All Formats

Essay Templates
19+ best microsoft word essay templates.
On the search for college templates ? We can help you with that. We have here an array of essay templates for you to choose from. For some, essay writing can be a stressful endeavor, but that should not be the case. Writing is a positive and professional way of channeling your deepest thoughts and sentiments.

Simple Narrative Essay Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Three-Paragraph Essay Template

Biography Essay Outline Format Template

Sample Essay Plan Template

Microsoft Word High School Persuasive Essay Template

Microsoft Word Basic Paragraph Reflective Essay Template

Free Microsoft Word MLA Format Argumentative Essay

Microsoft Word Introduction Expository Essay Template

Free Microsoft Word Narrative Research Essay Template

Microsoft Word Short Informative Essay Template

Relevance of Essay Templates
- As a marketing strategy in the business world . Behind every successful and famous product is a great writer. Advertisers also used essays as a tool for making quality content in their ads, particularly on websites.
- As an academic requirement . Inevitably, a student will not encounter essay writing in school regardless of the level. From your elementary to your college years, essays are mostly required by your professors as a partial requirement for the fulfillment of your course or program .
- As a means of career elevation . For those institutions that are sponsoring great minds and letting them proceed with their post-graduate courses, essays are usually one of the requirements before a scholarship grant is given. Part of the evaluation process is the quality of your writing, which will give them an idea of your degree of expertise.
Free Microsoft Word Personal Elementary Essay Template

Microsoft Word University Academic Scholarship Essay

Microsoft Word Professional College Essay Template

Microsoft Word Middle School Descriptive Essay Template

Free Microsoft Word Essay Layout Template

Microsoft Word Outline Paragraph Essay Template
Free Microsoft Word APA Essay Template

Free Microsoft Word 5th Grade Essay Template

Free 6th Grade Persuasive Essay Template

Free 4th Grade Essay Template

Important Factors to Note about Different Types of Essays
- Argumentative essay . This type of essay requires you to present and explain your stand on a certain issue. This is tricky because you’re not just arguing for the argument’s sake but is also a requirement to provide substantial evidence.
- Descriptive essay . Here, you are required to layout and write about the salient characteristics and dynamics of a certain issue, person, or event, depending on the topic. This will channel your capability to express your observations in an organized manner.
- Narrative essay . This refers to the ones that tell a story whether fictional or based on real-life events.
More in Essay Templates
Promotion Policy Outline HR Template
Recruitment policy outline hr template, code of ethics outline hr template, future training scope outline hr template, goal setting session outline hr template, school sports program brochure template, research essay outline template, colorful outline template, personal career case study interview essay template, reflective leadership interview essay template.
- How to Make/Create a College Essay [Templates + Examples] 2023
- How to Make/Create a Rhetorical Analysis Essay [Templates + Examples] 2023
- 5+ Free Descriptive Essay Templates – PDF
- 15+ Essay Format Templates – PDF
- 11+ Free Descriptive Essay Templates – PDF, DOC
- 19+ Essay Templates in PDF
- How to Make/Create a Narrative Essay [Templates + Examples] 2023
- 14+ 5 Paragraph Essay Templates – PDF
- How To Make/Create a 5-Paragraph Essay Outline [Templates + Examples] 2023
- 10+ Argumentative Essay Outline Templates – PDF
- 20+ Interview Essay Templates
- 9+ Leadership Essays
- 13+ Literary Essay Templates in Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
- 7+ Extended Essay Templates
- 9+ Free Downloadable Informative Essay Samples and Examples
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
Trying to devise a structure for your essay can be one of the most difficult parts of the writing process. Making a detailed outline before you begin writing is a good way to make sure your ideas come across in a clear and logical order. A good outline will also save you time in the revision process, reducing the possibility that your ideas will need to be rearranged once you've written them.
The First Steps
Before you can begin outlining, you need to have a sense of what you will argue in the essay. From your analysis and close readings of primary and/or secondary sources you should have notes, ideas, and possible quotes to cite as evidence. Let's say you are writing about the 1999 Republican Primary and you want to prove that each candidate's financial resources were the most important element in the race. At this point, your notes probably lack much coherent order. Most likely, your ideas are still in the order in which they occurred to you; your notes and possible quotes probably still adhere to the chronology of the sources you've examined. Your goal is to rearrange your ideas, notes, and quotes—the raw material of your essay—into an order that best supports your argument, not the arguments you've read in other people's works. To do this, you have to group your notes into categories and then arrange these categories in a logical order.
Generalizing
The first step is to look over each individual piece of information that you've written and assign it to a general category. Ask yourself, "If I were to file this in a database, what would I file it under?" If, using the example of the Republican Primary, you wrote down an observation about John McCain's views on health care, you might list it under the general category of "Health care policy." As you go through your notes, try to reuse categories whenever possible. Your goal is to reduce your notes to no more than a page of category listings.
Now examine your category headings. Do any seem repetitive? Do any go together? "McCain's expenditure on ads" and "Bush's expenditure on ads," while not exactly repetitive, could easily combine into a more general category like "Candidates' expenditures on ads." Also, keep an eye out for categories that no longer seem to relate to your argument. Individual pieces of information that at first seemed important can begin to appear irrelevant when grouped into a general category.
Now it's time to generalize again. Examine all your categories and look for common themes. Go through each category and ask yourself, "If I were to place this piece of information in a file cabinet, what would I label that cabinet?" Again, try to reuse labels as often as possible: "Health Care," "Foreign Policy," and "Immigration" can all be contained under "Policy Initiatives." Make these larger categories as general as possible so that there are no more than three or four for a 7-10 page paper.
With your notes grouped into generalized categories, the process of ordering them should be easier. To begin, look at your most general categories. With your thesis in mind, try to find a way that the labels might be arranged in a sentence or two that supports your argument. Let's say your thesis is that financial resources played the most important role in the 1999 Republican Primary. Your four most general categories are "Policy Initiatives," "Financial Resources," "Voters' Concerns," and "Voters' Loyalty." You might come up with the following sentence: ÒAlthough McCain's policy initiatives were closest to the voters' concerns, Bush's financial resources won the voters' loyalty.Ó This sentence should reveal the order of your most general categories. You will begin with an examination of McCain's and Bush's views on important issues and compare them to the voters' top concerns. Then you'll look at both candidates' financial resources and show how Bush could win voters' loyalty through effective use of his resources, despite his less popular policy ideas.
With your most general categories in order, you now must order the smaller categories. To do so, arrange each smaller category into a sentence or two that will support the more general sentence you've just devised. Under the category of "Financial Resources," for instance, you might have the smaller categories of "Ad Expenditure," "Campaign Contributions" and "Fundraising." A sentence that supports your general argument might read: "Bush's early emphasis on fundraising led to greater campaign contributions, allowing him to have a greater ad expenditure than McCain."
The final step of the outlining process is to repeat this procedure on the smallest level, with the original notes that you took for your essay. To order what probably was an unwieldy and disorganized set of information at the beginning of this process, you need now only think of a sentence or two to support your general argument. Under the category "Fundraising," for example, you might have quotes about each candidate's estimation of its importance, statistics about the amount of time each candidate spent fundraising, and an idea about how the importance of fundraising never can be overestimated. Sentences to support your general argument might read: "No candidate has ever raised too much money [your idea]. While both McCain and Bush acknowledged the importance of fundraising [your quotes], the numbers clearly point to Bush as the superior fundraiser [your statistics]." The arrangement of your ideas, quotes, and statistics now should come naturally.
Putting It All Together
With these sentences, you have essentially constructed an outline for your essay. The most general ideas, which you organized in your first sentence, constitute the essay's sections. They follow the order in which you placed them in your sentence. The order of the smaller categories within each larger category (determined by your secondary sentences) indicates the order of the paragraphs within each section. Finally, your last set of sentences about your specific notes should show the order of the sentences within each paragraph. An outline for the essay about the 1999 Republican Primary (showing only the sections worked out here) would look something like this:
I. POLICY INITIATIVES
II. VOTERS' CONCERNS
III. FINANCIAL RESOURCES
A. Fundraising
a. Original Idea
b. McCain Quote/Bush Quote
c. McCain Statistics/Bush Statistics
B. Campaign Contributions
C. Ad Expenditure
IV. VOTERS' LOYALTY
Copyright 2000, David Kornhaber, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Words to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay .
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
To use the words of X
According to X
As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
In this essay, I will…
The purpose of this essay…
This essay discusses…
In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
There are three main arguments for…

Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
First and foremost
First of all
To begin with
Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
Additionally
In addition
Furthermore
Another key thing to remember
In the same way
Correspondingly
Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
In other words
To put it another way
That is to say
To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
For instance
To give an illustration of
To exemplify
To demonstrate
As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
As a result
Accordingly
As you can see
This suggests that
It follows that
It can be seen that
For this reason
For all of those reasons
Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”

When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
What’s more
Not only…but also
Not to mention
To say nothing of
Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
On the one hand / on the other hand
Alternatively
In contrast to
On the contrary
By contrast
In comparison
Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
Having said that
Differing from
In spite of
With this in mind
Provided that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
Notwithstanding
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
Accommodate
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
Verbs that show increase:
Verbs that show decrease:
Deteriorate
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
Comprises of
Is composed of
Constitutes
Encompasses
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
Misconstrue

Verbs that show a positive stance:
Substantiate
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
Corroborate
Demonstrate
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
Contemplate
Hypothesize
Investigate
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
Significant
Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
Controversial
Insignificant
Questionable
Unnecessary
Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
Comprehensively
Exhaustively
Extensively
Respectively
Surprisingly
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
In conclusion
To summarize
In a nutshell
Given the above
As described
All things considered
Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
Unquestionably
Undoubtedly
Particularly
Importantly
Conclusively
It should be noted
On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Last places remaining for July 14th and July 28th courses . Enrol now and join students from 175 countries for the summer of a lifetime
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.
General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.

