

Essay on Disaster Management
Students are often asked to write an essay on Disaster Management in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Disaster Management
Understanding disaster management.
Disaster management is the process of preparing for, responding to, and recovering from disasters. It’s like a game plan to handle emergencies.
The Importance of Disaster Management
Disaster management is important because it helps to reduce the impact of disasters. It saves lives and protects property.
Steps in Disaster Management
There are four steps: mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. Mitigation and preparedness happen before a disaster, while response and recovery happen after.
Role of Everyone
Everyone has a role in disaster management. We should all be prepared and know what to do in case of a disaster.
250 Words Essay on Disaster Management
Introduction.
Disaster management refers to the organization and management of resources for dealing with all aspects of emergencies, particularly when they have catastrophic consequences. Its primary aim is to minimize the harmful effects of disasters on humanity and the environment.
The Cycle of Disaster Management
Disaster management operates in a cycle, encompassing four phases: mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. Mitigation attempts to prevent hazards from developing into disasters or reduce the effects of disasters. Preparedness involves developing plans and systems to respond effectively when disasters occur. Response is the immediate reaction to a disaster, while recovery aims to restore the affected area to its previous state.
Importance of Disaster Management
Disaster management is crucial in ensuring a systematic response to natural or man-made disasters. It helps in saving lives, reducing economic losses, and maintaining societal functions. Furthermore, it aids in building resilient communities that can withstand and recover from disasters.
Challenges in Disaster Management
Despite its importance, disaster management faces several challenges, such as inadequate funding, lack of public awareness, and coordination issues among different agencies. Achieving effective disaster management requires overcoming these obstacles through increased funding, public education, and improved inter-agency coordination.
In a world where disasters are becoming increasingly frequent and severe due to climate change and other factors, effective disaster management is more important than ever. By understanding and addressing the challenges in this field, we can build a safer, more resilient world for future generations.
500 Words Essay on Disaster Management
Introduction to disaster management.
Disasters, whether natural or man-made, have the potential to alter the course of life, causing extensive damage to life, property, and the environment. Effective disaster management strategies can significantly reduce the negative impacts of such events. For instance, they can minimize loss of life, ensure faster recovery, and safeguard the socio-economic fabric of the community.
Phases of Disaster Management
Disaster management can be divided into four critical phases: mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.
Preparedness
This phase involves the provision of emergency services and public assistance during or immediately following a disaster. The main aim is to reduce the impact of the disaster and facilitate recovery operations.
Role of Technology in Disaster Management
Effective disaster management is a collective and coordinated effort that involves various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, communities, and individuals. It requires a proactive approach that focuses not only on responding to disasters but also on preventing and mitigating their effects. By incorporating advanced technologies and fostering community participation, we can improve our resilience to disasters and ensure a safer and more secure future.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


Essay on Disaster Management
Essay generator.
In the contemporary world, disasters have become a frequent, albeit unwelcome, part of human life. From natural calamities like earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes to man-made crises such as industrial accidents and terrorist attacks, the spectrum of disasters is vast and varied. The omnipresent threat posed by these disasters necessitates an effective and efficient disaster management strategy. This essay delves into the essence of disaster management, its phases, the challenges involved, and the role of technology and community participation in enhancing disaster resilience.
Disaster Management
Disaster management refers to the systematic process of creating strategies aimed at limiting the adverse impacts of disasters. It encompasses a broad range of activities, including preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation efforts, to safeguard lives, property, and the environment. Effective disaster management is imperative not only for saving lives but also for maintaining economic stability and ensuring sustainable development.
The Phases of Disaster Management
Disaster management can be delineated into four critical phases, each of which plays a pivotal role in managing disasters.
1. Mitigation
Mitigation involves efforts to reduce the risk of disaster occurrences or diminish their effects. These measures include constructing buildings that can withstand earthquakes, improving drainage systems to prevent flooding, and implementing strict zoning and land-use practices. Mitigation strategies aim at preventing disasters from occurring and, failing that, reducing the impact of disasters when they occur.
2. Preparedness
Preparedness focuses on planning how to respond when a disaster strikes. This phase includes training emergency responders, establishing warning systems, conducting disaster drills, and developing evacuation plans. Preparedness efforts ensure that when a disaster occurs, the response is swift, coordinated, and effective, thereby minimizing loss of life and damage to property.
3. Response
The response phase is activated once a disaster occurs. It involves the mobilization of emergency services, volunteers, and other resources to save lives, provide shelter, and meet the basic needs of those affected. The effectiveness of the response phase heavily relies on the preparedness measures that have been put in place.
4. Recovery
Recovery is the process of restoring the affected community to its pre-disaster state. It includes rebuilding infrastructure, restoring public services, and providing support to the impacted individuals and businesses. Recovery can be a long-term process, focusing on not only the restoration of the physical aspects but also the emotional, economic, and social recovery of the community.
Challenges in Disaster Management
Despite the best efforts, disaster management faces numerous challenges. These include:
- Lack of Resources: Many regions, especially in developing countries, lack the necessary resources, including finances, equipment, and trained personnel, to effectively manage disasters.
- Communication Breakdown: Effective communication is crucial during disasters. However, disasters often disrupt communication infrastructure, making it challenging to coordinate response efforts and disseminate information to the public.
- Coordination Among Agencies: Multiple agencies are involved in disaster management, including local, state, and federal governments, NGOs, and international bodies. Ensuring seamless coordination among these entities is often a daunting task.
- Climate Change: The increasing impact of climate change is exacerbating the frequency and intensity of natural disasters, posing new challenges to disaster management strategies.
The Role of Technology in Disaster Management
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of disaster management. Innovations such as satellite imagery, GIS (Geographic Information Systems), and drones provide critical information for disaster preparedness and response. Social media and mobile technology have revolutionized the way information is disseminated and have improved communication between disaster management agencies and the public. Additionally, early warning systems powered by advanced forecasting technologies can save countless lives by providing timely alerts about impending disasters.
Community Participation in Disaster Management
Community participation is fundamental to the success of disaster management efforts. Local communities are the first to respond to disasters and thus, empowering them through education and training is vital. Community-based disaster management programs encourage local involvement in disaster preparedness activities, such as evacuation drills and first aid training, ensuring that communities are better equipped to cope with disasters. Engaging communities also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards local disaster management initiatives.
In conclusion, Disaster management is a complex and multifaceted field that requires the concerted efforts of governments, organizations, communities, and individuals. By understanding the phases of disaster management and addressing the associated challenges, we can enhance our resilience to disasters. The integration of technology and the active participation of communities further strengthen disaster management frameworks, making our societies more robust and better prepared to face the inevitable challenges posed by disasters. As we move forward, it is imperative that disaster management strategies evolve in tandem with the changing dynamics of disasters, ensuring a safer and more resilient world for future generations.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate an essay on the importance of extracurricular activities for student development
Write an essay discussing the role of technology in modern education.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Disaster Management

- Updated on
- May 10, 2023

Disaster Management has been essentially included in the study curriculums of secondary education. Whether it is natural or man-made, disasters can wreak havoc on our surroundings and cost human lives as well. To familiarise students with efficiently preventing and ensuring the safety of living beings and our environment from unprecedented events, the study of Disaster Management has been included as an important part of the Geography class 10 syllabus. This blog aims to focus on imparting how you can draft a well-written essay on Disaster Management.
This Blog Includes:
What is disaster management, essay on disaster management: tips & tricks, sample format for essay on disaster management in 150 words, sample essay of disaster management (150 words), sample essay on disaster management (300 words) , sample essay on disaster management (500 words), essay on disaster management for class 9 onwards, essay on disaster management in india.
To begin with your essay on Disaster Management, the most important thing is to comprehend this concept as well as what it aims to facilitate. In simple terms, Disaster Management is termed as the management and utilisation of resources as well as responsibilities to tackle different emergencies, be it man-made disasters or natural ones. It concentrates on preparing human beings for a varied range of calamities and helping them respond in a better way as well as ensure recovery thus lessening their overall impact.
Preparing for the Writing Section for Your English Exam? Then Check Out Message Writing and Letter Writing !
Before drafting your essay on Disaster Management, another thing you need to ensure is familiarising yourself with the structure of essay writing. To help you understand the do’s and don’ts, we have listed down some of the major things you need to keep in mind.

- Research thoroughly about your topic. For example, while writing an essay on Disaster Management, explore the recent happenings and mention them to provide the reader with a view into your understanding of this concept.
- Create important pointers while researching that you can further incorporate into your essay.
- Don’t mug up the definitions but comprehend them through examples.
- Use transitions between paragraphs to keep a coherent flow for the reader as a long paragraph might seem too lengthy and segregating your introduction and conclusion can provide a better structure.
- Quote important examples not only in your introduction but also in the following paragraphs where you detail the given topic.
- Revise and add finishing touches once you have completed the essay to locate any grammatical errors as well as other mistakes.
Now that you are aware of the key elements of writing an essay on Disaster Management, take a look at the format of essay writing first:
Introduction (30-40 words)
Begin with defining your topic explained in simple terms. For Disaster Management, You can make it more interesting by adding a question or a recent instance. The introduction should be understandable aiming to become more specific in the subsequent paragraphs.
Related Article: Geography for UPSC Preparation
Body of Content (80 words)
Also termed as the thesis statement , the content after the introduction should explain your given topic in detail. It should contain the maximum content out of the whole format because it needs to be detailed. For Disaster Management, you can delve deeper into its process, how it is carried out for different situations as well as prevention and protection.
Conclusion (30-40 words)
This section should mainly wrap up what you have described in the above paragraphs. For an essay on Disaster Management, you can focus on summing it up by writing its aim, types and purposes briefly.

Disaster can be simply termed as a sudden incident or happening which can be either natural or man-made and can potentially cause damage to the surroundings or loss of human life. To facilitate preparedness and better responsiveness to unforeseen events which can harm human beings and the environment, Disaster Management came into the picture.
Disaster Management aims to lessen the impact of natural and man-made calamities by designing and planning efficient ways to tackle them. It centrally comprises ensuring better control of the situation, its immediate evaluation, calling up required medical aids and transports, supplying drinking and food sources, among others and during this whole process, protecting the surroundings from more harm and keeping the lawfulness. The importance of Disaster Management has further increased in the contemporary scenario with the prevalent climate change and some of its latest examples include the unprecedented Australian wildfires.
Thus, the planet is getting bogged down by infinite technological devices, and their possible effects on the climate and the environment are inescapable. This has led to Disaster Management becoming the need of the hour as every country is aiming to become efficient and prepared to face both natural and man-made calamities.
Since the dawn of time, disasters, whether natural or man-made, have been a part of man’s evolution. Tsunamis, cyclones, earthquakes, floods, accidents, plane crashes, forest fires, chemical disasters, and other natural disasters frequently strike without notice, leading to massive loss of life and property. Disaster management refers to the strategies and actions put in place to lessen and prevent the effects of a disaster.
The word “disaster management” refers to all aspects of catastrophe mitigation, including preventive and protective measures, preparedness, and relief activities. The disaster management process can be separated into two phases: pre-disaster planning and post-disaster recovery. This encompasses measures such as prevention, mitigation, and preparedness aimed at minimising human and property losses as a result of a possible danger.
The second category is activity post-disaster recovery in which response, rehabilitation, and reconstruction are all included. Search and rescue evacuation, meeting the victims’ basic needs, and rapid medical support from regional, national, and international authorities were all part of the response phase. The immediate purpose of the recovery phase is to restore some degree of normalcy to the afflicted areas. In resource-scarce countries, ex-ante risk mitigation investment in development planning is critical for decreasing disaster damage. It would be prudent to go from a risk-blind to a risk-informed investment decision.
We cannot prevent disasters, but we can reduce their severity and arm ourselves with knowledge so that too many lives are spared.
Introduction:
The globe is plagued with disasters, some of which are terrible and others that are controllable. Natural calamities, for example, are sudden occurrences that wreak significant devastation to lives and property. Disasters can occur either naturally or are man-made. To repair the damage caused by these disasters, emergency management is required. Through a disaster management procedure, the damage is contained and the hazards of the event are controlled. The procedure is aimed at averting disasters and reducing the effects of those that are unavoidable. Floods, droughts, landslides, and earthquakes are all threats to India. The Indian government’s disaster management measures have vastly improved over time.
The Process of Disaster Management:
The disaster management process is split into four stages. The first phase is mitigation, which involves reducing the likelihood of a disaster or its negative consequences. Public education on the nature of the calamity and how people may prepare to protect themselves, as well as structural construction projects, are among the actions. These projects are intended at reducing the number of people killed and property destroyed in the event of a disaster.
Preparedness is the second phase of disaster management, and it aims to improve government-led preparedness to deal with emergencies. The majority of the preparations are aimed toward life-saving activities. Plan writing, communication system development, public education, and drills are all part of the preparation process. The disaster management team implements measures to keep people alive and limit the number of people affected in the third phase, reaction. Transport, shelter, and food are provided to the afflicted population as part of the response. Repairs are being made, and temporary solutions, such as temporary housing for the impacted population, are being sought.
Recovery is the ultimate stage of disaster management. This normally happens after the tragedy has subsided and the harm has been done. During the recovery process, the team works to restore people’s livelihoods and infrastructure. Short-term or long-term recovery is possible. The goal is to return the affected population to a normal or better way of life. During public education, the importance of health safety is highlighted. The recovery phase allows catastrophe management to move forward with long-term solutions.
Disaster Management Challenges:
The management of disasters is a difficult task, and there are certain flaws to be found. Since the individual dangers and disasters in some countries are not well understood, the government is unable to deploy disaster management in the event of an unforeseen disaster. There’s also the issue of a country’s technical and framework capabilities being insufficient. Government support is required for disaster management frameworks. Due to the generally large population, the disaster management approach includes public education, but there is no psychological counselling for individuals. People are more likely to develop post-traumatic stress disorder and psychiatric illnesses.
Conclusion:
Disaster management is a very important activity that countries should embrace to prevent disasters and lessen the negative consequences of disasters. However, disaster management has limitations that restrict the techniques’ ability to be implemented successfully.
Disasters can cause chaos, mass death of humans and animals, and a rise in crime rates. Disasters are unfavourable events that cause widespread anxiety and terror. They also make it difficult for society to respond to its causes.
Natural or man-made disasters can emerge. In both circumstances, they have the potential to cause significant loss of life and property. A combination of man-made and natural disasters can occur in severe circumstances. For example, violent conflicts and food scarcity. As a result, disaster management is required to limit or prevent massive loss and damage.
Disaster management includes disaster avoidance, disaster awareness, and disaster planning. These ideas will be discussed further down.
Prevention of Disaster:
Countries all across the world have taken precautions to prevent diseases or viruses from spreading. These initiatives include the funding of research into natural disaster aversion. Other sources of revenue include food distribution, healthcare services, and so on. In Africa and the Middle East, the latter is commonly used in economically challenged areas.
Improved scientific research has also made it feasible to predict potential natural disasters. For example, equipment to detect earthquakes and tsunamis has been developed. As a result, more people are concerned about the environment. In this sense, consciousness translates to a reduction in all forms of pollution in the environment.
Disaster Awareness :
Another strategy to minimise the excesses of widespread epidemics is to raise disaster awareness. Members of the public must be made aware of the importance of maintaining peace, de-escalating dangerous circumstances, and prioritising safety in the face of any possible tragedy.
The goal of disaster management is to reduce human death and suffering. The impact of disasters can be reduced if all of these factors are successfully managed. As a result, the necessity of disaster management cannot be emphasised.
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is the main agency charged with establishing rules and guidelines for disaster management in order to ensure prompt and effective disaster response. There is also a separate fund for mitigation called the “national disaster management fund” (NDMF). Functions performed by this agency are:
- Administration
- Formation of policies for disaster management
- Approval of the strategies made up for disaster mitigation
- Formation of revenue or funds for disaster mitigation
- Managing multiple programmes and disseminating instructions.
The disaster has had both direct and indirect repercussions on human life, both of which have been deadly devastating and detrimental. There have been fatalities as well as stock losses. Natural disasters are unavoidable; even if we have mechanisms in place to predict or forecast them, we cannot prevent them from occurring. While preparing plans for our disaster management, the best that can be done is to prevent behaviours that are detrimental to the environment and lead to environmental deterioration. When a disaster strikes, it causes widespread devastation and loss of life. In the event of a disaster such as earthquakes, floods, or other natural disasters, a large number of people are displaced, and a large number of people die as a result of the disaster. This is when the true emergency begins by providing first aid to the injured, as well as rescue and relief efforts for the victims. To limit the risk of human life, everyone must participate actively in disaster management. When a crisis happens, the appropriate disaster management team can seize over as soon as possible.
Also Read: Career in Ecology and Environment
The 4 phases of disaster management are Mitigation, Preparedness, Response, and Recovery.
The 3 types of disasters are natural, man-made, and hybrid disasters.
On 23 December 2005, the Government of India enacted the Disaster Management Act
Hence, we hope that this blog has helped you understand the key steps to writing a scoring essay on Disaster Management. If you are at the conclusion of the 10th grade and confused about which stream to take in the next standard, reach out to our Leverage Edu expert and we’ll guide you in choosing the right stream of study as well as gain clarity about your interests and aspirations so that you take an informed step towards a rewarding career.
Sonal is a creative, enthusiastic writer and editor who has worked extensively for the Study Abroad domain. She splits her time between shooting fun insta reels and learning new tools for content marketing. If she is missing from her desk, you can find her with a group of people cracking silly jokes or petting neighbourhood dogs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Disaster Management Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on disaster management.
Nature has various manifestations both gentle as well as aggressive. We see how sometimes it is so calm while the other times it becomes fierce. The calm side is loved by everyone, of course, however, when the ferocious side is shown, devastation happens. As humans cannot control everything, certain things of nature are out of our control.

