- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

What is Research: Definition, Methods, Types & Examples

The search for knowledge is closely linked to the object of study; that is, to the reconstruction of the facts that will provide an explanation to an observed event and that at first sight can be considered as a problem. It is very human to seek answers and satisfy our curiosity. Let’s talk about research.
Content Index
What is Research?
What are the characteristics of research.
- Comparative analysis chart
Qualitative methods
Quantitative methods, 8 tips for conducting accurate research.
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, “research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.”
Inductive methods analyze an observed event, while deductive methods verify the observed event. Inductive approaches are associated with qualitative research , and deductive methods are more commonly associated with quantitative analysis .
Research is conducted with a purpose to:
- Identify potential and new customers
- Understand existing customers
- Set pragmatic goals
- Develop productive market strategies
- Address business challenges
- Put together a business expansion plan
- Identify new business opportunities
- Good research follows a systematic approach to capture accurate data. Researchers need to practice ethics and a code of conduct while making observations or drawing conclusions.
- The analysis is based on logical reasoning and involves both inductive and deductive methods.
- Real-time data and knowledge is derived from actual observations in natural settings.
- There is an in-depth analysis of all data collected so that there are no anomalies associated with it.
- It creates a path for generating new questions. Existing data helps create more research opportunities.
- It is analytical and uses all the available data so that there is no ambiguity in inference.
- Accuracy is one of the most critical aspects of research. The information must be accurate and correct. For example, laboratories provide a controlled environment to collect data. Accuracy is measured in the instruments used, the calibrations of instruments or tools, and the experiment’s final result.
What is the purpose of research?
There are three main purposes:
- Exploratory: As the name suggests, researchers conduct exploratory studies to explore a group of questions. The answers and analytics may not offer a conclusion to the perceived problem. It is undertaken to handle new problem areas that haven’t been explored before. This exploratory data analysis process lays the foundation for more conclusive data collection and analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Descriptive Analysis
- Descriptive: It focuses on expanding knowledge on current issues through a process of data collection. Descriptive research describe the behavior of a sample population. Only one variable is required to conduct the study. The three primary purposes of descriptive studies are describing, explaining, and validating the findings. For example, a study conducted to know if top-level management leaders in the 21st century possess the moral right to receive a considerable sum of money from the company profit.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Explanatory: Causal research or explanatory research is conducted to understand the impact of specific changes in existing standard procedures. Running experiments is the most popular form. For example, a study that is conducted to understand the effect of rebranding on customer loyalty.
Here is a comparative analysis chart for a better understanding:
| Approach used | Unstructured | Structured | Highly structured |
| Conducted through | Asking questions | Asking questions | By using hypotheses. |
| Time | Early stages of decision making | Later stages of decision making | Later stages of decision making |
It begins by asking the right questions and choosing an appropriate method to investigate the problem. After collecting answers to your questions, you can analyze the findings or observations to draw reasonable conclusions.
When it comes to customers and market studies, the more thorough your questions, the better the analysis. You get essential insights into brand perception and product needs by thoroughly collecting customer data through surveys and questionnaires . You can use this data to make smart decisions about your marketing strategies to position your business effectively.
To make sense of your study and get insights faster, it helps to use a research repository as a single source of truth in your organization and manage your research data in one centralized data repository .
Types of research methods and Examples

Research methods are broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative .
Both methods have distinctive properties and data collection methods .
Qualitative research is a method that collects data using conversational methods, usually open-ended questions . The responses collected are essentially non-numerical. This method helps a researcher understand what participants think and why they think in a particular way.
Types of qualitative methods include:
- One-to-one Interview
- Focus Groups
- Ethnographic studies
- Text Analysis
Quantitative methods deal with numbers and measurable forms . It uses a systematic way of investigating events or data. It answers questions to justify relationships with measurable variables to either explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
Types of quantitative methods include:
- Survey research
- Descriptive research
- Correlational research
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
Remember, it is only valuable and useful when it is valid, accurate, and reliable. Incorrect results can lead to customer churn and a decrease in sales.
It is essential to ensure that your data is:
- Valid – founded, logical, rigorous, and impartial.
- Accurate – free of errors and including required details.
- Reliable – other people who investigate in the same way can produce similar results.
- Timely – current and collected within an appropriate time frame.
- Complete – includes all the data you need to support your business decisions.
Gather insights

- Identify the main trends and issues, opportunities, and problems you observe. Write a sentence describing each one.
- Keep track of the frequency with which each of the main findings appears.
- Make a list of your findings from the most common to the least common.
- Evaluate a list of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats identified in a SWOT analysis .
- Prepare conclusions and recommendations about your study.
- Act on your strategies
- Look for gaps in the information, and consider doing additional inquiry if necessary
- Plan to review the results and consider efficient methods to analyze and interpret results.
Review your goals before making any conclusions about your study. Remember how the process you have completed and the data you have gathered help answer your questions. Ask yourself if what your analysis revealed facilitates the identification of your conclusions and recommendations.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Life@QuestionPro: The Journey of Kristie Lawrence
Jun 7, 2024

How Can I Help You? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 5, 2024

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024

Raked Weighting: A Key Tool for Accurate Survey Results
May 31, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
What is Research? – Purpose of Research
- By DiscoverPhDs
- September 10, 2020

The purpose of research is to enhance society by advancing knowledge through the development of scientific theories, concepts and ideas. A research purpose is met through forming hypotheses, collecting data, analysing results, forming conclusions, implementing findings into real-life applications and forming new research questions.
What is Research
Simply put, research is the process of discovering new knowledge. This knowledge can be either the development of new concepts or the advancement of existing knowledge and theories, leading to a new understanding that was not previously known.
As a more formal definition of research, the following has been extracted from the Code of Federal Regulations :
While research can be carried out by anyone and in any field, most research is usually done to broaden knowledge in the physical, biological, and social worlds. This can range from learning why certain materials behave the way they do, to asking why certain people are more resilient than others when faced with the same challenges.
The use of ‘systematic investigation’ in the formal definition represents how research is normally conducted – a hypothesis is formed, appropriate research methods are designed, data is collected and analysed, and research results are summarised into one or more ‘research conclusions’. These research conclusions are then shared with the rest of the scientific community to add to the existing knowledge and serve as evidence to form additional questions that can be investigated. It is this cyclical process that enables scientific research to make continuous progress over the years; the true purpose of research.
What is the Purpose of Research
From weather forecasts to the discovery of antibiotics, researchers are constantly trying to find new ways to understand the world and how things work – with the ultimate goal of improving our lives.
The purpose of research is therefore to find out what is known, what is not and what we can develop further. In this way, scientists can develop new theories, ideas and products that shape our society and our everyday lives.
Although research can take many forms, there are three main purposes of research:
- Exploratory: Exploratory research is the first research to be conducted around a problem that has not yet been clearly defined. Exploration research therefore aims to gain a better understanding of the exact nature of the problem and not to provide a conclusive answer to the problem itself. This enables us to conduct more in-depth research later on.
- Descriptive: Descriptive research expands knowledge of a research problem or phenomenon by describing it according to its characteristics and population. Descriptive research focuses on the ‘how’ and ‘what’, but not on the ‘why’.
- Explanatory: Explanatory research, also referred to as casual research, is conducted to determine how variables interact, i.e. to identify cause-and-effect relationships. Explanatory research deals with the ‘why’ of research questions and is therefore often based on experiments.
Characteristics of Research
There are 8 core characteristics that all research projects should have. These are:
- Empirical – based on proven scientific methods derived from real-life observations and experiments.
- Logical – follows sequential procedures based on valid principles.
- Cyclic – research begins with a question and ends with a question, i.e. research should lead to a new line of questioning.
- Controlled – vigorous measures put into place to keep all variables constant, except those under investigation.
- Hypothesis-based – the research design generates data that sufficiently meets the research objectives and can prove or disprove the hypothesis. It makes the research study repeatable and gives credibility to the results.
- Analytical – data is generated, recorded and analysed using proven techniques to ensure high accuracy and repeatability while minimising potential errors and anomalies.
- Objective – sound judgement is used by the researcher to ensure that the research findings are valid.
- Statistical treatment – statistical treatment is used to transform the available data into something more meaningful from which knowledge can be gained.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Types of Research
Research can be divided into two main types: basic research (also known as pure research) and applied research.
Basic Research
Basic research, also known as pure research, is an original investigation into the reasons behind a process, phenomenon or particular event. It focuses on generating knowledge around existing basic principles.
Basic research is generally considered ‘non-commercial research’ because it does not focus on solving practical problems, and has no immediate benefit or ways it can be applied.
While basic research may not have direct applications, it usually provides new insights that can later be used in applied research.
Applied Research
Applied research investigates well-known theories and principles in order to enhance knowledge around a practical aim. Because of this, applied research focuses on solving real-life problems by deriving knowledge which has an immediate application.
Methods of Research
Research methods for data collection fall into one of two categories: inductive methods or deductive methods.
Inductive research methods focus on the analysis of an observation and are usually associated with qualitative research. Deductive research methods focus on the verification of an observation and are typically associated with quantitative research.

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a method that enables non-numerical data collection through open-ended methods such as interviews, case studies and focus groups .
It enables researchers to collect data on personal experiences, feelings or behaviours, as well as the reasons behind them. Because of this, qualitative research is often used in fields such as social science, psychology and philosophy and other areas where it is useful to know the connection between what has occurred and why it has occurred.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a method that collects and analyses numerical data through statistical analysis.
It allows us to quantify variables, uncover relationships, and make generalisations across a larger population. As a result, quantitative research is often used in the natural and physical sciences such as engineering, biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, finance, and medical research, etc.
What does Research Involve?
Research often follows a systematic approach known as a Scientific Method, which is carried out using an hourglass model.
A research project first starts with a problem statement, or rather, the research purpose for engaging in the study. This can take the form of the ‘ scope of the study ’ or ‘ aims and objectives ’ of your research topic.
Subsequently, a literature review is carried out and a hypothesis is formed. The researcher then creates a research methodology and collects the data.
The data is then analysed using various statistical methods and the null hypothesis is either accepted or rejected.
In both cases, the study and its conclusion are officially written up as a report or research paper, and the researcher may also recommend lines of further questioning. The report or research paper is then shared with the wider research community, and the cycle begins all over again.
Although these steps outline the overall research process, keep in mind that research projects are highly dynamic and are therefore considered an iterative process with continued refinements and not a series of fixed stages.

The term rationale of research means the reason for performing the research study in question.

Impostor Syndrome is a common phenomenon amongst PhD students, leading to self-doubt and fear of being exposed as a “fraud”. How can we overcome these feelings?

A thesis and dissertation appendix contains additional information which supports your main arguments. Find out what they should include and how to format them.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

In Finland, all new PhD holders are given a traditional Doctoral Hat and Doctoral Sword during a Conferment Ceremony, symbolising the freedom of research.

An abstract and introduction are the first two sections of your paper or thesis. This guide explains the differences between them and how to write them.

Kat is in the second year of her PhD at the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) in Perth, Western Australia (WA). Her research involves studying supermassive black holes at the centres of distant galaxies.

Carlos is a third year PhD student at the Centre for Doctoral Training in Intelligent Games and Games Intelligence (IGGI), as part of the University of York and Goldsmiths, University of London.
Join Thousands of Students
What Is Research, and Why Do People Do It?
- Open Access
- First Online: 03 December 2022
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- James Hiebert 6 ,
- Jinfa Cai 7 ,
- Stephen Hwang 7 ,
- Anne K Morris 6 &
- Charles Hohensee 6
Part of the book series: Research in Mathematics Education ((RME))
18k Accesses
Abstractspiepr Abs1
Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain, and by its commitment to learn from everyone else seriously engaged in research. We call this kind of research scientific inquiry and define it as “formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses.” By “hypotheses” we do not mean the hypotheses you encounter in statistics courses. We mean predictions about what you expect to find and rationales for why you made these predictions. Throughout this and the remaining chapters we make clear that the process of scientific inquiry applies to all kinds of research studies and data, both qualitative and quantitative.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Part I. What Is Research?
Have you ever studied something carefully because you wanted to know more about it? Maybe you wanted to know more about your grandmother’s life when she was younger so you asked her to tell you stories from her childhood, or maybe you wanted to know more about a fertilizer you were about to use in your garden so you read the ingredients on the package and looked them up online. According to the dictionary definition, you were doing research.
Recall your high school assignments asking you to “research” a topic. The assignment likely included consulting a variety of sources that discussed the topic, perhaps including some “original” sources. Often, the teacher referred to your product as a “research paper.”
Were you conducting research when you interviewed your grandmother or wrote high school papers reviewing a particular topic? Our view is that you were engaged in part of the research process, but only a small part. In this book, we reserve the word “research” for what it means in the scientific world, that is, for scientific research or, more pointedly, for scientific inquiry .
Exercise 1.1
Before you read any further, write a definition of what you think scientific inquiry is. Keep it short—Two to three sentences. You will periodically update this definition as you read this chapter and the remainder of the book.
This book is about scientific inquiry—what it is and how to do it. For starters, scientific inquiry is a process, a particular way of finding out about something that involves a number of phases. Each phase of the process constitutes one aspect of scientific inquiry. You are doing scientific inquiry as you engage in each phase, but you have not done scientific inquiry until you complete the full process. Each phase is necessary but not sufficient.
In this chapter, we set the stage by defining scientific inquiry—describing what it is and what it is not—and by discussing what it is good for and why people do it. The remaining chapters build directly on the ideas presented in this chapter.
A first thing to know is that scientific inquiry is not all or nothing. “Scientificness” is a continuum. Inquiries can be more scientific or less scientific. What makes an inquiry more scientific? You might be surprised there is no universally agreed upon answer to this question. None of the descriptors we know of are sufficient by themselves to define scientific inquiry. But all of them give you a way of thinking about some aspects of the process of scientific inquiry. Each one gives you different insights.

Exercise 1.2
As you read about each descriptor below, think about what would make an inquiry more or less scientific. If you think a descriptor is important, use it to revise your definition of scientific inquiry.
Creating an Image of Scientific Inquiry
We will present three descriptors of scientific inquiry. Each provides a different perspective and emphasizes a different aspect of scientific inquiry. We will draw on all three descriptors to compose our definition of scientific inquiry.
Descriptor 1. Experience Carefully Planned in Advance
Sir Ronald Fisher, often called the father of modern statistical design, once referred to research as “experience carefully planned in advance” (1935, p. 8). He said that humans are always learning from experience, from interacting with the world around them. Usually, this learning is haphazard rather than the result of a deliberate process carried out over an extended period of time. Research, Fisher said, was learning from experience, but experience carefully planned in advance.
This phrase can be fully appreciated by looking at each word. The fact that scientific inquiry is based on experience means that it is based on interacting with the world. These interactions could be thought of as the stuff of scientific inquiry. In addition, it is not just any experience that counts. The experience must be carefully planned . The interactions with the world must be conducted with an explicit, describable purpose, and steps must be taken to make the intended learning as likely as possible. This planning is an integral part of scientific inquiry; it is not just a preparation phase. It is one of the things that distinguishes scientific inquiry from many everyday learning experiences. Finally, these steps must be taken beforehand and the purpose of the inquiry must be articulated in advance of the experience. Clearly, scientific inquiry does not happen by accident, by just stumbling into something. Stumbling into something unexpected and interesting can happen while engaged in scientific inquiry, but learning does not depend on it and serendipity does not make the inquiry scientific.
Descriptor 2. Observing Something and Trying to Explain Why It Is the Way It Is
When we were writing this chapter and googled “scientific inquiry,” the first entry was: “Scientific inquiry refers to the diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based on the evidence derived from their work.” The emphasis is on studying, or observing, and then explaining . This descriptor takes the image of scientific inquiry beyond carefully planned experience and includes explaining what was experienced.
According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, “explain” means “(a) to make known, (b) to make plain or understandable, (c) to give the reason or cause of, and (d) to show the logical development or relations of” (Merriam-Webster, n.d. ). We will use all these definitions. Taken together, they suggest that to explain an observation means to understand it by finding reasons (or causes) for why it is as it is. In this sense of scientific inquiry, the following are synonyms: explaining why, understanding why, and reasoning about causes and effects. Our image of scientific inquiry now includes planning, observing, and explaining why.

We need to add a final note about this descriptor. We have phrased it in a way that suggests “observing something” means you are observing something in real time—observing the way things are or the way things are changing. This is often true. But, observing could mean observing data that already have been collected, maybe by someone else making the original observations (e.g., secondary analysis of NAEP data or analysis of existing video recordings of classroom instruction). We will address secondary analyses more fully in Chap. 4 . For now, what is important is that the process requires explaining why the data look like they do.
We must note that for us, the term “data” is not limited to numerical or quantitative data such as test scores. Data can also take many nonquantitative forms, including written survey responses, interview transcripts, journal entries, video recordings of students, teachers, and classrooms, text messages, and so forth.

Exercise 1.3
What are the implications of the statement that just “observing” is not enough to count as scientific inquiry? Does this mean that a detailed description of a phenomenon is not scientific inquiry?
Find sources that define research in education that differ with our position, that say description alone, without explanation, counts as scientific research. Identify the precise points where the opinions differ. What are the best arguments for each of the positions? Which do you prefer? Why?
Descriptor 3. Updating Everyone’s Thinking in Response to More and Better Information
This descriptor focuses on a third aspect of scientific inquiry: updating and advancing the field’s understanding of phenomena that are investigated. This descriptor foregrounds a powerful characteristic of scientific inquiry: the reliability (or trustworthiness) of what is learned and the ultimate inevitability of this learning to advance human understanding of phenomena. Humans might choose not to learn from scientific inquiry, but history suggests that scientific inquiry always has the potential to advance understanding and that, eventually, humans take advantage of these new understandings.
Before exploring these bold claims a bit further, note that this descriptor uses “information” in the same way the previous two descriptors used “experience” and “observations.” These are the stuff of scientific inquiry and we will use them often, sometimes interchangeably. Frequently, we will use the term “data” to stand for all these terms.
An overriding goal of scientific inquiry is for everyone to learn from what one scientist does. Much of this book is about the methods you need to use so others have faith in what you report and can learn the same things you learned. This aspect of scientific inquiry has many implications.
One implication is that scientific inquiry is not a private practice. It is a public practice available for others to see and learn from. Notice how different this is from everyday learning. When you happen to learn something from your everyday experience, often only you gain from the experience. The fact that research is a public practice means it is also a social one. It is best conducted by interacting with others along the way: soliciting feedback at each phase, taking opportunities to present work-in-progress, and benefitting from the advice of others.
A second implication is that you, as the researcher, must be committed to sharing what you are doing and what you are learning in an open and transparent way. This allows all phases of your work to be scrutinized and critiqued. This is what gives your work credibility. The reliability or trustworthiness of your findings depends on your colleagues recognizing that you have used all appropriate methods to maximize the chances that your claims are justified by the data.
A third implication of viewing scientific inquiry as a collective enterprise is the reverse of the second—you must be committed to receiving comments from others. You must treat your colleagues as fair and honest critics even though it might sometimes feel otherwise. You must appreciate their job, which is to remain skeptical while scrutinizing what you have done in considerable detail. To provide the best help to you, they must remain skeptical about your conclusions (when, for example, the data are difficult for them to interpret) until you offer a convincing logical argument based on the information you share. A rather harsh but good-to-remember statement of the role of your friendly critics was voiced by Karl Popper, a well-known twentieth century philosopher of science: “. . . if you are interested in the problem which I tried to solve by my tentative assertion, you may help me by criticizing it as severely as you can” (Popper, 1968, p. 27).
A final implication of this third descriptor is that, as someone engaged in scientific inquiry, you have no choice but to update your thinking when the data support a different conclusion. This applies to your own data as well as to those of others. When data clearly point to a specific claim, even one that is quite different than you expected, you must reconsider your position. If the outcome is replicated multiple times, you need to adjust your thinking accordingly. Scientific inquiry does not let you pick and choose which data to believe; it mandates that everyone update their thinking when the data warrant an update.
Doing Scientific Inquiry
We define scientific inquiry in an operational sense—what does it mean to do scientific inquiry? What kind of process would satisfy all three descriptors: carefully planning an experience in advance; observing and trying to explain what you see; and, contributing to updating everyone’s thinking about an important phenomenon?
We define scientific inquiry as formulating , testing , and revising hypotheses about phenomena of interest.
Of course, we are not the only ones who define it in this way. The definition for the scientific method posted by the editors of Britannica is: “a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the tests and experiments” (Britannica, n.d. ).

