How to Write a Thematic Essay

A thematic essay explores a central message or theme that runs through a piece of literature, a historical event, or even a societal trend. It analyzes evidence like characters' actions, plot development, or real-world examples to explain how this matter is revealed and unpack its significance, showing a deeper understanding of the subject at hand.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what is a thematic essay :
- Analyzes a central message (theme) in a text.
- Explains how the text explores that theme.
- Uses evidence (quotes, details) to support your analysis.
- Shows how the evidence connects to the overall theme.
This article explains how to craft a thematic essay by analyzing a central theme in a text, using evidence like quotes and thematic essay examples to support analysis. It provides step-by-step guidance, from understanding the theme to structuring an essay effectively.
If you’re having trouble with this type of assignment, feel free to use our paper writing service and streamline the process.
Dissecting a text's central message and how it unfolds can be a rewarding challenge. Here's a step-by-step breakdown to conquer your next thematic essay:
If you're seeking 'someone to do my homework fast' – contact us without hesitation!

Thematic Essay Checklist
- State a focused main argument about the theme.
- Hook the reader and introduce the theme.
- Begin each with a clear topic sentence related to the theme.
- Use specific examples, quotes, or facts.
- Explain how the evidence supports the thesis.
- Link analysis back to the central theme throughout.
- Ensure paragraphs and ideas progress logically.
- Summarize key points and restate the thesis.
- Check for clarity, coherence, and grammar.
- Properly cite sources used.
How to Pick a Thematic Topic
A crucial aspect of writing a good thematic essay is choosing a theme. Follow the hints listed below to help you create a thematic topic:
Thematic Essay Topics
Picking the right theme for your essay can really shape how engaging and insightful it turns out. The topic you choose will guide your whole approach, letting you dive deep into meaningful ideas that connect with your readers.
To help you get started, here are some thematic essay topics that offer plenty of room for exploration:
- Star-Crossed Fate: Destiny in "Romeo and Juliet"
- Gatsby's Illusion: The Mirage of the American Dream
- Thoreau's Call to Action: Civil Disobedience and Its Echoes
- Grit and Grind: Industrial Strife in "Hard Times"
- Monster or Man? Isolation in "Frankenstein"
- Voices of Change: The Civil Rights Movement Unveiled
- Big Brother's Watch: Propaganda in "1984"
- Silent Scars: The Aftermath of War in "All Quiet on the Western Front"
- Pride, Prejudice, and Power: Women in Austen's World
- Cultural Cracks: Colonialism in "Things Fall Apart"
- Echoes of Justice: Moral Struggles in "To Kill a Mockingbird"
- Surviving Hard Times: Life During the Great Depression
- Invisible Chains: Identity in "Invisible Man"
- Worlds Apart: Control and Conformity in "Brave New World"
- Chains of Oppression: Freedom in "Uncle Tom's Cabin"
- Hester's Burden: Sin and Redemption in "The Scarlet Letter"
- Wired Society: The Tech Revolution's Impact
- Vengeance and Virtue: The Journey in "The Count of Monte Cristo"
- Island Power Struggles: Leadership in "Lord of the Flies"
- Dreams of Freedom: Martin Luther King Jr.'s Enduring Impact
- Survival and Humanity: The Struggle in "The Road"
- The Power of Words: Propaganda in "Animal Farm"
- Isolation and Madness: The Descent in "The Yellow Wallpaper"
- Social Class and Ambition: The Divide in "Great Expectations"
- The Burden of Guilt: Consequences in "Crime and Punishment"
- The Quest for Freedom: Oppression in "The Handmaid’s Tale"
- Family Ties: Loyalty and Betrayal in "King Lear"
- The Corruption of Power: Greed in "The Lord of the Rings"
- The American Dream: Reality vs. Illusion in "Death of a Salesman"
- War and Its Aftermath: Trauma in "The Things They Carried"
How to Start a Thematic Essay
Knowing how to start a thematic essay is key to setting the right tone for your entire paper. Every strong thematic essay begins with a captivating introduction that grabs the reader's attention right from the start:
- Hook the reader: Grab their attention with a thought-provoking question, a relevant quote, or an interesting anecdote related to the theme.
- Introduce the topic: Briefly mention the literary work you'll be analyzing.
- State the theme: Clearly identify the central theme you'll be exploring.
- Preview the analysis: Briefly hint at how the theme is developed in the work.
Here's an example of a thematic essay introduction:
“Have you ever wondered why some stories keep coming back to the idea of forgiveness? In Harper Lee's classic novel To Kill a Mockingbird , the seemingly simple town of Maycomb grapples with racial injustice. However, beneath the surface lies a powerful exploration of the theme of forgiveness, where characters must confront their own prejudices and learn to let go of resentment. This essay will analyze how Lee uses character interactions, symbolism, and the trial of Tom Robinson to demonstrate the transformative power of forgiveness.”
Feeling difficult to write a thematic essay? Leave us notice, and our persuasive essay writer we'll help.
Let our custom essay writing service do all the work for you. Check out our price calculator to estimate the cost of your assignment.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Need Help with a Thematic Essay?
Understanding the central themes of literary works is quite hard, so let our writers show you how it’s done!
Thematic Essay Outline
A thematic essay structure has several key components. Primarily, it should be five paragraphs or more, depending on the depth of the theme. Next, it should have a concrete thesis statement, which is the thematic statement that comes from the main subject.
The introduction presents the reader with the subject and the thesis statement. The body paragraphs each discuss one literary element or more to defend the validity of your thesis, all the while providing many supporting details from the text itself.
Lastly, the thematic essay conclusion summarizes the main points presented and finishes off with a statement of significance.
Learn more: How to create a winning outline .
Introduction
When you sit down to write a thematic essay, it’s good to start by laying out the basics: What is a thematic essay? It’s an essay where you dig into a specific theme and explore it from different angles within a text.
The thematic essay introduction presents the main subject of discussion captivatingly. The first sentence of the intro should be a hook statement that makes some intriguing claims about the subject of discussion. If done correctly, this will grab your reader's attention.
As you start your essay, try to catch your reader’s attention with something that ties directly into your theme, like a quote. For instance, if you're focusing on the theme of identity in To Kill a Mockingbird , you might use a quote like, “You never really understand a person … until you climb into his skin and walk around in it.”
This not only sets the tone but also smoothly leads into your thematic thesis statement. Keep things clear and straightforward so your readers know exactly what theme you’ll be diving into.
Then, provide any necessary background information from the literature to help the audience understand your claims later. Lastly, put together a well-thought-out thesis statement that reflects the novel's central theme.
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs follow a thematic essay format. Since each body paragraph’s purpose should be to present a literary device as evidence, the topic sentence should introduce the claim and gateway into the evidence. Every topic sentence must mention a literary device and its relationship to the literature.
When you’re writing the body of your thematic essay, you’ve got some flexibility. You can use two, three, or even four paragraphs — whatever it takes to cover your theme without dragging things out. Just make sure everything you include is relevant and adds value to your argument.
Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that gets straight to the point. Stick to the facts and avoid slipping in personal opinions. For example, if you’re exploring the theme of justice in To Kill a Mockingbird , mention specific events like Tom Robinson’s trial, focusing on the key details and backing them up with evidence from the text.
Make sure to explain and analyze the points you bring up. Help your readers understand why these details matter. For instance, you could discuss how the trial scene highlights the deep-rooted racial inequalities of the time, making the theme of justice clear and powerful.
The key to a strong thematic essay structure is thoroughly evaluating your main points. This will help you build a strong case for your thesis.
Afterward, to validate your claim, use examples from the book that strengthen the reasoning of your statement. These can be actions from the plot or quotations parallel with the central theme. Explaining how the action/quote links back to your thesis statement is imperative, as it shows that you can support your logic.
Remember : Each claim must use a literary device. It can not just be a random moment or inference. Thematic essays are all about proving thesis statements through critical literary devices.
The thematic essay conclusion has three main objectives before wrapping up the paper. It should not present any new information or facts but summarize the information already given. First of all, restate your thesis statement in a new way.
Then, summarize the central claims you made within the body of your paper and their influence on the thesis statement. To finish off the entire work, present an overall concluding statement with a global analysis of the subject. Leave your reader with another hook, making him/her interested in digging deeper into the topic.
Proofreading and Taking Advice
Once you’ve wrapped up writing your thematic essays, it’s time to give them a good review.
Start by going through your essay carefully, checking it against the rubric your professor gave you. For example, if your essay is on the theme of power in 1984 , make sure every point you’ve made is backed by solid evidence from the text and that it fits what the rubric asks for.
Next, get a second opinion. Ask a friend or classmate to read your essay. They might catch something you missed, like a theme that needs more explanation or an example that doesn’t quite hit the mark.
Don’t be shy about asking your teacher for feedback, too. They can offer valuable advice, especially if they know the theme well. This step is all about crafting your essay as strong and clear as possible. It’s easier to cut down extra details later, so don’t be afraid to add more substance where needed.
Learn more: Poetry analysis essay .
Try also read an article on poetry analysis essay , it could be useful and can give you new insights.
Thematic Essay Example: How to Write Guide
The best way to familiarize yourself with this type of writing is to learn from thematic essay examples. In this section, we’re going to walk you through how to craft an essay using a real example. By breaking down the steps and showing you exactly how it’s done, this thematic essay example will give you a clear idea of how to approach your own essay.
Thematic Essay Introduction
When figuring out how to write a thematic essay, starting with a solid introduction is crucial. A solid thematic essay introduction should introduce the theme, give some background, and present your thesis in a way that’s easy to follow.
Let’s say you’re writing about Athens and Sparta.
- You’d want to kick things off by briefly mentioning that these two ancient Greek cities, though close in distance, were worlds apart in terms of culture, lifestyle, and politics. This sets the scene and lets your readers know what to expect.
- Next, you’ll want to give a bit of background to help your readers understand why this comparison is significant. You might explain how the differences between Athens and Sparta shaped their citizens' lives and left a lasting mark on Western civilization. This gives context to the discussion that will follow in the body of your essay.
- Finally, wrap up your introduction with your thesis statement—the main point you’ll be arguing throughout the essay. For the Athens vs. Sparta example, your thesis could focus on how their differing values and political systems influenced their historical legacy.
Thematic Essay Main Body
The main body of your essay is where you really get into the heart of your argument. This is the part where you present the evidence that supports your thesis, using facts, examples, and analysis to make your points clear and convincing.
Let’s break down how to structure this section with the Athens vs. Sparta example, while following a strong thematic essay format.
- Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that connects directly to your thesis. For instance, if you’re focusing on the different political systems in Athens and Sparta, you might begin with something like, “One of the key differences between Athens and Sparta was how they governed their citizens.”
- After setting up the main idea of the paragraph, back it up with specific evidence. You could explain how Athens operated under a democratic system, where citizens had a voice in government decisions. In contrast, Sparta was more oligarchic, with two kings holding power.
- Once you’ve laid out the evidence, take a moment to analyze it. Show how these differences in governance reflected the broader values of each city-state and contributed to their unique identities. This is where you connect the dots and demonstrate how the details support your overall thesis.
Thematic Essay Conclusion
Wrapping up your thematic essay is about bringing your ideas full circle and reinforcing the points you've made throughout the paper. A good thematic essay conclusion should tie everything together, restate your thesis with the insights gained, and leave your reader with a strong final thought.
- Start by briefly going over the main points you made in your essay. Think of this as a quick reminder for the reader about what you’ve covered. For example, if your essay compared Athens and Sparta, you’d mention how their different political systems and values shaped their cultures and identities.
- Next, take your original theme thesis and rephrase it to reflect what you’ve discussed. Don’t just repeat your thesis word-for-word but show how your essay has proven it. For example, you might say, “The unique political and cultural systems of Athens and Sparta not only defined their societies but also left a lasting mark on Western civilization.”
- End with a closing thought that ties everything together. It could be a reflection on why these themes are still relevant today or just a simple statement that emphasizes the importance of what you’ve discussed.
Wrap Things Up
Thematic essays are a powerful tool for students. They unlock deeper meaning in texts, sharpen critical thinking and analytical skills, and build strong writing foundations.
Writing thematic essays doesn’t have to be complicated. Start by choosing a theme that resonates with you, then structure your essay with a clear introduction, detailed body paragraphs, and a strong conclusion. Use evidence from your text to support your thesis and make sure to review your work for clarity and flow. Finally, don’t forget to check your citations and formatting.
Before submitting your thematic essay, cross off all these items from the to-do list.
Learn more: Jem Finch character traits .
Got Little Time Left Until Submission?
Use our service to obtain a first-class thematic essay overnight.
What Is a Thematic Essay?
How to write a thematic essay, what is the main point of a thematic essay.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