Similarly, when natural disasters happen, humans cannot control them. However, we can prevent them. In other words, whenever a calamitous situation arises that may disturb the life and ecosystem, we need emergency measures to save and preserve lives. As natural disaster are not predictable, they can take place anywhere at any time. To understand disaster management thoroughly, we need to first identify the types of disasters.
Types of Disasters
If we look at the disasters that have taken place earlier, we can easily say that nature is not merely responsible for them to happen. They happen due to other reasons too. This is why we have classified them in different categories. First comes the natural disasters which are caused by natural processes. They are the most dangerous disaster to happen which causes loss of life and damage to the earth. Some of the deadliest natural disasters are earthquakes , floods, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, and more.

As no country is spared from any kind of disasters, India also falls in the same category. In fact, the geographical location of India makes it a very disaster-prone country. Each year, India faces a number of disasters like floods, earthquakes, tsunami, landslides, cyclones, droughts and more. When we look at the man-made disasters, India suffered the Bhopal Gas Tragedy as well as the plague in Gujarat. To stop these incidents from happening again, we need to strengthen our disaster management techniques to prevent destructive damage.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Disaster Management
Disaster management refers to the efficient management of resources and responsibilities that will help in lessening the impact of the disaster. It involves a well-planned plan of action so we can make effective efforts to reduce the dangers caused by the disaster to a minimum.
Most importantly, one must understand that disaster management does not necessarily eliminate the threat completely but it decreases the impact of the disaster. It focuses on formulating specific plans to do so. The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) in India is responsible for monitoring the disasters of the country. This organization runs a number of programs to mitigate the risks and increase the responsiveness.
Proper disaster management can be done when we make the citizens aware of the precautionary measures to take when they face emergency situations. For instance, everyone must know we should hide under a bed or table whenever there is an earthquake. Thus, the NDMA needs to take more organized efforts to decrease the damage that disasters are causing. If all the citizens learn the basic ways to save themselves and if the government takes more responsive measures, we can surely save a lot of life and vegetation.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the types of disasters?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “There are essentially two types of disasters. One is natural disasters which include floods, earthquake, tsunami, volcanic eruptions and more. The other is man-made disaster including oil spills, fires” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How can we effectively manage disasters?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”We must make people aware of the consequences of disasters. Moreover, we can teach them actions and measures to take when they face emergency situations.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Disaster Management

Introduction
Disasters, whether natural or man-made, have the capacity to inflict immense destruction and disrupt the lives of millions. Effective disaster management is crucial to mitigate these risks and build community resilience. For instance, Japan’s 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami highlighted the importance of preparedness and swift response. Japan’s strict construction regulations and preemptive alert systems were instrumental in preserving countless lives, although it was one of the most potent earthquakes ever documented. This event underscores the need for comprehensive disaster management strategies encompassing mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. The essay will delve into the different facets of disaster management and its importance in protecting communities around the globe.

Importance of Disaster Management
Disaster management holds immense significance as it protects lives, reduces property damage, and fosters sustainable development. Here are several vital reasons why disaster management is essential:
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
- Lifesaving : Effective disaster management measures such as early warning systems, evacuation plans, and emergency response protocols can significantly reduce casualties during disasters. Timely action can mean the difference between life and death for those affected.
- Minimization of Damage : Disaster management helps mitigate the impact of disasters on infrastructure, buildings, and natural resources. Implementing measures such as building codes, land-use planning, and ecosystem restoration can help minimize the extent of damage caused by disasters.
- Resilience Building : Through disaster preparedness initiatives, communities can enhance their resilience to future disasters. This includes educating the public, training emergency responders, and establishing robust communication networks to facilitate swift responses.
- Economic Stability : Disasters often result in significant economic losses due to property damage, disruption of business activities, and the cost of recovery efforts. Disaster management helps reduce these economic losses by investing in risk-reduction measures and ensuring the continuity of essential services.
- Social Cohesion : Disaster management fosters community cohesion and solidarity by promoting collaboration among government agencies, non-governmental organizations, businesses, and individuals. Collaborating towards the shared objective of disaster preparedness and response enhances social cohesion and fosters mutual assistance during challenging times.
- Environmental Protection : Numerous disasters have negative environmental impacts, including pollution, habitat destruction, and loss of biodiversity . Disaster management minimizes these environmental impacts and promotes sustainable recovery and reconstruction practices.
- Long-term Development : Integrating disaster risk reduction into development planning ensures that investments in infrastructure and livelihoods are resilient to potential hazards. This approach helps reduce vulnerability and promote sustainable development that can withstand future disasters.
Types of Disasters
There are several types of disasters, broadly categorized into natural and man-made disasters . Here’s a breakdown of each:
1. Natural Disasters
- Earthquakes : Earthquakes result from sudden movements of tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface, causing the ground to shake.
- Hurricanes/Typhoons : Intense tropical cyclones characterized by strong winds, heavy rain, and storm surges, forming over warm ocean waters.
- Floods : Floods occur when water overflows onto dry land due to heavy rainfall, river overflow, or storm surges.
- Wildfires : Uncontrolled fires that spread rapidly through vegetation, often fueled by dry conditions and high winds.
- Tornadoes : Tornadoes are intense, rotating columns of air extending from thunderstorms to the ground, with the potential to cause significant damage along their path.
2. Man-made Disasters
- Industrial Accidents : Mishaps occurring in industrial facilities, such as chemical spills, explosions, or structural failures, leading to environmental contamination and human casualties.
- Nuclear Incidents : Accidents or malfunctions in nuclear power plants release radioactive materials, posing health risks and environmental contamination.
- Terrorist Attacks : Deliberate acts of violence targeting civilians or infrastructure, causing fear, destruction, and loss of life.
- Transportation Accidents : Crashes involving airplanes, trains, ships, or automobiles, resulting in casualties, property damage, and environmental pollution .
- Urban Fires : Large-scale fires occur in urban areas due to various causes, such as electrical faults, gas leaks, or arson, leading to extensive property damage and loss of life.
Phases of Disaster Management
The phases of disaster management are crucial for effective disaster preparedness and response. Here is a brief description of each phase:
- Mitigation : This phase involves measures taken to reduce the risk of disasters and minimize their impact. This includes activities such as enforcing building codes, implementing land-use planning, and conducting public awareness campaigns to reduce vulnerability to hazards.
- Preparedness : Preparedness involves planning and capacity-building activities undertaken to ensure an effective response to disasters. This includes developing emergency response plans, conducting drills and exercises, and pre-positioning resources and supplies.
- Response : The response phase involves the immediate actions taken to address the needs of those affected by a disaster. This includes search and rescue operations, providing emergency medical care, and distributing food, water, and shelter to survivors.
- Recovery : The recovery phase is when affected communities rebuild and recuperate from the effects of a disaster. This includes restoring infrastructure, providing psychosocial support to survivors, and implementing measures to prevent future disasters.
- Risk Reduction : Risk reduction is a continual process that seeks to diminish the risk of disasters through long-term measures like enhancing infrastructure, improving early warning systems, and advocating for sustainable development practices.
Role of Government in Disaster Management
The role of government in disaster management is pivotal in ensuring effective coordination, response, and recovery efforts. Here are several key aspects of the government’s role in disaster management:
- Policy and Planning : Governments are responsible for developing policies, regulations, and guidelines related to disaster management. This includes creating national disaster management frameworks, establishing regulatory standards for infrastructure resilience, and drafting contingency plans for various types of disasters.
- Coordination and Collaboration : Governments coordinate disaster management efforts across different levels (national, regional, and local) and sectors (government agencies, non-governmental organizations, private sector, etc.). This involves establishing coordination mechanisms, conducting joint exercises and drills, and fostering stakeholder collaboration.
- Resource Allocation : Governments allocate resources, including funding, personnel, and equipment, to support disaster preparedness, response, and recovery activities. This may involve budgeting for emergency response agencies, procuring supplies and equipment, and mobilizing personnel from various government agencies.
- Risk Assessment and Early Warning : Governments conduct risk assessments to identify hazards, vulnerabilities, and disaster exposure. They also establish early warning systems to monitor and alert communities about impending disasters, such as floods, hurricanes, or tsunamis, allowing for timely evacuation and preparedness measures.
- Emergency Response : During disasters, governments take the lead in emergency response efforts by mobilizing emergency services, which include search and rescue teams, medical personnel, and law enforcement agencies. They also establish emergency shelters, provide medical assistance, and coordinate the distribution of relief supplies to affected populations.
- Public Awareness and Education : Governments are crucial in raising public awareness about disaster risks and promoting preparedness measures. This includes disseminating information through public campaigns, educational programs, and community outreach activities to ensure that individuals and communities are well-informed and prepared to respond to disasters.
- Recovery and Reconstruction : Governments lead efforts to support the recovery and reconstruction of affected communities following a disaster. This includes assessing damage and needs, providing financial assistance and resources for rebuilding infrastructure, and facilitating the restoration of essential services and livelihoods.
Role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are vital in disaster management as they supplement the endeavors of governments and other stakeholders. Here are several key roles that NGOs play in disaster management:
- Service Provision : NGOs often provide essential services during disasters, such as shelter, food, water, and medical care. They may also offer psychosocial support, counseling, and rehabilitation services to survivors.
- Community Engagement : NGOs work closely with communities to raise awareness about disaster risks, build local capacity for preparedness and response, and facilitate community-led initiatives for disaster risk reduction.
- Advocacy and Policy Influence : NGOs advocate for policies and practices that promote disaster risk reduction, climate change adaptation, and sustainable development. They also work to hold governments and other stakeholders accountable for their disaster management responsibilities.
- Capacity Building : NGOs support the capacity building of local organizations and communities to enhance their resilience to disasters. This includes providing training, resources, and technical assistance to build local capacity for disaster preparedness, response, and recovery.
- Coordination and Networking : NGOs often play a crucial role in coordinating disaster response efforts, both among themselves and with government agencies and other stakeholders. They also facilitate information sharing and collaboration to ensure a more effective and coordinated response.
- Monitoring and Evaluation : NGOs conduct assessments and evaluations to monitor the effectiveness of disaster management programs and interventions. This helps to identify lessons learned and best practices for future disaster response and preparedness efforts.
- Innovation and Learning : NGOs often pioneer innovative approaches to disaster management, including the use of technology , community-based approaches, and participatory methods. They also facilitate learning and knowledge sharing among stakeholders to improve disaster management practices.
Community Involvement
Community involvement is a critical component of effective disaster management. Involving communities in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery can bolster resilience and mitigate the impact of disasters. Communities can involve themselves in disaster management in several ways:
- Risk Assessment : Communities can participate in identifying and assessing local disaster risks. This includes understanding the hazards they face, mapping vulnerable areas, and evaluating their capacity to cope with disasters.
- Planning and Preparedness : Communities can participate in developing disaster preparedness plans. This includes identifying evacuation routes, establishing communication networks, and conducting drills and exercises to ensure readiness.
- Early Warning Systems : Communities can help disseminate early warnings and alerts to residents. This includes establishing communication channels, such as sirens, text messages, or community networks, to ensure everyone receives timely information.
- Search and Rescue : Following a disaster, individuals within a community can provide aid in search and rescue efforts within the affected area. This includes helping to locate missing persons, providing first aid, and supporting emergency responders.
- Emergency Shelter and Care : Communities can establish emergency shelters and provide care for displaced persons. This involves establishing temporary shelters, providing food and water, and offering medical assistance.
- Post-Disaster Recovery : Communities can participate in the recovery and reconstruction process. This includes clearing debris, rebuilding infrastructure, and restoring essential services.
- Education and Training : Communities can educate themselves about disaster risks and preparedness measures. This includes conducting awareness campaigns, training sessions, and workshops to build capacity and resilience.
- Community Networks : Establishing community networks and partnerships can enhance communication and coordination during disasters. This includes collaborating with local organizations, government agencies, and NGOs to ensure a coordinated response.
Technologies and Innovations in Disaster Management
Technologies and innovations are instrumental in improving the effectiveness of disaster management efforts. Here are some key technologies and innovations used in disaster management:
- Early Warning Systems : These systems use various technologies, such as satellites, weather stations, and sensors, to detect and monitor potential disasters, such as hurricanes, tsunamis, and floods. They provide early warnings to at-risk communities, allowing them to take timely actions to mitigate the impact of the disaster.
- GIS and Remote Sensing : GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and remote sensing technologies are employed to map and analyze disaster risks, vulnerable populations, and critical infrastructure. They help plan evacuation routes, identify safe shelter locations, and assess damage after a disaster.
- Drones : The use of drones in disaster management is increasing for various purposes, such as conducting search and rescue operations, assessing damage, and delivering supplies to remote or inaccessible areas. They can provide real-time aerial images and videos, helping responders make informed decisions.
- Mobile and Web-based Applications : Mobile apps and web-based platforms are used for disaster preparedness, communication, and coordination. These tools can provide information on evacuation routes, emergency contacts, shelter locations, and real-time updates during a disaster.
- Social Media : Organizations and individuals use social media platforms for disaster communication and situational awareness. They allow emergency responders to disseminate information quickly to a large audience and receive real-time updates from affected communities.
- Big Data and Analytics : Big data analytics processes and analyzes large volumes of data, such as social media feeds, satellite imagery, and sensor data, to identify trends and patterns related to disasters. This helps in making data-driven decisions for disaster response and recovery efforts.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) : AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, are used in disaster management for various applications, including predictive modeling, damage assessment, and decision support. Artificial intelligence (AI) can analyze extensive datasets and offer insights that aid in effective disaster response.
- Internet of Things (IoT) : Sensors and wearable devices, among other IoT devices, collect data in real time on various factors such as environmental conditions, infrastructure performance, and human activities. This data can be used for early warning, situational awareness, and disaster decision-making.
Case Studies
Here are a few case studies highlighting the use of technologies and innovations in disaster management:
- Hurricane Katrina (2005) : Hurricane Katrina stands out as one of the most devastating hurricanes in U.S. history. The storm caused widespread flooding and destruction along the Gulf Coast, particularly in New Orleans. One key lesson from Hurricane Katrina was the importance of early warning systems and communication technologies. In response to this, the U.S. government invested in improving its early warning systems and implementing better communication strategies to alert residents about impending disasters.
- Haiti Earthquake (2010) : The earthquake that struck Haiti in 2010 caused widespread destruction and loss of life. Various technologies aided in the response and recovery efforts in the aftermath of the disaster. For example, response teams used GIS technology to map out the affected areas and assess the damage. Authorities used drones to survey the damage and identify areas requiring assistance.
- Typhoon Haiyan (2013) : Typhoon Haiyan, one of the strongest typhoons ever recorded, struck the Philippines in 2013, causing massive devastation. In response to the disaster, the Philippine government utilized various technologies to aid in the recovery efforts. Mobile and web-based applications coordinated rescue and relief operations, while social media platforms disseminated information and gathered real-time updates from affected communities.
- Nepal Earthquake (2015) : The earthquake that struck Nepal in 2015 caused widespread destruction and loss of life. After the disaster, surveying the damage and assessing the needs of affected communities was done using drones. Additionally, response teams used mobile and web-based applications to coordinate rescue and relief efforts and provide information to affected individuals.
Disaster management faces several challenges that can complicate response and recovery efforts. Here are some key challenges:
- Limited Resources : One key challenge in disaster management is the scarcity of resources, including funding, personnel, and equipment. This can hinder the ability to respond effectively to disasters, especially in low-resource settings.
- Coordination and Communication : Successful disaster response relies on effective coordination and communication among various stakeholders, including government agencies, NGOs, and affected communities. However, challenges such as communication breakdowns, conflicting priorities, and lack of information sharing can impede coordination efforts.
- Complexity of Disasters : Disasters are often complex and multifaceted, involving multiple hazards and impacts. This complexity can present challenges in assessing risks, planning responses, and coordinating efforts, mainly when dealing with cascading or concurrent disasters.
- Vulnerability of Populations : Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and people with disabilities, are disproportionately affected by disasters. Ensuring the safety and well-being of vulnerable populations during disasters demands special attention and resources, which can pose challenges.
- Climate Change and Urbanization : Climate change and rapid urbanization exacerbate the frequency and intensity of disasters, including floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. These trends pose new challenges for disaster management, requiring adaptation strategies and long-term planning.
- Information Overload : During disasters, there is often an influx of information from various sources, including social media, news outlets, and official channels. Managing this information overload and distinguishing between reliable and inaccurate information can be challenging for responders.
- Logistical Challenges : Logistics, including transportation, supply chain management, and distribution of relief supplies, can be challenging during disasters, especially in remote or hard-to-reach areas. Ensuring timely delivery of aid requires careful planning and coordination.
- Community Engagement and Participation : Engaging communities in disaster management is essential for effective response and recovery. However, meaningful community participation can be challenging to achieve due to factors such as language barriers, cultural differences, and lack of trust in authorities.
Future Directions
In the future, disaster management is likely to evolve in several key directions:
- Technology Integration : Advanced technologies, such as drones, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence, will be increasingly integrated into disaster management practices. These technologies will enhance early warning systems, improve disaster response coordination, and enable more efficient damage assessments.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making : The use of big data analytics and real-time data monitoring will enable more data-driven decision-making in disaster management. This will help predict disasters, identify vulnerable populations, and allocate resources more effectively.
- Community Resilience Building : There will be a greater focus on building community resilience to disasters through education, training, and community-based initiatives. This will involve empowering communities to take proactive measures to reduce risks and enhance their ability to recover from disasters.
- Climate Change Adaptation : Due to the growing impacts of climate change, disaster management will increasingly prioritize climate change adaptation. This will involve implementing measures to reduce vulnerability to climate-related disasters like floods, droughts, and storms.
- Cross-Sector Collaboration : In disaster management, there will be increased collaboration among government agencies, non-governmental organizations, the private sector, and academia. This will involve sharing resources, expertise, and best practices to enhance overall capabilities.
- Policy and Governance : There will be a greater emphasis on improving policy frameworks and governance structures for disaster management. This will involve strengthening legal and institutional frameworks, enhancing coordination mechanisms, and promoting accountability and transparency.
- Sustainable Development : Sustainable development planning will increasingly integrate disaster management. This will involve promoting resilient infrastructure, sustainable land use practices, and environmental conservation to reduce disaster risks.
- Global Cooperation : There will be a greater emphasis on global cooperation in disaster management, particularly in response to transboundary disasters and emerging threats. This will involve sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise across borders to enhance global disaster resilience.
Effective disaster management is imperative for safeguarding lives, minimizing damage, and promoting community resilience worldwide. By implementing comprehensive strategies encompassing mitigation, preparedness, response, recovery, and risk reduction, societies can better withstand the impact of disasters. Integrating advanced technologies, community engagement, and global cooperation are crucial for addressing the evolving challenges of disaster management. As we move forward, it is essential to prioritize investment in disaster preparedness and resilience-building measures to mitigate the growing risks posed by natural and man-made disasters. Collectively, we can forge a safer and more resilient future for everyone.

