The Impact of Online Games on Student Academic Performance
21 Pages Posted: 1 Jun 2023

Beimbet Beibit
Nazarbayev Intellectual School
Date Written: May 12, 2023
Online video gaming has become a popular leisure activity among students, but concerns have been raised about its potential impact on academic performance. While some argue that video games can enhance cognitive skills, others claim that excessive gaming can lead to poor academic performance and even addiction. This research aims to investigate the influence of online video gaming on the academic performance of students. The study will examine the relationship between online gaming and academic performance, as well as factors that may moderate this relationship, such as the days of gaming sessions, gender, and academic performance. A survey was conducted among a sample of students from NIS school(73 participants), to collect data on their gaming habits and academic performance. The data collected will be analyzed using statistical methods to determine whether there is a significant correlation between online gaming and academic performance. The findings of this study can be used to inform educational policy and practice, and to promote healthy gaming habits among students.
Keywords: video games, academic performance, addiction, influence
JEL Classification: I
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Beimbet Beibit (Contact Author)
Nazarbayev intellectual school ( email ), do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on ssrn, paper statistics.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
The effects of online game addiction on reduced academic achievement motivation among chinese college students: the mediating role of learning engagement.

- 1 BinZhou College of Science and Technology, Binzhou, China
- 2 Binzhou Polytechnic, Binzhou, China
- 3 Faculty of Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
- 4 National Institute of Vocational Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
Introduction: The present study aimed to examine the effects of online game addiction on reduced academic achievement motivation, and the mediating role of learning engagement among Chinese college students to investigate the relationships between the three variables.
Methods: The study used convenience sampling to recruit Chinese university students to participate voluntarily. A total of 443 valid questionnaires were collected through the Questionnaire Star application. The average age of the participants was 18.77 years old, with 157 males and 286 females. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS and AMOS.
Results: (1) Chinese college students’ online game addiction negatively affected their behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement (the three dimensions of learning engagement); (2) behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement negatively affected their reduced academic achievement motivation; (3) learning engagement mediated the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation.
1. Introduction
Online games, along with improvements in technology, have entered the daily life of college students through the popularity of computers, smartphones, PSPs (PlayStation Portable), and other gaming devices. Online game addiction has recently become a critical problem affecting college students’ studies and lives. As early as 2018, online game addiction was officially included in the category of “addictive mental disorders” by the World Health Organization (WHO), and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) was updated specifically to include the category of “Internet Gaming Disorder” (IGD). Prior research investigating Chinese college students’ online game addiction status mostly comprised regional small-scale studies. For example, a study on 394 college students in Chengde City, Hebei province, China showed that the rate of online game addiction was about 9% ( Cui et al., 2021 ). According to the results of an online game survey conducted by China Youth Network (2019) on 682 Chinese college students who played online games, nearly 60% of participants played games for more than 1 h a day, over 30% stayed up late because of playing games, over 40% thought that playing games had affected their physical health, over 70% claimed that games did not affect their studies, and over 60% had spent money on online games. This phenomenon has been exacerbated by the fact that smartphones and various portable gaming devices have become new vehicles for gaming with the development of technology. The increase in the frequency or time spent on daily gaming among adolescents implies a growth in the probability of gaming addiction, while an increase in the level of education decreases the probability of gaming addiction ( Esposito et al., 2020 ; Kesici, 2020 ). Moreover, during the COVID-19 pandemic, adolescents’ video game use and the severity of online gaming disorders increased significantly ( Teng et al., 2021 ).
A large body of literature on the relationship between problematic smartphone use and academic performance has illustrated the varying adverse effects of excessive smartphone obsession ( Durak, 2018 ; Mendoza et al., 2018 ; Rozgonjuk et al., 2018 ). These effects are manifested in three critical ways: first, the more frequently cell phones are used during study, the greater the negative impact on academic performance and achievement; second, students are required to master the basic skills and cognitive abilities to succeed academically, which are negatively affected by excessive cell phone use and addiction ( Sunday et al., 2021 ); third, online game addiction negatively affects students’ learning motivation ( Demir and Kutlu, 2018 ; Eliyani and Sari, 2021 ). However, there is currently a lack of scientifically objective means of effective data collection regarding online game addiction among college students in China, such as big data. Hong R. Z. et al. (2021) and Nong et al. (2023) suggested that the impact of addiction on students’ learning should be explored more deeply.
Since the 1990s, learning engagement has been regarded as a positive behavioral practice in learning in Europe and the United States, and plays an important role in the field of higher education research ( Axelson and Flick, 2010 ). Recently, studies on learning engagement among college students have also been a hot topic in various countries ( Guo et al., 2021 ). According to Fredricks et al. (2004) , learning engagement includes three dimensions: behavioral, emotional, and cognitive.
The concept of behavioral engagement encompasses three aspects: first, positive behavior in the classroom, such as following school rules and regulations and classroom norms; second, engagement in learning; and third, active participation in school activities ( Finn et al., 1995 ). Emotional engagement refers to students’ responses to their academic content and learning environment. The emotional responses to academic content include students’ emotional responses such as interest or disinterest in learning during academic activities ( Kahu and Nelson, 2018 ), while the emotional responses to the learning environment refer to students’ identification with their peers, teachers, and the school environment ( Stipek, 2002 ). Cognitive engagement is often associated with internal processes such as deep processing, using cognitive strategies, self-regulation, investment in learning, the ability to think reflectively, and making connections in daily life ( Khan et al., 2017 ). Cognitive engagement emphasizes the student’s investment in learning and self-regulation or strategies.
According to Yang X. et al. (2021) , learning engagement refers to students’ socialization, behavioral intensity, affective qualities, and use of cognitive strategies in performing learning activities. Besides, Kuh et al. (2007) argued that learning engagement was “the amount of time and effort students devote to instructional goals and meaningful educational practices.” Learning engagement is not only an important indicator of students’ learning process, but also a significant predictor of students’ academic achievement ( Zhang, 2012 ). It is also an essential factor in promoting college students’ academic success and improving education quality.
As one of the crucial components of students’ learning motivation ( Han and Lu, 2018 ), achievement motivation is the driving force behind an individual’s efforts to put energy into what he or she perceives to be valuable and meaningful to achieve a desired outcome ( Story et al., 2009 ). It can be considered as achievement motivation when an individual’s behavior involves “competing at a standard of excellence” ( Brunstein and Heckhausen, 2018 ). Students’ achievement motivation ensures the continuity of learning activities, achieving academic excellence and desired goals ( Sopiah, 2021 ). Based on the concept of achievement motivation, academic achievement motivation refers to the mental perceptions or intentions that students carry out regarding their academic achievement, a cognitive structure by which students perceive success or failure and determine their behavior ( Elliot and Church, 1997 ). Related research also suggests that motivation is one variable that significantly predicts learning engagement ( Xiong et al., 2015 ).
Therefore, it is worthwhile to investigate the internal influence mechanism of college students’ online game addiction on their reduced academic achievement motivation and the role of learning engagement, which is also an issue that cannot be ignored in higher education research. The present study explored the relationship between online game addiction, learning engagement, and reduced academic achievement motivation among college students by establishing a structural equation model (SEM) to shed light on the problem of online game addiction among college students.
2. Research model and hypotheses
2.1. research model.
Previous research usually regarded learning engagement as a variable of one or two dimensions, and scholars tend to favor the dimension of behavioral engagement. However, other ignored dimensions are inseparable parts of learning engagement ( Dincer et al., 2019 ). In a multi-dimensional model, the mutual terms of each dimension form a single composite structure. Therefore, the present study took the structure proposed by Fredricks et al. (2004) as a reference, divided learning engagement into behavioral, emotional, and cognitive dimensions as mediating variables, and explored the relationship between online game addiction, learning engagement, and reduced academic achievement motivation. The research frame diagram is shown in Figure 1 .
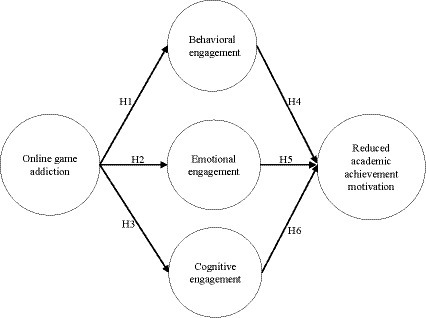
Figure 1 . The research model.
2.2. Research questions
2.2.1. the relationship between online game addiction and learning engagement.
Learning engagement has been viewed as a multidimensional concept in previous studies. Finn (1989) proposed the participation-identification model to make pioneering progress in learning engagement study. Schaufeli et al. (2002) suggested that learning engagement was an active, fulfilling mental state associated with learning. Chapman (2002) pointed out affective, behavioral, and cognitive criteria for assessing students’ learning engagement based on previous research. Fredricks et al. (2004) systematically outlined learning engagement as an integration of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement. The updated International Classification of Diseases [ World Health Organization (WHO), 2018a , b ] specifies several diagnostic criteria for gaming addiction, including the abandonment of other activities, the loss of interest in other previous hobbies, and the loss or potential loss of work and social interaction because of gaming. Past studies have shown the adverse effects of excessive Internet usage on students’ learning. Short video addiction negatively affects intrinsic and extrinsic learning motivation ( Ye et al., 2022 ). Students’ cell phone addiction negatively affects academic commitment, academic performance, and relationship facilitation, all of which negatively affect their academic achievement ( Tian et al., 2021 ). The amount of time spent surfing the Internet and playing games has been identified to negatively affect students’ cognitive ability ( Pan et al., 2022 ). College students’ cell phone addiction, mainly reflected in cell phone social addiction and game entertainment addiction, has also been noted to impact learning engagement; specifically, the higher the level of addiction, the lower the learning engagement ( Qi et al., 2020 ). Gao et al. (2021) also showed that cell phone addiction among college students could negatively affect their learning engagement. Choi (2019) showed that excessive use of cell phones might contribute to smartphone addiction, which also affects students’ learning engagement. Accordingly, the following three research hypotheses were proposed.
H1 : Online game addiction negatively affects behavioral engagement.
H2 : Online game addiction negatively affects emotional engagement.
H3 : Online game addiction negatively affects cognitive engagement.
2.2.2. The relationship between learning engagement and reduced academic achievement motivation
Achievement motivation is people’s pursuit of maximizing individual value, which embodies an innate drive, including the need for achievement, and can be divided into two parts: the intention to succeed and the intention to avoid failure ( McClelland et al., 1976 ). On this basis, Weiner (1985) proposed the attributional theory of achievement motivation, suggesting that individuals’ personality differences, as well as the experience of success and failure, could influence their achievement attributions and that an individual’s previous achievement attributions would affect his or her expectations and emotions for the subsequent achievement behavior while expectations and emotions could guide motivated behavior. Birch and Ladd (1997) indicated that behavioral engagement involved positive behavioral attitudes such as hard work, persistence, concentration, willingness to ask questions, and active participation in class discussions to complete class assignments. Students’ attitudes toward learning are positively related to achievement motivation ( Bakar et al., 2010 ). Emotional engagement involves students’ sense of identity with their peers, teachers, and the school environment ( Stipek, 2002 ). Students’ perceptions of the school environment influence their achievement motivation ( Wang and Eccles, 2013 ). Cognitive engagement encompasses the ability to use cognitive strategies, self-regulation, investment in learning, and reflective thinking ( Khan et al., 2017 ). Learning independence and problem-solving abilities predict student motivation ( Saeid and Eslaminejad, 2017 ). Hu et al. (2021) indicated that cognitive engagement had the most significant effect on students’ academic achievement among the learning engagement dimensions, and that emotional engagement was also an important factor influencing students’ academic achievement. Therefore, the following three research hypotheses were proposed:
H4 : Behavioral engagement significantly and negatively affects the reduced academic achievement motivation.
H5 : Emotional engagement significantly and negatively affects the reduced academic achievement motivation.
H6 : Cognitive engagement significantly and negatively affects the reduced academic achievement motivation.