- Updated writing steps.
- Added new topics.
- Added a new example.
- Added a checklist.
- https://www.wboro.org/cms/lib/NY01914047/Centricity/Domain/1006/Thematic%20Essays%20Helpful%20Hints.pdf
- Thematic Essay - Regents Exam Rubric | New Visions - Social Studies. (n.d.). New Visions - Social Studies. https://curriculum.newvisions.org/social-studies/resources/resource/thematic-essay-regents-exam-rubric/
- How to Structure Your Essay Introduction | Essay Writing Part 2. (2023, October 31). Matrix Education. https://www.matrix.edu.au/essay-writing-guide/how-to-structure-your-essay-introduction/
.webp)
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Thematic Analysis – A Guide with Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 16th, 2021 , Revised On August 29, 2023
Thematic analysis is one of the most important types of analysis used for qualitative data . When researchers have to analyse audio or video transcripts, they give preference to thematic analysis. A researcher needs to look keenly at the content to identify the context and the message conveyed by the speaker.
Moreover, with the help of this analysis, data can be simplified.
Importance of Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis has so many unique and dynamic features, some of which are given below:
Thematic analysis is used because:
- It is flexible.
- It is best for complex data sets.
- It is applied to qualitative data sets.
- It takes less complexity compared to other theories of analysis.
Intellectuals and researchers give preference to thematic analysis due to its effectiveness in the research.
How to Conduct a Thematic Analysis?
While doing any research , if your data and procedure are clear, it will be easier for your reader to understand how you concluded the results . This will add much clarity to your research.
Understand the Data
This is the first step of your thematic analysis. At this stage, you have to understand the data set. You need to read the entire data instead of reading the small portion. If you do not have the data in the textual form, you have to transcribe it.
Example: If you are visiting an adult dating website, you have to make a data corpus. You should read and re-read the data and consider several profiles. It will give you an idea of how adults represent themselves on dating sites. You may get the following results:
I am a tall, single(widowed), easy-going, honest, good listener with a good sense of humor. Being a handyperson, I keep busy working around the house, and I also like to follow my favourite hockey team on TV or spoil my two granddaughters when I get the chance!! Enjoy most music except Rap! I keep fit by jogging, walking, and bicycling (at least three times a week). I have travelled to many places and RVD the South-West U.S., but I would now like to find that special travel partner to do more travel to warm and interesting countries. I now feel it’s time to meet a nice, kind, honest woman who has some of the same interests as I do; to share the happy times, quiet times, and adventures together
I enjoy photography, lapidary & seeking collectibles in the form of classic movies & 33 1/3, 45 & 78 RPM recordings from the 1920s, ’30s & ’40s. I am retired & looking forward to travelling to Canada, the USA, the UK & Europe, China. I am unique since I do not judge a book by its cover. I accept people for who they are. I will not demand or request perfection from anyone until I am perfect, so I guess that means everyone is safe. My musical tastes range from Classical, big band era, early jazz, classic ’50s & 60’s rock & roll & country since its inception.
Development of Initial Coding:
At this stage, you have to do coding. It’s the essential step of your research . Here you have two options for coding. Either you can do the coding manually or take the help of any tool. A software named the NOVIC is considered the best tool for doing automatic coding.
For manual coding, you can follow the steps given below:
- Please write down the data in a proper format so that it can be easier to proceed.
- Use a highlighter to highlight all the essential points from data.
- Make as many points as possible.
- Take notes very carefully at this stage.
- Apply themes as much possible.
- Now check out the themes of the same pattern or concept.
- Turn all the same themes into the single one.
Example: For better understanding, the previously explained example of Step 1 is continued here. You can observe the coded profiles below:
Make Themes
At this stage, you have to make the themes. These themes should be categorised based on the codes. All the codes which have previously been generated should be turned into themes. Moreover, with the help of the codes, some themes and sub-themes can also be created. This process is usually done with the help of visuals so that a reader can take an in-depth look at first glance itself.
Extracted Data Review
Now you have to take an in-depth look at all the awarded themes again. You have to check whether all the given themes are organised properly or not. It would help if you were careful and focused because you have to note down the symmetry here. If you find that all the themes are not coherent, you can revise them. You can also reshape the data so that there will be symmetry between the themes and dataset here.
For better understanding, a mind-mapping example is given here:
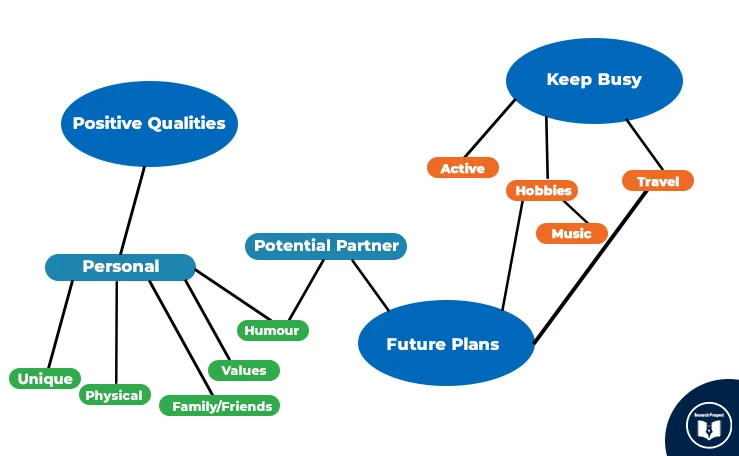
Reviewing all the Themes Again
You need to review the themes after coding them. At this stage, you are allowed to play with your themes in a more detailed manner. You have to convert the bigger themes into smaller themes here. If you want to combine some similar themes into a single theme, then you can do it. This step involves two steps for better fragmentation.
You need to observe the coded data separately so that you can have a precise view. If you find that the themes which are given are following the dataset, it’s okay. Otherwise, you may have to rearrange the data again to coherence in the coded data.
Corpus Data
Here you have to take into consideration all the corpus data again. It would help if you found how themes are arranged here. It would help if you used the visuals to check out the relationship between them. Suppose all the things are not done accordingly, so you should check out the previous steps for a refined process. Otherwise, you can move to the next step. However, make sure that all the themes are satisfactory and you are not confused.
When all the two steps are completed, you need to make a more précised mind map. An example following the previous cases has been given below:
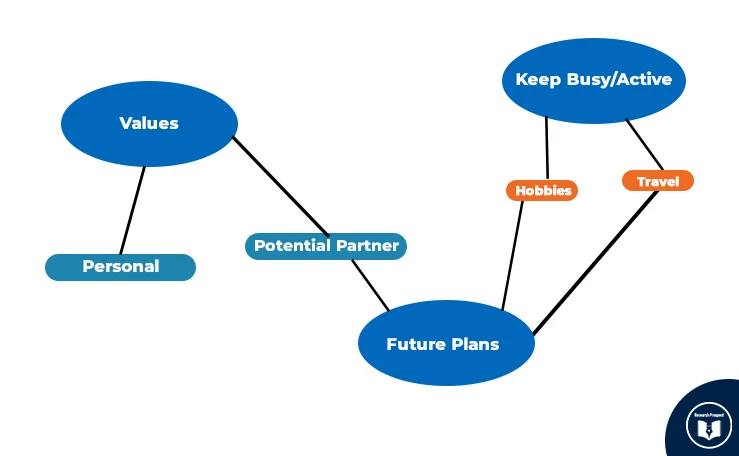
Define all the Themes here
Now you have to define all the themes which you have given to your data set. You can recheck them carefully if you feel that some of them can fit into one concept, you can keep them, and eliminate the other irrelevant themes. Because it should be precise and clear, there should not be any ambiguity. Now you have to think about the main idea and check out that all the given themes are parallel to your main idea or not. This can change the concept for you.
The given names should be so that it can give any reader a clear idea about your findings. However, it should not oppose your thematic analysis; rather, everything should be organised accurately.
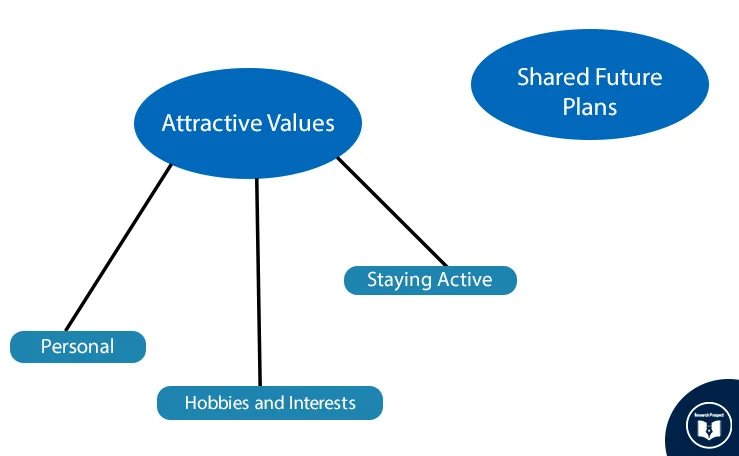
Does your Research Methodology Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Research Methodology strong.

Also, read about discourse analysis , content analysis and survey conducting . we have provided comprehensive guides.
Make a Report
You need to make the final report of all the findings you have done at this stage. You should include the dataset, findings, and every aspect of your analysis in it.
While making the final report , do not forget to consider your audience. For instance, you are writing for the Newsletter, Journal, Public awareness, etc., your report should be according to your audience. It should be concise and have some logic; it should not be repetitive. You can use the references of other relevant sources as evidence to support your discussion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meant by thematic analysis.
Thematic Analysis is a qualitative research method that involves identifying, analyzing, and interpreting recurring themes or patterns in data. It aims to uncover underlying meanings, ideas, and concepts within the dataset, providing insights into participants’ perspectives and experiences.
You May Also Like
Inductive and deductive reasoning takes into account assumptions and incidents. Here is all you need to know about inductive vs deductive reasoning.
You can transcribe an interview by converting a conversation into a written format including question-answer recording sessions between two or more people.
Disadvantages of primary research – It can be expensive, time-consuming and take a long time to complete if it involves face-to-face contact with customers.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works

What Is Thematic Analysis?
Plain-Language Explanation, Definition & Examples

T hematic analysis is one of the most popular qualitative analysis techniques we see students opting for at Grad Coach – and for good reason. Despite its relative simplicity, thematic analysis can be a very powerful analysis technique when used correctly. In this post, we’ll unpack thematic analysis using plain language (and loads of examples) so that you can conquer your analysis with confidence.
Thematic Analysis 101
- Basic terminology relating to thematic analysis
- What is thematic analysis
- When to use thematic analysis
- The main approaches to thematic analysis
- The three types of thematic analysis
- How to “do” thematic analysis (the process)
- Tips and suggestions
First, the lingo…
Before we begin, let’s first lay down some terminology. When undertaking thematic analysis, you’ll make use of codes . A code is a label assigned to a piece of text, and the aim of using a code is to identify and summarise important concepts within a set of data, such as an interview transcript.
For example, if you had the sentence, “My rabbit ate my shoes”, you could use the codes “rabbit” or “shoes” to highlight these two concepts. The process of assigning codes is called qualitative coding . If this is a new concept to you, be sure to check out our detailed post about qualitative coding .
Codes are vital as they lay a foundation for themes . But what exactly is a theme? Simply put, a theme is a pattern that can be identified within a data set. In other words, it’s a topic or concept that pops up repeatedly throughout your data. Grouping your codes into themes serves as a way of summarising sections of your data in a useful way that helps you answer your research question(s) and achieve your research aim(s).
Alright – with that out of the way, let’s jump into the wonderful world of thematic analysis…
What is thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is the study of patterns to uncover meaning . In other words, it’s about analysing the patterns and themes within your data set to identify the underlying meaning. Importantly, this process is driven by your research aims and questions , so it’s not necessary to identify every possible theme in the data, but rather to focus on the key aspects that relate to your research questions .
Although the research questions are a driving force in thematic analysis (and pretty much all analysis methods), it’s important to remember that these questions are not necessarily fixed . As thematic analysis tends to be a bit of an exploratory process, research questions can evolve as you progress with your coding and theme identification.
When should you use thematic analysis?
There are many potential qualitative analysis methods that you can use to analyse a dataset. For example, content analysis , discourse analysis , and narrative analysis are popular choices. So why use thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is highly beneficial when working with large bodies of data , as it allows you to divide and categorise large amounts of data in a way that makes it easier to digest. Thematic analysis is particularly useful when looking for subjective information , such as a participant’s experiences, views, and opinions. For this reason, thematic analysis is often conducted on data derived from interviews , conversations, open-ended survey responses , and social media posts.
Your research questions can also give you an idea of whether you should use thematic analysis or not. For example, if your research questions were to be along the lines of:
- How do dog walkers perceive rules and regulations on dog-friendly beaches?
- What are students’ experiences with the shift to online learning?
- What opinions do health professionals hold about the Hippocratic code?
- How is gender constructed in a high school classroom setting?
These examples are all research questions centering on the subjective experiences of participants and aim to assess experiences, views, and opinions. Therefore, thematic analysis presents a possible approach.
In short, thematic analysis is a good choice when you are wanting to categorise large bodies of data (although the data doesn’t necessarily have to be large), particularly when you are interested in subjective experiences .
What are the main approaches?
Broadly speaking, there are two overarching approaches to thematic analysis: inductive and deductive . The approach you take will depend on what is most suitable in light of your research aims and questions. Let’s have a look at the options.
The inductive approach
The inductive approach involves deriving meaning and creating themes from data without any preconceptions . In other words, you’d dive into your analysis without any idea of what codes and themes will emerge, and thus allow these to emerge from the data.
For example, if you’re investigating typical lunchtime conversational topics in a university faculty, you’d enter the research without any preconceived codes, themes or expected outcomes. Of course, you may have thoughts about what might be discussed (e.g., academic matters because it’s an academic setting), but the objective is to not let these preconceptions inform your analysis.
The inductive approach is best suited to research aims and questions that are exploratory in nature , and cases where there is little existing research on the topic of interest.
The deductive approach
In contrast to the inductive approach, a deductive approach involves jumping into your analysis with a pre-determined set of codes . Usually, this approach is informed by prior knowledge and/or existing theory or empirical research (which you’d cover in your literature review ).
For example, a researcher examining the impact of a specific psychological intervention on mental health outcomes may draw on an existing theoretical framework that includes concepts such as coping strategies, social support, and self-efficacy, using these as a basis for a set of pre-determined codes.
The deductive approach is best suited to research aims and questions that are confirmatory in nature , and cases where there is a lot of existing research on the topic of interest.
Regardless of whether you take the inductive or deductive approach, you’ll also need to decide what level of content your analysis will focus on – specifically, the semantic level or the latent level.
A semantic-level focus ignores the underlying meaning of data , and identifies themes based only on what is explicitly or overtly stated or written – in other words, things are taken at face value.
In contrast, a latent-level focus concentrates on the underlying meanings and looks at the reasons for semantic content. Furthermore, in contrast to the semantic approach, a latent approach involves an element of interpretation , where data is not just taken at face value, but meanings are also theorised.
“But how do I know when to use what approach?”, I hear you ask.
Well, this all depends on the type of data you’re analysing and what you’re trying to achieve with your analysis. For example, if you’re aiming to analyse explicit opinions expressed in interviews and you know what you’re looking for ahead of time (based on a collection of prior studies), you may choose to take a deductive approach with a semantic-level focus.
On the other hand, if you’re looking to explore the underlying meaning expressed by participants in a focus group, and you don’t have any preconceptions about what to expect, you’ll likely opt for an inductive approach with a latent-level focus.
Simply put, the nature and focus of your research, especially your research aims , objectives and questions will inform the approach you take to thematic analysis.