Word Choice
What this handout is about.
This handout can help you revise your papers for word-level clarity, eliminate wordiness and avoid clichés, find the words that best express your ideas, and choose words that suit an academic audience.
Introduction
Writing is a series of choices. As you work on a paper, you choose your topic, your approach, your sources, and your thesis; when it’s time to write, you have to choose the words you will use to express your ideas and decide how you will arrange those words into sentences and paragraphs. As you revise your draft, you make more choices. You might ask yourself, “Is this really what I mean?” or “Will readers understand this?” or “Does this sound good?” Finding words that capture your meaning and convey that meaning to your readers is challenging. When your instructors write things like “awkward,” “vague,” or “wordy” on your draft, they are letting you know that they want you to work on word choice. This handout will explain some common issues related to word choice and give you strategies for choosing the best words as you revise your drafts.
As you read further into the handout, keep in mind that it can sometimes take more time to “save” words from your original sentence than to write a brand new sentence to convey the same meaning or idea. Don’t be too attached to what you’ve already written; if you are willing to start a sentence fresh, you may be able to choose words with greater clarity.
For tips on making more substantial revisions, take a look at our handouts on reorganizing drafts and revising drafts .
“Awkward,” “vague,” and “unclear” word choice
So: you write a paper that makes perfect sense to you, but it comes back with “awkward” scribbled throughout the margins. Why, you wonder, are instructors so fond of terms like “awkward”? Most instructors use terms like this to draw your attention to sentences they had trouble understanding and to encourage you to rewrite those sentences more clearly.
Difficulties with word choice aren’t the only cause of awkwardness, vagueness, or other problems with clarity. Sometimes a sentence is hard to follow because there is a grammatical problem with it or because of the syntax (the way the words and phrases are put together). Here’s an example: “Having finished with studying, the pizza was quickly eaten.” This sentence isn’t hard to understand because of the words I chose—everybody knows what studying, pizza, and eating are. The problem here is that readers will naturally assume that first bit of the sentence “(Having finished with studying”) goes with the next noun that follows it—which, in this case, is “the pizza”! It doesn’t make a lot of sense to imply that the pizza was studying. What I was actually trying to express was something more like this: “Having finished with studying, the students quickly ate the pizza.” If you have a sentence that has been marked “awkward,” “vague,” or “unclear,” try to think about it from a reader’s point of view—see if you can tell where it changes direction or leaves out important information.
Sometimes, though, problems with clarity are a matter of word choice. See if you recognize any of these issues:
- Misused words —the word doesn’t actually mean what the writer thinks it does. Example : Cree Indians were a monotonous culture until French and British settlers arrived. Revision: Cree Indians were a homogenous culture.
- Words with unwanted connotations or meanings. Example : I sprayed the ants in their private places. Revision: I sprayed the ants in their hiding places.
- Using a pronoun when readers can’t tell whom/what it refers to. Example : My cousin Jake hugged my brother Trey, even though he didn’t like him very much. Revision: My cousin Jake hugged my brother Trey, even though Jake doesn’t like Trey very much.
- Jargon or technical terms that make readers work unnecessarily hard. Maybe you need to use some of these words because they are important terms in your field, but don’t throw them in just to “sound smart.” Example : The dialectical interface between neo-Platonists and anti-disestablishment Catholics offers an algorithm for deontological thought. Revision : The dialogue between neo-Platonists and certain Catholic thinkers is a model for deontological thought.
- Loaded language. Sometimes we as writers know what we mean by a certain word, but we haven’t ever spelled that out for readers. We rely too heavily on that word, perhaps repeating it often, without clarifying what we are talking about. Example : Society teaches young girls that beauty is their most important quality. In order to prevent eating disorders and other health problems, we must change society. Revision : Contemporary American popular media, like magazines and movies, teach young girls that beauty is their most important quality. In order to prevent eating disorders and other health problems, we must change the images and role models girls are offered.
Sometimes the problem isn’t choosing exactly the right word to express an idea—it’s being “wordy,” or using words that your reader may regard as “extra” or inefficient. Take a look at the following list for some examples. On the left are some phrases that use three, four, or more words where fewer will do; on the right are some shorter substitutes:
| I came to the realization that | I realized that |
| She is of the opinion that | She thinks that |
| Concerning the matter of | About |
| During the course of | During |
| In the event that | If |
| In the process of | During, while |
| Regardless of the fact that | Although |
| Due to the fact that | Because |
| In all cases | Always |
| At that point in time | Then |
| Prior to | Before |
Keep an eye out for wordy constructions in your writing and see if you can replace them with more concise words or phrases.
In academic writing, it’s a good idea to limit your use of clichés. Clichés are catchy little phrases so frequently used that they have become trite, corny, or annoying. They are problematic because their overuse has diminished their impact and because they require several words where just one would do.
The main way to avoid clichés is first to recognize them and then to create shorter, fresher equivalents. Ask yourself if there is one word that means the same thing as the cliché. If there isn’t, can you use two or three words to state the idea your own way? Below you will see five common clichés, with some alternatives to their right. As a challenge, see how many alternatives you can create for the final two examples.
| Agree to disagree | Disagree |
| Dead as a doornail | Dead |
| Last but not least | Last |
| Pushing the envelope | Approaching the limit |
| Up in the air | Unknown/undecided |
Try these yourself:
| Play it by ear | _____?_____ |
| Let the cat out of the bag | _____?_____ |
Writing for an academic audience
When you choose words to express your ideas, you have to think not only about what makes sense and sounds best to you, but what will make sense and sound best to your readers. Thinking about your audience and their expectations will help you make decisions about word choice.
Some writers think that academic audiences expect them to “sound smart” by using big or technical words. But the most important goal of academic writing is not to sound smart—it is to communicate an argument or information clearly and convincingly. It is true that academic writing has a certain style of its own and that you, as a student, are beginning to learn to read and write in that style. You may find yourself using words and grammatical constructions that you didn’t use in your high school writing. The danger is that if you consciously set out to “sound smart” and use words or structures that are very unfamiliar to you, you may produce sentences that your readers can’t understand.
When writing for your professors, think simplicity. Using simple words does not indicate simple thoughts. In an academic argument paper, what makes the thesis and argument sophisticated are the connections presented in simple, clear language.
Keep in mind, though, that simple and clear doesn’t necessarily mean casual. Most instructors will not be pleased if your paper looks like an instant message or an email to a friend. It’s usually best to avoid slang and colloquialisms. Take a look at this example and ask yourself how a professor would probably respond to it if it were the thesis statement of a paper: “Moulin Rouge really bit because the singing sucked and the costume colors were nasty, KWIM?”
Selecting and using key terms
When writing academic papers, it is often helpful to find key terms and use them within your paper as well as in your thesis. This section comments on the crucial difference between repetition and redundancy of terms and works through an example of using key terms in a thesis statement.
Repetition vs. redundancy
These two phenomena are not necessarily the same. Repetition can be a good thing. Sometimes we have to use our key terms several times within a paper, especially in topic sentences. Sometimes there is simply no substitute for the key terms, and selecting a weaker term as a synonym can do more harm than good. Repeating key terms emphasizes important points and signals to the reader that the argument is still being supported. This kind of repetition can give your paper cohesion and is done by conscious choice.
In contrast, if you find yourself frustrated, tiredly repeating the same nouns, verbs, or adjectives, or making the same point over and over, you are probably being redundant. In this case, you are swimming aimlessly around the same points because you have not decided what your argument really is or because you are truly fatigued and clarity escapes you. Refer to the “Strategies” section below for ideas on revising for redundancy.
Building clear thesis statements
Writing clear sentences is important throughout your writing. For the purposes of this handout, let’s focus on the thesis statement—one of the most important sentences in academic argument papers. You can apply these ideas to other sentences in your papers.
A common problem with writing good thesis statements is finding the words that best capture both the important elements and the significance of the essay’s argument. It is not always easy to condense several paragraphs or several pages into concise key terms that, when combined in one sentence, can effectively describe the argument.
However, taking the time to find the right words offers writers a significant edge. Concise and appropriate terms will help both the writer and the reader keep track of what the essay will show and how it will show it. Graders, in particular, like to see clearly stated thesis statements. (For more on thesis statements in general, please refer to our handout .)
Example : You’ve been assigned to write an essay that contrasts the river and shore scenes in Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn. You work on it for several days, producing three versions of your thesis:
Version 1 : There are many important river and shore scenes in Huckleberry Finn.
Version 2 : The contrasting river and shore scenes in Huckleberry Finn suggest a return to nature.
Version 3 : Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
Let’s consider the word choice issues in these statements. In Version 1, the word “important”—like “interesting”—is both overused and vague; it suggests that the author has an opinion but gives very little indication about the framework of that opinion. As a result, your reader knows only that you’re going to talk about river and shore scenes, but not what you’re going to say. Version 2 is an improvement: the words “return to nature” give your reader a better idea where the paper is headed. On the other hand, they still do not know how this return to nature is crucial to your understanding of the novel.
Finally, you come up with Version 3, which is a stronger thesis because it offers a sophisticated argument and the key terms used to make this argument are clear. At least three key terms or concepts are evident: the contrast between river and shore scenes, a return to nature, and American democratic ideals.
By itself, a key term is merely a topic—an element of the argument but not the argument itself. The argument, then, becomes clear to the reader through the way in which you combine key terms.
Strategies for successful word choice
- Be careful when using words you are unfamiliar with. Look at how they are used in context and check their dictionary definitions.
- Be careful when using the thesaurus. Each word listed as a synonym for the word you’re looking up may have its own unique connotations or shades of meaning. Use a dictionary to be sure the synonym you are considering really fits what you are trying to say.
- Under the present conditions of our society, marriage practices generally demonstrate a high degree of homogeneity.
- In our culture, people tend to marry others who are like themselves. (Longman, p. 452)
- Before you revise for accurate and strong adjectives, make sure you are first using accurate and strong nouns and verbs. For example, if you were revising the sentence “This is a good book that tells about the Revolutionary War,” think about whether “book” and “tells” are as strong as they could be before you worry about “good.” (A stronger sentence might read “The novel describes the experiences of a soldier during the Revolutionary War.” “Novel” tells us what kind of book it is, and “describes” tells us more about how the book communicates information.)
- Try the slash/option technique, which is like brainstorming as you write. When you get stuck, write out two or more choices for a questionable word or a confusing sentence, e.g., “questionable/inaccurate/vague/inappropriate.” Pick the word that best indicates your meaning or combine different terms to say what you mean.
- Look for repetition. When you find it, decide if it is “good” repetition (using key terms that are crucial and helpful to meaning) or “bad” repetition (redundancy or laziness in reusing words).
- Write your thesis in five different ways. Make five different versions of your thesis sentence. Compose five sentences that express your argument. Try to come up with four alternatives to the thesis sentence you’ve already written. Find five possible ways to communicate your argument in one sentence to your reader. (We’ve just used this technique—which of the last five sentences do you prefer?)Whenever we write a sentence we make choices. Some are less obvious than others, so that it can often feel like we’ve written the sentence the only way we know how. By writing out five different versions of your thesis, you can begin to see your range of choices. The final version may be a combination of phrasings and words from all five versions, or the one version that says it best. By literally spelling out some possibilities for yourself, you will be able to make better decisions.
- Read your paper out loud and at… a… slow… pace. You can do this alone or with a friend, roommate, TA, etc. When read out loud, your written words should make sense to both you and other listeners. If a sentence seems confusing, rewrite it to make the meaning clear.
- Instead of reading the paper itself, put it down and just talk through your argument as concisely as you can. If your listener quickly and easily comprehends your essay’s main point and significance, you should then make sure that your written words are as clear as your oral presentation was. If, on the other hand, your listener keeps asking for clarification, you will need to work on finding the right terms for your essay. If you do this in exchange with a friend or classmate, rest assured that whether you are the talker or the listener, your articulation skills will develop.
- Have someone not familiar with the issue read the paper and point out words or sentences they find confusing. Do not brush off this reader’s confusion by assuming they simply doesn’t know enough about the topic. Instead, rewrite the sentences so that your “outsider” reader can follow along at all times.
- Check out the Writing Center’s handouts on style , passive voice , and proofreading for more tips.
Questions to ask yourself
- Am I sure what each word I use really means? Am I positive, or should I look it up?
- Have I found the best word or just settled for the most obvious, or the easiest, one?
- Am I trying too hard to impress my reader?
- What’s the easiest way to write this sentence? (Sometimes it helps to answer this question by trying it out loud. How would you say it to someone?)
- What are the key terms of my argument?
- Can I outline out my argument using only these key terms? What others do I need? Which do I not need?
- Have I created my own terms, or have I simply borrowed what looked like key ones from the assignment? If I’ve borrowed the terms, can I find better ones in my own vocabulary, the texts, my notes, the dictionary, or the thesaurus to make myself clearer?
- Are my key terms too specific? (Do they cover the entire range of my argument?) Can I think of specific examples from my sources that fall under the key term?
- Are my key terms too vague? (Do they cover more than the range of my argument?)
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Cook, Claire Kehrwald. 1985. Line by Line: How to Improve Your Own Writing . Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Grossman, Ellie. 1997. The Grammatically Correct Handbook: A Lively and Unorthodox Review of Common English for the Linguistically Challenged . New York: Hyperion.
Houghton Mifflin. 1996. The American Heritage Book of English Usage: A Practical and Authoritative Guide to Contemporary English . Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
O’Conner, Patricia. 2010. Woe Is I: The Grammarphobe’s Guide to Better English in Plain English , 3rd ed. New York: Penguin Publishing Group.
Tarshis, Barry. 1998. How to Be Your Own Best Editor: The Toolkit for Everyone Who Writes . New York: Three Rivers Press.
Williams, Joseph, and Joseph Bizup. 2017. Style: Lessons in Clarity and Grace , 12th ed. Boston: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- How to Order
Essay Writing Guide
500 Word Essay
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
11 min read

People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
A Catalog of 370+ Essay Topics for Students
Common Types of Essays - Sub-types and Examples
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
How to Write an Essay Outline in 5 Simple Steps
How to Start an Essay? Tips for an Engaging Start
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
Tips On How to Make an Essay Longer: 15 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay Properly- An Easy Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
A Guide to Writing a Five-Paragraph Essay
How To Write A Strong Body Paragraph
A 500-word essay is a common format assignment that students have to deal with. It is a three-part paper that provides vivid descriptions of an event, object, or phenomenon.
This format of essay writing is very easy if you know the correct techniques to put down your ideas within a specific word limit.
The best way to write an essay in this format is by using specific words and making your ideas flow well. This essay enables you to learn how to be concise but also poses significant essay writing challenges .
In this blog, we will learn about 500-word essays in detail and explore everything about this type of essay format with examples. Keep reading!

