Find cars with the safety features you want at AARP Auto Buying Program powered by TrueCar. Learn more.
AARP daily Crossword Puzzle
Hotels with AARP discounts
Life Insurance
AARP Dental Insurance Plans
AARP MEMBERSHIP
AARP Membership — $12 for your first year when you sign up for Automatic Renewal
Get instant access to members-only products, hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP the Magazine. Find how much you can save in a year with a membership. Learn more.
- right_container
Work & Jobs
Social Security
AARP en Español
- Membership & Benefits
- Members Edition
AARP Rewards
- AARP Rewards %{points}%
Conditions & Treatments
Drugs & Supplements
Health Care & Coverage
Health Benefits

AARP Hearing Center
Advice on Tinnitus and Hearing Loss

Get Happier
Creating Social Connections

Brain Health Resources
Tools and Explainers on Brain Health

Your Health
8 Major Health Risks for People 50+
Scams & Fraud
Personal Finance
Money Benefits

View and Report Scams in Your Area

AARP Foundation Tax-Aide
Free Tax Preparation Assistance

AARP Money Map
Get Your Finances Back on Track

How to Protect What You Collect
Small Business
Age Discrimination

Flexible Work
Freelance Jobs You Can Do From Home

AARP Skills Builder
Online Courses to Boost Your Career

31 Great Ways to Boost Your Career

ON-DEMAND WEBINARS
Tips to Enhance Your Job Search

Get More out of Your Benefits

When to Start Taking Social Security

10 Top Social Security FAQs

Social Security Benefits Calculator

Medicare Made Easy
Original vs. Medicare Advantage

Enrollment Guide
Step-by-Step Tool for First-Timers

Prescription Drugs
9 Biggest Changes Under New Rx Law

Medicare FAQs
Quick Answers to Your Top Questions
Care at Home
Financial & Legal
Life Balance

LONG-TERM CARE
Understanding Basics of LTC Insurance

State Guides
Assistance and Services in Your Area

Prepare to Care Guides
How to Develop a Caregiving Plan

End of Life
How to Cope With Grief, Loss
Recently Played
Word & Trivia
Atari® & Retro
Members Only
Staying Sharp
Mobile Apps
More About Games

Right Again! Trivia

Right Again! Trivia – Sports

Atari® Video Games

Throwback Thursday Crossword
Travel Tips
Vacation Ideas
Destinations
Travel Benefits

Beach Vacation Ideas
Fun Beach Vacations

Road Trips For Every Personality

Passport Access
Passports Can Be Renewed Online

AARP National Park Guide
Black Canyon of the Gunnison
Entertainment & Style
Family & Relationships
Personal Tech
Home & Living
Celebrities
Beauty & Style

Movies for Grownups
Summer Movie Preview

Jon Bon Jovi’s Long Journey Back

Looking Back
50 World Changers Turning 50

Sex & Dating
Spice Up Your Love Life

Friends & Family
How to Host a Fabulous Dessert Party

Home Technology
Caregiver’s Guide to Smart Home Tech

Virtual Community Center
Join Free Tech Help Events

Create a Hygge Haven

Soups to Comfort Your Soul

AARP Solves 25 of Your Problems
Driver Safety
Maintenance & Safety
Trends & Technology

AARP Smart Guide
How to Clean Your Car

We Need To Talk
Assess Your Loved One's Driving Skills

AARP Smart Driver Course

Building Resilience in Difficult Times

Tips for Finding Your Calm

Weight Loss After 50 Challenge

Cautionary Tales of Today's Biggest Scams

7 Top Podcasts for Armchair Travelers

Jean Chatzky: ‘Closing the Savings Gap’

Quick Digest of Today's Top News

AARP Top Tips for Navigating Life

Get Moving With Our Workout Series
You are now leaving AARP.org and going to a website that is not operated by AARP. A different privacy policy and terms of service will apply.

What is Medicare assignment and how does it work?
Kimberly Lankford,
Because Medicare decides how much to pay providers for covered services, if the provider agrees to the Medicare-approved amount, even if it is less than they usually charge, they’re accepting assignment.
A doctor who accepts assignment agrees to charge you no more than the amount Medicare has approved for that service. By comparison, a doctor who participates in Medicare but doesn’t accept assignment can potentially charge you up to 15 percent more than the Medicare-approved amount.
That’s why it’s important to ask if a provider accepts assignment before you receive care, even if they accept Medicare patients. If a doctor doesn’t accept assignment, you will pay more for that physician’s services compared with one who does.

Get instant access to members-only products and hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP the Magazine. Find out how much you could save in a year with a membership. Learn more.
How much do I pay if my doctor accepts assignment?
If your doctor accepts assignment, you will usually pay 20 percent of the Medicare-approved amount for the service, called coinsurance, after you’ve paid the annual deductible. Because Medicare Part B covers doctor and outpatient services, your $240 deductible for Part B in 2024 applies before most coverage begins.
All providers who accept assignment must submit claims directly to Medicare, which pays 80 percent of the approved cost for the service and will bill you the remaining 20 percent. You can get some preventive services and screenings, such as mammograms and colonoscopies , without paying a deductible or coinsurance if the provider accepts assignment.
What if my doctor doesn’t accept assignment?
A doctor who takes Medicare but doesn’t accept assignment can still treat Medicare patients but won’t always accept the Medicare-approved amount as payment in full.
This means they can charge you up to a maximum of 15 percent more than Medicare pays for the service you receive, called “balance billing.” In this case, you’re responsible for the additional charge, plus the regular 20 percent coinsurance, as your share of the cost.
How to cover the extra cost? If you have a Medicare supplement policy , better known as Medigap, it may cover the extra 15 percent, called Medicare Part B excess charges.
All Medigap policies cover Part B’s 20 percent coinsurance in full or in part. The F and G policies cover the 15 percent excess charges from doctors who don’t accept assignment, but Plan F is no longer available to new enrollees, only those eligible for Medicare before Jan. 1, 2020, even if they haven’t enrolled in Medicare yet. However, anyone who is enrolled in original Medicare can apply for Plan G.
Remember that Medigap policies only cover excess charges for doctors who accept Medicare but don’t accept assignment, and they won’t cover costs for doctors who opt out of Medicare entirely.
Good to know. A few states limit the amount of excess fees a doctor can charge Medicare patients. For example, Massachusetts and Ohio prohibit balance billing, requiring doctors who accept Medicare to take the Medicare-approved amount. New York limits excess charges to 5 percent over the Medicare-approved amount for most services, rather than 15 percent.

