©Copyright Mandy Barrow 2013 primaryhomeworkhelp.com
Follow me on Twitter @mbarrow
Woodlands Junior School, Hunt Road Tonbridge Kent TN10 4BB UK


Viking Cuisine Explored: Diet, Meals & Feasts of Norse Life
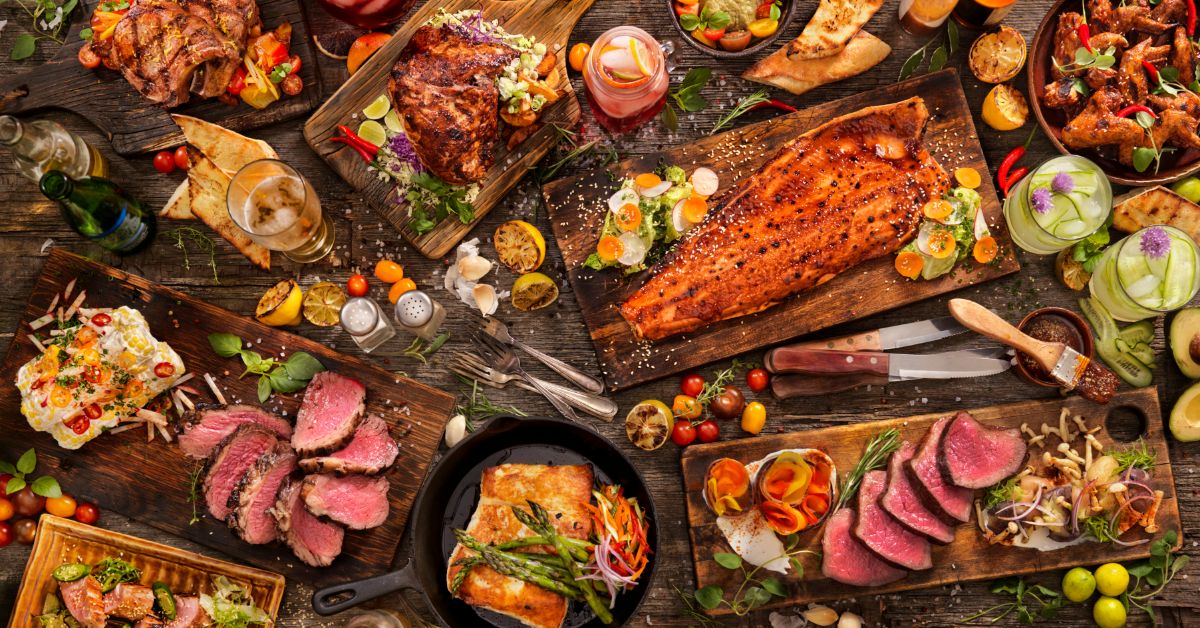

The Vikings, known for their seafaring prowess, were equally remarkable in their culinary customs. Their diet was a reflection of the rugged landscapes and the bountiful seas that surrounded them.
This post delves into the depths of Viking cuisine, exploring the nourishment that fueled these legendary warriors and settlers.
Introduction to Viking Culinary Traditions
The culinary traditions of the Vikings were deeply intertwined with their lifestyle, environment, and the changing seasons.
They were not just raiders but also farmers, fishermen, and traders, with a diet that reflected the diversity of these roles.
The Historical Context of Viking Cuisine
The Viking Age, from the late 8th to the early 11th century, was a time of great exploration and cultural exchange.
The Vikings’ diet evolved with their travels, incorporating elements from the lands they visited, traded with, or settled in.

Understanding the Viking Age Through Food
Food is a powerful indicator of a civilization’s way of life. By examining the remains of Viking meals, we gain insights into their daily life, health, and even social structures.
Primary Food Sources in the Viking Age
Vikings depended largely on their local environment for food. Their primary sources were agriculture, hunting, and fishing, which together provided a balanced diet.
Agricultural Practices and Crops
Agriculture in the Viking Age included the cultivation of barley, oats, and rye. The grains were used to make bread, porridge, and ale, which were staples in the Viking diet.
Livestock and Meat Consumption
Livestock such as cattle, sheep, and pigs were central to Viking farming, providing meat, milk, cheese, and wool.
Meat was often preserved through smoking or salting to last through the winter months.
Fishing Techniques and Seafood
The seas and rivers provided a rich source of food. Vikings were adept at fishing, and their catches included herring, salmon, and cod, which were also dried or salted for preservation.
Everyday Meals: From Field to Table
The daily meals of a Viking were simple yet nourishing, often comprising of a stew or porridge, with meat and fish being more common during feasts or in wealthier households.
Typical Daily Diet of a Viking Family
A typical Viking family ate two meals a day: ‘dagmal’ in the morning and ‘nattmal’ in the evening.
These meals consisted of a base of grains with additions of vegetables, legumes, and occasionally meat or fish.
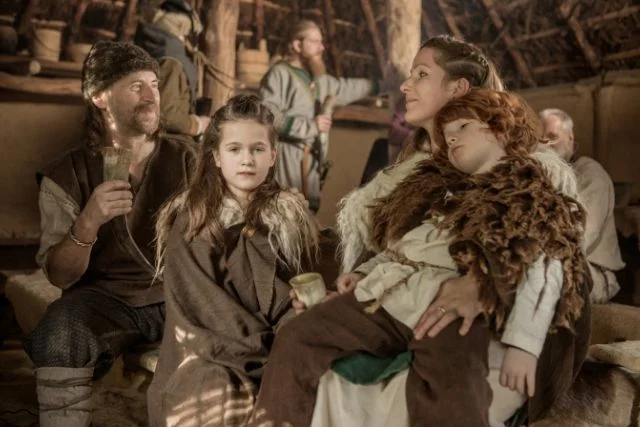