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Disaster Management Essay

Essay on Disaster Management
Disaster Management is the arrangement and management of the resources following a disaster, be it natural or man-made. There are so many organizations who are dealing with various types of disastrous situations from the humanitarian aspect. Some disasters are just the consequences of human hazards and some are caused by natural calamity. However, we can prevent them by taking the necessary emergency measures to save and preserve lives. As natural disasters cannot be predicted, they can take place anywhere at any time.
Vedantu has provided an essay on Disaster management on this page. Students who have received an assignment to write an essay on Disaster Management or preparing an essay for examination can refer to this page to understand the pattern. Any student or parent can directly visit Vedantu site or download the app on the phone to get access to the study materials.
Disaster Management’ is the simple term of management which embraces loads of disaster-related activities. Disaster occurs frequently in some parts of the world. Japan is the best example of it. Japanese people are annoyed on Tsunamis and earthquakes. The local scene is not much different from the global one. No one could forget the cyclone in Orissa, Earthquake in Gujarat or even the Mumbai Terrorist Attack.
Natural and man-made are the two categories of the disaster. Natural disasters are those which occurred due to sudden changes in the environment or topography causing uncountable human as well as economic loss. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods and cloudbursts are few of the natural disasters. Manual intentional made disasters are man-made disasters. For example, Gas leakage, terrorist attacks, fire, oil spills. Man-made disasters are the result of human intentions or might be because of workmanship or technical errors. The count of man-made and natural disasters is rising rapidly.
Here are a few things which will help us to deal with earthquakes. The significant information about Natural calamities is predicted easier and is being shared within the public by the central bureau. Furthermore, earthquake-resistant structures are constructed considering, ‘Precaution is Better Than Cure’. Reflexes are made so strong that cover of solid platforms such as a table and chair should be taken as soon as the danger is sensible while the cover of trees, electric poles or buildings is avoided as far as possible. Keep in touch with local news during heavy rainy days. Any flood is preceded with significant time. Making proper use of divine buffer time for safety is advisable. Strategically planning of water reservoirs, land uses, tree plantation, rainwater harvesting techniques help us increase immunity power to fight against the drought.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), American Red Cross, Federal Emergency Management Agency, International Association of Emergency Managers etc. are the best disaster management authorities. NDMA is a core body which obeys the law of Disaster Management. The reputed disaster managers are stuck in finding plans for rescuing from the loss of disaster. Moreover, to counteract the effect of disaster Rajya Sabha passed the ‘Disaster Management Act’ on 23 December 2005 which includes 11 chapters and 79 sections in it. Honourable Prime Minister of India Mr Narendra Modi holds the position of chairman of it.
Youngsters should motivate themselves to learn and practice plenty of disaster management techniques and arrange the camps regarding it. Today, everyone is fighting against one of the breathtaking disasters named COVID-19 which is as big as fighting in world war. Avoiding the crowd, wearing the mask are the basic precautions suggested by the World Health Organization (WHO) during this period of fighting. This disease spreads mostly amongst the people who come in close contact with the infected one. So, it's suggested to keep a safe distance of around 3 meters within the others. This is being termed as ‘Social Distancing’. Nature is not cruel nor is it human. Just small management skills help us withstand before, in and after disasters. Uncountable suggestions and instructions in disaster management but few which apply every time must be followed.
Stages of Disaster Management
With proper implementation and structured action, we can prevent or lessen the impact of natural or man-made disasters. There are certain stages involving the cycle for disaster management plan which incorporates policies and emergency responses required for a prospectively complete recovery. The stages are –
The most preferred way to deal with disasters is to be proactive in their prevention rather than rushing later for their cure. This implies recognition of potential hazards and working towards infrastructure to mitigate their impact. This stage in the management cycle involves setting up permanent measures to minimize disaster risk.
Setting up an evacuation plan in a school, training the teachers to lead the students towards safe structures in the event of earthquake, tornado or fire, planning a strong base for high raised sky-scrapers to prepare for earthquakes and designing a city in such a manner that reduces the risk of flooding are some examples of measures takes for disaster prevention.
Mitigation is the first and the foremost attempt to save human lives during the time of disaster or their recovery from the aftermath. The measures which are taken can be both structural and non-structural.
Structural mitigation measures could include transforming the physical characteristics of a building or the surroundings to curb the effect, for example, clearing out of the trees around your house, ensuring that storms don’t knock down the trees and send them crashing into the house. Non-structural measures could include amending the building or locality codes to enhance safety and prevent disasters.
Preparedness
Preparedness is a process that involves a social community where the trained, or the head of the community, businesses and institutions demonstrate the plan of action which is supposed to be executed during the event of a disaster. It is an ongoing continuous process with anticipation of a calamity, which involves training, evaluating and taking corrective action with the highest level of alertness. Some examples of such prevention measures are fire drills, shooter drills and evacuation rehearsals.
The response is the action taken after the disaster has occurred to retrieve some life from it. It includes short-term and long-term responses. In ideal situations, the disaster-management leader will coordinate the use of resources in the restoration process and minimize the risk of further property damage.
During this stage, the area of the calamity is cleared if it poses any further threat to human as well as environmental life. For example, evacuation of the city of Chernobyl, Ukraine, is a responsive action against a disaster.
The fifth and last stage in the process of the disaster management plan is the recovery stage. This can sometimes take years or decades to happen. The larger mass of a city is also sometimes part of the recovery from a disaster. The greatest and the most infamous example of this is the Hiroshima and Nagasaki nuclear attacks on Japan, it took the people of those cities years and decades to recover from that man-made calamity.
It took years of effort to stabilize the area and restore essential community or individual functions. The recovery stage prioritizes the basic essential needs of human survival like food, drinkable water, utilities, transportation and healthcare over less-essential services. Eventually, this stage is all about coordinating with individuals, communities and businesses to help each other to restore a normal or a new normal, as in the case of Covid-19.
How to Act as a Responsible Person During a Time of Disaster?
Some people have more experience than others with managing natural or man-made disasters and their prevention of them. Although this is that subject of life which should be studied and implemented by every business or community. As it is said rightly, “prevention is better than cure”, and any organization or an individual or a community can be hit by a disaster sooner or later, whether it's something as minor as a prolonged power cut or a life-threatening hurricane or an earthquake. Usually, the pandemics train us, as a social and political community, to deal with natural calamities and compel the organizations responsible for it, to build an infrastructure for its prevention.
To act responsibly and pro-actively during the event of a disaster, we have got to be prepared and equipped as a nation, individually and as a social community. To be well-educated and read with the aspects of disaster management is to be responsible for the handling of it.

