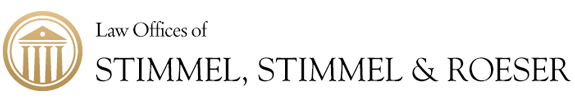
- assignments basic law

Assignments: The Basic Law
The assignment of a right or obligation is a common contractual event under the law and the right to assign (or prohibition against assignments) is found in the majority of agreements, leases and business structural documents created in the United States.
As with many terms commonly used, people are familiar with the term but often are not aware or fully aware of what the terms entail. The concept of assignment of rights and obligations is one of those simple concepts with wide ranging ramifications in the contractual and business context and the law imposes severe restrictions on the validity and effect of assignment in many instances. Clear contractual provisions concerning assignments and rights should be in every document and structure created and this article will outline why such drafting is essential for the creation of appropriate and effective contracts and structures.
The reader should first read the article on Limited Liability Entities in the United States and Contracts since the information in those articles will be assumed in this article.
Basic Definitions and Concepts:
An assignment is the transfer of rights held by one party called the “assignor” to another party called the “assignee.” The legal nature of the assignment and the contractual terms of the agreement between the parties determines some additional rights and liabilities that accompany the assignment. The assignment of rights under a contract usually completely transfers the rights to the assignee to receive the benefits accruing under the contract. Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court , 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950).
An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment in the underlying contract or lease. Where assignments are permitted, the assignor need not consult the other party to the contract but may merely assign the rights at that time. However, an assignment cannot have any adverse effect on the duties of the other party to the contract, nor can it diminish the chance of the other party receiving complete performance. The assignor normally remains liable unless there is an agreement to the contrary by the other party to the contract.
The effect of a valid assignment is to remove privity between the assignor and the obligor and create privity between the obligor and the assignee. Privity is usually defined as a direct and immediate contractual relationship. See Merchants case above.
Further, for the assignment to be effective in most jurisdictions, it must occur in the present. One does not normally assign a future right; the assignment vests immediate rights and obligations.
No specific language is required to create an assignment so long as the assignor makes clear his/her intent to assign identified contractual rights to the assignee. Since expensive litigation can erupt from ambiguous or vague language, obtaining the correct verbiage is vital. An agreement must manifest the intent to transfer rights and can either be oral or in writing and the rights assigned must be certain.
Note that an assignment of an interest is the transfer of some identifiable property, claim, or right from the assignor to the assignee. The assignment operates to transfer to the assignee all of the rights, title, or interest of the assignor in the thing assigned. A transfer of all rights, title, and interests conveys everything that the assignor owned in the thing assigned and the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor. Knott v. McDonald’s Corp ., 985 F. Supp. 1222 (N.D. Cal. 1997)
The parties must intend to effectuate an assignment at the time of the transfer, although no particular language or procedure is necessary. As long ago as the case of National Reserve Co. v. Metropolitan Trust Co ., 17 Cal. 2d 827 (Cal. 1941), the court held that in determining what rights or interests pass under an assignment, the intention of the parties as manifested in the instrument is controlling.
The intent of the parties to an assignment is a question of fact to be derived not only from the instrument executed by the parties but also from the surrounding circumstances. When there is no writing to evidence the intention to transfer some identifiable property, claim, or right, it is necessary to scrutinize the surrounding circumstances and parties’ acts to ascertain their intentions. Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998)
The general rule applicable to assignments of choses in action is that an assignment, unless there is a contract to the contrary, carries with it all securities held by the assignor as collateral to the claim and all rights incidental thereto and vests in the assignee the equitable title to such collateral securities and incidental rights. An unqualified assignment of a contract or chose in action, however, with no indication of the intent of the parties, vests in the assignee the assigned contract or chose and all rights and remedies incidental thereto.
More examples: In Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs ., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998), the court held that the assignee of a party to a subordination agreement is entitled to the benefits and is subject to the burdens of the agreement. In Florida E. C. R. Co. v. Eno , 99 Fla. 887 (Fla. 1930), the court held that the mere assignment of all sums due in and of itself creates no different or other liability of the owner to the assignee than that which existed from the owner to the assignor.
And note that even though an assignment vests in the assignee all rights, remedies, and contingent benefits which are incidental to the thing assigned, those which are personal to the assignor and for his sole benefit are not assigned. Rasp v. Hidden Valley Lake, Inc ., 519 N.E.2d 153, 158 (Ind. Ct. App. 1988). Thus, if the underlying agreement provides that a service can only be provided to X, X cannot assign that right to Y.
Novation Compared to Assignment:
Although the difference between a novation and an assignment may appear narrow, it is an essential one. “Novation is a act whereby one party transfers all its obligations and benefits under a contract to a third party.” In a novation, a third party successfully substitutes the original party as a party to the contract. “When a contract is novated, the other contracting party must be left in the same position he was in prior to the novation being made.”
A sublease is the transfer when a tenant retains some right of reentry onto the leased premises. However, if the tenant transfers the entire leasehold estate, retaining no right of reentry or other reversionary interest, then the transfer is an assignment. The assignor is normally also removed from liability to the landlord only if the landlord consents or allowed that right in the lease. In a sublease, the original tenant is not released from the obligations of the original lease.
Equitable Assignments:
An equitable assignment is one in which one has a future interest and is not valid at law but valid in a court of equity. In National Bank of Republic v. United Sec. Life Ins. & Trust Co. , 17 App. D.C. 112 (D.C. Cir. 1900), the court held that to constitute an equitable assignment of a chose in action, the following has to occur generally: anything said written or done, in pursuance of an agreement and for valuable consideration, or in consideration of an antecedent debt, to place a chose in action or fund out of the control of the owner, and appropriate it to or in favor of another person, amounts to an equitable assignment. Thus, an agreement, between a debtor and a creditor, that the debt shall be paid out of a specific fund going to the debtor may operate as an equitable assignment.
In Egyptian Navigation Co. v. Baker Invs. Corp. , 2008 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 30804 (S.D.N.Y. Apr. 14, 2008), the court stated that an equitable assignment occurs under English law when an assignor, with an intent to transfer his/her right to a chose in action, informs the assignee about the right so transferred.
An executory agreement or a declaration of trust are also equitable assignments if unenforceable as assignments by a court of law but enforceable by a court of equity exercising sound discretion according to the circumstances of the case. Since California combines courts of equity and courts of law, the same court would hear arguments as to whether an equitable assignment had occurred. Quite often, such relief is granted to avoid fraud or unjust enrichment.
Note that obtaining an assignment through fraudulent means invalidates the assignment. Fraud destroys the validity of everything into which it enters. It vitiates the most solemn contracts, documents, and even judgments. Walker v. Rich , 79 Cal. App. 139 (Cal. App. 1926). If an assignment is made with the fraudulent intent to delay, hinder, and defraud creditors, then it is void as fraudulent in fact. See our article on Transfers to Defraud Creditors .
But note that the motives that prompted an assignor to make the transfer will be considered as immaterial and will constitute no defense to an action by the assignee, if an assignment is considered as valid in all other respects.
Enforceability of Assignments:
Whether a right under a contract is capable of being transferred is determined by the law of the place where the contract was entered into. The validity and effect of an assignment is determined by the law of the place of assignment. The validity of an assignment of a contractual right is governed by the law of the state with the most significant relationship to the assignment and the parties.
In some jurisdictions, the traditional conflict of laws rules governing assignments has been rejected and the law of the place having the most significant contacts with the assignment applies. In Downs v. American Mut. Liability Ins. Co ., 14 N.Y.2d 266 (N.Y. 1964), a wife and her husband separated and the wife obtained a judgment of separation from the husband in New York. The judgment required the husband to pay a certain yearly sum to the wife. The husband assigned 50 percent of his future salary, wages, and earnings to the wife. The agreement authorized the employer to make such payments to the wife.
After the husband moved from New York, the wife learned that he was employed by an employer in Massachusetts. She sent the proper notice and demanded payment under the agreement. The employer refused and the wife brought an action for enforcement. The court observed that Massachusetts did not prohibit assignment of the husband’s wages. Moreover, Massachusetts law was not controlling because New York had the most significant relationship with the assignment. Therefore, the court ruled in favor of the wife.
Therefore, the validity of an assignment is determined by looking to the law of the forum with the most significant relationship to the assignment itself. To determine the applicable law of assignments, the court must look to the law of the state which is most significantly related to the principal issue before it.
Assignment of Contractual Rights:
Generally, the law allows the assignment of a contractual right unless the substitution of rights would materially change the duty of the obligor, materially increase the burden or risk imposed on the obligor by the contract, materially impair the chance of obtaining return performance, or materially reduce the value of the performance to the obligor. Restat 2d of Contracts, § 317(2)(a). This presumes that the underlying agreement is silent on the right to assign.
If the contract specifically precludes assignment, the contractual right is not assignable. Whether a contract is assignable is a matter of contractual intent and one must look to the language used by the parties to discern that intent.
In the absence of an express provision to the contrary, the rights and duties under a bilateral executory contract that does not involve personal skill, trust, or confidence may be assigned without the consent of the other party. But note that an assignment is invalid if it would materially alter the other party’s duties and responsibilities. Once an assignment is effective, the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor and assumes all of assignor’s rights. Hence, after a valid assignment, the assignor’s right to performance is extinguished, transferred to assignee, and the assignee possesses the same rights, benefits, and remedies assignor once possessed. Robert Lamb Hart Planners & Architects v. Evergreen, Ltd. , 787 F. Supp. 753 (S.D. Ohio 1992).
On the other hand, an assignee’s right against the obligor is subject to “all of the limitations of the assignor’s right, all defenses thereto, and all set-offs and counterclaims which would have been available against the assignor had there been no assignment, provided that these defenses and set-offs are based on facts existing at the time of the assignment.” See Robert Lamb , case, above.
The power of the contract to restrict assignment is broad. Usually, contractual provisions that restrict assignment of the contract without the consent of the obligor are valid and enforceable, even when there is statutory authorization for the assignment. The restriction of the power to assign is often ineffective unless the restriction is expressly and precisely stated. Anti-assignment clauses are effective only if they contain clear, unambiguous language of prohibition. Anti-assignment clauses protect only the obligor and do not affect the transaction between the assignee and assignor.
Usually, a prohibition against the assignment of a contract does not prevent an assignment of the right to receive payments due, unless circumstances indicate the contrary. Moreover, the contracting parties cannot, by a mere non-assignment provision, prevent the effectual alienation of the right to money which becomes due under the contract.
A contract provision prohibiting or restricting an assignment may be waived, or a party may so act as to be estopped from objecting to the assignment, such as by effectively ratifying the assignment. The power to void an assignment made in violation of an anti-assignment clause may be waived either before or after the assignment. See our article on Contracts.
Noncompete Clauses and Assignments:
Of critical import to most buyers of businesses is the ability to ensure that key employees of the business being purchased cannot start a competing company. Some states strictly limit such clauses, some do allow them. California does restrict noncompete clauses, only allowing them under certain circumstances. A common question in those states that do allow them is whether such rights can be assigned to a new party, such as the buyer of the buyer.
A covenant not to compete, also called a non-competitive clause, is a formal agreement prohibiting one party from performing similar work or business within a designated area for a specified amount of time. This type of clause is generally included in contracts between employer and employee and contracts between buyer and seller of a business.
Many workers sign a covenant not to compete as part of the paperwork required for employment. It may be a separate document similar to a non-disclosure agreement, or buried within a number of other clauses in a contract. A covenant not to compete is generally legal and enforceable, although there are some exceptions and restrictions.
Whenever a company recruits skilled employees, it invests a significant amount of time and training. For example, it often takes years before a research chemist or a design engineer develops a workable knowledge of a company’s product line, including trade secrets and highly sensitive information. Once an employee gains this knowledge and experience, however, all sorts of things can happen. The employee could work for the company until retirement, accept a better offer from a competing company or start up his or her own business.
A covenant not to compete may cover a number of potential issues between employers and former employees. Many companies spend years developing a local base of customers or clients. It is important that this customer base not fall into the hands of local competitors. When an employee signs a covenant not to compete, he or she usually agrees not to use insider knowledge of the company’s customer base to disadvantage the company. The covenant not to compete often defines a broad geographical area considered off-limits to former employees, possibly tens or hundreds of miles.
Another area of concern covered by a covenant not to compete is a potential ‘brain drain’. Some high-level former employees may seek to recruit others from the same company to create new competition. Retention of employees, especially those with unique skills or proprietary knowledge, is vital for most companies, so a covenant not to compete may spell out definite restrictions on the hiring or recruiting of employees.
A covenant not to compete may also define a specific amount of time before a former employee can seek employment in a similar field. Many companies offer a substantial severance package to make sure former employees are financially solvent until the terms of the covenant not to compete have been met.
Because the use of a covenant not to compete can be controversial, a handful of states, including California, have largely banned this type of contractual language. The legal enforcement of these agreements falls on individual states, and many have sided with the employee during arbitration or litigation. A covenant not to compete must be reasonable and specific, with defined time periods and coverage areas. If the agreement gives the company too much power over former employees or is ambiguous, state courts may declare it to be overbroad and therefore unenforceable. In such case, the employee would be free to pursue any employment opportunity, including working for a direct competitor or starting up a new company of his or her own.
It has been held that an employee’s covenant not to compete is assignable where one business is transferred to another, that a merger does not constitute an assignment of a covenant not to compete, and that a covenant not to compete is enforceable by a successor to the employer where the assignment does not create an added burden of employment or other disadvantage to the employee. However, in some states such as Hawaii, it has also been held that a covenant not to compete is not assignable and under various statutes for various reasons that such covenants are not enforceable against an employee by a successor to the employer. Hawaii v. Gannett Pac. Corp. , 99 F. Supp. 2d 1241 (D. Haw. 1999)
It is vital to obtain the relevant law of the applicable state before drafting or attempting to enforce assignment rights in this particular area.
Conclusion:
In the current business world of fast changing structures, agreements, employees and projects, the ability to assign rights and obligations is essential to allow flexibility and adjustment to new situations. Conversely, the ability to hold a contracting party into the deal may be essential for the future of a party. Thus, the law of assignments and the restriction on same is a critical aspect of every agreement and every structure. This basic provision is often glanced at by the contracting parties, or scribbled into the deal at the last minute but can easily become the most vital part of the transaction.
As an example, one client of ours came into the office outraged that his co venturer on a sizable exporting agreement, who had excellent connections in Brazil, had elected to pursue another venture instead and assigned the agreement to a party unknown to our client and without the business contacts our client considered vital. When we examined the handwritten agreement our client had drafted in a restaurant in Sao Paolo, we discovered there was no restriction on assignment whatsoever…our client had not even considered that right when drafting the agreement after a full day of work.
One choses who one does business with carefully…to ensure that one’s choice remains the party on the other side of the contract, one must master the ability to negotiate proper assignment provisions.
Founded in 1939, our law firm combines the ability to represent clients in domestic or international matters with the personal interaction with clients that is traditional to a long established law firm.
Read more about our firm
© 2024, Stimmel, Stimmel & Roeser, All rights reserved | Terms of Use | Site by Bay Design