Cooking Methods and Kitchen Tools
Viking cooking methods were straightforward, involving boiling or roasting over an open fire. Kitchen tools included iron pots, wooden utensils, and stone querns for grinding grain.
The Role of Women in Food Preparation
Women played a crucial role in Viking society as the primary food preparers. They managed the farms, preserved food for the long winters, and cooked meals for their families.
Feasts and Festivities: Celebratory Foods
Feasts were a significant part of Viking culture, marking important events with an abundance of food and drink that went beyond their daily fare.
Special Occasion Dishes and Recipes
During feasts , dishes such as roasted meats, thick stews, and bread made with finer flour were served. Sweetened with honey, desserts, and fruits were also enjoyed when available.
Alcoholic Beverages and Brewing Methods
Mead, ale, and beer were the primary alcoholic beverages of the Vikings , brewed from barley and flavored with herbs or fruits. These drinks were a staple at any large gathering.

Rituals and Food: The Spiritual Connection
Food also had a spiritual significance for Vikings, with certain meals and toasts being an integral part of their rituals and offerings to the gods.
Trading and Influence: Exotic Foods and Spices
Trade expanded the Viking palate with spices, fruits, and other luxuries that were previously unknown, showcasing their connections with the wider medieval world.
Trade Routes and Imported Ingredients
Viking traders brought back goods like wheat, honey, wine, and exotic spices from their travels, which were then incorporated into their cuisine.
The Impact of Foreign Culinary Practices
These imported goods influenced Viking cooking, introducing new flavors and techniques that added variety to their diets.
Viking Cooking Techniques and Preservation
To survive the harsh northern winters, Vikings developed effective food preservation techniques, which also enhanced their food’s flavor and longevity.
Smoking, Drying, and Salting: Preserving Food
Methods like smoking fish and meats over fires, drying them in the open air, or salting were commonplace and essential for ensuring a year-round food supply.
Fermentation: A Taste of Viking Innovation
Fermentation was another preservation method, leading to foods like skyr (a type of yogurt) and various pickled vegetables.
Nutrition and Diet: The Health of a Viking
While the Vikings are often associated with robust health, their diet was varied enough to provide them with the necessary nutrients to survive in their harsh environment.

Analyzing the Nutritional Value of Viking Meals
Studies of Viking remains indicate a diet rich in protein and vitamins but also show evidence of diseases related to diet and lifestyle.
Common Diseases and Diet-Related Health
Dental wear and deficiencies point to some of the challenges Vikings faced, possibly due to a lack of certain vegetables and fruits during the long winters.
Archaeological Insights: What Remains Tell Us
Archaeological discoveries continue to shed light on the Viking diet, providing a tangible link to the past through the study of food residues, utensils, and even ship remains.
Discoveries from Viking Settlement Excavations
Excavations of Viking settlements have unearthed kitchen middens, which are full of clues about their daily meals, such as bones, seeds, and shells.
Reconstructing Diets from Bones and Seeds
Analysis of these materials allows researchers to reconstruct the Viking diet in detail, offering a window into their everyday life.
Recreating Viking Cuisine Today
Today, there is a growing interest in recreating Viking cuisine. Modern cooks and historians alike are bringing ancient recipes to life, using them to connect with Viking heritage.
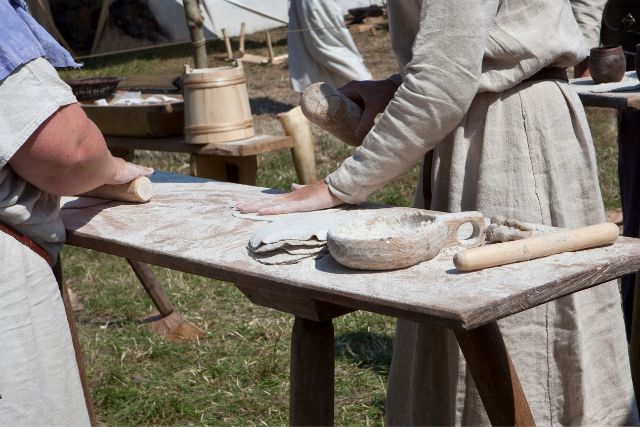