What are the types of thematic analysis?
Now that you’ve got an understanding of the overarching approaches to thematic analysis, it’s time to have a look at the different types of thematic analysis you can conduct. Broadly speaking, there are three “types” of thematic analysis:
- Reflexive thematic analysis
- Codebook thematic analysis
- Coding reliability thematic analysis
Let’s have a look at each of these:
Reflexive thematic analysis takes an inductive approach, letting the codes and themes emerge from that data. This type of thematic analysis is very flexible, as it allows researchers to change, remove, and add codes as they work through the data. As the name suggests, reflexive thematic analysis emphasizes the active engagement of the researcher in critically reflecting on their assumptions, biases, and interpretations, and how these may shape the analysis.
Reflexive thematic analysis typically involves iterative and reflexive cycles of coding, interpreting, and reflecting on data, with the aim of producing nuanced and contextually sensitive insights into the research topic, while at the same time recognising and addressing the subjective nature of the research process.
Codebook thematic analysis , on the other hand, lays on the opposite end of the spectrum. Taking a deductive approach, this type of thematic analysis makes use of structured codebooks containing clearly defined, predetermined codes. These codes are typically drawn from a combination of existing theoretical theories, empirical studies and prior knowledge of the situation.
Codebook thematic analysis aims to produce reliable and consistent findings. Therefore, it’s often used in studies where a clear and predefined coding framework is desired to ensure rigour and consistency in data analysis.
Coding reliability thematic analysis necessitates the work of multiple coders, and the design is specifically intended for research teams. With this type of analysis, codebooks are typically fixed and are rarely altered.
The benefit of this form of analysis is that it brings an element of intercoder reliability where coders need to agree upon the codes used, which means that the outcome is more rigorous as the element of subjectivity is reduced. In other words, multiple coders discuss which codes should be used and which shouldn’t, and this consensus reduces the bias of having one individual coder decide upon themes.

Quick Recap: Thematic analysis approaches and types
To recap, the two main approaches to thematic analysis are inductive , and deductive . Then we have the three types of thematic analysis: reflexive, codebook and coding reliability . Which type of thematic analysis you opt for will need to be informed by factors such as:
- The approach you are taking. For example, if you opt for an inductive approach, you’ll likely utilise reflexive thematic analysis.
- Whether you’re working alone or in a group . It’s likely that, if you’re doing research as part of your postgraduate studies, you’ll be working alone. This means that you’ll need to choose between reflexive and codebook thematic analysis.
Now that we’ve covered the “what” in terms of thematic analysis approaches and types, it’s time to look at the “how” of thematic analysis.

How to “do” thematic analysis
At this point, you’re ready to get going with your analysis, so let’s dive right into the thematic analysis process. Keep in mind that what we’ll cover here is a generic process, and the relevant steps will vary depending on the approach and type of thematic analysis you opt for.
Step 1: Get familiar with the data
The first step in your thematic analysis involves getting a feel for your data and seeing what general themes pop up. If you’re working with audio data, this is where you’ll do the transcription , converting audio to text.
At this stage, you’ll want to come up with preliminary thoughts about what you’ll code , what codes you’ll use for them, and what codes will accurately describe your content. It’s a good idea to revisit your research topic , and your aims and objectives at this stage. For example, if you’re looking at what people feel about different types of dogs, you can code according to when different breeds are mentioned (e.g., border collie, Labrador, corgi) and when certain feelings/emotions are brought up.
As a general tip, it’s a good idea to keep a reflexivity journal . This is where you’ll write down how you coded your data, why you coded your data in that particular way, and what the outcomes of this data coding are. Using a reflexive journal from the start will benefit you greatly in the final stages of your analysis because you can reflect on the coding process and assess whether you have coded in a manner that is reliable and whether your codes and themes support your findings.
As you can imagine, a reflexivity journal helps to increase reliability as it allows you to analyse your data systematically and consistently. If you choose to make use of a reflexivity journal, this is the stage where you’ll want to take notes about your initial codes and list them in your journal so that you’ll have an idea of what exactly is being reflected in your data. At a later stage in the analysis, this data can be more thoroughly coded, or the identified codes can be divided into more specific ones.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Search for patterns or themes in the codes
Step 2! You’re going strong. In this step, you’ll want to look out for patterns or themes in your codes. Moving from codes to themes is not necessarily a smooth or linear process. As you become more and more familiar with the data, you may find that you need to assign different codes or themes according to new elements you find. For example, if you were analysing a text talking about wildlife, you may come across the codes, “pigeon”, “canary” and “budgerigar” which can fall under the theme of birds.
As you work through the data, you may start to identify subthemes , which are subdivisions of themes that focus specifically on an aspect within the theme that is significant or relevant to your research question. For example, if your theme is a university, your subthemes could be faculties or departments at that university.
Step 3: Review themes
By now you’ll have a good idea of your codes, themes, and potentially subthemes. Now it’s time to review all the themes you’ve identified . In this step, you’ll want to check that everything you’ve categorised as a theme actually fits the data, whether the themes do indeed exist in the data, whether there are any themes missing , and whether you can move on to the next step knowing that you’ve coded all your themes accurately and comprehensively . If you find that your themes have become too broad and there is far too much information under one theme, it may be useful to split this into more themes so that you’re able to be more specific with your analysis.

Step 4: Finalise Themes
By this point, your analysis will really start to take shape. In the previous step, you reviewed and refined your themes, and now it’s time to label and finalise them . It’s important to note here that, just because you’ve moved onto the next step, it doesn’t mean that you can’t go back and revise or rework your themes. In contrast to the previous step, finalising your themes means spelling out what exactly the themes consist of, and describe them in detail . If you struggle with this, you may want to return to your data to make sure that your data and coding do represent the themes, and if you need to divide your themes into more themes (i.e., return to step 3).
When you name your themes, make sure that you select labels that accurately encapsulate the properties of the theme . For example, a theme name such as “enthusiasm in professionals” leaves the question of “who are the professionals?”, so you’d want to be more specific and label the theme as something along the lines of “enthusiasm in healthcare professionals”.
It is very important at this stage that you make sure that your themes align with your research aims and questions . When you’re finalising your themes, you’re also nearing the end of your analysis and need to keep in mind that your final report (discussed in the next step) will need to fit in with the aims and objectives of your research.
In your reflexivity journal, you’ll want to write down a few sentences describing your themes and how you decided on these. Here, you’ll also want to mention how the theme will contribute to the outcomes of your research, and also what it means in relation to your research questions and focus of your research.

Step 5: Produce your report
You’re nearly done! Now that you’ve analysed your data, it’s time to report on your findings. A typical thematic analysis report consists of:
- An introduction
- A methodology section
- Your results and findings
- A conclusion
When writing your report, make sure that you provide enough information for a reader to be able to evaluate the rigour of your analysis. In other words, the reader needs to know the exact process you followed when analysing your data and why. The questions of “what”, “how”, “why”, “who”, and “when” may be useful in this section.
So, what did you investigate? How did you investigate it? Why did you choose this particular method? Who does your research focus on, and who are your participants? When did you conduct your research, when did you collect your data, and when was the data produced? Your reflexivity journal will come in handy here as within it you’ve already labelled, described, and supported your themes.
If you’re undertaking a thematic analysis as part of a dissertation or thesis, this discussion will be split across your methodology, results and discussion chapters . For more information about those chapters, check out our detailed post about dissertation structure .
Quick Recap: How to “do” thematic analysis
Getting familiar with your data: Here you’ll read through your data and get a general overview of what you’re working with. At this stage, you may identify a few general codes and themes that you’ll make use of in the next step.
Search for patterns or themes in your codes : Here you’ll dive into your data and pick out the themes and codes relevant to your research question(s).
Review themes : In this step, you’ll revisit your codes and themes to make sure that they are all truly representative of the data, and that you can use them in your final report.
Finalise themes : Here’s where you “solidify” your analysis and make it report-ready by describing and defining your themes.
Produce your report : This is the final step of your thematic analysis process, where you put everything you’ve found together and report on your findings.
Tips & Suggestions
In the video below, we share 6 time-saving tips and tricks to help you approach your thematic analysis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Wrapping Up
In this article, we’ve covered the basics of thematic analysis – what it is, when to use it, the different approaches and types of thematic analysis, and how to perform a thematic analysis.
If you have any questions about thematic analysis, drop a comment below and we’ll do our best to assist. If you’d like 1-on-1 support with your thematic analysis, be sure to check out our research coaching services here .

Learn More About Methodology

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Triangulation: The Ultimate Credibility Enhancer
Triangulation is one of the best ways to enhance the credibility of your research. Learn about the different options here.

Research Limitations 101: What You Need To Know
Learn everything you need to know about research limitations (AKA limitations of the study). Includes practical examples from real studies.

In Vivo Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about in vivo coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies where the nuances of language are central to the aims.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
27 Comments
I really appreciate the help
Hello Sir, how many levels of coding can be done in thematic analysis? We generate codes from the transcripts, then subthemes from the codes and themes from subthemes, isn’t it? Should these themes be again grouped together? how many themes can be derived?can you please share an example of coding through thematic analysis in a tabular format?
I’ve found the article very educative and useful
Excellent. Very helpful and easy to understand.
This article so far has been most helpful in understanding how to write an analysis chapter. Thank you.
My research topic is the challenges face by the school principal on the process of procurement . Thematic analysis is it sutable fir data analysis ?
It is a great help. Thanks.
Best advice. Worth reading. Thank you.
Where can I find an example of a template analysis table ?
Finally I got the best article . I wish they also have every psychology topics.
Hello, Sir/Maam
I am actually finding difficulty in doing qualitative analysis of my data and how to triangulate this with quantitative data. I encountered your web by accident in the process of searching for a much simplified way of explaining about thematic analysis such as coding, thematic analysis, write up. When your query if I need help popped up, I was hesitant to answer. Because I think this is for fee and I cannot afford. So May I just ask permission to copy for me to read and guide me to study so I can apply it myself for my gathered qualitative data for my graduate study.
Thank you very much! this is very helpful to me in my Graduate research qualitative data analysis.
Thank you very much. I find your guidance here helpful. Kindly let help me understand how to write findings and discussions.
i am having troubles with the concept of framework analysis which i did not find here and i have been an assignment on framework analysis
I was discouraged and felt insecure because after more than a year of writing my thesis, my work seemed lost its direction after being checked. But, I am truly grateful because through the comments, corrections, and guidance of the wisdom of my director, I can already see the bright light because of thematic analysis. I am working with Biblical Texts. And thematic analysis will be my method. Thank you.
lovely and helpful. thanks
very informative information.
thank you very much!, this is very helpful in my report, God bless……..
Thank you for the insight. I am really relieved as you have provided a super guide for my thesis.
Thanks a lot, really enlightening
excellent! very helpful thank a lot for your great efforts
I am currently conducting a research on the Economic challenges to migrant integration. Using interviews to understand the challenges by interviewing professionals working with migrants. Wouks appreciate help with how to do this using the thematic approach. Thanks
The article cleared so many issues that I was not certain of. Very informative. Thank you.
i really appreciate the learning that learned from here
This was absolutely informative! I’ll certainly be using Grad Coach often 🙂 thank you!
Hi can you use thematic analysis on two variables?

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
How to Write a Theme Essay
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A thematic essay is a type of writing assignment that focuses on a specific theme or topic. It requires you to identify a central theme, discuss it in detail, and make connections between various facts. Your main goal is to demonstrate understanding and interpretation of the given subject matter. This type of essay is commonly used in literature classes or history exams.
If you’ve got an assignment to write a theme essay, you might wonder where you should even start from. No worries, we’ve got you covered here! The first thing you must know about this specific type of paper is that it aims to analyze a certain well-known theme and make an interesting statement about it. Here, you must explain meaning and relevance or complexity of your topic. You should summarize details that support your conclusion. In this article, we will conduct a detailed review of theme essay concept. We will also provide you a step by step guide on how to write a proper one. Let's dive right into it!
Thematic Essay Definition
Let’s start with defining what is a thematic essay and its purpose. In this type, one should select a thesis and form unique statement related to its aspects. You should write about it, explaining or elaborating to your audience the following:
- How is your statement related to your topic?
- Which important or interesting aspects does it highlight?
- What approaches and literary devices are you using for analysis ? How do you explain your general theme? This can be comparison, metaphor, personification etc.
When composing such an essay, you must formulate and defend your statement. Here, you will demonstrate abilities of analysis and literary devices usage. At least several paragraphs would be needed to display such skills properly.
Thematic Essay Outline: What's Inside
The best way to begin is creating a theme essay outline for your topic. An outline should contain all key parts, concepts and ideas of your paper. You should put it in a sketchy but logical manner. This way you'll quickly prepare a shortened version of your assignment. It will also help you in reviewing it. Adding missing points and correcting significant mistakes would be easier at this early stage. Outline should include all main essay parts:
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body section
- Conclusion.
Keeping it brief, you should not provide complete sentences to describe your statements, ideas and arguments. A few words would suffice for each important point. Purpose is to make it readable for yourself! You should review it quickly and spot any inconsistencies.
How to Write a Thematic Essay Step-By-Step
Now it is time to focus on how to write a theme analysis essay – the complete text from scratch. Is your goal to impress readers and achieve a good grade? Then it is important that you create a proper essay structure template and don't lose any of your key questions! Stay methodical and keep it logical! Make sure your audience is engaged and don’t disappoint them in the end. Below we’ll provide a general idea for each step of this process.
Step 1. Define the Topic for Your Thematic Essay
When it comes to choosing among thematic essay topics, it is important that you pick an interesting and maybe even a controversial one. At the same time, make sure you can actually provide some meaningful input about it. Your assignment should impress readers with detailed analysis and its author’s writing skills. That's why your chosen topic must provide enough material for that. There is a diverse choice of topics. Choose the one you are really interested in whether it is Bullying essay or Happiness essay . If you need some ideas for great essay topics, feel free to check out our other articles.
Step 2. Create a Thematic Essay Outline
We've already covered the main points of theme essay outline concept. When writing it, include all the main parts of your future work. Keep it as short as possible, one paragraph per each key point will be enough. It isn’t even necessary to describe everything with complete sentences! A few words would suffice. Once done, review it first and make necessary corrections. It is advised to review an outline several times. That's how any noticeable gaps or mistakes would be spotted early.
Step 3. Start a Thematic Essay with a Hook
A good thematic essay introduction ought to captivate readers right from the start. That’s why it is always advised to add some ‘hook’ into it. You can begin with an unexpected statement, use wordplay or a plot twist. Then you can explain this in the main body part. This way your audience would be interested to hear those explanations. As a result, your paper will have better chances of success. Apart from that, introduction should contain the main statement and some information about its content.
Step 4. Write Body Paragraphs for Your Theme Essay
Goal of thematic essay body is to answer all the questions stated in an introduction. You must elaborate the meaning of each key idea. Finally, display your usage of literary devices, as we’ve specified earlier. Common practice is to use at least one paragraph per a literary device disclosure. Besides, the main body is the right place to use all relevant sources that can support your analysis or provide you with helpful analogies. Keep the main body logical, so that every paragraph is somehow connected to the previous and the next ones.
Step 5. Create a Thematic Essay Conclusion
A strong thematic essay conclusion should highlight all important points from tyourhe essay while avoiding adding new facts or evidence. Just restate your thesis, answer all questions and summarize your arguments. It might be also useful to leave some final note for readers with some deeper analysis of your topic. You can also highlight the need for further exploration of the chosen theme and thus to prepare readers for your future works on this topic.
Step 6. Proofread Your Thematic Analysis Essay
After completing theme essay, it is highly recommended to review it thoroughly, even several times if possible. The goal is to find mistakes and to spot logical gaps or missing details. Even best essays typically have inconsistencies left at the early stage. Taking a fresh look at your text often reveals some issues. If possible, ask your friends or colleagues to review your text. They might notice something you could not.
How to Format a Thematic Essay
When it comes to thematic essay format, you need to find out what are the requirements in your assignment or which format is common in the institution you will be presenting your essay for. In case no special requirements were made for you, just choose one of the most popular formats for scholarly papers:
- APA paper format : typically used in natural sciences, education and psychology fields
- MLA: typically used for works in humanities
- Chicago: typically used in business, history, and fine arts fields.
Thematic Essay Example
Let’s illustrate the explanations above with a few theme essay examples. We’ll provide some real ones here so that your every question would be answered. Hopefully you’ll find some inspiration in these examples for your own winning paper! The examples can be found below. Please scroll down to find them.
Thematic Essay: Final Thoughts
In this article we have explored the theme essay concept in detail. Its central purpose and main definition were examined and a step by step guide for writing a strong one was suggested. We’ve also provided a few working examples for your convenience. Hopefully, all this information will be useful for your scholarly endeavors!
Feel free to check out our paper writing services ! We’ve got a team of skilled writers with expertise in different literary areas, ready to help you. They deliver high quality content, always on time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Theme Essay
1. what is the thematic statement.
A thematic statement typically takes the place of a thesis in a thematic essay. It consists of 1-2 complete sentences that express a theme which you have chosen for your work. This statement must convey the main message and also show what analysis will be done. It should be brief however as most of the details are to be provided in the main body.
2. What is the goal of thematic essay?
The thematic essay goal is to express an idea or some insights about the surrounding world and to change readers' minds about certain issues. As an author, you are expected to illustrate the team, provide all necessary explanations and conduct an analysis if needed. Besides, you typically should demonstrate familiarity with some literary interpretations and methods which are used to examine your theme.
3. How long should a theme essay be?
The minimum length of a theme essay is five paragraphs. One is for introduction, one for conclusion and remaining three for the main body. Of course, it can be more than that, depending on the depth of the theme that was chosen. The main rule is to keep your essay logical and concise, avoiding adding too many details. Otherwise your audience might get tired and the effect produced by your writing would be damaged.
4. What is a thematic essay history?
Thematic essay (history class) should be written to analyze some historical facts or significance of specific literary pieces. A typical case is examining different aspects of a controversial leader from the past or a political event that has produced a number of various important consequences. Or you might argue about a specific role of a certain book during a certain period or its influence on different nations or cultural groups.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

