
- Programs & Services
- Delphi Center

Ideas to Action (i2a)
- What is Critical Thinking?
The ability to think critically calls for a higher-order thinking than simply the ability to recall information.
Definitions of critical thinking, its elements, and its associated activities fill the educational literature of the past forty years. Critical thinking has been described as an ability to question; to acknowledge and test previously held assumptions; to recognize ambiguity; to examine, interpret, evaluate, reason, and reflect; to make informed judgments and decisions; and to clarify, articulate, and justify positions (Hullfish & Smith, 1961; Ennis, 1962; Ruggiero, 1975; Scriven, 1976; Hallet, 1984; Kitchener, 1986; Pascarella & Terenzini, 1991; Mines et al., 1990; Halpern, 1996; Paul & Elder, 2001; Petress, 2004; Holyoak & Morrison, 2005; among others).
After a careful review of the mountainous body of literature defining critical thinking and its elements, UofL has chosen to adopt the language of Michael Scriven and Richard Paul (2003) as a comprehensive, concise operating definition:
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.
Paul and Scriven go on to suggest that critical thinking is based on: "universal intellectual values that transcend subject matter divisions: clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness. It entails the examination of those structures or elements of thought implicit in all reasoning: purpose, problem, or question-at-issue, assumptions, concepts, empirical grounding; reasoning leading to conclusions, implication and consequences, objections from alternative viewpoints, and frame of reference. Critical thinking - in being responsive to variable subject matter, issues, and purposes - is incorporated in a family of interwoven modes of thinking, among them: scientific thinking, mathematical thinking, historical thinking, anthropological thinking, economic thinking, moral thinking, and philosophical thinking."
This conceptualization of critical thinking has been refined and developed further by Richard Paul and Linder Elder into the Paul-Elder framework of critical thinking. Currently, this approach is one of the most widely published and cited frameworks in the critical thinking literature. According to the Paul-Elder framework, critical thinking is the:
- Analysis of thinking by focusing on the parts or structures of thinking ("the Elements of Thought")
- Evaluation of thinking by focusing on the quality ("the Universal Intellectual Standards")
- Improvement of thinking by using what you have learned ("the Intellectual Traits")
Selection of a Critical Thinking Framework
The University of Louisville chose the Paul-Elder model of Critical Thinking as the approach to guide our efforts in developing and enhancing our critical thinking curriculum. The Paul-Elder framework was selected based on criteria adapted from the characteristics of a good model of critical thinking developed at Surry Community College. The Paul-Elder critical thinking framework is comprehensive, uses discipline-neutral terminology, is applicable to all disciplines, defines specific cognitive skills including metacognition, and offers high quality resources.
Why the selection of a single critical thinking framework?
The use of a single critical thinking framework is an important aspect of institution-wide critical thinking initiatives (Paul and Nosich, 1993; Paul, 2004). According to this view, critical thinking instruction should not be relegated to one or two disciplines or departments with discipline specific language and conceptualizations. Rather, critical thinking instruction should be explicitly infused in all courses so that critical thinking skills can be developed and reinforced in student learning across the curriculum. The use of a common approach with a common language allows for a central organizer and for the development of critical thinking skill sets in all courses.
- SACS & QEP
- Planning and Implementation
- Why Focus on Critical Thinking?
- Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
- Culminating Undergraduate Experience
- Community Engagement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is i2a?
Copyright © 2012 - University of Louisville , Delphi Center
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- Order Tracking
- Create an Account