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
- 1. What is 500 word Essay?
- 2. 500 Words Essay Format
- 3. How Long is a 500 Word Essay?
- 4. How to Write a 500-word Essay?
- 5. 500 Word Essay Examples
- 6. 500 Word Essay Topics
What is 500 word Essay?
A 500-word essay is a type of academic writing typically assigned in schools and colleges. This type of essay format requires the writer to express their thoughts, ideas, or arguments within a concise word limit.
A typical 500-word essay generally follows 4 to 5 paragraphs essay structure, with each paragraph containing approximately 75 to 200 words. The specific number and length of paragraphs can vary based on the type and structure of the essay.
A 500-word essay can be the easiest and the most difficult one to write, at the same time. It all depends on two things; the Topic and the Writer’s Abilities . Teachers often assign 500-word essay assignments as it can help them quickly assess the student’s critical, analytical, and writing skills.
500 Words Essay Format
Here is the format and structure of a well-crafted 500-word essay.
- Introduction (Approximately 50-75 words)
- Body Paragraphs (2-3 paragraphs, Approximately 150-200 words)
- Counterargument (Optional, Approximately 50-75 words)
- Conclusion (Approximately 50-75 words)
Let's take a closer look at how a 500-word essay is set up and what each part does to make the writing strong and clear.
that introduces the main point of the paragraph. between paragraphs to maintain the essay's coherence.
|
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How Long is a 500 Word Essay?
A 500-word essay is typically one to two pages long, depending on formatting and spacing. For APA style , use a 12-point font for serif (e.g., Times New Roman) and 11-point for sans-serif (e.g., Arial). With double spacing, it will extend to approximately 2 pages, while with single spacing, it usually fits onto 1 page.
How Long Should a 500 Word Essay Take?
Typically, for an average writer, composing a 500-word essay might take around 1 to 2 hours. However, this estimate can vary significantly based on individual factors such as familiarity with the topic, writing experience, and the need for extensive research or revision.
How Many Paragraphs is a 500 Word Essay?
A typical 500-word essay generally comprises 4 to 6 paragraphs. Each paragraph contains roughly 75 to 200 words. However, the exact number and length of paragraphs may vary depending on the essay's type and structure.
Word count is important in short essays. So, it’s best to aim for an introduction under 100 words, body paragraphs around 300 words each, and conclude within 100 words.
500-Word Essay vs. 250-Word Essay
A 500-word essay offers more depth than a 250-word one, allowing for additional detail and evidence. This extra content strengthens arguments or supports viewpoints, making the essay more effective.
500-Word Essay vs. 1000+ Word Essay
A 500-word essay is shorter than a 1000+ word essay. The 500-word one usually fits on one to two pages, while the longer essay can span several pages. With more words, the longer essay allows for a deeper exploration of topics and more detailed arguments. However, both essays require clear organization and effective communication of ideas.
How to Write a 500-word Essay?
Writing a 500-word essay is the same as classic essay writing. Here are some steps to keep in mind while writing a 500-word essay.
- Create an Outline
- Write a Strong Introduction
- Composing The Body Paragraphs
- Write an Impressive Conclusion
Below is a detailed description of each step.
Step 1: Create An Outline
First, make a clear and detailed essay outline , and do not miss anything at this point. It will serve as a backbone for your entire paper.
The purpose of this outline is to break down the ideas in a logical and structured manner.
Step 2: Write A Strong Introduction
The opening paragraph of an essay serves as the reader's initial window into the topic. Grab your reader from the start of this paragraph with an attention-grabbing hook . Make it as interesting and creative as you can so that they don't put down the essay before reading it all!
For writing an essay introduction , you need to introduce your main topic. And give an idea of what the reader may encounter in the rest of the essay. At the end of this paragraph pin your thesis statement .
For Example:
In our increasingly inactive world, where many of us spend long hours sitting in front of screens, the value of regular exercise becomes ever more apparent. Not only does exercise benefit us physically, but it also plays a significant role in promoting mental well-being. This essay aims to explore the various ways in which exercise positively impacts both our bodies and our minds. By shedding light on the transformative effects of exercise on our overall health and vitality, we hope to underscore its importance in maintaining a balanced and fulfilling lifestyle. |
Step 3: Composing The Body Paragraphs
The body section of the essay is mostly divided into 3 paragraphs as discussed above in the format section. It is the point where you need to explain the different types of arguments you make in the essay. Support these arguments with relevant examples, facts, or personal interpretations.
Regular physical activity strengthens muscles and bones, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, and enhances overall physical well-being. For instance, cardiovascular exercises, like jogging or swimming, improve heart health by increasing circulation and reducing the risk of heart disease. A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that individuals who engaged in regular cardiovascular exercise had a significantly lower risk of developing cardiovascular ailments compared to those leading sedentary lifestyles.
Exercise is not only good for the body but also the mind. Engaging in activities like yoga or aerobics triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. This can help alleviate stress, anxiety, and even symptoms of depression. Research published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that regular exercise can be as effective as medication in treating mild to moderate depression.
Furthermore, regular exercise enhances cognitive function by promoting neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to adapt and form new connections. It boosts memory, focus, and overall mental performance. Exercise also increases the production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, benefiting both mental acuity and emotional well-being. |
In a 500-word essay, it's best to stick to one main argument with supporting evidence. Longer essays, such as 1000-word essays , can explore multiple arguments as long as they're connected and contribute to a unified thesis.
Step 4: Write an Impressive Conclusion
Conclusion is the last part of the essay where you need to summarise the main argument of the essay. When writing the conclusion of your essay, begin by restating the thesis statement and explaining it with some strong points analyzed in the body section.
Make sure it does not completely iterate the introduction. Focus on providing critical insight into the main subject of discussion.
For Example:
In conclusion, regular exercise is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. It promotes physical well-being, reduces the risk of diseases, and enhances mental health. Incorporating exercise into your daily routine, even in small doses, can lead to a happier and healthier life. |
Always proofread your essay for mistakes and inconsistencies. Also, make sure the writing convention checklist is followed, as it will give you a clearer idea of what needs to be improved before submitting!
If you still need some guidance, here is a video on how to write a 500-word essay!
500 Word Essay Examples
All 500-word essays follow a different style and structure, making it difficult for a student to understand what their instructor expects. In such scenarios, 500-word essay examples can be of great help.
Below you can find some 500-word essay examples on different topics to better understand the various style formats.
500 Word Essay On Honesty
A 500-word essay on honesty is a commonly assigned task to high school and college students. It simply involves writing on how to develop a practice of speaking the truth always.
Here is an example 500-word essay on honesty that you can refer to for your understanding.
500 Word Essay on Honesty
500 Word Essay On Integrity
Below, you can find a great 500-word essay on integrity written by one of our expert writers for your help.
500 Word Essay On Leadership
Leadership essay discusses the quality of leading people. Get help from the following leadership essay example and learn how you can write on one of the important aspects of life.
500 Word Essay On Punctuality
Punctuality is an important trait that everyone should strive to possess. Take help from this punctual example essay and make your writing even more powerful.
500 Word Essay On Punctuality
500 Word Essay On Responsibility
Responsibility is an important value that everyone should possess. It dictates the way we interact with others and how we carry out our daily lives. Take a look at our example of an essay on responsibility to understand what it means to be responsible.
500 Word Essay On Responsibility
500 Word Essay On Why I Deserve a Scholarship
Writing an essay explaining why you deserve a scholarship can be a challenging experience since students often feel like they’re bragging about themselves. Learn how to write a 500-word essay for scholarship that will make a strong case for your academic excellence with our sample!
500 Word Essay On Why I Deserve a Scholarship Pdf
500 Word Essay on Respect
Respect is a very important concept in today's society. It is an essential component of any successful relationship, both personal and professional. Check out our essay example on Respect to begin learning more about this topic.
500 Word Essay On Respect
500 Word Essay on Why I Want to be a Teacher
Writing essays about something you are passionate about is never an easy task. When it comes to writing about why someone wants to be a teacher, you can always get help from some great sample essays.
500 Word Essay on Why I Want to be a Teacher
500 Word Essay on Why I Want to be a Nurse
Nursing is a passion for a lot of people. If you want to write an essay on why you want to be a nurse, you must look at our sample essay.
500 Word Essay on Why I Want to be a Nurse
500 Word Essay on Global Warming
Global warming is not just an environmental concern but a moral obligation for the well-being of our planet. Write a 500 word essay on global warming with the help of our sample.
Here are some more 500-word essay pdf samples on important topics for your understanding:
500 word essay about myself
500 word essay on corruption
500 word essay on social media
500 word essay on pollution
500 word essay about Islam
500 Word Essay Topics
Here are some topics that you may find interesting.
- Describe your favorite trip.
- Is it possible to earn on the Internet?
- What are the challenges of people living with disabilities?
- How to avoid problems at college.
- What is honesty?
- Abstract art and its impact on people.
- Causes of racism.
- The best day of your life.
- What is the objective of your life?
- What do you mean by punctuality?
If you want to look at more topics, feel free to choose from our interesting list of essay topics .
Wrapping it Up!
Writing essays in a concise 500-word format may seem straightforward, but the process can often be challenging for students. The biggest hurdle? Squeezing in all the essential details while staying within the limit.
If you're feeling overwhelmed or struggling to navigate this task, let MyPerfectWords.com handle it for you.
Our essay writer service is here to transform your academic journey. Whether it's crafting a compelling narrative or refining your arguments, our experts are dedicated to delivering excellence.
Connect now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How many sentences is a 500-word essay.
A 500-word essay typically contains around 5 to 10 sentences per paragraph, spread across 4 to 6 paragraphs.
Can a 500-word essay have 4 paragraphs?
Yes, a 500-word essay can have 4 paragraphs, though it's more commonly structured with 5 or 6 paragraphs.
How many references are needed for a 500-word essay?
The number of references needed for a 500-word essay can vary depending on the topic and requirements, but generally, 2 to 4 references are sufficient for supporting arguments and providing evidence.
Does a 500-word essay have to be exactly 500 words?
Yes, that’s because the general rule for any academic essay is to not exceed the given word count by more than 10%. So applying the same rule, your 500 word essay length should ideally not exceed 10%, that is 550 words, so you should try to wrap up your thoughts within that word count or otherwise risk a negative marking by the professor.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Paper and report design and layout templates
Pen perfect looking papers and reports every time when you start your assignment with a customizable design and layout template. whether you want your paper to pop off the page or you need your report to represent your data in the best light, you'll find the right template for your next paper..

Perfect your papers and reports with customizable templates
Your papers and reports will look as professional and well put together as they sound when you compose them using customizable Word templates . Whether you're writing a research paper for your university course or putting together a high priority presentation , designer-created templates are here to help you get started. First impressions are important, even for papers, and layout can make or break someone's interest in your content. Don't risk it by freestyling, start with a tried-and-true template. Remember, though: Papers and reports don't have to be boring. Professional can still pop. Tweak your favorite layout template to match your unique aesthetic for a grade A package.
How To Write An Essay
500 Word Essay

All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
16 min read
Published on: Mar 10, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
A 500-word essay is a very interesting type of essay writing. Like other academic writing assignments, this type of essay writing is quite often assigned to students at different academic levels.
A 500-word essay tends to polish the writing and analytical skills of a writer. It is not a very extensive composition, but still, it is meaningful and equally important.
This type of essay writing is interesting and very easy to write. You have to be on point, which means that you do not have to do a lot of research and stay focused on your point of view.
A 500-word essay format is one of the easiest formats to follow for essay writing.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a 500-Word Essay?
A 500-word essay is basically an essay with three sections that give clear depictions of an occasion or any item. This type of essay is a common article design that can be followed for composing any sort of exposition, for example, a descriptive essay, an argumentative essay, and so forth.
A 500-word essay is mostly doled out at secondary schools and universities. Almost every other student faces it multiple times throughout academic life. It doesn't have any broad heading, so you can show all your latent capacity by not relying on the subject and theme.
How to Format a 500-Word Essay?
The format of a 500-word essay is very simple and very similar to other types of essay formats. The only thing that makes it different is the essay length.
As the word count for this type of essay is less, thus the length of the paragraphs is also small, and the word count ranges from 75-125 words.
Each paragraph has 3-5 sentences. These sentences must be well-written so that despite being short in length, the sentence can explain its purpose.
Here is a standard format of a 500-word essay that has the following components with examples of each component.
The introduction is responsible for keeping the reader engaged. It provides a brief overview of the overall essay and contains the thesis statement for the essay topic.
It provides background information about your essayâs topic and mentions why you chose this topic in particular.
Also, there is a hook statement in the introduction paragraph. This is a statement that usually is a verse or a famous quotation. It is used as an opening sentence for the essay.
For Example
Cell phones have gone from a desired commodity to an essential item. While these devices offer us easy access to the rest of the world, they can cause problems for educators. High school teachers may be able to ask pupils in their classes to put away their mobiles, but should professors possess similar control over grown men and women? The solution is crafting cell phone usage rules that limit disruptions without impeding student liberties. |
After the introduction, the body of the essay starts. The body paragraphs make the body of an essay. For a 500-word essay, particularly, there are usually 4-6 paragraphs.
Each paragraph discusses a key element and provides the required evidence to give it a logical sense.
Like the body paragraph of any other essay, the paragraphs of the 500-word essay start with a topic sentence. This sentence acts as an introduction to the paragraph.
Each paragraph should end with a transition sentence to show a connection with the upcoming part.
Make sure that such a body paragraph is meaningful yet in a comprehensive form.
Here is a sample body paragraph to help you craft a winning 500-word essay
Continuation of the same examples⦠The principal basis for restricting cell phone use in the classroom is that phones can act as a distraction. Not only do students and teachers become diverted, but this has an analogous impact on someone glancing at their device during a movie screening - even if it's silent, the illuminated display will still divert oneâs focus away from what matters most! When debating mobile phone regulations in the classroom, safety is typically brought to the forefront. Emergencies may happen at any time and students should have their phones with them for peace of mind. Parents' needs come into play too; if a student has children, they could need access to call someone during medical emergencies. Furthermore, if an individual is on standby for work-related matters then having a cell phone accessible would be useful as well - there are endless plausible scenarios that make it difficult not to provide exceptions from these rules! To ensure all students have an opportunity to learn without distraction, the optimal choice is to establish and enforce mobile phone usage rules. With these guidelines in place, pupils should be able to carry their devices with them as long as they remain on silent during class hours. This way, phones are easily accessible for any necessary use but don't interfere with anyone's learning experience. Vibrate settings can be allowed if the instructor feels comfortable with it, as the buzz may not be heard in a crowded classroom. In an emergency situation, students can quickly step out of class to answer their phones. This will create a more relaxed environment for both instructors and students alike. Cell phone restrictions in the classroom should be enforced with clear and specific disciplinary measures for violations. For instance, if a student is caught using their cell phone during class, they can be excused from that day's classes. Professors should avoid seizing control of the device out of consideration for potential liability issues. Itâs safer to request students leave the classroom than take away their phones, as any damages incurred while in a professor's possession could result in liability for repairs on behalf of the school or instructor.
|
A conclusion paragraph is the extract of the whole essay. The writing skills of a writer are judged by the way they conclude an essay.
Writing the conclusion is the most complicated part of essay writing. To write a good conclusion, the writer must logically summarize all the key elements and reiterate the thesis statement.
Whatever is mentioned in the conclusion should give the reader a sense of closure and completion.
Let's continue with the cell phone example for a better understanding of the conclusion phase.
Every educational institution, professor, and student body holds a unique identity. Thus, educational organizations must adjust their regulations to fit the current needs of their scholars. Although prohibiting cell phone use in college courses is excessive, there are other ways to reconcile studentsâ rights with instructors' expectations. Allowing just the right amount of regulation and flexibility within colleges can cultivate an optimal learning atmosphere that ensures maximum safety for its members. |
500 Word Vs. 250 Word Essay
500-word scholarship essays provide you with a significantly greater degree of writing freedom than 250-word ones. When you're given fewer words, it can be tricky to express your views in concise and effective phrases without sacrificing clarity.
With 500 words at hand though, you have ample space to make sure that all the facets of your opinion are expressed - yet don't need footnotes and cited resources as often!
500 Word Essay Vs. 1000 Word Essay
The length of a 500-word essay and a 1000-word essay is quite different.
While a 500-word essay may not require much outside research or citations, it still requires more focus and organization than a 1000-word essay.
A 1000-word essay requires far more time and effort to write than a 500-word essay. Plus, it requires you to be more thorough in your research, analysis, and composition. It will also require you to use a greater degree of critical thinking skills when making arguments.
Additionally, a 1000-word essay may call for the use of outside sources to support points or draw conclusions. Thus, writing a 1000-word essay can be a much more challenging task than writing a 500-word essay.
How Long is a 500-word Essay?
You must be wondering how long exactly a 500-word essay is? As it is a very easy style of composing an essay, so every student prefers to complete it right away and get back to other activities.
One of the interesting facts about this essay type is that it is even shorter than we think. It depends on the formatting style, sizing, and spacing a writer chooses to use. If a writer wants a double-spaced writing format, that is also acceptable for writing such an essay.
To make sure that you write the essay with perfection, understand all the requirements provided by your instructor to compose this type of essay.
500-Word Essay Sample (PDF)

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!