FAQs on Disaster Management Essay
1. What is Disaster Management?
In simpler words, disaster management can be defined as the arrangement of resources and precautions to deal with all humanitarian aspects during an emergency. Disasters are the consequences of natural or human hazards. Earthquakes, floods, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes are some of the deadliest natural disasters to name a few. Examples of man-made disasters are bomb blast, radiations, transport accidents, terrorist attacks etc.
2. What is the Main Aim of Disaster Management?
The main aim of disaster management is prevention, rescue and recovery from the trauma, and development.
3. How to Write an Essay on Disaster Management?
Disaster management refers to the response to an emergency situation to make it as normal as possible. While writing an essay on Disaster Management, you can start with an introduction, then go on with the definition, the types of disaster management, a little in-depth explanation along with examples, and finish it off with a conclusion.
4. Can I Get a Sample Essay on Disaster Management from Vedantu?
Yes, the essay mentioned on this page is about Disaster Management. This essay has been written by the experts of Vedantu keeping the understanding ability of the students of each class.
5. What are the career opportunities in the field of Disaster management?
People looking for career opportunities in the field of disaster management have many pathways to approach it. Some examples of the jobs relating to this line of work are crisis-management leader, disaster-assistance specialist and emergency-planning coordinator. These are the roles which call for varying levels of responsibility in preparing a city or a company for catastrophic events. The job roles can be approached with earning a master’s degree in emergency and crisis management.
Geography Notes
Essay on disaster management: top 11 essays | geography.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Disaster Management’ for class 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays ‘Disaster Management’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Disaster Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Awareness Programmes for Disaster Management
Essay # 1. Introduction to Disaster Management:
India has been traditionally vulnerable to natural disasters on account of its unique geo- climatic conditions. Floods, droughts, cyclones, earthquakes and landslides have been recurrent phenomena. About 60% of the landmass is prone to earthquakes of various intensities; over 40 million hectares is prone to floods; about 8% of the total area is prone to cyclones and 68% of the area is susceptible to drought.
In the decade 1990-2000, an average of about 4344 people lost their lives and about 30 million people were affected by disasters every year. The loss in terms of private, community and public assets has been astronomical. At the global level, there has been considerable concern over natural disasters.
Even as scientific and material progress is made, the loss of lives and property due to disasters has not decision. In fact, the human toll and economic losses have mounted. It was in this background that the Nations General Assembly, in 1989, declared the decade 1990-2000 as the International Natural Disaster Reduction with the objective to reduce loss of lives and property and restrict economic damage through concerted international action, especially in developing countries.
Over the past couple of years, the Government of India has brought about a paradigm shift in approach to disaster management. The new approach proceeds from the conviction that develop cannot be sustainable unless disaster mitigation is built into the development process. Another stone of the approach is that mitigation has to be multi-disciplinary spanning across all sectors.
The new policy also emanates from the belief that investments in mitigation are much cost effective than expenditure on relief and rehabilitation. Disaster management occupies an important place in this country’s policy framework as it is poor and the underprivileged who are worst affected on account of calamities/disasters.
The steps being taken by the Government emanate from the approach outlined above. The app: has been translated into a National Disaster Framework [a roadmap] covering institutional mechanic; disaster prevention strategy, early warning system, disaster mitigation, preparedness and response human resource development.
The expected inputs, areas of intervention and agencies to be in at the national, state and district levels have been identified and listed in the roadmap. This road has been shared with all the State Governments and Union Territory Administrations.
Ministries Departments of Government of India, and the State Governments/UT Administrations have been develop their respective roadmaps taking the national roadmap as a broad guideline. There is, therefore: now a common strategy underpinning the action being taken by the entire participating organisation stakeholders.
The approach is being put into effect through:
1. Institutional changes
2. Enunciation of policy
3. Legal and techno-legal framework
4. Mainstreaming Mitigation into development process
5. Funding mechanism
6. Specific schemes addressing mitigation
7. Preparedness measures
8. Capacity building
9. Human resource development and, above all, community participation.
In India, the role of emergency management falls to National Disaster Management of India, a government agency subordinate to the Ministry of Home Affairs. In recent years, there has been a shift in emphasis, from response and recovery to strategic risk management and reduction, and from a government-centered approach to decentralized community participation.
Survey of India, an agency within the Ministry of Science and Technology, is also playing a role in this field, through bringing the academic knowledge and research expertise of earth scientists to the emergency management process.
Essay # 2. Meaning of Disaster Management:
Disaster management means a systematic response to a disaster. Earlier the approach to disaster was relief centric and was limited to providing relief to the disaster affected area. For the first time, the Tenth Five Year Plan devoted a chapter to disaster management. The approach subsequently changed and pre-empting the disaster, assessing disaster risk and taking preventive measures has also become a part of disaster management.
The Disaster Management Act was notified on 26th December, 2005 which defines disaster management as “a continuous and integrated process of planning, organising, coordinating and implementing measures which are necessary or expedient for-prevention of danger or threat of any disaster; mitigation or reduction of risk of any disaster or its severity or consequences; capacity building; preparedness to deal with any disaster; prompt response to any threatening disaster situation or disaster; assessing the severity of magnitude of effects of any disaster; evacuation, rescue and relief; and rehabilitation and reconstruction.”
The Act provided for a dedicated and institutionalized framework to coordinate various aspects of disaster management. A National Policy on Disaster Management, which provided detailed guidelines on disaster management, was announced in 2009.
Essay # 3. Institutions of Disaster Management:
The Disaster Management Act 2005 has provided the legal and institutional framework for disaster management in India at the national, state and district levels. In the federal policy of India the primary responsibility of disaster management vests with the State Governments.
The Central Government lays down policies and guidelines and provides technical, financial and logistic support while the district administration carries out most of the operations in collaboration with central and state level agencies.
In the Central Government there are existing institutions and mechanisms for disaster management while new dedicated institutions have been created under the Disaster Management Act of 2005.
The Cabinet Committee on Management of Natural Calamities (CCMNC) oversees all aspects relating to the management of natural calamities including assessment of the situation and identification of measures and programmes considered necessary to reduce its impact, monitor and suggest long term measures for prevention of such calamities, formulate and recommend programmes for public awareness for building up society’s resilience to them. The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) deals with the matters relating to nuclear, biological and chemical emergencies.
The National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) under the Cabinet Secretary oversees the Command, Control and Coordination of the disaster response. The Disaster Management Act, 2005 has created new institutions at the national, state, district and local levels.
The new institutional framework for disaster management in the country is as under:
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) under the Chairmanship of the Prime Minister is the apex body responsible for laying down policies, plans and guidelines for disaster management and for coordinating their enforcement and implementation throughout the country.
The policies and guidelines will assist the Central Ministries, State Governments and district administration to formulate their respective plans and programmes. NDMA has the power to approve the National Plans and the Plans of the respective Ministries and Departments of Government of India. The general superintendence, direction and control of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) are vested in and will be exercised by the NDMA.
The National Executive Committee (NEC) is mandated to assist the NDMA in the discharge of its functions and further ensure compliance of the directions issued by the Central Government. The NEC comprises of the Union Home Secretary as the Chairperson, and the Secretaries to the GOI in the Ministries/Departments of Agriculture, Atomic Energy, Defence, Drinking Water Supply, Environment and Forests, Finance (Expenditure), Health, Power, Rural Development, Science and Technology, Space, Telecommunications, Urban Development, Water Resources and the Chief of the Integrated Defence Staff of the Chiefs of Staff Committee as members.
Secretaries in the Ministry of External Affairs, Earth Sciences, Human Resource Development, Mines, Shipping, Road Transport and Highways and Secretary, NDMA are special invitees to the meetings of the NEC. The National Executive Committee is responsible to prepare the National Plan and coordinate and monitor the implementation of the National Policy and the guidelines issued by NDMA.
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) in the Central Government has the overall responsibility for disaster management in the country.
For a few specific types of disasters the concerned Ministries have the nodal responsibilities for management of the disasters, as under:
The National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) has the mandate for human resource development and capacity building for disaster management within the broad policies and guidelines laid down by the NDMA. NIDM is required to design, develop and implement training programmes, undertake research, formulate and implement a comprehensive human resource development plan, provide assistance in national policy formulation, assist other research and training institutes, state governments and other organizations for successfully discharging their responsibilities, develop educational materials for dissemination and promote awareness among stakeholders in addition to undertake any other function as assigned to it by the Central Government.
The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is the specialized force for disaster response which works under the overall supervision and control of the NDMA.
At the State Level the State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA), headed by the Chief Minister, lays down policies and plans for disaster management in the state. It is also responsible to coordinate the implementation of the State Plan, recommend provision of funds for mitigation and preparedness measures and review the developmental plans of the different departments of the state to ensure integration of prevention, preparedness and mitigation measures.
The State Disaster Management Department (DMD) which is mostly positioned in the Revenue and Relief Department is the nodal authority.
In the district level the District Disaster Management Authority (DDMA) is headed by the District Magistrate, with the elected representative of the local authority as the Co-Chairperson. DDMA is the planning, coordinating and implementing body for disaster management at district level. It will, inter alia prepare the District Disaster Management Plan and monitor the implementation of the National and State Policies and the National, State and the District Plans.
DDMA will also ensure that the guidelines for prevention, mitigation, preparedness and response measures laid down by the NDMA and the SDMA are followed by all departments of the State Government at the district level and the local authorities in the district.
The Local Authorities both the rural local self-governing institutions (Panchayati Raj Institutions) and urban local bodies (Municipalities, Cantonment Boards and Town Planning Authorities) These bodies will ensure capacity building of their officers and employees for managing disasters, carry out relief, rehabilitation and reconstruction activities in the affected areas and will prepare DM Plans in consonance with guidelines of the NDMA, SDMAs and DDMAs.
Disaster Management Act (2005):
The Disaster Management Act, 2005 came into the statute book on 26 December, 2005 by a Gazette notification, exactly on the first anniversary of the devastating tsunami of 2004, which killed nearly 13,000 people in India alone and affected 18 million people. The Act provides a legal and institutional framework for “the effective management of disasters and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.”
It provides for establishment of National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA) and District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMA) at the National, State and District levels with adequate financial and administrative powers and creation of the National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) with the mandate of undertaking training and capacity building, Develop Training Modules on various aspects of disaster management, Undertake Research and Documentation, Formulate and implement comprehensive HRD Plan covering all aspects of DM, Provide assistance in national level policy formulation and Provide assistance to state governments and State Training Institutions.
The act also provides guidelines for creation of National Disaster Response Fund, National Mitigation Fund, Establishment of funds by State Government and Allocation of funds by Ministries and Departments for Emergency Procurement. The act also provides for establishment of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).
National Policy on Disaster Management in 2009 :
The National Policy on Disaster Management was approved by the Government in November 2009. This comprehensive policy document lays down policies on every aspect of holistic management of disasters in the country.
The policy has thirteen chapters as under:
1. Preamble
2. Approach and Objectives
3. Institutional and Legal Arrangements
4. Financial Arrangements
5. Disaster Prevention, Mitigation and Preparedness
6. Techno-Legal Regime
7. Response
8. Relief and Rehabilitation
9. Reconstruction and recovery
10. Capacity development
11. Knowledge management
12. Research and development
13. Road ahead
Salient Features of India’s National Policy on Disaster Management:
India’s National Policy on Disaster Management was approved by the Union Cabinet of India on 22nd October, 2009 with the aim to minimize the losses to lives, livelihoods and property, caused by natural or manmade disasters with a vision to build a safe and disaster resilient India by developing a holistic, proactive, integrated, Multi-disaster oriented and technology driven strategy.
With this national policy in place in India, a holistic and integrated approach will be evolved towards disaster management with emphasis on building strategic partnerships at various levels. The themes underpinning the policy include Community based Disaster Management, Capacity development in all spheres, Consolidation of past initiatives and best practices and Cooperation with agencies at national and international levels with multi-sectoral synergy.
The Policy is also intended to promote a culture of prevention, preparedness and resilience at all levels through knowledge, innovation and education. It encourages mitigation measures based on environmental sustainability. It seeks to mainstream disaster management into the developmental planning process and provides for institutional and financial arrangements at national, state, and district-levels for Disaster Prevention, Mitigation, Preparedness and Response as it ensures adequate budgeting for disaster mitigation activities in all Ministries and Departments.
I. State Policies on Disaster Management:
The States of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Kerala have formulated State Disaster Management Policies. Tamil Nadu, Chattisgarh, Uttrakhand, Meghalaya, Bihar, Rajasthan, Delhi, Orissa and West Bengal have prepared draft policies.
II. State Relief Codes/DM Codes:
Many States have manuals and codes for management of drought, floods etc. Now many states are in the process of changing their State Relief codes into Disaster Management Manuals.