Modern Interpretations of Viking Recipes
Chefs and enthusiasts experiment with historical ingredients and methods to create dishes that provide a taste of the Viking age, adapted for the modern palate.
Themed Viking Feasts and Culinary Experiences
Themed events and restaurants offer immersive experiences, allowing people to dine like Vikings and engage with their history in a unique and flavorful way.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Viking Cuisine
The legacy of Viking cuisine is not only in the dishes that have been passed down or the historical records but also in the enduring curiosity and fascination with the Viking way of life.
Viking Influence on Modern Nordic Cuisine
Modern Nordic cuisine owes much to its Viking roots, with a focus on simplicity, purity, and freshness that echoes the diet of these ancient seafarers.
Preserving History Through Food Culture
By exploring and recreating Viking cuisine, we preserve a vital part of history, connecting the past to the present through the universal language of food.
Like this post? Please share.
Trending Viking Products

3 Piece Viking Knife Stainless Steel Set
The Topfeel 3PCS Butcher Knife Set offers hand-forged, multifunctional chef, cleaver, and Viking knives with high carbon steel blades and comfortable rosewood handles.
Check Best Price

12 Inch Stainless Steel Viking Fry Pan
The Viking 12-inch stainless steel fry pan offers even cooking, ergonomic handle, dishwasher safe, and works on all cooktops, including induction. Perfect for serious cooks.

Set of 5 10 Oz Carved Horn Shot Cups
Authentic 10oz Viking Drinking Horn Mugs Set, perfect for ale or whiskey, includes Medieval accessories, offering a unique, rustic gift with Norse runes.

8 Quart Stock Pot with Lid, Pasta & Steamer Insert
Viking's 8-quart stainless steel pasta pot excels in even heating and versatility, featuring a non-stick coating and compatibility with all cooktops, including induction.

Steel Chainmail Shirt & Coif – Natural / Silver / Black
The Mythrojan Chainmail Shirt and Coif offer authentic medieval armor for LARP and reenactments, featuring durable steel in a classic pattern with a lifetime guarantee.

Uniquely Designed Drinking Horn Tankard
Unique, handcrafted Viking Drinking Horn Mug, perfect for those who cherish medieval craftsmanship and authenticity. Elevates drinking experiences, making each sip historically immersive.
Related Articles
Exploring the use of color in viking clothing.
Dive into Viking culture through the vibrant spectrum of their clothing. Uncover the historical significance, symbolic meanings & modern misunderstandings

The Role of Music and Poetry in Viking Society
Dive deep into the world of Viking society, unraveling the intricate role of music & poetry in daily life, rituals & legacy. Discover the art & soul of Vikings

Land & Agriculture in Viking Society: Farming & Innovations
Explore Viking farming life, women's roles & sustainable practices. Discover how Vikings managed land & resources effectively from in-depth insights.

Viking Longhouses: Architecture, Purpose & Legacy Explored
Dive into the world of Viking longhouses, exploring their multifunctional purpose, intricate construction, and lasting impact on architecture & society

- Year 4 History Links
- Online Learning
- Key Stage 2
- BBC Bitesize - Vikings This site has learner guides and video clips about the Vikings.
- Children's British History Encyclopedia - The Vikings This site has lots of information about the Vikings and their invasion of Britain.
- DK Find Out - Vikings Click on the pictures to learn more about the Vikings.
- Primary Homework Help - Vikings This site covers lots of topics including settlements, food, clothes and Viking houses.
- Cook it! - Historical Cookbook - Saxons and Vikings This site has lots of information about Viking life as well as authentic recipes from the time you can make at home.
- BBC Viking Quest In this activity you need to build a ship and go exploring.
- BBC Schools Radio - Viking Sagas Listen to a selection of tales from Viking mythology featuring Thor and Loki.
- Write Your Name in Runes Type in your name and see what it would look like in the runic alphabet.
- BBC Schools Radio - Tudor Sketches Listen to audio clips about Tudor life and Tudor kings and queens.
- Children's British History Encyclopedia - The Tudors This site has lots of information about the Tudors including life in Tudor times, clothes and the royalty.
- DK Find Out - Tudors Learn about a range of topics including childhood, exploration and entertainment.
- BBC Class Clips - Tudors and Stewarts Watch videos about life in Tudor times.
- Primary Homework Help - Tudors This site covers lots of topics including Tudor houses, food, schools and the Mary Rose.
- Cook it! - Historical Cookbook - Tudors This site has information about the Tudors as well as authentic recipes from the time you can make at home.
- Tudor Britain This site has pictures of real documents and objects from Tudor times.
- BBC Schools - Famous People - Henry VIII This archived site covers the life of King Henry VIII.
- Object Lessons - Tudors This site lets you explore objects from the Tudor era and other periods from history.
Unfortunately not the ones with chocolate chips.
Our cookies ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Please make your choice!
Some cookies are necessary in order to make this website function correctly. These are set by default and whilst you can block or delete them by changing your browser settings, some functionality such as being able to log in to the website will not work if you do this. The necessary cookies set on this website are as follows:
Website CMS
A 'sessionid' token is required for logging in to the website and a 'crfstoken' token is used to prevent cross site request forgery. An 'alertDismissed' token is used to prevent certain alerts from re-appearing if they have been dismissed. An 'awsUploads' object is used to facilitate file uploads.
We use Matomo cookies to improve the website performance by capturing information such as browser and device types. The data from this cookie is anonymised.
Cookies are used to help distinguish between humans and bots on contact forms on this website.
Cookie notice
A cookie is used to store your cookie preferences for this website.
- Create new account
- Reset your password
Register and get FREE resources and activities
Ready to unlock all our resources?
The Vikings


