

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
| past simple | I bought a car | She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. |
| past continuous | I was walking along the street | She said (that) she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | I haven't seen Julie | She said (that) she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | I had taken English lessons before | She said (that) she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | I'll see you later | She said (that) she would see me later. |
| would* | I would help, but... | She said (that) she would help but... |
| can | I can speak perfect English | She said (that) she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | I could swim when I was four | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
| should* | I should call my mother | She said (that) she should call her mother |
| might* | I might be late | She said (that) she might be late |
| must | I must study at the weekend | She said (that) she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
| Where is the Post Office, please? | She asked me where the Post Office was. |
| What are you doing? | She asked me what I was doing. |
| Who was that fantastic man? | She asked me who that fantastic man had been. |
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
| Do you love me? | He asked me if I loved him. |
| Have you ever been to Mexico? | She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico. |
| Are you living here? | She asked me if I was living here. |
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
| Please don't smoke. | She asked me not to smoke. |
| Could you bring my book tonight? | She asked me to bring her book that night. |
| Could you pass the milk, please? | She asked me to pass the milk. |
| Would you mind coming early tomorrow? | She asked me to come early the next day. |
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don't worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don't smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
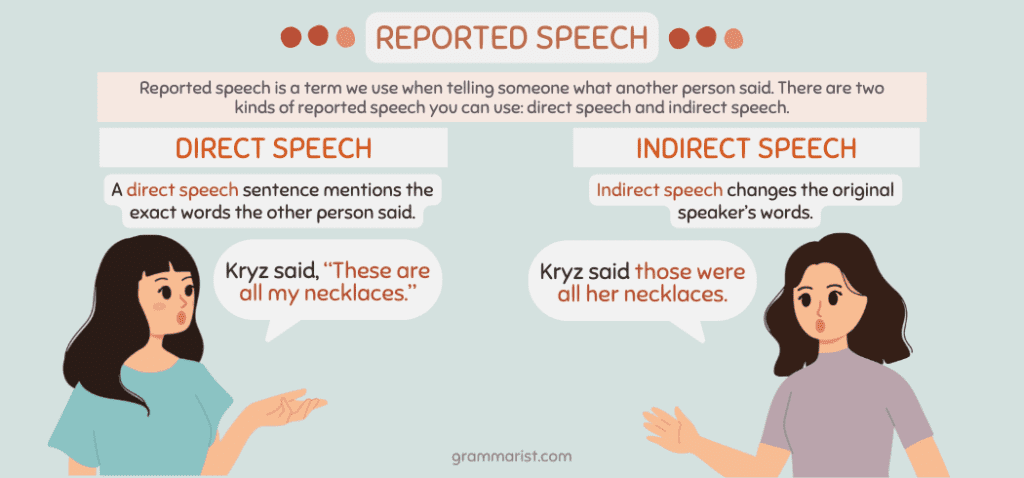
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
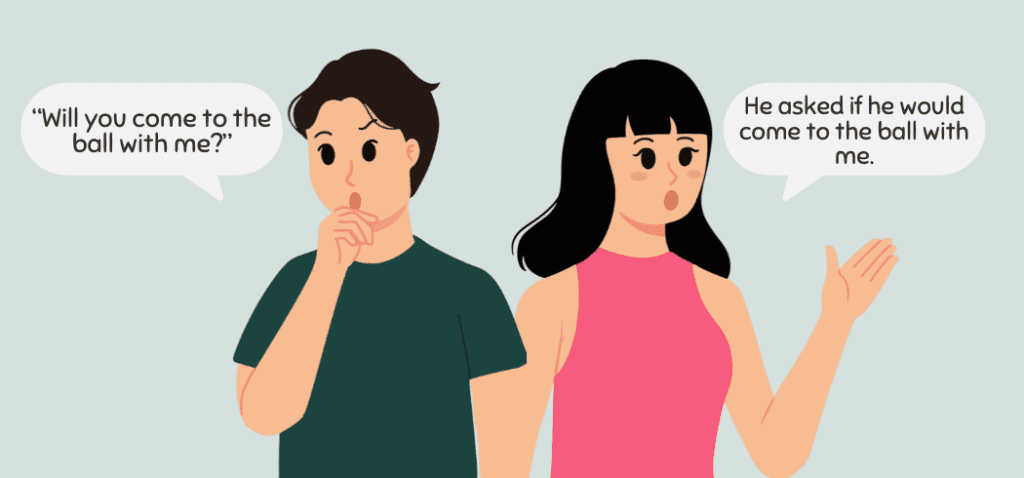

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.

Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
| Simple present “I to go home.” | Simple past She said she to go home. |
| Present continuous “I a good book.” | Past continuous She said she a good book. |
| Simple past “I pasta for dinner last night.” | Past perfect She said she pasta for dinner the night before. |
| Present perfect “I just cleaning my room.” “My mother never to Japan.” | Past perfect She said she just cleaning her room. She said her mother never to Japan. |
| Can/can’t “I meet with you next Monday.” “Sorry, I talk now; I’m at work.” | Could/couldn’t She said she meet with me next Monday. She said she talk at the moment because she was at work. |
| Will/won’t “I pick him up from the airport.” “I tell anyone your secret.” | Would/wouldn’t She said she pick him up from the airport. She said she tell anyone my secret. |
| Should “You apologize.” | Should She said I apologize. |
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to Backshift in Reported Speech
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Relative Clauses + Exercises

Advanced English Prepositions Quiz

Forming reported speech
- Direct speech: “I’m not playing football.” Reported later: “He said that he wasn’t playing football.”
- Direct speech: Jane: “I don’t like living here.” (Jane is referring to herself) Reported speech: Jane said (that) she didn’t like living here. (The pronoun she refers to Jane )
- Direct speech: “I like this car.” Reported speech: He said (that) he liked that car.
- Direct speech: “I went to Tokyo last week .” Reported speech: She said (that) she’d been to Tokyo the week before .
We use reported speech to tell someone what another person said:
Jim says to you:
“I don’t feel well.” “I can’t drive.” “My parents have gone on holiday.” “I’m going out now so you will have to wait until I get back.” “I’ll help you.”
Later, you tell your friend what Jim said:
Jim said (that) he didn’t feel well. He said (that) he couldn’t drive. He said (that) his parents had gone on holiday. He said (that) he was going out now so I would have to wait until he got back. He said that he would help me .
Additional points
- Direct speech: “My car is bigger than yours.”
- Reported speech: He said his car is/was bigger than mine.
- Direct speech: “The earthquake happened at half past seven.”
- Reported speech: The radio said that the earthquake happened at half past seven.
- Direct speech: “I should go to the dentist.”
- Reported speech: He said that he should go to the dentist.
Pronunciation
See the phonemic chart for IPA symbols used below.
If we use that in reported speech, we pronounce the weak form.
- I said that he’d do it: /ðət/
Related grammar points
Reported Questions Reporting Verbs Say and Tell
Got a teaching idea to share?
Share your activity or lesson plan with your fellow teachers. You'll be helping our community and contributing to a hub of valuable resources for teachers everywhere.