Assignment of Contract
Jump to section, what is an assignment of contract.
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the approved incoming party.
How Does Assignment of Contract Work?
An assignment of contract is simpler than you might think.
The process starts with an existing contract party who wishes to transfer their contractual obligations to a new party.
When this occurs, the existing contract party must first confirm that an assignment of contract is permissible under the legally binding agreement . Some contracts prohibit assignments of contract altogether, and some require the other parties of the agreement to agree to the transfer. However, the general rule is that contracts are freely assignable unless there is an explicit provision that says otherwise.
In other cases, some contracts allow an assignment of contract without any formal notification to other contract parties. If this is the case, once the existing contract party decides to reassign his duties, he must create a “Letter of Assignment ” to notify any other contract signers of the change.
The Letter of Assignment must include details about who is to take over the contractual obligations of the exiting party and when the transfer will take place. If the assignment is valid, the assignor is not required to obtain the consent or signature of the other parties to the original contract for the valid assignment to take place.
Check out this article to learn more about how assigning a contract works.
Contract Assignment Examples
Contract assignments are great tools for contract parties to use when they wish to transfer their commitments to a third party. Here are some examples of contract assignments to help you better understand them:
Anna signs a contract with a local trash company that entitles her to have her trash picked up twice a week. A year later, the trash company transferred her contract to a new trash service provider. This contract assignment effectively makes Anna’s contract now with the new service provider.
Hasina enters a contract with a national phone company for cell phone service. The company goes into bankruptcy and needs to close its doors but decides to transfer all current contracts to another provider who agrees to honor the same rates and level of service. The contract assignment is completed, and Hasina now has a contract with the new phone company as a result.
Here is an article where you can find out more about contract assignments.
Assignment of Contract in Real Estate
Assignment of contract is also used in real estate to make money without going the well-known routes of buying and flipping houses. When real estate LLC investors use an assignment of contract, they can make money off properties without ever actually buying them by instead opting to transfer real estate contracts .
This process is called real estate wholesaling.
Real Estate Wholesaling
Real estate wholesaling consists of locating deals on houses that you don’t plan to buy but instead plan to enter a contract to reassign the house to another buyer and pocket the profit.
The process is simple: real estate wholesalers negotiate purchase contracts with sellers. Then, they present these contracts to buyers who pay them an assignment fee for transferring the contract.
This process works because a real estate purchase agreement does not come with the obligation to buy a property. Instead, it sets forth certain purchasing parameters that must be fulfilled by the buyer of the property. In a nutshell, whoever signs the purchase contract has the right to buy the property, but those rights can usually be transferred by means of an assignment of contract.
This means that as long as the buyer who’s involved in the assignment of contract agrees with the purchasing terms, they can legally take over the contract.
But how do real estate wholesalers find these properties?
It is easier than you might think. Here are a few examples of ways that wholesalers find cheap houses to turn a profit on:
- Direct mailers
- Place newspaper ads
- Make posts in online forums
- Social media posts
The key to finding the perfect home for an assignment of contract is to locate sellers that are looking to get rid of their properties quickly. This might be a family who is looking to relocate for a job opportunity or someone who needs to make repairs on a home but can’t afford it. Either way, the quicker the wholesaler can close the deal, the better.
Once a property is located, wholesalers immediately go to work getting the details ironed out about how the sale will work. Transparency is key when it comes to wholesaling. This means that when a wholesaler intends to use an assignment of contract to transfer the rights to another person, they are always upfront about during the preliminary phases of the sale.
In addition to this practice just being good business, it makes sure the process goes as smoothly as possible later down the line. Wholesalers are clear in their intent and make sure buyers know that the contract could be transferred to another buyer before the closing date arrives.
After their offer is accepted and warranties are determined, wholesalers move to complete a title search . Title searches ensure that sellers have the right to enter into a purchase agreement on the property. They do this by searching for any outstanding tax payments, liens , or other roadblocks that could prevent the sale from going through.
Wholesalers also often work with experienced real estate lawyers who ensure that all of the legal paperwork is forthcoming and will stand up in court. Lawyers can also assist in the contract negotiation process if needed but often don’t come in until the final stages.
If the title search comes back clear and the real estate lawyer gives the green light, the wholesaler will immediately move to locate an entity to transfer the rights to buy.
One of the most attractive advantages of real estate wholesaling is that very little money is needed to get started. The process of finding a seller, negotiating a price, and performing a title search is an extremely cheap process that almost anyone can do.
On the other hand, it is not always a positive experience. It can be hard for wholesalers to find sellers who will agree to sell their homes for less than the market value. Even when they do, there is always a chance that the transferred buyer will back out of the sale, which leaves wholesalers obligated to either purchase the property themselves or scramble to find a new person to complete an assignment of contract with.
Learn more about assignment of contract in real estate by checking out this article .
Who Handles Assignment of Contract?
The best person to handle an assignment of contract is an attorney. Since these are detailed legal documents that deal with thousands of dollars, it is never a bad idea to have a professional on your side. If you need help with an assignment of contract or signing a business contract , post a project on ContractsCounsel. There, you can connect with attorneys who know everything there is to know about assignment of contract amendment and can walk you through the whole process.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Meet some of our Lawyers
Accident and injury attorney. Prior to going to law school I was a paralegal for 12+ years primarily in personal injury. I also worked for a local school district as the Risk Manager and a Buyer in Procurement where I facilitated solicitations and managed all the contracts for the district.
NY Admitted Lawyer 20+ years of experience. Focused on Startups , Entrepreneurs, Entertainers, Producers, Athletes and SMB Companies. I have been a part of numerous startups as Founder, CEO, General Counsel and Deal Executive. I have been through the full life cycle from boot strap to seed investors to large funds-public companies to successful exit. Let me use my experiences help you as you grow your business through these various stages. We saw a market for an on-line platform dedicated to Virtual General Counsel Services to Start Ups and Private Companies.
Attorney with a wide-range of experience
20 years experienced attorney, Corp/commercial RE/wills trusts/ contracts/ reg compliance
A. Browne Esq. is an entertainment, intellectual property, and business lawyer. Her goal is always to provide the best legal representation for your creative endeavors, both tangible and intangible. Always know that the best way to deal with legal issues is to take measures to avoid them. Learn how to protect your creative work at a law firm that’s passionate about ensuring that creatives own their stuff.
Brian M. Rokaw has negotiated, drafted, and reviewed a multitude of contracts, resolutions, and agreements for a wide array of business owners. Brian has represented clients who are starting a business, selling a business, buying a business, creating a partnership, establishing a corporate entity, as well as those that are dissolving a business throughout the State of Florida. Brian M. Rokaw is knowledgeable and experienced in all real estate related matters, both residential and commercial including closings, financing, and litigation. Brian has drafted hundreds of deeds, affidavits, bills of sale, and settlement statements. Brian has represented clients in all areas of the real estate industry, including buyers, sellers, developers, management companies, brokers, and investors throughout the State of Florida. Brian M. Rokaw has successfully defended against actions and negotiated settlement agreements involving all types of consumer debt. Brian has represented homeowners and commercial property owners that are facing foreclosure, being pursued by judgment creditors, consumers burdened by secured and unsecured financial obligations, as well as collection accounts throughout the State of Florida.
Christopher N.
Christopher Nuneviller has practiced in the securities, venture capital, corporate and emerging business sectors, and as a contract-advisor to the federal government, a federal government senior level executive, and as Army Judge Advocate. Like you, he also he is a partner in other business ventures and faces the same pressure to succeed, be profitable, and stay sane, all while making his clients, employees, family and business partners happy. As the managing partner for Philadelphia's MNB Meridian Law, Ltd., his focus is on assisting small and mid-sized businesses grow and thrive. As a business generalist, Christopher provides advice and counsel to businesses, their owners, investors and shareholders on matters ranging from formation, organization, governance, routine and special operations, and growth toward IPO. Christopher is also a former U.S. Army Judge Advocate having served seven years in Washington, D.C. where he gained significant experience with "above the fold" matters of great import and an unhealthy insight into the internal workings of the "beltway" underbelly. Mr. Nuneviller is admitted to practice in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, and before the Supreme Court of the United States, the Court of Federal Claims, and the Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces.
Find the best lawyer for your project

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
Need help with a Contract Agreement?
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
CONTRACT LAWYERS BY TOP CITIES
- Austin Contracts Lawyers
- Boston Contracts Lawyers
- Chicago Contracts Lawyers
- Dallas Contracts Lawyers
- Denver Contracts Lawyers
- Houston Contracts Lawyers
- Los Angeles Contracts Lawyers
- New York Contracts Lawyers
- Phoenix Contracts Lawyers
- San Diego Contracts Lawyers
- Tampa Contracts Lawyers
ASSIGNMENT OF CONTRACT LAWYERS BY CITY
- Austin Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Boston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Chicago Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Dallas Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Denver Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Houston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Los Angeles Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- New York Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Phoenix Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- San Diego Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Tampa Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
How It Works
Want to speak to someone.
Get in touch below and we will schedule a time to connect!
Find lawyers and attorneys by city
(404) 738-5471

Ultimate Checklist for Understanding Contract Assignment Rules
- February 28, 2024
- Moton Legal Group

In contracts, understanding assignment is key. Simply put, an assignment in contract law is when one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and responsibilities under a contract to another party (the assignee). This can include anything from leasing agreements to business operations. But why is this important? It’s because it allows for flexibility in business and personal dealings, a critical component in our world.
Here’s a quick rundown: – Contract Basics: The foundational agreements between parties. – Assignment Importance: Allowing the transfer of obligations and benefits to keep up with life’s changes.
Contracts are a staple in both personal and business worlds, acting as the backbone to many transactions and agreements encountered daily. Understanding the nuances, like assignments, can empower you to navigate these waters with confidence and ease. Whether you’re a business owner in the Southeast looking to expand or an individual managing personal agreements, grasp these basics, and you’re on the right path.
Understanding Contract Assignment
Contract Assignment sounds complicated, right? But, let’s break it down into simple terms. In contracts and legal agreements, knowing about assignment can save you a lot of headaches down the road. Whether you’re a business owner, a landlord, or just someone who deals with contracts, this is for you.
Legal Definition
At its core, contract assignment is about transferring rights or obligations under a contract from one party to another. Think of it as passing a baton in a relay race. The original party (the assignor) hands off their responsibilities or benefits to someone else (the assignee). But, there’s a twist – the race keeps going with the new runner without starting over.
Contract Law
In contract law, assignment comes into play in various ways. For example, if you’re a freelancer and you’ve agreed to complete a project but suddenly find yourself overbooked, you might assign that contract to another freelancer. This way, the job gets done, and your client is happy. However, not all contracts can be freely assigned. Some require the other party’s consent, and others can’t be assigned at all, especially if they involve personal skills or confidential trust.
Property Law
When it comes to property law, assignment often surfaces in landlord-tenant relationships. Say you’re renting a shop for your business, but you decide to move. If your lease allows it, you might assign your lease to another business. This means they take over your lease, stepping into your shoes, with all the rights and obligations that come with it.
The concept might seem straightforward, but there are important legal requirements and potential pitfalls to be aware of. For instance, an assignment could be prohibited by the contract itself, or it may significantly change the original deal’s terms in a way that’s not allowed. Plus, when you’re dealing with something that requires a unique skill set, like an artist or a consultant, those services typically can’t be passed on to someone else without agreement from all parties involved.
To navigate these complexities, understanding the fundamentals of assignment in contract law and property law is crucial. It ensures that when you’re ready to pass that baton, you’re doing it in a way that’s legal, effective, and doesn’t leave you tripping up before you reach the finish line.
The goal here is to make sure everyone involved understands what’s happening and agrees to it. That way, assignments can be a useful tool to manage your contracts and property agreements, keeping things moving smoothly even when changes come up.
For more detailed exploration on this topic, consider checking the comprehensive guide on Assignment (law)). This resource dives deeper into the nuances of contract assignment, offering insights and examples that can help clarify this complex area of law.
By grasping these basics, you’re well on your way to mastering the art of contract assignment. Whether you’re dealing with leases, business deals, or any agreement in between, knowing how to effectively assign a contract can be a game-changer.
Key Differences Between Assignment and Novation
When diving into contracts, two terms that often cause confusion are assignment and novation . While both deal with transferring obligations and rights under a contract, they are fundamentally different in several key aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in contract management or negotiation.
Rights Transfer
Assignment involves the transfer of benefits or rights from one party (the assignor) to another (the assignee). However, it’s important to note that only the benefits of the contract can be assigned, not the burdens. For instance, if someone has the right to receive payments under a contract, they can assign this right to someone else.
Novation , on the other hand, is more comprehensive. It involves transferring both the rights and obligations under a contract from one party to a new party. With novation, the original party is completely released from the contract, and a new contractual relationship is formed between the remaining and the new party. This is a key distinction because, in novation, all parties must agree to this new arrangement.
Obligations Transfer
Assignment doesn’t transfer the original party’s obligations under the contract. The assignor (the original party who had the rights under the contract) might still be liable if the assignee fails to fulfill the contract terms.
In contrast, novation transfers all obligations to the new party. Once a novation is complete, the new party takes over all rights and obligations, leaving the original party with no further legal liabilities or rights under the contract.
Written Agreement
While assignments can sometimes be informal or even verbal, novation almost always requires a written agreement. This is because novation affects more parties’ rights and obligations and has a more significant impact on the contractual relationship. A written agreement ensures that all parties are clear about the terms of the novation and their respective responsibilities.
In practice, the need for a written agreement in novation serves as a protection for all parties involved. It ensures that the transfer of obligations is clearly documented and legally enforceable.
For example, let’s say Alex agrees to paint Bailey’s house for $1,000. Later, Alex decides they can’t complete the job and wants Chris to take over. If Bailey agrees, they can sign a novation agreement where Chris agrees to paint the house under the same conditions. Alex is then relieved from the original contract, and Chris becomes responsible for completing the painting job.
Understanding the difference between assignment and novation is critical for anyone dealing with contracts. While both processes allow for the transfer of rights or obligations, they do so in different ways and with varying implications for all parties involved. Knowing when and how to use each can help ensure that your contractual relationships are managed effectively and legally sound.
For further in-depth information and real-life case examples on assignment in contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Next, we’ll delve into the legal requirements for a valid assignment, touching on express prohibition, material change, future rights, and the rare skill requirement. Understanding these will further equip you to navigate the complexities of contract assignments successfully.
Legal Requirements for a Valid Assignment
When dealing with assignment in contract law , it’s crucial to understand the legal backbone that supports a valid assignment. This ensures that the assignment stands up in a court of law if disputes arise. Let’s break down the must-know legal requirements: express prohibition, material change, future rights, and rare skill requirement.
Express Prohibition
The first stop on our checklist is to look for an express prohibition against assignment in the contract. This is a clause that outright states assignments are not allowed without the other party’s consent. If such language exists and you proceed with an assignment, you could be breaching the contract. Always read the fine print or have a legal expert review the contract for you.
Material Change
Next up is the material change requirement. The law states that an assignment cannot significantly alter the duties, increase the burdens, or impair the chances of the other party receiving due performance under the contract. For instance, if the contract involves personal services tailored to the specific party, assigning it to someone else might change the expected outcome, making such an assignment invalid.
Future Rights
Another important aspect is future rights . The rule here is straightforward: you can’t assign what you don’t have. This means that a promise to assign rights you may acquire in the future is generally not enforceable at present. An effective assignment requires that the rights exist at the time of the assignment.
Rare Skill Requirement
Lastly, let’s talk about the rare skill requirement . Some contracts are so specialized that they cannot be assigned to another party without compromising the contract’s integrity. This is often the case with contracts that rely on an individual’s unique skills or trust. Think of an artist commissioned for a portrait or a lawyer hired for their specialized legal expertise. In these scenarios, assignments are not feasible as they could severely impact the contract’s intended outcome.
Understanding these legal requirements is pivotal for navigating the complexities of assignment in contract law. By ensuring compliance with these principles, you can effectively manage contract assignments, safeguarding your interests and those of the other contracting party.
For anyone looking to delve deeper into the intricacies of contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Moving forward, we’ll explore the common types of contract assignments, from landlord-tenant agreements to business contracts and intellectual property transfers. This will give you a clearer picture of how assignments work across different legal landscapes.
Common Types of Contract Assignments
When we dive into assignment in contract law , we find it touches nearly every aspect of our business and personal lives. Let’s simplify this complex topic by looking at some of the most common types of contract assignments you might encounter.
Landlord-Tenant Agreements
Imagine you’re renting a fantastic apartment but have to move because of a new job. Instead of breaking your lease, you can assign your lease to someone else. This means the new tenant takes over your lease, including rent payments and maintenance responsibilities. However, it’s crucial that the landlord agrees to this switch. If done right, it’s a win-win for everyone involved.