Notice how defining scientific inquiry this way satisfies each of the descriptors. “Carefully planning an experience in advance” is exactly what happens when formulating a hypothesis about a phenomenon of interest and thinking about how to test it. “ Observing a phenomenon” occurs when testing a hypothesis, and “ explaining ” what is found is required when revising a hypothesis based on the data. Finally, “updating everyone’s thinking” comes from comparing publicly the original with the revised hypothesis.
Doing scientific inquiry, as we have defined it, underscores the value of accumulating knowledge rather than generating random bits of knowledge. Formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses is an ongoing process, with each revised hypothesis begging for another test, whether by the same researcher or by new researchers. The editors of Britannica signaled this cyclic process by adding the following phrase to their definition of the scientific method: “The modified hypothesis is then retested, further modified, and tested again.” Scientific inquiry creates a process that encourages each study to build on the studies that have gone before. Through collective engagement in this process of building study on top of study, the scientific community works together to update its thinking.
Before exploring more fully the meaning of “formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses,” we need to acknowledge that this is not the only way researchers define research. Some researchers prefer a less formal definition, one that includes more serendipity, less planning, less explanation. You might have come across more open definitions such as “research is finding out about something.” We prefer the tighter hypothesis formulation, testing, and revision definition because we believe it provides a single, coherent map for conducting research that addresses many of the thorny problems educational researchers encounter. We believe it is the most useful orientation toward research and the most helpful to learn as a beginning researcher.
A final clarification of our definition is that it applies equally to qualitative and quantitative research. This is a familiar distinction in education that has generated much discussion. You might think our definition favors quantitative methods over qualitative methods because the language of hypothesis formulation and testing is often associated with quantitative methods. In fact, we do not favor one method over another. In Chap. 4 , we will illustrate how our definition fits research using a range of quantitative and qualitative methods.
Exercise 1.4
Look for ways to extend what the field knows in an area that has already received attention by other researchers. Specifically, you can search for a program of research carried out by more experienced researchers that has some revised hypotheses that remain untested. Identify a revised hypothesis that you might like to test.
Unpacking the Terms Formulating, Testing, and Revising Hypotheses
To get a full sense of the definition of scientific inquiry we will use throughout this book, it is helpful to spend a little time with each of the key terms.
We first want to make clear that we use the term “hypothesis” as it is defined in most dictionaries and as it used in many scientific fields rather than as it is usually defined in educational statistics courses. By “hypothesis,” we do not mean a null hypothesis that is accepted or rejected by statistical analysis. Rather, we use “hypothesis” in the sense conveyed by the following definitions: “An idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved” (Cambridge University Press, n.d. ), and “An unproved theory, proposition, or supposition, tentatively accepted to explain certain facts and to provide a basis for further investigation or argument” (Agnes & Guralnik, 2008 ).
We distinguish two parts to “hypotheses.” Hypotheses consist of predictions and rationales . Predictions are statements about what you expect to find when you inquire about something. Rationales are explanations for why you made the predictions you did, why you believe your predictions are correct. So, for us “formulating hypotheses” means making explicit predictions and developing rationales for the predictions.
“Testing hypotheses” means making observations that allow you to assess in what ways your predictions were correct and in what ways they were incorrect. In education research, it is rarely useful to think of your predictions as either right or wrong. Because of the complexity of most issues you will investigate, most predictions will be right in some ways and wrong in others.
By studying the observations you make (data you collect) to test your hypotheses, you can revise your hypotheses to better align with the observations. This means revising your predictions plus revising your rationales to justify your adjusted predictions. Even though you might not run another test, formulating revised hypotheses is an essential part of conducting a research study. Comparing your original and revised hypotheses informs everyone of what you learned by conducting your study. In addition, a revised hypothesis sets the stage for you or someone else to extend your study and accumulate more knowledge of the phenomenon.
We should note that not everyone makes a clear distinction between predictions and rationales as two aspects of hypotheses. In fact, common, non-scientific uses of the word “hypothesis” may limit it to only a prediction or only an explanation (or rationale). We choose to explicitly include both prediction and rationale in our definition of hypothesis, not because we assert this should be the universal definition, but because we want to foreground the importance of both parts acting in concert. Using “hypothesis” to represent both prediction and rationale could hide the two aspects, but we make them explicit because they provide different kinds of information. It is usually easier to make predictions than develop rationales because predictions can be guesses, hunches, or gut feelings about which you have little confidence. Developing a compelling rationale requires careful thought plus reading what other researchers have found plus talking with your colleagues. Often, while you are developing your rationale you will find good reasons to change your predictions. Developing good rationales is the engine that drives scientific inquiry. Rationales are essentially descriptions of how much you know about the phenomenon you are studying. Throughout this guide, we will elaborate on how developing good rationales drives scientific inquiry. For now, we simply note that it can sharpen your predictions and help you to interpret your data as you test your hypotheses.

Hypotheses in education research take a variety of forms or types. This is because there are a variety of phenomena that can be investigated. Investigating educational phenomena is sometimes best done using qualitative methods, sometimes using quantitative methods, and most often using mixed methods (e.g., Hay, 2016 ; Weis et al. 2019a ; Weisner, 2005 ). This means that, given our definition, hypotheses are equally applicable to qualitative and quantitative investigations.
Hypotheses take different forms when they are used to investigate different kinds of phenomena. Two very different activities in education could be labeled conducting experiments and descriptions. In an experiment, a hypothesis makes a prediction about anticipated changes, say the changes that occur when a treatment or intervention is applied. You might investigate how students’ thinking changes during a particular kind of instruction.
A second type of hypothesis, relevant for descriptive research, makes a prediction about what you will find when you investigate and describe the nature of a situation. The goal is to understand a situation as it exists rather than to understand a change from one situation to another. In this case, your prediction is what you expect to observe. Your rationale is the set of reasons for making this prediction; it is your current explanation for why the situation will look like it does.
You will probably read, if you have not already, that some researchers say you do not need a prediction to conduct a descriptive study. We will discuss this point of view in Chap. 2 . For now, we simply claim that scientific inquiry, as we have defined it, applies to all kinds of research studies. Descriptive studies, like others, not only benefit from formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses, but also need hypothesis formulating, testing, and revising.
One reason we define research as formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses is that if you think of research in this way you are less likely to go wrong. It is a useful guide for the entire process, as we will describe in detail in the chapters ahead. For example, as you build the rationale for your predictions, you are constructing the theoretical framework for your study (Chap. 3 ). As you work out the methods you will use to test your hypothesis, every decision you make will be based on asking, “Will this help me formulate or test or revise my hypothesis?” (Chap. 4 ). As you interpret the results of testing your predictions, you will compare them to what you predicted and examine the differences, focusing on how you must revise your hypotheses (Chap. 5 ). By anchoring the process to formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses, you will make smart decisions that yield a coherent and well-designed study.
Exercise 1.5
Compare the concept of formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses with the descriptions of scientific inquiry contained in Scientific Research in Education (NRC, 2002 ). How are they similar or different?
Exercise 1.6
Provide an example to illustrate and emphasize the differences between everyday learning/thinking and scientific inquiry.
Learning from Doing Scientific Inquiry
We noted earlier that a measure of what you have learned by conducting a research study is found in the differences between your original hypothesis and your revised hypothesis based on the data you collected to test your hypothesis. We will elaborate this statement in later chapters, but we preview our argument here.
Even before collecting data, scientific inquiry requires cycles of making a prediction, developing a rationale, refining your predictions, reading and studying more to strengthen your rationale, refining your predictions again, and so forth. And, even if you have run through several such cycles, you still will likely find that when you test your prediction you will be partly right and partly wrong. The results will support some parts of your predictions but not others, or the results will “kind of” support your predictions. A critical part of scientific inquiry is making sense of your results by interpreting them against your predictions. Carefully describing what aspects of your data supported your predictions, what aspects did not, and what data fell outside of any predictions is not an easy task, but you cannot learn from your study without doing this analysis.

Analyzing the matches and mismatches between your predictions and your data allows you to formulate different rationales that would have accounted for more of the data. The best revised rationale is the one that accounts for the most data. Once you have revised your rationales, you can think about the predictions they best justify or explain. It is by comparing your original rationales to your new rationales that you can sort out what you learned from your study.
Suppose your study was an experiment. Maybe you were investigating the effects of a new instructional intervention on students’ learning. Your original rationale was your explanation for why the intervention would change the learning outcomes in a particular way. Your revised rationale explained why the changes that you observed occurred like they did and why your revised predictions are better. Maybe your original rationale focused on the potential of the activities if they were implemented in ideal ways and your revised rationale included the factors that are likely to affect how teachers implement them. By comparing the before and after rationales, you are describing what you learned—what you can explain now that you could not before. Another way of saying this is that you are describing how much more you understand now than before you conducted your study.
Revised predictions based on carefully planned and collected data usually exhibit some of the following features compared with the originals: more precision, more completeness, and broader scope. Revised rationales have more explanatory power and become more complete, more aligned with the new predictions, sharper, and overall more convincing.
Part II. Why Do Educators Do Research?
Doing scientific inquiry is a lot of work. Each phase of the process takes time, and you will often cycle back to improve earlier phases as you engage in later phases. Because of the significant effort required, you should make sure your study is worth it. So, from the beginning, you should think about the purpose of your study. Why do you want to do it? And, because research is a social practice, you should also think about whether the results of your study are likely to be important and significant to the education community.
If you are doing research in the way we have described—as scientific inquiry—then one purpose of your study is to understand , not just to describe or evaluate or report. As we noted earlier, when you formulate hypotheses, you are developing rationales that explain why things might be like they are. In our view, trying to understand and explain is what separates research from other kinds of activities, like evaluating or describing.
One reason understanding is so important is that it allows researchers to see how or why something works like it does. When you see how something works, you are better able to predict how it might work in other contexts, under other conditions. And, because conditions, or contextual factors, matter a lot in education, gaining insights into applying your findings to other contexts increases the contributions of your work and its importance to the broader education community.
Consequently, the purposes of research studies in education often include the more specific aim of identifying and understanding the conditions under which the phenomena being studied work like the observations suggest. A classic example of this kind of study in mathematics education was reported by William Brownell and Harold Moser in 1949 . They were trying to establish which method of subtracting whole numbers could be taught most effectively—the regrouping method or the equal additions method. However, they realized that effectiveness might depend on the conditions under which the methods were taught—“meaningfully” versus “mechanically.” So, they designed a study that crossed the two instructional approaches with the two different methods (regrouping and equal additions). Among other results, they found that these conditions did matter. The regrouping method was more effective under the meaningful condition than the mechanical condition, but the same was not true for the equal additions algorithm.
What do education researchers want to understand? In our view, the ultimate goal of education is to offer all students the best possible learning opportunities. So, we believe the ultimate purpose of scientific inquiry in education is to develop understanding that supports the improvement of learning opportunities for all students. We say “ultimate” because there are lots of issues that must be understood to improve learning opportunities for all students. Hypotheses about many aspects of education are connected, ultimately, to students’ learning. For example, formulating and testing a hypothesis that preservice teachers need to engage in particular kinds of activities in their coursework in order to teach particular topics well is, ultimately, connected to improving students’ learning opportunities. So is hypothesizing that school districts often devote relatively few resources to instructional leadership training or hypothesizing that positioning mathematics as a tool students can use to combat social injustice can help students see the relevance of mathematics to their lives.
We do not exclude the importance of research on educational issues more removed from improving students’ learning opportunities, but we do think the argument for their importance will be more difficult to make. If there is no way to imagine a connection between your hypothesis and improving learning opportunities for students, even a distant connection, we recommend you reconsider whether it is an important hypothesis within the education community.
Notice that we said the ultimate goal of education is to offer all students the best possible learning opportunities. For too long, educators have been satisfied with a goal of offering rich learning opportunities for lots of students, sometimes even for just the majority of students, but not necessarily for all students. Evaluations of success often are based on outcomes that show high averages. In other words, if many students have learned something, or even a smaller number have learned a lot, educators may have been satisfied. The problem is that there is usually a pattern in the groups of students who receive lower quality opportunities—students of color and students who live in poor areas, urban and rural. This is not acceptable. Consequently, we emphasize the premise that the purpose of education research is to offer rich learning opportunities to all students.
One way to make sure you will be able to convince others of the importance of your study is to consider investigating some aspect of teachers’ shared instructional problems. Historically, researchers in education have set their own research agendas, regardless of the problems teachers are facing in schools. It is increasingly recognized that teachers have had trouble applying to their own classrooms what researchers find. To address this problem, a researcher could partner with a teacher—better yet, a small group of teachers—and talk with them about instructional problems they all share. These discussions can create a rich pool of problems researchers can consider. If researchers pursued one of these problems (preferably alongside teachers), the connection to improving learning opportunities for all students could be direct and immediate. “Grounding a research question in instructional problems that are experienced across multiple teachers’ classrooms helps to ensure that the answer to the question will be of sufficient scope to be relevant and significant beyond the local context” (Cai et al., 2019b , p. 115).
As a beginning researcher, determining the relevance and importance of a research problem is especially challenging. We recommend talking with advisors, other experienced researchers, and peers to test the educational importance of possible research problems and topics of study. You will also learn much more about the issue of research importance when you read Chap. 5 .
Exercise 1.7
Identify a problem in education that is closely connected to improving learning opportunities and a problem that has a less close connection. For each problem, write a brief argument (like a logical sequence of if-then statements) that connects the problem to all students’ learning opportunities.
Part III. Conducting Research as a Practice of Failing Productively
Scientific inquiry involves formulating hypotheses about phenomena that are not fully understood—by you or anyone else. Even if you are able to inform your hypotheses with lots of knowledge that has already been accumulated, you are likely to find that your prediction is not entirely accurate. This is normal. Remember, scientific inquiry is a process of constantly updating your thinking. More and better information means revising your thinking, again, and again, and again. Because you never fully understand a complicated phenomenon and your hypotheses never produce completely accurate predictions, it is easy to believe you are somehow failing.
The trick is to fail upward, to fail to predict accurately in ways that inform your next hypothesis so you can make a better prediction. Some of the best-known researchers in education have been open and honest about the many times their predictions were wrong and, based on the results of their studies and those of others, they continuously updated their thinking and changed their hypotheses.
A striking example of publicly revising (actually reversing) hypotheses due to incorrect predictions is found in the work of Lee J. Cronbach, one of the most distinguished educational psychologists of the twentieth century. In 1955, Cronbach delivered his presidential address to the American Psychological Association. Titling it “Two Disciplines of Scientific Psychology,” Cronbach proposed a rapprochement between two research approaches—correlational studies that focused on individual differences and experimental studies that focused on instructional treatments controlling for individual differences. (We will examine different research approaches in Chap. 4 ). If these approaches could be brought together, reasoned Cronbach ( 1957 ), researchers could find interactions between individual characteristics and treatments (aptitude-treatment interactions or ATIs), fitting the best treatments to different individuals.
In 1975, after years of research by many researchers looking for ATIs, Cronbach acknowledged the evidence for simple, useful ATIs had not been found. Even when trying to find interactions between a few variables that could provide instructional guidance, the analysis, said Cronbach, creates “a hall of mirrors that extends to infinity, tormenting even the boldest investigators and defeating even ambitious designs” (Cronbach, 1975 , p. 119).
As he was reflecting back on his work, Cronbach ( 1986 ) recommended moving away from documenting instructional effects through statistical inference (an approach he had championed for much of his career) and toward approaches that probe the reasons for these effects, approaches that provide a “full account of events in a time, place, and context” (Cronbach, 1986 , p. 104). This is a remarkable change in hypotheses, a change based on data and made fully transparent. Cronbach understood the value of failing productively.
Closer to home, in a less dramatic example, one of us began a line of scientific inquiry into how to prepare elementary preservice teachers to teach early algebra. Teaching early algebra meant engaging elementary students in early forms of algebraic reasoning. Such reasoning should help them transition from arithmetic to algebra. To begin this line of inquiry, a set of activities for preservice teachers were developed. Even though the activities were based on well-supported hypotheses, they largely failed to engage preservice teachers as predicted because of unanticipated challenges the preservice teachers faced. To capitalize on this failure, follow-up studies were conducted, first to better understand elementary preservice teachers’ challenges with preparing to teach early algebra, and then to better support preservice teachers in navigating these challenges. In this example, the initial failure was a necessary step in the researchers’ scientific inquiry and furthered the researchers’ understanding of this issue.
We present another example of failing productively in Chap. 2 . That example emerges from recounting the history of a well-known research program in mathematics education.
Making mistakes is an inherent part of doing scientific research. Conducting a study is rarely a smooth path from beginning to end. We recommend that you keep the following things in mind as you begin a career of conducting research in education.
First, do not get discouraged when you make mistakes; do not fall into the trap of feeling like you are not capable of doing research because you make too many errors.
Second, learn from your mistakes. Do not ignore your mistakes or treat them as errors that you simply need to forget and move past. Mistakes are rich sites for learning—in research just as in other fields of study.
Third, by reflecting on your mistakes, you can learn to make better mistakes, mistakes that inform you about a productive next step. You will not be able to eliminate your mistakes, but you can set a goal of making better and better mistakes.
Exercise 1.8
How does scientific inquiry differ from everyday learning in giving you the tools to fail upward? You may find helpful perspectives on this question in other resources on science and scientific inquiry (e.g., Failure: Why Science is So Successful by Firestein, 2015).
Exercise 1.9
Use what you have learned in this chapter to write a new definition of scientific inquiry. Compare this definition with the one you wrote before reading this chapter. If you are reading this book as part of a course, compare your definition with your colleagues’ definitions. Develop a consensus definition with everyone in the course.
Part IV. Preview of Chap. 2
Now that you have a good idea of what research is, at least of what we believe research is, the next step is to think about how to actually begin doing research. This means how to begin formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses. As for all phases of scientific inquiry, there are lots of things to think about. Because it is critical to start well, we devote Chap. 2 to getting started with formulating hypotheses.
Agnes, M., & Guralnik, D. B. (Eds.). (2008). Hypothesis. In Webster’s new world college dictionary (4th ed.). Wiley.
Google Scholar
Britannica. (n.d.). Scientific method. In Encyclopaedia Britannica . Retrieved July 15, 2022 from https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-method
Brownell, W. A., & Moser, H. E. (1949). Meaningful vs. mechanical learning: A study in grade III subtraction . Duke University Press..
Cai, J., Morris, A., Hohensee, C., Hwang, S., Robison, V., Cirillo, M., Kramer, S. L., & Hiebert, J. (2019b). Posing significant research questions. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 50 (2), 114–120. https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.50.2.0114
Article Google Scholar
Cambridge University Press. (n.d.). Hypothesis. In Cambridge dictionary . Retrieved July 15, 2022 from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/hypothesis
Cronbach, J. L. (1957). The two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 12 , 671–684.
Cronbach, L. J. (1975). Beyond the two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 30 , 116–127.
Cronbach, L. J. (1986). Social inquiry by and for earthlings. In D. W. Fiske & R. A. Shweder (Eds.), Metatheory in social science: Pluralisms and subjectivities (pp. 83–107). University of Chicago Press.
Hay, C. M. (Ed.). (2016). Methods that matter: Integrating mixed methods for more effective social science research . University of Chicago Press.
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Explain. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved July 15, 2022, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/explain
National Research Council. (2002). Scientific research in education . National Academy Press.
Weis, L., Eisenhart, M., Duncan, G. J., Albro, E., Bueschel, A. C., Cobb, P., Eccles, J., Mendenhall, R., Moss, P., Penuel, W., Ream, R. K., Rumbaut, R. G., Sloane, F., Weisner, T. S., & Wilson, J. (2019a). Mixed methods for studies that address broad and enduring issues in education research. Teachers College Record, 121 , 100307.
Weisner, T. S. (Ed.). (2005). Discovering successful pathways in children’s development: Mixed methods in the study of childhood and family life . University of Chicago Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
James Hiebert, Anne K Morris & Charles Hohensee
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
Jinfa Cai & Stephen Hwang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Hiebert, J., Cai, J., Hwang, S., Morris, A.K., Hohensee, C. (2023). What Is Research, and Why Do People Do It?. In: Doing Research: A New Researcher’s Guide. Research in Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_1
Published : 03 December 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-19077-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-19078-0
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Summary
Definition:
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings. It is often used as a tool to quickly communicate the main findings of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or decision-makers.
Structure of Research Summary
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. It describes the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section presents the main findings of the study, including statistical analysis if applicable. It may include tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and explains their implications. It discusses the significance of the findings, compares them to previous research, and identifies any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the research and provides a conclusion based on the findings. It may also suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
How to Write Research Summary
Here are the steps you can follow to write a research summary:
- Read the research article or study thoroughly: To write a summary, you must understand the research article or study you are summarizing. Therefore, read the article or study carefully to understand its purpose, research design, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the main points : Once you have read the research article or study, identify the main points, key findings, and research question. You can highlight or take notes of the essential points and findings to use as a reference when writing your summary.
- Write the introduction: Start your summary by introducing the research problem, research question, and purpose of the study. Briefly explain why the research is important and its significance.
- Summarize the methodology : In this section, summarize the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. Explain the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Present the results: Summarize the main findings of the study. Use tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data if necessary.
- Interpret the results: In this section, interpret the results and explain their implications. Discuss the significance of the findings, compare them to previous research, and identify any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclude the summary : Summarize the main points of the research and provide a conclusion based on the findings. Suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- Revise and edit : Once you have written the summary, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors. Make sure that your summary accurately represents the research article or study.
- Add references: Include a list of references cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
Example of Research Summary
Here is an example of a research summary:
Title: The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis
Introduction: This meta-analysis examines the effects of yoga on mental health. The study aimed to investigate whether yoga practice can improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, stress, and quality of life.
Methodology : The study analyzed data from 14 randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of yoga on mental health outcomes. The sample included a total of 862 participants. The yoga interventions varied in length and frequency, ranging from four to twelve weeks, with sessions lasting from 45 to 90 minutes.
Results : The meta-analysis found that yoga practice significantly improved mental health outcomes. Participants who practiced yoga showed a significant reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as stress levels. Quality of life also improved in those who practiced yoga.
Discussion : The findings of this study suggest that yoga can be an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. The study supports the growing body of evidence that suggests that yoga can have a positive impact on mental health. Limitations of the study include the variability of the yoga interventions, which may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion : Overall, the findings of this meta-analysis support the use of yoga as an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal length and frequency of yoga interventions for different populations.
References :
- Cramer, H., Lauche, R., Langhorst, J., Dobos, G., & Berger, B. (2013). Yoga for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and anxiety, 30(11), 1068-1083.
- Khalsa, S. B. (2004). Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 48(3), 269-285.
- Ross, A., & Thomas, S. (2010). The health benefits of yoga and exercise: a review of comparison studies. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16(1), 3-12.
Purpose of Research Summary
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study.
Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
- Facilitating comprehension: A research summary allows readers to quickly understand the main points and findings of a research project or study without having to read the entire article or study. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the research and its significance.
- Communicating research findings: Research summaries are often used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public. The summary presents the essential aspects of the research in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for non-experts to understand.
- Supporting decision-making: Research summaries can be used to support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. This information can be used by policymakers or practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Saving time: Research summaries save time for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders who need to review multiple research studies. Rather than having to read the entire article or study, they can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
Characteristics of Research Summary
The following are some of the key characteristics of a research summary:
- Concise : A research summary should be brief and to the point, providing a clear and concise overview of the main points of the research.
- Objective : A research summary should be written in an objective tone, presenting the research findings without bias or personal opinion.
- Comprehensive : A research summary should cover all the essential aspects of the research, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research summary should accurately reflect the key findings and conclusions of the research.
- Clear and well-organized: A research summary should be easy to read and understand, with a clear structure and logical flow.
- Relevant : A research summary should focus on the most important and relevant aspects of the research, highlighting the key findings and their implications.
- Audience-specific: A research summary should be tailored to the intended audience, using language and terminology that is appropriate and accessible to the reader.
- Citations : A research summary should include citations to the original research articles or studies, allowing readers to access the full text of the research if desired.
When to write Research Summary
Here are some situations when it may be appropriate to write a research summary:
- Proposal stage: A research summary can be included in a research proposal to provide a brief overview of the research aims, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Conference presentation: A research summary can be prepared for a conference presentation to summarize the main findings of a study or research project.
- Journal submission: Many academic journals require authors to submit a research summary along with their research article or study. The summary provides a brief overview of the study’s main points, findings, and conclusions and helps readers quickly understand the research.
- Funding application: A research summary can be included in a funding application to provide a brief summary of the research aims, objectives, and expected outcomes.
- Policy brief: A research summary can be prepared as a policy brief to communicate research findings to policymakers or stakeholders in a concise and accessible manner.
Advantages of Research Summary
Research summaries offer several advantages, including:
- Time-saving: A research summary saves time for readers who need to understand the key findings and conclusions of a research project quickly. Rather than reading the entire research article or study, readers can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
- Clarity and accessibility: A research summary provides a clear and accessible overview of the research project’s main points, making it easier for readers to understand the research without having to be experts in the field.
- Improved comprehension: A research summary helps readers comprehend the research by providing a brief and focused overview of the key findings and conclusions, making it easier to understand the research and its significance.
- Enhanced communication: Research summaries can be used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public, in a concise and accessible manner.
- Facilitated decision-making: Research summaries can support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. Policymakers or practitioners can use this information to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Increased dissemination: Research summaries can be easily shared and disseminated, allowing research findings to reach a wider audience.
Limitations of Research Summary
Limitations of the Research Summary are as follows:
- Limited scope: Research summaries provide a brief overview of the research project’s main points, findings, and conclusions, which can be limiting. They may not include all the details, nuances, and complexities of the research that readers may need to fully understand the study’s implications.
- Risk of oversimplification: Research summaries can be oversimplified, reducing the complexity of the research and potentially distorting the findings or conclusions.
- Lack of context: Research summaries may not provide sufficient context to fully understand the research findings, such as the research background, methodology, or limitations. This may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the research.
- Possible bias: Research summaries may be biased if they selectively emphasize certain findings or conclusions over others, potentially distorting the overall picture of the research.
- Format limitations: Research summaries may be constrained by the format or length requirements, making it challenging to fully convey the research’s main points, findings, and conclusions.
- Accessibility: Research summaries may not be accessible to all readers, particularly those with limited literacy skills, visual impairments, or language barriers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...

Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...
Key Steps in the Research Process - A Comprehensive Guide

Embarking on a research journey can be both thrilling and challenging. Whether you're a student, journalist, or simply inquisitive about a subject, grasping the research process steps is vital for conducting thorough and efficient research. In this all-encompassing guide, we'll navigate you through the pivotal stages of what is the research process, from pinpointing your topic to showcasing your discoveries.
We'll delve into how to formulate a robust research question, undertake preliminary research, and devise a structured research plan. You'll acquire strategies for gathering and scrutinizing data, along with advice for effectively disseminating your findings. By adhering to these steps in the research process, you'll be fully prepared to confront any research endeavor that presents itself.
Step 1: Identify and Develop Your Topic
Identifying and cultivating a research topic is the foundational first step in the research process. Kick off by brainstorming potential subjects that captivate your interest, as this will fuel your enthusiasm throughout the endeavor.
Employ the following tactics to spark ideas and understand what is the first step in the research process:
- Review course materials, lecture notes, and assigned readings for inspiration
- Engage in discussions with peers, professors, or experts in the field
- Investigate current events, news pieces, or social media trends pertinent to your field of study to uncover valuable market research insights.
- Reflect on personal experiences or observations that have sparked your curiosity
Once you've compiled a roster of possible topics, engage in preliminary research to evaluate the viability and breadth of each concept. This initial probe may encompass various research steps and procedures to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the topics at hand.
- Scanning Wikipedia articles or other general reference sources for an overview
- Searching for scholarly articles, books, or media related to your topic
- Identifying key concepts, theories, or debates within the field
- Considering the availability of primary sources or data for analysis
While amassing background knowledge, begin to concentrate your focus and hone your topic. Target a subject that is specific enough to be feasible within your project's limits, yet expansive enough to permit substantial analysis. Mull over the following inquiries to steer your topic refinement and address the research problem effectively:
- What aspect of the topic am I most interested in exploring?
- What questions or problems related to this topic remain unanswered or unresolved?
- How can I contribute new insights or perspectives to the existing body of knowledge?
- What resources and methods will I need to investigate this topic effectively?
Step 2: Conduct Preliminary Research
Having pinpointed a promising research topic, it's time to plunge into preliminary research. This essential phase enables you to deepen your grasp of the subject and evaluate the practicality of your project. Here are some pivotal tactics for executing effective preliminary research using various library resources:
- Literature Review
To effectively embark on your scholarly journey, it's essential to consult a broad spectrum of sources, thereby enriching your understanding with the breadth of academic research available on your topic. This exploration may encompass a variety of materials.
- Online catalogs of libraries (local, regional, national, and special)
- Meta-catalogs and subject-specific online article databases
- Digital institutional repositories and open access resources
- Works cited in scholarly books and articles
- Print bibliographies and internet sources
- Websites of major nonprofit organizations, research institutes, museums, universities, and government agencies
- Trade and scholarly publishers
- Discussions with fellow scholars and peers
- Identify Key Debates
Engaging with the wealth of recently published materials and seminal works in your field is a pivotal part of the research process definition. Focus on discerning the core ideas, debates, and arguments that define your topic, which will in turn sharpen your research focus and guide you toward formulating pertinent research questions.
- Narrow Your Focus
Hone your topic by leveraging your initial findings to tackle a specific issue or facet within the larger subject, a fundamental step in the research process steps. Consider various factors that could influence the direction and scope of your inquiry.
- Subtopics and specific issues
- Key debates and controversies
- Timeframes and geographical locations
- Organizations or groups of people involved
A thorough evaluation of existing literature and a comprehensive assessment of the information at hand will pinpoint the exact dimensions of the issue you aim to explore. This methodology ensures alignment with prior research, optimizes resources, and can bolster your case when seeking research funding by demonstrating a well-founded approach.
Step 3: Establish Your Research Question
Having completed your preliminary research and topic refinement, the next vital phase involves formulating a precise and focused research question. This question, a cornerstone among research process steps, will steer your investigation, keeping it aligned with relevant data and insights. When devising your research question, take into account these critical factors:
Initiate your inquiry by defining the requirements and goals of your study, a key step in the research process steps. Whether you're testing a hypothesis, analyzing data, or constructing and supporting an argument, grasping the intent of your research is crucial for framing your question effectively.
Ensure that your research question is feasible, given your constraints in time and word count, an important consideration in the research process steps. Steer clear of questions that are either too expansive or too constricted, as they may impede your capacity to conduct a comprehensive analysis.
Your research question should transcend a mere 'yes' or 'no' response, prompting a thorough engagement with the research process steps. It should foster a comprehensive exploration of the topic, facilitating the analysis of issues or problems beyond just a basic description.
- Researchability
Ensure that your research question opens the door to quality research materials, including academic books and refereed journal articles. It's essential to weigh the accessibility of primary data and secondary data that will bolster your investigative efforts.
When establishing your research question, take the following steps:
- Identify the specific aspect of your general topic that you want to explore
- Hypothesize the path your answer might take, developing a hypothesis after formulating the question
- Steer clear of certain types of questions in your research process steps, such as those that are deceptively simple, fictional, stacked, semantic, impossible-to-answer, opinion or ethical, and anachronistic, to maintain the integrity of your inquiry.
- Conduct a self-test on your research question to confirm it adheres to the research process steps, ensuring it is flexible, testable, clear, precise, and underscores a distinct reason for its importance.
By meticulously formulating your research question, you're establishing a solid groundwork for the subsequent research process steps, guaranteeing that your efforts are directed, efficient, and yield productive outcomes.
Step 4: Develop a Research Plan
Having formulated a precise research question, the ensuing phase involves developing a detailed research plan. This plan, integral to the research process steps, acts as a navigational guide for your project, keeping you organized, concentrated, and on a clear path to accomplishing your research objectives. When devising your research plan, consider these pivotal components:
- Project Goals and Objectives
Articulate the specific aims and objectives of your research project with clarity. These should be in harmony with your research question and provide a structured framework for your investigation, ultimately aligning with your overarching business goals.
- Research Methods
Select the most appropriate research tools and statistical methods to address your question effectively. This may include a variety of qualitative and quantitative approaches to ensure comprehensive analysis.
- Quantitative methods (e.g., surveys, experiments)
- Qualitative methods (e.g., interviews, focus groups)
- Mixed methods (combining quantitative and qualitative approaches)
- Access to databases, archives, or special collections
- Specialized equipment or software
- Funding for travel, materials, or participant compensation
- Assistance from research assistants, librarians, or subject matter experts
- Participant Recruitment
If your research involves human subjects, develop a strategic plan for recruiting participants. Consider factors such as the inclusion of diverse ethnic groups and the use of user interviews to gather rich, qualitative data.
- Target population and sample size
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Recruitment strategies (e.g., flyers, social media, snowball sampling)
- Informed consent procedures
- Instruments or tools for gathering data (e.g., questionnaires, interview guides)
- Data storage and management protocols
- Statistical or qualitative analysis techniques
- Software or tools for data analysis (e.g., SPSS, NVivo)
Create a realistic project strategy for your research project, breaking it down into manageable stages or milestones. Consider factors such as resource availability and potential bottlenecks.
- Literature review and background research
- IRB approval (if applicable)
- Participant recruitment and data collection
- Data analysis and interpretation
- Writing and revising your findings
- Dissemination of results (e.g., presentations, publications)
By developing a comprehensive research plan, incorporating key research process steps, you'll be better equipped to anticipate challenges, allocate resources effectively, and ensure the integrity and rigor of your research process. Remember to remain flexible and adaptable to navigate unexpected obstacles or opportunities that may arise.
Step 5: Conduct the Research
With your research plan in place, it's time to dive into the data collection phase. As you conduct your research, adhere to the established research process steps to ensure the integrity and quality of your findings.
Conduct your research in accordance with federal regulations, state laws, institutional SOPs, and policies. Familiarize yourself with the IRB-approved protocol and follow it diligently, as part of the essential research process steps.
- Roles and Responsibilities
Understand and adhere to the roles and responsibilities of the principal investigator and other research team members. Maintain open communication lines with all stakeholders, including the sponsor and IRB, to foster cross-functional collaboration.
- Data Management
Develop and maintain an effective system for data collection and storage, utilizing advanced research tools. Ensure that each member of the research team has seamless access to the most up-to-date documents, including the informed consent document, protocol, and case report forms.
- Quality Assurance
Implement comprehensive quality assurance measures to verify that the study adheres strictly to the IRB-approved protocol, institutional policy, and all required regulations. Confirm that all study activities are executed as planned and that any deviations are addressed with precision and appropriateness.
- Participant Eligibility
As part of the essential research process steps, verify that potential study subjects meet all eligibility criteria and none of the ineligibility criteria before advancing with the research.
To maintain the highest standards of academic integrity and ethical conduct:
- Conduct research with unwavering honesty in all facets, including experimental design, data generation, and analysis, as well as the publication of results, as these are critical research process steps.
- Maintain a climate conducive to conducting research in strict accordance with good research practices, ensuring each step of the research process is meticulously observed.
- Provide appropriate supervision and training for researchers.
- Encourage open discussion of ideas and the widest dissemination of results possible.
- Keep clear and accurate records of research methods and results.
- Exercise a duty of care to all those involved in the research.
When collecting and assimilating data:
- Use professional online data analysis tools to streamline the process.
- Use metadata for context
- Assign codes or labels to facilitate grouping or comparison
- Convert data into different formats or scales for compatibility
- Organize documents in both the study participant and investigator's study regulatory files, creating a central repository for easy access and reference, as this organization is a pivotal step in the research process.
By adhering to these guidelines and upholding a commitment to ethical and rigorous research practices, you'll be well-equipped to conduct your research effectively and contribute meaningful insights to your field of study, thereby enhancing the integrity of the research process steps.
Step 6: Analyze and Interpret Data
Embarking on the research process steps, once you have gathered your research data, the subsequent critical phase is to delve into analysis and interpretation. This stage demands a meticulous examination of the data, spotting trends, and forging insightful conclusions that directly respond to your research question. Reflect on these tactics for a robust approach to data analysis and interpretation:
- Organize and Clean Your Data
A pivotal aspect of the research process steps is to start by structuring your data in an orderly and coherent fashion. This organizational task may encompass:
- Creating a spreadsheet or database to store your data
- Assigning codes or labels to facilitate grouping or comparison
- Cleaning the data by removing any errors, inconsistencies, or missing values
- Converting data into different formats or scales for compatibility
- Calculating measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Determining measures of variability (range, standard deviation)
- Creating frequency tables or histograms to visualize the distribution of your data
- Identifying any outliers or unusual patterns in your data
- Perform Inferential Analysis
Integral to the research process steps, you might engage in inferential analysis to evaluate hypotheses or extrapolate findings to a broader demographic, contingent on your research design and query. This analytical step may include:
- Selecting appropriate statistical tests (e.g., t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis)
- As part of the research process steps, establishing a significance threshold (e.g., p < 0.05) is essential to gauge the likelihood of your results being a random occurrence rather than a significant finding.
- Interpreting the results of your statistical tests in the context of your research question
- Considering the practical significance of your findings, in addition to statistical significance
When interpreting your data, it's essential to:
- Look for relationships, patterns, and trends in your data
- Consider alternative explanations for your findings
- Acknowledge any limitations or potential biases in your research design or data collection
- Leverage data visualization techniques such as graphs, charts, and infographics to articulate your research findings with clarity and impact, thereby enhancing the communicative value of your data.
- Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or subject matter experts to validate your interpretations
It's important to recognize that data interpretation is a cyclical process that hinges on critical thinking, inventiveness, and the readiness to refine your conclusions with emerging insights. By tackling data analysis and interpretation with diligence and openness, you're setting the stage to derive meaningful and justifiable inferences from your research, in line with the research process steps.
Step 7: Present the Findings
After meticulous analysis and interpretation of your research findings, as dictated by the research process steps, the moment arrives to disseminate your insights. Effectively presenting your research is key to captivating your audience and conveying the importance of your findings. Employ these strategies to create an engaging and persuasive presentation:
- Organize Your Findings :
Use the PEEL method to structure your presentation:
- Point: Clearly state your main argument or finding
- Evidence: Present the data and analysis that support your point
- Explanation: Provide context and interpret the significance of your evidence
- Link: Connect your findings to the broader research question or field
- Tailor Your Message
Understanding your audience is crucial to effective communication. When presenting your research, it's important to tailor your message to their background, interests, and level of expertise, effectively employing user personas to guide your approach.
- Use clear, concise language and explain technical terms
- Highlight what makes your research unique and impactful
- Craft a compelling narrative with a clear structure and hook
- Share the big picture, emphasizing the significance of your findings
- Engage Your Audience : Make your presentation enjoyable and memorable by incorporating creative elements:
- Use visual aids, such as tables, charts, and graphs, to communicate your findings effectively
- To vividly convey your research journey, consider employing storytelling techniques, such as UX comics or storyboards, which can make complex information more accessible and engaging.
- Injecting humor and personality into your presentation can be a powerful tool for communication. Utilize funny messages or GIFs to lighten the mood, breaking up tension and refocusing attention, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of humor in communication.
By adhering to these strategies, you'll be well-prepared to present your research findings in a manner that's both clear and captivating. Ensure you follow research process steps such as citing your sources accurately and discussing the broader implications of your work, providing actionable recommendations, and delineating the subsequent phases for integrating your findings into broader practice or policy frameworks.
The research process is an intricate journey that demands meticulous planning, steadfast execution, and incisive analysis. By adhering to the fundamental research process steps outlined in this guide, from pinpointing your topic to showcasing your findings, you're setting yourself up for conducting research that's both effective and influential. Keep in mind that the research journey is iterative, often necessitating revisits to certain stages as fresh insights surface or unforeseen challenges emerge.
As you commence your research journey, seize the chance to contribute novel insights to your field and forge a positive global impact. By tackling your research with curiosity, integrity, and a dedication to excellence, you're paving the way towards attaining your research aspirations and making a substantial difference with your work, all while following the critical research process steps.
Sign up for more like this.
8 Key Elements of a Research Paper Structure + Free Template (2024)
.webp)
Table of contents