Keith Taylor
Keith is the co-founder of Eslbase and School of TEFL . He's been a teacher and teacher trainer for over 20 years, in Indonesia, Australia, Morocco, Spain, Italy, Poland, France and now in the UK.
Grammar for English Teachers
Learn everything you need to feel confident with grammar as a teacher Online course - Save £30 this summer
16 comments
Hello, I’m not a teacher, I’m an ESL class student. So, I’m here to ask you guys a question about wich is still making me to be confused. I asked my teacher, ”if you say, ”I am a teacher”, should I make it a reported speech as ” she said she was a teacher?”. she answered that I needed to say ,” she said she is a teacher”. One more thing: I found a sentence in worksheet written , ”He told his birthday is next week”. Is it correct? I thought it had to be ” he told his birhday would be next week” So, is this modern English rule? Is that a difference? Can you pleeease, explain and help me to make sure to correct this hesitation.
Thanks for your questions.
1. “She said she was a teacher” and “She said she is a teacher” are both correct. Often we don’t change the tense if the fact that we are reporting is still true. So, if it is still true that she is a teacher, then she can report it with “She said she is a teacher” (see Additional point number 1 above).
2. “He told his birthday is next week”. First of all, if you use “told” then you must add a direct object, like this: “He told me his birthday is next week”.
Now, let’s look at the different ways we can use reported speech for this. If the person says “My birthday is next week” then we can report it like this: – He told me his birthday was next week – He told me his birthday is next week (it’s still true so we don’t need to change the tense)
If the person says “My birthday will be next week” then we can report it like this: – He told me his birthday would be next week.
I hope that helps!
This is what I wanted to know. Thanks a lot!
I ask one of my students to introduce him/herself (name, age, hobbies)… and ask other students to take notes. When they are finished, I ask “What did he say?”
I tell students to think about what happened to them before they came to class. For example, “what did your mom, dad, husband, wife say to them? They write down the direct speech and then the reported speech.
I prepare cards with several questions in different tenses, such as:
“What were you doing yesterday at 6?” “How long have you been studying English?” “Will you do your homework for tomorrow?”
I put my students in pairs and ask them to interview each other using the questions on the cards. Once they’ve got their answers, they change partners and share everything they’ve learnt about the previous student.
Cut a dialogue into four parts. Paste it on four walls. Students work in pairs. One of them is the messenger and the other one is a receiver. The messenger runs to the walls and remembers the sentences, comes back and narrates the same to the receiver.
I did a “Find someone who…” mingling activity with my students and then divided the group into two teams. I asked a member from the first team to report one of the replies to a question they had asked. If their reply was correctly put into reported speech, they got a point for their team. I repeated the process until I had covered all the responses from the activity. The team with the most points won the game and was rewarded with cream eggs!
I have students make 10 questions they would ask their favourite actor or actress. Then, they use these questions to interview another partner who pretends to be that famous person. He or she will answer those questions the same way the famous person would. Students end up reporting their answers to the teacher. In that way, they can practice reported speech in an interesting form.
If you have the resources, you can play a short listening/video about an important event, news, etc. Students then have to report to the teacher what they heard.
I show them some debate shows on the Internet after advising them to make notes of the main points. Then I ask them to report what different participants opined. SBS insight has nice discussions to be used for this purpose.
I showed some slides about a fire at a petrol station and the group had to make up a conversation between two witnesses to the fire. We then wrote it as a newspaper report.
I put students in groups of three. Two in the group are a couple quarrelling, but who will not speak to each other. The middle man/woman receives information from one and uses reported speech to relay the message(s).
I ask students to think of a fun sentence. I put them all in a line and the student at the end whispers their sentence to the one beside them, this student then reports the sentence to the following student, and so on. The last student says the sentence aloud and we see if they did it correctly… it is like the “telefono descompuesto” in Spanish.
I ask students to tell their partner three secrets. Then, this student tells other students in the class (a good way to explain the word: gossip!). This activity helps students practice reporting but in a fun way!
I give the students comic strips from the funny pages, and they have to summarize the direct speech. There are always lots of questions, and that makes especially good practice.
Leave your comment (Cancel Reply)
We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your experience. Agreeing to this helps us process data like your browsing habits and unique IDs, making our site work better for you. If you choose not to, some features won't work as smoothly.
The Reported Speech
Table of contents, what is reported speech.
is a reported speech, whereas:
Direct speech vs reported speech
1. We use direct speech to quote a speaker’s exact words. We put their words within quotation marks. We add a reporting verb such as “he said” or “she asked” before or after the quote.
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| She says: “I like tuna fish.” | She says that she likes tuna fish. |
| She said: “I’m visiting Paris next weekend.” | She said that she was visiting Paris the following weekend. |
| He asked Betty: “Do you like cheese?” | He wanted to know if Betty liked cheese. |
Different types of reported speech
When you use reported speech, you either report:
A. Reporting statements
1- pronouns.
| Shifting back tense | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| (no backshift) | “I poems.” | He that he poems. |
| (backshift) | “I poems | He that he poems. |
Do not change the tense if the introductory clause (i.e., the reporting verb) is in the present tense (e. g. He says ). Note, however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person singular).
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| He said: “I happy” | He said that he happy |
| He said: “I for my keys” | He said that he for his keys |
| He said: “I New York last year” | He said that he New York the previous year. |
| He said: ” I here for a long time “ | He said that he there for a long time |
| He said: “They the work when I “ | He said that they the work when he “ |
| He said: “I football when the accident “ | He said that football when the accident |
| He said: “I football for two hours.” | He said that football for two hours |
| He said: “I a newspaper when the light “ | He said that he a newspaper when the light |
| He said: “I the door.” | He said that the door. |
| He said: “I a Mercedes if I rich” | He said that he a Mercedes if he rich |
3. Modal verbs
| Modal | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| can | “I do it.” | He said that he do it. |
| may | “ I go out?” | He wanted to know if he go out. |
| must | “She apply for the job.” | He said that she apply for the job. |
| will | “They call you.” | He told her that they call her. |
4- Place, demonstratives, and time expressions
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Time Expressions | |
| today | that day |
| now | then |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before/the previous week |
| next year | the following year/the next year/ the year after |
| tomorrow | the next day/the following day |
| Place | |
| here | there |
| Demonstratives | |
| this | that |
| these | those |
B. Reporting Questions
| Types of questions | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| With question words (what, why, where, how…) | “Why don’t you speak English?” | He asked me why I didn’t speak English. |
| Without question words (yes or no questions) | “Do you speak English?” | He asked me whether/if I spoke English. |
C. Reporting requests/commands
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| “Nancy, do the exercise.” | He told Nancy to do the exercise. |
| “Nancy, give me your pen, please.” | He asked Nancy to give him her pen. |
| Tenses are not relevant for requests, simply use / + verb (infinitive without “to”) |
| For affirmative use + infinitive (without to) For negative requests, use + infinitive (without to). |
D. Other transformations
Main clauses connected with and/but, punctuation rules of the reported speech, can we omit that in the reported speech, list of reporting verbs.
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| simple present | simple past |
| simple past | past perfect |
| present continuous | past continuous |
| past continuous | past perfect continuous |
| will | would |
| shall | should |
| may | might |
| can | could |
| must | had to |
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
StoryLearning
Learn A Language Through Stories
A Comprehensive Guide To Reported Speech In English
There are times when someone tells you something and you’ll have to report what they said to someone else.
How can you do this in English?
You’ll need to know how to use what's called reported speech in English and this is what you’ll learn in this blog post.
What Is Reported Speech In English?
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of retelling what someone else has said without repeating their exact words.
For example, let’s say you have a friend called Jon and one called Mary. Mary has organised a house party and has invited you and Jon.
Jon, however, is not feeling well. He says to you, “Sorry but I cannot come to the party. I spent all day working outside under the rain and I feel ill today.”
A few days after the party, you meet Sarah. She’s another one of your friends and she was at the party too, but she arrived late – a moment before you left. You only had time to say hello to each other.
She asks you, “I saw you at the party but I didn’t see Jon. Where was he?”
When Sarah asks you, “Where was Jon?” you can say,
“Jon said, ‘Sorry but I cannot come to the party. I spent all day working outside under the rain and I feel ill today’.”
However, it would be more natural to use indirect speech in this case. So you would say, “Jon said he couldn’t come to the party. He had spent all day working outside under the rain and he felt ill that day .”
Did you notice how the sentence changes in reported speech?
Here’s what happened:
- “I” became “he”
- “Cannot” became “couldn’t”
- “Spent” became “had spent”
- “I feel ill today” became “he felt ill on that day”
Let’s take a closer look at how we form reported speech.
How To Form Reported Speech In English
To form reported speech, you might have to make a few changes to the original sentence that was spoken (or written).
You may have to change pronouns, verb tenses, place and time expressions and, in the case of questions, the word order.
There are certain patterns to learn for reporting promises, agreements, orders, offers, requests, advice and suggestions.
Let’s have a look at all these cases one by one.
Reported Speech In English: Changing Verb Tenses
In general, when we use reported speech, the present tenses become past tenses.
We do this because we are often reporting someone else’s words at a different time (Jon’s words were spoken 3 days before you reported them to Sarah).
Here’s an example:
Jenny (on Saturday evening) says, “I don't like this place. I want to go home now.”(present tenses)
Matt (on Sunday morning) talks to James and says, “Jenny said that she didn't like the place, and she wanted to go home. (past tenses)
So this is how different verb tenses change:
Simple Present → Simple Past
DIRECT: I need money.
INDIRECT: She said she needed money.
Present Progressive → Past Progressive
DIRECT: My French is improving.
INDIRECT: He said his French was improving.
Present Perfect → Past Perfect
DIRECT: This has been an amazing holiday.
INDIRECT: She told me that it had been an amazing holiday.
What if there is a past simple form of the verb in direct speech? Well, in this case, it can stay the same in reported speech or you can change it to past perfect .
Past Simple → Past Simple Or Past Perfect
DIRECT: I didn’t go to work.
INDIRECT: Mary said that she didn’t go to work / Mary said that she hadn’t gone to work
Past Perfect Tenses Do Not Change
DIRECT: I arrived late because I had missed the bus.
INDIRECT: He said he arrived (or had arrived) late because he had missed the bus.
Modal verbs like “can,” “may,” and “will” also change in reported speech.
Will → Would
DIRECT: The exam will be difficult.
INDIRECT: They said that the exam would be difficult.
Can → Could
DIRECT: I can’t be there.
INDIRECT: He told me he couldn’t be there.
May → Might
DIRECT: We may go there another time.
INDIRECT: They said they might go there another time.
However, past modal verbs don’t change (would, must, could, should, etc.) don’t change in reported speech.
DIRECT: It would be nice if we could go to Paris.
INDIRECT: He said it would be nice if we could go to Paris.
Here are some other examples:
| “I am going to the store,” said John. | John said that he was going to the store. |
| “I love pizza,” said Jane. | Jane said that she loved pizza. |
| “I will finish the project today,” said Mary. | Mary said that she would finish the project that day. |
| “I can't come to the party,” said Tom. | Tom said that he couldn't come to the party. |
| “I have a headache,” said Sarah. | Sarah said that she had a headache. |
| “I saw a movie last night,” said Peter. | Peter said that he had seen a movie the previous night. |
| “I want to learn Spanish,” said Emily. | Emily said that she wanted to learn Spanish. |
| “I have been working on this project for a week,” said Sam. | Sam said that he had been working on the project for a week. |
| “I don't like this food,” said Mark. | Mark said that he didn't like that food. |
| “I am not feeling well,” said Alice. | Alice said that she was not feeling well. |
So, in summary,
- am/is → were
- do/does → did
- have/has → had
- had done → had done
- will → would
- can → could
- may → might
- could → could
- would → would
- like/love/buy/see → liked/loved/bought/saw or had liked/ had loved/had bought/had seen.
You make these verb tense shifts when you report the original words at a different time from when they were spoken. However, it is often also possible to keep the original speaker’s tenses when the situation is still the same.
For example,
1. DIRECT: I am feeling sick.
INDIRECT: She said she is feeling sick.
2. DIRECT: We have to leave now.
INDIRECT: They said they have to leave now.
3. DIRECT: I will call you later.
INDIRECT: He said he will call me later.
4. DIRECT: She is not coming to the party.
INDIRECT: He said she is not coming to the party.
5. DIRECT: They are working on a new project.
INDIRECT: She said they are working on a new project.
What about conditional sentences? How do they change in reported speech?
Sentences with “if” and “would” are usually unchanged.
DIRECT: It would be best if we went there early.
INDIRECT: He said it would be best if they went there early.
But conditional sentences used to describe unreal situations (e.g. second conditional or third conditional sentences) can change like this:
DIRECT: If I had more money I would buy a new car.
INDIRECT: She said if she had had more money, she would have bought a new car OR She said if she had more money, she would buy a new car.
Reported Speech In English: Changing Pronouns
In reported speech, because you’re reporting someone else’s words, there’s a change of speaker so this may mean a change of pronoun.
An example:
Jenny says, “I don't like this place. I want to go home now.”
Matt says, “Jenny said that she didn't like the place, and she wanted to go home.”
In this example, Jenny says “I” to refer to herself but Matt, talking about what Jenny said, uses “she”.
So the sentence in reported speech becomes:
- Jenny said that she didn’t like . . . ( not Jenny said that I didn’t like . . .)
Some other examples:
1 . DIRECT: I have been studying for hours.
INDIRECT: He said he had been studying for hours.
2. DIRECT: I don’t like that movie.
INDIRECT: She said she didn’t like that movie.
3. DIRECT: He doesn't like coffee.
INDIRECT: She said he doesn't like coffee.
4. DIRECT: We have a new car.
INDIRECT: They told me they had a new car.
5. DIRECT: We are going on vacation next week.
INDIRECT: They said they are going on vacation next week.
Reported Speech In English: Place And Time Expressions
When you’re reporting someone’s words, there is often a change of place and time. This may mean that you will need to change or remove words that are used to refer to places and time like “here,” “this,” “now,” “today,” “next,” “last,” “yesterday,” “tomorrow,” and so on.
Check the differences in the following sentences:
DIRECT: I'll be back next month.
INDIRECT: She said she would be back the next month , but I never saw her again.
DIRECT: Emma got her degree last Tuesday.
INDIRECT: He said Emma had got her degree the Tuesday before.
DIRECT: I had an argument with my mother-in-law yesterday .
INDIRECT: He said he’d had an argument with his mother-in-law the day before .
DIRECT: We're going to have an amazing party tomorrow.
INDIRECT: They said they were going to have an amazing party the next day.
DIRECT: Meet me here at 10 am.
INDIRECT: He told me to meet him there at 10 am.
DIRECT: This restaurant is really good.
INDIRECT: She said that the restaurant was really good.
DIRECT: I'm going to the gym now.
INDIRECT: He said he was going to the gym at that time.
DIRECT: Today is my birthday.
INDIRECT: She told me that it was her birthday that day .
DIRECT: I'm leaving for Europe next week.
INDIRECT: She said she was leaving for Europe the following week.
Reported Speech In English: Word Order In Questions
What if you have to report a question? For example, how would you report the following questions?
- Where’s Mark?
- When are you going to visit your grandmother?
- What do I need to buy for the celebration?
- Where are your best friend and his wife staying?
- Do you like coffee?
- Can you sing?
- Who’s your best friend?
- What time do you usually wake up?
- What would you do if you won the lottery?
- Do you ever read nonfiction books?
In reported questions, the subject normally comes before the verb and auxiliary “do” is not used.
So, here is what happens when you're reporting a question:
DIRECT: Where’s Mark?
INDIRECT: I asked where Mark was.
DIRECT: When are you going to visit your grandmother?
INDIRECT: He wanted to know when I was going to visit my grandmother.
DIRECT: What do I need to buy for the celebration?
INDIRECT: She asked what she needed to buy for the celebration.
DIRECT: Where are your best friend and his wife staying?
INDIRECT: I asked where his best friend and his wife were staying.
DIRECT: Do you like coffee?
INDIRECT: I asked if she liked coffee.
DIRECT: Can you sing?
INDIRECT: She asked me if I could sing.
DIRECT: Who’s your best friend?
INDIRECT: They asked me who my best friend was.
DIRECT: What time do you usually wake up?
INDIRECT: She asked me what time I usually wake up.
DIRECT: What would you do if you won the lottery?
INDIRECT: He asked me what I would do if I won the lottery.
DIRECT: Do you ever read nonfiction books?
INDIRECT: She asked me if I ever read nonfiction books.
You might have noticed that question marks are not used in reported questions and you don’t use “say” or “tell” either.
Promises, Agreements, Orders, Offers, Requests & Advice
When you’re reporting these, you can use the following verbs + an infinitive:
Here are some examples:
DIRECT SPEECH: I’ll always love you.
PROMISE IN INDIRECT SPEECH: She promised to love me.
DIRECT SPEECH: OK, let’s go to the pub.
INDIRECT SPEECH: He agreed to come to the pub with me.
DIRECT SPEECH: Sit down!
INDIRECT SPEECH: They told me to sit down OR they ordered me to sit down.
DIRECT SPEECH: I can go to the post office for you.
INDIRECT SPEECH: She offered to go to the post office.
DIRECT SPEECH: Could I please have the documentation by tomorrow evening?
INDIRECT SPEECH: She requested to have the documentation by the following evening.
DIRECT SPEECH: You should think twice before giving him your phone number.
INDIRECT SPEECH: She advised me to think twice before giving him my phone number.
Reported Speech In English
All right! I hope you have a much clearer idea about what reported speech is and how it’s used.
And the good news is that both direct and indirect speech structures are commonly used in stories, so why not try the StoryLearning method ?
You'll notice this grammatical pattern repeatedly in the context of short stories in English.
Not only will this help you acquire it naturally, but you will also have a fun learning experience by immersing yourself in an interesting and inspiring narrative.
Have a wonderful time learning through books in English !
Language Courses
- Language Blog
- Testimonials
- Meet Our Team
- Media & Press
Our website uses cookies to provide you the best experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our use of cookies. For more information, read our Cookie Policy .
Download Your Free StoryLearning® Kit!
Discover the world famous story-based method that 1,023,037 people have used to learn a language quickly…, not interested.
What can we do better ? If I could make something to help you right now, w hat would it be?
Which language are you learning?
What is your current level in [language]?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips…
Where shall I send them?
We will protect your data in accordance with our data policy.
Download this article as a FREE PDF ?
What is your current level in Swedish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Swedish tips…
Where shall I send the tips and your PDF?
What is your current level in Danish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Danish tips…
What can we do better? If I could make something to help you right now, w hat would it be?
What is your current level in [language] ?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips, PLUS your free StoryLearning Kit…
Download this article as a FREE PDF?
Great! Where shall I send my best online teaching tips and your PDF?
Download this article as a FREE PDF ?
What is your current level in Arabic?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Arabic tips…
FREE StoryLearning Kit!
Join my email newsletter and get FREE access to your StoryLearning Kit — discover how to learn languages through the power of story!
Download a FREE Story in Japanese!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Japanese and start learning Japanese quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
What is your current level in Japanese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Japanese StoryLearning® Pack …
Where shall I send your download link?
Download Your FREE Natural Japanese Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Japanese Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Japanese grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Japanese Grammar Pack …
What is your current level in Portuguese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Portuguese Grammar Pack …
What is your current level in German?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural German Grammar Pack …
Train as an Online Language Teacher and Earn from Home
The next cohort of my Certificate of Online Language Teaching will open soon. Join the waiting list, and we’ll notify you as soon as enrolment is open!
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Portuguese tips…
What is your current level in Turkish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Turkish tips…
What is your current level in French?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the French Vocab Power Pack …
What is your current level in Italian?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Italian Vocab Power Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the German Vocab Power Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Japanese Vocab Power Pack …
Download Your FREE Japanese Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Japanese Vocab Power Pack and learn essential Japanese words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE German Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my German Vocab Power Pack and learn essential German words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE Italian Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Italian Vocab Power Pack and learn essential Italian words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)