Who were the Vikings?
The Vikings came from all around Scandinavia (where Norway, Sweden and Denmark are today). They sent armies to Britain about the year 700 AD to take over some of the land, and they lived here until around 1050.
Even though the Vikings didn’t stay in Britain, they left a strong mark on society – we’ve even kept some of the same names of towns. They had a large settlement around York and the Midlands, and you can see some of the artefacts from Viking settlements today.
Top 10 facts
- The Vikings are also called Norsemen, and came from Scandinavia.
- They spoke Norse , which had an alphabet made up of characters called runes.
- They travelled over the sea in longships, which are long, narrow wooden boats that could be sailed in both deep and shallow water.
- The Vikings left their homeland because they were looking for better places to farm than the kind of terrain that Scandinavia had.
- The Vikings first attacked Britain in 787 AD, but didn’t start to invade and settle in the British Isles until 793 .
- In 878, King Alfred the Great defeated the Vikings in battle and had them sign a treaty saying they had to keep to their own land in England – this section of land was called Danelaw.
- Jorvik was a large Viking kingdom around York ; the last king of Jorvik was Eric Bloodaxe in 954.
- Viking warriors believed that when they died in battle, they went to Valhalla – this is where the king of the gods lived, named Odin.
- England once had a Viking king: King Canute ruled from 1016-1035, and his descendants ruled until 1042.
- A few weeks before the Anglo-Saxons were defeated in the Battle of Hastings in 1066 , they defeated Viking warriors near York, led by Harald Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge.

- 793 The Vikings attacked a monastery at Lindisfarne in Northumbria and started to settle in England
- 866 The Vikings raided and conquered York, and established the Viking Kingdom of Jorvik

- 878 Alfred the Great defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Ethandun
- 886 The boundary between Anglo-Saxon and Viking territories was established, called Danelaw
- 950 Viking armies raided Wales
- 954 The Viking Kingdom of Jorvik became part of England again
- 994 Viking armies from Denmark and Norway attempted to raid London, but were defeated

- 25 September 1066 The Battle of Stamford Bridge took place near York, between the Anglo-Saxons and Viking invaders led by Harald Hardrada
- 14 October 1066 William from Normandy, "William the Conqueror", won the Battle of Hastings and the Normans began to rule England

