Essay Papers Writing Online
A comprehensive guide to writing a response essay that will help you ace your academic assignments.

Writing a response essay can be a challenging task, as it requires you to analyze a piece of literature, a movie, an article, or any other work and provide your personal reaction to it. This type of essay allows you to express your thoughts and feelings about the content you’re responding to, and it can help you develop critical thinking and analytical skills.
In order to craft a compelling response essay, you need to carefully read and understand the work you’re responding to, identify key themes and arguments, and formulate a clear and coherent response. This guide will provide you with tips and strategies to help you write an effective response essay that engages your readers and communicates your ideas effectively.

Key Elements of a Response Essay
A response essay typically includes the following key elements:
- Introduction: Begin with a brief summary of the text you are responding to and your main thesis statement.
- Summary: Provide a concise summary of the text, focusing on the key points and arguments.
- Analysis: Analyze and evaluate the text, discussing its strengths, weaknesses, and the effectiveness of its arguments.
- Evidence: Support your analysis with evidence from the text, including quotes and examples.
- Personal Reaction: Share your personal reaction to the text, including your thoughts, feelings, and opinions.
- Conclusion: Sum up your response and reiterate your thesis statement, emphasizing the significance of your analysis.
By incorporating these key elements into your response essay, you can effectively engage with the text and provide a thoughtful and well-supported response.
Understanding the Assignment
Before you start writing your response essay, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the assignment requirements. Read the prompt carefully and identify the main objectives of the assignment. Make sure you understand what the instructor expects from your response, whether it is a critical analysis of a text, a personal reflection, or a synthesis of different sources.
Pay attention to key elements such as:
- The topic or subject matter
- The purpose of the response
- The audience you are addressing
- The specific guidelines or formatting requirements
Clarifying any doubts about the assignment will help you focus your response and ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria for a successful essay.
Analyzing the Prompt
Before you start writing your response essay, it is crucial to thoroughly analyze the prompt provided. Understanding the prompt is essential for crafting a coherent and well-structured response that addresses the key points effectively. Here are some key steps to consider when analyzing the prompt:
- Carefully read the prompt multiple times to fully grasp the main question or topic that needs to be addressed.
- Identify the key words and phrases in the prompt that will guide your response and help you stay focused on the main theme.
- Consider any specific instructions or requirements outlined in the prompt, such as the length of the essay, the format to be used, or the sources to be referenced.
- Break down the prompt into smaller parts or components to ensure that you cover all aspects of the question in your response.
- Clarify any terms or concepts in the prompt that are unclear to you, and make sure you have a solid understanding of what is being asked of you.
By analyzing the prompt carefully and methodically, you can ensure that your response essay is well-structured, focused, and directly addresses the main question or topic at hand.
Developing a Thesis Statement

One of the most critical aspects of writing a response essay is developing a clear and strong thesis statement. A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of your essay. It sets the tone for your entire response and helps guide your reader through your arguments.
When developing your thesis statement, consider the following tips:
| 1. | Identify the main topic or issue you will be responding to. |
| 2. | State your position or stance on the topic clearly and concisely. |
| 3. | Provide a brief preview of the key points or arguments you will present in your essay to support your thesis. |
Remember, your thesis statement should be specific, focused, and debatable. It should also be located at the end of your introduction paragraph to ensure it captures the reader’s attention and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
Structuring Your Response
When structuring your response essay, it’s essential to follow a clear and logical format. Start with an introduction that provides background information on the topic and presents your thesis statement. Then, organize your body paragraphs around key points or arguments that support your thesis. Make sure each paragraph focuses on a single idea and provides evidence to back it up.
After presenting your arguments, include a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your thesis. Remember to use transitions between paragraphs to ensure a smooth flow of ideas. Additionally, consider the overall coherence and cohesion of your response to make it engaging and easy to follow for the reader.
Main Body Paragraphs

When writing the main body paragraphs of your response essay, it’s essential to present your arguments clearly and logically. Each paragraph should focus on a separate point or idea related to the topic. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, and then provide supporting evidence or examples to reinforce your argument.
- Make sure to organize your paragraphs in a coherent and sequential manner, so that your essay flows smoothly and is easy for the reader to follow.
- Use transition words and phrases, such as “furthermore,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand,” to connect your ideas and create a cohesive structure.
- Cite sources and provide proper references to strengthen your arguments and demonstrate the credibility of your analysis.
Remember to analyze and evaluate the information you present in each paragraph, rather than simply summarizing it. Engage critically with the texts, articles, or sources you are referencing, and develop your own perspective or interpretation based on the evidence provided.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
How to Write a Response Paper
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Most of the time when you are tasked with an essay about a book or article you've read for a class, you will be expected to write in a professional and impersonal voice. But the regular rules change a bit when you write a response paper.
A response (or reaction) paper differs from the formal review primarily in that it is written in the first person . Unlike in more formal writing, the use of phrases like "I thought" and "I believe" is encouraged in a response paper.
You'll still have a thesis and will need to back up your opinion with evidence from the work, but this type of paper spotlights your individual reaction as a reader or viewer.
Read and Respond
Grace Fleming
For a response paper, you still need to write a formal assessment of the work you're observing (this could be anything created, such as a film, a work of art, a piece of music, a speech, a marketing campaign, or a written work), but you will also add your own personal reaction and impressions to the report.
The steps for completing a reaction or response paper are:
- Observe or read the piece for an initial understanding.
- Mark interesting pages with a sticky flag or take notes on the piece to capture your first impressions.
- Reread the marked pieces and your notes and stop to reflect often.
- Record your thoughts.
- Develop a thesis.
- Write an outline.
- Construct your essay.
It may be helpful to imagine yourself watching a movie review as you're preparing your outline. You will use the same framework for your response paper: a summary of the work with several of your own thoughts and assessments mixed in.
The First Paragraph
After you have established an outline for your paper, you need to craft the first draft of the essay using all the basic elements found in any strong paper, including a strong introductory sentence .
In the case of a reaction essay, the first sentence should contain both the title of the work to which you are responding and the name of the author.
The last sentence of your introductory paragraph should contain a thesis statement . That statement will make your overall opinion very clear.
Stating Your Opinion
There's no need to feel shy about expressing your own opinion in a position paper, even though it may seem strange to write "I feel" or "I believe" in an essay.
In the sample here, the writer analyzes and compares the plays but also manages to express personal reactions. There's a balance struck between discussing and critiquing the work (and its successful or unsuccessful execution) and expressing a reaction to it.
Sample Statements
When writing a response essay, you can include statements like the following:
- I felt that
- In my opinion
- The reader can conclude that
- The author seems to
- I did not like
- This aspect didn't work for me because
- The images seemed to
- The author was [was not] successful in making me feel
- I was especially moved by
- I didn't understand the connection between
- It was clear that the artist was trying to
- The soundtrack seemed too
- My favorite part was...because
Tip : A common mistake in personal essays it to resort to insulting comments with no clear explanation or analysis. It's OK to critique the work you are responding to, but you still need to back up your feelings, thoughts, opinions, and reactions with concrete evidence and examples from the work. What prompted the reaction in you, how, and why? What didn't reach you and why?
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- How To Write an Essay
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- What Is a Critique in Composition?
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- How to Write a Great Process Essay
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- 10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How to Write a News Article That's Effective
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
- How to Write a Response Paper: Outline, Steps & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Response Paper: Outline, Steps & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Response essays are a frequent assignment in many academic courses. Professors often ask students to share their thoughts and feelings about a variety of materials, such as books, articles, films, songs, or poems. To write an effective response paper, you should follow a specific structure to ensure that your ideas are well-organized and presented in a logical manner.
In this blog post, we will explore how to write a good outline and how it is used to develop a quality reaction essay. You will also come across a response paper example to help you better understand steps involved in writing a response essay. Continue reading to explore writing tips from professional paper writers that you can use to improve your skills.
What Is a Response Paper?
It is vital to understand the meaning of a response essay before you start writing. Often, learners confuse this type of academic work with reviews of books, articles, events, or movies, which is not correct, although they seem similar. A response paper gives you a platform to express your point of view, feelings, and understanding of a given subject or idea through writing. Unlike other review works, you are also required to give your idea, vision, and values contained in literal materials. In other words, while a response paper is written in a subjective way, a review paper is written in a more objective manner. A good reaction paper links the idea in discussion with your personal opinion or experience. Response essays are written to express your deep reflections on materials, what you have understood, and how the author's work has impacted you.

Purpose of a Response Essay
Understanding reasons for writing a reaction paper will help you prepare better work. The purpose of a response essay will be:
- To summarize author's primary ideas and opinions: you need to give a summary of materials and messages the author wants you to understand.
- Providing a reflection on the subject: as a writer, you also need to express how you relate to authors' ideas and positions.
- To express how the subject affects your personal life: when writing a response paper, you are also required to provide your personal outcome and lesson learned from interacting with the material.
Response Essay Outline
You should adhere to a specific response paper outline when working on an essay. Following a recommended format ensures that you have a smooth flow of ideas. A good response paper template will make it easier for a reader to separate your point of view from author's opinion. The essay is often divided into these sections: introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs. Below is an example of a response essay outline template:
- Briefly introduce the topic of the response paper
- State your thesis statement or main argument
- Provide a brief summary of the source material you are responding to
- Include key details or arguments from the source
- Analyze the source material and identify strengths and weaknesses
- Evaluate the author's arguments and evidence
- Provide your own perspective on the source material
- Respond to the source material and critique its arguments
- Offer your own ideas and counterarguments
- Support your response with evidence and examples
- Summarize your main points and restate your thesis
- Provide final thoughts on the source material and its implications
- Offer suggestions for further research or inquiry

Save time and effort with our high-quality academic paper assistance. Buy college papers from experts and get an A+ with ease!
Response Paper Introduction
The success of response papers is partly dependent on how well you write the introductory paragraph. As with any academic paper, the introduction paragraph welcomes targeted readers and states the primary idea. Below is a guideline on how to start a response essay:
- Provide a compelling hook to capture the attention of your target audience.
- Provide background information about the material, including the name and author of the work.
- Provide a brief summary of main points to bring readers who are unfamiliar with the work up to task and enable them to follow up on your subsequent analysis.
- Write a thesis statement at the end of your introductory paragraph to inform readers about the purpose and argument you are trying to relay.
Response Essay Thesis Statement
A thesis statement summarizes a paper's content within a sentence or two. A response essay thesis statement is not any different! The final sentence of the introductory paragraph of a reaction paper should give readers an idea of the message that will be discussed in your paper. Do you know how to write a thesis statement for a response essay? If you follow the steps below, you should be able to write one:
- Review the material you are responding to, and pinpoint main points expressed by authors.
- Determine points of view or opinions you are going to discuss in the essay.
- Develop your thesis statement. It should express a summary of what will be covered in your reaction. The sentence should also consider logical flow of ideas in your writing.
- Thesis statement should be easy to spot. You should preferably place it at the end of your introductory paragraph.
Response Paper Body Paragraph
In most instances, the body section has between 1 and 3 paragraphs or more. You should first provide a summary of the article, book, or any other literature work you are responding to. To write a response essay body paragraph that will capture the attention of readers, you must begin by providing key ideas presented in the story from the authors' point of view. In the subsequent paragraph, you should tell your audience whether you agree or disagree with these ideas as presented in the text. In the final section, you should provide an in-depth explanation of your stand and discuss various impacts of the material.
Response Paper Conclusion
In this section of a response paper, you should provide a summary of your ideas. You may provide key takeaways from your thoughts and pinpoint meaningful parts of the response. Like any other academic work, you wind up your response essay writing by giving a summary of what was discussed throughout the paper. You should avoid introducing new evidence, ideas, or repeat contents that are included in body paragraphs in the conclusion section. After stating your final points, lessons learned, and how the work inspires you, you can wrap it up with your thesis statement.
How to Write a Response Paper?
In this section, we will provide you with tips on how to write a good response paper. To prepare a powerful reaction essay, you need to consider a two-step approach. First, you must read and analyze original sources properly. Subsequently, you also need to organize and plan the essay writing part effectively to be able to produce good reaction work. Various steps are outlined and discussed below to help you better understand how to write a response essay.