Business Contracts
In the business world, contract assignments are a daily occurrence. For example, if a company agrees to provide services but then realizes it’s overbooked, it can assign the contract to another company that can fulfill the obligations. This way, the project is completed on time, and the client remains happy. It’s a common practice that ensures flexibility and efficiency in business operations.

Intellectual Property
Intellectual property (IP) assignments are fascinating and complex. If an inventor creates a new product, they can assign their patent rights to a company in exchange for a lump sum or royalties. This transfer allows the company to produce and sell the invention, while the inventor benefits financially. However, it’s critical to note that with trademarks, the goodwill associated with the mark must also be transferred to maintain its value.
Understanding these types of assignments helps clarify the vast landscape of contract law. Whether it’s a cozy apartment, a crucial business deal, or a groundbreaking invention, assignments play a pivotal role in ensuring these transitions happen smoothly.
As we navigate through the realm of contract assignments, each type has its own set of rules and best practices. The key is to ensure all parties are on the same page and that the assignment is executed properly to avoid any legal pitfalls.
Diving deeper into the subject, next, we will explore how to execute a contract assignment effectively, ensuring all legal requirements are met and the process runs as smoothly as possible.
How to Execute a Contract Assignment Effectively
Executing a contract assignment effectively is crucial to ensure that all legal requirements are met and the process runs smoothly. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you navigate this process without any hiccups.
Written Consent
First and foremost, get written consent . This might seem like a no-brainer, but it’s surprising how often this step is overlooked. If the original contract requires the consent of the other party for an assignment to be valid, make sure you have this in black and white. Not just a handshake or a verbal agreement. This ensures clarity and avoids any ambiguity or disputes down the line.
Notice of Assignment
Next up, provide a notice of assignment to all relevant parties. This is not just common courtesy; it’s often a legal requirement. It informs all parties involved about the change in the assignment of rights or obligations under the contract. Think of it as updating your address with the post office; everyone needs to know where to send the mail now.
Privity of Estate
Understanding privity of estate is key in real estate transactions and leases. It refers to the legal relationship that exists between parties under a contract. When you assign a contract, the assignee steps into your shoes, but the original terms of the contract still apply. This means the assignee needs to be aware of and comply with the original agreement’s requirements.
Secondary Liability
Lastly, let’s talk about secondary liability . Just because you’ve assigned a contract doesn’t always mean you’re off the hook. In some cases, the original party (the assignor) may still hold some liability if the assignee fails to perform under the contract. It’s essential to understand the terms of your assignment agreement and whether it includes a release from liability for the assignor.
Executing a contract assignment effectively is all about dotting the I’s and crossing the T’s . By following these steps—securing written consent, issuing a notice of assignment, understanding privity of estate, and clarifying secondary liability—you’re setting yourself up for a seamless transition.
The goal is to ensure all parties are fully informed and agreeable to the changes being made. This not only helps in maintaining good relationships but also in avoiding potential legal issues down the line.
We’ll dive into some of the frequently asked questions about contract assignment to clear any lingering doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Contract Assignment
When navigating contracts, questions often arise, particularly about the concepts of assignment and novation. Let’s break these down into simpler terms.
What does assignment of a contract mean?
In the realm of assignment in contract law , think of assignment as passing the baton in a relay race. It’s where one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and benefits under a contract to another party (the assignee). However, unlike a relay race, the original party might still be on the hook for obligations unless the contract says otherwise. It’s like handing off the baton but still running alongside the new runner just in case.
Is an assignment legally binding?
Absolutely, an assignment is as binding as a pinky promise in the playground – but with legal muscle behind it. Once an assignment meets the necessary legal criteria (like not significantly changing the obligor’s duties or having express consent if required), it’s set in stone. This means both the assignee and the assignor must honor this transfer of rights or face potential legal actions. It’s a serious commitment, not just a casual exchange.
What is the difference between assignment and novation?
Now, this is where it gets a bit more intricate. If assignment is passing the baton, novation is forming a new team mid-race. It involves replacing an old obligation with a new one or adding a new party to take over an old one’s duties. Crucially, novation extinguishes the old contract and requires all original and new parties to agree. It’s a clean slate – the original party walks away, and the new party steps in, no strings attached.
While both assignment and novation change the playing field of a contract, novation requires a unanimous thumbs up from everyone involved, completely freeing the original party from their obligations. On the other hand, an assignment might leave the original party watching from the sidelines, ready to jump back in if needed.
Understanding these facets of assignment in contract law is crucial, whether you’re diving into a new agreement or navigating an existing one. Knowledge is power – especially when it comes to contracts.
As we wrap up these FAQs, the legal world of contracts is vast and sometimes complex, but breaking it down into bite-sized pieces can help demystify the process and empower you in your legal undertakings.
Here’s a helpful resource for further reading on the difference between assignment and cession.
Now, let’s continue on to the conclusion to tie all these insights together.
Navigating assignment in contract law can seem like a daunting task at first glance. However, with the right information and guidance, it becomes an invaluable tool in ensuring that your rights and obligations are protected and effectively managed in any contractual relationship.
At Moton Legal Group, we understand the intricacies of contract law and are dedicated to providing you with the expertise and support you need to navigate these waters. Whether you’re dealing with a straightforward contract assignment or facing more complex legal challenges, our team is here to help. We pride ourselves on our ability to demystify legal processes and make them accessible to everyone.
The key to successfully managing any contract assignment lies in understanding your rights, the obligations involved, and the potential impacts on all parties. It’s about ensuring that the assignment is executed in a way that is legally sound and aligns with your interests.
If you’re in need of assistance with a contract review, looking to understand more about how contract assignments work, or simply seeking legal advice on your contractual rights and responsibilities, Moton Legal Group is here for you. Our team of experienced attorneys is committed to providing the clarity, insight, and support you need to navigate the complexities of contract law with confidence.
For more information on how we can assist you with your contract review and other legal needs, visit our contract review service page .
In the constantly evolving landscape of contract law, having a trusted legal partner can make all the difference. Let Moton Legal Group be your guide, ensuring that your contractual dealings are handled with the utmost care, professionalism, and expertise. Together, we can navigate the complexities of contract law and secure the best possible outcomes for your legal matters.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the fundamentals of assignment in contract law. We hope you found this information helpful and feel more empowered to handle your contractual affairs with confidence.
For more information Call :
Reach out now.
" * " indicates required fields
Recent Blog Posts:

How to Understand Acceptance in Contract Law: Key Elements Explained

Essential Guide to the Core Elements of Contract Law

The Expanded Guide to Contract Law: Understanding All 8 Elements

Understanding Contracts: The 7 Fundamental Elements in Law

Building Better Business Deals: 6 Key Elements of Contract Law

Common Law Contracts: A Guide to Understanding Essential Elements
Choose Your Legal Category:
- Online Law Library
- Bankruptcy Law
- Business Law
- Civil Law
- Criminal Law
- Employment Law
- Family Law
- Finance Law
- Government Law
- Immigration Law
- Insurance Law
- Intellectual Property Law
- Personal Injury Law
- Products & Services Law
- Real Estate Law
- Wills, Trusts & Estates Law
- Attorney Referral Services
- Top 10 Most Popular Articles
- Legal Dictionary
- How It Works - Clients
- Legal Center
- About LegalMatch
- Consumer Satisfaction
- Editorial Policy
- Attorneys Market Your Law Practice Attorney Login Schedule a Demo Now Did LegalMatch Call You Recently? How It Works - Attorneys Attorney Resources Attorney Success Stories Attorney Success Story Videos Compare Legal Marketing Services Cases Heatmap View Cases
- Find a Lawyer
- Legal Topics
- Contract Law
Contract Assignments
(This may not be the same place you live)
What is a Contract Assignment?
In a contract assignment, one of the two parties to a contract may transfer their right to the other’s performance to a third party. This is known as “contract assignment.” Generally, all rights under a contract may be assigned. A provision in the contract that states the contract may not be assigned usually refers to the delegation of the assignor’s (person who assigns) duties under that contract, not their rights under the contract.
In modern law, the phrase “assignment of contract” usually means assignment of both rights and duties under a contract.
Who are the Various Parties Involved in a Contract Assignment?
How is a contract assignment created, when is a contract assignment prohibited, which parties are liable to each other in a contract assignment, are there issues with multiple assignments, should i hire a lawyer for contract assignments.
In a contract, there are two parties to the agreement, X and Y. The parties may agree to let X assign X’s rights to a third party . Once the third party enters the picture, each party has a special name. For instance, suppose X, a seller of bookmarks, contracts with Y, a purchaser of bookmarks. Y desires to have Y’s right to X’s performance (the sale of bookmarks on a monthly basis) to another person.
This third person, Z, is called the assignee. X is called the obligor , and Y is called the assignor , since Y has assigned its right to X’s performance . X, the obligor, is obligated to continue to perform its duties under the agreement.
There are no “magic words” needed to create an assignment. The law simply requires that the would-be assignor have an intent to immediately and completely transfer their rights in the agreement. In addition, writing is typically not required to create an assignment. As long as X and Y both adequately understand what right is being assigned, an assignment is created.
Words that indicate a transfer is to take place suffice, such as “I intend to transfer my rights under this agreement,” or, “I intend to give my rights to Z,” or “I intend to confer an assignment on Z.” In addition,consideration,which is a bargained-for exchange required for a contract to be valid, is not required for assignment.
In certain instances, an assignment of contract rights can be prohibited. If the contract contains a clause prohibiting assignment of “the contract,” without specifying more, the law construes this language as barring only delegation of the assignor’s duties, not their rights. If the assignment language states “assignment of contractual rights are prohibited,” the obligor may sue for damages if the assignor attempts to assign the agreement. If the contract language states that attempts to assign “will be void,” the parties can bar assignment.of rights.
Under modern contract law, the phrase “I assign the contract” is usually interpreted to mean that one is assigning rights and duties. What is an assignment of duties? An assignment of duties occurs where Y, called the obligor or delegator, promises to perform for X, the obligee. Y then delegates their duty to perform to Z, the delegate. Under the law, most duties can be delegated.
There are exceptions to this rule. Delegation can be prohibited when:
- The duties to be performed involve personal judgment and special skill (e.g., a portrait, creation of a custom-made dress).
- “Personal judgment” is the exercise of some kind of superior judgment when it comes to determining how, when, or where to do something. Examples of individuals who exercise personal judgment include talent scouts and financial advisors. Special skill is the unique ability to create a good or perform a service. A delegator can be prohibited from delegating duties when it is that specific delegator’s services are sought. For example, if the services of a specific famous chef are sought, and the original agreement was entered into on the understanding that the chef was hired for their specific talent, the delegator may not delegate the services;
- The assignment fundamentally changes risks or responsibilities under the agreement;
- The assignment is over future rights associated with a future contract that does not currently exist;
- Delegation would increase the obligation of the obligee. For example, if a shoe manufacturer contracts to deliver soles to a store in the same town as the shoe factory, the other party cannot assign the delivery to a different store in another state. Doing so would impose a greater obligation on the obligee than was originally contemplated;
- The obligee had placed special trust in the delegator. For example, assume that you have hired a patent attorney, based on that attorney’s significant skill and expertise, to obtain a valuable patent. You have placed special trust in this person, hiring them instead of other patent attorneys, because of their unique expertise. In such a situation, the attorney may not delegate his duties to another attorney (delegate), since the attorney was hired because of one person’s special capabilities;
- The delegation is of a promise to repay a debt; or
- The contract itself restricts or prohibits delegation. If the contract states, “any attempt to delegate duties under this contract is void,” a delegation will not be permitted.
In a contract involving assignment of rights, the assignee may sue the obligor. This is because the assignee, once the assignee has been assigned rights, is entitled to performance under the contract. If the obligor had a defense that existed in the original contract between obligor and assignor, the obligor may assert that defense against the assignee. Examples of such defenses include the original contract was not valid because of lack of consideration, or because there was never a valid offer or acceptance).
An assignee may also sue an assignor. Generally, if an assignment is made for consideration,it is irrevocable. Assignments not made for consideration, but under which an obligor has already performed, are also irrevocable. If an assignor attempts to revoke an irrevocable assignment,the assignee may sue for “wrongful revocation.”
In circumstances involving delegation of duties,an obligee must accept performance from the delegate of all duties that may be delegated. The delegator remains liable on the agreement. Therefore, the obligee may sue the delegator for nonperformance by the delegate. The obligee may sue the delegate for nonperformance, but can only require the delegate to perform if there has been an assumption by the delegate. An assumption by the delegate is a promise that the delegate will perform the delegated duty, which promise is supported by consideration.
Assignments that are not supported by consideration are revocable. If an initial assignment is revocable, a subsequent assignment can revoke it. If a first assignment is irrevocable, because consideration was present,the first assignment will usually prevail over a subsequent assignment. This means the person who can claim the assignment was first made to them will prevail over someone who claims a subsequent assignment.
If, however, the second person paid value for the assignment, and entered into the assignment without knowing of the first assignment, the “subsequent”assignee is entitled to proceeds the first judgment against the obligor (the original party who still must perform), in the event such a judgment is issued,
If you have an issue with assignment of rights or duties under a contract, you should contact a contract lawyer for advice. An experienced business lawyer near you can review the facts of your case, advise you of your rights, and represent you in court proceedings.
Save Time and Money - Speak With a Lawyer Right Away
- Buy one 30-minute consultation call or subscribe for unlimited calls
- Subscription includes access to unlimited consultation calls at a reduced price
- Receive quick expert feedback or review your DIY legal documents
- Have peace of mind without a long wait or industry standard retainer
- Get the right guidance - Schedule a call with a lawyer today!
Need a Contract Lawyer in your Area?
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Daniel Lebovic
LegalMatch Legal Writer
Original Author
Prior to joining LegalMatch, Daniel worked as a legal editor for a large HR Compliance firm, focusing on employer compliance in numerous areas of the law including workplace safety law, health care law, wage and hour law, and cybersecurity. Prior to that, Daniel served as a litigator for several small law firms, handling a diverse caseload that included cases in Real Estate Law (property ownership rights, residential landlord/tenant disputes, foreclosures), Employment Law (minimum wage and overtime claims, discrimination, workers’ compensation, labor-management relations), Construction Law, and Commercial Law (consumer protection law and contracts). Daniel holds a J.D. from the Emory University School of Law and a B.S. in Biological Sciences from Cornell University. He is admitted to practice law in the State of New York and before the State Bar of Georgia. Daniel is also admitted to practice before the United States Courts of Appeals for both the 2nd and 11th Circuits. You can learn more about Daniel by checking out his Linkedin profile and his personal page. Read More