How to Write a Thematic Essay with an Example

Samuel Gorbold
A thematic essay is a piece of writing that explores a central idea or theme that is common to multiple texts. To write it, you need to carefully analyze the texts, identify the theme, and develop a strong argument.
This article will explain what is a thematic essay and provide you with a step-by-step guide to writing one. We will cover everything from choosing a theme to revising and editing your final draft. If you're still struggling with your thematic essay after reading this article, EssayHub is your go-to resource for expert help. Remember, our team of skilled writers can tackle any essay, big or small - all you have to do is to just ask - write my essays online .
How to Write a Thematic Essay?
A thematic essay requires careful analysis and thoughtful interpretation. Follow these steps to craft an essay that effectively explores the theme of your chosen texts.
1. Choose a Theme
- Identify common elements: Look for recurring themes, symbols, motifs, or characters that appear across the texts.
- Consider the author's intent: Think about what the author might be trying to convey through these elements.
2. Analyze the Texts
- Gather evidence: Collect specific quotes, examples, and details from the texts that support your chosen theme.
- Analyze the evidence: Explain how these examples illustrate the theme and contribute to the overall meaning of the texts.
3. Develop a Thesis Statement
- Create a clear and concise statement: Your thesis statement should express the central idea of your essay and outline the main points you will discuss.
- Make a claim: Your thesis should go beyond simply stating the theme; it should make a claim about how the theme is significant or relevant.
4. Organize Your Essay
- Create a strong introduction: Your introduction should grab the reader's attention, provide necessary background information, and present your thesis statement.
- Develop your body paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of your thesis statement, providing evidence and analysis to support your argument.
- Write a conclusion: Your conclusion should summarize your main points and restate your thesis in a new way.
5. Revise and Edit
- Check for clarity and coherence: Make sure your ideas are clearly expressed and logically connected.
- Proofread for errors: Correct any grammatical, spelling, or punctuation mistakes.

How to Start a Thematic Essay?
The thematic essay introduction should provide necessary background information and clearly present your thesis statement. Here are some tips for writing a strong introduction:
- Hook the Reader: To effectively write a thematic essay introduction, pose a question that relates to your theme and makes the reader curious. Alternatively, share a brief story or illustration that connects to your theme and captures the reader's attention.
- Provide Necessary Background: Briefly mention the titles and authors of the works you will be analyzing. Afterward, give a brief overview of the historical, cultural, or social context of the texts if relevant.
- Present Your Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement should express the central idea of your essay. It should go beyond simply stating the theme and make a claim about how the theme is significant or relevant.
Example Introduction:
Theme: The theme of the corrupting influence of power is explored in both "Animal Farm" by George Orwell and "Lord of the Flies" by William Golding.
Introduction:
The abuse of power is a timeless theme that has been explored in countless works of literature. George Orwell's "Animal Farm" and William Golding's "Lord of the Flies" both delve into the destructive consequences of unchecked authority. In "Animal Farm," the pigs, who initially represent the ideals of equality and fairness, gradually become tyrannical dictators. Similarly, in "Lord of the Flies," the boys' descent into savagery is fueled by their struggle for dominance and control. By examining these texts, we can gain a deeper understanding of the human tendency to succumb to the temptations of power and the devastating consequences that can result.

