If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Digital SAT Reading and Writing
Course: digital sat reading and writing > unit 2, rhetorical synthesis | lesson.
- Rhetorical synthesis — Worked example
- Rhetorical Synthesis — Quick example
- Rhetorical synthesis: foundations
What are "rhetorical synthesis" questions?
- The novel David Copperfield by Charles Dickens focuses on the adventures of its title character, David Copperfield.
- David Copperfield is considered a bildungsroman.
- In a bildungsroman, the main character grows, learns, and changes from experience.
- The novel Tom Jones by Henry Fielding focuses on the adventures of its title character, Tom Jones.
- Tom Jones is considered a picaresque novel.
- In a picaresque novel, the main character has many experiences but stays fundamentally the same.
- (Choice A) David Copperfield and Tom Jones are both considered picaresque novels. A David Copperfield and Tom Jones are both considered picaresque novels.
- (Choice B) Both David Copperfield and Tom Jones focus on the adventures of their title characters. B Both David Copperfield and Tom Jones focus on the adventures of their title characters.
- (Choice C) David Copperfield was written by Charles Dickens; Tom Jones was written by Henry Fielding. C David Copperfield was written by Charles Dickens; Tom Jones was written by Henry Fielding.
- (Choice D) In David Copperfield , unlike in Tom Jones , the main character grows, learns, and changes from experience. D In David Copperfield , unlike in Tom Jones , the main character grows, learns, and changes from experience.
Choice A: This choice does not accurately represent the information in the bullet points! Bullet point 2 tells us that David Copperfield is considered a bildungsroman. The next bullet points tell us that in a bildungsroman, the main character changes, while in a picaresque novel, the main character basically stays the same. This means that a bildungsroman can't also be a picaresque novel.
Choice B: This choice emphasizes a similarity and accurately represents the information in the bullet points. Bullet point 1 says that David Copperfield focuses on the adventures of its title character, and bullet point 4 says that Tom Jones focuses on the adventures of its title character.
Choice C: This choice accurately represents the bulleted information, but it doesn't accomplish the goal. It highlights a difference between the two novels—the fact that they have different authors. But we're looking for a similarity.
Choice D: Like choice C, this choice accurately represents the bulleted information, but it doesn't accomplish the goal. It emphasizes a difference between the two novels, but, again, we're looking for a similarity.
How should we think about rhetorical synthesis questions?
Question structure.
- an introduction
- a series of bulleted facts
- a question prompt
- the choices
How to approach rhetorical synthesis questions
Step 1: Identify the goal
Step 2: Read the bullet points and identify relevant info
Step 3: Test the choices
Step 4: Select the choice that matches
Do two "passes" to eliminate choices!
Simplify the goal.
- Choice C emphasizes a difference between the two novels, not a similarity. We can eliminate choice C.
- Choice D also emphasizes a difference between the two novels, not a similarity. We can eliminate choice D.
Ignore the grammar
- Marine biologist Camille Jazmin Gaynus studies coral reefs.
- Coral reefs are vital underwater ecosystems that provide habitats to 25% of all marine species.
- Reefs can include up to 8,000 species of fish, such as toadfish, seahorses, and clown triggerfish.
- The Amazon Reef is a coral reef in Brazil.
- It is one of the largest known reefs in the world.
- (Choice A) Providing homes to 25% of all marine species, including up to 8,000 species of fish, coral reefs are vital underwater ecosystems and thus of great interest to marine biologists. A Providing homes to 25% of all marine species, including up to 8,000 species of fish, coral reefs are vital underwater ecosystems and thus of great interest to marine biologists.
- (Choice B) Marine biologist Camille Jazmin Gaynus studies coral reefs, vital underwater ecosystems that provide homes to 25% of all marine species. B Marine biologist Camille Jazmin Gaynus studies coral reefs, vital underwater ecosystems that provide homes to 25% of all marine species.
- (Choice C) Camilla Jazmin Gaynus is a marine biologist who exclusively studies the Amazon Reef, a coral reef that is home to 8,000 different species of fish. C Camilla Jazmin Gaynus is a marine biologist who exclusively studies the Amazon Reef, a coral reef that is home to 8,000 different species of fish.
- (Choice D) As Camille Jazmin Gaynus knows well, coral reefs are vital underwater ecosystems, providing homes to thousands of species of fish. D As Camille Jazmin Gaynus knows well, coral reefs are vital underwater ecosystems, providing homes to thousands of species of fish.
- Choice A doesn't mention the scientist at all. We can eliminate choice A.
- Remember to be strict : the goal is to introduce the scientist AND her field of study. Choice D names the scientist, but it doesn't introduce her field of study (it doesn't say she's a marine biologist). We can eliminate choice D.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
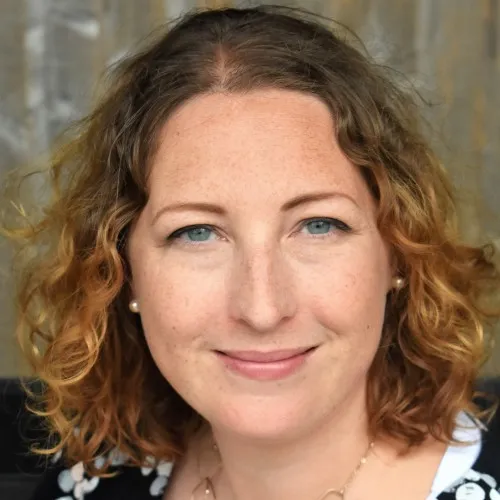
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
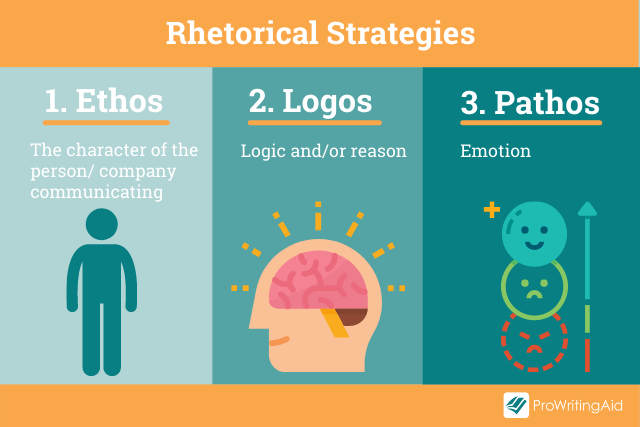
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
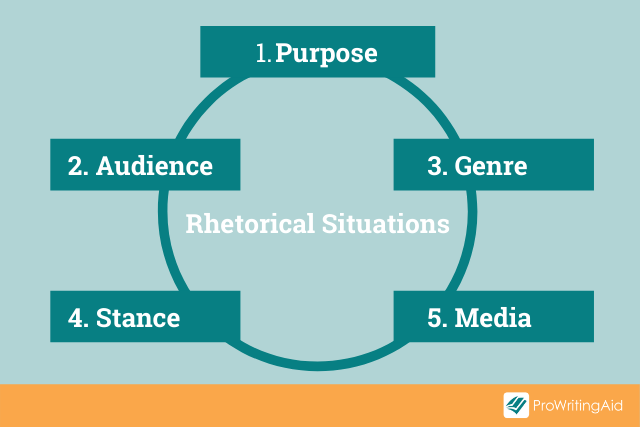
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
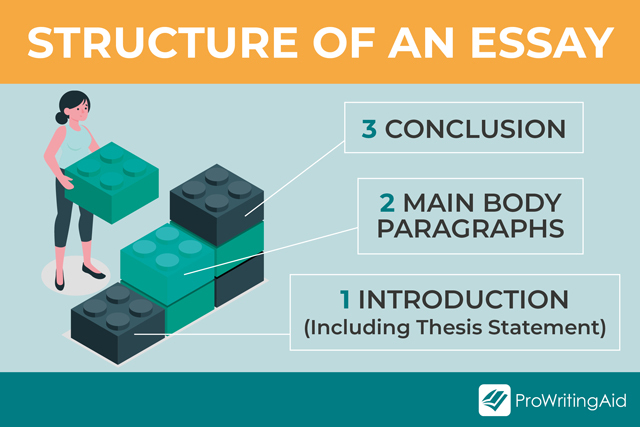
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- SAT / ACT Prep Services
- Rates & Prices
- About Our Founder
- Free Guides
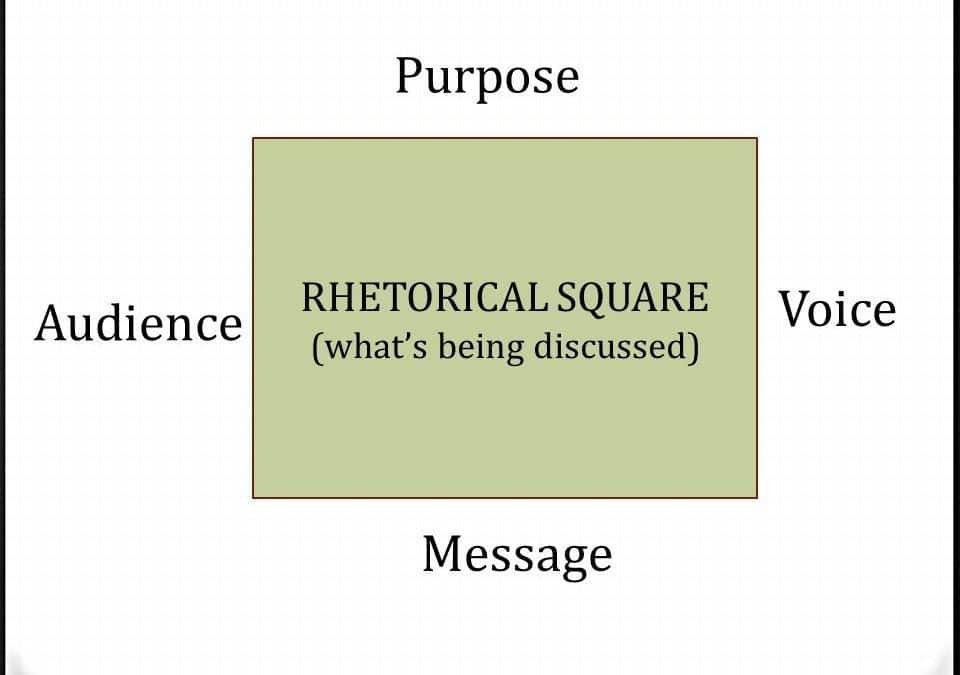
4 Key Components of an SAT Text to Analyze (The Rhetorical Square)
by Chris | Dec 25, 2017 | Learning Resources , SAT Prep | 0 comments
What is rhetoric?
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. Why is it an art? Well, to be a good rhetorician, you’ve got to be convincing, and being convincing involves knowing your audience and shaping your argument in a way that will be persuasive to that audience. When you want to convince someone of something, chances are you’ll be employing rhetoric to do so.
The SAT Essay asks you to analyze how authors use rhetoric to persuade the reader to agree with them. In addition to analyzing rhetorical devices, you’ll want to make sure you consider these 4 elements of rhetoric. Today, we’ll take a look at the rhetorical square, which is comprised of the 4 elements you should consider when analyzing a text.
The Rhetorical Square
The Rhetorical Square consists of four elements that matter when analyzing a text.
The four elements are: 1) Purpose, 2) Message, 3) Audience, and 4) Voice.
The first element of the rhetorical square is PURPOSE. Purpose has to do with WHY a text exists. What’s the point? What’s the purpose? When you understand what it is that motivates the writer to make his or her argument, you’ll be well on your way to analyzing the rhetorical choices the writer makes in order to convince the reader that his or her argument is sound. All of the writer’s choices will make sense in light of that writer’s purpose, so be sure you’re able to correctly identify it when analyzing a text.
No matter what text you’re dealing with, there’s a purpose for that text. Try to identify WHY the author is writing. Some possible purposes for texts could be…
