

Easy Peasy All-in-One High School
An extension of easy peasy all-in-one homeschool, acid rain lab.
Effects of Acid Rain Lab
Objectives:
To visualize the effects of acid rain on a living organism.
How does simulated acid rain affect the germination of a lima bean?
- 3 cups or containers
- 3 Ziploc bags
- 15 dry (not canned) lima beans (soak in warm water overnight before using)
- paper towels
- Number each of the cups or containers as 1, 2, or 3.
- Cup #1 “Rainwater:” Fill cup or container with 2 cups of plain water (tap water would be fine).
- Cup #2 “Mild Acid Rain:” Fill cup or container with ½ cup vinegar and 1 ½ cups of water.
- Cup #3 “Strong Acid Rain:” Fill cup or container 2 cups of vinegar.
- Soak a paper towel in each of the cups.
- Label each Ziploc bag as 1, 2, or 3.
- For each bag place the respective paper towel in with 5 presoaked lima beans.
- Write a hypothesis answering the question posed at the beginning of the lab.
- Observe their growth over the next 5 days adding more liquid if necessary to the paper towels.
Example of Data Table:
| Day | # of Beans that have Germinated | Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Bag 1 – Rainwater | ||
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| Bag 2 – Mild Acid Rain | ||
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| Bag 3 – Strong Acid Rain | ||
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 |
Lab Report:
Create a lab report that includes the following elements:
- What is acid rain?
- How does acid rain occur?
- Do background research. How does acid rain affect plants? Is it currently a problem for plantlife?
- Completed data table.
- Did your results support or refute your hypothesis? Why or why not?
- Summarize your results.
- What percentage of beans germinated in each type of “rain?”
- What were some sources of error in your experiment?
- Other than plants, what other things are damaged by acid rain?
- What are some ways of reducing acid rain so that it will not continue to harm organisms in the environment?
From a Georgia Virtual Learning assignment source
FREE K-12 standards-aligned STEM
curriculum for educators everywhere!
Find more at TeachEngineering.org .
- TeachEngineering
- Acid Rain Effects
Hands-on Activity Acid Rain Effects
Grade Level: 6 (5-6)
Time Required: 45 minutes
Expendable Cost/Group: US $2.00
Group Size: 4
Activity Dependency: None
Subject Areas: Chemistry
NGSS Performance Expectations:

Curriculum in this Unit Units serve as guides to a particular content or subject area. Nested under units are lessons (in purple) and hands-on activities (in blue). Note that not all lessons and activities will exist under a unit, and instead may exist as "standalone" curriculum.
- Acid and Base Rainbows
- Is That Legal? A Case of Acid Rain
- The Effects of Acid Rain
- Visual Literacy: Tears in Acid Rain
| Unit | Lesson | Activity |
TE Newsletter
Engineering connection, learning objectives, materials list, worksheets and attachments, more curriculum like this, introduction/motivation, troubleshooting tips, activity extensions, activity scaling, user comments & tips.

Acid rain is a complex environmental problem that concerns many environmental and chemical engineers. When engineers examine the acid rain damage to water, wildlife, forests, crops and structures, they consider the impact on human health. Engineers design many useful technologies that help industry reduce the amount of harmful pollutants released into our air. Engineers also help to develop laws that prevent or limit factories and industries from burning fossil fuels (which release pollutants), or require them to minimize their pollutant output.
After this activity, students should be able to:
- Discuss how engineers are working to prevent pollution and acid rain.
- Use an indicator to differentiate between acidic, basic and neutral solutions.
- Use their observations to describe the cause-effect relationship of acid rain.
- Observe and describe some of the harmful effects of acid rain on living and non-living items.
Educational Standards Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science, technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards. All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in TeachEngineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN) , a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org). In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g. , by state; within source by type; e.g. , science or mathematics; within type by subtype, then by grade, etc .
Ngss: next generation science standards - science.
| NGSS Performance Expectation | ||
|---|---|---|
| MS-ESS3-4. Construct an argument supported by evidence for how increases in human population and per-capita consumption of natural resources impact Earth's systems. (Grades 6 - 8) Do you agree with this alignment? Thanks for your feedback! | ||
| This activity focuses on the following aspects of NGSS: | ||
| Science & Engineering Practices | Disciplinary Core Ideas | Crosscutting Concepts |
| Apply scientific ideas to construct an explanation for real-world phenomena, examples, or events. Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for phenomena.Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! Conduct an investigation to produce data to serve as the basis for evidence that meet the goals of an investigation.Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! | Typically as human populations and per-capita consumption of natural resources increase, so do the negative impacts on Earth unless the activities and technologies involved are engineered otherwise. Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! | Cause and effect relationships may be used to predict phenomena in natural or designed systems. Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! All human activity draws on natural resources and has both short and long-term consequences, positive as well as negative, for the health of people and the natural environment.Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! Scientific knowledge can describe the consequences of actions but does not necessarily prescribe the decisions that society takes.Alignment agreement: Thanks for your feedback! |
Common Core State Standards - Math
View aligned curriculum
Do you agree with this alignment? Thanks for your feedback!
International Technology and Engineering Educators Association - Technology
State standards, colorado - math.
Each group needs:
- 1 cup vinegar
- 1 cup distilled water
- 2 medium-sized eggshell pieces
- 2 small green leaves
- 2 paperclips
- 2 small- or medium-sized glass jars
- masking tape and pen (for labeling containers)
- two 1.5-inch strips of wide-range (0-14 pH) litmus paper; since groups need to use the comparison chart included with the litmus container, obtain enough dispensers for each group to have one; litmus paper is available from chemistry supply companies (such as Fisher) and well-equipped hardware stores.
- Acid Rain Effects Worksheet , 1 per student (for recording data and answering questions)
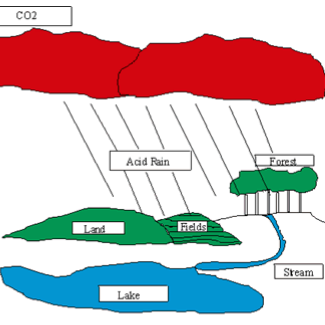
Acid rain is an environmental problem that concerns many environmental and chemical engineers. Engineers are always considering the possible effects of acid rain on the health of humans and the environment when they investigate damage to bodies of water, wildlife, forests and crops, and contamination of the drinking water supply.
Acid rain is defined as any form of wet precipitation (rain, snow, fog, dew or sleet) that has a pH less than 5.6 (on a scale of 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral). Large quantities can also be deposited in a dry form through dust. Acid rain is more acidic than normal rain and forms through a complex process of chemical reactions involving air pollution and water molecules in the air. The two most important pollutants that contribute to the formation of acid rain are nitrogen and sulfur compounds, which react with moisture in the atmosphere to form nitric and sulfuric acid.
The sulfur and nitrogen compounds that contribute to acid rain primarily come from combustion products (burning coal and oil) from large industrial and utility sites. Emissions also come from automobiles and other forms of transportation, and other industrial processes.
The effects of acid rain may not be immediately apparent. For example, at a glance, a lake might look clear and beautiful, but a closer look may reveal few living organisms. Some species of fish cannot survive in water with a pH of less than 5. Clams, snails, crayfish and other crustaceans, brook trout, walleyed pike and bullfrogs are especially sensitive to acid in their water supply. Thus, the pH does not have to decrease very much before fish cannot survive. Insects, birds and mammals are also highly affected by acid rain. Acid rain can alter soil chemistry, nutrient availability and plant growth. In their weakened condition, trees and shrubs become vulnerable to insects, diseases and fungus infestations. For more information, see the Acid Deposition Reading and Approximate pH of Common Substances References Sheet .
One way that we can help prevent acid rain is by burning less fossil fuel. Some types of industries that burn a lot of coal and oil include large power plants, and paper and wood processing plants. Engineers have helped to develop laws that prevent or limit large factories and industries from burning fossil fuels or that require them to minimize their pollutant output. Engineers have also developed many useful technologies to help industry reduce the harmful pollutants in the air, but the companies must adhere to the laws and use these technologies.
Before the Activity
- Practice this activity at home prior to using it in your classroom.
- Gather materials and make copies of the Acid Rain Effects Worksheet .
With the Students
- Divide the class into groups of four students each.
- Distribute supplies to each group.
- Ask students to use the pH paper to measure the pH of the vinegar and the distilled water, and record it on their worksheets.
- Ask the students to make some predictions. If vinegar contains acid (acetic acid), then how will the items placed in vinegar change? If these items are placed in water, will they change in the same ways as in the vinegar?
- Have students use masking tape and pens to label one jar "vinegar" and the other one "water."
- Pour 1 cup of vinegar into the vinegar jar. Place a paperclip, piece of eggshell and a green leaf in the vinegar. Put the lid on the container.
- Pour 1 cup of distilled water into the water jar. Place a paperclip, piece of eggshell and a green leaf in the distilled water. Put the lid on the container.
- Let the jars sit overnight on a windowsill or protected area.
- The next day, remove the container lids. Observe any changes in the condition of the items in the jars. Ask students to write their observations on their worksheets. (Expected results: In the water containers, the items show no noticeable changes. In the vinegar jars, the eggshells are soft, the leaf may have brown spots [this may take a few days], and the paperclip shows no noticeable changes.)
- After one week, look for more changes. Make observations again, as often as you wish.
- Direct students to complete the questions on their worksheets and/or discuss as a class.
Pre-Activity Assessment
Prediction : Using the Acid Rain Effects Worksheet , ask students to record some predictions. If vinegar contains acid (acetic acid), how will the items placed in vinegar change? If these items are placed in water, will they change in the same ways as in vinegar?
Activity Embedded Assessment
Observations : Using the Acid Rain Effects Worksheet , ask students to record their observations of what happens to the items after one day and one week.
Worksheet : Ask students to complete the questions on their Acid Rain Effects Worksheets . You may wish to discuss some of these as a class.
Post-Activity Assessment
It's a Community Issue! : Ask students to write a detailed description of how acid rain would affect their world. For example, the tree on the playground, the pencil they use, a local crop or a local park, etc.
Safety Issues
Remind students not to taste the "acid rain" even though it is made of vinegar.
Allow at least 24- 48 hours for the effects of the vinegar to appear in the leaf and eggshell.
Look at photographs on the Internet or in books/magazines that show evidence of damage due to acid rain. Discuss the general and specific types of damage to living and non-living things.
If you know of physical evidence of acid rain in your community, arrange a field trip to see and examine it.
Observe the effects of acid rain on living plants. Water a control plant with distilled water and the other with vinegar water (1 tablespoon vinegar per 1 cup distilled water). You can also water them both with distilled water and spritz them with distilled water or vinegar water to more accurately simulate rain. Discuss/explore materials that could be added to the soil to counteract the effects of the acid rain.
Try the vinegar experiment with a whole, raw egg, or a piece of chalk.
Make a third solution (perhaps of lemon juice or a vinegar/water mix) and compare/rank the results or make a bar graph.
Have students read and discuss the Acid Deposition Reading .
- While this activity is appropriate for all grade levels, for lower grades, consider observing and discussing the effects as a class. Encourage students to draw pictures of the results (and for assessment).
- For upper grades, have students measure a precise volume of vinegar and water.
- For upper grades, ask students to use graph paper (this may be easier with irregular shapes), or measure length and width to determine the area of the eggshell and leaf.
- For upper grades, have students measure the mass of the eggshell, leaf and paperclip before and after the experiment.
Students are introduced to acids and bases, and the environmental problem of acid rain. Students also conduct a simple experiment to model and discuss the harmful effects of acid rain on our living and non-living environment.