Boost Your Child's Learning Today!
- We'll created a tailored plan for your child...
- ...and add English & maths activities to it each week...
- ...so you can watch your child grow in skills & confidence
Did you know?
- The word ‘Viking’ means ‘a pirate raid’ in the Norse language, which is what the Vikings spoke.
- ‘-by’, as in Corby or Whitby, means ‘farm’ or ‘town’
- ‘-thorpe’, as in Scunthorpe, means ‘village’
- The Viking alphabet, ‘Futhark’, was made up of 24 characters called runes. Each one stood for entire words or gods, as well as sounds.
- There was a large Viking community around York called Jorvik. Archaeologists have found out a lot about the Vikings thanks to the artefacts they found there.
- The Vikings kept long benches in their homes that they’d use to sit on during the day, and then to sleep on at night. Only rich people had beds.
- In Viking times, people usually just took baths once a week! This was often on Saturdays.
- The Normans from France who defeated the Anglo-Saxons in the Battle of Hastings were actually descendants of Vikings! Vikings settled around more places than just Britain – they went to Ireland , Iceland, Greenland, France and Spain too.
Can you find the following in the gallery below?
- A map showing where the Vikings originally lived, and where they settled in Britain and Ireland
- A map showing the Danelaw
- A replica of a Viking longboat
- What a Viking warrior would have looked like
- A Viking warrior’s helmet
- What a Viking man would have worn
- What a Viking woman would have worn
- The names of clothing that the Vikings wore
- Weapons that the Vikings used
- A Viking ship reconstruction
- A Viking village reconstructed in Ukranenland, an archeological village-museum in Germany
- Viking gold bracelets
- A Viking boat sculpture in Iceland
- An illustration of a Viking boat
- A re-enactment of Viking life
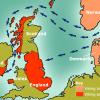
The Vikings wanted new land because the places where they came from in Scandinavia – Norway, Sweden and Denmark – weren’t very easy to live in. It was hard to grow crops, which meant there wasn’t a lot of food as the population got bigger. Britain and Europe had plenty of good farmland , so the Vikings tried to claim some of that land for themselves.
Even though the Anglo-Saxons were pretty well established in England, the Vikings would turn up every now and then to raid towns and take a bit of land. Sometimes, instead of fighting the Vikings, the Anglo-Saxons decided it was better to pay them money so they’d stay away. This payment was called Danegeld.
The first Viking attack on England was in 787 on the Isle of Portland. The Vikings went home straight afterwards, but they came back to England in 793 and raided a monastery at Lindisfarne. Monastaries made easy targets because the monks who lived there didn’t have any weapons, and they did have money and food.
The Vikings believed in many different gods , and they thought making sacrifices to the gods kept them all happy. They also told stories about the gods, called Norse mythology . Some of the gods included:
- Thor , the god of thunder
- Idun , the goddess of spring
- Odin , the king of gods and the god of war
The Vikings believed that if a warrior died while fighting in battle, he’d go to Valhalla , which is where Odin was. Other heroes who had died would also be there. Odin would send his warrior maidens, called Valkyries, across the sky to ferry dead warriors to Valhalla.
Viking warriors were very good fighters. They’d wear helmets and carry shields to defend themselves, and they’d also have one of these weapons:
- spear – a leaf shape or spike at the end of a wooden shaft
- sword – these were expensive to make and usually double-edged, and warriors would decorate the hilts
- battle axe – an axe with a long handle, and cheaper to make than a sword
Boats that the Vikings built are called longships – they are long, narrow boats that can be used in both deep and shallow water, making them perfect for travelling over the ocean and carrying lots of warriors onto the shore. Longships were symmetrical, meaning they looked the same at the front as they did at the back. They’d often have dragon heads carved at either end.
VIkings sailed all the way across the Atlantic Ocean to Newfoundland in North America in their longships!
Viking homes were long too – they were called longhouses ! They were rectangular, made from wood and were usually just one big room without any inside walls. There would be one big fire pit in the centre for cooking and keeping the house warm. The roof was covered in thatch, and there was a hole in the middle for smoke from the fire to go through. Benches around the house would be used both to sit on and to sleep on.
Most clothes that the Vikings had were made from wool, but they also had some clothes made from linen. They used dyes made from plants and minerals to make red, green, brown, yellow and blue, so their clothes were very colourful.
Viking men wore a long shirt, trousers with a drawstring tie and a coat with a belt around the waist. Viking women wore long dresses with a tunic over the top that was held up by two brooches pinned at the shoulders. Both men and women wore woollen socks and leather shoes.
Alfred the Great defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Ethandun (in modern day Wiltshire). After this, he and the Vikings agreed to set boundaries for their kingdoms. The area that the Vikings lived in was called Danelaw, and it meant that the land south of the diagonal line between London and Chester belonged to King Alfred (Wessex). Danelaw eventually became smaller and smaller as the Anglo-Saxons took more and more control.
Jorvik was a large Viking kingdom around York. The last king of Jorvik was Eric Bloodaxe, who was driven out in 954. The Vikings in England then agreed to be ruled by the king of England rather than having their own king.
But, that doesn’t mean that the king of England couldn’t be a Viking! The first Viking king of England was King Canute in 1016. He ruled until 1035, and then his sons were kings after that – but only for a total of seven years. Harold Harefoot was king until 1040, then Hardicanute was king until 1042.
Names to know:
King Canute (ruled as king of England from 1016-1035) – Canute was the first Viking king of England. He won a battle against Edmund II that divided their kingdoms, but when Edmund died Canute ruled both kingdoms. His sons, Harold Harefoot and then Hardicanute, ruled until 1042.
Harald Hardrada (c.1015-1066) – Harald Hardrada was the king of Norway. He led Viking armies into England, but was defeated at the Battle of Stamford Bridge in York by King Harold II.
Leif Erikson (c.970-1020) – Leif Erikson was a famous Viking explorer who sailed all the way to North America.
Eric Bloodaxe (died in 954) – Eric Bloodaxe was king of the Viking kingdom of Jorvik between 947-948 and 952-954. He was the last king of Jorvik before it became part of England.
Related Videos
Just for fun...
- Type your name into the box and see how it looks written in Viking runes!
- Have Mum or Dad help you make some porridge in the way that the Vikings would have had it
- Watch Horrible Histories songs about the Vikings, the Vikings & Garkunkel Song and The Vikings - Literally
- Print some Viking colouring sheets and a Viking Age boat to colour in
- Make your own Viking tortoise brooches and try Viking cord winding
- You'll find amazing artefacts from the Viking Age on the Jorvik Discover from Home webpage, as well as Viking colouring, puzzles, crafts, stories and videos
- Quiz yourself on the Vikings
- Make your own Viking name
- Bake your own Viking flatbread
- The Cbeebies television show Gudrun the Viking Princess offers a glimpse of what life might have been like for the Vikings a thousand years ago
- Listen to a collection of Viking sagas told by Loki, Viking god of fire, on BBC Schools Radio
- Read a National Geographic kids comic set on a Viking longboat
- Make your own Viking shield , Viking longboat and Viking helmet with step-by-step instructions and videos from Hobbycraft
- Try some Viking puzzles from the Yorvik Centre
- Step back to 876AD and make your own Viking longship, Viking longship figurehead and Viking helmet
Children's books about the Vikings