Essay # 4. Disaster Management Cycle:
Earthquakes, landslides, floods, hurricanes, famines typhoons, and other disasters affect millions of people and cause a lot of financial loss to the nation every year. Many of these events are impossible to predict precisely, but with the disaster response community has a variety of tools that can employ to reduce thereafter effects.
The community understands these tools as arrayed across a “disaster management cycle” that includes work from prevention efforts all the way through long-term recovery and “building back better.”
The disaster management cycle includes several phases:
1. Mitigation:
Disaster mitigation work involves directly preventing future emergencies and/or minimizing their negative effects. It requires hazard risk analysis and the application of strategies to reduce the likelihood that hazards will become disasters, such as flood-proofing homes or buying insurance.
2. Preparedness:
Disaster preparedness efforts include plans or preparations made in advance of an emergency that help individuals and communities get ready. Such preparations might include the stocking of food and water, medicine, or the gathering and screening of willing volunteers.
3. Response:
Disaster response work includes any actions taken in the midst of or immediately following an emergency, including efforts to save lives and to prevent further property damage. Ideally, disaster response involves putting already established disaster preparedness plans into motion. Typically, this phase of the disaster life cycle draws the most attention.
4. Recovery:
Disaster recovery happens after damages have been assessed, and involves actions to return the affected community to its pre-disaster state or better-and ideally to make it less vulnerable to future risk. Risk identification includes understanding the nature of hazards as well as understanding the nature of vulnerabilities. Subsequent efforts may range from physical upgrades to education, training, and public awareness campaigns.
Essay # 5. Plan Preparation for Disaster Management:
Programme staff has selected 100 villagers (including women) who will be given intensive disaster management training. This will include preparation for post-earthquake, cyclone and fire situations. The objective of the programme is to help build up, within a short period of time, a mechanism that can respond to natural calamities and help save lives.
Results of the training should include better coordination with relief and rescue efforts of the government and humanitarian agencies so as to avoid the common mismanagement that often hampers relief operations following natural disasters.
By prioritising measures for vulnerability reduction in a transparent, accountable and inclusive way, the programme aims to shape future disaster response and related development projects in other areas of Gujarat, as well as in other drought prone states.
Disaster Contingency Plan Preparation :
A good disaster contingency plan consists of organizing resources, assessing risks, developing a plan, implementing the plan and monitoring it. The plan is a constantly changing document. The plan needs to be flexible because communities and resources change over time.
The goal of the plan is to reduce or eliminate the loss of life. The plan strives to do the same for property damage resulting from natural hazards. Understand that your plan might be different for different types of emergencies.
You would respond differently to a house fire than you would a state emergency for disaster:
1. Organize your resources. Take an inventory of resources that would be needed and available in the event of various emergencies. Resources can be other people as well as organizations. Create an emergency list of contacts. Be sure to include area codes, especially if you have younger children. Create an inventory of household items and family assets. Keep it in a water and fire-proof safe.
2. Assess your risks. Determine the potential problems in your household and in your community. Include tornadoes or wind storms in your plan if you live in an area prone to these meteorological events.
3. Develop a plan and set priorities. Make an evacuation map of your house. Include each room and possible escape routes from each room. Consider where your family would meet if a disaster happened while your children were at school and you were at work. Learn how to turn off your utilities. Include your pets in your planning.
4. Implement the plan and monitor its progress. Hold regular drills at home. Make sure everyone knows where to go and what to do in an emergency.
5. Make an emergency kit. Include blankets, food and snacks high in protein, water, a flashlight and batteries. The Pennsylvania Emergency Management Agency also recommends a first aid kit, extra clothes, a tool kit, duct tape, a towline, a utility knife, and extra medication if applicable.
Disaster Management Plan Preparation :
The preparation of plans must fulfill the statutory requirements as laid down in the Disaster Management Act and must ensure that efforts have been made by the department to fulfill statutory duties-failure of which invites stringent liabilities including criminal proceedings by the law of the State.
This planning exercise is an effort made to mainstream all issues concerned with emergency preparedness, response and mitigation/risk reduction activities.
The department should include the following components in the department plan:
1. Planning on emergency response at all levels.
2. Planning on providing relief and recovery support (post-disaster).
3. Planning on prevention and mitigation issues (including mainstreaming mitigation into the development)
4. Programmes supported by schemes financed by the state government (multilateral bilateral and donor institutions).
5. Planning for resources such as financial and human resource to fulfill the above three components.
The roles and responsibilities (in fulfilling the above four components) of all the actors and agencies within the department should be clearly spelt out in the plan. This will avoid ambiguity and confusion while executing the plan in the times of crisis. Thus, the roles and responsibilities under the above listed heads/sections should be prepared and the responsibilities assigned.
Department plan must clearly identify and assess the current capacity of the department. In other words, the department assess the availability of human resources/manpower, equipment, need for training and further capacity building through human resource development plan. In addition, existing resource allocation by the department on disaster management functions and requirements of additional funds for a minimum period of next three years must be indicated in the plan.
Essay # 6. Principles of Disaster Management:
The principles of disaster management are:
1. Disaster management is the responsibility of all spheres of government. No single service or department in itself has the capability to achieve comprehensive disaster management. Each affected service or department must have a disaster management plan which is coordinated through the Disaster Management Advisory Forum.
2. Disaster management should use resources that exist for a day-to-day purpose. There are limited resources available specifically for disasters, and it would be neither cost effective nor practical to have large holdings of dedicated disaster resources. However, municipalities must ensure that there is a minimum budget allocation to enable appropriate response to incidents as they arise, and to prepare for and reduce the risk of disasters occurring.
3. Organisations should function as an extension of their core business. Disaster management is about the use of resources in the most effective manner. To achieve this during disasters, organisations should be employed in a manner that reflects their day-to-day role. But it should be done in a coordinated manner across all relevant organisations, so that it is multidisciplinary and multi-agency.
4. Individuals are responsible for their own safety. Individuals need to be aware of the hazards that could affect their community and the counter measures, which include the Municipal Disaster Management Plan, that are in place to deal with them.
5. Disaster management planning should focus on large-scale events. It is easier to scale down a response than it is to scale up if arrangements have been based on incident scale events. If you are well prepared for a major disaster you will be able to respond very well to smaller incidents and emergencies, nevertheless, good multi agency responses to incidents do help in the event of a major disaster.
6. Disaster management planning should recognise the difference between incidents and disasters. Incidents, e.g., fires that occur in informal settlements, floods that occur regularly, still require multi-agency and multi-jurisdictional coordination. The scale of the disaster will indicate when it is beyond the capacity of the municipality to respond, and when it needs the involvement of other agencies.
7. Disaster management operational arrangements are additional to and do not replace incident management operational arrangements. Single service incident management operational arrangements will need to continue, whenever practical, during disaster operations.
8. Disaster management planning must take account of the type of physical environment and the structure of the population. The physical shape and size of the Municipality and the spread of population must be considered when developing counter disaster plans to ensure that appropriate prevention, preparation, response and recovery mechanisms can be put in place in a timely manner.
9. Disaster management arrangements must recognize the involvement and potential role of non-government agencies. Significant skills and resources needed during disaster operations are controlled by non-government agencies. These agencies must be consulted and included in the planning process.
Goal of Disaster Management:
1. Reduce or avoid losses from hazards
2. Assure prompt assistance to victims
3. Achieve rapid and effective recovers.
Essay # 7. Financial Agreements for Disaster Management:
Financing of Relief Expenditures :
The policy arrangements for meeting relief expenditure related to natural disasters are, by and large, based on the recommendations of successive finance commissions. The two main windows presently open for meeting such expenditures are the Calamity Relief Fund (CRF) and National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF). The Calamity Relief Fund is used for meeting the expenditure for providing immediate relief to the victims of cyclone, drought, earthquake, fire, flood and hailstorm.
Expenditure on restoration of damaged capital works should ordinarily be met from the normal budgetary heads, except when it is to be incurred as part of providing immediate relief, such as restoration of drinking water sources or provision of shelters etc., or restoration of communication links for facilitating relief operations.
The amount of annual contribution to the CRF of each State for each of the financial years 2000-01 to 2004-05 is as indicated by the Finance Commission. Of the total contribution indicated, the Government of India contributes 75 per cent of the total yearly allocation in the form of a non-plan grant, and the balance amount is contributed by the State Government concerned. A total of Rs.11,007.59 crore was provided for the Calamity Relief Fund from 2000-05.
Pursuant to the recommendations of the Eleventh Finance Commission, apart from the CRF, a National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF) Scheme came into force with effect from the financial year 2000-01 and would be operative till the end of the financial year 2004-05.
NCCF is intended to cover natural calamities like cyclone, drought, earthquake, fire, flood and hailstorm, which are considered to be of severe nature requiring expenditure by the State Government in excess of the balances available in its own Calamity Relief Fund.
The assistance from NCCF is available only for immediate relief and rehabilitation. Any reconstruction of assets or restoration of damaged capital should be financed through re-allocation of Plan funds. There is need for defining the arrangements in this regard.
The initial corpus of the National Fund is Rs.500 crore, provided by the Government of India. This fund is required to be recouped by levy of special surcharge for a limited period on central taxes. An amount of about Rs.2,300 crore has already been released to States from NCCF. A list of items and norms of expenditure for assistance chargeable to CRF/NCCF in the wake of natural calamities is prescribed in detail from time to time.
Financing of Disaster Management through Five Year Plans :
Although not specifically addressed in Five Year Plan documents in the past, the Government of India has a long history of using funds from the Plan for mitigating natural disasters. Funds are 11 provided under plan schemes i.e., various schemes of Government of India, such as for drinking water, employment generation, inputs for agriculture and flood control measures etc.
There are also facilities for rescheduling short-term loans taken for agriculture purposes upon certification by the District/ State administration. Central Government’s assets/ infrastructure are to be repaired/rectified by the respective Ministry/Department of Government of India.
Besides this, at the occurrence of a calamity of great magnitude, funds flow from donors, both local and international, for relief and rehabilitation, and in few cases for long- term preparedness/preventive measures. Funds for the latter purposes are also available from multilateral funding agencies such as the World Bank. These form part of the state.
There are also a number of important ongoing schemes that specifically help reduce disaster vulnerability.
Some of these are:
a. Integrated Wasteland Development Programme (IWDP),
b. Drought Prone Area Programme (DPAP),
c. Desert Development Programme (DDP),
d. Flood Control Programme,
e. National Afforestation and Eco-development Programme (NA & ED),
f. Accelerated Rural Water Supply Programme (ARWSP),
g. Crop Insurance, Sampurn Grameen Rozgar Yojana (SGRY),
h. Food for Work etc.
Initiatives Proposed by Various Bodies Regarding Financing under the Plan :
References have recently been made to the role of the Plan in disaster management by the High Power Committee (HPC) on Disaster Management, as well as by the Eleventh Finance Commission. The HPC was constituted in 1999 and submitted its Report in October 2001. The HPC took an overview of all recent disasters (natural as well as manmade) in the country and identified common response and preparedness mechanisms on the basis of a series of consultations with a number of government, non-government, national and international agencies and media organisations.
An important recommendation of the Committee was that at least 10 per cent of plan funds at the national, state and district levels be earmarked and apportioned for schemes which specifically address areas such as prevention, reduction, preparedness and mitigation of disasters.
The Eleventh Finance Commission too paid detailed attention to the issue of disaster management and, in its chapter on calamity relief, came out with a number of recommendations, of which the following have a direct bearing on the Plan:
1. Expenditure on restoration of infrastructure and other capital assets, except those that are intrinsically connected with relief operations and connectivity with the affected area and population, should be met from the plan funds on priority basis.
2. Medium and long-term measures be devised by the concerned Ministries of the Government of India, the State Governments and the Planning Commission to reduce, and if possible, eliminate, the occurrences of these calamities by undertaking developmental works.
3. The Planning Commission, in consultation with the State Governments and concerned Ministries, should be able to identify works of a capital nature to prevent the recurrence of specific calamities. These works may be funded under the Plan.
Essay # 8. Challenges in Disaster Management:
Logistics and supply chain management underpin responses to humanitarian crises. Disaster management cannot be handled by single agency.
Following are the real factors that affect the most in any location:
1. Reconstruction challenges
2. De-forestation
3. Climate change
4. Geographical locations
5. Speed of delivery
6. Movement of people from disastrous zones
7. Influx of humanitarian staff
8. Gaps in NGO capacity
9. Funding biasness
10. Lack of depth in knowledge
11. Lack of investment in technology and communication
Essay # 9. Role of Indian Armed Forces and Government in Disaster Management:
Role of Indian Armed Forces in Disaster Management:
Whenever a disaster strikes, either it is natural or man-made, the Indian armed forces are called upon to handle the situation. They are always ready to move to any kind of disaster- affected areas and have the guts to work under adverse conditions.
India is one of the most vulnerable nations in the world, susceptible to multiple natural disasters owing to its unique topographic and climatic conditions. Its coastal states, particularly the eastern coast and Gujarat are exposed to cyclones, 40 million hectares (eight per cent) of land mass is flood prone, 68 per cent faces drought threat, 55 per cent of the area is in seismic zones III-IV and falls under earthquakes-prone belt and sub-Himalayan region and Western Ghats are threatened by landslides.
Moreover, India is increasingly getting susceptible to man-made disasters related to industrialization, transportation, environmental degradation and terrorist attacks. Besides, there is no legal ratification either at the Union or the state governments level to deal with such disasters in comprehensive manner as the subject of disaster management is not specified under any of the three lists (Central, state and concurrent) of Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
The government of India is aware of the urgent need for better disaster response mechanism, but the overall trend in the nation has indicated that the level of preparedness of the Centre as well as the states is extremely uneven and requires considerable strengthening.
Fortunately, the Centre and a number of states have displayed growing appreciation for the need of effective disaster management strategies. Of late, the nodal agency for coordination of relief, response and overall natural disaster management is positioned under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
However, when any disaster occurs in India, the armed forces under the Ministry of Defence are called upon to intervene and handle the situation. As the development oriented Indian Civil Administration is ill equipped for undertaking disaster response activities in the event of major disasters, they merely rely on the armed forces.
At the same time, the Indian armed forces, being one of the most dedicated, professional, modernised armed forces in the world with rapid strides in technology development, adequately equipped with the necessary technical competence, man power and material resources undertakes rescue and relief operations of any disasters.
For instance, when tsunami occurred in December 2004, the Indian army, navy and the air force coordinated by the Integrated Defence Staff (IDS) efficiently executed the relief, rescue and evacuation assignments under Operation Sea Wave, and also extended aid to Sri Lanka and Maldives under Operation Rainbow and Operation Castor at the request of their respective governments for assistance.
Whether the Kashmir earthquake of 2005, the cyclone in Bangladesh on 15 November, 2007, the fire breakout at Burrabazar in Kolkata on January 12, 2008, or the recent serial blasts at Bangalore and Ahmedabad on July 2008, the role played by the Indian armed forces is commendable.
Above and beyond its primary role, i.e., to defend the nation against any external aggression the Indian armed forces are inevitably involved in securing the country from diverse unconventional fronts. They are always in the state of operational readiness to move to any kind of disaster-affected areas and have the daring to work under adverse ground and climatic conditions, which is of immense help in assisting the civil authority during disasters.
Their performance in rescue and response action after disasters has been exemplary and with the ever increasing frequency of disasters in the South Asian region, they will continue to play a vital role in the years to come.
Furthermore, in spite of the disaster rescue and relief responsibilities, there is need for decisive modus operandi for operational coordination between the civil administration and the armed forces. Since, the armed forces’ effective response depends on immediate information made available by the state administration, delay in information has often caused loss of precious time due to lack of proper communication and coordination with the civil authority and concern for loss of lives. In this regard, the state institutions must appreciate the operational line of action in which the armed forces function.
The armed forces professional ethics are autonomous in character and do not encourage civil interference. At the same time, the armed forces need to acknowledge that the source of primary information for disaster response lies with the state.
As disaster management plan should incorporate the role expected of the armed forces so that the procedure for deploying them is well-organized, there is a need to encompass an interface personnel correlation between the state government and the armed forces for immediate effective delivery of relief to the victims affected by disasters.
Role of Government in Disaster Management:
i. Funding Mechanisms:
The policy and the funding mechanism for provision of relief assistance to those affected by natural calamities is clearly laid down. These are reviewed by the Finance Commission appointed by the Government of India every five years. The Finance Commission makes recommendation regarding the division of tax and non-tax revenues between the Central and the State Governments and also regarding policy for provision of relief assistance and the share of expenditure thereon.
A Calamity Relief Fund (CRF) has been set up in each State as per the recommendations of the Eleventh Finance Commission. The size of the Calamity Relief Fund has been fixed by the Finance Commission after taking into account the expenditure on relief and rehabilitation over the past 10 years.
The Government of India contributes 75% of the corpus of the Calamity Relief Fund in each State. 25% is contributed by the State. The requirement of funds for response and relief is met from the CRF. Overall norms for relief assistance are laid down by a national committee with representatives of States as members.
Different States can have State-specific norms to be recommended by State level committee under the Chief Secretary. Where the calamity is of such proportion that the funds available in the CRF will not be sufficient for provision of relief, the State seeks assistance from the National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF).
When such requests are received, the requirements are assessed by a team from the Central Government and thereafter the assessed requirements are assessed by a Central team and thereafter the requirements are placed before an Inter-Ministerial Group chaired by the Home Secretary.
A High Level Committee chaired by the Home Minister with the Agriculture Minister, Finance Minister and the Deputy Chairman Planning Commission take decision regarding the release of assistance from the NCCF based on the report of the Central Team and the recommendations of the IMG thereon. In brief, the institutional arrangements for response and relief are well established and have proved to be robust and effective.
ii. Role of Central Government :
At the national level, the Ministry of Home Affairs is the nodal Ministry for all matters concerning disaster management except drought, which continues to be handled by the Ministry of Agriculture. The Central Relief Commissioner (CRC) in the Ministry of Home Affairs is the nodal officer for coordinating relief assistance for the natural and manmade disasters.
The CRC receives information relating to forecasting/warning of a natural calamity from India Meteorological Department (IMD) or from Central Water Commission of Ministry of Water Resources on a continuing basis. These forecasts are also concurrently passed on to the State by the Agencies responsible for early warning.
Whenever assistance is required by the States for handling a natural calamity, the assistance is coordinated by the Ministry of Home Affairs. Nodal Officers have been appointed in each Ministry/Department responsible for emergency support functions in the event of a disaster. The Central Relief Commissioner coordinates with the Nodal Officers to ensure that the requisite assistance is made available to the State.
Essay # 10. National Policy on Disaster Mana gement:
Despite the fact that we lose thousands of lives and property worth thousands of crores each year in disasters, we have not had a National Policy on Disaster Management. Where a number of Ministries or where a broad segment of Government is involved; it is useful to have a National Policy as it serves as a framework for action by all the relevant Ministries/ Departments. A National Policy on Disaster Management has been drafted. In line with the changed focus, the policy proposes to integrate disaster mitigation into developmental planning.
Institutional Changes :
The primary objective is to change the focus from relief and rehabilitation to mitigation and preparedness. MHA is working towards putting in place institutions which will reflect this holistic approach. The States have been advised (HS had written to all Chief Secretaries and the former Dy.
Prime Minister has also written to all Chief Ministers in this regard) to convert their Departments of Relief and Rehabilitation into Department of Disaster Management. 10 States/UTs: Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, Nagaland, Andaman & Nicobar Administration and Lakshadweep have already acted on this.
The exercise of reducing vulnerabilities of mitigation or of preparedness or in fact of response is multi-disciplinary. It involves a number of Ministries/ Departments. Unfortunately, till date all Departments have had the feeling that disaster management/response is the responsibility of the Department of Relief and Rehabilitation alone.
The States have, therefore, been advised to set up Disaster Management Authorities under the Chief Minister with the Ministers of Water Resources, Agriculture, Home, Health, PWD, Animal Husbandry, Urban Development and other Ministers who may be relevant as members. 11 States and UTs: Tamil Nadu, Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Orissa, Gujarat, Kerala, Nagaland, Delhi, Goa, A&N administration and Chandigarh Administration have notified the authority.
The other States are in the process of setting up similar authorities. At the National level, a National Emergency Management Agency is being set up. The proposal for setting up NEMA and building up specialised capabilities was considered by the Committee of Secretaries (COS) on 21st April, 2004. Based on the recommendations of the COS, the Note for the Empowered Group of Ministers on Disaster Management is being revised for submission to Home Minister for approval.
Disaster Management Codes :
In line with the changed approach, we are converting the Relief Codes into Disaster Management Codes by building into it the process necessary for drawing up disaster management and mitigation plans as well as elements of preparedness apart from response and relief. A Committee constituted under the Executive Director, National Institute of Disaster Management is expected to submit the draft to the Ministry by 30th June, 2004.
Essay # 11. Awareness Programmes for Disaster Management:
i. School Safety Programme :
An Initiative under Govt of India (GOI) and UNDP Disaster Risk Management Programme:
The School Safety Programme under the GOI-UNDP Disaster Risk Management Programme essentially targets in promoting a culture of safety in school and draw in the commitment of providing safe learning environment for children and education professionals.
Primary strategies are to help inform, persuade, and integrate the issues of safety to create safe schools, while the goal of the programme is to promote a culture of disaster preparedness in the school community. The objective is to sensitize children and the school community on issues of disaster preparedness and safety measures and to motivate key stakeholders through direct participation in activities that would foster towards a disaster resilient community.
The School Safety Programme includes a series of ongoing activity. Following is the list of activity undertaken to create safe schools — placing of school safety in the education agenda —awareness raising, education, training and capacity building of the Government Officials, Educational Administrators, Teachers.
Students, Engineers, Masons, parents and community — development of School Disaster Management Plan / building level emergency response plan and practicing through mock drills — structural and non-structural mitigation (incorporate structural safety parameters into the new constructions) knowledge networking and capacity building of the institutions to address the challenge.
The programme is spearheaded by the School Safety Advisory Committee/ School Disaster Management Committee supported by representatives from all sections of the school community Educational Administrators, School Administrators, Emergency officials, Civil Defence, Engineering / Public Works Department, Local Administration Officials, Health and Emergency Response Officials and the local community.
The implementation framework and the programme strategies have been highlighted in the School Safety Handbook. The programme draws in key risk reduction elements and it encompasses-preparedness and mitigation measures.
ii. Safety Awareness Programs:
Objectives:
The purpose of Safety Awareness Programs is to promote interest, increase safety awareness, and gain acceptance of safe work practices. The aim is to secure maximum employee participation through the effective use of media and individual or group recognition. The cooperation of the local safety and health committee in the promotion of safety is to be encouraged.
Local Needs :
Effective promotional programs must be based on a thorough study of local needs. Accurate planning and analysis are essential to achieve program objectives.
Districts, plants, and other installations should procure or develop and distribute posters, publications, films, bulletins, pamphlets, newsletters, displays, etc., based on current and projected accident trends. The display of safety posters distributed by Headquarters must be kept current. Budgeting for safety promotional needs must be included in program planning.
Implementing 7 Steps to School Safety:
1. Develop and equitably enforce a Code of Conduct for the district and building :
School district must have a Code of Conduct that is updated annually. Students and parents are all given a copy of this booklet at the beginning of the year. Additionally, the assistant principal also reviews the contents of the code of conduct in an assembly with students at the beginning of the year.
Students and parents are required to sign and return a form acknowledging the understanding of its contents as well. Teachers are also given training during staff development on the proper procedures for filling out referral forms for breaches of the code of conduct and for the proper protocol for handling classroom removals.
2. Develop district safety plans and building emergency response plans to deal with serious situations and conduct drills, table tops and functional exercises to increase the level of preparedness. School regularly holds practice drills to ensure that students and staff are familiar with the proper procedures and protocols for emergency situations. Substitute folders are also equip with information and protocols for handling emergency situations for whenever there is a substitute teacher in the building.
3. Personalize the school environment:
School personalized its environment by having students in the school Tech class build “Help Boxes”. These colorful boxes have been placed throughout the school building. Students can fill out an anonymous “help slip” if they have a problem that they need help with and drop it in the locked box.
If the student chooses to include their name, one of the school counselors will address the issue with them discreetly. Anonymous issues are usually read aloud during the morning announcements, and a suggestion for handling the issue is offered by the principal.
4. Analyze Violent and Disruptive Incident Reports (VADIR) and other student conduct data to provide information regarding pockets of concern that require attention and program strengths that could be replicated. As mandated reporters to this system, our district has a SAVE team that meets regularly to address these reports. Data from these reports issued to help revise and update our district annual Code of Conduct.
5. Implement programs and activities that have a proven record of achieving positive results; Evaluate programs periodically for their effectiveness and potential improvement. District has annually provided an after school program for students. This program provides homework help as well as elective type courses where students can engage in activities that are of interest to them.
Additionally, city also has two other community based programs affiliated with the district where students can go for after school support. Finally, local library also has a homework help program for elementary students. For two hours after school daily, these students can simply drop by with their homework and receive assistance from certified teachers for free.
6. Actively involve and engage parents and other community members in addressing issues and concerns. School must maintain a policy of communicating with parents whenever there is an incident of misconduct. Teachers are required to inform parents via phone or email communication whenever there is an incident of concern in the classroom. Administrators also actively contact parents whenever a referral is issued. Additionally, the district also has attendance teachers that specifically address attendance and truancy issues.
7. Make sure students, teachers, parents, administrators, and other school staffs are aware of warning signs of violence and the need to communicate to others.
