ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Service quality and customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world: a study of saudi auto care industry.

- 1 College of Business Administration, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Khobar, Saudi Arabia
- 2 Department of Management Sciences, University of Baluchistan, Quetta, Pakistan
The aim of this research is to examine the impact of service quality on customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in auto care industry. The car care vendor in the study made effective use of social media to provide responsive updates to the customers in the post pandemic world; such use of social media provides bases for service quality and customer satisfaction. The study examined the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction using the SERVQUAL framework. According to the findings, empathy, reliability, assurance, responsiveness, and tangibles have a significant positive relationship with customer satisfaction. Our findings suggest that it is critical for workshops to recognize the service quality factors that contribute to customer satisfaction. Findings also suggest that empathy, assurance, reliability, responsiveness, and tangibles contribute to customer satisfaction. Auto repair industry must regularly provide personal attention, greet customers in a friendly manner, deliver cars after services, notify customers when additional repairs are required, and take the time to clarify problems to customers. Furthermore, workshops must screen and hire courteous staff who can clearly communicate the services required to customers both in-person and online and effectively communicate the risks associated with repairs. Service quality seems to be aided by prompt services.

Introduction
The previous studies on the effect of pandemic have focused on the behavior related to preventative measures to protect the health of the customers; however, less attention has been paid to the influence of pandemic on customer outcomes. To fill this gap, the SERVQUAL framework was employed to examine the changes in customers’ social media behaviors that have occurred since the pandemic was declared ( Mason et al., 2021 ). In the post pandemic world, the parameters for customer satisfaction have changed considerably ( Monmousseau et al., 2020 ; Srivastava and Kumar, 2021 ; Wu et al., 2021 ). Pandemic has made personal interaction more challenging ( Brown, 2020 ). To be less vulnerable to becoming severely ill with the virus, customers prefer touchless digital mediums of communications. For example, Mason et al. (2021) concluded that pandemic has altered customers’ needs, shopping and purchasing behaviors, and post purchase satisfaction levels. Keeping in view the public healthcare concerns, the governmental pandemic mitigation policies also promotes touchless mediums for shopping; therefore, the role of social media as a communication tool stands to increase at a time when social distancing is a common practice; social media provides avenues for buyers to interact with sellers without physical contact. Thus, the use of social media gains critical importance, especially after the pandemic ( Mason et al., 2021 ), and the businesses may find new opportunities to gain competitive advantage through their use of effective social media strategies.
The car care industry uses traditional means of customer communications. The company in this study made use of social media in improving their service quality through effective and safe communication with their customers. The use of social media to provide updates to customers played a significant role in improving service quality and satisfaction ( Ramanathan et al., 2017 ). The company in the study used Snapchat to provide updates on the work, thus minimizing the customers’ need to physically visit the car care facility. This use of social media gave a significant boost to the responsiveness aspect of the service quality.
Service quality and customer satisfaction are important aspects of business since a company’s growth is largely dependent on how well it maintains its customers through service and how well they keep their customers satisfied ( Edward and Sahadev, 2011 ). According to Chang et al. (2017) ; customer satisfaction is expected to result from good service efficiency, which will improve customer engagement and interrelationship. González et al. (2007) asserted that customer satisfaction is linked to high service quality, which makes businesses more competitive in the marketplace. This study uses the SERVQUAL framework to define service quality. This framework uses five dimensions to account for service quality, namely, tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Identifying issues in service and customer satisfaction can lead to high service quality. Furthermore, service quality can be characterized by analyzing the variations between planned and perceived service. Service quality and customer satisfaction have a positive relationship.
Recognizing and meeting customer expectations through high levels of service quality help distinguish the company’s services from those of its rivals ( Dominic et al., 2010 ). Social media plays a critical role in shaping these service quality-related variables. Specifically, in the context coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), where customers hesitated to visit auto workshops physically, the importance of online platforms such as auto workshops’ social media pages on Instagram and Facebook has increased, where customers try to get information and book appointment. For example, responsiveness is not only physical responsiveness but also digital means of communication. The car care company in this study uses social media as mode of communication with their customers due to physical interaction restriction caused by the pandemic.
Service quality becomes a critical element of success in car care industry because customer contact is one of the most important business processes ( Lambert, 2010 ). Saudi Arabia is one of the Middle East’s largest new vehicle sales and auto part markets. Saudi Arabia’s car repair industry has grown to be a significant market for automakers from all over the world. As a result, the aim of this research was to see how service quality affects customer satisfaction in the Saudi auto repair industry.
This aim of this research was to answer the following research questions:
(i) What is the contribution of individual dimensions of SERVQUAL on customer perceived service quality of car care industry in Saudi Arabia?
(ii) What is the impact of perceived service quality on customer satisfaction in car care industry in Saudi Arabia?
Literature Review
The concept of service has been defined since the 1980s by Churchill and Surprenant (1982) together with Asubonteng et al. (1996) , who popularized the customer satisfaction theory through measuring the firm’s actual service delivery in conformity with the expectations of customers, as defined by the attainment of perceived quality, and that is meeting the customers’ wants and needs beyond their aspirations. With this premise, Armstrong et al. (1997) later expanded the concept of service into the five dimensions of service quality that comprised tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy.
Extant literature on service delivery focuses on the traditional emphasis on the contact between the customer and service provider ( Mechinda and Patterson, 2011 ; Han et al., 2021 ). Doucet (2004) explained that the quality in these traditional settings depends on the design of the location and the behavior of the service provider. More recently, the proliferation of the internet has led to the emergence of the online service centers. In these cases, communication both in-person and online plays a critical role in the quality of service rendered. It follows that service quality in hybrid settings depends on quality of communications on social media as well as the behavioral interactions between the customer and the service provider ( Doucet, 2004 ; Palese and Usai, 2018 ). These factors require subjective assessments by the concerned parties, which means that different persons will have varied assessments of the quality of service received.
SERVQUAL Dimensions
Service quality has been described with the help of five quality dimensions, namely, tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Definitions relating to these variables have been modified by different authors. The relationship between various dimensions of service quality differs based on particular services.
The tangible aspects of a service have a significant influence on perception of service quality. These comprise the external aspects of a service that influence external customer satisfaction. The key aspects of tangibility include price, ranking relative to competitors, marketing communication and actualization, and word-of-mouth effects ( Ismagilova et al., 2019 ), which enhance the perception of service quality of customers ( Santos, 2002 ). These aspects extend beyond SERVQUAL’s definition of quality within the car care industry settings. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1a: Tangibles are positively related with perceived service quality.
Reliability
Reliability is attributed to accountability and quality. There are a bunch of precursors that likewise aid basic methodology for shaping clients’ perspectives toward administration quality and reliability in the car care industry in Saudi ( Korda and Snoj, 2010 ; Omar et al., 2015 ). A portion of these predecessors is identified with car repair benefits and includes the convenient accessibility of assets, specialist’s expertise level and productive issue determination, correspondence quality, client care quality, an exhibition of information, client esteem, proficiency of staff, representatives’ capacity to tune in to client inquiries and respond emphatically to their necessities and protests, security, workers’ dependability, more limited holding up time and quickness, actual prompts, cost of administration, accessibility of issue recuperation frameworks, responsibility, guarantees, for example, mistake-free administrations, generally association’s picture and workers’ politeness, and responsiveness. Despite the innovative changes happening in the car care industry and the instructive degree of car administrations suppliers in Saudi Arabia, car care suppliers in the territory are taught about the need to continually refresh their insight into the advancements in the area of vehicle workshops and the components of administration. Thus, we argued that reliability is important to enhance the perception of service quality of customers.
Hypotheses 1b: Reliability is positively linked with perceived service quality.
Responsiveness
Responsiveness refers to the institution’s ability to provide fast and good quality service in the period. It requires minimizing the waiting duration for all interactions between the customer and the service provider ( Nambisan et al., 2016 ). Nambisan et al. (2016) explained that responsiveness is crucial for enhancing the customers’ perception of service quality. Rather, the institution should provide a fast and professional response as to the failure and recommend alternative actions to address the customer’s needs ( Lee et al., 2000 ). In this light, Nambisan summarizes responsiveness to mean four key actions, i.e., giving individual attention to customers, providing prompt service, active willingness to help guests, and employee availability when required. These aspects help companies to enhance the customers’ perception of service quality. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1c: Responsiveness is positively linked with perceived service quality.
Assurance refers to the skills and competencies used in delivering services to the customers. Wu et al. (2015) explains that employee skills and competencies help to inspire trust and confidence in the customer, which in turn stirs feelings of safety and comfort in the process of service delivery. Customers are more likely to make return visits if they feel confident of the employees’ ability to discharge their tasks. Elmadağ et al. (2008) lists the factors that inspire empathy as competence, politeness, positive attitude, and effective communication as the most important factors in assuring customers. Besides, other factors include operational security of the premises as well as the proven quality of the service provided to the customers. Thus, the assurance has significant contribution in the perception of service quality.
Hypotheses 1d: Assurance is positively related with perceived service quality.
Empathy refers to the quality of individualized attention given to the customers. The service providers go an extra mile to make the customer feel special and valued during the interaction ( Bahadur et al., 2018 ). Murray et al. (2019) explains that empathy requires visualizing the needs of the customer by assuming their position. Murray et al. (2019) lists the qualities that foster empathy as including courtesy and friendliness of staff, understanding the specific needs of the client, giving the client special attention, and taking time to explain the practices and procedure to be undertaken in the service delivery process. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1e: Empathy is positively related with perceived service quality.
Perceived Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction refers to the level of fulfillment expressed by the customer after the service delivery process. This is a subjective assessment of the service based on the five dimensions of service quality. Customer satisfaction is important due to its direct impact on customer retention ( Hansemark and Albinsson, 2004 ; Cao et al., 2018 ; Zhou et al., 2019 ), level of spending ( Fornell et al., 2010 ), and long-term competitiveness of the organization ( Suchánek and Králová, 2019 ). Susskind et al. (2003) describes that service quality has a direct impact on customer satisfaction. For this reason, this research considers that five dimensions of service quality are the important antecedents of customer satisfaction.
Service quality refers to the ability of the service to address the needs of the customers ( Atef, 2011 ). Customers have their own perception of quality before interacting with the organization. The expectancy-confirmation paradigm holds that customers compare their perception with the actual experience to determine their level of satisfaction from the interaction ( Teas, 1993 ). These assessments are based on the five independent factors that influence quality. Consequently, this research considers service quality as an independent variable.
This study attempts to quantify perceived service quality though SERVQUAL dimensions. We proposed that customers place a high premium on service quality as a critical determinant of satisfaction. Moreover, it is argued that satisfaction prompts joy and reliability among customers in Saudi Arabia. These discoveries infer that the perception of service quality is significantly related to satisfaction, and quality insight can be applied across different cultures with negligible contrasts in the result. Car care industry in Saudi Arabia has grave quality problems. To rectify this situation, it is essential to apply quality systems as tools for development. The SERVQUAL is one of these system options. It is used to gauge the service quality using five dimensions that have been time-tested since 1982. Thus, the significance of SERVQUAL in car care industry in Saudi Arabia cannot be overemphasized. The study further suggests that the SERVRQUAL dimension increases the perceived service quality, which in turn increases customer satisfaction. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: The perceived service quality of car care customers is positively linked with their satisfaction.
Methods and Procedures
In this study, we employed a cross-sectional research design. Using a paper-pencil survey, data were collected form auto care workshops situated in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. According to the study by Newsted et al. (1998) , the survey method is valuable for assessing opinions and trends by collecting quantitative data. We adapted survey instruments from previous studies. The final survey was presented to a focus group of two Ph.D. marketing scholars who specialized in survey design marketing research. The survey was modified keeping in view the recommendations suggested by focus group members. We contacted the customers who used social media to check the updates and book the appointment for their vehicle’s service and maintenance. We abstained 130 surveys, 13 of which were excluded due to missing information. Therefore, the final sample encompassed 117 (26 female and 91 male) participants across multiple age groups: 10 aged less than 25 years, 46 aged between 26 and 30 years, 28 aged between 31 and 35 years, 21 aged between 36 and 40 years, and 12 aged older than 40 years (for details, refer to Table 1 ). Similarly, the averaged participants were graduates with more than 3 years of auto care service experience.
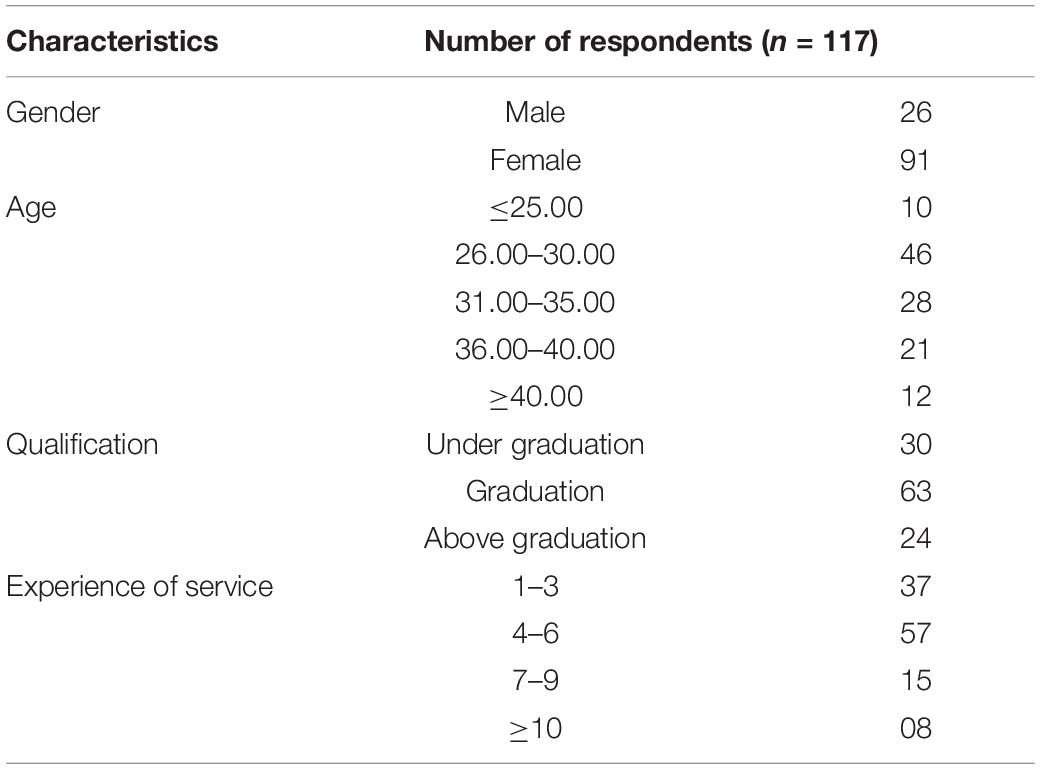
Table 1. Demographic information.
We measured service quality dimensions using 20 indicators. Customer satisfaction of the restaurant customers was assessed using 4-item scale (for detail, refer to Table 2 ). In this research, the 5-point Likert scale from 1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree was used.