2.2.3. The relationship between online game addiction, learning engagement, and reduced academic achievement motivation
Past studies have demonstrated the relationship between online game addiction and students’ achievement motivation. For example, a significant negative correlation between social network addiction and students’ motivation to progress has been reported ( Haji Anzehai, 2020 ), and a significant negative correlation between Internet addiction and students’ achievement motivation has been reported ( Cao et al., 2008 ). Students addicted to online games generally have lower academic achievement motivation because they lack precise academic planning and motivation ( Chen and Gu, 2019 ). Yayman and Bilgin (2020) pointed out a correlation between social media addiction and online game addiction. Accordingly, there might be a negative correlation between online game addiction and academic achievement motivation among college students.
Students addicted to online games generally have lower motivation for academic achievement because they lack precise academic planning and learning motivation ( Chen and Gu, 2019 ). Similarly, Haji Anzehai (2020) reported a significant negative correlation between social network addiction and students’ motivation to progress.
Learning engagement is often explored as a mediating variable in education research. Zhang et al. (2018) found that learning engagement was an essential mediator of the negative effect of internet addiction on academic achievement in late adolescence and is a key factor in the decline in academic achievement due to students’ internet addiction. Li et al. (2019) noted that college students’ social networking site addiction significantly negatively affected their learning engagement, and learning engagement mediated the relationship between social networking addiction and academic achievement. Accordingly, the following research hypothesis was proposed.
H7 : Learning engagement mediates the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation.
3. Research methodology and design
3.1. survey implementation.
The present study employed the Questionnaire Star application for online questionnaire distribution. Convenience sampling was adopted to recruit Chinese college students to participate voluntarily. The data were collected from October 2021 to January 2022 from a higher vocational college in Shandong province, China. Participants were first-and second-year students. According to Shumacker and Lomax (2016) , the number of participants in SEM studies should be approximately between 100 and 500 or more. In the present study, 500 questionnaires were returned, and 443 were valid after excluding invalid responses. The mean age of the participants was 18.77 years. There were 157 male students, accounting for 35.4% of the total sample, and 286 female students, accounting for 64.6%.
3.2. Measurement instruments
The present empirical study employed quantitative research methods by collecting questionnaires for data analysis. The items of questionnaires were adapted from research findings based on corresponding theories and were reviewed by experts to confirm the content validity of the instruments. The distributed questionnaire was a Likert 5-point scale (1 for strongly disagree , 2 for disagree , 3 for average , 4 for agree , and 5 for strongly agree ). After the questionnaire was collected, item analysis was conducted first, followed by reliability and validity analysis of the questionnaire constructs using SPSS23 to test whether the scale met the criteria. Finally, research model validation was conducted.
3.2.1. Online game addiction
In the present study, online game addiction referred to the addictive behavior of college students in online games, including mobile games and online games. The present study adopted a game addiction scale compiled by Wu et al. (2021) and adapted the items based on the definition of online game addiction. The adapted scale had 10 items. Two examples of the adapted items in the scale were: “I will put down what should be done and spend my time playing online games” and “My excitement or expectation of playing an online game is far better than other interpersonal interactions.”
3.2.2. Learning engagement
In the present study, learning engagement included students’ academic engagement in three dimensions: behavioral, emotional, and cognitive. The learning engagement scale compiled by Luan et al. (2020) was adapted based on its definition. The adapted scale had 26 questions in three dimensions: behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement. Two examples of the adapted items in the scale are: “I like to actively explore unfamiliar things when I am doing my homework” and “I will remind myself to double-check the places where I tend to make mistakes in my homework.”
3.2.3. Reduced academic achievement motivation
Reduced academic achievement motivation in the present study refers to the reduction in college students’ intrinsic tendency to enjoy challenges and achieve academic goals and academic success. The achievement motivation scale developed by Ye et al. (2020) was adapted to measure reduced academic achievement motivation. The adapted scale had 10 items. Two examples of the adapted items in the scale are: “Since playing online games, I do not believe that the effectiveness of learning is up to me, but that it depends on other people or the environment” and “Since I often play online games, I am satisfied with my current academic performance or achievement and do not seek higher academic challenges.”
4. Results and discussion
4.1. internal validity analysis of the measurement instruments.
In the present study, item analysis was conducted using first-order confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), which can reflect the degree of measured variables’ performance within a smaller construct ( Hafiz and Shaari, 2013 ). The first-order CFA is based on the streamlined model and the principle of independence of residuals. According to Hair et al. (2010) and Kenny et al. (2015) , it is recommended that the value of χ 2 / df in the model fitness indices should be less than 5; the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) value should be greater than 0.100; the values of the goodness of fit index (GFI) and adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI) should not be lower than 0.800; the factor loading (FL) values of the constructs should also be greater than 0.500. Based on the criteria above, the items measuring the online game addiction construct were reduced from 10 to seven; the items measuring the behavioral engagement construct were reduced from nine to six; the items measuring the emotional engagement construct were reduced from nine to six; the items measuring the cognitive engagement construct were reduced from eight to six; and the items measuring the reduced academic achievement motivation construct was reduced from 10 to six, as shown in Table 1 .
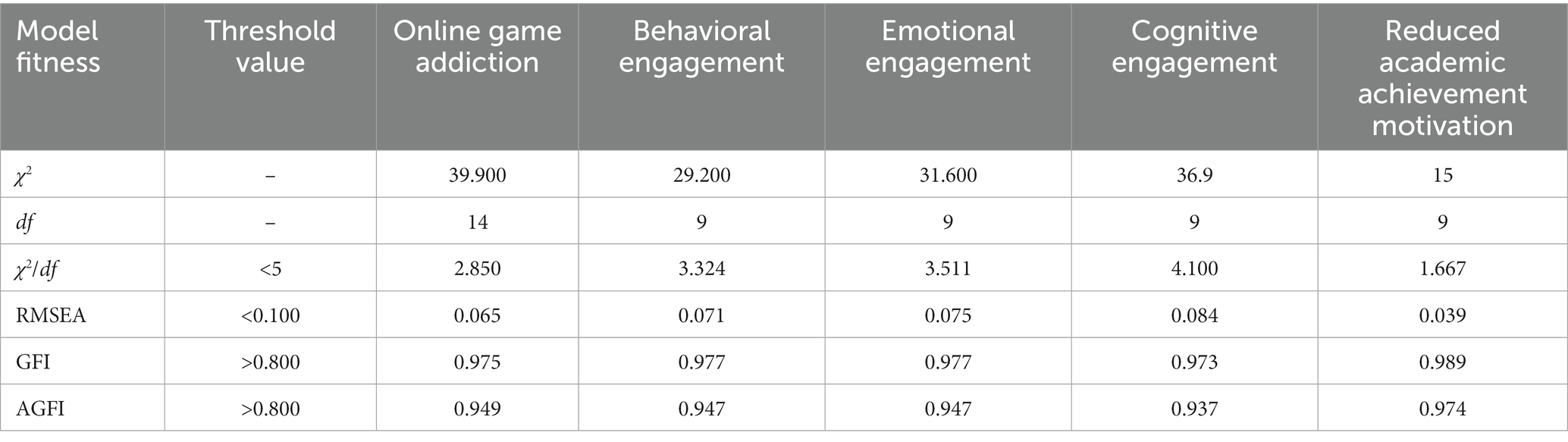
Table 1 . First-order confirmatory factor analysis.
4.2. Construct reliability and validity analysis
In order to determine the internal consistency of the constructs, the reliability of the questionnaire was tested using Cronbach’ s α value. According to Hair et al. (2010) , a Cronbach’ s α value greater than 0.700 indicates an excellent internal consistency among the items, and the constructs’ composite reliability (CR) values should exceed 0.700 to meet the criteria. In the present study, the Cronbach’ s α values for the constructs ranged from 0.911 to 0.960, and the CR values ranged from 0.913 to 0.916, which met the criteria, as shown in Table 2 .
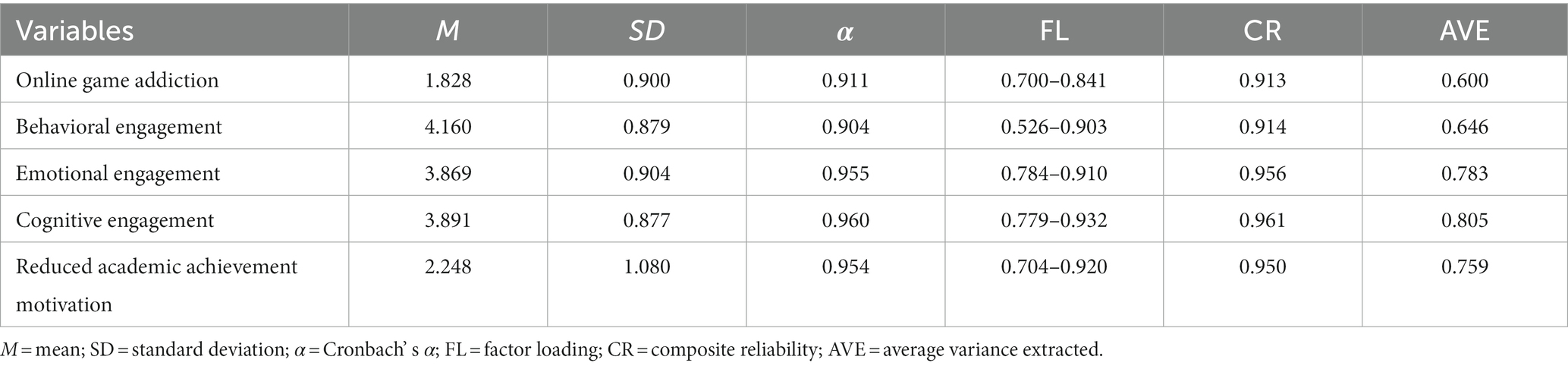
Table 2 . Construct reliability and validity of constructs.
In the present study, convergent validity was confirmed by two types of indicators, FL and average variance extracted (AVE). According to Hair et al. (2011) , an FL value should be greater than 0.500, and items with an FL value less than 0.500 should be removed; and AVE values should be greater than 0.500. In the present study, the FL values of the constructs ranged from 0.526 to 0.932, and the AVE values ranged from 0.600 to 0.805; all dimensions met the recommended criteria, as shown in Table 2 .
According to Awang (2015) and Hair et al. (2011) , the square root of the AVE of each construct (latent variable) should be greater than its correlation coefficient values with other constructs to indicate the ideal discriminant validity. The results of the present study showed that the three constructs of online game addiction, learning engagement, and reduced academic achievement motivation had good discriminant validity in the present study, as shown in Table 3 .
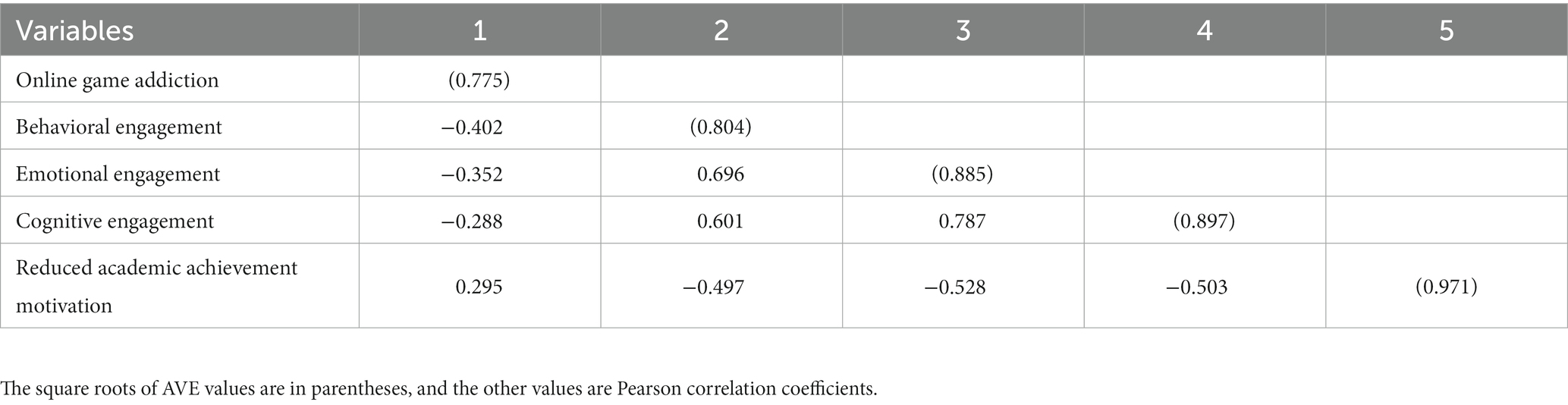
Table 3 . Discriminant validity analysis.