Students are introduced to the differences between acids and bases and how to use indicators, such as pH paper and red cabbage juice, to distinguish between them. They learn why it is important for engineers to understand acids and bases.

Students are introduced to the primary types of erosion—chemical, water, wind, glacier and temperature. Students investigate examples of each erosion type and discuss how erosion changes the surface of the Earth.

Students are introduced to the concepts of air pollution, air quality, and climate change. The three lesson parts (including the associated activities) focus on the prerequisites for understanding air pollution. First, students use M&M® candies to create pie graphs that express their understanding o...

Air Quality, Project A.I.R.E. (Air Information Resource for Educators). Last updated on October 15, 2002. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Accessed October 31, 2004. Originally found at: http://www.epa.gov/region01/students/teacher/airqual.html
Investigations in Science – Ecology . Huntington Beach, CA: Creative Teaching Press, 1995.
Contributors
Supporting program, acknowledgements.
The contents of this digital library curriculum were developed under grants from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), U.S. Department of Education and National Science Foundation (GK-12 grant no. 0338326). However, these contents do not necessarily represent the policies of the Department of Education or National Science Foundation, and you should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Last modified: May 21, 2021

Acid Rain Assignment
- Identify the causes of acid rain.
- Explain how acid rain is formed.
- Explain how acid rain impacts the environment.
- Identify ways to prevent the formation of acid rain.
- Explain sources of human impact on the environment from chemical disposal/production.
- Balance a chemical equation.
- Identify types of chemical reactions.
- Predict the products of chemical reactions.
- Calculate pH from concentration and vice versa.
- Calculate concentration using percent by mass and by volume.

Related Textbook
Please read section 17.9 of your textbook before completing this assignment. The information provided here will help you complete this assignment.
Introduction
Acid rain is caused by burning fossil fuels containing nitrogen and sulfur. When burned, fossil fuels release nitrogen and sulfur, which react with oxygen to form sulfur oxides (such as sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide) and nitrogen oxides (such as nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide). These chemicals then react with the water in the air to produce sulfurous acid, sulfuric acid, nitrous acid, and nitric acid. The presence of these acids in rainwater lowers the pH, making the rain more acidic.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration website, petroleum, natural gas, and coal, all of which are fossil fuels, have provided more than 80% of the total US energy consumption for the past century. In 2015, 81.5% of US energy consumption was met by the use of fossil fuels.
The resources below explain in more detail how acid rain is formed, the impacts of acid rain, and how to prevent the formation of acid rain. Review these resources to learn more about acid rain.
Environmental Protection Agency Information on Acid Rain:
- What is acid rain: https://www.epa.gov/acidrain/what-acid-rain
- Effects of Acid Rain: https://www.epa.gov/acidrain/effects-acid-rain
Acid Rain by Fuse School
Reducing acid rain and it’s effects by fuse school.
Answer the following questions using the information provided in the assignment introduction, your textbook, and the concepts we have learned in this class. Your assignment must be handwritten. Typed submissions will not be accepted and will earn a zero. You must show all of your work on the calculations to earn credit. Upload your completed assignment to the “Acid Rain assignment folder” on Brightspace. This assignment is worth 25 points.
- Explain how fossil fuels, which are made of carbon and hydrogen, contain sulfur compounds. (2 points)
- Explain how nitrogen is released into the air to form nitric acid and nitrous acid, causing acid rain. (2 points)
- What are 3 specific ways acid rain impacts the environment? (3 points)
- What are 3 specific ways to reduce the amount of acid rain produced? Be sure to address both the production of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides in your answer. (3 points)
- Acid rain is formed when sulfur dioxide or nitrogen dioxide is released into the air from burning fossil fuels and then reacts with the water in the air. Balance the equations for the formation of sulfur dioxide and nitric acid, illustrated below: (2 points each)
Reaction 1: FeS 2(s) + O 2(g) → Fe 2 O 3(s) + SO 2(g)
Reaction 2: NO (g) + O 2(g) → NO 2(g)
- What type of chemical reaction (single replacement, double replacement, combination, decomposition, combustion) is illustrated in Reaction 2 above? (1 point)
- Calcium oxide or sodium carbonate can be used to scrub the sulfur dioxide from emissions from power plants. One of the videos illustrated a reaction between calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to produce calcium sulfite. When sulfur dioxide reacts with sodium carbonate, sodium sulfite and carbon dioxide gas are produced. Using this information, write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of sulfur dioxide and sodium carbonate. (4 points)
- The pH of a sample of rainwater water is 5.6. What is the hydronium concentration in this sample of rainwater? (0.5 point)
- The pH of a sample of acid rain is 4.3. What is the hydronium concentration of this sample of acid rain? (0.5 point)
- According to data obtained from Statista.com, the United States burned 587 tons (532.5 metric tons) of coal in 2019. If coal contains 3.5% sulfur, how many grams of sulfur are released by coal burning in 2019 in the US? Write your answer in scientific notation. You must show your work to receive credit for this problem. (1 metric ton = 1,000,000 grams) (5 points)
“Acid Rain.” YouTube , Fuse School, 10 Aug. 2014, www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nf8cuvl62Vc .
“Reducing Acid Rain Or Its Effect.” YouTube , Fuse School, 10 Aug. 2014, www.youtube.com/watch?v=VILCk2CpUCw .
“Effects of Acid Rain.” EPA , Environmental Protection Agency, 4 May 2020, www.epa.gov/acidrain/effects-acid-rain .
Sönnichsen, Published by N., and Jul 14. “Coal Consumption United States 2006-2019.” Statista , 14 July 2020, www.statista.com/statistics/243934/coal-consumption-in-the-united-states/ .
“U.S. Energy Information Administration – EIA – Independent Statistics and Analysis.” Fossil Fuels Still Dominate U.S. Energy Consumption despite Recent Market Share Decline – Today in Energy – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) , 1 July 2016, www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=26912 .
“What Is Acid Rain?” EPA , Environmental Protection Agency, 12 May 2020, www.epa.gov/acidrain/what-acid-rain .
This page was created on February 15, 2023, and was last updated on August 4, 2023.
©2023 Catherine Haslag. All Rights Reserved.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Learning About Acid Rain: A Teacher's Guide for Grades 6 through 8
This book is intended for teachers of students in 6th-8th grade. It is written at a 6th grade level and the language, concepts, and experiments may need to be adapted for other grades accordingly.
View this book in the National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP)
Printable PDF:
- Acid Rain Teacher's Guide for Grades 6-8 (pdf) (4.6 MB)
- Acid Rain Home
- What is Acid Rain?
- Effects of Acid Rain
- Acid Rain Program
- Acid Rain Program Results
Search Filters:
Main Navigation
Search Cornell
Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers
- Labs & Activities
- Workshops & Events
- Equipment Lending Library
- Connect with Cornell
Labs & Activities
In this section:

Thanks to generous support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Science Foundation and the Cornell Biotechnology Program, CIBT has developed over 100 labs and classroom activities. Our materials have been developed through partnerships between science faculty and classroom teachers. Many of the labs require little equipment and elaborate supplies, while others are time and equipment intensive. Many of the labs are now kits that are made available to CIBT alumni teachers. For kits, see the Equipment Lending Library .
CIBT labs contain two sections. The first is a teacher section with extensive background information, suggestions for time management of the lab and lists of needed reagents and materials. The following section is for distribution to the students. It contains relevant background and data collection sheets.
All of our labs and classroom activities are available for download at no charge!
- 2012 CIBT Alumni Workshop
- Elementary School
- High School
- Human Health
- Inquiry/Scientific Method
- Microbiology
- Middle School
- Molecular Biology
- Physical Sciences
- Recently Added

Abuse-a-Cyst- University of Utah
Brine shrimp populations survive in some of the harshest environments. Subject brine shrimp cysts to extreme conditions then try to hatch them to see just how tough they are! Downloads Abuse a Cyst Lab (University of Utah)
Acid Rain Lab- Katherine Betrus Derrico
Students will design and conduct an experiment to test the effect of acid rain on the germination of seeds. They will utilize the data from their experiment to explain their conclusions, and also read a passage on acid rain. Downloads Acid Rain Lab Rubric (Katherine Betrus Derrico) Acid Rain Lab... read more of the article entitled "Acid Rain Lab- Katherine Betrus Derrico"
Battle-jar Galactica- Matt Downing
In this investigation students will study the types of bacteria that grow during the formation of sauerkraut, identify some characteristics of each, as well as research the type of respiratory pathway used by the organisms to break down the cabbage to get their energy. Downloads pH Questions (Matt Downing) Bacteria... read more of the article entitled "Battle-jar Galactica- Matt Downing"

Becoming a Plant
Students will plant seeds at various depths in the soil and make observations after seedlings emerge. Based on their observations, students will decide what measurements could be made. They will make these measurements and look for an explanation for differences in their measurements. They will write a hypothesis that describes... read more of the article entitled "Becoming a Plant"
Biological Shapes
Remember the old salad dressing commercial tag line “…because oil and vinegar don’t mix!” Water has that same love/hate relationship with many other molecules. Through this series of lessons, students will learn about the properties that make other molecules “love” or “hate” water. They will also begin to build a... read more of the article entitled "Biological Shapes"
Biomagnification Lab- Todd Shuskey
This lab demonstrates how contaminants can accumulate in organisms within a food web by using paper cutouts and M&M®s candies to simulate fish, osprey, and DDT. Students can see how the contamination levels increase as the trophic level increases. Downloads Biomagnification Lab Pictures (in color) Biomagnification Lab Pictures (in black and... read more of the article entitled "Biomagnification Lab- Todd Shuskey"
Blood Vessel Physiology
This lab investigates the physical mechanisms by which our blood vessels function in allowing the circulatory system to do its job. Blood vessels are not simply rigid tubes that conduct blood to our tissues like copper pipes carrying water to our houses, nor are they infinitely extensible balloons that can... read more of the article entitled "Blood Vessel Physiology"

Bottle Ecosystem- Tim Downs
The objective of this lab is to put together a suitable habitat (ecosystem) that will allow one or two guppies to survive to the end of the school year and beyond. Students will make observations of their ecosystems for the three weeks. The ecosystem in this experiment will be closed,... read more of the article entitled "Bottle Ecosystem- Tim Downs"

Bouquet of Flowers
This series of four different lab activities all relate to flower reproduction. They have been designed to relate to each other and to stand alone. Name that Pollinator focuses on adaptations for successful pollination. Both pollen and pollen vectors are examined. Observing, data gathering, making measurements through the microscope, and... read more of the article entitled "Bouquet of Flowers"
Bovine Uterus Dissection
The instructor will dissect an early to mid-pregnant bovine reproductive tract. Data on crown rump length and fetal mass can then be collected for use with CIBT’s Fetal Development Lab. Some appreciation of the form and function of the various organs should be developed by students. This exercise will also... read more of the article entitled "Bovine Uterus Dissection"
Building Blocks of Life
The shape of a protein determines its function. In this lab, students will be given a hypothetical DNA sequence for part of an enzyme. Using the Universal Genetic Code, they will then determine the amino acid sequence coded for by the DNA. Students will examine a “substrate” and predict the... read more of the article entitled "Building Blocks of Life"

Case of the Missing Diamond Maker
Students will learn about some of the techniques of forensic science. They will use fingerprinting, chromatography, and chemistry to gather and analyze evidence left behind at a crime scene. Students will exercise deductive reasoning to evaluate the evidence and determine the criminal’s identity. CIBT has prepared a Missing Diamond Maker... read more of the article entitled "Case of the Missing Diamond Maker"
The structure and function of enzymes is a central theme in cellular and molecular biology. In this laboratory exercise, a crude cell extract is prepared from potatoes. Activity of the enzyme, catalase [which catalyzes the reaction 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)], is then studied using a simple assay for O2. To... read more of the article entitled "Catalase"

Comparative Skulls
What can a skull tell you? A lot! If you look at a skull for clues about its origin, not only can you identify what species it might be from, but you can learn many details about the original animal. In this lab, students will determine what clues to analyze in... read more of the article entitled "Comparative Skulls"
Comparing Aquatic Communities
Teams of students measure physical and chemical characteristics of different sites in streams and/or ponds and collect benthic invertebrate organisms. They interpret patterns in the structure of the biological community at each site in light of the abiotic (physical and chemical) and biotic nature of the environment. Downloads Comparing Aquatic... read more of the article entitled "Comparing Aquatic Communities"

This lab uses two different sizes of dialysis tubing to represent cellular and organelle membranes. Students design experiments in which they place solutions of iodine, starch, and glucose on different sides of a membrane. The movement of these materials is monitored with the use of indicator solutions. Students are given... read more of the article entitled "Diffusion"
DNA Molecule Activity
This lab activity corresponds to CIBT’s DNA Molecule Model. Downloads DNA Molecule HS Student Edition (CIBT) DNA Molecule MS Student Edition (CIBT) DNA Molecule Post-Lab Questions (CIBT) Watson & Crick Reading (CIBT) Watson&Crick Reading Qs Student Edition (CIBT) Watson&Crick Reading Qs Teacher Edition (CIBT) DNA Blankenship Notes (CIBT)