Jose Rivera, J.D.
Managing Editor
Related Articles
- Acceleration Clause Lawyers
- What is Rescission of Contract?
- When Is a Contract Considered Void or Voidable?
- Illegal Contract Lawyers
- Nominal Damages in a Contracts Claim
- Breach of Contract Defense: Laches
- Breach of Contract Defenses: Unclean Hands
- Material Breach of Contract and Lawsuits
- Breaching vs. Non-Breaching Parties in a Contract
- What is a Contract?
- Fraudulent Inducement
- Contract Law: Fraud Cases
- Limitation of Liability Clauses in Construction Contracts
- Homeowners Hiring Unlicensed Contractors
- Business Licenses for Independent Contractors
- State Statute of Limitations for a Breach of Contract Action
- Email Contracts
- Employer Liability for Wage Violations of Subcontractors
- Employee or Independent Contractor?
- Tax Requirements for Independent Contractors
- Statutory Damages in Breach of Contract Cases
- Hiring an Independent Contractor
- Attorney's Fees in Breach of Contract Cases
- What Is the Proper Court for a Breach of Contract Lawsuit?
- Exclusive Dealing Contracts
- Defenses to Breach of Employment Contract
- Real Estate Contracts: Exclusive Right to Sell
- Exculpatory Clauses
- Exterminators Breach of Contract Liability
- Negligent Misrepresentation
Discover the Trustworthy LegalMatch Advantage
- No fee to present your case
- Choose from lawyers in your area
- A 100% confidential service
How does LegalMatch work?
Law Library Disclaimer

16 people have successfully posted their cases
- Practical Law
Practical Law UK Glossary 1-107-6442 (Approx. 4 pages)
- Lending: General
- After Death
- General Contract and Boilerplate
- Security and Quasi Security
The Law Dictionary
Your Free Online Legal Dictionary • Featuring Black’s Law Dictionary, 2nd Ed.
ASSIGNMENT Definition & Legal Meaning
Definition & citations:.
In contracts. 1. The act by which one person transfers to another, or causes to vest in that other, the whole of the right, interest, or property which he has in any realty or personalty, in possession or in action, or any share, interest, or subsidiary estate therein. Seventh Nat. Bank v. Iron Co. (C. C.) 35 Fed. 440; Haug v. Riley, 101 Ga. 372, 29 S. E. 44, 40 L It A. 244. More particularly, a written transfer of property, as distinguished from a transfer by mere delivery. 2. In a narrower sense, the transfer or making over of the estate, right, or title which one has in lands and tenements; and, in an especially technical sense, the transfer of the unexpired residue of a term or estate for life or years. Assignment does not include testamentary transfers. The idea of an assignment is essentially that of a transfer by one existing party to another existing party of some species of property or valuable interest, except in the case of an executor. Ilight v. Sackett, 34 N. Y. 447. 3. A transfer or making over by a debtor of all his property and effects to one or more assignees in trust for the benefit of his creditors. 2 Story, Eq. Jur.
This article contains general legal information but does not constitute professional legal advice for your particular situation. The Law Dictionary is not a law firm, and this page does not create an attorney-client or legal adviser relationship. If you have specific questions, please consult a qualified attorney licensed in your jurisdiction.
Browse Legal Articles
Business Formation
Business Law
Child Custody & Support
Criminal Law
Employment & Labor Law
Estate Planning
Immigration
Intellectual Property
Landlord-Tenant
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Personal Injury
Real Estate & Property Law
Traffic Violations
Browse by Area of Law
Powered by Black’s Law Dictionary, Free 2nd ed., and The Law Dictionary .
About The Law Dictionary
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
Assignment Law: Everything You Need to Know
In legal terms, the meaning of an assignment is a contractual obligation to transfer a property title or right from one party to another. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
The term assignment law is used in the law of real estate and in the law of contracts. In both instances, it relates to the transfer of rights held by one party (the assignor) to another party (the assignee).
Assignment Law
In legal terms, the meaning of an assignment is a contractual obligation to transfer a property title or right from one party to another. Generally, the assignment is transferred based on an entire interest in the property, chattel, estate, or other item assigned.
A grant is different from an assignment in that an assignment refers to the right to transfer the property. This is considered an intangible right. On the other hand, the grant is concerned about the physical transfer of property. This is a tangible right. For example, a payee can assign their rights to collect a note payment to a bank.
The terms of the contract must be analyzed to determine if the right of assignment is prohibited. For example, a property owner may allow a lease to be assigned, ordinarily along with an assumption agreement, where the new tenant is now responsible for the payments and duties of the lease.
The holder of a trademark may transfer it, either by giving or selling their interest in the trademark to another party. This is referred to as an assignment. The party that receives the benefit is called the assignee. Once transferred, the assignee has the ability to exclude others from using their trademark.
In order for the assignment to be enforceable, it must be in writing and have the goodwill of the company attached to the mark. For an assignment to be effective, it must contain the fundamental aspects of a contract, such as:
- Parties with legal capacity
- Legality of object
- Consideration consent
A contract assignment occurs when a party assigns their contractual rights to a third party. The benefit the issuing party would have received from the contract is now assigned to the third party. The party appointing their rights is referred to as the assignor, while the party obtaining the rights is the assignee. Essentially, the assignor prefers that the assignee reverses roles and assumes the contractual rights and obligations as stated in the contract. Before this can occur, all parties to the original contract must be notified.
How Assignments Work
The specific language used in the contract will determine how the assignment plays out. For example , one contract may prohibit assignment, while another contract may require that all parties involved agree to it before proceeding. Remember, an assignment of contract does not necessarily alleviate an assignor from all liability. Many contracts include an assurance clause guaranteeing performance. In other words, the initial parties to the contract guarantee the assignee will achieve the desired goal.
When Assignments Will Not Be Enforced
The following situations indicate when an assignment of a contract is not enforced:
- The contract specifically prohibits assignment
- The assignment drastically changes the expected outcome
- The assignment is against public policy or illegal
Delegation vs. Assignment
Occasionally, one party in a contract will desire to pass on or delegate their responsibility to a third party without creating an assignment contract. Some duties are so specific in nature that they cannot be delegated. Adding a clause in the contract to prevent a party from delegating their responsibilities and duties is highly recommended.
Three Steps to Follow if You Want to Assign a Contract
There are three main steps to take if you're looking to assign a contract:
- Make sure the current contract does not contain an anti-assignment clause
- Officially execute the assignment by transferring the parties' obligations and rights
- Notify the obligor of the changes made
Once the obligor is notified, the assignor will effectively be relieved of liability.
Anti-Assignment Clauses
If you'd prefer not to allow the party you're doing business with to assign a contract, you may be able to prevent this from occurring by clearly stating anti-assignment clauses in the original contract. The three most common anti-assignment clauses are:
- Consent required for assignment
- Consent not needed for new owners or affiliates
- Consent not unreasonably withheld
Based on these three clauses, no party in the contract is allowed to delegate or assign any obligations or rights without prior written consent from the other parties. Any delegation or assignment in violation of this passage shall be deemed void. It is not possible to write an anti-assignment clause that goes against an assignment that is issued or ordered by a court.
If you need help with assignment law, you can post your job on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Legal Assignment
- Assignment Contract Law
- Assignment of Rights and Obligations Under a Contract
- Assignment of Rights Example
- Assignment Legal Definition
- What Is the Definition of Assigns
- Consent to Assignment
- Assignment Of Contracts
- Delegation vs Assignment
- Assignment of Contract Rights
Contact us whenever you need it!
+1 855 997 0206
Contact Hours: Sun-Sat 8am - 10pm ET
- LawDistrict ❯
- Legal Dictionary
Assignment is a legal definition that refers to the transfer of rights, property, or other benefits between two parties. The party allocating the rights is known as the “assignor”, while the one receiving them is called the “assignee”. The other original party to the contract is known as the “ obligor ”.
A burden, duty, or detriment cannot be transferred as an assignment without the agreement of the assignee . Furthermore, the assignment can be carried out as a gift, or it may be paid for with a contractual consideration .
Keep reading to learn how this important legal term is used both in contract and property law and to see relevant examples.
- Assignment Examples
A common example of assignment within property law can be seen in rental agreements between landlords and tenants. For example, a tenant may be renting from a landlord but wants another party to take over the property . In this scenario, the tenant may be able to choose between assigning the lease to a new tenant or subleasing it.
If assigning it, the new tenant will be given the entire balance of the term, with no reversion to anyone else being possible. In other words, the new tenant would have a legal relationship with the landlord. On the other hand, if subleasing the property, the new tenant would be given a limited term and no legal responsibility towards the property owner, only towards the original tenant.
Another example of assignment can be seen within contract law . Let’s say that a school hires a piano teacher for a monthly employment contract with a salary of $2000 per month. As long as there is consent from all parties, the teacher could assign their contract to another qualified piano instructor.
This would be an assignment both of the piano teacher’s rights to receive $2000 per month, and a delegation of their duty to teach piano lessons. This illustrates the fact that under contract law, assignment always includes a transfer of both rights and duties between the parties. If a breach of contract is made by either party, for example for defective performance, then the new teacher or the school can sue each other accordingly.
- Legal Requirements for Assignment
For an assignment to be legally valid, it must meet certain requirements . If these are not met, a trial court can determine that the transfer of rights did not occur. The legal requirements for assignment are as follows:
- All parties must consent and be legally capable to carry out the assignment.
- The objects, rights, or benefits being transferred must be legal.
- The assignment is not against public policy or illegal.
- Some type of consideration is included if necessary.
- The contract in question must already be in place and doesn’t prohibit assignment.
- If a duty is being transferred, and it requires a rare genius or skill, then it cannot be delegated.
- The assignment doesn’t significantly change the expected outcome of a contract.
- Assignment Steps
To successfully assign a contract, certain steps must be followed to ensure the process is legally valid. The necessary assignment steps are listed below:
- Ensuring there is no anti-assignment clause in the contract.
- Executing the assignment by transferring the obligations and rights to a third party.
- Notifying the obligor of the transfer, which in turn relieves the assignor of any liability.
- Avoiding Assignment
In certain situations, one of the two parties may not want to allow their counterpart to assign the contract. This can be prevented by setting anti-assignment clauses in the original contract. An example of this is making it necessary for prior written consent to be attained from the other parties before the assignment is approved. Nevertheless, an anti-assignment clause cannot be included in an assignment that was issued or ordered by a court.
- Assignment vs. Novation
Novation occurs when a party would like to transfer both the benefits and burden of a contract to another party. This is similar to assignment in the sense that the benefits are transferred, but in this case, the burden is also passed on. When novation is finalized, the original contract is deleted and a new one is created, in which a third party becomes responsible for all the obligations and rights of the original contract.
- Assignment vs. Delegation
Although delegation and assignment are similar in purpose, they are two different concepts. Delegation refers to transferring the obligation to a third party without an assignment contract . While in assignment an entire contract and its rights and benefits can be passed on, in delegation only a particular contractual task or activity is transferred.
Let’s look at an example . Lisa is a homeowner that wants to hire Michael with an independent contractor agreement to remodel her garage. He plans to do all the work himself, but he’s not a painter, so he wants to delegate the painting work to his friend Valentina.
In this example, the contract is between Lisa, the obligor, and Michael, the delegator. Valentina would then be known as a delegatee, she doesn’t assume responsibility for the contract nor does she receive the contractual benefits, which in this case would be monetary compensation. However, Michael may have a separate agreement with Valentina to pay her in return for her work.
It’s also important to note that some duties are so specific in nature that it’s not possible to delegate them. In addition, if a party wants to avoid delegation , it’s recommended to add a clause to prevent the other party from delegating their duties.
Create a Customizable Legal Form Now
Get 7 Days Total Access to Our Entire Catalog!
Related Content
- checklists (0)
- practice notes (1432)
- precedents (702)
- q&as (792)
- News (1558)
Assignment definition
What does assignment mean.
An assignment is 'an immediate transfer of an existing proprietary right, vested or contingent from one party to another'. Assignments can occur by consent or by operation of law.
A consensual assignment occurs by way of a gift or consideration. Assignments by law can occur during life or on death and will transfer the benefit of rights to the assignee but will not make the assignee personally liable. An attempt to transfer benefits under a contract of personal performance will not be effective.
View the related checklists about Assignment
Isda documentation in a finance transaction—checklist.
ISDA documentation in a finance transaction—checklist This checklist sets out the key ISDA documentary requirements which need to be considered...
Unauthorised payments—checklist
Unauthorised payments—checklist Under the Finance Act 2004 (FA 2004) and underlying regulations, payments from a registered pension scheme to, or...
View the related practice notes about Assignment
Subcontracting.
This Practice Note examines the following legal and practical matters in relation to entering into a subcontract or when granting...
What constitutes a valid assignment of a contract?
This Practice Note identifies what can be transferred when assigning rights under a contract and how to effect a valid...
Discover our 1432 Practice Notes on Assignment
View the related precedents about Assignment
Property warranties (short-form) in an asset purchase, step-in rights and sra compliance clauses: law firm outsourcing agreement.
Dive into our 702 Precedents related to Assignment
View the related q&as about Assignment
How might the european commission proposal for new conflict of law rules for assigned claims impact the secondary loan market.
How might the European Commission proposal for new conflict of law rules for assigned claims impact the secondary...
How do the provisions of paragraph 4 of Part 1 of Schedule 1 to the Academies Act 2010 impact consideration of whether or not a maintained school can let part of the school premises to a third party for use as a nursery two–four years olds?
How do the provisions of paragraph 4 of Part 1 of Schedule 1 to the Academies Act 2010 impact consideration...
See the 792 Q&As about Assignment
View the related News about Assignment
Restructuring & insolvency weekly highlights—11 july 2024.
This week's edition of Restructuring & Insolvency weekly highlights includes: the convening order for a scheme of arrangement for VTB...
IP weekly highlights—4 July 2024
This week's edition of IP weekly highlights includes: a hand-picked summary of news analysis, updates and new content from the...
Read the latest 1558 News articles on Assignment
Speed up all aspects of your legal work with tools that help you to work faster and smarter. Win cases, close deals and grow your business–all whilst saving time and reducing risk.
Access this content for free with a 7 day trial of LexisNexis and benefit from:
- Instant clarification on points of law
- Smart search
- Workflow tools
- 41 practice areas
** Trials are provided to all LexisNexis content, excluding Practice Compliance, Practice Management and Risk and Compliance, subscription packages are tailored to your specific needs. To discuss trialling these LexisNexis services please email customer service via our online form. Free trials are only available to individuals based in the UK, Ireland and selected UK overseas territories and Caribbean countries. We may terminate this trial at any time or decide not to give a trial, for any reason. Trial includes one question to LexisAsk during the length of the trial.
"Because of the pure breadth and depth of black letter law research and practical guidance that LexisNexis provides, we don't have to rely on counsel as much as perhaps firms that don't use LexisNexis."
KaurMaxwell
Access all documents on Assignment