Warning signs of youth violence that have been seen as an educator include:
1. Anger and aggression toward other students and adults
2. Isolating oneself from friends and loved ones
3. Arguing with group members during paired group activities
4. Complaints from other students about behaviour or language
5. Bullying behaviors
6. Attempting to justify violence as rough “horseplay”
7. Students bullying their parents or sibling in the home environment
8. Signs of gang affiliation
9. Frequent bruises or disheveled appearance
10. Long sleeves, coats during hot weather could be signs of a self-mutilator (cutting on various parts of the body).
Related Articles:
- Institutional Framework of Disaster Management in India | Geography
- Phases of Disaster Management Cycle (With Diagram) | Disaster Management
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) | India | Disaster Management
- Role of Various Agencies in Disaster Management | India
Essay , Geography , Disaster Management , Essay on Disaster Management
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Essay on Disaster Management: 122 Topics + Writing Guide
Without a doubt, a natural disaster essay is a tough paper to write.
To begin with, when people encounter a disaster risk, it’s a tragedy. Emergency situations can affect hundreds, thousands, and millions of people. These are the crises and events that change people’s lives drastically. So, disaster and emergency management essay topics aren’t that fun to discuss.
Moreover, an essay on disaster management requires thorough research. Mentioning how people handle natural hazards and recovery from such tragedies is essential for the paper. But you can approach the discussion from different sides.
In this article, our experts will help you with the following:
- How to nail disaster management essay writing.
- What to write your paper about.
- Types of disaster management and their importance.
And good luck!
- 👨💼 Disaster Management Definition
✍️ Disasters to Write About
- 🌎 Essay Topics
- ❓ Essay Questions
- 🔥 Essay Title Ideas
- 📑 Writing Guide
- 🖊️ Essay Example 300 Words
🔗 Resources
👨💼 essay on disaster management: what is it about.
What is natural disaster management , anyway? What is the role of adults and youth in it?
Disaster management is the management and organization of responsibilities and resources. Its goal is to deal with the humanitarian aspects of an emergency. Put simply, how to help victims of natural disasters.
There are five stages of the disaster management process:
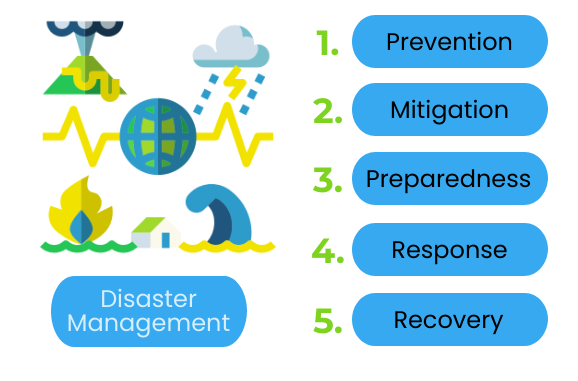
Let’s see what each of these stages entails.
The name of this stage explains its purpose. Its primary focus is on preventing hazards and potential natural disasters.
Measures are usually taken on different scales, including international and domestic levels. They’re designed to provide reliable protection from possible disasters.
Of course, it isn’t possible to stop all disasters. But there’s always a chance to minimize the risks of injuries and loss of life. All thanks to environmental planning, evacuation plans, and the introduction of specific design standards.
Mitigation measures are those that are taken before a disaster or emergency happens. It aims to reduce or eliminate the risks and impact a hazard can have on people and the environment.
Mitigation measures come in different forms depending on the hazard itself.
Here are some examples of possible actions:
- Structural changes to buildings
- Securing items inside buildings
- Installation of generators
- Construction of shelters
- Large-scale mitigation measures on the national level
- Preparedness
The focus of this stage is to prepare supplies and equipment. It also involves developing usage procedures when a disaster happens.
The primary goal is to reduce the level of people’s vulnerability to a disaster. Also, to mitigate a disaster’s impact. And to be able to have a more effective response in case of an emergency.
Organizations like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) even develop a disaster management plan. They also make disaster supply kit lists. Other agencies and organizations use them to teach people how to help each other. Or they modify those plans to increase their effectiveness. Those can be found on the web in the form of downloadable PDF files or printed handouts.
The response stage aims at fulfilling the humanitarian needs of the population affected by a disaster. Depending on the consequences, anyone can provide such assistance, including individuals, social workers, organizations, national and international agencies.
The most important part of the proper response is the effective coordination of assistance, especially if there’s a misbalance in the amounts of demand and the available answers.
In the case of massive and overwhelming disasters, donations play a crucial role in the response process. They range from all kinds of gifts to money (which is the most efficient type of assistance).
The question is: can communities recover after the disaster happens?
The recovery stage begins after the threat to human life is gone. The goal here is to bring the affected area back to normal condition as quickly and efficiently as possible.
This stage usually involves numerous processes—reconstructing buildings, refilling food availability, and preparing the equipment.
As we’ve mentioned earlier, disasters are divided into two categories—natural and man-made.
| Natural Disasters | Man-Made Disasters |
|---|---|
| Natural disasters happen regardless of human actions. | Man-made disasters are hazards caused by humans. |
| With resources and possibilities, the reduction of disaster risk is minimal; | Natural calamities might be made worse by humans. A wrong response to the disaster, or lack of such, might cause severe damage. |
| Cause damage to property, physical damage, and deaths. | Cause damage, loss of life, and property. Additionally, it might cause evacuation from certain areas and overuse of health resources in the affected regions. |
🌪️ Natural Disasters
Natural disasters are phenomena or processes that occur due to a force of nature and hurt the environment and people. They can cause injuries, property damage, environmental damage, and loss of life or other health impacts.
There are two types of natural disasters—geological hazards (involving geological processes) and meteorological hazards (or climate hazards).
Geological Hazards
A geological hazard is an extreme natural event in Earth’s crust that represents a threat to life and property. Now, let’s take a closer look at them.
| Geological Hazards | Description |
|---|---|
| They are characterized by shaking or displacement of the ground. If it happens on the sea, an earthquake can often result in a tsunami. The cause of an earthquake is a sudden release of energy from lithospheric plates that lead to seismic waves. | |
| It’s a vast mass of snow or rock that slides down a mountain. This rapid slide or falling of material is due to the force of gravity. People usually consider the size of the avalanche and some harmful consequences caused by it. They use the information to classify this natural disaster. | |
| They are closely related to a volcanic eruption. It involves a large mass of material from a glaciated volcano eruption. It slides rapidly away from the volcano. The material usually includes rocks, ash, and mud from the melted ice. These kinds of flows are capable of destroying entire small towns, forming flood basalts. | |
| It involves shifting or changing of shorelines in coastal areas. Currents and waves usually cause coastal erosion. Those result from storm surges and tides. It can also be a consequence of severe tropical cyclones. Long-term processes like beach evolution are also a cause. | |
| It is a massive ground movement that can include slope failure, falling rocks, or debris flows. Landslides can also happen in coastal areas or underwater. The original driving force of such an event is gravity. But quite often, landslides are a cause of other factors that decrease the stability of slopes. | |
| It happens during the active state of a volcano. Eruptions may come in various forms. There can be small daily explosions or less frequent ones, but a much more considerable amount of material erupted. Apart from that, volcanoes can form pyroclastic flows. Those are hot clouds consisting of steam and ash. They descend from the mountain at very high speed. | |
| It is a localized depression in the surface. The most usual cause of sinkholes is the collapse of a subterranean structure (like a cave). They appear rarely, but suddenly. They can bring a great deal of damage to highly populated areas, especially with lots of buildings that can collapse. |
Meteorological Hazards
Meteorological hazards are calamities caused by extreme weather factors, such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed. So, let’s talk in more detail about these.
| Meteorological Hazards | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| It happens when hailstones (balls of ice) are produced during a thunderstorm. Hailstones are damaging to locations where they fall. The consequences are especially severe if the hailstorm rains down on a farm field. It can damage equipment and ruin crops. | |
| A blizzard is a severe storm in winter. It is characterized by heavy snow, strong winds, and low temperatures and usually lasts for three or more hours. And the speed of the wind is at least 35 mph. There’s also a ground blizzard. The snow isn’t falling but is instead lifted from the ground and blown around during it. | |
| This is a rare phenomenon that might be related to global warming. It involves masses of hot air appearing in an area where such temperatures are unusual. Or even extreme. Heatwaves arise due to a combination of multiple weather events. They include katabatic winds and temperature inversions. Building resilience is needed, as extreme heat is quite harmful. | |
| This is a period of low precipitation. It results in shortages of water supply, including atmospheric water, groundwater, and surface water. Droughts can last for quite a long time, ranging from months to years. It’s harmful to the region’s economy, agriculture, and ecosystem. | |
| It’s a type of winter storm that involves freezing rain. The main characteristic of an ice storm is that the ice accumulates on surfaces. The rain itself isn’t severe. And the temperature is just below freezing. But it can still bring a lot of damage. Glaze ice covers all the surfaces, adding extra weight. It results in fallen branches or even whole trees. The weight of the ice also snaps power lines and breaks power or utility poles. | |
| This phenomenon comes in different forms and under various names: typhoon, hurricane, a tropical cyclone. But all those names mean practically the same thing. This is a storm system that forms over the ocean because of evaporated water. The storm also spins due to the Coriolis effect. The average wind speed is 74 mph. This is probably one of the most common U.S. natural disasters. | |
| This natural disaster usually comes as a result of a thunderstorm. It’s a rotating air column. The airspeed in it ranges from 50 mph up to 300 mph (and sometimes even higher). They can appear one at a time or in clusters or outbreaks. Tornadoes can happen both on the land and over the water. It’s easy to find videos of this disaster online to understand how severe it can get. | |
| This is a temporary interruption of the planet’s magnetosphere. The primary cause of it is a solar wind shockwave. It forms a magnetic field cloud. And it goes into interaction with the magnetic field of the Earth. It can cause electrical systems disruptions and affect communication facilities, satellite, and navigation systems. | |
| This is an unplanned fire that burns uncontrollably. Wildfire can be a consequence of either natural events or human activity. Many natural phenomena can cause a fire. These include rockfall sparks, lightning strikes, volcanic eruptions, and spontaneous combustion. | |
| This is an overflow of water in typically dry areas. It usually happens due to rivers, lakes, or oceans spilling out of their boundaries. Or because of rainwater that accumulates on the saturated ground. Floods can have different development speeds, from slow ones to flash floods that can start in a matter of minutes. Numerous documental movies have enough evidence of floods being a severe issue for people, regardless of whether they live in a developed country or not. |
⚡ Man-Made Disasters
Man-made disasters (also known as anthropogenic) are events caused by the action or inaction of humans. These disasters also affect the environment, humans, other organisms, and ecosystems.
Let’s now move to describe disasters themselves to give you ideas for your future essay.
Societal Hazards
Most societal hazards can be prevented by taking proper measures and actions. These hazards usually appear due to anti-social and criminal behavior. It all can be reported if spotted at the right time.
| Societal Hazards | Description |
|---|---|
| This broad term covers any disturbance that involves many people that all have a common aim. Reasons for such disorders vary widely. The condition is mainly hazardous for specific groups of people: for those directly involved in it, for people controlling it, and for passers-by. For those staying out of the disorder, it’s usually not dangerous. | |
| Crimes involve behavior that imposes a risk of injury or death for other people. Another risk factor is the difficulty of preventing such actions. It depends on many factors, such as place and time. | |
| It is the use of violence to achieve individual goals. Threatening the use of violence is also considered terrorism. The intentions vary from ideological to religious and political. The greatest danger of terrorism is that anyone can be a target, from regular citizens to government officials. | |
| It’s a conflict between large groups of people that involves the use of weapons – war results in destroyed countries, cities, economies, and cultures. Wars can easily be considered some of the worst disasters in history, regardless of their origin. | |
| Engineering hazards include the failure of structures that people use. Or the use of hazardous materials. The failure can often be the result of the poor structural design. The involvement of inexperienced workers is another reason for it. The low quality of materials used can also cause an engineering hazard. | |
| Industrial hazards usually include accidents resulting from the release of hazardous materials. Those accidents often happen in a commercial context. They endanger the lives of people involved in the accident. Industrial hazards also have an environmental impact and can harm people close to the disaster. | |
| Even a fire that started as a result of natural events can turn into a man-made disaster, especially if people ignore it and don’t take any action to stop it. Fires can also start due to negligence or arson (starting a fire to cause damage). | |
| There’s a single major cause of this problem. It’s putting hazardous materials into commercial and domestic waste streams. | |
| This is an interruption of electrical energy sources. Short-term (up to a couple of hours) outages don’t have much of an adverse effect. At the same time, long-term ones influence personal and business activities. It can also cause emergencies in medical and rescue services. Extended power outages usually occur due to natural disasters such as hurricanes or floods. |
Hazards Related to Dangerous Materials
Dangerous materials released from man-made or natural hazards threaten human health by increasing the possibility of human exposure to hazardous materials. So, now, let’s take a look at them.
| Dangerous Materials Hazards | Description |
|---|---|
| Those include metals and salts of metals. Elements such as copper, mercury, lead, and transuranic metals, may expose humans to toxicity. It has a long-term negative influence on health. The longer the exposure—the worse the effect. | |
| This acronym is referring to chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear hazards. The term usually describes a terror threat with the usage of mentioned hazards. | |
| These are synthetic organic molecules that contain atoms of halogens. They were considered to be harmless when first produced. But they have a negative physiological effect on organisms in the long run. Some of the compounds are also soluble and can make it into the food chain. | |
| Such materials are capable of producing ionizing radiation, which has an extremely harmful effect on living organisms. Even a short exposure to radioactive materials can have long-term health consequences. |
Transportation Hazards
Transportation hazards include disastrous events that can happen anywhere. On the road, in aviation, on railways, in sea travel, and even in space. Several reasons can cause a crash, from mechanism malfunctions to trivial inattention or carelessness. Such catastrophes not only endanger the people involved in them. They also harm the environment, for example, when freight vehicles are involved.
Environmental Hazards
A man-made disaster is classified as environmental if it affects ecosystems and biomes. Such disasters include air pollution, uncontrollable deforestation, oil spills, and water pollution.
🌎 Disaster Management Topics for Essays
- The role of the government oeganizations in mitigation of natural disasters.
- Discuss how to address the needs and demands of vulnerable population in disaster management.
- Explain why earthquakes are among the most dangerous natural disasters.
- Natural disasters and the strategies of disaster management in Katmandu.
- Natural disasters and vulnerable health populations.
- Describe the ways to improve disaster response.
- Discuss the cases of post-disaster fraud and how to prevent them.
- Analyze the level of natural disaster preparedness in Texas.
- Compare international and South Africa’s disaster management.
- What disaster mitigation strategies can reduce the consequences of flash floods.
- Examine how natural disasters influence various systems.
- Describe the ways media responds to natural disasters.
- The vital role of SNS in a case of a disaster.
- Analyze ethical and legal issues that arise in case of a natural disaster.
- Explain why hurricane Katrina is considered one of the worst national disasters in the USA.
- Describe 2 different global disasters and explain their causes.
- Discuss the importance of emergency planner in effective disaster preparedness.
- Issues that may arise during rebuilding and recovery after natural disaster.
- The main aspects of safety and disaster training for healthcare workers.
- Analyze winter snow disaster in Philadelphia and its impact on the community.
- Describe the effect of natural disasters on the supply chain.
- Examine the reasons and consequences of the Budalangi flood.
- Explain why the 1900 Galveston hurricane is regarded as disaster management failure.
- Explain why the problem of wildfire in California is getting out of control.
- Discuss the response to the Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami .
- Compare and analyze the earthquakes in California and Armenia .
- What were the causes and consequences of Haiti earthquake.
- The management of evacuations from Gulf Coast hurricanes.
- Describe what the emergency response to a volcano eruption should be.
- Why was the blizzard of 1888 so deadly?
- Is it possible to avoid catastrophic drought?
- Analyze how media depicts droughts in Africa.
- Discuss economic and environmental consequences of earthquakes .
- The importance of proper training for an effective disaster management.
- Explain the meaning of “New Normal” concept after disaster.
- What steps should government take for better protection from wildfire?
- Basic aspects of disaster management in big cities.
- Analyze the issues and lessons of hurricane Katrina.
- Compare the preparedness and response strategies to Haiti and Japan’s earthquake.
- Describe tsunami causes and countermeasures.
❓ Essay-Type Questions on Disaster Management
- What is the role of community-based organizations in managing regional disasters?
- What are the major global trends in disaster management?
- How can we help children cope and adjust after a disaster?
- What are the pros and cons of AI technology in catastrophe management?
- What role does early warning play in disaster management?
- Why is family unification one of the critical issues in disaster planning?
- What are the social and economic consequences of natural disasters?
- What characterizes disaster management in developing countries?
- How does natural ecosystem restoration contribute to disaster risk reduction?
- What are the key components of a comprehensive disaster management plan?
- What are the problems associated with organizing international disaster relief efforts?
- Why is psychological support a critical component of post-disaster management?
- What key elements should hospital evacuation plans consider?
- What are the peculiarities of disaster management plans for people with disabilities?
- How can climate change adaptation strategies be used in disaster management?
- What are the benefits of the disaster management cycle ?
- What can a regular person do to help their community recover from a disaster?
- How can cyberattacks on critical infrastructure exacerbate disaster scenarios?
- What is the importance of international cooperation in disaster management?
- How can disaster management motivate individuals to be active in their own safety?
- What are the ethical considerations in providing humanitarian aid in a disaster zone?
- How can you help others who might be more vulnerable during disasters?
- What common mistakes do people make when preparing for a disaster?
- Why is it important to have a disaster plan for your family or community?
- What are the specific risks of highly populated urban areas during natural disasters?
- How can psychological support programs be effective in post-disaster recovery?
- What is the role of land-use planning in mitigating disaster risks?
- How can collaboration between hospitals improve response to disaster?
- Why is mitigation one of the most critical phases of disaster management?
- How can physiotherapists effectively contribute in disaster situations?
- What are the key aspects of disaster preparedness?
- Why is it critical to invest in technologies for improving disaster response strategies?
- Why do different types of disasters require different management strategies?
- What are the ethical considerations in disaster mitigation and recovery?
- Why is effective communication essential during and after a disaster event?
- What technologies and methods are used to warn people about impending disasters?
- What role can education programs play in preventing anthropogenic catastrophes?
- How can urban planning help to minimize the impact of disasters on cities?
- What are the most effective ways to stay safe during a flood?
- What is the connection between cultural diversity and disaster preparedness?
🔥 Disaster Title Ideas for Essays
- Explore the role of disaster preparedness in reducing the effects of disasters.
- Flood prevention measures and their importance in vulnerable regions.
- The efficiency of scientific methods and technologies in predicting volcanic activity.
- Write about the function of social workers in China’s disaster management programs.
- How past disaster experiences can help prevent future catastrophes.
- The effectiveness of reforestation programs in restoring ecosystems.
- Housing programs and their role in post-disaster recovery.
- Compare the US and UK disaster management systems.
- Earthquake-resistant materials and their role in mitigating damage during earthquakes.
- Evaluate the use of coastal infrastructure in protecting from wave surges.
- The potential of green infrastructure in preventing floods.
- Cultural heritage preservation and its role in disaster management.
- The use of the Incident Command System in effective disaster management.
- Study the factors leading to building collapses and measures to prevent such disasters.
- The role of volunteers in the disaster management process.
- Biodegradable disaster cleanup technology and its pitfalls.
- Ethics in the practices and policies of disaster management.
- Review the challenges for preserving cultural heritage in coastal areas affected by wave surges.
- Energy-efficient buildings and their role in temperature regulation.
- Assess the importance of community education in minimizing the impact of volcanic eruptions.
- The influence of economic disparities on post-disaster recovery.
- Insurance and its role in mitigating the financial impacts of disaster.
- The importance of vaccination programs in preventing pandemics.
- Man-made disasters and their prevention strategies.
- Review the key methods of protecting vulnerable populations during heatwaves.
- The role of NGOs and international aid in volcano recovery.
- Potential challenges of global disaster management systems.
- Study the key pitfalls of tourism disaster management.
- Evacuation plans and their use in minimizing the risks of wildfires.
- Look into the social-cultural aspects influencing community resilience to disaster.
- Circular economy principles and their application in waste management.
- Evaluate the importance of international collaboration in preventing biosecurity risks.
- Safety practices and regulations to prevent dam failures.
- The use of risk management protocols in chemical plant explosion prevention.
- Sustainable agriculture practices and their use in reducing soil erosion.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of emergency response plans during extreme heat events.
- Post-tsunami mental health support and its importance.
- The strategies for minimizing economic impact in regions with active volcanoes.
- Study how social networks can assist in coordination during disaster events.
- Cyclone disaster management system and its main issues.
- Review the core components of a disaster response and their peculiarities.
- The efficiency of investing in resilience to reduce the impact of future disasters.
📑 Essay on Disaster Management: How to Write
If you’re writing an essay on such a serious topic, a how-to guide will be of great help. Here, we explore the ideas and issues to explore in your paper and the way to organize it.
Check what information your natural disasters essay can include.
Start with the Basics
We skipped it in this post, but you shouldn’t do this in your paper.
When writing a natural disasters essay of 500 words, or 1000 words, it’s essential to start with some general facts:
- A natural disaster definition would be a good beginning. Tell about various types, too.
- You can also provide information about a national disaster of your choice.
- Talk about countries that suffer from it more frequently than others, like India, Japan, etc.
- You can also write a quick rundown of the latest natural disasters.
Don’t forget to make this part meaningful, leading to your thesis statement, where you state your position.
Go into More In-Depth Details
In the main body, provide specific details about the catastrophe you’ve decided to describe:
- the locations where it can happen,
- causes of natural disasters,
- effects this particular disaster can have (both on the environment and in people’s lives),
Elaborating on each issue, offer evidence. For example, the disaster’s effect on transportation, infrastructure, economy, and so on can be supported by worldwide statistics data. A previously made outline might be a great help here.
Another thing you can do:
You can compare the disaster in question with other ones of the same type. Talk about the damages caused by them and how people dealt with the aftermath. Provide a couple of examples to prove your point.
Be sure to provide as many details as possible. As a result, your essay is maximally useful.
Talk About Disaster Management
Now, you can pass on the details of handling the situation. To be more specific, you’re going to tell your readers what to do in case of a catastrophe.
In this part of your essay on disaster management, you will have to talk about its phases. They are:
We’ll talk more about disaster management later on in the article.
Make Your Disaster Essay Even More Helpful
Do you want to make your disaster management essay more informative and impressive? Then tell about various organizations that deal with managing disasters. These resources can also help natural disaster victims or those who want to be aware of all the necessary information if something terrible happens.
Say a few words about the following organizations:
- International Association of Emergency Managers
- PreventionWeb
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction
- FEMA Recovery Resources
- Disaster Resource Guide
- Disaster Assistance
- American Red Cross
- Habitat for Humanity
- The Salvation Army
- World Confederation for Physical Therapy disaster management resources
These resources provide information about the prevention of natural disasters and what types of assistance are available. How to find missing friends or family members? What are the ways of recovering after disaster strikes? There are also community resources that can help with recovery.
End on a High Note
You don’t want to frustrate your reader, leaving them with a bitter impression. No matter how long your natural disaster essay is – 200 words, 300 words, or a thousand. It’s crucial to deliver a positive message.
Here’s what you can do;
- Talk about the consequences. Tell about the lessons that catastrophic events you’ve described teach us, as human beings. Spreading awareness about the consequences is essential, especially if we talk about man-made disasters. You might mention the role of the media in spreading awareness about environmental disasters.
- Talk about dealing with disasters. It might be a natural disaster, such as a tsunami, or human-made, like the Chernobyl disaster. Your essay should include info about how people dealt with them. The experience individuals get from dealing with disasters is priceless.
- Mention the value of human life. Encountering natural disasters reminds people of how fragile their lives are. It shows the importance of cherishing the life given.
In the end, you’ll have to summarize your essay and restate your thesis. While you try not to leave a negative message, don’t present any new thoughts or concepts. Draw a clear conclusion from the info mentioned in the body.
🖊️ Natural Disasters Essay 300 Words
Check out our essay example on natural disasters below to learn more about structuring your paper. And if you want more examples, try our free Chat GPT Essay Writer to generate a custom-made disaster essay sample tailored to your requirements.
Hurricane Katrina: Disaster Management Strategies
Introduction
In August 2005, Hurricane Katrina hit the southeastern United States. It became one of the most devastating natural disasters in the history of the country, resulting in 1,833 fatalities and $108 billion in damage . The experience learned from Hurricane Katrina, including both successes and failures, provides important insights for improving disaster management strategies.
Among the effective measures implemented were immediate rescue and social media coordination. Despite initial logistical challenges, the quick deployment of rescue teams, including the Coast Guard and volunteer organizations, saved countless lives. At the same time, social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook have become effective tools for spreading information as well as reuniting families and organizing volunteers. The emergence of crowdfunding websites such as GoFundMe also helped affected communities and families by providing them with financial support.
Despite all efforts, Katrina also revealed shortcomings in disaster response and preparedness. Levee failures, in particular, which are a result of inadequate infrastructure, made the flooding more destructive. Besides, the government faced long-term recovery challenges due to bureaucratic obstacles. There were also challenges caused by inequitable resource distribution and limited access to mental health services. All these factors made reconstruction more difficult and isolated some communities, which highlighted the need for more inclusive and equitable strategies for recovery.
The struggle with the consequences of Hurricane Katrina became a lesson for the United States and the whole world. Recognizing both successful and unsuccessful strategies allows us to draw important conclusions for the next decades. In the event of future disasters, it will be crucial to prioritize community-based preparedness, efficient communication, a robust infrastructure, and equitable resource distribution to boost resilience and save more lives.
Want to see a fully-formatted natural disasters essay sample? Feel free to download it in PDF format below:
The inevitability of natural disasters and the frequent occurrence of human-made disasters necessitate well-planned effective emergency management approaches that employ functional and cost-efficient methods. Since disasters entail multiple financial losses, property damage, and most importantly, impose a significant threat to human health and life, medical preparedness constitutes a pivotal part of the disaster management process.
Hopefully, you’ve found this guide on natural disaster essay writing useful.
If you have any thoughts on writing disaster essays—make sure to leave a comment about it below. You can also leave a comment if you want to share more disaster resources. Have any questions, suggestions, or even a story to tell? Leave a comment!
This might be interesting for you:
- Efficient Essays on Environment vs. Development: Useful Tips
- Responsibility Essay: How to Write, Topic Ideas and Examples
- How to Write a Narrative Essay: Easy Guide and Useful Tips
- What is a Disaster?
- Natural Disaster
- Has volcanic activity been increasing?
- What is disaster management?
- What is a Disaster Management Specialist?
- Disaster Planning
- Types of Disasters
- Effects of Disasters: Risk and Resilience Factors
- Proper Emergency Kit Essential to Hurricane Preparedness
- Preventing Natural Hazards From Becoming Societal Disasters
- Natural hazards and disaster risk reduction
- Disaster Preparation and Recovery
- Emergency Response Resources
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Exemplification essays, which are also called illustration essays, are considered one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the easiest tasks require some experience and practice. So, if you are not experienced enough in writing exemplification essays, you will face certain challenges.