Download Your FREE French Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my French Vocab Power Pack and learn essential French words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Portuguese StoryLearning® Pack …
What is your current level in Russian?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Russian Grammar Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Russian StoryLearning® Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Italian StoryLearning® Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Italian Grammar Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the French StoryLearning® Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural French Grammar Pack …
What is your current level in Spanish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Spanish Vocab Power Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Spanish Grammar Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Spanish StoryLearning® Pack …
Where shall I send them?
What is your current level in Korean?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Korean tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Russian tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Japanese tips…
What is your current level in Chinese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Chinese tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Spanish tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Italian tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] French tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] German tips…
Download Your FREE Natural Portuguese Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Portuguese Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Portuguese grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural Russian Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Russian Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Russian grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural German Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural German Grammar Pack and learn to internalise German grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural French Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural French Grammar Pack and learn to internalise French grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural Italian Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Italian Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Italian grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download a FREE Story in Portuguese!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Brazilian Portuguese and start learning Portuguese quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in Russian!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Russian and start learning Russian quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in German!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in German and start learning German quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the German StoryLearning® Pack …
Download a FREE Story in Italian!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Italian and start learning Italian quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in French!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in French and start learning French quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in Spanish!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Spanish and start learning Spanish quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
FREE Download:
The rules of language learning.
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Rules of Language Learning and discover 25 “rules” to learn a new language quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Spanish Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Spanish Vocab Power Pack and learn essential Spanish words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE Natural Spanish Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Spanish Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Spanish grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Free Step-By-Step Guide:
How to generate a full-time income from home with your English… even with ZERO previous teaching experience.
What is your current level in Thai?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Thai tips…
What is your current level in Cantonese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Cantonese tips…
Steal My Method?
I’ve written some simple emails explaining the techniques I’ve used to learn 8 languages…
I want to be skipped!
I’m the lead capture, man!
Join 84,574 other language learners getting StoryLearning tips by email…
“After I started to use your ideas, I learn better, for longer, with more passion. Thanks for the life-change!” – Dallas Nesbit
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips…
Find The Perfect Language Course For You!
Looking for world-class training material to help you make a breakthrough in your language learning?
Click ‘start now’ and complete this short survey to find the perfect course for you!
Do you like the idea of learning through story?
Do you want…?
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Reported Speech in English
“Reported speech” might sound fancy, but it isn’t that complicated.
It’s just how you talk about what someone said.
Luckily, it’s pretty simple to learn the basics in English, beginning with the two types of reported speech: direct (reporting the exact words someone said) and indirect (reporting what someone said without using their exact words ).
Read this post to learn how to report speech, with tips and tricks for each, plenty of examples and a resources section that tells you about real world resources you can use to practice reporting speech.
How to Report Direct Speech
How to report indirect speech, reporting questions in indirect speech, verb tenses in indirect reported speech, simple present, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, simple past, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, simple future, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, authentic resources for practicing reported speech, novels and short stories, native english videos, celebrity profiles.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Direct speech refers to the exact words that a person says. You can “report” direct speech in a few different ways.
To see how this works, let’s pretend that I (Elisabeth) told some people that I liked green onions.
Here are some different ways that those people could explain what I said:
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” Elisabeth said.
- Thousands of learner friendly videos (especially beginners)
- Handpicked, organized, and annotated by FluentU's experts
- Integrated into courses for beginners

Direct speech: “I like green onions,” she told me. — In this sentence, we replace my name (Elisabeth) with the pronoun she.
In all of these examples, the part that was said is between quotation marks and is followed by a noun (“she” or “Elisabeth”) and a verb. Each of these verbs (“to say,” “to tell [someone],” “to explain”) are ways to describe someone talking. You can use any verb that refers to speech in this way.
You can also put the noun and verb before what was said.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like spaghetti.”
The example above would be much more likely to be said out loud than the first set of examples.
Here’s a conversation that might happen between two people:
- Interactive subtitles: click any word to see detailed examples and explanations
- Slow down or loop the tricky parts
- Show or hide subtitles
- Review words with our powerful learning engine
1: Did you ask her if she liked coffee?
2: Yeah, I asked her.
1: What did she say?
2. She said, “Yeah, I like coffee.” ( Direct speech )
Usually, reporting of direct speech is something you see in writing. It doesn’t happen as often when people are talking to each other.
Direct reported speech often happens in the past. However, there are all kinds of stories, including journalism pieces, profiles and fiction, where you might see speech reported in the present as well.
This is sometimes done when the author of the piece wants you to feel that you’re experiencing events in the present moment.
- Learn words in the context of sentences
- Swipe left or right to see more examples from other videos
- Go beyond just a superficial understanding