How to Write a 500-word Essay?
Writing a 500-word essay is a very simple task to do. But things might get complicated if you do not follow a standard way of writing.
The following are the steps you should consider while writing a 500-word essay.
Before you start writing an essay, the first thing you should do is to understand the requirements provided by your instructor.
Understanding the requirements will help you to complete your essay without any mess and up to the mark. Proceeding according to the requirements will keep you composed through the essay writing process.
Once you have understood all the requirements, the next step is to think of some interesting ideas. Brainstorming helps you to use the creativity of your mind, especially when it comes to essay writing.
Note down all the elements that you come up with within your mind. Make a rough list of all the ideas and later on organize them to compose an effective essay.
After you have understood all the instructions and spent enough time brainstorming different ideas, it is time you choose a topic.
Always choose a unique and interesting topic. A good topic is highly responsible for making your essay attractive. Also, try that you have selected a topic that is not overdone. An overdone and repetitive topic would make your audience boring.
For a 500-word essay, a topic must be very interesting as you have to make the essay interesting within a very limited word count. Make sure that you choose such a topic about which you can easily collect evidence and facts to support it and make it stronger.
Conducting research on the selected topic is an essential part of essay writing. The research will help you collect all the relevant information that is necessary to make your essay stronger.
Also, researching a topic will make the writing process very smooth for you as you will have all the information that is needed for the essay.
Collect all information only from reliable sources as you donât want to misguide your audience.
The outline is an element of an essay that can save time, make things easy, and earn a better grade.
Just write down all the main features and arguments you want to discuss in your 500-word essay. This will help you to get back on track if you forget the things you wanted to write about.
Moreover, your essay will always be structured and clear, so the audience will read it easily and will follow your thoughts without any challenges.
Since you have your topic and all the information related to the topic thus, you are all set to start writing your essay.
Essay writing starts with writing an introduction. As you are writing an essay of 500 words, an introduction should have only one paragraph. In that paragraph, you should explain the main topic and its importance and also the thesis statement.
After introducing the topic, state the body paragraph, and explain all the key elements in it. Usually, there are three body paragraphs in such essays to explain different key elements.
Donât forget to add transition words, which will make the text smooth and readable. Also, ensure that you use the standard font styles, preferably Arial or Times New Roman.
The same as an introduction, your conclusion should be one paragraph long. Summarize all the key elements in a very precise way and do not add any new points.
Devoting some extra time to proofreading, revision, and editing can make your essay a whole lot better.
This is the simplest thing to do, but most students still skip it and make the biggest mistake. Proofreading ensures that there are no mistakes left behind in your document.
Always make sure that you revise your essay at least once and do the required editing.
Watch this video that shows cases the 5 common mistakes you might make in your 500-word essay writing. Learn how to avoid them to get the desired grade.
500-Word Essay Examples
To understand any type of essay, one needs to look into some good examples. Unfortunately, when it comes to writing a 500-word essay, things become a bit technical for the writer.
To understand the method of writing a good 500-word essay on any topic, look at the following 500-word essay sample pdf examples.
Leadership essays are written to discuss all the qualities of being a leader. Look at the given example and learn how you can write a 500-word essay on leadership
500-Word Essay on Leadership (PDF)
500-word essay writing assignments are often assigned to high school students. If you are a high school and want to see how you can perfectly write such an essay, look at the example given below.
500-Word Essay for High School (PDF)
Our changing environment is an important issue these days. An essay can be composed of different things related to it. The given example is a 500-word essay that discusses the environment in general.
500-Word Essay on the Environment (PDF)
Punctuality is one of the significant qualities of an individual. A well-written 500-word essay on punctuality is mentioned below to help you through.
500-Word Essay on Punctuality (PDF)
Teachers are the backbone of any educational system, and they play an essential role in developing studentsâ skills. However, many students aspiring teachers get confused writing 500-word essays due to their shortened length. Here is an example to help you out.
500 Word Essay on Why I Want to be a Teacher
Writing on nursing topics helps you to develop an understanding of the complexities of this field while also honing critical thinking skills. Below is a 500-word essay that can help future nurses.
500 Word Essay on Why I Want to be a Nurse
Honesty is an important value that must be cultivated in students from a young age. It helps to establish trust between individuals and sets the foundation for strong character development. Below is a 500 word essay on honesty to guide you on how to write on such a theme.
500 Word Essay on Honesty
500-word essay on why I deserve a scholarship is often dreaded among students. These essays require you to shorten yet express a compelling story that can win over the panel. Here is a pdf to help you out.
500 Word Essay On Why I Deserve a Scholarship PDF
Anger management is a difficult topic to tackle. It requires you to find effective solutions and ideas within such a limited word count. Check out the example given below for help.
500 Word Essay on Anger
The Second World War is one of the most important events in human history and its impact can still be felt today. Writing a 500-word essay on this subject requires research, understanding, and war insight. Below is a sample to help you get an idea about how to tackle such a topic.
500 word essay on ww2
Now that you know exactly what a 500 word essay looks like. Continue reading to select the perfect 500-word essay topic.
Great 500-Word Essay Topics
This type of essay is mostly assigned to high school and middle school students. The following are some amazing topics for 500-word essays.
- Difference between Love and passion.
- The love story of Romeo and Juliet.
- Why is there a belief that marriage destroys love?
- A religious aspect of love.
- What is real love?
- Is it possible to make a person truly love somebody?
- The influence of love on a personâs life?
- Why is real love often depicted in fairy tales?
- How to write a 100 words essay in Times New Roman?
- Can animals feel love for their owners?
- The effects of single space formatting in an essay.
- A journey to remember.
- How to prepare for an exam?
- Thoughts on spacecraft?
- How do people earn from the Internet?
- How can money influence people?
- How can disabilities be a challenge?
- Carrying guns by people underage.
- Telling lies is sometimes useful.
- Why is smoking the greatest threat to youngsters?
Writing assignments can be really daunting sometimes. To write an essay perfectly, you need to have strong writing skills and a lot of time to complete it. Instead of being stressed out, the best option is to seek professional help.
At CollegeEssay.org , we have a qualified team of expert writer who can take care of any writing assignment. From writing a good college essay to providing you with the best research paper, we have got you covered.
You can always make the most of AI essay writing tools to refine and enhance your writing skills.
Get in touch with us now and place an order now for your 500-word scholarship essay or any other essay you need. We provide you with the best custom essay writing service and an amazing experience.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
How many pages is a 500 word essay.
A 500-word essay page is approximately one page single-spaced, or two pages double-spaced. This may vary depending on your writing style and font size.Usually time new roman 12 is used. Typically, a 500 word essay will be about one page single or two pages double spaced.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
10 Simple Design Rules for Professional Microsoft Word Documents

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
How a Well-Placed Break Can Tidy Up Your Google Docs
These 6 ai tools give you real job interview practice, 5 must-have free chrome extensions i rely on as a student.
Microsoft Word is packed with so many features that you can produce pretty much whatever you want with it. But these features don't always result in the kind of beautiful, high-quality, and professional document designs that you may expect.
It's one thing to know everything about Microsoft Word, all of its intricacies and quirks and functions—it's something else entirely to know what makes a great document. Here, we'll show you how to format a Word document to make it look professional.
1. Keep It Simple, Less Is More
Want to know how to make a Word document look good? Just keep it simple, and take advantage of the hidden features that Microsoft Word comes with. If you remember one thing from this article, let it be this, and you'll be able to make the right design decisions in the future!
When writing a document, the content should be the main focus. Document formatting guidelines exist to make that content easier to read and digest.
Eliminate the temptation to introduce eye-catching elements that only serve to distract. Maximize whitespace. Keep your wording tight and revise any wordy sentences or paragraphs. Simple and minimal rules overall.
2. Choose a Context-Appropriate Typeface

Your first big design decision should be which typeface you're going to use. Traditional knowledge says that serif fonts are easier to read in printed documents, whereas sans-serif fonts are better on the eyes when read on a digital screen.
Good examples of serif fonts include Garamond, Georgia, Hoefler Text, and Palatino, while good examples of sans-serif fonts include Arial, Gill Sans, Helvetica, and Lucida Sans.
Skip Comic Sans if you want to avoid one of the most common presentation design mistakes . And whatever you end up using, stick to the same typeface throughout to make your Word document professional. If desired, you can use a different typeface for headings.
3. Use Standard Font Size and Color
You can't learn how to format a word document to look professional without paying attention to the look of the text. Business and academic papers generally use 12-point font sizes, which produce the most readable paragraphs when used in combination with the guidelines discussed below for page size, margins, and line spacing.
Some information-dense reports may sometimes go down to 10-point font size, but never less than that.
In general, it's best to keep your hands off of anything related to colors, especially for printed documents. You'll have to pay more for the color ink, and it won't carry over if the document ever gets copied. For digital documents, reserve colored text for critical warnings and the like. Prefer to emphasize using bolded and italic text.
4. Use Standard Page Size and Margins
Nearly all office documents are formatted to the same page size as they are printed for standard 8½" x 11" pages, known as US Letter size (also known as A4 elsewhere, which is 210mm x 297mm). This is the only size that's guaranteed to be available regardless of which printer you use.
As for margins, most style manuals and style guides call for a 1" margin on all sides of the page, which produces the best readability for line lengths and allows for written annotations if necessary. In Word, you can select Normal under Margins to do so. However, if the document is going to be bound in a binder, you may want to use Custom Margins to increase the side margins to 1½" to accommodate the rings.
5. Align Paragraphs to the Left
You may be tempted to use justified alignment because that's what's used in newspapers, novels, and some textbooks, but it's the wrong choice for office and academic documents. Why is it important to make a document formal? Without formality, your document becomes unreadable.
What you want is left alignment for text. This produces jaggedness on the right side of paragraphs, but it keeps letter spacing as intended by whatever typeface you're using, and that means optimal legibility.
Otherwise, you may end up with typographic rivers , which are extremely distracting and simply look ugly. This is something you certainly want to avoid when you want to make your Word document look professional.
6. Indent the First Lines of Paragraphs
Paragraphs should have no extra spacing between them, and the first lines of paragraphs should be indented to make each paragraph stand out. The only exception is for paragraphs that directly follow a section heading, which can be left unindented because the surrounding context makes it clear that it's its own paragraph.
To make a document look professional, a general rule of thumb is to have the indent size the same as the font size. Make sure you use Word's paragraph styling features to handle the indents rather than using the Tab key!
7. Place Images Between Paragraphs
Inserting images is a part of designing your Word document. It may be okay to place images inside a paragraph and allow the surrounding text to flow around it, and if your organization follows this document formatting guideline, then go ahead and do that.
But generally speaking, it can damage readability, especially in data-driven reports. The safest option, particularly for graphs, charts, and tables, is to put images in between paragraphs and keep them center aligned. That way, your images help to make your document attractive, but they are never vying for attention with the surrounding text. It also helps captions to stand out.
8. Choose Context-Appropriate Line Spacing
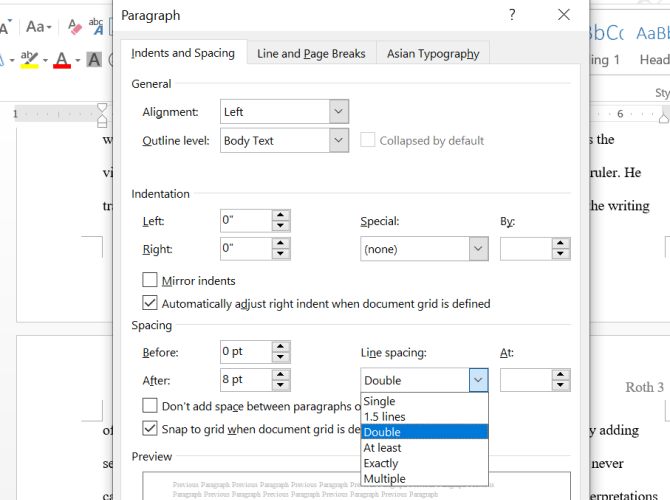
To format a document to look professional, the right choice for line spacing (the whitespace that separates a line of text from the next line of text) really depends on what kind of document you're writing.
Academic papers should first follow any academic style guides in place, then prefer double-spacing if no style guide exists. Business and office documents tend to be single-spaced to minimize the number of pages needed when printing, but digital documents may be easier to read if spaced at somewhere between 120-150 percent.
9. Break Up Text With Headings and Lists
The longer the document, the more important headings become. Would you rather read a 20-page report that's nothing but a wall of text from end to end? Or a 30-page report that's organized into proper sections, subsections, and headings? It’s highly likely you’ll prefer the latter.
Lists are also good for breaking up walls of text and drawing eyes to important points. In Word, use Numbering to create numbered lists when counting a set of items (e.g., "the five attributes of a successful entrepreneur") or when providing step-by-step instructions. Otherwise, use Bullets to make bulleted lists .
Just be sure to avoid overusing lists, which detracts readability from your Word document design. This is especially important when it comes to using Word to format a screenplay .
10. Separate Sections With Breaks
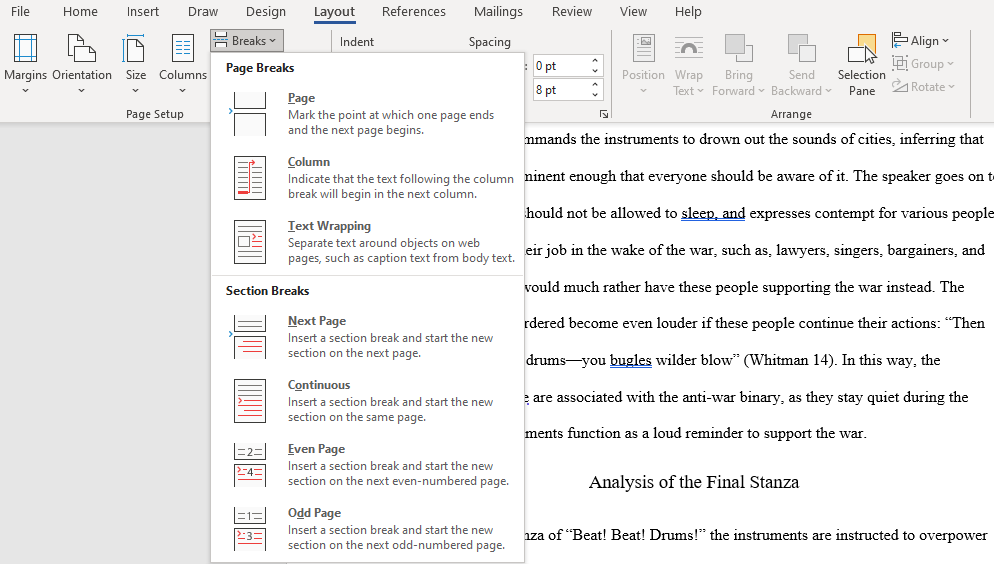
When you want to learn how to make your report look professional, you need to get acquainted with section breaks. In Microsoft Word, section breaks allow you to differentiate certain pages with changes in orientation, columns, headers, footers, page numbers, and more. Section breaks come in four forms:
- Next Page: Start the next section on the following page.
- Continuous: Start the next section on the current page.
- Even Page: Start the next section on the next even page.
- Odd Page: Start the next section on the next even page.
If your document is large enough to need chapters, this is the best way to format them in a clean way. Each chapter should be made with a Next Page section break, or the Even Page or Odd Page section breaks if you're going to place it within a binder. We've shown how to remove page breaks if needed, too.
Learn How to Format a Word Document to Look Professional
Unless your organization or school requires a specific layout and format, you can skip the hard work of setting up your own template and just download one instead. This helps you quickly achieve a professional document design.
- Productivity
- Digital Document
- Microsoft Word
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Create a document Article
- Save your document to OneDrive Article
- Design and edit Article
- Collaborate Article
- Set up your mobile apps Article
- Learn more Article

Design and edit
Design and edit in word.
Styles templates apply a consistent font, font size, font color, and spacing to headings, paragraphs, and titling throughout your document.
Select the words, paragraph, list or table to edit.
On the Home tab, select a style.