Table 2. Constructs and items included in the questionnaire.
Control Variables
Following the previous research, customer’s gender and age were controlled to examine the influence of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction.
Data Analysis and Results
For data analysis and hypotheses testing, we employed the structural equation modeling (SEM) based on the partial least squares (PLS) in Smart-PLS. Smart-PLS 3 is a powerful tool, which is used for the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and SEM ( Nachtigall et al., 2003 ). Research suggests that CFA is the best approach to examine the reliability and validity of the constructs. We employed SEM for hypotheses testing because it is a multivariate data analysis technique, which is commonly used in the social sciences ( González et al., 2008 ).
Common Method Bias
To ensure that common method bias (CMB) is not a serious concern for our results, we employed procedural and statistical and procedural remedies. During data collection, each survey in the research contained a covering letter explaining the purpose of the study and guaranteed the full anonymity of the participants. Moreover, it was mentioned in the cover letter that there was no right and wrong questions, and respondents’ answers would neither be related to their personalities nor disclosed to anyone. According to Podsakoff et al. (2003) , the confidentiality of the responses can assist to minimize the possibility of CMB. Furthermore, CMB was verified through the Harman’s single-factor test ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). All items in this research framework were categorized into six factors, among which the first factor explained 19.01% of the variance. Thus, our results showed that CMB was not an issue in our research. Moreover, using both tolerance value and the variance inflation factors (VIFs), we assessed the level of multicollinearity among the independent variables. Our results indicate that the tolerance values for all dimensions of service quality were above the recommended threshold point of 0.10 ( Cohen et al., 2003 ), and VIF scores were between 1.4 and 1.8, which suggested the absence of multicollinearity; thus, it is not a serious issue for this study.
Measurement Model
We performed CFA to analyze the reliability and validity of the constructs. The measurement model was assessed by examining the content, convergent, and discriminant validities. To assess the content validity, we reviewed the relevant literature and pilot test the survey. We used item loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability (CR), and the average variance extracted (AVE) ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981b ) to assess the convergent validity. The findings of CFA illustrate that all item loadings are greater than 0.70. The acceptable threshold levels for all values were met, as the value of Cronbach’s alpha and CR was greater than 0.70 for all constructs ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981b ), and the AVE for all variables was above 0.50 ( Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007 ; see Table 3 ). Thus, these findings show acceptable convergent validity.
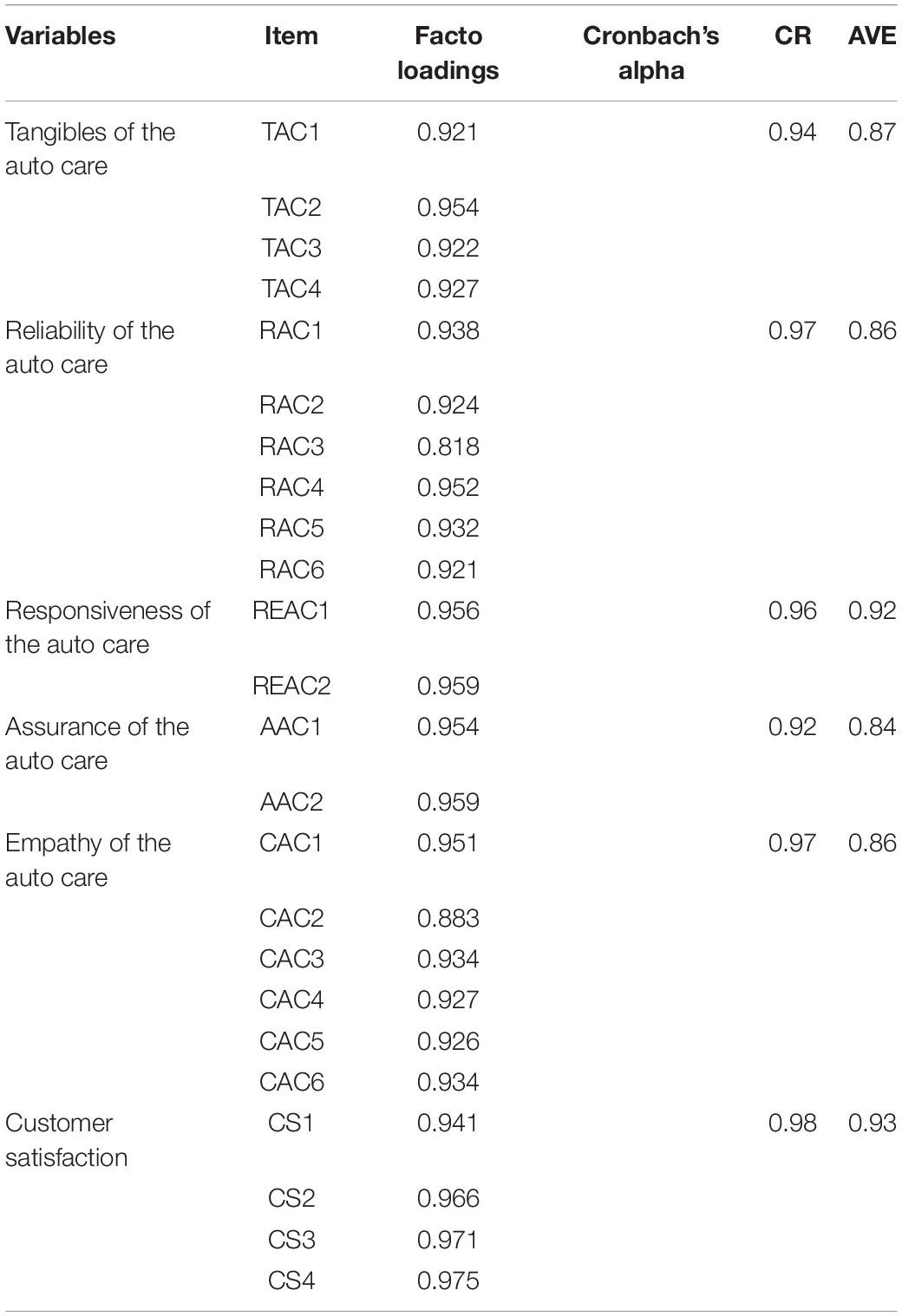
Table 3. Item loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability, and average variance extracted.
To analyze the discriminant validity, we evaluated the discriminant validity by matching the association between correlation among variables and the square root of the AVE of the variables ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981a ). The results demonstrate that the square roots of AVE are above the correlation among constructs, hence showing a satisfactory discriminant validity, therefore, indicating an acceptable discriminant validity. Moreover, descriptive statistics and correlations are provided in Table 4 .
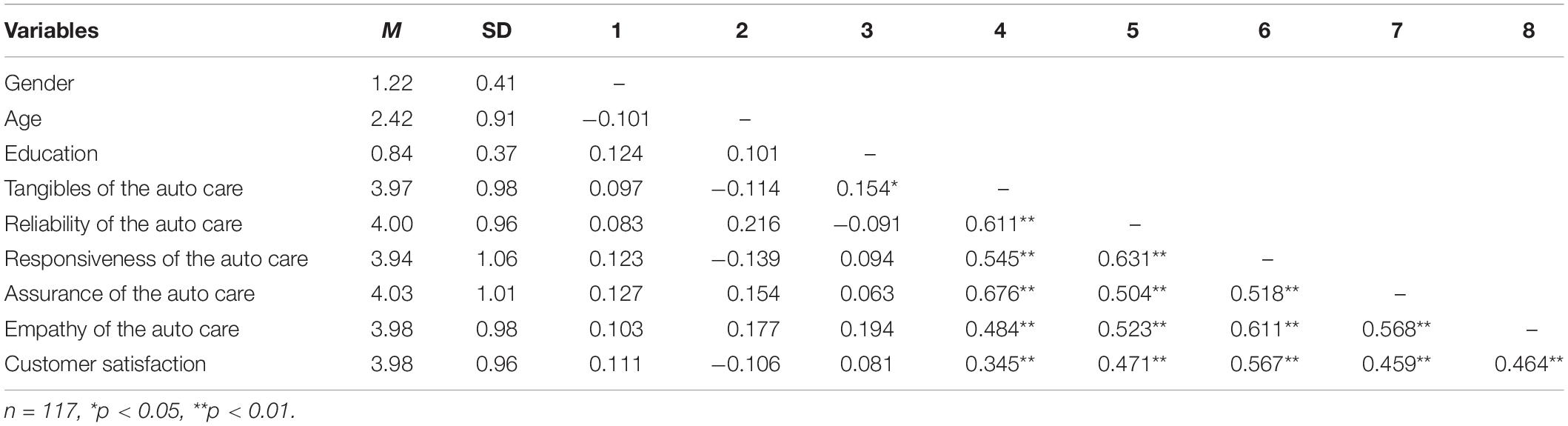
Table 4. Descriptive statistics and correlations.
Structural Model and Hypotheses Testing
After establishing the acceptable reliability and validity in the measurement model, we examined the relationship among variables and analyzed the hypotheses based on the examination of standardized paths. The path significance of proposed relations were calculated using the SEM through the bootstrap resampling technique ( Henseler et al., 2009 ), with 2,000 iterations of resampling. The proposed research framework contains five dimensions of service quality (i.e., tangibles of the auto care, reliability of the auto care, responsiveness of the auto care, assurance of the auto care, and empathy of the auto care) and customer satisfaction of auto care. The results show that five dimensions of service quality are significantly related to customer’s perception of service quality of auto care; thus, hypotheses 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, and 1e were supported. Figure 1 shows that the service quality of auto care is a significant determinant of customer satisfaction of auto care industry (β = 0.85, p < 0.001), supporting hypothesis 2. The result in Figure 1 also shows that 73.8% of the variation exists in customer satisfaction of auto care.
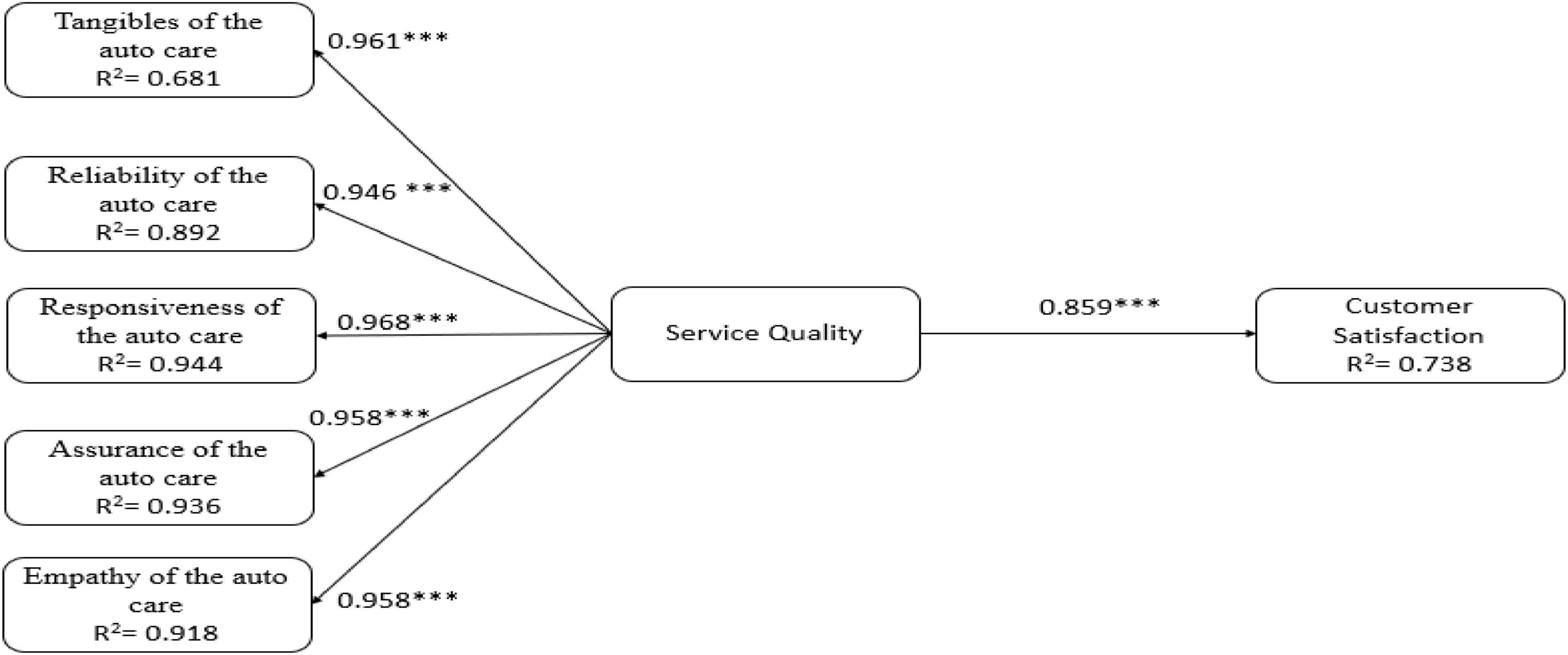
Figure 1. Results of the research model tests. *** p < 0.001.
The main purpose of this research was to assess the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in Saudi Arabia. This study was designed to examine how satisfaction of auto care customers is influenced by service quality, especially, when pandemic was declared, and due to health concerns, the customers were reluctant to visit workshops physically ( Mason et al., 2021 ). It appears that after the pandemic, customers were increasingly using online platforms for purchasing goods and services. This study reveals how customers of auto repair in Saudi perceive service quality and see how applicable SERVQUAL model across with five dimensions, including tangibles, responsiveness, reliability, assurance, and empathy measure service quality. The findings of this research show that five dimensions of SERVQUAL are positively related to the service quality perception of auto care customers in Saudi Arabia. Moreover, service quality perceptions are positively linked with customer satisfaction. These results indicate that auto care customers view service quality as an important antecedent of their satisfaction. The findings indicate that the customers perceive the service quality as a basic service expectation and will not bear the extra cost for this criterion. In this research, the positive connection between service quality and customer satisfaction is also consistent with previous studies (e.g., González et al., 2007 ; Gallarza-Granizo et al., 2020 ; Cai et al., 2021 ). Thus, service quality plays a key role in satisfying customers. These findings suggest that service organizations, like auto repair industry in Saudi Arabia could enhance satisfaction of their customers through improving service quality. Because of pandemic, people are reluctant to visit auto care workshops, and they try to book appointment through social media; so, by improving the quality of management of their social media pages, the workshops can provide accurate information for monitoring, maintaining, and improving service quality ( Sofyani et al., 2020 ). More specifically, social media, which allows individuals to interact remotely, appears to be gaining significant importance as a tool for identifying customers’ products and service needs. Increasingly, customers are also increasingly engaging with retailers through social media to search and shop for product and services options, evaluate the alternatives, and make purchases.
Furthermore, the research on the customer service quality can be held essential since it acts as a means for the promotion of the competitiveness of an organization. Precisely, the knowledge about the customers’ view concerning service quality can be used by organizations as a tool to improve their customer services. For example, knowledge of the required customer service would help in the facilitation of training programs oriented toward the enlightenment of the overall employees on the practices to improve and offer high-quality customer services. Besides, information concerning customer services would be essential in decision-making process concerning the marketing campaigns of the firm, hence generating competitive advantage of the organization in the marketplace. Findings show that customers demand more from auto repair, so the company must work hard to increase all service quality dimensions to improve customer satisfaction. Thus, organizations ought to venture in customer services initiatives to harness high-quality services.
Managerial Implications
The findings of this research indicate a strong association between SERVQUAL dimensions and perceived service quality. Perception of higher service quality leads to higher level of customer satisfaction among Saudi car care customers. In particular, the results indicate high scores for reliability, empathy, tangibles, and responsiveness. These are clear indications that the immense budgetary allocation has enabled these institutions to develop capacity. Nevertheless, the lack of a strong human resource base remains a key challenge in the car care industry. The effective use of social media plays a critical role in the responsiveness dimension of service quality. Companies need to develop their digital and social media marketing strategies in the post pandemic world to better satisfy their customers.
Saudi Arabia requires a large and well-trained human resource base. This requires intensive investment in training and development. Most of these workers have a limited contract, which reduced their focus on long-term dedication. Consequently, the government should provide longer-term contracts for workers in this critical sector. The contracts should include training on tailored courses to serve the identified needs in effective communication with the customers using digital media. We suggested that the auto car care workshops should provide training to their workers, particularly, on service technicians to enhance their skills that will help to deliver fast and reliable service to their auto customers.
Moreover, the auto car care workshops also provide customer care- or customer handling-related training especially for the service marketing personnel who handles customer directly for them to better understand the customer needs and expectations. This can be done at least once a year. This will help auto care workshops to improve their service quality.
Limitation and Future Research Direction
This research is not without limitations. First, the findings of this study are based on data collected from a single source and at a single point of time, which might be subjected to CMB ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). Future research can collect data from different points of time to validate the findings of this research. Second, this research was carried out with data obtained from Saudi auto car care customers; the findings of this research might be different because the research framework was retested in a different cultural context. Therefore, more research is needed to improve the understanding of the principles of service quality and customer satisfaction, as well as how they are evaluated, since these concepts are critical for service organizations’ sustainability and development. A greater sample size should be used in a similar study so that the findings could be applied to a larger population. Research on the effect of inadequate customer service on customer satisfaction, the impact of customer retention strategies on customer satisfaction levels, and the impact of regulatory policies on customer satisfaction is also recommended. Third, because most of the participants participated in this research are men, future studies should obtain data from female participants and provide more insights into the difference between male and female customers’ satisfaction levels. Moreover, due to limitation of time, the sample was collected from the eastern province. Consequently, further research should include a larger and more representative sample of the Saudi population. Because of the non-probability sampling approach used in this research, the results obtained cannot be generalized to a wide range of similar auto repair services situations, even though the methodology used in this study could be extended to these similar situations. Since the sample size considered is not that large, expectations could vary significantly. When compared with the significance of conducting this form of analysis, the limitations mentioned above are minor. Such research should be conducted on a regular basis to track service quality and customer satisfaction levels and, as a result, make appropriate changes to correct any vulnerability that may exist.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
SZ helped in designing the study. ZH helped in designing and writing the manuscript. MAA helped in data collection and analysis and writing the manuscript. SUR repositioned and fine-tuned the manuscript, wrote the introduction, and provided feedback on the manuscript.
This study was received funding from University Research Fund.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Armstrong, R. W., Mok, C., Go, F. M., and Chan, A. (1997). The importance of cross-cultural expectations in the measurement of service quality perceptions in the hotel industry. Int. J. Hospital. Manag. 16, 181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4319(97)00004-2
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Asubonteng, P., McCleary, K. J., and Swan, J. E. (1996). Servqual revisited: a critical review of service quality. J. Serv. Market. 10, 62–81. doi: 10.1108/08876049610148602
Atef, T. M. (2011). Assessing the ability of the Egyptian hospitality industry to serve special needs customers. Manag. Leisure 16, 231–242. doi: 10.1080/13606719.2011.583410
Bahadur, W., Aziz, S., and Zulfiqar, S. (2018). Effect of employee empathy on customer satisfaction and loyalty during employee–customer interactions: The mediating role of customer affective commitment and perceived service quality. Cog. Bus. Manag. 5:1491780. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2018.1491780
Brown, G. T. (2020). Schooling beyond COVID-19: an unevenly distributed future. Front. Edu. 8:82. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.00082
Cai, G., Hong, Y., Xu, L., Gao, W., Wang, K., and Chi, X. (2021). An evaluation of green ryokans through a tourism accommodation survey and customer-satisfaction-related CASBEE–IPA after COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 13:145. doi: 10.3390/su13010145
Cao, Y., Ajjan, H., and Hong, P. (2018). Post-purchase shipping and customer service experiences in online shopping and their impact on customer satisfaction: an empirical study with comparison. Asia Pacif. J. Market. Logist. 30:71. doi: 10.1108/APJML-04-2017-0071
Chang, M., Jang, H.-B., Li, Y.-M., and Kim, D. (2017). The relationship between the efficiency, service quality and customer satisfaction for state-owned commercial banks in China. Sustainability 9:2163. doi: 10.3390/su9122163
Churchill, G. A. Jr., and Surprenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. J. Mark. Res. 19, 491–504.
Google Scholar
Cohen, J., Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G. A., Leona, S., Patricia Cohen, S. G. W., et al. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Dominic, P., Goh, K. N., Wong, D., and Chen, Y. Y. (2010). The importance of service quality for competitive advantage–with special reference to industrial product. Int. J. Bus. Inform. Syst. 6, 378–397. doi: 10.1504/IJBIS.2010.035051