4.3. Correlation analysis
Pearson’s correlation coefficient is usually used to determine the closeness of the relationship between variables. A correlation coefficient greater than 0.8 indicates a high correlation between variables; a correlation coefficient between 0.3 and 0.8 indicates a moderate correlation between variables; while a correlation of less than 0.3 indicates a low correlation. Table 4 shows the Correlation Analysis results. Online game addiction was moderately negatively correlated with behavioral engagement ( r = −0.402, p < 0.001), moderately negatively correlated with emotional engagement ( r = −0.352, p < 0.001), slightly negatively correlated with cognitive engagement ( r = −0.288, p < 0.001), and slightly positively correlated with reduced academic achievement motivation ( r = 0.295, p < 0.001). Behavioral engagement was moderately positively correlated with emotional engagement ( r = 0.696, p < 0.001), moderately positively correlated with cognitive engagement ( r = 0.601, p < 0.001), and moderately negatively correlated with reduced academic achievement motivation ( r = −0.497, p < 0.001). Emotional engagement was moderately positively correlated with cognitive engagement ( r = 0.787, p < 0.001) and moderately negatively correlated with reduced academic achievement motivation ( r = −0.528, p < 0.001). Cognitive engagement was moderately negatively correlated with reduced motivation for academic achievement ( r = −0.528, p < 0.001).
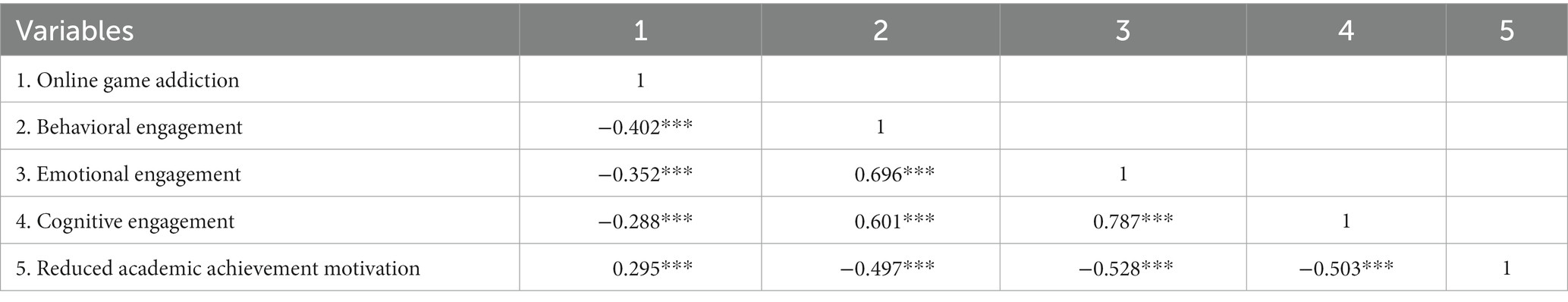
Table 4 . Correlation analysis.
4.4. Analysis of fitness of the measurement model
According to Hair et al. (2010) and Abedi et al. (2015) , the following criteria should be met in the analysis for measurement model fitness: the ratio of chi-squared and degree of freedom ( χ 2 / df ) should be less than 5; the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) should not exceed 0.100; the goodness of fit index (GFI), adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI), normed fit index (NFI), non-normed fit index (NNFI), comparative fit index (CFI), incremental fit index (IFI) and relative fit index (RFI) should be higher than 0.800; and the parsimonious normed fit index (PNFI) and the parsimonious fitness of fit index (PGFI) should be higher than 0.500. The model fitness indices in the present study were χ 2 = 1434.8, df = 428, χ 2 / df = 3.352, RMSEA = 0.073, GFI = 0.837, AGFI = 0.811, NFI = 0.899, NNFI = 0.920, CFI = 0.927, IFI = 0.927, RFI = 0.890, PNFI = 0.827, and PGFI = 0.722. The results were in accordance with the criteria, indicating a good fitness of the model in the present study ( Table 5 ).
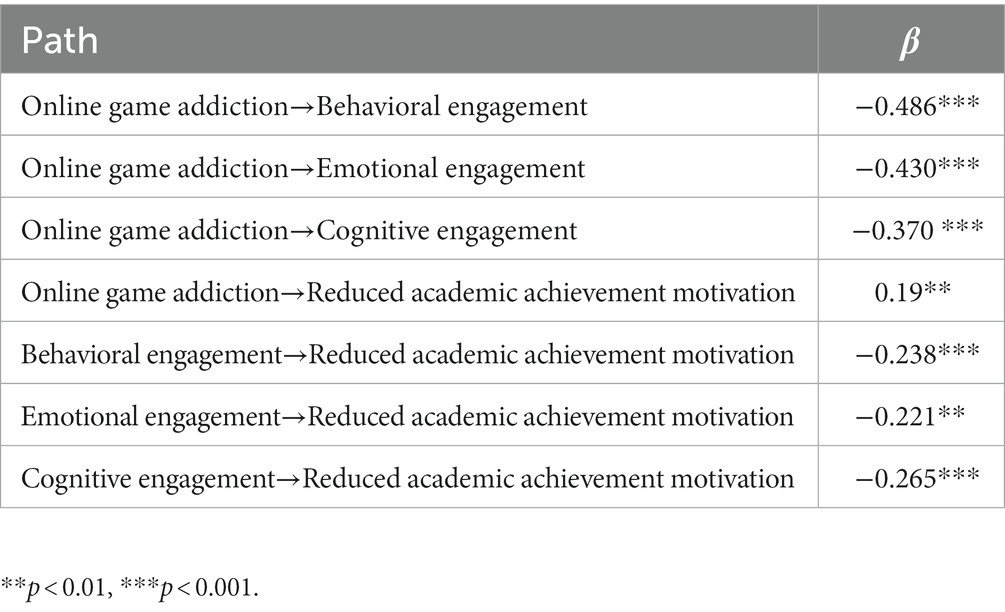
Table 5 . Direct effects analysis.
4.5. Validation of the research model
Online game addiction had a negative effect on behavioral engagement ( β = −0.486; t = −9.143; p < 0.001). Online game addiction had a negative effect on emotional engagement ( β = −0.430; t = −8.054; p < 0.001). Online game addiction had a negative effect on cognitive engagement ( β = −0.370; t = −7.180; p < 0.001). Online game addiction had a positive effect on reduced academic achievement motivation ( β = 0.19; t = −2.776; p < 0.01). Behavioral engagement had a negative effect on reduced academic achievement motivation ( β = −0.238; t = −3.759; p < 0.001). Emotional engagement had a negative effect on reduced academic achievement motivation ( β = −0.221; t = −2.687; p < 0.01), and cognitive engagement had a negative effect on reduced academic achievement motivation ( β = −0.265; t = −3.581; p < 0.01), as shown in Figure 2 Table 6 .
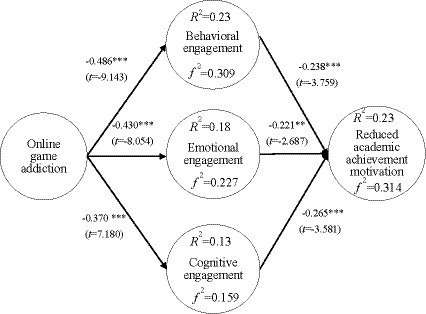
Figure 2 . Validation of the research model. *** p < 0.001.
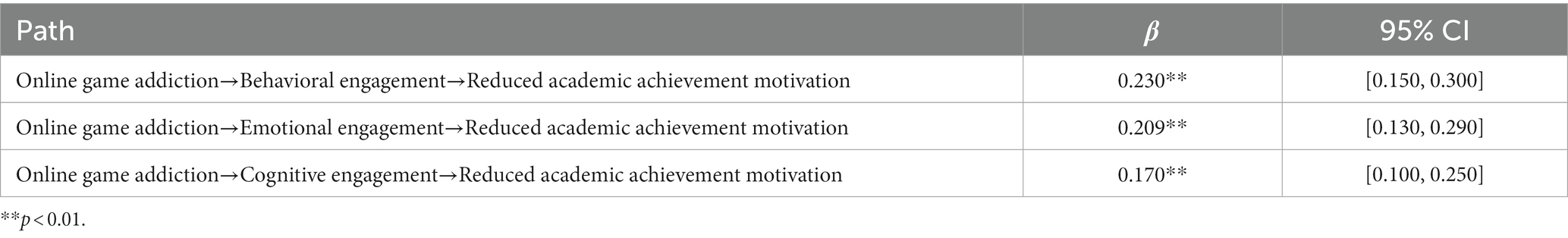
Table 6 . Indirect effects analysis.
Cohen’ s f 2 is an uncommon but valuable standardized effect size measure that can be used to assess the size of local effects ( Selya et al., 2012 ). When f 2 reaches 0.02 it represents a small effect size, 0.150 represents a medium effect size, and 0.350 represents a high effect size ( Hair et al., 2014 ). The explanatory power of online game addiction on behavioral engagement was 23.6%, and f 2 was 0.309. The explanatory power of online game addiction on emotional engagement was 18.5%, and f 2 was 0.227. The explanatory power of online game addiction on cognitive engagement was 13.7%, and f 2 was 0.159. The explanatory power of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement on reduced academic achievement motivation was 23.9%, and f 2 was 0.314. Figure 2 illustrates the above findings.
4.6. Indirect effects analysis
Scholars are often interested in whether variables mediate the association between predicting and outcome variables. Therefore, mediating variables can partially or entirely explain the association ( Hwang et al., 2019 ). In research fields such as psychology and behavior, where the research situation is often more complex, multiple mediating variables are often required to clearly explain the effects of the independent variables on the dependent variables ( MacKinnon, 2012 ). Scientific quantitative research requires tests of confidence interval (CI; Thompson, 2002 ), and the standard value of the test numbers is often determined by 95% CI ( Altman and Bland, 2011 ). CI value not containing 0 indicates the statistical significance of the analysis results ( Nakagawa and Cuthill, 2007 ). According to the statistical results shown in Table 4 , behavioral engagement significantly positively mediated the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation with a path coefficient of 0.230 and 95% CI ranging from 0.150 to 0.300 (excluding 0), p < 0.01; emotional engagement positively mediated the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation with a path coefficient of 0.209, 95% CI ranging from 0.130 to 0.292 (excluding 0), p < 0.01; cognitive engagement positively mediated the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation with a path coefficient of 0.170, 95% CI ranging from 0.100 to 0.250 (excluding 0), p < 0.01, as shown in Table 6 .
4.7. Discussion
4.7.1. analysis of the relationship between online game addiction and learning engagement.
Online game addiction is often negatively associated with students’ learning. For example, the problematic use of short videos was reported as negatively affecting students’ behavioral engagement, while behavioral engagement positively affected students’ emotional and cognitive engagement ( Ye et al., 2023 ). Meral (2019) highlighted that students’ learning attitudes and academic performance had a negative relationship with students’ addiction to online games. Demir and Kutlu (2018) found that online game addiction negatively affects students’ learning motivation. As the level of students’ game addiction increased, the level of their communication skills decreased ( Kanat, 2019 ). Furthermore, Tsai et al. (2020) pointed out a negative correlation between online game addiction and peer relationships as well as students’ learning attitudes. According to the results of the research model validation, it can be observed that: online game addiction negatively affected behavioral engagement, emotional engagement, and cognitive engagement. Therefore, it can be stated that online game addiction had significant and negative effects on all dimensions of learning engagement.