You push the snooze button once again and finally open your eyes. It is already 8:50, and your classes start at 9. “I’m going to be late again!”— you think, already in full panic mode. In a minute, you rush out the door half-dressed, swallowing your sandwich on the go. ...

An essay about Harriet Tubman is to focus on the biography and accomplishments of a famous American abolitionist and political activist of the 19th century. Harriet Tubman was born into slavery, escaped it herself, and helped others escape it. She changed many jobs throughout her lifetime, being a housekeeper, a...

What is a documented essay and what is the purpose of it? It is a type of academic writing where the author develops an opinion relying on secondary resources. A documented essay can be assigned in school or college. You should incorporate arguments and facts from outside sources into the...

What is a reflexive essay? If you have just received the assignment and think there is a typo, you’re in the right place. Long story short, no, there is no mistake. You actually need to write a reflexive essay, not a reflective one. The thing is that reflective and reflexive...

Fairies and evil spirits, noble kings and queens, beautiful princesses and brave princes, mysterious castles and abandoned huts somewhere in a thick a wood… This is all about fairy tales. Fairy tales are always associated with childhood. Fairy tales always remind us that love rules the world and the Good...

Subjective or objective essay writing is a common task students have to deal with. On the initial stage of completing the assignment, you should learn how to differentiate these two types of papers. Their goals, methods, as well as language, tone, and voice, are different. A subjective essay focuses on...

Writing All About Me paragraph is probably one of the most usual assignments. For example, students might write it when entering an academic institution. Such work gives an opportunity to introduce yourself, your skills, and goals. However, it is not the only possible situation.

Coral reefs can be called one of the most amazing things created by nature. These structures can be found in tropical and temperate waters. Like many other unique natural phenomena, coral reefs are influenced by human activity these days. This negative impact is one of the significant issues to consider when...

An ambition essay focuses on one’s strong desire to achieve success in one or several areas. It might be one’s career, finance, family, art, health, or all at once. Writing an ambition essay, you might want to consider your own life or examples from the world literature. You can describe...
![essay a rc disaster management centre is at Essay for Primary School: Simple Guide for Kids [with Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/pupils-raising-hand-classroom-284x153.jpg)
The age of primary school students ranges from 5 to 11 years. At this stage of education, children start developing their writing skills. They make their first steps to analyzing and proving their points of view. Besides, they study how to write an essay for elementary school. Correctly preparing all...