See for yourself
- Visit Jorvik Viking Centre in York to go back in time and see what it was like to live as a Viking
- See a Viking coin made in England for a Viking ruler
- Step into a Viking Longhouse reconstruction at the Ancient Technology Outdoor Education Centre
- At the National Museum of Scotland, see the Galloway Hoard , the richest collection of rare and unique Viking-age objects ever found in the British Isles
Find out more:
- Watch BBC Bitesize animations about the Vikings
- A children's introduction to the Vikings from DKfindout!
- See an animated film about the life of a ten-year-old Viking boy
- Learn about everyday life in the Viking age
- Find out about the Vikings in Scotland with BBC Bitesize animations
- Watch a virtual tour of the British Museum's Vikings Live exhibition
- Discover the secrets of Viking ships
- "Walk" through a real Viking village
- Read stories and sagas from the Viking world – we've collected the best kids' books about the Vikings
- Find out about the Viking words we use in English place names . Did you know that words like berserk, ugly, muck, knife, die and cake come from Old Norse, the Viking language ?
- Information about Viking gods and mythology
- Did Vikings have horned helmets? Find out!
- See some images of Viking clothes and Viking jewellery and find out about Viking pets
- The Vikings were warriors of the sea. Find out more about Viking voyages and sea-faring life
- Download a Viking information booklet, packed with pictures
- Watch a video about the Vikings Eric the Red and his son Leif Ericson, who explored areas of Greenland and North America

Give your child a headstart
- FREE articles & expert information
- FREE resources & activities
- FREE homework help
You'll need JavaScript enabled to experience the full functionality of this site. Please enable JavaScript by following the instructions at enable-javascript.com .
Sorry, the browser you're currently using is not supported by this site. Please upgrade your browser by following the instructions at browser-update.org .

Vikings — An Introduction (Years 5-6)
Write a review

Choose your format:
Save to Your Lessons
Save to Homework
Share resource
Your download limit has been reached!
Check out our FAQs for more info.
Who were the Vikings and where do they fit in to history? This PowerPoint is a great resource to introduce the class to the Viking era, or equally to recap their general learning of the topic. Children will think about where the Vikings fit in on a timeline of history, where they came from, the transport that they used and the importance of their raids.
- Key Stage: Key Stage 2
- Subject: History
- Topic: Vikings
- Topic Group: Settlers & Invaders in Britain
- Year(s): Years 5-6
- Media Type: PowerPoint
- Resource Type: PowerPoint
- Last Updated: 19/07/2022
- Resource Code: H2PAT85
Related Topics:
Other Teachers Downloaded...

Vikings Timeline (Years 5-6)
- Key Stage 2 History

Vikings Map — Early Viking Exploration (Years 5-6)

Vikings — Raiding and Trading (Years 5-6)

Vikings — Label a Long Ship (Years 5-6)

Vikings — Lindisfarne (Years 5-6)

Viking Food (Years 5-6)
1 customer rating
Related Resources

Reputation of the Vikings (Years 5-6)

The Vikings — Crossword and Wordsearch (Years 5-6)

The Vikings — Crossword and Wordsearch: Foundation (Years 5-6)

Vikings Timeline: Foundation (Years 5-6)

Norse God Trading Card Game (Years 5-6)

Viking Voyages (Years 5-6)

Viking Imports and Exports Trading Card Game (Years 5-6)

Stone Age to Iron Age Timeline (Years 3-4)
- Stone Age to Celts

Battle of Hastings — Points of View Activity (Years 5-6)

Roman Britain — Scotland (Years 3-4)
Cookies are disabled on your browser. This means some features of the site won't be fully available to you.
CGP uses cookies to give you a smooth shopping experience and to help us understand how well our site is working. To agree to us using all cookies, click 'Accept', or to reject optional cookies click 'Customise'.
Accept cookies Customise cookies
Restaurant Globus