To persuade someone to buy something.
To persuade someone to do something.
To persuade someone to think something.
To prove something’s true.
To disprove something.
When reading, always ask yourself WHY the author is writing the piece? What does he or she hope to achieve? What are they hoping to convince us?
And when you’re writing, it’s very important to consider YOUR purpose for writing. When you know your purpose, you’ll be better equipped to persuade the reader.
Every day, we hear many messages. “Buy this,” “do that,” “Please RSVP,” “Like and share,” “Vote for so-and-so,” and so on. Messages can often be quite simple, but they can also be subtle and complex. For example, we might see a celebrity on TV endorsing a haircare product. The message is, I’m a celebrity, I use this haircare product, you want to be like me, so use this haircare product. When you read a text, take to identify what the writer’s message is.
What exactly is the writer hoping to get across? Why does the writer believe that this message is significant to readers? How does the message affect me? How might it affect other readers? What consequences will arise as a function of agreeing with the author and acting accordingly? What is at stake?
In most pieces of writing, especially academic writing, the message is the most important thing. We focus all our attention on what it is we want to say. There are many ways to convey a message and to strengthen it, and these methods include rhetorical devices and persuasive techniques. If you’re telling an anecdote or making an emotional appeal, chances are they’ll both be in service to the message you’re trying to get across.
3) Audience
This is a very important element of the rhetorical square! Writers need to be conscious of their audience when writing a text, and readers need to be conscious of the writer being conscious of his or her audience. Why does audience matter? Well, depending on your audience, you might say or do different things in an effort to persuade them. Different audiences might necessitate different strategies, different voices, different tones, different diction, different techniques. An audience of literary theorists will likely read a paper different than an audience of high school freshman. If you’re talking to your mother-in-law, you might speak differently than you do when talking to your best friend. The best rhetoricians will have carefully considered their audience before deciding the most effective methods to persuade that audience.
As readers, we can ask ourselves: Who is the intended audience for this piece? Is it a specific audience? A general audience? Is the writer aware of his or her audience? Is the writer making any choices specifically designed to appeal to this audience? Is the writer ignorant of his or her potential audience? All of these factors, and more, come into play when analyzing rhetoric.
As writers, it’s vital to have our intended audience in mind. Who might be reading our piece or listening to our argument? What techniques will appeal to these readers or listeners? Most people want to be spoken to in a language they can understand. If you’re writing for a general audience, it’s important not to use highly technical terms and leaving those terms unexplained. On the other hand, if you’re writing for a highly specialized audience, the types of claims you’ll make and the diction you use may be different.
The last element of the rhetorical square that we’ll discuss today is voice, and voice is quite important!
All texts can be said to have a “voice,” and the voice of a text is shaped by a variety of factors. A lawyer writing or speaking to another lawyer might use a very different voice than a toddler trying to persuade his mother to get him an ice cream cone. Audience and voice are closely linked; one shapes the other. By considering your audience, you’ll be ready to tailor your voice to that audience’s beliefs, intelligence, needs, desires, and so on.
As readers, we want to pay attention to the author’s voice. How does he or she write or speak? What type of tone does he or she take? What type of diction does the author use? Ask yourselves these questions during your reading and note-taking process, and when you need to write an analytical essay, be sure to discuss the nuances of how voice is employed in service of a message!
That’s it! Remember to keep the rhetorical square in mind whenever you’re reading an argumentative text or listening to a speaker make an argument. A thoughtful consideration of purpose, voice, audience, and message will lead you to a greater understanding of the speaker’s persuasive techniques. For more essay-writing tips, as well as plenty of SAT and ACT prep tips to help you ace the big test, check out the rest of our blog . Looking for 1-on-1 tutoring or small group SAT or ACT classes? Contact us today.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- College Readiness
- Entertainment, Family, and Fun
- Group Classes
- Learning Resources
- Love the SAT News
- Online Tutoring
- Practice Tests
- Reading Lists
- Reviews: Books and Products
- SAT Subject Tests
- Student Success
- Test-Taking Skills
- Time Management
Online Courses and Books
- Conquer SAT Vocabulary
- Winning College Scholarships
- Ultimate Time Management for Teens
- SAT Grammar Crammer
- Top 30 Examples for the SAT Essay
Absolutely Essential SAT Writing Strategies
tl;dr: The SAT essay is graded on three metrics — Reading, Analysis, and Writing — each on a scale from 1-4. To score an 8/8/8 on the SAT essay, you need to understand the rubric and keep in mind the three important parts of the essay: analyzing the prompt, outlining, and writing. Analyzing the prompt requires you to identify the author’s claim, purpose, tone, and persuasive elements that help build the argument. Outlining helps you answer the three questions for each device—why, how, and affect—to ensure you have strong analysis. Finally, when writing the essay, make sure to include an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. With these tips, you can write a great SAT essay and get the top score!
❓ What are the SAT Sections?
In the SAT, you will have 4-5 sections on the test (depending on whether you choose to take the essay section or not)! The sections are:
- Check out this video with an overview of the reading section of the SAT .
- Writing and Language (aka the Grammar section)
- Make sure to watch this video with tips and tricks for the grammar section of the SAT .
- Math (No-Calculator)
- Review the important aspects of the math section with this SAT math review part 1 and part 2 .
- Math (Calculator Allowed)
- Writing/Essay (⚠️OPTIONAL ⚠️)
If you signed up for the essay portion of the SAT, you have a relaxing 2-minute break after the math calculator section. You're going to need it, as you have 50 minutes to write a rhetorical analysis essay. ⏲️
If you are taking AP Lang or have already taken the exam, you should be pretty familiar with this format of essay. It is very similar to FRQ 2, or the rhetorical analysis essay. 📰
✍️ Mastering the Rubric
Your essay is graded on these three metrics on a scale from 1-4:
Two readers will score your essay , so the highest score you can receive is an 8 on each of the three sections. Unlike the other SAT sections, there is no percentile for the SAT essay nor a composite score (the three categories aren't "added"). 💯 Let's break down each of these three scoring categories and how you can score an 8 in all three.