1. Pick a Topic for Your Response Essay
Picking a topic for response essay topics can be affected either by the scope of your assignment as provided by your college professor or by your preference. Irrespective of your reason, the guideline below should help you brainstorm topic ideas for your reaction:
- Start from your paper's end goal: consider what outcomes you wish to attain from writing your reaction.
- Prepare a list of all potential ideas that can help you attain your preferred result.
- Sort out topics that interest you from your list.
- Critique your final list and settle on a topic that will be comfortable to work on.
Below are some examples of good topics for response essay to get you started:
- Analyzing ideas in an article about effects of body shaming on mental health .
- Reaction paper on new theories in today's business environment.
- Movies I can watch again and again.
- A response essay on a documentary.
- Did the 9/11 terror attacks contribute to issues of religious intolerance?
2. Plan Your Thoughts and Reactions
To better plan your thoughts and reactions, you need to read the original material thoroughly to understand messages contained therein. You must understand author's line of thinking, beliefs, and values to be able to react to their content. Next, note down ideas and aspects that are important and draw any strong reactions. Think through these ideas and record potential sequences they will take in your response paper. You should also support your opinions and reactions with quotes and texts from credible sources. This will help you write a response essay for the college level that will stand out.
3. Write a Detailed Response Paper Outline
Preparing a detailed response paper outline will exponentially improve the outcome of your writing. An essay outline will act as a benchmark that will guide you when working on each section of the paper. Sorting your ideas into sections will not only help you attain a better flow of communication in your responsive essay but also simplify your writing process. You are encouraged to adopt the standard response essay outline provided in the sample above. By splitting your paper into introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs, you will be able to effectively introduce your readers to ideas that will be discussed and separate your thoughts from authors' messages.
4. Write a Material Summary
For your audience to understand your reaction to certain materials, you should at first provide a brief summary of authors' points of view. This short overview should include author's name and work title. When writing a response essay, you should dedicate a section to give an informative summary that clearly details primary points and vital supporting arguments. You must thoroughly understand the literature to be able to complete this section. For important ideas, you can add direct quotes from the original sources in question. Writers may sometimes make a mistake of summarizing general ideas by providing detailed information about every single aspect of the material. Instead of addressing all ideas in detail, focus on key aspects. Although you rely on your personal opinion and experience to write a response paper, you must remain objective and factual in this section. Your subjective opinion will take center stage in the personal reaction part of the essay.
Example of a Response Summary
Below is a sample summary response essays example to help you better understand how to write one. A Summary of The Adventures of Robin Hood (1938)
The classic film The Adventure of Robin Hood (1938), as directed by Michael Curtis and William Keighley, stars an infamous outlaw, Robin Hood, who "robbed from the rich and gave to the poor''. The charismatic and charming Saxon lord, Robin Hood (Flynn), becomes an outlaw and seeks justice for poor people by fighting Sir Guy of Gisborne (Rathbone), Sheriff of Nottingham (Copper), and Prince John (Rains), who were oppressing people. After assembling an outlaw group, Robin defies the excessive taxes imposed on poor people by stealing from wealthy individuals and redistributing wealth to the destitute in society. Robin Hood is eventually lured into an archery tournament and gets arrested, but survives an execution. He later helps King Richard to regain his lost throne and banish Prince John.
5. Share Your Reaction
After summarizing the original material, the second part of a response paper involves writing your opinion about author’s point of view. After a thorough review of the material, you should be able to express your perspective on the subject. In this section, you are expected to detail how the material made you feel and how it relates to your personal life, experience, and values. Within the short response essay, you may also be required to state whether you agree or disagree with author's line of thinking. How does the material relate to current issues, or in what way does it impact your understanding of a given subject? Does it change your opinion on the subject in any way? Your reaction should answer these questions. In addition, you may also be required to outline potential advantages and shortcomings of the material in your reaction. Finally, you should also indicate whether or not you would endorse the literal work to others.
Reaction in Response Body Paragraph Example
Below is a reaction in a response essay body paragraph sample to help you improve your skills in writing the response body paragraph: Reaction Paragraph Example
My main takeaway from watching The Adventure of Robin Hood (1938) is that society should prioritize good and justice over laws if the set rules oppress people. Prince John, Sir Guy, and Sheriff Cooper were cruel and petty and used existing laws to oppress and exploit poor people. In response, Robin Hood employed unorthodox means and tried to help oppressed people in society. I agree with his way of thinking. Laws are made to protect people in society and ensure justice is served. Therefore, when legislation fails to serve its purpose, it becomes redundant. Even in current society, we have seen democratic governments funding coups when presidents start oppressing their people. Such coups are supported despite the fact that presidency is protected by law. Although Robin Hood's actions might encourage unlawfulness if taken out of context, I would still recommend this film because its main message is advocating for justice in the community.
6. Conclude Your Response Essay
Do you know how to write a response paper conclusion? It should be the icing on the cake. Irrespective of how good previous sections were, your reaction essay will not be considered to be exceptional if you fail to provide a sum up of your reaction, ideas, and arguments in the right manner. When writing a response essay conclusion , you should strive to summarize the outcome of your thoughts. After stating your final point, tell readers what you have learned and how that material inspired or impacted you. You can also explain how your perspective and the author's point of view intertwine with each other. Never introduce new ideas in the conclusion paragraph. Presenting new points will not only disrupt the flow of ideas in the paper but also confuse your readers because you may be unable to explain them comprehensively. You are also expected to link up your discussions with the thesis statement. In other words, concluding comments and observations need to incorporate the reaffirmation of the thesis statement.
Example of Response Paper Conclusion
You can use the responsive essay conclusion sample below as a benchmark to guide you in writing your concluding remarks: Conclusion Example
There are a lot of similarities between the film's message and my opinion, values, and beliefs. Based on my personal principles, I believe the actions of the main character, Robin Hood, are justifiable and acceptable. Several people in modern society would also agree with my perspective. The movie has provided me with multiple lessons and inspirations. The main lesson acquired is that laws are not ultimate and that we should analyze how they affect people rather than adhere to them blindly. Unless legislation protects people and serves justices, it should be considered irrelevant. Also, morality outweighs legislation. From the movie, I gathered that morality should be the foundation for all laws, and at any time, morality and greater good should be prioritized above laws. The main inspiration relates to being brave in going against some legislation since the end justifies the means sometimes. My point of view and that of the movie creators intertwine. We both advocate for human decency and justice. The argument discussed supports the idea that good and justice is greater than law.
Proofread Your Response Paper
It is important to proofread your response paper before submitting it for examination. Has your essay met all instructional requirements? Have you corrected every grammatical error in your paper? These are common questions you should be asking yourself. Proofreading your work will ensure that you have eliminated mistakes made when working on your academic work. Besides, you also get the opportunity to improve your logical flow of ideas in your paper by proofreading. If you review your work thoroughly before submitting it for marking, you are more likely to score more marks! Use our Paper Rater , it is a tool that can help you pinpoint errors, which makes going through your work even simpler.
Response Essay Examples
If you have never written this type of academic paper before, responsive essay examples should help you grasp the primary concepts better. These response paper samples not only help you to familiarize yourself with paper's features but also help you to get an idea of how you should tackle such an assignment. Review at least one written response essay example from the compilation below to give you the confidence to tackle a reaction paper. Response essay example: Book
Response paper example: Poem
Response paper sample: Movie
Example of a response paper: Article
Sample response essay: Issue
Response Paper Format
It is important to follow a recommended response essay format in order to adhere to academic writing standards needed for your assignment. Formats depend on your institution or the discipline. A reaction paper can be written in many different academic writing styles, including APA, MLA, and Chicago, with each demanding a slightly different format. The outlook of the paper and referencing varies from one writing style to another. Despite the format for a response paper, you must include introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs.
Response Essay Writing Tips
Below are some of the best tips you can use to improve your response papers writing skills:
- Review your assignment instructions and clarify any inquiries before you start a response paper.
- Once you have selected topics for response essay, reviewed your original materials, and came up with your thesis statement, use topic sentences to facilitate logical flow in your paper.
- Always ensure that you format your work as per the standard structure to ensure that you adhere to set academic requirements. Depending on the academic writing style you will be using, ensure that you have done your in-text citation as per the paper format.
- If you have never worked on this kind of academic paper, you should review examples and samples to help you familiarize yourself with this type of work. You should, however, never plagiarize your work.
- You can use a first-person perspective to better stress your opinion or feelings about a subject. This tip is particularly crucial for reaction part of your work.
- Finally, before submitting your work, proofread your work.
Bottom Line on Response Paper Writing
As discussed in this blog post, preparing a response paper follows a two-step approach. To successfully work on these sections, you need to plan properly to ensure a smooth transition from the reading and analyzing the original material to writing your reaction. In addition, you can review previous works to improve your writing skills. So, what is a response essay that will immediately capture the attention of your instructor? Well, it should have a captivating introduction, evidence backed reaction, and a powerful conclusion. If you follow various tips outlined above and sum up your work with thorough proofreading, there is no chance that you can fail this type of assignment.
Order a response essay from our academic writing platform! Send us a ‘ write my college paper ’ message and our experienced writers will provide you with a top-notch essay according to your instructions.
FAQ About Response Paper
1. how long is a short response essay.
The length of a short response essay varies depending on topic and your familiarity with the subject. Depending on how long original sources are and how many responsive points you have, your reaction paper can range from a single paragraph of 150-400 words to multiple paragraphs of 250-500 words.
2. How to start a response body paragraph?
Use an argumentative topic sentence to start your responsive paper paragraph. Failing to begin a paragraph with an elaborate topic sentence will confuse your readers. Topic sentences give readers an idea of what is being discussed in the section. Write a responsive body paragraph for every new idea you add.
3. Is reaction paper similar to a response paper?
Yes. Reaction papers and response essays are used interchangeably. Responsive essays analyze author's point of view and compare them with your personal perspective. This type of academic writing gives you freedom to share your feelings and opinion about an idea. People also discuss how ideas, concepts, and literature material influence them in a response paper.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
24 How do I Write a Response Essay?
Pre-writing steps:
- Read the essay prompt carefully.
- Activate schema
Actively read the assigned article.
Analyze the article to determine the rhetorical situation.
- Consider your own thoughts about the article.
- Decide how you want to respond.
Conference #1
Structure your essay.
- Outline the essay you want to write.
Draft a working thesis.
Drafting the essay:
Write a summary of the article as your introduction.
Write 3 or more body paragraphs in response to the article.
Review your draft so far.
Write the conclusion to summarize your thoughts.
Revising steps:
Peer review
Conference #2
- Revise your essay.
- Proofread your essay.
—————————————–
Read the essay prompt carefully
- Highlight or note the important points
- Ask questions for any part that isn’t clear to you.
- Retrieve your assigned article.
Activate schema.
- Skim and scan the article to identify the topic and the author(s). Look for subtitles and boldly printed words. Read the author’s bio which is often located at the beginning or at the end of the article. Identify the publication. Read the first sentence of each paragraph. Ask yourself, “Am I familiar with this topic?” This will help you to activate your schema.
- identify the key points and ideas
- make note of where you agree or disagree
- highlight impactful sentences to quote the author later
- paraphrase the author’s words
- summarize the article
- What is the message?
- What is the context?
- Who is the author?
- What is the author’s purpose?
- What is the structure of the text?
- Who is the audience?
Consider your own thoughts about the author and their message.
- What do I think about this topic?
- Is this author trustworthy?
- Is the article written to inform or persuade me?
- If it is written to persuade, on which points do I agree or disagree?
- Is the author biased?
- Does the article have an objective or subjective tone?
- What did I like or dislike about what the author has written in this article?
- What made the most sense to me? What was confusing about this article?
Decide how to respond.
There are several ways in which to respond to an article. You may choose a type of response from the following list:
- Before/After- Discuss your thoughts about this topic before you read the article, then explain what you learned from the article using evidence from the text.
- Persuasion- Discuss which parts of the articles you found convincing and/or which parts of the article you did not find convincing.
- Agreement or Disagreement- Discuss an idea that the author presented to which you agree or disagree. If there were two points of view that were presented, explain which one you agree with and explain why.
- Affect- Explain the emotional effect that the article had on you. Explain why you responded that way including your own background and your own thoughts/ experiences.
- Association- Share something from the article that is similar to your own experience. Or relate the information to a different article that you have read before this article.
- Most students wait until they have a draft, but seriously, this is the best time to talk to a writing tutor about your project.
- HCC has several options for free tutoring. Best choice: after class, drop in at the Composition and Learning Center (CLC) in Duncan Hall 210. This is staffed by current HCC English professors, and you can talk to one for 10-20 minutes about your assignment and your ideas for your topic, and what to include in your essay.
- There are also drop-in tutors at the Learning Assistance Center (LAC) in RCF 340.
- an introduction- a summary paragraph of the article
- a response- 3 or more body paragraphs responding to the author
- a conclusion- a concluding paragraph summing up your thoughts.
Outline the essay your want to write.
- Use the structure of the response essay to determine the order of each paragraph. Gather your notes. Review the way you chose to respond. Write a main idea statement for each paragraph of your essay. Then, list (using bullet points) the details that you want to include under each main idea statement. You can also list relevant quotes from the article that support your ideas.
- A thesis includes your topic and what you are going to say about this topic.
- A thesis always has two parts: a topic AND something important about this topic that your essay is going to discuss.
- A thesis is NEVER a question.
- Use your notes and the rhetorical situation of the article to write a summary. Begin with an introductory sentence that introduces the publisher, author, topic, purpose, and the main idea of the article.
- Next, write a few sentences to describe the key points the author made to support the main idea.
- End your summary with your thesis.
- During your pre-writing, you decided how you might want to respond to the article. Use your outline to draft your body paragraphs. Use your synthesis skills to corporate relevant quotes from the article into paragraphs to support your ideas.
- Is your summary of the article concise, objective, and accurate?
- Do your body paragraphs respond to the article?
- Do you have a main idea for each of the body paragraphs?
- Do the sentences in each paragraph support each main idea?
- This question is extremely important. If you find that you did not respond to the article in the way you had originally planned, revise your thesis.
- End your essay by summarizing the main points you shared in your body paragraphs.
- A classmate; a friend; a relative: ask someone to read over your work. Note their questions as they read.
- At the very least, read your essay aloud to yourself, stopping when you get tripped up in words or sentences. Consider how to make these rough spots easier to read.
- Schedule a conference with your instructor, or drop in on their student/office hours, or send them a Zoom request to talk about any questions you have about your draft.
- You can also drop in at the CLC in DH210 or LAC in RCF 340 to have a conference with a tutor.
Revise your essay
- Look at your outline: have you forgotten anything?
- Do a paragraph outline of just main idea sentences for each paragraph: you’ll have a 5-7 sentence summary of your whole essay.
Proofread your essay
- take on an objective tone?
- introduce the article properly?
- capture the main point of the article?
- respond to the article?
- capture your thoughts and opinions?
- begin with a main idea statement followed by detail?
- include quotes from the article?
- concisely review your thoughts about the article?
- Major grammar errors include run-on sentences, comma splices, and sentence fragments.
- You are responsible for running Grammarly or another grammar/spellcheck before your essay is submitted.
- Your instructors want to focus on improving your WRITING—not technical errors that machines can catch easily.
- Use Modern Language Association (MLA) guidelines for formatting your academic essay and for any in-text citations or a Works Cited page.
College Reading & Writing: A Handbook for ENGL- 090/095 Students Copyright © by Yvonne Kane; Krista O'Brien; and Angela Wood. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Home ➔ How to Write an Essay ➔ Response (Reaction) Paper
Response Paper Guide
A response paper, also called a reaction paper, is a unique form of written assignment often encountered in academic settings. Its primary aim is to prompt the writer to articulate their perspective, analysis, and personal reflection on a given text, which could be an article, book, film, or another form of media.

- A response paper is a critical reflection on a specific piece of work. It goes beyond mere summary, urging the writer to engage with the text deeper, analyzing its content, and expressing a personalized viewpoint.
- The purpose of a response paper is multifaceted. It demonstrates the writer’s understanding of the text, allowing for the expression of personal thoughts and opinions. It also encourages the development of critical reading skills, fostering the ability to evaluate arguments, identify strengths and weaknesses in a text, and articulate a reasoned response to its ideas.
- In academic contexts, response papers are valuable tools for assessing a student’s comprehension, analytical abilities, and engagement with course material. They allow students to synthesize and interpret information, enhancing their ability to argue effectively and thoughtfully.
- Beyond academia, response essays hold relevance in various professional fields, particularly those that require critical analysis and thoughtful reflection on texts and concepts. For example, in journalism, research, and policy-making, crafting coherent and insightful responses to texts is crucial for informing decisions, presenting arguments, and contributing to scholarly and public discourse.
Response papers are a vital component of both academic and professional landscapes, offering a platform for critical engagement, thoughtful analysis, and the expression of personalized viewpoints on diverse topics and texts.
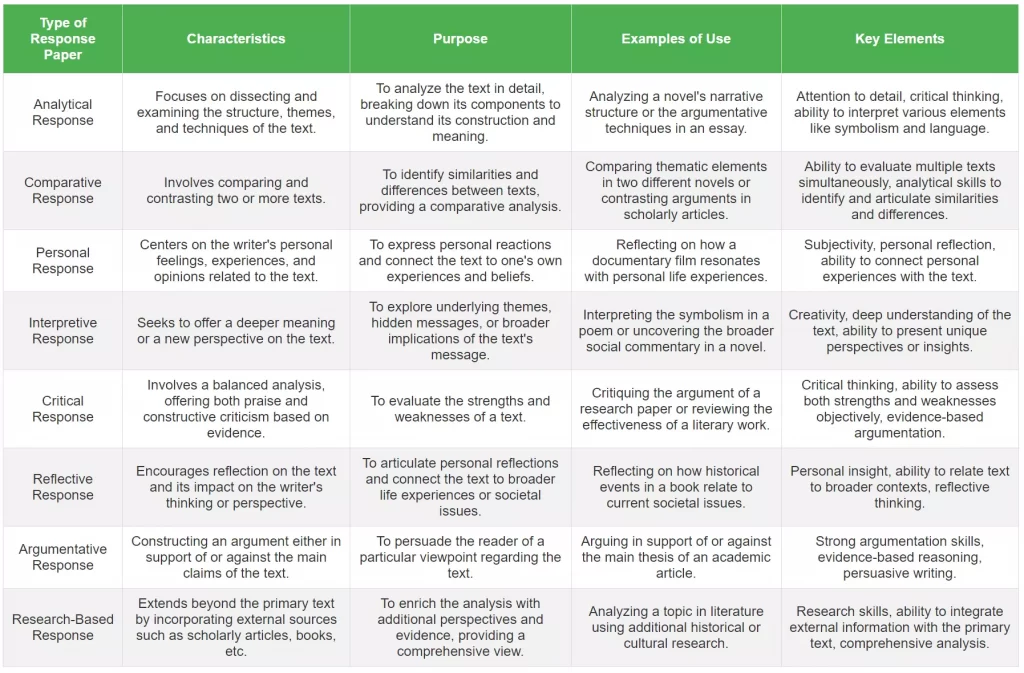
Types of Response Papers
Response papers come in various formats, each designed to cater to different analytical needs and perspectives. This section provides an overview of the various types of response essays, highlighting their unique features and objectives. These types include:
- Focuses on breaking down the text into its core components to examine and interpret its structure, themes, and techniques. This type of response requires a deep analysis of elements like symbolism, language use, and narrative structure.
- Involves analyzing two or more texts to identify similarities and differences. This type of response paper emphasizes understanding each text in the context of the others, comparing themes, styles, or arguments.
- Centers on the writer’s feelings, experiences, and opinions related to the text. It is subjective, allowing the writer to connect personal life experiences or beliefs with the content of the text.
- Seeks to offer a more profound meaning or a new perspective on the text. This type often involves exploring underlying themes, hidden messages, or the broader implications of the text’s message.
- Focuses on evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of a text. It involves a balanced analysis, offering both praise and constructive criticism based on evidence from the text and other scholarly sources.
- Encourages the writer to reflect on the text and its impact on their thinking or perspective. This type often includes personal reflections, connecting the text to broader life experiences or societal issues.
- Involves constructing an argument either in support of or against the main claims of the text. This type requires the writer to present clear arguments backed by evidence to persuade the reader of their viewpoint.
- Extends beyond the primary text by incorporating external sources such as scholarly articles, books, or interviews. This type of response paper enriches the analysis with additional perspectives and evidence, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Each type of response paper serves a specific purpose and requires a different approach. Understanding these variations allows writers to choose the most suitable type for their objectives and the text they are responding to, enhancing the depth and quality of their analysis and reflection.
Pre-Writing Steps
The pre-writing process phase is a critical step in crafting a response paper. It sets the foundation for a well-structured and insightful paper. This section outlines the key pre-writing steps: thorough reading and analysis of the text, effective note-taking and highlighting, developing a clear thesis statement, and creating a structured outline.
- The first and foremost step is to read and analyze the text thoroughly. This involves more than a cursory glance; it requires deep engagement with the text’s content, structure, and style. Pay close attention to the author’s main arguments, themes, and the use of language. Consider the context in which the text was written and its relevance to contemporary issues.
- While reading, taking detailed notes and highlighting key points is crucial. This practice helps in organizing thoughts and forming a basis for the response. Jot down initial reactions, questions, and observations. Highlight significant quotes, evidence, and arguments that stand out. This step is instrumental in identifying patterns and crucial insights within the text.
- A thesis statement forms the backbone of your response paper. It should clearly articulate your main argument or perspective regarding the text. This statement should be based on your analysis and personal viewpoint. Ensure that it is specific, focused, and reflective of your engagement with the text. A well-crafted thesis statement guides the direction of your argument and provides coherence to your paper.
- An outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and structuring your paper. It helps map out the paper’s flow, ensuring that each point and argument is logically placed. The outline should include an introduction that presents the thesis, body paragraphs that expand on your arguments with evidence from the text, and a conclusion that ties together your main points and reiterates the thesis.
These pre-writing steps are integral to writing a response paper that is coherent, well-argued, and reflective of a deep engagement with the text. They provide a structured approach to dissecting and understanding the text, enabling a more nuanced and informed response.