Online game addiction in the present study included aspects of computer game addiction and mobile phone game addiction. The results of the present study are consistent with the findings of Gao et al. (2021) , Choi (2019) , and Qi et al. (2020) , who pointed out that college students’ addiction to cell phones negatively affected their learning engagement.
4.7.2. Analysis of the relationship between learning engagement and reduced academic achievement motivation
For technology education in higher education, students’ intrinsic motivation for academic study predicts their learning engagement ( Dunn and Kennedy, 2019 ). In addition, learning engagement is positively correlated with academic achievement ( Fredricks and McColskey, 2012 ). Based on the research model validation results, behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement all negatively affected reduced academic achievement motivation. The findings are consistent with Hu et al.’s (2021) study which pointed out that cognitive engagement in the learning engagement dimension had the most significant effect on students’ academic achievement, and that emotional engagement was also an essential factor influencing students’ academic achievement. Lau et al. (2008) showed that achievement motivation positively predicted cognitive engagement in the learning engagement dimension. Mih et al. (2015) noted that achievement motivation positively predicted behavioral and emotional engagement in the learning engagement dimension. The present study supported the above discussion by confirming the association between learning engagement and reduced academic achievement motivation.
4.7.3. Analysis of the mediating role of learning engagement
According to the indirect effects analysis results of the present study, learning engagement negatively mediated the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation. The findings support Haji Anzehai’s (2020) conclusion that social network addiction negatively correlated with students’ motivation to progress ( Haji Anzehai, 2020 ). It is also consistent with the findings of Chen and Gu (2019) that students addicted to online games generally had lower academic achievement motivation due to a lack of precise academic planning and motivation. Cao et al. (2008) found a significant negative correlation between Internet addiction and students’ achievement motivation. Similarly, Zhang et al. (2018) explored the intrinsic influencing mechanism of students’ Internet addiction on academic achievement decline in their late adolescence by identifying learning engagement as the important mediating variable. Li et al. (2019) proposed that social networking site addiction among college students significantly negatively affected learning engagement and that learning engagement mediated the relationship between social network addiction and students’ academic achievement. The present study findings also support the discussion above.
5. Conclusion and suggestions
5.1. conclusion.
Currently, the problem of online game addiction among college students is increasing. The relationship between online game addiction, learning engagement, and reduced academic achievement motivation still needs to be explored. The present study explored the relationships between the three aforementioned variables by performing SEM. The results of the study indicated that: (1) online game addiction negatively affected behavioral engagement; (2) online game addiction negatively affected emotional engagement; (3) online game addiction negatively affected cognitive engagement; (4) behavioral engagement negatively affected reduced academic achievement motivation; (5) emotional engagement negatively affected reduced academic achievement motivation; (6) cognitive behavioral engagement negatively affected reduced academic achievement motivation; (7) learning engagement mediated the relationship between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation.
According to the research results, when college students are addicted to online games, their learning engagement can be affected, which may decrease their behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement; their academic achievement motivation may be further reduced and affect their academic success or even prevent them from completing their studies. The mediating role of learning engagement between online game addiction and reduced academic achievement motivation indicates that reduced academic achievement motivation influenced by online game addiction could be prevented or weakened by enhancing learning engagement.
5.2. Suggestions
Universities and families play a crucial role in preventing online game addiction among college students. One of the main reasons college students play online games may be that they lack an understanding of other leisure methods and can only relieve their psychological pressure through online games ( Fan and Gai, 2022 ). Therefore, universities should enrich college students’ after-school leisure life and help them cultivate healthy hobbies and interests. Besides, a harmonious parent–child relationship positively affects children’s learning engagement ( Shao and Kang, 2022 ). Parents’ stricter demands may aggravate children’s game addiction ( Baturay and Toker, 2019 ). Therefore, parents should assume a proper perspective on the rationality of gaming and adopt the right approach to guide their children.
One key factor influencing the quality of higher education is students’ learning engagement. The integration of educational information technology has disrupted traditional teaching methods. This trend has accelerated in the context of COVID-19. College students’ growth mindset can impact their learning engagement through the role of the perceived COVID-19 event strength and perceived stress ( Zhao et al., 2021 ). Moreover, students’ self-regulated learning and social presence positively affect their learning engagement in online contexts ( Miao and Ma, 2022 ). Students’ liking of the teacher positively affects their learning engagement ( Lu et al., 2022 ). Their perceived teacher support also positively affects their learning engagement ( An et al., 2022 ). Hence, educators should focus on teacher support and care in the teaching and learning process.
Students’ motivation for academic achievement can often be influenced by active interventions. Cheng et al. (2022) noted that the cumulative process of students gaining successful experiences contributed to an increased sense of self-efficacy, motivating them to learn. Zhou (2009) illustrated that cooperative learning motivated students’ academic achievement. In addition, Hong J. C. et al. (2021) showed that poor parent–child relationships (such as the behavior of “mama’ s boy” in adults) had a negative impact on students’ academic achievement motivation, and they concluded that cell phone addiction was more pronounced among students with low academic achievement motivation. Hence, enhancing students’ academic achievement motivation also requires family support.
5.3. Research limitations and suggestions for future research
Most of the past studies on the impact of online game addiction on academics have used quantitative research as the research method. The qualitative research approach regarding students’ online game addiction should not be neglected. By collecting objective factual materials in the form of qualitative research such as interviews a greater understanding of students’ actual views on games and the psychological factors of addiction can be achieved. Therefore, future studies could introduce more qualitative research to study online game addiction.
To pay attention to the problem of students’ online game addiction, universities and families should not wait until they become addicted and try to remedy it, but should start to prevent it before it gets to that stage. In terms of developing students’ personal psychological qualities, students’ sensation-seeking and loneliness can significantly affect their tendency to become addicted to online games ( Batmaz and Çelik, 2021 ). Adolescents’ pain intolerance problems can also contribute to Internet overuse ( Gu, 2022 ). Emotion-regulation methods affect the emotional experience and play a vital role in Internet addiction ( Liang et al., 2021 ). In this regard, it is necessary to pay attention to students’ mental health status and to guide them to establish correct values and pursue goals through psychological guidance and other means.
In addition to individual factors, different parenting can considerably impact adolescents. Adolescents who tend to experience more developmental assets are less likely to develop IGD ( Xiang et al., 2022a ), and external resources can facilitate the development of internal resources, discouraging adolescents from engaging in IGD ( Xiang et al., 2022b ). Relevant research indicates that the most critical factor in adolescents’ game addiction tendency comes from society or their parents rather than being the adolescents’ fault ( Choi et al., 2018 ). Adolescents who tend to be addicted to online games may have discordant parent–child relationships ( Eliseeva and Krieger, 2021 ). Better father-child and mother–child relationships predict lower initial levels of Internet addiction in adolescents ( Shek et al., 2019 ). Family-based approaches such as improved parent–child relationships and increased communication and understanding among family members can be a direction for adolescent Internet addiction prevention ( Yu and Shek, 2013 ).
At the school level, a close teacher-student relationship is one of the main factors influencing students’ psychological state. Students’ participation in and control over the teaching and learning process as well as their closeness to teachers can increase their satisfaction and thus enhance their learning-related well-being ( Yang J. et al., 2021 ). More school resources can lead to higher adolescent self-control, attenuating students’ online gaming disorders ( Xiang et al., 2022c ).
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. Written informed consent was not obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
R-QS, and J-HY: concept and design and drafting of the manuscript. R-QS, and J-HY: acquisition of data and statistical analysis. G-FS, and J-HY: critical revision of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by Beijing Normal University First-Class Discipline Cultivation Project for Educational Science (Grant number: YLXKPY-XSDW202211). The Project Name is “Research on Theoretical Innovation and Institutional System of Promoting the Modernization of Vocational Education with Modern Chinese Characteristics”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abedi, G., Rostami, F., and Nadi, A. (2015). Analyzing the dimensions of the quality of life in hepatitis B patients using confirmatory factor analysis. Global J. Health Sci. 7, 22–31. doi: 10.5539/gjhs.v7n7p22
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Altman, D. G., and Bland, J. M. (2011). How to obtain the confidence interval from a p value. Br. Med. J. 2011:343. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d2090
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
An, F., Yu, J., and Xi, L. (2022). Relationship between perceived teacher support and learning engagement among adolescents: mediation role of technology acceptance and learning motivation. Front. Psychol. 13:992464. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.992464
Awang, Z. (2015). SEM made simple, a gentle approach to learning structural equation modeling . MPWS Rich Publication. Bangi.
Google Scholar
Axelson, R. D., and Flick, A. (2010). Defining student engagement. Change 43, 38–43. doi: 10.1080/00091383.2011.533096
Bakar, K. A., Tarmizi, R. A., Mahyuddin, R., Elias, H., Luan, W. S., and Ayub, A. F. M. (2010). Relationships between university students’ achievement motivation, attitude and academic performance in Malaysia. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2, 4906–4910. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.793
Batmaz, H., and Çelik, E. (2021). Examining the online game addiction level in terms of sensation seeking and loneliness in university students. Addicta 8, 126–130. doi: 10.5152/ADDICTA.2021.21017
Baturay, M. H., and Toker, S. (2019). Internet addiction among college students: some causes and effects. Educ. Inf. Technol. 24, 2863–2885. doi: 10.1007/s10639-019-09894-3
Birch, S., and Ladd, G. (1997). The teacher-child relationship and children’s early school adjustment. Journal of School Psychology 35, 61–79. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4405(96)00029-5
Brunstein, J. C., and Heckhausen, H. (2018). “Achievement motivation,” in Motivation and action . eds. J. Heckhausen and H. Heckhausen (New York, NY: Springer), 221–304.
Cao, H., Cao, P., Wang, P., and Wang, X. H. (2008). An exploration of the interrelationship between internet addiction and achievement motivation among middle school students. J. Beijing Youth Polit. College 2008, 31–38.