200+ Award-Winning Educational Textbooks, Activity Books, & Printable eBooks!
- Compare Products
Reading, Writing, Math, Science, Social Studies
- Search by Book Series
- Algebra I & II Gr. 7-12+
- Algebra Magic Tricks Gr. 2-12+
- Algebra Word Problems Gr. 7-12+
- Balance Benders Gr. 2-12+
- Balance Math & More! Gr. 2-12+
- Basics of Critical Thinking Gr. 4-7
- Brain Stretchers Gr. 5-12+
- Building Thinking Skills Gr. Toddler-12+
- Building Writing Skills Gr. 3-7
- Bundles - Critical Thinking Gr. PreK-9
- Bundles - Language Arts Gr. K-8
- Bundles - Mathematics Gr. PreK-9
- Bundles - Multi-Subject Curriculum Gr. PreK-12+
- Bundles - Test Prep Gr. Toddler-12+
- Can You Find Me? Gr. PreK-1
- Complete the Picture Math Gr. 1-3
- Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Gr. 5-12+
- Cranium Crackers Gr. 3-12+
- Creative Problem Solving Gr. PreK-2
- Critical Thinking Activities to Improve Writing Gr. 4-12+
- Critical Thinking Coloring Gr. PreK-2
- Critical Thinking Detective Gr. 3-12+
- Critical Thinking Tests Gr. PreK-6
- Critical Thinking for Reading Comprehension Gr. 1-5
- Critical Thinking in United States History Gr. 6-12+
- CrossNumber Math Puzzles Gr. 4-10
- Crypt-O-Words Gr. 2-7
- Crypto Mind Benders Gr. 3-12+
- Daily Mind Builders Gr. 5-12+
- Dare to Compare Math Gr. 2-7
- Developing Critical Thinking through Science Gr. 1-8
- Dr. DooRiddles Gr. PreK-12+
- Dr. Funster's Gr. 2-12+
- Editor in Chief Gr. 2-12+
- Fun-Time Phonics! Gr. PreK-2
- Half 'n Half Animals Gr. K-4
- Hands-On Thinking Skills Gr. K-1
- Inference Jones Gr. 1-6
- James Madison Gr. 10-12+
- Jumbles Gr. 3-5
- Language Mechanic Gr. 4-7
- Language Smarts Gr. 1-4
- Mastering Logic & Math Problem Solving Gr. 6-9
- Math Analogies Gr. K-9
- Math Detective Gr. 3-8
- Math Games Gr. 3-8
- Math Mind Benders Gr. 5-12+
- Math Ties Gr. 4-8
- Math Word Problems Gr. 4-10
- Mathematical Reasoning Gr. Toddler-11
- Middle School Science Gr. 6-8
- Mind Benders Gr. PreK-12+
- Mind Building Math Gr. K-1
- Mind Building Reading Gr. K-1
- Novel Thinking Gr. 3-6
- OLSAT® Test Prep Gr. PreK-K
- Organizing Thinking Gr. 2-8
- Pattern Explorer Gr. 3-9
- Practical Critical Thinking Gr. 8-12+
- Punctuation Puzzler Gr. 3-8
- Reading Detective Gr. 3-12+
- Red Herring Mysteries Gr. 4-12+
- Red Herrings Science Mysteries Gr. 4-9
- Science Detective Gr. 3-6
- Science Mind Benders Gr. PreK-3
- Science Vocabulary Crossword Puzzles Gr. 4-6
- Sciencewise Gr. 4-12+
- Scratch Your Brain Gr. 2-12+
- Senior Brain Health Program Gr. 4-8
- Sentence Diagramming Gr. 3-12+
- Smarty Pants Puzzles Gr. 3-12+
- Snailopolis Gr. K-4
- Something's Fishy at Lake Iwannafisha Gr. 5-9
- Teaching Technology Gr. 3-12+
- Tell Me a Story Gr. PreK-1
- Think Analogies Gr. 3-12+
- Think and Write Gr. 3-8
- Think-A-Grams Gr. 4-12+
- Thinking About Time Gr. 3-6
- Thinking Connections Gr. 4-12+
- Thinking Directionally Gr. 2-6
- Thinking Skills & Key Concepts Gr. PreK-2
- Thinking Skills for Tests Gr. PreK-5
- U.S. History Detective Gr. 8-12+
- Understanding Fractions Gr. 2-6
- Visual Perceptual Skill Building Gr. PreK-3
- Vocabulary Riddles Gr. 4-8
- Vocabulary Smarts Gr. 2-5
- Vocabulary Virtuoso Gr. 2-12+
- What Would You Do? Gr. 2-12+
- Who Is This Kid? Colleges Want to Know! Gr. 9-12+
- Word Explorer Gr. 4-8
- Word Roots Gr. 3-12+
- World History Detective Gr. 6-12+
- Writing Detective Gr. 3-6
- You Decide! Gr. 6-12+
- Special of the Month
- Sign Up for our Best Offers
- Bundles = Greatest Savings!
- Sign Up for Free Puzzles
- Sign Up for Free Activities
- Toddler (Ages 0-3)
- PreK (Ages 3-5)
- Kindergarten (Ages 5-6)
- 1st Grade (Ages 6-7)
- 2nd Grade (Ages 7-8)
- 3rd Grade (Ages 8-9)
- 4th Grade (Ages 9-10)
- 5th Grade (Ages 10-11)
- 6th Grade (Ages 11-12)
- 7th Grade (Ages 12-13)
- 8th Grade (Ages 13-14)
- 9th Grade (Ages 14-15)
- 10th Grade (Ages 15-16)
- 11th Grade (Ages 16-17)
- 12th Grade (Ages 17-18)
- 12th+ Grade (Ages 18+)
- Test Prep Directory
- Test Prep Bundles
- Test Prep Guides
- Preschool Academics
- Store Locator
- Submit Feedback/Request
- Sales Alerts Sign-Up
- Technical Support
- Mission & History
- Articles & Advice
- Testimonials
- Our Guarantee
- New Products
- Free Activities
- Libros en Español
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical Thinking Definition
September 2, 2005, by The Critical Thinking Co. Staff
The Critical Thinking Co.™ "Critical thinking is the identification and evaluation of evidence to guide decision making. A critical thinker uses broad in-depth analysis of evidence to make decisions and communicate their beliefs clearly and accurately."
Other Definitions of Critical Thinking: Robert H. Ennis , Author of The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests "Critical thinking is reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe and do."
A SUPER-STREAMLINED CONCEPTION OF CRITICAL THINKING Robert H. Ennis, 6/20/02
Assuming that critical thinking is reasonable reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do, a critical thinker:
1. Is open-minded and mindful of alternatives 2. Tries to be well-informed 3. Judges well the credibility of sources 4. Identifies conclusions, reasons, and assumptions 5. Judges well the quality of an argument, including the acceptability of its reasons, assumptions, and evidence 6. Can well develop and defend a reasonable position 7. Asks appropriate clarifying questions 8. Formulates plausible hypotheses; plans experiments well 9. Defines terms in a way appropriate for the context 10. Draws conclusions when warranted, but with caution 11. Integrates all items in this list when deciding what to believe or do
Critical Thinkers are disposed to:
1. Care that their beliefs be true, and that their decisions be justified; that is, care to "get it right" to the extent possible. This includes the dispositions to
a. Seek alternative hypotheses, explanations, conclusions, plans, sources, etc., and be open to them b. Endorse a position to the extent that, but only to the extent that, it is justified by the information that is available c. Be well informed d. Consider seriously other points of view than their own
2. Care to present a position honestly and clearly, theirs as well as others'. This includes the dispositions to
a. Be clear about the intended meaning of what is said, written, or otherwise communicated, seeking as much precision as the situation requires b. Determine, and maintain focus on, the conclusion or question c. Seek and offer reasons d. Take into account the total situation e. Be reflectively aware of their own basic beliefs
3. Care about the dignity and worth of every person (a correlative disposition). This includes the dispositions to
a. Discover and listen to others' view and reasons b. Avoid intimidating or confusing others with their critical thinking prowess, taking into account others' feelings and level of understanding c. Be concerned about others' welfare
Critical Thinking Abilities:
Ideal critical thinkers have the ability to (The first three items involve elementary clarification.)
1. Focus on a question
a. Identify or formulate a question b. Identify or formulate criteria for judging possible answers c. Keep the situation in mind
2. Analyze arguments
a. Identify conclusions b. Identify stated reasons c. Identify unstated reasons d. Identify and handle irrelevance e. See the structure of an argument f. Summarize
3. Ask and answer questions of clarification and/or challenge, such as,
a. Why? b. What is your main point? c. What do you mean by…? d. What would be an example? e. What would not be an example (though close to being one)? f. How does that apply to this case (describe a case, which might well appear to be a counter example)? g. What difference does it make? h. What are the facts? i. Is this what you are saying: ____________? j. Would you say some more about that?
(The next two involve the basis for the decision.)
4. Judge the credibility of a source. Major criteria (but not necessary conditions):
a. Expertise b. Lack of conflict of interest c. Agreement among sources d. Reputation e. Use of established procedures f. Known risk to reputation g. Ability to give reasons h. Careful habits