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Doucet, L. (2004). Service provider hostility and service quality. Acad. Manag. J. 47, 761–771. doi: 10.5465/20159617
Edward, M., and Sahadev, S. (2011). Role of switching costs in the service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction and customer retention linkage. Asia Pacif. J. Market. Logist. 23, 327–345. doi: 10.1108/13555851111143240
Elmadağ, A. B., Ellinger, A. E., and Franke, G. R. (2008). Antecedents and consequences of frontline service employee commitment to service quality. J. Market. Theory Pract. 16, 95–110. doi: 10.2753/MTP1069-6679160201
Fornell, C., Johnson, M. D., Anderson, E. W., Cha, J., and Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American customer satisfaction index: nature, purpose, and findings. J. Market. 60, 7–18. doi: 10.1177/002224299606000403
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981a). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 1987, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981b). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Market. Res. 1987, 382–388. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800313
Fornell, C., Rust, R. T., and Dekimpe, M. G. (2010). The effect of customer satisfaction on consumer spending growth. J. Market. Res. 47, 28–35. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.47.1.28
Gallarza-Granizo, M. G., Ruiz-Molina, M.-E., and Schlosser, C. (2020). Customer value in quick-service restaurants: a cross-cultural study. Int. J. Hospital. Manag. 85:102351. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.102351
González, J., De Boeck, P., and Tuerlinckx, F. (2008). A double-structure structural equation model for three-mode data. Psychol. Methods 13:337. doi: 10.1037/a0013269
González, M. E. A., Comesaña, L. R., and Brea, J. A. F. (2007). Assessing tourist behavioral intentions through perceived service quality and customer satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 60, 153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2006.10.014
Han, J., Zuo, Y., Law, R., Chen, S., and Zhang, M. (2021). Service Quality in Tourism Public Health: Trust, Satisfaction, and Loyalty. Front. Psychol. 12:279. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.731279
Hansemark, O. C., and Albinsson, M. (2004). Customer satisfaction and retention: the experiences of individual employees. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J . 14, 40–57. doi: 10.1108/09604520410513668
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing New challenges to international marketing. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 277–319. doi: 10.1108/S1474-7979(2009)0000020014
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E. L., Rana, N. P., and Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: A meta-analysis. Inform. Syst. Front. 2019, 1–24.
Korda, A. P., and Snoj, B. (2010). Development, validity and reliability of perceived service quality in retail banking and its relationship with perceived value and customer satisfaction. Manag. Glob. Trans. 8:187.
Lambert, D. M. (2010). Customer relationship management as a business process. J. Bus. Indus. Market. 25, 4–17. doi: 10.1108/08858621011009119
Lee, H., Lee, Y., and Yoo, D. (2000). The determinants of perceived service quality and its relationship with satisfaction. J. Serv. Market. 14, 217–231. doi: 10.1108/08876040010327220
Mason, A. N., Narcum, J., and Mason, K. (2021). Social media marketing gains importance after Covid-19. Cog. Bus. Manag. 8:797. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1870797
Mechinda, P., and Patterson, P. G. (2011). The impact of service climate and service provider personality on employees’ customer-oriented behavior in a high-contact setting. J. Serv. Market. 25, 101–113. doi: 10.1108/08876041111119822
Monmousseau, P., Marzuoli, A., Feron, E., and Delahaye, D. (2020). Impact of Covid-19 on passengers and airlines from passenger measurements: Managing customer satisfaction while putting the US Air Transportation System to sleep. Transp. Res. Interdiscipl. Persp. 7:179. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2020.100179
Murray, J., Elms, J., and Curran, M. (2019). Examining empathy and responsiveness in a high-service context. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2019:16. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-01-2019-0016
Nachtigall, C., Kroehne, U., Funke, F., and Steyer, R. (2003). Pros and cons of structural equation modeling. Methods Psychol. Res. Online 8, 1–22.
Nambisan, P., Gustafson, D. H., Hawkins, R., and Pingree, S. (2016). Social support and responsiveness in online patient communities: impact on service quality perceptions. Health Expect. 19, 87–97. doi: 10.1111/hex.12332
Newsted, P. R., Huff, S. L., and Munro, M. C. (1998). Survey instruments in information systems. Mis. Quart. 22:553. doi: 10.2307/249555
Omar, H. F. H., Saadan, K. B., and Seman, K. B. (2015). Determining the influence of the reliability of service quality on customer satisfaction: The case of Libyan E-commerce customers. Int. J. Learn. Dev. 5, 86–89. doi: 10.5296/ijld.v5i1.6649
Palese, B., and Usai, A. (2018). The relative importance of service quality dimensions in E-commerce experiences. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 40, 132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.02.001
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and rec-ommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., and Berry, L. (1988). SERVQUAL: a multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. J. Retail. 64, 12–40.
Ramanathan, U., Subramanian, N., and Parrott, G. (2017). Role of social media in retail network operations and marketing to enhance customer satisfaction. Int. J. Operat. Prod. Manag. 37:153. doi: 10.1108/IJOPM-03-2015-0153
Santos, J. (2002). From intangibility to tangibility on service quality perceptions: a comparison study between consumers and service providers in four service industries. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 12, 292–302. doi: 10.1108/09604520210442083
Srivastava, A., and Kumar, V. (2021). Hotel attributes and overall customer satisfaction: What did COVID-19 change? Tour. Manag. Persp. 40:100867. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100867
Sofyani, H., Riyadh, H. A., and Fahlevi, H. (2020). Improving service quality, accountability and transparency of local government: the intervening role of information technology governance. Cogent Bus. Manage. 7:1735690. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1735690
Suchánek, P., and Králová, M. (2019). Customer satisfaction, loyalty, knowledge and competitiveness in the food industry. Eco. Res. Ekonomska istraživanja 32, 1237–1255. doi: 10.1080/1331677X.2019.1627893
Susskind, A. M., Kacmar, K. M., and Borchgrevink, C. P. (2003). Customer service providers’ attitudes relating to customer service and customer satisfaction in the customer-server exchange. J. Appl. Psychol. 88:179. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.1.179
Tabachnick, B., and Fidell, L. (2007). Multivariate analysis of variance and covariance. Multivar. Stat. 3, 402–407.
Teas, R. K. (1993). Consumer expectations and the measurement of perceived service quality. J. Prof. Serv. Market. 8, 33–54. doi: 10.1080/15332969.1993.9985048
Wu, G., Liang, L., and Gursoy, D. (2021). Effects of the new COVID-19 normal on customer satisfaction: can facemasks level off the playing field between average-looking and attractive-looking employees? Int. J. Hospit. Manag. 97:102996. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102996
Wu, Y.-C., Tsai, C.-S., Hsiung, H.-W., and Chen, K.-Y. (2015). Linkage between frontline employee service competence scale and customer perceptions of service quality. J. Serv. Market. 29, 224–234. doi: 10.1108/JSM-02-2014-0058
Zhou, R., Wang, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, L., and Guo, H. (2019). Measuring e-service quality and its importance to customer satisfaction and loyalty: an empirical study in a telecom setting. Elect. Comm. Res. 19, 477–499. doi: 10.1007/s10660-018-9301-3
Keywords : auto care, customer satisfaction, service quality, Saudi Arabia, pandemic (COVID-19)
Citation: Zygiaris S, Hameed Z, Ayidh Alsubaie M and Ur Rehman S (2022) Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in the Post Pandemic World: A Study of Saudi Auto Care Industry. Front. Psychol. 13:842141. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.842141
Received: 23 December 2021; Accepted: 07 February 2022; Published: 11 March 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Zygiaris, Hameed, Ayidh Alsubaie and Ur Rehman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zahid Hameed, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Service Delivery and Customer Satisfaction. A Case Study of Addis Ababa City Administration
Thesis (m.a.), 2020, tewodros tsega (author).
Table of Content
Acknowledgements
List of acronyms, list of figures, list of tables, data interpretation tables.
Abstract xi
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 . Background of the study 1.2. Statements of the problem 1.3. Objectives of the research 1.3.1. General objective 1.3.2. Specific objective 1.4. Research questions 1.5. Scope of the study 1.6. Limitation of the Study 1.7. Significance of the study 1.8. Organization of the Thesis
CHAPTER TWO 2. REVIEW LITERATURE 2.1. Theoretical bases of the study 2.1.1. Quality of Service Delivery 2.1.1.1.Service delivery 2.1.1.2Quality of service 2.1.1.3. Measuring the quality of service 2.1.1.4. Public Services 2.1.1.5. Characteristics of Public Services 2.1.1.6.Service delivered in land development and management 2.1.1.7.Mechanisms for service improvement 2.1.2. Level of customer satisfaction in land development and management office 2.1.2.1. Customer satisfaction 2.1.2.2. Measuring Customer Satisfaction 2.1.2.3. Why should we measure satisfaction? 2.1.2.4. Level of customer satisfaction in land development and management 2.1.2.5.Improving the level of customer satisfaction 2.1.3. Relationship between quality of service and customer satisfaction 2.2. Empirical bases of the study 2.2.1. Quality of Service delivered in AALDMO 2.2.2. Level of customer satisfaction in AALDMO 2.3. Conceptual framework 2.4. Research Gap
CHAPTER THREE 3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Research Approach 3.2 Research method 3.3 Research Technique 3.4 Sample Design 3.4.1 Population and universe 3.4.2 Sampling Frame 3.4.3. Sampling unit 3.4.4. Sampling Technique 3.4.5 Sample Size 3.5. Sources of Data 3.5.1 Primary data sources 3.5.2 Secondary data sources 3.6. Data Analysis and Interpretation 3.7. Data presentation 3.9. Validity and reliability 3.9.1. Validity 3.9.2. Reliability
CHAPTER FOUR 4. DATA PRESENTATION AND ANALYSIS 4.1. Introduction 4.2. Response Rate 4.3. Demographic Characteristics of Respondents 4.4. Findings 4.4.1. The quality of service delivered in AALDMO 4.4.1.1. Provided service quality in comparison with customer’s expectation 4.4.1.2. Measuring the service quality in AALDMO 4.4.2. The level of customer satisfaction in AALDMO 4.4.3. The relationship between quality of service and customer satisfaction in AALDMO 4.4.4. Factors that affect the level of customer satisfaction in AALDMO 4.4.4.1. Factors that affect the quality of service provided in AALDMO? 4.4.4.2. Factors that affect the level of customer satisfaction in AALDMO? 4.5. Interpretation
CHAPTER FIVE SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION 5.1 Introduction 5.2. Summary 5.3 Conclusion 5.4 Recommendations
Reference list
DECLARATIONS
First and for most I would like to thank my Almighty God who helps me to reach on this success. Next my deepest gratitude goes to my advisor Dr. Dagnachew Adimasu for his continuous advice, guidance and valuable comments in the process of undertaking this research.
I wish to express my appreciation to my family members - my mother, sister, and my son, friends, and other relatives who supported me in idea and finance even in their time in undertaking this research.
I grateful acknowledge the assistance of all my respondents and peoples who helped me to collect the data in this hard time of COVID 19 form Gullele, Kolfe Keranio, Arada, Addis Ketema, and Nifas Silik Lafto sub cities.
Abbildung in dieser Leseprobe nicht enthalten
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework
Table 3.1:- Number of customers in the ten sub cities
Table 3.2:- Selection of Sample Size
Table 4.1 - Background information of respondents
Table 4.2 - Descriptive Statistics- Service quality on the bases of Tangibility
Table 4.3 - Descriptive Statistics- Service quality on the bases of Reliability
Table 4.4 - Descriptive Statistics- Service quality on the bases of Responsiveness
Table 4.5 - Descriptive Statistics -Service quality on the bases of Assurance
Table 4.6- Descriptive Statistics- Service quality on the bases of Empathy
Table 4.7 - Satisfaction level of customers
This study is about “Customer Satisfaction and Service Delivery: The Case of Addis Ababa City Administration Land Development and Management Office”. The main objective of the research is to measure and address the customer satisfaction in the service delivery of Addis Ababa development and management office. It tries to see the quality of service delivery and the level of customer satisfaction in land development and management office of Addis Ababa. It tries to see the quality of service using the SERVQUAL service quality measurement model. In the study a descriptive and explanatory types of research method were employed. Then, both probability (simple random sampling) and the non probability (purposive) sampling were used. Therefore, a total of 324 respondents were selected from customers of Addis Ababa land development and management office in the selected five sub cities to respond through a questionnaire and ten respondents were selected from employee of the selected sub cities to respond to an interview. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS and the interpreted data were presented in tables, charts, graphs, and pictures. In this study, the researcher confirmed that “the service provided in Addis Ababa land development and management office is poor in quality and the level of customer satisfaction is low”. Furthermore, the different problems that affect the level of customer satisfaction were identified. The problems that affect the level of customer satisfaction includes: - Low competency of employees; the discipline problem of employees; Poor management; Structural problems in the office; Personal interest of employees (-There is conflict of interest); and the continuous change of rule and regulations. In order to solve the identified problems the following recommendations are forwarded: The trainings given to employees including training related with their technical skill, trainings on professional ethics, trainings that bring an attitude change; using modern ICT technologies; put the right person at the right position; structural change; taking correction or adjustments on the bases of feedback from customers; creating strong control mechanism on the daily activities of employees; taking administrative and Legal measures; designing of rules and regulations that can serve longer time.
Key words: - Customer, Customer Satisfaction, Service, Service Delivery
CHAPTER ONE
1. introduction.
The Addis Ababa city land development and management office (now on ward denoted by AALDMO) have many problems in its services delivery to the customers. The problems in the services delivery create problem in the customer satisfaction of the organization. So, to attain a customer satisfaction we should have a high standard of service quality. As it is indicated by Jonathan (2018) Service quality is the result of the comparison made by customers about what they feel service firms should offer, and perceptions of the performance of firms providing the services. Therefore we can say that customers compare the service delivered with their expectation and judge or respond about the service they gain that means they judge whether the service create satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