RESTAURANT GLOBUS, Elektrostal - Restaurant Reviews & Photos - Tripadvisor

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

XL Flag Elektrostal Moscow oblast | landscape flag | 2.16m² | 23sqft | 120x180cm | 4x6ft - 100% Made in Germany - long lasting outdoor flag
Purchase options and add-ons, about this item.
- 100% Made in Germany » ... because the first impression last, quality flag for representative purposes *****
- State-of-the-art High-Tech Outdoor Fabric » One air-permeable 110 GSM Polyester to keep wind forces low and lifetime high
- Mirrored Back » Image printed on the front, mirrored image 100% visible on the rear side
- Landscape flag | 2.16m² | 23sqft | 120x180cm | 4x6ft
- Show your pride for your hometown with the Elektrostal flag! Made with quality materials and vibrant colors, this flag is the perfect way to display your patriotism and love for your city. Fly it proudly at home, at events, or even in your car. Get yours today and show your Elektrostal pride!
- The flag of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, is a striking combination of Old Glory red, representing strength and courage at 81%, complemented by a subtle touch of light grey at 5% for balance and harmony. The bold black stripe at 3% adds a touch of sophistication, while the shimmering gold stripes at 3% each symbolize prosperity and success. The flag is completed with a touch of very dark grey at 1%, representing the city s resilience and
- Elektrostal Moscow oblast
Product information
Warranty & support, looking for specific info, product description.
Flag: Elektrostal Moscow oblast landscape flag | 2.16m² | 23sqft | 120x180cm | 4x6ft Elektrostal Moscow oblast Elektrostal obwód moskiewski , flaga ???????????? ?????????? ??????? Since we know how important your external presentation is, we print our Elektrostal Moscow oblast flag for your representative appearance using the most modern machines in Germany. To ensure your maximum flexibility, we have equipped the flags with quality metal eyelets, to let you simply attach these flags to any flagpole. To let you use the flags for a long time, we have strengthened the flag using double safety seams and a tear proof strap at the side of the pole. Due to the quality of this business flag, you show a particular degree of the closeness to Elektrostal Moscow oblast. Details about this flag This landscape Elektrostal Moscow oblast flag is a quality product Made in Germany made of 110g/m² gloss polyester. This Elektrostal Moscow oblast flag is wind- and weather-resistant and highly durable. The flag colors are intensive and UV-resistant. This flag is specially made for outer space. This Elektrostal Moscow oblast flag will be delivered with a double safety-seam as well as with 2 metal eyelets to hoist at the flag pole. The metal eyelets give you great flexibility for placing this flag on any flagstaff. The mast side is reinforced with a white hem. The quality flag material and the metal eyelets will take care of a long endurance of this Elektrostal Moscow oblast flag. If required, the flag can be washed at 60 degrees Celsius. Recommended height of flag pole Elektrostal Moscow oblast flags of 2.16m² | 23sqft | 120x180cm | 4x6ft look best with flagpoles of around 6m | 18ft height. Need a bigger size or an other configuration? We can provide bigger sizes, other configurations, exclusive indoor ...
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
Current time by city
For example, New York
Current time by country
For example, Japan
Time difference
For example, London
For example, Dubai
Coordinates
For example, Hong Kong
For example, Delhi
For example, Sydney
Geographic coordinates of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, Russia
City coordinates
Coordinates of Elektrostal in decimal degrees
Coordinates of elektrostal in degrees and decimal minutes, utm coordinates of elektrostal, geographic coordinate systems.
WGS 84 coordinate reference system is the latest revision of the World Geodetic System, which is used in mapping and navigation, including GPS satellite navigation system (the Global Positioning System).
Geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) define a position on the Earth’s surface. Coordinates are angular units. The canonical form of latitude and longitude representation uses degrees (°), minutes (′), and seconds (″). GPS systems widely use coordinates in degrees and decimal minutes, or in decimal degrees.
Latitude varies from −90° to 90°. The latitude of the Equator is 0°; the latitude of the South Pole is −90°; the latitude of the North Pole is 90°. Positive latitude values correspond to the geographic locations north of the Equator (abbrev. N). Negative latitude values correspond to the geographic locations south of the Equator (abbrev. S).
Longitude is counted from the prime meridian ( IERS Reference Meridian for WGS 84) and varies from −180° to 180°. Positive longitude values correspond to the geographic locations east of the prime meridian (abbrev. E). Negative longitude values correspond to the geographic locations west of the prime meridian (abbrev. W).
UTM or Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system divides the Earth’s surface into 60 longitudinal zones. The coordinates of a location within each zone are defined as a planar coordinate pair related to the intersection of the equator and the zone’s central meridian, and measured in meters.
Elevation above sea level is a measure of a geographic location’s height. We are using the global digital elevation model GTOPO30 .
Elektrostal , Moscow Oblast, Russia
Time in Elektrostal , Moscow Oblast, Russia now
- Tokyo 05:51PM
- Beijing 04:51PM
- Kyiv 11:51AM
- Paris 10:51AM
- London 09:51AM
- New York 04:51AM
- Los Angeles 01:51AM
Time zone info for Elektrostal
- The time in Elektrostal is 8 hours ahead of the time in New York when New York is on standard time, and 7 hours ahead of the time in New York when New York is on daylight saving time.
- Elektrostal does not change between summer time and winter time.
- The IANA time zone identifier for Elektrostal is Europe/Moscow.
Time difference from Elektrostal
Sunrise, sunset, day length and solar time for elektrostal.
- Sunrise: 03:43AM
- Sunset: 09:07PM
- Day length: 17h 24m
- Solar noon: 12:25PM
- The current local time in Elektrostal is 25 minutes ahead of apparent solar time.
Elektrostal on the map
- Location: Moscow Oblast, Russia
- Latitude: 55.79. Longitude: 38.46
- Population: 144,000
Best restaurants in Elektrostal
- #1 Tolsty medved - Steakhouses food
- #2 Ermitazh - European and japanese food
- #3 Pechka - European and french food
Find best places to eat in Elektrostal
- Best pubs & bars in Elektrostal
- Best steak restaurants in Elektrostal
- Best bbqs in Elektrostal
The 50 largest cities in Russia