AARP NEWSLETTERS

%{ newsLetterPromoText }%
%{ description }%
Privacy Policy
ARTICLE CONTINUES AFTER ADVERTISEMENT
How do I find doctors who accept assignment?
Before you start working with a new doctor, ask whether he or she accepts assignment. About 98 percent of providers billing Medicare are participating providers, which means they accept assignment on all Medicare claims, according to KFF.
You can get help finding doctors and other providers in your area who accept assignment by zip code using Medicare’s Physician Compare tool .
Those who accept assignment have this note under the name: “Charges the Medicare-approved amount (so you pay less out of pocket).” However, not all doctors who accept assignment are accepting new Medicare patients.
AARP® Vision Plans from VSP™
Vision insurance plans designed for members and their families
What does it mean if a doctor opts out of Medicare?
Doctors who opt out of Medicare can’t bill Medicare for services you receive. They also aren’t bound by Medicare’s limitations on charges.
In this case, you enter into a private contract with the provider and agree to pay the full bill. Be aware that neither Medicare nor your Medigap plan will reimburse you for these charges.
In 2023, only 1 percent of physicians who aren’t pediatricians opted out of the Medicare program, according to KFF. The percentage is larger for some specialties — 7.7 percent of psychiatrists and 4.2 percent of plastic and reconstructive surgeons have opted out of Medicare.
Keep in mind
These rules apply to original Medicare. Other factors determine costs if you choose to get coverage through a private Medicare Advantage plan . Most Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks, and they may charge more or not cover services from out-of-network providers.
Before choosing a Medicare Advantage plan, find out whether your chosen doctor or provider is covered and identify how much you’ll pay. You can use the Medicare Plan Finder to compare the Medicare Advantage plans and their out-of-pocket costs in your area.
Return to Medicare Q&A main page
Kimberly Lankford is a contributing writer who covers Medicare and personal finance. She wrote about insurance, Medicare, retirement and taxes for more than 20 years at Kiplinger’s Personal Finance and has written for The Washington Post and Boston Globe . She received the personal finance Best in Business award from the Society of American Business Editors and Writers and the New York State Society of CPAs’ excellence in financial journalism award for her guide to Medicare.
Unlock Access to AARP Members Edition
Already a Member? Login

More on Medicare

How Do I Create a Personal Online Medicare Account?
You can do a lot when you decide to look electronically

I Got a Medicare Summary Notice in the Mail. What Is It?
This statement shows what was billed, paid in past 3 months

Understanding Medicare’s Options: Parts A, B, C and D
Making sense of the alphabet soup of health care choices
Recommended for You
AARP Value & Member Benefits

Learn, earn and redeem points for rewards with our free loyalty program

AARP® Dental Insurance Plan administered by Delta Dental Insurance Company
Dental insurance plans for members and their families

The National Hearing Test
Members can take a free hearing test by phone

AARP® Staying Sharp®
Activities, recipes, challenges and more with full access to AARP Staying Sharp®
SAVE MONEY WITH THESE LIMITED-TIME OFFERS
Does your provider accept Medicare as full payment?
You can get the lowest cost if your doctor or other health care provider accepts the Medicare-approved amount as full payment for a covered service. This is called “accepting assignment.” If a provider accepts assignment, it’s for all Medicare-covered Part A and Part B services.
Using a provider that accepts assignment
Most doctors, providers, and suppliers accept assignment, but always check to make sure that yours do.
If your doctor, provider, or supplier accepts assignment:
- Your out-of-pocket costs may be less.
- They agree to charge you only the Medicare deductible and coinsurance amount, and usually wait for Medicare to pay its share before asking you to pay your share.
- They have to submit your claim directly to Medicare and can't charge you for submitting the claim.
How does assignment impact my drug coverage?
Using a provider that doesn't accept Medicare as full payment
Some providers who don’t accept assignment still choose to accept the Medicare-approved amount for services on a case-by-case basis. These providers are called "non-participating."
If your doctor, provider, or supplier doesn't accept assignment:
- You might have to pay the full amount at the time of service.
- They should submit a claim to Medicare for any Medicare-covered services they give you, and they can’t charge you for submitting a claim. If they refuse to submit a Medicare claim, you can submit your own claim to Medicare. Get the Medicare claim form .
- They can charge up to 15% over the Medicare-approved amount for a service, but no more than that. This is called "the limiting charge."
Does the limiting charge apply to all Medicare-covered services?
Using a provider that "opts-out" of Medicare
- Doctors and other providers who don’t want to work with the Medicare program may "opt out" of Medicare.
- Medicare won’t pay for items or services you get from provider that opts out, except in emergencies.
- Providers opt out for a minimum of 2 years. Every 2 years, the provider can choose to keep their opt-out status, accept Medicare-approved amounts on a case-by-case basis ("non-participating"), or accept assignment.
Find providers that opted out of Medicare.
Private contracts with doctors or providers who opt out
- If you choose to get services from an opt-out doctor or provider you may need to pay upfront, or set up a payment plan with the provider through a private contract.
- Medicare won’t pay for any service you get from this doctor, even if it’s a Medicare-covered service.
What are the rules for private contracts?
You may want to contact your State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP) for help before signing a private contract with any doctor or other health care provider.
What do you want to do next?
- Next step: Get help with costs
- Take action: Find a provider
- Get details: How to get Medicare services
You are using an unsupported browser ×
You are using an unsupported browser. This web site is designed for the current versions of Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Safari.
Site Feedback
The Office of the Federal Register publishes documents on behalf of Federal agencies but does not have any authority over their programs. We recommend you directly contact the agency associated with the content in question.
If you have comments or suggestions on how to improve the www.ecfr.gov website or have questions about using www.ecfr.gov, please choose the 'Website Feedback' button below.
If you would like to comment on the current content, please use the 'Content Feedback' button below for instructions on contacting the issuing agency
Website Feedback
- Incorporation by Reference
- Recent Updates
- Recent Changes
- Corrections
- Reader Aids Home
- Using the eCFR Point-in-Time System
- Understanding the eCFR
- Government Policy and OFR Procedures
- Developer Resources
- My Subscriptions
- Sign In / Sign Up
Hi, Sign Out
The Electronic Code of Federal Regulations
Enhanced content :: cross reference.
Enhanced content is provided to the user to provide additional context.
Navigate by entering citations or phrases (eg: suggestions#fillExample" class="example badge badge-info">1 CFR 1.1 suggestions#fillExample" class="example badge badge-info">49 CFR 172.101 suggestions#fillExample" class="example badge badge-info">Organization and Purpose suggestions#fillExample" class="example badge badge-info">1/1.1 suggestions#fillExample" class="example badge badge-info">Regulation Y suggestions#fillExample" class="example badge badge-info">FAR ).
Choosing an item from citations and headings will bring you directly to the content. Choosing an item from full text search results will bring you to those results. Pressing enter in the search box will also bring you to search results.
Background and more details are available in the Search & Navigation guide.
- Title 42 —Public Health
- Chapter IV —Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Department of Health and Human Services
- Subchapter B —Medicare Program
- Part 424 —Conditions for Medicare Payment
- Subpart F —Limitations on Assignment and Reassignment of Claims
Enhanced Content - Table of Contents
The in-page Table of Contents is available only when multiple sections are being viewed.
Use the navigation links in the gray bar above to view the table of contents that this content belongs to.
Enhanced Content - Details
42 U.S.C. 1302 and 1395hh .
53 FR 6634 , Mar. 2, 1988, unless otherwise noted.
Enhanced Content - Print
Generate PDF
This content is from the eCFR and may include recent changes applied to the CFR. The official, published CFR, is updated annually and available below under "Published Edition". You can learn more about the process here .
Enhanced Content - Display Options
The eCFR is displayed with paragraphs split and indented to follow the hierarchy of the document. This is an automated process for user convenience only and is not intended to alter agency intent or existing codification.
A separate drafting site is available with paragraph structure matching the official CFR formatting. If you work for a Federal agency, use this drafting site when drafting amendatory language for Federal regulations: switch to eCFR drafting site .
Enhanced Content - Subscribe
Subscribe to: 42 CFR 424.73
Enhanced Content - Timeline
No changes found for this content after 1/03/2017.
Enhanced Content - Go to Date
Enhanced content - compare dates, enhanced content - published edition.
View the most recent official publication:
- View Title 42 on govinfo.gov
- View the PDF for 42 CFR 424.73
These links go to the official, published CFR, which is updated annually. As a result, it may not include the most recent changes applied to the CFR. Learn more .
Enhanced Content - Developer Tools
This document is available in the following developer friendly formats:
- Hierarchy JSON - Title 42
- Content HTML - Section 424.73
- Content XML - Section 424.73
Information and documentation can be found in our developer resources .
eCFR Content
The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) is the official legal print publication containing the codification of the general and permanent rules published in the Federal Register by the departments and agencies of the Federal Government. The Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (eCFR) is a continuously updated online version of the CFR. It is not an official legal edition of the CFR.
§ 424.73 Prohibition of assignment of claims by providers.
( a ) Basic prohibition. Except as specified in paragraph (b) of this section, Medicare does not pay amounts that are due a provider to any other person under assignment, or power of attorney, or any other direct payment arrangement.
( b ) Exceptions to the prohibition —
( 1 ) Payment to a government agency or entity. Subject to the requirements of the Assignment of Claims Act ( 31 U.S.C. 3727 ), Medicare may pay a government agency or entity under an assignment by the provider.
( 2 ) Payment under assignment established by court order. Medicare may pay under an assignment established by, or in accordance with, the order of a court of competent jurisdiction if the assignment meets the conditions set forth in § 424.90 .
( 3 ) Payment to an agent. Medicare may pay an agent who furnishes billing and collection services to the provider if the following conditions are met:
( i ) The agent receives the payment under an agency agreement with the provider;
( ii ) The agent's compensation is not related in any way to the dollar amounts billed or collected;
( iii ) The agent's compensation is not dependent upon the actual collection of payment;
( iv ) The agent acts under payment disposition instructions that the provider may modify or revoke at any time; and
( v ) The agent, in receiving the payment, acts only on behalf of the provider.
Payment to an agent will always be made in the name of the provider.
Reader Aids
Information.
- About This Site
- Legal Status
- Accessibility
- No Fear Act
- Continuity Information
42 CFR § 424.73 - Prohibition of assignment of claims by providers.
(a) Basic prohibition. Except as specified in paragraph (b) of this section, Medicare does not pay amounts that are due a provider to any other person under assignment, or power of attorney , or any other direct payment arrangement.
(b) Exceptions to the prohibition —(1) Payment to a government agency or entity. Subject to the requirements of the Assignment of Claims Act ( 31 U.S.C. 3727 ), Medicare may pay a government agency or entity under an assignment by the provider.
(2) Payment under assignment established by court order. Medicare may pay under an assignment established by, or in accordance with, the order of a court of competent jurisdiction if the assignment meets the conditions set forth in § 424.90 .
(3) Payment to an agent. Medicare may pay an agent who furnishes billing and collection services to the provider if the following conditions are met:
(i) The agent receives the payment under an agency agreement with the provider;
(ii) The agent's compensation is not related in any way to the dollar amounts billed or collected;
(iii) The agent's compensation is not dependent upon the actual collection of payment ;
(iv) The agent acts under payment disposition instructions that the provider may modify or revoke at any time; and
(v) The agent, in receiving the payment , acts only on behalf of the provider.