This scoring category covers comprehension! Essentially, the scorers want to see if you understand the relationship between the main idea(s) and important details. To get an 8 in this scoring category, you cannot misstate facts from the passage, nor make an interpretation about facts not in the passage.
One of the main things that SAT Essay scorers will check is to ensure you have textual evidence (quotations and/or paraphrases) throughout the essay to ensure that you have a true understanding of the text. 📚
What separates an 8 from a lower score in this category is whether you have thorough (as opposed to effective) comprehension of the text and whether you are making skillful (as opposed to appropriate) use of textual evidence. The line between thorough and skillful is drawn at your consistency; if you make a misrepresentation of text in just one place, that may lower you to a 6.
To earn a 8 in the analysis category, you should be accomplishing the following:
- Offering an insightful analysis of source text.
- Evaluating the author's choice of evidence, reasoning, stylistic & persuasive elements, and/or other features that you noticed.
- Using relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for your claims or points.
- Consistently focusing on features that are most relevant to addressing the task.

What separates an 8 in analysis from a lower score is whether you have strategically chosen support for claims and whether your essay is consistent in its analysis and its focus on "features most relevant to addressing the task."
The writing rubric category is exactly what it sounds like—checking your ability to write an essay! There are a number of guidelines that SAT essay scorers will be looking at, and here are a few of them that will help you earn an 8:
- A cohesive essay that effectively uses and commands language
- A precise central claim
- Skillful introduction and conclusion
- Progression of ideas that is highly effective both within paragraphs and throughout the essay
- Wide variety in sentence structures
- Consistent use of precise word choice
- Formal style and objective tone
- Strong command of English conventions, an essay free of errors

Consistency is also key to getting a high score in this category. Having a mostly cohesive essay or including a few errors could bump your score down to a 6 or below!
📖 Analyzing Prompt and Passage
On test day, you're not going to see the rubric or even the three scoring categories. All you will get is the prompt and passage. It's important you analyze and annotate the prompt and passage to ensure you can write an effective essay.
On test day, you'll see this at the beginning of the essay.

The most important thing to do before you even start reading the passage is to read the given context. In this example, we know that the article is from the Huffington Post and the author Peter Goodman is writing about crisis and foreign policy. 🔥
Then, you'll read a passage about an argument written for a broad audience. In that passage, the author will make a claim, and use different techniques to persuade the audience of that claim.
Since you will be writing about how the author uses different techniques in the passage to make their argument more persuasive, that is exactly what you should look out for while writing your essay. 🔍
When reading the passage, you'll want to look at the three bullet points given in the prompt: specific factual evidence or examples, reasoning that connects evidence and claims, and other stylistic or persuasive elements that helps the author build the argument. 🚧
Here's a short bullet list of stylistic or persuasive elements that you can look out for:
- Shifts of any kind (in diction 🗣️, tone 😤, imagery 🖼️, etc.)
- Appeals to emotion 💕, logic 🧠, or credibility 👩🏽🎓
- Syntax (organization of paragraphs 📑, length of sentences ↔️)
- Unique diction or imagery (make sure to describe diction/imagery with an adjective )
After you find the rhetorical devices you want to analyze, you'll need to answer three important questions:
- Why does the author use this device or strategy?
- How does this device or strategy help them achieve their purpose?
- How does the device or strategy affect or change the audience?
You can strengthen your analysis and answer these three questions for each of your devices by outlining.
🗒️ Outlining
There are a few components to an outline that will help you secure an 8/8/8 on the SAT essay:
- Identifying audience & author's purpose
- Writing a thesis
- Identifying rhetorical devices
- Answering the three important "analysis" questions for each rhetorical device
On test day, find some white space under the article (or on the next page) to write your outline. Knowing and writing down these elements will make the writing process go a lot smoother!
📝 Writing the Essay
Let's break down how to write each section of the SAT essay portion: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Introduction
There are a few elements that you should explicitly include in your introduction:
- Author's claim in the passage
- Author's tone & purpose
- Audience of passage
- Specific rhetorical choices or persuasive elements in the passage that "enhance logic/persuasiveness" of the argument
One example template for an introduction is:

Here's an example:
Writer Marcus Stern in his article, "How to Prevent an Oil Train Disaster," asserts that new Obama-era regulations in 2015 were insufficient in protecting the public's safety and needed to be expanded. Stern adopts a critical tone to persuade his audience, the general public, of his purpose of supporting stricter, comprehensive regulations that reduce oil volatility. To achieve his purpose, Stern utilizes a variety of rhetorical techniques, including but not limited to specific credible evidence, appeals to the general public's fear of disaster, and emotional word choice that enhances the logic and persuasiveness of his argument.
Body Paragraphs
Your body paragraphs should create a line of reasoning , which is just a fancy of way of saying that it should follow the structure you outline in the essay. For instance, from the introduction paragraph above, I would make my first body paragraph about the "specific credible evidence," my second body paragraph about the appeals to the general public, and so on. 🤩
⚠️ Note: There is no minimum or maximum number of body paragraphs that you should include —focus on developing solid body paragraphs rather than including as many as possible!
You should include the following in a body paragraph to earn high scores on reading, analysis, and writing:
- A strong introduction sentence tied to the thesis
- Embedded quote or paraphrase with context
- Why the author uses this rhetorical strategy or persuasive element
- How it affects the audience and/or how it helps the author achieve their purpose
- Link back to thesis
Let's see these five elements in an example!
- Stern furthers his argument by appealing to the general public’s fear of disaster.
- He invokes specific visual imagery when asserting that an oil tanker rupture would send a “mushroom-shaped fireball” into the sky. In fact, Stern further builds his argument by citing the “nine other places in North America” in which oil tanker explosions materialized.
- Stern uses these appeals to logic and emotion primarily because they highlight a somber reality of the impacts of continued inaction.
- Because Stern includes multiple instances of oil explosions, the audience feels logically impacted. This sense of urgency communicated by the visual imagery makes the audience more convinced that action must be taken, specifically because it could harm them very soon.
- Ultimately, Stern successfully leaves the audience convinced that lax oil restriction could lead to devastating consequences that could harm the audience, which strengthens the persuasion of his argument that we should enact strict regulation that decreases volatility.

You may hear sometimes from your teacher that the conclusion is not that important, or that it can simply be one sentence. This is not true for the SAT; in fact, you could get points taken off the writing section with an oversimplified or non-existent conclusion.
However, you can score highly with a slightly reworded introduction! Here's what you should include in your conclusion:
- Author's central claim (reworded from intro)
- Persuasive elements/rhetorical choices
- Audience & author's purpose
Here's an example conclusion paragraph that includes those elements (and you can see its parallel to the intro):
Author Olmer Stern communicates to the general public that there is a necessity for stricter safety regulations that decrease oil volatility. To convince the audience of his purpose, Stern effectively invokes fearful emotion of the general public, cites specific evidence from the oil industry, and communicates powerful diction about the imminent oil threat to strengthen the logic and persuasiveness of his argument.
📂 Resources and Example Essays
There are some fantastic ways to practice for the SAT essay! Here are some useful resources and example essays :
- Two sample SAT Essay prompts from College Board's website
- 50 CrackSAT Practice Essays and Prompts
Guide Outline
Related content, sat math: guide to quadratic equations & radicals, sat math: guide to linear equations, sat math: how to use your calculator, sat reading: guide to the social science passage, how to study for the sat/psat english sections, sat language: guide to word choice & passive flow.
.png)
Stay Connected
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, tips for writing a rhetorical analysis essay.
In my English class, we have to write a rhetorical analysis essay and I've never done one before. Can anyone give me some advice on how to break down the text and write a solid essay? I'd really appreciate any help you guys can provide!
First and foremost, it's essential to understand the basic structure of a rhetorical analysis essay and what the purpose is. Rhetorical analysis essays focus on examining how authors use rhetorical strategies (such as ethos, pathos, and logos) to create an argument or persuade the audience. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective rhetorical analysis essay:
1. Carefully read the text: Begin by reading the text multiple times to ensure that you thoroughly understand the arguments presented. Note down significant points, arguments, and claims made by the author.
2. Identify rhetorical strategies: After understanding the text, identify the rhetorical strategies the author uses, such as ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical appeal). Keep in mind that authors may also utilize rhetorical devices like analogy, juxtaposition, or irony to enrich their arguments.
3. Analyze the effectiveness of rhetorical strategies: Examine how the rhetorical strategies contribute to the author's purpose and message. Assess the effectiveness of each strategy and how they work in tandem to persuade the audience.
4. Develop a thesis statement: Craft a concise and clear thesis statement that outlines your essay's focus. The thesis should articulate the author's purpose, the rhetorical strategies used, and your analysis of their effectiveness.
5. Outline your essay: Create an outline that includes the introduction, main points supporting your thesis, and a conclusion. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a coherent flow throughout the essay.
6. Write the introduction: In the introduction, provide some background on the text and author, as well as a brief summary of the main arguments. Your thesis statement should be placed at the end of the introduction.
7. Develop body paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on one rhetorical strategy, starting with a topic sentence that connects to your thesis statement. Then, provide evidence from the text to illustrate the strategy's use and effectiveness. Finally, analyze how the strategy contributes to the author's overall message and purpose.
8. Write the conclusion: Summarize your analysis, restate your thesis, and discuss the implications or significance of your findings. Avoid introducing new ideas in this section.
9. Revise and edit: Make sure to proofread your essay and revise any errors in grammar, syntax, or punctuation. Also, check for clarity, coherence, and cohesion throughout the essay.
By following these steps and maintaining a clear focus on the author's rhetorical strategies, you'll be well on your way to crafting a strong rhetorical analysis essay. Good luck!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.