DNA Profiling
This lab was designed to complement CIBT’s DNA Gel Electrophoresis kit. Students will cut DNA with restriction enzymes. The DNA fragments will be separated electrophoretically on an agarose gel. The results will simulate a DNA profile. Students can learn how this type of evidence is prepared and interpreted. Downloads DNA Profiling Teacher... read more of the article entitled "DNA Profiling"

Easy Stats Lab
Downloads Easy Stats Intro Activity (CIBT) Easy Stats Lab (CIBT) Easy Stats Data Table (CIBT) Easy Stats Post-Lab Questions (CIBT)

Edible Earth Parfaits- Groundwater Foundation
This activity uses soda, ice cream, sprinkles, colored sugars, and food coloring to represent the layers of Earth and aquifers under the surface. Students are instructed to “drill a well” with a straw and “pump the well” by sucking on the straw, as they watch the decline in the water... read more of the article entitled "Edible Earth Parfaits- Groundwater Foundation"

This lab involves the qualitative measurement of the changes in carbon dioxide concentration associated with respiration and photosynthesis in the freshwater plant Elodea. Bromthymol blue is used as an indicator for the presence of CO2 in solution. When CO2 dissolves in water, carbonic acid is formed. A bromthymol blue solution, acidified... read more of the article entitled "Elodea"
Evolving Trees
This exercise introduces the basic methods of phylogenetic analysis. Students are asked to hypothesize the evolutionary relationships of groups of organisms based on traits, and to become familiar with the methods for building evolutionary trees using the basic principles of taxonomy and classification. Downloads Evolving Trees (Teacher Edition) Evolving Trees... read more of the article entitled "Evolving Trees"
Fetal Development
Students will measure pictures of developing cow embryos, or use data from the pregnant bovine uterus dissection, to generate size data. Then they will interpret data from graphs to determine age and mass. Students will compare changes of mass during fetal development with changes in size. Finally, students will contrast developmental... read more of the article entitled "Fetal Development"

Floating Leaf Disk- Brad Williamson
This lab tangibly demonstrates the abstract concept of photosynthesis to students. Normally, disks punched out of leaves (with a hole punch) would float. When the air spaces are infiltrated with a sodium bicarbonate solution, the overall density of the leaf disks increase and they sink. Bicarbonate ion serves as the... read more of the article entitled "Floating Leaf Disk- Brad Williamson"
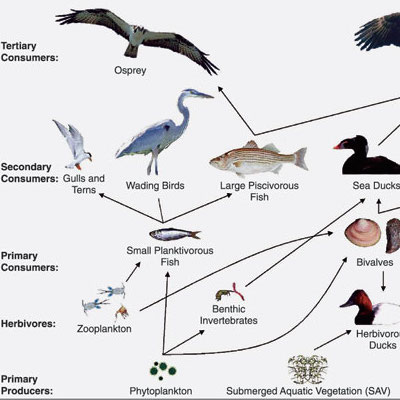
Food Chain Game- Delta Education
In this activity, students investigate food chains by assuming the roles of animals that are part of a food chain. Downloads

Goldenrod Galls
This investigation examines natural selection and coevolution using goldenrod (Solidago canadensis), its stem gall insect (Eurosta solidaginis), and associated parasites, parasitoids, and predators that feed upon the stem gall insect (i.e., Eurytoma obtusiventris, Eurytoma gigantea, Mordellistena unicolor, and birds). Through measurements of gall size and an investigation of events occurring... read more of the article entitled "Goldenrod Galls"
HIV Transmission
“This is the best way I can imagine to introduce such a sensitive/vital issue in a non-embarrassing way and still get the message across: the HIV virus is transmitted by sharing body fluids, there are specific high risk behaviors, and what you choose to do is the greatest determining factor... read more of the article entitled "HIV Transmission"
How Many CATs
In this paper simulation, students will “cut” DNA samples from a mother, a baby, a husband, and a rape suspect using a “restriction endonuclease.” They will then “run” the DNA fragments on a “gel” to simulate the process of electrophoresis. A fluorescent probe is then washed over the gel. Finally,... read more of the article entitled "How Many CATs"
I’ll Have a Bite! – Greg Panzanaro
This lab was designed by one of our alumni teachers to complement CIBT’s Forensics Odontology kit. Downloads I’ll Have A Bite (Greg Panzanaro)

Insect GENEration
Students build a model insect based upon genetic information provided to them in the lab directions. Gene forms (alleles) contributed by each parent are determined by tossing a coin with one side representing the dominant form of the gene and the other side representing the recessive form. Student teams record... read more of the article entitled "Insect GENEration"


Lichens on Tree Trunks- Scott LaGreca
Students will learn to recognize moss and lichens, identify various trees, record observations using a mapping technique, use a compass, and think about the conditions mosses and lichens need to grow. They will identify and mark trees with mosses and lichens growing on their trunks, and try to figure out... read more of the article entitled "Lichens on Tree Trunks- Scott LaGreca"

Mark-Recapture- Nancy Wright
This lab presents a popular method often used to estimate the population size of a single species of highly mobile animals, such as insects or vertebrates. Students use other students in the school as their population and the Lincoln-Peterson method to determine population size. “Real ecologists” also use this method... read more of the article entitled "Mark-Recapture- Nancy Wright"

Medical Importance of Biodiversity- Mary Keymel
Students assume the role of an ethnobotanist for a start-up pharmaceutical company, who is about to journey to the rainforest, coral reef, or another natural source of medicine in the world. Their mission is to catalog 1 plant or animal species that may be useful to medical research. They will... read more of the article entitled "Medical Importance of Biodiversity- Mary Keymel"
Metric Measurement
Downloads Metric Measurement (Student Edition)
Microscopy and Cell Biology
Students will identify the parts of a microscope. Students will observe, manipulate, write and memorize. Students will also compute total magnification of the objective lenses. The lab can be modified to suit higher grade levels using the attached handouts for various observation stations. Downloads Pollen Station Red Onion Cell Station... read more of the article entitled "Microscopy and Cell Biology"

Mollusk Dichotomous Key
In this lab, students will be introduced to the concept of a dichotomous key through the use of preliminary activities modeled by the teacher. They will then learn about the ecology and biology of selected marine mollusks, before putting their dichotomous key reading skills to the test on 8 or... read more of the article entitled "Mollusk Dichotomous Key"

Mystery of the (Hominin) Skulls
In this laboratory activity students will examine nine hominin skulls for specialized features and take measurements that will enable them to determine the relatedness of these species. They will identify the placement of each specimen on a phylogenetic tree that also reveals the geological time frame in which each species... read more of the article entitled "Mystery of the (Hominin) Skulls"
Oh Deer- Project WILD
Students simulate a deer population and its “limiting factors” of water, food, and shelter, which are represented by strips of colored paper. “Deer” who are unable to find a match for their limiting factor do not survive the round, and instead becoming limiting factors. The data is collected and graphed,... read more of the article entitled "Oh Deer- Project WILD"

Oil Spills Lab- Kristen Pizarro
This activity, used as a 7th grade science laboratory final exam, comes in three sections. Students will first model an oil spill and test materials for cleaning it up. This experiment will help them understand why it is such a difficult task. Next they will examine data about the effects... read more of the article entitled "Oil Spills Lab- Kristen Pizarro"

In this lab students will investigate the application of physical principles to a living organism. Students will analyze the foot and its function as a machine by applying lever mechanics to the “walking” foot. Analysis will incorporate anatomical terms for some of the muscles and bones involved in plantigrade motion.... read more of the article entitled "Phoot Lab"

This exercise helps students think about how plants grow in a fun and enticing manner. Teams of students “grow a plant” composed of “leaves,” “roots,” and “flowers.” The goal of the game is to produce a maximum number of flowers, which is possible only if the students have a good strategy to... read more of the article entitled "Plant Game"
Predator-Prey Population Oscillation- Bridget Henshaw
This activity introduces students to the oscillating relationship between predator and prey population sizes. Students manipulate small “creatures” (anything from gummy worms to animal crackers to plastic animals) with differing numbers of predators/prey and calculate population changes between rounds of predation. Data is graphed in Excel at the end. Downloads... read more of the article entitled "Predator-Prey Population Oscillation- Bridget Henshaw"