Brinda Gulati
Welcome to the twilight zone of research writing. You’ve got your thesis statement and research evidence, and before you write the first draft, you need a wireframe — a structure on which your research paper can stand tall.
When you’re looking to share your research with the wider scientific community, your discoveries and breakthroughs are important, yes. But what’s more important is that you’re able to communicate your research in an accessible format. For this, you need to publish your paper in journals. And to have your research published in a journal, you need to know how to structure a research paper.
Here, you’ll find a template of a research paper structure, a section-by-section breakdown of the eight structural elements, and actionable insights from three published researchers.
Let’s begin!
Why is the Structure of a Research Paper Important?
A research paper built on a solid structure is the literary equivalent of calcium supplements for weak bones.
Richard Smith of BMJ says, “...no amount of clever language can compensate for a weak structure."
There’s space for your voice and creativity in your research, but without a structure, your paper is as good as a beached whale — stranded and bloated.
A well-structured research paper:
- Communicates your credibility as a student scholar in the wider academic community.
- Facilitates accessibility for readers who may not be in your field but are interested in your research.
- Promotes clear communication between disciplines, thereby eliminating “concept transfer” as a rate-limiting step in scientific cross-pollination.
- Increases your chances of getting published!
Research Paper Structure Template
.webp)
Why Was My Research Paper Rejected?
A desk rejection hurts — sometimes more than stubbing your pinky toe against a table.
Oftentimes, journals will reject your research paper before sending it off for peer review if the architecture of your manuscript is shoddy.
The JAMA Internal Medicine , for example, rejected 78% of the manuscripts it received in 2017 without review. Among the top 10 reasons? Poor presentation and poor English . (We’ve got fixes for both here, don’t you worry.)
5 Common Mistakes in a Research Paper Structure
- Choppy transitions : Missing or abrupt transitions between sections disrupt the flow of your paper. Read our guide on transition words here.
- Long headings : Long headings can take away from your main points. Be concise and informative, using parallel structure throughout.
- Disjointed thoughts : Make sure your paragraphs flow logically from one another and support your central point.
- Misformatting : An inconsistent or incorrect layout can make your paper look unprofessional and hard to read. For font, spacing, margins, and section headings, strictly follow your target journal's guidelines.
- Disordered floating elements : Ill-placed and unlabeled tables, figures, and appendices can disrupt your paper's structure. Label, caption, and reference all floating elements in the main text.
What Is the Structure of a Research Paper?
The structure of a research paper closely resembles the shape of a diamond flowing from the general ➞ specific ➞ general.
We’ll follow the IMRaD ( I ntroduction , M ethods , R esults , and D iscussion) format within the overarching “context-content-conclusion” approach:
➞ The context sets the stage for the paper where you tell your readers, “This is what we already know, and here’s why my research matters.”
➞ The content is the meat of the paper where you present your methods, results, and discussion. This is the IMRad (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) format — the most popular way to organize the body of a research paper.
➞ The conclusion is where you bring it home — “Here’s what we’ve learned, and here’s where it plays out in the grand scheme of things.”
Now, let’s see what this means section by section.
1. Research Paper Title
A research paper title is read first, and read the most.
The title serves two purposes: informing readers and attracting attention . Therefore, your research paper title should be clear, descriptive, and concise . If you can, avoid technical jargon and abbreviations. Your goal is to get as many readers as possible.
In fact, research articles with shorter titles describing the results are cited more often .
An impactful title is usually 10 words long, plus or minus three words.
For example:
- "Mortality in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria" (word count = 7)
- “A Review of Practical Techniques For the Diagnosis of Malaria” (word count = 10)
2. Research Paper Abstract
In an abstract, you have to answer the two whats :
- What has been done?
- What are the main findings?
The abstract is the elevator pitch for your research. Is your paper worth reading? Convince the reader here.

✏️ NOTE : According to different journals’ guidelines, sometimes the title page and abstract section are on the same page.
An abstract ranges from 200-300 words and doubles down on the relevance and significance of your research. Succinctly.
This is your chance to make a second first impression.
If you’re stuck with a blob of text and can’t seem to cut it down, a smart AI elf like Wordtune can help you write a concise abstract! The AI research assistant also offers suggestions for improved clarity and grammar so your elevator pitch doesn’t fall by the wayside.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. Introduction Section
What does it do.
Asks the central research question.
Pre-Writing Questions For the Introduction Section
The introduction section of your research paper explains the scope, context, and importance of your project.
I talked to Swagatama Mukherjee , a published researcher and graduate student in Neuro-Oncology studying Glioblastoma Progression. For the Introduction, she says, focus on answering three key questions:
- What isn’t known in the field?
- How is that knowledge gap holding us back?
- How does your research focus on answering this problem?
When Should You Write It?
Write it last. As you go along filling in the body of your research paper, you may find that the writing is evolving in a different direction than when you first started.
Organizing the Introduction
Visualize the introduction as an upside-down triangle when considering the overall outline of this section. You'll need to give a broad introduction to the topic, provide background information, and then narrow it down to specific research. Finally, you'll need a focused research question, hypothesis, or thesis statement. The move is from general ➞ specific.
✨️ BONUS TIP: Use the famous CARS model by John Swales to nail this upside-down triangle.
4. methods section.
Describes what was done to answer the research question, and how.
Write it first . Just list everything you’ve done, and go from there. How did you assign participants into groups? What kind of questionnaires have you used? How did you analyze your data?
Write as if the reader were following an instruction manual on how to duplicate your research methodology to the letter.
Organizing the Methods Section
Here, you’re telling the story of your research.
Write in as much detail as possible, and in the chronological order of the experiments. Follow the order of the results, so your readers can track the gradual development of your research. Use headings and subheadings to visually format the section.

This skeleton isn’t set in stone. The exact headings will be determined by your field of study and the journal you’re submitting to.
✨️ BONUS TIP : Drowning in research? Ask Wordtune to summarize your PDFs for you!
5. results section .
Reports the findings of your study in connection to your research question.
Write the section only after you've written a draft of your Methods section, and before the Discussion.
This section is the star of your research paper. But don't get carried away just yet. Focus on factual, unbiased information only. Tell the reader how you're going to change the world in the next section. The Results section is strictly a no-opinions zone.
How To Organize Your Results
A tried-and-true structure for presenting your findings is to outline your results based on the research questions outlined in the figures.
Whenever you address a research question, include the data that directly relates to that question.
What does this mean? Let’s look at an example:
Here's a sample research question:
How does the use of social media affect the academic performance of college students?
Make a statement based on the data:
College students who spent more than 3 hours per day on social media had significantly lower GPAs compared to those who spent less than 1 hour per day (M=2.8 vs. M=3.4; see Fig. 2).
You can elaborate on this finding with secondary information:
The negative impact of social media use on academic performance was more pronounced among freshmen and sophomores compared to juniors and seniors ((F>25), (S>20), (J>15), and (Sr>10); see Fig. 4).
Finally, caption your figures in the same way — use the data and your research question to construct contextual phrases. The phrases should give your readers a framework for understanding the data:
Figure 4. Percentage of college students reporting a negative impact of social media on academic performance, by year in school.
Dos and Don’ts For The Results Section

✔️ Related : How to Write a Research Paper (+ Free AI Research Paper Writer)
6. discussion section.
Explains the importance and implications of your findings, both in your specific area of research, as well as in a broader context.
Pre-Writing Questions For the Discussion Section
- What is the relationship between these results and the original question in the Introduction section?
- How do your results compare with those of previous research? Are they supportive, extending, or contradictory to existing knowledge?
- What is the potential impact of your findings on theory, practice, or policy in your field?
- Are there any strengths or weaknesses in your study design, methods, or analysis? Can these factors affect how you interpret your results?
- Based on your findings, what are the next steps or directions for research? Have you got any new questions or hypotheses?
Before the Introduction section, and after the Results section.
Based on the pre-writing questions, five main elements can help you structure your Discussion section paragraph by paragraph:
- Summary : Restate your research question/problem and summarize your major findings.
- Interpretations : Identify patterns, contextualize your findings, explain unexpected results, and discuss if and how your results satisfied your hypotheses.
- Implications: Explore if your findings challenge or support existing research, share new insights, and discuss the consequences in theory or practice.
- Limitations : Acknowledge what your results couldn’t achieve because of research design or methodological choices.
- Recommendations : Give concrete ideas about how further research can be conducted to explore new avenues in your field of study.
Dos and Don’ts For the Discussion Section

Aritra Chatterjee , a licensed clinical psychologist and published mental health researcher, advises, “If your findings are not what you expected, disclose this honestly. That’s what good research is about.”
7. Acknowledgments
Expresses gratitude to mentors, colleagues, and funding sources who’ve helped your research.
Write this section after all the parts of IMRaD are done to reflect on your research journey without getting distracted midway.
After a lot of scientific writing, you might get stumped trying to write a few lines to say thanks. Don’t let this be the reason for a late or no-submission.
Wordtune can make a rough draft for you.

All you then have to do is edit the AI-generated content to suit your voice, and replace any text placeholders as needed:


8. References
Lists all the works/sources used in your research with proper citations.
The two most important aspects of referencing are:
- Following the correct format; and
- Properly citing the sources.
Keep a working document of the works you’ve referenced as you go along, but leave the finishing touches for last after you’ve completed the body of your research paper — the IMRaD.
Tips For Writing the References Section
The error rate of references in several scientific disciplines is 25%-54% .
Don’t want to be a part of this statistic? We got you.
- Choose quality over quantity : While it's tempting to pad your bibliography to seem more scholarly, this is a rookie mistake. Samantha Summers , a museum professional based in Canada, is a published researcher in Medieval History and Critical Philanthropy studies. According to her, “Adding in a citation just to lengthen your bibliography and without engaging deeply with the cited work doesn’t make for good writing.” We ought to listen to her advice — she has three Master’s degrees to her name for a reason.
- Select the correct referencing guide : Always cross-check with your chosen journal’s or institution’s preference for either Harvard, MLA, APA, Chicago, or IEEE.
- Include recent studies and research : Aim to cite academically ripe sources — not overripe. Research from the past half-decade or so is ideal, whereas studies from the 80s or 90s run a higher risk of being stale.
- Use a reliable reference manager software : Swagatama recommends several free resources that have helped her get her research organized and published — Zotero and Mendeley are top contenders, followed by EndNote .
By the end, your References section will look something like this:

Ready, Get, Set, Publish!
Dust yourself off, we've made it out of the twilight zone. You’ve now got the diamond of the structure of a research paper — the IMRaD format within the “context-content-conclusion” model.
Keep this structure handy as you fill in the bones of your research paper. And if you’re stuck staring at a blinking cursor, fresh out of brain juice?
An AI-powered writing assistant like Wordtune can help you polish your diamond, craft great abstracts, and speed through drafts!
You've got this.
Share This Article:
.webp)
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.1 Determining Your Main Ideas
Learning objectives.
- Revisit the function of a specific purpose.
- Understand how to make the transition from a specific purpose to a series of main points.
- Be able to narrow a speech from all the possible points to the main points.
- Explain how to prepare meaningful main points.