Write the Introduction
The introduction of a response paper sets the tone for the entire essay and is crucial for capturing the reader’s interest. It should be engaging, informative, and clearly state the purpose of your paper.
- Begin the introductory paragraph with a compelling hook : a thought-provoking question, a striking fact, or a brief anecdote related to the text. This captures the reader’s attention and piques their curiosity.
- Provide a brief overview or preview of the main points you will discuss, creating intrigue and setting expectations for the reader.
- Introduce the text by mentioning the author, title, and publication details. This provides the reader with necessary background information.
- Offer a brief summary of the text’s main argument or theme, setting the stage for your response. This helps readers who may not be familiar with the text understand your perspective.
- Conclude the introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement . This statement should briefly present your main argument or reaction to the text.
- Ensure that your thesis reflects your analysis and viewpoint, providing a roadmap for the rest of your response essay.
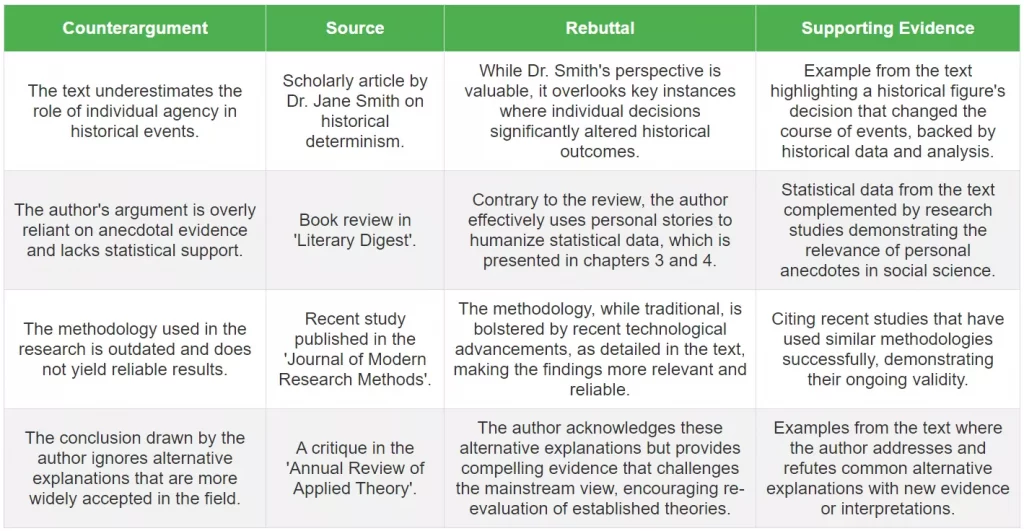
Craft the Body of the Paper
The body of a response paper is where you delve into your analysis and argument, supported by evidence from the text.
- Support your arguments with relevant quotes, examples, and details from the text. This demonstrates a thorough understanding and provides a solid foundation for your analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence is relevant to your argument, making connections explicit.
- Critically engage with the text, analyzing key themes, arguments, and stylistic elements. Discuss how these aspects support or contradict your thesis statement.
- Interpret the text in the context of your argument, offering a unique perspective or insight.
- Consider potential counterarguments or differing interpretations of the text. Acknowledge these perspectives and provide reasoned responses to them.
- This approach demonstrates critical thinking and adds depth to your analysis.
The Summary and Response Format
A response paper’s summary and response format involves two distinct sections: a summary of the text and a personal reaction or critique.
- Start with a concise summary that covers the main ideas of the text. This should be neutral and factual, providing a foundation for your response.
- Avoid including your opinions in the summary; focus on the author’s arguments and key points.
- The response section is where you present your analysis and viewpoints. Here, engage critically with the text, offering your interpretations and evaluations.
- Back up your opinions with evidence, and relate them to the main themes or arguments of the text.
- One common format is to present the summary and response in separate blocks: first summarizing the text, followed by your response.
- Alternatively, you can integrate the summary and response, addressing each main point of the text and immediately following with your reaction.
Conclude the Paper
The conclusion of a response paper is where you wrap up your analysis and restate your main points.
- Briefly summarize the main arguments of your paper, reinforcing how they support your thesis.
- Avoid introducing new ideas; focus on bringing closure to the points you’ve already made.
- Restate your thesis to reflect the insights and arguments you have presented in the body of the paper.
- This reaffirms your stance and provides a coherent end to your response essay.
- Conclude with a final thought or question that leaves the reader pondering your perspective or the text itself.
- This creates a lasting impression, encouraging further reflection on the topic.

Read for more insights:
- Graff, G., & Birkenstein, C. (2014). They Say / I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing. W. W. Norton & Company. This book provides a comprehensive guide to academic writing, focusing on argumentation and the integration of one’s own voice with others’ ideas, which is crucial for response papers.
- Rosenwasser, D., & Stephen, J. (2011). Writing Analytically . Cengage Learning. This text offers strategies for developing analytical skills in writing, which are essential for crafting effective response papers.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., & Williams, J. M. (2016). The Craft of Research, Fourth Edition . University of Chicago Press. This book is valuable for response paper writing as it guides developing a research question, gathering evidence, and constructing an argument.
- Lunsford, A. A. (2020). The Everyday Writer . Bedford/St. Martin’s. This guide provides practical advice on the nuts and bolts of writing, including structure and style, which are key components of a well-written response paper.
- Harris, M. (2017). Rewriting: How To Do Things With Texts, Second Edition . Utah State University Press. This book delves into revising and rewriting texts, a crucial skill for refining response papers and strengthening arguments.
Was this article helpful?
📕 Studying HQ
How to write a response essay., carla johnson.
- June 13, 2023
- How to Guides
A response essay is an important part of academic writing because they give students a chance to think about the ideas and arguments in a text and give their own thoughts and opinions on the subject. Response essays are different from other types of essays because students not only have to summarize the text, but also analyze and evaluate it in a critical way.
These essays are important because they help students learn how to think critically, improve their writing skills, and deal with complicated ideas and arguments. In this article, we’ll talk about how to write response essays and give students tips, examples, and ideas for topics to help them learn this important skill.
In this article, readers will learn what response essays are, how to write a good response essay, and what kinds of topics are good for this type of assignment. By the end of this article, readers will know exactly what it takes to write a good response essay and have the tools and knowledge they need to confidently take on this type of assignment.
What You'll Learn
What is a Response Essay?
In a response essay, the writer talks about how they feel about a certain text, article, or book. The goal of a response essay is to analyze the text critically and share the writer’s thoughts and opinions about the topic.
Response essays are different from argumentative and expository essays in that the writer must give their own opinion on the topic. Even though a summary of the text is often part of a response essay, it is not the main point.
An introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion are the most important parts of a response essay. The introduction should give background information about the text and include a thesis statement that shows the writer’s opinion about the text. The writer’s argument should be backed up by evidence and examples from the text in the body paragraphs. The conclusion should restate the essay’s main points and give a final opinion on the text.
Elements of a Response Essay
To write an effective response essay, it is important to include several key elements in the essay . These include:
Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on the text, including the author, title, and publication date. It should also include a thesis statement that expresses the writer’s opinion about the text.
Body Paragraphs: The writer’s argument should be backed up by evidence and examples from the text in the body paragraphs. It’s important to think critically about the text and give specific examples to back up the writer’s ideas and opinions. Each paragraph in the body should be about a different part of the text, and the writer should use transitions to link the paragraphs and keep the flow of ideas smooth.
Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points of the essay and provide a final opinion on the text. It should not introduce any new ideas or information, but rather provide closure for the reader and reinforce the writer’s thesis statement .
Thesis Statement: The thesis statement is a critical component of a response essay, as it expresses the writer’s opinion on the text. The thesis statement should be clear, concise, and focused on the main argument of the essay. It should provide a roadmap for the reader and guide the writer’s analysis and evaluation of the text.
Evidence and Examples: In a response essay, the writer’s argument needs to be backed up by evidence and examples from the text. The writer should back up their ideas and thoughts with specific examples and quotes from the text. It is important to think carefully about the evidence and explain how it backs up the writer’s argument .
Writing a response essay means carefully analyzing and judging a piece of writing, as well as being able to say what you think and feel about it. By including the key points talked about in this article, writers can effectively communicate their ideas and make sense of complicated texts.
Don’t forget to use clear, concise language, give specific examples and proof, and stick to the main point of your essay . With these tips, writers can learn how to write response essays and effectively respond to academic texts in their writing.
How to Write a Response Essay
Writing a response essay can be a challenging task, but it can also be a rewarding one. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a response essay:
Before you start writing your response essay, it is important to read the text carefully and take notes on important ideas and concepts . Consider the main argument of the text and evaluate the evidence and examples used to support it. Think about your own experiences and opinions on the subject matter and how they relate to the text.
Once you’re done with your planning, you can start writing your response essay. Start with an introduction that tells what the text is about and includes a clear thesis statement that shows what you think about it. Use body paragraphs to analyze and evaluate the text critically , using evidence and examples from the text to support your arguments. Use transitions between paragraphs to make sure the ideas flow smoothly. Finish with a summary of your main points and your final thoughts on the text.
After you finish the first draft of your essay, you should go back and fix any mistakes. Read your essay carefully , making sure there are no spelling or grammar mistakes and that it makes sense. Think about how your essay is put together and make any changes you need to make sure your argument is clear and well-supported. It’s important to follow a clear and logical format when setting up and organizing your response essay. Start with an introduction that gives background information about the text and a thesis statement that is clear and focused. Use the body paragraphs to back up your thesis statement with evidence and examples from the text, and make sure to use clear, concise language. Use transitions to link your paragraphs and keep your ideas moving smoothly. Finish with a summary of your main points and your final thoughts on the text. When writing a response essay, common mistakes to avoid include summarizing the text instead of analyzing and evaluating it, not giving specific examples and evidence to back up your arguments, and not revising and editing your essay carefully .
Response Essay Examples
Here are 10 fascinating response essay examples from different academic fields:
1. The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers” by Jane Smith
2. “The Role of Art in Society” by John Doe
3. “The Ethics of Genetic Engineering” by Sarah Johnson
4. The Importance of Education in Developing Countries” by Michael Brown
5. The Significance of the Civil Rights Movement” by Angela Davis
6. “The Future of Renewable Energy” by David Lee
7. The Effects of Climate Change on Marine Life” by Rachel Wilson
8. The Impact of Technology on Human Relationships” by Emily Jones
9. “The Role of Women in Politics” by Susan Lee
10. The Importance of Cultural Diversity in the Workplace” by Maria Hernandez
Each of these response essay examples provides a clear and focused thesis statement that expresses the writer’s opinion on the subject matter. The body paragraphs use specific examples and evidence from the text to support the arguments, and the conclusion summarizes the main points of the essay and provides a final opinion on the subject.
For example, in “The Ethics of Genetic Engineering” by Sarah Johnson, the thesis statement is clear and focused: “Genetic engineering poses ethical dilemmas that must be carefully considered before any scientific advances are made.” The body paragraphs provide specific examples and evidence to support this argument, such as the potential for genetic discrimination and the unknown long-term effects of genetic engineering. The conclusion summarizes the main points of the essay and provides a final opinion on the subject, emphasizing the need for caution and ethical considerations in genetic engineering.
Readers can use these examples to learn how to write effective response essays in their own academic fields. They can also analyze the key features of each example, such as the use of specific examples and evidence to support the argument, and use these techniques in their own writing. By learning from these examples, readers can become skilled response essay writers and effectively engage with complex texts in their academic writing.
Response Essay Topics
Here are 50 response essay topics that are sure to impress your professors:
1. The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
2. The Ethics of Animal Testing
3. The Role of Government in Healthcare
4. The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture
5. The Importance of Diversity in the Workplace
6. The Role of Art in Society
7. The Impact of Technology on Education
8. The Ethics of Cloning
9. The Significance of the Civil Rights Movement
10. The Future of Renewable Energy
11. The Effects of Immigration on the Economy
12. The Role of Women in Politics
13. The Impact of Video Games on Youth
14. The Ethics of Capital Punishment
15. The Importance of Voting Rights
16. The Effects of Globalization on Culture
17. The Role of Religion in Society
18. The Impact of Technology on Human Relationships
19. The Ethics of Stem Cell Research
20. The Significance of the Women’s Suffrage Movement
21. The Future of Space Exploration
22. The Effects of Social Media on Politics
23. The Role of Education in Reducing Poverty
24. The Importance of Mental Health Awareness
25. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Job Market
26. The Ethics of Euthanasia
27. The Significance of the American Revolution
28. The Future of Self-Driving Cars
29. The Effects of Income Inequality on Society
30. The Role of Media in Shaping Public Opinion
31. The Impact of COVID-19 on Education
32. The Ethics of Gene Editing
33. The Importance of Free Speech in Democracy
34. The Effects of Technology on Privacy
35. The Role of Sports in Society
36. The Impact of Climate Change on Public Health
37. The Ethics of Cybersecurity
38. The Significance of the Industrial Revolution
39. The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
40. The Effects of Social Media on Body Image
41. The Role of Animal Rights in Society
42. The Importance of Cultural Diversity in the Workplace
43. The Impact of Technology on Mental Health
44. The Ethics of Abortion
45. The Significance of the Women’s Rights Movement
46. The Future of Green Energy
47. The Effects of Immigration on Cultural Identity
48. The Role of Music in Society
49. The Impact of Technology on Privacy
50. The Ethics of Human Cloning
Each of these topics is interesting and important, providing ample opportunity for critical analysis and evaluation. They cover a broad range of subjects, including social issues, technology, ethics, history, and the environment . By choosing one of these topics for your response essay, you can demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in the subject matter and engage with complex ideas and arguments.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is the difference between a response essay and a summary.
A response essay requires critical analysis and evaluation of a text, while a summary simply provides a brief overview of the text. In a response essay, the writer provides their own opinions and thoughts on the text, while in a summary, the writer remains objective and simply summarizes the main points of the text.
2. What is the appropriate tone for a response essay?
The tone for a response essay should be professional and objective, while also expressing the writer’s personal opinions and thoughts. It is important to remain respectful and avoid using emotional language, while also conveying a sense of passion and engagement in the subject matter.
3. What are some tips for writing a strong conclusion for a response essay?
A strong conclusion for a response essay should summarize the main points of the essay and provide a final opinion on the text. It should also provide closure for the reader and reinforce the writer’s thesis statement. To write a strong conclusion, it is important to avoid introducing any new ideas or information and to end on a strong and memorable note.
Response Essay Outline and Structure
A clear and logical structure is essential for writing an effective response essay. Here is a sample response essay outline:
I. Introduction
A. Background information on the text
B. Thesis statement
II. Body Paragraph 1
A. Topic sentence
B. Evidence and examples from the text
C. Analysis and evaluation of evidence
III. Body Paragraph 2
IV. Body Paragraph 3
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of main points
B. Final opinion on the text
This outline can be customized for different topics and purposes by adjusting the number of body paragraphs and the amount of evidence and analysis required for each paragraph. For example, a more complex topic may require additional body paragraphs with more evidence and analysis, while a simpler topic may only require two or three body paragraphs.
Transitions are also important for maintaining a clear and logical structure in a response essay. Transitions help to connect the paragraphs and ensure a smooth flow of ideas. Some effective transition words and phrases to use in a response essay include “furthermore,” “in addition,” “however,” “on the other hand,” and “finally.”
In conclusion, response essays are an important part of academic writing that require critical analysis and evaluation of a particular text. To write an effective response essay, it is important to include key components such as an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. It is also important to use a clear and logical structure, including transitions between paragraphs, to ensure that the essay is easy to read and understand.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business Analysis Examples Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Nursing
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Cookie Policy
- Free College Essay Examples
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📧 [email protected]
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