For example, a profile of Kristen Stewart in Vanity Fair has a funny moment that describes how the actress isn’t a very good swimmer:
Direct speech: “I don’t want to enter the water, ever,” she says. “If everyone’s going in the ocean, I’m like, no.”
Here, the speech is reported as though it’s in the present tense (“she says”) instead of in the past (“she said”).
In writing of all kinds, direct reported speech is often split into two or more parts, as it is above.
Here’s an example from Lewis Carroll’s “ Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland ,” where the speech is even more split up:
Direct speech: “I won’t indeed!” said Alice, in a great hurry to change the subject of conversation. “Are you—are you fond—of—of dogs?” The Mouse did not answer, so Alice went on eagerly: “There is such a nice little dog near our house I should like to show you!”
Reporting indirect speech is what happens when you explain what someone said without using their exact words.
- FluentU builds you up, so you can build sentences on your own
- Start with multiple-choice questions and advance through sentence building to producing your own output
- Go from understanding to speaking in a natural progression.
Let’s start with an example of direct reported speech like those used above.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like coffee.”
As indirect reported speech, it looks like this:
Indirect speech: Elisabeth said she liked coffee.
You can see that the subject (“I”) has been changed to “she,” to show who is being spoken about. If I’m reporting the direct speech of someone else, and this person says “I,” I’d repeat their sentence exactly as they said it. If I’m reporting this person’s speech indirectly to someone else, however, I’d speak about them in the third person—using “she,” “he” or “they.”
You may also notice that the tense changes here: If “I like coffee” is what she said, this can become “She liked coffee” in indirect speech.
- Images, examples, video examples, and tips
- Covering all the tricky edge cases, eg.: phrases, idioms, collocations, and separable verbs
- No reliance on volunteers or open source dictionaries
- 100,000+ hours spent by FluentU's team to create and maintain
However, you might just as often hear someone say something like, “She said she likes coffee.” Since people’s likes and preferences tend to change over time and not right away, it makes sense to keep them in the present tense.
Indirect speech often uses the word “that” before what was said:
Indirect speech: She said that she liked coffee.
There’s no real difference between “She said she liked coffee” and “She said that she liked coffee.” However, using “that” can help make the different parts of the sentence clearer.
Let’s look at a few other examples:
Indirect speech: I said I was going outside today.

Indirect speech: They told me that they wanted to order pizza.
Indirect speech: He mentioned it was raining.
Indirect speech: She said that her father was coming over for dinner.
You can see an example of reporting indirect speech in the funny video “ Cell Phone Crashing .” In this video, a traveler in an airport sits down next to another traveler talking on his cell phone. The first traveler pretends to be talking to someone on his phone, but he appears to be responding to the second traveler’s conversation, which leads to this exchange:
Woman: “Are you answering what I’m saying?”
Man “No, no… I’m on the phone with somebody, sorry. I don’t mean to be rude.” (Direct speech)
Woman: “What was that?”
Man: “I just said I was on the phone with somebody.” (Indirect speech)
When reporting questions in indirect speech, you can use words like “whether” or “if” with verbs that show questioning, such as “to ask” or “to wonder.”
Direct speech: She asked, “Is that a new restaurant?”
Indirect speech: She asked if that was a new restaurant.
In any case where you’re reporting a question, you can say that someone was “wondering” or “wanted to know” something. Notice that these verbs don’t directly show that someone asked a question. They don’t describe an action that happened at a single point in time. But you can usually assume that someone was wondering or wanted to know what they asked.
Indirect speech: She was wondering if that was a new restaurant.
Indirect speech: She wanted to know whether that was a new restaurant.
It can be tricky to know how to use tenses when reporting indirect speech. Let’s break it down, tense by tense.
Sometimes, indirect speech “ backshifts ,” or moves one tense further back into the past. We already saw this in the example from above:
Direct speech: She said, “I like coffee.”
Indirect speech: She said she liked coffee.
Also as mentioned above, backshifting doesn’t always happen. This might seem confusing, but it isn’t that difficult to understand once you start using reported speech regularly.
What tense you use in indirect reported speech often just depends on when what you’re reporting happened or was true.
Let’s look at some examples of how direct speech in certain tenses commonly changes (or doesn’t) when it’s reported as indirect speech.
To learn about all the English tenses (or for a quick review), check out this post .
Direct speech: I said, “I play video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I played video games (simple past) or I said that I play video games (simple present).
Backshifting into the past or staying in the present here can change the meaning slightly. If you use the first example, it’s unclear whether or not you still play video games; all we know is that you said you played them in the past.
If you use the second example, though, you probably still play video games (unless you were lying for some reason).
However, the difference in meaning is so small, you can use either one and you won’t have a problem.
Direct speech: I said, “I’m playing video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I was playing video games (past continuous) or I said that I’m playing video games (present continuous).
In this case, you’d likely use the first example if you were telling a story about something that happened in the past.
You could use the second example to repeat or stress what you just said. For example:
Hey, want to go for a walk?
Direct speech: No, I’m playing video games.
But it’s such a nice day!
Indirect speech: I said that I’m playing video games!
Direct speech: Marie said, “I have read that book.”
Indirect speech: Marie said that she had read that book (past perfect) or Marie said that she has read that book (present perfect).
The past perfect is used a lot in writing and other kinds of narration. This is because it helps point out an exact moment in time when something was true.
The past perfect isn’t quite as useful in conversation, where people are usually more interested in what’s true now. So, in a lot of cases, people would use the second example above when speaking.
Direct speech: She said, “I have been watching that show.”
Indirect speech: She said that she had been watching that show (past perfect continuous) or She said that she has been watching that show (present perfect continuous).
These examples are similar to the others above. You could use the first example whether or not this person was still watching the show, but if you used the second example, it’d probably seem like you either knew or guessed that she was still watching it.
Direct speech: You told me, “I charged my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had charged your phone (past perfect) or You told me that you charged your phone (simple past).
Here, most people would probably just use the second example, because it’s simpler, and gets across the same meaning.
Direct speech: You told me, “I was charging my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had been charging your phone (past perfect continuous) or You told me that you were charging your phone (past continuous).
Here, the difference is between whether you had been charging your phone before or were charging your phone at the time. However, a lot of people would still use the second example in either situation.
Direct speech: They explained, “We had bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Indirect speech: They explained that they had bathed the cat on Wednesday. (past perfect)
Once we start reporting the past perfect tenses, we don’t backshift because there are no tenses to backshift to.
So in this case, it’s simple. The tense stays exactly as is. However, many people might simplify even more and use the simple past, saying, “They explained that they bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Direct speech: They said, “The cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time!”
Indirect speech: They said that the cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time. (past perfect continuous)
Again, we don’t shift the tense back here; we leave it like it is. And again, a lot of people would report this speech as, “They said the cat was going outside and getting dirty for a long time.” It’s just a simpler way to say almost the same thing.
Direct speech: I told you, “I will be here no matter what.”
Indirect speech: I told you that I would be here no matter what. (present conditional)
At this point, we don’t just have to think about tenses, but grammatical mood, too. However, the idea is still pretty simple. We use the conditional (with “would”) to show that at the time the words were spoken, the future was uncertain.
In this case, you could also say, “I told you that I will be here no matter what,” but only if you “being here” is still something that you expect to happen in the future.
What matters here is what’s intended. Since this example shows a person reporting their own speech, it’s more likely that they’d want to stress the truth of their own intention, and so they might be more likely to use “will” than “would.”
But if you were reporting someone else’s words, you might be more likely to say something like, “She told me that she would be here no matter what.”
Direct speech: I said, “I’ll be waiting for your call.”
Indirect speech: I said that I would be waiting for your call. (conditional continuous)
These are similar to the above examples, but apply to a continuous or ongoing action.
Direct speech: She said, “I will have learned a lot about myself.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would have learned a lot about herself (conditional perfect) or She said that she will have learned a lot about herself (future perfect).
In this case, using the conditional (as in the first example) suggests that maybe a certain event didn’t happen, or something didn’t turn out as expected.
However, that might not always be the case, especially if this was a sentence that was written in an article or a work of fiction. The second example, however, suggests that the future that’s being talked about still hasn’t happened yet.
Direct speech: She said, “By next Tuesday, I will have been staying inside every day for the past month.”
Indirect speech: She said that by next Tuesday, she would have been staying inside every day for the past month (perfect continuous conditional) or She said that by next Tuesday, she will have been staying inside every day for the past month (past perfect continuous).
Again, in this case, the first example might suggest that the event didn’t happen. Maybe the person didn’t stay inside until next Tuesday! However, this could also just be a way of explaining that at the time she said this in the past, it was uncertain whether she really would stay inside for as long as she thought.
The second example, on the other hand, would only be used if next Tuesday hadn’t happened yet.
Let’s take a look at where you can find resources for practicing reporting speech in the real world.
One of the most common uses for reported speech is in fiction. You’ll find plenty of reported speech in novels and short stories . Look for books that have long sections of text with dialogue marked by quotation marks (“…”). Once you understand the different kinds of reported speech, you can look for it in your reading and use it in your own writing.
Writing your own stories is a great way to get even better at understanding reported speech.
One of the best ways to practice any aspect of English is to watch native English videos. By watching English speakers use the language, you can understand how reported speech is used in real world situations.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
Celebrity profiles, which you can find in print magazines and online, can help you find and practice reported speech, too. Celebrity profiles are stories that focus on a famous person. They often include some kind of interview. The writer will usually spend some time describing the person and then mention things that they say; this is when they use reported speech.
Because many of these profiles are written in the present tense, they can help you get used to the basics of reported speech without having to worry too much about different verb tenses.
While the above may seem really complicated, it isn’t that difficult to start using reported speech.
Mastering it may be a little difficult, but the truth is that many, many people who speak English as a first language struggle with it, too!
Reported speech is flexible, and even if you make mistakes, there’s a good chance that no one will notice.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