Thematic Essay Outline
Once you have a strong thesis statement, it's time to organize your ideas into a coherent thematic essay structure. An outline will help you structure your essay and ensure that all of your points are relevant and well-supported. Let's consider this example outline:
- Theme: The corrupting influence of power in "Animal Farm" and "Lord of the Flies"
- Hook: Quote about the dangers of unchecked power
- Background information on the novels
- Thesis statement: Both "Animal Farm" and "Lord of the Flies" explore the corrupting influence of power, demonstrating how unchecked authority can lead to tyranny and violence.
- Topic sentence: In "Animal Farm," the pigs gradually become tyrannical dictators.
- Evidence: Cite specific examples of the pigs' abuse of power.
- Analysis: Explain how the pigs' actions demonstrate the corrupting influence of power.
- Transition: Similarly, in "Lord of the Flies," the boys' descent into savagery is fueled by their struggle for dominance.
- Evidence: Cite specific examples of the boys' violent behavior.
- Analysis: Explain how the boys' actions demonstrate the corrupting influence of power.
- Topic sentence: Both novels explore the theme of the loss of innocence.
- Evidence: Cite specific examples of characters losing their innocence.
- Analysis: Explain how the loss of innocence is connected to the corrupting influence of power.
- Restatement of thesis
- Summary of main points
- Final thought: The corrupting influence of power is a timeless theme that has relevance in today's world.
Thematic Essay Format
The format of your thematic essay should be clear, consistent, and easy to follow. Here are some guidelines to keep in mind:
Thematic Essay Example
We've crafted a thematic essay example to illustrate the principles discussed in the previous sections. It's a great way to learn how to structure your own essay and make a strong argument.
Final Thoughts
To summarize, writing a thematic essay involves several key steps:
- Identifying a common theme across multiple texts.
- Gathering and analyzing evidence to support your theme.
- Crafting a clear thesis statement.
- Organizing your essay with a strong introduction, well-developed body paragraphs, and a compelling conclusion.
- Revising and editing for clarity, coherence, and accuracy.
If you're struggling with your thematic essay, we can provide expert guidance and support. Don't forget, our team of writers can help you with any type of essay, from argumentative to expository.
.png)
How to Write a Good Hook for a Thematic Essay?
What is the point of a thematic essay, how do you start a thematic essay.
Samuel Gorbold , a seasoned professor with over 30 years of experience, guides students across disciplines such as English, psychology, political science, and many more. Together with EssayHub, he is dedicated to enhancing student understanding and success through comprehensive academic support.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
Student Examples of Good Practice
Sometimes it’s good to know what ‘doing a good job’ looks like… To help those wanting to understand what describing the reflexive TA process well might look like, we offer some good examples here, from student projects. This may be particularly helpful for students doing research projects, and for people very well-trained in positivism.
As well as the example(s) we provide here, you can find a much more detailed discussion in our book Thematic Analysis: A Practical Guide (SAGE, 2022).
Suzy Anderson (Professional Doctorate)
The following sections are by Suzy Anderson, from her UWE Counselling Psychology Professional Doctorate thesis – The Problem with Picking: Permittance, Escape and Shame in Problematic Skin Picking.
An example of a description of the thematic analysis process:
Process of Coding and Developing Themes
Coding and analysis were guided by Braun and Clarke’s (2006, 2013) guidelines for using thematic analysis. Each stage of the coding and theme development process described below was clearly documented ensuring that the evolution of themes was clear and traceable. This helped to ensure research rigour and means that process and dependability may be demonstrable.
I familiarised myself with the data by reading the transcripts several times while making rough notes. As data collection took place over a protracted period of time, coding of transcribed interviews began before the full dataset was available. Transcripts were read line-by-line and initial codes were written in a column alongside the transcripts. These codes were refined and added to as interviews were revisited over time. Throughout this process I was careful to note and re-read areas of relatively sparse coding to ensure they were not neglected. My supervisor also independently coded three of the interviews for purposes of reflexivity, providing an interesting alternative standpoint. I cross-referenced our two perspectives to notice and reflect on our differences of perspective.
Once initial coding was complete, I looked for larger patterns across the dataset and grouped the codes into themes (Braun & Clarke, 2006). I found it helpful to think of the theme titles as spoken in the first person, and imagine participants saying them, to check whether they reflected the dataset and participants’ meanings. I tried not to have my coding and themes steered by ideas, categories and definitions from previous research, to allow a more inductive, data-driven approach, while recognising my role as researcher in co-creation of themes (Braun & Clarke, 2013). However, there were times when the language of previous research appeared a good fit, such as in the discussion of ‘automatic’ and ‘focussed’ picking. Given that the experience of SP is an under-researched area, particularly from a qualitative perspective, and that the aim is for this study to contribute to therapeutic developments, themes were developed with the entire dataset in mind (Braun & Clarke, 2006), such that they would more likely be relevant to someone presenting in therapy for help with SP. There was clear heterogeneity in the interviews, and in cases where I have taken a narrower perspective on an experience (such as when describing an experience only true for some of the participants), I have tried to give a loose indication of prevalence and alternative views.
I created a large ‘directory’ of themes and smaller sub-themes, with the relevant participant quotations filed under each theme or sub-theme heading. This helped me to adjust theme titles, boundaries and position, meant that I could check that themes were faithful to the data at a glance, and was of practical help when writing the analysis.
The process of coding and developing themes was intended to have both descriptive and interpretive elements (using Braun & Clarke’s definitions, 2013). The descriptive element was intended to represent what participants said, while the interpretative element drew on my subjectivity to consider less directly evident patterns, such as those that might be influenced by social context or forces such as shame. This interpretation was of particular value to the current study as participants often struggled to find words for their experience and several reported or implied that they did not understanding the mechanisms of their picking. An interpretative stance meant that I could develop ideas about what they were able to describe and consider the relationships between these experiences, making sense of them alongside previous literature (Braun & Clarke, 2006). Writing was considered an integral part of the analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2013) and it helped me to adjust the boundaries of themes, notice more latent patterns and considered how themes and their content were related.
Given the known heterogeneity of picking I was keen to make sure my analysis did not become skewed towards one type of SP experience to the detriment of another. I actively looked for participant experiences that diverged from those of the developing themes (with similar intentions to a ‘deviant case analysis’; Lincoln & Guba, 1985) so that the final analysis would represent themes in context and with balance. When adding quotations to the prose of my analysis I re-read them in their original context to ensure that my representation of their words appeared to be a credible reflection of what was said.
An example of researcher reflexivity in relation to analysis process
Subjectivity as a Resource
I considered my subjectivity to be a resource when conducting interviews and analysing data (Gough & Madill, 2012). It guided my judgement when interviewing, helping me to respond to participants’ explicit, implicit and more verbally concealed distress. I allowed aspects of my own experience to resonate with those of participants meaning that I could listen to their stories with empathy and a genuine curiosity. During analysis, themes were actively created and categorised, demanding my use of self (DeSantis & Ugarriza, 2000). I sought to interpret the data rather than simply describe it, which necessarily requires acknowledgement of both researcher and participant subjectivity. I strongly feel that we can only make sense of another’s story by relating it to our own phenomenology (Smith & Shinebourne, 2012), and that we re-construct their stories on frameworks formed by our own subjective experience. As such it is useful to be aware of my personal experiences and assumptions.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3 (2), 77-101.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: A practical guide for beginners. Sage.
DeSantis, L., & Ugarriza, D. N. (2000). The concept of theme as used in qualitative nursing research. Western Journal of Nursing Research, 22 (3), 351-372.
Gough, B., & Madill, A. (2012). Subjectivity in psychological research: From problem to prospect. Psychological Methods, 17 (3), 374-384.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Establishing trustworthiness. Naturalistic Inquiry, 289 (331), 289-327.
Smith, J. A., & Shinebourne, P. (2012). Interpretative phenomenological analysis. In H. Cooper, P. M. Camic, D. L. Long, A. T. Panter, D. Rindskopf, & K. J. Sher (Eds.), APA handbook of research methods in psychology, Vol. 2. Research designs: Quantitative, qualitative, neuropsychological, and biological (p. 73–82). American Psychological Association.
Gina Broom (Research Master's)
The following extract is by Gina Broom, from her University of Auckland Master’s thesis (2020): “Oh my god, this might actually be cheating”: Experiencing attractions or feelings for others in committed relationships .
A detailed description of reflexive TA analytic approach and process
I analysed data through a process of reflexive thematic analysis (reflexive TA), as outlined by Braun, Clarke, Hayfield, and Terry (2019), who describe reflexive TA as a method by which a researcher will “explore and develop an understanding of patterned meaning across the dataset” with the aim of producing “a coherent and compelling interpretation of the data, grounded in the data” (p. 848). I utilized Braun and colleagues’ reflexive approach to TA, as opposed to alternative models of TA, due to my alignment with critical qualitative research. I did not select a c oding reliability TA approach, for example, due to its foundation of (post)positivist assumptions and processes (such as predetermined hypotheses, the aim of discovering ‘accurate’ themes or “domain summaries”, and efforts to ‘remove’ researcher bias while evidencing reliability/replicability), which were not suitable for the critical realist epistemology underpinning this thesis. In contrast, Reflexive TA is a ‘Big Q’ qualitative approach, constructing patterns of meaning as an ‘output’ from the data (rather than as predetermined domain summaries) while valuing “researcher subjectivity as not just valid but a resource” (Braun et al., 2019, p. 848). As the critical realist and feminist approaches of this thesis theorize knowledge as contextual, subjective, and partial, with reflexivity valued as a crucial process, a reflexive TA was the most appropriate method for this analysis.
Braun and colleagues’ (2019) reflexive TA process involves six-phases, including familiarization with the data, generating codes, constructing themes, revising and defining themes, and producing the report of the analysis. I outline my process for each of these below:
Phase 1, familiarization: Much of my initial engagement with the data was done through my transcription of the interviews, as the process provided extended time with each interview, both listening to the audio of the participant, and in the writing of the transcript. Some qualitative researchers describe transcription as an essential process for a researcher to perform themselves, as “transcribing discourse, like photographing reality, is an interpretive practice” (Riessman, 1993, p. 13), and as a result, “analysis begins during transcription” (Bird, 2005, p. 230). Braun and Clarke (2012) suggest certain questions to consider during the process of familiarization: “How does this participant make sense of their experiences? What assumptions do they make in interpreting their experience? What kind of world is revealed through their accounts?” (p. 61). During transcription, I took notes of potential points of interest for the analysis, using these types of questions as a guide. In exploring attractions or feelings for others in committed relationships, these questions (and my notes) often related to the meaning participants applied to their feelings and relationships, particularly in terms of morality and social acceptability, while the ‘world’ of their accounts was conveyed through their discourse of the contemporary relational context.
Phase 2, generating initial codes : Following transcription, I systematically coded each interview, searching for instances of talk that produced snippets of meaning relevant to the topic of attractions or feelings for others. I coded interviews using the ‘comment’ feature in the Microsoft Word document of each transcript, highlighting the relevant text excerpt for each code comment. I used this approach, rather than working ‘on paper’, so that I would later be able to easily export my coded excerpts for use in my theme construction. The coding of thematic analysis can be either an inductive ‘bottom up’ approach, or a deductive or theoretical ‘top down’ approach, or a combination of the two, depending on the extent to which the analysis is driven by the content of the data, and the extent to which theoretical perspectives drive the analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006, 2013). Coding can also be semantic , where codes capture “explicit meaning, close to participant language”, or latent , where codes “focus on a deeper, more implicit or conceptual level of meaning” (Braun et al., 2019, p. 853). I used an inductive approach due to the need for exploratory research on experiences attractions or feelings for others, as it is a relatively new topic without an existing theoretical foundation. The focus of my coding therefore developed throughout the process of engaging with the data, focusing on segments of participants’ meaning-making in relation to general, personal, or partner-centred experiences of: attractions or feelings for others in the contemporary relational context, implied moral and/or social acceptability (or unacceptability), related affective experiences and responses, and enacted or recommended management of attractions or feelings for others. At the beginning of the process, I mostly noted semantic codes such as ‘feels guilty about attractions or feelings for others’, particularly as my coding was exploratory and inductive, rather than guided by a knowledge of ‘deeper’ contextual meaning. As I progressed, however, I began to notice and code for more latent meanings, such as ‘love = effortless emotional exclusivity’ or ‘monogamy compulsory/unspoken relationship default’. When all interviews had been systematically and thoroughly coded (and when highly similar codes had been condensed into single codes), I had a final list of roughly 200 codes to take into the next phase of analysis.
Phase 3, constructing themes : When developing my initial candidate themes, I utilized the approach described by Braun and colleagues (2019) as “using codes as building blocks”, sorting my codes into topic areas or “clusters of meaning” (p. 855) with bullet-point lists in Microsoft Word. From this grouping of codes, I produced and refined a set of candidate themes through visual mapping and continuous engagement with the data. These candidate themes were grouped into two overarching themes: the first encompassed 2 themes and 6 sub-themes evidencing pervasive ‘traditional’ conceptions of committed relationships (as monogamous by default with an assumption of emotionally exclusivity), and the way attractions or feelings for others were positioned as an unexpected threat within this context; the second encompassed four themes and eight sub-themes exploring modern contradictions (which problematized the quality of the relationship or the ‘maturity’ of those within it, rather than the attractions or feelings), and the way attractions or feelings for others were positioned as ‘only natural’ or even positive agents of change. This process of candidate theme development was still explorative and inductive, as I worked closely with the coded data and had only brief engagement with potentially relevant theoretical literature at this stage. Further engagement with contextually relevant literature, and a deductive integration of it into the analysis, was developed in the next phases.
Phases 4 and 5, revising and defining themes : My process of revising and defining themes started by using a macro (that was developed for this project) to export all of my initial codes and their associated excerpts into a single master sheet in Microsoft Excel, with columns indicating the source interview for each excerpt, as well as relevant participant demographic information (e.g. age, gender, relationship as monogamous or non-monogamous). This master sheet contained 6006 coded excerpts. In two new columns (one for themes and one for sub-themes), I ‘tagged’ excerpts relevant to my candidate analysis by writing the themes and/or sub-themes that they fit into. I was then able to export these excerpts, using the macro designed for this project, sorting the relevant data for each theme and sub-theme into separate tabs. I then reviewed all the excerpts for each individual theme and sub-theme, which allowed me to revise and define my candidate themes into my first full thematic analysis for the writing phase.
The thematic analysis at this stage included 13 themes and seven sub-themes, and these differed from the original candidate themes in a number of ways. In reviewing the collated data, I noted that some sub-themes were nuanced and prominent enough to be promoted to themes; the sub-theme ‘stay or go? (partner or other)’, for example, became the theme ‘you have to choose’. Similarly, I found other themes or sub-themes to be ‘thin’, and either removed them, or integrated them into other parts of the analysis; the sub-theme roughly titled ‘families at stake (marriage, children)’, for example, became a smaller part of the ‘safety in exclusivity’ theme. I also noted that the first overarching theme in the candidate analysis was ‘messy’, and in an effort to improve focus and clarity, I split this first overarching theme into three new ones, each with its own “central organizing concept” (Braun et al., 2019, p. 48): the first evidenced the contemporary relational context as one of default monogamy with an idealization of exclusivity; the second evidenced infidelity as an unforgivable offence, while associating attractions or feelings for others with this threat of infidelity; the third evidenced discourses in which someone must be to blame (either the person with the feelings or their partner). The second half of the candidate analysis became a fourth and final overarching theme, which encompassed a revised list of themes evidencing favourable talk of attractions or feelings for others.
Phase 6, writing the report : In writing my first draft of my analysis, I developed an even deeper sense of which themes and sub-themes were ‘falling into place’, and which did not fit so well with the overall analysis. At this point I was also engaging in a deeper exploration of relevant literature, and writing my chapter on the context of sexuality and relationships, which provided a foundation of theoretical knowledge that I could deductively integrate into my analysis. Through a process of supervisor feedback on my initial draft, engagement with literature, and revision of the data, I developed the analysis into the final thematic structure. My initial research question of ‘how do people make sense of attractions or feelings for others in committed relationships?’ also developed into three final research questions, each of which is explored across the three overarching themes of the final analysis:
Upon revision, both of the first two overarching themes from the second (revised) thematic map (‘the safety of default monogamy’ and ‘the danger of infidelity’) involved themes and sub-themes which situated attractions or feelings for others within the dominant contemporary relational context. I combined relevant parts of these into one overarching theme in the final analysis, which explored the research question: What is the contemporary relational context, and how are attractions or feelings for others made sense of within that context? Two themes and five sub-themes together evidenced attractions or feelings for others as a threat (by association with infidelity) within the mononormative sociocultural context.
The third overarching theme from the second (revised) thematic map (‘there’s gotta be someone to blame’) did not require much revision to fit with the final analysis. I refined information that was too similar or redundant in the original analysis, such as the sub-themes ‘partner is flawed’ and ‘deficit in partner’ which were combined into one sub-theme. I also added a third theme, ‘the relationship was wrong’, from a later part of the original analysis, as this also fit with the central organizing concept of wrongness and accountability. Together, these three themes and two sub-themes formed the second overarching theme of the final analysis, exploring the question: What accountabilities are at stake with attractions or feelings for others in committed relationships? This chapter also explores the affective consequences of these attributed accountabilities, as described by participants and interpreted by myself as researcher.
I revised and developed the final overarching theme most, in contrast to the analysis previously done, as my process of writing, feedback, and revision demonstrated that this section was the least coherent, and the central organizing concept required development. There were various themes and sub-themes across the initial analysis that explored imperatives or choices that were either made or recommended by participants. These parts of the original analysis were combined to produce the third overarching theme of the final analysis, including four (contradictory) themes and four sub-themes exploring the research question: How do people navigate, or recommend navigating, attractions or feelings for others?.
Combined, these three final overarching themes tell a story of (dominant or ‘normative’) initial sense making of attractions or feelings for others, subsequent attributions of accountability, and various (often contradictory and moralized) ways these feelings are navigated. Braun and Clarke (2006) describe thematic analysis as an active production of knowledge by the researcher, as themes aren’t ‘discovered’ or a pre-existing form of knowledge that will ‘emerge’, but rather patterns that a researcher identifies through their perspective of the data. My thematic analysis was influenced by my own social context, experiences, and theoretical positioning. In the context of critical research, ethical considerations are often complex, and researcher reflexivity is a crucial part of the process (Bott, 2010; L. Finlay, 2002; Lafrance & Wigginton, 2019; Mauthner & Doucet, 2003; Price, 1996; Teo, 2019; Weatherall et al., 2002). As the theoretical foundation of this thematic analysis was a combination of critical realism and critical feminist psychology, I engaged in an ongoing consideration of ethics and reflexivity throughout my data collection and analysis, which I discuss in the following section.
Bird, C. M. (2005). How I stopped dreading and learned to love transcription. Qualitative Inquiry , 11 (2), 226–248.
Bott, E. (2010). Favourites and others: Reflexivity and the shaping of subjectivities and data in qualitative research. Qualitative Research , 10 (2), 159–173.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3 (2), 77–101.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2012). Thematic analysis. In H. Cooper, P. M. Camic, D. L. Long, A. T. Panter, D. Rindskopf, & K. J. Sher (Eds.), APA Handbook of Research Methods in Psychology (Vol. 2: Research Designs: Quantitative, qualitative, neuropsychological, and biological, pp. 57-71). APA books.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: A practical guide for beginners . Sage.
Braun, V., Clarke, V., Hayfield, N., & Terry, G. (2019). Thematic analysis. In P. Liamputtong (Ed.), Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences (pp. 843-860). Springer.
Finlay, L. (2002). “Outing” the researcher: The provenance, process, and practice of reflexivity. Qualitative Health Research , 12 (4), 531–545.
Lafrance, M. N., & Wigginton, B. (2019). Doing critical feminist research: A Feminism & Psychology reader. Feminism & Psychology , 29 (4), 534–552.
Mauthner, N. S., & Doucet, A. (2003). Reflexive accounts and accounts of reflexivity in qualitative data analysis. Sociology , 37 (3), 413–431.
Price, J. (1996). Snakes in the swamp: Ethical issues in qualitative research. In R. Josselson (Ed.), Ethics and Process in the Narrative Study of Lives (pp. 207–215). Sage.
Riessman, C. K. (1993). Narrative analysis . Sage.
Teo, T. (2019). Beyond reflexivity in theoretical psychology: From philosophy to the psychological humanities. In T. Teo (Ed.), Re-envisioning Theoretical Psychology (pp. 273–288). Palgrave Macmillan.
Weatherall, A., Gavey, N., & Potts, A. (2002). So whose words are they anyway? Feminism & Psychology , 12 (4), 531–539.
Lucie Wheeler (Professional Doctorate)
The following sections are by Lucie Wheeler, from her UWE Counselling Psychology Professional Doctorate thesis – “It’s such a hard and lonely journey”: Women’s experiences of perinatal loss and the subsequent pregnancy .
Data from the qualitative surveys and interviews were analysed using reflexive thematic analysis within a contextualist approach, as this allows the flexibility of combining multiple sources of data (Braun & Clarke, 2006; 2020). Both forms of data provided accounts of perinatal experiences, and therefore were considered as one whole data set throughout analysis, rather than analysed separately. The inclusion of data from different perspectives, by not limiting the type of perinatal loss experienced, and offering multiple ways to engage with the research, allowed a rich understanding of the experiences being studied (Polkinghorne, 2005). However, despite the data providing a rich and complex picture of the participants’ experiences, I acknowledge that any understanding that has developed though this analysis can only ever be partial, and therefore does not aim to completely capture the phenomenon under scrutiny (Tracy, 2010). An inductive approach was taken to analysis, working with the data from the bottom-up (Braun & Clarke, 2013), exploring the perspectives of the participants, whilst also examining the contexts from which the data were produced. Through the analysis I sought to identify patterns across the data in order to tell a story about the journey through loss and the next pregnancy. The six phases of Braun and Clarke’s (2006; 2020) reflexive thematic analysis were used through an iterative process, in the following ways:
Phase 1 – Data familiarisation and writing familiarisation notes:
By conducting every aspect of the data collection myself, from developing the interview schedule and survey questions, to carrying out the face-to-face interviews, and then transcribing them, I was immersed in the data from the outset. Particularly for the interviews, the experience allowed me to engage with participants, build rapport, explore their stories with them, and then listen to each interview multiple times through the transcription process. I therefore felt familiar with the interview data before actively engaging with analysis. I found the process of transcribing the interviews a particularly useful way to engage with the data, as it slowed the interview process down, with a need to take in every word, and therefore led me to notice things that hadn’t been apparent when carrying out the interviews. The surveys, as well as the interview transcripts, were read through several times. I used a reflective journal throughout this process to makes notes about anything that came to mind during data collection and transcription. This included personal reflections, what the data had reminded me of, led me to think about, as well as what I noticed about the participant and the way in which they framed their experiences.
Phase 2 – Systematic data coding:
Coding of the data was done initially for the interviews, and then for the survey responses. I began by going line by line through each transcript, paying equal attention to each part of the data, and applying codes to anything identified as meaningful. The majority of coding was semantic, sticking closely to the participants’ understanding of their own experiences, however, as the process developed, and each transcript was re-visited, some latent coding was applied, that sought to look below the surface level meaning of what participants had said. Again, throughout this process, a reflective journal was used in order to make notes about my own experience of the data, to capture anything I felt may be drawing on my own experience, and to reflect on what I was being drawn to in the data.
Due to the quantity of data (over 70,000 words in the transcripts, and over 23,000 words of survey responses), this was a slow process, and required repeatedly stepping away from the data and coming back to it in a different frame of mind, reviewing data items in a different order, and discussions with peers and supervisors in the process. I noticed that my coding tended to be longer phrases, rather than one-to-two words, as it felt important to maintain some element of context for the codes, particularly as the stories being told had a sense of chronology to them, that seemed related to the way in which experiences were understood. The codes were then collated into a Word document. Writing up the codes in this way separately to the data, it was important to ensure that the codes captured meaning in a way that could be understood in isolation. Therefore, the wording of some of the codes was developed further at this stage. During the coding process I began to notice a number of patterns in the data, so alongside coding, I also developed some rough diagrams of ideas that could later be used in the development of thematic maps.
Phase 3: Generating initial themes from coded and collated data:
The process of generating themes from the data was initially a process of collating the codes from both the interviews and the surveys, and organising them in a way that reflected some of the commonality in what participants had expressed. Despite each of the participants having a unique story to tell, with details specific to their personal context, there was also commonality found in these experiences. Through reflecting on the codes themselves, going back to the data, and using notes and diagrams that had been made throughout the process in my reflective journal, I began to further develop ideas about the patterns that I had developed from the data. Related codes were collated, and developed into potential theme and sub theme ideas. I used thematic maps to develop my thinking, and changed these as my understanding of the data developed. I was conscious that in the development of codes and theme ideas, I wanted to ensure that my analysis was firmly grounded in the data, and therefore, repeatedly returned to the raw data during this process. The use of my reflective notes was also vital at this stage, to ensure that I did not become too fixated on limited ways of seeing the data, but was able to remain open and willing to let initial ideas go.
Phase 4: Developing and reviewing themes:
Theme development was an iterative process of going back and fore between the codes, and the way that patterns had been identified, and the data, collating quotes to illustrate ideas. A number of thematic maps were created that aimed to illustrate the way in which participants made sense of their experiences across the data set, including identifying areas of contradiction and overlap. The use of thematic maps was particularly useful as a visual tool of the way in which different ideas and patterns were connected and related.
Phase 5: Refining, defining and naming themes:
Through the process of developing thematic maps, areas of overlap became evident, which led to further refinement of ideas. There were many possible ways in which the data could be described, and therefore defining and articulating ideas to colleagues and supervisors brought helpful clarity about what could be defined as a theme, where related ideas fitted together into sub themes, and also where separation of ideas was necessary. The theme names were developed once there were clear differences between ideas, and with the use of participants’ quotes where appropriate, in order to keep close links between the themes and the data itself.
Phase 6: Writing the report:
Writing up each theme required further clarity as I sought to articulate ideas, and illustrate these through multiple participant quotes. The process of writing a theme report required further refinement of ideas, and rather than just a final part of the process, still required the iterative process of revisiting earlier phases to ensure that the ideas being presented closely represented the data whilst meeting the research aims. At this stage links were also made to existing literature in order to expand upon patterns identified in the data. Referring to relevant existing literature also helped me to further question my interpretation of the data, and to expand upon my understanding of the participants’ experiences.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: A practical guide for beginners . London: SAGE.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2020). One size fits all? What counts as quality practice in (reflexive) thematic analysis? Qualitative Research in Psychology , 1-25. [online first]
Polkinghorne, D. E. (2005). Language and meaning: Data collection in qualitative research. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 137-145.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write a Thematic Essay: The Complete Guide
by Antony W
June 24, 2024

