

Department Business Plans Template

Department business plans outline a department’s goals, what steps or initiatives the department will undertake to achieve those goals, and the timeline during which these goals should be achieved. Department business plan templates should include sections in which each department can specify the current state of affairs, the goals and strategies that will be the focus of the upcoming business plan, and what metrics will be used to track progress toward achieving each goal.
Qualitative Analysis

When creating dashboards, a lot of emphasis is placed on quick visualizations of important numbers that can tell a story at a glance. However, there is a time and place for qualitative analysis, especially when it comes to dashboards for business plans. Numbers will not always be able to describe the full picture. With ClearPoint, department leaders can create custom fields to describe their goals and strategy for the coming year and use this qualitative analysis to complement the data they are already tracking in ClearPoint. Adding qualitative features to a department business plan dashboard can help give users situational awareness, better enabling departments to accomplish their goals.

A department business plans template can easily be adapted to suit different audiences. Organizational leadership may only wish to view department business plans at a very high-level, with only an outline of what goals each department will undertake. Members of the department, by contrast, will likely require more information on what and how the department will seek to accomplish in the months to come.An effective business plan template like the one shown in ClearPoint above makes it easy for viewers to drill down for further details on the goals, initiatives, and measures included in the business plan.
Key Elements for Department Business Plans Templates
- Visualization of department goals, measures, and initiatives
Without visuals of department goals, measures and initiatives, department leaders cannot get a quick glimpse into the health of their department. The visual is key to allowing managers to quickly see how their department is doing and see where they should focus their attention to make sure they meet their (and the organization’s) strategic goals.
- Ability to drill down for more information on each strategic element
Once managers get an understanding of where improvements might be needed, they should be able to drill down into the element to see why that element may be behind and lagging. Or, on the opposite end, if an initiative is doing well, drilling down for more information allows managers to see what’s working and allows them to apply that information to other places.
- Qualitative update or summary on progress and next steps
Qualitative updates allow managers and leaders to see next steps for a project and provide any missing context from the dashboard. This allows the dashboard to serve as the one-stop location for all the needed information for that department, meaning managers and leaders don’t have to e-mail or reach out to their team to gain more information. By seeing next steps, managers can easily see what course of action is being taken by their team and intervene if they believe it’s necessary.
Intended Audience
This dashboard is intended to be viewed by the leaders of various departments and shared both during department meetings and leadership meetings across departments. Managers in various industries can utilize this dashboard to gain an understanding of how they’re meeting goals in their specific department and how that may impact the organization’s goals.
Latest posts

"State" Spotlight: Canada

Quality Assurance Advice from the Experts

How Healthcare Providers Use ClearPoint for Impactful Strategy Management
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
How to Write a Business Plan: Beginner’s Guide (& Templates)

Written by: Chloe West

Thinking about starting a business? One of the first steps you’ll need to take is to write a business plan. A business plan can help guide you through your financial planning, marketing strategy, unique selling point and more.
Making sure you start your new business off on the right foot is key, and we’re here to help. We’ve put together this guide to help you write your first business plan. Or, you can skip the guide and dive right into a business plan template .
Ready to get started?
Here’s a short selection of 8 easy-to-edit business plan templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

8-Step Process for Writing a Business Plan
What is a business plan, why is a business plan important, step #1: write your executive summary, step #2: put together your company description, step #3: conduct your market analysis, step #4: research your competition, step #5: outline your products or services, step #6: summarize your financial plan, step #7: determine your marketing strategy, step #8: showcase your organizational chart, 14 business plan templates to help you get started.
A business plan is a document that helps potential new business owners flesh out their business idea and put together a bird’s eye view of their business. Writing a business plan is an essential step in any startup’s ideation process.
Business plans help determine demographics, market analysis, competitive analysis, financial projections, new products or services, and so much more.
Each of these bits of information are important to have on hand when you’re trying to start a business or pitching investors for funds.
Here’s an example of a business plan that you can customize to incorporate your own business information.

We’re going to walk you through some of the most important parts of your business plan as well as how to write your own business plan in 8 easy steps.
If you’re in the beginning stages of starting a business , you might be wondering if it’s really worth your time to write out your business plan.
We’re here to tell you that it is.
A business plan is important for a number of reasons, but mostly because it helps to set you up for success right from the start.
Here are four reasons to prove to you why you need to start your business off on the right foot with a plan.
Reason #1: Set Realistic Goals and Milestones
Putting together a business plan helps you to set your objectives for growth and make realistic goals while you begin your business.
By laying out each of the steps you need to take in order to build a successful business, you’re able to be more reasonable about what your timeline is for achieving everything as well as what your financial projections are.
The best way to set goals is using the SMART goals guidelines, outlined below.

Reason #2: Grow Your Business Faster
Having a business plan helps you be more organized and strategic, improving the overall performance of your business as you start out. In fact, one study found that businesses with a plan grow 30% faster than businesses that don’t.
Doesn’t that sound reason enough alone to start out your business venture with a solidified plan? We thought so too, but we’ve still got two more reasons.
Reason #3: Minimize Risk
Starting a new business is uncharted territory. However, when you start with a roadmap for your journey, it makes it easier to see success and minimize the risks that come with startups.
Minimize risk and maximize profitability by documenting the most important parts of your business planning.
Reason #4: Secure Funding
And finally, our last reason that business plans are so important is that if you plan to pitch investors for funding for your new venture, they’re almost always going to want to see a detailed business plan before deciding whether or not to invest.
You can easily create your business plan and investor pitch deck right here with Visme. Just sign up for a free account below to get started.
Hey executives! Looking to cut design costs?
- Spend less time on presentations and more time strategizing
- Ensure your brand looks and feels visually consistent across all your organization's documents
- Impress clients and stakeholders with boardroom ready presentations
Sign up. It’s free.

The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire business plan, giving anyone who reads through your document a quick understanding of what they’re going to learn about your business idea.
However, you need to remember that some of the people who are going to read your business plan don’t want to or have time to read the entire thing. So your executive summary needs to incorporate all of the most important aspects of your plan.
Here’s an example of an executive summary from a business plan template you can customize and turn into your own.

Your executive summary should include:
- Key objective(s)
- Market research
- Competitor information
- Products/services
- Value proposition
- Overview of your financial plan
- How you’re going to actually start your business
One thing to note is that you should actually write your executive summary after the rest of your business plan so that you can properly summarize everything you’ve already created.
So at this point, simply leave a page blank for your executive summary so you can come back to it at the end of your business plan.

The next step is to write out a full description of your business and its core offerings. This section of your business plan should include your mission statement and objectives, along with your company history or overview.
In this section, you may also briefly describe your business formation details from a legal perspective.
Mission Statement
Don’t spend too much time trying to craft this. Your mission statement is a simple “why” you started this business. What are you trying to achieve? Or what does your business solve?
This can be anything from one single quote or a paragraph, but it doesn’t need to be much longer than that. In fact, this could be very similar to your value proposition.

What are your goals? What do you plan to achieve in the first 90 days or one year of your business? What kind of impact do you hope to make on the market?
These are all good points to include in your objectives section so anyone reading your business plan knows upfront what you hope to achieve.
History or Overview
If you’re not launching a brand new business or if you’ve previously worked on another iteration of this business, let potential investors know the history of your company.
If not, simply provide an overview of your business, sharing what it does or what it will do.

Your third step is to conduct a market analysis so you know how your business will fit into its target market. This page in your business plan is simply meant to summarize your findings. Most of your time should be spent actually doing the research.
Your market analysis needs to look at things like:
- Market size, and if it’s grown in recent years or shrinking
- The segment of the market you plan to target
- Demographics and behavior of your target audience
- The demand for your product or service
- Your competitive advantage or differentiation strategy
- The average price of your product or service
Put together a summary of your market analysis and industry research in a 1-2 page format, like we see below.

Your next step is to conduct a competitive analysis. While you likely touched on this briefly during your market analysis, now is the time to do a deep dive so that you have a good grasp on what your competitors are doing and how they are generating customers.
Start by creating a profile of all your existing competitors, or at the very least, your closest competitors – the ones who are offering very similar products or services to you, or are in a similar vicinity (if you’re opening a brick and mortar store).
Focus on their strengths and what they’re doing really well so that you can emulate their best qualities in your own way. Then, look at their weaknesses and what your business can do better.
Take note of their current marketing strategy, including the outlets you see a presence, whether it’s on social media, you hear a radio ad, you see a TV ad, etc. You won’t always find all of their marketing channels, but see what you can find online and on their website.

After this, take a minute to identify potential competitors based on markets you might try out in the future, products or services you plan to add to your offerings, and more.
Then put together a page or two in your business plan that highlights your competitive advantage and how you’ll be successful breaking into the market.
Step five is to dedicate a page to the products or services that your business plans to offer.
Put together a quick list and explanation of what each of the initial product or service offerings will be, but steer clear of industry jargon or buzzwords. This should be written in plain language so anyone reading has a full understanding of what your business will do.

You can have a simple list like we see in the sample page above, or you can dive a little deeper. Depending on your type of business, it might be a good idea to provide additional information about what each product or service entails.
The next step is to work on the financial data of your new business. What will your overhead be? How will your business make money? What are your estimated expenses and profits over the first few months to a year? The expenses should cover all the spending whether they are recurring costs or just one-time LLC filing fees .
There is so much that goes into your financial plan for a new business, so this is going to take some time to compile. Especially because this section of your business plan helps potential cofounders or investors understand if the idea is even viable.

Your financial plan should include at least five major sections:
- Sales Forecast: The first thing you want to include is a forecast or financial projection of how much you think your business can sell over the next year or so. Break this down into the different products, services or facets of your business.
- Balance Sheet: This section is essentially a statement of your company’s financial position. It includes existing assets, liabilities and equity to demonstrate the company’s overall financial health.
- Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), this covers your projected expenses and revenue, showcasing whether your business will be profitable or not.
- Operating Budget: A detailed outline of your business’s income and expenses. This should showcase that your business is bringing in more than it’s spending.
- Cash Flow Statements: This tracks how much cash your business has at any given point, regardless of whether customers or clients have paid their bills or have 30-60+ days to do so.
While these are the most common financial statements, you may discover that there are other sections that you want to include or that lenders may want to see from you.
You can automate the process of looking through your documents with an OCR API , which will collect the data from all your financial statements and invoices.
The next step is coming up with a successful marketing plan so that you can actually get the word out about your business.
Throughout your business plan, you’ve already researched your competitors and your target market, both of which are major components of a good marketing strategy. You need to know who you’re marketing to, and you want to do it better than your competition.

On this page or throughout this section of your business plan, you need to focus on your chosen marketing channels and the types of marketing content you plan to create.
Start by taking a look at the channels that your competitors are on and make sure you have a good understanding of the demographics of each channel as well. You don’t want to waste time on a marketing channel that your target audience doesn’t use.
Then, create a list of each of your planned marketing avenues. It might look something like:
- Social media ( Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest)
- Email newsletter
- Digital ads
Depending on the type of business you’re starting, this list could change quite a bit — and that’s okay. There is no one-size-fits-all marketing strategy, and you need to find the one that brings in the highest number of potential customers.
Your last section will be all about your leadership and management team members. Showcasing that you have a solid team right from the start can make potential investors feel better about funding your venture.
You can easily put together an organizational chart like the one below, with the founder/CEO at the top and each of your team leaders underneath alongside the department they’re in charge of.

Simply add an organizational chart like this as a page into your overall business plan and make sure it matches the rest of your design to create a cohesive document.
If you want to create a good business plan that sets your new business up for success and attracts new investors, it’s a good idea to start with a template.
We’ve got 14 options below from a variety of different industries for you to choose from. You can customize every aspect of each template to fit your business branding and design preferences.
If you're pressed for time, Visme's AI business plan generator can churn out compelling business plans in minutes. Just input a detailed prompt, choose the design, and watch the tool generate your plan in a few seconds.
Template #1: Photography Business Plan Template

This feminine and minimalistic business plan template is perfect for getting started with any kind of creative business. Utilize this template to help outline the step-by-step process of getting your new business idea up and running.
Template #2: Real Estate Business Plan Template

Looking for a more modern business plan design? This template is perfect for plainly laying out each of your business plans in an easy-to-understand format. Adjust the red accents with your business’s colors to personalize this template.
Template #3: Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Creating a business and marketing plan for your nonprofit is still an essential step when you’re just starting out. You need to get the word out to increase donations and awareness for your cause.
Template #4: Restaurant Business Plan Template

If your business plan needs to rely heavily on showcasing photos of your products (like food), this template is perfect for you. Get potential investors salivating at the sight of your business plan, and they’re sure to provide the capital you need.
Template #5: Fashion Business Plan Template

Serifs are in. Utilize this template with stunning serif as all the headers to create a contemporary and trendy business plan design that fits your business. Adjust the colors to match your brand and easily input your own content.
Template #6: Daycare Business Plan Template

Creating a more kid-friendly or playful business? This business plan template has bold colors and design elements that will perfectly represent your business and its mission.
Use the pages you need, and remove any that you don’t. You can also duplicate pages and move the elements around to add even more content to your business plan.
Template #7: Consulting Business Plan Template

This classic business plan template is perfect for a consulting business that wants to use a stunning visual design to talk about its services.
Template #8: Coffee Shop Business Plan Template

Customize this coffee shop business plan template to match your own business idea. Adjust the colors to fit your brand or industry, replace photos with your own photography or stock photos that represent your business, and insert your own logo, fonts and colors throughout.
Template #9: SaaS Business Plan Template

A SaaS or service-based company also needs a solid business plan that lays out its financials, list of services, target market and more. This template is the perfect starting point.
Template #10: Small Business Plan Template

Every startup or small business needs to start out with a strong business plan in order to start off on the right foot and set yourself up for success. This template is an excellent starting point for any small business.
Template #11: Ecommerce Business Plan Template

An ecommerce business plan is ideal for planning out your pricing strategy of all of your online products, as well as the site you plan to use for setting up your store, whether WordPress, Shopify, Wix or something else.
Template #12: Startup Business Plan Template

Customize this template and make it your own! Edit and Download
This is another generic business plan template for any type of startup to customize. Switch out the content, fonts and colors to match your startup branding and increase brand equity.
Template #13: One-Page Business Plan Template

Want just a quick business plan to get your idea going before you bite the bullet and map out your entire plan? This one-page template is perfect for those just starting to flesh out a new business idea.
Template #14: Salon Business Plan Template

This salon business plan template is easy on the design and utilizes a light color scheme to put more focus on the actual content. You can use the design as is or keep it as a basis for your own design elements.
Create Your Own Business Plan Today
Ready to write your business plan? Once you’ve created all of the most important sections, get started with a business plan template to really wow your investors and organize your startup plan.
Design beautiful visual content you can be proud of.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Chloe West is the content marketing manager at Visme. Her experience in digital marketing includes everything from social media, blogging, email marketing to graphic design, strategy creation and implementation, and more. During her spare time, she enjoys exploring her home city of Charleston with her son.
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

How To Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (2024)
Business plans aren’t just for entrepreneurs who need to secure funding—they can help you plan and evaluate new ideas or growth plans, too. Find out how to write a business plan and get the most out of the process in this comprehensive guide.

A great business plan can help you clarify your strategy, identify potential roadblocks, determine necessary resources, and evaluate the viability of your idea and growth plan before you start a business .
Not every successful business launches with a formal business plan, but many founders find value in taking time to step back, research their idea and the market they’re looking to enter, and understand the scope and the strategy behind their tactics. That’s where writing a business plan comes in.
Learn how to write a business plan with a step-by-step guide, get tips for getting the most of your plan, and see real business plan examples to inspire you.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines a company's goals, strategies for achieving them, and the time frame for their achievement. It covers aspects like market analysis , financial projections, and organizational structure, serving as a roadmap for business growth and a tool to secure funding.
Often, financial institutions and investors need to see a business plan before funding any project. Even if you don’t plan to seek outside funding, a well-crafted plan becomes the guidance for your business as it scales.
How to write a business plan in 9 steps
- Draft an executive summary.
- Write a company description.
- Perform a market analysis.
- Outline the management and organization.
- List your products and services.
- Perform customer segmentation.
- Define a marketing plan.
- Provide a logistics and operations plan.
- Make a financial plan.
Few things are more intimidating than a blank page. Starting your business plan with a structured outline and key elements for what you’ll include in each section is the best first step you can take.
Since an outline is such an important step in the process of writing a business plan, we’ve put together a high-level overview to get you started (and avoid the terror of facing a blank page).
Once you have your business plan template in place, it’s time to fill it in. We’ve broken it down by section to help you build your plan step by step.
1. Draft an executive summary.
A good executive summary is one of the most crucial sections of your plan—it’s also the last section you should write.
The executive summary distills everything that follows and gives time-crunched reviewers (e.g., potential investors and lenders) a high-level overview of your business that persuades them to read further.
Again, it’s a summary, so highlight the key points you’ve uncovered while writing your plan. If you’re writing for your own planning purposes, you can skip the summary altogether—although you might want to give it a try anyway, just for practice.