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Viking Food. There were no supermarkets or shops to buy food so the Vikings ate what food they could grow or hunt. Vegetables e.g. leeks, onions, turnips, parsnips and carrots. Wild nuts e.g. hazelnuts and walnuts. Berries e.g. gooseberries, blackberries and blueberries. Wild animals e.g. deer, wild boar, fox, beaver, and bear.
Vikings ate fruit and vegetables and kept animals for meat, milk, cheese and eggs. They had plenty of fish as they lived near the sea. Bread was made using quern stones, stone tools for hand ...
This would make a great experiment, both as homework or as an in-school activity. After completing the Viking food recipes, children can review the appearance, taste, smell and texture of the food. Every recipe comes with a list of ingredients and details of the equipment you'll need to get started.
Vikings had a varied diet of vegetables, fruit, fish, eggs, cheese, meat and bread. Vikings could catch fish as they were used to living by the sea, they could farm animals such as pigs, chickens and sheep, and they could grow crops such as corn, leeks and carrots. Bread could be made using stone tools to hand-grind the grain.
In the 9th century ad seafaring warriors known as Vikings began raiding the coasts of Europe, burning, plundering, and killing as they went. These marauders, or pirates, came from Scandinavia —what is now Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. The people who lived there were known as Norsemen, or Northmen. Their expression for these campaigns of swift ...
Primary Homework Help The Vikings. by Mandy Barrow : Celts. Romans. Saxons. Vikings. Normans. Tudors. Victorians. WW ll. 500 BC . AD 43. 450. ... Food: Religion: Viking Houses: Clothes: Timeline: ... mandybarrow.com . Where did the Vikings come from? Where did the Vikings come from? The Vikings came from the three countries in Scandinavia (in ...
8 + Resources to Use When Teaching The Vikings to Children. 8 min. November 18, 2022. The Vikings were a seafaring people who sailed from Scandinavia to explore and raid other lands from the 8th century to the 11th century. In this blog post, we've put together a list of eight amazing resources for teaching Vikings to children.
Help children to learn about the Viking diet with this worksheet. Children will match each Viking menu with the type of Viking family that would have eaten it, as well as complete the Viking shopping list. In the second activity, they must read the information on the table and decide what is true and what is false. Answers are provided. Key ...
Typical Daily Diet of a Viking Family. A typical Viking family ate two meals a day: 'dagmal' in the morning and 'nattmal' in the evening. These meals consisted of a base of grains with additions of vegetables, legumes, and occasionally meat or fish.
Primary Homework Help - Vikings This site covers lots of topics including settlements, food, clothes and Viking houses. Cook it! - Historical Cookbook - Saxons and Vikings This site has lots of information about Viking life as well as authentic recipes from the time you can make at home.
Welcome to our Homework Help guide all about the Vikings. Click through the chapters on the left-hand side to learn more about this famous period of time! As well as help with your homework, these guides contain lots of exciting activities that you can try at home and plenty of fun facts that you can impress your family and friends with.
About. The Vikings wanted new land because the places where they came from in Scandinavia - Norway, Sweden and Denmark - weren't very easy to live in. It was hard to grow crops, which meant there wasn't a lot of food as the population got bigger. Britain and Europe had plenty of good farmland, so the Vikings tried to claim some of that land for themselves.
Vikings had many weapons, but longswords were their most prized possessions. They were doubled-edged and so sharp that they could cut through a human skull. Vikings gave their swords fierce-sounding names like 'widow-maker'. 3. Vikings believed that the first man and woman came from the sweat of a giant's armpit. 4.
Children will think about where the Vikings fit in on a timeline of history, where they came from, the transport that they used and the importance of their raids. Browse our fun and colourful online KS2 History resources for Years 3-6 (ages 7-11) — covering Mayan Civilisation, Ancient Greece, the 20th Century and more!
Review. Share. 67 reviews. #2 of 28 Restaurants in Elektrostal $$ - $$$, European, Contemporary, Vegetarian Friendly. Fryazevskoye Hwy., 14, Elektrostal Russia. + Add phone number + Add website + Add hours Improve this listing. There aren't enough food, service, value or atmosphere ratings for Restaurant Globus yet.
Amazon.com : magFlags XL Flag Elektrostal Moscow oblast | landscape flag | 2.16m² | 23sqft | 120x180cm | 4x6ft - 100% Made in Germany - long lasting outdoor flag : Outdoor Flags : Patio, Lawn & Garden
Geographic coordinates of Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast, Russia in WGS 84 coordinate system which is a standard in cartography, geodesy, and navigation, including Global Positioning System (GPS). Latitude of Elektrostal, longitude of Elektrostal, elevation above sea level of Elektrostal.
Sunset: 09:07PM. Day length: 17h 24m. Solar noon: 12:25PM. The current local time in Elektrostal is 25 minutes ahead of apparent solar time.