In this guide, you'll learn exactly how to write a thematic essay step-by-step.
Thematic essays, or theme essays, require you to really examine a literary object such as a book, journal, paper, or other art form and pick out the main ideas (themes).
You will then explain how these themes are brought on and what literary devices are used to do that.
Key Takeaways
To write an outstanding theme essay, you should:
- Select a literary work to base your thematic analysis on.
- Choose a primary theme.
- Identify supporting evidence and literary devices used.
- Plan and outline the essay.
- Write the first draft.
- Edit and proofread your work for submission.
What is a Thematic Essay?

A thematic essay is a one in which you identify the main idea (theme) expressed in a chosen literary object and explore how the writer of that literature chooses to address that theme through various literary devices.
The devices can be metaphors, hyperbole, imagery, allegory, and many others.
Writing a thematic analysis essay is a great way to learn how to pick out themes in the literature you read as well as how to improve your writing skills.
A thematic essay will be at least five paragraphs long , but usually longer depending on the complexity of the work being reviewed.
You can write a thematic essay based on a book, a speech, a magazine article, a video, audio, or any other art form.
Choosing a Theme for a Thematic Essay
Choosing the main idea or theme of such a work is not a straightforward process.
It is highly subjective, and what you consider the main theme in a book may not be somebody else’s.
You have to make sure that what you pick as your main theme is fully supported throughout the book and makes significant appearances in most chapters, if not all of them.
How to Write a Thematic Essay Step by Step
Writing a thematic essay is easy. You just have to:
1. Choose a Literary Object
If your instructor does not provide the topic, think back to a book or article that made a strong impression to you, or think about your favorite pieces of literature.
Another option is to brainstorm. Brainstorming hardly fails, especially if you incorporate the help of your friends and even your instructor.
Collect different ideas and be sure to write each of them down, no matter how unlikely they sound. From there, eliminate most of these the following criteria:
- The topic should be interesting and captivating. Avoid those that are too common and overly used in academia unless you can provide a fresh twist or insight.
- The topic needs to have one or more important themes running through.
- It should be a literary work that is relatively well known and in the public domain.
- Some of the shorter works are best because they guarantee your essay won’t be too long.
This process will likely leave you with one or two possible topics, but make sure to confirm with your instructor that what you choose to focus on is acceptable.
2. Find a Relevant Theme
A theme is a significant idea that recurs throughout the literary work you have chosen. You can think of it as the main message the author is trying to pass across.
There are major and minor themes differentiated by how much attention the author gives to each.
For the best outcome, your theme should be one of the major themes addressed throughout the work.
There are a few things you can do to figure out what major themes are present:
- As you read the work, note and write down what tone, setting, language styles, and characterization the writer is using.
- What is the plot of the book and what does it lead to? Think about what you would tell somebody else about the book.
- Identify who the protagonist (main character) is and what they represent. Do they change at all in the book?
For example, in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird, Atticus Finch does not change and represents morality, love, fairness, and good reason to the end.
- Put yourself in the author’s shoes and observe from their point of view. What message do you think they want to pass on as the most important?
3. Pick Material for the Essay
Read through the book again with the main theme in mind.
See how the author plays with it, what literary devices are used to highlight their thematic approach, and write down all these for reference.
What you are doing at this stage is a literary analysis.
The tools in the author’s hands include character development, mood, setting, irony, allegory, simile, alliteration, symbolism, metaphor, among many others.
Think about how effective these tools are in shining the light upon the main theme. It helps to read between the lines as well because sometimes the most important thing is what the author leaves unsaid.
4. Planning: Thematic Essay Outline
A thematic essay is very simple and straightforward. Like most essays, it will have an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Each of these parts should be considered carefully in the planning stage and map out which ideas will go where.
Introduction
The introduction serves to catch the reader’s interest, set the background, and mention what exactly you intend to discuss in the essay.
The first one or two sentences should be a hook, that is, a statement that will be intriguing enough to make the reader want to keep reading. It can be a clever observation, a surprising statement, or even a relevant question.
Second, provide a very brief background on which to build your essay.
However, you will be assuming that the reader has already read the literary work that is the subject of the essay. So you don’t have to give too much detail.
In winding up the introductory, write your thesis statement . This is a one-sentence statement that tells the reader what your essay is about.
However, don’t say it like this: “My thesis statement is ... “ Instead, let the introduction flow and link smoothly up to this point.
Body paragraphs
You will have three or more body paragraphs detailing your arguments about the main theme. In a thematic essay, each of the body paragraphs will be focusing on one literary device and how it is useful in presenting the theme message.
As with most essays, body paragraphs will follow the TEEL format.
- Topic Sentence : The introductory sentence introduces the idea that the paragraph is about. Think of it as a mini-thesis statement. The rest of the paragraph will be explaining and supporting this one statement.
- Explanation: Explain your topic idea clearly.
- Evidence : Give compelling evidence for your claims. It can be a quote, a direct observation, similar use of the same method elsewhere in the book, a citation from an authoritative work, etc.
- Link : Show how the idea you just described links with the rest of the essay and thesis statement. Again, you won’t say, “this idea relates to my thesis statement because …” Instead, let the whole paragraph flow smoothly and seamlessly.
The number of body paragraphs will depend on how much evidence you have collected. However, make sure to keep within the reasonable word count parameters as given by your instructor.
Recap the main arguments in your body and restate your thesis statement.
The purpose of the conclusion is to give your “take-home” argument, what you feel the reader should retain from the whole work.
Customize your theme essay outline accordingly; don’t make it as generic as this example here.
Fill it with details like what ideas you will include in your first paragraph, what your thesis statement will be, and what your introduction hook is. With this thematic essay format, you are now ready to do the write-up.
5. Write the Essay
With a good outline, writing a thematic essay becomes a piece of cake. You will simply be fleshing out the template.
6. Proofreading and Revision
Make sure to read through your essay at least twice.
Note how well your ideas flow, how the arguments and evidence presented link back to the thesis statement, and of course, clear any grammatical errors.
Thematic Essay Writing Help
If you don’t have the time to read your subject thoroughly and analytically, you can hire Help for Assessment’s essay writing service . We have a suitable writer that can help you get the assignment completed on time.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. how do you start a theme essay.
The introduction of your theme essay should be an intriguing hook about the subject you wish to discuss.
Ensure the hook is concise and strong enough to grab your reader’s attention.
2. What are the Elements of a Thematic Essay?
The elements of a thematic essay are the introduction, body paragraphs, and the conclusion.
Ensure the introduction includes a thesis statement. The body paragraphs should support the thesis using relevant examples, evidence, and arguments.
Lastly, the conclusion should be logical enough to tie everything together at the end.
3. What is the Main Point of a Thematic Essay?
The main point of a thematic essay is to identify themes from a source, present a theme statement, and address a specific issue within the requirement of the assignment.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Thematic Essay: Guidelines for an A+ Paper
- Icon Calendar 8 August 2024
- Icon Page 6445 words
- Icon Clock 29 min read
Thematic essays are common writing assignments in college across all disciplines. Basically, this guide begins with a definition of a thematic essay and its format and provides examples of topics and papers for illustration. Further on, this manual deconstructs a specific process of writing a thematic essay. Moreover, a presented guide covers three core stages of thematic essay writing: preliminary actions, establishing a paper’s foundation, and writing. In turn, a working manual presents an outline template and an example of a thematic essay to demonstrate a real writing situation where a student implements these guidelines of thematic paper writing correctly. Finally, a discussed guide presents information on what people can include in their theme essays and common mistakes to avoid. Hence, students need to learn how to write a good thematic essay and excel in their academic endeavors.
General Aspects
A thematic essay is a form of academic writing that requires an author to react to a particular question or theme. In this case, instructors expect students to develop a written reaction to a question or theme by connecting various pieces of information to reach a reasonable conclusion. Moreover, writing a thematic essay has a high demand for research and a critical examination of subtle relationships that exist between sources. Then, an entire research process yields a significant amount of information, which learners may use to generate numerous logical relationships that lead to rational inferences. Consequently, students may select any set of evidence with a clear, logical association provided that their central claim centers on a theme of interest.
What Is a Thematic Essay and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a thematic essay is a focused piece and type of writing that revolves around a specific theme, unique subject, or central idea. For example, the main purpose of writing a thematic essay is to analyze and understand underlying themes, concepts, or ideas presented in a given text, artwork, historical event, or any other subject of study (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Basically, such papers encourage critical thinking and comprehension by requiring students to make connections between a particular theme and various elements within a given subject, such as characters, settings, events, and symbols. Further on, this type of essay also aims to demonstrate people’s abilities to organize their thoughts coherently, present well-supported arguments, and engage with an assigned material on a deeper level (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Moreover, these compositions often serve a particular educational purpose and help students to improve their analytical skills, writing proficiency, and ability to synthesize information. In terms of pages and words, the length of a thematic essay depends on academic levels and specific assignment criteria, while general writing guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 2-3 pages
- Word Count: 500-750 words
- Length: 3-5 pages
- Word Count: 750-1,250 words
University (Undergraduate)
- Length: 5-7 pages
- Word Count: 1,250-1,750 words
- Length: 10-15 pages
- Word Count: 2,500-3,750 words
- Length: 15-20 pages (or longer, depending on a complexity of a chosen topic and depth of research)
- Word Count: 3,750-5,000 words (or more, depending on specific dissertation requirements)