Primary Productivity Lab- modified by Sean McGlynn
Students will use LaMotte Test Kits to determine the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO) in various water samples. The process involves adding some chemicals to the water to “fix” the free oxygen (O2). Once the O2 is fixed, they will add an acid powder, some starch, and titrate to determine... read more of the article entitled "Primary Productivity Lab- modified by Sean McGlynn"
Protein Gel Electrophoresis
Students will separate a mixture of proteins from skeletal muscle using SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). PAGE is a powerful analytical technique having numerous applications in modern biology. Evidence for evolutionary relatedness amongst organisms can be determined using this technique. Suggested organisms to compare include various fishes, mammals, poultry and/or... read more of the article entitled "Protein Gel Electrophoresis"
Protein Synthesis and Words- Comet
mRNA is genetic information found in the nucleus of cells. Protein synthesis occurs in ribosomes found in the cytoplasm and on rough endoplasmic reticulum. If protein is to be synthesized, then the genetic information in the nucleus must be transferred to these ribosomes. This is done by mRNA (messenger ribonucleic... read more of the article entitled "Protein Synthesis and Words- Comet"
Pseudomonas Labs
Module 1: This classroom activity demonstrates interactions between plants and specific strains of Pseudomonas (a plant-pathogenic bacteria). Students will design an experiment that demonstrates the specificity of the hypersensitive response. This serves as a starting point to learn the importance of model systems through comparisons of two pathogens. Both Pseudomonas,... read more of the article entitled "Pseudomonas Labs"

Radish Seed Lab- Chris Courtsunis
This laboratory activity will test the effects of various household chemicals on the germination and growth of radish seeds in the lab. Downloads Radish Seed Lab (Chris Courtsunis) Radish Seed Lab Rubrics (Chris Courtsunis)
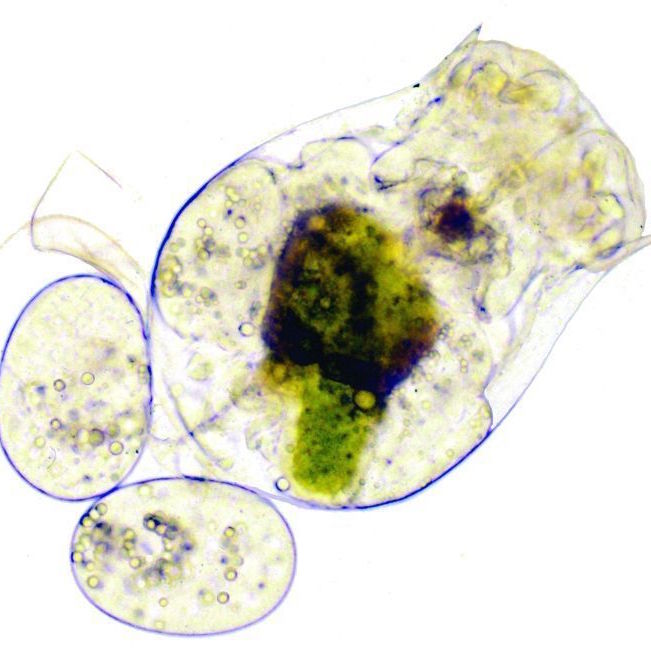
Rotifers Lab- Beth Chagrasulis
These instructions detail how to collect bdelloid rotifers from moss, extract them, and view them under a microscope along with protozoa, nematodes, and tardigrades that also live in moss. Download Rotifer Article (Beth Chagrasulis) Rotifer & Tardigrade Collecting (Beth Chagrasulis)

Shake and Break: An Earthquake Simulation
An earthquake simulator, or seismic table is constructed and then used to test the structural soundness of several types of student built houses. Several different construction materials are used to demonstrate what type best survives an earthquake. Two different geological foundations, bedrock and water-saturated sand, are tested to show the... read more of the article entitled "Shake and Break: An Earthquake Simulation"

Students will investigate the food preferences of garden slugs (Arion subfuscus) using simple equipment including margarine tubs, graph paper, scissors, and common plants, both wild and cultivated. The exercise is genuine scientific research in that: a) the student devises his/her own “research question” about slug feeding behavior, and b) the... read more of the article entitled "Slug Lab"

Students will investigate the bacteria (plant pathogens) that cause soft rot on grocery produce (that mushy mess you often see on vegetables). By bringing some of this rotting produce from the store back to the lab students can isolate bacteria that are responsible for the disease (and sometimes yeasts, other... read more of the article entitled "Soft Rot"

Downloads Spice Lab (Student Edition) Spice Lab (Teacher Edition) Supplemental Reading: Why Cilantro Tastes Like Soap, for Some Supplemental Reading: Why 10% of the Population Hates Cilantro Supplemental Reading: Antimicrobial Functions of Spices
Stomata Safari- Carolyn Wilczynski
On a “stomata safari,” students will view and compare the number and location of stomata from leaves of several species of plants. Once they have learned how to sample stomata, they will be able to investigate how plants distribute their stomata depending on the environment. Downloads Stomata Safari Lab (Carolyn... read more of the article entitled "Stomata Safari- Carolyn Wilczynski"
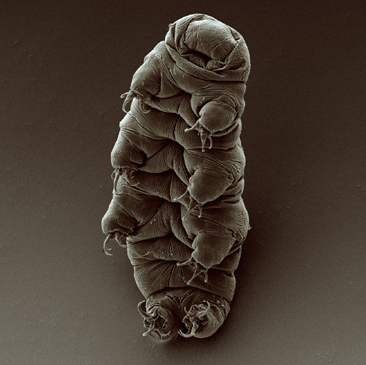
Tardigrade Lab
Downloads Students will explore the microscopic world found living on lichens and mosses. Using a simple collection and extraction process, students will observe extremophiles called tardigrades. This lab includes a reading activity with questions as well as an anticipation guide handout for use with a YouTube video Tardigrade Lab (Student... read more of the article entitled "Tardigrade Lab"
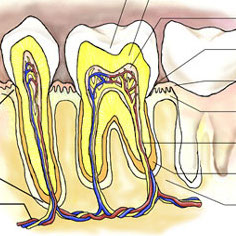
Students will investigate the characteristics of teeth and what teeth can tell about an animal’s lifestyle: Students will sort and categorize 10 to 12 teeth. Given information about what canines, incisors and molars are, students will identify which teeth are which and why. They will predict which teeth came from... read more of the article entitled "Teeth Unit"
Tell-Tale Heart
“The Tell Tale Heart” is an activity during which students familiarize themselves with the structure of the heart through a dissection. They locate the atria, ventricles, and major blood vessels. Through “surgical” procedures, students perform coronary bypass surgery and correct patent ductus arteriosus. Human and dog hearts are compared in terms... read more of the article entitled "Tell-Tale Heart"
Vegevaders- PPI
Playing this game allows students to experience through game-play the continuing co-evolution between plants and their microbial pathogens that occurs during the battle to detect/defend (plants) versus evade/invade (pathogens). This battle is ongoing in nature over evolutionary time and observable in agricultural fields from one season to another, where crop... read more of the article entitled "Vegevaders- PPI"

Vocabulary and Story Writing- Karen Cook
The RAFT strategy (Santa, 1988) employs writing-to-learn activities to enhance understanding of informational text. Instead of writing a traditional essay explaining a concept learner, students demonstrate their understanding in a nontraditional format. This technique encourages creative thinking and motivates students to reflect in unusual ways about concepts they have read.... read more of the article entitled "Vocabulary and Story Writing- Karen Cook"

Web of Gold Activity- Robert Raguso
“Web of Gold” uses common autumn wildflowers to explore the hidden lessons of food webs. Different insects visit flowers in search of different resources, in varying levels of abundance. Students will observe visitors to a flower (or area of flowers) and record their species and abundance. Older students can explore... read more of the article entitled "Web of Gold Activity- Robert Raguso"

The Whale Kit full teachers’ manual provided below contains background information, handouts, games, and laboratory exercises related to all aspects of whale biology, from the massive blue whale to the smallest harbor porpoise. Students will explore anatomy, evolution, feeding strategies, migration, communication, behavior, conservation, and cultural whale tales. Kit activities target elementary and middle school ocean science... read more of the article entitled "Whales"

Lab 1 Goal: To introduce students to the incredible diversity and abundance of insects and to prepare specimens for DNA analysis. Upon completion of this activity, students will: Describe the diversity of insects collected in one location. Identify insects using taxonomic classification. Sort insects into “morphospecies” – similar looking species.... read more of the article entitled "Wolbachia"

World of Crickets
“The World of Crickets” is a series of lab activities involving live crickets kept in the classroom that can be modified to suit students of all ages. Lab 4 is best suited for older students, as it requires experimental design and execution. Lab 1: What Do Crickets Eat? Students will... read more of the article entitled "World of Crickets"
-->Cornell University --> ©2014 ↑

Teacher Resource Center
Pasco partnerships.