5. Observe, and judge observation reports. Major criteria (but not necessary conditions, except for the first):
a. Minimal inferring involved b. Short time interval between observation and report c. Report by the observer, rather than someone else (that is, the report is not hearsay) d. Provision of records. e. Corroboration f. Possibility of corroboration g. Good access h. Competent employment of technology, if technology is useful i. Satisfaction by observer (and reporter, if a different person) of the credibility criteria in Ability # 4 above.
(The next three involve inference.)
6. Deduce, and judge deduction
a. Class logic b. Conditional logic c. Interpretation of logical terminology in statements, including (1) Negation and double negation (2) Necessary and sufficient condition language (3) Such words as "only", "if and only if", "or", "some", "unless", "not both".
7. Induce, and judge induction
a. To generalizations. Broad considerations: (1) Typicality of data, including sampling where appropriate (2) Breadth of coverage (3) Acceptability of evidence b. To explanatory conclusions (including hypotheses) (1) Major types of explanatory conclusions and hypotheses: (a) Causal claims (b) Claims about the beliefs and attitudes of people (c) Interpretation of authors’ intended meanings (d) Historical claims that certain things happened (including criminal accusations) (e) Reported definitions (f) Claims that some proposition is an unstated reason that the person actually used (2) Characteristic investigative activities (a) Designing experiments, including planning to control variables (b) Seeking evidence and counter-evidence (c) Seeking other possible explanations (3) Criteria, the first five being essential, the sixth being desirable (a) The proposed conclusion would explain the evidence (b) The proposed conclusion is consistent with all known facts (c) Competitive alternative explanations are inconsistent with facts (d) The evidence on which the hypothesis depends is acceptable. (e) A legitimate effort should have been made to uncover counter-evidence (f) The proposed conclusion seems plausible
8. Make and judge value judgments: Important factors:
a. Background facts b. Consequences of accepting or rejecting the judgment c. Prima facie application of acceptable principles d. Alternatives e. Balancing, weighing, deciding
(The next two abilities involve advanced clarification.)
9. Define terms and judge definitions. Three dimensions are form, strategy, and content.
a. Form. Some useful forms are: (1) Synonym (2) Classification (3) Range (4) Equivalent expression (5) Operational (6) Example and non-example b. Definitional strategy (1) Acts (a) Report a meaning (b) Stipulate a meaning (c) Express a position on an issue (including "programmatic" and "persuasive" definitions) (2) Identifying and handling equivocation c. Content of the definition
10. Attribute unstated assumptions (an ability that belongs under both clarification and, in a way, inference)
(The next two abilities involve supposition and integration.)
11. Consider and reason from premises, reasons, assumptions, positions, and other propositions with which they disagree or about which they are in doubt -- without letting the disagreement or doubt interfere with their thinking ("suppositional thinking")
12. Integrate the other abilities and dispositions in making and defending a decision
(The first twelve abilities are constitutive abilities. The next three are auxiliary critical thinking abilities: Having them, though very helpful in various ways, is not constitutive of being a critical thinker.)
13. Proceed in an orderly manner appropriate to the situation. For example:
a. Follow problem solving steps b. Monitor one's own thinking (that is, engage in metacognition) c. Employ a reasonable critical thinking checklist
14. Be sensitive to the feelings, level of knowledge, and degree of sophistication of others
15. Employ appropriate rhetorical strategies in discussion and presentation (orally and in writing), including employing and reacting to "fallacy" labels in an appropriate manner.
Examples of fallacy labels are "circularity," "bandwagon," "post hoc," "equivocation," "non sequitur," and "straw person."
Dewey, John Critical thinking is "active, persistent, and careful consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds that support it and the further conclusions to which it tends (Dewey 1933: 118)."
Glaser (1) an attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that come within the range of one's experiences, (2) knowledge of the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning, and (3) some skill in applying those methods. Critical thinking calls for a persistent effort to examine any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the evidence that supports it and the further conclusions to which it tends. (Glaser 1941, pp. 5-6).
Abilities include: "(a) to recognize problems, (b) to find workable means for meeting those problems, (c) to gather and marshal pertinent information, (d) to recognize unstated assumptions and values, (e) to comprehend and use language with accuracy, clarity and discrimination, (f) to interpret data, (g) to appraise evidence and evaluate statements, (h) to recognize the existence of logical relationships between propositions, (i) to draw warranted conclusions and generalizations, (j) to put to test the generalizations and conclusions at which one arrives, (k) to reconstruct one's patterns of beliefs on the basis of wider experience; and (l) to render accurate judgments about specific things and qualities in everyday life." (p.6)
MCC General Education Initiatives "Critical thinking includes the ability to respond to material by distinguishing between facts and opinions or personal feelings, judgments and inferences, inductive and deductive arguments, and the objective and subjective. It also includes the ability to generate questions, construct, and recognize the structure of arguments, and adequately support arguments; define, analyze, and devise solutions for problems and issues; sort, organize, classify, correlate, and analyze materials and data; integrate information and see relationships; evaluate information, materials, and data by drawing inferences, arriving at reasonable and informed conclusions, applying understanding and knowledge to new and different problems, developing rational and reasonable interpretations, suspending beliefs and remaining open to new information, methods, cultural systems, values and beliefs and by assimilating information."
Nickerson, Perkins and Smith (1985) "The ability to judge the plausibility of specific assertions, to weigh evidence, to assess the logical soundness of inferences, to construct counter-arguments and alternative hypotheses."
Moore and Parker , Critical Thinking Critical Thinking is "the careful, deliberate determination of whether we should accept, reject, or suspend judgment about a claim, and the degree of confidence with which we accept or reject it."
Delphi Report "We understand critical thinking to be purposeful, self-regulatory judgment which results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation, and inference, as well as explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations upon which that judgment is based. CT is essential as a tool of inquiry. As such, CT is a liberating force in education and a powerful resource in one's personal and civic life. While not synonymous with good thinking, CT is a pervasive and self-rectifying human phenomenon. The ideal critical thinker is habitually inquisitive, well-informed, trustful of reason, open-minded, flexible, fair-minded in evaluation, honest in facing personal biases, prudent in making judgments, willing to reconsider, clear about issues, orderly in complex matters, diligent in seeking relevant information, reasonable in the selection of criteria, focused in inquiry, and persistent in seeking results which are as precise as the subject and the circumstances of inquiry permit. Thus, educating good critical thinkers means working toward this ideal. It combines developing CT skills with nurturing those dispositions which consistently yield useful insights and which are the basis of a rational and democratic society."