Consider a sampling of the things we might be asked to respond to--an individual event, experience, or feeling; a series of events, experiences, or feelings; a person or several persons; objects, attitudes, trends, art, film, literature, historical artifact, cultural practice-and this is just a beginning. All of these, for purposes of our discussion here, can be thought of as "texts" to be responded to and all of them can provide occasion for the writing of a response essay.
Consider the range of texts that might be grounds for a response assignment, and remember, this is just a sampling.
Primary documents from any period, a moment from history, the biography of an historical figure, an artifact, an autobiography.
Literature and Art
A novel, short story, poem, essay, book, a passage from any piece of literature, a book review, literary criticism, a specialized lexicon, biography, autobiography; any art object, any criticism of an art object, a series of objects by an individual artist.
Film or Theater
A feature-length film, a full theater production, a one-woman show, a commercial advertisement, a clip, an individual performance within film or theater, stage features: scenery, lighting, costuming, etc.
A case study, an observation of a subject, an interview with a subject, a testing procedure, a developmental model, a treatment model, developmental transitions, group practices, individual practices, a statistical analysis.
A cultural practice or tradition, cultural norms or taboos, a case study, an ethnography, a rite of passage, funereal or baptismal practices-rituals, games and play, group processes.
Political Science
A Supreme Court ruling, a political speech, a demonstration, role of the media in public life, definitions in constitutional issues such as the definitions of "obscenity" and "pornography".
Lab report, household experiment, biography of a scientist, history of a scientific notion, lay writings on technical topics, funding sources for research, experimental procedures, science and culture interface/overlap, breakthroughs and slowdowns, research methodologies, professional/technical journal articles on groundbreaking research, data.
Am I Qualified to Respond?
Responses allow writers, even novice writers, the opportunity to do original thinking and writing. In fact, the writing of academic responses is one way to enter the conversation of the academic community. Arguably, it is an obligatory part of being a college student.
Goals of Academic Response
The goal of dialogue in academe, of responses and responses to the responses, is less about ratification, or confirmation of what we already know and more about risk-taking, or what is sometimes called "reading against the grain" or functioning as the "loyal opposition." Implicit here is the assumption that we learn by keeping an open and enlarging mind, and that at the same time we acknowledge the incomplete nature of each of our perspectives. We do the best we can at any given time, with the material and resources available to us, and the way we respond today may differ from the way we respond tomorrow.
Further, because no two people are alike, neither are their ways of responding to "texts." Yet the power to interpret belongs to everyone. So even though we may not feel qualified to respond to a text, may not believe we possess sufficient background or expertise on a topic, nevertheless we find ourselves capable of responding to it and, in fact, often are required to do so.
Becoming Informed and Staying That Way
It has always been challenging to become informed, but as information proliferates and knowledge grows more complex and specialized, it becomes increasingly difficult to stay informed. Therefore, the struggle you are engaged today as a novice is not so much different than the struggle you'll be engaged in throughout your professional career.
Do not despair! More to the point, do not allow your incomplete grasp of all aspects of a situation (or of a text) to deter you from entering the conversation or providing your own best response at any given time.
In a sense, we are all in the same boat, even your professors--and increasingly so given the rapid expansion of knowledge and its transmittal in the Information Age. Embrace your membership in this community-college--which supports an evolution or development of response from basic to sophisticated; further, continue to approach your responses with the candor and openness of the novitiate and you'll go far in academe. You probably are that novice right now, and yet you are simultaneously an important voice whose point of view is valued. As a novice, you do well to approach your role as did the villagers of Ballybran, who entered the conversation out of desire and necessity and then busied to make themselves knowledgeable. Then, as you learn more about subjects, approach your knowledge with the same fresh approach as the learned Stanford anthropologist Nancy Scheper-Hughes, who, in studying the villagers of Ballybran, was unafraid to look at her own area of expertise with fresh eyes. That is the nature of academic inquiry when it is functioning well.
Take Courage From an Example: The Anthropologist and the Ballybrans
Stanford anthropologist Nancy Scheper-Hughes, went to a village in western Ireland, Ballybran, to study the relationship there between longstanding social customs and mental illness. Scheper-Hughes lived amongst the Ballybrans, engaging in a kind of study known as ethnography. As a result of her study, some of the inhabitants of the village became angry about the way Scheper-Hughes depicted them. They spoke out about it, even argued about it. Others began to examine some of the complicated problems of their community and started discussing them. In any case, the inhabitants of this village were changed by having been studied, and they looked at their circumstances with fresh eyes, with a perspective gained from having a foreign observer in their midst.
Similarly, because Scheper-Hughes was concerned about the way her new friends in the village became bitter about her findings, she reexamined the purposes and methods of her field. She began to challenge some of anthropology's ethical obligations to the people it studies.
Thus, both the villagers and the visiting expert were changed; they learned from each other. Further, there can be little doubt that both were qualified to respond to the study, and they did so, though in quite different ways.
Reading to Respond: Encountering the Text
In preparing to respond there's no substitute for coming face-to-face with the text you'll be responding to and opening yourself up to it fully. Don't be one of those people who "reads around" the text, reading criticism of the text but never quite getting to the text itself. Eventually you may want to look at some of the secondary sources, the criticism, but start with the primary text. Immerse yourself in it. Know it, inside and out. Think of "reading" the text, regardless of whether it's a written text or a piece of art or a film or an historical artifact. Resolve from the beginning that this is going to take some time.
Survey or Preview the Text
Try to begin your encounter with the text by surveying or previewing it, which is to say, coming at it with a wide-angle lens, looking it over in its entirety, and activating your schema (your storehouse of accumulated knowledge and experience). Think of this encounter as similar to the strategy you take when downhill skiing at a new location, when shopping at a new mall, or when visiting a city for the first time. You want to get the lay of the land, know what you're getting into before you take a lift at the ski resort, before buying shoes at the mall, or before trying to traverse the city. You could waste precious time taking a lift to slopes you've no interest in; you could spend too much money by not doing comparison shopping; and you could get lost in traffic if you don't know where you're going. A little time up front can save you a lot of time over the long haul, so learn to get the broad view of a text before you try to read, analyze, and respond to it, and know that taking a look at your text this way is one of the most valuable skills you can learn as a writer, as a reader, and as a life-long learner.
Formulate Questions About the Text
Based upon your initial survey and upon the response assignment you've been given, develop questions that are pertinent to the reading you are about to do. These questions should help you focus and stay active during your reading. Use your predictive capabilities to forecast what the text will say and the questions you will have. Think more in terms of "Why" questions than "What" questions. Think of the "connective tissue" of the text, the margins, the movements from point to point, or those areas where relationships among ideas are explored, exceptions taken, distinctions made, and then ask how the text proceeds from point to point, paying particular attention to these boundary areas.
Use Prediction
When an active reader prepares to read and as he or she reads, an act of prediction often occurs. The reader develops expectations, logical guesses about where the text is taking him or her. This predictive capacity is not something to avoid but something to develop. Doing so suggests your engagement with the material, and even a wrong prediction is a valuable one, because the correction to your expectation is often the source of new knowledge that surprises and informs you.
Read the Text
Read the text all the way through, perhaps making some quick checks in the margin for places that surprise or challenge you. As you read, look for answers to the questions you developed after you surveyed the text.
Annotate/Mark theText
Now read the text again with pen in hand, prepared to do some serious marking this time around. This will involve a slower re-reading. Notice that you do not annotate (or highlight for that matter) on the first reading. Doing so tends to produce wanton, or indiscriminate, marking and highlighting, and the pen and highlighter tend to become pacers leading you through the text and turning a nice white page into a nice yellow one. Don't deceive yourself into thinking that this sort of activity is what is meant by textbook marking!
Before you start this more careful re-reading, return again to the questions you formulated after your initial survey. Develop a shorthand for your annotations, perhaps always using a double underline on the text to indicate a thesis or main focusing statement. Try writing marginal summaries as you go along as well, since the ability to summarize a text is the surest way to show your command or "ownership" of the material. Also, respond intuitively in the margins; after all, your feelings as you read are important and sometimes provide the most important insights, even suggesting your overall reaction to the text. The more you interact with the text the better able you will be to do your response to it. You will know the text well.
Special Problems of The Non-Print Text
Doing these activities is a much simpler notion when you have a written text in front of you than if you are watching a film or studying a work of art. However, there are ways to record your reactions even with non-written texts, ways to keep a running log as you experience the "text." (One notable difficulty may be if you're sitting in a dimly lit theater; there it will be difficult to take notes so you'll want to make some mental notes and then record your ideas immediately after the viewing. Keep your notebook handy! Anything you can learn about the production before you see it will also help, so read the reviews and the synopses and the production notes and the handbill before watching a production in film or theater.)
Multi-Pass Reading
Some people refer to the process we're describing here as multi-pass reading. On your first pass, you're getting the lay of the land, thinking about the audience for the text, its apparent approach. On your next pass you're reading all the way through a text but you're not responding but are instead coming to terms with the text as a whole document. On the next pass you're re-reading and responding through annotations and text marking and marginal summary, essentially coming to terms with the text's message. On yet another reading you're skimming and scanning and thinking about the speaker (the name we sometimes give to the human being, the writer, behind the words you're reading). You ask yourself what you know about the speaker in terms of facts, whether directly stated or alluded to, (gender, race, age, affiliations, etc.), emotions (evidence in the text of the speaker's emotional response to his or her topic), and attitudes (evidence from the text of the speaker's intellectual response to his or her topic and conveyed as judgments or conclusions). Think throughout your multiple reading about audience and purpose. For whom did the writer write? What purpose(s) did the text serve? These kinds of questions can help you move from an objective restatement of a text's substance toward more penetrating observation and analysis of the text's aims and accomplishments. How did the writer hope to influence his or her readers' way of thinking or acting? And why?
Write In My Book? No Way!
As a final note here, the idea of annotating a written text sometimes causes consternation among students. They say they plan to return their textbooks at the end of the semester for a refund. This is a foolhardy approach, a false economy of a most dangerous kind. It simply won't work for the serious college student who knows that texts are returned to throughout an education, not read and then discarded. Real encounters with written texts are a messy business. Further, you are building a library, and if that image doesn't appeal to you, think of it this way: you're being invited to deface a published document. Have fun, be a rebel, make it yours! Someday you can show your children the outrageous things you once wrote in the margins of your texts. And by that time you may well appreciate the library you began to build back there during your college days.
Making Inferences
For our purposes, a text will be defined as anything we study closely for purposes of an academic response. When we respond to a text, we make inferences from a text.
Defining Inference
An inference is a conclusion based upon available information. We infer all the time, sometimes less wisely than others. For instance, we are pulled over by a policeman when driving across town and infer that we've made a moving violation. Or this: we receive a phone call from the Internal Revenue Service and infer that we're about to be audited. But we can't properly infer anything from the sketchy information provided here. The policeman could be looking for a lost child and hoping that we've seen her. The IRS could be calling to send us a lifetime achievement award for our conscientious income tax reporting. (All right, so that last one is unlikely, but you get the idea.) In order to convince an audience that an inference is correct, we must provide evidence sufficient to support our claims or suppositions.
The Inferential Thesis
To give a response is a way of talking back to a text-and remember a text can be any number of things, even an experience you've had which can be "read" or interpreted and reinterpreted through response. Notice the use of the phrase "talking back." Think of the response as a way of conversing, of engaging in dialogue, but think also of the slightly rebellious possibilities of talking back to someone. When you "talk back" there is an element of challenge, of healthy questioning, of constructive criticism. Something is out there, a text of some sort, and then there is a long pause, the silence that anticipates a response. The response you give will no doubt be expressive but probably it also will be persuasive. It should reflect what you know or have learned about a topic. It will take the conversation forward, not simply repeat what has already been said in the text itself. It will involve some risk, not mere ratification. It will question boundaries and will suggest a position, or what is sometimes called a "critical stance" or "critical position."
That is why a critical stance or position is the written demonstration of critical thinking, the goal of which is new intellectual territory. When you think critically you view a text in its entirety. You see the text via its parts, but you ask how it all adds up. The result is a thorough examination that captures the essence of the text and responds to it, resulting in a whole new shaping of the topic.
Sometimes in the early stages of developing an inferential thesis we may call it a working message . That sends the message that we're working on it, attempting in our drafts to state clearly and simply the position we're taking in our response and why we are taking it.
More on Evidence: Making Choices
Your response is only as good as your evidence, and your effectiveness as a response writer, your authority as it is sometimes called, will depend in large part upon your evidence. The kind of evidence you choose to use will vary according to the thesis you are proposing and the subject you are addressing. If, for instance, you are comparing two texts, then some of your evidence will be drawn from each of those texts and will no doubt require summary of both texts.
In general, a response is only as good as its understanding of the text being responded to. Therefore, thorough familiarity with the text is absolutely necessary, and the text itself provides the first and most important evidence for your thesis. Beyond that, however, your own experiences, observations, and knowledge can inform your thesis. Information gleaned from additional sources and experts in the field can form a further pillar of support.
When you select the evidence that best contributes to and develops your thesis, remember that simple summary at this point will not do. Rather, analysis of the material is needed. You are always endeavoring to explain how the evidence contributes to or develops your thesis, your line of thinking.
Further, strive to be both concrete and analytical. Refer back frequently to the text itself, providing brief, concrete details from the text to support your thesis. From these concrete pieces of evidence, derive analytical conclusions . As you write from these analytical conclusions, provide ample examples from the text, clarifying how those examples support your thesis. Strive to be thorough but not repetitive.
How Do I Get Started? Preliminary Considerations
Ask questions. Ask questions that probe beyond the obvious, the clearly stated, the facts. Instead the questions should ask "why," "how," "what does this mean," and "how does this connect to (or differ from or relate similarly to)" other things I know or think. You ask yourself about the context of the text and its author, suppositions inherent to that context. Then you go back to the original, skimming or scanning for places that address your questions. You look for specific kinds of information, rather like scanning a telephone book until you find what you're looking for. Once you find an area that looks promising, then you read the text more closely, looking for cues that answer the probing questions you've developed.
Do I Need Outside Sources?
Studying the original alone may be enough for purposes of your response, or you may need to draw upon outside or additional sources to provide the context and the contrast that you need for your analysis. The answer to the question depends upon many factors, including, perhaps most importantly, the expectations of your teacher for this assignment.
It is always appropriate to ask yourself what you know about a topic, activating your schema, your storehouse of accumulated knowledge, perhaps even personal experience with the topic if you have any. Then you ask yourself how the text you're studying challenges your experience, your expectations, your additional sources, your understanding because you're hoping to do something beyond mere reporting. Having found these challenges, these distinguishing features, distinctions, or areas of debate, you have also found the area(s) most promising for a response from you. For here, where you notice either surprise, contrast, movement into new space, or tension, lies the material waiting for a response from you, a response that is authentically yours. And now you get a sense of why response can be a creative and original act, which is not in any way to suggest that creativity and originality cannot also be collaboratively derived. The next step is to mine your response for an inferential thesis that will guide your formal, written response.
The Connection of Summary and Comprehension
To begin a critical stance or position you must first be able to summarize the thing being responded to. Critical thinking and the development of a critical position is movement from true understanding to original statement. You might use reporting expressions such as she "claims," he "recommends," and they "argue" to suggest in summary what the text has seemed to say. Keep in mind, too, that you simply must know the original text well before you can begin to respond in an informed way.