2024 Catalogs & Brochures
Acid rain and seed germination.
In this lab, students will use pH sensors to determine the effect of acid rain on the germination of bean seeds.
Grade Level: Middle School
Subject: Life Science
Student Files
| 424.50 KB | ||
| 230.69 KB |
Featured Equipment

Wireless pH Sensor
Here’s the best tool for measuring pH since litmus paper. The Wireless pH Sensor connects via Bluetooth® to monitor the pH of solutions.
Many lab activities can be conducted with our Wireless , PASPORT , or even ScienceWorkshop sensors and equipment. For assistance with substituting compatible instruments, contact PASCO Technical Support . We're here to help. Copyright © 2018 PASCO
Source Collection: Lab #01
Middle School Life Science Teacher Guide
More experiments.
Middle School
- Venous Blood Flow
- Optimize Water Movement in a Greenhouse
- Muscle Fatigue
- Photosynthesis
- Air Pressure and the Lungs
- Program a Greenhouse Sense and Control System (Function-Based)
- Renew Membership
AACT Member-Only Content
You have to be an AACT member to access this content, but good news: anyone can join!
- AACT member benefits »
- Forgot User Name or Password?
Save Your Favorite AACT Resources! ×
Log in or join now to start building your personalized "My Favorites" page. Easily save all the resources you love by logging in and clicking on the star icon next to any resource title.
Investigating Acid Rain Mark as Favorite (25 Favorites)
ACTIVITY in Observations , Chemical Change , Interdisciplinary , Acid Base Reactions , Classification of Reactions , Chemical Change , Acid Rain , pH . Last updated March 11, 2022.
In this activity, students will investigate the chemistry of acid rain through web based research. Students will also have the opportunity to observe the reaction between a common acid and a material in a week long simulation and relate their findings to the effects of acid rain.
Grade Level
High school
By the end of this activity, students should be able to
- Describe the components of acid rain as well as its effects on various environments.
- Interpret observations of chemical change in an acid reaction.
Chemistry Topics
This activity supports students’ understanding of
- Chemical Reactions
- Chemical Change
Teacher Preparation : 10 minutes
Lesson : 30 minutes for web assignment; 15 minutes/day, for 3-4 days for observations
(Per group)
- 25 ml vinegar
- One uncooked egg
- Glass container with lid
- pH paper with pH chart
- Graduated cylinder
- Small paint brush
- Always wear safety goggles when handling chemicals in the lab.
- Wash your hands thoroughly before leaving the lab.
- Follow the teacher’s instructions for cleanup of materials and disposal of chemicals.
- When working with acids, if any solution gets on your skin immediately rinse the area with water.
Teacher Notes
- This resource could be used as a post-AP Chemistry exam activity.
- On the first day students should complete the webquest portion of this activity in the beginning of the class period, followed by the set-up of the acid rain simulation with the egg and vinegar.
- Materials listed are per student group. I would suggest placing students in groups of 2-3 for the simulation portion of the activity.
- The vinegar used in the simulation can be any type of vinegar (apple cider, white, etc.)
- It is possible that an egg may break at some point, so it is helpful to have multiple jars within a class so students can observe the entire process even if their egg doesn’t last through the entire week.
- Observation check-ins can be adjusted as needed with your class schedule. I would suggest having 3-4 observations after the start of the simulation.
- Students should be familiar with molecular names, formulas and reactions at this point. If students haven’t been exposed to this content yet, adjust the analysis questions as needed.
Cross-Disciplinary Extensions
Connect to Reading Read articles linking the declining bird population with acid rain.
- Songbird Population Declines, linked to acid rain
- Acid Rain Linked to Bird Decline
Connect to Writing Write a summary essay explaining the types of acid rain and the effects on the bird population.
Connect to Social Studies | Track the governmental regulations that have been enacted since the early 1960’s to the present for diminishing the emissions of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides.
For the Student
Visit the EPA website to thoroughly answer the next five questions using your own words.
Navigate through the information provided to help answer each of the questions.
- What is acid rain?
- What are causes of some acid rain?
- Why is acid rain harmful?
- What is being done to reduce acid rain?
- What can you do to help reduce acid rain?
Visit the SoftSchools.com website to thoroughly answer the next five questions using your own words.
- When was acid rain first recognized?
- When did people begin to note the crisis and looked for solutions?
- What is the general pH range of acid rain?
- What emissions do power plants produce that contribute to acid rain?
- What emissions do vehicles produce that contribute to acid rain?
- What consumer products have similar pH values as acid rain?
Visit the YPTE website to thoroughly answer the next five questions using your own words.
- How does acid rain spread?
- Why is nitrogen a problem?
- How can the damage be restored?
- What can be done to help reduce acid rain?
- Describe how mass transit would play a role in diminishing acid rain.
Part 2: Acid Rain Simulation
Acid rain and vinegar have similar pH values. Over the next week you will observe and record the effect that vinegar has on an egg shell.
- Carefully place a single egg inside one of the glass containers.
- Record your qualitative observations about the egg shell in the data table (color, hardness, etc.)
- Measure 25 ml of vinegar in a graduated cylinder.
- Pour all the vinegar onto the egg in the jar. Using the paint brush, apply the vinegar to the shell of the egg, so that the entire surface has been saturated with vinegar.
- Touch the paint brush to a strip of pH paper. Compare the color change with the pH color chart. Record the pH value in the data table.
- Seal the jar with the lid, and place the jar in a safe place.
- After 24 hours return to the jar.
- Remove the lid, and dip your paint brush in the jar and touch it to a new piece of pH paper. Record this value in your data table.
- Again record your qualitative observations about the egg shell in the data table, specify color, hardness, etc. Wear gloves if you remove the egg from the jar.
- Seal the jar with a lid, and place the jar in a safe place.
- Repeat steps 7-9 several times during a week (complete 3-4 observations after the first day).
- After a week, wearing gloves remove the egg from the jar and gently rinse the egg with water. Record your final observations.
Observations
| | ||
- How does the pH of vinegar compare with the average pH of acid rain? Refer to your webquest if needed.
- What indicators of chemical change did you observe on the egg shell during the week trial?
- Research to find out what the main chemical component of an egg shell is. Record its chemical name and chemical formula.
- Research to find out what the acid in vinegar is called. Record its chemical name and chemical formula.
- What kind of reaction took place between the egg shell and the vinegar?
What other materials contain the same chemical as the one found in egg shells? Reflect on the egg and vinegar reaction, why was this done, and how was it helpful as you learned about acid rain?
Hobart and William Smith Colleges
Acid rain lesson student worksheet.
- Finger Lakes Institute
- Intern Opportunities
- Finger Lakes Community Development Center
- Finger Lakes Research Conference
- Archived Projects
- Centers for Experiential Education
What is acid rain? Acid Rain is a term used to describe the phenomena of rainfall that contains lower than normal readings of pH due to inputs of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide compounds into the atmosphere. These compounds come from power plants and other industries that burn fossil fuels for energy. Scientists are concerned about acid rain and its impact on the environment. For this lesson we will focus specifically on the affects of acid rain on lakes and aquatic life although acid rain's impacts are much broader.
How Acidic is Rain in New York State? A pH scale is used to measure acidity, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 the most alkaline. A value of 7 is neutral. Solutions with a pH of less than 7 are acids, while those with a pH greater than 7 are bases. A decrease in pH represents an increase in acidity, and an increase in pH represents a decrease in acidity. The scale also is logarithmic, meaning that a one-unit change actually represents a tenfold change. Rainfall is somewhat acidic by nature, due to atmospheric carbon dioxide (gas) reacting with precipitation (rain drops) to make carbonic acid, a weak acid. The acidity of rainfall is critical for the weathering of rocks and formation of soils on land. Without it there would not be the needed minerals and nutrients in soils to grow plants. However, acid rain is intensifying this weathering process and can have negative impacts on the landscape and surface waters where transported ions and sediments end up. While normal rainfall is slightly acidic (about 5.5) the average pH of rainfall in New York State ranges from 4.0 to 4.5 - 30 times more acidic than "normal". Below is a graph that illustrates the acid rain cycle.