What You Need to Know About Medicare Assignment
If you are one of the more than 63 million Americans enrolled in Medicare and are on the lookout for a new provider, you may wonder what your options are. A good place to start? Weighing the pros and cons of choosing an Original Medicare plan versus a Medicare Advantage plan—both of which have their upsides.
Let’s say you decide on an Original Medicare plan, which many U.S. doctors accept. In your research, however, you come across the term “Medicare assignment.” Cue the head-scratching. What exactly does that mean, and how might it affect your coverage costs?
What is Medicare Assignment?
It turns out that Medicare assignment is a concept you need to understand before seeing a new doctor. First things first: Ask your doctor if they “accept assignment”—that exact phrasing—which means they have agreed to accept a Medicare-approved amount as full payment for any Medicare-covered service provided to you. If your doctor accepts assignment, that means they’ll send your whole medical bill to Medicare, and then Medicare pays 80% of the cost, while you are responsible for the remaining 20%.
A doctor who doesn’t accept assignment, however, could charge up to 15% more than the Medicare-approved amount for their services, depending on what state you live in, shouldering you with not only that additional cost but also your 20% share of the original cost. Additionally, the doctor is supposed to submit your claim to Medicare, but you may have to pay them on the day of service and then file a reimbursement claim from Medicare after the fact.
Worried that your doctor will not accept assignment? Luckily, 98% of U.S. physicians who accept Medicare patients also accept Medicare assignment, according to the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). They are known as assignment providers, participating providers, or Medicare-enrolled providers.
It can be confusing. Here’s how to assess whether your provider accepts Medicare assignment, and what that means for your out-of-pocket costs:
The 3 Types of Original Medicare Providers
1. participating providers, or those who accept medicare assignment.
These providers have an agreement with Medicare to accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment for their services. You don’t have to pay anything other than a copay or coinsurance (depending on your plan) at the time of your visit. Typically, Medicare pays 80% of the cost, while you are responsible for the remaining 20%, as long as you have met your deductible.
2. Non-participating providers
“Most providers accept Medicare, but a small percentage of doctors are known as non-participating providers,” explains Caitlin Donovan, senior director of public relations at the National Patient Advocate Foundation (NPAF) in Washington D.C. “These may be more expensive,” she adds. Also known as non-par providers, these physicians may accept Medicare patients and insurance, but they have not agreed to take assignment Medicare in all cases. That means they’re not held to the Medicare-approved amount as payment in full. As a reminder, a doctor who doesn’t accept assignment can charge up to 15% more than the Medicare-approved amount, depending on what part of the country you live in, and you will have to pay that additional amount plus your 20% share of the original cost.
What does that mean for you? Besides being charged more than the Medicare-approved amount, you might also be required to do some legwork to get reimbursed by Medicare.
- You may have to pay the entire bill at the time of service and wait to be reimbursed 80% of the Medicare-approved amount. In most cases, the provider will submit the claim for you. But sometimes, you’ll have to submit it yourself.
- Depending on the state you live in, the provider may also charge you as much as 15% more than the Medicare-approved amount. (In New York state, for example, that add-on charge is limited to 5%.) This is called a limiting charge—and the difference, called the balance bill, is your responsibility.
There are some non-par providers, however, who accept Medicare assignment for certain services, on a case-by-case basis. Those may include any of the services—anything from hospital and hospice care to lab tests and surgery—available from any assignment-accepting doctor, with a key exception: If a non-par provider accepts assignment for a particular service, they cannot bill you more than the regular Medicare deductible and coinsurance amount for that specific treatment. Just as it’s important to confirm whether your doctor accepts assignment, it’s also important to confirm which services are included at assignment.
3. Opt-out providers
A small percentage of providers do not participate in Medicare at all. In 2020, for example, only 1% of all non-pediatric physicians nationwide opted out, and of that group, 42% were psychiatrists. “Some doctors opt out of providing Medicare coverage altogether,” notes Donovan.“In that case, the patient would pay privately.” If you were interested in seeing a physician who had opted out of Medicare, you would have to enter a private contract with that provider, and neither you nor the provider would be eligible for reimbursement from Medicare.