SAT Essay Prompts: Analysis and Practice

Analyzing and practicing SAT essay prompts is crucial for success on the Writing and Language section of the SAT. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you understand SAT essay prompts, analyze them effectively, and practice writing essays that meet the SAT's expectations:
Understanding SAT Essay Prompts
1. Prompt Structure: SAT essay prompts typically consist of a passage or excerpt followed by a question that asks you to analyze the author's argument, rhetorical strategies, or persuasive techniques.
2. Key Components: Pay attention to the main argument or thesis presented in the passage, as well as the evidence and rhetorical devices used to support it.
3. Purpose of Analysis: The SAT essay prompt is designed to assess your ability to analyze and evaluate an author's argument, rather than to express your own opinion or personal experiences.
Analyzing SAT Essay Prompts
1. Identify the Main Argument: Read the passage carefully to understand the author's main argument or thesis. Highlight key points and evidence used to support it.
2. Evaluate Rhetorical Strategies: Identify and analyze the rhetorical devices and persuasive techniques used by the author, such as appeals to emotion, logic, or authority.
3. Consider Tone and Style: Pay attention to the author's tone and writing style, as well as any patterns or recurring themes in the passage.
4. Assess Effectiveness: Evaluate how effectively the author presents their argument and persuades the reader to agree with their point of view.
Practicing SAT Essay Writing
1. Time Yourself: Set a timer for 50 minutes (the allotted time for the SAT essay) and practice writing essays under timed conditions to simulate test-day conditions.
2. Choose Prompts: Select SAT essay prompts from official SAT practice tests, review books, or online resources. Aim to practice with a variety of prompts to improve your versatility.
3. Outline Your Response: Before writing your essay, create a brief outline outlining your main points and the structure of your argument. This will help you stay focused and organized.
4. Write Clear, Concise Responses: Write in clear, concise language, and provide specific examples and evidence from the passage to support your analysis.
5. Edit and Revise: Take time to review and revise your essay after you've finished writing. Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, and make any necessary revisions to strengthen your argument.
6. Seek Feedback: Ask a teacher, tutor, or knowledgeable peer to review your essays and provide constructive feedback. Use their suggestions to improve your writing skills.
Tips for Success
1. Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to improving your SAT essay writing skills. Aim to practice writing essays on a regular basis to build confidence and familiarity with the format.
2. Read Critically: Read a variety of texts, including articles, essays, and editorials, and practice analyzing the author's argument, tone, and rhetorical strategies.
3. Stay Updated: Familiarize yourself with current events and social issues, as SAT essay prompts often draw from contemporary topics and debates.
4. Stay Calm and Focused: On test day, stay calm and focused, and trust in your preparation and practice. Remember to manage your time effectively and pace yourself throughout the essay-writing process.
By understanding SAT essay prompts, analyzing them effectively, and practicing writing essays that meet the SAT's expectations, you can improve your performance on the SAT Writing and Language section and work towards achieving your target score.
You Might Also Like

The Perfect College Essay Structure
The Fundamentals of writing an Essay which includes the process of brainstorming, drafting, and finalizing.

The Secret to Getting off the Waitlist
So how would you go about making a letter of continued interest while you’re on the waiting status? Here’s a guide we’ve got for you.

Know How to Write Supplemental College Essays
Learn some tactics to write out standing supplemental college essay. Here is a blog that provide guidance to write effective supplemental essays - Read a blog


Free Resources
9.7 Evaluation: Rhetorical Analysis
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Evaluate the elements of a rhetorical analysis.
- Identify and correct errors involving mixed sentence structures.
- Evaluate an essay for clarity, coherence, and language.
At various points in your writing, especially after you complete the first draft, check the rubric provided here. Your instructor is likely to use a similar rubric to evaluate your rhetorical analysis. Aligning your writing to applicable points in the rubric—especially to those reflecting a score of 5— will keep you focused and guide you in your work.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/9-7-evaluation-rhetorical-analysis
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: Full Guide