0330 161 1234
- International Sales(Includes Middle East)
- Latin America and the Caribbean
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Philippines
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- United States
Popular Links
- Supplier Payment Terms
- Partner Alliance Programme
HELP & SUPPORT
- Legal Help and Support
- Tolley Tax Help and Support
LEGAL SOLUTIONS
- Compliance and Risk
- Forms and Documents
- Legal Drafting
- Legal Research
- Magazines and Journals
- News and Media Analysis
- Practice Management
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Settings
- Terms & Conditions
- Data Protection Inquiry
- Protecting Human Rights: Our Modern Slavery Agreement
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Law School Toolbox®
All the tools you need for law school success
Five Tips for a Great Legal Writing Assignment
September 25, 2012 By Lee Burgess 2 Comments

- Follow the format outlined by your professor. It is likely your legal writing professor has given you instructions for the overall format of your legal writing assignment. In addition, your professor may have given you formatting instructions for the body of your assignment, such as that you need to follow IRAC. Whatever the instructions, follow them . Sure, you may think it is an overly formal or a frustrating way to write—but to be honest, no one cares. You need to write for your professor . It is more important to write in the way your professor has outlined, than as you personally prefer. And it is not going to be the last time your writing will need to conform to someone else’s rules. As a working attorney you often need to write in the format requested by your boss or even by the court. So get used to it!
- Remember, your writing doesn’t need to be full of legalese—the best legal writing is often simple! So many law students make the mistake of thinking that to “sound like a lawyer” they must use every possible legal term out there. This is just not the case. Often the most effective legal writing is very clear and concise and only uses legal terms or “legalese” when appropriate (say, when you are using a term of art). It is also important to work on writing in a clear, concise way because your assignments may have maximum word count. So using extra words to sound “more professional” won’t really help your grade in the end.
- Answer the question asked by your assignment. Often students get so caught up in writing their assignment that they forget to focus on the question that was asked of them. It is important to read and re-read (and even read again) the assignment sheet. You don’t want to make a mistake and write something off topic. Remember, answering the question is key to getting a good grade!
- Plan before you write. A great legal writing assignment is organized. And for most of us this means that you need to plan your paper just as you would plan an essay or any other project. Organization is key and it takes time to sit with the research and develop your answer. Make sure you build this time into your plan of how you are going to get your assignment done.
- Proofread and double-check citations. As an attorney-in-training, it is very important to present yourself in a professional way. That means that you need to proofread your assignments to present yourself in a professional way to your professor as well. If your assignment is riddled with typos, it is distracting for the professor and likely will cause your grade to drop. Also, students often are lax when handling citations. You are typically graded on the accuracy of your citations. Citations are not hard, but you must be detail oriented and look things up! I have seen many a legal writing grade go down because students didn’t spend adequate time or energy on citations. Don’t let this happen to you.
Legal writing, like most things, gets easier the more that you do it. So do every practice assignment assigned and get as much feedback as you can. This will help you become an excellent legal writer, which is a critical skill in our profession.
Check out these other helpful posts:
- Surviving the first weeks of law school .
- Law school exam prep 101 .
- Getting feedback on past exams is critical .
- Pay attention in class, it can save you time !
Are you on our mailing list? Sign up now and we’ll send you lots of great stuff, totally free!
Image by nh313066 via stock.xchng .

Looking for some help to do your best in law school? Find out about our law school tutoring options.
About Lee Burgess
Lee Burgess, Esq. is the co-founder of the Law School Toolbox , a resource for law students that demystifies the law school experience and the Bar Exam Toolbox , a resource for students getting ready for the bar exam. Lee has been adjunct faculty at two bay area law schools teaching classes on law school and bar exam preparation. You can find Lee on Twitter at @leefburgess , @lawschooltools , & @barexamtools .
Reader Interactions
Thank very much for the tips i have just read they been beneficial to me because am a distance law school student.
I need more guide to legal writing because am lecturing this course for Magistrates
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Want Better Law School Grades?
Sign Up for Our Exam Tips!
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Copyright 2024 Law School Toolbox®™
What is a notice of assignment?
An assignment takes place when one party is holding a right to property, claims, bills, lease, etc., of another party and wishes to pass it along (or sell it) to a third party. As complicated as that sounds, it really isn’t. Strangely enough, many assignments can be made under the law without immediately informing, or obtaining the permission, of the personal obligated to perform under the contract. An example of this is when your mortgage is sold to another mortgage company. The original mortgage company may not inform you for several weeks, and they certainly aren’t going to ask your permission to make the sale.
If a person obligated to perform has received notice of the assignment and still insists on paying the initial assignor, the person will still be obligated to pay the new assignee according to the agreement. If the obligated party has not yet been informed of the assignment and pays the original note holder (assignor), the assignor is obligated to turn those funds over to the new assignee. But, what are the remedies if this doesn’t take place? Actually, the new assignee may find themselves in a difficult position if the assignor simply takes off with their funds or payment. They are limited to taking action against the person they bought the note from (assignor) and cannot hold the obligator liable. Therefore, it is important to remember that if any note or obligation is assigned to another party, each party should be well aware of their responsibilities in the transaction and uphold them according to the laws of their state. Assignment forms should be well thought out and written in a manner which prevents the failure of one party against another.
Related posts:
- Does your Agreement Require an Assignment Legal Form?
- Why Every Landlord and Tenant Needs a Lease Agreement
- Why you need a Power of Attorney and How to Assign One
Related Posts
- Seven Slip-and-Fall Accidents FAQs That You Should Know
- What is a mutual non-disclosure agreement?
- Can I use a form to change my name?
- When do I need a mechanic’s lien?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
CAPTCHA Code *
- Platform Overview All-in-one legal research and workflow software
- Legal Research Unmetered access to primary and secondary sources
- Workflow Tools AI-powered tools for smarter workflows
- News & Analysis Paywall-free premium Bloomberg news and coverage
- Practical Guidance Ready-to-use guidance for any legal task
- Contract Solutions New: Streamlined contract workflow platform
- Introducing Contract Solutions Experience contract simplicity
- Watch product demo
- Law Firms Find everything you need to serve your clients
- In-House Counsel Expand expertise, reduce cost, and save time
- Government Get unlimited access to state and federal coverage
- Law Schools Succeed in school and prepare for practice
- Customer Cost Savings and Benefits See why GCs and CLOs choose Bloomberg Law
- Getting Started Experience one platform, one price, and continuous innovation
- Our Initiatives Empower the next generation of lawyers
- Careers Explore alternative law careers and join our team
- Press Releases See our latest news and product updates
- DEI Framework Raising the bar for law firms
- Request Pricing
Master the Legal Memo Format
September 20, 2022
[Bloomberg Law’s Essential Career Toolkit can help you excel in class and jump-start your legal career to successfully transition from law student to lawyer.]
What is the legal memo assignment?
The legal memo is an objective memorandum that provides you the opportunity to review and research relevant case law, investigate relevant facts using available resources, analyze those facts under that law, and impartially assess the potential outcome of a matter. The legal memo is an assignment that law firm associates are frequently asked to provide to senior attorneys.
Far too often, however, the assigning attorney takes one look at the result and replies, “I knew this already.” To prevent this outcome, it’s important to write a legal memo with sufficient understanding of audience, scope, purpose, and format. With proper planning, law firm associates can maximize the odds of favorable reception at the outset.
Bloomberg Law can help you understand and apply legal issues to your legal memo assignment, so your final product addresses all relevant points right out of the gate.
What’s the difference between a closed legal memo and an open legal memo?
A closed legal memo is an assignment where you are given the case law or other primary law to be used in your writing. Far more challenging is an open legal memo, where you will need to research and identify the relevant law, investigate and analyze the most legally significant facts involving a particular client, and provide a critical assessment of how the court may apply the law to the matter.
By extension, unlike a court brief, the legal memo is not the place to wager a legal opinion or argue facts. The legal memorandum serves as an objective standalone document and identifies the risks and any unknown facts that need investigation. It should maintain an impartial tone, with no implied preference for one side or the other.
What’s the standard legal memo format?
Generally, a legal memorandum comprises six sections, with the following information:
1. Heading or caption
A section, titled, “Memorandum,” identifies the recipient (To: _______), the author (From: ____), the assignment submission date (typically in MMMM DD YYYY format), and subject of the memo (Re: __________).
2. Question presented
A brief one-sentence statement that defines how the law applies to the legal question at hand, and the jurisdiction where the matter will be decided. The question presented is specific and impartial and doesn’t assume a legal conclusion.
3. Brief answer
A quick-hit legal prediction to the question presented, based on a short (four to five sentences) explanation that references relevant law and facts.
4. Statement of facts
A concise, impartial statement of the facts that captures the heart of the legal matter, as well as current and past legal proceedings related to the issue. The facts can be chronological or grouped thematically, whichever format presents the facts in the clearest manner.
5. Discussion
Restates the main facts and delineates the overarching legal rule. Several paragraphs outline the various legal topics to be addressed in the case and provide an analysis of the legal issues, usually ordered in subsections.
6. Conclusion
The assigning attorney will likely read this section first. It predicts how the court will apply the law, and how confident you are in your prediction based on the data. With an impartial advisory tone, you identify next steps and propose a legal strategy to proceed.
How to write a legal memo
Legal research memos can come in many forms—from broad 50-state surveys to more nuanced research on a particular point of law—but whatever the format, it’s important that you fully understand the task entrusted to you before you start typing.
If you tackle your assignment by following the recommended approaches in the legal memo example below, you’ll be more likely to find an appreciative supervising attorney, deliver better work product, cut down on the number of drafts required to arrive at a final product, and, most importantly, please the client.
Learn the essentials of litigation writing, research, and document review with our Core Litigation Skills Practical Guidance Toolkit , available to Bloomberg Law subscribers.
Legal memorandum sample assignment
Assignment: Prepare an open legal memo on whether, under the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause, there is personal jurisdiction over a foreign car manufacturer involving a products liability case.
Step 1: Understand the legal issues
Review legal memo assignment materials.
In an open legal memo, you will be tasked with researching relevant primary and secondary resources, such as from national, single, or multiple state entities, as well as appeals circuits, to include in your analysis.

Locate secondary sources
Secondary sources, such as books, treatises, law reviews, legal analysis publications, and Practical Guidance are a great starting point to assist with your legal memo research. Although secondary sources are not binding on courts, meaning courts are not required to follow these sources, they are still helpful tools to use when you know little about a topic.
However, remember that while you may know little about a topic, the same may not hold true for your audience. Readers like law partners and assigning attorneys will already know general law. Identify your audience’s presumed level of knowledge, then the most mission-critical questions to address. These identified gaps will inform your fact-finding and research.
Use secondary resources to better fill in the main legal topics and issues as they relate to the facts in the legal memo assignment. Your legal research should help frame the issue and lead to other relevant materials, including cases and statutes.
Throughout, utilize legal memo space wisely. Remember, legal memo length varies by subject. Some topics require only a short summary, while others compel long-form treatment. For guidance, search your firm’s office document management system for previous legal memos.
Sample assignment – Step 1
Understand the legal issues: Legal research depends on the right search terms. In the case, for example, you can use the keywords: (“personal jurisdiction” and manufacture!)) to locate relevant resources on the Bloomberg Law platform.
More broadly, while your search into secondary sources may span books and treatises, law review articles, and other legal analysis publications, make sure to vet all legal authorities for relevance.
[Research tip: It can be challenging to know all relevant keywords. Bloomberg Law provides a convenient search results page, where relevant article blurbs showcase additional keywords to explore. Based on targeted keywords, you can better gather the most relevant background information to assist with your analysis.]
Step 2: Develop a research plan
Identify primary law.
Primary sources can often be identified with research tools, such as court opinions searches for relevant case law. However, primary sources are not always apparent. In such cases, work your way backward. Reviewing secondary sources can help you identify a list of relevant primary law resources, like case law and related statutes. Keep your research organized and create a research plan to identify key resources. The research plan will list the relevant primary law and how the case or statute relates to your comprehensive legal analysis.
Stay organized
Save the relevant cases and statutes to a designated workspace. Bloomberg Law provides a streamlined and secure digital working area where you can add your notes as well as upload and store your drafts to keep organized.
Sample assignment – Step 2
Develop a research plan: In the assignment, some legal research may mention cases on what contacts a foreign defendant must have for the court to have personal jurisdiction over it, such as Ford Motor Co. v. Montana Eighth Judicial District Court . Read through these articles to reveal additional relevant cases and statutes to support your analysis.
Step 3: Confirm your legal memo research
Once you have your research plan, you want to verify all your research to make sure you’re relying on the most current case law available. Bloomberg Law’s litigation tools like the BCite citator tool help you work smarter and faster to validate your case law research—specifically, to determine whether a citation still represents good law and can be relied upon—and helps you to conduct additional research to find more cases and resources that support your legal memo’s findings and conclusions.
Robust verification should ensure you know the following information:
- Composite analysis – the overall treatment of the cited case by other courts.
- Direct history – How a cited case has moved through the court system.
- Case analysis – Cases that have subsequently cited to the case.
- Authorities – Cases relied on by the court in the main case.
- Citing documents – Legal materials, such as court opinions, administrative decisions, and secondary sources that reference your case by citation.
Sample assignment – Step 3
Confirm your research: To see whether Ford Motor Co. v. Montana Eighth Judicial District Court is still good law, you will of course need to pull up and review the case status. As part of this verification, you should review how other courts have treated the case. Once you have verified case status, you can better find additional secondary cases and other sources that cite to your case.
[Research tip: Carefully review whether case law citation can be relied on in your legal memo. While a legal memo is written for internal stakeholders like the assigning attorney, and not for the court system, it may nonetheless serve as a primer for future material.]
Attorneys may later incorporate any case law citations within the legal memo into court filings in support of their arguments. Given this broad potential reach, it’s imperative to verify all case law within your legal memo. Any unverified case law that later makes its way into public documents will result in an admonition from the court.
It is also important not to cherry-pick case citations. Remember the legal memo’s purpose is to inform, not to argue the facts. The legal memo must therefore provide an objective summary of all relevant case law and how it applies to the facts at hand. The omission of negative case law only compromises future legal strategy and heightens client legal exposure.
Step 4: Write an objective analysis
The legal memo showcases your critical legal thinking skills. Use your research plan and research materials to help organize your analysis. Remember to clearly state the law and the facts, in the active voice, and present your analysis in a logical manner.
Even with the IRAC legal memo format (Issue, Rule, Application, and Conclusion), it can be a challenge to write with precision. For example, it may not be clear which details to include in the statement of facts. Skilled legal memo writers often begin with the discussion. With complementary considerations of legal authority and factual criteria, this section clarifies the most legally significant facts and informs other earlier sections like the question presented and brief answer.
Across all stages, Bloomberg Law provides a vast trove of articles and resources to assist you in preparing your legal memo. Whether this is your first or fiftieth legal memo assignment, you can showcase clear and impartial legal analysis in your legal memo and other writing assignments in ways that establish you as a strong legal mind.
Reference Shelf
11 resume rules every law student should follow
Succeeding in the modern legal classroom
The right answers to law interview questions
Three things to know before starting your law career
Turn your passion for social justice into a law career
Recommended for you
See bloomberg law in action.
From live events to in-depth reports, discover singular thought leadership from Bloomberg Law. Our network of expert analysts is always on the case – so you can make yours. Request a demo to see it for yourself.
- Personal Profile
- See all online law products
- Guided Tour
- Subscriber Services