Matt Wynn – Lightbulb! – CC BY 2.0.
When creating a speech, it’s important to remember that speeches have three clear parts: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction establishes the topic and whets your audience’s appetite, and the conclusion wraps everything up at the end of your speech. The real “meat” of your speech happens in the body. In this section, we’re going to discuss how to think strategically about the body of your speech.
We like the word strategic because it refers to determining what is important or essential to the overall plan or purpose of your speech. Too often, new speakers just throw information together and stand up and start speaking. When that happens, audience members are left confused and the reason for the speech may get lost. To avoid being seen as disorganized, we want you to start thinking critically about the organization of your speech. In this section, we will discuss how to take your speech from a specific purpose to creating the main points of your speech.
What Is Your Specific Purpose?
Before we discuss how to determine the main points of your speech, we want to revisit your speech’s specific purpose, which we discussed in detail in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” . Recall that a speech can have one of three general purposes: to inform, to persuade, or to entertain. The general purpose refers to the broad goal for creating and delivering the speech. The specific purpose, on the other hand, starts with one of those broad goals (inform, persuade, or entertain) and then further informs the listener about the who , what , when , where , why , and how of the speech.
The specific purpose is stated as a sentence incorporating the general purpose, the specific audience for the speech, and a prepositional phrase that summarizes the topic. Suppose you are going to give a speech about using open-source software. Here are three examples (each with a different general purpose and a different audience):
| General Purpose | To inform |
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of school administrators about the various open-source software packages that could be utilized in their school districts |
| General Purpose | To persuade |
| Specific Purpose | To persuade a group of college students to make the switch from Microsoft Office to the open-source office suite OpenOffice |
| General Purpose | To entertain |
| Specific Purpose | To entertain members of a business organization with a mock eulogy of for-pay software giants as a result of the proliferation of open-source alternatives |
In each of these three examples, you’ll notice that the general topic is the same—open-source software—but the specific purpose is different because the speech has a different general purpose and a different audience. Before you can think strategically about organizing the body of your speech, you need to know what your specific purpose is. If you have not yet written a specific purpose for your current speech, please go ahead and write one now.
From Specific Purpose to Main Points
Once you’ve written down your specific purpose, you can now start thinking about the best way to turn that specific purpose into a series of main points. Main points are the key ideas you present to enable your speech to accomplish its specific purpose. In this section, we’re going to discuss how to determine your main points and how to organize those main points into a coherent, strategic speech.
How Many Main Points Do I Need?
While there is no magic number for how many main points a speech should have, speech experts generally agree that the fewer the number of main points the better. First and foremost, experts on the subject of memory have consistently shown that people don’t tend to remember very much after they listen to a message or leave a conversation (Bostrom & Waldhart, 1988). While many different factors can affect a listener’s ability to retain information after a speech, how the speech is organized is an important part of that process (Dunham, 1964; Smith, 1951; Thompson, 1960). For the speeches you will be delivering in a typical public speaking class, you will usually have just two or three main points. If your speech is less than three minutes long, then two main points will probably work best. If your speech is between three and ten minutes in length, then it makes more sense to use three main points.
You may be wondering why we are recommending only two or three main points. The reason comes straight out of the research on listening. According to LeFrancois, people are more likely to remember information that is meaningful, useful, and of interest to them; different or unique; organized; visual; and simple (LeFrancois, 1999). Two or three main points are much easier for listeners to remember than ten or even five. In addition, if you have two or three main points, you’ll be able to develop each one with examples, statistics, or other forms of support. Including support for each point will make your speech more interesting and more memorable for your audience.
Narrowing Down Your Main Points
When you write your specific purpose and review the research you have done on your topic, you will probably find yourself thinking of quite a few points that you’d like to make in your speech. Whether that’s the case or not, we recommend taking a few minutes to brainstorm and develop a list of points. In brainstorming, your goal is simply to think of as many different points as you can, not to judge how valuable or important they are. What information does your audience need to know to understand your topic? What information does your speech need to convey to accomplish its specific purpose? Consider the following example:
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of school administrators about the various open-source software packages that could be utilized in their school districts |
| Brainstorming List of Points | Define open-source software. |
| Define educational software. | |
| List and describe the software commonly used by school districts. | |
| Explain the advantages of using open-source software. | |
| Explain the disadvantages of using open-source software. | |
| Review the history of open-source software. | |
| Describe the value of open-source software. | |
| Describe some educational open-source software packages. | |
| Review the software needs of my specific audience. | |
| Describe some problems that have occurred with open-source software. |
Now that you have brainstormed and developed a list of possible points, how do you go about narrowing them down to just two or three main ones? Remember, your main points are the key ideas that help build your speech. When you look over the preceding list, you can then start to see that many of the points are related to one another. Your goal in narrowing down your main points is to identify which individual, potentially minor points can be combined to make main points. This process is called chunking because it involves taking smaller chunks of information and putting them together with like chunks to create more fully developed chunks of information. Before reading our chunking of the preceding list, see if you can determine three large chunks out of the list (note that not all chunks are equal).
| Specific Purpose | To inform a group of school administrators about the various open-source software packages that could be utilized in their school districts |
| Define educational software. | |
| List and describe the software commonly used by school districts. | |
| Define open-source software. | |
| Review the history of open-source software. | |
| Explain the advantages of using open-source software. | |
| Describe the value of open-source software. | |
| Explain the disadvantages of using open-source software. | |
| Describe some problems that have occurred with open-source software. | |
| Review the software needs of my specific audience. | |
| Describe some educational open-source software packages. |
You may notice that in the preceding list, the number of subpoints under each of the three main points is a little disjointed or the topics don’t go together clearly. That’s all right. Remember that these are just general ideas at this point. It’s also important to remember that there is often more than one way to organize a speech. Some of these points could be left out and others developed more fully, depending on the purpose and audience. We’ll develop the preceding main points more fully in a moment.
Helpful Hints for Preparing Your Main Points
Now that we’ve discussed how to take a specific purpose and turn it into a series of main points, here are some helpful hints for creating your main points.
Uniting Your Main Points
Once you’ve generated a possible list of main points, you want to ask yourself this question: “When you look at your main points, do they fit together?” For example, if you look at the three preceding main points (school districts use software in their operations; what is open-source software; name some specific open-source software packages that may be appropriate for these school administrators to consider), ask yourself, “Do these main points help my audience understand my specific purpose?”
Suppose you added a fourth main point about open-source software for musicians—would this fourth main point go with the other three? Probably not. While you may have a strong passion for open-source music software, that main point is extraneous information for the speech you are giving. It does not help accomplish your specific purpose, so you’d need to toss it out.
Keeping Your Main Points Separate
The next question to ask yourself about your main points is whether they overlap too much. While some overlap may happen naturally because of the singular nature of a specific topic, the information covered within each main point should be clearly distinct from the other main points. Imagine you’re giving a speech with the specific purpose “to inform my audience about the health reasons for eating apples and oranges.” You could then have three main points: that eating fruits is healthy, that eating apples is healthy, and that eating oranges is healthy. While the two points related to apples and oranges are clearly distinct, both of those main points would probably overlap too much with the first point “that eating fruits is healthy,” so you would probably decide to eliminate the first point and focus on the second and third. On the other hand, you could keep the first point and then develop two new points giving additional support to why people should eat fruit.
Balancing Main Points
One of the biggest mistakes some speakers make is to spend most of their time talking about one of their main points, completely neglecting their other main points. To avoid this mistake, organize your speech so as to spend roughly the same amount of time on each main point. If you find that one of your main points is simply too large, you may need to divide that main point into two main points and consolidate your other main points into a single main point.
Let’s see if our preceding example is balanced (school districts use software in their operations; what is open-source software; name some specific open-source software packages that may be appropriate for these school administrators to consider). What do you think? Obviously, the answer depends on how much time a speaker will have to talk about each of these main points. If you have an hour to talk, then you may find that these three main points are balanced. However, you may also find them wildly unbalanced if you only have five minutes to speak because five minutes is not enough time to even explain what open-source software is. If that’s the case, then you probably need to rethink your specific purpose to ensure that you can cover the material in the allotted time.
Creating Parallel Structure for Main Points
Another major question to ask yourself about your main points is whether or not they have a parallel structure. By parallel structure, we mean that you should structure your main points so that they all sound similar. When all your main points sound similar, it’s simply easier for your audiences to remember your main points and retain them for later. Let’s look at our sample (school districts use software in their operations; what is open-source software; name some specific open-source software packages that may be appropriate for these school administrators to consider). Notice that the first and third main points are statements, but the second one is a question. Basically, we have an example here of main points that are not parallel in structure. You could fix this in one of two ways. You could make them all questions: what are some common school district software programs; what is open-source software; and what are some specific open-source software packages that may be appropriate for these school administrators to consider. Or you could turn them all into statements: school districts use software in their operations; define and describe open-source software; name some specific open-source software packages that may be appropriate for these school administrators to consider. Either of these changes will make the grammatical structure of the main points parallel.
Maintaining Logical Flow of Main Points
The last question you want to ask yourself about your main points is whether the main points make sense in the order you’ve placed them. The next section goes into more detail of common organizational patterns for speeches, but for now we want you to just think logically about the flow of your main points. When you look at your main points, can you see them as progressive, or does it make sense to talk about one first, another one second, and the final one last? If you look at your order, and it doesn’t make sense to you, you probably need to think about the flow of your main points. Often, this process is an art and not a science. But let’s look at a couple of examples.
| School Dress Codes Example | |
|---|---|
| Main Point 1 | History of school dress codes |
| Main Point 2 | Problems with school dress codes |
| Main Point 3 | Eliminating school dress codes |
| Rider Law Legislation | |
|---|---|
| Main Point 1 | Why should states have rider laws? |
| Main Point 2 | What are the effects of a lack of rider laws? |
| Main Point 3 | What is rider law legislation? |
When you look at these two examples, what are your immediate impressions of the two examples? In the first example, does it make sense to talk about history, and then the problems, and finally how to eliminate school dress codes? Would it make sense to put history as your last main point? Probably not. In this case, the main points are in a logical sequential order. What about the second example? Does it make sense to talk about your solution, then your problem, and then define the solution? Not really! What order do you think these main points should be placed in for a logical flow? Maybe you should explain the problem (lack of rider laws), then define your solution (what is rider law legislation), and then argue for your solution (why states should have rider laws). Notice that in this example you don’t even need to know what “rider laws” are to see that the flow didn’t make sense.
Key Takeaways
- All speeches start with a general purpose and then move to a specific purpose that gives the who , what , where , and how for the speech.
- Transitioning from the specific purpose to possible main points means developing a list of potential main points you could discuss. Then you can narrow your focus by looking for similarities among your potential main points and combining ones that are similar.
- Shorter speeches will have two main points while longer speeches will generally have three or more main points. When creating your main points, make sure that they are united, separate, balanced, parallel, and logical.
- Generate a specific purpose for your current speech. Conduct a brainstorming activity where you try to think of all the possible points you could possibly make related to your specific purpose. Once you’ve finished creating this list, see if you can find a meaningful pattern that helps you develop three main points.
- Pair up with a partner. Take the three main points you developed in the previous exercise, exchange papers with your partner and ask him or her to see whether or not they are united, separate, balanced, parallel, and logical. You do the same for your partner’s main points. If they are not, what can you or your partner do to fix your main points?
Bostrom, R. N., & Waldhart, E. S. (1988). Memory models and the measurement of listening. Communication Education, 37 , 1–13.
Dunham, J. R. (1964). Voice contrast and repetition in speech retention (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from: http://etd.lib.ttu.edu/theses .
LeFrancois, G. R. (1999). Psychology for teaching (10th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Smith, R. G. (1951). An experimental study of the effects of speech organization upon attitudes of college students. Speech Monographs, 18 , 292–301.
Thompson, E. C. (1960). An experimental investigation of the relative effectiveness of organizational structure in oral communication. Southern Speech Journal, 26 , 59–69.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is research methodology?

The basics of research methodology
Why do you need a research methodology, what needs to be included, why do you need to document your research method, what are the different types of research instruments, qualitative / quantitative / mixed research methodologies, how do you choose the best research methodology for you, frequently asked questions about research methodology, related articles.
When you’re working on your first piece of academic research, there are many different things to focus on, and it can be overwhelming to stay on top of everything. This is especially true of budding or inexperienced researchers.
If you’ve never put together a research proposal before or find yourself in a position where you need to explain your research methodology decisions, there are a few things you need to be aware of.
Once you understand the ins and outs, handling academic research in the future will be less intimidating. We break down the basics below:
A research methodology encompasses the way in which you intend to carry out your research. This includes how you plan to tackle things like collection methods, statistical analysis, participant observations, and more.
You can think of your research methodology as being a formula. One part will be how you plan on putting your research into practice, and another will be why you feel this is the best way to approach it. Your research methodology is ultimately a methodological and systematic plan to resolve your research problem.
In short, you are explaining how you will take your idea and turn it into a study, which in turn will produce valid and reliable results that are in accordance with the aims and objectives of your research. This is true whether your paper plans to make use of qualitative methods or quantitative methods.
The purpose of a research methodology is to explain the reasoning behind your approach to your research - you'll need to support your collection methods, methods of analysis, and other key points of your work.
Think of it like writing a plan or an outline for you what you intend to do.
When carrying out research, it can be easy to go off-track or depart from your standard methodology.
Tip: Having a methodology keeps you accountable and on track with your original aims and objectives, and gives you a suitable and sound plan to keep your project manageable, smooth, and effective.
With all that said, how do you write out your standard approach to a research methodology?
As a general plan, your methodology should include the following information:
- Your research method. You need to state whether you plan to use quantitative analysis, qualitative analysis, or mixed-method research methods. This will often be determined by what you hope to achieve with your research.
- Explain your reasoning. Why are you taking this methodological approach? Why is this particular methodology the best way to answer your research problem and achieve your objectives?
- Explain your instruments. This will mainly be about your collection methods. There are varying instruments to use such as interviews, physical surveys, questionnaires, for example. Your methodology will need to detail your reasoning in choosing a particular instrument for your research.
- What will you do with your results? How are you going to analyze the data once you have gathered it?
- Advise your reader. If there is anything in your research methodology that your reader might be unfamiliar with, you should explain it in more detail. For example, you should give any background information to your methods that might be relevant or provide your reasoning if you are conducting your research in a non-standard way.
- How will your sampling process go? What will your sampling procedure be and why? For example, if you will collect data by carrying out semi-structured or unstructured interviews, how will you choose your interviewees and how will you conduct the interviews themselves?
- Any practical limitations? You should discuss any limitations you foresee being an issue when you’re carrying out your research.
In any dissertation, thesis, or academic journal, you will always find a chapter dedicated to explaining the research methodology of the person who carried out the study, also referred to as the methodology section of the work.
A good research methodology will explain what you are going to do and why, while a poor methodology will lead to a messy or disorganized approach.
You should also be able to justify in this section your reasoning for why you intend to carry out your research in a particular way, especially if it might be a particularly unique method.
Having a sound methodology in place can also help you with the following:
- When another researcher at a later date wishes to try and replicate your research, they will need your explanations and guidelines.
- In the event that you receive any criticism or questioning on the research you carried out at a later point, you will be able to refer back to it and succinctly explain the how and why of your approach.
- It provides you with a plan to follow throughout your research. When you are drafting your methodology approach, you need to be sure that the method you are using is the right one for your goal. This will help you with both explaining and understanding your method.
- It affords you the opportunity to document from the outset what you intend to achieve with your research, from start to finish.
A research instrument is a tool you will use to help you collect, measure and analyze the data you use as part of your research.
The choice of research instrument will usually be yours to make as the researcher and will be whichever best suits your methodology.
There are many different research instruments you can use in collecting data for your research.
Generally, they can be grouped as follows:
- Interviews (either as a group or one-on-one). You can carry out interviews in many different ways. For example, your interview can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. The difference between them is how formal the set of questions is that is asked of the interviewee. In a group interview, you may choose to ask the interviewees to give you their opinions or perceptions on certain topics.
- Surveys (online or in-person). In survey research, you are posing questions in which you ask for a response from the person taking the survey. You may wish to have either free-answer questions such as essay-style questions, or you may wish to use closed questions such as multiple choice. You may even wish to make the survey a mixture of both.
- Focus Groups. Similar to the group interview above, you may wish to ask a focus group to discuss a particular topic or opinion while you make a note of the answers given.
- Observations. This is a good research instrument to use if you are looking into human behaviors. Different ways of researching this include studying the spontaneous behavior of participants in their everyday life, or something more structured. A structured observation is research conducted at a set time and place where researchers observe behavior as planned and agreed upon with participants.
These are the most common ways of carrying out research, but it is really dependent on your needs as a researcher and what approach you think is best to take.
It is also possible to combine a number of research instruments if this is necessary and appropriate in answering your research problem.
There are three different types of methodologies, and they are distinguished by whether they focus on words, numbers, or both.
| Data type | What is it? | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
Quantitative | This methodology focuses more on measuring and testing numerical data. What is the aim of quantitative research? | Surveys, tests, existing databases. |
Qualitative | Qualitative research is a process of collecting and analyzing both words and textual data. | Observations, interviews, focus groups. |
Mixed-method | A mixed-method approach combines both of the above approaches. | Where you can use a mixed method of research, this can produce some incredibly interesting results. This is due to testing in a way that provides data that is both proven to be exact while also being exploratory at the same time. |
➡️ Want to learn more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative research, and how to use both methods? Check out our guide for that!
If you've done your due diligence, you'll have an idea of which methodology approach is best suited to your research.
It’s likely that you will have carried out considerable reading and homework before you reach this point and you may have taken inspiration from other similar studies that have yielded good results.
Still, it is important to consider different options before setting your research in stone. Exploring different options available will help you to explain why the choice you ultimately make is preferable to other methods.
If proving your research problem requires you to gather large volumes of numerical data to test hypotheses, a quantitative research method is likely to provide you with the most usable results.
If instead you’re looking to try and learn more about people, and their perception of events, your methodology is more exploratory in nature and would therefore probably be better served using a qualitative research methodology.
It helps to always bring things back to the question: what do I want to achieve with my research?
Once you have conducted your research, you need to analyze it. Here are some helpful guides for qualitative data analysis:
➡️ How to do a content analysis
➡️ How to do a thematic analysis
➡️ How to do a rhetorical analysis
Research methodology refers to the techniques used to find and analyze information for a study, ensuring that the results are valid, reliable and that they address the research objective.
Data can typically be organized into four different categories or methods: observational, experimental, simulation, and derived.
Writing a methodology section is a process of introducing your methods and instruments, discussing your analysis, providing more background information, addressing your research limitations, and more.
Your research methodology section will need a clear research question and proposed research approach. You'll need to add a background, introduce your research question, write your methodology and add the works you cited during your data collecting phase.
The research methodology section of your study will indicate how valid your findings are and how well-informed your paper is. It also assists future researchers planning to use the same methodology, who want to cite your study or replicate it.

How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
How to Write a Psychology Essay

How to Find The Main Points in an Article: A Simple Guide
Anthony metivier.
- April 5, 2023
- Learning , Podcast
Podcast: Download
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | RSS

You are being tested on your ability to figure out what they are and why they’re important.
Teachers worth their salt won’t give you the answers because to do so violates your ability to learn this skill.
Why is this true?
Because all of human progress relies upon unique and innovative solutions to problems.
And knowing how to find the key points in an article is something that is learned by doing.
Plus, content is not king in this regard.
Instead, context is god.
So you not only need to practice identifying what the key points are.
You need to justify in your own words why those points are so important.
The best part?
I have tips for you that will help you improve your skills in not only finding the main points, but also explaining why those points count.
And I’ll teach you how I as a person with two MAs and a PhD earned my degrees by doing just that: finding, outlining and justifying each key point.
Ready to see A+ written all over your report cards and university transcripts?
Let’s get started!
What Is A Main Point?
A main point has several aspects to it. For starters, we have:
- What the author meant
- What the author actually said

Now, you might think that this is splitting hairs.
But as Stanley Fish put it , “the world is one thing, words another.”
Fish is the author of How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read One . A huge part of his point is that there’s a difference between what a person actually means and how words can be interpreted in many different ways.
There’s a word for this problem: Polysemy . We face it when “a single word, phrase, or concept has more than one meaning or connotation.”
Because many sentences have this issue, the main idea of a passage almost always requires interpretation in your own words.
And if you want to interpret really well, you need to give evidence to demonstrate why your take on the meaning of the passage is valid.
So we might as well face an uncomfortable truth:
To a certain extent, a main point is what you say it is plus what you can validate through argumentation.
Main Points In The Classroom
The definition I’ve just given applies to all aspects of life, but might not be what a teacher in a classroom is looking for from you.
It may be that you need to give a specific answer. This is why I say that “context is god.” In order to pass a test or get an A+ on a paper, the right answer might not be in your control no matter how much evidence you provide.
I’ve personally suffered situations several times where in multiple choice exams, the wording of the question made it impossible to give the best possible answer.

That’s why I’m glad that I used to follow a few simple steps:
- Read the textbooks thoroughly and answer any section or chapter quizzes
- Talk to my teachers to make sure I knew exactly what they were looking for
- Go through sample exams from previous years
- Attend study groups to discuss possible exam questions in advance
Once in the exam setting, if I could not figure out what answer the person grading the exam considered correct, I took a detour.
I would handwrite on the exam that I could not give an answer in good faith. Then I would write on the back of one of the pages a full explanation of why I thought the question was worded poorly. Finally, I gave the answer in prose that I felt was correct.
Although I cannot advise you to do the same, this strategy saved my skin in several exams. I always passed and did complete most of my degrees with honors, something that would have been impossible if I followed the “rules.”
In my case, my main idea paragraphs (or what I sometimes called “paragrowls”) saved my skin many times.
The Best Way To Identify A Main Point
At the end of the day, the best way to know the main point is to question everything .
Ask yourself:
- What is the author trying to tell me?
- What are the words the author uses?
- How is the topic introduced and concluded?
- What do any diagrams or illustrations tell me about the main points?
- What references to other research does the author make?
- What do commentators on the author say about the main points made by the author?
- Can I find where in the book or article those commentators drew their conclusions?

By asking and answering questions like these, in combination with the strategies I’ve shared for how I used to pass exams, you should feel confident that you can find the main points much easier now.
What Are Subpoints?
Subpoints are easier to define.
Remember how I said that we need to validate our opinion about what counts as a main point?
Authors of books and articles need to do this too. And subpoints is how they do it.
A subpoint typically involves:
- Giving an example
- Providing evidence in order to substantiate a claim
- Paraphrasing another source
- Quoting a source
- Analyzing a secondary text
- Providing a variation on a key point
- Performing historical or theoretical analysis on a main point
For a quick example of a subpoint, just scroll up.
When I mentioned that I’ve passed all my exams so well that I’ve earned the highest degrees you can get at a university, that was a subpoint. It is providing evidence to support the claim that my strategy is valid.