Apply Themes
Themes add a professional look to your document.
Select Design > Themes .
Point to a theme to preview how it will look.
Select the theme you want.

Check spelling and grammar
Word marks misspelled words with a red squiggly underline and grammar mistakes with a blue double underline.
Right-click the word.
Select a correction, or select Ignore .
Note: Spelling and grammar check work a little differently in newer versions of Word and Microsoft 365. For more, see Editor - your writing assistant .
Find and replace text
Select Home > Replace .
For Find what , enter a word or phrase to search. For Replace with , enter the new text.
Select Find next , and then select:
Replace to replace the first instance, or
Replace all to replace all instances.
Next: Collaborate in Word

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
How-To Geek
Everything you need to know about microsoft word's styles.

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Quick Links
Why use styles, before you start, view all styles in word, modify a style for your purpose, create a new style, use existing text to define a style, power user tips.
Styles are to Microsoft Word what gridlines are to Microsoft Excel—you can't have a fully functioning file without having them. They save time, help you to cut out bad Microsoft Word habits, and secure your document's structure. Let's look into what they are, what they do, and how to use them.
Whether you apply them to headings, captions, or the main body of your document, styles define how your text is formatted, spaced, and positioned. Using styles has several benefits:
- They're a time-saver —Instead of manually reformatting your headings and paragraphs, assigning styles to your work means that you can repeat layouts with just a single click.
- They aid consistency —Not only does using styles mean that your text layout is consistent, but you can change the formatting of large volumes of your work at the same time.
- Certain styles have quirky benefits —For example, text assigned to a heading style automatically stays next to the corresponding text and can be used in tables of contents.
The default style is Normal, which is used for the main body of a Word document. Any text that contains formatting that differs from the Normal style should have its own style name.
While you can view a paragraph's style by clicking any word within that section and seeing which style is selected in the Style Gallery in the Home tab, a much easier way to see them in action is to use Word's Draft View. Open the "View" tab on the ribbon, and click "Draft." You will then see the Style Area Pane on the left of your document.
Once you've finished organizing your styles, click "Print Layout" to return to a more familiar view.
If you still can't see the Style Area Pane, click File > Options to launch the Word Options dialog box, and click "Advanced" in the left-hand-side menu. Then, scroll down to find the Display options, set the Style Area Pane Width to 5 cm or 2 in , and click "OK."
Styles are set to paragraphs. Each time you press Enter, you create a new paragraph, so this is the opportunity to set a new style or continue using the same one. To amend a style, you don't need to select the whole paragraph—simply place your cursor anywhere within the paragraph, and press Ctrl+Shift+S. This will launch the Apply Styles dialog box.
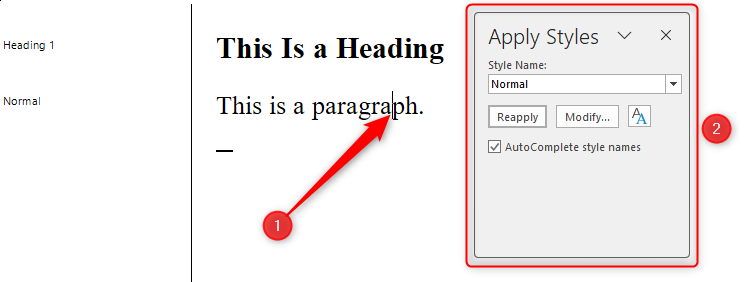
When working with styles and paragraphs, it's always advisable to display paragraph markers. Click "Show/Hide" (¶) in the Paragraph group of the Home tab to do this.
The Style Gallery in the Home tab is intended to give you quick access to the styles you use more frequently. However, to see more, click the icon in the bottom-right corner of the Styles Gallery or, if you have enough fingers, press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S—this will launch the Style Pane.
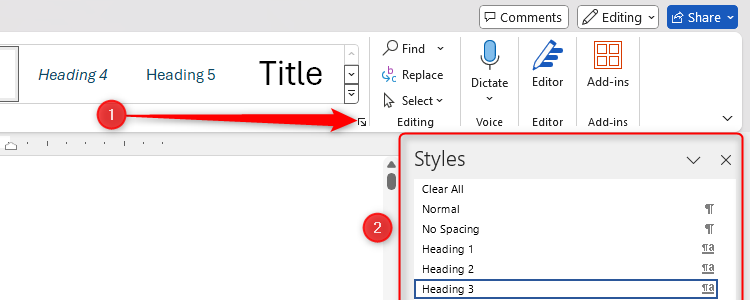
Next, click "Options" to launch the Style Pane Options dialog box, where you can choose from the "Select Styles To Show" options to define what you see in the Style Pane. Clicking "All Styles" will bring up all the default options you can use. Click "OK" when you've decided what you want to display.
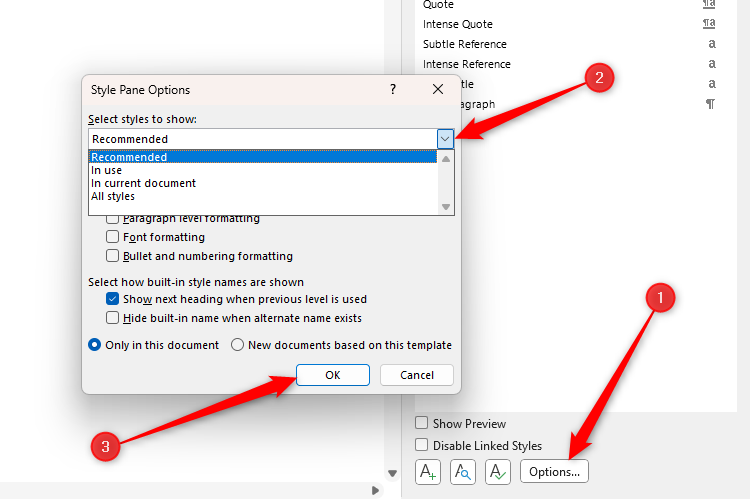
Right-clicking a style in the Style Pane will give you the option to add or remove it from the Style Gallery.
Many people are put off by how the preset styles appear in the Style Gallery, but they're easy to amend to suit your needs.
To modify a style, either place your cursor within the text assigned to that particular style and press Ctrl+Shift+S, or right-click a style in the Style Gallery in the Home tab on the ribbon. Whichever method you use, you'll then have the option to click "Modify."
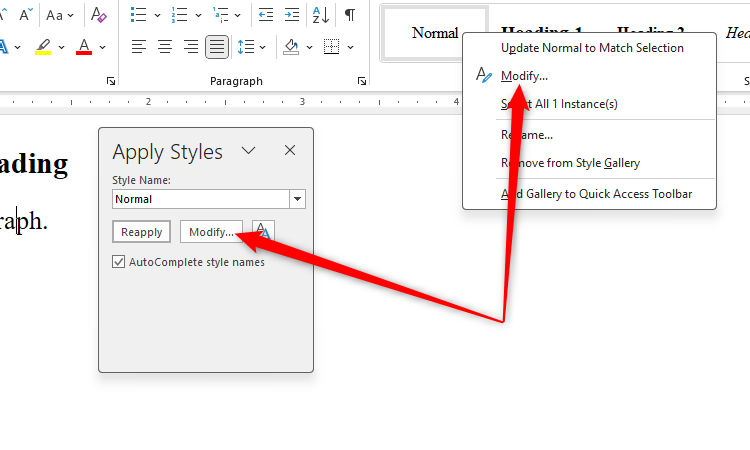
When the Modify Style dialog box opens, click "Format" to see the different elements of this style you can modify.
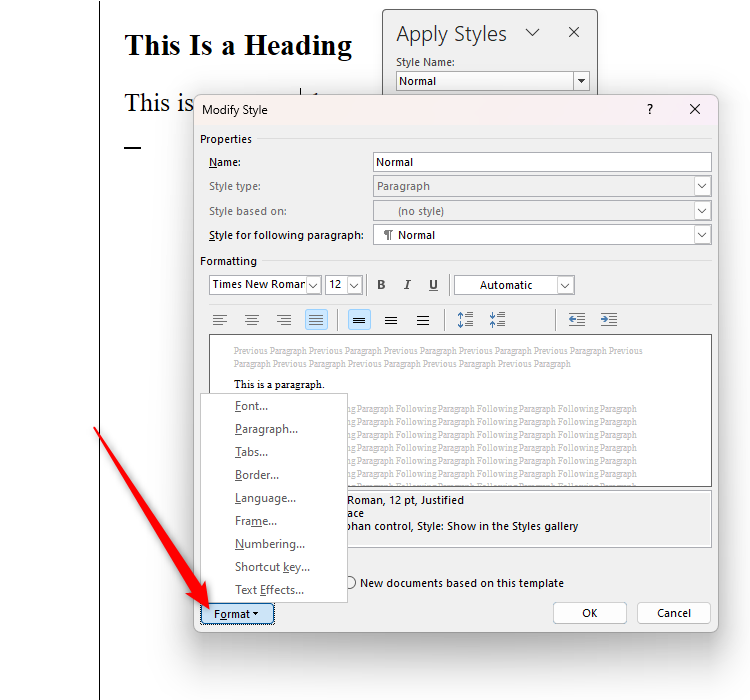
- Font —Here, you can change the font typeface, size, and color, as well as other formatting options, such as underlining, bold, and all caps. For more options—such as font character spacing—click the "Advanced" tab.
- Paragraph —This option is the place to go if you want to amend the spacing between lines and paragraphs, or add a consistent indentation to this style. You can also go to the "Lines And Page Breaks" tab to tell Word to keep lines in this style together or keep text in this style directly next to the following paragraph.
- Tabs —Linked to the Paragraph options, Tabs lets you add tab stops to the ruler whenever you use the chosen style.
- Border —You can force Word to add borders or shading anytime you use the selected style.
- Language —This is a great option if you're typing in more than one language in a document. Whenever you use this style, Microsoft Editor will automatically switch to check for spelling and punctuation errors in the specified language.
- Frame —Here, you can add invisible borders to your style so that the text fits into a smaller space.
- Numbering —If a certain style repeatedly contains lists within your document, you can decide on the bullet and numbering formatting using the Numbering settings.
- Shortcut Key —If you find yourself becoming tired of clicking in the Style Gallery, you can assign a shortcut key to a style to quickly apply it to a given paragraph.
- Text Effects —For a more artistic style, you can adjust the effects applied to the text. However, I'd recommend that you don't do this, as it can significantly reduce the credibility and formality of your work.
Remember, when you click "OK," all paragraphs assigned to this style will adjust according to any changes you make.
Press Enter at the end of any paragraph to move to the next paragraph and revert to the Normal style. However, don't press Enter repeatedly to create a larger gap between paragraphs—instead, amend the Space After value in the Paragraph section of the Modify Style dialog box.
As well as modifying and using existing styles in Word, you can create your own. The best way to do this is to first type and format text manually using the Font and Paragraph groups in the Home tab on the ribbon.
In this example, after selecting the whole paragraph, I clicked "Bold" and "Italics," as well as changing the font size to 28 pt and the font color to red. I also clicked the Paragraph dialog box launcher and changed the Space After to 24 pt.
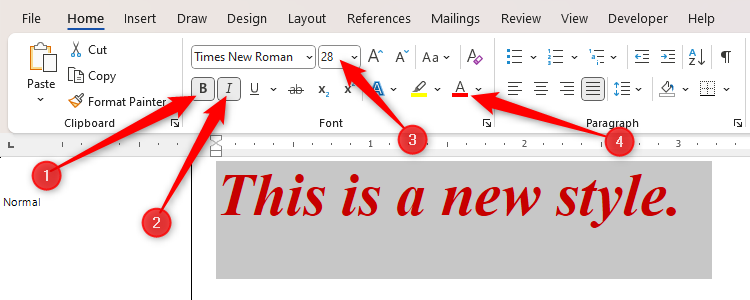
You'll see that the Style Area Pane still displays this newly formatted font as being in the Normal style. Don't worry—as you're applying formatting manually here, it won't affect existing styles in your document.
Now, with your cursor anywhere within that new paragraph, press Ctrl+Alt+S, name your new style, and click "New."
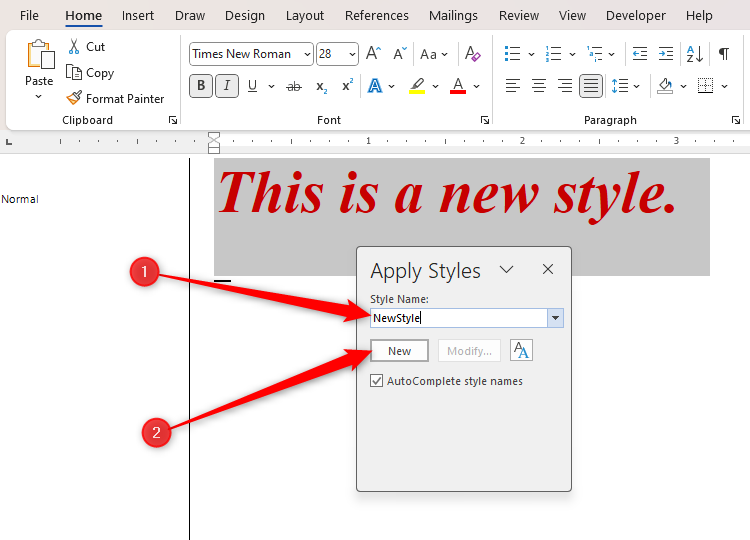
You will then see the Style Area Pane and Style Gallery reflect the addition of this new style.
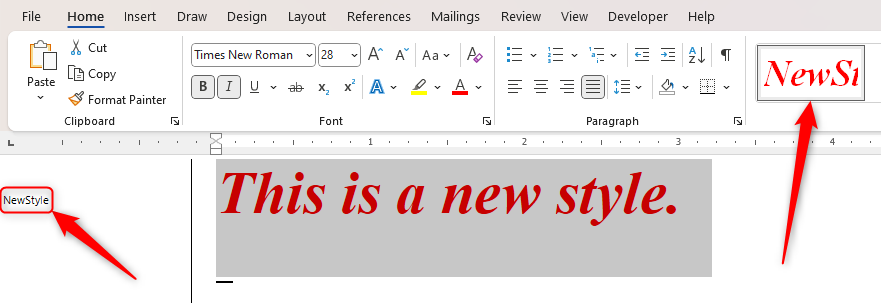
You can use a similar method to apply manual formatting to an existing style name or copy an existing style's properties to another style name.
Place your cursor within some text you have formatted manually, and head to the Style Gallery in the Home tab on the ribbon. There, right-click the style you want to modify to match this text, and click "Update [Style Name] To Match Selection."
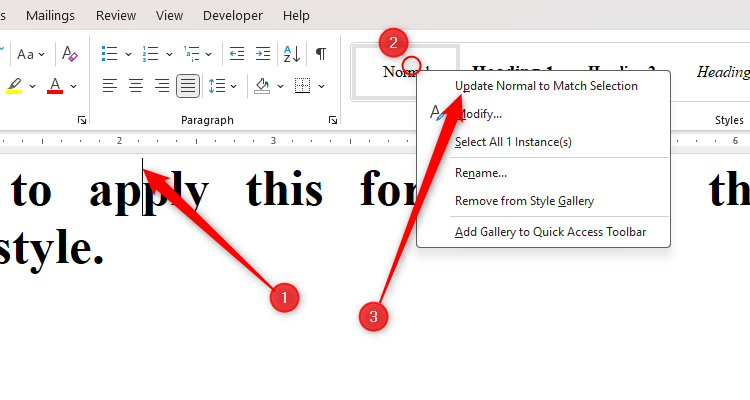
You will then see the Style Gallery update to display the new formatting for that style. You might also see the other styles change within the Style Gallery, as Microsoft Word wants to help you keep your font sizes consistent.
You can easily get by with Word's styles using the tips in the previous sections of this article. However, knowing the following will help you to use and implement Word's styles even more effectively:
- You can copy styles between Word documents if you're working on two related pieces.
- Once you have modified the styles or created your own to suit your preferences or match your client's style guide, save your Word document as a template , so that you don't have to recreate them each time.
- While styles are usually reserved for differentiating between different paragraph types—such as body text or headings—you can add a style separator to use more than one style within a single paragraph.
Now that you know that it's better to use styles than formatting paragraphs and headings individually, check out some other tips to avoid making mistakes in Word that would inevitably lead to issues down the line.
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft 365
MS Word Cover Page Templates
Download, personalize & print, cover pages for essay.
Posted By: admin 30/07/2019
The cover page for the essay is, usually, its first page, which is also referred to as the title page. It presents the basic information about the essay content and the author or authors as well as helps in creating the interest of the reader.
When a professional essay is being written, the cover page holds great significance due to many reasons, and hence require enough consideration.
- It serves as a marketing and promotional tool for the author, so it should be prepared carefully with the right emphasis on the author’s credentials and skills.
- It is the first page that a reader, usually, glances at. Therefore, if it is attractive enough, the reader might get pushed to look at the complete essay.
- What the essay is all about.
- If he is interested in the essay.
- The font, colors, images, etc., should match with the essay topic and content. For instance, if it is a serious topic, like the Kashmir issue, the use of bright colors on the cover page may not be suitable.
- Chicago style.
There are many templates available online and in programs, such as Microsoft Word, for making cover pages for essays. At the same time, the individual can even design the cover page himself from scratch, as well. However, in the former option, time and effort get saved, as the templates have been professionally developed and are easily usable and customizable.
The author can choose the details to be included on the cover page, as long as the rules of the selected formatting style get followed. The general details included are:
- Running head (not in all formats).
- Topic or title.
- The subtitle, if any.
- Name of author.
- The course of the author, if applicable.
- School, university or institute of the author.
- Any other details of the author, if required.
- Name of the person to which the essay is being submitted.
- Date of submission.
Based on the formatting style, few of the above-mentioned details may or may not be provided on the cover page of the essay. In addition, the sequence of the information on the cover page also varies with the formatting style used.
If the rules of the formatting style have been properly followed and the cover page has been designed professionally and attractively, it would certainly improve the value of the essay in the eyes of the reader, which will, in turn, increase the worth of the essay author or authors.
Be the first to comment on "Cover Pages for Essay"
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to Use Styles in Word: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
How to use styles in word.
Want to make your Word documents look more professional and easier to read? Using styles in Word is the way to go. Styles allow you to apply consistent formatting across your document with just a few clicks. Here’s a simple guide to get you started.
Using styles in Word will organize and beautify your document with consistent formatting, making it easier to read and navigate.
Step 1: Open Your Document
First, open the Word document you want to format.
Once your document is open, you can start applying styles to the text. Make sure you have the Home tab selected, as that’s where you’ll find the styles menu.
Step 2: Select the Text
Next, highlight the text you want to format.
This can be a heading, a paragraph, or even a single word. Just click and drag your mouse over the text, or use your keyboard to select it.
Step 3: Choose a Style
In the Home tab, go to the Styles group and choose the style you want to apply.
You’ll see options like Heading 1, Heading 2, and Normal. Click on the style that suits your needs. Your selected text will instantly update with the new format.
Step 4: Modify a Style (Optional)
If you want to customize a style, right-click on it and select Modify.
This will open a dialog box where you can change things like font, size, color, and alignment. Once you’re satisfied, click OK to save your changes.
Step 5: Apply Styles Throughout the Document
Repeat steps 2-4 for other sections of your document.
Applying consistent styles to all headings, subheadings, and body text will make your document look polished and professional.
After completing these steps, your document will have a consistent and professional appearance. Each section will be clearly defined, making it easier for readers to follow along.
Tips for Using Styles in Word
- Always start with a clean, unformatted document to avoid conflicts with existing formatting.
- Use Heading 1 for main sections, Heading 2 for subsections, and so on.
- Create custom styles for specific needs, like quotations or code snippets.
- Make use of the Styles Pane for a visual overview of all the styles used in your document.
- Save your custom styles in a template for future use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are styles in word.
Styles are predefined sets of formatting options that you can apply to text to ensure consistency throughout your document.
How do I create a custom style?
Right-click in the Styles group and select "New Style." Customize the settings and click OK to save.
Can I apply multiple styles to one piece of text?
No, each piece of text can only have one style applied at a time.
How do I remove a style from text?
Highlight the text and select the "Normal" style to remove any custom formatting.
Why should I use styles instead of manual formatting?
Styles save time and ensure consistency, making your document look more professional and easier to navigate.
- Open your document.
- Select the text.
- Choose a style.
- Modify a style (optional).
- Apply styles throughout the document.
Using styles in Word is a game-changer for anyone who wants to create professional-looking documents quickly and efficiently. Not only does it save you time, but it also ensures that your formatting is consistent throughout the entire document. This can be particularly helpful when you’re working on long reports, essays, or any form of content that requires a clear structure.
So, why not give it a try? Open up Word, play around with the styles, and see how much easier it makes your life. Once you get the hang of it, you’ll wonder how you ever managed without them. For further reading, you might want to check out Microsoft’s official guide on using styles in Word. Happy formatting!