Chapman, E. (2002). Alternative approaches to assessing student engagement rates. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 8:13. doi: 10.7275/3e6e-8353
Chen, C. G., and Gu, X. Q. (2019). The impact of online games on students’ subject literacy and social inclusion - an analysis based on PISA 2015 test data from four Chinese provinces and cities. Open Educat. Res. 25, 73–87. doi: 10.13966/j.cnki.kfjyyj.2019.05.008
Cheng, B. J., Chen, P., and Chen, Y. S. (2022). The influence of academic achievement motivation on technical learning engagement of students with specialization in physical education faculty: the mediating role of self-efficacy. J. Southwest Univ. 47, 96–106. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xsxb.2022.04.014
China Youth Network (2019). Survey on online hames for college students . Available at: http://edu.youth.cn/jyzx/jyxw/201904/t20190415_11926323.htm
Choi, S. (2019). Relationships between smartphone usage, sleep patterns and nursing students’ learning engagement. J. Korean Biol. Nurs. Sci. 21, 231–238. doi: 10.7586/jkbns.2019.21.3.231
Choi, C., Hums, M. A., and Bum, C. H. (2018). Impact of the family environment on juvenile mental health: eSports online game addiction and delinquency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:2850. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122850
Cui, J., Yang, K. B., Yang, Q. Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, R. J., Wu, W., et al. (2021). Psychological influences of online game addiction among college students in Chengde City. Chin. J. Drug Depend 30, 296–300+305. doi: 10.13936/j.cnki.cjdd1992.2021.04.011
Demir, Y., and Kutlu, M. (2018). Relationships among Internet addiction, academic motivation, academic procrastination and school attachment in adolescents. Int. Online J. Educat. Sci. 10, 315–332. doi: 10.15345/iojes.2018.05.020
Dincer, A., Yeşilyurt, S., Noels, K. A., and Vargas Lascano, D. I. (2019). Self-determination and classroom engagement of EFL Learners: a mixed-methods study of the self-system model of motivational development. SAGE Open 9:215824401985391. doi: 10.1177/2158244019853913
Dunn, T. J., and Kennedy, M. (2019). Technology enhanced learning in higher education; motivations, engagement and academic achievement. Comput. Educ. 137, 104–113. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.04.004
Durak, H. Y. (2018). Investigation of nomophobia and smartphone addiction predictors among adolescents in Turkey: demographic variables and academic performance. Soc. Sci. J. 56, 492–517. doi: 10.1016/j.soscij.2018.09.003
Eliseeva, M. I., and Krieger, E. E. (2021). The peculiarities of parent-child relationship among teenagers who are addicted to online games. Psychol. Educat. Stud. 13, 51–67. doi: 10.17759/psyedu.2021130304
Eliyani, E., and Sari, N. F. (2021). The effect of online game activities on student learn motivation. Jurnal Pelita Pendidikan 9, 65–70. doi: 10.24114/jpp.v9i2.23843
Elliot, A. J., and Church, M. A. (1997). A hierarchical model of approach and avoidance achievement motivation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 72, 218–232. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.218
Esposito, M. R., Serra, N., Guillari, A., Simeone, S., Sarracino, F., Continisio, G. I., et al. (2020). An investigation into video game addiction in pre-adolescents and adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Medicina 56:221. doi: 10.3390/medicina56050221
Fan, H., and Gai, X. Y. (2022). A survey study on contemporary college students’ leisure activities and online gaming behavior. Campus Life Mental Health 20, 12–16. doi: 10.19521/j.cnki.1673-1662.2022.01.002
Finn, J. D. (1989). Withdrawing from school. Rev. Educ. Res. 59, 117–142. doi: 10.3102/00346543059002117
Finn, J. D., Pannozzo, G. M., and Voelkl, K. E. (1995). Disruptive and inattentive-withdrawn behavior and achievement among fourth graders. Elem. Sch. J. 95, 421–434. doi: 10.1086/461853
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., and Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 74, 59–109. doi: 10.3102/00346543074001059
Fredricks, J. A., and McColskey, W. (2012). “The measurement of student engagement: a comparative analysis of various methods and student self-report instruments,” in Handbook of research on student engagement (New York, NY: Springer), 763–782.
Gao, B., Zhu, S. J., and Wu, J. L. (2021). The relationship between cell phone addiction and learning engagement among college students: the mediating role of self-control and the moderating role of core self-evaluation. Psychol. Dev. Educ. 37, 400–406. doi: 10.16187/j.cnki.issn1001-4918.2021.03.11
Gu, M. (2022). Understanding the relationship between distress intolerance and problematic internet use: the mediating role of coping motives and the moderating role of need frustration. J. Adolesc. 94, 497–512. doi: 10.1002/jad.12032
Guo, J. P., Liu, G. Y., and Yang, L. Y. (2021). Mechanisms and models influencing college students’ learning engagement – a survey based on 311 undergraduate higher education schools. Educ. Res. 42, 104–115.
Hafiz, B., and Shaari, J. A. N. (2013). “Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) of first order factor measurement model-ICT empowerment in Nigeria,” in International Journal of Business Management and Administration . 2, 81–88.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., and Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th. New York Pearson Prentice Hall.
Hair, J. F., Hult, T. M., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2014). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) . Thousand Oaks, CA SAGE.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: indeed a silver bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 19, 139–152. doi: 10.2753/MTP1069-6679190202
Haji Anzehai, Z. (2020). Correlation between self-efficacy and addiction to social networks with the motivation of academic achievement in high school students in Tehran. J. Health Promot. Manag. 9, 72–86.
Han, J., and Lu, Q. (2018). “A correlation study among achievement motivation, goal-setting and L2 learning strategy in EFL context,” in English Language Teaching . 11, 5–14.
Hong, J. C., Ye, J. N., Ye, J. H., Wang, C. M., and Cui, Y. T. (2021). Perceived helicopter parenting related to vocational senior high school students’ academic achievement and smartphone addiction. J. Res. Educat. Sci. 66, 1–33. doi: 10.6209/JORIES.202112_66(4).0001
Hong, R. Z., Ye, J. N., Ye, J. H., Wang, C. M., and Cui, Y. T. (2021). A study on the correlation between “mummy’s boys” behavior awareness, academic achievement motivation and cell phone addiction among technology-based high school students. J. Educat. Sci. Res. 66, 1–33. doi: 10.6209/JORIES.202112_66(4).0001
Hu, Q. Z., Wang, L. Y., and Gao, S. B. (2021). The effect of physics teacher trainees’ learning engagement on academic achievement. Higher Educat. Sci. 2021, 53–60.
Hwang, M. Y., Hong, J. C., Ye, J. H., Wu, Y. F., Tai, K. H., and Kiu, M. C. (2019). Practicing abductive reasoning: the correlations between cognitive factors and learning effects. Comput. Educ. 138, 33–45. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.04.014
Kahu, E. R., and Nelson, K. (2018). Student engagement in the educational interface: understanding the mechanisms of student success. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 37, 58–71. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2017.1344197
Kanat, S. (2019). The relationship between digital game addiction, communication skills and loneliness perception levels of university students. Int. Educ. Stud. 12, 80–93. doi: 10.5539/ies.v12n11p80
Kenny, D. A., Kaniskan, B., and McCoach, D. B. (2015). The performance of RMSEA in models with small degrees of freedom. Sociol. Methods Res. 44, 486–507. doi: 10.1177/0049124114543236
Kesici, A. (2020). The effect of conscientiousness and gender on digital game addiction in high school students. J. Educ. Fut. 18, 43–53. doi: 10.30786/jef.543339
Khan, A., Ahmad, F. H., and Malik, M. M. (2017). Use of digital game based learning and gamification in secondary school science: the effect on student engagement, learning and gender difference. Educ. Inf. Technol. 22, 2767–2804. doi: 10.1007/s10639-017-9622-1
Kuh, G. D., Kinzie, J., Cruce, T., Shoup, R., and Gonyea, R. M. (2007). Connecting the dots: multi-faceted analyses of the relationships between student engagement results from the NSSE, and the institutional practices and conditions that foster student success . Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Center for Postsecondary Research.
Lau, S., Liem, A. D., and Nie, Y. (2008). Task-and self-related pathways to deep learning: the mediating role of achievement goals, classroom attentiveness, and group participation. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 78, 639–662. doi: 10.1348/000709907X270261
Li, Y., Yao, C., Zeng, S., Wang, X., Lu, T., Li, C., et al. (2019). How social networking site addiction drives university students’ academic achievement: the mediating role of learning engagement. J. Pac. Rim Psychol. 13:e19. doi: 10.1017/prp.2019.12
Liang, L., Zhu, M., Dai, J., Li, M., and Zheng, Y. (2021). The mediating roles of emotional regulation on negative emotion and internet addiction among Chinese adolescents from a development perspective. Front. Psych. 12:608317. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.608317
Lu, L., Zhang, L., and Wang, L. (2022). The relationship between vocational college students’ liking of teachers and learning engagement: a moderated mediation model. Front. Psychol. 13:998806. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.998806
Luan, L., Hong, J. C., Cao, M., Dong, Y., and Hou, X. (2020). Exploring the role of online EFL learners’ perceived social support in their learning engagement: a structural equation model. Interact. Learn. Environ. 31, 1703–1714. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1855211
MacKinnon, D. P. (2012). Introduction to statistical mediation analysis . New York Routledge.
McClelland, D. C., Atkinson, J. W., Clark, R. A., and Lowell, E. L. (1976). The achievement motive . Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York.
Mendoza, J. S., Pody, B. C., Lee, S., Kim, M., and McDonough, I. M. (2018). The effects of cellphones on attention and learning: the influence of time, distraction, and nomophobia. Comput. Hum. Behav. 86, 52–60. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2018.04.027
Meral, S. A. (2019). Students’ attitudes towards learning, a study on their academic achievement and internet addiction. World J. Educat. 9, 109–122. doi: 10.5430/wje.v9n4p109
Miao, J., and Ma, L. (2022). Students’ online interaction, self-regulation, and learning engagement in higher education: the importance of social presence to online learning. Front. Psychol. 13:815220. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.815220
Mih, V., Mih, C., and Dragoş, V. (2015). Achievement goals and behavioral and emotional engagement as precursors of academic adjusting. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 209, 329–336. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.11.243
Nakagawa, S., and Cuthill, I. C. (2007). Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biol. Rev. 82, 591–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00027.x
Nong, W., He, Z., Ye, J.-H., Wu, Y.-F., Wu, Y.-T., Ye, J. N., et al. (2023). The relationship between short video flow, addiction, serendipity, and achievement motivation among Chinese vocational school students: the post-epidemic era context. Healthcare 11:462. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11040462
Pan, Y., Zhou, D., and Shek, D. T. L. (2022). Participation in after-school extracurricular activities and cognitive ability among early adolescents in China: moderating effects of gender and family economic status. Front. Pediatr. 10:839473. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.839473
Qi, H. Y., Liu, J. H., Hou, Y. H., Fan, W. F., Hou, J. P., and Wang, X. Y. (2020). The effect of cell phone addiction types on college students’ learning engagement. Health Prot. Promot. 2020, 88–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0223(x).2020.05.023
Rozgonjuk, D., Saal, K., and That, K. (2018). Problematic smartphone use, deep and surface approaches to learning, and social media use in lectures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:92. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15010092
Saeid, N., and Eslaminejad, T. (2017). Relationship between student’s self-directed-learning readiness and academic self-efficacy and achievement motivation in students. Int. Educ. Stud. 10, 225–232. doi: 10.5539/ies.v10n1p225
Schaufeli, W. B., Martinez, I. M., Pinto, A. M., Salanova, M., and Bakker, A. B. (2002). Burnout and engagement in university students: a cross-national study. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 33, 464–481. doi: 10.1177/0022022102033005003
Selya, A. S., Rose, J. S., Dierker, L. C., Hedeker, D., and Mermelstein, R. J. (2012). A practical guide to calculating Cohen’s f 2 , a measure of local effect size, from PROC MIXED. Front. Psychol. 3:111. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00111
Shao, Y., and Kang, S. (2022). The link between parent-child relationship and learning engagement among adolescents: the chain mediating roles of learning motivation and academic self-efficacy. Front. Educat. 7:854549. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.854549
Shek, D. T., Zhu, X., and Dou, D. (2019). Influence of family processes on internet addiction among late adolescents in Hong Kong. Front. Psych. 10:113. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00113
Shumacker, R. E., and Lomax, R. G. (2016). A beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling (4th) New York, NY: Routledge.