- Financial Law [FBL]
- International Commercial Arbitration [ICMA]
- Private International Law [PRIL]
- International Commercial Law [ICML]
Recently viewed (0)
- Save Search

- Find at OUP.com
The Law of Assignment (3rd Edition)
Marcus smith, nico leslie.
This book is the leading text on the law relating to intangible property or choses in action. Its clear and approachable structure covers all forms of intangible property (debts, rights under contract, securities, intellectual property, leases, rights/causes of action, and equitable rights), considering the nature of intangible property, how it comes into being, and how it is transferred or assigned. The first part of the book analyses the general principles regarding intangibles and their transfer, and the second examines the practical considerations relating to particular types of intangibles, securities, insurance contracts, leases, and intellectual property under the law. This new edition includes new chapters on powers of attorney and factoring, areas particularly important to legal practice. Other significant developments include the expansion of the chapter on leases to include leasing of chattels, and more material on securities, especially regarding the operation of settlement systems.
Bibliographic Information
Affiliations are at time of print publication..
Marcus Smith, author
Nico Leslie, author
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
- Foreword to The Third Edition
- Foreword to the Second Edition
- Foreword to the First Edition
- Preface to The Third Edition
- Preface to the First Edition
- Summary Contents
- Detailed Contents
- Table of Cases
- Statutory Instruments
- Netherlands
- United States
- Conventions
- Regulations
- International Conventions
- List of References
- List of Authority Abbreviations
- Preliminary Material
- Part III.01
- [185.80.149.115]
- 185.80.149.115

Top 14 Assignments Law Students Have to Deal With

4 Effective Ways to Build a Reputation As a New Lawyer

Advice For Students Who Want to Become Car Accident Lawyers

Being a student always means having to deal with loads of homework. This statement is true for all students, regardless of their academic level or the major they choose to study. However, while the scope of homework is about the same for everyone, the types of assignments can slightly vary depending on the subject that you study.
In this article, we are going to tell you about the four main homework types facing law students, in particular. So, if you are a law student yourself, read on to learn what will be expected of you in a law school.
Practice Homework
The first and the most common of the four main homework types is practice homework. The core goal of such assignments is to help students expand their knowledge and reinforce their newly-acquired skills by means of putting them to practice. This kind of homework is the one that makes the most of the academic program, which is why law students struggle with it the most.
The most common assignment that represents this type of homework is essay writing. Just like the rest of their peers, law students are being assigned dozens of essays and other academic papers every year. A load of such assignments is so huge that students often look for the write my essay online writing services and platforms. But, it is an integral part of the educational process, so there is no way to avoid academic writing.
Some other examples of practice homework that you can face in a law school can include:
- Memorizing local laws;
- Reading court records;
- Examining subject-related literature, etc.
Extension Homework
The second one of the four main homework types is extension homework. In a nutshell, this type of homework is used by professors to encourage their students to pursue knowledge individually and in ways that are more imaginative than simply reading a textbook. Also, extension assignments are used to help students connect what they learn in the classroom with real-life and apply their existing skills to expand their knowledge.
Common types of law assignments that represent this type of homework include:
- Writing literature reviews;
- Researching local law news;
- Compare and contrast events, etc.
Creative Homework
Despite the fact that law students spend most of their time studying complex and serious subjects, there is still a place for the next type of homework – creative homework in their curriculums. As you can guess from its name, this type of homework often takes different creative forms. The key goal is to help students develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills through completing creative projects.
There are plenty of examples of creative homework assignments that you can face in a law school. Basically, pretty much any type of individual project can be considered a creative homework assignment. However, to help you grasp the idea, here are a few examples of the most common law assignments of this type:
- Research projects;
- Photo essays;
- PowerPoint presentations, etc.
Preparatory Homework
Finally, the last of the four types of homework is preparatory homework. The key goal of such homework is to help students gain solid background on a specific unit of study in order to prepare them for future lessons. Simply put, preparatory homework is the type of homework that helps you collect initial knowledge on the subject you are studying. And it can also be called one of the most common types of assignments facing law and other students.
What assignments can be considered as preparatory homework? In fact, there are many. To name a few, here are some of the most common examples of this type of homework:
- Tests and exams;
- Completing exercises from the workbook;
- Reading textbook chapters to prepare for the next lesson, test, discussion, etc.
The Bottom Line
Whether you are just planning to enroll in a law school or are already a law student, knowing about different types of homework that you will have to deal with can empower you for better academic achievements.
After reading this article, you should have a better idea of different homework types that you can face studying in a law school. Hopefully, this will help you prepare for your academic path and ensure success.
Camilla Uppal
Related posts.

6 Reasons to Hire a Car Accident Lawyer

How to Navigate Family-Based Immigration: A Brief Guide

What Not to Do After a Motorcycle Accident
Comments are closed.
Primary tabs
Assignee is a person to whom a right is transferred by the person holding such rights under the transferred contract (the “assignor”). The act of transferring is referred to as “ assigning ” or “ assignment ” and is a concept found in both contract and property law.
Contract Law
Under contract law, when one party assigns a contract, the assignment represents both: (1) a transfer of rights; and (2) a delegation of duties . For example, if A contracts with B to teach B guitar for $50, A can assign this contract to C. Here, A has both: assigned A’s rights under the contract to receive the $50 to C, and delegated A’s duty to teach guitar to C. In this example, A is the “assignor” because he/she assigns the contract to C. A is also the “primary obligor ,” meaning he/she will still be liable to B if C fails to teach B guitar. C is the “assignee,” since C is the party to whom A transfers the contract. C is also the “secondary obligor,” since he/she must perform the obligations to B. B is the ultimate recipient of the duty under the assignment, and is the “ obligee .”
There are a few notable rules regarding assignments under contract law. First, if an individual has not yet secured the contract to perform duties to another, he/she cannot assign his/her future right to an assignee. That is, if A has not yet contracted with B to teach B guitar, A cannot assign his/her rights to C. Second, rights cannot be assigned when they materially change the obligor’s duty and rights. Third, the primary obligor can sue the assignee directly if the assignee does not perform the assigned duty. In guitar assignment example, if C does not teach B guitar, A can sue C for any liability that A incurs as a result of C’s failure to perform the assigned contract. Fourth, if the promised performance requires a rare genius or skill, then the primary obligor cannot assign the contract.
Lastly, a related concept is novation , which is when the secondary obligor substitutes and releases the primary obligor. If novation occurs, then the primary obligor’s duties are extinguished under the contract. However, novation requires the obligee’s consent . In the guitar example, if A, B, and C agree to novation, then A would not be liable if C fails to teach B guitar.
Property Law
Under property law, assignment typically arises in landlord-tenant situations. For example, A might be renting from landlord B but wants C, a new tenant, to take over the lease. In this scenario, A might be able to choose between assigning and subleasing the property to C. If assigning , A would be giving C the entire balance of the term, with no reversion to anyone. If subleasing , A would be giving C for a limited period of the remaining term. Significantly, under assignment, C would have privity of estate with the landlord, while under a sublease, C would not.
[Last updated in December of 2021 by the Wex Definitions Team ]
- business law
- landlord & tenant
- property & real estate law
- trusts, inheritances & estates
- wex definitions
Business development
- Billing management software
- Court management software
- Legal calendaring solutions
Practice management & growth
- Project & knowledge management
- Workflow automation software
Corporate & business organization
- Business practice & procedure
Legal forms
- Legal form-building software
Legal data & document management
- Data management
- Data-driven insights
- Document management
- Document storage & retrieval
Drafting software, service & guidance
- Contract services
- Drafting software
- Electronic evidence
Financial management
- Outside counsel spend
Law firm marketing
- Attracting & retaining clients
- Custom legal marketing services
Legal research & guidance
- Anywhere access to reference books
- Due diligence
- Legal research technology
Trial readiness, process & case guidance
- Case management software
- Matter management
Recommended Products
Conduct legal research efficiently and confidently using trusted content, proprietary editorial enhancements, and advanced technology.
Accelerate how you find answers with powerful generative AI capabilities and the expertise of 650+ attorney editors. With Practical Law, access thousands of expertly maintained how-to guides, templates, checklists, and more across all major practice areas.
A business management tool for legal professionals that automates workflow. Simplify project management, increase profits, and improve client satisfaction.
- All products
Tax & Accounting
Audit & accounting.
- Accounting & financial management
- Audit workflow
- Engagement compilation & review
- Guidance & standards
- Internal audit & controls
- Quality control
Data & document management
- Certificate management
- Data management & mining
- Document storage & organization
Estate planning
- Estate planning & taxation
- Wealth management
Financial planning & analysis
- Financial reporting
Payroll, compensation, pension & benefits
- Payroll & workforce management services
- Healthcare plans
- Billing management
- Client management
- Cost management
- Practice management
- Workflow management
Professional development & education
- Product training & education
- Professional development
Tax planning & preparation
- Financial close
- Income tax compliance
- Tax automation
- Tax compliance
- Tax planning
- Tax preparation
- Sales & use tax
- Transfer pricing
- Fixed asset depreciation
Tax research & guidance
- Federal tax
- State & local tax
- International tax
- Tax laws & regulations
- Partnership taxation
- Research powered by AI
- Specialized industry taxation
- Credits & incentives
- Uncertain tax positions
A powerful tax and accounting research tool. Get more accurate and efficient results with the power of AI, cognitive computing, and machine learning.
Provides a full line of federal, state, and local programs. Save time with tax planning, preparation, and compliance.
Automate work paper preparation and eliminate data entry
Trade & Supply
Customs & duties management.
- Customs law compliance & administration
Global trade compliance & management
- Global export compliance & management
- Global trade analysis
- Denied party screening
Product & service classification
- Harmonized Tariff System classification
Supply chain & procurement technology
- Foreign-trade zone (FTZ) management
- Supply chain compliance
Software that keeps supply chain data in one central location. Optimize operations, connect with external partners, create reports and keep inventory accurate.
Automate sales and use tax, GST, and VAT compliance. Consolidate multiple country-specific spreadsheets into a single, customizable solution and improve tax filing and return accuracy.
Risk & Fraud
Risk & compliance management.
- Regulatory compliance management
Fraud prevention, detection & investigations
- Fraud prevention technology
Risk management & investigations
- Investigation technology
- Document retrieval & due diligence services
Search volumes of data with intuitive navigation and simple filtering parameters. Prevent, detect, and investigate crime.
Identify patterns of potentially fraudulent behavior with actionable analytics and protect resources and program integrity.
Analyze data to detect, prevent, and mitigate fraud. Focus investigation resources on the highest risks and protect programs by reducing improper payments.
News & Media
Who we serve.
- Broadcasters
- Governments
- Marketers & Advertisers
- Professionals
- Sports Media
- Corporate Communications
- Health & Pharma
- Machine Learning & AI
Content Types
- All Content Types
- Human Interest
- Business & Finance
- Entertainment & Lifestyle
- Reuters Community
- Reuters Plus - Content Studio
- Advertising Solutions
- Sponsorship
- Verification Services
- Action Images
- Reuters Connect
- World News Express
- Reuters Pictures Platform
- API & Feeds
- Reuters.com Platform
Media Solutions
- User Generated Content
- Reuters Ready
- Ready-to-Publish
- Case studies
- Reuters Partners
- Standards & values
- Leadership team
- Reuters Best
- Webinars & online events
Around the globe, with unmatched speed and scale, Reuters Connect gives you the power to serve your audiences in a whole new way.
Reuters Plus, the commercial content studio at the heart of Reuters, builds campaign content that helps you to connect with your audiences in meaningful and hyper-targeted ways.
Reuters.com provides readers with a rich, immersive multimedia experience when accessing the latest fast-moving global news and in-depth reporting.
- Reuters Media Center
- Jurisdiction
- Practice area
- View all legal
- Organization
- View all tax
Featured Products
- Blacks Law Dictionary
- Thomson Reuters ProView
- Recently updated products
- New products
Shop our latest titles
ProView Quickfinder favorite libraries
- Visit legal store
- Visit tax store
APIs by industry
- Risk & Fraud APIs
- Tax & Accounting APIs
- Trade & Supply APIs
Use case library
- Legal API use cases
- Risk & Fraud API use cases
- Tax & Accounting API use cases
- Trade & Supply API use cases
Related sites
United states support.
- Account help & support
- Communities
- Product help & support
- Product training
International support
- Legal UK, Ireland & Europe support
New releases
- Westlaw Precision
- 1040 Quickfinder Handbook
Join a TR community
- ONESOURCE community login
- Checkpoint community login
- CS community login
- TR Community
Free trials & demos
- Westlaw Edge
- Practical Law
- Checkpoint Edge
- Onvio Firm Management
- Proview eReader