Reported speech
Tense changes in reported speech
Indirect speech (reported speech) focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired.
| Phrase in Direct Speech | Equivalent in Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| "I always coffee", she said | She said that she always coffee. |
| "I a book", he explained. | He explained that he a book |
| "Bill on Saturday", he said. | He said that Bill on Saturday. |
| "I to Spain", he told me. | He told me that he to Spain. |
| "I the light," he explained. | He explained that he the light. |
| They complained, "We for hours". | They complained that they for hours. |
| "We in Paris", they told me. | They told me that they in Paris. |
| "I in Geneva on Monday", he said. | He said that he in Geneva on Monday. |
| She said, " the car next Friday". | She said that she the car next Friday. |
You do not need to change the tense if the reporting verb is in the present, or if the original statement was about something that is still true (but this is only for things which are general facts, and even then usually we like to change the tense) , e.g.
- He says he has missed the train but he'll catch the next one.
- We explained that it is very difficult to find our house.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
These modal verbs do not change in reported speech: might, could, would, should, ought to :
- We explained, "It could be difficult to find our house." = We explained that it could be difficult to find our house.
- She said, "I might bring a friend to the party." = She said that she might bring a friend to the party.
Course Curriculum
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
My English Grammar
Ultimate English Grammar, Vocabulary, and Names Database
Changes in Indirect Speech
Welcome to a comprehensive tutorial providing guidance on the proper use, types, and rules of indirect speech in English grammar. Indirect speech, also called reported speech, allows us to share another person’s exact words without using quotes. It is particularly useful in written language. This tutorial aims to brief you about the changes that occur when switching from direct speech to indirect speech. It further explains the necessary rules which must be followed during this transition.
Table of Contents
Understanding Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct speech refers to the exact wording that someone uses when performing an act of speech. However, indirect speech implicitly shares the content of the person’s original words.
Direct Speech: He said, “I am hungry.” Indirect Speech: He said that he was hungry.
Notably, an essential component of indirect speech is the change in verb tense. In the direct speech example, the speaker uses the present tense “am.” In the indirect version, even though the speaker is still hungry, the tense changes to the past “was.”
Changes in Verb Tenses
The verb tense in indirect speech is one step back in time from the tense in the direct speech. Here are the common changes:
- Present Simple becomes Past Simple.
- Present Continuous becomes Past Continuous.
- Present Perfect becomes Past Perfect.
- Present Perfect Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous.
- Past Simple becomes Past Perfect.
Direct: He says, “I need help.” Indirect: He said he needed help.
Direct: She is saying, “I am reading a book.” Indirect: She was saying that she was reading a book.
Changes in Time and Place References
Besides the tense, word usage for place and time often changes when converting from direct to indirect speech.
- ‘Now’ changes to ‘then’.
- ‘Today’ changes to ‘that day’.
- ‘Yesterday’ turns into ‘the day before’ or ‘the previous day’.
- ‘Tomorrow’ changes to ‘the next day’ or ‘the following day’.
- ‘Last week/month/year’ switches to ‘the previous week/month/year’.
- ‘Next week/month/year’ changes to ‘the following week/month/year’.
- ‘Here’ turns into ‘there’.
Direct: He said, “I will do it tomorrow.” Indirect: He said that he would do it the next day.
Direct: She said, “I was here.”
Indirect: She said that she was there.
Changes in Modals
Modals also change when transforming direct speech into indirect speech. Here are some common changes:
- ‘Can’ changes to ‘could’.
- ‘May’ changes to ‘might’.
- ‘Will’ changes to ‘would’.
- ‘Shall’ changes to ‘should’.
Direct: She said, “I can play the piano.” Indirect: She said that she could play the piano.
Direct: He said, “I will go shopping.” Indirect: He said that he would go shopping.
Reporting Orders, Requests, and Questions
When reporting orders, requests, and questions, the structure also changes. The following is the structure:
- ‘To’ + infinitive for orders.
- Interrogative word + subject + verb for questions.
- Could/Would + subject + verb for polite requests.
Direct: He said to her, “Close the door.” Indirect: He told her to close the door.
Direct: She asked, “Where is the station?” Indirect: She asked where the station was.
In conclusion, reported speech becomes easier to understand and use effectively with practice. Understanding the transition from direct to indirect speech is vital to expressing yourself accurately and professionally, especially in written English. This guide provides the foundational information for mastering the changes in indirect speech. Practice these rules to become more fluent and confident in your English communication skills.
Related Posts:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Indirect Speech Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Indirect speech is a report on what someone else said or wrote without using that person's exact words (which is called direct speech). It's also called indirect discourse or reported speech .
Direct vs. Indirect Speech
In direct speech , a person's exact words are placed in quotation marks and set off with a comma and a reporting clause or signal phrase , such as "said" or "asked." In fiction writing, using direct speech can display the emotion of an important scene in vivid detail through the words themselves as well as the description of how something was said. In nonfiction writing or journalism, direct speech can emphasize a particular point, by using a source's exact words.
Indirect speech is paraphrasing what someone said or wrote. In writing, it functions to move a piece along by boiling down points that an interview source made. Unlike direct speech, indirect speech is not usually placed inside quote marks. However, both are attributed to the speaker because they come directly from a source.
How to Convert
In the first example below, the verb in the present tense in the line of direct speech ( is) may change to the past tense ( was ) in indirect speech, though it doesn't necessarily have to with a present-tense verb. If it makes sense in context to keep it present tense, that's fine.
- Direct speech: "Where is your textbook? " the teacher asked me.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook was.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook is.
Keeping the present tense in reported speech can give the impression of immediacy, that it's being reported soon after the direct quote,such as:
- Direct speech: Bill said, "I can't come in today, because I'm sick."
- Indirect speech: Bill said (that) he can't come in today because he's sick.
Future Tense
An action in the future (present continuous tense or future) doesn't have to change verb tense, either, as these examples demonstrate.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I'm going to buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he's going to buy a new car.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I will buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he will buy a new car.
Indirectly reporting an action in the future can change verb tenses when needed. In this next example, changing the am going to was going implies that she has already left for the mall. However, keeping the tense progressive or continuous implies that the action continues, that she's still at the mall and not back yet.
- Direct speech: She said, "I'm going to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she was going to the mall.
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she is going to the mall.
Other Changes
With a past-tense verb in the direct quote, the verb changes to past perfect.
- Direct speech: She said, "I went to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she had gone to the mall.
Note the change in first person (I) and second person (your) pronouns and word order in the indirect versions. The person has to change because the one reporting the action is not the one actually doing it. Third person (he or she) in direct speech remains in the third person.
Free Indirect Speech
In free indirect speech, which is commonly used in fiction, the reporting clause (or signal phrase) is omitted. Using the technique is a way to follow a character's point of view—in third-person limited omniscient—and show her thoughts intermingled with narration.
Typically in fiction italics show a character's exact thoughts, and quote marks show dialogue. Free indirect speech makes do without the italics and simply combines the internal thoughts of the character with the narration of the story. Writers who have used this technique include James Joyce, Jane Austen, Virginia Woolf, Henry James, Zora Neale Hurston, and D.H. Lawrence.
- Indirect Speech in the English Language
- How to Teach Reported Speech
- Question Mark Definition and Examples
- Figure of Speech: Definition and Examples
- Backshift (Sequence-of-Tense Rule in Grammar)
- What Is Attribution in Writing?
- Using Reported Speech: ESL Lesson Plan
- Constructed Dialogue in Storytelling and Conversation
- What Are Reporting Verbs in English Grammar?
- Dialogue Guide Definition and Examples
- Ellipsis: Definition and Examples in Grammar
- Sequence of Tenses in English Grammar
- Direct Speech Definition and Examples
- French Grammar: Direct and Indirect Speech
- Definition and Examples of Context Clues
- Definition and Examples of Direct Quotations

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.
Time and Place in Reported Speech
When we report something, we may need to make changes to:
- time (now, tomorrow)
- place (here, this room)
| direct speech | reported speech |
|---|---|
| She said, "I saw Mary yesterday." | She said she had seen Mary the day before. |
| He said: "My mother is here." | He said that his mother was there. |
If we report something around the same time, then we probably do not need to make any changes to time words . But if we report something at a different time, we need to change time words. Look at these example sentences:
- He said: "It was hot yesterday ." → He said that it had been hot the day before .
- He said: "We are going to swim tomorrow ." → He said they were going to swim the next day .
Here is a list of common time words, showing how you change them for reported speech:
| direct speech | reported speech |
|---|---|
| now | then, at that time |
| today | that day, on Sunday, yesterday |
| tonight | that night, last night, on Sunday night |
| tomorrow | the next day/ the following day, on Sunday, today |
| yesterday | the day before/ the previous day, on Sunday |
| last night | the night before/ the previous night, on Sunday night |
| this week | that week, last week |
| last month | the month before/ the previous month, in May |
| next year | the following year, in 2014 |
| two minutes ago | two minutes before |
| in one hour | one hour later |
Place words
If we are in the same place when we report something, then we do not need to make any changes to place words . But if we are in a different place when we report something, then we need to change the place words. Look at these example sentences:
- He said: "It is cold in here ." → He said that it was cold in there .
- He said: "How much is this book ?" → He asked how much the book was.
Here are some common place words, showing how you change them for reported speech:
| direct speech | indirect speech |
|---|---|
| here | there, in Starbucks |
| this | that |
| this book | the book, that book, |
| in this room | in the room, in that room, in the kitchen |

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
direct | indirect | reported clause | |
statement | ) I was tired. | -clause | |
question | . . | clause clause clause | |
command | . | -infinitive clause |
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| not very happy at work.’ | not very happy at work. |
| going home.’ | going home. |
| be late.’ | be late. |
| been working,’ she said. | . |
| to make her so angry?’ he asked. | to make her so angry. |
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
direct | indirect | |
present simple | → | past simple |
present continuous | → | past continuous |
present perfect simple | → | past perfect simple |
present perfect continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
past simple | → | past perfect simple |
past continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
future (will) | → | future-in-the-past (would) |
past perfect | ↔ | past perfect (no change) |
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Direct speech | Indirect speech |
| already left. |
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
direct speech | indirect speech | change | |
| be there,’ he promised. | be there. | becomes |
| need more money.’ I open it?’ she asked. | need more money. open it. | usually becomes in reported questions, becomes |
| see you at 2.30,’ he added. | see me at 2.30. | becomes |
| be back later,’ she said. wait in the hallway,’ he said. | be back later. wait in the hallway. | (possibility) becomes (permission) becomes |
| pay by 30th April.’ be awful to live in such a noisy place,’ she said. | pay by 30th April. be awful to live in such a noisy place. | (obligation) usually becomes (speculation) does not change |
| sell it for about 2,000 euros,’ he said. | sell it for about 2,000 euros. | no change |
| go there immediately,’ she said. | go there immediately. | no change |
| buy it if I had the money,’ he said. | buy it if he had the money. | no change |
| snow tonight,’ he warned. | snow that night. | no change |
| come till six o’clock,’ he said. | come till six o’clock. | no change |
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
direct | indirect | |
| don’t want to shock people,’ Tom said. | said he didn’t want to shock people. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| ’ll look after Toby,’ I said. | said I would look after Toby. | same speaker (no change) |
| need to be here at nine o’clock,’ George told Beatrice. | told Beatrice she needed to be there at nine o’clock. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| hope you will join us tonight,’ I said to James. | told James I hoped he would join us that night. | same speaker (no change to ; changes to ) |
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| .’ | the next/following day. |
| this moment in time.’ | . |
| .” | . |
| ,’ the boy protested. | . |
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
direct | indirect | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect speech: typical errors
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
be over the moon
to be very pleased