Kermit Matthews is a freelance writer based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania with more than a decade of experience writing technology guides. He has a Bachelor’s and Master’s degree in Computer Science and has spent much of his professional career in IT management.
He specializes in writing content about iPhones, Android devices, Microsoft Office, and many other popular applications and devices.
Read his full bio here .
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- How to Curve Text in Word for Office 365
- How to Format Word Document Automatically: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Change Bitmoji Style on iPhone 14: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Add a Heading to an Outline in Google Docs
- How to Add a Heading in Google Docs
- How to Use Microsoft Word 2007: A Comprehensive Guide
- Step-by-Step Guide: Saving Word Docs on Mac
- How to Use and Insert WordArt in Microsoft Word: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Rotate Text in Word 365
- How to Download a Microsoft Word Document on Mac: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Step-by-Step Guide to Removing Page Borders in Word 365
- How to Show Invisibles & Formatting Marks in Google Docs: A Guide
- How to Remove Section Breaks in Word Documents
- How to Get Out of Compatibility Mode in MS Word: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Open a PDF in Microsoft Word: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Save a Microsoft Word Document: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Use Microsoft Word: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- Creating Graphs in Word for Office 365: A Guide
- How to Do a Google Docs Hanging Indent
- Securing Your Word Document with Password Protection
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, design – the visual language that shapes our world.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley
Design refers to much more than how something looks or works: Design is a powerful tool of communication that empowers writers, graphic designers, and product developers to reach their target audience at a viscera, visual level. Good design makes information easier to understand, more engaging, and more memorable. It creates emotional connections, influences perceptions, and shapes decisions. If your design is unappealing or confusing, you've lost your chance at engaging your audience in the 8 seconds they're willing to give attention to your work. The essay below defines design based on research and scholarship, explores the importance of design in our contemporary information ecology, and serves as an introduction to design resources @ Writing Commons.

What is Design?
Design , most conventionally, refers to how something looks or works . For instance, by any measure, the Apple iPhone is well designed: the colors it displays are brilliant; it fits in your pocket; it’s easy to use as a camera, a recording device, or phone; and it provides easy access to friends, music, and the internet.
Yet, design may refer to more than whether or not a text or product looks good or accomplishes its aims . For instance, d esign may also be defined as
- a social construct
- a form of visual language , a mode of human communication
- a signifier of identity and community
- a subject of study, an academic discipline, a catechism regarding usr, an interpretative framework , based on principles of design .
Related Concepts: Composition ; Composing Processes ; Design Thinking ; Gestalt ; Information Architecture ; Information Design ; Semiotics
Definitions of Design
1. design refers to how a text, application, or product looks or works.
“ Design is a fun word. Some people think design means how it looks. But of course, if you dig deeper, it’s really how it works.” Steve Jobs
Design refers to the aesthetics and functionality of a text , application, or product—concepts often encapsulated under the banner of “look and feel.”
Aesthetics (Look):
This dimension of design involves the visual, tactile, and sometimes auditory elements of a product or system. It encompasses attributes such as color , shape , texture , typography , and layout . In terms of a digital application, for example, the choice of icons , the color scheme , typography , and the overall user interface (UI) fall under aesthetic considerations. These elements contribute to the overall visual appeal and user experience.
Functionality (Works):
This refers to the operational aspect of a design. It involves how well the product, application, or system serves its intended purpose. The functionality of a design is often evaluated based on its efficiency, effectiveness, and ease of use. In the case of a digital application, it would include aspects like navigation flow, load times, responsiveness, and overall usability.
In essence, the balance between aesthetics and functionality is key in design. A design that excels in both dimensions creates an engaging, user-friendly, and effective product or system. This outlook is crucial in fields like product design, web design, graphic design, and user experience (UX) design, among others.
For writers, d esign largely concerns
- the use of data visualizations and other elements of design and visual language
- the page design & scannability of a text .
2. Design is a Social, Historical Construct
Design, a social and historical construct, stands at the intersection of art, culture, history, and technology. It serves as a mirror to our collective intellect, reflecting our beliefs, history, and advancements. Each culture, each epoch has its unique interpretation and manifestation of design, thus weaving a rich, multifaceted tapestry of human creativity and evolution.
Art and Culture
Art and cultural norms seep deep into the core of design, infusing it with distinctive colors and patterns. Take, for example, the traditional Mexican design. Its bright geometric patterns symbolize the nation’s vibrant culture and rich historical narratives. It’s a testament to the cultural sensibilities that pervade design.
But look closer, and you see a paradox: despite periods of hardship and scarcity, Mexican people devoted resources to create opulent gold temples and intricate religious artifacts for the Catholic Church. This underscores design’s role as a reflection of cultural priorities and beliefs, sometimes extending beyond immediate practical needs.
Design reflects the dialogues , epistemologies , and circumstances of particular cultures and specific time periods. Consider, e.g., in the heart of the desert, the ancient Egyptians designed pyramids and temples that continue to astound us millennia later. These structures, built with an extraordinary precision that baffles modern engineers, stand as a testament to the design sensibilities of a civilization that existed over 4,000 years ago. Their hieroglyphic scripts and symbolic art formed a design language that communicated spiritual beliefs and pharaonic authority.
Fast forward to the Victorian era, characterized by its industrial growth and prosperity, and you see a markedly different design narrative. The Victorian designs embraced opulence and ornamentation, with an emphasis on detailing and a penchant for grandeur. This was reflected in their architecture, fashion, and even their typography.
In stark contrast, the 21st century has been marked by a shift towards minimalism in design. Embodying the mantra ‘less is more,’ modern design trends advocate simplicity and functionality. From the sleek lines of contemporary architecture to the user-friendly design of digital interfaces, the present-day design ethos emphasizes usability and clarity .
3. Design is a Form of Visual Language
Design refers to much more than how something looks or works. Design, at its core, is a sophisticated form of visual language . More than just aesthetically pleasing arrangements of elements, it holds the power to communicate, provoke thought, and stir emotions.
This communication occurs at a fundamental, prelinguistic level–as a form of felt sense . While conventional languages use words and syntax to convey meaning, design communicates through a rich vocabulary of visual elements: lines, shapes, colors, spaces, and typography. These elements are arranged using principles like alignment, balance, and contrast to create a cohesive visual message.
When the audience interacts with a design, they are not just passively observing. They are actively ‘reading’ these visual elements and interpreting them. This interpretation often happens instinctively, tapping into our innate human capacity for visual perception. We are, as a species, highly attuned to visual information. Our brains are wired to recognize patterns, discern contrasts, and respond to visual stimuli.
Audiences read the design of a text or product just as they read words and sentences . Yet rather than words or sentences , they read design elements : They trace the line on the page or screen. They note the images, colors , shapes , contrast , spaces , and typography of the copy . They consider the alignment , balance , proximity , repetition of symbols. And then they interpret these symbolic elements to mean something. Their interpretation may be experienced as a form of felt sense of gestalt . In other words, they engage in acts of communication .
4. Design May Function as a Signifier of Identity and Community
In business, companies spend small fortunes defining their brand. They aim to distinguish their products and services. Thus, it’s fairly commonplace for business and nonprofit organizations to have style guidelines.
Typically style guidelines
- call for standard written English
- call for a professional writing style
- call for a particular citation style
- define logo, color, and photo-usage guidelines.
5. Design May Refer to a Curriculum, a Catechism, a Subject of Study
Design is an extraordinarily broad field, a convergence point where disciplines such as arts, engineering, sciences, and humanities intersect and engage in a dynamic discourse . Its interdisciplinary nature stems from the fact that design problems often require diverse perspectives and multi-faceted solutions. Hence, design isn’t just about aesthetics or usability; it’s about crafting solutions that reconcile functionality, sustainability, social impact, and user experience.
In academic settings, design manifests as a robust field of study, encompassing a broad spectrum of topics, including
- accommodation s(how designs cater to different user needs)
- aesthetics (the principles that guide visual harmony and appeal)
- information architecture (how information is organized and structured in a design),
- information design (how information is presented)
- usability (how user-friendly a design is).
Communities of Practice: Shaping the Design Landscape
Alongside academia, communities of practice contribute significantly to the evolution of design as a field. These communities, composed of practitioners and scholars, engage in rigorous scholarship and empirical research. Their primary objective is to enhance clarity in communication and improve design outcomes.
These communities continually shape the design landscape through the development of conventions and best practices. They respond dynamically to technological advancements and societal shifts, adapting design practices to better fit new paradigms. This iterative process of exploration, adaptation, and refinement is what keeps design relevant and effective in a rapidly changing world.
Through this ongoing conversation of humankind and the ever-evolving technological landscape, design continues to evolve, offering innovative solutions to both old and new problems. This is a testament to design’s versatile nature and its inherent capacity to adapt, innovate, and inspire.
Related Concepts
Writers, designers, and usability experts design texts and products by composing with design elements (e.g., Color – Color Theory ; Line ; Shape ; Space ; Typography ). Additionally, they consult their knowledge of design principles — (e.g., alignment ; balance ; color ; Contrast ; Emphasis ; Gestalt, Gestalt Theory ; Proximity ; Repetition ) in order to inform their compositions.
Recommended Books on Design
- Cooper, A., Reimann, R., Cronin, D., & Noessel, C. (2014). About face: The essentials of interaction design (4th ed.). Wiley.
- Krug, S. (2013). Don’t make me think, revisited: A common sense approach to web usability (3rd ed.). New Riders.
- Norman, D. (2013). The design of everyday things: Revised and expanded edition . Basic Books.
- Williams, R. (2014). Non-designer’s design book (4th ed.). Peachpit Press.
Why does design matter?
In 2023, we’re living in a world where attention spans are shrinking, digital content is proliferating, and consumer expectations are escalating. The average person spent around 6 hours and 42 minutes online every day, and this time is scattered across various platforms – social media, news sites, video streaming, online shopping, and much more. The explosion of digital content means people are inundated with information, choices, and distractions, making it harder than ever to stand out. In this context, excellent design isn’t just nice to have – it’s a necessary tool for survival. It’s a way to respect your audience’s time, to reward their attention, and to rise above the noise.
Related Articles:
Data Visualization - Information Visualization - The Art of Visualizing Meaning For Better Decision-Making