An executive summary shouldn’t exceed one page. Admittedly, that space constraint can make squeezing in all of the salient information a bit stressful—but it’s not impossible. Your business plan’s executive summary should include:
- Business concept. What does your business do?
- Business goals and vision. What does your business want to do?
- Product description and differentiation. What do you sell, and why is it different?
- Target market. Who do you sell to?
- Marketing strategy. How do you plan on reaching your customers?
- Current financial state. What do you currently earn in revenue?
- Projected financial state. What do you foresee earning in revenue?
- The ask. How much money are you asking for?
- The team. Who’s involved in the business?
2. Write a company description.
This section of your business plan should answer two fundamental questions: who are you, and what do you plan to do?
Answering these questions with a company description provides an introduction to why you’re in business, why you’re different, what you have going for you, and why you’re a good investment.
For example, clean makeup brand Saie shares a letter from its founder on the company’s mission and why it exists.

Clarifying these details is still a useful exercise, even if you’re the only person who’s going to see them. It’s an opportunity to put to paper some of the more intangible facets of your business, like your principles, ideals, and cultural philosophies.
Here are some of the components you should include in your company description:
- Your business structure (Are you a sole proprietorship, general partnership, limited partnership, or incorporated company?)
- Your business model
- Your industry
- Your business’s vision, mission, and value proposition
- Background information on your business or its history
- Business objectives, both short and long term
- Your team, including key personnel and their salaries
Brand values and goals
To define your brand values , think about all the people your company is accountable to, including owners, employees, suppliers, customers, and investors. Now consider how you’d like to conduct business with each of them. As you make a list, your core values should start to emerge.
Your company description should also include both short- and long-term goals. Short-term goals, generally, should be achievable within the next year, while one to five years is a good window for long-term goals. Make sure your goal setting includes SMART goals : specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound.
Vision and mission statements
Once you know your values, you can write a mission statement . Your statement should explain, in a convincing manner, why your business exists, and should be no longer than a single sentence.
Next, craft your vision statement : What impact do you envision your business having on the world once you’ve achieved your vision? Phrase this impact as an assertion—begin the statement with “We will” and you’ll be off to a great start. Your vision statement, unlike your mission statement, can be longer than a single sentence, but try to keep it to three at most. The best vision statements are concise.
3. Perform a market analysis.
No matter what type of business you start, it’s no exaggeration to say your market can make or break it. Choose the right market for your products—one with plenty of customers who understand and need your product—and you’ll have a head start on success. If you choose the wrong market, or the right market at the wrong time, you may find yourself struggling for each sale.
Market analysis is a key section of your business plan, whether or not you ever intend for anyone else to read it.
This is why market research and analysis is a key section of your business plan, whether or not you ever intend for anyone else to read it. It should include an overview of how big you estimate the market is for your products, an analysis of your business’s position in the market, and an overview of the competitive landscape. Thorough research supporting your conclusions is important both to persuade investors and to validate your own assumptions as you work through your plan.
Here is an example to illustrate how to approach this section:

How big is your potential market?
The potential market is an estimate of how many people need your product. While it’s exciting to imagine sky-high sales figures, you’ll want to use as much relevant independent data as possible to validate your estimated potential market.
Since this can be a daunting process, here are some general tips to help you begin your research:
- Understand your ideal customer profile. Look for government data about the size of your target market , learn where they live, what social channels they use, and their shopping habits.
- Research relevant industry trends and trajectory. Explore consumer trends and product trends in your industry by looking at Google Trends, trade publications, and influencers in the space.
- Make informed guesses. You’ll never have perfect, complete information about your total addressable market. Your goal is to base your estimates on as many verifiable data points as necessary.
Some sources to consult for market data include government statistics offices, industry associations, academic research, and respected news outlets covering your industry.
Read more: What is a Marketing Analysis? 3 Steps Every Business Should Follow
SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis looks at your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. What are the best things about your company? What are you not so good at? What market or industry shifts can you take advantage of and turn into opportunities? Are there external factors threatening your ability to succeed?
SWOT is often depicted in a grid or visual way. With this visual presentation, your reader can quickly see the factors that may impact your business and determine your competitive advantage in the market.
Competitive analysis
There are three overarching factors you can use to differentiate your business in the face of competition:
- Cost leadership. You have the capacity to maximize profits by offering lower prices than the majority of your competitors. Examples include companies like Mejuri and Endy .
- Differentiation. Your product or service offers something distinct from the current cost leaders in your industry and banks on standing out based on your uniqueness. Think of companies like Knix and QALO .
- Segmentation. You focus on a very specific, or niche, target market, and aim to build traction with a smaller audience before moving on to a broader market. Companies like TomboyX and Heyday Footwear are great examples of this strategy.
To understand which is the best fit, you’ll need to understand your business as well as the competitive landscape.
You’ll always have competition in the market, even with an innovative product, so it’s important to include a competitive overview in your business plan. If you’re entering an established market, include a list of a few companies you consider direct competitors and explain how you plan to differentiate your products and business from theirs.
For example, if you’re selling jewelry , your competitive differentiation could be that, unlike many high-end competitors, you donate a percentage of your profits to a notable charity or pass savings on to your customers.
If you’re entering a market where you can’t easily identify direct competitors, consider your indirect competitors—companies offering products that are substitutes for yours. For example, if you’re selling an innovative new piece of kitchen equipment, it’s too easy to say that because your product is new, you have no competition. Consider what your potential customers are doing to solve the same problems.
4. Outline the management and organization.

If you have a management team, use an organizational chart to show your company’s internal structure, including the roles, responsibilities, and relationships between people in your chart. Communicate how each person will contribute to the success of your startup.
5. List your products and services.
Your products or services will feature prominently in most areas of your business plan, but it’s important to provide a section that outlines key details about them for interested readers.
If you sell many items, you can include more general information on each of your product lines. If you only sell a few, provide additional information on each. For example, bag shop BAGGU sells a large selection of different types of bags, in addition to home goods and other accessories. Its business plan would list out those categories and key details about the products within each.

Describe new products you’ll launch in the near future and any intellectual property you own. Express how they’ll improve profitability. It’s also important to note where products are coming from—handmade crafts are sourced differently than trending products for a dropshipping business, for instance.
6. Perform customer segmentation.

To give a holistic overview of your ideal customer, describe a number of general and specific demographic characteristics. Customer segmentation often includes:
- Where they live.
- Their age range.
- Their level of education.
- Some common behavior patterns.
- How they spend their free time.
- Where they work.
- What technology they use.
- How much they earn.
- Where they’re commonly employed.
- Their values, beliefs, or opinions.
This information will vary based on what you’re selling, but you should be specific enough that it’s unquestionably clear who you’re trying to reach—and more importantly, why you’ve made the choices you have based on who your customers are and what they value.
For example, a college student has different interests, shopping habits, and pricing sensitivity than a 50-year-old executive at a Fortune 500 company. Your business plan and decisions would look very different based on which one was your ideal customer.
Put your customer data to work with Shopify’s customer segmentation
Shopify’s built-in segmentation tools help you discover insights about your customers, build segments as targeted as your marketing plans with filters based on your customers’ demographic and behavioral data, and drive sales with timely and personalized emails.
7. Define a marketing plan.

If you’re planning to invest heavily in Instagram marketing or TikTok ads , for example, it might make sense to include whether Instagram and TikTok are a leading platform for your audience—if it’s not, that might be a sign to rethink your marketing plan.
Market your business with Shopify’s customer marketing tools
Shopify has everything you need to capture more leads, send email campaigns, automate key marketing moments, segment your customers, and analyze your results. Plus, it’s all free for your first 10,000 emails sent per month.
Most marketing plans include information on four key subjects. How much detail you present on each will depend on both your business and your plan’s audience.
- Price: How much do your products cost, and why have you made that decision?
- Product: What are you selling and how do you differentiate it in the market?
- Promotion: How will you get your products in front of your ideal customer?
- Place: Where will you sell your products? On what channels and in which markets?
Promotion may be the bulk of your plan since you can more readily dive into tactical details, but the other three areas should be covered at least briefly—each is an important strategic lever in your marketing mix.
Here is an example of a marketing plan for a new business:

8. Provide a logistics and operations plan.
Logistics and operations are the workflows you’ll implement to make your business idea a reality. If you’re writing a business plan for your own planning purposes, this is still an important section to consider, even though you might not need to include the same level of detail as if you were seeking investment.
Cover all parts of your planned operations, including:
- Suppliers . Where do you get the raw materials you need for production, or where are your products produced?
- Production . Will you make, manufacture, wholesale , or dropship your products? How long does it take to produce your products and get them shipped to you? How will you handle a busy season or an unexpected spike in demand?
- Facilities . Where will you and any team members work? Do you plan to have a physical retail space? If yes, where?
- Equipment . What tools and technology do you require to be up and running? This includes everything from computers to lightbulbs and everything in between.
- Shipping and fulfillment. Will you be handling all the fulfillment tasks in-house, or will you use a third-party fulfillment partner?
- Inventory . How much will you keep on hand, and where will it be stored? How will you ship it to partners if required, and how will you approach inventory management ?
This section should signal to your reader that you’ve got a solid understanding of your supply chain and strong contingency plans in place to cover potential uncertainty. If your reader is you, it should give you a basis to make other important decisions, like how to price your products to cover your estimated costs, and at what point you plan to break even on your initial spending.
9. Make a financial plan.

The level of detail required in your financial plan will depend on your audience and goals, but typically you’ll want to include three major views of your financials: an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash-flow statement. It also may be appropriate to include financial data and projections.
Here’s a spreadsheet template that includes everything you’ll need to create an income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement, including some sample numbers. You can edit it to reflect projections if needed.
Let’s review the types of financial statements you’ll need.
Income statements
Your income statement is designed to give readers a look at your revenue sources and expenses over a given time period. With those two pieces of information, they can see the all-important bottom line or the profit or loss your business experienced during that time. If you haven’t launched your business yet, you can project future milestones of the same information.
Balance sheets
Your balance sheet offers a look at how much equity you have in your business. On one side, you list all your business assets (what you own), and on the other side, all your liabilities (what you owe). This provides a snapshot of your business’s shareholder equity, which is calculated as:
Assets - Liabilities = Equity
Cash flow statements
Your cash flow statement is similar to your income statement, with one important difference: it takes into account when revenues are collected and when expenses are paid.
When the cash you have coming in is greater than the cash you have going out, your cash flow is positive. When the opposite scenario is true, your cash flow is negative. Ideally, your cash flow statement will help you see when cash is low, when you might have a surplus, and where you might need to have a contingency plan to access funding to keep your business solvent .
It can be especially helpful to forecast your cash-flow statement to identify gaps or negative cash flow and adjust operations as required.
📚 Read more: What Is Cash Flow Management: Template and Examples
Why write a business plan?
Investors rely on business plans to evaluate the feasibility of a business before funding it, which is why business plans are commonly associated with getting a loan.
Business plans also help owners identify areas of weakness before launching, potentially avoiding costly mistakes down the road. “Laying out a business plan helped us identify the ‘unknowns’ and made it easier to spot the gaps where we’d need help or, at the very least, to skill up ourselves,” says Jordan Barnett, owner of Kapow Meggings .
There are several other compelling reasons to consider writing a business plan, including:
- Strategic planning. Writing out your plan is an invaluable exercise for clarifying your ideas and can help you understand the scope of your business, as well as the amount of time, money, and resources you’ll need to get started.
- Evaluating ideas. If you’ve got multiple ideas in mind, a rough business plan for each can help you focus your time and energy on the ones with the highest chance of success.
- Research. To write a business plan, you’ll need to research your ideal customer and your competitors—information that will help you make more strategic decisions.
- Recruiting. Your business plan is one of the easiest ways to communicate your vision to potential new hires and can help build their confidence in the venture, especially if you’re in the early stages of growth.
- Partnerships. If you plan to collaborate with other brands , having a clear overview of your vision, your audience, and your business strategy will make it much easier for them to identify if your business is a good fit for theirs.
- Competitions. There are many business plan competitions offering prizes such as mentorships, grants, or investment capital.
If you’re looking for a structured way to lay out your thoughts and ideas, and to share those ideas with people who can have a big impact on your success, a business plan is an excellent starting point.
Business plan types
Business plan types can span from one page to multiple pages with detailed graphs and reports. There’s no one way to create a business plan. The goal is to convey the most important information about your company for readers.
Common business plans we see include, but are not limited to, the following types:
Traditional business plans
These are the most common business plans. Traditional business plans take longer to write and can be dozens of pages long. Venture capitalist firms and lenders ask for this plan. Traditional business plans may not be necessary if you don’t plan to seek outside funding. That’s where the next type comes in.
Lean business plans
A lean business plan is a shorter version of a traditional business plan. It follows the same format, but only includes the most important information. Businesses use lean business plans to onboard new hires or modify existing plans for a specific target market.
Nonprofit business plans
A nonprofit business plan is for any entity that operates for public or social benefit. It covers everything you’ll find in a traditional business plan, plus a section describing the impact the company plans to make. For example, a speaker and headphone brand that aims to help people with hearing disabilities. Donors often request this plan.
📚 Read more: The Road to Success: Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own .
7 tips for creating a small business plan
There are a few best practices when it comes to writing a business plan. While your plan will be unique to your business and goals, keep these tips in mind as you write.
1. Know your audience.
When you know who will be reading your plan—even if you’re just writing it for yourself to clarify your ideas—you can tailor the language and level of detail to them. This can also help you make sure you’re including the most relevant information and figure out when to omit sections that aren’t as impactful.
2. Have a clear goal.
When creating a business plan, you’ll need to put in more work and deliver a more thorough plan if your goal is to secure funding for your business versus working through a plan for yourself or even your team.
3. Invest time in research.
Sections of your business plan will primarily be informed by your ideas and vision, but some of the most crucial information you’ll need requires research from independent sources. This is where you can invest time in understanding who you’re selling to, whether there’s demand for your products, and who else is selling similar products or services.
4. Keep it short and to the point.
No matter who you’re writing for, your business plan should be short and readable—generally no longer than 15 to 20 pages. If you do have additional documents you think may be valuable to your audience and your goals, consider adding them as appendices.
5. Keep the tone, style, and voice consistent.
This is best managed by having a single person write the plan or by allowing time for the plan to be properly edited before distributing it.
6. Use a business plan template.
You can also use a free business plan template to provide a skeleton for writing a plan. These often guide you through each section from financial projects to market research to mission statement ensuring you don’t miss a step.
7. Try business plan software.
Writing a business plan isn’t the easiest task for business owners. But it’s important for anyone starting or expanding a business. Fortunately, there are tools to help with everything from planning, drafting, creating graphics, syncing financial data, and more. Business plan software also has business plan templates and tutorials to help you finish a comprehensive plan in hours, rather than days.
A few curated picks include:
- LivePlan : the most affordable option with samples and templates
- Bizplan : tailored for startups seeking investment
- Go Small Biz : budget-friendly option with industry-specific templates
📚 Read more: 6 Best Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
Common mistakes when writing a business plan
Other articles on business plans would never tell you what we’re about to tell you: Your business plan can fail. The last thing you want is for time and effort to go down the drain. Avoid these common mistakes:
- Bad business idea. Sometimes your idea may be too risky for potential investors, too expensive to run, or there’s no market. Aim for small business ideas that require low startup costs.
- No exit strategy. If you don’t show an exit strategy, or a plan for investors to leave the business with maximum profits, you’ll have little luck finding capital.
- Unbalanced teams. A great product is the cost of entry to starting a business. But an incredible team will take it to the top. Unfortunately, many business owners overlook a balanced team. They focus on potential profits, without worrying about how it will be done.
- Missing financial projections. Don’t leave out your balance sheet, cash flow statements, P&L statements, and income statements. Include your break-even analysis and return-on-investment calculations in your financial projections to create a successful business plan.
- Spelling and grammar errors. All the best organizations have an editor review their documents. If someone spots typos while reading your business plan, how can they believe you’ll run a successful company?
Prepare your business plan today

Whether you’re working on starting a new online business idea , building a retail storefront, growing your established business, or purchasing an existing business , you now understand how to write a business plan that suits your business’s goals and needs.
Feature illustration by Rachel Tunstall
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- AliExpress Dropshipping- How to Dropship From AliExpress
- How to Start a Clothing Line in 12 Steps (2024)
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- How To Do Crowdfunding: With Expert Tips and Examples From Successful Campaigns
- How to Start a Candle Business (with Examples)
- What Is Affiliate Marketing and How to Get Started
- Pinterest Marketing 101- How to Promote Your Business on Pinterest
- Getting Started on IG- A Beginner’s Guide to Instagram Marketing
Business plan FAQ
How do i write a business plan.
Learning how to write a business plan is simple if you use a business plan template or business plan software. Typically, a traditional business plan for every new business should have the following components :
- Executive summary
- Company description, including value proposition
- Market analysis and competitive analysis
- Management and organization
- Products and services
- Customer segmentation
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations
- Financial plan and financial projections
What is a good business plan?
A good business plan starts with a strong executive summary. It also adequately outlines idea feasibility, target market insights, and the competitive landscape. A business plan template can help businesses be sure to follow the typical format of traditional business plans which include financial projections, details about the management team, and other key elements that venture capital firms and potential investors want to see.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are:
- To clarify your plans for growth
- To understand your financial needs
- To attract funding from investors or secure a business loan
What are the different types of business plans?
The types of business plans include startup, refocusing, internal, annual, strategic, feasibility, operations, growth, and scenario-based. Each type of business plan has a different purpose. Business plan formats include traditional, lean, and nonprofit. Find a business plan template for the type of plan you want to write.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts
The most intuitive, powerful
Shopify yet
Shopify Editions Summer ’24

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jul 12, 2024
Jul 11, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.