I could actually make the claim even more valid by providing proof that I have a Ph.d., such as by giving you this link to the alumni page of York University’s graduate program in Humanities.
Are subpoints more important than the main points?
In many ways, yes. They are often the evidence that substantiates the main point. Or they provide the nuances or historical background that help explain what makes the main point important.
How to Find the Key Points in an Article in 3 Steps
Now that we have defined main ideas and subpoints, let’s talk about some powerful ways to find them.
The following steps do not have to be followed in any particular order, though I do suggest always starting with the first one.
Step One: Know Your Goal
As I mentioned, a teacher or examiner may have a definition of what counts as the main point. I’ve given you some strategies for figuring that out.
All you have to do after determining what counts as a main point in your particular context is to read the books with that definition in mind. Searching for information based on a goal is a key part of reading faster , so take a second to write out the specific goal every time you sit down to read.
If you’re completing a doctoral dissertation or writing a book like I often do, the burden is a bit heavier. Your goal is to have a research question before you start reading.

Answering this question, and any sub-questions you may have, is your goal.
Step Two: Keep Detailed & Moveable Notes
Because it’s not always possible to know the main idea of a story or scholarly book I’m reading, I take notes on cards.
I shared a detailed tutorial on how I do this in How to Memorize a Textbook .
As I discuss in that post, there are several benefits to taking notes on cards. The main one is studying faster . Another is how using physical cards helps you constantly reshape your “deck of notes.”
The more you read, the more your idea of what counts as an important point might change, as will the subpoints you notice.
Keep in mind that subpoints don’t always have to come from the same source. As a former university professor myself, I can tell you that one way to make sure you get an A+ on your essays is to cross-reference several articles.
By doing this as much as possible in your writing and when answering exam questions, you’re demonstrating reflective thinking . This impresses your graders and will later impress hiring managers too.
Step Three: Test For Validity
One of the best things you can do is test your assumption that a point is as important as it seems.
You can test the validity of what you’ve decided are the most important details in your reading by:
- Checking introductions and conclusions again for confirmation
- Looking through the index for the terms you’ve selected
- Follow-up reading online and in other books
- Asking your teacher or professor if you’ve understood the reading correctly
- Talking with others to see if they’ve reached similar conclusions

Ultimately, having your test, submitted assignment or the things you write yourself graded or scored by others is the ultimate validation. You need either the feedback of your teacher or comments from the court of public opinion to know if you’ve hit paydirt.
And that’s a very good thing. External validation is a huge part of how we grow.
Yes, it takes some courage and sometimes you might get things wrong. Being willing to admit that and then commit to improving in the future is the best response. And so long as you commit to doing that, you cannot lose.
A Final, Powerful Way To Find Main Points
There’s an ancient technique for finding out what really matters in any given text.
It involves using a Memory Palace .
Basically, you memorize a few details, or entire quotes. Then, you analyze them from within memory.
By doing this, you’re able to consider them in a way that is much deeper than if they are only partially absorbed in your mind.
If you’d like to learn more about this technique, consider going through my Free Memory Improvement Kit:

This approach has helped me many times throughout the years, not only for academic goals, but also personal progress in other areas of life. I’m talking about health, mindfulness and professional matters.
Give it a try, and let me know:
What questions do you still have about identifying the main points in the texts that you’re reading? I love updating posts and answering questions in the comments.
And that’s another strategy you might consider:
Online discussion. It’s a great way to figure out what matters most to yourself and others.
Related Posts
Autobiographical memory can be complex to understand. This article is packed with autobiographical memory examples…
Understanding anterograde vs retrograde amnesia is a challenge. This post is packed with examples that…
Here's an audio presentation of The Magnetic Memory Method "Memory Training Consumer Awareness Guide."
4 Responses
Very interesting topic, got a lot out of it.
Thanks for stopping by and commenting, James!
Great blog post! I came across it while researching how to find key points in an article.
The additional information, strategies, and powerful ways memory helps are fascinating. I will attempt to utilize these methods and look into the free memory course.
Thanks, Dr. Metivier.
Thanks, Cindy.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
I accept the Privacy Policy
WANT TO LEARN SIMPLE EVERYDAY THINGS WITHOUT FORGETTING?
Enter your email below to get instant access to my FREE course that gives you a proven step-by-step process for remembering anything you want . You'll discover how to:
- Speak any language fluently
- Recall complicated formulas, math equations, or numbers.
- Master the technical terms for your field of work or study.
- Recite poetry, jokes, and even long speeches word-for-word
- Quickly absorb the most important ideas from books, textbooks, or lectures...
Unlock your natural ability to learn and remember anything 3x faster now!
ABOUT ANTHONY METIVIER

Anthony Metivier is the founder of the Magnetic Memory Method, a systematic, 21st century approach to memorizing foreign language vocabulary, names, music, poetry and more in ways that are easy, elegant, effective and fun.
Dr. Metivier holds a Ph.D. in Humanities from York University and has been featured in Forbes, Viva Magazine, Fluent in 3 Months, Daily Stoic, Learning How to Learn and he has delivered one of the most popular TEDx Talks on memory improvement.
His most popular books include, The Victorious Mind and… Read More
Anthony Metivier taught as a professor at:
POPULAR POSTS
Recent posts, how to use the memory palace technique for math in 8 steps, the ultimate guide to using mnemonics in your everyday life, how to remember what you read: 11 proven steps, 10 intellectual activities to mix with mnemonics for personal growth, how to memorize paragraphs, sentences, and passages fast, pay with confidence.

P.O. Box 933 Mooloolaba, QLD 4557 Australia
MEMORY COURSES
Quick links, memory boosting tips & tutorials.
Copyright © 2012 – 2024 Anthony Metivier · Advanced Education Methodologies Pty Ltd

COOL MEMORY TECHNIQUES!

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
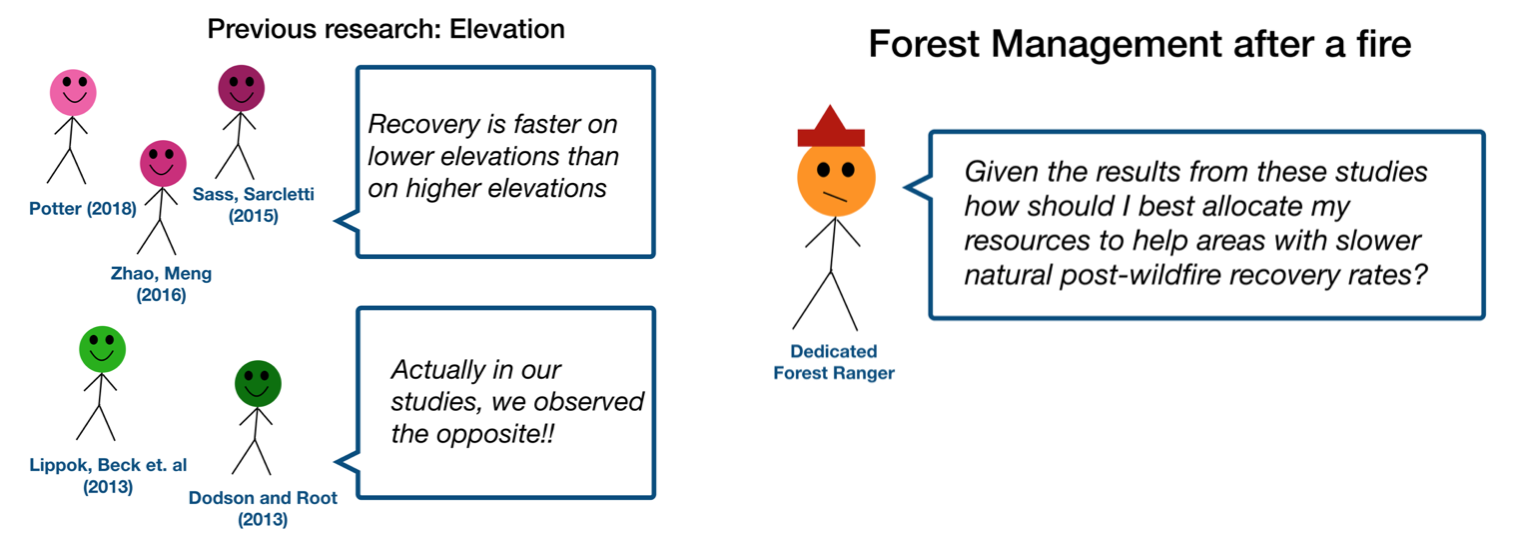
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Find the right market research agencies, suppliers, platforms, and facilities by exploring the services and solutions that best match your needs
list of top MR Specialties
Browse all specialties
Browse Companies and Platforms
by Specialty
by Location
Browse Focus Group Facilities

Manage your listing
Follow a step-by-step guide with online chat support to create or manage your listing.
About Greenbook Directory
IIEX Conferences
Discover the future of insights at the Insight Innovation Exchange (IIEX) event closest to you
IIEX Virtual Events
Explore important trends, best practices, and innovative use cases without leaving your desk
Insights Tech Showcase
See the latest research tech in action during curated interactive demos from top vendors
Stay updated on what’s new in insights and learn about solutions to the challenges you face
Greenbook Future list
An esteemed awards program that supports and encourages the voices of emerging leaders in the insight community.
Insight Innovation Competition
Submit your innovation that could impact the insights and market research industry for the better.
Find your next position in the world's largest database of market research and data analytics jobs.

For Suppliers
Directory: Renew your listing
Directory: Create a listing
Event sponsorship
Get Recommended Program
Digital Ads
Content marketing
Ads in Reports
Podcasts sponsorship
Run your Webinar
Host a Tech Showcase
Future List Partnership
All services