How do I know if my doctor accepts Medicare assignment?
The best way to find out whether your provider accepts Medicare assignment is simply to ask. First, confirm whether they are participating or non-participating—and if they are non-participating, ask whether they accept Medicare assignment for certain services.
Also, make sure to ask your provider exactly how they will be billing Medicare and what charges you might expect at the time of your visit so that you’re on the same page from the start.
Is seeing a non-participating provider who accepts Medicare assignment more expensive?
The short answer is yes. There are usually out-of-pocket costs after you’re reimbursed. But it may not cost as much as you think, and it may not be much more than if you see a participating provider. Still, it could be challenging if you’re on a fixed income.
For example, let’s say you’re seeing a physical therapist who accepts Medicare patients but not Medicare assignment. Medicare will pay $95 per visit to the provider; but your provider bills the service at $115. In most states, you’re responsible for a 15% limiting charge above $95. In this case, your bill would be 115% of $95, or $109.25.
Once you get your $95 reimbursement back from Medicare, your cost for the visit—the balance bill—would be $14.25 (plus any deductibles or copays) .
In some states, the maximum cap on the limiting charge is less than 15%. As mentioned earlier, New York state, for instance, allows only a 5% surcharge, which means that physical therapy appointment would cost you just $4.75 extra.
Bottom line: Medicare assignment providers and non-participating providers who agree to accept Medicare assignment are both viable options for patients. So if you want to see a particular provider, don’t rule them out just because they’re non-par.
While seeing a non-participating provider may still be affordable, ultimately, the biggest headache may be keeping track of claims and reimbursements, or simply setting aside the right amount of money to pay for your visit up front.
Before you schedule a visit, be sure to ask how much the service will cost. You can also estimate the payment amount based on Medicare-approved charges. A good place to start is this out-of-pocket expense calculator provided by the CMS.
What if I see a provider who opts out of Medicare altogether?
An opt-out provider will create a private contract with you, underscoring the terms of your agreement. But Medicare will not reimburse either of you for services.
Seeing a provider who does not accept Medicare will likely be more expensive. And your visits won’t count toward your deductible. But you may be able to work out paying reduced fees on a sliding scale for that provider’s services, all of which would be laid out in your contract.

Speak with a Licensed Insurance Agent
- (888) 335-8996
Medicare Assignment
Home / Medicare 101 / Medicare Costs / Medicare Assignment
Summary: If a provider accepts Medicare assignment, they accept the Medicare-approved amount for a covered service. Though most providers accept assignment, not all do. In this article, we’ll explain the differences between participating, non-participating, and opt-out providers. You’ll also learn how to find physicians in your area who accept Medicare assignment. Estimated Read Time: 5 min
What is Medicare Assignment
Medicare assignment is an agreement by your doctor or other healthcare providers to accept the Medicare-approved amount as the full cost for a covered service. Providers who “accept assignment” bill Medicare directly for Part B-covered services and cannot charge you more than the applicable deductible and coinsurance.
Most healthcare providers who opt-in to Medicare accept assignment. In fact, CMS reported in its Medicare Participation for Calendar Year 2024 announcement that 98 percent of Medicare providers accepted assignment in 2023.
Providers who accept Medicare are divided into two groups: Participating providers and non-participating providers. Providers can decide annually whether they want to participate in Medicare assignment, or if they want to be non-participating.
Providers who do not accept Medicare Assignment can charge up to 15% above the Medicare-approved cost for a service. If this is the case, you will be responsible for the entire amount (up to 15%) above what Medicare covers.
Below, we’ll take a closer look at participating, non-participating, and opt-out physicians.
Medicare Participating Providers: Providers Who Accept Medicare Assignment
Healthcare providers who accept Medicare assignment are known as “participating providers”. To participate in Medicare assignment, a provider must enter an agreement with Medicare called the Participating Physician or Supplier Agreement. When a provider signs this agreement, they agree to accept the Medicare-approved charge as the full charge of the service. They cannot charge the beneficiary more than the applicable deductible and coinsurance for covered services.
Each year, providers can decide whether they want to be a participating or non-participating provider. Participating in Medicare assignment is not only beneficial to patients, but to providers as well. Participating providers get paid by Medicare directly, and when a participating provider bills Medicare, Medicare will automatically forward the claim information to Medicare Supplement insurers. This makes the billing process much easier on the provider’s end.
Medicare Non-Participating Providers: Providers Who Don’t Accept Assignment
Healthcare providers who are “non-participating” providers do not agree to accept assignment and can charge up to 15% over the Medicare-approved amount for a service. Non-participating Medicare providers still accept Medicare patients. However they have not agreed to accept the Medicare-approved cost as the full cost for their service.
Doctors who do not sign an assignment agreement with Medicare can still choose to accept assignment on a case-by-case basis. When non-participating providers do add on excess charges , they cannot charge more than 15% over the Medicare-approved amount. It’s worth noting that providers do not have to charge the maximum 15%; they may only charge 5% or 10% over the Medicare-approved amount.
When you receive a Medicare-covered service at a non-participating provider, you may need to pay the full amount at the time of your service; a claim will need to be submitted to Medicare for you to be reimbursed. Prior to receiving care, your provider should give you an Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) to read and sign. This notice will detail the services you are receiving and their costs.
Non-participating providers should include a CMS-approved unassigned claim statement in the additional information section of your Advanced Beneficiary Notice. This statement will read:
“This supplier doesn’t accept payment from Medicare for the item(s) listed in the table above. If I checked Option 1 above, I am responsible for paying the supplier’s charge for the item(s) directly to the supplier. If Medicare does pay, Medicare will pay me the Medicare-approved amount for the item(s), and this payment to me may be less than the supplier’s charge.”
This statement basically summarizes how excess charges work: Medicare will pay the Medicare-approved amount, but you may end up paying more than that.
Your provider should submit a claim to Medicare for any covered services, however, if they refuse to submit a claim, you can do so yourself by using CMS form 1490S .
Opt-Out Providers: What You Need to Know
Opt-out providers are different than non-participating providers because they completely opt out of Medicare. What does this mean for you? If you receive supplies or services from a provider who opted out of Medicare, Medicare will not pay for any of it (except for emergencies).
Physicians who opt-out of Medicare are even harder to find than non-participating providers. According to a report by KFF.org, only 1.1% of physicians opted out of Medicare in 2023. Of those who opted out, most are physicians in specialty fields such as psychiatry, plastic and reconstructive surgery, and neurology.
How to Find A Doctor Who Accepts Medicare Assignment
Finding a doctor who accepts Medicare patients and accepts Medicare assignment is generally easier than finding a provider who doesn’t accept assignment. As we mentioned above, of all the providers who accept Medicare patients, 98 percent accept assignment.
The easiest way to find a doctor or healthcare provider who accepts Medicare assignment is by visiting Medicare.gov and using their Compare Care Near You tool . When you search for providers in your area, the Care Compare tool will let you know whether a provider is a participating or non-participating provider.
If a provider is part of a group practice that involves multiple providers, then all providers in that group must have the same participation status. As an example, we have three doctors, Dr. Smith, Dr. Jones, and Dr. Shoemaker, who are all part of a group practice called “Health Care LLC”. The group decides to accept Medicare assignment and become a participating provider. Dr. Smith decides he does not want to accept assignment, however, because he is part of the “Health Care LLC” group, he must remain a participating provider.
Using Medicare’s Care Compare tool, you can select a group practice and see their participation status. You can then view all providers who are part of that group. This makes finding doctors who accept assignment even easier.
To ensure you don’t end up paying more out-of-pocket costs than you anticipated, it’s always a good idea to check with your provider if they are a participating Medicare provider. If you have questions regarding Medicare assignment or are having trouble determining whether a provider is a participating provider, you can contact Medicare directly at 1-800-633-4227. If you have questions about excess charges or other Medicare costs and would like to speak with a licensed insurance agent, you can contact us at the number above.
Announcement About Medicare Participation for Calendar Year 2024, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Accessed January 2024
https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-participation-announcement.pdf
Annual Medicare Participation Announcement, CMS.gov. Accessed January 2024
https://www.cms.gov/medicare-participation
Does Your Provider Accept Medicare as Full Payment? Medicare.gov. Accessed January 2024
https://www.medicare.gov/basics/costs/medicare-costs/provider-accept-Medicare