Your Context: The Assignment
Refer to the assignment you've been given. This should clarify the audience and purpose for the response you are giving. Since so much depends upon audience and purpose, it is wise to spend some dedicated time making this evaluation. Ask yourself these kinds of questions: Who is my audience? What is the purpose of this assignment? What can I safely assume about my audience's knowledge? What might I have to offer to the conversation on this topic, or how might I further the thinking on this topic, given what I know and what my audience knows? What are the expectations for this assignment? Is there a specific task implied by the assignment-for instance, a comparison of two texts? There may be other questions that come to mind for you, and since no one knows the context of the assignment better than you, we would expect your questions to differ somewhat from the suggested ones given here.
The Text's Context
Then step back from the reporting and ask some questions about the text, such as "Why would he/she/they say this/do this/make this, etc? What do I know about this source? What is its context? Its author's context? Is the text predictable? What would you expect from this context, or does it somehow surprise? What position would be taken by persons coming from other contexts? These kinds of questions can begin the formulation of your own critical stance or position.
Ideas for Finding and Developing a Critical Stance
Next, think back to your summarization process. If there were places where you had difficulty summarizing, these problematic areas may provide clue as to one or more weaknesses in the text's statement or argument or they may suggest areas of new information for you. With any text, you can ask:
1) Are the connections of the parts to the whole reasonable and clear?
2) Are all the parts of the text easily made to fit, to follow, or developed as logically and reasonably as you might expect
3) Is the evidence appropriate and sufficient?
You might also think of these questions as tests-tests for logical consistency, for inherent assumptions, for degree of examination.
If Your Tests Reveal Weaknesses
If, upon further examination of the text, you are able to discern weaknesses in argument, or use of evidence or something else, then you may well have begun to find your critical stance. There may be questions the studied text failed to respond to fully. There may be an underrepresented or misrepresented side of the story with which you are familiar. There may be one or more faults in logic or use of evidence. You may be aware of these problems from your own life experiences or you may find that in doing further reading there are issues on which the text is inadequate.
If Your Tests Reveal Few Weaknesses or You Essentially Concur With the Text
What if you find yourself agreeing completely with the text you are responding to? Is it still possible to respond? The answer is yes. Even agreement can yield an important critical position or stance. By having looked closely, you should be able to describe what is there, and your reader will appreciate your thorough knowledge of the text. Further, an aggressive counterpoint to the text is not always necessary; sometimes, in fact, you may choose to support and enlarge or amplify a text's claims, rather than to refute them. In other words, perhaps you could extend a text with which you essentially agree, suggest through your own evidence ways to beef up the author's presentation.
Other Ideas for Developing a Critical Stance
- Construct a different side to the text's position, even if this construction involves some imagination on your part and is not really in keeping with your beliefs. Try writing this conflicting view in a single draft called "The Other Side."
- Ask yourself what the contribution of the text is to a body of knowledge, the text's contribution to general knowledge. Locate the text within a larger framework. How does this text differ or appear to be the same as previous texts?
- Read the text for tone. What does the text additionally communicate via subtle (or not so subtle) cues?
- Read the text for structural decisions and overall intent. Ask yourself: Is this text, as a whole, reflecting, reporting, explaining, persuading? Is it composed of a series of structural decisions-in other words, does it report, then explain, and finally persuade?
The injection of one's own thoughts distinguishes response from summary. Remember that with summary you remain true, or close, to the original text. As such you remind your reader over and over (through author tags, for instance) that the ideas you are representing are not your own but belong to someone else.
When summary ends and response begins, you should provide some clear markers. One clear way to do this is with a paragraph change. Additionally, it is a good idea to declare your presence through use of the first person "I," as in "I believe," "I think," "I have found." Do not be shy about this; despite the familiar advice to keep your academic writing away from the first person, there are occasions where first person is not only acceptable but desirable. A response essay can be one such occasion. If, however, you are nervous about this, the best recommendation is always to check with the individual instructor for whom the response is being completed.
Collaboration and Conversation
When it comes to response there are few strategies more powerful for generating ideas and a solid response than collaboration through conversation. When we converse we engage in a dynamic give and take of minds that is aided by our proximity to others, especially when that dialogue occurs in person and, though to a lesser degree, also when we converse via telephonic or electronic exchange. Talking alongside another we gain the benefit of facial expressions, gestures, interruptions for clarification, inflections of voice, and other nonverbal forms of communication. Additionally, we are the beneficiaries of adjustments and accommodations that are made almost instantaneously as we tailor our response to the audience we confront. Clarification is done almost without thinking, and we are nearly without limitation as to our ability to modify spontaneously.
Negotiated Meaning
Perhaps most importantly, when we converse we reap immediate benefit from the ideas of others around us. Thus, conversation serves a broad social function as we strive in our dialogue with others to work out cooperative understanding, or what is sometimes called "negotiated meaning." We extend our understanding by hearing other voices and alternative perspectives, and, in turn, those others benefit from hearing us. Conversation is thus a powerful mechanism for furthering insight.
Small Groups
When you can, you should seek out small groups for just this purpose, especially when you are initially dealing with new texts. Exploration, divergence, discussion, examination, interpretation, and resolution are some of the things a member of a conversing small group might hope to gain from such an experience. And with both amplification and challenge, your responses will improve-almost certainly.
Internalized Audience: Strive to Develop
By the same token, it will not always be possible for you to engage in conversation regarding every text you respond to in your college career. On those occasions when dialogue is not possible, you lose all the benefits of hearing outside interpretations, and this can be a significant handicap. However, it is possible to develop a voice of dissension, what we might call the voice of the loyal opposition, that voice or internalized audience whose position you are able to imagine and hence profit from. Since your own response will stand up better after being subjected to the imagined criticism of others, it is always wise to engage in dialogue with at least your internalized audience.
Developing a Response
Depending upon the assignment and upon your preferences, one or more of the following approaches to response should get you started on a suitable response.
Development Approaches
Kinds of evidence, structuring the response, inductive and deductive presentations of response, interpolating and extrapolating.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the text. Here the response focuses on the most important elements of the text and evaluates their effectiveness (the clarity of the main idea, the organization of the argument, the quality of the evidence, the overall effect of the text, conveyed through tone and apparent attitude of the text's author.) We might also think of this option as critique or review.
- Agree or disagree with the ideas in the text. Here the response focuses on a respondent's reaction to the ideas or effect of the text. It is important to note here that often it is not necessary (or even desirable) to completely agree or complete disagree. In fact, a quite reasonable and credible response will agree with some points and disagree with others.
- Interpret and reflect on the text. Here the respondent explains, examines, and/or theorizes on the meaning of the whole and the parts of the text, its implications and its contributions to understanding of the topic.
Different kinds of evidence can be chosen to support these response types. You might well use:
- evidence from the text itself
- personal experience
- outside sources
- or some combination of these.
It is rarely necessary to use all three of these kinds of evidence, but the important thing is to have sufficient evidence to support the ideas you're proposing, the point you're making, and to ensure that you are indeed providing a main, overall point-the inferential thesis--that is coherent. A simple laundry list will not do.
Typically a response will take one of the forms suggested below in outline or skeletal form.
- Introduction to text(s)
- Summary of text(s)
- Point 3, etc.
Or here's another format. Notice the initial focus upon key issues.
- Introduction to key issues
- Point 2, etc.
Or here's another, integrating summary and response.
- Introduction to issues and/or text(s)
- Summary of text's point 1/response to point 1
- Summary of text's point 2/response to point 2
- Summary of text's point 3/response to point 3, etc.
Sometimes it also helps to think of sequencing or arranging your response in either an inductive format or a deductive format. An inductive format builds toward a conclusion, since an inductive process is "emergent," one thing leading to another, building upon another, like scaffolding. The inferential thesis with an inductive approach would come near the end of the essay. With a deductive format, the inferential thesis is delivered at the beginning, right up front. Think of this approach as "spilling the beans," essentially telling all that you know from the beginning and then using the rest of the essay to support or defend (provide evidence for) your thesis. In theory, either development is suitable, but it should also be said that there is a rather strong preference in much of college writing for the deductive approach.
Another way to think about the development of your response is to consider the concepts of interpolation and extrapolation. To interpolate is to bring external ideas to a text so that these external ideas inform, enlarge, elucidate, or even refute the text. To extrapolate is to take what you learn in one place or one text and apply it to a different context, one that perhaps seems to bear little resemblance to the original context.
Example of Interpolation and Extrapolation
Consider an example of Sally Smith, college student. She is taking several humanities courses and has recently learned in a philosophy course that a human's interpretation of experience can vary widely and according to the cultural background and context of the person. Among other things Sally is studying in this philosophy course are Native American representations of the relationship between humans and the earth. At the same time Sally is assigned to read and respond to Moby Dick along with selected secondary sources for her American Lit class. She finds that none of the assigned secondary sources was written from a Native American perspective.
As a point of fact, the philosophy course and Native American culture really have no direct relationship to Sally's American Lit course, but she sees a relationship between what isn't being discussed there and what she is learning in another class. Further, she feels she has been changed by studying a non-European way of looking at and living in nature, and she believes her audience might be newly informed themselves if she were to bring something of her new perspective to her response paper. Increasingly she believes that she can't ignore her increasingly sophisticated ways of viewing the world, is gaining confidence as she learns and connects her learning among classes. As a matter of course, then, Sally finds she can't help but "extrapolate" some of this new-found knowledge, as she reflects upon the novel from what she thinks would be a Native American perspective, or at least as close as she can come to that from her admittedly limited knowledge. During a discussion period of the literature class Sally finds herself wondering how differently the discussion might go if a Native American perspective were articulated.
Sally is extrapolating, applying newfound knowledge to a novel situation.
Then comes the next step, the paper Sally must write. As she applies her newly informed knowledge of the sacredness of non-human living things to her response to Moby Dick (and its secondary sources) she is interpolating, bringing an external idea into the text she's studying. Perhaps she even winds up questioning how "American" this American classic is.
A Process for Writing a Response
There is no one correct process, only approaches and strategies as varied as people. However, some practices seem to work well for many people, and so an example is presented here to get you started. This is not a prescription; adapt and adjust the process to meet your needs, your best practices, and your assignment requirements.
Getting Started
Because response always comes as a result of something, some text that precedes it, which must be read and responded to, the process of writing a response actually begins with reading. Don't shortchange this part of the process because your success throughout the process will depend on your initial attentiveness to the text you are responding to.
One important thing to think about as you begin a response process is the assignment itself. What do you know about the audience and the purpose of the response you are about to write? What more do you need to find out?
A second thing to consider is the deadline for the assignment. Be clear in your own mind about due dates, and then backward plan from that due date to the current date. Divide up the tasks of the response, allowing yourself time to read, react, draft, collaborate, revise, and even seek a full-scale peer response or workshop opportunity.
Don't allow yourself to procrastinate simply because the task seems overwhelming; instead, chip away at it, a little bit at a time, and you may be surprised at how smoothly things go. Among other things, when you address the assignment early and give yourself time to think (and actually do that thinking instead of avoiding it) you actually end up incubating ideas even when you're not fully conscious that you are doing so. This mulling over of your response will tend to make the writing of the response go much more easily and should actually help you produce a better response because of your full engagement with the material. Starting early will help you filter out less good responses over the course of the assignment period.
Just as soon as your initial reading of the text has been accomplished, then critical thinking can begin, and this is perhaps the most essential component of your pre-writing efforts. A good place to start is with a double-entry journal.
Double-entry Journal
Consider using a journal to first explore your initial and individual responses to the text. One particularly helpful form of journal for responses is called the dialectic or double-entry journal. In this kind of journal, you divide a standard piece of notebook paper down the middle and first record your summary of a text in one column and your ideas, questions, and reactions in the second column. If you have trouble getting started or are worried about getting full coverage with a double-entry journal, try thinking of the text in terms of four elements:
- the text's audience
- the text's main idea or main effect
- the text's organization, its forms and features of support used to create, enhance, and amplify the main idea or effect
- the text's style and tone
Early Collaboration Strategies: The Importance of Peers
Even at this stage it is not too early to begin collaborating and conversing with peers to strengthen and enlarge your response. In fact, you could begin even before you have made your first entry into your journal. Instead, you could read the text in a small group, stopping ever few paragraphs to record together what has happened so far and to predict where the text is going.
Try Collaborative Prediction as a group strategy. With this approach, the group reads a text for the first time together. A member reads two paragraphs aloud and then stops. Members of the group summarize aloud what has happened in the text and discuss what the group predicts will happen next. Then the group reads a full page, stops and predicts again. Do this a third time, reading another full page and summarizing in one sentence what has happened and predicting the next step. Now the group stops and writes a forecast for the whole essay. The group then reads through to the end to see how close they've come to anticipating the text's direction.
Once your initial journal entry is complete, try doing a Collaborative Annotation of the text. First, each member records (probably before class) his or her response in the margins of the individual's text; then each member of the group reads (one paragraph at a time) his or her response aloud and the group collaborates to choose the best of the responses. The group then records a consensus response (selecting best responses as you go along) in the margins of a common copy of the text.
Alternatively, your group could debate the strengths and weaknesses of the text.
No matter how or when you do a collaboration or conversation, however, make sure to record your personal reflections on the collaborative subject. What new responses did you hear in the discussion? How has the conversation affected your initial response? Where might you revise your reactions? How will your focus be altered by exposure to these other responses?
The Exploratory Draft
You're at the point now of trying an exploratory draft, writing just for yourself, to find out how you feel and what you have to say in response to the text at hand. At this stage, you are not thinking about communicating with others so much as you are writing to think, or to discover what you think.
Once you have an exploratory draft, you're at another juncture where collaborating and conversing with a peer may be helpful. When you involve a peer or a small group of peers in reading your exploratory draft, you can direct their reading by asking them to tell you what they find to be your central point as well as what they find most surprising or intriguing. By directing their reading, your peers will be less likely to treat your exploratory draft as a finished product and will seek instead to answer your questions. You might ask your collaborators to name their concerns about the things you have said in the response, to take issue where they disagree and say a bit about their beliefs. Taking into account such additional information will inform and improve your subsequent drafts.
You may find that you need several exploratory drafts before you really know what it is you mostly want to say.
A Rough Draft of Your Response
Perhaps you have now written several exploratory drafts, have collaborated and conversed with peers until you have a fairly good idea of what you want to do in the response paper. Now you can begin to plan your draft, thinking more concretely about your audience, about the work you'll need to do to convey your main idea, to enlarge and amplify the supporting points, to reduce and cut and less important information, to rearrange and sequence your points.
Now you are thinking less about focus because that is clear in your mind. You are beginning to think more about presentation. The goal now is to provide sufficient support of the right kind and to organize it in such a way that you achieve maximum effect.
At this point you will also want to think about your tone in the response, whether you are conveying the attitude you intend. Your collaborators may be better judges of the overall effect of your writing than you are. Ask your peers to read this draft for that issue only. Do I sound smug? Sarcastic? Unnecessarily hostile? Inappropriate humorous or flip? Does my tone fit my message and my subject?
You may also be ready at this point to start putting final touches on things so by all means do the very best job you can with proofreading and mechanics, and then do not hesitate to ask a peer reader to look at your response for these matters as well.
Checking Your Inferential Thesis
Ask yourself if you have an inferential thesis, a statement of your critical stance regarding this text. Remember that an inference is a conclusion based upon available information. Reliable inferences are grounded in the text itself and demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the text. Remember that your audience will not believe your inference, regardless of how true it is, unless you are able to show why the inference is reasonable and accurate. Your job essentially is to persuade your reader, using evidence which supports your conclusion or inference.
Checking Your Development Decisions
A hundred different developments might well be possible for your response, and so it should not be concluded that a rigid format for response is a reliable tool. It's not as simple as taking a formatted approach and simply plugging in your data, your evidence. Rather, the subject, the assignment, the audience, and the text itself should inform your decisions about the development options for your response. Given this caution, however, three of the most common methods of responding include:
- agree or disagreeing with text's points or presentation
- interpreting or analyzing the text's points or presentation
- critiqueing or reviewing the text's effectiveness
Checking Your Evidence
The development of your response is completely dependent upon the kinds of evidence you choose to use to support your inferential thesis. Typical kinds of evidence for responses are drawn from personal experience, from outside sources, and, most importantly, from the text itself. It is not necessary to include all of three of these kinds of evidence for every kind of response, but almost certainly your evidence will include references to the text itself.
Choose the kind of evidence that makes sense for your essay. There is nothing wrong with drawing upon personal experience unless it really doesn't cast light on the topic or unless other forms of evidence would work better. Outside sources can often provide perspectives you might not have possessed before reading them; however, the use of outside sources does not eliminate the need for you to formulate your own conclusions and your own inferential thesis. Use outside sources, if you choose to use them at all, to add credibility and authority to your points.
Most importantly, remember that your primary task in a response is to react to the text itself. Stay close to the text, whatever form it may take, in formulating and delivering your response. Regardless of the other kinds of evidence you select for your response, your first and more important one is always the text itself.
Late Collaboration: Formalized Peer Response
It may not be possible to engage your peers for as many responses to your paper as this process suggests, but having completed your rough draft with all the thoughts of focus, organization, and mechanics at the forefront of your mind, you may wish for one last peer response, and this one might take a more formal, wholistic approach. At this point you might seek out an in-class workshop in which the entire class or a small group responds to your paper, or you might engage in a reciprocal take-home review with a peer, or you may want to send a computer copy to one or more people in your class.
At this stage, since you will probably not seek additional peer assistance after this point, you want to get the most you can from your peers. On your draft, label summary and label response. Underline your thesis statement. Perhaps underline the topic sentences for the paragraphs that introduce the main lines of development or support of that thesis. Accompany the draft with the one or two most important questions you have at this point regarding your paper. Write your most urgent questions for your readers at either the top or the bottom of your response.
Draft One and Draft Two Questions: Another Way to Approach Process
Here's another idea that may help you think further about your response. Try a Draft One that provides your response from the point of view you are inclined to take and then follow this draft with a Draft Two that introduces a new perspective into the discussion. A Draft One/Draft Two approach ensures that you are looking at your topic from multiple perspectives, which is not only good for enlarging your way of looking at things but is also practical and effective at helping you write a better paper. Deep knowledge of another perspective will help you anticipate the possible questions and doubts of your audience. Deep knowledge of another perspective also will tend to help you develop better explanations for your judgments.
The Final Draft
In truth there are no final drafts, only final deadlines, so as you complete the last draft you will be able to do before your deadline, return to your original assignment and goals for the response assignment. Think one last time about your audience. Have you responded to the assignment and its implicit audience?
Review your thesis. Is it clearly stated? Do all of your supporting points really support your thesis? What method of response did you select-agree/disagree, interpret/analyze, critique/review? What forms of evidence or support did you choose to use in addition to the text itself-personal experience, additional sources?
Take a final look at your level of amplification. Did you say enough? Is there proper balance among the parts, or are the proportions right for the points you are making? Did you sequence these points to maximum effect?
How about sentences and paragraphs? Are your paragraphs unified and coherent? Do they all contribute to your points? Are your sentences varied and emphatic? Does each contribute to the paragraph to which it belongs? What about proofreading? Did you use the spell check function on your word processing software and then follow up with a rereading to catch words spell check misses? How about punctuation? Have you gone back over your draft and considered the patterns of mechanical error you typically have problems with and attempted to correct them? If you have printed out your final draft and it's due in ten minutes, pencil in changes rather than turn in a paper that has errors. Most of your professors would rather see that you've attempted to make corrections than see a pristinely typed, though uncorrected manuscript.
Doe, Sue. (2004). Responding. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=34
Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
How to write response essay: guidelines from expert team.
January 31, 2022