Building a strong in-house legal team: Structure and strategy
Today's general counsel plays a critical part in shaping the success of their organization. A key question they must continuously ask is: "Is my legal department's structure optimized to provide strategic support and meet the needs of the business?"
This question typically emerges when the general counsel starts in their role. However, it becomes vital during leadership transitions, significant company changes, service quality concerns, and the aftermath of a crisis or failure during which the department didn't perform as expected.
Consider several things when evaluating your legal department structure.
Types of legal department structures
There are three types of legal team structures to consider:
- Functional . Lawyers specialize in distinct legal areas — contracts, IP, litigation, etc. — forming a centralized team that promotes efficiency and consistent advice.
- Client focused . Attorneys are integrated directly into business units or geographical regions , which fosters strong client relationships and a deep understanding of specific business needs.
- Hybrid . This model aims to balance the strengths of both functional and client-focused structures. It provides flexibility and customization but can be complex to manage.
Each structure has pros, including efficiency, consistency of advice, and cost. The cons might include the strength of client relationships, visibility into problems, and divided loyalties among the lawyers. Career development opportunities can also vary depending on the structure.
AI in legal departments
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the legal landscape and should factor into decisions about your legal department structure. There are many opportunities for efficiency and optimization, so legal departments must proactively assess how AI can support their chosen structure and develop guidelines around its use. Critical applications include automating tasks like contract review, legal research, and due diligence, freeing attorneys to focus on higher-value strategic work.
However, selecting industry-specific AI solutions trained on reliable legal data is crucial to mitigate potential risks like biased outputs or poor legal judgment. By carefully integrating AI tools and investing in training, legal departments can use AI to enhance service delivery, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge.
Choosing your legal department structure
There is no “one time and forever” decision for legal structure — innovative general counsel review structures yearly and in consultation with senior management.
Factors to consider include:
- Nature of the business
- Size of the legal team
- Location of the attorneys
- Skills of the existing legal team, like generalists versus specialists
- The team's reaction to change and the impact of the structure on job satisfaction
- Service needs of the business
- What the CEO wants
Sometimes, the decision is clear — but not always. For example, despite its complexities and costs, a hybrid model may be the answer when no right structure is clear from other models.
Legal team best practices
No matter your chosen structure, there are a few “must-dos” to ensure cohesion and mitigate any possible negatives.
These include:
- Consistent communication with the legal team through regularly scheduled meetings, intranet site or portal announcements, department newsletter, project collaboration, and recognition of birthdays and significant events.
- Career development opportunities for in-house legal teams, such as allowing team members to develop areas of responsibility; get exposure to senior management ; move into different sections or geographies, even if only short-term assignments; train the business; help with department administrative tasks; and focus on promoting from within.
- Use of technology, like webcast and video conferencing and “Slack”; common matter; budget; legal document management systems ; templates database; dashboards; document assembly; and more.
The evolving role of the general counsel
The role of general counsel is shifting. Today, it often extends beyond just legal expertise. Usually, general counsel play vital roles in the business, acting as partners and strategic decision makers. They must use their knowledge of the legal landscape, company goals, and industry insights to weigh in on everything from compliance and regulatory requirements to litigation prevention and cost controls.
This skill set requires balancing proactive risk management with business growth, which is especially difficult when faced with ever-present budget constraints. "Do more with less" is a common refrain; research shows that 69% of general counsel globally are under moderate to significant cost pressure from business leaders. Collaborating with the rest of the C-suite can help general counsel demonstrate department value and their value as critical contributors to the organization's overall success.
Benchmarking and performance metrics
Data-driven insights are critical in today's legal department, especially as cost controls are among the highest priorities . Focusing on automation and efficiency and using data-driven insights can help general counsel track key performance indicators (KPIs) to optimize efficiency, control costs, and better inform strategic decisions. Doing so can also identify trends and anticipate challenges, keeping the organization agile.
Key areas to benchmark include:
- Operational efficiency . Track metrics like matter turnaround times, cycle times, and technology adoption rates.
- Budget management . Analyze internal legal spend, external counsel costs, and alternative legal service provider usage.
- Departmental staffing . Track the size and skill mix of the legal team, identifying potential gaps or opportunities for right-sizing.
Benchmarking against industry standards helps general counsel identify areas for improvement and demonstrate value to the C-suite, especially as volume increases across the board. By embracing data and metrics, legal departments can evolve from cost centers into strategically aligned drivers of business success.
Find the right structure for your organization's needs
Your organization's legal department structure is critical to the success of the team and the quality of the services provided to the business. To provide the best possible service and meet today's challenges , general counsel must review their structures on a regular basis, consider the specific needs of their businesses, and ensure that they have the right mix of skills on their teams.
General counsel can ensure that they’ve structured the legal department for success by taking the time to consider all the factors involved and communicating regularly.
Related insights
Measuring what matters: efficient legal department structure, challenges for general counsel structuring an effective global law department.

Advise your business more confidently and reduce outside costs with the legal know-how solution built by Thomson Reuters for in-house counsel
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
Trademark Assignment: What You Need To Know Before Transferring Ownership
Contributor.
Trademark assignment is the process of transferring ownership of a trademark. It is a significant legal process that requires careful consideration and adherence to relevant laws and regulations. Failing to understand the intricacies of trademark assignment can lead to legal disputes, loss of rights, and financial implications for both parties involved. Therefore, it is essential for individuals and businesses involved in trademark transactions to have a clear understanding of the process and its implications.
UNDERSTANDING TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
Trademark assignment refers to the formal transfer of ownership rights of a trademark (Registered or Pending)from one individual or entity to another. It involves the conveyance of all associated rights, including the right to use, licence, or sell the trademark, to the assignee.
IMPORTANCE OF PROPER DOCUMENTATION
Proper documentation is essential in the process of trademark assignment to ensure clarity, legality, and enforceability of the transfer. Documentation typically includes a written agreement outlining the terms and conditions of the assignment, as well as any associated considerations or payments. Without proper documentation, the assignment may be deemed invalid or unenforceable, leading to potential disputes or challenges in the future.
TYPES OF TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
Trademark assignment can take several forms, depending on the nature and extent of the transfer:
- Complete Assignment : In a complete assignment, the assignor transfers all rights and interests in the trademark (Registered or Pending) to the assignee. This includes the right to use the trademark for any purpose, as well as the right to sublicense or transfer the trademark to third parties.
- Partial Assignment : A partial assignment involves the transfer of only specific rights or interests in the trademark (Registered or Pending). This may include limiting the assignment to certain products, services, or geographical regions, while retaining ownership rights over other rights or interests of the trademark.
- Assignment with Goodwill : When a trademark is assigned with goodwill of the business, the assignor transfers not only the rights to the trademark but also the associated value and reputation of the trademark. This allows the assignee to benefit from the established goodwill and reputation of the trademark.
- Assignment without Goodwill : In contrast, an assignment without goodwill involves the transfer of only the rights to the trademark, without any associated value or reputation. .
PREREQUISITES FOR TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
Before proceeding with a trademark assignment, certain prerequisites must be met to ensure the validity and enforceability of the transfer.
REQUIREMENT OF A WRITTEN AGREEMENT
A trademark assignment must be documented in writing to provide clarity and evidence of the transfer. This written agreement, often referred to as a trademark assignment agreement, outlines the terms and conditions of the transfer, including the rights and obligations of both the assignor and the assignee. Without a written agreement, the assignment may be subject to disputes or challenges regarding the terms of the transfer.
IDENTIFICATION OF PARTIES INVOLVED
The parties involved in the trademark assignment must be clearly identified in the agreement. The assignor, who is the current owner of the trademark, and the assignee, who is the intended recipient of the trademark rights, must be accurately identified to establish their respective roles and responsibilities in the transfer process.
CONSENT FROM THE ASSIGNOR
Consent from the assignor is essential for a valid trademark assignment. The assignor must willingly agree to transfer the ownership rights of the trademark to the assignee. Without the assignor's consent, the assignment would be considered invalid and unenforceable. Therefore, obtaining explicit consent from the assignor is a fundamental requirement in the trademark assignment process.
CONSIDERATION
Consideration refers to the value exchanged between the parties as part of the trademark assignment in the form monetary consideration.
TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT AGREEMENT
A well-drafted trademark assignment agreement is essential to ensure clarity, enforceability, and protection of rights for both the assignor and the assignee. It helps to avoid misunderstandings or disputes between the parties involved and provides a legal framework for the transfer of trademark rights.
The trademark assignment agreement must be executed by both parties in accordance with legal formalities. It should be signed by the assignor and the assignee, with their signatures witnessed by independent witnesses. The agreement will be stamped based on the consideration amount of the assignment. Notary may also be required.
PROCESS OF TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
The process of trademark assignment involves several steps that must be followed meticulously to ensure the legal transfer of ownership.
FILING OF TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT APPLICATION (FORM TM-P)
The first step in the process is to file a trademark assignment application with the appropriate authority, usually the Registrar of trademarks. This application is typically submitted on Form TM-P, formally notifies the registrar of the intention to transfer ownership of the trademark. The application must contain all necessary details, including information about the assignor, assignee, and the trademarks being transferred along with a copy of the assignment deed..
ADVERTISEMENT OF THE ASSIGNMENT AS DIRECTED BY THE REGISTRAR
Upon receipt of the trademark assignment application, the registrar may direct the parties to advertise the assignment in a specified manner and within a specified period.This is only in case of partial assignment or in the case of assignment without goodwill This advertisement serves to notify the public of the impending transfer of ownership and provides an opportunity for any interested parties to raise objections or concerns regarding the assignment.
REGISTRAR'S REGISTRATION OF THE ASSIGNEE AS THE NEW PROPRIETOR
Once the advertisement requirements have been met and any objections addressed, the Rregistrar will proceed to register the assignee as the new proprietor of the trademark/s. This registration formally recognises the transfer of ownership and updates the official records accordingly. The assignee will now have full legal rights and responsibilities associated with the ownership of the trademark/s.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
Several essential documents must be prepared and submitted during the process of trademark assignment to ensure the legality and validity of the transfer.
RESTRICTIONS ON TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
Certain restrictions are in place to ensure fair use and prevent confusion or deception among consumers.
- Parallel use restriction: This restriction prohibits the assignor from assigning a trademark in a manner that creates exclusive rights in different individuals or entities for the same or similar products or services. Essentially, it aims to prevent multiple parties from using the same trademark in a way that could lead to consumer confusion. This is applicable in the case of partial assignment.
- Multiple territorial use restriction: This restriction prevents the assignor from assigning a trademark in a manner that creates exclusive rights in different regions or territories for the same or similar products or services. It aims to maintain consistency and clarity in the use of trademarks within specific geographical areas.This is applicable in the case of partial assignment.
BENEFITS OF TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT
Trademark assignment offers several advantages for both the assignor and the assignee, making it a valuable tool for transferring ownership of intellectual property rights.
MONETISATION OF BRAND VALUE FOR THE ASSIGNOR
By transferring ownership rights to another party, the assignor can receive financial compensation in exchange for granting the assignee the exclusive rights to use the trademark. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to capitalise on the value they have built through branding efforts over time.
ACQUISITION OF ESTABLISHED BRAND RIGHTS FOR THE ASSIGNEE
For the assignee, trademark assignment provides the opportunity to acquire the established rights and recognition associated with a well-known brand. Instead of building a brand from scratch, the assignee gains immediate access to the market presence, reputation, and consumer trust that the trademark represents. This can expedite market entry and enhance the assignee's competitive position in their industry.
SUPPORT FOR BUSINESS EXPANSION
For the assignor, transferring ownership of underutilised trademarks or brands can free up resources and focus on core business activities. Meanwhile, the assignee can leverage the acquired trademarks to diversify their product offerings, enter new markets, or strengthen their existing market position, driving growth and revenue opportunities.
ESTABLISHMENT OF LEGAL RIGHTS IN CASE OF DISPUTES
By formalising the transfer of trademark ownership through a legally binding agreement, both the assignor and the assignee establish clear legal rights and obligations. In the event of disputes or challenges to the ownership of the trademark, the assignment agreement serves as evidence of the parties' intentions and commitments. This can streamline dispute resolution processes and provide legal recourse to protect the interests of both parties.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
1. what is the full assignment of a trademark.
The full assignment of a trademark refers to the transfer of all rights, interests, and ownership of the trademark from one party (the assignor) to another party (the assignee). In a full assignment, the assignor relinquishes all control and benefits associated with the trademark, including the right to use, licence, or sell the mark. This comprehensive transfer ensures that the assignee gains exclusive ownership and control over the trademark for all relevant goods or services.
2. WHAT IS LICENCE AND ASSIGNMENT OF TRADEMARK?
A licence and assignment of a trademark involve two distinct legal arrangements. A licence grants permission to a third party (the licensee) to use the trademark under specified terms and conditions, while the ownership and control of the trademark remain with the licensor. In contrast, an assignment transfers the entire ownership rights of the trademark from one party to another. While a licence allows for the authorised use of the trademark, an assignment results in the complete transfer of ownership, including all associated rights and benefits.
3. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TRANSMISSION AND ASSIGNMENT?
Transmission and assignment are both methods of transferring ownership of a trademark, but they differ in scope and application. Transmission refers to the automatic transfer of trademark rights due to changes in legal status, such as inheritance, bankruptcy, or corporate restructuring. In contrast, assignment is a deliberate and voluntary act where the current owner (assignor) transfers ownership rights to another party (assignee) through a written agreement. While transmission occurs by operation of law, assignment requires the explicit consent and agreement of the parties involved.
4. WHAT IS CONSIDERATION FOR TRADEMARK ASSIGNMENT?
Consideration for trademark assignment refers to the value exchanged between the assignor and the assignee as part of the transfer agreement which is in monetary form. It serves as the legal basis for the contract and ensures that both parties receive something of value in exchange for the transfer of trademark rights..
In conclusion, understanding trademark assignment is crucial before transferring ownership. It's essential to ensure proper documentation, consent, and consideration to facilitate a smooth transfer. Seeking professional assistance from legal experts can help navigate the complexities of trademark assignment and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

Intellectual Property
Mondaq uses cookies on this website. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies as set out in our Privacy Policy.

- Corporate & In-House
- Law & Policy
- Law Schools
- The Recruiters
- Working Title
- Moot Courts
- Conferences & Paper presentations
- Recruitment Tracker

What influence has ChatGPT had in Indian law schools?
The advent of ChatGPT over eighteen months ago has changed the way we access information. Although still in a nascent stage, the artificial intelligence (AI) tool's influence has invariably caught the eye of law school students in India.
Law faculty have been constantly adapting to ensure integrity of online legal research done by students. The use of technology like Turnitin has aided them in checking whether projects are plagiarised, albeit with its own shortcomings of falsely reflecting original content as AI-generated.
So how are they now adapting to the latest technological change in the research field? Have students become lackadaisical with their assignments or has this tool been used to fairly aid them in projects assigned to them?
We caught up with law students and legal academicians to understand the influence that this tool can have on legal education, and how professors have tactfully integrated ChatGPT and re-imagined the way assignments are disbursed and assessed.
How are law students using the AI tool?
In a candid chat with about 30 law students across law schools on their experience of ChatGPT for and what exactly they utilise the tool for, it came to light that 29% students used the tool for summarising concepts or notes. Students opined that the responses can pass off as human.
54% used the tool for studying and found it particularly helpful for conceptual clarifications. 50% students used the tool for research and 47% used it for creating content while writing e-mails, blogs and projects.
Of these, 82% students found the tool useful, while 18% felt otherwise. In terms of the reliability of the output, 47% reported positively, while 24% responded negatively given its tendency to hallucinate and produce fake case laws.
Another 21% students mentioned that the reliability of the output depends from instance to instance. In the case of complex prompts, the accuracy of the output needs to be cross-verified, and sometimes the content gets repeated after the first 500 words of response to a prompt.
Testing the tool
While running a prompt of a research project undertaken during my time at law school through ChatGPT, the tool did a decent job in dividing the content into chapters, headings and sub-headings. On asking the tool to produce content under each heading, there is a tendency for the tool to stray away from the main topic unless the prompt is very specific to what the user is expecting to address. Further, given that the output by the tool is a product of recombining existing information, the tool lacks the ability to critically analyse and provide innovative solutions to issues posed before it. The tool also falls short of creativity in presenting information and responding soundly to application-based questions.
On cross-checking the responses produced by it, most times it seems to be able to circumvent basic plagiarism tools like Grammarly. However, similar tools like Turnitin also have their shortcomings by virtue of it being an AI tool in itself. There may be a tendency for it to detect false positives which may tend to create unnecessary doubts and apprehension in the minds of facutly. Further, the lack of academic sourcing to the content generated by ChatGPT also mandates its users to ensure that the output generated by the AI tool is cross-verified.
What are faculty saying about the tool?
Krishna Deo Singh Chauhan , Associate Professor at Jindal Global Law School, opines that introducing ChatGPT formally as part of the law school curriculum may not be feasible at the moment, given the complexity of the application. However, he admits that law schools cannot afford to ignore the presence of the AI tool. He added,
"Possibly it could be part of the basic training on library resources that students undergo. That too can only be done under supervision of how students must develop a critical faculty during its use. Do the students test and verify the responses they get from it? How do they do it? Does that ensure that work is scientific and trustworthy?"