Thomas Liquori

Ashlee Zareczny

- Medicare Eligibility Requirements
- Medicare Enrollment Documents
- Apply for Medicare While Working
- Guaranteed Issue Rights
- Medicare by State
- Web Stories
- Online Guides
- Calculators & Tools
© 2024 Apply for Medicare. All Rights Reserved.
Owned by: Elite Insurance Partners LLC. This website is not connected with the federal government or the federal Medicare program. The purpose of this website is the solicitation of insurance. We do not offer every plan available in your area. Currently we represent 26 organizations which offer 3,740 products in your area. Please contact Medicare.gov or 1-800-MEDICARE or your local State Health Insurance Program to get information on all of your options.
Let us help you find the right Medicare plans today!
Simply enter your zip code below
Get the Reddit app
All things coding and billing.
Medicare Assignment Violation
I am a Medicare recipient. I also have Medicaid. Medicare shows that Medicaid covers all copays and deductibles. This is news to me because I’ve been getting and paying bills.
I contacted Medicare last week about a question related to billing, trying to understand how the process works. I’m not sure what specially I said that triggered them calling me today asking for details.
They are calling me again next week after they review a number of claims and indicated that if providers are billing me after Medicare pays them that it’s an “assignment violation”
Looking back, none of the hospitals or hospital affiliated providers have billed me. The national DME companies haven’t nor have specialty pharmacies. The only claims I’m receiving are from independent providers using their own billing platforms.
what is an assignment violation?
what should I prepare for as the patient/consumer?
am I or my providers likely to face a consequence for this?
are these common and do I need to look out for this?
My entire medical system involvement is atypical so I can’t grasp is this is one of those unusual situations that happens only to me or if this is a common issue and I just happened to get a Medicare rep who identified a problem and then took action
Happy to do the reading, but I’m not sure what the best resource is or what terminology will help me locate info that addresses my questions.
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
Paying a Visit to the Doctor: Current Financial Protections for Medicare Patients When Receiving Physician Services
Cristina Boccuti Published: Nov 30, 2016
- Issue Brief
Under current law, Medicare has several financial protections in place that are designed to safeguard Medicare beneficiaries—seniors and people with permanent disabilities—from unexpected and confusing charges when they seek care from doctors and other practitioners. These protections include the participating provider program, limitations on balance billing, and conditions on private contracting. This issue brief describes these three protections, explains why they were enacted, and examines the implications of modifying them for beneficiaries, providers, and the Medicare program.
Main Findings
- The participating provider program was enacted in 1984 for two purposes: (1) to assist Medicare patients with identifying and choosing providers who charge Medicare-approved rates; and (2) to encourage providers to accept these rates. Given this program’s strong provider incentives, the number of participating providers grew rapidly across all states and today, the vast majority (96%) of eligible physicians and practitioners are “participating providers”—agreeing to charge Medicare’s standard fees when they see beneficiaries.
- The Congress instituted limitations on balance billing in 1989, in conjunction with implementation of the Medicare physician fee schedule. This financial protection limits the amount that “non-participating” providers may charge beneficiaries through balance billing—whereby beneficiaries are responsible for the portion of the provider’s charge that exceeds Medicare’s fee-schedule rate. Total out-of-pocket liability from balance billing has declined significantly over the past few decades dropping from $2.5 billion in 1983 ($5.65 billion in 2011 dollars) to $40 million in 2011.
- In 1997, the Congress codified several conditions for private contracting that apply to physicians and practitioners who “opt out” of Medicare and see beneficiaries only under individual private contracts. These restrictions were instituted to ensure that beneficiaries are aware of the financial ramifications of entering into these private contracts, and to safeguard patients and Medicare from fraud and abuse. In general, private contracting is relatively rare with only 1 percent of practicing physicians opting out of Medicare.
Background: Current Provider Options for Charging Medicare Patients
Under current law, physicians and practitioners have three options for how they will charge their patients in traditional Medicare. They may register with Medicare as (1) a participating provider, (2) a non-participating provider, or (3) an opt-out provider who privately contracts with each of his or her Medicare patients for payment (Figure 1). This issue brief describes these three options and then examines three current provisions in Medicare that provide financial protections for Medicare beneficiaries.
Participating providers: Physicians and practitioners who register with Medicare as participating providers agree to “accept assignment” for all of their Medicare patients. Accepting assignment entails two conditions: agreeing to accept Medicare’s fee-schedule amount as payment-in-full for a given service and collecting Medicare’s portion directly from Medicare, rather than the patient. Therefore, when Medicare patients see participating providers, they can be certain that these providers will not charge fees higher than Medicare’s published fee-schedule amount and that they will not face higher out-of-pocket liability than the maximum 20-percent coinsurance for most services. The vast majority (96%) of providers who provide Medicare-covered services are participating providers.
Non-participating providers: Non-participating providers do not agree to accept assignment for all of their Medicare patients; instead they may choose—on a service-by-service basis—to charge Medicare patients higher fees, up to a certain limit. When doing so, their Medicare patients are liable for higher cost sharing to cover the higher charges. This arrangement is called “balance billing” and means that the Medicare patient is financially responsible for the portion of the provider’s charge that is in excess of Medicare’s assigned rate, in addition to standard applicable coinsurance and deductibles for Medicare services. When non-participating providers do not accept assignment, they may not collect reimbursement from Medicare; rather, they bill the Medicare patient directly, typically up front at the time of service. Non-participating providers must submit claims to Medicare on behalf of their Medicare patients, but Medicare reimburses the patient, rather than the nonparticipating provider, for its portion of the covered charges. A small share (4%) of providers who provide Medicare-covered services are non-participating providers.