Dana Stanley
Greenbook’s Chief Revenue Officer
Research Methodologies
June 5, 2024
Primary Market Research Explained: WHY and How to Do It
Discover the power of primary market research for your business strategies. Uncover valuable insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and opportunities.
by Ashley Shedlock
Content Coordinator at Greenbook
Primary market research is essential for business strategies, offering direct insights into customers, markets, and competitors, unlike secondary research that relies on existing data. This hands-on approach gathers new data tailored to specific needs, providing fresh, current, and specific information not available through secondary research.
Methods like surveys, interviews, and observational research offer valuable insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and opportunities, helping businesses make informed strategic decisions. Embracing primary research methods allows businesses to understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors better, align their offerings with market demands, and drive business growth through targeted marketing efforts.
Primary Market Research Explained
In the world of business, primary market research serves as a powerful tool for steering growth and success. By implementing the findings derived from thorough primary research, companies can strategically position themselves in the market to capitalize on opportunities and overcome challenges effectively. It is not enough to conduct research; the real value lies in the strategic implementation of the insights garnered.
Continuous improvement is at the heart of every successful business, and primary market research plays a pivotal role in this process. By consistently engaging in research activities, companies can stay ahead of industry trends, consumer preferences, and competitive landscapes. This ongoing cycle of gathering, analyzing, and implementing data ensures that businesses remain agile, adaptable, and relevant in a dynamic marketplace.
It is essential to emphasize the significance of primary market research as a cornerstone of informed decision-making. Every data point, every insight, and every analysis contributes to a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics, customer behaviors, and emerging opportunities. By investing in primary research, businesses equip themselves with the knowledge needed to make strategic, data-driven decisions that lead to sustainable growth and long-term success.
Why is Primary Market Research Essential?
To excel in primary market research, one must adopt a customer-centric approach that goes beyond surface-level interactions. By delving deep into understanding customer needs, businesses can tailor their products and services to precisely meet those requirements. This approach not only fosters customer loyalty but also cultivates a deeper connection with the target audience, leading to long-term success.
Secondary Should Always Come Before Primary
When conducting primary market research, identifying market trends is instrumental in staying ahead of the curve. By analyzing patterns and shifts in consumer behavior, businesses can proactively adapt their strategies to capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate potential risks. This proactive stance demonstrates market responsiveness and positions the company as an industry leader poised for sustainable growth.
Uncovering consumer behavior patterns is like unraveling the DNA of a market. By closely examining how consumers interact with products or services, businesses can gain profound insights into purchase decisions. This knowledge empowers companies to fine-tune their marketing efforts, optimize their offerings, and create a seamless customer experience that resonates with the target demographic.
The true essence of primary market research lies in gaining valuable insights that transcend mere data points. These insights serve as the cornerstone of informed decision-making, guiding businesses towards strategic moves that drive sustainable success. By leveraging primary research findings, companies can uncover hidden opportunities, address underlying challenges, and pivot their operations to achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Primary market research is essential for businesses to succeed in today's ever-changing landscape. It is more than just collecting data - it is a strategic necessity. By embracing a customer-centric ethos, responding nimbly to market trends, understanding the intricacies of consumer behavior, and harnessing valuable insights, organizations can forge a path towards sustained growth and industry leadership. The competitive advantage derived from such deep-rooted insights is unparalleled, positioning businesses for success not just in the short term, but for years to come.
Different Types of Primary Research
Primary market research encompasses various types, each offering unique insights crucial for informed decision-making.
- Surveys: Which involve gathering feedback directly from individuals to understand their preferences, behaviors, and needs. Researchers can conduct surveys through online platforms, emails, or in-person interviews, gathering valuable data for analyzing trends and customer satisfaction.
- In-depth Interviews: Unlike surveys that rely on structured questions, interviews are a primary research method that offers a more personalized approach, allowing researchers to delve deeper into respondents' thoughts, emotions, and experiences. This qualitative method is particularly useful for gaining in-depth insights into consumer behavior, motivations, and perceptions.
- Focus groups: A valuable primary research method where a small group discusses specific topics or products, allowing researchers to gather insights into consumer opinions and preferences through group dynamics. This approach yields qualitative data not easily obtained through individual interviews or surveys.
- Observational Research: Involves directly observing and recording consumer behaviors in real-world settings. This method is particularly useful for studying consumer habits, preferences, and interactions with products or services in their natural environment. By observing without interference, researchers can gain valuable insights into how consumers behave without relying on self-reported data.
- Experimental Research: The manipulating variables to observe the effects on consumer behavior. This method allows researchers to control and test specific factors to understand their impact on consumer preferences and decision-making. By conducting experiments, researchers can draw valuable conclusions about causality and make informed predictions about consumer reactions to different stimuli.
Using a variety of research methods can help understand consumer behavior, market trends, and customer preferences more fully. Each type offers unique advantages in collecting data, analyzing consumer insights , and making informed decisions to drive business strategy and product development. Businesses can gain an advantage by using different types of primary research to understand their target market's needs and preferences.
How to Do Primary Market Research
When conducting primary market research, it is crucial to begin by setting clear and specific research objectives. This initial step lays the foundation for the entire research process, guiding the focus and scope of your study. By defining these goals from the outset, you establish a roadmap that shapes all subsequent decisions and actions.
In designing and implementing your research, it is essential to carefully consider the most appropriate research design for your objectives. Choosing the right research approach, whether exploratory, descriptive, or causal, helps you collect accurate data to answer your research questions effectively. The design stage creates the blueprint for your study, outlining the methodologies and procedures to follow.
When it comes to data collection methods, the key is to leverage a mix of techniques that best suit your research goals. Surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, and experiments are just a few methods at your disposal. Each method offers unique advantages and insights, so choosing the right combination can provide a comprehensive view of your target market and its preferences. Variety in data collection approaches helps ensure the robustness and depth of your findings.
Analyzing research findings is a critical step that transforms raw data into actionable insights. This process involves interpreting the collected data, identifying patterns, trends, and relationships within the information. By delving deep into the analysis, you can uncover valuable nuggets of information that lead to informed decision-making. The ability to draw meaningful conclusions from your research findings is what ultimately drives strategic business initiatives and shapes future success.
Conducting primary market research involves a systematic approach that starts with defining clear research goals and progresses through thoughtful design, diverse data collection methods, and insightful analysis. By following these steps diligently, businesses can unlock a wealth of knowledge about their target market, consumer behavior, and industry trends, enabling them to make informed decisions and stay ahead in today's competitive landscape.
What is the Difference Between Primary and Secondary Market Research?
Primary market research and secondary market research serve distinct purposes in the world of business analysis. While secondary research involves gathering information from existing sources like reports, articles, and studies, primary research entails collecting original data directly from the source. Imagine secondary research as reading a book about a place, while primary research is like visiting that place yourself to experience it firsthand.
Primary research allows businesses to ask specific questions and get current information directly from their target audience or market. This method enables companies to delve deeper into a particular issue, gaining a more nuanced understanding compared to secondary research findings. By engaging in primary research, businesses can gather unique insights and data that are relevant and timely for their decision-making processes.
On the other hand, secondary research is valuable for providing background information, industry trends, and competitor analysis. It offers a broad overview of the market landscape, serving as a foundation for further exploration through primary research. While secondary research is efficient and cost-effective, it may not always address the specific needs or nuances that primary research can uncover.
The primary vs. secondary research debate boils down to depth versus breadth. Primary research offers depth by allowing businesses to customize their approach and dive deeply into specific issues, whereas secondary research provides breadth by offering a wide range of existing data and insights. Each type of research has its place in informing business decisions, with primary research being essential for uncovering firsthand insights tailored to the unique needs of a company.
What are the Key Challenges in Collecting Primary Market Research Data?
Collecting primary market research data presents various challenges that researchers need to navigate effectively.
- Researchers must focus on designing methodologies that reduce biases and errors to ensure the reliability and validity of the data collected for primary market research.
- Conducting primary market research is resource-intensive due to the costs and time involved. It requires investments in manpower, technology, and research tools, demanding wise budgeting of time and financial resources for efficient data collection and valuable insights.
- Accessing the target population in primary market research can be challenging due to issues like respondent fatigue, privacy concerns, and hesitancy to participate. Establishing trust and rapport with participants is crucial to boost their involvement and obtain genuine feedback.
- In primary market research, it is essential to choose participants that mirror the target market's diversity accurately to ensure a representative sample. Failure to do so can result in biased results and compromise the research's validity.
- In primary market research, staying current with evolving market trends and changing consumer preferences is crucial. Researchers must adjust methodologies to capture valuable insights amidst the dynamic nature of markets and consumer behavior.
Addressing these challenges requires meticulous planning, strategic decision-making, and a deep understanding of research principles. By recognizing and proactively mitigating these challenges, researchers can enhance the quality and reliability of their primary market research data, leading to meaningful and actionable insights that drive informed business decisions.
Ashley Shedlock
The views, opinions, data, and methodologies expressed above are those of the contributor(s) and do not necessarily reflect or represent the official policies, positions, or beliefs of Greenbook.
Comments are moderated to ensure respect towards the author and to prevent spam or self-promotion. Your comment may be edited, rejected, or approved based on these criteria. By commenting, you accept these terms and take responsibility for your contributions.
More from Ashley Shedlock
Brand Strategy
Brand Tracking Tech 101
Gain valuable insights into consumer preferences and behaviors with brand tracking. Stay ahead of the competition by monitoring key brand metrics cons...
June 11, 2024
Read article
Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG)
Market Research For CPG Companies: The Best Methods
Gain a competitive edge in the consumer goods industry with effective market research strategies. Understand consumer behavior and how to use data ana...
May 15, 2024
5 Secrets to Effective Competitor Research
Gain valuable insights with competitor research. Understand trends, customer preferences, and industry opportunities. Stay ahead in the competitive la...
March 27, 2024
Is Walmart the Future of Market Research?
Editor’s Note: Earlier this year, we had Linda Lomelino on our podcast to discuss how Walmart is now leveraging shopper data and serving commercial cu...
December 1, 2022
Top in Quantitative Research
Moving Away from a Narcissistic Market Research Model
Why are we still measuring brand loyalty? It isn’t something that naturally comes up with consumers, who rarely think about brand first, if at all. Ma...
Devora Rogers
Chief Strategy Officer at Alter Agents
May 31, 2023
Qualitative Research
The Stepping Stones of Innovation: Navigating Failure and Empathy with Carol Fitzgerald
Natalie Pusch
Senior Content Producer at Greenbook
March 16, 2023
Play Episode
Sign Up for Updates
Get content that matters, written by top insights industry experts, delivered right to your inbox.
67k+ subscribers
Weekly Newsletter
Greenbook Podcast
Event Updates
I agree to receive emails with insights-related content from Greenbook. I understand that I can manage my email preferences or unsubscribe at any time and that Greenbook protects my privacy under the General Data Protection Regulation.*
Get the latest updates from top market research, insights, and analytics experts delivered weekly to your inbox
Your guide for all things market research and consumer insights
Create a New Listing
Manage My Listing
Find Companies
Find Focus Group Facilities
Tech Showcases
GRIT Report
Expert Channels
Get in touch
Marketing Services
Future List
Publish With Us
Privacy policy
Cookie policy
Terms of use
Copyright © 2024 New York AMA Communication Services, Inc. All rights reserved. 234 5th Avenue, 2nd Floor, New York, NY 10001 | Phone: (212) 849-2752
Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Stress management
Positive thinking: Stop negative self-talk to reduce stress
Positive thinking helps with stress management and can even improve your health. Practice overcoming negative self-talk with examples provided.
Is your glass half-empty or half-full? How you answer this age-old question about positive thinking may reflect your outlook on life, your attitude toward yourself, and whether you're optimistic or pessimistic — and it may even affect your health.
Indeed, some studies show that personality traits such as optimism and pessimism can affect many areas of your health and well-being. The positive thinking that usually comes with optimism is a key part of effective stress management. And effective stress management is associated with many health benefits. If you tend to be pessimistic, don't despair — you can learn positive thinking skills.
Understanding positive thinking and self-talk
Positive thinking doesn't mean that you ignore life's less pleasant situations. Positive thinking just means that you approach unpleasantness in a more positive and productive way. You think the best is going to happen, not the worst.
Positive thinking often starts with self-talk. Self-talk is the endless stream of unspoken thoughts that run through your head. These automatic thoughts can be positive or negative. Some of your self-talk comes from logic and reason. Other self-talk may arise from misconceptions that you create because of lack of information or expectations due to preconceived ideas of what may happen.
If the thoughts that run through your head are mostly negative, your outlook on life is more likely pessimistic. If your thoughts are mostly positive, you're likely an optimist — someone who practices positive thinking.
The health benefits of positive thinking
Researchers continue to explore the effects of positive thinking and optimism on health. Health benefits that positive thinking may provide include:
- Increased life span
- Lower rates of depression
- Lower levels of distress and pain
- Greater resistance to illnesses
- Better psychological and physical well-being
- Better cardiovascular health and reduced risk of death from cardiovascular disease and stroke
- Reduced risk of death from cancer
- Reduced risk of death from respiratory conditions
- Reduced risk of death from infections
- Better coping skills during hardships and times of stress
It's unclear why people who engage in positive thinking experience these health benefits. One theory is that having a positive outlook enables you to cope better with stressful situations, which reduces the harmful health effects of stress on your body.
It's also thought that positive and optimistic people tend to live healthier lifestyles — they get more physical activity, follow a healthier diet, and don't smoke or drink alcohol in excess.
Identifying negative thinking
Not sure if your self-talk is positive or negative? Some common forms of negative self-talk include:
- Filtering. You magnify the negative aspects of a situation and filter out all the positive ones. For example, you had a great day at work. You completed your tasks ahead of time and were complimented for doing a speedy and thorough job. That evening, you focus only on your plan to do even more tasks and forget about the compliments you received.
- Personalizing. When something bad occurs, you automatically blame yourself. For example, you hear that an evening out with friends is canceled, and you assume that the change in plans is because no one wanted to be around you.
- Catastrophizing. You automatically anticipate the worst without facts that the worse will happen. The drive-through coffee shop gets your order wrong, and then you think that the rest of your day will be a disaster.
- Blaming. You try to say someone else is responsible for what happened to you instead of yourself. You avoid being responsible for your thoughts and feelings.
- Saying you "should" do something. You think of all the things you think you should do and blame yourself for not doing them.
- Magnifying. You make a big deal out of minor problems.
- Perfectionism. Keeping impossible standards and trying to be more perfect sets yourself up for failure.
- Polarizing. You see things only as either good or bad. There is no middle ground.
Focusing on positive thinking
You can learn to turn negative thinking into positive thinking. The process is simple, but it does take time and practice — you're creating a new habit, after all. Following are some ways to think and behave in a more positive and optimistic way:
- Identify areas to change. If you want to become more optimistic and engage in more positive thinking, first identify areas of your life that you usually think negatively about, whether it's work, your daily commute, life changes or a relationship. You can start small by focusing on one area to approach in a more positive way. Think of a positive thought to manage your stress instead of a negative one.
- Check yourself. Periodically during the day, stop and evaluate what you're thinking. If you find that your thoughts are mainly negative, try to find a way to put a positive spin on them.
- Be open to humor. Give yourself permission to smile or laugh, especially during difficult times. Seek humor in everyday happenings. When you can laugh at life, you feel less stressed.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle. Aim to exercise for about 30 minutes on most days of the week. You can also break it up into 5- or 10-minute chunks of time during the day. Exercise can positively affect mood and reduce stress. Follow a healthy diet to fuel your mind and body. Get enough sleep. And learn techniques to manage stress.
- Surround yourself with positive people. Make sure those in your life are positive, supportive people you can depend on to give helpful advice and feedback. Negative people may increase your stress level and make you doubt your ability to manage stress in healthy ways.
- Practice positive self-talk. Start by following one simple rule: Don't say anything to yourself that you wouldn't say to anyone else. Be gentle and encouraging with yourself. If a negative thought enters your mind, evaluate it rationally and respond with affirmations of what is good about you. Think about things you're thankful for in your life.
Here are some examples of negative self-talk and how you can apply a positive thinking twist to them:
| Negative self-talk | Positive thinking |
|---|---|
| I've never done it before. | It's an opportunity to learn something new. |
| It's too complicated. | I'll tackle it from a different angle. |
| I don't have the resources. | Necessity is the mother of invention. |
| I'm too lazy to get this done. | I couldn't fit it into my schedule, but I can re-examine some priorities. |
| There's no way it will work. | I can try to make it work. |
| It's too radical a change. | Let's take a chance. |
| No one bothers to communicate with me. | I'll see if I can open the channels of communication. |
| I'm not going to get any better at this. | I'll give it another try. |
Practicing positive thinking every day
If you tend to have a negative outlook, don't expect to become an optimist overnight. But with practice, eventually your self-talk will contain less self-criticism and more self-acceptance. You may also become less critical of the world around you.
When your state of mind is generally optimistic, you're better able to handle everyday stress in a more constructive way. That ability may contribute to the widely observed health benefits of positive thinking.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
- Forte AJ, et al. The impact of optimism on cancer-related and postsurgical cancer pain: A systematic review. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2021; doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.09.008.
- Rosenfeld AJ. The neuroscience of happiness and well-being. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 2019;28:137.
- Kim ES, et al. Optimism and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2016; doi:10.1093/aje/kww182.
- Amonoo HL, et al. Is optimism a protective factor for cardiovascular disease? Current Cardiology Reports. 2021; doi:10.1007/s11886-021-01590-4.
- Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://health.gov/paguidelines/second-edition. Accessed Oct. 20, 2021.
- Seaward BL. Essentials of Managing Stress. 4th ed. Burlington, Mass.: Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2021.
- Seaward BL. Cognitive restructuring: Reframing. Managing Stress: Principles and Strategies for Health and Well-Being. 8th ed. Burlington, Mass.: Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2018.
- Olpin M, et al. Stress Management for Life. 5th ed. Cengage Learning; 2020.
- A very happy brain
- Being assertive
- Bridge pose
- Caregiver stress
- Cat/cow pose
- Child's pose
- COVID-19 and your mental health
- Does stress make rheumatoid arthritis worse?
- Downward-facing dog
- Ease stress to reduce eczema symptoms
- Ease stress to reduce your psoriasis flares
- Forgiveness
- Job burnout
- Learn to reduce stress through mindful living
- Manage stress to improve psoriatic arthritis symptoms
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Meditation is good medicine
- Mountain pose
- New School Anxiety
- Seated spinal twist
- Standing forward bend
- Stress and high blood pressure
- Stress relief from laughter
- Stress relievers
- Support groups
- Tips for easing stress when you have Crohn's disease
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Positive thinking Stop negative self-talk to reduce stress
We’re transforming healthcare
Make a gift now and help create new and better solutions for more than 1.3 million patients who turn to Mayo Clinic each year.
Common Comorbidities with Substance Use Disorders Research Report Part 1: The Connection Between Substance Use Disorders and Mental Illness
Many individuals who develop substance use disorders (SUD) are also diagnosed with mental disorders, and vice versa. 2,3 Although there are fewer studies on comorbidity among youth, research suggests that adolescents with substance use disorders also have high rates of co-occurring mental illness; over 60 percent of adolescents in community-based substance use disorder treatment programs also meet diagnostic criteria for another mental illness. 4
Data show high rates of comorbid substance use disorders and anxiety disorders—which include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. 5–9 Substance use disorders also co-occur at high prevalence with mental disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder, 6,9–11 attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 12,13 psychotic illness, 14,15 borderline personality disorder, 16 and antisocial personality disorder. 10,15 Patients with schizophrenia have higher rates of alcohol, tobacco, and drug use disorders than the general population. 17 As Figure 1 shows, the overlap is especially pronounced with serious mental illness (SMI). Serious mental illness among people ages 18 and older is defined at the federal level as having, at any time during the past year, a diagnosable mental, behavior, or emotional disorder that causes serious functional impairment that substantially interferes with or limits one or more major life activities. Serious mental illnesses include major depression, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder, and other mental disorders that cause serious impairment. 18 Around 1 in 4 individuals with SMI also have an SUD.
Data from a large nationally representative sample suggested that people with mental, personality, and substance use disorders were at increased risk for nonmedical use of prescription opioids. 19 Research indicates that 43 percent of people in SUD treatment for nonmedical use of prescription painkillers have a diagnosis or symptoms of mental health disorders, particularly depression and anxiety. 20
Youth—A Vulnerable Time
Although drug use and addiction can happen at any time during a person’s life, drug use typically starts in adolescence, a period when the first signs of mental illness commonly appear. Comorbid disorders can also be seen among youth. 21–23 During the transition to young adulthood (age 18 to 25 years), people with comorbid disorders need coordinated support to help them navigate potentially stressful changes in education, work, and relationships. 21
Drug Use and Mental Health Disorders in Childhood or Adolescence Increases Later Risk
The brain continues to develop through adolescence. Circuits that control executive functions such as decision making and impulse control are among the last to mature, which enhances vulnerability to drug use and the development of a substance use disorder. 3,24 Early drug use is a strong risk factor for later development of substance use disorders, 24 and it may also be a risk factor for the later occurrence of other mental illnesses. 25,26 However, this link is not necessarily causative and may reflect shared risk factors including genetic vulnerability, psychosocial experiences, and/or general environmental influences. For example, frequent marijuana use during adolescence can increase the risk of psychosis in adulthood, specifically in individuals who carry a particular gene variant. 26,27
It is also true that having a mental disorder in childhood or adolescence can increase the risk of later drug use and the development of a substance use disorder. Some research has found that mental illness may precede a substance use disorder, suggesting that better diagnosis of youth mental illness may help reduce comorbidity. One study found that adolescent-onset bipolar disorder confers a greater risk of subsequent substance use disorder compared to adult-onset bipolar disorder. 28 Similarly, other research suggests that youth develop internalizing disorders, including depression and anxiety, prior to developing substance use disorders. 29
Untreated Childhood ADHD Can Increase Later Risk of Drug Problems
Numerous studies have documented an increased risk for substance use disorders in youth with untreated ADHD, 13,30 although some studies suggest that only those with comorbid conduct disorders have greater odds of later developing a substance use disorder. 30,31 Given this linkage, it is important to determine whether effective treatment of ADHD could prevent subsequent drug use and addiction. Treatment of childhood ADHD with stimulant medications such as methylphenidate or amphetamine reduces the impulsive behavior, fidgeting, and inability to concentrate that characterize ADHD. 32
That risk presents a challenge when treating children with ADHD, since effective treatment often involves prescribing stimulant medications with addictive potential. Although the research is not yet conclusive, many studies suggest that ADHD medications do not increase the risk of substance use disorder among children with this condition. 31,32 It is important to combine stimulant medication for ADHD with appropriate family and child education and behavioral interventions, including counseling on the chronic nature of ADHD and risk for substance use disorder. 13,32
- Global (EN)
- Africa (EN)
- Australia (EN)
- Belgium (EN)
- Brasil (PT)
- Canada (EN)
- Canada (FR)
- France (FR)
- Germany (DE)
- Germany (EN)
- Hong Kong (EN)
- Indonesia (EN)
- Ireland (EN)
- Latin America (ES)
- Malaysia (EN)
- Middle East (EN)
- Netherlands (EN)
- 2024 TRUST BAROMETER
- About Edelman
- Diversity, Equity, Inclusion & Belonging
- Citizenship
- Edelman Trust Barometer
- Edelman Trust Institute
- Edelman Trust Management
- Research Archive
- News & Awards

- Home …
- Why we study Trust …
- 2023 …
- 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer …
- Special Report — Brand Trust 2023
The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel
In a volatile world rife with pressures on consumers, from health and the economy to challenges to rights and freedoms and an eroding sense of community, consumers are demanding more from brands.
The relationship between consumers and brands must evolve, as people feel more vulnerable, and their expectations of brands grow. The 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer Special Report: The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel tells us that consumers are looking for ongoing engagement after the point of purchase and their need for trust grows with feelings of vulnerability.
Featured Content
Gen z on gen z: the collapse of the purchase funnel.
Giselle Huasipoma and Gabe Gomez, Edelman Gen Z Lab ambassadors, sit down to unpack findings from the Edelman Trust Barometer Special Report: The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel. They discuss Gen Z asking more questions throughout their purchasing journeys, the future of online versus brick-and-mortar retail experiences, and why they don't want to be "ghosted" by brands.

Personal and societal threats have led to a more discerning consumer

are more price conscious
are doing more research before they buy
are making fewer impulse purchases

say there are brands they will not buy because of the countries in which they are HQ'd
Gen Z is impacting the entire buying ecosystem
79% of Gen Z say it’s more important than ever to trust the brands they buy, more than any other generation surveyed
68% of consumers say Gen Z influences where and how they shop, with a staggering 12-point increase in one year on those age 59+
The purchase funnel no longer reflects the modern brand-consumer relationship
Purchase is just the beginning

of consumers say that they uncover things that attract them to a brand and drive loyalty after the first purchase .
1. Purchase is often the starting point
2. ongoing engagement builds attraction, 3. brand action builds trust, 4. trust drives growth.
Trusted brands are rewarded with purchase, loyalty and advocacy

are more likely to purchase new products when they trust the brand, even irrespective of price

are more likely to stay loyal to and advocate for a brand they trust
Building Brands in a Vulnerable World
Move beyond the funnel.
Today’s consumers want an ongoing relationship with brands, and most consideration happens after the purchase. Build your brand and measurement strategy around the Trust Loop.
Work with Z, don’t underestimate them

Gen Z is changing the face of global commerce. They are pragmatic and highly influential. Even if they’re not your target, work with them to unlock consumer action at scale.
Make trust your growth engine

With trust, brand action fuels consumer action – buying, advocacy and loyalty. Through a reciprocal relationship that builds trust, you can unlock growth.
Featured Insights
Trust and Brands: The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel

Richard Edelman, CEO.
Edelman’s most recent Trust Barometer special report, The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel, finds that today’s buying behavior is too dynamic for a linear funnel and that purchase is no longer the end point but the start of an ongoing relationship with the consumer.
Three Mandates Marketers Must Adopt to Build Brand Trust in 2023

Jackie Cooper, Global Chief Brand Officer & Senior Advisor.
When we ask ourselves, what has really changed in the last year? The truth is that everything has. Consumers are feeling the pressure from every corner of our world - from the micro, everyday things like paying their bills to the macro, big picture things, like the smog outside their city windows..
Gen Z Harnesses Vulnerabilities, Asking Brands to Stand Up for All Consumers

Bianca Brown, Senior Account Executive and a U.K. Ambassador to Edelman’s Gen Z Lab, in conversation with Ellie Smith, Content Supervisor at the Edelman Trust Institute.
The Edelman Trust Institute sat down with Bianca Brown, Senior Account Executive and a U.K. Ambassador to Edelman’s Gen Z Lab, to discuss findings about Gen Z in the 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer Special Report: The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel.
Subscribe to receive our latest research and insights directly to your inbox
Methodology.
Fieldwork conducted: May 1 – May 12, 2023
Respondents
Respondents / Country
What does this mean for your business?
Subscribe to receive our latest research and insights directly to your inbox
- Accessibility Policy
- Skip to content
- QUICK LINKS
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications
- Download Java
- Careers at Oracle
What Is Big Data?
Sherry Tiao | Senior Manager, AI & Analytics, Oracle | March 11, 2024

In This Article
Big Data Defined
The three “vs” of big data, the value—and truth—of big data, the history of big data, big data use cases, big data challenges, how big data works, big data best practices.
What exactly is big data?
The definition of big data is data that contains greater variety, arriving in increasing volumes and with more velocity. This is also known as the three “Vs.”
Put simply, big data is larger, more complex data sets, especially from new data sources. These data sets are so voluminous that traditional data processing software just can’t manage them. But these massive volumes of data can be used to address business problems you wouldn’t have been able to tackle before.
| Volume | The amount of data matters. With big data, you’ll have to process high volumes of low-density, unstructured data. This can be data of unknown value, such as X (formerly Twitter) data feeds, clickstreams on a web page or a mobile app, or sensor-enabled equipment. For some organizations, this might be tens of terabytes of data. For others, it may be hundreds of petabytes. |
| Velocity | Velocity is the fast rate at which data is received and (perhaps) acted on. Normally, the highest velocity of data streams directly into memory versus being written to disk. Some internet-enabled smart products operate in real time or near real time and will require real-time evaluation and action. |
| Variety | Variety refers to the many types of data that are available. Traditional data types were structured and fit neatly in a . With the rise of big data, data comes in new unstructured data types. Unstructured and semistructured data types, such as text, audio, and video, require additional preprocessing to derive meaning and support metadata. |
Two more Vs have emerged over the past few years: value and veracity . Data has intrinsic value. But it’s of no use until that value is discovered. Equally important: How truthful is your data—and how much can you rely on it?
Today, big data has become capital. Think of some of the world’s biggest tech companies. A large part of the value they offer comes from their data, which they’re constantly analyzing to produce more efficiency and develop new products.
Recent technological breakthroughs have exponentially reduced the cost of data storage and compute, making it easier and less expensive to store more data than ever before. With an increased volume of big data now cheaper and more accessible, you can make more accurate and precise business decisions.
Finding value in big data isn’t only about analyzing it (which is a whole other benefit). It’s an entire discovery process that requires insightful analysts, business users, and executives who ask the right questions, recognize patterns, make informed assumptions, and predict behavior.
But how did we get here?
Although the concept of big data itself is relatively new, the origins of large data sets go back to the 1960s and ‘70s when the world of data was just getting started with the first data centers and the development of the relational database.
Around 2005, people began to realize just how much data users generated through Facebook, YouTube, and other online services. Hadoop (an open source framework created specifically to store and analyze big data sets) was developed that same year. NoSQL also began to gain popularity during this time.
The development of open source frameworks, such as Hadoop (and more recently, Spark) was essential for the growth of big data because they make big data easier to work with and cheaper to store. In the years since then, the volume of big data has skyrocketed. Users are still generating huge amounts of data—but it’s not just humans who are doing it.
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), more objects and devices are connected to the internet, gathering data on customer usage patterns and product performance. The emergence of machine learning has produced still more data.
While big data has come far, its usefulness is only just beginning. Cloud computing has expanded big data possibilities even further. The cloud offers truly elastic scalability, where developers can simply spin up ad hoc clusters to test a subset of data. And graph databases are becoming increasingly important as well, with their ability to display massive amounts of data in a way that makes analytics fast and comprehensive.