Acid Rain and the Environment When acid rain falls to the earth it interacts with landscape features which affects how it will impact the environment. Much of the research on the detrimental effects of acid rain has been conducted in the Adirondack region of New York State where the igneous/metamorphic bedrock in this region and the thin, slightly acidic soils lack the ability to neutralize the inputs from acid rain. In the Finger Lakes region however, calcareous soils and limestone outcrops which contain Ca CO 3 (calcium carbonate) are dominant in the landscape and provide a "buffer" against acid rain. Source: Lajewski, C. K. et. al. Geological Society Bulletin 2003.
Below are links to bedrock maps of the regions discussed:
Finger Lakes Adirondacks
Acid rain has many negative impacts on the environment. Acid rain can alter the pH of surface water such as lakes and streams stressing aquatic life that is adapted to certain pH levels. Acid rain also can erode to concrete buildings and monuments. And the particles in acid rain can contribute to health problems for people with respiratory illness like asthma or bronchitis.
Below are links that provide some good background information about water quality and pH and the impacts of acid rain. You may ask students to do some of their own research as well.
Glossary of Terms pH and Water Quality What is Acid Rain? Acid Rain Impacts on the Environment
Lesson Outcomes
Through this lesson and accompanying activity students will:
- Understand the dynamics of acid rain and its impact on the living and non-living environment.
- Hypothesize how acid rain affects water pH levels in two lake systems with differing watershed features.
- Learn to make scatter plot charts of data sets using MS Excel computer software.
- Analyze trends in charts.
- Interpret data from charts and table.
MST Standards
- Standard 1 Key 1, Key 3
- Standard 2 Key 1
- Standard 4 Key 2, Key 6
- Standard 5 Key 3, Key 6
Lesson Objectives
In this lesson you will be investigating the relationship between acid rain and pH levels in two lakes: Morehouse Lake in the Adirondacks and Seneca Lake in the Finger Lakes. To do this you will be using data on pH levels collected from both lakes for the years 1993-2007 and making two charts. You will be using these charts along with the charts provided in the lesson to answer the questions A-E. Although the charts will help you to answer some of the questions you will need to refer to the website links found at the bottom of the page for further information. At the end of this lesson you should have completed:
- Two charts: Avg pH in Morehouse Lake; Avg pH Seneca Lake
- Answered questions A-E using your generated charts, the charts and table provided and the website links as references.
In this activity you will make two charts showing a line graph of the average pH concentrations in the surface waters of a lake in the Adirondacks - Morehouse Lake, and for a lake in the Finger Lakes region - Seneca Lake, for the years 1993-2007. Follow the steps below to complete the activity.
Step 1) Copy and paste to copy the data sets (including the headers) shown here into an Excel file.
Morehouse and Seneca lakes data
Activity for Users of Excel Before 2007
Activity for Users of Excel Version 2007
The two charts that students generate should look like this:

Answer the questions below. Additional information can be found at the websites listed.
A. What is the general trend of the pH levels in the lakes over the past ten years? The general trend has been for the pH levels to increase. The magnitude of these increases may not seem apparent to the students when they view the charts and see only a unit increase in pH levels from one year to the next. Remind students however that the increase in pH from one unit to the next is logarithmic or exponential. The articles enphasize that scientists are claiming the increase in pH levels are apparent but may not keep going up if there are not more restrictions placed on emissions from power plants and vehicles.
B. How would you explain this trend? The increase in pH values over the past ten years has been linked to the Amendments to the Clean Air Act of 1990. Although scientists agree that the 1990 Amendments have helped reduce the impacts of sulfur dioxide emissions, they are unclear whether the Amendments have had as great an impact on Nitrogen Oxide emissions. Scientists from Syracuse University and the University of Maine caution that further reductions in emissions may be needed to bring the lakes in the Northeast back to health.
C. Which lake system has a greater potential to buffer the effects of acid rain and why? Recent research conducted by scientists from Syracuse University has shown that the soils and underlying bedrock in the Finger Lakes region buffer the effects of acid rain and actually contribute to an "alkalization" of the lakes. Scientists call this phenomena a "chemical weathering" of the bedrock in the region which increased rapidly in the 1820s when the region was deforested, leveling off and then beginning again after World War II and into the 1990s. See links below for the actual study and the a synthesis of the study for the student handout.
Lajewski Study of Finger Lakes and Acid Rain Acid Rain in the Finger Lakes Acid Rain in the Adirondacks
D. Charts A & B show the annual average pH of rainfall at a monitoring site in Huntington NY (Adirondacks) and Aurora NY (Finger Lakes) over the past ten years.
- For each region acid rain precipitation shows an increase in pH levels.
- The reductions of sulfur emissions due to the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 which reduced the amount of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere reducing the amount of sulfur in acid rain.
- The data show the most obvious upward trends for both regions. In the 1990's the pH levels of the acid rain were actually lower in the Finger Lakes region than in the Adirondacks. Students are then asked to observe why then would we see lower pH levels in Morehouse Lake in the Adirondacks vs. Seneca Lake during this period of time?
- As the pH levels in the acid precipitation have increased for both regions, the pH levels in the lakes reflect this trend with higher pH levels in the surface waters.
- When acid precipitation falls in the Adirondacks the soils and bedrock lack the ability to buffer the effects of the acids. Morehouse Lake is also more acidic to begin with so the pH levels have remained acidic. However, in the Finger Lakes region the limestone bedrock and calcareous soils are able to buffer the effects of acid rain by the chemical weathering of calcium carbonate and the pH levels of the lake have remained basic.

- 1993-1999 were critical years for Morehouse Lake as pH levels dipped to 4.0 at one point before going back up to 6.0. The health level of the lake was at an all time low of 4 where insects and frogs and some fish may have been affected. Fish eggs would not have hatched.
E. Using the charts you made on pH levels in Seneca Lake and Morehouse Lake and the table below answer the following questions about the health of the water body if pH is the only factor.
pH and Effect on Aquatic Organisms
| Health Level | pH | Effect |
|---|---|---|
Source: Center for Earth and Environmental Science at Indiana University - Purdue University Indianapolis.
Bonus Question: Hypothesize and explain two factors that may cause a body of water to change pH. pH levels are also affected by photosynthesis and respiration of plant life in the lakes. During photosynthesis plants take up CO2 which causes the pH levels to increase,at night when plants are respiring the pH levels will naturally decrease as CO2 is released. Episodic acidification is also possible when there is a sudden snow melt or rainfall releasing acidic pollutants into watersheds. Other factors that will affect pH are the release of chemicals from industrial pollution and vehicle emissions.
Link to other lesson plans on pH
pH and plants pH Effects on Aquatic Life
Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology
Molecular level seasonality of dissolved organic matter in freshwater and its impact on drinking water treatment †.