Opt-out providers, privately contracting: Physicians and practitioners who choose to enter into private contracts with their Medicare patients “opt-out” of the Medicare program entirely. These opt-out providers may charge Medicare patients any fee they choose. Medicare does not provide any reimbursement—either to the provider or the Medicare patient—for services provided by these providers under private contracts. Accordingly, Medicare patients are liable for the entire cost of any services they receive from physicians and practitioners who have opted out of Medicare. Several protections are in place to ensure that patients are clearly aware of their financial liabilities when seeing a provider under a private contract. An extremely small portion of physicians (less than 1% of physicians in clinical practice) have chosen to “opt-out” of the Medicare program, of whom 42 percent are psychiatrists.
These provider options have direct implications on the charges and out-of-pocket liabilities that beneficiaries face when they receive physician services (Figure 2). They also play a major role in several financial protections in current law—namely, the physician participation program, limitations on balance billing, and conditions for private contracting—which help beneficiaries understand the financial implications of their provider choices and encourage providers to accept Medicare’s standard fees.
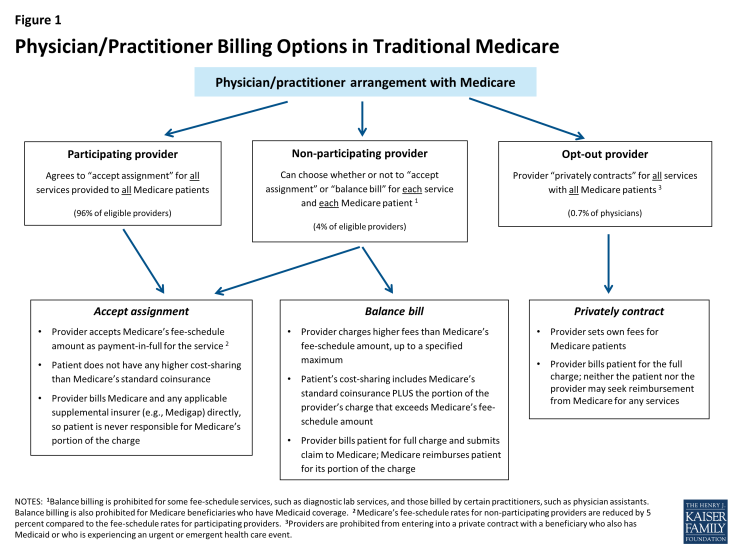
Figure 1: Physician/Practitioner Billing Options in Traditional Medicare
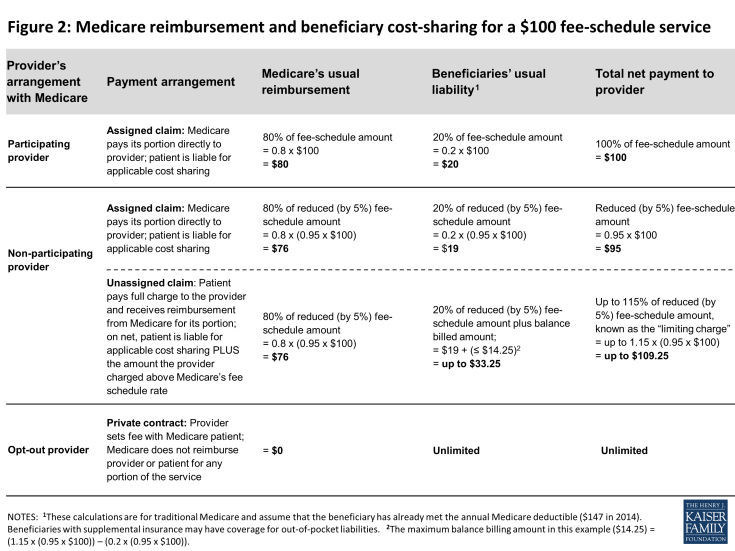
Figure 2: Medicare reimbursement and beneficiary cost-sharing for a $100 fee-schedule service
Medicare’s Participating Provider Program
Medicare’s participating provider program includes several incentives (both financial and nonfinancial) to encourage physicians and practitioners to “accept assignment” for all of their Medicare patients. When providers accept assignment, they agree to accept Medicare’s fee-schedule amount as payment-in-full for a given service and are allowed to bill Medicare directly for its portion of the reimbursement. Physicians and practitioners who agree to accept assignment on all services that they provide to Medicare patients are “participating providers” and are listed in Medicare provider directories. Beneficiaries who select a participating provider are assured that, after meeting the deductible, their coinsurance liability will not exceed 20 percent of the charge for the services they receive (Figure 2).
Congress established the participating provider program in the 1984 Deficit Reduction Act (DEFRA) to address two main concerns: confusion among beneficiaries about the fees they were being charged when they saw a doctor and escalating rates of balance billing from charges that exceeded Medicare’s established “usual, customary, and reasonable” rates for their area. 1 At that time, aside from Medicaid-eligible beneficiaries, Medicare had no limits on the amount that physicians and practitioners could balance bill for their services. Surveys conducted by the Physician Payment Review Commission (PPRC), a congressional advisory body and predecessor of the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC), revealed that prior to the participating provider program, beneficiaries often did not know from one physician to the next whether they would face extra out-of-pocket charges due to balance billing and how much those amounts might be. 2 By 1984, beneficiaries’ payment for balance billing reached 27 percent of total Medicare Part B out-of-pocket liability and was jeopardizing their access to affordable physician services. 3
The establishment of the participating provider program in Medicare instituted multiple incentives to encourage providers to accept assignment for all their patients and become participating providers. For example, Medicare payment rates for participating providers are 5 percent higher than the rates paid to non-participating providers. Also, participating providers may collect Medicare’s reimbursement amount directly from Medicare, in contrast to non-participating providers who may not collect payment from Medicare and typically bill their Medicare patients upfront for their charges. (Non-participating providers must submit claims to Medicare so that their patients are reimbursed for Medicare’s portion of their charges.) Participating providers also gain the benefit of having electronic access to Medicare beneficiaries’ supplemental insurance status, such as their Medigap coverage. This information makes it considerably easier for providers to file claims to collect beneficiary coinsurance amounts, as well as easing the paperwork burden on patients. Additionally, Medicare helps beneficiaries in traditional Medicare seek and select participating providers by listing them by name with their contact information on Medicare’s consumer-focused website (www.Medicare.gov).
Given the strong incentives of the participation program, combined with limits on balance billing (discussed in the next section), it is not surprising that the share of physicians and practitioners electing to be participating providers has risen to high levels across the country. Overall, the rate of providers with participation agreements has grown to 96 percent in 2011, up considerably from about 30 percent in 1986, two years after the start of the participating provider program (Figure 3). 4 As a result, across all states, most beneficiaries now encounter predictable expenses for Medicare-covered services, and are never responsible for Medicare’s portion of the fee (Appendix 1).
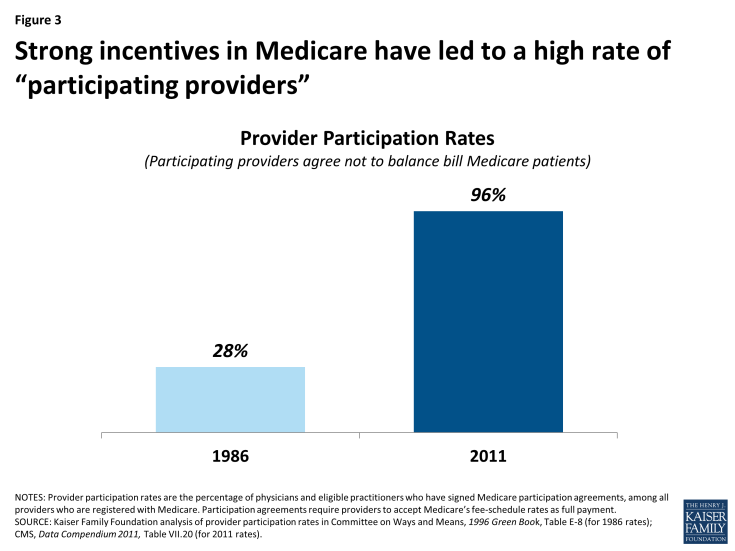
Figure 3: Strong incentives in Medicare have led to a high rate of “participating providers”
Medicare’s Balance Billing Limitations
Despite the incentives to become participating providers, a small share (4%) of physicians and practitioners who are registered with Medicare are non-participating providers. These providers can—on a service-by-service basis—charge patients in traditional Medicare higher fees than Medicare’s fee-schedule amount, up to a specified maximum. When charging higher fees, beneficiaries are responsible for the difference between Medicare’s approved amount and the providers’ total charge—essentially the balance of the bill remaining after accounting for Medicare’s reimbursement. This higher cost-sharing arrangement is called “balance billing” and means that the Medicare patient is financially liable for not only the applicable coinsurance and deductible, but also for any amount in which the provider’s charge exceeds Medicare’s assigned rate. Providers may not balance bill Medicare beneficiaries who also have Medicaid coverage. 5