Department Business Plan Template

What is a Department Business Plan?
A department business plan outlines the focus areas, objectives, and projects of a team or department within a company. It is used to develop a roadmap to success and ensure that the team is working towards the same goals. It can also be used to track progress and measure the results of the team’s efforts.
What's included in this Department Business Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Department Business Plan template for?
This department business plan template is for department heads and business leaders in all industries. It provides a framework to help create a plan for their department or team as well as a way to track their progress and results.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
Focus areas are the main topics that your team or department needs to address. Examples of focus areas could include improving internal communication, streamlining onboarding processes, or improving customer experience. These focus areas should be specific and measurable.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the goals that you want to achieve for each focus area. It is important to set measurable objectives for each focus area that you can track and measure. This will help you to determine if you are making progress towards the goals. Examples of some objectives for the focus area of Improve Internal Communication could be: Increase Team Collaboration, and Improve Team Communication.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
Setting measurable targets, or Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), are important for each objective to help track progress. KPIs should have an initial value, a target value, and a unit. Examples of KPIs could include increasing team collaboration usage from 20% to 80%, or decreasing onboarding process time from 30 days to 15 days.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects, or actions, are the steps that need to be taken in order to achieve the KPIs. These could include increasing team meetings, automating onboarding processes, or increasing customer surveys. It is important to ensure that the projects are related to the objectives and KPIs.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade Strategy Execution platform helps teams or departments develop, track, and measure their business plans. Cascade makes it easy to collaborate, communicate, and execute on your strategy and see faster results from your efforts.
How to Write a Department Business Plan
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Write a Business Plan
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Role of Financial Management in Corporate Structure
Lease contract administration functions, how to create a business plan as an entrepreneur.
- How Is a Budget Used to Motivate a Staff?
- How to Make a Business Budget Plan
Even a small business can be organized into separate departments, each one being assigned its own goals, such as revenue targets or units to be produced, and having its own expense budget. Each manager writes a department business plan, usually with guidance from the small-business owner and the finance staff. The managers of each department are held accountable for meeting these goals and staying within budgeted – often called forecast – expenses.
Review Last Year's Finances
Compare actual results to what had been in the forecast. Determine the reasons for significant variances. Analyze whether negative variances were due to one-time events or are likely to recur in the upcoming year and should be taken into account in the forecast.
Analyze Overall Performance
Review the productivity of the department as a whole and each member of the department. Set goals for productivity improvement – including better teamwork – in the upcoming year. Transmit these goals to each member of the department.
Align with Company-wide Goals
Determine departmental goals and make sure they conform with the expectations expressed in the company-wide goals and assumptions about the economy and industry. If the business owner seeks to keep cost increases to less than 2 percent in order to build up cash reserves, make sure your department budget is in line with that expectation.
Create Department Mission Statement
Express how the department will contribute to the company’s overall growth and productivity. State the value the department provides to the company as a whole. For example, the purchasing division’s mission could be to have critical inventory items available at all times while keeping inventory costs as low as possible.
Create a Financial Forecast
Create a forecast for revenues and expenses based on past results combined with the goals the company owner expressed for the upcoming year. The business owner may have set a goal of opening three new retail locations. Each department must determine what additional resources it needs to operate, in light of these expansion goals, and the cost of these resources, including personnel.
Transmit the Plan
Review the plan with the owner and his finance staff and justify proposed expenditure increases included in the departmental plan. Modify the plan based on recommendations from the business owner.
Final Review
Review the final plan with each member of the department to ensure all team members are aware of the expectations the business owner has for the department and the goals that have been set for it.
- When submitting the department budget to top management, include detailed analysis of the logic behind the revenue and expense forecast line items. This will increase the chance that proposed expense increases will be approved.
Each department manager should expect back-and-forth negotiations with top management, including the small-business owner, during the finalization of the department budgets. A department manager should not have the attitude that he is being singled out – in most instances all departments will be asked to make modifications to their plans.
- Forbes: New Managers: How To Create Your Department's Tactical Plan
- SBA.gov: Write Your Business Plan
- Strathcona: Department Business Plan
- nibusinessinfo.co.uk: Prepare a business plan for growth
- Each department manager should expect back-and-forth negotiations with top management, including the small-business owner, during the finalization of the department budgets. A department manager should not have the attitude that he is being singled out -- in most instances all departments will be asked to make modifications to their plans.
Brian Hill is the author of four popular business and finance books: "The Making of a Bestseller," "Inside Secrets to Venture Capital," "Attracting Capital from Angels" and his latest book, published in 2013, "The Pocket Small Business Owner's Guide to Business Plans."
Related Articles
How to put a business plan in motion, what are quotas & goals, organization strategy & division strategy, how to forecast profits for a business plan, how to run an effective hr department, the importance of a financial plan for a small business, what is a quarterly budget, how to write a golf club business plan, budgetary control techniques, most popular.
- 1 How to Put a Business Plan in Motion
- 2 What Are Quotas & Goals?
- 3 Organization Strategy & Division Strategy
- 4 How to Forecast Profits for a Business Plan

Department Strategic Plan

A department strategic plan can be a five-year strategic plan or it may also contain action plans and strategies that will be implemented for a short time period.
- 9+ Non-Profit Strategic Plan Examples
- 13+ Museum Strategic Plan Examples
A department strategic plan is an important business document that allows a department or a division to present all their projects and activities that can help further improve the entire operations or areas of the business. This document also showcases the initiatives, strategies, and action plans that are needed to be executed so that it can support the vision and corporate objectives of the company.
One of the most important things that you have to remember when creating a department strategic plan is that its content must be aligned with the overall strategic plan of the business. Hence, the content that can be seen in the document must be precise, specific, and relevant. We have put together a number of department strategic plan examples that you can refer to if you want to start developing the strategic plan of your department.
Detailed Department of Finance Strategic Plan Example

Department of Early Education and Care Strategic Plan Example

Size: 409 KB
Department of Finance and Management Strategic Plan Example

Size: 267 KB
First Time to Create a Department Strategic Plan?
Department strategic plans can be created by the human resource department , the managers or supervisors of the division, the management, or the third parties that the business have hired to assess the current condition of each department and come up with a strategic plan based on their expert insights and observations.
If this is your first time to be tasked or be required to develop a department strategic plan, here are some of the things that you need to be aware of:
1. Your strategic plan must be tactical. It is important for you to consider the ability of the entire department to attain the objectives that you have listed. Make sure to match the deliverable of the team with the things that you would like to implement. In this manner, you can create a realistic and attainable model for the department strategic plan. You may also see strategic planning checklist examples .
2. Consider how your department strategic plan can possibly affect the operations of the business as well as the things that it would like to achieve. You first need to look into the overall impacts and effects of the strategies and action plans that you have set so that you can measure its feasibility when applied into actual processes. You may also like sales strategic plan examples .
3. Ensure that your department strategic plan is time-bound. The next entire operational year of the department will mostly rely on the plans that you have created, which is why it is very important for you to come up with time frames that can present the specific milestones that must be achieved in certain periods for these results to have a maximum contribution to the growth and development of the business. You may also check out security strategic plan examples .
4. Just like when creating a compliance strategic plan , you have to look into the general corporate procedural policies and other rules of the business first. You have to be knowledgeable of the regulations and protocols that are essential to be considered so that you will not negate the objectives of the business or the processes that are done by other departments.
5. If the department where you are assigned at have previous strategic plans, compile all these documents so you can see the trends when it comes to action plan creation and strategy incorporation. Having the knowledge of previous processes can make it easier for you to create new decisions for the department. More so, it can give you an overview of the strategies and simple action plans that worked and those that did not.
Human Resources Department Strategic Plan Example

Police Department Strategic Plan Example

Tribal Health Department Strategic Plan Example

Size: 924 KB
How to Come Up with an Impressive Department Strategic Plan
In comparison to the creation of recruitment strategic plan examples and all the other kinds of strategic plan documents, it is also evident that not all department strategic plans are in the same level of effectiveness and efficiency. This being said, there are actually a lot of factors and elements that can affect the successful development and implementation of this document.
One of which is the process followed by the department when creating the strategic plan. A basic procedure that you can always execute if you want to come up with a simple department strategic plan is listed below.
1. Browse through the business strategic plan of the company first. Familiarize with the processes followed by the business and the plans that will be executed for the next operational plan . Again, it is very important for you to align the content of the department strategic plan with the information presented in the business strategic plan.
2. Evaluate the department’s existing issues, problems, and concerns. More so, have an idea about the current condition of the department’s operations as well as the strengths that you can capitalize on. Being able to understand the dynamics of the team can help you allocate resources and maximize the potential of skills, abilities, expertise, and other deliverable. You may also see health and safety strategic plan examples .
3. Conduct internal and external analysis. As you may have noticed, the initial steps of creating a department strategic plan is mostly focused on the acquisition of data from surveys questionnaires , and other data-gathering tools. It is important for you to know a lot about the environment, the potential effects of your strategic plan and the ways in which the document can develop the relationship and performance of each department members.
4. Have a goal in mind. What would you like the department strategic plan to achieve in the future? What is the vision that you have for the department and how can it help the business achieve its vision? Setting your goals can make it easier for you to be more direct and precise when creating the content of the department strategic plan.
5. If you are already aware of what you will be working on, you can already specify the action plans, programs, and other efforts that you would like the department to execute. Alongside these plans are the set of time duration in which milestones should already be identified. Come up with tactics and backup plans so you can make your department strategic plan more flexible and dynamic. You may also like personal strategic plan examples .
6. Put all the details that you have gathered together with the strategic plans that you will execute. Use templates and other references that can help you present your discussion in a presentable and understandable manner. Make sure to review the document before sending it to your target audience. You may also check out school strategic plan examples .
7. In some instances or if you have the budget allocation for this activity, you can also seek for an expert’s advice so you can ensure the quality of the document that you came up with. There are already professionals who offer their services so they can help you come up with an effective department strategic plan. You might be interested in one-page strategic plan examples .
Health Department Strategic Plan Example

Size: 480 KB
Department of Finance Strategic Plan Example

Size: 559 KB
Law Department Strategic Plan Example

Size: 469 KB
Useful Recommendations and Tips to Help You Make a Department Strategic Plan Successfully
From a club strategic plan to a restaurant strategic plan , there are different departments who can make use of a variety of strategic plans based on the nature of their processes and the activities that the workforce within the department needs to execute to comply with the business standards, requirements, and expectations.
Even if there are different kinds of strategic plans, there are also some similarities when it comes to the development of these documents.
Some useful recommendations and tips that you can use as references and guides when making a successful department strategic plan are as follows:
1. Ensure that your department strategic plan contains all the action plans that can help you achieve particular goals and objectives . Whether it is to connect with your target market more effectively or to help the business obtain competitive advantage, what is important is for your call-to-actions to be relevant.
2. Gather all your team members and have an initial meeting about the potential content of the department strategic plan. You have to look into all issues and problems in different angles so you can create a department strategic plan that has a high potential of being effective. You have to understand root causes, previous effects, and actual implications so you can ensure the efficiency of the document that you will create. You may also see procurement strategy plan examples .
3. Set proper expectations. You have to ensure that the items that you will include in the department strategic plan are realistic and measurable. Keep in mind that the attainability of your goals and objectives can affect the implementation of your general action plans and strategies.
4. Designate responsibilities and work processes accordingly. You have to make sure that all action plans are given to responsible entities so that lapses and loopholes during the plan execution can be minimized or even be eliminated. You also have to make sure that the workforce is aware of what is expected from them so they can function accordingly. You may also like audit strategic plan examples .
5. Create a department strategic plan that is brief and concise. You have to include necessary information that targets the key areas of the department’s operations. If you can successfully do this, then it will be easier for you to present your discussion in an understandable manner. You may also check out community strategic plan examples .
Finance Department Strategic Plan Example

Size: 387 KB
Department of Conservation: Information Systems Strategic Plan Example

Strategic Planning Guide for Offices and Department Managers Example

The Role of References in Department Strategic Plan Drafting
An outstanding department strategic plan, may it be an HR strategic plan or any strategic plan made and used by other departments, is one that considers the content of the overall business strategic plan of the company and all the other factors that are essential in the successful usage of the document.
Listed below are some of the ways on how references can help you draft a department strategic plan.
1. Downloadable and existing examples of department strategic plans can help you identify all the information that are considered necessary and relevant to be included in the document that you generally plan to make. With the usage of these examples, you will know whether you have already completed all the things that are expected to be included in your own department strategic plan.
2. Aside from downloadable examples, you can also refer to templates specifically for formatting purposes. A department strategic plan must be well-presented so that it can appeal to the target audience of the department especially to the decision-makers within the management. You may also see real estate strategic plan examples .
The discussion flow can be more understandable if you can put all details in their proper places within the document. This can reflect the quality standards that you have considered when making the document.
3. There are also organizational tools that you can use as references. Examples of these are the previous outlines, checklists, drafts, and summaries of the department strategic plans used by the business. Using these references can help you become aware of the loopholes that made the previous documents weak or irrelevant. You may also like strategic action plan examples .
We suggest you to browse through and download the department strategic plan examples in PDF that we have put together in this post for your advantage. Using these existing examples can further develop your knowledge when it comes to the factors and elements that you need to consider when creating a department strategic plan. Create a department strategic plan draft now so your department, your team, and the business can already benefit from the effects of the document’s usage.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.

Content , Strategic Development
How to build a department from ground zero.