Design Principles - The Big Design Principles You Need to Know to Create Compelling Messages

Elements of Art - How to Leverage the Power of Art to Make Visually Compelling Documents
Elements of design – master the fundamentals of visual composition.

Page Design - How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Universal design principles - how to design for everyone.

Usability - How to Research & Improve Usability
Visual representation, recommended.

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
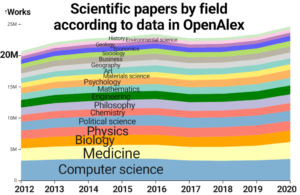
Review research and theory on the information visualization. Unlock the power of data visualization to make complex data accessible and engaging. Learn the art and science of transforming numbers into...

- Joseph M. Moxley
Principles of design refer to the discourse conventions, artistic traditions, and theories that inform the design of messages, products, and services. P.A.R.C. refers to the four primary design principles (proximity,...

The Elements of Art (also known as The Elements of Design) refers to color, form, line, shape, space, texture, and value. Working as a gestalt that communicates with audiences at...

Page design refers to the strategic placement of information on a page or digital screen: Good page design can help you hook your readers’ curiosity and improve readability. Good page...
Universal design focuses on all potential users’ needs, abilities, and limitations. Rather than target a narrow user/customer segment, universal design values inclusivity: designers practicing universal design aim to make their...

Usability refers to the ease with which audiences can accurately interpret your message, understand your purpose, and navigate your information architecture. Whether you’re writing an essay, a research paper, or...
Featured Articles

Pictionary Word Generator
Start generating pictionary word for free below.
If you need help, please refer to the detailed step-by-step instructions entitled below.
Write about
Generate pictionary word in these simple steps.
Enter topic
Select language, tone and word count
Click on the Generate button
Revamp Game Night with WriteCream’s Instant Pictionary Words!
Introducing WriteCream’s Pictionary Word Generator, a versatile tool designed to simplify the selection of Pictionary words with just a single click. Whether you’re hosting a game night with friends, organizing a team-building activity, or looking to spark creativity in classrooms, this generator offers a wide array of words suitable for all ages and settings. Powered by intuitive algorithms, it ensures that each generated word is stimulating, easy to illustrate, and guarantees hours of fun and laughter. With WriteCream’s Pictionary Word Generator, creating memorable moments and fostering creativity has never been easier.
How It Works:
1. Input Selection: Choose from various categories or themes such as “Easy,” “Medium,” or “Hard,” depending on the difficulty level desired.
2. Algorithmic Selection: Utilizes algorithms to randomly select appropriate words within the chosen category or theme.
3. Immediate Generation: Generates a single word instantly with a click of a button, eliminating the need for manual word selection.
4. Versatility: Suitable for diverse settings including parties, classrooms, and virtual gatherings, providing words that are engaging and easy to draw.
5. Customization Options: Allows users to adjust settings or categories to better fit specific preferences or game requirements, enhancing flexibility and enjoyment.
Key Features:
1. Ease of Use: Quickly generate Pictionary words with a single click, making game preparation effortless.
2. Diverse Categories: Offers a variety of categories such as “Objects,” “Actions,” and “Animals,” catering to different game preferences and player ages.
3. Randomization: Utilizes random selection algorithms to ensure each word is unique and unpredictable, adding excitement to every round.
4. Clear and Concise: Provides clear and easy-to-understand words that are suitable for drawing, enhancing the game’s enjoyment and accessibility.
5. Instant Accessibility: Generates words instantly, allowing for smooth gameplay transitions and minimizing downtime between rounds.
In conclusion, WriteCream’s Pictionary Word Generator is an indispensable tool for anyone looking to spice up game nights, classroom activities, or team-building exercises. With its user-friendly interface, diverse categories, and instant word generation, it simplifies the process of selecting engaging and easy-to-draw words. Whether you’re playing with family and friends or facilitating a group activity, this generator ensures hours of fun and creativity, making every game of Pictionary memorable and enjoyable.
Create content in minutes, not weeks.
© Copyright 2024 Writecream | All Rights Reserved
Wait! Before you go...
Sign up to get 10,000 words per month for free, please enter your name and email below:.

New novel 'Long Island Compromise' looks at generational trauma
-jlv9et.jpg)
Watch Morning Joe Highlights: July 12

'Clearly he's made some missteps': Democratic governor on Biden

Ron Klain: It's a mistake to underestimate Joe Biden

Rev. Al: Offensive and elitist for Black, Latino voices to be out of the discussion on Biden

Idea of replacing Biden has sent a chill through Trump campaign, says reporter

Rep. Clyburn says conversation should focus on Biden's record

A real sense of despair on the Hill: Biden faces more congressional defections

Biden campaign polls Harris' viability against Trump

Biden increased the odds he'll be the candidate after speech: Richard Haass

Society for the Rule of Law releases statement of principles

NATO officials preparing for Biden to lose set about Trump-proofing organization

'Call it out in real time': Mika urges men to call out workplace sexism
-dgqvxw.jpg)
Watch Morning Joe Highlights: July 11

'Unit X' looks at the connection between the Pentagon and Silicon Valley

'Donald Trump Is Unfit to Lead': NYT releases 5,000 word essay warning voters

Chris Matthews: Biden is not quitting; he is not built to quit

Joe slams Trump for planned meeting with Viktor Orbán

Our support for Ukraine is not just rhetoric; it is a reality: White House

DNC Chair: Stop the hand-wringing and focus on Joe Biden
Morning joe, 'donald trump is unfit to lead': nyt releases 5,000 word essay warning voters.
- Share this -
The New York Times' Mara Gay joins Morning Joe to discuss the editorial board's 5,000 word essay 'Donald Trump Is Unfit to Lead'. July 11, 2024
MSNBC HIGHLIGHTS (BEST OF MSNBC)

New York Times editorial board calls Donald Trump 'unfit to lead,' urges voters to reject reelection bid

WASHINGTON - The New York Times' editorial boar d called on voters to reject Donald Trump' s reelection bid, alleging that the former president is "unfit to lead" a second term.
“Mr. Trump has shown a character unworthy of the responsibilities of the presidency. He has demonstrated an utter lack of respect for the Constitution, the rule of law and the American people,” wrote the Times editorial board, made up of opinion journalists, in a piece published Thursday.
“Instead of a cogent vision for the country’s future, Mr. Trump is animated by a thirst for political power: to use the levers of government to advance his interests, satisfy his impulses and exact retribution against those who he thinks have wronged him,” they added.
In the piece, the editorial board outlined five “essential” qualities and values that they feel a president must have - and that they say Trump fails on: moral fitness, principled leadership, character, a president’s words and rule of law.
“We urge voters to see the dangers of a second Trump term clearly and to reject it,” they wrote.
Last month, the New York Times editorial board published a piece calling on President Joe Biden to drop out of the 2024 race following a disastrous debate performance. The president struggled to complete sentences during the showdown and articulate his pitch to voters.
The Times argued in its op-ed piece at the time that "the president is engaged in a reckless gamble," adding that "it's too big a bet to simply hope Americans will overlook or discount Mr. Biden's age and infirmity that they see with their own eyes."
Since the debate, a growing handful of Democratic lawmakers have called on Biden to pass the torch and exit the 2024 race for the White House.
Rep. Hillary Scholten, D-Mich., on Thursday became the 10th House member to publicly call for Biden to leave the presidential race, adding to the drip of lawmakers pushing for change.
Contributing: Riley Beggin, USA TODAY

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Green India Mission Essay 150 and 500 words in English
- Updated on
- Jul 3, 2024

Green India Mission Essay: The Green India Mission is the profound mission of the Government of India. It is the eighth mission which indicates the aim of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC). The mission was launched in 2014 with a vision to plant more trees, improve forests, and fight climate change. Further, this mission wants to increase the forest in India from 21 percent to 22 percent of its land. It also helps India keep its promise regarding the global commitment to protect the environment.