When non-participating providers balance bill, they bill the beneficiary directly, typically for the full charge of the service—including Medicare’s share, applicable coinsurance and deductible, and any balance billed amount. Non-participating providers are then required to submit a claim to Medicare, so that Medicare can process the claim and reimburse the patient for Medicare’s share of the charge. Two Medigap insurance policies, which beneficiaries may purchase to supplement their Medicare coverage, include coverage for balance billing. 6 Balance billing is prohibited for Medicare-covered services in the Medicare Advantage program, except in the case of private fee-for-service plans.
In traditional Medicare, the maximum that non-participating providers may charge for a Medicare-covered service is 115 percent of the discounted fee-schedule amount. (Medicare’s fee-schedule rates for non-participating physicians are reduced by five percent.) Accordingly, non-participating providers may bill Medicare patients up to 9.25 percent more than participating providers (i.e., 1.15 x 0.95= 109.25). If the non-participating physician or practitioner balance bills the maximum amount permitted (not including any unmet deductible), total beneficiary liability for Medicare-covered services is about 33 percent of Medicare’s regular fee schedule amount (Figure 2).
Balance billing limitations were implemented in conjunction with the institution of Medicare’s physician fee-schedule in the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1989. At the time, Medicare’s charge-based methodology for physician services gave rise to rapid spending growth and confusion among beneficiaries about what charges they would face for physician services. 7 Moreover, high cost-sharing liabilities weighed disproportionately on beneficiaries who were sickest and used the most physician services. Despite physician reports that they took patient incomes into account when determining whether to charge higher-than Medicare rates, PPRC research did not find a relationship between beneficiary income and the probability that claims would be assigned. 8
While the Congress constrained growth in provider fees through the implementation of the fee schedule, it also implemented maximum “limiting charges” to establish further certainty and predictability for patients on their expected costs for services. In trying to rein in Medicare fee-schedule payments, the Congress sought to protect beneficiaries from excess charges that providers could otherwise impose in response to restrictions on their fees. 9
The continued desire to protect beneficiary spending during the implementation of the new physician fee schedule gave rise to the question of whether Congress might consider imposing even greater restrictions on balance billing or even mandate assignment (prohibiting balance billing) for all claims. 10 Ultimately, the rationale in Congress for allowing limited balance billing was that it would provide for: (1) a “safety valve” for physicians who believed that the fee schedule did not adequately reflect the quality of services that they provided; (2) a means to correct any underpricing of resource costs in the fee schedule; and (3) necessary financial protections for beneficiaries, particularly in areas of the country where choice of physicians was limited. 11
As limits on balance billing were implemented and incentives for physicians and practitioners to take assignment took hold, beneficiary liability for balance billing declined dramatically. CMS data show that in 2011, total balance billing amounted to $40 million, down significantly from $2.5 billion in 1983, (which equals $5.6 billion in 2011 dollars) (Figure 4). Concurrently, the rate of assigned claims to total covered charges climbed from 51% in 1983 to 99% in 2011.
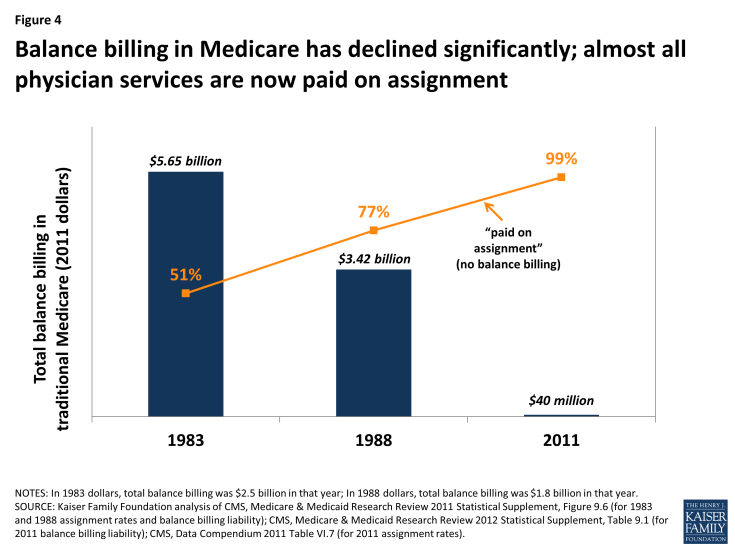
Figure 4: Balance billing in Medicare has declined significantly; almost all physician services are now paid on assignment
Private Contracting Conditions for Providers who Opt Out of Medicare
A very small share of providers (less than 1 percent of physicians) have elected to “opt out” of Medicare and contract privately with all of their Medicare patients, individually. 12 Their fees are not bound by Medicare’s physician fee schedule in any way, which means that these providers have no limits on the amounts they may charge beneficiaries for their services. Medicare does not reimburse either the provider or the patient for any services furnished by opt-out providers. Therefore, Medicare patients are financially responsible for the full charge of services provided by providers who have formally opted out of Medicare. 13
Serving as beneficiary protections, several important conditions exist for providers who elect to contract privately with Medicare patients. One condition is that prior to providing any service to Medicare patients, physicians and practitioners must inform their Medicare patients that they have opted out of Medicare and provide their Medicare patients with a written document stating that Medicare will not reimburse either the provider or the patient for any services furnished by opt-out providers. Their Medicare patients must sign this document to signify their understanding of it and their right to seek care from a physician or other practitioner who has not opted-out of Medicare.
Providers opt-out by submitting a signed affidavit to Medicare agreeing to applicable terms and affirming that their contracts with patients include all the necessary information. Physicians or practitioners who opt out of Medicare must privately contract with all of their Medicare patients, not just some. Once a physician or practitioner opts out of Medicare, this status lasts for a two-year period and is automatically renewed unless the physician or practitioner actively cancels it. 14 Providers may not enter into a private contract with a beneficiary who also has Medicaid benefits or who is experiencing an urgent or emergent health care event. 15
These conditions, which provide protections for both beneficiaries and the Medicare program, were included in the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 as part of the legislation that first codified physicians’ ability to privately contract with Medicare beneficiaries. Requiring opt-out providers to privately contract for all services they provide to Medicare patients (rather than being able to select by individual patients or services) was intended to prevent confusion among Medicare patients as to whether or not each visit would be covered under Medicare and how much they could expect to pay out-of-pocket. Similarly, requiring providers to opt out for a minimum period of time—two years—was intended to ensure that beneficiaries had consistent information to make knowledgeable choices when selecting their physicians. Both of these provisions also addressed Medicare’s duty to guard against fraudulent billing in an administratively feasibly manner. If, for example, physicians contracted with only some of their patients and/or services, Medicare would have to examine each contract for each submitted claim to discern which claims were eligible for Medicare reimbursement and which were not.