“The only constant is change.”
Heraclitus, Greek Philosopher of the late 6th century BCE
Delivery of a specific product or service requires work is accomplished using a system of clearly defined processes to achieve a common goal. This is the core definition of a department. Much of the work that Pacific Crest Group does is based on building departments for our clients’ businesses designed explicitly to assist them in being more efficient and profitable.
Benefits of Building a Department
The purpose of creating a department is to provide a structure that increases the ability of a team of individuals in planning, problem solving and decision making for the company. In order to be effective in this directive, it is critical the department remains focused on fulfilling a specific value proposition.
Creating the Department’s Value Proposition
Each department’s value proposition must be in alignment with the organization’s overall strategic initiatives. Review the entity’s long-term business plan, vision, mission and objectives. Know how progress is tracked, measured and managed. What are the company’s Key Performance Indicators (KPI)?
Given your analysis, what role will the department play in meeting one or more of the organization’s goals?
Identifying Resource Needs
What knowledge, talent and skills will team members need to realize the value proposition? How many participants do you need to be successful? How do you select, develop and retain these people?
What support will be required to get the work done? How will you create a positive and collaborative culture? What systems and processes are required to allow people in the department to communicate and work together efficiently and effectively?
The best approach is to create job descriptions, skill profiles and work specifications for all department employees. Create definitive policies, procedures and standards for advancement. Invest in technologies that help team members excel.
Installing Metrics for Success
It is imperative to install solid analytics, systems for testing and for measuring performance right from the start. This is the only way to determine which processes work and which do not. It is also the most effective way to track the Return on Investment (ROI) the department will contribute to the achievement of the company’s long-term goals.
Designing a Process Map
The process map defines visually what and how a department will fulfill its value proposition. It indicates what needs to be measured to identify and assess performance improvements. The map documents each step that will be taken and when.
Preparing for Constant Change
Invest the time and effort required to document the processes that keep the department running efficiently. The documentation must emphasize the roles, objectives and tasks of each participant. Plan on employee transitions occurring no matter what systems you have in place.
How We Can Help You
Pacific Crest Group provides professional services that keep your business focused on your critical objectives. We provide strategic Accounting and Human Resource (HR) services created specifically to help you meet your goals. Through exemplary customer service, clearly defined policies and procedures as well as a forward looking perspective, we provide the outsourced solutions your business needs to grow. A PCG professional is happy to meet with you to discuss solutions for your unique requirements designed to maximize all of your business opportunities.
Marin Business Forum Event
Join us for a special event on “Understanding Personalities to Optimize the Use of Talent” on Thursday October 13, 2016 from 5 PM to 7 PM in the Community Room located at 300 Drake’s Landing Road in Greenbrae. The Community Room is adjacent to Jason’s Restaurant.
How to Develop a Departmental Business Plan
by Danielle Smyth
Published on 28 May 2019
Departmental business plans are essential for all department managers, as they help to guide the growth of the company. However, many managers, even established ones, have trouble nailing down the specifics of a departmental business plan. From reviewing the plan with your team to running it by company higher-ups to proper formatting, there is a lot that can be murky when it comes to creating this sort of document.
Departmental Business Plan Basics
A departmental business plan is a planning document focused on a specific department within a company. It should discuss your past metrics and discover any pain points that your team experienced. After you've focused on these problems, the document should focus on how you will address those problems going forward. If you feel like you need more staff, for example, you should work on how to justify that need to upper management.
Your departmental business plan should finish on a high note; specifically, you should focus on goals and what your team will do to meet them. Ideally, this plan would deal with how you will develop and groom your direct reports. In short, your departmental business plan is both a reflection and a game plan.
Departmental Business Plan Template
The following is a departmental business plan example, or business growth plan template, that could be applied to a variety of businesses.
[Department Name] Departmental Business Plan - [Date]
- Review of Annual Metrics.
- Annual Goals vs. Metric Comparison.
- Adjusted Annual Goals.
- Departmental Needs to Meet Goals.
- Individual Staff Metrics.
- Staff Development Plans.
- Raw Data for Reference.
Above you can see a generic template for a departmental business plan. This plan should be adjusted based upon your specific needs. Some departments won't need to discuss individual metrics because of their size, but they should focus on extremely high and extremely low performers. The focus on the outliers will allow your star staff to get recognition for their work while also providing you a dedicated PIP (performance improvement plan) to assist your lower-achieving employees.
Strategic Plan Templates
Strategic plan templates are adjustable by department, company and industry to be as useful as possible. Depending on your company’s needs, there may be other metrics that you should focus on, which would require adding to a traditional strategic plan template.
If you are new to your department, reviewing past strategy plans can give you a good sense for how a template should be updated. Some companies have pre-approved templates for strategic planning, so make sure that you ask your reporting manager before taking the time to make your template.
What Is a Business Growth Plan
Business growth plans focus on both your performance and the performance of competitors. The goal for a business growth plan is to find room for your business to grow while maintaining its current foothold in your industry. The significant difference between a business growth plan and a strategic plan is that the strategic plan focuses more on strategy and goal meeting. A growth plan should focus on growth goals, increasing visibility and offering you knowledge of competitor markets.

Benefits to Nonprofits and Startups
Organizations, particularly nonprofits and startups, may have a different workflow, structure, budget or even employees that work entirely remotely. Large corporations with branches throughout the country or even internationally might have very different needs from smaller companies or nonprofits. Having a departmental business plan saved in a central location allows all staff to access it and focus on the specific goals that are set out before them. Workflows should be easier for the entire team if it is specific to your company’s needs and all players are on the same page.
Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
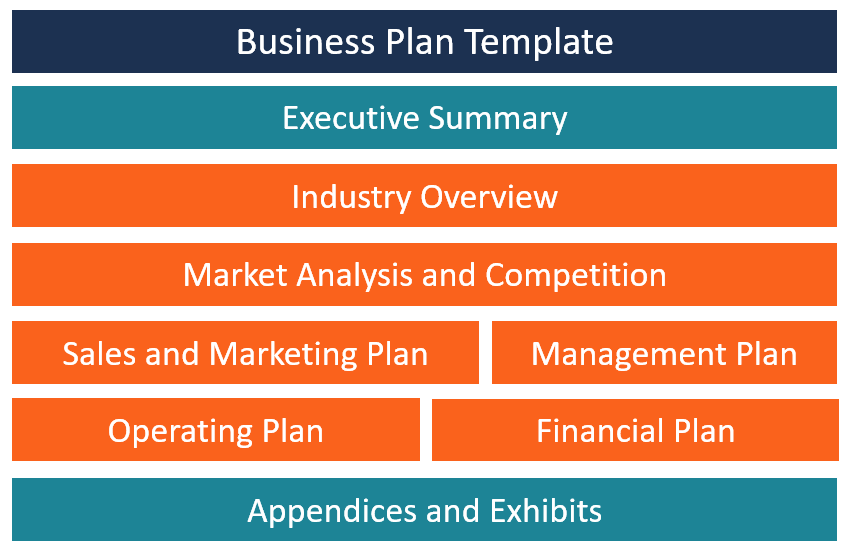
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many, or all, of the products featured on this page are from our advertising partners who compensate us when you take certain actions on our website or click to take an action on their website. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

LLC Formation
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.

- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![business plan for a new department [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management

How to create a CRM strategy: 6 steps (with examples)
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework
- The Grossman Group Difference
- Internal Communications
- Leadership Communication
- Change Management
- Organizational Culture Change
- Resource Center
- Heart First Giveaway
- Case Studies

100 Day Plan for Leaders New in Role (Examples + Template)

When I dropped my son off at school on his first day of kindergarten, he looked at me and said, “I can’t wait to not be new anymore.” Thinking about the many people changing roles and companies these days, I can’t help but wonder how many may be counting the days until they’re not new anymore, too.
No matter how many years of experience a person has – even the most senior of leaders – being the “newbie” is daunting for most and hard enough that many avoid taking the new job in the first place. Add to it the complexity of the workplace these days – exhausted teams, workforce shortages, supply chain and business disruption, the war for talent, and constantly shifting ways of working and connecting as teams and organizations – being a leader in a new role is even more challenging.
For those talented and brave souls venturing to new roles and opportunities, congratulations. Instead of a new coffee mug or new decoration for your Zoom background (or at least, in addition to it), give yourself the gift of preparedness so you make the most of your first months on the job and set yourself up for success.
Is a 100 Day Plan Necessary for Leaders New in Role?
In short, yes. As a newly appointed leader, it’s easy to fall into the trap of waiting for the dust to settle – for you to get comfortable in your role and get a lay of the land, for your employees and teams to get accustomed to having a new leader before you start making any plans. However, waiting to form your plan means you lose the opportunity to set the right tone from the start by being purposeful, organized, and action-oriented.
What is a 100 Day Plan for New Leaders?
A 100 Day Plan is an action plan to guide executive leaders through their first critical months in a new role – outlining strategies and tactics to identify and engage key stakeholders and to build relationships, understand the business, set goals, and gain traction quickly so you can set up a foundation for long-term success in an organization.
While a plan needs to be customized for each leader – and you can download a 100 Day Plan Template here to get started – our experience points to six critical strategies all leaders can deploy to ace their first 100 days regardless of industry or function.
What should a 100 Day Plan include?
While a 100 Day Plan for executive leaders in a new role can take on many forms and is as unique as the business challenges leaders face, there are some core components that the best plans have. Use this 100 Day Plan example framework as a guide:
- Situation Summary – Outline the current business landscape, strengths, opportunities and other important headlines that capture the context you’re stepping into as the leader in your role. This might include the state of engagement at your organization, cost pressures, how employees perceive you as the new leader and more. Take an employee-centric point of view by key audience segments and then try to understand the challenge they need to overcome in today’s environment. You may need to set up informational interviews with a few key colleagues to help confirm some of your assumptions and to highlight details that you wouldn’t yet know.
- Longer-term: What do you want people to say about you and the business 18 months from now and what are some of the big actions you might consider taking to make your vision a reality?
- Near-term: Where do you want to be 100 days in on the job? What impact do you want to have made and how does that line up with your longer-term goals? List your goals, ensuring there are business metrics and relationship goals.
- Evolve the vision and goals for the organization’s future (if needed)
- Retain top talent
- Know : What facts do they need from me? What new information can I provide them? Examples: Key milestones I’m setting, changes from how the role was previously defined and new priorities / expectations I’m establishing.
- Feel: What do I want to be top of mind when they walk away from meeting with me? What pain point are they currently experiencing that I might be able to begin alleviating? Example: Confidence in the path forward, comfort in their ability to talk to me.
- Do: Is there an action that you need them to take right now? Is there a behavior that you want to see them demonstrate going forward? Example: Share the information you’ve provided them with their team, commit to asking questions and keeping the lines of communication open and adopt a mindset that assumes good intent even when faced with challenges or times of change.
- Key Messages – Articulate what the main messages are that you want to convey as you get to know your various key stakeholders. These may be key themes that you know you want to highlight about your leadership style and vision for the role, high-level examples of how you view your function tying into broader company goals and strategies, or a list of commitments you are making to your staff and the actions you are asking them to take while you settle in.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Communication Plan – Make a plan for how you’ll purposefully reach your stakeholders and how you’ll communicate over time to accomplish your goals. When you consider your stakeholders, think about big “centers of gravity” so you can separate out how to allocate time and where you can have the greatest impact by investing time and energy. Also, consider what key relationships you need to build because they’re critical to establishing bridges and sponsorship across the organization. Look for communication channels that already exist so you can simply plug in without having to build infrastructure – don’t underestimate the value of informal conversations and small group huddles as a powerful vehicle while people are getting to know you.
- Quick Win Tactics – Identify opportunities to generate quick and meaningful wins that demonstrate progress toward your overall goals. It is easy for leaders to get caught up in the long game, focusing on the notable impact they aspire to make within a business, but it’s the small wins along the way that both give you something to celebrate and help your stakeholders appreciate the impact you are already making.
- Measures for Success – Consider how you’ll know when success is achieved. Identify the metrics and how you’ll monitor progress – remember, this is a 100 Day Plan, so the metrics should fit accordingly with that timeline. For example, a measure could be around moving sentiment – such as belief in the company, confidence and optimism in the future, and clarity around where we’re heading and why. Use the progress in your stakeholder engagement and communication plans to show momentum.
Want help getting started? Download our free 100 Day Plan Template .

100 Day Plan Example – Your 3 Month Action Plan
The following is a sample 100 Day Plan that shows how to quickly and strategically build out your approach. You can simply customize this list, or you can use the list for inspiration to develop a more detailed plan in alignment with your or your new organization’s preferred format.
Before you get started:
- Continue to learn as much as you can about the organization and your team
- Have pre-meetings with identified stakeholders to discuss the game plan and listen for key expectations, core issues and opportunities
- Begin to map key stakeholders
- Get briefed on the employee, culture and communication landscape (set up an initial meeting with the Communications team, if possible)
- Consider having an informal visit with your new team over breakfast or lunch
- Prepare your elevator speech and/or your initial message platform
- Create a list for your Listening plans, outlining who all you need to meet with to hear perspectives, observe and tap for insights; set up meetings with key stakeholders (including senior leaders, peers, direct reports and skip-level reports/teams) ; if you don’t yet know their names, list their roles to prompt you to then find out the right point of contact
- Begin your listening “tour;” reinforce that you’re hearing what people are saying and make a point to circle back with anyone who asked a question that you couldn’t answer in the moment
- Connect with Communications and HR partners to understand the company culture and how communication happens
- Set the stage with your team and stakeholders with what to expect these first days and weeks, including what to continue to focus on and do
- Identify key contributors and any key people who are flight risks on your team and engage with them, including conducting stay interviews
- Actively participate in company onboarding so you experience what others also experience
- Continue listening tour
- Work with team members to codify strategy; involve people representing a cross-section of the organization whenever possible
- Identify communication channels you’ll regularly use to share updates on what you’re hearing, doing and thinking in advance of the formal launch of your communications plan
- Finalize your strategy and plan and socialize with key stakeholders for alignment
- Develop a communication plan for playback of listening and to share strategy going forward
- Refresh key messages and leader platform
- Implement communication plan
- Continue a steady cadence of employee listening, and update/amend the plan and messages in real-time based on new, viable insights that come from listening and any key changes within the business or your work environment
6 Strategies to Learn and Lead in Your First 100 Days
From our years of experience working with senior leaders as they navigate being new in their role while leading teams and organizations, we’ve compiled a list of six strategies that will help you learn while leading yourself and others with confidence and credibility.
1. Study up
Learn everything there is about the team or company you’re joining, but also spend the time where it counts so you don’t get caught up in analysis paralysis. Have a game plan leading up to your start date for what you need to know to hit the ground running, what you can learn along the way and how you want to get immersed. There’s plenty you can read online, but there’s so much more you can learn from inside the organization, especially by speaking with those who have the pulse.
Get to know the Communications and HR/People/Culture teams early on because they likely have a wealth of information about employee mindsets, hot-button issues and the best ways to reach and interact with employees. Many Communications teams we work with would be happy to help you know how information flows in the organization and what channels are best for leaders like you to get information and communicate effectively with your teams.
When an incoming senior executive was getting ready to join the organization, we partnered with the Communications team to develop an executive briefing book on the state of the workforce and how communication happens inside the company. There was a briefing meeting, great discussion and an opportunity for the leader to get to know the Communications team as they discussed shared needs and expectations so the leader could get connected and communicate effectively with key audiences. All of this led to a better, more actionable 100 Day Plan.
2. Figure out where to start
The first months are an exercise in drinking from a fire hose. Prioritizing is essential, but it can be hard to know where to start. Many leaders we’ve worked with have found it helpful to have a “working session.” In those sessions, we work with the leader to sort through critical business and communication demands and needs and then map their 100 Day Plan – with a particular eye on the next 30 days. These sessions give the leader a chance to step out of the day-to-day, assess the situation, determine priorities and frame a practical action plan for how to spend their time – always with business outcomes and stakeholder needs in mind. This session also sets the foundation for the key messages to convey and what to communicate and when.
3. Hit the road
Get out of your office . Whether you’re rounding, doing listening tours, road shows or coffees, get in front of as many people as you can so you get to know people across levels and roles in the organization. There’s nothing like being in person to ask questions, surface ideas and stories, read the room, feel the vibe and get a sense of what’s being said (and not said). If you can’t be in person, do your best to hit the road virtually with virtual office visits, coffees and the like. Make a commitment to visit those teams and sites as soon as possible when you can. This one is easy to put on the back burner, so make a point to schedule a set number of meet-and-greets per week to hold yourself accountable.
Asking questions during your onsite or virtual meetings is an important part of your listening. The best leaders lead by listening . They seek to understand, not to judge, and make this a regular part of how they lead. Find out why things are the way they are. Get to know people’s stories. Ask them what gets them excited to come to work, and what pain points or barriers they see and experience that get in the way. Make it about them, while also giving them a window into who you are.
As important as listening is, that doesn’t mean you can’t also share your story. As a leader, people need to know you first before they’ll get on board with your vision or strategy. Help them know who you are as a person and as a leader – what gets you excited, why you want to be a part of the team, how people who know you best describe you, what principles you live by and what brings you joy outside of work. All these things give others a chance to know you, how you tick and how you think about the world, which gives them a chance to have a human connection with you and to be able to help you deliver on your vision.
Another key part of sharing your story is being ready with your elevator speech and core messages. The elevator speech is the main message that you want to convey succinctly to your key stakeholders and audiences. Have your story ready and use it regularly from day one. You may customize this a bit for your various audiences and over time, but there’s power in being consistent overall.
Determining your Elevator Speech as a Leader New in Role
Keep it short and make it conversational. Speak to what your role is and how you’ve been here before in your previous role. Write it out so you’re thoughtful about what you want to convey. This is how many people will first remember you. For example:
Example Elevator Speech 1:
I’ve seen the power of transforming the employee experience and am excited to lead our team as we make it happen here together.
- This says you know employee experience and that you’ve been here before, which speaks to credibility and confidence in the role and where you’re going to take the team.
- This shows that you’re bringing energy and enthusiasm, and that you want to be part of the team because you view yourselves on a common journey aimed at getting results. This is motivating, speaks to a shared end game, and reinforces camaraderie and collaboration.
Example Elevator Speech 2:
Having a child with medical issues, I have immense appreciation for how much work goes into making great healthcare possible . I’m grateful to be part of this team and to partner together with you to improve access to great care for those we serve.
- Self discloses something personal and relatable, and establishes that this is a field of work that the person respects and appreciates.
- Sharing gratitude signals a person with character, humility and heart.
- Speaks to leading the team as colleagues, not subordinates, and that we’re in this together.
- Signals a vision of what’s possible that you want the team to work toward.
For senior-most executives, a best practice is having your own leadership message platform. Much like a “stump speech” for politicians, this is a set of key messages and stories to help you tell your story in a way that connects to your audiences and drives line of sight and engagement. It’s a useful tool for driving message consistency across communications and channels, as well as for saving time preparing for meetings and communications (for both the leader and the communicators who support them).
When leaders are new in role, the method of developing this platform is especially powerful in helping leaders think purposefully about how to articulate their story, their vision and their approach to shaping the strategy.
4. Have a stakeholder engagement and communication plan
The complement to your core messages is an engagement and communication plan. Whether you’re preparing your own, or have the support of your Communications team, this is a must so that you are intentional in your first 100 days (and beyond) about which stakeholders and audiences you are reaching, the best approach to do so and the outcome you want to see.
Take a few minutes to follow this 5-step method to plan your communication:
- OUTCOME: What’s the business goal for your engagement and outreach? As a leader new in role, your business goal may be to keep people focused on the current strategy, while you listen and determine the path forward. Or perhaps you need to stabilize the business and/or team. Whatever the situation, pinpoint what your business outcome is for the first 100 days.
- AUDIENCE: Who are the key audiences you need to engage and where are they coming from? Different audiences will have different perceptions and information needs – and the more you know about each, the more effective you’ll be at connecting with them and ultimately moving them to action. If you discover that you don’t know much about some audiences, it’s a signal you need to go and get to know them more.
- Why (rationale and context)
- What (what’s happening and what to focus on for now)
- When (a sense of timing for what’s happening and what’s to come)
- How (how you’re approaching the coming weeks, how they can help, how you’ll use their insights to develop your action plan)
- Who (who you are, what brings you here, what’s important to you, what they can expect from you and what you expect from them)
- WIIFM (what’s in it for “me” – in other words, what all of this means for them)
- METHOD: What’s the best way to reach them? Map your plan for how to connect with people in ways that foster conversation and the ability to share information freely and candidly. In-person is ideal. Consider where you need one-on-one conversations vs. where small group sessions or larger sessions – such as town halls – can be helpful. Maybe there are feedback channels you want to use or initiate. Consider the mix of methods.
- MEASURE: How do you know if the plan is working? You can learn a lot about what’s working based on the nature of the conversations you’re having, whether you sense people are sharing their views openly and the questions you’re getting. Engage your direct reports and Communications team to share insights and feedback on what they’re hearing. Consider whether informal or formal pulse checks would be useful to get a sense of things as well.
TIP: Having a stakeholder engagement and communication plan is a critical tool beyond your first 100 days, too. The best leaders are always purposeful about how they stay connected with stakeholders and audiences and how they’re showing up regularly through communications.