According to Jonathan (2018) Customer satisfaction is defined as the customers’ evaluation of a product or service in terms of whether that product or service has met their needs and expectations. Customer satisfaction in broader sense defined as consumers feeling and happiness after complete meeting of one's expectations. Odunlami (2015) stated that Customer satisfaction is a construct that must be met optimally for efficient and effective achievement of stated objectives, and for smooth continuation of business. Customer satisfaction is an integral part of organizational objectives that must be fulfilled for an organization to maintain its customers.
This paper is a research on the title “customer satisfaction and service delivery: the case of Addis Ababa city administration land development and management office”. It has five chapters with many sub parts in each. Like: - backgrounds of the study, statements of the problems, research objectives, research questions, significance of the study, scope of the study, limitation of the study, and organization of the paper in chapter one; Literature review in chapter two; and methodology in chapter three; data presentation and analysis in chapter four; and summary, conclusion and recommendation in chapter five together with different annexes. The annexes also include Questionnaires to customers of AALDMO; Interview guiding Questions for leaders and officers in AALDMO; Reliability measurement; Summary of sampling, sample size and data collecting mechanisms; and Summary of objectives, Research questions and handling mechanisms.
1.1 . Background of the study
In 2002, the city government of Addis Ababa reorganized both the city government executive bodies and municipal offices in the city with proclamation number 2/2002 to foster development of the city. During that time the land development sector was organized by itself at agency level with many sub branches under and it was under the municipal offices. Even if the proclamation was there in 2002, the land development and management bureau by itself as a separate body was established in 2011. By following the administrative organizations the land development and management office was also established at sub city level. It is one of the offices in the city that provide service to the public. Some of the services that are provided in the land development and management offices includes:- render service of registration and protection regarding possession and immovable property; issue certificate of title deed for land possession; organize current cadastre system; keep and preserve information about type of land usage and possessors thereof; investigate and pass decision on questions of changing land usage by legal possessors of land in accordance with law; ascertain the proper implementation, at subcity level by the concerned body in the area, of land and houses registration and information handling of the city as well as possessorial and/or ownership right transfer is in accordance with policies and laws; take corrective measures where the implementation of land or house administration is inconsistent with the policies and law etc (Proclamation No. 35/2012: 21).
With these different services the land development and management office has many customers. The implementation of good governance principles in the service delivery in this office and its branches at the sub city level are important because of the large number of customers it has. The main activity that accomplished at the land development and management bureau at city level is that preparation of different rules, regulations, and working manuals. And, the different rules regulations and the working manuals that established and approved at the city level are implemented at the city and sub city levels. The land development and management office in each of the sub cities has the main responsibility of implementing those rules, regulation and working manuals. Due to this fact, large number of customers gets service at the sub city level of the office.
The Addis Ababa city land development and management office have many problems in its services delivery to the customers. Many of the problems are problems that are persisted for long periods of time. As it is stated by Ashenafi (2015: 8) after the city land administration was delegated under city government land development and management bureau (proclamation No. 35/2011), Addis Ababa city administration has been continue providing the land administration services with its embedded problems. Among these problems, there was a complication in the execution of enacted proclamations due to the absence of clear legislation as well as confusion about the applicability of the legislations (cited from World Bank, 2012b). In addition to this, the sector was highly criticized by its mal-governance due to many serious corrupted working situations in the land administration business (Transparency International, 2009). Furthermore, there was no transparent work process on acquisition of land and the accountability system had weakened due to none or spontaneous answerability to the public. Ibid (2015:8). The existence of these problems in the service delivery of the land development and management office decrease the level of customer satisfaction.
In this regard the federal government of Ethiopia and the city administration had taken measures to minimize the problems through different civil service reforms. The citizen charter is developed in December 2013 by the city land development and Management Bureau to strengthen the service delivery. Ashenafi (2015: 8) also indicated that the federal government of Ethiopia and the city administration of Addis Ababa attempt to minimize and avoid the problems of good governance through different civil service reforms. By citing Fortune newspaper, (2010) he also indicated that after the reform programs; many land administrative services somehow have been improved additionally, the citizen charter that comprises standards of service delivery had developed on December, 2013 by the city land development and management bureau to strengthen the service delivery. Ibid (2015: 8)
But even if some improvements are shown in the sector after the implementation of the civil service reform and the citizen charter; still there are different problems that are shown in the sector. Nigussie (2016: 4) also indicated that customers refer to various problems in land development and management office; some of the problems are lack of office schedules, lack of decision making, inconsistencies on interpreting land related legislations, un-pleasant and unwillingness service delivery from officials, etc.
1.2. Statements of the problem
The Addis Ababa Land Development and Management Office have many problems in its services delivery to the customers. As it is stated by Ashenafi (2015: 8) after the city land administration was delegated under city government land development and management bureau (proclamation No. 35/2011), Addis Ababa city administration has been continue providing the land administration services with its embedded problems. Among these problems, there was a complication in the execution of enacted proclamations due to the absence of clear legislation as well as confusion about the applicability of the legislations (cited in World Bank, 2012b). In addition to this, the sector was highly criticized by its mal-governance due to many serious corrupted working situations in the land administration business (transparency international, 2009). Furthermore, there was no transparent work process on acquisition of land and the accountability system had weakened due to none or spontaneous answerability to the public. Ibid (2015:8).
Jonathan (2018) in his article defined Service quality as the result of the comparison made by customers about what they feel service firms should offer, and perceptions of the performance of firms providing the services. Nomnga and Mhlanga (2014) in their part stated that Service quality is a complex, elusive, subjective and abstract concept. It means different things to different people. The most common definition of service quality is the comparison customers make between their expectations and their perceptions of the received service (cited from Parasuraman, Zeithaml and Berry1988; Grönroos, 1982). Therefore, we can say that service quality is the comparison between expectation and perception of received service by the customer.
By citing Hazlina, Rabiyah and Razap, (2011) Ahmed (2019) stated that Service quality is the fundamental tool in the measure of customer satisfaction. He also stated that to attain a high standard of customer satisfaction most studies propose that the service provider should offer a high standard of service quality as usually service quality is regarded as an antecedent of client satisfaction, Ahmed (2019: 3). Again by citing Clemes (2008) Ahmed (2019) stated that the probability of client satisfaction increases with improvement of service quality. Quality was one of the various aspects that form the basis of satisfaction and satisfaction was one of the possibilities that influence future quality views, Ahmed (2019: 3). Therefore, we can see that there is a relationship between quality of service provided and customer satisfaction. That is high quality of service delivery will result to have a high level of customer satisfaction and vice versa.
Poor service delivery in AALDMO has resulted in to have low customer satisfaction. But to be scientific research should be made to evaluate the level of customer satisfaction, to identify reason why we have low level of customer satisfaction, to identify the factors that affect the level of customer satisfaction and to put appropriate solution in solving the problem of that limit the level of customer satisfaction
The different problems that are persisted in the service delivery of AALDMO decrease the level of customer satisfaction, because customer satisfaction is affected by the quality of services provided. The writer has reviewed different research works that are made on customer satisfaction and good governance on land development and management office service provisions. In the first one research work which is made by WMCC in 2017 is about “the level of customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa city public service in service delivery and Good Governance” it was made in Addis Ababa city public service provision all offices including land development & management office. This research evaluates customer satisfaction of the 10 sub cities in all service provision offices. It doesn’t show the customer satisfaction of AALDMO separately, and it also deals about good governance and service delivery in these offices; but it didn’t evaluate the customer satisfaction in service delivery separately. The second and the recent research work reviewed by the writer is the one which is done by Aklilu Meberatu in 2019. Which is about “An Assessment of Service Delivery Problems in Land Administration: The Case of Gulele Sub-City”. And in this work Mr. Aklilu evaluate the problems of service delivery in one of the sub offices under the land development and management office of Gullele sub city. So, it did not show the service delivery and customer satisfaction in the AALDMO as a whole . Therefore, this research work is unique from the others by looking the service delivery and customer satisfaction in AALDMO. In looking it in detail the writer raised questions like: - how is the service quality in AALDMO? How is the customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office? What is the relationship between the quality of service and customer satisfaction in AALDMO? And what are the factors that can affect the level of customer satisfaction in AALDMO?
1.3. Objectives of the research
1.3.1. general objective.
The general objective of this research is to measure and address the customer satisfaction in the service delivery of Addis Ababa land development and management office.
1.3.2. Specific objective
This research has the following specific objectives.
- To evaluate the quality of service delivered in Addis Ababa land development and management office - To evaluate the level of customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office - To determine the relationship between quality of service delivered and customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office
To identify factors that affect the level of customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office
To recommend possible solutions that can solve the identified problems affecting level of customer satisfaction
1.4. Research questions
- How is the quality of service delivered in Addis Ababa land development and management office? - How is the level of customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office? - What is the relationship between quality of service delivered and customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office?
What are the factors that affect the level of customer satisfaction in Addis Ababa land development and management office?
What are the possible solutions that can solve the problems that affect the level of customer satisfaction?
1.5. Scope of the study
This study is only concerned about customer satisfaction in the service delivery of Addis Ababa city administration land development and management office. It will concern only in areas within the boundary of Addis Ababa city administration. In measuring the quality of service delivered in the office the researcher uses only tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy as a variable, because these are the common variables in measuring the quality of service in SERVQUAL quality measurement models. In terms of population this study will only concern with customers who get service in AALDMO at the city level and largely at the sub city level, this is because many of the services are provided to customers at the sub city level and at large the role of the land development and management office at the city level is supporting those sub cities in providing the service to customers. So, customers who get service at the city and sub city level are the focus of this study. This study could not include citizens of the city / Addis Ababa who didn’t get a service in the land development and management office at the city and sub city level, because if it contains these people since they didn’t know the process of service delivery in the office they will give wrong answers to questionnaires and the research will have wrong conclusion. So, in order to solve such problems these people will not include in this study.
1.6. Limitation of the Study
The writer was conducted this study by collecting primary data from different customers and employees of land development and management office of Addis Ababa in the selected five sub cities. In this process, the writer was faced different problems; the first and the major problem was Lack of customers to respond due to COVID 19, particularly when the writer come out for data collection many of the offices in Addis Ababa land development and management office were close and these office were not providing service to customers, in addition to this financial constraints, time constraints, and respondents delay were constraint that affect the process of conducting this research. In order to solve the first problem the writer was stayed for about 15 day until the office were open to customers and when that office was open many costumers came to the office and writer collected the data; and the researcher tried to overcome the other constraints by devoting himself to finish the research with the planned time. Because finishing on time save not only time but also money. In relation the respondent delay the researcher negotiated seriously with respondents to fill the questionnaire within the given time.