Canadian identity is something that has become really important for many Canadians in the past fifty years. Canada is a big, multinational country with its own traditions, culture, and history. However, because of quite a large number of foreigners and even Americans, its culture and people are associated with the...
It’s really superb!
Wow. It is very helpful. Thanks.
What is the most effective process of prevention disasters?

It’s quite a complex process, and there’s definitely more than one choice.
Thank you a lot. I found this post very helpful in writing my essay on disaster management. Best regards, Michael
Thanks for the excellent guide to writing an essay on disaster management. Very helpful points to include in a disaster management paper! I wish you good luck!

Essay on Disaster Management
Disasters, whether natural or human-made, can strike without warning, causing immense destruction and suffering. Disaster management is a crucial process that involves preparing for, responding to, and recovering from these catastrophic events. In this essay, we will explore the vital importance of disaster management, its key components, and the role it plays in safeguarding lives and communities.
Understanding Disaster Management
Disaster management encompasses a range of activities aimed at reducing the impact of disasters. It involves planning, organizing, coordinating, and implementing measures to protect people, property, and the environment.
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, can have devastating consequences. Effective disaster management helps communities prepare for these events and respond swiftly when they occur.
Preparedness and Planning
A crucial aspect of disaster management is preparedness. Communities must develop emergency plans, conduct drills, and establish communication systems to ensure a coordinated response in times of crisis.
Response and Rescue
When disaster strikes, immediate response and rescue efforts are essential. Trained professionals and volunteers work tirelessly to save lives, provide medical care, and offer shelter to those affected.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery is a long-term process that follows the initial response phase. Communities must rebuild infrastructure, restore essential services, and support the emotional and psychological well-being of survivors.
Mitigating Risk
Disaster management also involves measures to reduce the risk of disasters. This includes land-use planning, building codes, and environmental conservation to minimize the impact of future events.
Human-Made Disasters
Human-made disasters, such as industrial accidents, terrorist attacks, and nuclear incidents, require a different approach to disaster management. It involves prevention, preparedness, and response strategies tailored to these specific threats.
Technology and Early Warning Systems
Advances in technology have improved disaster management. Early warning systems, weather forecasts, and satellite imagery help predict and monitor natural disasters, giving communities more time to prepare.
The Role of Governments
Governments play a central role in disaster management. They allocate resources, create policies, and coordinate efforts at the local, regional, and national levels. Government agencies like FEMA in the United States are dedicated to disaster response and recovery.
Community Involvement
Disaster management is a collective effort that involves individuals, communities, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and international agencies. Community participation is vital for a resilient response.
Lessons from Past Disasters
Studying past disasters provides valuable lessons for disaster management. It helps identify weaknesses in response and recovery efforts and informs improvements for the future.
Global Collaboration
Disasters can transcend borders, requiring international collaboration. Organizations like the United Nations and the Red Cross work together to provide aid and support to affected regions worldwide.
Conclusion of Essay on Disaster Management
In conclusion, disaster management is a critical process that saves lives, reduces suffering, and safeguards communities. It encompasses preparedness, response, recovery, and risk reduction strategies that are essential for addressing both natural and human-made disasters. As we witness the increasing frequency and severity of disasters in our changing world, the importance of effective disaster management cannot be overstated. It is a shared responsibility that requires cooperation at all levels of society. By investing in disaster preparedness and response, we can protect lives and ensure a more resilient and secure future for ourselves and generations to come. Disaster management is not merely a choice; it is a necessity for the safety and well-being of our global community.
Also Check: The Essay on Essay: All you need to know

- Classroom Programme
- Interview Guidance
- Online Programme
- Drishti Store
- My Bookmarks
- My Progress
- Change Password
- From The Editor's Desk
- How To Use The New Website
- Help Centre
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
- Disaster Management
Make Your Note
Disaster Management–I
- 10 Jun 2019
- 15 min read
- GS Paper - 3
- Important Geophysical Phenomena
Why in News?
- In May 2019, more than 20 young people died due to a deadly fire at a coaching centre in Surat.
- According to National Crime Records Bureau data, India’s record is appalling on fire safety. More than 17,000 people nationwide died in fire related incidences in 2015.
- These tragedies highlight the gaps in Disaster Management framework of India.
- In this context, there is a need to understand the various facets of Disaster Management and what should be done for fixing accountability and updation of disaster management protocol countrywide.
What is a Disaster?
- A disaster is a result of natural or man-made causes that leads to sudden disruption of normal life, causing severe damage to life and property to an extent that available social and economic protection mechanisms are inadequate to cope.
- It is an undesirable occurrence resulting from forces that are largely outside human control. It strikes quickly with little or no warning and requires major efforts in providing statutory emergency service.
Classification of Disasters
- Disasters are classified as per origin, into natural and man-made disasters. As per severity, disasters are classified as minor or major (in impact).
- Natural disasters can be broadly classified into categories including geophysical such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions; hydrological such as floods; meteorological such as hurricanes; climatological such as heat and cold waves and droughts; and biological such as epidemics.
- Man-made disasters can include hazardous material spills, fires, groundwater contamination, transportation accidents, structure failures, mining accidents, explosions and acts of terrorism.
Causes for Occurrence of Disaster
- Environmental degradation: Removal of trees and forest cover from a watershed area have caused, soil erosion, expansion of flood plain area in upper and middle course of rivers and groundwater depletion.
- Developmental process: Exploitation of land use, development of infrastructure, rapid urbanization and technological development have caused increasing pressure over the natural resources.
- Political issues: War, nuclear power aspirations, fight between countries to become super power and conquering land, sea and skies. These have resulted into wide range of disaster events such as Hiroshima nuclear explosion, Syrian civil war, growing militarisation of oceans and outer space.
- Industrialization: This has resulted into warming of earth and frequency of extreme weather events has also increased.
Impacts of Disaster
- Disaster impacts individuals physically (through loss of life, injury, health, disability) as well as psychologically .
- Disaster results in huge economic loss due to destruction of property, human settlements and infrastructure etc.
- Disaster can alter the natural environment , loss of habitat to many plants and animals and cause ecological stress that can result in biodiversity loss.
- After natural disasters, food and other natural resources like water often becomes scarce resulting into food and water scarcity .
- The disaster results in displacement of people , and displaced population often face several challenges in new settlements, in this process poorer becomes more poor.
- Disaster increases the level of vulnerability and hence multiply the effects of disaster.
Vulnerability Profile of India
- India is vulnerable, in varying degrees, to a large number of disasters. Around 59% of the landmass is prone to earthquakes of moderate to very high intensity.
- About 12% (over 40 million hectares) of its land is prone to floods and river erosion.
- Close to 5,700 kms, out of the 7,516 kms long coastline is prone to cyclones and tsunamis .
- 68% of its cultivable area is vulnerable to droughts; and, the hilly areas are at risk from landslides and avalanches .
- Moreover, India is also vulnerable to chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) emergencies and other man-made disasters.
- Disaster risks in India are further compounded by increasing vulnerabilities related to changing demographics and socio-economic conditions, unplanned urbanization, development within high-risk zones, environmental degradation, climate change, geological hazards, epidemics and pandemics .
- Clearly, all these contribute to a situation where disasters seriously threaten India’s economy, its population and sustainable development.
Worst Disasters in India
- Kashmir Floods (2014) affected Srinagar, Bandipur, Rajouri etc. areas of J&K have resulted into death of more than 500 people.
- Uttarakhand Flash Floods (2013) affected Govindghat, Kedar Dome, Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand and resulted into death of more than 5,000 people.
- The Indian Ocean Tsunami (2004) affected parts of southern India and Andaman Nicobar Islands, Sri Lanka, Indonesia etc., and resulted in the death of more than 2 lakh people.
- Gujarat Earthquake (2001) affected Bhuj, Ahmedabad, Gandhinagar, Kutch, Surat, Surendranagar, Rajkot district, Jamnagar and Jodia districts of Gujarat and resulted in death of more than 20,000 people.
- Odisha Super Cyclone or Paradip cyclone (1999) affected the coastal districts of Bhadrak, Kendrapara, Balasore, Jagatsinghpur, Puri, Ganjam etc., and resulted into death of more than 10,000 people.
- The Great Famine (1876-1878) affected Madras, Mysore, Hyderabad, and Bombay and resulted into death of around 3 crore people. Even today, it is considered as one of the worst natural calamities in India of all time.
- Coringa Cyclone (1839) that affected Coringa district of Andhra Pradesh and Calcutta Cyclone (1737) are some other instances of natural calamities faced by the country in the past.
- The Bengal Famine in the years 1770 and 1943 affected Bengal, Odisha, Bihar very badly and resulted into death of nearly 1 crore people.
- Bhopal Gas tragedy (December, 1984) is one of the worst chemical disasters globally that resulted in over 10,000 losing their lives (the actual number remains disputed) and over 5.5 lakh persons affected and suffering from agonizing injuries.
- cases of railway accidents (Dussehra gathering on the railway tracks crushed by the trains in 2018),
- fire accidents in hospitals due to negligence and non implementation of existing mandatory fire safety norms,
- collapse of various infrastructure constructs like flyovers, metro tracks and residential buildings due to poor quality of construction, illegal addition of floors and recurring floods.
- Stampede at large public gathering like Kumbh Mela caused by poor people management and lack of adequate infrastructure to monitor and manage large crowd gathering.
Stages in Disaster Management
- Disaster Management efforts are geared towards disaster risk management .
- Disaster Risk Management implies the systematic process of using administrative decisions, organisation, operational skills, and capacities to implement policies, strategies and coping capacities of the society and communities to lessen the impact of natural hazards and related environmental and technological disasters.
- These comprise all forms all activities including structural and non- structural measures to avoid (prevention) or to limit (mitigation and preparedness) adverse effects of hazards.
- There are three key stages of activities in disaster management:
- Before a disaster: to reduce the potential for human, material, or environmental losses caused by hazards and to ensure that these losses are minimised when disaster strikes;
- During a disaster: to ensure that the needs and provisions of victims are met to alleviate and minimise suffering; and
- After a disaster: to achieve rapid and durable recovery which does not reproduce the original vulnerable conditions.
- The different phases of disaster management are represented in the disaster cycle diagram.
Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR)
- Disaster risk reduction is the concept and practice of reducing disaster risks through systematic efforts to analyse and reduce the causal factors of disasters.
- Mitigation: To eliminate or reduce the impacts and risks of hazards through proactive measures taken before an emergency or disaster occurs.
- Preparedness: To take steps to prepare and reduce the effects of disasters.
- Rescue: Providing warning, evacuation, search, rescue, providing immediate assistance.
- Relife: To respond to communities who become victims of disaster, providing relief measures such as food packets, water, medicines, temporary accommodation, relief camps etc.
- Recovery: This stage emphasises upon recovery of victims of disaster, recovery of damaged infrastructure and repair of the damages caused.
Disaster Risk Reduction in Sustainable Development Goals
- Goal 1: Target 1.5, which relates to building the resilience of the poor, further strengthens the position of disaster risk reduction as a core development strategy for ending extreme poverty.
- Goal 2: Target 2.4 supports the immediate need to advance actions in mainstreaming disaster risk reduction and climate adaptation into agriculture sector planning and investments in order to promote resilient livelihoods, food production and ecosystems.
- Goal 3: Target 3.d, relates to strengthening early warning and risk reduction of national and global health risks presents an opportunity to further actions to promote resilient health.
- Goal 4: Target 4.7 focusing on building and upgrading education facilities and promoting education for sustainable development, contribute significantly to resilience-building in the education sector.’
- Goal 6: Target 6.6, which relates to protecting and restoring water-related ecosystems , will significantly contribute to strengthening the resilience of communities to water-related hazards.
- Goal 9: Targets 9.1 related to developing sustainable and resilient infrastructure development are vital not only to protect existing infrastructure but also future infrastructure investments.
- Goal 11: Action targets under this goal (11.1, 11.3, 11.4, 11.5, 11.b and 11.c) focusing on upgrading urban slums, integrated urban planning, reducing social and economic impacts of disaster risk, building the resilience of the urban poor, adopting and implementing urban policies in line with the Sendai Framework and building sustainable and resilient urban infrastructure, are strategic opportunities to ensure increased capacity to support cities, to protect current and future development prospects and to build safer, more resilient cities throughout the world.
- Goal 13: Target actions under this goal, focusing on strengthening resilience and adaptive capacity , capacity building and integrating climate change measures into policies and plans, awareness raising on climate adaptation and early warning (Targets 13.1 to 13.3 and 13.a to 13.b) provide opportunities to strengthen the integration between disaster and climate resilience and to protect broader development paths at all levels.
- Goal 14: Target action 14.2, focusing on the sustainable management and protection as well as strengthening resilience of marine and coastal ecosystems, can contribute to reducing disaster risk and increase in demand for healthy marine and coastal ecosystems.
- Goal 15: Target actions 15.1 to 15.4 and 15.9, focus on managing and restoring forests , combating land degradation and desertification, conserving mountain ecosystems and their biodiversity and integrating ecosystem and biodiversity values into national and local planning, development processes, poverty reduction strategies.
- These targets are also in line with the Sendai Framework focus on building environmental resilience through the inclusion of ecosystems in risk analysis and planning.
Challenges in Disaster Risk Reduction
- There are insufficient levels of implementation for each monitored activity. For example, Disaster risk management plans or a risk sensitive building codes exist but they are not enforced because of a lack of government capacity or public awareness.
- There is lack of local capacities to implement disaster risk management. Weak capacity at the local levels undermines the implementation Disaster preparedness plans.
- Absence of integration of climate change into Disaster risk management plans.
- There is divergence of obtaining political and economic commitments due to other competing needs and priorities such as poverty reduction, social welfare, education etc. require greater attention and funding.
- Due to poor coordination between stakeholders, there is inadequate access with respect to risk assessment, monitoring, early warning, disaster response and other Disaster related activities.
- Insufficient investment in building disaster resilient strategies, also private sector are least contributors in the share of investment.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Disaster management is crucial in ensuring a systematic response to natural or man-made disasters. It helps in saving lives, reducing economic losses, and maintaining societal functions. Furthermore, it aids in building resilient communities that can withstand and recover from disasters.
This essay delves into the essence of disaster management, its phases, the challenges involved, and the role of technology and community participation in enhancing disaster resilience.
How to Write an Essay on Disaster Management? Learn the format and find samples for 150, 300, and 500 words; including tips & tricks!
Disaster management refers to the efficient management of resources and responsibilities that will help in lessening the impact of the disaster. It involves a well-planned plan of action so we can make effective efforts to reduce the dangers caused by the disaster to a minimum.
Introduction. Disasters, whether natural or man-made, have the capacity to inflict immense destruction and disrupt the lives of millions. Effective disaster management is crucial to mitigate these risks and build community resilience.
While writing an essay on Disaster Management, you can start with an introduction, then go on with the definition, the types of disaster management, a little in-depth explanation along with examples, and finish it off with a conclusion.
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Disaster Management’ for class 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays ‘Disaster Management’ especially written for school and college students.
Analyze winter snow disaster in Philadelphia and its impact on the community. Describe the effect of natural disasters on the supply chain. Examine the reasons and consequences of the Budalangi flood. Explain why the 1900 Galveston hurricane is regarded as disaster management failure.
Disaster management is a crucial process that involves preparing for, responding to, and recovering from these catastrophic events. In this essay, we will explore the vital importance of disaster management, its key components, and the role it plays in safeguarding lives and communities.
Disaster Management. Important Geophysical Phenomena. Why in News? In May 2019, more than 20 young people died due to a deadly fire at a coaching centre in Surat. According to National Crime Records Bureau data, India’s record is appalling on fire safety. More than 17,000 people nationwide died in fire related incidences in 2015.