5. Resist the urge to make change right away
Most leaders are hired to be change agents, so it’s counterintuitive to say don’t come in and change things right away. Even if you think you know what needs to change, try to avoid making big changes in those first 100 days as it can usually cause more harm than help.
Typically, leaders use the first 100 days to listen and formulate an informed strategy, gain key stakeholder buy-in, and then they roll out the strategy in a thoughtful way, so the right audiences are reached at the right time and with the right message. To the greatest extent possible, let others be part of the strategy shaping so it’s the collective plan, not “your” plan alone. WATCH OUT: Without adequate upfront listening in the first 100 days, there’s an assumption that the leader may be uninterested, uninformed or misaligned with the company’s heritage, culture and people. Any which way, it’s a bad look, and it hinders your and the team’s ability to get things done if you come out of the gate with your mind made up about what needs to happen.
There are a few exceptions when making changes in the first 100 days could be the right option. Perhaps there are things you’ve heard and seen that are clearly broken and getting in the way of the employee experience that could be fixed right away and that signal your focus on the people. Or, perhaps something is happening that’s putting the organization at major risk and cannot wait for action. In those cases, immediate change may be the answer to stop the bleeding and/or to signal important and meaningful change right away.
Engage key stakeholders who have institutional perspective in the planning so you’re aware of blind spots or bright spots and leverage your Communications team so what’s communicated is done in the right way and casts a positive light on your approach and intention.
6. Be yourself
All eyes are on you as the new manager or leader, especially those first 100 days, and people are searching for meaning in everything you do (or don’t do). Consider your leadership style and what has served you well and will continue to serve you. Bring that forward with intentionality in how you show up. Check the old habits or ways of working that may not have been as effective at the door. Communicate with purpose.
Lead with heart – knowing that the best leaders today are those who bring authenticity, empathy and humanity to the workplace, so teams can be their best selves and deliver on their mission and goals in the best way.
Empathy is not a “soft” skill
Leaders who practice empathy have more engaged and higher-performing teams, as well as more profitable businesses overall. (Catalyst research study: “The Power of Empathy in Times of Crisis and Beyond,” Sept 2021)
- 79% of US workers agree empathetic leadership decreases employee turnover. (EY Consulting survey, Oct. 2021)
- 85% of employees report that empathetic leadership in the workplace increases productivity. (EY Consulting survey, Oct. 2021)
The Bottom Line
Being an executive leader in a new role comes with big responsibility and a lot of hard work. With the right preparation and thoughtful approach to how you lead and communicate in your first 100 days – and year – you can make your first weeks and months ones that recharge, inspire, motivate and chart the path for great work together to accomplish your goals and strengthen your company’s future.
Don’t feel you need to do this important work on your own. Let those with expertise in these areas partner with you so you can elevate your presence, focus your time where you can have the greatest impact on the business, and achieve the results you want faster and better. If you’d like to discuss ways we can help you get quick wins and plan for long-term impact, contact us today.
—Kate Bushnell
Set the right tone in your new role from the start by being purposeful, organized, and action-oriented with the help of this 100 Day Plan Template. Click the image below to download the 100 Day Plan Template today!

Comments on this post
Other posts you might be interested in, 4 ways to differentiate communication from information, reasons why your business strategy activation fails, communicating your strategic plan to employees, subscribe to the leadercommunicator blog.
Get new blog posts delivered directly to your inbox.

Check this posts
Future entrepreneurs should use cds to raise capital, what entrepreneurs saving for retirement must know about cfds, safeguarding your brand with online image moderation, how much does it cost to hire a marketing consultant, how to make your trucking company more profitable, 8 common mistakes to avoid when launching your startup.
- Human Resources
- Investments
Build A New Business Department The Easy Way
When a new startup business is created, it often relies on a skeleton staff. This is usually due to financial restrictions. Even though the entrepreneur might want to employ more employees to help them get their new business up and running, there’s a likely chance that they don’t have the money to do so. So, they just employ the bare-minimum team that they need in order to take care of the current workload. Once the business starts to make a bit more money, though, it is time to start thinking about expanding the company and taking things further.
Once you do start to hire more employees, you will no doubt hire people who are a lot more focused in their work. In the early days of your business, people will have helped out in various different aspects of the company. But now you have more staff, you can afford to hire dedicated employees for the likes of your finance, marketing, and HR. Of course, this means that you will need to start establishing a few departments in your company. This will bring some structure and order to your business, which can help it stay efficient and productive.
You might think that establishing a new department within your business would be easy. After all, you just need to give it a name and hire some employees to take care of it, right? Well, unfortunately, it isn’t quite that easy. In fact, it can be very easy to get it wrong, and this could make it difficult to set the necessary structure in place to ensure that the department is a seamless addition to your company. Are you starting to wonder how you can go about creating a new business department successfully? If so, read on. You just need to follow these next few tips.
Be Clear About Why You Need This New Department
First of all, you need to be 100% sure that you do in fact need this new department in your company in its current state. If you think that you would be able to hold off establishing one for a certain business aspect for a few more months, then it is usually best to do so. That’s because setting up a brand-new department can be extremely expensive. If you end up creating one prematurely, then it could end up becoming a huge strain on your business’s finances. That’s mainly because you will end up taking on new hires before you can really afford them. So, before you do decide to create a new department, it’s really worth taking the time to research your business’s current situation and making sure that it is at the right point to take on one more department.
Set Up A Department Action Plan
Next, once you’ve decided that setting up a department is the best course of action for you and your company, you need to create a plan that can help you do just that. This plan should include a few steps detailing how you will establish the department, including information such as how many employees you will need for it. Other things that should be included in the plan need to be things like the scope of work that it will take care of. Ideally, you should write down this plan and publish it so that all of your current employees can see it and are made aware of what is going on in their place of employment. You might also need to share this plan with your bank manager and investors if you will need some more money to help fund this new department.
Find The Space For It
Are you sure that you have the physical space for a new department? This is often one point that many entrepreneurs forget to consider. You will be hiring new employees to help populate this department, and they will need to have space in your office. Hopefully, there will be some space for a few extra desks next to each other in your current work environment. If there isn’t any extra room, you might have to consider moving into a larger office . In fact, when they start to create different departments, some entrepreneurs like to move into large offices that offer them plenty of individual rooms. That way, each department can have its own room for its employees so that they can easily work and collaborate together.
How to Sell an eCommerce Website for the Highest Possible Price?
10 out-of-office autoresponder email messages, amazon business vs. amazon prime: what's the difference between the two, digital marketing trends you must not miss out on in 2021.
Consider Who Will Be Right For The Team
Of course, you might not need to hire anyone new to join this new department – you might have enough employees currently working for you that can be moved into it. This might take some company restructuring, but it could be worth it as it will be a lot cheaper than hiring some new staff. If you are taking this route, you need to consider your current employees and figure out who will be the best fit for the new department. This will largely be based on their skill set and previous experience. You should also take this into consideration when you are hiring new employees too as everyone who works in the new department needs to be a good fit for it.
Create A Specific Budget for This New Department
Once you start adding departments to your business, you will need to start creating specific budgets for each of them. These shouldn’t replace your overall company budget , though. The department-specific budgets will give you numbers and figures that can be used in the larger one. These department budgets will give each manager the chance to see exactly how much money they have to use on the various items and appliances that they will need to buy throughout the course of the year. They also keep spending on track and ensure that no department manager ever overspends on accident.
Build Its Own IT Network
You also need to take some IT and tech considerations into account when setting up a brand new department in your company. There’s a good chance that the department will benefit from its own IT network or setup. You can get a reliable company like Down To Earth Technology to help you with this. It’s also a good idea to consider whether the department will need any specific software of computer programs. These are often worth it as they can help automate processes, which will help to increase the overall efficiency and productivity of the department.
Create Some Goals and Targets for The Department
While you are still working on building the department and incorporating it into the company, it’s a good idea to think about a few goals and targets for it. These are things that the employees in the department can work towards. It’s a good idea to put some short-term and long-term goals in place. The short-term ones can be achieved over the first year of the department while the longer ones might take a few years to achieve. Working towards these targets will give all of the employees something to work towards, which can help them feel highly motivated at all times.
OK The Department Plan With All Managers
Before you do start setting up a new department, you will need to ok your plan with each of your managers. Even though they may not be working within the new department, there’s a good chance that the establishment of a new one could impact on theirs. So, you will need to make sure that the new department won’t lead to you neglecting the needs and wants of other necessary departments within your company. Plus, your managers will be the main people who liaise with the new head of the department. Because of this, it’s a good idea to set up a management-wide meeting that they can all attend. This will give them the chance to voice any concerns and uncertainties that they may have.
Make Sure All Stakeholders and Investors Are Onboard with The Idea
It’s not just your managers who you will need to run your new department idea by. You also need to let all of your stakeholders and investors know these plans as well. After all, they have a financial interest in your business so will be intrigued to know all about the running of it. Not only that, though, but if they are unhappy with the plans for a new department, then they could put their foot down and prevent you from setting it up in the first place. So, when you meet with them make sure that you are ready to pitch to them and that you are able to tell them multiple benefits of creating a brand-new department. I’m sure that you will be able to win them over if they seem to be a bit cautious at first!
As you can see then, setting up a new department in your company will be no easy feat. But with a little dedication and elbow grease, it should go off without a hitch.
About author
Catalyst For Business is award winning blog (previously owned by Adobe) is geared to cover technology related stories with innovative techniques. We welcome experts to join and contribute to CFB.
Buffalo, New York, USA [email protected]
Forgot your password?
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive mail with link to set new password.
Back to login
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Simple Business Plan Template (2024)

Updated: May 4, 2024, 4:37pm

Table of Contents
Why business plans are vital, get your free simple business plan template, how to write an effective business plan in 6 steps, frequently asked questions.
While taking many forms and serving many purposes, they all have one thing in common: business plans help you establish your goals and define the means for achieving them. Our simple business plan template covers everything you need to consider when launching a side gig, solo operation or small business. By following this step-by-step process, you might even uncover a few alternate routes to success.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Whether you’re a first-time solopreneur or a seasoned business owner, the planning process challenges you to examine the costs and tasks involved in bringing a product or service to market. The process can also help you spot new income opportunities and hone in on the most profitable business models.
Though vital, business planning doesn’t have to be a chore. Business plans for lean startups and solopreneurs can simply outline the business concept, sales proposition, target customers and sketch out a plan of action to bring the product or service to market. However, if you’re seeking startup funding or partnership opportunities, you’ll need a write a business plan that details market research, operating costs and revenue forecasting. Whichever startup category you fall into, if you’re at square one, our simple business plan template will point you down the right path.
Copy our free simple business plan template so you can fill in the blanks as we explore each element of your business plan. Need help getting your ideas flowing? You’ll also find several startup scenario examples below.
Download free template as .docx
Whether you need a quick-launch overview or an in-depth plan for investors, any business plan should cover the six key elements outlined in our free template and explained below. The main difference in starting a small business versus an investor-funded business is the market research and operational and financial details needed to support the concept.
1. Your Mission or Vision
Start by declaring a “dream statement” for your business. You can call this your executive summary, vision statement or mission. Whatever the name, the first part of your business plan summarizes your idea by answering five questions. Keep it brief, such as an elevator pitch. You’ll expand these answers in the following sections of the simple business plan template.
- What does your business do? Are you selling products, services, information or a combination?
- Where does this happen? Will you conduct business online, in-store, via mobile means or in a specific location or environment?
- Who does your business benefit? Who is your target market and ideal customer for your concept?
- Why would potential customers care? What would make your ideal customers take notice of your business?
- How do your products and/or services outshine the competition? What would make your ideal customers choose you over a competitor?
These answers come easily if you have a solid concept for your business, but don’t worry if you get stuck. Use the rest of your plan template to brainstorm ideas and tactics. You’ll quickly find these answers and possibly new directions as you explore your ideas and options.
2. Offer and Value Proposition
This is where you detail your offer, such as selling products, providing services or both, and why anyone would care. That’s the value proposition. Specifically, you’ll expand on your answers to the first and fourth bullets from your mission/vision.
As you complete this section, you might find that exploring value propositions uncovers marketable business opportunities that you hadn’t yet considered. So spend some time brainstorming the possibilities in this section.
For example, a cottage baker startup specializing in gluten-free or keto-friendly products might be a value proposition that certain audiences care deeply about. Plus, you could expand on that value proposition by offering wedding and other special-occasion cakes that incorporate gluten-free, keto-friendly and traditional cake elements that all guests can enjoy.

3. Audience and Ideal Customer
Here is where you explore bullet point number three, who your business will benefit. Identifying your ideal customer and exploring a broader audience for your goods or services is essential in defining your sales and marketing strategies, plus it helps fine-tune what you offer.
There are many ways to research potential audiences, but a shortcut is to simply identify a problem that people have that your product or service can solve. If you start from the position of being a problem solver, it’s easy to define your audience and describe the wants and needs of your ideal customer for marketing efforts.
Using the cottage baker startup example, a problem people might have is finding fresh-baked gluten-free or keto-friendly sweets. Examining the wants and needs of these people might reveal a target audience that is health-conscious or possibly dealing with health issues and willing to spend more for hard-to-find items.
However, it’s essential to have a customer base that can support your business. You can be too specialized. For example, our baker startup can attract a broader audience and boost revenue by offering a wider selection of traditional baked goods alongside its gluten-free and keto-focused specialties.
4. Revenue Streams, Sales Channels and Marketing
Thanks to our internet-driven economy, startups have many revenue opportunities and can connect with target audiences through various channels. Revenue streams and sales channels also serve as marketing vehicles, so you can cover all three in this section.
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams are the many ways you can make money in your business. In your plan template, list how you’ll make money upon launch, plus include ideas for future expansion. The income possibilities just might surprise you.
For example, our cottage baker startup might consider these revenue streams:
- Product sales : Online, pop-up shops , wholesale and (future) in-store sales
- Affiliate income : Monetize blog and social media posts with affiliate links
- Advertising income : Reserve website space for advertising
- E-book sales : (future) Publish recipe e-books targeting gluten-free and keto-friendly dessert niches
- Video income : (future) Monetize a YouTube channel featuring how-to videos for the gluten-free and keto-friendly dessert niches
- Webinars and online classes : (future) Monetize coaching-style webinars and online classes covering specialty baking tips and techniques
- Members-only content : (future) Monetize a members-only section of the website for specialty content to complement webinars and online classes
- Franchise : (future) Monetize a specialty cottage bakery concept and sell to franchise entrepreneurs
Sales Channels
Sales channels put your revenue streams into action. This section also answers the “where will this happen” question in the second bullet of your vision.
The product sales channels for our cottage bakery example can include:
- Mobile point-of-sale (POS) : A mobile platform such as Shopify or Square POS for managing in-person sales at local farmers’ markets, fairs and festivals
- E-commerce platform : An online store such as Shopify, Square or WooCommerce for online retail sales and wholesale sales orders
- Social media channels : Facebook, Instagram and Pinterest shoppable posts and pins for online sales via social media channels
- Brick-and-mortar location : For in-store sales , once the business has grown to a point that it can support a physical location
Channels that support other income streams might include:
- Affiliate income : Blog section on the e-commerce website and affiliate partner accounts
- Advertising income : Reserved advertising spaces on the e-commerce website
- E-book sales : Amazon e-book sales via Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing
- Video income : YouTube channel with ad monetization
- Webinars and online classes : Online class and webinar platforms that support member accounts, recordings and playback
- Members-only content : Password-protected website content using membership apps such as MemberPress
Nowadays, the line between marketing and sales channels is blurred. Social media outlets, e-books, websites, blogs and videos serve as both marketing tools and income opportunities. Since most are free and those with advertising options are extremely economical, these are ideal marketing outlets for lean startups.
However, many businesses still find value in traditional advertising such as local radio, television, direct mail, newspapers and magazines. You can include these advertising costs in your simple business plan template to help build a marketing plan and budget.