* Corresponding authors
a Department of Thematic Studies – Environmental Change, Linköping University, SE-581 83 Linköping, Sweden E-mail: [email protected]
b Department of Chemistry, State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry, Syracuse, New York 13210, USA
c Research Unit Analytical BioGeoChemistry, Helmholtz Munich, Ingolstaedter Landstraße 1, 85764 Neuherberg, Germany
d Chair of Analytical Food Chemistry, Technical University of Munich, 85354 Freising, Germany
e University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science, Chesapeake Biological Laboratory, Solomons, Maryland 20688, USA
f Research Unit: Environmental Sciences and Management, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
g Norrvatten, Kvalitet och Utveckling, SE-169 02 Solna, Sweden
h Nodra, Borgs vattenverk, SE-603 36 Norrköping, Sweden
Improved characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in source waters used for drinking water treatment is necessary to optimize treatment processes and obtain high drinking water quality. In this study, seasonal differences in freshwater DOM composition and associated treatment-induced changes, were investigated at four drinking water treatment plants (DWTPs) in Sweden, during all seasons and a full-year. The objective was to understand how effectively DWTPs can adapt to seasonal changes and compare how optical and mass spectrometry methods detected these changes. In addition to bulk DOM analysis, this work focused on excitation–emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence including parallel factor (PARAFAC) analysis, and molecular level non-target analysis by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS). Overall, seasonal variability of raw water DOM composition was small and explained primarily by changes in the contributions of DOM with aromatic and phenolic moieties, which were more prevalent during spring in two surface water sources as indicated by absorbance measurements at 254 nm, computed specific ultraviolet absorbance (SUVA) and phenol concentrations. These changes could be balanced by coagulation, resulting in seasonally stable DOM characteristics of treated water. While EEM fluorescence and PARAFAC modelling effectively revealed DOM fingerprints of the different water sources, FT-ICR MS provided new insights into treatment selectivity on DOM composition at the molecular level. Future DOM monitoring of surface waters should target more specific seasonal DOM changes, such as features with a known impact on certain treatment processes or target certain events, like algal or cyanobacterial blooms.

Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (4569K)
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
Molecular level seasonality of dissolved organic matter in freshwater and its impact on drinking water treatment
A. Andersson, L. Powers, M. Harir, M. Gonsior, N. Hertkorn, P. Schmitt-Kopplin, H. Kylin, D. Hellström, Ä. Pettersson and D. Bastviken, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4EW00142G
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications without requesting further permissions from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cup #1 "Rainwater:" Fill cup or container with 2 cups of plain water (tap water would be fine). Cup #2 "Mild Acid Rain:" Fill cup or container with ½ cup vinegar and 1 ½ cups of water. Cup #3 "Strong Acid Rain:" Fill cup or container 2 cups of vinegar. Soak a paper towel in each of the cups. Label each Ziploc bag as 1, 2, or 3.
Acid rain is a general term that describes how acids fall out of the atmosphere. A better term would be acid deposition, which occurs in two ways: wet and dry. Acid rain, fog, and snow are known as wet deposition. Dry deposition is made up of acid gases and particles, and these constitute about 50% of all acidic fallout from the atmosphere.
Acid rain is defined as any form of wet precipitation (rain, snow, fog, dew or sleet) that has a pH less than 5.6 (on a scale of 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral). Large quantities can also be deposited in a dry form through dust. Acid rain is more acidic than normal rain and forms through a complex process of chemical reactions involving air ...
Air pollution from the burning of fossil fuels is the major cause of acid rain. The main chemicals in air pollution that create acid rain are sulfur dioxide (SO2) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx). Acid rain usually forms high in the clouds where sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides react with water, oxygen, and oxidants.
Abstract Give an overview of the experiment, including purpose, approach, results, and conclusion. The purpose of this experiment is to find out the effects of acid rain on organisms in a freshwater pond by counting and comparing animal populations before and after acid rain contamination. To solve this problem, I used a model provided by my ...
Please read section 17.9 of your textbook before completing this assignment. The information provided here will help you complete this assignment. Acid rain is caused by burning fossil fuels containing nitrogen and sulfur. When burned, fossil fuels release nitrogen and sulfur, which react with oxygen to form sulfur oxides (such as sulfur ...
Acid Rain Lab Assignment chidi name acid rain lab assignment what is acid rain? points) any form of precipitation that contains acidic components.m complete the
Acid Rain Lab. Flashcards. ... Terms in this set (14) SO2. sulfur dioxide. sulfur dioxide. what is one of the principle gases involved in the formation of acid rain. 90. what % of the gaseous SO2 in the US comes from man made activities. 4.0-4.5. average pH of rainfall in the U.S. 5.6. normal pH of unpolluted rain. 7.
Learning About Acid Rain: A Teacher's Guide for Grades 6 through 8. This book is intended for teachers of students in 6th-8th grade. It is written at a 6th grade level and the language, concepts, and experiments may need to be adapted for other grades accordingly. View this book in the National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP)
Students test different pH solutions on radish seeds to determine the optimal level for seed germination and use the results to identify effects of acid rain. Students will be able to: Determine the acidity of a substance by testing with pH paper. Measure and graph the results of a lab experiment with radish seeds.
Acid Rain Lab- Katherine Betrus Derrico. Students will design and conduct an experiment to test the effect of acid rain on the germination of seeds. They will utilize the data from their experiment to explain their conclusions, and also read a passage on acid rain. Downloads Acid Rain Lab Rubric (Katherine Betrus Derrico) Acid Rain Lab...
2. Complete the data tables below using the Acid Rain Lab PowerPoint. (75 points: 25 points/table) Record in the table below your predictions (what you think will happen to each item). Next, record your observations (a detailed description of what actually happened to each item) after Day 1, Day 2, Day 3, and Day 7 in each liquid.
Acid Rain and Seed Germination. In this lab, students will use pH sensors to determine the effect of acid rain on the germination of bean seeds. Grade Level: Middle School. Subject: Life Science. Student Files. Acid Rain and Seed Germination: 424.50 KB: Acid Rain and Seed Germination: 230.69 KB:
Because CaSO4 is somewhat soluble in water, significant damage to the structure can result. The biological effects of acid rain are more complex. As indicated in Figure 4.8.2 4.8. 2, biological fluids, such as blood, have a pH of 7-8. Organisms such as fish can maintain their internal pH in water that has a pH in the range of 6.5-8.5.
Measure 25 ml of vinegar in a graduated cylinder. Pour all the vinegar onto the egg in the jar. Using the paint brush, apply the vinegar to the shell of the egg, so that the entire surface has been saturated with vinegar. Touch the paint brush to a strip of pH paper. Compare the color change with the pH color chart.
Acid Rain is a term used to describe the phenomena of rainfall that contains lower than normal readings of pH due to inputs of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide compounds into the atmosphere. These compounds come from power plants and other industries that burn fossil fuels for energy. Scientists are concerned about acid rain and its impact on ...
View Acid+Rain+Lab+Assignment.pdf from EDUC 637 at Liberty University Online Academy. Dwayne scott Name _ Acid Rain Lab Assignment 1. What is acid rain? (5 points) Acid rain, or acid deposition, is a
2. Complete the data tables below using the Acid Rain Lab PowerPoint. (75 points: 25 points/table) Record in the table below your predictions (what you think will happen to each item). Next, record your observations (a detailed description of what actually happened to each item) after Day 1, Day 2, Day 3, and Day 7 in each liquid.
the assignment acid rain make copy of this assignment. complete it, and submit the completed version in canvas the ph scale is used to determine if substance is. Skip to document. ... Copy of Island Biogeography Theory Lab. AP Environmental Science 98% (40) 51. Smedes You Tube Unit 5 Fill In APES Notes. AP Environmental Science 100% (18 ...
Add 5 drops of 0.1 M HCl (hydrochloric acid) to test tubes A and B. Record the pH using pH paper. Add 5 drops of 0.1 M NaOH (sodium hydroxide) to test tubes C and D. Record the pH using pH paper. 10.1: Acid, Bases and pH Lab Procedure is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
Enhanced Document Preview: Grace Leardini Name _____ Acid Rain Lab Assignment 1. What is acid rain? (5 points). Acid rain is a broad term that includes any form of precipitation that contains acidic components, such as sulfuric acid or nitric acid. 2. Complete the data tables below using the Acid Rain Lab PowerPoint.
Summarize the findings of this experiment in terms of damage acid rain can do. Pre-lab assignment. This is a three week lab, determine the best way to divide up your time between the three weeks. Write it out in your notebook. How many grams of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt do you need to make 2 liters of a 0.005M solution?
Improved characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in source waters used for drinking water treatment is necessary to optimize treatment processes and obtain high drinking water quality. In this study, seasonal differences in freshwater DOM composition and associated treatment-induced changes, were investi
2. Complete the data tables below using the Acid Rain Lab PowerPoint. (75 points: 25 points/table) Record in the table below your predictions (what you think will happen to each item). Next, record your observations (a detailed description of what actually happened to each item) after Day 1, Day 2, Day 3, and Day 7 in each liquid.