Have you ever been completely fascinated by a speech or ad, wondering how it managed to convince you so effectively? From powerful political speeches to catchy commercials, persuasion is all around us, shaping our thoughts and choices every day.
In this guide, we'll explain all about a rhetorical analysis essay. We'll break down the clever tricks writers and speakers use to win over their audience, like how they choose their words carefully and play with our emotions. This article will give you the tools you need to understand and analyze texts more deeply. So, let’s jump right in and start by understanding the nature of this assignment first.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of essay where you examine how authors or speakers use words, phrases, and other techniques to influence or persuade their audience. This type of essay focuses on analyzing the strategies used by the writer or speaker to achieve their purpose, whether it's to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke.
You'll dissect the text or speech into its components, looking at how each part contributes to the overall message. This might involve examining the introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, evidence, and conclusion.
Once you've identified the strategies used, you'll assess their effectiveness in achieving the author's or speaker's purpose. This involves considering the intended audience, context, and the impact of the communication.
As per our essay writing service , some common topics for rhetorical analysis include analyzing speeches by influential leaders, dissecting political advertisements, or examining the rhetoric used in literary works.
Do You Want to Ease Your Academic Burden?
Order a rhetorical analysis essay from our expert writers today and experience the power of top-notch academic writing.
Rhetorical Analysis Topic Ideas
Now that we've grasped the essence of a rhetorical analysis essay let's explore some potential topics you might consider for your own analysis. Here are 15 specific ideas to get you started:
- The Use of Metaphors in Barack Obama's 'Yes We Can' Speech
- Visual Rhetoric in Dove's 'Real Beauty' Advertising Campaign
- The Role of Irony in Jonathan Swift's 'A Modest Proposal'
- The Manipulation of Emotions in Coca-Cola's 'Share a Coke' Campaign
- The Repetition Technique in Winston Churchill's 'We Shall Fight on the Beaches' Speech
- The Argument Structure in Michelle Obama's Speech on Education
- The Use of Imagery in Edgar Allan Poe's 'The Raven'
- Gender Stereotypes in Old Spice's 'The Man Your Man Could Smell Like' Ad
- Satirical Elements in George Orwell's 'Animal Farm'
- The Influence of Tone in Greta Thunberg's Climate Change Speeches
- Political Symbolism in Banksy's Street Art
- Humor as Persuasion in Ellen DeGeneres' Stand-Up Comedy
- The Power of Silence in Emma Watson's UN Speech on Gender Equality
- Ethical Appeals in ASPCA's Animal Rights Advertisements
- The Cultural References in Super Bowl Commercials: A Case Study
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Understanding how to start a rhetorical analysis essay involves dissecting a piece of communication to learn how it works and what effect it aims to achieve. This analytical process typically includes five paragraphs and three main parts: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below, our analytical essay writing service will explain each in more detail
.webp)
Major Rhetorical Elements
Before heading towards the analysis process, it's essential to grasp some key rhetorical concepts that will help guide your examination of the text or speech. These concepts provide a framework for understanding how authors and speakers use language to persuade and influence their audience.
Ethos, pathos logos in rhetorical analysis form the foundation of persuasive communication and are often intertwined in rhetorical strategies. Ethos refers to the credibility or authority of the speaker or author. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, while logos appeals to reason and logic.
There are also other rhetorical devices that are specific techniques or patterns of language used to convey meaning or evoke particular responses. Examples include metaphor, simile, imagery, irony, repetition, and hyperbole. Recognizing and analyzing these devices can provide insight into the author's intended message and its impact on the audience.
Tone and mood also play crucial roles in shaping the audience's perception and response to the communication. Tone refers to the author's attitude toward the subject matter, while mood describes the emotional atmosphere created by the text.
Whether you ask us - write my essay , or tackle the task yourself, familiarizing yourself with these concepts will help you analyze the text and persuade the audience more effectively.
Understanding Rhetorical Appeals
.webp)
First off, what is ethos in rhetorical analysis? Well, it revolves around establishing the credibility and authority of the speaker or author. This appeal seeks to convince the audience that the communicator is trustworthy, knowledgeable, and reliable. Ethos in rhetorical analysis can be built through various means, including:
- Professional Credentials : Demonstrating expertise in the subject matter through relevant qualifications or experience.
- Personal Character : Highlighting traits such as honesty, integrity, and sincerity to engender trust and respect.
- Association : Aligning oneself with respected individuals, institutions, or causes to enhance credibility by association.
For instance, in a health-related speech, a doctor might leverage their medical expertise and professional experience (credentials) to establish ethos. Similarly, a celebrity endorsing a product is using their fame and reputation (association) to persuade consumers.
Now, let's understand what is pathos in rhetorical analysis. Pathos involves appealing to the audience's emotions, aiming to evoke feelings such as empathy, sympathy, joy, anger, or fear. This emotional connection can be a powerful tool for persuasion, as it resonates with the audience on a personal level. Strategies for employing pathos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Vivid Imagery : Painting a vivid picture or narrative that elicits strong emotional responses from the audience.
- Anecdotes : Sharing personal stories or anecdotes that evoke empathy or sympathy and make the message more relatable.
- Language Choice : Using emotive language, sensory details, and rhetorical devices to evoke specific emotional reactions.
For example, in a charity advertisement for children in need, images of impoverished and suffering children coupled with heart-wrenching stories (anecdotes) are used to evoke feelings of compassion and a desire to help.
Lastly, what is logos in rhetorical analysis, you may ask. It appeals to reason and logic, aiming to persuade the audience through rational argumentation and evidence. This appeal relies on facts, statistics, logical reasoning, and sound arguments to convince the audience of the validity of the message. Strategies for employing logos in rhetorical analysis include:
- Factual Evidence : Providing empirical data, research findings, or expert opinions to support the argument.
- Logical Reasoning : Presenting a well-structured argument with clear premises and conclusions that logically follow one another.
- Counterarguments : Addressing potential counterarguments and refuting them with logical reasoning and evidence.
For instance, in a persuasive essay advocating for environmental conservation, the author might present scientific data on climate change (factual evidence) and use logical reasoning to explain the consequences of inaction.
Text and Context
Text analysis involves closely examining the language, structure, and rhetorical devices employed within the communication. This includes identifying key themes, rhetorical appeals, persuasive strategies, and stylistic elements used by the author or speaker to convey their message.
For example, in a political speech advocating for healthcare reform, text analysis might involve identifying the use of rhetorical appeals such as ethos (e.g., highlighting the speaker's experience in healthcare policy), pathos (e.g., sharing anecdotes of individuals struggling with medical costs), and logos (e.g., presenting statistics on healthcare affordability).
Contextual analysis involves considering the broader social, cultural, and historical factors that shape communication and influence its reception. This includes examining the audience demographics, the political and cultural climate, the historical events surrounding the communication, and any relevant societal norms or values.
For instance, when analyzing a historical speech advocating for civil rights, contextual research paper writers might involve considering the social and political context of the time, including prevailing attitudes towards race, ongoing civil rights movements, and recent legislative developments.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
A claim is a statement or assertion that the author or speaker is advocating for or seeking to prove. Claims can take various forms, including factual claims (assertions of fact), value claims (judgments about what is good or bad), and policy claims (proposals for action). For example, in an argumentative essay about the importance of exercise, the claim might be that regular physical activity is essential for maintaining good health.
Supports are the evidence, reasoning, or examples provided to substantiate and strengthen the claims being made. Supports can take many forms, including empirical data, expert testimony, personal anecdotes, logical reasoning, and analogies. The quality and relevance of the supports provided play a critical role in the persuasiveness of the argument.
Continuing with the example of the argumentative essay about exercise, supports might include scientific studies demonstrating the health benefits of physical activity, testimonials from fitness experts, and personal stories of individuals who have experienced positive changes from incorporating exercise into their routine.
Warrants are the underlying assumptions or principles that connect the supports to the claims. They provide the reasoning or justification for why the supports are relevant and valid evidence for supporting the claims. Warrants are often implicit rather than explicit and require careful analysis to uncover. In the context of the essay on exercise, the warrant connecting the supports to the claim might be the assumption that actions that promote good health are inherently valuable and worthy of pursuit.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Whether you opt for the option to buy essay or start writing it yourself, it's important to use a clear plan to organize your thoughts well. This plan usually includes four main steps, each looking at different parts of your analysis.
Analyzing the Text
Before writing a rhetorical analysis, take the time to thoroughly analyze the text you'll be examining. This means more than just skimming through it; it requires a thorough understanding of its subtleties and complexities. Here are some questions to guide your analysis:
- How does the text try to sway its audience? What methods does it use to convince or influence them?
- Which rhetorical appeals—ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), logos (logic)—does the author use, and how do they contribute to the overall argument?
- What specific rhetorical devices and strategies does the author employ to effectively convey their message? Are there any patterns or recurring motifs?
- How does the structure of the text contribute to its persuasive power or overall impact?
- Are there any cultural, historical, or contextual factors that influence how the text is perceived or understood?
By scrutinizing the text in this manner, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how it functions and the techniques employed by the author to achieve their desired effect.
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your analysis by providing essential context and framing the discussion. Start by introducing the text you're analyzing, including the author's name and the title of the work. Provide some background information to give context to your analysis. For example, if you're analyzing a speech, mention the occasion or event where it was delivered.
Next, summarize the main arguments or claims made by the author. Highlight the rhetorical techniques they use to persuade their audience. Are they appealing to logic, emotion, credibility, or a combination of these? Use specific examples from the text to illustrate these techniques discussed by our dissertation service .
For instance, if you're analyzing a speech on climate change, mention the speaker's expertise in environmental science to establish credibility. Summarize the key points they make about the consequences of inaction and the urgent need for change.
Finally, conclude your introduction with a clear thesis statement. This statement should encapsulate the main argument or purpose of your analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph
The body paragraphs form the crux of your analysis, where you delve into the details of the text and dissect its rhetorical strategies. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the text, such as the use of ethos, pathos, logos, or specific rhetorical devices.
Utilize Aristotle's rhetorical triangle and other key concepts introduced earlier to guide your analysis. Provide quotations or examples from the text to illustrate your points and explain why the author chose certain approaches. Evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies in achieving the author's goals and persuading the audience.
For instance, if you're discussing the use of pathos in a marketing campaign, analyze the emotional appeal of the imagery or language used and consider how it resonates with the target audience.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
In the conclusion, it's crucial to reinforce your main arguments and evaluate the author's effectiveness in achieving their goals, whether you're writing an MLA or APA essay format . Reflect on the overall impact of the text on both its immediate audience and society at large, underscoring the importance of your analysis.
Resist the temptation to introduce new ideas in the conclusion. Instead, draw upon the points you've already explored in the body of your essay to strengthen your analysis. Conclude with a poignant statement that resonates with your readers, encapsulating the essence of your interpretation and leaving a lasting impression. This final remark should tie together the threads of your analysis, leaving the reader with a deeper understanding of the text's rhetorical strategies and significance.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In this section, you'll discover two essay samples that skillfully demonstrate the application of rhetorical analysis. These examples offer insightful insights into the effective use of rhetorical techniques in writing.
5 Rhetorical Analysis Essay Tips
Here are five focused tips that will help you lay a solid foundation for your examination.
- Dissect Rhetorical Strategies : Break down the text to identify specific rhetorical devices such as metaphor, simile, or parallelism.
- Evaluate Tone and Diction : Pay attention to the author's tone and word choice. Analyze how these elements contribute to the overall mood of the text.
- Probe Ethos, Pathos, Logos : Explore how the author establishes credibility (ethos), evokes emotions (pathos), and employs logic (logos) to sway the audience.
- Contextualize Historical Significance : Consider the historical, cultural, and social backdrop against which the text was written.
- Craft a Structured Analysis : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs focusing on specific rhetorical elements, and a conclusion that synthesizes your findings.
Final Words
As we near the end, it's important to analyze carefully whether you're examining a speech, an advertisement, or a story. Pay attention to the smart tactics that influence our thinking. It's all about revealing how we communicate and relate to one another. Ultimately, understanding rhetoric offers a fresh perspective on the world beyond just academic success.
Looking to Take Your Academic Performance to the Next Level?
Say goodbye to stress, endless research, and sleepless nights - and hello to a brighter academic future.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How to structure a rhetorical analysis essay, how to write a rhetorical analysis essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, sat essay prompts: the complete list.
SAT Writing , SAT Essay