5. Structure, Suppliers and Operations
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and responsibilities, supplier logistics and day-to-day operations. Also, include any certifications or permits needed to launch your enterprise in this section.
Our cottage baker example might use a structure and startup plan such as this:
- Business structure : Sole proprietorship with a “doing business as” (DBA) .
- Permits and certifications : County-issued food handling permit and state cottage food certification for home-based food production. Option, check into certified commercial kitchen rentals.
- Roles and responsibilities : Solopreneur, all roles and responsibilities with the owner.
- Supply chain : Bulk ingredients and food packaging via Sam’s Club, Costco, Amazon Prime with annual membership costs. Uline for shipping supplies; no membership needed.
- Day-to-day operations : Source ingredients and bake three days per week to fulfill local and online orders. Reserve time for specialty sales, wholesale partner orders and market events as needed. Ship online orders on alternating days. Update website and create marketing and affiliate blog posts on non-shipping days.
Start A Limited Liability Company Online Today with ZenBusiness
Click to get started.
6. Financial Forecasts
Your final task is to list forecasted business startup and ongoing costs and profit projections in your simple business plan template. Thanks to free business tools such as Square and free marketing on social media, lean startups can launch with few upfront costs. In many cases, cost of goods, shipping and packaging, business permits and printing for business cards are your only out-of-pocket expenses.
Cost Forecast
Our cottage baker’s forecasted lean startup costs might include:
| Business Need | Startup Cost | Ongoing Cost | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
Gross Profit Projections
This helps you determine the retail prices and sales volume required to keep your business running and, hopefully, earn income for yourself. Use product research to spot target retail prices for your goods, then subtract your cost of goods, such as hourly rate, raw goods and supplier costs. The total amount is your gross profit per item or service.
Here are some examples of projected gross profits for our cottage baker:
| Product | Retail Price | (Cost) | Gross Profit |
|---|---|---|---|
Bottom Line
Putting careful thought and detail in a business plan is always beneficial, but don’t get so bogged down in planning that you never hit the start button to launch your business . Also, remember that business plans aren’t set in stone. Markets, audiences and technologies change, and so will your goals and means of achieving them. Think of your business plan as a living document and regularly revisit, expand and restructure it as market opportunities and business growth demand.
Is there a template for a business plan?
You can copy our free business plan template and fill in the blanks or customize it in Google Docs, Microsoft Word or another word processing app. This free business plan template includes the six key elements that any entrepreneur needs to consider when launching a new business.
What does a simple business plan include?
A simple business plan is a one- to two-page overview covering six key elements that any budding entrepreneur needs to consider when launching a startup. These include your vision or mission, product or service offering, target audience, revenue streams and sales channels, structure and operations, and financial forecasts.
How can I create a free business plan template?
Start with our free business plan template that covers the six essential elements of a startup. Once downloaded, you can edit this document in Google Docs or another word processing app and add new sections or subsections to your plan template to meet your specific business plan needs.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best LLC Services
- Best Registered Agent Services
- Best Trademark Registration Services
- Top LegalZoom Competitors
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Plan Software
- ZenBusiness Review
- LegalZoom LLC Review
- Northwest Registered Agent Review
- Rocket Lawyer Review
- Inc. Authority Review
- Rocket Lawyer vs. LegalZoom
- Bizee Review (Formerly Incfile)
- Swyft Filings Review
- Harbor Compliance Review
- Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC
- LLC vs. Corporation
- LLC vs. S Corp
- LLP vs. LLC
- DBA vs. LLC
- LegalZoom vs. Incfile
- LegalZoom vs. ZenBusiness
- LegalZoom vs. Rocket Lawyer
- ZenBusiness vs. Incfile
- How To Start A Business
- How to Set Up an LLC
- How to Get a Business License
- LLC Operating Agreement Template
- 501(c)(3) Application Guide
- What is a Business License?
- What is an LLC?
- What is an S Corp?
- What is a C Corp?
- What is a DBA?
- What is a Sole Proprietorship?
- What is a Registered Agent?
- How to Dissolve an LLC
- How to File a DBA
- What Are Articles Of Incorporation?
- Types Of Business Ownership
Next Up In Company Formation
- Best Online Legal Services
- How To Write A Business Plan
- Member-Managed LLC Vs. Manager-Managed LLC
- Starting An S-Corp
- LLC Vs. C-Corp
- How Much Does It Cost To Start An LLC?

Best West Virginia Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Best Vermont Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Rhode Island Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Wisconsin Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best South Dakota Registered Agent Services Of 2024

B2B Marketing In 2024: The Ultimate Guide
Krista Fabregas is a seasoned eCommerce and online content pro sharing more than 20 years of hands-on know-how with those looking to launch and grow tech-forward businesses. Her expertise includes eCommerce startups and growth, SMB operations and logistics, website platforms, payment systems, side-gig and affiliate income, and multichannel marketing. Krista holds a bachelor's degree in English from The University of Texas at Austin and held senior positions at NASA, a Fortune 100 company, and several online startups.
TechRepublic
Account information.

Share with Your Friends
4 lessons on how to develop a new business department
Your email has been sent
As companies grow and develop, so do the departments needed to facilitate different functions. IT, quality assurance, training, human resources, and marketing are all examples of this. Creating a new department is an exhilarating experience for many managers because it’s an opportunity to develop something out of nothing, and there is enormous potential for creativity, recognition, and promotion.There are managers, though, who refuse these department innovation assignments, preferring to stay in roles that are already established in the company because creating a new department can be risky. If it doesn’t achieve recognition and acceptance as quickly as stakeholders expect it to, those managers could lose their job.
However, if you are a manager with an entrepreneurial bent and you want to innovate a new department, there are several best practices from business startups that you can take with you as you develop a new business union.
1. Understand who your stakeholders and investors are and what they expect
A company starts a new department for a reason–there is a perceived need for the new department, and that need has reached the point where there is resolve to create it and fund it. If you are the one heading up the new department, you should make it a point to understand who your stakeholders and investors are and what their expectations are. It will be your job to meet or exceed those expectations.
2. Recruit strong people
You will beat the drums for your new department as it develops a reputation and a place within the organization. You can’t do this if you are also doing all of the daily work. This is why it is important to recruit strong people into your organization and to develop an excellent working team.
3. Understand the company’s pain points
If a company wants to establish a separate quality assurance department, there is probably a reason for it. Perhaps the company has been experiencing product or process failures. If a separate IT department is being called for when IT used to be a function within finance, it might be because the tasks of technical IT and daily IT security have outgrown the resources and skillsets of the finance department. If marketing is the new department being called for, it might be because sales has realized that it only wants to sell–not chart demographics, develop strategic plans, and organize promotions and campaigns. The sooner you get a handle on what the company’s pain points are, the sooner you’ll know where the new department can produce both value and pain relief.
4. Focus on developing a brand
A new department, like a new company, must develop an identity and also deliver value that its customers want. It is up to the new department’s manager to develop this departmental identity and to create the value that the department can bring to the other departments within the company. Once others within the company see what the new department can deliver and what it is all about, the department can begin to root itself into the corporate fabric and assume its place among the other company departments.
There are many similarities between creating a new department within a company and launching a startup. As a manager of a new business entity, you have to cultivate trust in your constituents, develop a brand and an identity for your organization, and build credibility. Value is created when you continuously demonstrate that you can eliminate pain points and move the company forward. At the beginning of the process, promoting the new department–as well as developing it–will be primary functions. If you can recruit strong performers and build a cohesive team, the job will be that much easier.
Subscribe to the Executive Briefing Newsletter
Discover the secrets to IT leadership success with these tips on project management, budgets, and dealing with day-to-day challenges. Delivered Tuesdays and Thursdays
- Money talks: Why all managers need to understand their company's financials
- IT security spending: It's time to rethink our priorities
- What CXOs can learn about consistency from fast food chains
- IT budgeting: The smart person's guide
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.
Three Steps To Create A New Department for your Growing Business
When your business is growing, it demands more of you. It requires much of your time, energy, and ideas. You need to be quick to decide and to adjust especially when your business is rapidly expanding .
As expansion of your business comes to a head, the company will require a higher level of organization in order to function efficiently.
When only you and maybe a few workers constitute a business, the requirements are minimal. But say you want to diversify services or expand operations, things need to pick up in a significant way.
This is where you want to start thinking about adding departments to your business. This way, you can streamline production by compartmentalizing all tasks, and running your business as sum of all its operations.
It may seem easy to just create a department and let it run on its own. However, It requires tons of planning to ensure everything falls into place.
To help you out, here are the basic steps to effectively expand a business with the introduction of new departments.
Analyze the path of the company
When thinking about planning and strategizing , it’s critical to view pre-execution steps with the same importance as the implementation phase. As the saying goes, “if your fail to plan, you plan to fail.”
In other words, you need to consider where your company is going.
In the beginning, you may have just wanted to stay afloat, but taking that next step requires you to set a course. You need to sit down and contemplate, whether by yourself or with your core staff, to determine your overall business goals.
It’s also important to know where you are right now. Let’s call it your ‘Point A.’ This serves as the starting point from where you can move forward your business goals. In the same way as knowing your end goal is essential, you also need to know where you are coming from in order to reach your Point B, Point C, and so forth.
During your planning session , realize your current situation and check for alignment with your company’s original mission and vision. As you strategize on which department needs to be established, you’ll develop a better understanding of all the requirements that need to be addressed.
You also need to understand how your company appears from an outside perspective. This can be done by getting feedback from clients, from taking a look at your online reputation through Google search and evaluating your online presence, and through evaluation by your employees.
When you see how the company is viewed in every way, you can now decide what departments are necessary to be created.
Plan how to execute the introduction of new departments
Once you decide which department or departments to create, it’s time to get the ball rolling. This is where you need to execute what you have envisioned and start implementing guidelines for the new structure of your overall business system.
This is where it’s important to ask key questions. You have to decide who will run this department, whether you need a larger staff, and how this all fits into existing infrastructure.
For example, say you want to expand your sales department. Up to this point, you have been exceeding your expectations in terms of sales per month. Things snowball and there are more opportunities than you can reasonably handle with the existing structure.
If you’re hiring new people, you need to decide whether you’re going to post jobs online and where. You can try the large job post aggregators like Indeed or Monster, or you can rely on local sites. For example, if you’re in New York, it might be a good idea to post on a site that caters specifically to jobs in New York . You can also lean on employee referrals or take a look to social media sites like Linkedin for recruitment.
Also, establishing departments in the company could happen one department at a time or multiple departments all at once.
The former allows an option to test out the growth and follow through accordingly. The latter takes on more duties all at the same time, which is what happens when a business expands rapidly.
Regardless, the infrastructure needs to be there. You need to know who is handling what. For this, it’s best to put one qualified person in charge of the department and allow them to grow it as needed.
This person can report directly to the business owner, and can be held accountable for deciding what is and isn’t needed at any time. This process can usually happen slowly.
But sometimes you don’t have the choice to move slowly. If things aren’t coming together immediately, that is okay. It may take time for everything to fall into place.
Constantly review the progression
A new system needs guidance.
In order for you to make sure that the departments are in line with the company mission and vision, you need to establish a set of Key Performance Indicators (KPI) for every department.
This allows you to see if one department is working effectively or not. It is like a grading system for the business. If one fails, you need to see why it failed and then do corrective actions. If it passes, you recognize the workers and see that they continue producing.
It’s also important to make sure your staff is staying aligned with the duties as they were laid out. At first, it may be difficult to them because everything might seem new or different. However, if everyone cooperates and works according to the set guidelines, things should run smoothly.
It’s important to empower whoever you have running a new department. Ask if they have other ideas on how to help the company succeed.
You can also ask your clients or customers if they have been experiencing more effective service with the way things are now. This feedback allows you to grow more and learn more as things continue to grow for your company.

High Speed Internet very fast moving and changing world

Management Across Industries: Is It All The Same?

Centrinity Blog Provides Information and Tips about Business and Tech

Build plans, manage results, & achieve more
Learn about the AchieveIt Difference vs other similar tools
We're more than just a software, we're a true partner
- Strategic Planning
- Business Transformation
- Enterprise PMO
- Project + Program Management
- Operational Planning + Execution
- Integrated Plan Management
- Federal Government
- State + Local Government
- Banks + Credit Unions
- Manufacturing
Best practices on strategy, planning, & execution
Real-world examples of organizations that have trusted AchieveIt
Ready-to-use templates to take planning to the next level
Research-driven guides to help your strategy excel
Pre-recorded & upcoming webinars on everything strategy & planning
- *NEW!* Podcast 🎙️
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Government Department or Agency
RELATED TAGS:
Budgets and deadlines are two of the most crucial elements when it comes to getting things done in a local government. To be as efficient as possible, you’ll need a robust strategic plan for your government department that outlines how you’ll spend your provincial budget and how you and your subcontractors will achieve public project deadlines. Building a long-term and multiyear strategic plan with goals and objectives can be challenging. We also understand how complicated it is to transform your ideas into tangible results for your community, and we’re here to help.
In This Article
Why Government Departments and Agencies Need Strategic Plans
Why current government strategic processes and tools fall short, conduct internal and external analysis, consider the vision and mission , perform a holistic risk-assessment , list the focus areas , develop strategic objectives, set up an actionable game plan , utilize measurable kpis , put the plan into action , evaluate the results , transform government strategic planning and execution with achieveit, ready to accelerate your planning and execution efforts let’s actually do this..
Why should the state and municipal governments consider strategic planning? Isn’t having a yearly budget sufficient? After all, things may change when heavy rains overflow the city sewers or roadway repairs exceed the budget. What difference does additional planning make? What exactly is department strategic planning?
A department strategic plan is a comprehensive and systematic management tool that assists governmental departments, agencies and organizations in assessing their current environment, anticipating changes and responding appropriately to issues. Strategic planning involves envisioning the future, improving effectiveness, developing commitment to the department’s mission and reaching a consensus on strategies and objectives for achieving that mission. It involves influencing the future rather than merely preparing for or responding to it.
While combining community vision with available resources is critical, the resources should not stifle the vision. The objectives of a departmental strategic plan will involve identifying how the resources available may be linked to future ambitions. A long-term financial plan, created with the department strategy plan, is crucial to the departmental strategic planning process. A government should have an established financial planning mechanism that evaluates the long-term economic consequences of current and planned policies and programs. A financial plan depicts the expected financial repercussions of certain activities.
Regarding strategic planning in government positions, the notion is that leaders must be good strategists if their departments and agencies are to achieve their goals, accomplish their mandates and, most importantly, satisfy their communities in the coming years. The strategic planning department must lay out effective strategies to deal with changing conditions and governmental leaders must create a cohesive and defensible framework for their judgments. Ultimately, a department strategy provides a big-picture document that directs resources and activities toward a well-defined vision.
A state department strategic plan is a long-term commitment to various governmental objectives. Selecting the correct solutions to support the department’s strategic plan is critical to attaining them. The strategic planning department requires integrated and holistic systems and tools to increase productivity and improve the overall management of the various objectives while keeping operations running smoothly. An adequate system also keeps communication channels open between different departments.
Many procedures and systems on the market can help manage a department’s strategic plan but mainly focuses on short-term success. Business intelligence, project management, strategy development tools and other mainstream options focus on something other than integrated plans that span departments and locations. Each focuses on a specific function of planning, developing, executing or reporting strategies, so finding a single system that keeps everything in one secure place is challenging.