Response writing can be tricky, but if you follow our step-by-step guide, you’ll have no trouble coming up with a great one! We will walk you through exactly how to write a response paragraph, how to properly structure it, and even give you some helpful tips to make your essay shine!
So, let’s get writing!
Table Of Contents
What is a response essay, structure of a response essay, steps to write a good response essay, 5 key features needed in a response essay, tips to write a stellar response essay, response essay example.
First things first – what exactly is a response essay? A response essay is a type of writing that allows the writer to respond to a piece of work. It can be a text, image, or event. It’s essentially a reaction paper – you’re giving your thoughts and feelings about whatever it is you’re responding to.
Response essays allow you to freely communicate your thoughts and feelings about any topic. Unlike summary essays where you just restate what you read, response essays require you to genuinely understand the content and context of the work you’re assigned.
Once you have a strong grasp of the subject material, you have to concisely put forth your insights, opinions, and analysis.
Now that you know what a response essay is, it’s time to learn how to structure one. A good response essay follows a specific format, which allows your ideas to be conveyed clearly and concisely.
Here’s the basic essay response format :
- Introduction
- Summary Of The Work
- Reaction, Response, and Analysis
Let’s take a closer look at each of these elements that form the response paper format.
- Introduction Your introduction should introduce the work that you’re responding to and mention the name of the author. You should also include your thesis statement in this section – this is your position on the subject matter. Overall, this part should be about 1-2 paragraphs long and it should keep the reader interested to read the rest of the response paper.
For example : “Should America atone for its past sins against black people? This is the question raised by Ta-Nehisi Coates in his powerful article ‘The Case For Reparations’. The author strongly believes that America should make reparations to the African-American community, and after much contemplation, I wholeheartedly agree with him”.
- Summary Of The Work In your summary, you want to give a general overview of the content without giving away too much. You’ll highlight the main points of the work, provide direct quotations, and keep the writing objective and factual.
For example : “Ta-Nehisi Coates makes many compelling arguments for why America should make reparations to the African-American community. He cites statistics, historical evidence, and personal stories to support his position. According to him, “To celebrate freedom and democracy while forgetting American’s origins in a slavery economy is patriotism à la carte.”.
- Reaction, Response, and Analysis In this section, you’ll want to go into detail about your reaction to the work. What did you like or dislike? What were your thoughts and feelings? Be sure to back up your claims with evidence from the text.
For example : “I found Coates’ argument to be very convincing. He makes a strong case for reparations by providing ample evidence to support his position. I was also moved by his personal stories about the impact of slavery on African-Americans today. His writing is powerful and emotional, and it made me think about America’s history in a new light”.
Many students struggle with writing a good response essay simply because they’re confused about how to write response essay, where to begin, how to begin, and what to do next. Let’s take a look at the step-by-step process of writing a fabulous response paper that is sure to get the attention of your teachers and professors.
- Step 1 – Read and Understand the Work Before you can write a good response essay, you first need to read and understand the work that you’re responding to. Whether it’s a book, movie, article, or poem, the quality of your response paper is directly proportional to how well you’ve understood the source material. Take notes as you read and highlight important passages so that you can refer back to them later. This is an important step in learning how to start a response essay.
- Step 2 – Brainstorm Your Ideas Once you’ve read and understood the work, it’s time to brainstorm your ideas. This is the part of the process where you let your thoughts flow freely and write down any and all responses that come to mind. Don’t worry about making sense or sorting them out yet – just get everything down on paper.
- Step 3 – Write Your Thesis Statement Your thesis statement is your position on the subject matter – it should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. This is what you’ll be arguing for or against in your essay. Don’t be afraid to genuinely put forth your opinion, whether it’s positive or negative.
- Step 4 – Support Your Thesis with Evidence Now it’s time to support your thesis statement with evidence from the text. Quote directly from the work and provide a brief explanation of how it supports your argument. Don’t forget to cite your sources! The summary of the work and your personal opinion on the matter will form the core content of your paper.
- Step 5 – Write a Conclusion Once you’ve finished arguing for your position, it’s time to write a conclusion. Restate your thesis and summarize your main points. You may also want to leave readers with something to think about or a call to action. A solid conclusion can sometimes make all the difference between a great response essay and a mediocre one!
By following these steps, you’ll be able to write some of the best response essays that are well-organized, informative, and persuasive. All it takes is a little time and practice! On the contrary, you can choose buying custom college papers and be free of this assignment.
When writing a response essay, there are certain key features that you need to keep in mind. Whether it’s for school, college, or university, these five features will make your response essay unique and interesting.
- Summarizing – This is probably the most important feature of writing a response essay. You need to be able to summarize the work succinctly, highlighting the most important points without giving away too much of the plot or story.
- Paraphrasing/Quoting – In order to support your argument, you’ll need to quote and paraphrase the work extensively. Make sure that you always credit your sources!
- Organization – Your essay should be well-organized and easy to follow. Start with a strong introduction, then move on to your main points. Wrap things up with a conclusion that reiterates your position. No professor likes reading a haphazardly put-together essay!
- Transitions – To keep your essay cohesive, you’ll need to use strong transitions and connecting words between paragraphs. This way, the reader can move between different portions of your writing (e.g. Introduction > Summary > Thesis > Conclusion) without losing interest.
- Argumentation – Last but not least, your essay needs to be filled with strong argumentation. Make sure to back up your points with evidence from the text, and don’t be afraid to state your opinion openly. This is what will set your response essay apart from the rest!
We’ll share with you a few of our tried and tested essay writing tips that will masterfully elevate your response essay.
- Take your time and read the source material carefully.
- Write a strong thesis statement that reflects your position on the matter.
- When stating definitive opinions, cite instances from the text to strengthen your stand.
- Argument your points persuasively and with conviction.
- Proofread your essay for errors such as grammar, language, punctuation, and spelling.
- Have someone else, like a trusted friend or teacher, read it over for you as well – fresh eyes can sometimes catch mistakes that you’ve missed.
- Use the help of a reliable paper writing service to assist you in the process.
Now that you’ve read all our instructions, there’s only one thing left to do. You have a chance to ged extended response essay sample and see all our tips in practice.
Response Paper In his article “The Militarization of the Police”, James Bouie argues that recent traegy in Ferguson is only one symptom of the broad problem of increasing police militarization in the USA. The purpose of the author is to bring this question into light and warn American citizens about the danger it entails for the whole society, with a special emphasis being placed on racial minorities. Bouie addresses the general public who are concerned with political and social tendencies in the US. The author begins his article with discussion of the photographs from Ferguson demonstration, pointing out the signs of inadequate aggression of the police toward the citizens. He puts the Ferguson tragedy in the context of increasing militarization of the US police force, which he believes to be one of the major problems of the American society. Bouie asserts that this process began with the war on drugs in the 1980s and intensified after the 9/11 attacks and the wars in the Middle East. He estimates that the value of military hardware owned by U.S. police agencies increased at 450 times from 1990 to 2013, despite the falling crime rates. Bouie also discusses the issue of increased SWAT deployment, which is disproportionately utilized in black and Latino neighborhoods. The conclusion the author draws is that the availability of heavy military weapons and a long-standing tradition of punitive policing toward racial minorities are the major factors that are likely to cause repressive reactions of the police. The Ferguson tragedy has recently riveted the attention of the whole U.S. population. While we may lament the deaths of Michael Brown and Eric Garner, it is important to view these events in the broader context of police misconduct, as the author does it. Despite numerous changes and advancements in law enforcement over the last decade, such as community policing and recruiting more officers from racial minorities, the society is still staunchly opposed to the police force, and the negative sentiment has predictably grown after the Ferguson unrest. The frequent SWAT raids are definitely an overreaction, given that they are mostly deployed for low-level offenses, such as drug use. Repressive and punitive actions with the disproportionate targeting of racial minorities suggest that positive changes in the police were of purely decorative nature and were not effective to eradicate stereotypes, prejudices and aggression from the mind of law enforcement officers. While the author does not explore this perspective in detail, the increasing militarization of the police is often viewed as a logical consequence of the militarization of the whole US politics, which is obsessed with identifying and eliminating national enemies. Incessant employment of war rhetoric by the officials has the power to alter the mindset of the whole society, not only police officers. The article provides a comprehensive account of the author’s opinion. No doubts arise as to the appropriateness of his observations, largely because they are aligned with the common social reaction to Ferguson tragedy. However, the author does not explore any potential solutions to the problem, thus leaving this question open for the readers to consider. Another overlooked issue, which may interest the readers, is how the situation in the USA compares to other developed countries and what policies they implement to prevent the overreaction of police force. The author has achieved the purpose of persuading his readers that events in Ferguson are linked to a broader social problem, as his arguments appeal to the common sense and show clear causality between acquisition of military equipment and overreaction to offenses and unrest. The author made his article more persuading by referring to Ferguson photographs, statistics and authoritative specialists to support his argument.
Want Someone To Write An Essay For You?
We hope this guide has taught you everything you need to know about how to write a strong response essay. Keep these key points in mind, and you’re guaranteed to produce a top-notch paper! If you want additional advice on how to write a response paper, simply hire someone to write an essay . Our team of professional, educated academic writers will write high-quality papers and essays that will get you in the good books of any of your teachers! It’s fast, affordable, and always 100% original. You won’t be disappointed! Good luck with all of your future academic endeavours!

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics
- How It Works
- Essay Examples
What Response Essays Are and How to Tackle Them
Writing a response essay might seem like a challenging task at first. Firstly, you need to understand to a great extent what the study that you are responding to is talking about and then make sure that you write an insightful, true to the source essay about it. Even if you need to write a response essay as part of your homework for faculty studies or high school assignments or you want to exercise your argumentative skills, it might seem like a lot of work at first. However, having in mind a clear structure of your future response essay is essential.
Before beginning to go through the main structure points that you need to check when writing a response essay, there are some tips that you need to know and that will help you lay your thoughts on paper in a more efficient way. First of all, after reading the essay or the article that you are responding to, you need to settle on whether you want to attack the ideas presented in that article or to agree with them. Based on that, you will structure the components of your response essay. For example, if your response essay is talking about protecting the environment and you want to show your agreement with the ideas presented in the original essay, then you should build your response essay around the idea of consolidating the thoughts in the main source.
Secondly, it is important that your readers clearly understand your position after reading your response essay. This means that you need to expose all possible arguments which might strengthen or attack the ideas presented in the main article. In order for you to achieve a strong position, it might be helpful to also expose a personal experience that can be related to the topic you are writing an essay about. This will not only make your argument points stronger but will also help your readers empathize with your writing. Also, it is important that you keep in mind that your response essay should be a response to something you have read, something that is a hot topic at the moment in various social contexts or something that has been debated for a long time and you want to present a new approach to things.
You also have to keep in mind that the more knowledge you show to your audience in your response essay about the author and the topic that is being debated, the more credibility you will gain. Read some cause or effect essay topics to get inspired. This is why it is important to also present a context in your response essay, such as details about the author and the paper you are choosing to respond to. Finally, after debating the ideas of the original text, you can also choose to talk about the effectiveness of the source text. It can be about how the main paper managed to reach the audience, if the writing style was effective, and how the author you are responding to had chosen to expose their ideas.
If we were to summarize the main points you should keep in mind before starting to tackle the components of a response essay, these would be:
- Make sure to clearly expose your position regarding the article or paper you are responding to
- Don’t forget to expose the personal experiences or thoughts that might help you relate to the matter in question and your reader to empathize with your way of writing
- Prove that you have knowledge about the author of the main text and can put your response essay in a context
- Evaluate the main text’s effectiveness and how it managed to reach the audience
Get Started: Write an Introduction
One important thing when writing a response essay is the way you structure the introduction. This is one of the key parts of your essay, as it embodies the topic you are about to debate and the premises you are basing your essay on. The introduction will make your audience decide if they want to keep reading your response essay or not. This is why it is important that you keep in mind the following tips:
- Introduction is all about catching your audience’s attention
- It should provide a brief description of the topic
- You should be able to briefly summarize your thesis
- Don’t forget to give a short description of the author and the article you are responding to
It might be the case that the source article that you are about to discuss contains several parts or has different ideas which can be debated and your response article refers only to a part of them. In this case, don’t forget to also mention this. Do not forget that you need to keep it short and catchy.
How to Make Your Introduction Catchy – Introduction Ideas
Writing a catchy introduction that will make your reader read the whole response article is challenging. This is why you will find here some ideas to start with, such as:
- Making use of a statistic: some puzzling conclusion that researchers might have reached at some point and which is relevant to the topic you are about to respond to.
- Citing someone who is related to the area of expertise of your topic or is known for having deep knowledge about the topic. The more popular the person you are citing is, the more efficient your introduction will be.
- Story-telling or reproducing a dialogue might also help, provided they are relevant and short.
- Starting with a question or with a situation regarding the topic you are about to talk about might also be a good introduction idea.
You might even want to combine some of these ideas and write your introduction based on an example and a statistic or any other possible combination. Whatever you choose, make sure it stays to the point and is catchy to the eye of the reader.
How You Can Connect Introduction to Conclusion
Another important aspect that you need to consider when writing your introduction to the response essay is that you need to somehow connect it to the conclusion. In order for you to achieve a perfectly cyclic response essay, you need to find a way to make the two feel correspondent. This will help your response essay have a “frame” and will help your writing style be more efficient.
It might be a bit difficult at first to start with an introduction and end with a conclusion that are connected, mostly if you want to write very long and thorough response essays. However, one important suggestion that might help is to always make sure that before starting off your response essay, you are clear about the ideas and position you want to present. This will help you avoid changing your position as you advance in writing your essay and make your introduction and conclusion connected, giving a sense of symmetry to your text.
Below you can find some examples of how you can connect your introduction with the conclusion:
- If you are writing about the usage of mobile devices in our everyday life, you could start your introduction by exposing a real-life experience, maybe someone who is driving to work on a normal day and is stuck in traffic. You could start by asking your readers what they would do on their phones as they wait in traffic and end with several possible outcomes of this scenario.
- If you are choosing to present an essay about a personal experience and you start with an introduction about how a certain day started in your life, you could end your essay with how that day ended. This way, you will make sure you keep your readers connected to the story and have their attention all throughout the essay.
- If you decide to write about any other topic, such as a topic of national importance or even an environmental topic, you could start by stating the facts to which you want to draw the attention and end with the facts about the current situation or how it can be improved.
How to Write a Strong Thesis
After making sure that you have caught your readers’ attention, it is all about making it clear to them what your position regarding the source article is. However, you should also provide a context to your response article by mentioning details about the author and the main ideas in the article that you have chosen to respond to. It can be that you are choosing to respond only partially, to a few of the ideas presented there, so this is the reason why it is important to clearly state the ideas of the article you want to respond to. Make sure to give an account of whatever it is debated in the article, by presenting the information in an objective way. At this point, it is more important for your readers to understand what you are trying to agree or disagree with than hear your personal opinion. Also, exposing the ideas of the source text in an objective, impersonal way will help your readers decide for themselves if the position you are taking is one that they would take or not.
Afterwards, it is vital that you expose what is known as “thesis statement” by allocating one paragraph in which you clearly state if you agree or disagree with the main topic presented in the source text. This should start with “I agree/I don’t agree with” and should be followed by a short and powerful message about the main reason why you are taking this position regarding that text.
The next step is to talk more about the reasons you are considering attacking or agreeing with the ideas presented in the original text. This can be done by either reviewing what the author is saying or just expanding on the main ideas. You can, for example, try to understand why the author has reached a certain conclusion that you are debating by trying to relate it to the author’s background or career. It can be that the author has chosen to promote oil drilling because they work in a factory that wants to make this process a sustainable one. It is important that you stay true to your debate and present the situation from both points of view: yours and the author’s.
How to Respond to Articles – Ideas
After tackling the introduction and the conclusion, the main body of your response essay is left to deal with. This is mainly the way in which you choose to present the source text and where you are standing regarding it. It is up to you if you choose to agree or disagree, however, what you have to keep in mind is that you need to be consistent and stay true to the topic you have chosen to debate.
One way to do that is to map the main three components of the response essay, namely, the introduction, body, and conclusion. Here are some helpful suggestions on how to structure your responding ideas:
- Whether you agree or disagree, you can state 3 or more reasons for which you are doing so. Make sure to start each new paragraph and allocate enough space for your ideas to be clearly distinguished and stated.
- If you are partially agreeing or disagreeing, make sure to always mention that so that your readers will clearly understand your position.
- It is always important to see how the author’s ideas managed to reach the audience and in which ways the ideas were brought forward.
How to Better Structure the Body of the Response Essay
Make sure to utilize evidence to back-up your thesis. In order to do this, you can use quotes, author tags or simply rely on other readings and give references.
Make sure that you achieve a personal voice throughout the text. This can be done by differentiating yourself from the author and using author tags.
By using author tags, you communicate to your readers the fact that it is the author you are responding to who has a certain idea or it is their article that makes this reference. You can use any of these suggestions when talking about someone’s article:
- The author mentions
- The author refers to
- The author is suggesting
- The author writes
- The author asks
- The author recommends
- The author is presenting
- The author points out
- The author relates
- The author pleads
- The author denies
- The author’s remarks point to
- The author explains
Write a Conclusion Your Readers Won’t Forget
One important thing to keep in mind when writing a conclusion to your response essay is that you shouldn’t repeat the arguments in the same form in which you have presented them in the body. Offering a conclusion to your response article is still needed, as this will help your readers make a clear decision whether they agree or disagree with the ideas presented in your response essay.
Besides making sure that your essay is built around a very powerful introduction and a conclusion that sums up the main ideas of your position regarding this essay, you can also:
- Present the topic that you have been debating throughout the essay in a broader perspective; for example, if the topic you are tackling is national, you can connect this topic to the situation in other countries worldwide
- Promote an organization or an event that has some influence on the topic you have been responding to
- Present the current situation of the topic you are talking about and ring the alarm if anything needs to be done about it
- Summarize how your arguments shed a new light on the topic
A Brief Summary of How a Response Essay Should Look Like
Keeping everything in mind, the essential parts of a response essay and the main suggestions that you have to keep in mind when starting to write are:
- Paragraph 1: The first part of the introduction which needs to be vivid, catchy and reflect the point you are about to make.
- Paragraph 2: Provide a context to your response essay: details about the source-text and the author and what the main points in the article are.
- State your position regarding the ideas presented in the introduction and if you agree with the author’s take on the matter or not.
- Clearly mention if you are going to question the author’s position or expand on the author’s account of the facts.
- Give clear arguments pro or against the matter and allocate one paragraph to each of these arguments.
- Use statistics, story-telling, research findings, scientific discoveries, and any other tools suggested in this article.
- Provide an insightful and catchy conclusion that correlates with the introduction you have chosen for your response essay.