Discover the Insights in Your Data
- Who are the criminals passing dirty money around and committing financial services fraud?
- Who has been in contact with an infected person and needs to go into quarantine?
- How can feature engineering for data science be made simpler and more efficient?
Click below to access the 17 Use Cases for Graph Databases and Graph Analytics ebook.
Big Data Benefits
- Big data makes it possible for you to gain more complete answers because you have more information.
- More complete answers mean more confidence in the data—which means a completely different approach to tackling problems.
Big data can help you address a range of business activities, including customer experience and analytics. Here are just a few.
| Product development | Companies like Netflix and Procter & Gamble use big data to anticipate customer demand. They build predictive models for new products and services by classifying key attributes of past and current products or services and modeling the relationship between those attributes and the commercial success of the offerings. In addition, P&G uses data and analytics from focus groups, social media, test markets, and early store rollouts to plan, produce, and launch new products. |
| Predictive maintenance | Factors that can predict mechanical failures may be deeply buried in structured data, such as the year, make, and model of equipment, as well as in unstructured data that covers millions of log entries, sensor data, error messages, and engine temperature. By analyzing these indications of potential issues before the problems happen, organizations can deploy maintenance more cost effectively and maximize parts and equipment uptime. |
| Customer experience | The race for customers is on. A clearer view of customer experience is more possible now than ever before. Big data enables you to gather data from social media, web visits, call logs, and other sources to improve the interaction experience and maximize the value delivered. Start delivering personalized offers, reduce customer churn, and handle issues proactively. |
| Fraud and compliance | When it comes to security, it’s not just a few rogue hackers—you’re up against entire expert teams. Security landscapes and compliance requirements are constantly evolving. Big data helps you identify patterns in data that indicate fraud and aggregate large volumes of information to make regulatory reporting much faster. |
| Machine learning | Machine learning is a hot topic right now. And data—specifically big data—is one of the reasons why. We are now able to teach machines instead of program them. The availability of big data to train machine learning models makes that possible. |
| Operational efficiency | Operational efficiency may not always make the news, but it’s an area in which big data is having the most impact. With big data, you can analyze and assess production, customer feedback and returns, and other factors to reduce outages and anticipate future demands. Big data can also be used to improve decision-making in line with current market demand. |
| Drive innovation | Big data can help you innovate by studying interdependencies among humans, institutions, entities, and process and then determining new ways to use those insights. Use data insights to improve decisions about financial and planning considerations. Examine trends and what customers want to deliver new products and services. Implement dynamic pricing. There are endless possibilities. |

Download your free ebook to learn about:
- New ways you can use your data
- Ways the competition could be innovating
- Benefits and challenges of different use cases
While big data holds a lot of promise, it is not without its challenges.
First, big data is…big. Although new technologies have been developed for data storage, data volumes are doubling in size about every two years. Organizations still struggle to keep pace with their data and find ways to effectively store it.
But it’s not enough to just store the data. Data must be used to be valuable and that depends on curation. Clean data, or data that’s relevant to the client and organized in a way that enables meaningful analysis, requires a lot of work. Data scientists spend 50 to 80 percent of their time curating and preparing data before it can actually be used.
Finally, big data technology is changing at a rapid pace. A few years ago, Apache Hadoop was the popular technology used to handle big data. Then Apache Spark was introduced in 2014. Today, a combination of the two frameworks appears to be the best approach. Keeping up with big data technology is an ongoing challenge.
Discover more big data resources:
Big data gives you new insights that open up new opportunities and business models. Getting started involves three key actions:
1. Integrate Big data brings together data from many disparate sources and applications. Traditional data integration mechanisms, such as extract, transform, and load (ETL) generally aren’t up to the task. It requires new strategies and technologies to analyze big data sets at terabyte, or even petabyte, scale.
During integration, you need to bring in the data, process it, and make sure it’s formatted and available in a form that your business analysts can get started with.
2. Manage Big data requires storage. Your storage solution can be in the cloud, on premises, or both. You can store your data in any form you want and bring your desired processing requirements and necessary process engines to those data sets on an on-demand basis. Many people choose their storage solution according to where their data is currently residing. The cloud is gradually gaining popularity because it supports your current compute requirements and enables you to spin up resources as needed.
3. Analyze Your investment in big data pays off when you analyze and act on your data. Get new clarity with a visual analysis of your varied data sets. Explore the data further to make new discoveries. Share your findings with others. Build data models with machine learning and artificial intelligence. Put your data to work.
To help you on your big data journey, we’ve put together some key best practices for you to keep in mind. Here are our guidelines for building a successful big data foundation.
| Align big data with specific business goals | More extensive data sets enable you to make new discoveries. To that end, it is important to base new investments in skills, organization, or infrastructure with a strong business-driven context to guarantee ongoing project investments and funding. To determine if you are on the right track, ask how big data supports and enables your top business and IT priorities. Examples include understanding how to filter web logs to understand ecommerce behavior, deriving sentiment from social media and customer support interactions, and understanding statistical correlation methods and their relevance for customer, product, manufacturing, and engineering data. |
| Ease skills shortage with standards and governance | One of the biggest obstacles to benefiting from your investment in big data is a skills shortage. You can mitigate this risk by ensuring that big data technologies, considerations, and decisions are added to your IT governance program. Standardizing your approach will allow you to manage costs and leverage resources. Organizations implementing big data solutions and strategies should assess their skill requirements early and often and should proactively identify any potential skill gaps. These can be addressed by training/cross-training existing resources, hiring new resources, and leveraging consulting firms. |
| Optimize knowledge transfer with a center of excellence | Use a center of excellence approach to share knowledge, control oversight, and manage project communications. Whether big data is a new or expanding investment, the soft and hard costs can be shared across the enterprise. Leveraging this approach can help increase big data capabilities and overall information architecture maturity in a more structured and systematic way. |
| Top payoff is aligning unstructured with structured data | It is certainly valuable to analyze big data on its own. But you can bring even greater business insights by connecting and integrating low density big data with the structured data you are already using today. Whether you are capturing customer, product, equipment, or environmental big data, the goal is to add more relevant data points to your core master and analytical summaries, leading to better conclusions. For example, there is a difference in distinguishing all customer sentiment from that of only your best customers. Which is why many see big data as an integral extension of their existing business intelligence capabilities, data warehousing platform, and information architecture. Keep in mind that the big data analytical processes and models can be both human- and machine-based. Big data analytical capabilities include statistics, spatial analysis, semantics, interactive discovery, and visualization. Using analytical models, you can correlate different types and sources of data to make associations and meaningful discoveries. |
| Plan your discovery lab for performance | Discovering meaning in your data is not always straightforward. Sometimes we don’t even know what we’re looking for. That’s expected. Management and IT needs to support this “lack of direction” or “lack of clear requirement.” At the same time, it’s important for analysts and data scientists to work closely with the business to understand key business knowledge gaps and requirements. To accommodate the interactive exploration of data and the experimentation of statistical algorithms, you need high-performance work areas. Be sure that sandbox environments have the support they need—and are properly governed. |
| Align with the cloud operating model | Big data processes and users require access to a broad array of resources for both iterative experimentation and running production jobs. A big data solution includes all data realms including transactions, master data, reference data, and summarized data. Analytical sandboxes should be created on demand. Resource management is critical to ensure control of the entire data flow including pre- and post-processing, integration, in-database summarization, and analytical modeling. A well-planned private and public cloud provisioning and security strategy plays an integral role in supporting these changing requirements. |
Learn More About Big Data at Oracle
- Try a free big data workshop
- Infographic: How to Build Effective Data Lakes
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on November 23, 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Summarizing , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or evaluating the source . You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).
Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about summarizing.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarize an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyze or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarizing is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organized into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction , methods , results , and discussion .
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
| Introduction | or problem was addressed? |
|---|---|
| Methods | |
| Results | supported? |
| Discussion/conclusion |
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.
Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarize this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
Davis et al. (2015) set out to empirically test the popular saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.” Apples are often used to represent a healthy lifestyle, and research has shown their nutritional properties could be beneficial for various aspects of health. The authors’ unique approach is to take the saying literally and ask: do people who eat apples use healthcare services less frequently? If there is indeed such a relationship, they suggest, promoting apple consumption could help reduce healthcare costs.
The study used publicly available cross-sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were categorized as either apple eaters or non-apple eaters based on their self-reported apple consumption in an average 24-hour period. They were also categorized as either avoiding or not avoiding the use of healthcare services in the past year. The data was statistically analyzed to test whether there was an association between apple consumption and several dependent variables: physician visits, hospital stays, use of mental health services, and use of prescription medication.
Although apple eaters were slightly more likely to have avoided physician visits, this relationship was not statistically significant after adjusting for various relevant factors. No association was found between apple consumption and hospital stays or mental health service use. However, apple eaters were found to be slightly more likely to have avoided using prescription medication. Based on these results, the authors conclude that an apple a day does not keep the doctor away, but it may keep the pharmacist away. They suggest that this finding could have implications for reducing healthcare costs, considering the high annual costs of prescription medication and the inexpensiveness of apples.
However, the authors also note several limitations of the study: most importantly, that apple eaters are likely to differ from non-apple eaters in ways that may have confounded the results (for example, apple eaters may be more likely to be health-conscious). To establish any causal relationship between apple consumption and avoidance of medication, they recommend experimental research.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or meta analysis you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Using national survey data, Davis et al. (2015) tested the assertion that “an apple a day keeps the doctor away” and did not find statistically significant evidence to support this hypothesis. While people who consumed apples were slightly less likely to use prescription medications, the study was unable to demonstrate a causal relationship between these variables.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarizing many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words. Want to make your life super easy? Try our free text summarizer today!
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarizing, and on the purpose of the summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarize or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarizing an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Cite the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarize the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarize a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
All can be done within seconds with our free text summarizer .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 31). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 7, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-summarize/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, the basics of in-text citation | apa & mla examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Paediatric medicines: applications and procedures
How to submit paediatric applications.
As of 4 June 2024, applicants should use the IRIS platform for the following types of procedure:
- Initial paediatric investigation plan (PIP)
- Modification of an agreed PIP
- Product-specific waiver
- Compliance check
- Annual report on paediatric deferred measures
- Confirmation of applicability of a class waiver, or inclusion of an indication within a condition
- Discontinuation of paediatric development.
Further guidance on the use of the IRIS platform and how to prepare submissions is available on the dedicated IRIS website:
- IRIS: A secure online platform for handling product-related scientific and regulatory procedures with EMA
For ongoing applications submitted before 4 June 2024, the previous process will apply ( eSubmission: Projects (europa.eu) ). This includes validation issues and documents to be provided during initial assessment. PIPs in clock-stop may have a case-by-case arrangement.
Procedural advice on paediatric applications
In addition to the guidance provided on this IRIS platform , applicants should consult the procedural advice below:
English (EN) (341.93 KB - PDF)
Submission deadlines
Applicants should check the submission deadlines for paediatric procedures for the 2024-2026 period:
Submission deadlines for paediatric applications 2024-2026
English (EN) (106.55 KB - PDF)
Templates and forms
The relevant templates and forms are available at below.
Please make sure to first download and save the forms and templates before filling them out.
Please also use the latest published version of all templates and forms unless stated otherwise. Do not re-use previously-downloaded documents
To report any technical issues with the form, contact the EMA Service Desk.
- Paediatric investigation plans: Templates, forms and submission dates
Template for scientific document
English (EN) (281.95 KB - DOCX)
Request for modification of an agreed paediatric investigation plan
English (EN) (58.5 KB - DOC)
Paediatric investigation plan (PIP) - Key elements guidance
English (EN) (343.4 KB - PDF)
Template - Request for compliance check on an agreed paediatric investigation plan (PIP)
English (EN) (31.65 KB - DOCX)
Notification of discontinuation of an agreed PIP decision
English (EN) (41 KB - DOC)
Contact points
To contact EMA, please see the options listed on below:
- Paediatric medicines: Research and development: Contact points
Related content
Share this page.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, "research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.".
The purpose of research is to further understand the world and to learn how this knowledge can be applied to better everyday life. It is an integral part of problem solving. Although research can take many forms, there are three main purposes of research: Exploratory: Exploratory research is the first research to be conducted around a problem ...
In a research proposal, you present your main research question, any related subquestions you plan to explore, and your working thesis. Step 2: Planning and Scheduling. Before you start researching your topic, take time to plan your researching and writing schedule. Research projects can take days, weeks, or even months to complete.
College-level research can be difficult, even for students who have previously done research. This guide is a great starting point for learning about how to successfully conduct literature-based research, such as secondary research or a literature review. College-level research can be difficult, even for students who have previously done research. This guide is a great starting point for ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
Abstractspiepr Abs1. Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain ...
Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance.
Research Summary. Definition: A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings.
Step 7: Present the Findings. After meticulous analysis and interpretation of your research findings, as dictated by the research process steps, the moment arrives to disseminate your insights. Effectively presenting your research is key to captivating your audience and conveying the importance of your findings.
1. Research Paper Title. A research paper title is read first, and read the most. The title serves two purposes: informing readers and attracting attention. Therefore, your research paper title should be clear, descriptive, and concise. If you can, avoid technical jargon and abbreviations.
The reason comes straight out of the research on listening. According to LeFrancois, people are more likely to remember information that is meaningful, useful, and of interest to them; different or unique; organized; visual; and simple (LeFrancois, 1999). ... Main Point 3: Name some specific open-source software packages that may be appropriate ...
The purpose of a research methodology is to explain the reasoning behind your approach to your research - you'll need to support your collection methods, methods of analysis, and other key points of your work. Think of it like writing a plan or an outline for you what you intend to do. When carrying out research, it can be easy to go off-track ...
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
The main paragraphs must focus on the research problem and arguments with supporting evidence. Experts suggest using headings and sub-heads to help organize ideas and data into sub-groups. The concluding section should have a summary of your study's main points and key takeaways with recommendations for future research. ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
main body of the paper: say it . 3. summary and conclusion: tell the reader what you've said. B. Don't worry about spelling, punctuation, etc. at this stage. C. Stick to the point, avoid digression. State each major idea quickly and then develop it through examples and explanations. D.
Step One: Know Your Goal. As I mentioned, a teacher or examiner may have a definition of what counts as the main point. I've given you some strategies for figuring that out. All you have to do after determining what counts as a main point in your particular context is to read the books with that definition in mind.
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
Every data point, every insight, and every analysis contributes to a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics, customer behaviors, and emerging opportunities. By investing in primary research, businesses equip themselves with the knowledge needed to make strategic, data-driven decisions that lead to sustainable growth and long-term ...
The Problem With Behavioral Nudges. The benefits of steering people toward making better decisions has become conventional wisdom. But the evidence suggests it doesn't work quite as well as we ...
Positive thinking often starts with self-talk. Self-talk is the endless stream of unspoken thoughts that run through your head. These automatic thoughts can be positive or negative. Some of your self-talk comes from logic and reason. Other self-talk may arise from misconceptions that you create because of lack of information or expectations due ...
Try Creative Cloud today. After your free trial, your Adobe Creative Cloud membership is only. US$19.99/mo US$59.99/mo . See terms. Buy now. Free trial. Purchase by phone: 800-585-0774. Students and teachers are eligible for over 60% discount on Adobe Creative Cloud. Get access to Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, Premiere Pro and more.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
Many individuals who develop substance use disorders (SUD) are also diagnosed with mental disorders, and vice versa.2,3 Although there are fewer studies on comorbidity among youth, research suggests that adolescents with substance use disorders also have high rates of co-occurring mental illness; over 60 percent of adolescents in community-based substance use disorder treatment programs also ...
The relationship between consumers and brands must evolve, as people feel more vulnerable, and their expectations of brands grow. The 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer Special Report: The Collapse of the Purchase Funnel tells us that consumers are looking for ongoing engagement after the point of purchase and their need for trust grows with feelings ...
The definition of big data is data that contains greater variety, arriving in increasing volumes and with more velocity. This is also known as the three "Vs.". Put simply, big data is larger, more complex data sets, especially from new data sources. These data sets are so voluminous that traditional data processing software just can't ...
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about summarizing.
Submission deadlines. Applicants should check the submission deadlines for paediatric procedures for the 2024-2026 period: Submission deadlines for paediatric applications 2024-2026. Reference Number: EMA/21598/2024. English (EN) (106.55 KB - PDF) First published: 25/01/2024.