Taking an analytical look into these traditional options, we can see some pros to utilizing them. Still, some cons can lead to your government’s strategic processes falling short:
- Business intelligence tools: Although business intelligence tools provide visual dashboards, reports and a data-driven understanding of how the government is performing, they miss the “why” behind the strategic plan — the vision and future forecasts.
- Project management tools: These tools are excellent for providing detailed project statuses but lack the big-picture view and are typically challenging to use and connect with other projects.
- Strategy management tools: Strategy development tools can most certainly help organize plans and foster project alignment. However, these tools are less proficient at enabling the effective execution of these plans. They have limited flexibility and make it difficult to manage multiple plans across the agency.
- Mainstream tools: You might recognize mainstream and user-friendly tools like PowerPoint and Excel. Despite being customizable, these tools lack format and version control.
Strategic planning in government can be challenging. You must include stakeholder input, ensure that your department’s strategy is consistent across all municipal agencies, connect capital projects to multiple plans and ensure that everyone engaged is on board with the strategy. The good news is that it’s possible and the approach may be more straightforward than you think.
Follow these tips for creating your government agency’s strategic plan:

Conduct an environmental scan, where the local government can investigate and assess the current and developing factors within their own area’s internal and external environments. The internal and external analysis provides detailed information on the government’s existing conditions, including prospective opportunities, strengths, threats and weaknesses to control or prevent.
An internal analysis looks at the government’s internal environment to analyze its abilities, resources and competitive advantages. An internal analysis helps you identify strengths and weaknesses and the opportunities and threats that government departments or agencies face. This information assists government officials in making strategic decisions as they carry out the strategy development and implementation process. In a nutshell, the following topics should be included in your internal analysis:
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis can help you comprehensively understand your area’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
- Strategy analysis: This analysis assists you in evaluating how well you performed against your current department strategy plan, what you can improve on and where you can focus your efforts.
- Internal stakeholder analysis: This analysis enables you to gain insight into the issues and perspectives of your area’s internal stakeholders and their influence.
- VRIO Analysis: A VRIO analysis can assist you in identifying any competitive advantages you may have and how to convert them into long-term competitive advantages.
An external analysis investigates and evaluates the government’s external environment to understand possibilities and risks in its area. Forces outside a local government’s immediate control affect them, and they need to be able to plan accordingly. For example, changes in legislation and policies, demographic shifts or climate concerns can influence a government’s decisions. An external analysis should usually consider the following:
- PESTEL analysis: Conducting a PESTEL analysis can help you discover the many scopes that may influence an area.
- External stakeholder analysis: This analysis enables you to gain insight into the issues and perspectives of your local government’s external stakeholders and their influence.
The government’s vision statement defines where they want to go — it’s the anchor that keeps them from being stranded at sea. A clear vision statement will aid in directing the strategic plan toward the best results for the community. Everything written into the plan will eventually help the government department or agency get closer to its vision. Additionally, your local government should base its department’s strategic plan on its mission statement. Consider asking the following questions to articulate the critical components of the strategy:
- What are the top concerns that your government must address?
- Which forthcoming public projects are most important to your constituents?
Every government has risks that require attention through policy and infrastructure developments. A comprehensive assessment of the different risks to your community may include the following:
- National issues: At the federal level, social and economic concerns arise and citizens on both sides may be dissatisfied with their government’s shortcomings. Considering which issues are most essential at the national level can enable your community to make localized efforts to address them.
- Constituent dissatisfaction: Angry constituents equals a poor reelection campaign. To avoid unfavorable government-constituent relations, your local government should examine which topics are most beneficial to your community and analyze these concerns.
- Economic hardship: Local governments must examine the impact of inflation on local companies, citizens and budgets.
- Natural disasters: Which natural disasters are the greatest threat to your area? What steps have been taken or are being made to address these events, reduce risks and communicate with the public?
- Cybercrime: Cybercriminals have been creating data breaches in municipal governments for years, and attacks are increasing daily. Have your local government invested in cyber-safe technologies and backed up its data?
- International challenges: Do you need help attracting new government employees due to intergovernmental challenges? Do your internal procedures need to be more effective and costly? Do you have an up-to-date information technology strategy? One of the leading reasons for inefficient bureaucracy is a failure to recognize and handle such difficulties.
- Public policies: Which national and state legislation are the most important for your municipality to handle in the near future in terms of public policy? What consequences will you face if you do not address these policies?
After reviewing all the significant risks, it’s time to prioritize the most critical ones and develop a strategy to manage them. List the top focus areas that are crucial to your citizens or represent significant risks to your community’s health, safety, quality and economy. Your focus areas should also align with the local government’s and community’s future aspirations. Although it would be ideal to address all areas immediately, it could be more realistic. Try to prioritize a few critical issues.
Strategic objectives indicate what your city genuinely wants to achieve — they’re quite high-priority and should have a date attached. Your strategic goals should align with one or more of your focus areas and provide some tangibility to how you envision attaining your focus areas. Similar to selecting a few focus areas at a time, you can develop a few realistic and achievable strategic objectives. An example of a strategic objective can be to “improve the community’s safety by implementing a new reporting system by June 30, 2023.”
Now that you’ve decided on the primary focus areas and objectives, it’s time to consider how to execute them. A game plan defines what the government will need to do to achieve its goals. An actionable game plan assists in breaking down the bigger picture into smaller, more attainable results and activities. At this phase in your strategic planning process, you will begin to define the steps you will take to attain specific goals and the talents, expertise and resources required.

KPIs track progress toward your strategic goals. KPIs are quantitative metrics that demonstrate your government’s progress toward essential strategic objectives. KPIs tell you whether or not you have met your strategic target. Once KPIs have been determined, describe who is responsible for what and give them a job using your local government management tool to keep everyone organized and accountable.
Following your department’s strategy’s completion and policymakers’ approval of budgets and deadlines for major projects, it’s time to begin implementing your government initiatives. File requests for proposals (RFPs) for private-sector partnerships, fill out the necessary documentation and clarify who is doing what and when.
Taking strategic action to address concerns entails some risk in and of itself. You’ll need to pay close attention to your KPIs and adjust if problems with fulfilling timelines and budgets develop. If such problems arise, you must assess whether parts of the process may be expedited using government technology. Automation will save you time and money while increasing the likelihood of project success in your management planning.
A government strategic plan is the first vital step toward achieving governmental goals. The execution of these plans also plays a pivotal role in the goals’ success. A government runs high-level plans that cascade down and across multiple departments — which can make managing the execution of strategic plans more challenging. This is because different departments work with tools that support their specific work and role. As a result, information is stockpiled across these departments, making planning and organization a manual process.
Transform your strategic planning and execution process with strategic planning software built for your organization. AchieveIt is a FedRAMP-authorized cloud-based platform that connects, manages and executes mission-critical plans and activities for federal government agencies. AchieveIt is a platform that easily tracks the performance of all your integrated plans while automating time-consuming update collection. Managing all these moving parts goes from multiple spreadsheets to a single, easy-to-use platform.
By utilizing AchieveIt, federal government agencies can:
- Establish uniformity in data collection and reporting.
- Create visibility across plans and initiatives to know what needs attention.
- Promote accountability for mission execution.
- Make informed decisions with real-time data and proper context.
- Monitor the performance of long-term initiatives with dashboards and reports.
- Connect all its plans and strategies in one single place.

Do you need help developing and aligning your plans? Since planning and executing is more than just software, AcieveIt’s expert team will partner with you. Our strategy experts can ensure you stay on track and offer advice on how other federal agencies approach planning and execution. Allow AchieveIt to make your agency more efficient, so you can better serve the public while focusing on achieving mission-critical objectives. Request a demo or give us a call at 1-800-535-1559 today.
Meet the Author Chelsea Damon
Chelsea Damon is the Content Strategist at AchieveIt. When she's not publishing content about strategy execution, you'll likely find her outside or baking bread.
Related Posts

Everything You Need to Know About Business Mission and Vision Statements

How to Run a Successful Strategic Planning Session

The Differences Between Long-Term, Mid-Term, and Short-Term Planning
Hear directly from our awesome customers
See first-hand why the world's best leaders use AchieveIt
See AchieveIt in action
Stay in the know. Join our community of subscribers.
Subscribe for plan execution content sent directly to your inbox.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Appeals court allows part of Biden student loan repayment plan to go forward
FILE - President Joe Biden speaks about student loan debt relief at Delaware State University, Oct. 21, 2022, in Dover, Del. A federal appeals court has allowed the U.S. Education Department to move ahead with a plan to lower monthly payments for millions of student loans borrowers. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci, File)

- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — A federal appeals court has allowed the U.S. Education Department to move ahead with a plan to lower monthly payments for millions of student loan borrowers, putting on hold a ruling last week by a lower court.
The ruling from the 10th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals puts back on track a central part of President Joe Biden’s efforts to address student debt — a rule that lowers from 10% of discretionary income to 5% the amount that some borrowers qualifying for a repayment plan need to pay.
The reduced payment threshold was set to take effect July 1, but federal judges in Kansas and Missouri last week blocked much of the administration’s student loan repayment plan in two separate rulings. The ruling on Sunday means the department can move ahead with the reduced payments already calculated while it pursues an appeal.
The rulings have created a difficult environment for borrowers to navigate, said Persis Yu, deputy executive director of the Student Borrower Protection Center, which advocates for eliminating student debt. The stay granted by the 10th Circuit is temporary, Yu said, leaving many borrowers in the dark about future financial obligations.
“Borrowers are having to make decisions right now about their financial lives, and they don’t know the very basic information that they need in order to make informed decisions,” Yu said.
The Biden administration created the SAVE plan last year to replace other existing income-based repayment plans offered by the federal government. It allowed many to qualify for lower payments, and forgiveness was granted to borrowers who had made payments for at least 10 years and originally borrowed $12,000 or less.
U.S. Education Secretary Miguel Cardona said the Biden administrations remains committed “to our work to fix a broken student loan system and make college more affordable for more Americans.”
The appeals court ruling does not impact the injunction issued by a federal judge in Missouri, which prevents the Education Department from forgiving loan balances going forward.
The injunctions are the result of lawsuits from Republican-led states seeking to invalidate the Biden administration’s entire loan forgiveness program, which was first available to borrowers in the summer of 2023, and at least 150,000 have had their loans cancelled. The suing states argued that the administration’s plan was a workaround after the Supreme Court struck down the original plan for student loan forgiveness earlier that year.
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .

Watch CBS News
What is Project 2025? What to know about the conservative blueprint for a second Trump administration
By Melissa Quinn , Jacob Rosen
Updated on: July 11, 2024 / 9:40 AM EDT / CBS News
Washington — Voters in recent weeks have begun to hear the name "Project 2025" invoked more and more by President Biden and Democrats, as they seek to sound the alarm about what could be in store if former President Donald Trump wins a second term in the White House.
Overseen by the conservative Heritage Foundation, the multi-pronged initiative includes a detailed blueprint for the next Republican president to usher in a sweeping overhaul of the executive branch.
Trump and his campaign have worked to distance themselves from Project 2025, with the former president going so far as to call some of the proposals "abysmal." But Democrats have continued to tie the transition project to Trump, especially as they find themselves mired in their own controversy over whether Mr. Biden should withdraw from the 2024 presidential contest following his startling debate performance last month.
Here is what to know about Project 2025:
What is Project 2025?
Project 2025 is a proposed presidential transition project that is composed of four pillars: a policy guide for the next presidential administration; a LinkedIn-style database of personnel who could serve in the next administration; training for that pool of candidates dubbed the "Presidential Administration Academy;" and a playbook of actions to be taken within the first 180 days in office.
It is led by two former Trump administration officials: Paul Dans, who was chief of staff at the Office of Personnel Management and serves as director of the project, and Spencer Chretien, former special assistant to Trump and now the project's associate director.
Project 2025 is spearheaded by the Heritage Foundation, but includes an advisory board consisting of more than 100 conservative groups.
Much of the focus on — and criticism of — Project 2025 involves its first pillar, the nearly 900-page policy book that lays out an overhaul of the federal government. Called "Mandate for Leadership 2025: The Conservative Promise," the book builds on a "Mandate for Leadership" first published in January 1981, which sought to serve as a roadmap for Ronald Reagan's incoming administration.
The recommendations outlined in the sprawling plan reach every corner of the executive branch, from the Executive Office of the President to the Department of Homeland Security to the little-known Export-Import Bank.

The Heritage Foundation also created a "Mandate for Leadership" in 2015 ahead of Trump's first term. Two years into his presidency, it touted that Trump had instituted 64% of its policy recommendations, ranging from leaving the Paris Climate Accords, increasing military spending, and increasing off-shore drilling and developing federal lands. In July 2020, the Heritage Foundation gave its updated version of the book to then-White House Chief of Staff Mark Meadows.
The authors of many chapters are familiar names from the Trump administration, such as Russ Vought, who led the Office of Management and Budget; former acting Defense Secretary Chris Miller; and Roger Severino, who was director of the Office of Civil Rights at the Department of Health and Human Services.
Vought is the policy director for the 2024 Republican National Committee's platform committee, which released its proposed platform on Monday.
John McEntee, former director of the White House Presidential Personnel Office under Trump, is a senior advisor to the Heritage Foundation, and said that the group will "integrate a lot of our work" with the Trump campaign when the official transition efforts are announced in the next few months.
Candidates interested in applying for the Heritage Foundation's "Presidential Personnel Database" are vetted on a number of political stances, such as whether they agree or disagree with statements like "life has a right to legal protection from conception to natural death," and "the President should be able to advance his/her agenda through the bureaucracy without hindrance from unelected federal officials."
The contributions from ex-Trump administration officials have led its critics to tie Project 2025 to his reelection campaign, though the former president has attempted to distance himself from the initiative.
What are the Project 2025 plans?
Some of the policies in the Project 2025 agenda have been discussed by Republicans for years or pushed by Trump himself: less federal intervention in education and more support for school choice; work requirements for able-bodied, childless adults on food stamps; and a secure border with increased enforcement of immigration laws, mass deportations and construction of a border wall.
But others have come under scrutiny in part because of the current political landscape.
Abortion and social issues
In recommendations for the Department of Health and Human Services, the agenda calls for the Food and Drug Administration to reverse its 24-year-old approval of the widely used abortion pill mifepristone. Other proposed actions targeting medication abortion include reinstating more stringent rules for mifepristone's use, which would permit it to be taken up to seven weeks into a pregnancy, instead of the current 10 weeks, and requiring it to be dispensed in-person instead of through the mail.
The Alliance Defending Freedom, a conservative legal group that is on the Project 2025 advisory board, was involved in a legal challenge to mifepristone's 2000 approval and more recent actions from the FDA that made it easier to obtain. But the Supreme Court rejected the case brought by a group of anti-abortion rights doctors and medical associations on procedural grounds.
The policy book also recommends the Justice Department enforce the Comstock Act against providers and distributors of abortion pills. That 1873 law prohibits drugs, medicines or instruments used in abortions from being sent through the mail.

Now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade , the volume states that the Justice Department "in the next conservative administration should therefore announce its intent to enforce federal law against providers and distributors of such pills."
The guide recommends the next secretary of Health and Human Services get rid of the Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force established by the Biden administration before Roe's reversal and create a "pro-life task force to ensure that all of the department's divisions seek to use their authority to promote the life and health of women and their unborn children."
In a section titled "The Family Agenda," the proposal recommends the Health and Human Services chief "proudly state that men and women are biological realities," and that "married men and women are the ideal, natural family structure because all children have a right to be raised by the men and women who conceived them."
Further, a program within the Health and Human Services Department should "maintain a biblically based, social science-reinforced definition of marriage and family."
During his first four years in office, Trump banned transgender people from serving in the military. Mr. Biden reversed that policy , but the Project 2025 policy book calls for the ban to be reinstated.
Targeting federal agencies, employees and policies
The agenda takes aim at longstanding federal agencies, like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The agency is a component of the Commerce Department and the policy guide calls for it to be downsized.
NOAA's six offices, including the National Weather Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, "form a colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future U.S. prosperity," the guide states.
The Department of Homeland Security, established in 2002, should be dismantled and its agencies either combined with others, or moved under the purview of other departments altogether, the policy book states. For example, immigration-related entities from the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice and Health and Human Services should form a standalone, Cabinet-level border and immigration agency staffed by more than 100,000 employees, according to the agenda.