- Writing a Cause and Effect Essay Outline
- A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Research Paper Outline
- 20 Classification Essay Topics To Inspire You
- How To Write A Poetry Analysis Essay
- Prep Courses and Classes: What They Are and How They Work

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Studying Literature
How to Write a Response Paper
Last Updated: January 31, 2023 Fact Checked
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 82,454 times. Learn more...
For a response paper, you must read a text, understand the point of the text, and determine what your own response to that point is. The response paper is more analytical than argumentative. Moreover, even though you need to write about your personal response, that response must be credible and not emotional. Keep reading to learn more about how to go about writing a response paper.
Understanding the Text

- Highlighting draws your attention to words and passages you found significant in the text you read, but it does not allow you to record your initial thoughts regarding those passages.
- Take notes on a separate piece of paper. Include paraphrases and quotes taken from the passage as well as your own thoughts about the information you write down.

- What is the main issue that the author or creator is attempting to address?
- What stance does the author take on this issue? What is the author's main claim or point?
- Are there any assumptions the author makes in forming his or her claim? Are these assumptions valid or biased?
- What sort of evidence does the author offer in support of his or her point?
- What points of the argument are strong?
- What points of the argument are weak?
- What are some possible counterarguments to the claims or arguments made by the author?
- What, if anything, makes the main issue or author's main claim important?

- How does this work relate to others within a collection of works on the same topic, or with regards to another work on a similar topic written by a different author?
- Do the authors of comparable works agree or disagree?
- Do the authors of comparable works address the same part of the same issue or different aspects of it? Do they view the matter being discussed in a similar or different way?
- Does the author who wrote the piece you're responding to have past works that address the same topic? How has that author's views become stronger or weaker in comparison to past works?
- Does the information from one text strengthen or weaken the text you're responding to, and if so, how?

- Even if you think your ideas would benefit from simmering for a little while before performing a thorough analysis, you should still take the time to write down your initial reaction while it is fresh. In many ways, your initial reaction is the most honest. You can talk yourself into another reaction as time passes, and that other reaction may seem more “intellectual,” but your initial response was your true reaction to the text and should be kept in mind.

- How does the text relate to you personally, whether in the past, present, or future? How does the text relate to the human experience as a whole?
- Does the text agree or disagree with your worldview and sense of ethics?
- Did the text help you to learn about the topic or understand an opposing view? Were your opinions or previous assumptions challenged or confirmed?
- Does the text directly address topics that you care about or consider important?
- Was the text enjoyable or admirable for its genre? In other words, if the text was fictional, was it enjoyable as entertainment or art? If it was historical, was it admirable from the perspective of a historian? If it was philosophical, was it adequately logical?
- What is your overall reaction? Would you recommend the work to another person?
- As you progress through these questions, write your answers down. In addition to writing down your answers and reactions, also provide evidence from the text to support these answers. Evidence can be in the form of direct quotations and paraphrasing.

- Re-examining your notes
- Recording new ideas as they come
- Using pro/con analysis
- Raising questions about your reactions and using your notes from the text to answer them
- Comparing your reactions directly to your notes and determining which topics have the most overlap

- Depending on the requirements of the assignment, you may need to come up with one organizing argument or multiple arguments to discuss. Even when you have multiple points to bring up, however, they should still be somewhat connected to each other.
- A key difference between a traditional thesis and an organizing argument is that a thesis usually exists to prove a point, fact, or thought. An organizing argument demands that the writer analyze the reading in an ongoing manner. [6] X Research source
Block Response Format

- For a four to five page paper, your introduction can extend to one or two paragraphs. For a shorter paper, though, restrict it to a short paragraph made up of three to five sentences.
- Introduce the work by describing how the work to which you are responding fits in within the broader topic it addresses.
- You could also introduce the work by explaining your own beliefs or assumptions about the topic the work agrees with before explaining how the work challenges or supports your beliefs.

- For a four to five page paper, this section should only take up about two to three paragraphs.
- Describe the content of the work and present the author's main arguments, especially as they affect your response.
- The summary should be somewhat analytical in nature instead of a strict retelling. As you present the details of the author's work and argument, you should use an analytical tone and discuss how well the author managed to get those points across.

- Note that this response format is best to use when you are focusing on a single major theme or argument in a work. It does not work as well if you are discussing multiple ideas presented by a work.
- Back up your analysis with quotes and paraphrases. Make sure that each example is properly cited.
- If you took the time to find textual evidence to support your responses during the prewriting stage, this portion of your paper should be fairly easy. All you really need to do is arrange your argument in a coherent manner and write in the details of the support you have already gathered.

- Even for a four to five page paper, you only need one standard paragraph to accomplish this. For a shorter paper, make this paragraph only three to five sentences long.
- State how this work has a broader effect on you and to the genre or community in which it is a part.
Mixed Response Format

- Your introduction can span one to two paragraphs for a four to five page paper, but for a short one to two page paper, keep the introduction down to a single short paragraph.
- You can either introduce the work by describing how it fits into the topic it addresses as a whole or by explaining how it impacts your own beliefs on the topic.
- By the end of the introduction, you should have mentioned your "thesis" or organizing argument.

- Note that this mixed response format is a better option when you have many loosely connected themes or ideas you want to react to instead of a single overarching one.
- This method allows you to weave your summary and analysis together more naturally and more cohesively. As you bring up a point or example from the text, address your own interpretation of that point directly following your mention of it.

- Continue on as you did with your first point. As you summarize a point or argument from the original text, immediately follow it with your own intellectual response to the argument.

- For a four to five page paper, your conclusion should be a standard size paragraph. For a shorter paper, keep this paragraph down to about three sentences.
- When appropriate, explain how the work has a widespread effect on the genre or community it fits into.
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-response-paper
- ↑ https://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/invention/Writing-a-Response-or-Reaction-Paper
- ↑ https://twp.duke.edu/sites/twp.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/response-paper.original.pdf
- ↑ https://www.awelu.lu.se/genres/student-writing-genres/response-paper/
- ↑ http://faculty.washington.edu/momara/Reader%20Response.pdf
- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/writing/how-to-write-a-strong-response-essay.html
- ↑ https://writing.colostate.edu/comparchive/rst/resource9.cfm
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-reaction-paper
- ↑ http://writing.colostate.edu/comparchive/rst/resource9.cfm
- ↑ http://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/invention/Writing-a-Response-or-Reaction-Paper
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

About This Article
If you need to write a response paper, read through the original texts, and take thorough notes, including paraphrases and quotes as well as your own thoughts. As soon as you finish reading the text, start drafting your ideas, since the thoughts will still be fresh in your mind. Open the paper with an introduction stating the major theme in the work you’re responding to, along with an overview of your reaction to it. Include a section briefly summarizing the original text, then go into detail about whether you agree or disagree with the work. Conclude by restating and defending the significance of your stance. For tips on writing a response to a work with multiple themes, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

4 Easy & Simple Step On How To Write A Responsive Essay
Writing a responsive essay can be challenging for many students because this type of essay requires you to now only summarize the content of a piece of literature, an article, or a film but also to provide a thoughtful and analytical response to it.
It demands that you engage with the material on a deeper level, making the connection between the author’s ideas and your own experiences and opinions.
It also requires strong critical thinking skills and the skills to express your thoughts and ideas clearly and coherently in writing.
That’s why many students find it difficult to write a responsive essay and also search online for how to write a responsive essay.
If you are one of them, then don’t worry! Because I have provided some of the best tips to write an effective responsive essay. So, let’s start with the definition of a Responsive essay.
What Is A Response Essay?
Table of Contents
A response essay is also different from formal writing because it contained the use of the phrase “I,” such as “I thought,” “I believe,” etc. The use of ‘I’ is also a key significant point of this essay that made it different from other formal writing.
When you write an essay on a book or article, then read for a class, and it describes the professional or impersonal voice, but when we write a response essay, the rules changed. It provides an opinion upon the article or book that is read by you. The opinion or thought contained your vision. It also depends upon you what you thought or experienced. It also considered a personal reflection on the matter.
Importance Of Writing An Effective Responsive Essay

If you want to write an effective responsive essay, then it should be well-structured and thoughtful piece of writing that presents a personal response to a particular topic or issue. Here are 5 important reasons why writing an effective responsive essay is important:
Develop Critical Thinking Skills
An effective responsive essay requires you to evaluate and analyze a topic critically. It helps you to build critical skills . And also enable you to assess various perspective and viewpoints on a topic.
Improve Writing Skills
You can improve your writing skills because when you write a responsive essay requires you to organize your thoughts, present ideas coherently, and articulate your opinions clearly.
Communication Skills
Writing an effective responsive essay also involves engaging with other people’s ideas and opinions. It can develop your skill to communicate your thoughts and ideas.
Develop Understanding
Writing an effective responsive essay also requires you to consider other people’s perspectives, opinions, and experiences. So, you can develop an understanding of people who hold different views. They will help you build strong relationships and communicate more effectively with others.
Improve Personal Growth
You can also develop a deeper understanding of yourself, your values, and your belief. It helps you to grow and develop as a person.
Steps On How To Write A Responsive Essay
Step-1 read carefully.
Before writing a response essay, first of all, read the article carefully, understand what is and what the concept of the article. Highlight the major points of the article and consider or make an analysis of the article. In your mind, analyze the article widely and try to consider everything. After becoming well aware of the concept of the article, try to make thought analysis in your mind then also effort to explain them briefly.
Start By Reading Introduction, Not Abstract
You must start reading the article from the part of the introduction rather than the abstract. Most of the students start reading from the abstract that is also a big mistake of the reader. Because the abstract contained some information on the whole article, and it also depends upon the author’s results after reading the article.
Identify the Big Question
What concerned the paper and identify what the major question is and what problem or issue efforts to solve by the entire article or paper. These are the major facts that defined why the article was written.
Read the Result Section
You must read the result section of the article carefully to write an excellent response essay. The result section contained the whole over outcomes of the result which helps to provide an excellent reflection on the paper. You need to summarize the results of each experiment in a very brief manner.
Final Reading
In the end, you must go to the abstract and read it appropriately. It helps you to provide a significant belief or thought in the response essay.
Step-2. The First Paragraph
After developing the outline of the paper, you must create the beginning draft for the essay. The first paragraph should contain a strong introductory sentence structure as well as a strong sense. In the area of a response essay, the beginning part should involve the title of the work and the name of the author. The first paragraph in the last sentence must contain this statement of the essay. The statement provides the overall thought or idea of the research very clearly.
Step-3. Stating Your Opinion
When starting your opening, don’t need to be shy; make everything confidently. Even though it may look as peculiar to write, “I thought,” or I believe.
Step-4. Final Format
Introduction.
Part of the introduction also a significant or beginning part of the essay in which you must make an effort to grab the attention of the reader. The part of the introduction contained only one to two paragraphs.
Quick Links
- A Comprehensive Guide On How To Balance Equations
- A Comprehensive Guide On Chicago Style Citation Generator
- The part of the body contained three or more paragraphs
- The part of the body summarizes the whole matter.
- What you considered or understood about the article, do you agree with the concept of the article if yes, then why? If not, why not?
- How does the article associate with you?
- What do you understand about how the article was written?
Conclusion
Provide a final decision or judgment on the article and also link it with the introduction.From the above steps, it may become quite easy for you to write the responsive essay. This guide will help you a lot when you are going to write a responsive essay. Furthermore, if you are still finding it difficult to write a responsive essay. Then we are here to provide you the best essay writing help and essay writing services at a nominal charge.
How do I start a response paragraph?
While writing an effective response paragraph, you should include the author’s name and the title of the text you are writing about. You should state precisely and concisely what you are going to prove, argue, or analyze about the text.
How many paragraphs should I use in a responsive essay?
You should use at least 3-5 paragraphs that give details from the story and the reader’s own thoughts to back up the ideas.
Similar Articles

13 Best Tips To Write An Assignment
Whenever the new semester starts, you will get a lot of assignment writing tasks. Now you enter the new academic…