A little reformatting helps make this definition more comprehensible:
We understand critical thinking to be purposeful, self-regulatory judgment which results in
- interpretation
as well as explanation of the
- methodological
- criteriological
considerations upon which that judgment is based.
Francis Bacon (1605) "For myself, I found that I was fitted for nothing so well as for the study of Truth; as having a mind nimble and versatile enough to catch the resemblances of things … and at the same time steady enough to fix and distinguish their subtler differences; as being gifted by nature with desire to seek, patience to doubt, fondness to meditate, slowness to assert, readiness to consider, carefulness to dispose and set in order; and as being a man that neither affects what is new nor admires what is old, and that hates every kind of imposture."
A shorter version is "the art of being right."
Or, more prosaically: critical thinking is "the skillful application of a repertoire of validated general techniques for deciding the level of confidence you should have in a proposition in the light of the available evidence."
HELPFUL REFERENCE: http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/logic-informal/
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
Defining Critical Thinking
- Humanities ›
- English Grammar ›
Critical Thinking in Reading and Composition
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
gawrav/Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Critical thinking is the process of independently analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information as a guide to behavior and beliefs.
The American Philosophical Association has defined critical thinking as "the process of purposeful, self-regulatory judgment. The process gives reasoned consideration to evidence , contexts , conceptualizations, methods, and criteria" (1990). Critical thinking is sometimes broadly defined as "thinking about thinking."
Critical thinking skills include the ability to interpret, verify, and reason, all of which involve applying the principles of logic . The process of using critical thinking to guide writing is called critical writing .
Observations
- " Critical Thinking is essential as a tool of inquiry. As such, Critical Thinking is a liberating force in education and a powerful resource in one’s personal and civic life. While not synonymous with good thinking, Critical Thinking is a pervasive and self-rectifying human phenomenon. The ideal critical thinker is habitually inquisitive, well-informed, trustful of reason, open-minded, flexible, fair-minded in evaluation, honest in facing personal biases, prudent in making judgments, willing to reconsider, clear about issues, orderly in complex matters, diligent in seeking relevant information, reasonable in the selection of criteria, focused in inquiry, and persistent in seeking results which are as precise as the subject and the circumstances of inquiry permit." (American Philosophical Association, "Consensus Statement Regarding Critical Thinking," 1990)
- Thought and Language "In order to understand reasoning [...], it is necessary to pay careful attention to the relationship between thought and language . The relationship seems to be straightforward: thought is expressed in and through language. But this claim, while true, is an oversimplification. People often fail to say what they mean. Everyone has had the experience of having their \ misunderstood by others. And we all use words not merely to express our thoughts but also to shape them. Developing our critical thinking skills, therefore, requires an understanding of the ways in which words can (and often fail to) express our thoughts." (William Hughes and Jonathan Lavery, Critical Thinking: An Introduction to the Basic Skills , 4th ed. Broadview, 2004)
- Dispositions That Foster or Impede Critical thinking "Dispositions that foster critical thinking include [a] facility in perceiving irony , ambiguity , and multiplicity of meanings or points of view; the development of open-mindedness, autonomous thought, and reciprocity (Piaget's term for the ability to empathize with other individuals, social groups, nationalities, ideologies, etc.). Dispositions that act as impediments to critical thinking include defense mechanisms (such as absolutism or primary certitude, denial, projection), culturally conditioned assumptions, authoritarianism, egocentrism, and ethnocentrism, rationalization, compartmentalization, stereotyping and prejudice." (Donald Lazere, "Invention, Critical Thinking, and the Analysis of Political Rhetoric." Perspectives on Rhetorical Invention , ed. by Janet M. Atwill and Janice M. Lauer. University of Tennessee Press, 2002)
- Critical Thinking and Composing - "[T]he most intensive and demanding tool for eliciting sustained critical thought is a well-designed writing assignment on a subject matter problem. The underlying premise is that writing is closely linked with thinking and that in presenting students with significant problems to write about—and in creating an environment that demands their best writing—we can promote their general cognitive and intellectual growth. When we make students struggle with their writing, we are making them struggle with thought itself. Emphasizing writing and critical thinking , therefore, generally increases the academic rigor of a course. Often the struggle of writing, linked as it is to the struggle of thinking and to the growth of a person's intellectual powers, awakens students to the real nature of learning." (John C. Bean, Engaging Ideas: The Professor's Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom , 2nd ed. Wiley, 2011) - "Finding a fresh approach to a writing assignment means that you must see the subject without the blinders of preconception. When people expect to see a thing in a certain way, it usually appears that way, whether or not that is its true image. Similarly, thinking based on prefabricated ideas produces writing that says nothing new, that offers nothing important to the reader. As a writer, you have a responsibility to go beyond the expected views and present your subject so that the reader sees it with fresh eyes. . . . [C]ritical thinking is a fairly systematic method of defining a problem and synthesizing knowledge about it, thereby creating the perspective you need to develop new ideas. . . . " Classical rhetoricians used a series of three questions to help focus an argument . Today these questions can still help writers understand the topic about which they are writing. An sit? (Is the problem a fact?); Quid sit (What is the definition of the problem?); and Quale sit? (What kind of problem is it?). By asking these questions, writers see their subject from many new angles before they begin to narrow the focus to one particular aspect." (Kristin R. Woolever, About Writing: A Rhetoric for Advanced Writers . Wadsworth, 1991)
Logical Fallacies
Ad Misericordiam
Appeal to Authority
Appeal to Force
Appeal to Humor
Appeal to Ignorance
Appeal to the People
Begging the Question
Circular Argument
Complex Question
Contradictory Premises
Dicto Simpliciter , Equivocation
False Analogy
False Dilemma
Gambler's Fallacy
Hasty Generalization
Name-Calling
Non Sequitur
Poisoning the Well
Red Herring
Slippery Slope
Stacking the Deck
- Stipulative Definitions in English
- What Is a Synopsis and How Do You Write One?
- What is Disjunction in Grammar?
- Definition and Examples of Explication (Analysis)
- online reading
- What Does It Mean to Make a Claim During an Argument?
- Critical Analysis in Composition
- What is Tu Quoque (Logical Fallacy) in Rhetoric?
- The Meaning of Innuendo
- Learn How to Use Extended Definitions in Essays and Speeches
- Rhetorical Analysis Definition and Examples
- What Is a Hasty Generalization?
- Ware, Wear, and Where: How to Choose the Right Word
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- Historic vs. Historical: How to Choose the Right Word
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition

- Table of Contents
- New in this Archive
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Back to Entry
- Entry Contents
- Entry Bibliography
- Academic Tools
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Supplement to Critical Thinking
This supplement elaborates on the history of the articulation, promotion and adoption of critical thinking as an educational goal.
John Dewey (1910: 74, 82) introduced the term ‘critical thinking’ as the name of an educational goal, which he identified with a scientific attitude of mind. More commonly, he called the goal ‘reflective thought’, ‘reflective thinking’, ‘reflection’, or just ‘thought’ or ‘thinking’. He describes his book as written for two purposes. The first was to help people to appreciate the kinship of children’s native curiosity, fertile imagination and love of experimental inquiry to the scientific attitude. The second was to help people to consider how recognizing this kinship in educational practice “would make for individual happiness and the reduction of social waste” (iii). He notes that the ideas in the book obtained concreteness in the Laboratory School in Chicago.
Dewey’s ideas were put into practice by some of the schools that participated in the Eight-Year Study in the 1930s sponsored by the Progressive Education Association in the United States. For this study, 300 colleges agreed to consider for admission graduates of 30 selected secondary schools or school systems from around the country who experimented with the content and methods of teaching, even if the graduates had not completed the then-prescribed secondary school curriculum. One purpose of the study was to discover through exploration and experimentation how secondary schools in the United States could serve youth more effectively (Aikin 1942). Each experimental school was free to change the curriculum as it saw fit, but the schools agreed that teaching methods and the life of the school should conform to the idea (previously advocated by Dewey) that people develop through doing things that are meaningful to them, and that the main purpose of the secondary school was to lead young people to understand, appreciate and live the democratic way of life characteristic of the United States (Aikin 1942: 17–18). In particular, school officials believed that young people in a democracy should develop the habit of reflective thinking and skill in solving problems (Aikin 1942: 81). Students’ work in the classroom thus consisted more often of a problem to be solved than a lesson to be learned. Especially in mathematics and science, the schools made a point of giving students experience in clear, logical thinking as they solved problems. The report of one experimental school, the University School of Ohio State University, articulated this goal of improving students’ thinking:
Critical or reflective thinking originates with the sensing of a problem. It is a quality of thought operating in an effort to solve the problem and to reach a tentative conclusion which is supported by all available data. It is really a process of problem solving requiring the use of creative insight, intellectual honesty, and sound judgment. It is the basis of the method of scientific inquiry. The success of democracy depends to a large extent on the disposition and ability of citizens to think critically and reflectively about the problems which must of necessity confront them, and to improve the quality of their thinking is one of the major goals of education. (Commission on the Relation of School and College of the Progressive Education Association 1943: 745–746)
The Eight-Year Study had an evaluation staff, which developed, in consultation with the schools, tests to measure aspects of student progress that fell outside the focus of the traditional curriculum. The evaluation staff classified many of the schools’ stated objectives under the generic heading “clear thinking” or “critical thinking” (Smith, Tyler, & Evaluation Staff 1942: 35–36). To develop tests of achievement of this broad goal, they distinguished five overlapping aspects of it: ability to interpret data, abilities associated with an understanding of the nature of proof, and the abilities to apply principles of science, of social studies and of logical reasoning. The Eight-Year Study also had a college staff, directed by a committee of college administrators, whose task was to determine how well the experimental schools had prepared their graduates for college. The college staff compared the performance of 1,475 college students from the experimental schools with an equal number of graduates from conventional schools, matched in pairs by sex, age, race, scholastic aptitude scores, home and community background, interests, and probable future. They concluded that, on 18 measures of student success, the graduates of the experimental schools did a somewhat better job than the comparison group. The graduates from the six most traditional of the experimental schools showed no large or consistent differences. The graduates from the six most experimental schools, on the other hand, had much greater differences in their favour. The graduates of the two most experimental schools, the college staff reported:
… surpassed their comparison groups by wide margins in academic achievement, intellectual curiosity, scientific approach to problems, and interest in contemporary affairs. The differences in their favor were even greater in general resourcefulness, in enjoyment of reading, [in] participation in the arts, in winning non-academic honors, and in all aspects of college life except possibly participation in sports and social activities. (Aikin 1942: 114)
One of these schools was a private school with students from privileged families and the other the experimental section of a public school with students from non-privileged families. The college staff reported that the graduates of the two schools were indistinguishable from each other in terms of college success.
In 1933 Dewey issued an extensively rewritten edition of his How We Think (Dewey 1910), with the sub-title “A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process”. Although the restatement retains the basic structure and content of the original book, Dewey made a number of changes. He rewrote and simplified his logical analysis of the process of reflection, made his ideas clearer and more definite, replaced the terms ‘induction’ and ‘deduction’ by the phrases ‘control of data and evidence’ and ‘control of reasoning and concepts’, added more illustrations, rearranged chapters, and revised the parts on teaching to reflect changes in schools since 1910. In particular, he objected to one-sided practices of some “experimental” and “progressive” schools that allowed children freedom but gave them no guidance, citing as objectionable practices novelty and variety for their own sake, experiences and activities with real materials but of no educational significance, treating random and disconnected activity as if it were an experiment, failure to summarize net accomplishment at the end of an inquiry, non-educative projects, and treatment of the teacher as a negligible factor rather than as “the intellectual leader of a social group” (Dewey 1933: 273). Without explaining his reasons, Dewey eliminated the previous edition’s uses of the words ‘critical’ and ‘uncritical’, thus settling firmly on ‘reflection’ or ‘reflective thinking’ as the preferred term for his subject-matter. In the revised edition, the word ‘critical’ occurs only once, where Dewey writes that “a person may not be sufficiently critical about the ideas that occur to him” (1933: 16, italics in original); being critical is thus a component of reflection, not the whole of it. In contrast, the Eight-Year Study by the Progressive Education Association treated ‘critical thinking’ and ‘reflective thinking’ as synonyms.
In the same period, Dewey collaborated on a history of the Laboratory School in Chicago with two former teachers from the school (Mayhew & Edwards 1936). The history describes the school’s curriculum and organization, activities aimed at developing skills, parents’ involvement, and the habits of mind that the children acquired. A concluding chapter evaluates the school’s achievements, counting as a success its staging of the curriculum to correspond to the natural development of the growing child. In two appendices, the authors describe the evolution of Dewey’s principles of education and Dewey himself describes the theory of the Chicago experiment (Dewey 1936).
Glaser (1941) reports in his doctoral dissertation the method and results of an experiment in the development of critical thinking conducted in the fall of 1938. He defines critical thinking as Dewey defined reflective thinking:
Critical thinking calls for a persistent effort to examine any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the evidence that supports it and the further conclusions to which it tends. (Glaser 1941: 6; cf. Dewey 1910: 6; Dewey 1933: 9)
In the experiment, eight lesson units directed at improving critical thinking abilities were taught to four grade 12 high school classes, with pre-test and post-test of the students using the Otis Quick-Scoring Mental Ability Test and the Watson-Glaser Tests of Critical Thinking (developed in collaboration with Glaser’s dissertation sponsor, Goodwin Watson). The average gain in scores on these tests was greater to a statistically significant degree among the students who received the lessons in critical thinking than among the students in a control group of four grade 12 high school classes taking the usual curriculum in English. Glaser concludes:
The aspect of critical thinking which appears most susceptible to general improvement is the attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that come within the range of one’s experience. An attitude of wanting evidence for beliefs is more subject to general transfer. Development of skill in applying the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning, however, appears to be specifically related to, and in fact limited by, the acquisition of pertinent knowledge and facts concerning the problem or subject matter toward which the thinking is to be directed. (Glaser 1941: 175)
Retest scores and observable behaviour indicated that students in the intervention group retained their growth in ability to think critically for at least six months after the special instruction.
In 1948 a group of U.S. college examiners decided to develop taxonomies of educational objectives with a common vocabulary that they could use for communicating with each other about test items. The first of these taxonomies, for the cognitive domain, appeared in 1956 (Bloom et al. 1956), and included critical thinking objectives. It has become known as Bloom’s taxonomy. A second taxonomy, for the affective domain (Krathwohl, Bloom, & Masia 1964), and a third taxonomy, for the psychomotor domain (Simpson 1966–67), appeared later. Each of the taxonomies is hierarchical, with achievement of a higher educational objective alleged to require achievement of corresponding lower educational objectives.
Bloom’s taxonomy has six major categories. From lowest to highest, they are knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Within each category, there are sub-categories, also arranged hierarchically from the educationally prior to the educationally posterior. The lowest category, though called ‘knowledge’, is confined to objectives of remembering information and being able to recall or recognize it, without much transformation beyond organizing it (Bloom et al. 1956: 28–29). The five higher categories are collectively termed “intellectual abilities and skills” (Bloom et al. 1956: 204). The term is simply another name for critical thinking abilities and skills:
Although information or knowledge is recognized as an important outcome of education, very few teachers would be satisfied to regard this as the primary or the sole outcome of instruction. What is needed is some evidence that the students can do something with their knowledge, that is, that they can apply the information to new situations and problems. It is also expected that students will acquire generalized techniques for dealing with new problems and new materials. Thus, it is expected that when the student encounters a new problem or situation, he will select an appropriate technique for attacking it and will bring to bear the necessary information, both facts and principles. This has been labeled “critical thinking” by some, “reflective thinking” by Dewey and others, and “problem solving” by still others. In the taxonomy, we have used the term “intellectual abilities and skills”. (Bloom et al. 1956: 38)