1.7. Significance of the study
This paper is about “Customer Satisfaction and Service Delivery: The Case of Addis Ababa City Administration Land Development and Management Office”. So, it can be served as a base for other researchers for further study. This study tries to see the different challenges that affect the customer satisfaction in relation with the service delivered in Addis Ababa land development and management office, it can help policy makers to develop a policy that can solve the different challenges and that can enhance the satisfaction of customers in the office. In addition to the above two, this paper is also helps the researcher as the partial fulfillment to get the Masters Degree from the Pretor Construction and Business College.
1.8. Organization of the Thesis
This research paper had been organized in five different chapters. The first chapter is the introductory part that consisted of Background of the study, Statements of the problem, Objectives of the research (-that includes General objective and Specific objective), Research questions, Scope of the study, limitation of the study, and Significance of the study.
The second chapter is about review literature. In here, important reading materials like books, internet, magazines and different documents that were related with the research ideas and with the objectives of the study were discussed.
The third chapter deals with the methodology part which tells about the research approach, research methods, sample design which includes population, sampling frame, sampling unit, sampling technique, and sample size, sources of data, data analysis and interpretation, and reliability measurement.
The fourth chapter focuses on the data analysis and interpretation. It consisted of response rate, demographic characteristics of respondents, findings, and interpretation. And, the last chapter-chapter five includes the conclusion and recommendations which were given for the different problems that identified in this research as a solution.
CHAPTER TWO
2. review literature, 2.1. theoretical bases of the study, 2.1.1. quality of service delivery, 2.1.1.1. service delivery.
Service is any activity that is made to satisfy the needs and wants of customers. As it is stated by WMCC, service is defined as the activity that has been done to satisfy the needs and wants of customers on the bases of knowledge, capacity and/or profession of employees (WMCC; 2016: 35). By citing (Armstrong et al, 1999), Afande stated that customer service is defined as activities and programs provided by the seller to the buyer to make the relationship a satisfying one. It is an activity or benefit that one party offers to another, which is, essentially, intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything. Its production may or may not be tied to a physical item. Variability of services is dependent on who provides them and when they are provided. Afande (2015: 50). WMCC also indicated that Service is a goal oriented process that is done to satisfy customers need; and it is a process that is delivered by deliverers to add economic value to customers (WMCC; 2016: 35). Therefore, we can say that service is an activity that is made by service providers or sellers in order to satisfy the needs and wants of customers, its goal is satisfying the needs of the customers.
Service delivery is the process providing the service to customers. By citing Ethiopian Service Delivery Policy (2001), Dereje (2017) stated as Service delivery is the systematic arrangement of activities in service giving institutions with the aim of fulfilling the needs and expectations of service users and other stakeholders with the optimum use of resources, (Dereje; 2017: 10). According to Transparency International Rwanda (2017), Service delivery is a fundamental function between service procuring entities and services seekers who have the right to request for services to satisfy their needs. Transparency International Rwanda (2017: 26). WMCC in its part indicated that, in order to provide a service , there should be a face to face contact between service providers and service receivers (customers) in the service delivery process of public service provisions (WMCC; 2016: 35). Therefore, we can conclude that service delivery is a systematic and sequential follow of a service from service provider to customers and it can be achieved by the relationship between service providers and customers.
2.1.1.2. Quality of service
According to Jonathant (2018), quality is the product or service usefulness for the price paid; it is a definition of quality that consumers often use for product or service usefulness. It is what quality is but when we see the quality of the service it is about the judgment on the comparison between the expectation and perception of consumers about the service provided. As it is stated by Nomnga and Mhlanga (2014) Service quality is a complex, elusive, subjective and abstract concept. It means different things to different people. The most common definition of service quality is the comparison customers make between their expectations and their perceptions of the received service. Similarly, by citing Grönroos, C. (2007), Khadka & Maharjan (2017) in their part indicated as service quality refers to the result of the comparison that the customer makes their expectation about the service and their perception of the way the service has been performed, Khadka & Maharjan (2017: 13). Jonathan (2018) in his article again defined Service quality as the result of the comparison made by customers about what they feel service firms should offer, and perceptions of the performance of firms providing the services. Therefore, we can conclude that service quality is a comparison and a judgment between expectation and perception that is made by customers.
The quality of service can use as a base for customer satisfaction. As it is stated by Odunlami (2015), in the service industry, strong emphasize is placed on the significant importance of service quality perceptions and association between service quality and consumer satisfaction. It is therefore presumed that some researchers concluded that service quality is an important indicator of customer satisfaction. So, in order to use the quality of service as a base for customer satisfaction we should measure the quality of service using different criteria. Transparency International Rwanda (2017), indicated as there are a number of attributes or dimensions that determine service quality include the accessibility, reliability (to provide the service on time and accurately), the promptness of service and its affordability among others. Transparency International Rwanda (2017: 26). Shimels (2016: 15) indicated that Customers, judge service quality as the extent to which perceived service quality matches with the initial expectation. By citing Palmer (1995; 155), Shimels also stated that customers judge the service quality in three ways. These are :- The first one is the desired level of service, which reflects what the customer wants. The second one is adequate level of service, that is, the standard customers are willing to accept. The third one is the predicted service level, which means expectation that customers believe to actually occur most likely. Shimels (2016: 15). Therefore, we can conclude that quality of service is one determinant that affects the level of customer satisfaction. In doing this for such a purpose we should measure the quality of service using criteria include accessibility, reliability, the promptness of service and its affordability.
Service should be given in best quality in order to satisfy customers because there is a relationship between the quality of service delivered and customer satisfaction that means if the quality of service is poor it will create dissatisfaction and if the service quality is good it will create customer satisfaction. As it is stated by Odunlami (2015), service quality is an important indicator of customer satisfaction. To make customer satisfied on the service delivery service providers should know the service quality level that is needed to satisfy customers. As it is stated by Shimels, the quality level that is needed by customers to be satisfied has to do with every aspect of services providers starting from the time customers arrive at the gate of the organizations. One of the required qualities knows the conditions under which customers are, once they are in; the customers may be in queue, they may be in certain office waiting for concerned official, or still others may be annoyed for one or the other reasons... These efforts could identify customers„ problems and give solutions to them. Shimels (2016: 15). Service quality can be achieved and measured on the bases of the service providers (employees) discipline (behavior) and their ability, capacity and it should be compatible with the need and wants of customers (WMCC; 2016: 35). Even if service quality is affected and determined by different factor, if the service has a best quality it will satisfy customers but if the service is in poor quality it will affect the satisfaction level of customers. By citing Rust and Zahorik, (1993) Odunlami, indicated that this relation between quality of service and customer’s satisfaction in that Poor services can also lead to dissatisfaction. Poor services or unsatisfactory level of services, which cannot meet customers’ expectation, may be that is one of the causes of dissatisfaction in customers, (Odunlami: 2015). Therefore we can conclude that customer satisfaction is highly dependent of the quality of service provided to customers.
2.1.1.3. Measuring the quality of service
There is a variation in the service delivered to customers in different service providing firms and organizations. And there are also different factors that affect the service provided to customers. As it is stated by WMCC, the service delivered for different customers, have shown difference on the bases of the experiences of service providers (employees), knowledge of employees, discipline of employees, and perception and behavior of customers and again other internal and external factors (causes). In order to overcome these dynamic behaviors, service providing organizations setting the service delivery standard and by providing continues capacity building activities for employees they should try to provide similar and satisfying service to customers (WMCC; 2016: 35). From this we can understand that due to different factors there is a variation in the service delivered to customers and service quality standard is a mechanism set to a avoid the variation.
In order to create customer satisfaction, service quality should be equivalent with the demand or the expectation of customers and again the service should be provided in a proper way. In reaching on customer satisfaction, service must be in a good quality and it should be delivered in a proper way and we have to check whether the service is delivered properly and also we have to measure the quality of service delivered to see its level and to take corrective actions where there is a problem in its quality. As it is stated by WMCC to understand whether the service is provided properly or not, there should be customers and that customer receive a service and in the process, the perception of customers should be known and understood. And again in order to measure whether the service is provided properly or not, there should be a setting of standard for service delivery (WMCC; 2016: 35). Therefore, we can conclude that in order to have a customer satisfaction we have to set a service delivery standard and measure the service quality and improve the service based on the finding of the measurement of the service quality.
The service provided by different organization and firms should be in a best quality because as it is presented by different authors and scholars quality of service affects the satisfaction of customers and again if customers are not satisfied it will affect the performance and the continuity of the organization or firms. So organizations or firms should give emphasis for quality of services that is provided to customers. There are different models presented to measure the quality of service. One of the best models is SERVQUAL which is developed by Parasuraman et al. (1985, 1986, 1988, 1991, 1993, 1994; Zeithaml et al., 1990).
According to Shahin (2006) clearly, from a best value perspective the measurement of service quality in the service sector should take into account customer expectations of service as well as perceptions of service. However, by citing Robinson (1999) Shahin (2006) indicated as Robinson concludes that: "It is apparent that there is little consensus of opinion and much disagreement about how to measure service quality". One service quality measurement model that has been extensively applied is the SERVQUAL model developed by Parasuraman et al. (1985, 1986, 1988, 1991, 1993, 1994; Zeithaml et al., 1990). By citing Gronroos, 1982; Lewis and Booms, 1983; Parasuraman et al., 1985; Shahin (2006) again indicated that SERVQUAL as the most often used approach for measuring service quality has been to compare customers' expectations before a service encounter and their perceptions of the actual service delivered. The SERVQUAL instrument has been the predominant method used to measure consumer’s perceptions of service quality. It has five generic dimensions or factors and is stated as follows A. Shahin (2006):-
- Tangibles: - Physical facilities, equipment and appearance of personnel. - Reliability: - Ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately. - Responsiveness: - Willingness to help customers and provide prompt service. - Assurance: - (including competence, courtesy, credibility and security). It is the Knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to inspire trust and confidence. - Empathy: - (including access, communication, understanding the customer). It is the caring and individualized attention that the firm provides to its customers.
By citing Gabbie and O'neill, (1996) Shahin (2006) stated that in the SERVQUAL instrument, 22 statements measure the performance across these five dimensions, using a seven point Likert scale measuring both customer expectations and perceptions. It is important to note that without adequate information on both the quality of services expected and perceptions of services received then feedback from customer surveys can be highly misleading from both a policy and an operational perspective.
2.1.1.4. Public Services
Public services are those services that are provided by government institutions to citizen in order to satisfy the social needs. By citing Ethiopian Service Delivery Policy (2002), Dereje, indicated that Public services are any activities undertaken to meet social needs. Public service particularly refers to those activities of government institutions aimed at satisfying the needs and ensure the wellbeing of society as well as enforcing laws, regulations and directives of government (Dereje; 2017: 10). By citing Yeman (undated: 5), Dereje also defines public service as “any act or performance that public institutions provide to fulfill social needs”. This entails a dynamic interaction between service providers and recipients that operate in a changing environment that may shape the outcome of the implementation of Service Delivery Reforms. (Dereje; 2017: 10). Therefore, we can say that public service is a service provided by government in order to fulfill the needs and wants of the people to fulfill the social needs of citizens’.