On every SAT Essay, you'll have to read an argument meant to persuade a broad audience and discuss how well the author argues his or her point. The passage you'll have to read will change from test to test, but you'll always need to analyze the author's argument and write a coherent and organized essay explaining this analysis.
In this article, we've compiled a list of the 14 real SAT essay prompts that the College Board has released (either in The Official SAT Study Guide or separately online) for the new SAT. This is the most comprehensive set of new SAT essay prompts online today.
At the end of this article, we'll also guide you through how to get the most out of these prompts and link to our expert resources on acing the SAT essay. I'll discuss how the SAT essay prompts are valuable not just because they give you a chance to write a practice essay, but because of what they reveal about the essay task itself.
UPDATE: SAT Essay No Longer Offered
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});.
In January 2021, the College Board announced that after June 2021, it would no longer offer the Essay portion of the SAT (except at schools who opt in during School Day Testing). It is now no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school is one of the small number who choose to offer it during SAT School Day Testing.
While most colleges had already made SAT Essay scores optional, this move by the College Board means no colleges now require the SAT Essay. It will also likely lead to additional college application changes such not looking at essay scores at all for the SAT or ACT, as well as potentially requiring additional writing samples for placement.
What does the end of the SAT Essay mean for your college applications? Check out our article on the College Board's SAT Essay decision for everything you need to know.
SAT essay prompts always keep to the same basic format. Not only is the prompt format consistent from test to test, but what you're actually asked to do (discuss how an author builds an argument) also remains the same across different test administrations.
The College Board's predictability with SAT essay helps students focus on preparing for the actual analytical task, rather than having to think up stuff on their feet. Every time, before the passage, you'll see the following:
- evidence, such as facts or examples, to support claims.
- reasoning to develop ideas and to connect claims and evidence.
- stylistic or persuasive elements, such as word choice or appeals to emotion, to add power to the ideas expressed.
And after the passage, you'll see this:
"Write an essay in which you explain how [the author] builds an argument to persuade [her/his] audience that [whatever the author is trying to argue for]. In your essay, analyze how [the author] uses one or more of the features listed in the box above (or features of your own choice) to strengthen the logic and persuasiveness of his argument. Be sure that your analysis focuses on the most relevant features of the passage.
Your essay should not explain whether you agree with [the author]'s claims, but rather explain how [the author] builds an argument to persuade [her/his/their] audience."
Now that you know the format, let's look at the SAT essay prompts list.
14 Official SAT Essay Prompts
The College Board has released a limited number of prompts to help students prep for the essay. We've gathered them for you here, all in one place. We'll be sure to update this article as more prompts are released for practice and/or as more tests are released.
SPOILER ALERT : Since these are the only essay prompts that have been released so far, you may want to be cautious about spoiling them for yourself, particularly if you are planning on taking practice tests under real conditions . This is why I've organized the prompts by the 10 that are in the practice tests (so you can avoid them if need be), the ones that are available online as sample prompts, and the ones that are in the text of the Official SAT Study Guide (Redesigned SAT), all online for free.
Practice Test Prompts
These 10 prompts are taken from the practice tests that the College Board has released.
Practice Test 1 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Jimmy Carter builds an argument to persuade his audience that the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge should not be developed for industry."
Practice Test 2 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Martin Luther King Jr. builds an argument to persuade his audience that American involvement in the Vietnam War is unjust."
Practice Test 3 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Eliana Dockterman builds an argument to persuade her audience that there are benefits to early exposure to technology."
Practice Test 4 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Paul Bogard builds an argument to persuade his audience that natural darkness should be preserved."
Practice Test 5 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Eric Klinenberg builds an argument to persuade his audience that Americans need to greatly reduce their reliance on air-conditioning."
Practice Test 6 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Christopher Hitchens builds an argument to persuade his audience that the original Parthenon sculptures should be returned to Greece."
Practice Test 7 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Zadie Smith builds an argument to persuade her audience that public libraries are important and should remain open"
Practice Test 8 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Bobby Braun builds an argument to persuade his audience that the US government must continue to invest in NASA."
Practice Test 9 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Todd Davidson builds an argument to persuade his audience that the US government must continue to fund national parks."
Practice Test 10 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Richard Schiffman builds an argument to persuade his audience that Americans need to work fewer hours."
Special note: The prompt for Practice Test 4 also appears on the College Board's site with real sample essays written in response. If you've written a practice essay for practice test 4 and want to see what essays of different score levels look like for that particular prompt, you can go there and look at eight real student essays.

Free Online Practice
This prompt comes from the College Board website .
"Write an essay in which you explain how Dana Gioia builds an argument to persuade his audience that the decline of reading in America will have a negative effect on society."
This prompt comes from Khan Academy , where it is listed as an alternate essay prompt to go along with Practice Test 2:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Leo W. Gerard builds an argument to persuade his audience that American colleges and universities should be affordable for all students."
The Official SAT Study Guide 2020
The Official SAT Study Guide (editions published in 2015 and later available online for free) contains all 10 of the previously mentioned practice tests at the end of the book. In the section about the new SAT essay , however, there are two additional sample essay prompts (accompanied by articles to analyze).
Sample Prompt 1:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Peter S. Goodman builds an argument to persuade his audience that news organizations should increase the amount of professional foreign news coverage provided to people in the United States."
Sample Prompt 2:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Adam B. Summers builds an argument to persuade his audience that plastic shopping bags should not be banned."

How Do You Get the Most Out of These Prompts?
Now that you have all the prompts released by the College Board, it's important to know the best way to use them. Make sure you have a good balance between quality and quantity, and don't burn through all 14 of the real prompts in a row— take the time to learn from your experiences writing the practice essays.
Step By Step Guide on How to Practice Using the Article
#1: Understand how the SAT essay is graded .
#2: Follow along as we write a high-scoring SAT essay, step by step .
#3: Plan a set of features you'll look for in the SAT essay readings and practice writing about them fluidly. This doesn't just mean identifying a technique, like asking a rhetorical question, but explaining why it is persuasive and what effect it has on the reader in the context of a particular topic. We have more information on this step in our article about 6 SAT persuasive devices you can use .
#4: Choose a prompt at random from above, or choose a topic that you think is going to be hard for you to detach from (because you'll want to write about the topic, rather than the argument) set timer to 50 minutes and write the essay. No extra time allowed!
#5: Grade the essay, using the official essay rubric to give yourself a score out of 8 in the reading, analysis, and writing sections.
#6: Repeat steps 4 and 5. Choose the prompts you think will be the hardest for you so that you can so that you're prepared for the worst when the test day comes
#7: If you run out of official prompts to practice with, use the official prompts as models to find examples of other articles you could write about . Start by looking for op-ed articles in online news publications like The New York Times, The Atlantic, LA Times , and so on. For instance, the passage about the plastic bag ban in California (Official SAT Study Guide sample essay prompt 2, above) has a counterpoint here —you could try analyzing and writing about that article as well.
Any additional articles you use for practice on the SAT essay must match the following criteria:
- ideally 650-750 words , although it'll be difficult to find an op-ed piece that's naturally that short. Try to aim for nothing longer than 2000 words, though, or the scope of the article is likely to be wider than anything you'll encounter on the SAT.
- always argumentative/persuasive . The author (or authors) is trying to get readers to agree with a claim or idea being put forward.
- always intended for a wide audience . All the information you need to deconstruct the persuasiveness of the argument is in the passage. This means that articles with a lot of technical jargon that's not explained in the article are not realistic passage to practice with.
What's Next?
We've written a ton of helpful resources on the SAT essay. I f you're just getting started, we recommend beginning with our top SAT essay tips for a quick overview of the essay task and what you need to know.
A little more familiar with the SAT essay but still not quite sure how to write one? Follow along with our step-by-step guide to writing the SAT essay .
Looking to earn a high score? Learn what it takes to get the highest score possible on the SAT essay here .
Plus, if you want a reference linking you to all of our great articles on the SAT essay, be sure to check out our ultimate SAT essay guide .
Laura graduated magna cum laude from Wellesley College with a BA in Music and Psychology, and earned a Master's degree in Composition from the Longy School of Music of Bard College. She scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and GRE and loves advising students on how to excel in high school.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
11 min read