On whether ChatGPT can be used as a legitimate research aid Chauhan said,
“This can happen only if we get students on board with the idea that this is a tool for better work, not a justification for less work...I have personally interacted with ChatGPT extensively and while awe-striking at first, it is nearly not as good as a student who reads diligently, thinks critically and wants to create an impact with her writing.
The rise of ChatGPT is no doubt a watershed event. All stakeholders must engage with it and use it to improve their work. Used mindlessly and unethically, it would stunt the intellectual development of the user, and the end product would be uncritical and sub-optimal.”
Deo shared that one of the ways he ensures students have not blindly used ChatGPT for projects is to have viva voce to find out whether the student has engaged with the work they have submitted.
Aman Gupta , Assistant Professor of Law and Technology at West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences (WBNUJS), admitted that large language models (LLMs) have become a concern when students submit written assignments.
“These concerns and solutions are not new and have been implemented in various forms over the years. Even before ChatGPT became popular, there were concerns regarding plagiarism and the use of paraphrasing tools. However, the popularity of ChatGPT has certainly resulted in a greater focus on the problem in the last two years.
The initial response involved asking students to submit projects on issues that have emerged over the last three years (as September 2021 was the initial cut-off point for ChatGPT’s knowledge)."

On some of the other methods incorporated to circumvent the reliance on AI tools like ChatGPT by students, Gupta said,
“A few approaches have emerged. One has been to require students to undertake empirical research, which can involve statistical analysis of legal trends that have emerged over the last few years. Another option has been to retain the written components (either in the form of a position paper or a moot court memo) and link them to a viva component where the knowledge of the students regarding their written submission is tested.
One option, which I find interesting, has been to use AI to generate information using prompts and then require the students to find faults and improvements within the information using knowledge gained in class and/or research. Several of these solutions have been implemented at WBNUJS.”
Gupta admitted that it is crucial for law teachers to thoroughly read the project submitted by students.
“Personally speaking, the primary test for judging GPT use is reading the project as the AI tends to hallucinate. I have seen it produce legislation and sections within legislation that do not exist, which is often a clear giveaway of GPT output. The second level of scrutiny comes from the Turnitin AI Writing Detection Tool. Having seen it in action, it does yield fairly accurate results on whether something is written by AI or is an original work of the student. However, as Turnitin itself warns its users, it is not completely accurate and may yield false positives.”
Commenting on the integration of ChatGPT in law school curriculum, Gupta noted that there is not much difference between ChatGPT and other LLMs from any internet-based resources.
“I do not think we should be averse to integrating it into our law school curriculum in the future. Even law firms appear to be using AI (including LLMs) to automate various tasks, which include creating the first draft of agreements/clauses.
However, we must ensure that students understand that the LLMs represent only research starting point, and not its end. The emphasis must be on two elements: (i) originality in writing; and (ii) critical analysis. Students’ primary use of ChatGPT appears to be to finish assignments without putting in requisite effort or to meet deadlines.”
As an ardent user of ChatGPT, Nikhil Naren , Assistant Professor at JGLS, firmly believes that the tool is here to stay and that incorporating the AI tool into law school curriculum is crucial.
“Prior to such incorporation, we will need to make the understanding of GPT (General Purpose Technology) such as AI; and Generative Pre-trained Transformer Models such as ChatGPT clear. Due to its extensive database, ChatGPT may become an important tool. Assessing the STAR - Safety, Transparency, Accountability, and Reliability of AI-enabled systems is a must. Users must be sensitised to societal issues raised by AI such as bias and privacy challenges as much as ethical issues behind using ChatGPT.”

Elaborating on the techniques he adopts to integrate ChatGPT as part of assignments, Naren said,
“I give a legal factual situation like a moot problem. I ask the students to feed the prompt to ChatGPT and to critically analyse the prompt given by the tool. I ask students to review privacy policies of oft-used apps like Instagram and notice dark patterns. This makes them go through policies in real time and make observations. I also make them present their findings through PPTs. For any take-home assignment, it is a given that students are going to take the assistance of an AI tool, so to circumvent the complete reliance on the tool, I started disseminating these kinds of assignments. This makes the students put their mind to assessing the GPT model as well. So it is both a critical analysis and an encouragement to use ChatGPT without compromising on the effort required to complete a task.”
On the overall sentiment around the influence of technology on academia and jobs, Naren drew an analogy to the time when computers were newly introduced.
“The same fear is surfacing today. But the purpose of technology is not to replace, but to use it as a tool to become more efficient and for better work.”
Prof Dr Shashikala Gurpur , Director of Symbiosis Law School, Pune, opined that AI tools like ChatGPT can make students future-ready. However, they cannot replace the crucial skills required by a lawyer.
“In legal education, the legal acumen of problem solving can not be fully addressed by ready data, as human operations are ingenuous. People are unpredictable. It has limits to address human transformation and innovation. Merit of public service, client commitment, designing society or activity in regulated fashion is a synthesis of intuition, information and thinking. A machine cannot substitute the wonders of multilayered human possibility. It can support meritocracy and caution should be exercised not to let it destroy meritocracy.”

How is the tool being used in international law schools?
At the University of Minnesota earlier last year, ChatGPT was made to respond to 95 multiple choice questions and 12 essay-based questions and its responses were shuffled with the responses of other law students. The responses generated by the tool secured passing grades, although it scored a below average with a C+. This experiment was done across subjects and the results were more or less the same throughout. It also mentioned that if its performance was consistent throughout, it would possibly even pass the JD exam.
A professor at the University of Pennsylvania Carey Law School opined that banning the tool is not a solution and that students need to become aware of when the tool can be relied on. Another teacher from the University of Michigan is of the view that integrating ChatGPT in law schools would prove as a nudge for students to enhance their legal writing skills. To circumvent the use of the tool in exams, he asks questions which are more focused on the teachings in class and avoids generic questions which can be easily answered by the tool.
In Australia, a specialised AI tool called Australia Law School SuperGPT has been developed. It assists students on a range of tasks from reviewing, and writing drafts, and understanding and applying complex legal principles and doctrines. While schools in Australia had initially restricted the use of ChatGPT, the government developed a framework for the use of emerging technologies in consultation with a national AI schools taskforce, education unions, experts and other key stakeholders.
What influence has ChatGPT had in Indian law schools? writes @Jelsyna1 https://t.co/2yyZ4Xh7Zk — Bar and Bench (@barandbench) July 9, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assignment (law) Assignment [a] is a legal term used in the context of the laws of contract and of property. In both instances, assignment is the process whereby a person, the assignor, transfers rights or benefits to another, the assignee. [1] An assignment may not transfer a duty, burden or detriment without the express agreement of the assignee.
assignment. Assignment is a legal term whereby an individual, the "assignor," transfers rights, property, or other benefits to another known as the " assignee .". This concept is used in both contract and property law. The term can refer to either the act of transfer or the rights /property/benefits being transferred.
Assignments: The Basic Law. The assignment of a right or obligation is a common contractual event under the law and the right to assign (or prohibition against assignments) is found in the majority of agreements, leases and business structural documents created in the United States. As with many terms commonly used, people are familiar with the ...
A legal assignment occurs when: In the Purman Estate case, the court stated that a legal assignment is a transfer of property, or of some right or interest, from one person to another. It also stated that it must be the proper transfer of one whole interest in that property. An assignment of rights occurs when an assignor gives up or transfers ...
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the ...
The assignment violates the law or public policy. Some laws limit or prohibit assignments. For example, many states prohibit the assignment of future wages by an employee, and the federal government prohibits the assignment of certain claims against the government. Other assignments, though not prohibited by a statute, may violate public policy.
When dealing with assignment in contract law, it's crucial to understand the legal backbone that supports a valid assignment. This ensures that the assignment stands up in a court of law if disputes arise. Let's break down the must-know legal requirements: express prohibition, material change, future rights, and rare skill requirement. ...
An assignment of a legal claim occurs when one party (the "assignor" ) transfers its rights in a cause of action to another party (the "assignee" ). 1. The Supreme Court has held that a private litigant may have standing to sue to redress an injury to another party when the injured party has assigned at least a portion of its claim for ...
Assign is the act of transferring rights, property, or other benefits to another party (the assignee) from the party who holds such benefits under contract (the assignor). This concept is used in both contract and property law. Contract Law Under contract law, when one party assigns a contract, the assignment represents both: (1) an assignment of rights; and (2) a delegation of duties.
This is known as "contract assignment.". Generally, all rights under a contract may be assigned. A provision in the contract that states the contract may not be assigned usually refers to the delegation of the assignor's (person who assigns) duties under that contract, not their rights under the contract. In modern law, the phrase ...
The best approach when you're assigning a contract is to make a written assignment agreement with the assignee. A lawyer can help you draft an agreement tailored to your circumstances, with language that clearly spells out your rights and obligations and the rights and obligations of the assignee. That way, you are less likely to be left ...
All parties must be legally capable. The objects being transferred must be legal. Consideration should be included. All parties must consent to the assignment. One of the most common forms of assignment is a wage assignment. For instance, if you owe child support, alimony, back taxes, or some other form of debt, the court can require your ...
Assignment. The transfer of a right from one party to another. For example, a party to a contract (the assignor) may, as a general rule and subject to the express terms of a contract, assign its rights under the contract to a third party (the assignee) without the consent of the party against whom those rights are held. Obligations cannot be ...
The idea of an assignment is essentially that of a transfer by one existing party to another existing party of some species of property or valuable interest, except in the case of an executor. Ilight v. Sackett, 34 N. Y. 447. 3. A transfer or making over by a debtor of all his property and effects to one or more assignees in trust for the ...
Assignment Law. In legal terms, the meaning of an assignment is a contractual obligation to transfer a property title or right from one party to another. Generally, the assignment is transferred based on an entire interest in the property, chattel, estate, or other item assigned. A grant is different from an assignment in that an assignment ...
Assignment vs. Delegation. Assignment is a legal definition that refers to the transfer of rights, property, or other benefitsbetween two parties. The party allocating the rights is known as the "assignor", while the one receiving them is called the "assignee". The other original party to the contractis known as the "obligor".
An assignment is the process of transferring responsibility and accountability. [i] Delegation is the process by which responsibility and authority for performing a task or activity is transferred to another person. The consent of the third party contracting is not necessary in an assignment. [ii] In contrast, in delegation, the person to whom ...
Commercial. An assignment is 'an immediate transfer of an existing proprietary right, vested or contingent from one party to another'. Assignments can occur by consent or by operation of law. A consensual assignment occurs by way of a gift or consideration. Assignments by law can occur during life or on death and will transfer the benefit of ...
It is important to read and re-read (and even read again) the assignment sheet. You don't want to make a mistake and write something off topic. Remember, answering the question is key to getting a good grade! Plan before you write. A great legal writing assignment is organized. And for most of us this means that you need to plan your paper ...
An assignment takes place when one party is holding a right to property, claims, bills, lease, etc., of another party and wishes to pass it along (or sell it) to a third party. As complicated as that sounds, it really isn't. Strangely enough, many assignments can be made under the law without immediately informing, or obtaining the permission,…
A closed legal memo is an assignment where you are given the case law or other primary law to be used in your writing. Far more challenging is an open legal memo, where you will need to research and identify the relevant law, investigate and analyze the most legally significant facts involving a particular client, and provide a critical ...
Competing equitable assignments of a legal chose. 27.94; One or more of the competing assignments is a legal assignment. 27.95; 27.96; Priorities between assignments and other interests. The interest of a trustee in bankruptcy. 27.97; The interest of a judgment creditor who has obtained a charging order. 27.98; 27.99; Another equitable interest ...
Also, extension assignments are used to help students connect what they learn in the classroom with real-life and apply their existing skills to expand their knowledge. Common types of law assignments that represent this type of homework include: Writing literature reviews; Researching local law news; Compare and contrast events, etc. Creative ...
These resources address a broad range of legal writing issues, and will be updated periodically. Please contact [email protected] with questions or feedback. For information about the Law School Writing Center, or to make an appointment, please visit the Writing Center main page. Handouts: Structure, Organization, and Clarity.
Assignee is a person to whom a right is transferred by the person holding such rights under the transferred contract (the "assignor"). The act of transferring is referred to as "assigning" or "assignment" and is a concept found in both contract and property law. Contract Law Under contract law, when one party assigns a contract, the assignment represents both: (1) a transfer of ...
Career development opportunities for in-house legal teams, such as allowing team members to develop areas of responsibility; get exposure to senior management; move into different sections or geographies, even if only short-term assignments; train the business; help with department administrative tasks; and focus on promoting from within.
Law document from London Met, 2 pages, LEVEL 7-PROFESSIONAL GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN LAW LEADING TO LLM (UK) Assignment Submission Course Name: LLM (Top Up) Module Name: International Corporate Law Proposed Topic: Assignment Submission Module Code: LWM 02 Tutor(s): Submission date: Tutor's Email: S
In contrast, assignment is a deliberate and voluntary act where the current owner (assignor) transfers ownership rights to another party (assignee) through a written agreement. While transmission occurs by operation of law, assignment requires the explicit consent and agreement of the parties involved. 4.
(2) An assignee of a lien on real property shall record the assignment in the county clerk's office as required by KRS 382.360. Failure of an assignee to record a mortgage assignment shall not affect the validity or perfection, or invalidity or lack of perfection, of a mortgage lien under applicable law.
Elaborating on the techniques he adopts to integrate ChatGPT as part of assignments, Naren said, "I give a legal factual situation like a moot problem. I ask the students to feed the prompt to ChatGPT and to critically analyse the prompt given by the tool. I ask students to review privacy policies of oft-used apps like Instagram and notice ...