In for a penny, in for a pound: Idioms in The Thursday Murder Club

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Rules/Help/FAQ Help/FAQ
- Members Current visitors
- Interface Language
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- English Only
the reported speech -went to -had gone or had been
- Thread starter iris yang
- Start date Feb 28, 2017
- Feb 28, 2017
Senior Member
I think your version of sentence 1 makes more sense, personally. It might be different in British English, but as an American English speaker I think "went/had gone" is a more logical transformation than "went/had been".
JamesM said: I think your version of sentence 1 makes more sense, personally. It might be different in British English, but as an American English speaker I think "went/had gone" is a more logical transformation than "went/had been". Click to expand...
Rep. Schiff calls on Biden to drop out, citing ‘serious concerns’ that he can’t win

- Copy Link URL Copied!
Rep. Adam B. Schiff has called on President Biden to drop out of the White House race, becoming the most prominent Democrat in Congress to do so.
Wednesday’s statement from Schiff — the heavy favorite in his U.S. Senate bid and a frequent guest on cable news — brought a jolt to an effort that had grown quieter after the weekend assassination attempt on former President Trump.
The Burbank congressman cited “serious concerns” about Biden’s ability to beat Trump in November.
He is the latest Democrat to call for the president of his own party to exit the race amid growing questions about Biden’s age and mental fitness to do the job — worries that became more public last month after a disastrous debate performance, in which the incumbent at times appeared confused.
In a statement reported first by The Times, Schiff said Biden “has been one of the most consequential presidents in our nation’s history, and his lifetime of service as a Senator, a Vice President, and now as President has made our country better.”
“But our nation is at a crossroads,” he said. “A second Trump presidency will undermine the very foundation of our democracy, and I have serious concerns about whether the President can defeat Donald Trump in November.”

Column: Republican National Convention is an exercise in collective amnesia
Republicans claim to be the party of law and order. But there’s been scant acknowledgement of Trump’s felony conviction and no mention of Jan. 6.
July 17, 2024
Schiff said that the “choice to withdraw from the campaign is President Biden’s alone,” but that he believes it is time for Biden, who tested positive Wednesday for COVID-19, “to pass the torch” and “secure his legacy of leadership” by allowing another Democrat to beat Trump.
The congressman also said he will fully support whoever ends up at the top of the Democratic ticket.
“I will do everything I can to help them succeed,” Schiff said. “There is only one singular goal: defeating Donald Trump. The stakes are just too high.”
Before his announcement, the Washington Post had tallied 22 other Democrats in Congress asking Biden to drop out. Schiff is a notable addition to the list.
He is considered close with Rep. Nancy Pelosi (D-San Francisco), a party leader whose position on Biden has been guarded — though she suggested at one point that the president was running out of time to decide whether to leave the race.
When she was speaker, Pelosi used her authority to appoint Schiff to lead the House Intelligence Committee, which is among the most important posts in Congress. She later appointed him to lead the first impeachment against Trump, one of the highest-stakes decisions in her career — and one that helped Schiff rise to national prominence.
When Schiff decided to run for Senate, she endorsed him against two progressive women.
A source close to Pelosi, who requested anonymity to speak candidly about her communications on the matter, said that Schiff’s announcement “came as news to her” and that Schiff “did not consult her” on it.
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
Late Wednesday, ABC News reported that during a private meeting over the weekend, Senate Majority Leader Charles E. Schumer (D-N.Y.) told Biden it would be “better for the Democratic Party and better for the country if he were to bow out.”
A Schumer spokesperson called the report “idle speculation. Leader Schumer conveyed the views of his caucus directly to President Biden on Saturday.”
White House spokesman Andrew Bates said Biden told Schumer, as well as House Democratic leader Hakeem Jeffries, that “he is the nominee of the party, he plans to win, and looks forward to working with both of them to pass his 100 days agenda to help working families,” the Associated Press reported.
Biden has dismissed the calls to step aside. He has said that he has a strong record in the Oval Office and that “average Democrats” want him to remain in the race even if “big names” do not.
He has tried to run out the clock on those critics and withstand their pressure long enough to make replacing him as the nominee logistically difficult, if not impossible.
“I’m all in,” he told a cheering crowd at the NAACP national convention in Las Vegas on Tuesday.
Biden has also suggested that those voicing concerns about his candidacy may be more concerned about their own chances of winning in down-ballot races.
“The truth of the matter is, I understand the self-interest of a candidate. If they think that, you know, running with Biden at the top of the ticket is going to hurt them, then they’re going to run away,” he said at a news conference Thursday.
Schiff is expected to win a Senate seat that was long held by Sen. Dianne Feinstein and is currently held by Sen. Laphonza Butler, whom Gov. Gavin Newsom appointed to serve out the remainder of Feinstein’s term after her death in September.
Schiff faces former Dodgers All-Star Steve Garvey , a Republican, after beating other leading Democratic contenders in a crowded primary this year.
After Trump was shot at a campaign rally in Pennsylvania on Saturday, the pace and volume of calls for Biden to get out of the race fell, leading some political observers to wonder whether the shooting would end such calls. Schiff’s announcement — delivered in the middle of a Republican National Convention, where Republicans have appeared unified and Trump’s former rivals in the party have lined up behind him — shows that is not the case.
Schiff’s decision also came the day an Associated Press poll showed that nearly two-thirds of Democrats believe Biden should withdraw.
A polling memo by the Democratic firm BlueLabs Analytics, first published by Politico, found that alternative candidates perform 3 percentage points better than Biden in a theoretical matchup with Trump in battleground states.
Though Vice President Kamala Harris was among those who tested better than Biden, she performed worse than several other would-be replacements, including Arizona Sen. Mark Kelly, Maryland Gov. Wes Moore, Pennsylvania Gov. Josh Shapiro and Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer.

Nearly two-thirds of Democrats want Biden to withdraw, poll finds
The AP-NORC survey also says only about 3 in 10 Democrats are extremely or very confident that President Biden has the mental capability to serve, down from 40% in February.
But Harris would have advantages if Biden were to drop out. She would have the easiest access to the campaign’s infrastructure, including its fundraising account.
And she was on the ticket with Biden when he was elected in 2020 and in office when he became the presumed nominee this year.
Harris has many backers if Biden withdraws, including Rep. James E. Clyburn, an influential South Carolina Democrat with deep ties to Biden.
But many Democrats have been pushing for a new process that would allow alternatives, often citing Harris’ poor poll numbers.
“We have a deep bench,” Rep. Scott Peters, a San Diego Democrat who has argued Biden should drop out, said in a recent interview with The Times. “I would love to hear from a lot of folks about their perspectives. I think that it could be exciting and could get a lot of attention if we paraded out all the amazing leaders we have who are governors, senators, many elected from the swing states themselves.”
Asked why he did not mention Harris, Peters said she was one of the people he was referring to. “She’s got a strong case and is very talented,” he said. “But we have to be really focused on who can win.”
Newsom also has been floated as a potential candidate. But the governor, a Biden surrogate, has said he has no intention of running and would not run against Harris.
Biden has been dismissive of polls, calling them inaccurate and misleading. “I can give you a series of polls where you have likely voters, me versus Trump, where I win all the time,” he said.
Get the L.A. Times Politics newsletter
Deeply reported insights into legislation, politics and policy from Sacramento, Washington and beyond. In your inbox three times per week.
Democrats are planning to hold a virtual vote before the Aug. 19 convention in Chicago, perhaps this month. But some members of Congress are pushing back, circulating a letter urging the party to wait.
Peters said Biden “is being protected” from bad news by his advisors if he’s not seeing polls that show he can’t win, “because that’s what the polling shows.”
The New York Times reported Tuesday that Schiff had warned attendees at a Democratic fundraiser on Saturday that the party would lose the Senate and miss out on a chance to take the House if Biden didn’t drop out.
Schiff’s statement further increases the pressure on Biden and could prompt other lawmakers who have private concerns to come out publicly.
More to Read

Republicans are mentioning ‘Ka-MAL-a’ a lot. But Trump shooting lowers pressure on Biden to drop out
July 16, 2024

California’s delegation could be pivotal at Democratic National Convention — depending on Biden

The members of Congress pushing Biden to step aside are nearly all white. Reasons for a racial divide
July 12, 2024

Kevin Rector is a legal affairs reporter for the Los Angeles Times covering the California Supreme Court, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals and other legal trends and issues, and chipping in on coverage of the 2024 election. He started with The Times in 2020 and previously covered the Los Angeles Police Department for the paper. Before that, Rector worked at the Baltimore Sun for eight years, where he was a police and investigative reporter and part of a team that won the 2020 Pulitzer Prize in local reporting. More recently, he was part of a Times team awarded the 2023 Everett McKinley Dirksen Award for Distinguished Reporting of Congress for coverage of Sen. Dianne Feinstein. He is from Maryland.

Noah Bierman is an enterprise reporter focusing on clashes between red and blue states in the Washington bureau for the Los Angeles Times. He previously covered the White House and wrote for the paper’s national desk.
More From the Los Angeles Times

After a U.S. citizen shot at Trump, GOP sticks to the message that migrants are dangerous

At RNC, vice presidential nominee J.D. Vance calls Trump ‘America’s last, best hope’

Biden tests positive for COVID-19 while campaigning in Las Vegas; ‘mild symptoms’ reported

World & Nation
Why Ukraine — and much of Europe — is alarmed over Trump’s selection of J.D. Vance as his running mate
We fact-checked some of the rumors spreading online about the Trump assassination attempt
- Medium Text

MISIDENTIFIED SHOOTERS
Altered images, false claims shooting was staged, predictive programming conspiracy theories.
Reporting by Seana Davis; additional reporting Esther Chan; editing by Stephanie Burnett and Christina Agnagnostopoulos
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Fact Check: No evidence Biden had medical emergency aboard Air Force One on July 5
There is no evidence that U.S. President Joe Biden had a medical emergency aboard Air Force One on July 5, despite speculative posts on X.
Hours after being released from prison, Peter Navarro delivers speech at RNC
'i went to prison so you won't have to,' navarro said..