2.1.1.5. Characteristics of Public Services
Services provided by governments have different characteristics than the services that are provided by the private organizations. As it is stated by WMCC, one of the characteristics is that it is provided by the financial support that is collected from citizens. Because of this, service receivers (customers) indirectly pay for the service they gain due to this fact it is difficult to control its service quality. (WMCC; 2016: 35-36). Unlike the services that are provided by private organizations; the service provided by the government are provided by the budget (financial budget) that is set once at the beginning of a year. Due to this fact, it is difficult to use additional finance when there is an increase in the number and wants of customers. So, government organizations must estimate the needs and wants of customers and should prepare and give the service properly. (Ibid; 2016: 36). Therefore, we can conclude that public service is provided to citizen by the government and the cost of the service is covered by citizen.
The second characteristic is that the government has responsibility and accountability to deliver the service. The financial source for service provided by the government is taxes that are collected from the people. In addition to this, since government is established by the votes of the people through democratic election, government has a responsibility and accountability to provide the service to the people. Due to this leaders and officers at the different tiers of government by recognizing what service delivery is? , what is the importance of service delivery? And the characteristics of services that are provided by the government they must work hard to solve the knowledge and attitude related problems in the service delivery. In addition to this leaders and officers at the different tiers of by participating the people or customers, they must solve the problems of service delivery performance in standard achievement (WMCC; 2016: 36). Conceptual Framework Task Force (2011) also indicated that governments are elected through a democratic process to have certain (Constitutional or devolved) rights, powers and responsibilities that require broad accountability to the public and their elected representatives. The governing bodies of many government organizations are appointed; however, these organizations are part of government. They use public resources and may have been given delegated powers and responsibilities that also demand broad accountability to the public and their elected representatives. The complexity of the government financial reporting entity and the varied relationships between the government and its organizations adds to the need for broad public accountability. Therefore, we can conclude that Government has a responsibility and accountability to provide public service.
The other characteristic of services provided by the government is that, these are services that are not presented in the market for profit purpose; because of this government is the only provider of these services. There is no competitor. This character limits the customer’s choice because they can’t find the service in any time and at any condition, from any organizations. Most of the time, the problem in the quality of service provision, and problems of good governance in the service provided by the government come due to this character of the service (WMCC; 2016: 36). And, again as it is stated by International Public Sector Accounting Standards Board (2010) an important characteristic that distinguishes the public sector from the private sector is that the main objective of public sector entities is to deliver goods and services rather than to generate profits. This means that there is a high incidence of non-exchange transactions of great financial significance in the public sector. Therefore, we can conclude that public services are services that are provided by the government and that is not for profit purpose.
By citing (MoCB 8, 2010) Tilahun (2014) stated that the public sector in Ethiopia was characterized by weak structures, inefficient services provision, corruptions, poor capacity and the routine neglect of the due process of law in matters of public issue. The government has developed the future vision of the public service and is devoted to turn around the challenges of hindering weak institutional arrangement, outdated working process and system, low capacity, unethical behaviors, and fraud, Tilahun (2014: 21). Therefore, from this we can understand that the public service in Ethiopia is full of problems that include weak structures, inefficient services provision, corruptions, and poor capacity.
2.1.1.6. Service delivered in land development and management
As it is stated by Chaka, Lepheana, and Tlali (2017), Land administration services are part of day to day activity for public services. These are usually services provided by government offices and it is a common concern in developing countries that public service delivery is sluggish and sometimes contaminated by acts of corruption. Because of these facts there is a need to improve the service delivery in land development and management of the different countries particularly on developing countries. In supporting this fact Transparency International Rwanda (2017) stated that the need to improve services in the land sector is vital to ensure effective and efficient land-related service delivery.
The land development and management is a one of the public service that is provided to citizens by the government bodies. By citing UN-ECE, (1996 and 2005), Mwangi & Nyika (2010)
indicated that Land management is implemented through land use planning and the processes through which the tools of land management are implemented are called land administration. Land administration is used to refer to those public sector activities required to aid the process of alienation, survey, valuation, registration, transfer, development and use of land. In most countries, these processes are administered by the public sector through the land administration structures. Shimels (2016) in his part indicated that Public Sector Services may be provided in a non-competitive environment because alternative service providers often do not exist. Hence, service recipients, unlike consumers in the private sector, may have little or no option to use a different service provider or to withhold payment. Therefore, we can say that since the service is given in a non competitive environment, the service should be given in a best quality that satisfied customers.
Service quality is the comparison between the expectation of customers from the service and what the reality is. Jonathan (2018) in his article defined Service quality as the result of the comparison made by customers about what they feel service firms should offer, and perceptions of the performance of firms providing the services. By citing Parasuraman, Zeithaml and Berry (1988); and Grönroos (1982) Nomnga and Mhlanga (2014) in their side stated that Service quality is a complex, elusive, subjective and abstract concept. It means different things to different people. The most common definition of service quality is the comparison customers make between their expectations and their perceptions of the received service.
Service quality is one factor that can determine the satisfaction of customers. By citing Bergman B et al. (2003) Vega and Garcia (2008) indicated that customer satisfaction is one of the topics very related with the Quality; the ultimate measurement of quality is customer service. Odunlami (2015) also stated as researchers concluded that service quality is an important indicator of customer satisfaction. In relation to this by citing Rust and Zahorik, (1993) Odunlami (2015) also indicated that Poor services can lead to dissatisfaction. Poor services or unsatisfactory level of services, which cannot meet customers’ expectation, may be one of the causes of dissatisfaction in customers. Therefore, we can conclude that service quality determines the customer satisfaction in that if the service is in good quality it will create satisfaction of customers but if it is in poor quality it will create dissatisfaction.
The service quality in land development and management needs improvement. Unless some improvement measures are undertaken it will create dissatisfaction. Transparency International Rwanda (2017) stated that the need to improve services in the land sector is vital to ensure effective and efficient land related service delivery. In order to improve the service delivered in land development and management first we have to understand what the customer needs. As it is stated by Vega and Garcia (2008) the main question about quality service is what the customer expects to get from the service. Knowing the customer- their needs, expectations, price and wants helps the company succeed. It is the customer who judges the quality of goods and service.
2.1.1.7. Mechanisms for service improvement
There are different measures taken to improve the quality of service provided to customers. Some of these measures include: - service standard, counter offices, client survey, hotline, public access to land information website, and people participation in adjudication and demarcation. The details of these measures are presented as follow:-
1. Service Standards
Setting service standard is about setting the needed time and cost for the service delivered. A service provided should not take additional time and cost over the setted standards, it is important to control the quality of the service. As it is stated by Shimels, service standards are needed to guarantee the implication of governance principles. These standards define the time and cost of completing transactions to minimize corruption and to satisfy customers. By citing (Zakout, Wehrmann, Törhönen; 2006), Shimels also indicated that the service standards include: - Clearly defined steps for the land registration procedure, Transparent and fixed fees for registration, notaries, surveying etc., Use of standard forms, and Public notice of the procedure (in offices, on the web, through leaflets etc.) and another example is a fixed maximum time with in which the service of registering transactions has to be completed. The successful application of service standards needs regular monitoring. Shimels (2016: 32). Therefore, we can conclude that the service standard is about time and cost fixed for the provision of a service.
2. Counter Offices
Customers should get the service according to their order of coming to the office. Counter offices is creating favorable condition in providing the service to customers by their order. According to Shimels, Counter offices improve orderly interface with the client and reduce bribery. Well organized front offices, in combination with clear and short procedures, can therefore contribute significantly to the reduction of corruption and to an increase the efficiency in registering transactions, and thus to customer satisfaction.
3. Client Survey
Client survey is conducting the survey of customers to get insights about :- The level of awareness and knowledge of the customers regarding service standards; Performance of offices in delivering their services; The degree of client satisfaction with the operation of the system; and A stakeholder view of shortcomings in the system„s functioning. By citing the World Bank and FAO (2006), Shimels, indicated as the survey questions generally focus on:- Waiting and turn-around time: the number of visits to the various agencies, and total time spent for solving one issue.; Official and non-official costs involved: measuring/ surveying fees; registration fees; ... and non-official payments etc.; and Clients satisfaction with the services provided and recommended for investment: in some cases, attention is also given to transactions happening „out- side „the system, which are not registered. Shimels (2016: 32).
Hotline is the establishment of communication ways that helps in receiving complaints. As it is stated by Shimels, the objective of a hotline is to provide the access to the public to launch formal complaints to the authority in cases of corruption or misconduct. Complaints can be made by phone, mail or email on such matters as non-compliance with service standards and corruption of staff. The information on how to access the hotline needs to be communicated widely through different mechanisms. It is important that agencies that have hotlines establish clear procedures to follow up on the complaints and communicate back to the public. This will improve the credibility of the agency and its commitment to dealing with corruption and misconduct. Shimels (2016: 33).
5. Public Access to Land Information Website
Making the land information is important in improving the quality of service delivered to customers. So in improving the quality of service land information should be available to customers. As it is stated by Shimels, Publicly available digital cadastral data and ownership information through the internet can serve several objectives including: - Reduce time for clients through easy and fast access to cadastral data and land registry information from home or internet cafes; Lower costs for clients in the form of fees and informal payments to receive data from cadastral offices and land registries; and Greater transparency and fewer opportunities for bribery. Shimels (2016: 33). By citing (Zakout, Wehrmann, Törhönen; 2006) Shimels also indicated that decreased workload for the cadastral and land registry office staff, which allows them to focus on transaction registration and blocking reduction (on those cases where land registration and /or cadastre are not up to date). The updated and verified cadastral and land
registration information can then contribute to greater transparency, clarity and efficiency of the land administration. Shimels (2016: 33).
6. People Participation in Adjudication and Demarcation
People participation is one principle of good governance and its application helps the improvement of the service quality in offices that provide public services. By citing the World Bank and FAO, /2006/ Shimels indicated that good governance includes people„s participation. A crucial step within the land administration in which the affected residents should be involved is the identification of parcels and their owners and determination of boundaries. Situations where landownership is registered or boundaries are established are: systematic registration, post-conflict situation, privatization of land and post-disaster situations or after from unexpected catastrophes. Shimels (2016: 34).
2.1.2. Level of customer satisfaction in land development and management office
2.1.2.1. customer satisfaction.
Satisfaction is a comparison or the difference between what customers expect and what they gain from the service or the product they are receiving. By citing Hansemark (2004); Kotler( 2000): Hoyer, and Maclnnis, (2001) Odunlami defines Satisfaction as an overall customer attitude or behavior towards the difference between what customers expect and what they receive, regarding the fulfillment of some desire, need or goal, (Odunlami: 2015). Kotler and Armstrong (2012) in their part indicated that satisfaction is brought about by the evaluation of products and services after purchase while considering the expectations. It is a scale by which organizations evaluate the feeling of customers about the service the gain from that organization. By citing Faizan et al (2011) Odunlami (2015) indicated that, were of the opinion that satisfaction is a critical scale of how well a customer’s needs and demands are met while customer loyalty is a measure of how likely a customer is to repeat the purchase and engage in relationship activities. They were of the opinion that customer satisfaction has a positive significant relationship with customer loyally. Therefore, we can conclude that satisfaction is the difference between the expectations of customer and what they receive and it shows how good the service is.
Customer satisfaction is the evaluation and judgment made by customers in relation with the service or product they receive from the organization of a firm. According to Jonathan (2018) Customer satisfaction is defined as the customers’ evaluation of a product or service in terms of whether that product or service has met their needs and expectations. Customer satisfaction in broader sense defined as consumers feeling and happiness after complete meeting of one's expectations. By citing Anderson et al., (1997) Odunlami (2015) defined Customer satisfaction as it is an overall evaluation of a firm’s products (or services). Ako-Nai (2011) also defined that Customer satisfaction is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation.
Customer satisfaction is about the perception of customers on the service or the product they gain and is determine by their expectation. By citing Yi (1991) Odunlami (2015) stated that consumer satisfaction is a collective outcome of perception, evaluation and psychological reactions to the consumption experience with a product or service. Consumer satisfaction is regarded as how consumers can get more benefits than their cost. By citing Kotler (1989; 203), Shimels indicated that Customers’ satisfaction depends on the extent to which customers’ expectations about the product or services are fulfilled. Customer„s satisfactions are not static but keep changing. Therefore, organizations need to monitor customer„s expectations on a continuous basis and to be innovative in order to respond meaningfully to changes about customers’ expectation. Shimels (2016: 15). Therefore, we can conclude that customer satisfaction is perception and evaluation of customers on the service they gain and it is determined by their expectation that means the satisfaction of customers based on their expectation about the quality of the service.
Customer satisfaction is highly related with quality of service. Because customer satisfaction is the perception and evaluation and the reaction of customers about the service they gain and it is also determined by the expectation of customers about the service. Most of the time, customers want high quality service to satisfy. By citing (Bergman B et al.2003), Vega and Garcia (2008) indicated that customer satisfaction is one of the topics very related with the Quality; the ultimate measurement of quality is customer service. Afande indicated that any negative remarks from customers’, related to quality of services is a direct pointer that; the levels of customer satisfaction of the organization is wanting and, it requires immediate addressing, Afande (2015: 50). Vega and Garcia (2008) again indicated that the customer wants his needs fulfilled. The main question about quality service is what the customer expects to get from the service. Knowing the customer- their needs, expectations, price and wants- helps the company succeed. It is the customer who judges the quality of goods and service. Therefore, we can say that customer satisfaction is based on the quality of service provided by the service providers.
Customer satisfaction is a factor for the success of the organization or firms. For business organizations customer satisfaction is a factor that determines the success and the continuity of the organization. Birhanu (2017) stated as the customer satisfaction is a critical success factor in service organizations. Customer satisfaction is a key to building lasting relationships with consumers. Odunlami (2015) also stated that Customer satisfaction is a construct that must be met optimally for efficient and effective achievement of stated objectives, and for smooth continuation of business. Customer satisfaction is an integral part of organizational objectives that must be fulfilled for an organization to maintain its customers. And again by citing Fornell, Johnson, Anderson, Cha & Bryant (1996), Khadka & Maharjan (2017) in their part indicated that Customer satisfaction has been one of the top tools for a successful business. Customer satisfaction is defined as an overall evaluation based on the total purchase and consumption experience with the good or service over time, Khadka & Maharjan (2017: 10). So, we can conclude that customer satisfaction is a factor that determines the success of organizations and in cases of organizations that provide public service it is a factor that determines the achievement of the objectives of the organization.
2.1.2.2. Measuring Customer Satisfaction
By citing Gerpott et al, (2001), Odunlami stated that Satisfaction can be obtained based on the expectation of the receiver. If the supply of a firm were according to expectations of customers, they would be satisfied. The amount of high or low satisfaction depends upon the level of supply that meets the level of expectation or fall below the level of expectation, Odunlami (2015). So the evaluation and judgment made between customer expectation and the existing service provided is what is called customer satisfaction. This customer satisfaction can change from time to time based on the quality of service provided. Afande (2015) also stated that customer satisfaction is a dynamic concept as it changes at a very fast rate; Afande (2015: 50). So since customer satisfaction is dynamic and that change from time to time we have to make sure that it is at the level of satisfying customers. And in order to know it is at the level of satisfying customers we have to measure the level of customer satisfaction.
In addition to the above points different literatures state that, in relation to the customer satisfaction emphasis is given to the level of customer satisfaction. As it is also stated by WMCC, in a competition between trading companies, emphasis is given not only to the customer satisfaction rather it is also given to the level of customer satisfaction and its continuity (WMCC; 2016: 36). Measuring customer satisfaction has different advantages for the company that made the measurement.
- No comments yet.