Sopiah, C. (2021). The influence of parenting style, achievement motivation and self-regulation on academic achievement. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 12, 1730–1742. doi: 10.17762/turcomat.v12i10.4635
Stipek, D. (2002). “Good instruction is motivating” in Development of achievement motivation . eds. A. Wigfield and J. Eccles (San Diego, CA: Academic Press)
Story, P. A., Hart, J. W., Stasson, M. F., and Mahoney, J. M. (2009). Using a two-factor theory of achievement motivation to examine performance-based outcomes and self-regulatory processes. Personal. Individ. Differ. 46, 391–395. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2008.10.023
Sunday, O. J., Adesope, O. O., and Maarhuis, P. L. (2021). The effects of smartphone addiction on learning: a meta-analysis. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 4:100114. doi: 10.1016/j.chbr.2021.100114
Teng, Z., Pontes, H. M., Nie, Q., Griffiths, M. D., and Guo, C. (2021). Depression and anxiety symptoms associated with internet gaming disorder before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal study. J. Behav. Addict. 10, 169–180. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00016
Thompson, B. (2002). What future quantitative social science research could look like: confidence intervals for effect sizes. Educ. Res. 31, 25–32. doi: 10.3102/0013189X031003025
Tian, J., Zhao, J. Y., Xu, J. M., Li, Q. L., Sun, T., Zhao, C. X., et al. (2021). Mobile phone addiction and academic procrastination negatively impact academic achievement among Chinese medical students. Front. Psychol. 12:758303. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.758303
Tsai, S. M., Wang, Y. Y., and Weng, C. M. (2020). A study on digital games internet addiction, peer relationships and learning attitude of senior grade of children in elementary school of Chiayi county. J. Educat. Learn. 9, 13–26. doi: 10.5539/jel.v9n3p13
Wang, M. T., and Eccles, J. S. (2013). School context, achievement motivation, and academic engagement: a longitudinal study of school engagement using a multidimensional perspective. Learn. Instr. 28, 12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2013.04.002
Weiner, B. (1985). An attributional theory of achievement motivation and emotion. Psychol. Rev. 92, 548–573. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.92.4.548
World Health Organization (WHO) (2018a). Inclusion of “gaming disorder” in ICD-11 . Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/14-09-2018-inclusion-of-gaming-disorder-in-icd-11
World Health Organization (WHO) (2018b). WHO releases new international classification of diseases (ICD11) . Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/18-06-2018-who-releases-new-international-classification-of-diseases-(icd-11)
Wu, Y.-T., Hong, J.-C., Wu, Y.-F., and Ye, J.-H. (2021). eSport addiction, purchasing motivation and continuous purchasing intention on eSport peripheral products. Int. J. e-Education e-Business e-Management e-Learning 11, 21–33. doi: 10.17706/ijeeee.2021.11.1.21-33
Xiang, G. X., Gan, X., Jin, X., and Zhang, Y. H. (2022a). The more developmental assets, the less internet gaming disorder? Testing the cumulative effect and longitudinal mechanism during the COVID-19 pandemic. Curr. Psychol. 1–12, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-03790-9
Xiang, G. X., Gan, X., Jin, X., Zhang, Y. H., and Zhu, C. S. (2022b). Developmental assets, self-control and internet gaming disorder in adolescence: testing a moderated mediation model in a longitudinal study. Front. Public Health 10:808264. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.808264
Xiang, G. X., Li, H., Gan, X., Qin, K. N., Jin, X., and Wang, P. Y. (2022c). School resources, self-control and problem behaviors in Chinese adolescents: a longitudinal study in the post-pandemic era. Curr. Psychol. 1-13, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-04178-5
Xiong, Y., Li, H., Kornhaber, M. L., Suen, H. K., Pursel, B., and Goins, D. D. (2015). Examining the relations among student motivation, engagement, and retention in a MOOC: a structural equation modeling approach. Glob. Educ. Rev. 2, 23–33.
Yang, J., Peng, M. Y. P., Wong, S., and Chong, W. (2021). How E-learning environmental stimuli influence determinates of learning engagement in the context of COVID-19? SOR model perspective. Front. Psychol. 12:584976. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.584976
Yang, X., Zhang, M., Kong, L., Wang, Q., and Hong, J. C. (2021). The effects of scientific self-efficacy and cognitive anxiety on science engagement with the “question-observation-doing-explanation” model during school disruption in COVID-19 pandemic. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 30, 380–393. doi: 10.30773/pi.2020.0034
Yayman, E., and Bilgin, O. (2020). Relationship between social media addiction, game addiction and family functions. Int. J. Evaluat. Res. Educat. 9, 979–986. doi: 10.11591/ijere.v9i4.20680
Ye, J. H., Wang, C. M., and Ye, J. N. (2020). An analysis of the relationship between achievement motivation, learning engagement and continuous improvement attitudes of technical vocational college students. J. Natl. Taichung Univ. Sci. Technol. 7, 1–20. doi: 10.6902/JNTUST.202012_7(2).0001
Ye, J. H., Wu, Y. F., Nong, W., Wu, Y. T., Ye, J. N., and Sun, Y. (2023). The association of short-video problematic use, learning engagement, and perceived learning ineffectiveness among Chinese vocational students. Healthcare 11:161. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11020161
Ye, J. H., Wu, Y. T., Wu, Y. F., Chen, M. Y., and Ye, J. N. (2022). Effects of short video addiction on the motivation and well-being of Chinese vocational college students. Front. Public Health 10:847672. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.847672
Yu, L., and Shek, D. T. L. (2013). Internet addiction in Hong Kong adolescents: a three-year longitudinal study. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 26, S10–S17. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2013.03.010
Zhang, N. (2012). A review of Chinese domestic and international research on learning engagement and its school influences. Psychol. Res. 5, 83–92.
Zhang, Y., Qin, X., and Ren, P. (2018). Adolescents’ academic engagement mediates the association between internet addiction and academic achievement: the moderating effect of classroom achievement norm. Comput. Hum. Behav. 89, 299–307. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.018
Zhao, H., Xiong, J., Zhang, Z., and Qi, C. (2021). Growth mindset and college students’ learning engagement during the COVID-19 pandemic: a serial mediation model. Front. Psychol. 12:621094. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.621094
Zhou, H. (2009). The effect of cooperative learning in basketball teaching on social behavior and academic achievement motivation. Zhejiang Sport Sci. 31, 109–112.
Keywords: college students, online game addiction, learning engagement, reduced academic achievement motivation, online games
Citation: Sun R-Q, Sun G-F and Ye J-H (2023) The effects of online game addiction on reduced academic achievement motivation among Chinese college students: the mediating role of learning engagement. Front. Psychol . 14:1185353. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1185353
Received: 13 March 2023; Accepted: 08 June 2023; Published: 13 July 2023.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Sun and Ye. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian-Hong Ye, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

- Advanced Search
A theoretical framework for online game society: the case of league of legends
New citation alert added.
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
Information & Contributors
Bibliometrics & citations.
- Aguerri J Santisteban M Miró-Llinares F (2023) The Enemy Hates Best? Toxicity in League of Legends and Its Content Moderation Implications European Journal on Criminal Policy and Research 10.1007/s10610-023-09541-1 29 :3 (437-456) Online publication date: 24-May-2023 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10610-023-09541-1
Index Terms
Applied computing
Law, social and behavioral sciences
Human-centered computing
Human computer interaction (HCI)
HCI design and evaluation methods
User models
Recommendations
Playing with streakiness in online games: how players perceive and react to winning and losing streaks in league of legends.
Streakiness refers to observed tendency towards consecutive appearances of particular patterns. In video games, streakiness is oftentimes inevitable, where a player keeps winning or losing for a short period. However, the phenomenon remains understudied ...
Prosocial behavior in an online game community: an ethnographic study
We report an ethnographic study of prosocial behavior inconnection to League of Legends, one of the most popular games in the world. In this game community, the game developer, Riot Games, implemented a system that allowed players to volunteer their ...
Using Machine Learning to Predict Game Outcomes Based on Player-Champion Experience in League of Legends
League of Legends (LoL) is the most widely played multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) game in the world. An important aspect of LoL is competitive ranked play, which utilizes a skill-based matchmaking system to form fair teams. However, players’ ...
Information
Published in.

- General Chairs:
Leibniz University Hannover & L3S Research Center, Germany
University of Southampton, UK
- Program Chairs:
Stanford University
University of Koblenz, Germany
- SIGWEB: ACM Special Interest Group on Hypertext, Hypermedia, and Web
Association for Computing Machinery
New York, NY, United States
Publication History
Check for updates, author tags.
- empirical study
- human-computer interaction
- league of legends
- theoretical framework
- theory formation
- user behaviors and models
- Extended-abstract
Funding Sources
- University of Southampton
Acceptance Rates
Contributors, other metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics.
- 1 Total Citations View Citations
- 493 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 21
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 3
View Options
Login options.
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
View options.
View or Download as a PDF file.
View online with eReader .
Share this Publication link
Copying failed.
Share on social media
Affiliations, export citations.
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.
- Golden Eagles
- Sports Awards
- Motor Sports
Giannis Antetokounmpo leads Greece over Slovenia, one game away from Olympics
The Greek national men’s basketball team is one game away from its first Olympic Games since 2008 after Giannis Antetokounmpo scored 13 points in a 96-68 victory over Luka Dončić and the Slovenian national team in an Olympic qualifying tournament in Greece on Saturday afternoon.
The Greek-Slovenian matchup was the most anticipated of the FIBA qualifying tournament, which also features the Dominican Republic and Croatia. But an ailing Dončić – whose NBA season in Dallas concluded with an NBA Finals loss on June 17 – and the Slovenians unexpectedly lost to Croatia in pool play on July 2. That set up a matchup between the two NBA superstars in Saturday’s semifinal, as opposed to the winner-take-all finals matchup most predicted.
The Greeks held Dončić to 21 points on 14 shots despite not having Thanasis Antetokounmpo, who tore his left Achilles tendon in June. The eldest of the basketball-playing Antetokounmpo brothers was expected to be the primary defender on Dončić.
Giannis Antetokounmpo added four rebounds in about 20 minutes of play, as the Slovenians had no answer for the 29-year-old Bucks star in the early going.
He scored seven points in the opening minutes as Greece took a 15-4 first-quarter lead and never looked back.
This tournament, held in Piraeus, Greece, has been Giannis Antetokounmpo’s first game action since straining a left soleus (calf) muscle against the Boston Celtics on April 9.
Dominican High School alumnus Kostas Antetokounmpo did not play in the game.
Greece will face the winner of the Dominican Republic and Croatia in the qualifying tournament final on Sunday. Greece easily dispatched the Dominican Republic 109-82 on July 3. The Dominican Republic is playing without Minnesota star Karl-Anthony Towns, who represented the country in the 2023 World Cup.
Should they win, as expected, it will mark the first Olympic appearance for the Greek men’s basketball team since 2008.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Impact of Online Games In Study Habit of Senior High School Students In Particial Fulfillmentof the Requirements for the Subject Research in daily life The Problem and its Background

Related Papers
bernadette basilan
king omambac
Alfredo Baula Jr.
pasca.if.its.ac.id
Yaya Heryadi
Maria Louella Sierra
FKDFFJSFJSD
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- High Schools
- SportsbookWire
- USA TODAY Sports
What channel is Phillies vs. Braves game on Friday? How to watch on Apple TV+

The Philadelphia Phillies open a three-game series against the rival Atlanta Braves Friday at Truist Park in Atlanta.
Did the Phillies win last night?
Cubs 10, phillies 2.
Jameson Taillon and the Cubs' bullpen limited the Phillies' offense to six hits as Chicago avoided a three-game sweep.
Who are the Phillies playing tonight?
Philadelphia faces Atlanta at 7:20 p.m. Friday at Truist Park in Atlanta. Philadelphia right-hander Aaron Nola (9-4, 3.43 ERA) will face Atlanta left-hander Max Fried (7-3, 2.91 ERA).

What channel is the Phillies game on tonight?
The game will be on Apple TV+. The radio broadcast will be on 94WIP and WDEL 101.7 FM/1150 AM.
How can I watch the Phillies on Apple TV+?
While there's still time before the game, you'll need a subscription to Apple TV+ if you want to watch it. A monthly subscription to Apple TV+ is $9.99 . However, Apple TV+ is offering a free trial with the requirement of an email or Apple ID.
When do the Phillies play on Apple TV+ this season?
At this point, the Phillies aren't scheduled for another game on "Friday Night Baseball" on Apple TV+ . However, Apple's schedule is only announced through July. The Phillies could be on Apple TV+ again in August or September.
How can I stream today's Phillies game?
Every Phillies game is streamed on MLB.com with the MLB TV package , which you have to pay for. You can also stream the radio broadcasts with MLB audio.

Copa America 2024: Results, highlights as Canada defeats Venezuela on penalties
A 1-1 draw through regulation Friday night in Arlington, Texas pushed the Copa America quarterfinal matchup between Venezuela and Canada to penalty kicks.
The teams were even at 3-3 after five attempts each. Following a miss from Venezuela's Wilker Ángel, Ismaël Koné stepped into the box for Canada with a chance to win the game.
He hesitated slightly before burying the ball in the left corner of the net to advance Canada to the semifinals of the team's first Copa America.
Friday's quarterfinal match saw an early goal by Canada's Jacob Shaffelburg in the 13th minute. The Copa America debutant kept that lead through halftime and into the second half as Venezuela turned up the energy and pressure.