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

How to Write a Discursive Essay: Awesome Guide and Template

The term "discursive" comes from the Latin word "discursus," meaning to move around or traverse. A discursive essay reflects this by exploring multiple viewpoints and offering a thorough discussion on a specific topic.
In this article, our term paper writing service will define what a discursive essay is, distinguish it from an argumentative essay, provide practical tips on how to write one effectively, and examine essay examples to illustrate its structure and approach.
What Is a Discursive Essay
A discursive essay is a type of essay where you discuss a topic from various viewpoints. The goal is to provide a balanced analysis by exploring different perspectives. Your essay should present arguments on the topic, showing both sides to give a comprehensive view.
Features of discursive essays typically include:
- Thesis Statement: Clearly states your position or argument on the topic.
- Discussion of Perspectives: Examines different viewpoints or aspects of the issue.
- Evidence and Examples: Supports arguments with relevant evidence and examples.
- Counterarguments: Addresses opposing viewpoints to strengthen your position.
- Logical Organization: Structured to present arguments coherently and persuasively.
Ready to Transform Your Essays?
From discursive writing to academic triumphs, let your words soar with our essay writing service!
How to Write a Discursive Essay
Writing a discursive essay involves examining a topic from different angles and presenting balanced viewpoints. Whether you're tackling a controversial issue or analyzing a complex subject, following these steps will help you craft a well-structured discursive essay.
.webp)
1. Understand the Topic
Before you start writing, make sure you grasp the topic thoroughly. Identify key terms and concepts to clarify what you need to discuss. Consider the different aspects and perspectives related to the topic that you will explore in your essay.
2. Research and Gather Evidence
Research is crucial for a discursive essay. Gather information from reliable sources such as books, academic journals, and reputable websites. Collect evidence that supports various viewpoints on the topic. Note down quotes, statistics, and examples that you can use to strengthen your arguments.
3. Plan Your Structure
Organize your essay effectively to ensure clarity and coherence. Start with an introduction that states your thesis or main argument. Outline the main points or perspectives you will discuss in the body paragraphs. Each paragraph should focus on a different aspect or viewpoint, supported by evidence. Consider including a paragraph that addresses counterarguments to strengthen your position.
4. Write the Introduction
Begin your essay with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader's attention. Start with a hook or an intriguing fact related to the topic. Clearly state your thesis statement, which outlines your position on the issue and previews the main points you will discuss. The introduction sets the tone for your essay and provides a roadmap for what follows.
5. Develop the Body Paragraphs
The body of your essay should present a balanced discussion of the topic. Each paragraph should focus on a different perspective or argument. Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea. Support your points with evidence, examples, and quotes from your research. Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs to maintain the flow of your argument.
6. Conclude Effectively
Wrap up your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes the main points and reinforces your thesis statement. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion. Instead, reflect on the significance of your arguments and how they contribute to the broader understanding of the topic. End with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action, encouraging readers to consider the complexities of the issue.
If you find this kind of writing challenging, simply say ' write my paper ', and professional writers will handle it for you.
Discursive Guide Checklist
| Aspect 📝 | Checklist ✅ |
|---|---|
| Understanding the Topic | Have I thoroughly understood the topic and its key terms? Have I identified the different perspectives or viewpoints related to the topic? |
| Research and Evidence | Have I conducted comprehensive research using reliable sources? Have I gathered sufficient evidence, including quotes, statistics, and to support each perspective? |
| Structuring the Essay | Have I planned a clear and logical structure for my essay? Does my introduction include a strong thesis statement that outlines my position? |
| Introduction | Does my introduction effectively grab the reader's attention? Have I clearly stated my thesis statement that previews the main arguments? |
| Body Paragraphs | Do my body paragraphs each focus on a different perspective or argument? Have I provided evidence and examples to support each argument? |
| Counterarguments | Have I addressed potential counterarguments to strengthen my position? Have I acknowledged and responded to opposing viewpoints where necessary? |
| Conclusion | Does my conclusion effectively summarize the main points discussed? Have I reinforced my thesis statement and the significance of my arguments? |
| Clarity and Coherence | Are my ideas presented in a clear and coherent manner? Do my paragraphs flow logically from one to the next? |
| Language and Style | Have I used clear and concise language throughout the essay? Is my writing style appropriate for the academic context, avoiding overly casual language? |
| Editing and Proofreading | Have I proofread my essay for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors? Have I checked the overall structure and flow of my essay for coherence? |
Discursive Essay Examples
Here, let’s take a look at our samples and see how different topics are discussed from different viewpoints in real discursive essays.
If you found these examples helpful, you can order custom essay now and receive one on any topic you choose.
Discursive Essay Topics
Here are a range of topics that encourage exploration of different perspectives and critical analysis. Choose a topic that interests you and allows for a balanced analysis of arguments and evidence.
- Should governments impose higher taxes on sugary drinks to combat obesity?
- Is homeschooling beneficial for children's education?
- Should the use of drones for military purposes be restricted?
- Should the legal drinking age be lowered or raised?
- Is online education as effective as traditional classroom learning?
- Should parents be held legally responsible for their children's actions?
- Is artificial intelligence a threat to human employment?
- Are video games a positive or negative influence on young people?
- Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
- Should schools teach mindfulness and meditation techniques?
- Is cultural diversity in the workplace beneficial for companies?
- Should prisoners have the right to vote?
- Is social media addiction a real problem?
- Should plastic packaging be replaced with eco-friendly alternatives?
- Is it ethical to clone animals for agricultural purposes?
- Should the government provide subsidies for electric vehicles?
- Is privacy more important than national security?
- Should school uniforms be mandatory?
- Is renewable energy the future of our planet?
- Should parents have access to their children's social media accounts?
By the way, we also have a great collection of narrative essay topics to inspire your creativity.
What is the Difference Between a Discursive and Argumentative Essay
Discursive essays and argumentative essays share similarities but have distinct differences in their approach and purpose. While both essay types involve critical thinking and analysis, the main difference lies in the writer's approach to the topic and the overall goal of the essay—whether it aims to explore and discuss multiple perspectives (discursive) or to argue for a specific viewpoint (argumentative). Here’s a more detailed look at how they differ:
| Key Differences 📌 | Discursive Essay 📝 | Argumentative Essay 🗣️ |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose 🎯 | Provides a balanced discussion on a topic | Persuades the reader to agree with a specific viewpoint. |
| Approach 🔍 | Examines multiple perspectives without taking a definitive stance | Takes a clear position and argues for or against it throughout the essay. |
| Thesis Statement 📜 | Often states a general overview or acknowledges different viewpoints. | States a strong and specific thesis that outlines the writer's position clearly. |
| Argumentation 💬 | Presents arguments from various angles to provide a comprehensive view. | Presents arguments that support the writer's position and refute opposing views. |
Types of Discursive Essay
Before writing a discursive essay, keep in mind that they can be categorized into different types based on their specific purposes and structures. Here are some common types of discursive essays:
.webp)
Opinion Essays:
- Purpose: Expressing and supporting personal opinions on a given topic.
- Structure: The essay presents the writer's viewpoint and provides supporting evidence, examples, and arguments. It may also address counterarguments to strengthen the overall discussion.
Problem-Solution Essays:
- Purpose: Identifying a specific problem and proposing effective solutions.
- Structure: The essay introduces the problem, discusses its causes and effects, and presents possible solutions. It often concludes with a recommendation or call to action.
Compare and Contrast Essays:
- Purpose: Analyzing similarities and differences between two or more perspectives, ideas, or approaches.
- Structure: The essay outlines the key points of each perspective, highlighting similarities and differences. A balanced analysis is provided to give the reader a comprehensive understanding.
Cause and Effect Essays:
- Purpose: Exploring the causes and effects of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Structure: The essay identifies the primary causes and examines their effects or vice versa. It may delve into the chain of events and their implications.
Argumentative Essays:
- Purpose: Presenting a strong argument in favor of a specific viewpoint.
- Structure: The essay establishes a clear thesis statement, provides evidence and reasoning to support the argument, and addresses opposing views. It aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer's perspective.
Pro-Con Essays:
- Purpose: Evaluating the pros and cons of a given issue.
- Structure: The essay presents the positive aspects (pros) and negative aspects (cons) of the topic. It aims to provide a balanced assessment and may conclude with a recommendation or a summary of the most compelling points.
Exploratory Essays:
- Purpose: Investigating and discussing a topic without necessarily advocating for a specific position.
- Structure: The essay explores various aspects of the topic, presenting different perspectives and allowing the reader to form their own conclusions. It often reflects a process of inquiry and discovery.
These types of discursive essays offer different approaches to presenting information, and the choice of type depends on the specific goals of the essay and the preferences of the writer.
Discursive Essay Format
Writing a discursive essay needs careful planning to make sure it’s clear and flows well while presenting different viewpoints on a topic. Here’s how to structure your discursive essay:
Introduction
- Start with an interesting opening sentence to catch the reader's attention. Give some background information on the topic to show why it’s important.
- Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic, and mention that you’ll be discussing different viewpoints.
"Should genetically modified foods be more strictly regulated for consumer safety? This question sparks debates among scientists, policymakers, and consumers alike. This essay explores the different perspectives on genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to give a complete view of the issues."
Body Paragraphs
- Begin each paragraph with a sentence that introduces a key point or perspective about GMOs.
- Present arguments, evidence, and examples to support each perspective. Consider the benefits, risks, and ethical issues around GMOs.
- Address possible objections or opposing viewpoints to show a balanced analysis.
"Supporters of GMOs argue that genetically engineered crops can help solve global food shortages by increasing crop yields and resistance to pests. For example, studies have shown that GMOs like insect-resistant corn have reduced the need for chemical pesticides, which benefits both farmers and the environment."
Counterarguments
- Recognize the counterarguments or concerns raised by opponents of GMOs.
- Provide reasoned responses or rebuttals to these counterarguments, acknowledging the complexity of the issue.
"However, critics of GMOs worry about potential long-term health effects and environmental impacts. They argue that there isn’t enough research to ensure the safety of eating genetically modified foods over long periods."
- Summarize the main points discussed in the essay about GMOs.
- Reinforce your thesis statement while considering the different arguments presented.
- Finish with a thought-provoking statement or suggest what should be considered for future research or policy decisions related to GMOs.
"In conclusion, the debate over genetically modified foods highlights the need to balance scientific innovation with public health and environmental concerns. While GMOs offer potential benefits for global food security, ongoing research and transparent regulation are essential to address uncertainties and ensure consumer safety."
Formatting Tips
- Use clear and straightforward language throughout the essay.
- Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs to maintain the flow of ideas.
- Use headings and subheadings if they help organize different perspectives.
- Properly cite sources when referencing research findings, quotes, or statistics.
Remember, besides writing compositions, you’ll also need to do math homework , something we can assist you with right away.
Yays and Nays of Writing Discourse Essays
In learning how to write a discursive essay, certain do's and don'ts serve as guiding principles throughout the writing process. By adhering to these guidelines, writers can navigate the complexities of presenting arguments, counterarguments, and nuanced analyses, ensuring the essay resonates with clarity and persuasiveness.
| Yays 👍 | Nays 👎 |
|---|---|
| Conduct thorough research to ensure a well-informed discussion. | Don’t express personal opinions in the body of the essay. Save personal commentary for the conclusion. |
| Explore various arguments and viewpoints on the issue. | Don't introduce new information or arguments in the conclusion. This section should summarize and reflect on existing content. |
| Maintain a balanced and neutral tone. Present arguments objectively without personal bias. | Don’t use overly emotional or subjective language. Maintain a professional and objective tone. |
| Structure your essay with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Use paragraphs to organize your ideas. | Ensure your arguments are supported by credible evidence. Don’t rely on personal opinions without sufficient research. |
| Include clear topic sentences at the beginning of each paragraph to guide the reader through your arguments. | Don’t have an ambiguous or unclear thesis statement. Clearly state the purpose of your essay in the introduction. |
| Use credible evidence from reputable sources to support your arguments. | Don’t ignore counterarguments. Address opposing viewpoints to strengthen your overall argument. |
| Ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas with transitional words and phrases. | Don’t use overly complex language if it doesn’t add to the clarity of your arguments. Aim for clarity and simplicity. |
| Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments and viewpoints. | Don’t present ideas in a disorganized manner. Ensure a logical flow between paragraphs and ideas. |
| Recap key points in the conclusion, summarizing the main arguments and perspectives discussed. | Don’t excessively repeat the same points. Present a variety of arguments and perspectives to keep the essay engaging. |
| Correct any grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors by proofreading your essay. | Don’t ignore the guidelines provided for your assignment. Follow any specific instructions or requirements given by your instructor or institution. |
Wrapping Up
Throughout this guide, you have acquired valuable insights into the art of crafting compelling arguments and presenting diverse perspectives. By delving into the nuances of topic selection, structuring, and incorporating evidence, you could hone your critical thinking skills and sharpen your ability to engage in informed discourse.
This guide serves as a roadmap, offering not just a set of rules but a toolkit to empower students in their academic journey. As you embark on future writing endeavors, armed with the knowledge gained here, you can confidently navigate the challenges of constructing well-reasoned, balanced discursive essays that contribute meaningfully to academic discourse and foster a deeper understanding of complex issues. If you want to continue your academic learning journey right now, we suggest that you read about the IEEE format next.
Overwhelmed by Essays?
Let professional writers be your writing wingman. No stress - just success!
What is a Discursive Example?
What is the difference between a discursive and argumentative essay, what are the 2 types of discursive writing.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Updated old sections including definition, outline, writing guide.
- Added new topics, examples, checklist, FAQs.
- Discursive writing - Discursive Writing - Higher English Revision. (n.d.). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zpdwwmn/revision/1
- Prepare for Exam Success: C1 Advanced self-access learning Writing Part 1 -the discursive essay Lesson summary. (n.d.). Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://www.cambridgeenglish.org/Images/583526-c1-advanced-self-access-learning-writing-part-1-discursive-essay.pdf
- Tomeu. (n.d.). Advanced C1.1: How to write a DISCURSIVE ESSAY. Advanced C1.1. Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://englishadvanced2.blogspot.com/2013/10/speakout-advanced-p-25-examples-of.html
.webp)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Thomas L. Friedman
Joe Biden Is a Good Man and a Good President. He Must Bow Out of the Race.

By Thomas L. Friedman
Opinion Columnist, reporting from Lisbon
I watched the Biden-Trump debate alone in a Lisbon hotel room, and it made me weep. I cannot remember a more heartbreaking moment in American presidential campaign politics in my lifetime, precisely because of what it revealed: Joe Biden, a good man and a good president, has no business running for re-election. And Donald Trump, a malicious man and a petty president, has learned nothing and forgotten nothing. He is the same fire hose of lies he always was, obsessed with his grievances — nowhere close to what it will take for America to lead in the 21st century.
The Biden family and political team must gather quickly and have the hardest of conversations with the president, a conversation of love and clarity and resolve. To give America the greatest shot possible of deterring the Trump threat in November, the president has to come forward and declare that he will not be running for re-election and is releasing all of his delegates for the Democratic National Convention.
The Republican Party, if its leaders had an ounce of integrity, would demand the same, but it won’t, because they don’t. That makes it all the more important that Democrats put the country’s interests first and announce that a public process will begin for different Democratic candidates to compete for the nomination — town halls, debates, meetings with donors, you name it. Yes, it could be chaotic and messy when the Democratic convention starts on Aug. 19 in Chicago, but I think the Trump threat is sufficiently grave that delegates could quickly rally around a consensus nominee.
If Vice President Kamala Harris wants to compete, she should. But voters deserve an open process in search of a Democratic presidential nominee who can unite not only the party but also the country, by offering something neither man on that Atlanta stage did on Thursday night: a compelling description of where the world is right now and a compelling vision for what America can and must do to keep leading it — morally, economically and diplomatically.
Because this is no ordinary hinge of history we are at. We are at the start of the biggest technological disruptions and the biggest climate disruption in human history. We are at the dawn of an artificial intelligence revolution that is going to change EVERYTHING FOR EVERYONE — how we work, how we learn, how we teach, how we trade, how we invent, how we collaborate, how we fight wars, how we commit crimes and how we fight crimes. Maybe I missed it, but I did not hear the phrase “artificial intelligence” mentioned by either man at the debate.
If there was ever a time that the world needed an America at its best, led by its best, it is now — for great dangers and opportunities are now upon us. A younger Biden could have been that leader, but time has finally caught up with him. And that was painfully and inescapably obvious on Thursday.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When writing a response essay, it is crucial to thoroughly analyze the source material provided. This process involves carefully examining and understanding the key ideas, arguments, and evidence presented by the author without bias or preconceived notions. By effectively analyzing the source material, you can ensure that your response essay is ...
1. Identify the main topic or issue you will be responding to. 2. State your position or stance on the topic clearly and concisely. 3. Provide a brief preview of the key points or arguments you will present in your essay to support your thesis. Remember, your thesis statement should be specific, focused, and debatable.
Record your thoughts. Develop a thesis. Write an outline. Construct your essay. It may be helpful to imagine yourself watching a movie review as you're preparing your outline. You will use the same framework for your response paper: a summary of the work with several of your own thoughts and assessments mixed in.
Get an outline of the process for how to write a response essay from the prewriting to the final piece. See all the different steps in action to make writing a response essay a breeze.
Various steps are outlined and discussed below to help you better understand how to write a response essay. 1. Pick a Topic for Your Response Essay. Picking a topic for response essay topics can be affected either by the scope of your assignment as provided by your college professor or by your preference.
Carefully Read and Analyze the Text. The first step in response paper creation is to carefully read and analyze the text. This involves more than just reading the words on the page; it requires critical thinking and analysis. As you read, pay attention to the author's tone, style, and use of language.
A response essay consists of 5-7 paragraphs: an introduction- a summary paragraph of the article; a response- 3 or more body paragraphs responding to the author; a conclusion- a concluding paragraph summing up your thoughts. Outline the essay your want to write. Use the structure of the response essay to determine the order of each paragraph.
Use concise and short paragraphs to cover each topic, theme or reaction. Use a new paragraph for each new topic discussed. Go into detail on your findings and reactions related to the text and try to maintain consistency and a clear flow throughout the body of your response paper. 5. Summarize your thoughts.
Write the Introduction. The introduction of a response paper sets the tone for the entire essay and is crucial for capturing the reader's interest. It should be engaging, informative, and clearly state the purpose of your paper. Engage the Reader. Begin the introductory paragraph with a compelling hook: a thought-provoking question, a striking fact, or a brief anecdote related to the text.
To write an effective response essay, it is important to include several key elements in the essay. These include: Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on the text, including the author, title, and publication date. It should also include a thesis statement that expresses the writer's opinion about the text.
A response essay can be one such occasion. If, however, you are nervous about this, the best recommendation is always to check with the individual instructor for whom the response is being completed. ... the process of writing a response actually begins with reading. Don't shortchange this part of the process because your success throughout the ...
Conclusion. tell a personal story. finish your personal story. explain the history of the topic. ask the reader what they think. tell why you found this interesting. suggest why this article might interest the reader. explain what you expected the article to be about. tell how you were surprised by the article.
5 Responses. Your reaction will be one or more of the following: Agreement/disagreement with the ideas in the text. Reaction to how the ideas in the text relate to your own experience. Reaction to how ideas in the text relate to other things you've read. Your analysis of the author and audience. Your evaluation of how this text tries to ...
Step 1 - Read and Understand the Work. Before you can write a good response essay, you first need to read and understand the work that you're responding to. Whether it's a book, movie, article, or poem, the quality of your response paper is directly proportional to how well you've understood the source material.
Introduction. Paragraph 1: The first part of the introduction which needs to be vivid, catchy and reflect the point you are about to make. Paragraph 2: Provide a context to your response essay: details about the source-text and the author and what the main points in the article are. Body.
As you summarize a point or argument from the original text, immediately follow it with your own intellectual response to the argument. 4. Wrap things up with a conclusion. Restate your stance or reactions to the text in a short paragraph. If desired or appropriate, explain why the matter is important overall.
Importance Of Writing An Effective Responsive Essay. If you want to write an effective responsive essay, then it should be well-structured and thoughtful piece of writing that presents a personal response to a particular topic or issue. Here are 5 important reasons why writing an effective responsive essay is important:
Essay Writing Response. A response paper (also known as a reflection or reaction paper) tends to be the most personal type of academic writing. Its purpose is to explain to a reader how you think or feel about a particular text. You may agree or disagree with an author, and in either case you'll want to explain to your reader why.
A response essay is generally meant to provide the reader with a better understanding of how you personally feel about a particular subject. As such, when you complete a response or reaction essay, you'll discuss your personal thoughts and feelings on the subject at hand. In many cases, a response or reaction essay is completed in response to a video, reading assignment, or special event. For ...
Sample response paper "Typography and Identity" in PDF with margin notes. Sample response paper "Typography and Identity" accessible version with notes in parentheses. This page titled 5.7: Sample Response Essays is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anna Mills ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources ...
Response Paper. In a reaction or response paper, writers respond to one or more texts they have read. A popular assignment with instructors in the social sciences and humanities, such papers require students to understand each text individually and evaluate how well each accomplishes its own objectives. If you are responding to multiple texts ...
A response is a commentary on another piece of writing. Developing a response will help you make personal connections with the ideas in the essay. Instructors might use question prompts to help guide you in creating a focused response on a particular aspect of an assigned reading.
Discursive Essay Format. Writing a discursive essay needs careful planning to make sure it's clear and flows well while presenting different viewpoints on a topic. Here's how to structure your discursive essay: Introduction. Start with an interesting opening sentence to catch the reader's attention.
Donald Trump is too grave a threat to America. Democrats need a nominee who can unite the country and articulate a compelling vision for it.