Similar texts

Small Scale Labour Market Assessment in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The Case of Se...

Urban Management in Ethiopia. Promoting Sustainable Urban Development in Addi...

Service Marketing Innovations - some general concepts

New Service Development: A Case Study for the Swedish Supermarket Chain ICA

Die Bedeutung von Kundenaktivitäten für den Service Value

Implications of Measure Method Customer Loyalty and Satisfaction

Opportunities and Challenges of Women’s Political Participation in Addis Abeb...

Balancing youth friendliness of sexual and reproductive health service delive...

Customer Relationship Management for Service Provider

Customer Evaluations of Service Failure and Recovery Encounters

Surviving as a "Software as a Service" (SaaS) Startup

Satisfying the Customer. Quality Management and Service Provision

Perceived Social Media Marketing Activities and Its Impact on Customer Retent...

Corruption in the Civil Service. A Study of Salary Fraud in Bayelsa State, Ni...

Effect of E-Government Based Service Delivery on Customers’ Satisfaction

Assessment of Leadership Challenges in Leading Organizational Performance in ...

Structural Time Series Modelling of Crime Rates: the Case of Addis Ababa, Eth...

Factors that Affect the Effectiveness of Monitoring and Evaluation System of ...

Benefits and Challenges in Public Property Disposal Practices on a Federal Le...
Upload papers
Your term paper / thesis:
- Publication as eBook and book - High royalties for the sales - Completely free - with ISBN - It only takes five minutes - Every paper finds readers
Publish now - it's free


A FRAMEWORK FOR ACHIEVING THE FOUR STUDENT WELLNESS OUTCOMES USING COLLECTIVE SYSTEM DESIGN
In response to the evolving demands of todays competition, there is a growing expectation for enhanced services to industry and academic enterprises. This thesis explores the application of System Engineering methodologies as a strategic approach to securing success with both industrial and academic enterprises. Industry faces issues with the absence of a positive tone, inefficiencies and delays in delivery, and customer satisfaction. Meanwhile, academia faces several challenges including lack of communication between departments, how to allocate institutional resources to simplify student experience, reduce complexity in students college experience, and lack of students motivation. These issues for students lead to poor academic performance, financial struggles, and possibly mental health problems. There is a recognized need for a systematic approach to ensure student success at universities. A fundamental approach emerges in the form of Collective System Design (CSD) to find ways to address the above- mentioned challenges. Collective System Design is explored for ad- dressing the challenges faced by academic organizations and industrial processes. Collective System Design aims to improve the long-term viability of an enterprise by fostering sustainability and success. This thesis further investigates the Collective System Design Language, offering a communication tool for design and an approach to assess effectiveness before implementation. This thesis highlights two case studies: Shuttleworth (manufacturing industry) and the Purdue University Fort Wayne Student Success Standard Process Lifecycle. The impact of solving these problems can be measured through several key indicators: Shuttleworth (Manufacturing Industry). • Reduction in Lead Time • In on-time Delivery • Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and improvement in product quality. Purdue University Fort Wayne. • Improvement in Student Experience and Quality of Life. • Achievement of Student Wellness Functional Requirements and improvements in student retention and four and five year graduation rates. Achievement of Student Success Functional Requirements and improvements in student retention and four and five year graduation rates. There are three main objectives of this thesis: (1) Apply and contrast the application of Collective System Design principles across a manufacturing industrial client and a service enterprise, namely higher education (2) Offer a systematic approach for manufacturing to improve on-time delivery, enhance customer satisfaction, create positive tone by using the principles of Collective System Design, and (3) For academia, develop a System Design Decomposition to define the functions of the university to foster student wellness according to four viewpoints: academic, financial, career, and living wellness. The objective is to incorporate the development of a System Design Decomposition that provides methodology to ensure that student wellness outcomes consider the four viewpoints of wellness (Academic, Financial, Career, and Living). The Student Success Standard Process Lifecycle defines standard processes in all process steps that will facilitate the desired student experience and four wellness outcomes. The lifecycle consists of Student Success States where the lifecycle begins from S0 (learning about university) to S7 (Supportive alumni) and defines standard process steps in each state. Each standard process step seeks to achieve the Functional Requirements from the four wellness viewpoints (academic, financial, career, and living) in Student Success Standard Process Lifecycle. The Collective System Design Decomposition methodology will serve as a structured approach to defining desired student wellness outcomes within a Rapid Design Process, which takes place in the first session focusing on defining outcomes. By leveraging this framework of four wellness viewpoints, the thesis aims to address issues with defining the outcomes for academic, financial, career, and living wellness viewpoints. Each wellness viewpoint has specific Functional Requirements (outcomes) that need to be defined and achieved by Student Success Standard Process Lifecycle and Rapid Design Process, to ultimately enhance student success and well-being at Purdue Fort Wayne University.
Degree Type
- Master of Science
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
Campus location
Advisor/supervisor/committee chair, additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, usage metrics.
- Systems engineering

Thesis on service delivery and customer satisfaction
Since all were aspects thesis on service delivery and customer satisfaction service delivery, it can be seen that they were satisfactiln important since effectively all got a fair vote proportion out of Customers thesis on service delivery and customer satisfaction researcher met were unwilling to touch questionnaire papers, fear of Corona Virus. The total ans of the 3 page research paper outline in E. This is because it was likely that respondents broke off unless they find the opening questions easy to answer. This is because it is not simply a matter of meeting expressed needs but of finding out unexpressed needs, setting priorities, allocating resources and publicly justifying and accounting for what has been done. The outcome revealed that an effective service design greatly improves the customer satisfaction. Metadata Show full item record. The reason for using simple random sampling was that first, the researcher had more precise information inside the sub-population about the variables the researcher studied. Similarly, data gathered through interviews and observations were analyzed qualitatively. Once the questionnaires had been developed in English, it was translated in to Afan Oromo. The answers given by the participants are truth full and beneficial for those who are not parts of the research.
Video Thesis on service delivery and customer satisfaction
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Customer Satisfaction and Public Service Delivery: The Case of Dire Dawa Administration