Sample 1: Green India Mission Essay in 150+ words
| The Green India Mission has revitalised the country’s forests. Initiated under the supervision of the Indian government, the project aims to make the nation greener and healthier. It combats climate change by planting more trees and preserving our green forests. The Green India Mission has several important goals. The first goal is to plant trees on bare land and make existing forests denser. This helps clean our air and provides animals with a safer habitat. Secondly, the mission creates jobs for people living near forests. Growing and selling forest products like herbs and fruit helps local people earn money for a balanced livelihood. The people engaged with the mission are busy planting millions of trees across the country. New parks are created, and streets are lined with trees under the mission. Rural areas are provided with assistance to help farmers grow trees along with crops. This method of smart farming, called agroforestry, gives farmers extra income and helps them protect their soil. The Green India Mission also aims to teach how to take care of forests. It helps villagers prevent forest fires and the illegal cutting down of trees. By involving local communities, the mission ensures that people understand the importance of forests in their lives and for the environment. |
Also Read: Essay on Green Energy PDF: 150 and 250 Words
Sample 2: Green India Mission Essay in 500+ words
| The government of India started ¨Green India Mission¨ in 2014 to increase the cover of forest from 21.54 percent to 33 percent of its total land area. The mission is an integral part of the National Action Plan on Climate Change and aligns with profound global efforts to save the environment, such as the Paris Agreement. With an estimated budget of ₹46,000 crores (approximately $6.2 billion). The mission aims to transform the landscape of India over a 10-year period. Goals of the Green India MissionThe Green India Mission has several important goals. Let us look at what it wants to achieve: The motive behind the Green India mission is to increase the forest cover by 5 million hectares and improve the quality of the forest cover by another 5 million hectares. Here it should be noted that for perspective, the 5 million hectares are about the size of the country of Bhutan. The mission works to enhance the density of the existing forests. It also targets an increase from the current average of 0.5 to 0.7 tons of carbon per hectare per year. By 2020 the mission of ¨Green India Mission¨ aimed to improve ecosystem services like carbon sequestration by 100 million tonnes annually. The aim was successful in taking away a part and making the environment more sustainable. Yet another target of the mission is to provide direct benefits to 3 million forest-dependent households, focusing on sustainable livelihoods and the conservation of forests. Key Projects and Initiatives of the Mission To reach the goals of Green India Mission many different projects are running successfully across the country. In many states, the mission is organizing events like massively planting trees. Thousands of people come together to plant trees in a single day to make the event and mission successful. These events not only add more trees but also teach people about the importance of forests. Further, the mission also works with the villages to protect the nearby villages. This community-based forest management teaches the villagers how to take care of the forest and use its resources wisely. This method of protection helps the villagers as well as the forest mutually. Another exciting project that is running successfully under the Green India Mission is the creation of green corridors. These corridors are strips of forest that connect the larger forest areas. The implementation of the project helps the animals to survive safely between forests. Yet another lucrative sub-project of the Green India Mission is running successfully in the state of Uttarakhand. Here, the mission has helped in planting over 6 million trees. These newly planted trees have prevented the soil from washing away in the hilly areas and have also provided homes for many animals. Green India Mission not only helped the trees and animals, but it has also turned the lives of people far better. The mission helps to create jobs in rural areas by providing them with work in nurseries for growing young trees. This helps them fulfill their monetary needs and helps them connect with nature. Learning new skills like how to make products from forest materials, like basket making or preparing herbal medicine, makes them earn money while using the forest sustainably. The Green India Mission is the foundation of the environmental strategy of the Government of India. While there are still many challenges, comparatively, there has been more significant and impressive progress. As per the report of India State of Forest Report, there was a successful increase in the cover of the forest by 1,540 km between 2019 to 2012. With continuous effort and participation from all sectors, especially the youth, India is on the way to achieving further more ambitious targets. Achieving these targets will certainly contribute significantly to the global climate and livelihoods as well. |
Also Read: Essay on Earth Day in 150, 250, and 450 words
Ans: The Green India Mission is a national initiative launched by the Government of India to change and enhance the forest cover of the country. The mission aims to increase the forest and tree cover on 5 million hectares of land. Further, the mission also aims at improving the quality of the forest, afforestation, and eco-restoration. The mission is a successful part of the National Action Plan on climate change and aims for adaptation to the climate.
Ans: The features of the Green India Mission include: – Increasing forest cover and density – Improving biodiversity conservation – Enhancing carbon sequestration – Protecting and restoring mangroves – Supporting livelihood opportunities for local communities
Ans: The government launched Green India Clean India to make the country cleaner and greener. It focuses on planting more trees and keeping cities and villages clean. People join in to pick up litter and recycle waste. The program teaches everyone about the importance of a clean environment. It creates green spaces in urban areas. The mission also works to reduce air and water pollution. It encourages the use of renewable energy sources.
Related Essay Topics For Students
| | |
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Deepika Joshi
Deepika Joshi is an experienced content writer with expertise in creating educational and informative content. She has a year of experience writing content for speeches, essays, NCERT, study abroad and EdTech SaaS. Her strengths lie in conducting thorough research and ananlysis to provide accurate and up-to-date information to readers. She enjoys staying updated on new skills and knowledge, particulary in education domain. In her free time, she loves to read articles, and blogs with related to her field to further expand her expertise. In personal life, she loves creative writing and aspire to connect with innovative people who have fresh ideas to offer.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
How the Rise of the Camera Launched a Fight to Protect Gilded Age Americans’ Privacy
Early photographers sold their snapshots to advertisers, who reused the individuals’ likenesses without their permission
Sohini Desai, History News Network
:focal(512x380:513x381)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f2/82/f2822079-c144-4c0e-9b0c-d3585995cad6/service-pnp-ggbain-04000-04049v.jpg)
In 1904, a widow named Elizabeth Peck had her portrait taken at a studio in a small Iowa town. The photographer sold the negatives to Duffy’s Pure Malt Whiskey, a company that avoided liquor taxes for years by falsely advertising its product as medicinal. Duffy’s ads claimed the fantastical: that it cured everything from influenza to consumption, that it was endorsed by clergymen, that it could help you live until the age of 106. The portrait of Peck ended up in one of these dubious ads , published in newspapers across the country alongside what appeared to be her unqualified praise : “After years of constant use of your Pure Malt Whiskey, both by myself and as given to patients in my capacity as nurse, I have no hesitation in recommending it.”
Duffy’s lies were numerous. Peck (misleadingly identified as “Mrs. A. Schuman”) was not a nurse, and she had not spent years constantly slinging back malt beverages. In fact, she fully abstained from alcohol. Peck never consented to the ad.
The camera’s first great age—which began in 1888 when George Eastman debuted the Kodak—is full of stories like this one. Beyond the wonders of a quickly developing art form and technology lay widespread lack of control over one’s own image, perverse incentives to make a quick buck, and generalized fear at the prospect of humiliation and the invasion of privacy.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/20/94/2094ec41-60d5-4bae-bb9c-a06335e153d7/too_funny_to_not_clip.jpg)
Prior to 1888, cameras often existed in a realm of mystical unknowability. In one famed story from the early days of photography, a man asks for a picture of his recently buried wife, not understanding that someone must be present in order to be photographed. The French writer Honoré de Balzac confessed to fearing that each time a daguerreotype was taken of him, a layer of his skin would be peeled off. Early cameras required a level of technical mastery that evoked mystery—a scientific instrument understood only by professionals.
All of that changed when Eastman invented flexible roll film and debuted the first Kodak camera. Instead of developing their own pictures, customers could mail their devices to the Kodak factory and have their rolls of film developed, printed, and replaced. “You press the button,” Kodak ads promised , “we do the rest.” This leap from obscure science to streamlined service forever transformed the nature of looking and being looked at.
By 1905, less than 20 years after the first Kodak camera debuted, Eastman’s company had sold 1.2 million devices and persuaded nearly a third of the United States’ population to take up photography. Kodak’s record-setting yearly ad spending—$750,000 by the end of the 19th century (roughly $28 million in today’s dollars)—and the rapture of a technology that scratched a timeless itch facilitated the onset of a new kind of mass exposure.
“The impulse to peer into others’ affairs—an age-old feature of village life—had never actually subsided,” writes historian Sarah E. Igo in The Known Citizen: A History of Privacy in Modern America . Photography became such a phenomenon that “ Kodak fiends ,” a phrase used to describe those seduced by the devilish pleasures of photography, entered the vernacular.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/76/5c/765c1aef-d55d-45e0-92c8-5641bdea7768/service-pnp-cph-3c20000-3c20000-3c20100-3c20158v.jpg)
No one quite knew what to make of or how to control the fiendishness, and privacy was further unspooled by money-making schemes just as ferociously inventive as the new technology.
The same year Kodak cameras hit the marketplace, the Brooklyn Daily Eagle reported that Anthony Comstock—the anti-obscenity crusader after whom the 1873 Comstock Act is named—had arrested an amateur photographer for selling manually photoshopped pictures that placed “the heads of innocent women on the undraped bodies of other females.” In 1890, a mugshot photographer for the New York Police Department was fired for selling copies of the mugshots to arrestees themselves—an arrangement the New York Times described as a “lucrative business.” Boundless fascination with photographs created a bustling economy. People bought and collected random photographs from dry goods stores, general junk shops, vending machines and even cigarette packs. Demand was so robust that amateurs were just as able to sell to this market as professionals.
The ubiquity of advertising by the end of the 19th century only intensified this demand. “As the growth in productive capacity outpaced the needs of the population, commercial entrepreneurs became obsessed with creating demand for consumer products,” writes historian Samantha Barbas in Laws of Image: Privacy and Publicity in America . “The key agent in this project was advertising.”
By 1900, photography began to replace earlier image-making methods as the ad technology of choice. Photos of women were especially desirable, given their association with respectability and the belief that a pretty face could sell anything. But dominant values around modesty, avoiding indulgence and anti-consumerism meant that most people had no desire to be featured in an advertisement. Commercial modeling and stock photos did not yet exist. Faced with few choices, advertisers resorted to backdoor purchases. In an arrangement Barbas dubs “the crisis of the ‘circulating portrait,’” advertisers began buying portraits from photographers without the permission of the photos’ subjects—as was the case with Peck, temperate widow turned whiskey hound by the magic and obfuscation of advertising.
It wasn’t just ordinary people who found themselves newly exposed. Mass photography was an equalizer twice over: Nearly anybody could use a camera, and nearly anybody might be violated by one. To their grave displeasure, even the elite were unable to assert control over the frenzy. The New York Times reported that President Theodore Roosevelt was “known to exhibit impatience on discovering designs to Kodak him”; the same column mentioned that Reginald Claypoole Vanderbilt horsewhipped a man he alleged took a picture of him without permission.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/a4/86/a48623e8-f616-4c8f-a1f4-4af167ff4d20/flour-of-the-family.png)
Though newspapers across the country cautioned Americans to “beware the Kodak,” as the cameras were “deadly weapons” and “deadly little boxes,” many were also primary facilitators of the craze. The perfection of halftone printing coincided with the rise of the Kodak and allowed for the mass circulation of images. Newly empowered, newspapers regularly published paparazzi pictures of famous people taken without their knowledge, paying twice as much for them as they did for consensual photos taken in a studio.
Lawmakers and judges responded to the crisis clumsily. Suing for libel was usually the only remedy available to the overexposed. But libel law did not protect against your likeness being taken or used without your permission unless the violation was also defamatory in some way. Though results were middling, one failed lawsuit gained enough notoriety to channel cross-class feelings of exposure into action. A teenage girl named Abigail Roberson noticed her face on a neighbor’s bag of flour, only to learn that the Franklin Mills Flour Company had used her likeness in an ad that had been plastered 25,000 times all over her hometown.
After suffering intense shock and being temporarily bedridden, she sued. In 1902, the New York Court of Appeals rejected her claims and held that the right to privacy did not exist in common law. It based its decision in part on the assertion that the image was not libelous; Chief Justice Alton B. Parker wrote that the photo was “a very good one” that others might even regard as a “compliment to their beauty.” The humiliation, the lack of control over her own image, the unwanted fame—none of that amounted to any sort of actionable claim.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/6b/ce/6bceab94-6a55-4b29-aab4-7ff6dbb930bb/alton_b_parker_lccn2014694378.jpg)
Public outcry at the decision reached a fever pitch, and newspapers filled their pages with editorial indignation. In its first legislative session following the court’s decision and the ensuing outrage, the New York state legislature made history by adopting a narrow “right to privacy,” which prohibited the use of someone’s likeness in advertising or trade without their written consent. Soon after, the Supreme Court of Georgia became the first to recognize this category of privacy claim. Eventually, just about every state court in the country followed Georgia’s lead. The early uses and abuses of the Kodak helped cobble together a right that centered on profiting from the exploitation of someone’s likeness, rather than the exploitation itself.
Not long after asserting that no right to privacy exists in common law, and while campaigning to be the Democratic nominee for president, Parker told the Associated Press, “I reserve the right to put my hands in my pockets and assume comfortable attitudes without being everlastingly afraid that I shall be snapped by some fellow with a camera.” Roberson publicly took him to task over his hypocrisy, writing , “I take this opportunity to remind you that you have no such right.” She was correct then, and she still would be today. The question of whether anyone has the right to be free from exposure and its many humiliations lingers, intensified but unresolved. The law—that reactive, slow thing—never quite catches up to technology, whether it’s been given one year or 100.
This essay is from History News Network , a University of Richmond project dedicated to new interpretations of the past. Read more and subscribe to HNN’s newsletter here .
Get the latest History stories in your inbox?
Click to visit our Privacy Statement .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Use a Professional Example Layout to Outline a University, Basic, Academic, or Argumentative Essay. Grab a Blank Essay Template Today for Google Docs, MS Word, or Other Platforms.
Learn how to write an effective essay outline with clear guidelines and examples, and improve your argument and structure in academic writing.
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction, focused paragraphs, clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion.
This guide is designed to teach you to write and edit an essay, or another argumentative piece, from start to finish. It will help you align your motivations with the work and to choose a topic that grips you. This page will take you on a journey designed to convince you that writing an essay is a worthwhile endeavour, and to guide you through ...
The final step of the outlining process is to repeat this procedure on the smallest level, with the original notes that you took for your essay. To order what probably was an unwieldy and disorganized set of information at the beginning of this process, you need now only think of a sentence or two to support your general argument.
Templates for every kind of writing. Make your pages pop with a customizable template for you to put your words into. Everything from academic and research papers to work assignments to personal writing and journaling can benefit from starting your writing with a template. See which one gets the words flowing for you. Category.
In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words to use in an essay. Use these words to include your essay vocabulary.
• What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g. analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
Learn how to use 40 effective words and phrases to improve your essays and impress your readers. Oxford Royale offers you expert guidance and tips.
This handout can help you revise your papers for word-level clarity, eliminate wordiness and avoid clichés, find the words that best express your ideas, and choose words that suit an academic audience.
A hassle-free way to create custom, beautiful Word documents. Create useful and inviting templates for resumes, cover letters, cards, flyers, brochures, letters, certificates, and more with no design experience needed. Here's how: 1. Find your perfect Word template. Search documents by type or topic, or take a look around by browsing the catalog.
Learn how to write a 500-word essay with our easy guide and examples. Know about the format and structure of this type of short essay. Read to learn more!
Paper and report design and layout templates. Pen perfect looking papers and reports every time when you start your assignment with a customizable design and layout template. Whether you want your paper to pop off the page or you need your report to represent your data in the best light, you'll find the right template for your next paper.
A 500-word essay is a commonly assigned essay. To write such an essay, you should understand its concept. Read this blog and learn about it.
Write great papers with Microsoft Word. You may already use Microsoft Word to write papers, but you can also use for many other tasks, such as collecting research, co-writing with other students, recording notes on-the-fly, and even building a better bibliography! Explore new ways to use Microsoft Word below.
Want to create professional-looking business reports or academic papers? Use these tips for formatting your Word documents.
Academic writing. Students and researchers can benefit from Ahrefs' Paragraph Generator when working on papers, essays, or research articles. By providing the necessary instructions, the tool can generate well-structured paragraphs that present key arguments, evidence, and analysis, aiding in the writing process.
To write a strong essay, you need an introduction, a main body organized into paragraphs, and a conclusion. See how it's done with examples.
Select the words, paragraph, list or table to edit. On the Home tab, select a style. If you don't see the style you want, click the More button to expand the gallery. Apply Themes. Themes add a professional look to your document. Select Design > Themes. Point to a theme to preview how it will look.
A well-crafted essay can potentially win students thousands of dollars in scholarships, experts say.
Styles are to Microsoft Word what gridlines are to Microsoft Excel—you can't have a fully functioning file without having them. They save time, help you to cut out bad Microsoft Word habits, and secure your document's structure.
There are many templates available online and in programs, such as Microsoft Word, for making cover pages for essays. At the same time, the individual can even design the cover page himself from scratch, as well.
How to Use Styles in Word. Want to make your Word documents look more professional and easier to read? Using styles in Word is the way to go. Styles allow you to apply consistent formatting across your document with just a few clicks.
Explore how design shapes our perceptions, influences society, and communicates without words. Learn to use design to enhance your authority.
The Instant Essay Typer by WriteCream streamlines the writing process, allowing you to concentrate on refining ideas rather than grappling with words.-Tailored Precision: Customize your essay to align with your preferences. Edit, revise, and infuse personal insights, ensuring the final output is an authentic reflection of your thoughts.
The New York Times' Mara Gay joins Morning Joe to discuss the editorial board's 5,000 word essay 'Donald Trump Is Unfit to Lead'.
The New York Times editorial board called on voters to reject a second Donald Trump presidency, saying that the former president is unfit for a second term.
Check out the Green India Mission Essay in 150 and 200 words to understand the initiative launched by the Indian government!
The New York Times reported that President Theodore Roosevelt was "known to exhibit impatience on discovering designs to Kodak him"; ... This essay is from History News Network, ...