Comprehension and application objectives, as their names imply, involve understanding and applying information. Critical thinking abilities and skills show up in the three highest categories of analysis, synthesis and evaluation. The condensed version of Bloom’s taxonomy (Bloom et al. 1956: 201–207) gives the following examples of objectives at these levels:
- analysis objectives : ability to recognize unstated assumptions, ability to check the consistency of hypotheses with given information and assumptions, ability to recognize the general techniques used in advertising, propaganda and other persuasive materials
- synthesis objectives : organizing ideas and statements in writing, ability to propose ways of testing a hypothesis, ability to formulate and modify hypotheses
- evaluation objectives : ability to indicate logical fallacies, comparison of major theories about particular cultures
The analysis, synthesis and evaluation objectives in Bloom’s taxonomy collectively came to be called the “higher-order thinking skills” (Tankersley 2005: chap. 5). Although the analysis-synthesis-evaluation sequence mimics phases in Dewey’s (1933) logical analysis of the reflective thinking process, it has not generally been adopted as a model of a critical thinking process. While commending the inspirational value of its ratio of five categories of thinking objectives to one category of recall objectives, Ennis (1981b) points out that the categories lack criteria applicable across topics and domains. For example, analysis in chemistry is so different from analysis in literature that there is not much point in teaching analysis as a general type of thinking. Further, the postulated hierarchy seems questionable at the higher levels of Bloom’s taxonomy. For example, ability to indicate logical fallacies hardly seems more complex than the ability to organize statements and ideas in writing.
A revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy (Anderson et al. 2001) distinguishes the intended cognitive process in an educational objective (such as being able to recall, to compare or to check) from the objective’s informational content (“knowledge”), which may be factual, conceptual, procedural, or metacognitive. The result is a so-called “Taxonomy Table” with four rows for the kinds of informational content and six columns for the six main types of cognitive process. The authors name the types of cognitive process by verbs, to indicate their status as mental activities. They change the name of the ‘comprehension’ category to ‘understand’ and of the ‘synthesis’ category to ’create’, and switch the order of synthesis and evaluation. The result is a list of six main types of cognitive process aimed at by teachers: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create. The authors retain the idea of a hierarchy of increasing complexity, but acknowledge some overlap, for example between understanding and applying. And they retain the idea that critical thinking and problem solving cut across the more complex cognitive processes. The terms ‘critical thinking’ and ‘problem solving’, they write:
are widely used and tend to become touchstones of curriculum emphasis. Both generally include a variety of activities that might be classified in disparate cells of the Taxonomy Table. That is, in any given instance, objectives that involve problem solving and critical thinking most likely call for cognitive processes in several categories on the process dimension. For example, to think critically about an issue probably involves some Conceptual knowledge to Analyze the issue. Then, one can Evaluate different perspectives in terms of the criteria and, perhaps, Create a novel, yet defensible perspective on this issue. (Anderson et al. 2001: 269–270; italics in original)
In the revised taxonomy, only a few sub-categories, such as inferring, have enough commonality to be treated as a distinct critical thinking ability that could be taught and assessed as a general ability.
A landmark contribution to philosophical scholarship on the concept of critical thinking was a 1962 article in the Harvard Educational Review by Robert H. Ennis, with the title “A concept of critical thinking: A proposed basis for research in the teaching and evaluation of critical thinking ability” (Ennis 1962). Ennis took as his starting-point a conception of critical thinking put forward by B. Othanel Smith:
We shall consider thinking in terms of the operations involved in the examination of statements which we, or others, may believe. A speaker declares, for example, that “Freedom means that the decisions in America’s productive effort are made not in the minds of a bureaucracy but in the free market”. Now if we set about to find out what this statement means and to determine whether to accept or reject it, we would be engaged in thinking which, for lack of a better term, we shall call critical thinking. If one wishes to say that this is only a form of problem-solving in which the purpose is to decide whether or not what is said is dependable, we shall not object. But for our purposes we choose to call it critical thinking. (Smith 1953: 130)
Adding a normative component to this conception, Ennis defined critical thinking as “the correct assessing of statements” (Ennis 1962: 83). On the basis of this definition, he distinguished 12 “aspects” of critical thinking corresponding to types or aspects of statements, such as judging whether an observation statement is reliable and grasping the meaning of a statement. He noted that he did not include judging value statements. Cutting across the 12 aspects, he distinguished three dimensions of critical thinking: logical (judging relationships between meanings of words and statements), criterial (knowledge of the criteria for judging statements), and pragmatic (the impression of the background purpose). For each aspect, Ennis described the applicable dimensions, including criteria. He proposed the resulting construct as a basis for developing specifications for critical thinking tests and for research on instructional methods and levels.
In the 1970s and 1980s there was an upsurge of attention to the development of thinking skills. The annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Educational Reform has attracted since its start in 1980 tens of thousands of educators from all levels. In 1983 the College Entrance Examination Board proclaimed reasoning as one of six basic academic competencies needed by college students (College Board 1983). Departments of education in the United States and around the world began to include thinking objectives in their curriculum guidelines for school subjects. For example, Ontario’s social sciences and humanities curriculum guideline for secondary schools requires “the use of critical and creative thinking skills and/or processes” as a goal of instruction and assessment in each subject and course (Ontario Ministry of Education 2013: 30). The document describes critical thinking as follows:
Critical thinking is the process of thinking about ideas or situations in order to understand them fully, identify their implications, make a judgement, and/or guide decision making. Critical thinking includes skills such as questioning, predicting, analysing, synthesizing, examining opinions, identifying values and issues, detecting bias, and distinguishing between alternatives. Students who are taught these skills become critical thinkers who can move beyond superficial conclusions to a deeper understanding of the issues they are examining. They are able to engage in an inquiry process in which they explore complex and multifaceted issues, and questions for which there may be no clear-cut answers (Ontario Ministry of Education 2013: 46).
Sweden makes schools responsible for ensuring that each pupil who completes compulsory school “can make use of critical thinking and independently formulate standpoints based on knowledge and ethical considerations” (Skolverket 2011: 15). Subject syllabi incorporate this requirement, and items testing critical thinking skills appear on national tests in history, Swedish, mathematics and physics that are a required step toward university admission. For example, the physics syllabus emphasizes the importance of “critical examination of information and arguments which students meet in sources and social discussions related to physics” (Skolverket 2011: 124). Correspondingly, the 2013 national test on physics included a question asking students to provide arguments for a recommendation to the Swedish minister of energy on what energy sources to use for electricity production. Other jurisdictions similarly embed critical thinking objectives in curriculum guidelines.
At the college level, a new wave of introductory logic textbooks, pioneered by Kahane (1971), applied the tools of logic to contemporary social and political issues. In their wake, colleges and universities in North America transformed their introductory logic course into a general education service course with a title like ‘critical thinking’ or ‘reasoning’. In 1980, the trustees of California’s state university and colleges approved as a general education requirement a course in critical thinking, described as follows:
Instruction in critical thinking is to be designed to achieve an understanding of the relationship of language to logic, which should lead to the ability to analyze, criticize, and advocate ideas, to reason inductively and deductively, and to reach factual or judgmental conclusions based on sound inferences drawn from unambiguous statements of knowledge or belief. The minimal competence to be expected at the successful conclusion of instruction in critical thinking should be the ability to distinguish fact from judgment, belief from knowledge, and skills in elementary inductive and deductive processes, including an understanding of the formal and informal fallacies of language and thought. (Dumke 1980)
Since December 1983, the Association for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking has sponsored sessions at the three annual divisional meetings of the American Philosophical Association. In December 1987, the Committee on Pre-College Philosophy of the American Philosophical Association invited Peter Facione to make a systematic inquiry into the current state of critical thinking and critical thinking assessment. Facione assembled a group of 46 other academic philosophers and psychologists to participate in a multi-round Delphi process, whose product was entitled Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction (Facione 1990a). The statement listed abilities and dispositions that should be the goals of a lower-level undergraduate course in critical thinking.
Contemporary political and business leaders express support for critical thinking as an educational goal. In his 2014 State of the Union address (Obama 2014), U.S. President Barack Obama listed critical thinking as one of six skills for the new economy targeted with his Race to the Top program. An article in the business magazine Forbes reported that the number one job skill, found in nine out of 10 of the most in-demand jobs, was critical thinking, defined as “using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems” (Casserly 2012). In response to such claims, the European Commission has funded “Critical Thinking across the European Higher Education Curricula”, a nine-country research project to develop guidelines for quality in critical thinking instruction in European institutions of higher education, on the basis of the researchers’ findings of the critical thinking skills and dispositions that employers expect of recent graduates (Dominguez 2018a; 2018b). The Centre for Educational Research and Innovation of the Organization for Economic Development (OECD) in early 2018 issued a call for institutions of higher education to participate in a two-year study, with control groups, of interventions in undergraduate or teacher education designed to improve creative and critical thinking (OECD Centre for Educational Research and Innovation 2018).
Copyright © 2018 by David Hitchcock < hitchckd @ mcmaster . ca >

Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites

The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2016 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Center for the Study of Language and Information (CSLI), Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

CriticalThinking.NET
thinking in practice
What is critical thinking?
How can we define critical thinking?
Critical thinking is reasonable reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do.
A brief conception is below. For a longer definition, please see long definition . A BRIEF CONCEPTION OF CRITICAL THINKING A critical thinker: 1. Is open-minded and mindful of alternatives 2. Desires to be, and is, well-informed 3. Judges well the credibility of sources 4. Identifies reasons , assumptions , and conclusions 5. Asks appropriate clarifying questions 6. Judges well the quality of an argument , including its reasons , assumptions , evidence , and their degree of support for the conclusion 7. Can well develop and defend a reasonable position regarding a belief or an action, doing justice to challenges 8. Formulates plausible hypotheses 9. Plans and conducts experiments well 10. Defines terms in a way appropriate for the context 11. Draws conclusions when warranted – but with caution 12. Integrates all of the above aspects of critical thinking Last revised 11/26/10
(Note that this conception of critical thinking is not negative. It is also not mere persuasion, though critical thought will often be persuasive — but perhaps not often enough – the challenge of this century.)
Developed (revised 11/26/10) by Robert H. Ennis, Professor Emeritus, Univ. of Illinois. [email protected]
- Undergraduate Courses
- Postgraduate Taught Courses
- Professional, Part-time and Evening Courses
- PhDs and Research Masters
- Online Courses
- Micro-credentials
- How to Apply
- Fees & Funding
- Modes of Study
- Scholarships

Choosing a course is one of the most important decisions you'll ever make! View our courses and see what our students and lecturers have to say about the courses you are interested in at the links below.
View Courses
- Accommodation Advisory Service
- Campus Activities
- Student Support
- Study Abroad
- International Office
- Mature Students
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Ambassador Programme
- For Parents and Guardians
- Access Student Information
- Life in Galway

University Life
Each year more than 4,000 choose University of Galway as their University of choice. Find out what life at University of Galway is all about here.
Read about life at University of Galway
- News & Events
- Strategy 2020-2025
- Cois Coiribe (Publication)
- University Leadership
- Sustainability

About University of Galway
Since 1845, University of Galway has been sharing the highest quality teaching and research with Ireland and the world. Find out what makes our University so special – from our distinguished history to the latest news and campus developments.
About University of Galway
- Adult Learning and Professional Development
- College of Arts, Social Sciences, & Celtic Studies
- College of Business, Public Policy and Law
- College of Medicine, Nursing & Health Sciences
- College of Science and Engineering

Colleges & Schools
University of Galway has earned international recognition as a research-led university with a commitment to top quality teaching across a range of key areas of expertise.
Colleges and Schools
- Research Areas
- Research Office
- Innovation Office
- Researcher Development Centre
- Research Community Portal
- Research centres, institutes, and units

Research & Innovation
University of Galway’s vibrant research community take on some of the most pressing challenges of our times.
- Career Development Centre (for Employers)
- Business Innovation Centre
- Conference & Event Centre

Guiding Breakthrough Research at University of Galway
We explore and facilitate commercial opportunities for the research community at University of Galway, as well as facilitating industry partnership.
- Latest News
- Alumni Services
- Cois Coiribe
- Alumni Awards
- Follow our Social Channels
- Update Your Details
- Upcoming Alumni Events
- Previous Alumni Events
- NUI Elections

Alumni & Friends
There are 128,000 University of Galway alumni worldwide. Stay connected to your alumni community! Join our social networks and update your details online.
- About Engagement
- Learning with Community
- Community Partnerships
- Research with Communities
- University of Sanctuary