Former Trump adviser Peter Navarro on Tuesday slammed the United States’ criminal justice system after taking the stage at the Republican National Convention hours after completing a four-month federal prison sentence.
Navarro, who received thunderous applause when he walked on stage, accused Democrats of targeting him and accused the justice system of corruption despite no evidence .
"I went to prison, so you won't have to,” he said.
Navarro was convicted on two charges of contempt of Congress for defying subpoenas from the House committee that investigated the Capitol attack of Jan. 6, 2021. Navarro served a four month sentence at the Federal Correctional Institution, Miami and was released Wednesday.

“The Department of Justice, hear me out on this, if Congress slaps a subpoena on a senior White House adviser like me, the advisor's duty is to politely tell them to go pound sand,” Navarro said. “That's exactly what I did.”
The top Trump ally warned convention-goers that Democrats will “come for you” like they came for him and former President Donald Trump.
“If they can come for me, and if they can come for Donald Trump,” Navarro said. “Be careful – they will come for you.”
Navarro was joined on stage by his fiancee, Bonnie. He closed his speech with the parting words she gave him before he went to prison: "We got this."
Contributing: Savannah Kuchar and Karissa Waddick
- How to Submit
'A night of hope': JD Vance accepts GOP vice president nomination. Read his RNC speech.
Editor's note: The following is the pre-released prepared GOP Vice Presidential Nomination Acceptance Speech delivered by U.S. Sen. JD Vance of Ohio at the 2024 Republican National Convention in Milwaukee.
My fellow Americans, my name is JD Vance , from the great state of Ohio.
Tonight is a night of hope. A celebration of what America once was, and with God’s grace, what it will soon be again.
And it is a reminder of the sacred duty that we have to preserve the American experiment, to choose a new path for our children and grandchildren.
But as we meet tonight, we cannot forget that this evening could have been much different. Instead of a day of celebration, this could have been a day of heartache and mourning.For the last eight years, President Trump has given everything he has to fight for the people of our country. He didn’t need politics, but the country needed him.
Prior to running for president, he was one of the most successful businessmen in the world. He had everything anyone could ever want in a life. And yet, instead of choosing the easy path, he chose to endure abuse, slander, and persecution.
But don’t take my word for it, go and watch the video of a would-be assassin coming a quarter of an inch from taking his life. Consider the lies they told you about Donald Trump. And then look at the photo of him defiant – fist in the air.
When Donald J. Trump rose to his feet in that Pennsylvania field – all of America stood up with him.
Even in his most perilous moment we were on his mind. His instinct was for US. To call us to something higher. To something greater. To once again be citizens who ask what our country needs of us.
He called for national unity, for calm. He remembered the victims of the terrible attack, especially the brave Corey Comperatore , who gave his life to protect his family.
And then President Trump Flew to Milwaukee and got back to work.
Letter to the editor: JD Vance is no hillbilly – and knows nothing about real conservative values
Who is JD Vance? What to know about Donald Trump's VP pick
Who is JD Vance's wife? Here's what we know about Usha Chilukuri Vance
That is the man I’ve gotten to know personally over the last few years.
He is our once and future president future president of the United States.
And I want to respond to his call for unity myself.
And my message to my fellow Americans is: shouldn’t we be governed by a party that is unafraid to debate ideas and come to the best solution?
That’s the Republican Party of the next four years: united in our love for America and committed to free speech and the open exchange of ideas.
So tonight, I stand here humbled, and I am overwhelmed with gratitude, to say..
I officially accept your nomination to be vice president of the United States of America.
Never in my wildest imagination would I have believed that I could be standing here tonight.
Who is JD Vance? Ohioans have not-so-pretty things to say about Trump's VP pick.
I grew up in Middletown, Ohio, a small town where people spoke their minds, built with their hands, and loved their God, family, community, and country with their whole hearts.
But it was also a place that had been cast aside and forgotten by America’s ruling class in Washington.
When I was in the fourth grade, a career politician by the name of Joe Biden supported NAFTA , a bad trade deal that sent countless good American manufacturing jobs to Mexico.
When I was a sophomore in high school, a career politician by the name of Joe Biden gave China a sweetheart trade deal that destroyed even more good middle class jobs.
And when I was a senior in high school, Joe Biden supported the disastrous invasion of Iraq.
And at each step of the way, in small towns like mine in Ohio, or next door in Pennsylvania, or in Michigan and other states across our country, jobs were sent overseas and children were sent to war.
Somehow, a real estate developer from New York by the name of Donald Trump was right on all of these issues while Joe Biden was wrong. Donald Trump knew, even then, that we needed leaders who would put America First.
Thanks to these policies that Biden and the other out-of-touch politicians in Washington gave us, our country was flooded with cheap Chinese goods and cheap foreign labor… And in the decades to come, deadly Chinese fentanyl.
Joe Biden screwed up, and my community paid the price.
Now, I was lucky. Despite the closing factories and the growing addiction in towns like mine, in my life, I had a guardian angel by my side. She was an old woman who could barely walk but was tough as nails.
I called her “Mamaw,” the name we hillbillies gave to our grandmothers.
Mamaw raised me as her own as my own mother struggled with addiction.
Thanks to Mamaw, things worked out for me.
After 9/11, I did what thousands of other young men my age did in that time of soaring patriotism and love of country: I enlisted in the United States Marines.
I left the Marines after four years and went to the Ohio State, and then to law school at Yale—where I met my beautiful wife—and then started businesses to create jobs in the kinds of places I grew up.
My work taught me that there is still so much talent and grit in the American heartland. But for these places to thrive, we need a leader who fights for the people who built this country.
We need President Donald J. Trump.
Some people tell me I’ve lived the American Dream, and they are right.
But the American Dream that always counted most was not starting a business or becoming a senator or even being here with you fine people, it was becoming a good husband and a good dad, and of giving my family the things I never had as a kid.
And that’s the accomplishment I’m proudest of.
That tonight I’m joined by my beautiful wife, Usha, an incredible lawyer and a better mom, and our three kids — Ewan, Vivek, Mirabel—hopefully in bed.
Things did not work out well for a lot kids I grew up with. Every now and then I will get a call from a relative back home who asks, did you know “so and so.” And I’ll remember a face from years ago. And then I’ll hear, “they died of an overdose.”
As always, America’s ruling class wrote the checks; communities like mine paid the price.
For decades, that divide between the few, with their power and comfort in Washington, and the rest of us only widened.
From Iraq to Afghanistan, from the financial crisis to the Great Recession, from open borders to stagnating wages, the people who govern this country have failed and failed again.
That is, until President Donald J. Trump came along.
Donald Trump represents America’s last best hope to restore what – if lost – may never be found again.
But my fellow Americans, this moment is not about me, it’s about all of us, and who we’re fighting for.
It’s about the auto worker in Michigan, wondering why out of touch politicians are destroying your jobs.
It’s about the factory worker in Wisconsin, who makes things with their hands and is proud of American craftsmanship.
It’s about the energy worker in Pennsylvania and Ohio, who doesn’t understand why Joe Biden is willing to buy energy from tinpot dictators but not hard-working Americans right here at home.
BUCKEYE STATE: JD Vance would be first Ohio resident to be vice president, is first in 80 years on ticket
And, it’s about single moms like mine, who struggled with money and addiction but never gave up.
And I am proud to say that tonight my mom is here, 10 years clean and sober.
I love you, mom.
It's about grandparents all across this country, who are living on Social Security and raising grandchildren they didn't expect to raise.
Joe Biden has been a politician in Washington for longer than I've been alive.
For half-a-century, he's been the champion of every major policy initiative to make America weaker and poorer.
In four years, Donald Trump reversed decades of betrayals inflicted by Joe Biden and the rest of the corrupt Washington insiders.
He created the greatest economy in history for workers. Just imagine what he can do with four more years in the White House.
Months ago, I heard some young family member observe that their parents’ generation—the baby boomers—could afford to buy a home when they first entered the workforce. “But I don’t know if I’ll ever be able to afford a home,” they said sadly.
The absurd cost of housing is the result of many failures of America’s leadership class. And I can tell you exactly how it happened.
Wall Street barons crashed the economy and American builders went out of business.
As tradesmen scrambled for jobs, houses stopped being built.
The lack of good jobs led to stagnant wages.
Then Democrats flooded the country with illegal immigrants.
So citizens had to compete – with people who shouldn’t even be here – for precious housing.
Joe Biden’s inflation crisis is really an affordability crisis.
Many of the people that I grew up with can't afford to pay more for groceries, more for gas, more for rent, and that's exactly what Joe Biden’s economy has given them. So prices soared and dreams were shattered.
And China and the cartels sent fentanyl across the border, adding addiction to the heartache.
But that’s not the end of our story.
We’ve heard about the villains and their victims. But let me tell you about the future.
President Trump’s vision is simple - we won’t cater to Wall Street, we’ll commit to the working man
We won’t import foreign labor, we’ll fight for American citizens.We won’t buy energy from countries that hate us, we’ll get it right here from American Workers.We won’t sacrifice our supply chains to unlimited global trade, we’ll stamp every product Made in the USA. We will build factories again, put people to work making real products for American families, made with the hands of American workers.Together, we will protect the wages of American workers—union and non-union alike—and stop the Chinese Communist Party from building THEIR middle class on the backs of our hard-working citizens.Together, we will make our allies share in the burden of securing world peace: no more free rides for nations that betray the generosity of the American taxpayer.Together, we will send our kids to war only when we must.
ELECTION 2024: What has JD Vance written about state, national issues?
But as President Trump showed with the elimination of ISIS, when we punch, we will punch hard.Together, we will put the citizens of America first, whatever the color of their skin. We will, in short, make America great again. I am married to the daughter of South Asian immigrants to this country, incredible people, people who genuinely have enriched the country in so many ways.And of course, I'm biased, because I love my wife, but I believe that it's true.
When I proposed to my wife, we were in law school, and I said, Honey, I come with $120,000 worth of law school debt, and a cemetery plot on a mountainside in eastern Kentucky.That cemetery plot in Eastern Kentucky is near my family’s ancestral home. Like a lot of people, we came from the mountains of Appalachia into the factories of Ohio, Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Wisconsin.This is Kentucky coal country, by the way, one of the 10 poorest counties in the entire United States of America.They are very hardworking people, and they're very good people, and they would give you the shirt off their back.The media call them “privileged” and look down on them.But they love this country, not only because it's a good idea. But because in their bones, they know that this is their home, and it will be their children's home, and they would die fighting to protect it. That is the source of America's greatness.
As a U.S. senator , I get to represent millions of people in the state of Ohio with similar stories, and it’s the great honor of my life.
But never forget that the reason why this united Republican Party exists, why we do this, why we care about all those great ideas and that great history, is that we want this nation to thrive for centuries to come.
Eventually, in that mountain cemetery, my children will lay me to rest. And when they do, I would like them to know that thanks to the work of this Republican Party, the United States of America is as strong and as proud and as great as ever.And the thing that we have to do, right now, to make that happen, is to re-elect President Donald J. Trump!Mr. President, I will never take for granted the trust you have put in me. And what an honor it is to help achieve the extraordinary vision you have for our country.
I pledge to every American - no matter your party, I will give everything I have to serve you and to make this country a place where every dream you have for yourself, your family, and your country will be possible once again.
And I promise you one more thing - the people of Middletown, Ohio, and all the forgotten communities in Michigan, Wisconsin, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and every corner of our nation…
I promise you this - I will never forget where I came from.
And every single day for the next four years, when I walk into that White House to help President Trump,I will be doing it for you and for your family and for your future.
Thank you, God bless you, and God bless the United States of America.
Advertisement
Widow of Slain Rally Attendee Says She Received Call From Trump
Corey Comperatore, 50, was killed while attending a rally for Donald J. Trump for the first time.
- Share full article