Note: Some sections of a thematic essay can be added, deleted, or combined with each other, and such a paper typically ranges from 500 to 1,500 words, depending on academic levels and specific assignment requirements. For example, a standard format of a thematic essay includes an introduction with a single thesis statement sentence that covers a central theme, several body paragraphs that explore different aspects of a chosen topic with supporting evidence, and a conclusion that summarizes an entire analysis and reinforces a central claim (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). As such, a specific theme in an essay is a central topic or underlying message that a writer explores and analyzes throughout an entire text. In writing, a main point of a thematic essay is to analyze and interpret a central theme within a specific text or subject, demonstrating how it is developed and its significance (Laurens, 2018). Moreover, students need to write a thematic essay when they are assigned to analyze and interpret a central theme in a particular text or subject, often in literature, history, or social studies courses. In turn, a thematic way of writing involves focusing on a central theme or idea, exploring its various aspects through structured analysis and evidence, and connecting it to broader contexts or implications (Braun & Clarke, 2022). An example of thematic writing is an essay analyzing a particular theme of sacrifice in “The Hunger Games,” discussing how characters’ actions and an overall plot illustrate key sacrifices made for survival and freedom. Finally, to start a thematic essay, people begin with an engaging and interesting introduction that clearly presents a central theme, provides relevant background information, and states their thesis or main argument.
- Cybersecurity Laws: Are They Adequate in Combating Cybercrime?
- Historical Overview of Abortion Laws Across the Globe
- Examination of Mental Health Disparities Within the LGBTQ+ Community
- Facebook’s Data Privacy Controversy: A Deep Dive
- A Pure Democracy
- Privacy Rights in the Big Data Age
- Life in Prison and the Ex-Convict Experience
- Understanding the Impact of Social Media on Teenage Self-Image
- Cultural Factors Influencing Eating Disorders
- Racial Profiling and Its Impact on Modern Society
- Cultural Shifts in Privacy Perception Post-Social Media
- Major Parenting Issues of the 21 st Century
- Thematic Family Bonds in Immigrant Families
- Escaping the Cycle of Poverty
- Modern Interpretations of Shakespeare’s Female Characters
- Narrative Techniques in “Lord of the Flies” by William Golding
- Exploring Symbolism and Other Themes in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby”
- Embracing the Gothic: Examination of “The Castle of Otranto” by Horace Walpole
- A Thematic Significance of a Muse
- Corruption in 18th-Century Short Stories
- Female Authors Who Left a Mark on Classical Literature
- History of Cryptography and Its Modern Applications
- Racial Dynamics in the Harlem Renaissance: A Detailed Study
- The Impact of the Printing Press on Renaissance Europe
- Examination of Manifest Destiny’s Influence on Territorial Expansion
- Memories of the Holocaust
- Landmines on a Modern Political Landscape
- A Cause of a Collapse of Middle East Alliances in the 20 th Century
- Roles of Parental Attachment in Child Development
- Influence of Colors on Mood and Behavior
- Importance of Dream Analysis in Understanding Subconscious Thoughts
- Impacts of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance
- Teenage Confidence After a Thematic Emergence of Social Media.
- An Impact of Abuse on a Formation of Relationships
- An Efficacy of Proactive Counseling
How to Know
A student can readily identify a thematic essay topic because such a subject boldly pronounces a writing theme but does not hint at any specific point of view. In writing, the primary goal of a topic of a thematic essay is to inform readers of a specific theme rather than a particular approach of an author, which becomes more apparent in an introductory paragraph (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Specifically, a thematic essay topic does not allow students to develop a particular supposition concerning a theme because authors realize there may be multiple points of view concerning a main idea of a theme essay. In turn, to write a thematic essay, people develop a clear and well-formulated thesis statement, support this claim with detailed analysis and evidence related to a specific theme, and organize an entire content into a structured format with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Steps on How to Write a Thematic Essay
Step 1: Preliminary Actions
Defining a Thematic Topic
A particular ability of students to define a topic is dependent on an extent to which they understand essay rubrics and instructions. Basically, once learners receive thematic essay instructions, they should critically read their prompts to ensure they comprehend all demands of writing requirements. Then, writers should use keywords from their instructions to write one or more questions, which represent corresponding expectations of instructors (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Based on developed questions, students can create a good topic that adequately captures a specific content of possible responses holistically. Moreover, authors must consider the information in given instructions, which establishes a particular leeway they have in a further selection of a topic, for example, choosing a theme not covered in-class readings.
Identifying a Purpose for Writing
A unique procedure of identifying a purpose occurs in two distinct stages: selecting a general goal and defining a specific purpose. Basically, authors may write a thematic essay to achieve two general purposes: explanation and persuasion. In writing, basic expectations of instructors influence a specific choice of a general purpose of a theme essay to a large extent (Laurens, 2018). As such, students should write a thematic essay on a book that deeply explores significant themes, such as “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee, where an author addresses themes of racism, morality, and social justice. After learners pick a general purpose for writing a paper, they should create a specific purpose that shows a particular effect their papers must have on readers. Mostly, writers generate a specific purpose from questions that represent thematic essay instructions. In turn, a nearly determination of a main purpose is crucial because it affects a specific student’s approach to research and word choice during drafting.
Analyzing an Audience
Before writing a thematic essay, students need to determine key characteristics and expectations of readers. Basically, knowledge concerning crucial characteristics and expectations of an intened audience is valuable because writing allows authors to understand a specific interaction between defined characteristics and attitudes toward a topic, a readers’ level of expertise, and an actual significance of misconceptions, which aid in selecting an appropriate presentation approach. For example, a thematic essay in history is a paper that focuses on a specific theme or concept within a historical context, analyzing how this theme has influenced events, societies, or periods and providing evidence to support an entire analysis (Laurens, 2018). Specifically, learners can determine the most effective organization patterns, identify the best evidence, and employ an accepted documentation style. Moreover, students ensure a suitable level of explanation accompanies specialized writing terms that appear in a theme essay.
Generating and Writing Ideas
After learners define a main purpose and comprehend unique needs and traits of a target audience, they begin to develop ideas for an entire content of a thematic essay. Mostly, theme essay assignments for writing a particular subject focus on topics lecturers discuss in classrooms and other course readings (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Consequently, students may generate ideas through brainstorming based on the relevant information from a single unit and other related units they encounter during their schooling. During brainstorming, writers engage in idea mapping and clustering, which enables them to keep track of relationships between ideas.
Step 2: Establishing a Foundation for Writing
Searching for Sources
Author’s initial ideas regarding a topic act as a starting point for acquiring credible sources that support and refine those ideas. Basically, contemporary scholars engage in electronic searches to find useful and reliable sources for thematic compositions (Goddard et al., 2022). In this case, students should begin their search on a library’s website, which provides them with material that is reliable for academic writing. Further on, library search engines have complex filter functionalities, which make a particular process of searching for academic sources quite simple. Then, authors turn to open-web searches using Google Scholar or other public search engines that generate a significantly larger number of sources. However, some articles may not be accessible to students. Moreover, a particular burden of determining an overall reliability of sources falls on authors when they use open-web search engines (Naeem et al., 2023). In turn, students rely entirely on keywords or keyword combinations to generate working bibliographies.
Evaluating Sources Before Writing
Working bibliographies undergo an intensive evaluation process to establish whether they meet necessary quality standards for inclusion in writing a college-level thematic essay. For example, a main goal of a thematic essay is to analyze and interpret a central theme within a text or subject, demonstrating its development and significance through structured evidence and coherent argumentation (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). In writing, an evaluation process involves two primary stages: relevance determination and reliability test. During relevance determination, authors should examine each source by using three criteria:
- A level of attention that a specific source gives to a chosen topic.
- A suitability of a source’s sophistication to a particular purpose and audience’s needs.
- An impact of publication date on an actual relevance of its information.
Next, a reliability test investigates five critical writing aspects:
- An origin of a thematic source.
- A level of expertise of authors.
- Biases of a source in a context of existing literature.
- Availability and quality of given evidence supporting source’s claims.
- Objectivity in a presentation of author’s claims and handling of evidence.
Writing a Thematic Annotated Bibliography
At this point, a revised working bibliography now contains fewer sources that are relevant and reliable. In particular, students should engage in critical reading of all sources in a working bibliography to identify useful pieces of information they may incorporate into a theme essay. After reading each source, learners write an annotation that contains a summary of a source, ideas for using this source, and an assessment of this source (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Besides the three main elements of an annotated bibliography entry, writers may choose to mention specific pieces of evidence, which are the most significant contributions of a source to a thematic essay. Typically, they develop an annotated bibliography from notes they make as they read through a text.
Developing an Outline
Based on an annotated bibliography, students create an essay outline. Basically, a particular content of an annotated bibliography entry allows learners to develop relationships between sources, which is essential because such a paper begins to shape an essay structure. In this case, writers identify and group sources that support a general point, which splits a body of a thematic essay into discernible sections (Laurens, 2018). Then, authors break down each general point into specific points that can exist as a body paragraph and assign appropriate sources to individual body paragraphs. Furthermore, scholars logically organize particular points and establish some form of flow within each section of a body paragraph. In turn, they document an overall organization of general and specific ideas and a distribution of evidence in a list, like a format that allows for easy identification of hierarchy.
Step 3: Writing a Thematic Essay
Designing a Working Thesis
A student develops a working thesis statement, which presents his or her central claim. For example, to write a thesis for a thematic essay, people clearly state a central theme and outline main points they will discuss to demonstrate how this topic is developed and its significance (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Basically, questions that writers derive from assignment instructions and specific minor arguments listed in a thematic essay outline are main pieces of information they use to generate a thesis statement. Initially, writing a working thesis statement may appear as a simple combination of individual responses to assignment questions in a context of given information that forms an outline (Laurens, 2018). However, authors must unite individual answers under a specific inference that demonstrates a real significance of writing a thematic essay. Besides, a working thesis statement undergoes multiple revisions, which occur randomly during a writing process. In turn, some examples of sentence starters for beginning a thematic essay are:
- In [text/work], [author/creator] vividly explores a specific topic of [topic], revealing how this theme shapes unique characters’ actions and an overall narrative through … .
- A profound theme of [theme] is central to [text/work], as [author/creator] uses various literary devices to highlight its significance and impact on an entire plot, including … .
- After reading [text/work], it becomes clear that [theme] is not only a recurring motif but also a driving force behind characters’ developments and an unfolding of events, particularly through … .
- Throughout [text/work], a particular exploration of [theme] is paramount, with [author/creator] skillfully using [specific elements, such as symbolism or imagery] to underscore its importance in … .
- A unique theme of [theme] is clearly covered in [text/work], as [author/creator] employs [literary techniques] to examine its various dimensions and its influence on … .
- By focusing on a theme of [theme] in [text/work], [author/creator] provides a deep and complex analysis of [specific aspect], shedding light on its broader implications for … .
- A pervasive presence of [topic] in [text/work] is evident from an outset, with [author/creator] using [specific examples] to illustrate how this theme permeates an overall narrative and affects characters’ journeys … .
- In [text/work], an interesting topic of [theme] is explored through a complex approach, where [author/creator] implements [specific elements], offering a comprehensive understanding of its role and significance … .
- An intricate depiction of [topic] in [text/work] serves as a valid foundation for [author/creator]’s exploration of [specific aspect], highlighting how this theme influences a story’s progression and characters’ experiences … .
- Through a lens of [theme], [author/creator] in [text/work] shows a complex use of [specific elements], providing readers with a deeper appreciation of its impact and underlying messages conveyed … .
Reviewing an Outline
Once an author writes a working thesis statement, a person subjects an informal outline to a revision that results in a particular creation of a formal outline for a thematic essay. Basically, body paragraphs of a thematic essay are building blocks for a central claim. Consequently, learners must review an informal outline to ensure there is an apparent logical build-up to the inference, which they announce in a written thesis statement (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). During this review, students focus on a standard organization of minor arguments to ensure body paragraphs contain a single minor idea while maintaining a rational relationship with other body paragraphs. Moreover, writing a formal outline contains a systematic arrangement where information with the same level of significance or roles has identical indentation or numbering.
Selecting Correct Sources for Writing
Based on writing a formal outline, students make a final assessment of sources for each body paragraph. In particular, a formal outline contains some changes in its organization and the framing of minor arguments of a thematic essay (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). As such, these changes may affect the relevance of sources to each body paragraph’s argument. Then, a subdivision or merging of minor arguments may cause some sources to become inadequate because they do not extensively cover new minor ideas. Therefore, writers should check an overall suitability of each source to arguments it supports to ensure each source provides strong, relevant, and accurate evidence before commencing a drafting process.
Drafting a Thematic Paper
During a drafting stage, authors expand a thematic outline into a complete paper by changing statements and brief notes into coherent paragraphs. Basically, there is no fixed approach to drafting a thematic essay because students may start writing at any point by using a formal outline (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Nonetheless, it is an excellent practice for learners to begin drafting from a paragraph they understand the best because such a strategy ensures they waste very little time trying to overcome a particular fear of creating a first draft. In turn, scholars should allocate adequate time for drafting.
How to Improve
Self-Critic
After completing a first draft, students undertake a self-conducted revision process, which involves rethinking and rewriting. Basically, such a process of revision focuses on a particular evaluation of the evidence and organization of body paragraphs to ensure they support a working thesis statement entirely (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Further on, learners revisit a working thesis statement to refine its wording and a central claim it presents. Before starting a revision process, writers should take a break, which allows a human brain to reset and attain a higher level of objectivity while revising. In writing, a thematic statement is a unique sentence that expresses a central theme or underlying message of a text, summarizing an author’s main insight or viewpoint on a subject (Laurens, 2018). Moreover, scholars should use a checklist to reduce a risk of overlooking various crucial theme essay dynamics during individual revision.
Peer Review
An individual revision process identifies apparent flaws in content presentation, but numerous flaws may go unnoticed due to authors’ subconscious biases concerning their writing styles. As a result, students should subject their thematic essays to a peer review by a classmate, tutor, parent, or writing center staff (Laurens, 2018). In this case, learners should select a peer reviewer that best represents a member of the target audience. Moreover, authors may provide peer reviewers with a checklist to guide them through a revision process, especially if a person is not an expert editor. Then, students should assign adequate time to a peer review process to allow reviewers to carry out a revision task comfortably. In turn, once writers receive feedback from peer reviewers, they consider comments when making a final revision of a paper.
Clarity and Effectiveness
A first consideration in a editing process is an overall clarity and effectiveness of sentences in a thematic essay. Basically, authors should edit each sentence to ensure statements convey an intended meaning to readers. In this case, it is advisable to focus on six clarity issues, which are the most common in writing theme papers: lack of parallelism, dangling modifiers, vague references to pronouns, incomplete sentences, and incorrect separation of sentences (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Besides clarity, learners should evaluate a particular efficacy of each statement separately and as part of a paragraph. In turn, an entire effectiveness of writing statements revolves around a smoothness of transitions, conciseness, variability in sentence structure and length, a distinctiveness of an author’s voice, and emphasis on core ideas.
Surface Errors
A subsequent stage of an editing process involves editing for thematic surface and documentation errors. In particular, students should strive to eliminate all surface errors because they divert a reader’s attention to meaning, although some writing errors do not necessarily change an actual meaning of sentences. For example, learners can edit surface errors by using six-item criteria: spelling errors, comma splices, sentence fragments, verb errors, punctuation errors, and pronoun errors (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Moreover, students should not attempt to conduct clarity and effectiveness editing simultaneously with surface error editing, which may result in poor writing because of an extensive nature of rules governing the English language. In turn, the final step in editing a thematic essay is a correction of any documentation errors while referring to an appropriate style manual, such as APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, or Harvard.
Outline Template
I. Introduction
A. Hook sentence. B. Background information. C. Thematic thesis statement.
A. First body paragraph
1. A single idea for writing a first thematic paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of evidence.
- First specific deduction from evidence.
- Second specific deduction from evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates a specific link between a first paragraph’s claim and a central thesis statement.
B. Second body paragraph
1. A single idea for writing a second thematic paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates a specific link between a second paragraph’s claim and a central thesis statement.
C. Third body paragraph
1. A single idea for writing a third thematic paragraph. 2. Evidence supporting this paragraph’s claim. 3. Interpretation and analysis of evidence.
4. A concluding statement that demonstrates a specific link between a third paragraph’s claim and a central thesis statement.
III. Conclusion
A. Restatement of a central thesis statement written in a thematic essay. B. Summary of three minor arguments mentioned in body paragraphs. C. Closing remarks emphasizing an actual significance of a central claim in a unique context of three minor arguments.
Commentary on a Thematic Outline Template
Identifying a Central Theme
Any audience can determine a central theme of a thematic essay from a thesis statement or an overview of topic statements. Basically, writing a well-composed thesis statement must explicitly mention a central theme or implicitly hint at a central theme. Alternatively, an audience can read through topic sentences and correctly speculate a central theme of a thematic essay because minor arguments in individual body paragraphs are building blocks of a thesis statement (Laurens, 2018). However, a reader’s ability to identify a central theme from a formal outline is dependent on their pre-existing knowledge concerning a topic because an outline uses statements and annotations with little explanation.
A thematic essay stands out from other types of essays because of a high level of freedom writers enjoy during authorship. During a writing process of a theme essay, authors can choose any purpose or a combination of purposes to use in different sections of 5 parts of an essay, which is a luxury that argumentative and expository papers do not extend to writers (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Further on, essay instructions for writing a thematic essay tend to define a broad scope for research, which implies authors may develop a wide variety of arguments. In turn, an expansive nature of a subject of a paper is not present for argumentative essays, which forces students to choose one of the two sides of a controversial issue.
Introduction
An introduction section is a first part of a thematic essay, which consists of three main elements: hook, background information, and thesis statement. For example, a hook is a first statement of any paper that plays a crucial role in capturing an audience’s attention through creative wording, which gives them a reason to read an entire paper (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Since students know how to write a hook, they provide the essential background information that readers require to understand a thesis statement. Moreover, the background information element does not have a fixed length. Instead, it is dependent on a complexity of a thesis statement and an overall length of a thematic essay. As a result, writing a thematic thesis statement is a final item of an introductory paragraph. In turn, a standard length of introductions is approximately 10% of an essay’s word count.
Body Paragraphs
Topic Sentence
A topic sentence contains a minor claim that an author discusses within a paragraph. For example, its primary role is to establish content boundaries, which ensures students focus on a particular idea in each paragraph (Laurens, 2018). Moreover, a topic statement should present a minor argument and mention a relation that such a sentence has to a central idea of writing a thematic essay or make a tacit suggestion of its link to a main thesis. Therefore, writers should avoid a particular use of in-text citations in a topic statement because it implies an idea is not original.
After a topic sentence, students unveil the evidence that supports their claims. In college writing, an in-text citation should accompany any evidence learners introduce into a thematic essay to direct readers to its origin (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). Moreover, learners should rely heavily on summary and paraphrasing in their writing, as opposed to direct quotations from sources. Nevertheless, some theme essay instructions may specify a particular technique writers must use when integrating evidence into a paper.
This element of a paragraph structure allows authors to explain an actual significance of the evidence to a paragraph’s argument. In this section of a thematic essay, students provide an interpretation of the evidence, which informs a target audience of a real meaning of the evidence in a particular context of a source text (Laurens, 2018). Then, they explain an actual value of the evidence in developing a reasonable justification for a single idea proposed in topic sentences. In turn, learners should avoid a particular inclusion of lengthy pieces of evidence because it creates a situation where a specific voice of sources is more dominant than an author’s voice.
Concluding Statement
A concluding statement emphasizes a logical relationship that exists between a topic sentence, evidence, evaluation, and thesis statement. In some cases, such s sentence may establish a specific relationship of a paragraph with a preceding paragraph (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). As such, students should ensure a concluding sentence of a paragraph does not contain a meaningless summary of key pieces of evidence. Then, a concluding statement of a thematic essay must not contain any new evidence because there is no opportunity to explain a particular contribution of the evidence in supporting a paragraph’s argument.
A concluding paragraph has three critical features: a restatement of a main claim, a summary of minor arguments, and closing remarks. Basically, an opening statement of a thematic essay reminds students of a central argument by using new words and syntax (Kirszner & Mandell, 2024). After an opening statement, learners summarize minor claims that appear in individual body paragraphs while maintaining a logical organization, which is identical to a particular arrangement of ideas in a body. Further on, authors write a strong closing statement that knits together an introduction, thesis statement, and minor claims to create a lasting impression on a target audience (Laurens, 2018). Moreover, students should ensure they do not introduce new evidence or arguments in a concluding paragraph. In turn, authors must not apologize for a lack of expertise on a topic or make absolute claims because it diminishes an overall efficacy of writing a good conclusion.
Thematic Essay Example
Topic: Recruitment of Terrorists
Terrorism is a global problem, which appears to be spreading despite an increment in the efforts to suppress its growth. Basically, a prevention of recruitment is a crucial counterterrorism strategy. Moreover, its efficacy is dependent on the understanding of key terrorists’ recruitment techniques. In turn, terrorist groups’ recruitment methods focus on a target’s identity crisis, which puts a potential member at risk of falling for an ‘appeal’ of terrorism.
An individual’s desire to be part of a movement that is effecting a radical change in society is a significant motivator for participation in terrorism. For example, recent studies show that terrorist groups begin conversations with most young recruits on social media platforms, which discuss topics concerning social, political, and economic oppression (Weisburd et al., 2022). Basically, this finding suggests young people in contemporary society have a desire to correct the ‘wrongs’ in society as a means of identity. Consequently, terrorists use an increased sensitivity to social injustices as a common ground to initiate and build a relationship with a prospective recruit. In turn, a youth’s strong desire to do something to stop social injustices that their respective governments ignore leaves them vulnerable to radicalization by terrorist groups.
Religious Beliefs
Fanatical religious belief may drive an individual to support or participate in terrorism for a sake of being part of a group. According to Alakoc et al. (2021), a constant pressure from religious parents causes a blind indoctrination of adolescents and young adults, which enables recruiters from terrorist groups to present religious concepts as justifications for terrorism, for example, the holy war. In this case, a mosque is an ideal site for a particular recruitment of terrorism because of a presence of youth with highly impressionable minds. Moreover, youths depend on teachings at places of worship for knowledge that defines their perspective of the world. As a result, terrorist recruiters disguised as spiritual leaders can easily nurture fanatical beliefs that endorse terrorist activities. Eventually, a feeling of separation from conservative believers pushes them to pursue groups that share their fanatical religious beliefs.
A loss of a family member to counterterrorism activities may act as a motivation factor for grievers who are trying to re-establish their identities because they no longer fit into traditional social structures. For example, Binder and Kenyon (2022) argue that recruiters prey on a particular pain of grieving family members by offering them retribution as a solution to an overwhelming feeling of incompleteness and using Internet platforms to achieve this objective. After a particular death of a family member, emotional turmoil increases an overall susceptibility of individuals to an idea that terrorist acts are an appropriate response to the ‘killers’ of their loved ones. Often, recruitment occurs during this unstable state and encourages an individual to relive a pain each day, which results in a permanent erosion of their former identity. Accordingly, grievers may find themselves as sympathizers of terrorism, which leads to active or passive participation.
Most members of terrorist organizations experience an identity crisis at the time of recruitment. Basically, a particular need to gain membership to a group that fights against social injustices tolerates fanatical religious beliefs or seeks revenge for a death of loved ones is a sign that identity crisis is a common characteristic in recruits. In turn, current counterterrorism initiatives should seek to break a cycle of recruitment, which will weaken terrorist groups.
List of References
Alakoc, B. P., Werner, S., & Widmeier, M. (2021). Violent and nonviolent strategies of terrorist organizations: How do mixed strategies influence terrorist recruitment and lethality? Studies in Conflict & Terrorism , 46 (12), 2598–2621. https://doi.org/10.1080/1057610x.2021.1935706
Binder, J. F., & Kenyon, J. (2022). Terrorism and the Internet: How dangerous is online radicalization? Frontiers in Psychology , 13 , 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.997390
Weisburd, D., Wolfowicz, M., Hasisi, B., Paolucci, M., & Andrighetto, G. (2022). What is the best approach for preventing recruitment to terrorism? Findings from ABM experiments in social and situational prevention. Criminology & Public Policy , 21 (2), 461–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/1745-9133.12579
What to Include
Common Mistakes
- Lack of a Clear Thesis: Failing to present a clear, well-formulated, and concise thesis statement that outlines a main argument of a thematic essay.
- Biased Analysis: Providing a shallow analysis that does not cover a specific theme deeply or its implications.
- Ignoring a Theme: Straying from a central theme and including irrelevant information or tangents.
- Weak Evidence: Using insufficient or weak evidence to support claims, leading to a lack of credibility.
- Poor Organization: Lacking a coherent structure, making a thematic essay difficult to follow and understand.
- Repetition: Repeating same points or ideas without adding new insights or depth to an entire analysis.
- Grammar and Spelling Errors: Neglecting to proofread, resulting in numerous grammatical and spelling mistakes that undermine a paper’s quality.
- Inconsistent Tone: Shifting between formal and informal language, which disrupts a composition’s cohesiveness.
- Neglecting a Conclusion: Failing to provide a strong and logical conclusion that summarizes key points and reinforces a central thesis.
- Overgeneralization: Making broad, unsupported statements that do not accurately reflect a unique complexity of a chosen theme.
A thematic essay involves a structured approach to analyzing a central theme in a given text, requiring clear and coherent argumentation supported by evidence. Basically, its writing process includes several key steps: introducing a specific theme with a compelling hook and background information, formulating a precise thesis statement, and developing body paragraphs that provide detailed evidence and analysis supporting a central argument. Moreover, each paragraph should start with a topic sentence, include supporting evidence, and end with a concluding statement that ties back to a main thesis. In writing, a conclusion should restate a central thesis, summarize key points, and highlight broader implications of a chosen theme. Additionally, it is crucial to undergo thorough editing and peer review to ensure clarity, coherence, and correctness. Finally, common pitfalls to avoid include weak thesis statements, lack of organization, poor transitions, insufficient evidence, and unclear analysis. As a result, this structured writing approach helps to produce a well-organized and insightful thematic essay. In turn, some key takeaways to remember include:
- Students should define a narrow writing topic to guide them in generating ideas in response to a thematic paper prompt.
- Key characteristics and expectations of an intended audience are vital in determining an appropriate presentation approach.
- Before drafting a thematic essay, authors must write a formal outline and annotated bibliography, which are critical for organization and evidence selection.
- A particular maintenance of a high level of fluidity during drafting is critical because it allows writers to experiment with different styles of expression.
- Revision and editing are aspects of a writing process a student should not take lightly.
- All body paragraphs must adhere to a four-element paragraph structure.
- A conclusion paragraph of a thematic essay should not contain any new evidence or arguments.
- Learners must write a thesis statement that captures a specific theme instructors highlight in essay prompts.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2022). Toward good practice in thematic analysis: Avoiding common problems and be(com)ing a knowing researcher. International Journal of Transgender Health , 24 (1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/26895269.2022.2129597
Campbell, K. H., & Latimer, K. (2023). Beyond the five-paragraph essay . Routledge.
Goddard, Y. L., Ammirante, L., & Jin, N. (2022). A thematic review of current literature examining evidence-based practices and inclusion. Education Sciences , 13 (1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13010038
Kirszner, L. G., & Mandell, S. R. (2024). Patterns for college writing: A rhetorical reader and guide . Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Laurens, A. (2018). How to theme: Understanding and analysing the connection between theme and story for writers and students . Inkprint Press.
Naeem, M., Ozuem, W., Howell, K., & Ranfagni, S. (2023). A step-by-step process of thematic analysis to develop a conceptual model in qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods , 22 , 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069231205789
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