Community Engagement
At University of Galway, we believe that the best learning takes place when you apply what you learn in a real world context. That's why many of our courses include work placements or community projects.
Real Learning
Gateway Pages
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Ollscoil na Gaillimhe
- A High Contrast
- Registration
- Office 365 (Email)
- Student Registry Helpdesk
- Fees & Grants
- Exam Timetables
- Academic Skills Hub
- Student Services
- Student Volunteering
- Students' Union
- Financial System (Agresso)
- Academic Records
- Human Resources
- Academic Terms Dates
- Information Solutions & Services (IT Services)
- Buildings & Estates
- Service Desk
- Colleges & Schools
- What is Critical Thinking?
- Getting Started
- Getting Organised
- Communication Skills
- IT and Digital Skills
- Reading and Research Skills
- How to develop your critical thinking skills
- Evaluating arguments and evidence
- Reflective practice and reflective writing
- Assignments and Exams
- Galway Exams 101
Critical thinking skills are sometimes described as ‘higher order’ skills – that is, skills requiring ways of thinking that are deeper and more complex than the kind of ‘everyday’ thinking that we use to, say, cook a meal or learn our times tables.
A well known framework that describes different levels of thinking is Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (1956) – an updated version of which is shown below.
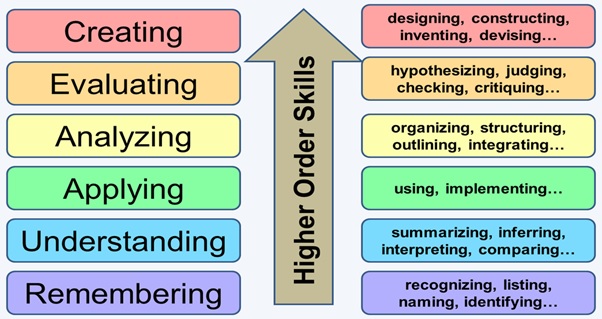
Image source: http://ezsnips.squarespace.com/blooms-taxonomy/
This framework suggests that remembering, understanding, and even applying facts, figures, concepts, or other learning are ‘lower order’ skills. Of course it’s important to be able to do these things, but they are just a beginning. To do really well academically, you will also need to be able to analyse and evaluate the information that you encounter in the course of your studies, and then make inferences or draw conclusions based upon your analysis and evaluation.
These three key higher order skills are core to critical thinking. Ultimately, the aim is to create original academic work of your own (while acknowledging the ideas and work of others, of course).
This involves close reading or scrutiny of a piece of work to detect and identify its main points, arguments, and conclusions, and the evidence offered in support of them. Analysis often involves comparing and contrasting the work of different authors, identifying key themes or areas of contention, or making connections between different ideas or approaches towards the topic under consideration. Analysis may also involve the detailed examination of other data, such as the outcome of an experiment or a computer simulation, or responses to a survey.
Evaluation involves assessing and probing the various points, arguments and evidence that you have found, in order to make a judgement about their credibility, relevance, and strength. It may involve considering what has been omitted as well as included, and questioning the conclusions that have been reached. Evaluation often requires you to consider how well the evidence or argument 'fits' with a particular theory.
Inference involves building on your analysis and evaluation of the available information, by using them to reach a conclusion of your own. This may involve agreeing or disagreeing with the theories, arguments and conclusions of others, discussing the implications of the information that you have considered, and possibly making suggestions or recommendations for the future.
Developing these skills will make it possible for you to master the key academic skill of reflective judgement or the ability to make a reasoned judgement, based on the available information, while also being cognisant of the nature and limits of knowledge and knowing. As your critical thinking skills develop, you should feel more confident about creating original work of your own, knowing that your ideas rest on solid critical foundations.
It’s important to understand that being critical does not imply being negative. For some students, the word ‘critical’ has negative connotations, and they take it to mean that they should only find fault with an idea or a piece of work. This is incorrect. Being critical means considering things in a balanced and objective way, and using reason and logic – rather than instinct, emotion, or belief – to reach a conclusion.

Arguments, non-arguments, and evidence PDF (181 KB)

Top tips for reflective practice and writing PDF (156 KB)
Manage Cookies
Some features need cookies to work properly. Cookies also let us (a) remember your preferences, (b) collect anonymous usage statistics, and (c) see how well our online ads are working.
No personal data is stored on these cookies but, under EU law, we still need to ask you this every 6 months. To learn more about our use of cookies, view our Privacy Policy .
Founded in 1845, we've been inspiring students for over 175 years. University of Galway has earned international recognition as a research-led university with a commitment to top quality teaching.
University of Galway, University Road, Galway, Ireland H91 TK33 T. +353 91 524411
Get Directions Send Us an Email
Twitter Instagram Facebook YouTube LinkedIn RSS

© 2023 University of Galway. All Rights Reserved. Server AWS University of Galway is a registered charity. RCN 20002107
- Privacy & Cookies
- Contact & Enquiries
- Accessibility

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
Critical Thinking. Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the type of goal, the criteria and norms ...
Critical thinking, in educational theory, mode of cognition using deliberative reasoning and impartial scrutiny of information to arrive at a possible solution to a problem. ... policy and in such guidelines as the Common Core State Standards in the United States generated some criticism that the concept itself was both overused and ill-defined ...
Critical Theory refers to a way of doing philosophy that involves a moral critique of culture. A "critical" theory, in this sense, is a theory that attempts to disprove or discredit a widely held or influential idea or way of thinking in society. Thus, critical race theorists and critical gender theorists offer critiques of traditional ...
Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments in order to form a judgement by the application of rational, skeptical, and unbiased analyses and evaluation. [1] In modern times, the use of the phrase critical thinking can be traced to John Dewey, who used the phrase reflective thinking. [2] The application of critical thinking includes self-directed ...
Critical thinking is a rich concept that has been developing throughout the past 2500 years. The term "critical thinking" has its roots in the mid-late 20th century. We offer here overlapping definitions, together which form a substantive, transdisciplinary conception of critical thinking. Critical Thinking as Defined by the National Council ...
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. ... assumptions, concepts, empirical grounding ...
The concept of critical thinking we adhere to reflects a concept embedded not only in a core body of research over the last 30 to 50 years but also derived from roots in ancient Greek. The word ''critical'' derives etymologically from two Greek roots: "kriticos" (meaning discerning judgment) and "kriterion" (meaning standards). ...
Critical thinking is a kind of thinking in which you question, analyse, interpret, evaluate and make a judgement about what you read, hear, say, or write. The term critical comes from the Greek word kritikos meaning "able to judge or discern". Good critical thinking is about making reliable judgements based on reliable information.
Critical thinking is the identification and evaluation of evidence to guide decision making. A critical thinker uses broad in-depth analysis of evidence to make decisions and communicate his/her beliefs clearly and accurately. Other Definitions of Critical Thinking:Robert H. Ennis, Author of The Cornell Critical Thinking Tests "Critical ...
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings. Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful ...
Critical thinking is a rich concept that has been developing throughout the past 2,500 years. The term "critical thinking" has its roots in the mid-late 20th century. Below, we offer overlapping definitions which together form a substantive and trans-disciplinary conception of critical thinking.
Critical thinking is the process of independently analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information as a guide to behavior and beliefs. The American Philosophical Association has defined critical thinking as "the process of purposeful, self-regulatory judgment. The process gives reasoned consideration to evidence, contexts, conceptualizations ...
Critical thinking is one of the thinking abilities that must be given in 21 st -century education, because by having it, the student can think reasonably, reflectively and systematically that ...
1. Identify the problem or situation, then define what influenced this to occur in the first place. 2. Investigate the opinions and arguments of the individuals involved in this process.
A landmark contribution to philosophical scholarship on the concept of critical thinking was a 1962 article in the Harvard Educational Review by Robert H. Ennis, with the title "A concept of critical thinking: A proposed basis for research in the teaching and evaluation of critical thinking ability" (Ennis 1962). Ennis took as his starting ...
Critical thinking is reasonable reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do. A brief conception is below. For a longer definition, please see long definition. 1. Is open-minded and mindful of alternatives. 2. Desires to be, and is, well-informed. 3. Judges well the credibility of sources.
The concept of critical thinking we adhere to reflects a concept embedded not only in a core body of research over the last 30 to 50 years but also derived from roots in ancient Greek. The word "critical'' derives etymologically from two Greek roots: "kriticos"
Critical thinking skills are sometimes described as 'higher order' skills - that is, skills requiring ways of thinking that are deeper and more complex than the kind of 'everyday' thinking that we use to, say, cook a meal or learn our times tables. A well known framework that describes different levels of thinking is Bloom's ...
An overview of critical thinking with examples. Thought Experiment The use of abstractions to experiment with ideas. For example, Einstein used a thought experiment about a street car moving away from a clock tower at the speed of light to develop his theory of special relativity. This thought experiment resulted in a moment of serendipity as Einstein realized that time would appear to be ...