Venezuela's vice captain Salomón Rondón notched the equalizer in the 65th minute and that score held through the end of stoppage time. Koné's shot secured Canada's second win in the tournament to move them on to another matchup with tournament favorite Argentina.
Down to the wire: Argentina bails out Messi in shootout to advance past Ecuador in Copa América thriller
When does Canada play next?
Canada will be back in action on Tuesday in East Rutherford, New Jersey to take on Argentina for the second time in the Copa America. The two teams faced off in Group A with Argentina winning 2-0. Kick off is set for 8 p.m. ET.
Canada vs. Venezuela highlights
Canada got on the board early behind Shaffelburg's shot in front of the goal.
CANADA TAKES THE LEAD 🇨🇦 Jacob Shaffelburg puts Canada on top 💪 pic.twitter.com/SiaqN3fDOc — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
In honor of teammate Tajon Buchanan, who is sidelined with an injury from training, Shaffelburg sprinted to the sideline to raise Buchanan's jersey up in celebration.
Jacob Shaffelburg ran over to the sideline after scoring to hold up Tajon Buchanan's jersey who was injured earlier this week in training ❤️🇨🇦 pic.twitter.com/uRl8ydUaW0 — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
Venezuela finally got on the board thanks to Rondón - the most experienced player in the national team's history - floating the ball past Canadian keeper Maxime Crépeau for his third goal of the tournament.
Salomón Rondón caught Crépeau out of the box for a massive equalizer 🤯 pic.twitter.com/GWZU4njLnm — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
After 11 penalty kicks, Koné made the 12th and final shot of the night to give Canada the victory.
The kick that sent Canada through. 🤩 pic.twitter.com/l5nwJ7L44x — Major League Soccer (@MLS) July 6, 2024
The teams traded makes and misses over the first 10 shots before Ángel's miss and Koné's make.
Canada made history after advancing in penalties 🇨🇦👏 Watch all TWELVE penalty kicks from the Canada-Venezuela shootout ⬇️ pic.twitter.com/6RF5pzd3Vt — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
Ismaël Koné seals the win for Canada
The second-half substitution fired the ball into the left corner for Canada to get the 4-3 edge in penalties and win their quarterfinal match with Venezuela.
Alphonso Davies makes clutch penalty kick
Venezuela's Jhonder Cádiz made it 3-2 with the game on the line for Davies. Canada's captain sank his attempt to make it 3-3.
Both teams miss fourth kick
Venezuela's Jefferson Savarino and Canada's Stephen Eustáquio missed their team's fourth shot.
Penalties at 2-2 following third kick
Tomás Rincón made the third shot for Venezuela. Canada's Moïse Bombito responded with a make in the far right corner of the net.
Both teams trade makes, misses
Salomón Rondón and Jonathan David each made the first kick for Venezuela and Canada, respectively. Venezuela's Angel Herrera and Canada's Liam Millar missed the second penalty kick.
End of regulation: Venezuela 1, Canada 1
Multiple shots for both teams in the final 15 minutes failed to connect and, after four minutes of stoppage time, referees ended regulation to send this matchup to penalties. Yesterday's Argentina-Ecuador match went to penalties as well.
Yellow card for Venezuela (94')
Canada's Liam Millar had a breakaway attempt and Venezuela's Jon Aramburu tripped him up to avoid a shot at goal. His effort earned a yellow card.
Canada misses multiple shots in closing minutes (89')
Ali Ahmed had a great chance on goal but his shot went wide left. A minute later, Ismaël Koné's curving shot went wide right of goal.
Substitutions for Venezuela (83')
Matías Lacava enters the game for his international debut for Eduard Bello and Jefferson Savarino enters the pitch for Yeferson Soteldo.
Another substitution for Canada (82')
Ismaël Koné enters the game for Jonathan Osorio.
Oluwaseyi's first shot misses high (77')
Minutes after entering the game, Tani Oluwaseyi earned a great opportunity from the center of the box from a pass by Derek Cornelius. The shot barely missed the crossbar as the game remains 1-1.
Substitutions for Canada (73')
Cyle Larin and Richie Laryea are out with Tani Oluwaseyi and Ali Ahmed taking their places.
GOAL: Venezuela 1, Canada 1 (64')
A clearance by Jon Aramburu left Venezuelan vice-captain Salomón Rondón one-on-one on the attacking side and he floated a shot over Canadian keeper Maxime Crépeau, who was too far outside of the box to catch it.
VENEZUELA WITH AN UNREAL GOAL TO LEVEL THE SCORE 😱🤯 pic.twitter.com/V17zWlgJV0 — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
Crépeau deflects a shot from Bello (58')
Venezuelan winger Eduard Bello nearly scored his third goal of the tournament after a cross from Yeferson Soltedo. Crépeau leapt up and knocked it above the goal to keep it 1-0.
Larin's shot sails over the net (52')
A great pass down the right side of the field put Canada in a great spot in the box. Cyle Larin - the active scoring leader for Canada - hastily put up a shot and it went over the net to remain 1-0.
Yellow card No. 2 for Canada (50')
Centre-back Derek Cornelius was shown the yellow for contact with Venezuela's Yeferson Soteldo.
HALFTIME: Canada 1, Venezuela 0
Jacob Shaffelburg's goal in the 13th minute remains the difference in the game as both teams head to the locker room.
Possession is nearly even over the first 45 minutes of play. Venezuela's outshot Canada 10-7 but Canada has more shots on goal with four to Venezuela's two.
Eustáquio ends chance for Venezuela (45')
Four minutes of stoppage time were added at the end of the first half. Venezuela had a good chance with a set piece but Stephen Eustáquio intercepted a pass and cleared out the chance to keep it 1-0 for at least a few minutes longer.
Yellow card for Shaffelburg (36')
Canada's Jacob Shaffelburg went down with an injury and went off the field. He re-entered the field too soon afterward and was given a yellow card.
Jacob Shaffelburg runs onto the field too early and receives a yellow card 🟨 pic.twitter.com/C0CnqmANnu — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
Canada misses another chance on goal (31')
After a deflection, Cyle Larin's pass missed Jonathan David's left foot by mere inches and kept the side from scoring another first-half goal.
Canada with ANOTHER huge chance 😳 pic.twitter.com/4qphQ4mSsQ — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
David's shot misses wide right for Canada (26')
Shaffelburg had a breakaway counter attack from a pass by Alphonso Davies. He found Jonathan David with only Venezuela's keeper Romo in the way. David fired a shot past Romo but it sailed wide right of the goal.
Shaffelburg nearly scores again (24')
After multiple attempts from Venezuela, Canada had one of their better chances at goal with Shaffelburg firing from the center of the box following a pass from Cyle Larin. Venezuelan keeper Rafael Romo blocked it away from goal.
Jacob Shaffelburg nearly had a second goal here 😳👀 pic.twitter.com/mNwtYp7tyr — FOX Soccer (@FOXSoccer) July 6, 2024
Venezuela can't connect from inside the box (20')
Salomón Rondón had another good chance at a goal in but Canadian keeper Maxime Crépeau blocked it. Minutes later, Crépeau blocked Yangel Herrera's header attempt from the center of the box.
Shaffelburg honors teammate Buchanan
Canadian striker Tajon Buchanan was injured during training earlier this week and will not play in today's match. Shaffelburg held up his teammate's jersey after scoring the first goal of the game.
Rondón's header just wide of the goal (15')
Venezuela's Yeferson Soteldo corraled a clearance and floated it perfectly to vice-captain Salomón Rondón in the middle of the box but his header attempt sailed wide left of the goal.
GOAL: Canada 1, Venezuela 0 (13')
After Cyle Larin's shot nearly led to a goal in the eighth minute, Jacob Shaffelburg capitalized on a deflection to find the right corner of the net from the center of the box. His goal is just the second of the tournament for Canada.
Crépeau earns early save for Canada
An attack from Venezuela in the opening minutes tested the Canadian keeper but he deflected the shot from Venezuela's vice captain Salomón Rondón.
Venezuela vs. Canada: Time, TV, Streaming and how to watch
- Time: 9 p.m. ET
- Location : AT&T Stadium, Arlington, Texas
- Streaming: FoxSports App, fuboTV
WATCH: Catch all of the action from the 2024 Copa America with a fubo subscription
Venezuela vs. Canada betting: Odds and spread for Copa America
Venezuela is slightly favored to move on to the semifinals of the 2024 Copa America, per BetMGM's latest soccer odds .
- Moneyline: Venezuela (+165), Tie (+188), Canada (+200)
- Over/under: 2.5 goals
WANNA BET? Check out new customer offers with the best online sportsbooks and sports betting apps
Venezuela starting lineup
Los 𝙉𝙐𝙀𝙎𝙏𝙍𝙊𝙎 📋🇻🇪 Alineación del profe @bochabatista para enfrentar a Canadá por los Cuartos de Final en el AT&T Stadium, Texas 🫡 #SiempreVinotinto #VibraElContinente pic.twitter.com/3GctfF1EZ1 — La Vinotinto (@SeleVinotinto) July 6, 2024
Canada starting lineup
Ready to write more history! ✍️ Here’s who we start with, presented by @GE_Appliances —— Nous sommes impatients d’écrire une nouvelle page d’histoire ! Voici avec qui nous commençons, présenté par @GE_Appliances #CANMNT #NoFearAllFight #SansPeurAvecCourage pic.twitter.com/G7Jcg4EjiE — CANMNT (@CANMNT_Official) July 5, 2024
Venezuela vs. Canada predictions
Sports mole : venzuela 1, canada 1 (venezuela advances on penalties).
Joel Lefevre writes: "The Canadians have been a resilient group, but in a match that could be about holding your nerve, we trust the experience of players like Rondon to carry the Venezuelans through."
Live Score : Venzuela wins
Aidan Perkins says: "Canada have some well-known players, including Davies and David, while Venezuela are led by experienced former West Brom and Everton forward Rondon, who has scored 41 goals for his country. It looks set to be tight but Venezuela can maintain their winning form and book themselves a place in the semis."
Sportskeeda : Venzuela 1, Canada 0
Soyoye Jedidiah writes: "Venezuela have been one of the standout sides in the Copa America so far and will head into the weekend clash with a three-game winning streak under their belt... Canada, meanwhile, have won just two of their last seven games across all competitions. They have struggled in front of goal of late and could exit the competition on Friday."
Copa America 2024 bracket: Remaining schedule
Quarterfinals.
Thursday, July 4
- Argentina 1, Ecuador 1 (Argentina wins 4-2 on penalties)
Friday, July 5
- Venezuela vs. Canada, 9 p.m. ET, Arlington, Texas
Saturday, July 6
- Panama vs. Colombia, 6 p.m. ET, Glendale, Arizona
- Uruguay vs. Brazil, 9 p.m. ET, Las Vegas
Tuesday, July 9
- Argentina vs. TBD, 8 p.m. ET, East Rutherford, New Jersey
Wednesday, July 10
- TBD vs. TBD, 8 p.m. ET, Charlotte, North Carolina
Saturday, July 13
- Third-place playoff, 8 p.m ET, Charlotte, North Carolina
Sunday, July 14
- Championship game, 8 p.m. ET, Miami
Copa America tickets: Prices and availability
As of Friday morning, tickets are still available for the quarterfinal matchup between Venezuela and Canada on SeatGeek starting at $115 each.
What is the Copa America tournament?
The Copa America is one of the oldest soccer competitions in the world. It began in 1916 with all of the national teams from South America. Since the 1990s, national teams from North America and Asia have also been invited.
This year's tournament includes 10 teams from the CONMEBOL (Confederación Sudamericana de Fútbol) and six teams from the CONCACAF (Confederation of North, Central America and Caribbean Association Football).
CONMEBOL teams:
CONCACAF teams:
Copa America odds: Favorites to win tournament
Argentina remains the favorite to win the 2024 Copa America, per BetMGM.