By Isabelle Taft
- July 16, 2024
The widow of the slain victim in Saturday’s shooting in Pennsylvania spoke with former President Donald J. Trump on Tuesday, she said in a social media post.
“He was very kind and said he would continue to call me in the days and weeks ahead,” Helen Comperatore wrote, adding that she had told the former president that her husband, Corey Comperatore, “left this world a hero, and God welcomed him in.”
Mr. Comperatore’s sister, Kelly Comperatore Meeder, said members of the family had also spoken with representatives of the Trump campaign on Monday night. Ms. Comperatore Meeder said they had declined an invitation to speak with President Biden.
Mr. Comperatore, 50, was an ardent supporter of Mr. Trump and was eager on Saturday to see the former president for the first time in person. His sister said on Tuesday that her family believed that anger toward Mr. Trump was sown by President Biden and media outlets and had led to the fatal shooting.
“We’re not offering them anything,” Ms. Comperatore Meeder, 56, said of President Biden and his administration.
Mr. Comperatore was a father of two daughters and worked at a local plastics manufacturing company. He was also a longtime volunteer firefighter.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Trump on Tuesday called the family of his supporter who died during the assassination attempt. On Monday, his wife told the New York Post he had not yet called
- The wife of Corey Comperatore, who died at the Trump rally, said Trump had not called her as of Monday.
- Corey Comperatore died shielding his family during an assassination attempt on Trump at a rally.
- Helen Comperatore said Biden called her. On Tuesday, she shared that Trump called her, per The New York Times.

The wife of Corey Comperatore , the man who was killed during the assassination attempt on former President Donald Trump, told The New York Post in an interview on Monday that the former president had not yet contacted her since the shooting on Saturday.
After the Post's report, Helen Comperatore said in a social media post that Trump called her on Tuesday, according to The New York Times .
Corey Comperatore, a 50-year-old former fire chief from Pennsylvania, was a supporter of Trump and attended the rally with his wife and daughters. His family said he was shot while shielding them from the gunfire.
In an interview with The New York Post that was published Monday at 4:44 p.m. ET, his wife, Helen Comperatore, said her husband was her "hero" and that the last thing he said to them was "get down!"
Helen Comperatore told the outlet that, at that point, she had not heard from Trump. The former president said he was shot during the rally ; two others were shot and critically wounded.
Representatives for the Trump campaign, the White House, and the Biden campaign did not immediately respond to requests for comment from Business Insider. BI attempted to reach Helen Comperatore through email.
"He was very kind and said he would continue to call me in the days and weeks ahead," she said of Trump on social media, according to The Times.
Corey Comperatore's sister told The Times the family also spoke with representatives of the Trump campaign on Monday night.
In his first statement after the shooting on Saturday, Trump wrote on Truth Social: "I want to thank The United States Secret Service, and all of Law Enforcement, for their rapid response on the shooting that just took place in Butler, Pennsylvania. Most importantly, I want to extend my condolences to the family of the person at the Rally who was killed, and also to the family of another person that was badly injured."
In another post on Sunday, Trump added, "Our love goes out to the other victims and their families. We pray for the recovery of those who were wounded, and hold in our hearts the memory of the citizen who was so horribly killed."
Related stories
Trump's team has also shared a link to a GoFundMe that was "authorized" by the former president and is raising funds that will go towards the victims' families. The page had accrued more than $4.5 million in donations as of Monday evening.
On Sunday, Trump arrived in Milwaukee for the Republican National Committee convention, which kicked off on Monday. Trump was formally nominated as the GOP candidate for president and announced he had selected Sen. JD Vance of Ohio as his vice presidential running mate.
Helen Comperatore told the Post her family did receive a call from President Joe Biden , but that she did not speak with him.
"I didn't talk to Biden. I didn't want to talk to him," she said. "My husband was a devout Republican, and he would not have wanted me to talk to him."
While some Republicans, including Vance , blamed Biden's rhetoric for the attempted assassination of Trump, the FBI has not identified a motive for the shooting.
Helen Comperatore said she did not think Biden was responsible for her husband's death. She told the Post she is voting for Trump but that she is not very involved in politics.
"I don't have any ill-will towards Joe Biden," she said, adding, "He didn't do anything to my husband. A 20-year-old despicable kid did."
Update, July 16, 2024: Helen Comperatore said in a social media post that Trump called her on Tuesday, according to The New York Times . Corey Comperatore's sister told the Times the family also spoke with representatives of the Trump campaign on Monday night.
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Here's an example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the store now," she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then.". 2.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
For example: Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken. Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
Yes, and you report it with a reporting verb. He said he wanted to know about reported speech. I said, I want and you changed it to he wanted. Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present continuous changes to the past continuous; the present perfect changes to the past perfect; can changes to could; will changes ...
Direct speech: "I like this car." Reported speech: He said (that) he liked that car. Direct speech: "I went to Tokyo last week." Reported speech: She said (that) she'd been to Tokyo the week before. Meaning. We use reported speech to tell someone what another person said: Jim says to you: "I don't feel well." "I can't drive."
1. We use direct speech to quote a speaker's exact words. We put their words within quotation marks. We add a reporting verb such as "he said" or "she asked" before or after the quote. Example: He said, "I am happy.". 2. Reported speech is a way of reporting what someone said without using quotation marks.
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of retelling what someone else has said without repeating their exact words. For example, let's say you have a friend called Jon and one called Mary. Mary has organised a house party and has invited you and Jon. Jon, however, is not feeling well.
"Reported speech" means talking about the things that other people have said. Read this post to learn about direct and indirect reported speech in English. Reported speech is an essential skill for gossiping, chatting with friends and keeping up with the news. ... The Mouse did not answer, so Alice went on eagerly: ...
In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command. Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired. Phrase in Direct Speech. Equivalent in Reported Speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Welcome to a comprehensive tutorial providing guidance on the proper use, types, and rules of indirect speech in English grammar. Indirect speech, also called reported speech, allows us to share another person's exact words without using quotes. It is particularly useful in written language. This tutorial aims to brief you about the changes ...
Future Tense. An action in the future (present continuous tense or future) doesn't have to change verb tense, either, as these examples demonstrate. Direct speech: Jerry said, "I'm going to buy a new car." Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he's going to buy a new car. Direct speech: Jerry said, "I will buy a new car."
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
Time and Place in Reported Speech. When we report something, we may need to make changes to: time (now, tomorrow) place (here, this room) direct speech. reported speech. She said, "I saw Mary yesterday." She said she had seen Mary the day before. He said: "My mother is here."
What is indirect speech or reported speech? When we tell people what another person said or thought, we often use reported speech or indirect speech. To do that, we need to change verb tenses (present, past, etc.) and pronouns (I, you, my, your, etc.) if the time and speaker are different.For example, present tenses become past, I becomes he or she, and my becomes his or her, etc.
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Here please change these sentence to reported speech start with he told me. The first sentence. "I went to the cinema yesterday.". My answer is He told me that he had gone to the cinema yesterday because I think went to should be changed to had gone. but the result showed it was wrong and showed the correct answer was He told me he had been ...
The New York Times reported Tuesday that Schiff had warned attendees at a Democratic fundraiser on Saturday that the party would lose the Senate and miss out on a chance to take the House if Biden ...
During a call with House Democrats, President Biden lashed out at Congressman Jason Crow after the Colorado Democrat bluntly told him that voters are concerned about his vigor and strength ...
Misinformation and conspiracy theories were spreading online after an assassination attempt on former U.S. President Donald Trump at a campaign rally on Saturday.
Model and reality TV star Amber Rose endorsed former President Donald Trump at the Republican National Convention. CNN political commentators Van Jones and Ashley Allison discuss whether her ...
"I went to prison, so you won't have to," he said. Navarro was convicted on two charges of contempt of Congress for defying subpoenas from the House committee that investigated the Capitol ...
Editor's note:The following is the pre-released prepared GOP Vice Presidential Nomination Acceptance Speech to be delivered by U.S. Sen. JD Vance of Ohio at the 2024 Republican National Convention ...
Wall Street barons crashed the economy and American builders went out of business. As tradesmen scrambled for jobs, houses stopped being built. The lack of good jobs, of course, led to stagnant wages.
In the 48 hours before he opened fire on former President Donald Trump, 20-year-old Thomas Matthew Crooks made a series of stops in and around his suburban Pittsburgh hometown. On Friday, he went ...
Corey Comperatore, 50, was killed while attending a rally for Donald J. Trump for the first time. By Isabelle Taft The widow of the slain victim in Saturday's shooting in Pennsylvania spoke with ...
Election 2024. Follow live updates from Day 2 of the Republican National Convention in Milwaukee. Catch up on the top takeaways from the first night, where Donald Trump made an appearance.. Trump ...
The wife of Corey Comperatore, who died during the Trump assassination attempt, said President Joe Biden called her but she didn't speak to him.