Profile Essay: Guidelines for an A+ Paper
- Icon Calendar 18 September 2020
- Icon Page 4518 words

680 Personal Essay Topics & Free Ideas
- Icon Calendar 16 September 2020
- Icon Page 7297 words

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thematic analysis is a good approach to research where you’re trying to find out something about people’s views, opinions, knowledge, experiences or values from a set of qualitative data – for example, interview transcripts, social media profiles, or survey responses.
This article explains how to craft a thematic essay by analyzing a central theme in a text, using evidence like quotes and thematic essay examples to support analysis. It provides step-by-step guidance, from understanding the theme to structuring an essay effectively.
Thematic Analysis is a qualitative research method that involves identifying, analyzing, and interpreting recurring themes or patterns in data. It aims to uncover underlying meanings, ideas, and concepts within the dataset, providing insights into participants’ perspectives and experiences.
By: Jenna Crosley (PhD). Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | April 2021. Thematic analysis is one of the most popular qualitative analysis techniques we see students opting for at Grad Coach – and for good reason. Despite its relative simplicity, thematic analysis can be a very powerful analysis technique when used correctly.
Learn what a thematic essay is and how to write it. See how a thematic essay outline looks like and the examples of this essay's parts.
A thematic essay is a type of writing assignment that focuses on a specific theme or topic. It requires you to identify a central theme, discuss it in detail, and make connections between various facts.
A thematic essay is a piece of writing that explores a central idea or theme that is common to multiple texts. To write it, you need to carefully analyze the texts, identify the theme, and develop a strong argument.
To help those wanting to understand what describing the reflexive TA process well might look like, we offer some good examples here, from student projects. This may be particularly helpful for students doing research projects, and for people very well-trained in positivism.
Key Takeaways. To write an outstanding theme essay, you should: Select a literary work to base your thematic analysis on. Choose a primary theme. Identify supporting evidence and literary devices used. Plan and outline the essay. Write the first draft. Edit and proofread your work for submission. What is a Thematic Essay?
For example, a main goal of a thematic essay is to analyze and interpret a central theme within a text or subject, demonstrating its development and significance through structured evidence and coherent argumentation (Campbell & Latimer, 2023).