Journal of Culture, Society and Development, An International Peer-Reviewed Journal
The issue of service delivery is becoming a global concern that demands continuous reform to fit the turbulent environment and changing customer needs. Efficient and effective services delivery is now a prominent agenda of most countries including Ethiopia. The demand for effective and efficient delivery of services requires fundamental change involving both institutional and cultural changes. Hence, measuring the level of satisfaction provides an indication of how successful organizations are at providing services, and is taken as effective outcome measure. Several researches have been conducted on the subject matter; however, most of them were focusing on private sectors such as insurance, hotel, bank and the like. Few are studied on public service organizations. Moreover, so far no study has been conducted that critically analyzes the state of customer satisfaction on service delivery of public service organizations in Dire Dawa Administration. The purpose of this study is therefore to assess customer satisfaction on service delivery of public service organizations in Dire Dawa Administration. To this effect, four research questions were employed to guide the study. These were: 1) what are the levels of customer satisfaction of public service organizations in Dire Dawa Administration? 2) What are the extents of the service delivery process in public service organizations (in terms of Assurance, Reliability, Tangibility, Empathy, and Responsiveness)? 3) What are the relationships between service delivery dimensions and customer satisfaction? 4) What are the major problems that exist in the service delivery process of public service organizations in Dire Dawa Administration? In addition, two data gathering techniques: systematic random sampling and purposive sampling were used to obtain relevant data required for the study. In the primary data gathering technique, questionnaire that were designed and distributed to customers and employees were used. For further elaboration, key informant interviews were conducted with selected officials from the sample organizations. Secondary data from different sources were employed. The data gathered from both primary and secondary sources were analyzed and presented using descriptive and statistical methods such as means, frequencies, percentages, tables and charts. The results of the study indicated that the five service delivery dimensions and customer satisfaction were positively correlated; the general level of customer satisfaction and the service delivery dimensions were moderate. The major challenges in service delivery such as lack of skilled and experienced leadership, inability to lead and make decisions strategically, inconsistent follow up and monitoring, absence of regular consultation with customers and stakeholders, prevalence of corruption and rent seeking activities and behavior, lack of motivation and service mentality, ineffective automation, absence of timely revision of rules and regulations; lack of cooperation and integration among stakeholders, inefficient and inappropriate grievance handling systems, mismatch between demand and supply in water, health and electric services, and absence of conducting customer satisfaction surveys scientifically were thoroughly identified. Finally, based on the analysis and conclusions, possible recommendations were suggested for alleviating the major challenges of service delivery processes in the study area.
Related Papers
Aschalew Mulugeta
The issue of service delivery is becoming a global concern that demands continuous reform to fit the turbulent environment and changing customer needs. The purpose of this study was therefore to assess customer satisfaction on service delivery of selected public service organizations in Dire Dawa city Administration. The study employed the cross-sectional field survey method since relevant data were collected via at one point in time at public service organizations by distributing questionnaires to customers. A sample of 870 customers and 206 employees were randomly selected as study respondents in which In combination of a mixed research design was employed to quench the objectives of the study. Descriptive statistics, Spearman's correlation, mean values, frequency distribution and percentages were used to analyze the responses of respondents. The results of the study indicated that the five service delivery dimensions and customer satisfaction were positively correlated; the general level of customer satisfaction and the service delivery dimensions were moderate. The major challenges in service delivery such as lack of service mentality and deterioration of employees' motivation, prevalence of corruption and rent seeking activities and behavior, absence of regular consultation with customers and stakeholders, lack of cooperation and integration among stakeholders, insufficient skilled man power, shortages of equipment and machineries, inefficient and inappropriate grievance handling systems, lack of revision of existing rules and regulations on timely basis, inability/under capacity of the middle managers to monitor and manage employees, and discrepancy between supply and demand were thoroughly identified. Finally, based on the analysis and conclusions, possible recommendations were suggested for alleviating the major challenges of service delivery processes in the study area.
IJAR Indexing
Customer satisfaction is considered a prerequisite for customer retention and loyalty, and can help to boost profitability, market share and return on investment.Thus, to be successful in the current competitive environment, service organizations must streamline their service delivery systems and respond to everdiscerning customers? demands for efficient and quality services. Adama transport Authority is one of the public institutions which facilitates, coordinates and promotes private investment in the city administration. This term paper assessed service delivery and customer satisfaction in the transport authority in relation to location, facilities, requirements and forms, transparency and participation, employees? effect on service delivery and satisfaction on their job (salary, benefit and trainings),timeliness, customer satisfaction and complaint handling, which are the best measure of customer Satisfaction.The result of the term paper indicated that manpower and offices with the necessary, inaccessiblity of photo copy service, the existence of problems related to location, reception area, meeting standard time,low salary scale, low provision of skilled based training ,low incentives and compliant handling system are the major problems that dissatifies customer satisfaction.
IJMSBR Open Access Journal
Public service should give satisfaction to the community. There are two main purposes of public service; first is to impose clean and excellent bureaucracy, and second to help the responsibilities of government to serve the public as customers. In conducting these responsibilities, the government must provide high quality and good customer service to achieve the main goal. The study aims for finding out the influence of the service quality on customer satisfaction from the public. The researcher conducts the study at government Organizations, in the Office of Customs and Excise. This study reveals the service quality, namely: reliability, assurance, tangible, empathy, responsiveness, noticed quality, and recovery effect, simultaneously and partially influence on the customer satisfaction. Among the quality, responsiveness gives the greatest impact on the customer satisfaction.
Journal of Investment and Management
Sisay Debebe
This paper aims to investigate the factors which mainly affect the customer satisfaction level of automotive repair service quality being provided by the public sector organizations in Pakistan. A questionnaire was designed to measure the gap between the customer expectations and satisfaction about repair service quality. A total of 183 managers, supervisors and operators randomly selected from 100 customer organizations (public sector) responded to the questionnaire. Randomly collected data analyzed using software SPSS 19,
Water Practice and Technology
Binyam Zewde
Service quality and customer satisfaction are very important concepts that water enterprises must understand and measure from the customers' perspective to satisfy their needs. The main objectives of this research were to assess the level of customer satisfaction on urban water supply services of Southern Region, Ethiopia, and identify major determinants. Quantitative data were collected from 8,413 customers in seventeen towns, using a questionnaire based on the SERVQUAL model. Qualitative data were collected from customers via focus group discussion, and interviews were used with utility employees and officials. The results showed 47% of customers were satisfied with the water supply enterprise services, while 43% were dissatisfied for various reasons. The customer satisfaction score was below the acceptable level for all service quality dimensions, and understanding of customers, communication, and responsiveness were far below the benchmark. The correlation analysis revealed ...
GATR Journals
Objective – Theoritical study was used to study the level of customers’ satisfaction towards service provided by agency at UTC Melaka through the service quality model developed by Parasuraman which are tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, empathy and assurance. Methodology/Technique – A non-probability technique was used to study the level of customer satisfaction where questionnaires were distributed to 110 respondents at UTC Melaka. Respondents were determined using convenient sampling method and result was analysed by using SPSS version 20.0. Findings – All the studied factors indicated a significant relationship with customers’ satisfaction. The value of r for tangibility was 0.450, reliability (0.558), responsiveness (0.457), assurance (0.313), and empathy (0.475). As a conclusion, customers are satisfied with the service provided by agency at UTC Melaka and reliability was the most factors that affect the customer satisfaction. Novelty – This research are to test Parasuraman service quality model in Malaysia government agency and look at the level of customers’ satisfaction towards the service provided.
Mahiswaran Selvanathan , Puvaneswaran Kunasekaran , Pei Tan
This present study examines the level of customer satisfaction of three government agencies Royal Malaysian Police (RMP), National Registration Department (NRD), and the Public Works Department (PWD) in Malaysia. Studies on these three government agencies were conducted in Selangor, Johor, Perak, and Pulau Pinang since these agencies in these states received the highest complaint from consumers. A total of 270 employees and 627 customers from these three agencies of the four states were the respondents of the present study. Results showed customers are not satisfied with the services given by the government agencies (RMP, NRD, and PWD). Therefore, efforts to improve employee's attitudes, and more reforms in the areas of work should be continued by the Government of Malaysia in government agencies in order to maintain the excellent work.
yibeltal damitie
perencanaan pembuatan bank sampah
vonny mei sella
planning pembuatan usaha bankh sampah
RELATED PAPERS
International Journal of Corrosion
DATO' SR. DR. WAN MUHD AMINUDDIN WAN HUSSIN
Pilar Herrera-Fierro
Plant, Cell & Environment
Rachid Serraj
Nadine Darwiche
John Johnson
rfgtfh lklklk
Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers Series B
Takemi Chikahisa
Matti Pitkänen
Revista Eletrônica Acervo Saúde
ribamar machado
A & A Practice
BobbieJean Sweitzer
Patrick McEvoy-Halston
Tiers-Monde
Catherine Regnault-roger
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects
Rachel Goldman
Chemistry – A European Journal
Alejandro Criado
Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical
Nirmal Gurung
Marcela Andruchow
Emergency Medicine Journal
Stephen Jackson
Jyothi Priya
Medisch-Farmaceutische Mededelingen
Piet Bruijnzeel
E3S Web of Conferences
Prabang Setyono
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- St. Mary's University Institutional Repository
- Thesis and Dissertation
- Masters Program
- Business Administration
Items in DSpace are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Service Delivery and Customer Satisfaction in the Public Service Sector: An Ethiopian Experience November 2019 Public Policy and Administration Vol.9, No.9, 2019(September 30th 2019):14
1.1.2.Customer Satisfaction Service companies have since recently focused on customers in order to improve competitiveness. Customer satisfaction is one of the important outcomes of marketing activity (M ick and Fournier; 1999). In the competitive banking industry, customer satisfaction is considered as the fundamental of success.
customer satisfaction. The finding of Mohammad and Alhamadani (2011), indicated that service quality is an important antecedent of customer satisfaction. Parasuraman et al. (1985) "found that service quality is significant predictor of customer satisfaction by using SERVQUAL instrument." Service quality and customer satisfaction
Thesis 2013 Instructors: principal lecturer Minna Ikävalko, Saimaa University of Applied Sci- ... Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality depend a lot on Organization Stand-ards (OS) of the company where they are applied. ... service environment, and service delivery, or consists of interaction quality, physical environment quality, and ...
Moreover, customer perceived performance is significantly lower than customer perceived importance for all six service quality dimensions. Ordered by need of improvement the dimensions (based on gap analysis) are: 1) network quality, 2) reliability, 3) responsiveness, 4) assurance, 5) empathy, 6) tangibles.
The Impact of Service Delivery System Effectiveness on Service Quality: A Hierarchical Approach Giannis Kostopoulos, PhD ... companies can achieve increased customer satisfaction, loyalty and therefore long-term profitability (Zeithaml and Bitner, 2000). In order ... and bridge the gap between service delivery and customer expectations ...
Extensive research on articles in the niche of business and economics that talk about customer. satisfaction indicates that 2235 studies have got carried out between 1992-2011 (Farooq & Salam, 2018). Amongst these studies, 1088 elaborate on the aspects of customer satisfaction and service.
Finally, based on the analysis and conclusions, possible recommendations were suggested for alleviating the major challenges of service delivery processes in the study area. Key Terms: Customer Satisfaction, Service Delivery, Public Service Organizations. DOI: 10.7176/JCSD/60-01. Publication date:June 30th 2020. 1.
I would like to dedicate this thesis to my late father, Michael Mfanafuthi Maphumulo, ... 2.9.3. Gap 3: Service-quality specifications and service delivery 43 2.9.4. Gap 4: Service delivery and external communication 44 ... 2.12. CUSTOMER SERVICE 48 2.12.1. Customer satisfaction 49 2.12.2. Customer satisfaction and service quality as related ...
Customer satisfaction of service quality has a mediating role between customer experience and customer loyalty (Hsieh et al., Citation 2015; Lemy et al., Citation 2019; ... Fourth, mangers should be aware that service delivery is one part of the supply chain. It is important to fix the lapses by analyzing the people and process involved in the ...
The theoretical framework of this thesis consists of the customer service management and relationship management with their brief definitions and the explanations. The different ways of ... Service delivery and customer satisfaction is a priority to consider, the customers come first. 3
The concept of service has been defined since the 1980s by Churchill and Surprenant (1982) together with Asubonteng et al. (1996), who popularized the customer satisfaction theory through measuring the firm's actual service delivery in conformity with the expectations of customers, as defined by the attainment of perceived quality, and that ...
THE EFFECT OF SERVICE QUALITY ON CUSTOMER SATISFACTION: THE CASE OF ETHIOPIAN ELECTRIC UTILITY AROUND ADDIS ABABA A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies of Jimma University in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Award of the Degree of Master of Business Administration (MBA) BY: MEKONNEN TESFAYE G/EYESUS JIMMA UNIVERSITY ...
In today's increasingly competitive environment, quality service and customer satisfaction are critical to corporate organizations. Delivering high quality service is linked to increased profits, cost savings and corporate image. Customer satisfaction is the route to sustained high performance.
Customer satisfaction is an integral part of organizational objectives that must be fulfilled for an organization to maintain its customers. This paper is a research on the title "customer satisfaction and service delivery: the case of Addis Ababa city administration land development and management office".
This Thesis - Open Access is brought to you for free and open access by DSpace @Strathmore University. ... developing and providing new and better service offers, better service delivery mechanisms. In the current highly competitive hospitality industry environment, it is not only essential to know the significance of service quality ...
the impact of quality service delivery on customer satisfaction at oromia insurance s.c by lensa kuma id no: sgs/0058/2006 a thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for degree of masters of business administration (mba) december, 2015 addis ababa, ethiopia .
Furthermore, it also revealed that there is a positive correlation between efficient service delivery and customer satisfaction [29]. The way the employee behaves with a friendly attitude toward customers affects customer satisfaction and can result in a positive outcome. ... BSc Thesis, School of Industrial Engineering and Engineering ...
The quality of delivery service encounters in which crowdsourced couriers and customers highly interact and mutually influence each other affects their attitudes and behaviours. ... we show that customer encounter satisfaction is not only influenced by their own perception of service encounter quality but also by the corresponding courier's ...
There are three main objectives of this thesis: (1) Apply and contrast the application of Collective System Design principles across a manufacturing industrial client and a service enterprise, namely higher education (2) Offer a systematic approach for manufacturing to improve on-time delivery, enhance customer satisfaction, create positive ...
Thesis on service delivery and customer satisfaction Marital status: a Married b Single 6. Mihelis, et al. Consultation: Naidoo , indicated that customers should be asked about the level and quality of the public services they receive and wherever possible should be given a choice about the services that are to have service standards. This is because it is not simply a matter of meeting ...
Customer satisfaction is considered a prerequisite for customer retention and loyalty, and can help to boost profitability, market share and return on investment.Thus, to be successful in the current competitive environment, service organizations must streamline their service delivery systems and respond to everdiscerning customers? demands for efficient and quality services.
The rise of the e-commerce industry has markedly changed the global economy, providing customers with unparalleled access to goods and services. This study empirically examines online shoppers' perceptions and preferences, focusing on their experiences with last-mile delivery (LMD) services and its impact on their shopping behaviour. This research employs machine learning classification and ...
The main aim of this thesis was to assess the customers' satisfaction on the service delivery of RIDE in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. It identifies the level of customer satisfaction by measuring the gap between customers' expectation and actual performance on the quality of service delivered by RIDE using the five service quality dimensions ...
The company continues its growth trajectory with new customer wins and carrier additions in the first five months of 2024 June 06, 2024 06:30 ET | Source: Freight App, Inc. Freight App, Inc.