If the policy recommendations are implemented, another federal agency that could come under the knife by the next administration, with action from Congress, is the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau.
The agenda seeks to bring a push by conservatives to target diversity, equity and inclusion, or DEI, initiatives in higher education to the executive branch by wiping away a slew of DEI-related positions, policies and programs and calling for the elimination of funding for partners that promote DEI practices.
It states that U.S. Agency for International Development staff and grantees that "engage in ideological agitation on behalf of the DEI agenda" should be terminated. At the Treasury Department, the guide says the next administration should "treat the participation in any critical race theory or DEI initiative without objecting on constitutional or moral grounds, as per se grounds for termination of employment."
The Project 2025 policy book also takes aim at more innocuous functions of government. It calls for the next presidential administration to eliminate or reform the dietary guidelines that have been published by the Department of Agriculture for more than 40 years, which the authors claim have been "infiltrated" by issues like climate change and sustainability.
Immigration
Trump made immigration a cornerstone of his last two presidential runs and has continued to hammer the issue during his 2024 campaign. Project 2025's agenda not only recommends finishing the wall along the U.S.-Mexico border, but urges the next administration to "take a creative and aggressive approach" to responding to drug cartels at the border. This approach includes using active-duty military personnel and the National Guard to help with arrest operations along the southern border.
A memo from Immigration and Customs Enforcement that prohibits enforcement actions from taking place at "sensitive" places like schools, playgrounds and churches should be rolled back, the policy guide states.
When the Homeland Security secretary determines there is an "actual or anticipated mass migration of aliens" that presents "urgent circumstances" warranting a federal response, the agenda says the secretary can make rules and regulations, including through their expulsion, for as long as necessary. These rules, the guide states, aren't subject to the Administration Procedure Act, which governs the agency rule-making process.
What do Trump and his advisers say about Project 2025?
In a post to his social media platform on July 5, Trump wrote , "I know nothing about Project 2025. I have no idea who is behind it. I disagree with some of the things they're saying and some of the things they're saying are absolutely ridiculous and abysmal. Anything they do, I wish them luck, but I have nothing to do with them."
Trump's pushback to the initiative came after Heritage Foundation President Kevin Roberts said in a podcast interview that the nation is "in the process of the second American Revolution, which will remain bloodless if the left allows it to be."
The former president continued to disavow the initiative this week, writing in another social media post that he knows nothing about Project 2025.
"I have not seen it, have no idea who is in charge of it, and, unlike our very well received Republican Platform, had nothing to do with it," Trump wrote. "The Radical Left Democrats are having a field day, however, trying to hook me into whatever policies are stated or said. It is pure disinformation on their part. By now, after all of these years, everyone knows where I stand on EVERYTHING!"
While the former president said he doesn't know who is in charge of the initiative, the project's director, Dans, and associate director, Chretien, were high-ranking officials in his administration. Additionally, Ben Carson, former secretary of Housing and Urban Development under Trump; John Ratcliffe, former director of National Intelligence in the Trump administration; and Peter Navarro, who served as a top trade adviser to Trump in the White House, are listed as either authors or contributors to the policy agenda.
Still, even before Roberts' comments during "The War Room" podcast — typically hosted by conservative commentator Steve Bannon, who reported to federal prison to begin serving a four-month sentence last week — Trump's top campaign advisers have stressed that Project 2025 has no official ties to his reelection bid.
Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita, senior advisers to the Trump campaign, said in a November statement that 2024 policy announcements will be made by Trump or his campaign team.
"Any personnel lists, policy agendas, or government plans published anywhere are merely suggestions," they said.
While the efforts by outside organizations are "appreciated," Wiles and LaCivita said, "none of these groups or individuals speak for President Trump or his campaign."
In response to Trump's post last week, Project 2025 reiterated that it was separate from the Trump campaign.
"As we've been saying for more than two years now, Project 2025 does not speak for any candidate or campaign. We are a coalition of more than 110 conservative groups advocating policy & personnel recommendations for the next conservative president. But it is ultimately up to that president, who we believe will be President Trump, to decide which recommendations to implement," a statement on the project's X account said.
The initiative has also pushed back on Democrats' claims about its policy proposals and accused them of lying about what the agenda contains.
What do Democrats say?
Despite their attempts to keep some distance from Project 2025, Democrats continue to connect Trump with the transition effort. The Biden-Harris campaign frequently posts about the project on X, tying it to a second Trump term.
Mr. Biden himself accused his Republican opponent of lying about his connections to the Project 2025 agenda, saying in a statement that the agenda was written for Trump and "should scare every single American." He claimed on his campaign social media account Wednesday that Project 2025 "will destroy America."
Congressional Democrats have also begun pivoting to Project 2025 when asked in interviews about Mr. Biden's fitness for a second term following his lackluster showing at the June 27 debate, the first in which he went head-to-head with Trump.
"Trump is all about Project 2025," Pennsylvania Sen. John Fetterman told CNN on Monday. "I mean, that's what we really should be voting on right now. It's like, do we want the kind of president that is all about Project '25?"
Rep. Jim Clyburn of South Carolina, one of Mr. Biden's closest allies on Capitol Hill, told reporters Monday that the agenda for the next Republican president was the sole topic he would talk about.
"Project 2025, that's my only concern," he said. "I don't want you or my granddaughter to live under that government."
In a statement reiterating her support for Mr. Biden, Rep. Frederica Wilson of Florida called Project 2025 "MAGA Republicans' draconian 920-page plan to end U.S. democracy, give handouts to the wealthy and strip Americans of their freedoms."
What are Republicans saying about Project 2025?
Two GOP senators under consideration to serve as Trump's running mate sought to put space between the White House hopeful and Project 2025, casting it as merely the product of a think tank that puts forth ideas.
"It's the work of a think tank, of a center-right think tank, and that's what think tanks do," Florida Sen. Marco Rubio told CNN's "State of the Union" on Sunday.
He said Trump's message to voters focuses on "restoring common sense, working-class values, and making our decisions on the basis of that."
Ohio Sen. J.D. Vance raised a similar sentiment in an interview with NBC's "Meet the Press," saying organizations will have good ideas and bad ideas.
"It's a 900-page document," he said Sunday. "I guarantee there are things that Trump likes and dislikes about that 900-page document. But he is the person who will determine the agenda of the next administration."
Jaala Brown contributed to this report.
Melissa Quinn is a politics reporter for CBSNews.com. She has written for outlets including the Washington Examiner, Daily Signal and Alexandria Times. Melissa covers U.S. politics, with a focus on the Supreme Court and federal courts.
More from CBS News

Project 2025 would overhaul U.S. taxes. Here's the impact for you.

Progressives look to Supreme Court to motivate voters in 2024 race

GOP effort to hold Garland in inherent contempt of Congress fails

Biden talks with Congressional Hispanic Caucus as he fights to stay in 2024 race
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

U.S. Department of Commerce
- Press Releases
Was this page helpful?
Biden-harris administration to invest up to $1.6 billion to establish and accelerate domestic capacity advanced packaging, office of public affairs.
Today, as part of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, the U.S. Department of Commerce issued a Notice of Intent (NOI) to open a competition for new research and development (R&D) activities that will establish and accelerate domestic capacity for semiconductor advanced packaging. The CHIPS for America program anticipates up to $1.6 billion in funding innovation across five R&D areas, as outlined in the vision for the National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Program (NAPMP). Through potential cooperative agreements, CHIPS for America would make several awards of approximately $150 million federal funding available per award in each research area. These awards will leverage private sector investments from industry and academia.
“President Biden was clear that we need to build a vibrant domestic semiconductor ecosystem here in the U.S., and advanced packaging is a huge part of that. Now, thanks to the Biden-Harris Administration’s commitment to investing in America, the U.S. will have multiple advanced packaging options across the country and push the envelope in new packaging technologies. This announcement is just the most recent example of our commitment to investing in cutting edge R&D that is critical to creating quality jobs in the U.S. and making our country a leader in advanced semiconductor manufacturing.” said U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo .
Advanced packaging capacity and R&D has never been in higher demand or more important to advances in semiconductor technology. Emerging artificial intelligence (AI)-driven applications are pushing the boundaries of current technologies like high performance computing and low power electronics, requiring leap-ahead advances in microelectronics capabilities, especially advanced packaging. Advanced packaging allows manufacturers to make improvements in all aspects of system performance and function and to shorten time to market. Additional benefits include a reduced physical footprint, lower power, decreased costs, as well as increased chiplet reuse. Achieving these goals requires coordinated investments to support integrated R&D activities to establish leading-edge domestic capacity for semiconductor advanced packaging.
“The National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Program will enable a packaging sector within the United States that outpaces the world through innovation driven by robust R&D,” said Under Secretary of Commerce for Standards and Technology and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Director Laurie E. Locascio . “Within a decade, through R&D funded by CHIPS for America, we will create a domestic packaging industry where advanced node chips manufactured in the U.S. and abroad can be packaged within the United States and where innovative designs and architectures are enabled through leading-edge packaging capabilities.
“Under President Biden’s leadership, we’re bringing semiconductor manufacturing back to the United States, teaming with industry to build factories, supply chains, and jobs in communities across the country. That’s how we win today, and CHIPS R&D is how we win tomorrow,” said Arati Prabhakar, Assistant to the President for Science and Technology and Director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy. “Investing in research to accelerate new advanced semiconductor packaging approaches will help this pivotal and fast-changing industry thrive here at home now and into the future.”
Funded activities are expected to be relevant to one or more of five R&D areas:
- Equipment, tools, processes, and process integration;
- Power delivery and thermal management;
- Connector technology, including photonics and radio frequency (RF);
- Chiplets ecosystem;
- and co-design/electronic design automation (EDA).
In addition to the R&D areas, the funding opportunity is expected to include opportunities for prototype developments.
More information about the NOI will be shared in an upcoming webinar. Follow CHIPS.gov for updates.
About CHIPS for America
CHIPS for America is part of President Biden’s economic plan to invest in America, stimulate private sector investment, create good-paying jobs, make more in the United States, and revitalize communities left behind. CHIPS for America includes the CHIPS Program Office, responsible for manufacturing incentives, and the CHIPS Research and Development (R&D) Office, responsible for R&D programs. Both offices sit within the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) at the Department of Commerce. NIST promotes U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life. NIST is uniquely positioned to successfully administer the CHIPS for America program because of the bureau’s strong relationships with U.S. industries, its deep understanding of the semiconductor ecosystem, and its reputation as fair and trusted.
CHIPS R&D released the first funding opportunity for the National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Program (NAPMP) in February 2024. That funding opportunity requested applications for R&D activities that will establish and accelerate domestic capacity for advanced packaging substrates and substrate materials, a key technology for manufacturing semiconductors.
Applicants submitted over 100 concept papers representing 28 states, and on May 22, 2024, the Department of Commerce announced that eight teams have been selected to submit full applications for the NAPMP funding opportunity for materials and substrate materials.
Final projects will play a vital role in helping to ensure that American innovation drives cutting-edge developments in semiconductor R&D and manufacturing. The CHIPS for America program anticipates awarding approximately $300 million in amounts up to approximately $100 million over up to 5 years per award. Program awards may be leveraged by voluntary co-investment. Full applications for the first NAPMP funding opportunity were due on July 3, 2024.
Visit https://www.chips.gov to learn more.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Offers $1.7 Billion to Help Factories Build Electric Vehicles
A Jeep plant that closed last year will be among those that will benefit from federal grants meant to help automotive manufacturers and protect jobs.

By Jack Ewing
The federal government will grant car and auto parts factories in eight states $1.7 billion to begin producing electric vehicles and other clean energy technology, the Biden administration announced on Thursday.
Among the 11 recipients will be a Jeep factory in Belvidere, Ill., that the brand’s parent company Stellantis closed last year. The money will allow the plant to reopen and produce electric vehicles, officials said, restoring almost 1,450 jobs.
Other beneficiaries include a factory in Georgia that plans to make Blue Bird electric school buses, a General Motors factory in Michigan that will shift production from gasoline to electric vehicles, and a Harley-Davidson factory in Pennsylvania that will increase production of electric motorcycles.
The funding helps to address fears that electric vehicles will endanger jobs at factories that make gasoline-powered vehicles or parts for internal combustion engines as the industry shifts to E.V.s. To qualify for the money, companies had to commit to retraining their existing workers.
Employees at all of the factories chosen are represented by unions. Officials said they gave priority to communities that suffered disproportionately from pollution or lack of investment.
Several of the factories are in Pennsylvania, Michigan or Georgia, states where narrow margins will determine the outcome of the presidential election. President Biden, in a statement, sought to contrast his industrial policies with those of former President Donald J. Trump.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As a new department manager, now that you've completed the initial six critical steps and established your rhythm of business model (ROB), next up is creating your department's tactical plan ...
A department business plans template allows department leaders to define their goals and strategy for the upcoming period. Department business plans outline a department's goals, what steps or initiatives the department will undertake to achieve those goals, and the timeline during which these goals should be achieved.
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Edit and Download. Step #2: Put Together Your Company Description. The next step is to write out a full description of your business and its core offerings. This section of your business plan should include your mission statement and objectives, along with your company history or overview.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Here is an example of a marketing plan for a new business: 8. Provide a logistics and operations plan. Logistics and operations are the workflows you'll implement to make your business idea a reality. If you're writing a business plan for your own planning purposes, this is still an important section to consider, even though you might not ...
A department business plan outlines the focus areas, objectives, and projects of a team or department within a company. It is used to develop a roadmap to success and ensure that the team is working towards the same goals. It can also be used to track progress and measure the results of the team's efforts.
To write a business plan for your department, start with an executive summary outlining your department's purpose and goals. Next, define clear objectives, conduct a market analysis, and detail ...
Here is a guide to help you get started on your business plan: 1. Executive Summary. What It Is: This section summarizes your business plan as a whole and outlines your company profile and goals.
Create a Financial Forecast. Create a forecast for revenues and expenses based on past results combined with the goals the company owner expressed for the upcoming year. The business owner may ...
A basic procedure that you can always execute if you want to come up with a simple department strategic plan is listed below. 1. Browse through the business strategic plan of the company first. Familiarize with the processes followed by the business and the plans that will be executed for the next operational plan.
In order to be effective in this directive, it is critical the department remains focused on fulfilling a specific value proposition. Creating the Department's Value Proposition. Each department's value proposition must be in alignment with the organization's overall strategic initiatives. Review the entity's long-term business plan ...
The following is a departmental business plan example, or business growth plan template, that could be applied to a variety of businesses. [Department Name] Departmental Business Plan - [Date] Outline: Review of Annual Metrics. Annual Goals vs. Metric Comparison. Adjusted Annual Goals. Departmental Needs to Meet Goals. Individual Staff Metrics.
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
A departmental business plan is a systematically positioned and strategically planned layout for each department in the organization. It is planned in accordance with the business plan usually under the guidance of the entrepreneurs of the organization so that it will meet organizations requirements and achieve its goals. Budgets and priorities of each department must fit in with those of the ...
A 100 Day Plan is an action plan to guide executive leaders through their first critical months in a new role - outlining strategies and tactics to identify and engage key stakeholders and to build relationships, understand the business, set goals, and gain traction quickly so you can set up a foundation for long-term success in an organization.
12049. 46. When a new startup business is created, it often relies on a skeleton staff. This is usually due to financial restrictions. Even though the entrepreneur might want to employ more employees to help them get their new business up and running, there's a likely chance that they don't have the money to do so.
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
2. Recruit strong people. You will beat the drums for your new department as it develops a reputation and a place within the organization. You can't do this if you are also doing all of the ...
Analyze the path of the company. When thinking about planning and strategizing, it's critical to view pre-execution steps with the same importance as the implementation phase. As the saying goes, "if your fail to plan, you plan to fail.". In other words, you need to consider where your company is going. In the beginning, you may have just ...
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Government Department or Agency. Conduct Internal and External Analysis. Consider the Vision and Mission. Perform a Holistic Risk-Assessment. List the Focus Areas. Develop Strategic Objectives. Set up an Actionable Game Plan. Utilize Measurable KPIs. Put the Plan Into Action.
The reduced payment threshold was set to take effect July 1, but federal judges in Kansas and Missouri last week blocked much of the administration's student loan repayment plan in two separate rulings. The ruling on Sunday means the department can move ahead with the reduced payments already calculated while it pursues an appeal.
The recommendations outlined in the sprawling plan reach every corner of the executive branch, from the Executive Office of the President to the Department of Homeland Security to the little-known ...
Health Secretary Wes Streeting said the Labour government's plan to overhaul the state-run National Health Service will be key to delivering its core pledge to boosting UK economic growth.
Today, as part of President Biden's Investing in America agenda, the U.S. Department of Commerce issued a Notice of Intent (NOI) to open a competition for new research and development (R&D) activities that will establish and accelerate domestic capacity for semiconductor advanced packaging. The CHIPS for America program anticipates up to $1.6 billion in funding innovation across five R&D ...
The White House on Thursday said it would hand out $1.7 billion to help convert closed-down or at-risk auto manufacturing and assembly facilities to make electric and hybrid vehicles. The funding ...
The funds will preserve 15,000 jobs and create almost 3,000 new ones, Jennifer Granholm, the energy secretary, said on a conference call with reporters on Wednesday.