- Argentina (-125)
- Brazil (+400)
- Colombia (+550)
- Uruguay (+550)
- Venezuela (+3300)
- Canada (+5000)
- Panama (+12500)
UEFA Euro Cup: Bracket, standings for remaining games
- Spain 2, Germany 1
- France 0, Portugal 0 (France wins 5-3 on penalties)
- England vs. Switzerland, Noon ET, Düsseldorf, Germany
- Netherlands vs. Turkey, 3 p.m. ET Berlin, Germany
- Spain vs. France, 3 p.m. ET, Munich, Germany
- Netherlands/Turkey vs. England/Switzerland, 3 p.m. ET, Dortmund, Germany
- TBD vs. TBD, 3 p.m. ET, Berlin, Germany
Canada national team roster
Professional club in parentheses.
- GK Dayne St. Clair (Minnesota United)
- DF Alistair Johnston (Celtic)
- DF Luc de Fougerolles (Fulham)
- DF Kamal Miller (Portland Timbers)
- DF Joel Waterman (CF Montréal)
- MF Samuel Piette (CF Montréal)
- MF Stephen Eustáquio (Porto) - vice-captain
- MF Ismaël Koné (Watford)
- FW Cyle Larin (Mallorca)
- FW Jonathan David (Lille)
- FW Theo Bair (Motherwell)
- FW Jacen Russell-Rowe (Columbus Crew)
- DF Derek Cornelius (Malmö FF)
- FW Jacob Shaffelburg (Nashville SC)
- DF Moïse Bombito (Colorado Rapids)
- GK Maxime Crépeau (Portland Timbers)
- FW Tajon Buchanan (Inter Milan)
- GK Tom McGill (Brighton & Hove Albion)
- DF Alphonso Davies (Bayern Munich) - captain
- DF Ali Ahmed (Vancouver Whitecaps)
- MF Jonathan Osorio (Toronto FC)
- DF Richie Laryea (Toronto FC)
- FW Liam Millar (Preston North End)
- MF Mathieu Choinière (CF Montréal)
- FW Tani Oluwaseyi (Minnesota United)
- DF Kyle Hiebert (St. Louis City)
Venezuela national team roster
- GK Joel Graterol (América de Cali)
- DF Nahuel Ferraresi (São Paulo)
- DF Yordan Osorio (Parma)
- DF Jon Aramburu (Real Sociedad)
- DF Jhon Chancellor (Metropolitanos)
- MF Yangel Herrera (Girona)
- MF Jefferson Savarino (Botafogo)
- MF Tomás Rincón (Santos) - captain
- FW Jhonder Cádiz (Famalicão)
- MF Yeferson Soteldo (Grêmio)
- MF Darwin Machís (Cádiz)
- GK José Contreras (Águilas Doradas)
- MF José Martínez (Philadelphia Union)
- DF Christian Makoun (Anorthosis Famagusta)
- DF Miguel Navarro (Talleres)
- MF Telasco Segovia (Casa Pia)
- MF Matías Lacava (Vizela)
- MF Cristian Cásseres (Toulouse)
- FW Eric Ramírez (Atlético Nacional)
- DF Wilker Ángel (Criciúma)
- DF Alexander González (Emelec)
- GK Rafael Romo (Universidad Católica)
- FW Salomón Rondón (Pachuca) - vice-captain
- MF Kervin Andrade (Fortaleza)
- MF Eduard Bello (Mazatlán)
- MF Daniel Pereira (Austin FC)
Canada players to watch:
FW Jonathan David: The Lille striker scored the team's lone goal of the tournament so far and drawn nine fouls, tied for third-most in the tournament. Though he didn't score against Chile, he led the squad by completing 88% of his passes.
DF Alphonso Davies: The Bayern Munich defender and captain has been a key player throughout the tournament for the Copa America debutants. If the squad makes it to the semifinals, Davies will be a huge part of it.
Venezuela players to watch:
FW Salomón Rondón : Venezuela's leading scorer and vice-captain has put on a show in this tournament. He'll set the record for most appearances on the Venezuelan national team with Friday's match. His experience and scoring will be key for Venezuela to win the race.
FW Eduard Bello: The midfielder's scored twice in the tournament as well in a secondary scoring role to Rondón in his first Copa America appearance. He'll also be a key part of the attack for La Vinotinto .
We occasionally recommend interesting products and services. If you make a purchase by clicking one of the links, we may earn an affiliate fee. USA TODAY Network newsrooms operate independently, and this doesn’t influence our coverage.
Gannett may earn revenue from sports betting operators for audience referrals to betting services. Sports betting operators have no influence over nor are any such revenues in any way dependent on or linked to the newsrooms or news coverage. Terms apply, see operator site for Terms and Conditions. If you or someone you know has a gambling problem, help is available. Call the National Council on Problem Gambling 24/7 at 1-800-GAMBLER (NJ, OH), 1-800-522-4700 (CO), 1-800-BETS-OFF (IA), 1-800-9-WITH-IT (IN). Must be 21 or older to gamble. Sports betting and gambling are not legal in all locations. Be sure to comply with laws applicable where you reside.
ONLINE GAMING ADDICTION AND ACADEMIC ATTITUDES: THE CASE OF COLLEGE STUDENTS IN THE PHILIPPINES

- J.H. Cerilles State College
Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Kathleen Seth Fancubila Farillon
- Eulalia Fancubila Farillon
- Ariel T. Gutierrez
- Neriza G. Guzman
- Ramilet Ramos
- Jan Katherine A. Uylengco
- Petrus Kondo
- Eldiani Bawone

- J Cognit Psychother

- Alan Watkins
- Rooij van A. J

- WIEN KLIN WOCHENSCHR

- Frank Benker

- Sara E Allison
- Lisa von Wahlde
- Tamra Shockley
- Glen O. Gabbard
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The negative effects of online games are obvious. In terms of education, a decline in aca demic. performance is one of the most apparent negative effects of online games. Besides that, due. to ...
DEFINITIONS OF ONLINE GAMES. This thesis will refer to all games that are played with multiple players simulta-neously. Other than single player games, which are often story based or stra-tegic, these games do require an active internet connection and offer different tools for communication within the game.
ENDORSEMENT SHEET The thesis entitled: "Effects of Online Games in Academic Performance among Senior High School in Mount Carmel School of Maria Aurora, Inc." Prepared and submitted by: Pauline Denise V. Rodica Hanes Andrew Q. Talania In partial fulfillment of the requirements for Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics (STEM) Strand ...
and online), dedicated portable hardware and software, PC games and games for mobile. devices such as smart phones, tablets and other devices that can play games as an added. Contact Author's ...
Online video gaming has become a popular leisure activity among students, but concerns have been raised about its potential impact on academic performance. While some argue that video games can enhance cognitive skills, others claim that excessive gaming can lead to poor academic performance and even addiction.
The search used the keywords "online game addiction", "mental health", and "youth". The inclusive criteria for the included literature in this study were as follow; the literature had to be ...
This online game allows non-traditional students to explore the following modules in a game format: a key to health, nutrient sources and significance, energy balance, vitamins, minerals and water, fitness and food safety, and a focus on life stages. Another nutrition GameScape that may be used in a Nutrition course for non-traditional learners ...
current thesis five superordinate themes were emerged, which are (1) escapist motivations to engage in excessive online gaming, (2) ambition to win and to be satisfied in online game spaces, (3) burst of emotions while playing online games, (4) omnipotent self-presentations as reflected in narratives of gameplay, and (5) reactive
1School of Nursing, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China, 2School of Mental Health, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China. Objectives: This study aimed to explore the positive effects of online games on college students' psychological demands and individual growth. Methods: A qualitative study design was carried out in September 2021.
These online games have a big factor that affects the students in their academic performances in school. According to Dondlinger (2007) much attention has been directed to the use of video games for learning in the recent years, in part due to the staggering amounts of capital spent on games in the entertainment industry, but also because of ...
What are the demographic profiles of the respondents in terms of: a. Frequency of playing online games b. Average time span of playing online games c. Length of period of playing online games (since they've started) 2. How does playing online games affect the academic performance of the students in relation with: a. Class Participation b.
have quickly reacted to the negative influence online games can have on students. China has set rules banning children from spending more than 90 minutes a day gaming and children are only able to play online games up until 10 pm (James, 2022) The negative effects of online games are obvious. In terms of education, a decline in academic
1 BinZhou College of Science and Technology, Binzhou, China; 2 Binzhou Polytechnic, Binzhou, China; 3 Faculty of Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China; 4 National Institute of Vocational Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China; Introduction: The present study aimed to examine the effects of online game addiction on reduced academic achievement motivation, and the ...
The Effects of Online Games Towards The Academic Performance Of Selected Information Technology Students A Research Proposal Presented to The Faculty Of College of Information and Computing Sciences In Partial Requirement for The Completion in The Course Methods of Research Submitted by: John Kristoffer G. Olesco Christian Mark Suguitan John ...
Based on the findings, online gaming has a positive relationship with social behavior. Online games can also be an avenue of socially interacting with other people. It was also found that playing online games can help improve one's psychological well-being if done moderately. Keywords: Online gaming, Social Behavior, Psychological Well-being
League of Legends is the largest online game in the world, but is under-represented in video game studies. Its community is large and multi-sited, but known for competitive and toxic behaviours. This paper presents a qualitative research project into video game sociology, using League of Legends as the research site. It draws on Bourdieu's established social theory alongside empirical ...
game research can benefit by including and comparing individuals from various generational/age. young adults, as GenX and Boomers also deal wit. video game stigmatization and stigma management. Most importantly, this thesis demonstrates how popular media and the medical commun. millions of peop.
Thesis statement: addiction to online games can tell negatively upon the academic . performance and success of students, be they children or adolescents. 2. Literature Review . 2.1.
ONLINE GAMING EFFECTS ON STUDENT-Final-Thesis-Research-docx - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This study examines the influence of online gaming on academic interest among senior high school students at Central Mindanao Colleges. It aims to understand how online gaming affects students' academic focus.
The aim of this study is to investigate high school students' online game addiction with respect to gender. The sample which was selected through the criterion sampling method, consists of 81 female (61.8 %) female, and 50 male (38.2 %), total 131 high school students. The "Online Game Addiction Scale" which was developed by Kaya and ...
and negligible. The study found out that majority of the respondents played online games. Online games players had an average academic performance while non-players had a high academic performance. The predominantly male players preferred multi-player online games and they spent an average 2.14 hours a day and 4.45 days a week in playing.
What channel is the Phillies game on tonight? The game will be on FOX. The radio broadcast will be on 94WIP and WDEL 101.7 FM/1150 AM.
Greece plays Canada on July 27 in its first pool play game at Pierre Mauroy Stadium in Villeneuve-d'Ascq, France. They then play Spain/Bahamas on July 30 and Australia on Aug. 2.
The Greek national men's basketball team is one game away from its first Olympic Games since 2008 after Giannis Antetokounmpo scored 13 points in a 96-68 victory over Luka Dončić and the ...
Based on established researches, the thesis is interested in discovering the reasons behind why young people start to play online games as well as now playing such games affects the study habit and daily lives of them. Many of us have stayed up late more than once playing our favorite computer or online games. ... Online games is a kind of ...
Jameson Taillon and the Cubs' bullpen limited the Phillies' offense to six hits as Chicago avoided a three-game sweep. Who are the Phillies playing tonight? Philadelphia faces Atlanta at 7:20 p.m ...
The game finished after that goal to make it 5-0. GOAL: Colombia 5, Panama 0 (90+5') Following the delay and yellow card, Miguel Borja took a penalty kick for Colombia and buried it in the right ...
Colombia have now scored 11 goals across their four games at Copa America, matching their highest-ever scoring output at the tournament.
Minutes after entering the game, Tani Oluwaseyi earned a great opportunity from the center of the box from a pass by Derek Cornelius. The shot barely missed the crossbar as the game remains 1-1.
Thesis. May 2023; Romar Jerome De Vega Claveria ... In the 2000s, online games became popular, while studies of Internet gaming addiction emerged, outlining the negative consequences of excessive ...