People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
320+ Best Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay for academics can be really demanding for students. This type of paper requires high-level analyzing abilities and professional writing skills to be drafted effectively.
As this essay persuades the audience, it is essential to know how to take a strong stance and develop a thesis.
This article will find some examples that will help you with your rhetorical analysis essay writing effortlessly.
- 1. Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
- 2. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023
- 3. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Writing a Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay with Example
- 5. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
The step-by-step writing process of a rhetorical analysis essay is far more complicated than ordinary academic essays. This essay type critically analyzes the rhetorical means used to persuade the audience and their efficiency.
The example provided below is the best rhetorical analysis essay example:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Sample
In this essay type, the author uses rhetorical approaches such as ethos, pathos, and logos . These approaches are then studied and analyzed deeply by the essay writers to weigh their effectiveness in delivering the message.
Let’s take a look at the following example to get a better idea;
The outline and structure of a rhetorical analysis essay are important.
According to the essay outline, the essay is divided into three sections:
- Introduction
- Ethos
- Logos
A rhetorical analysis essay outline is the same as the traditional one. The different parts of the rhetorical analysis essay are written in the following way:
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction Example
The introductory paragraph of a rhetorical analysis essay is written for the following purpose:
- To provide basic background information about the chosen author and the text.
- Identify the target audience of the essay.
An introduction for a rhetorical essay is drafted by:
- Stating an opening sentence known as the hook statement. This catchy sentence is prepared to grab the audience’s attention to the paper.
- After the opening sentence, the background information of the author and the original text are provided.
For example, a rhetorical analysis essay written by Lee Jennings on“The Right Stuff” by David Suzuki. Lee started the essay by providing the introduction in the following way:
Analysis of the Example:
- Suzuki stresses the importance of high school education. He prepares his readers for a proposal to make that education as valuable as possible.
- A rhetorical analysis can show how successful Suzuki was in using logos, pathos, and ethos. He had a strong ethos because of his reputation.
- He also used pathos to appeal to parents and educators. However, his use of logos could have been more successful.
- Here Jennings stated the background information about the text and highlighted the rhetorical techniques used and their effectiveness.
Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis Essay
A thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay is the writer’s stance on the original text. It is the argument that a writer holds and proves it using the evidence from the original text.
A thesis statement for a rhetorical essay is written by analyzing the following elements of the original text:
- Diction - It refers to the author’s choice of words and the tone
- Imagery - The visual descriptive language that the author used in the content.
- Simile - The comparison of things and ideas
In Jennings's analysis of “The Right Stuff,” the thesis statement was:
Example For Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph Example
In the body paragraphs of your rhetorical analysis essay, you dissect the author's work, analyze their use of rhetorical techniques, and provide evidence to support your analysis.
Let's look at an example that analyzes the use of ethos in David Suzuki's essay:
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion Example
All the body paragraphs lead the audience towards the conclusion.
For example, the conclusion of “The Right Stuff” is written in the following way by Jennings:
In the conclusion section, Jennings summarized the major points and restated the thesis statement to prove them.
Rhetorical Essay Example For The Right Stuff by David Suzuki
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023
Writing a rhetorical analysis for the AP Language and Composition course can be challenging. So drafting it correctly is important to earn good grades.
To make your essay effective and winning, follow the tips provided by professionals below:
Step #1: Understand the Prompt
Understanding the prompt is the first thing to produce an influential rhetorical paper. It is mandatory for this academic writing to read and understand the prompt to know what the task demands from you.
Step #2: Stick to the Format
The content for the rhetorical analysis should be appropriately organized and structured. For this purpose, a proper outline is drafted.
The rhetorical analysis essay outline divides all the information into different sections, such as the introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should explicitly state the background information and the thesis statement.
All the body paragraphs should start with a topic sentence to convey a claim to the readers. Provide a thorough analysis of these claims in the paragraph to support your topic sentence.
Step #3: Use Rhetorical Elements to Form an Argument
Analyze the following things in the text to form an argument for your essay:
- Language (tone and words)
- Organizational structure
- Rhetorical Appeals ( ethos, pathos, and logos)
Once you have analyzed the rhetorical appeals and other devices like imagery and diction, you can form a strong thesis statement. The thesis statement will be the foundation on which your essay will be standing.
AP Language Rhetorical Essay Sample
AP Rhetorical Analysis Essay Template
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students
Here are a few more examples to help the students write a rhetorical analysis essay:
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Outline
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example College
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example APA Format
Compare and Contrast Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Comparative Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
How to Start Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example High School
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example APA Sample
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example Of a Song
Florence Kelley Speech Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example MLA
Writing a Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay with Example
The visual rhetorical analysis essay determines how pictures and images communicate messages and persuade the audience.
Usually, visual rhetorical analysis papers are written for advertisements. This is because they use strong images to convince the audience to behave in a certain way.
To draft a perfect visual rhetorical analysis essay, follow the tips below:
- Analyze the advertisement deeply and note every minor detail.
- Notice objects and colors used in the image to gather every detail.
- Determine the importance of the colors and objects and analyze why the advertiser chose the particular picture.
- See what you feel about the image.
- Consider the objective of the image. Identify the message that the image is portraying.
- Identify the targeted audience and how they respond to the picture.
An example is provided below to give students a better idea of the concept.
Simplicity Breeds Clarity Visual Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Writing Tips
Follow the tips provided below to make your rhetorical writing compelling.
- Choose an engaging topic for your essay. The rhetorical analysis essay topic should be engaging to grab the reader’s attention.
- Thoroughly read the original text.
- Identify the SOAPSTone. From the text, determine the speaker, occasions, audience, purpose, subject, and tone.
- Develop a thesis statement to state your claim over the text.
- Draft a rhetorical analysis essay outline.
- Write an engaging essay introduction by giving a hook statement and background information. At the end of the introductory paragraph, state the thesis statement.
- The body paragraphs of the rhetorical essay should have a topic sentence. Also, in the paragraph, a thorough analysis should be presented.
- For writing a satisfactory rhetorical essay conclusion, restate the thesis statement and summarize the main points.
- Proofread your essay to check for mistakes in the content. Make your edits before submitting the draft.
Following the tips and the essay's correct writing procedure will guarantee success in your academics.
We have given you plenty of examples of a rhetorical analysis essay. But if you are still struggling to draft a great rhetorical analysis essay, it is suggested to take a professional’s help.
MyPerfectWords.com can assist you with all your academic assignments. The top essay writer service that we provide is reliable. If you are confused about your writing assignments and have difficulty meeting the deadline, get help from custom essay writing online .
Hire our analytical essay writing service today at the most reasonable prices.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay (With Example)
November 27, 2023
Feeling intimidated by the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? We’re here to help demystify. Whether you’re cramming for the AP Lang exam right now or planning to take the test down the road, we’ve got crucial rubric information, helpful tips, and an essay example to prepare you for the big day. This post will cover 1) What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? 2) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric 3) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt 4) AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example 5)AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
What is the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you to synthesize, analyze, and interpret texts and develop well-reasoned arguments. The three essays include:
Synthesis essay: You’ll review various pieces of evidence and then write an essay that synthesizes (aka combines and interprets) the evidence and presents a clear argument. Read our write up on How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay here.
Argumentative essay: You’ll take a stance on a specific topic and argue your case.
Rhetorical essay: You’ll read a provided passage, then analyze the author’s rhetorical choices and develop an argument that explains why the author made those rhetorical choices.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Rubric
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is graded on just 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . At a glance, the rubric categories may seem vague, but AP exam graders are actually looking for very particular things in each category. We’ll break it down with dos and don’ts for each rubric category:
Thesis (0-1 point)
There’s nothing nebulous when it comes to grading AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay thesis. You either have one or you don’t. Including a thesis gets you one point closer to a high score and leaving it out means you miss out on one crucial point. So, what makes a thesis that counts?
- Make sure your thesis argues something about the author’s rhetorical choices. Making an argument means taking a risk and offering your own interpretation of the provided text. This is an argument that someone else might disagree with.
- A good test to see if you have a thesis that makes an argument. In your head, add the phrase “I think that…” to the beginning of your thesis. If what follows doesn’t logically flow after that phrase (aka if what follows isn’t something you and only you think), it’s likely you’re not making an argument.
- Avoid a thesis that merely restates the prompt.
- Avoid a thesis that summarizes the text but does not make an argument.
Evidence and Commentary (0-4 points)
This rubric category is graded on a scale of 0-4 where 4 is the highest grade. Per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric, to get a 4, you’ll want to:
- Include lots of specific evidence from the text. There is no set golden number of quotes to include, but you’ll want to make sure you’re incorporating more than a couple pieces of evidence that support your argument about the author’s rhetorical choices.
- Make sure you include more than one type of evidence, too. Let’s say you’re working on your essay and have gathered examples of alliteration to include as supporting evidence. That’s just one type of rhetorical choice, and it’s hard to make a credible argument if you’re only looking at one type of evidence. To fix that issue, reread the text again looking for patterns in word choice and syntax, meaningful figurative language and imagery, literary devices, and other rhetorical choices, looking for additional types of evidence to support your argument.
- After you include evidence, offer your own interpretation and explain how this evidence proves the point you make in your thesis.
- Don’t summarize or speak generally about the author and the text. Everything you write must be backed up with evidence.
- Don’t let quotes speak for themselves. After every piece of evidence you include, make sure to explain your interpretation. Also, connect the evidence to your overarching argument.
Sophistication (0-1 point)
In this case, sophistication isn’t about how many fancy vocabulary words or how many semicolons you use. According to College Board , one point can be awarded to AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essays that “demonstrate sophistication of thought and/or a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation” in any of these three ways:
- Explaining the significance or relevance of the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Explaining the purpose or function of the passage’s complexities or tensions.
- Employing a style that is consistently vivid and persuasive.
Note that you don’t have to achieve all three to earn your sophistication point. A good way to think of this rubric category is to consider it a bonus point that you can earn for going above and beyond in depth of analysis or by writing an especially persuasive, clear, and well-structured essay. In order to earn this point, you’ll need to first do a good job with your thesis, evidence, and commentary.
- Focus on nailing an argumentative thesis and multiple types of evidence. Getting these fundamentals of your essay right will set you up for achieving depth of analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence connects to your thesis.
- Spend a minute outlining your essay before you begin to ensure your essay flows in a clear and cohesive way.
- Steer clear of generalizations about the author or text.
- Don’t include arguments you can’t prove with evidence from the text.
- Avoid complex sentences and fancy vocabulary words unless you use them often. Long, clunky sentences with imprecisely used words are hard to follow.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis: Sample Prompt
The sample prompt below is published online by College Board and is a real example from the 2021 AP Exam. The prompt provides background context, essay instructions, and the text you need to analyze. For sake of space, we’ve included the text as an image you can click to read. After the prompt, we provide a sample high scoring essay and then explain why this AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay example works.
Suggested time—40 minutes.
(This question counts as one-third of the total essay section score.)
On February 27, 2013, while in office, former president Barack Obama delivered the following address dedicating the Rosa Parks statue in the National Statuary Hall of the United States Capitol building. Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that analyzes the writer’s rhetorical choices.
- Select and use evidence to support your line of reasoning.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
In his speech delivered in 2013 at the dedication of Rosa Park’s statue, President Barack Obama acknowledges everything that Parks’ activism made possible in the United States. Telling the story of Parks’ life and achievements, Obama highlights the fact that Parks was a regular person whose actions accomplished enormous change during the civil rights era. Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.
Although it might be a surprising way to start to his dedication, Obama begins his speech by telling us who Parks was not: “Rosa Parks held no elected office. She possessed no fortune” he explains in lines 1-2. Later, when he tells the story of the bus driver who threatened to have Parks arrested when she refused to get off the bus, he explains that Parks “simply replied, ‘You may do that’” (lines 22-23). Right away, he establishes that Parks was a regular person who did not hold a seat of power. Her protest on the bus was not part of a larger plan, it was a simple response. By emphasizing that Parks was not powerful, wealthy, or loud spoken, he implies that Parks’ style of activism is an everyday practice that all of us can aspire to.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example (Continued)
Even though Obama portrays Parks as a demure person whose protest came “simply” and naturally, he shows the importance of her activism through long lists of ripple effects. When Parks challenged her arrest, Obama explains, Martin Luther King, Jr. stood with her and “so did thousands of Montgomery, Alabama commuters” (lines 27-28). They began a boycott that included “teachers and laborers, clergy and domestics, through rain and cold and sweltering heat, day after day, week after week, month after month, walking miles if they had to…” (lines 28-31). In this section of the speech, Obama’s sentences grow longer and he uses lists to show that Parks’ small action impacted and inspired many others to fight for change. Further, listing out how many days, weeks, and months the boycott lasted shows how Parks’ single act of protest sparked a much longer push for change.
To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By of including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.
Toward the end of the speech, Obama states that change happens “not mainly through the exploits of the famous and the powerful, but through the countless acts of often anonymous courage and kindness” (lines 78-81). Through carefully chosen diction that portrays her as a quiet, regular person and through lists and Biblical references that highlight the huge impacts of her action, Obama illustrates exactly this point. He wants us to see that, just like Parks, the small and meek can change the world for the better.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example: Why It Works
We would give the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay above a score of 6 out of 6 because it fully satisfies the essay’s 3 rubric categories: Thesis, Evidence and Commentary, and Sophistication . Let’s break down what this student did:
The thesis of this essay appears in the last line of the first paragraph:
“ Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did .”
This student’s thesis works because they make a clear argument about Obama’s rhetorical choices. They 1) list the rhetorical choices that will be analyzed in the rest of the essay (the italicized text above) and 2) include an argument someone else might disagree with (the bolded text above).
Evidence and Commentary:
This student includes substantial evidence and commentary. Things they do right, per the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis rubric:
- They include lots of specific evidence from the text in the form of quotes.
- They incorporate 3 different types of evidence (diction, long lists, Biblical references).
- After including evidence, they offer an interpretation of what the evidence means and explain how the evidence contributes to their overarching argument (aka their thesis).
Sophistication
This essay achieves sophistication according to the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis essay rubric in a few key ways:
- This student provides an introduction that flows naturally into the topic their essay will discuss. Before they get to their thesis, they tell us that Obama portrays Parks as a “regular person” setting up their main argument: Obama wants all regular people to aspire to do good in the world just as Rosa Parks did.
- They organize evidence and commentary in a clear and cohesive way. Each body paragraph focuses on just one type of evidence.
- They explain how their evidence is significant. In the final sentence of each body paragraph, they draw a connection back to the overarching argument presented in the thesis.
- All their evidence supports the argument presented in their thesis. There is no extraneous evidence or misleading detail.
- They consider nuances in the text. Rather than taking the text at face value, they consider what Obama’s rhetorical choices imply and offer their own unique interpretation of those implications.
- In their final paragraph, they come full circle, reiterate their thesis, and explain what Obama’s rhetorical choices communicate to readers.
- Their sentences are clear and easy to read. There are no grammar errors or misused words.
AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay—More Resources
Looking for more tips to help your master your AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay? Brush up on 20 Rhetorical Devices High School Students Should Know and read our Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension . If you’re ready to start studying for another part of the AP English Exam, find more expert tips in our How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis blog post.
Considering what other AP classes to take? Read up on the Hardest AP Classes .
- High School Success
Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This goal will be plainly stated. For instance, in the example item at the start of this lesson, the goal is "to emphasize a similarity between the two novels". Step 2: Read the bullet points and identify relevant info. Read the bullet points, looking for information is relevant to the goal you just identified.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
To hone your skills in analyzing rhetorical devices, practice with sample SAT Essay passages and analyze the devices used. Review sample essays that effectively incorporate rhetorical analysis, paying attention to how the analysis is structured and presented. Conclusion. Analyzing rhetorical devices is a crucial skill for success on the SAT Essay.
Rhetorical Devices and Persuasive Stategies to Analyze on the SAT Essay. Ethos - An appeal to authority aiming to establish the credibility of a speaker or source. For example, a writer might say "As a veteranarian…" or "a Harvard University study…" or "a constitutional scholar….". Pathos - An appeal to the reader's ...
Like all other essays, your rhetorical analysis essay will have an introduction with a thesis, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. WRITE - write your essay. Asher AP ELAC Name: _____ Step 3: Organizing and Writing Your Essay: Some of this is redundant, but this breaks down some of the steps from MAD TO WRITE even further. ...
The SAT Essay section assesses students' ability to analyze an author's argument and use of rhetorical devices to persuade the audience. Understanding rhetorical devices and their effects is essential for crafting effective analytical responses. In this guide, we'll examine sample SAT essays and analyze the rhetorical devices employed by the authors to convey their arguments persuasively.
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
5. State your thesis. Now that you've completed your analysis of the material, try to summarize it into one clear, concise thesis statement that will form the foundation of your essay. Your thesis statement should summarize: 1) the argument or purpose of the speaker; 2) the methods the speaker uses; and 3) the effectiveness of those methods ...
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
Follow this step-by-step guide to write your own effective rhetorical analysis essay. 1. Choose and study a text. Review the work you're analyzing more than once to become as familiar as possible with the author's argument and writing style. Make sure you have read the text thoroughly, and that you fully understand each point that the ...
To summarize, your SAT essay should stick to the following format: Introduction (with your thesis) - 2-5 sentences. Start with a statement about what the author of the passage is arguing. Thesis with a clear statement about what argumentative techniques you'll be examining in the essay. Example 1 - 6-10 sentences.
The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses " relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim (s) or point (s) made. " This means you can't just stick to abstract reasoning like this: The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches.
The SAT Essay asks you to analyze how authors use rhetoric to persuade the reader to agree with them. In addition to analyzing rhetorical devices, you'll want to make sure you consider these 4 elements of rhetoric. Today, we'll take a look at the rhetorical square, which is comprised of the 4 elements you should consider when analyzing a ...
Here are a couple of examples of statistics from an official SAT essay prompt, "Let There Be Dark" by Paul Bogard: Example: 8 of 10 children born in the United States will never know a sky dark enough for the Milky Way. Example: In the United States and Western Europe, the amount of light in the sky increases an average of about 6% every year.
Absolutely Essential SAT Writing Strategies. November 15, 2022. •. 10.8 min read. tl;dr: The SAT essay is graded on three metrics — Reading, Analysis, and Writing — each on a scale from 1-4. To score an 8/8/8 on the SAT essay, you need to understand the rubric and keep in mind the three important parts of the essay: analyzing the prompt ...
First and foremost, it's essential to understand the basic structure of a rhetorical analysis essay and what the purpose is. Rhetorical analysis essays focus on examining how authors use rhetorical strategies (such as ethos, pathos, and logos) to create an argument or persuade the audience. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective rhetorical analysis essay: 1.
1. Prompt Structure: SAT essay prompts typically consist of a passage or excerpt followed by a question that asks you to analyze the author's argument, rhetorical strategies, or persuasive techniques. 2. Key Components: Pay attention to the main argument or thesis presented in the passage, as well as the evidence and rhetorical devices used to ...
Evaluate the elements of a rhetorical analysis. Identify and correct errors involving mixed sentence structures. Evaluate an essay for clarity, coherence, and language. At various points in your writing, especially after you complete the first draft, check the rubric provided here. Your instructor is likely to use a similar rubric to evaluate ...
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of essay where you examine how authors or speakers use words, phrases, and other techniques to influence or persuade their audience. This type of essay focuses on analyzing the strategies used by the writer or speaker to achieve their purpose, whether it's to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke.
No extra time allowed! #5: Grade the essay, using the official essay rubric to give yourself a score out of 8 in the reading, analysis, and writing sections. #6: Repeat steps 4 and 5. Choose the prompts you think will be the hardest for you so that you can so that you're prepared for the worst when the test day comes.
This article will find some examples that will help you with your rhetorical analysis essay writing effortlessly. On This Page. 1. Good Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example. 2. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example AP Lang 2023. 3. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Examples for Students. 4.
Rhetoric. how a writer or speaker persuades his audience using specific techniques. The rhetorical analysis essay revolves around: the relationship between the communicator and the audience; what choices the writer makes and how they affect the audience. Rhetorical devices are also known as: - rhetorical strategies- rhetorical tools- literary ...
The AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay is one of three essays included in the written portion of the AP English Exam. The full AP English Exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long, with the first 60 minutes dedicated to multiple-choice questions. Once you complete the multiple-choice section, you move on to three equally weighted essays that ask you ...