Previous Kaiser Family Foundation analysis shows that psychiatrists are disproportionately represented among the 0.7 percent of physicians (4,863) who have opted out of Medicare—comprising 42 percent of all physicians who have opted out (Figure 5). 16 Another 1,775 clinical professionals with non-physician doctorate degrees (i.e. oral surgeon dentists, podiatrists, and optometrists) also have opted-out of the Medicare program. 17 Dentists who are oral surgeons comprise the majority of this group (95%). Earlier research that examined opt-out providers through 2002 found similarly low numbers of providers opting out (2,839) as well as relatively higher opt-out rates among psychiatrists compared with other specialties. 18
Some physician organizations attribute physician decisions to opt out of Medicare to frustration with Medicare’s fees and regulations. 19 Others have noted a similar trend in physician refusal to work with any insurers—including commercial insurance plans—especially in prosperous communities. 20 In these cases, providers require patients to pay them directly out-of-pocket, leaving the patient to seek reimbursement, if any, from their insurer. For providers with patients who have the resources to make the payments, this billing method significantly reduces providers’ paperwork.
| Addiction Medicine | NA | — | 4 | — | 0.1% |
| Allergy/Immunology | 3,668 | 0.5% | 35 | 1.0% | 0.7% |
| Anesthesiology | 36,462 | 5.4% | 30 | 0.1% | 0.6% |
| Cardiovascular Disease/Cardiology | 19,637 | 2.9% | 29 | 0.1% | 0.6% |
| Colorectal Surgery/Proctology | NA | — | 1 | — | 0.0% |
| Dermatology | 10,101 | 1.5% | 96 | 1.0% | 2.0% |
| Emergency Medicine | 30,094 | 4.4% | 53 | 0.2% | 1.1% |
| Endocrinology | 4,502 | 0.7% | 32 | 0.7% | 0.7% |
| Family Medicine/General Practice | 97,779 | 14.4% | 702 | 0.7% | 14.4% |
| Gastroenterology | 11,550 | 1.7% | 20 | 0.2% | 0.4% |
| General Surgery | 21,896 | 3.2% | 41 | 0.2% | 0.8% |
| Geriatric Medicine | 3,367 | 0.5% | 5 | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Hand Surgery | NA | — | 3 | — | 0.1% |
| Hematology/Oncology | 10,261 | 1.5% | 14 | 0.1% | 0.3% |
| Infectious Disease | 5,007 | 0.7% | 10 | 0.2% | 0.2% |
| Internal Medicine | 93,381 | 13.8% | 447 | 0.5% | 9.2% |
| Maxillofacial Surgery | NA | — | 245 | — | 5.0% |
| Nephrology | 7,020 | 1.0% | 2 | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Neurology | 10,748 | 1.6% | 47 | 0.4% | 1.0% |
| Neurosurgery | 4,505 | 0.7% | 36 | 0.8% | 0.7% |
| Obstetrics/Gynecology | 36,978 | 5.5% | 375 | 1.0% | 7.7% |
| Ophthalmology | 16,598 | 2.4% | 30 | 0.2% | 0.6% |
| Orthopedic Surgery | 18,625 | 2.7% | 140 | 0.8% | 2.9% |
| Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine | NA | — | 49 | — | 1.0% |
| Otolaryngology | 8,636 | 1.3% | 35 | 0.4% | 0.7% |
| Pain Mgt/Interventional Pain Mgt | NA | — | 21 | — | 0.4% |
| Pathology | 11,231 | 1.7% | 2 | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Pediatric Medicine | 55,686 | 8.2% | 52 | 0.1% | 1.1% |
| Physical Medicine And Rehab, Sports Medicine | 7,435 | 1.1% | 50 | 0.7% | 1.0% |
| Plastic And Reconstructive Surgery | 6,379 | 0.9% | 127 | 2.0% | 2.6% |
| Preventative Medicine | 4,060 | 0.6% | 24 | 0.6% | 0.5% |
| Psychiatry, Geriatric Psychiatry, Neuropsychiatry | 38,781 | 5.7% | 2,029 | 5.2% | 41.7% |
| Pulmonary Disease, Critical Care/Intensivists | 10,486 | 1.5% | 6 | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Radiation Oncology | 4,032 | 0.6% | 1 | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Radiology, Nuclear Medicine | 24,887 | 3.7% | 19 | 0.1% | 0.4% |
| Rheumatology | 4,069 | 0.6% | 12 | 0.3% | 0.2% |
| Thoracic Surgery | 4,222 | 0.6% | 4 | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Urology | 9,180 | 1.4% | 29 | 0.3% | 0.6% |
| Vascular Surgery | 2,582 | 0.4% | 6 | 0.2% | 0.1% |
| Other, unspecified specialty* | 44,479 | 6.6% | NA | — | — |
| Chiropractic | NA | — | 5 | — | 0.3% |
| Optometry | NA | — | 52 | — | 2.9% |
| Oral Surgery (Dentist Only) | NA | — | 1,692 | — | 95.3% |
| Podiatry | NA | — | 26 | — | 1.5% |
| 100.0% | |||||
| NOTES: Physician counts include active physicians in patient care with an MD (Medical Doctor) or DO (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) degree. NA (not available) indicates that the specified specialty category is not supplied in the applicable data source. *Physicians in specialties with fewer than 2,500 total physicians are not categorized by specialty in AAMC analysis of AMA data (see Sources); 44,749 is the difference between the total number of physicians in patient care (678,324) and the number categorized by specialty (633,845). | |||||
| SOURCES: Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of: Physician counts from Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) 2012 Physician Specialty Data Book, using American Medical Association (AMA) Physician Masterfile (December 2010); Unpublished data from the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services, September 2013; Physician counts from AAMC, 2011 State Physician Workforce Data Book, using AMA Physician Masterfile (December 31, 2010). | |||||
Concierge Practice Models
Some physicians are turning to concierge practice models (also called retainer-based care), in which they charge their patients annual membership fees and typically have smaller patient caseloads. Physicians in a concierge practice model do not necessarily need to opt-out of Medicare to see Medicare patients. However, if they do not opt-out of Medicare, these physicians are subject to Medicare’s balance billing rules, and therefore, cannot charge beneficiaries additional fees for services that are already covered by Medicare. 21 For example, the annual fee for a concierge practice may not be used for the yearly wellness visit covered by Medicare, but it could be applied to items such as a newsletter and high-end waiting room furniture. More controversy exists about concierge practices applying annual fees paid by Medicare beneficiaries to enhanced appointment access and extra time with patients. 22
While anecdotal reports suggest a significant migration of primary care physicians to concierge/retainer practices, particularly in areas around Washington D.C and other major east and west coast cities, reliable data on the number of these practices are lacking. In 2010, a report for MedPAC found listings for 756 concierge physicians, compared with 146 found by Government Accountability Office in 2005. 23 Other news articles have reported larger numbers (4,400 in 2012) according to the American Association of Private Physicians. 24
Implications of Proposals to Modify Incentives and Relax Certain Financial Protections—Pros and Cons
Proposals introduced by Rep. Tom Price, House Speaker Paul Ryan and others have sought to relax private contracting conditions either throughout the Medicare program or as a demonstration project that could be implemented by the Administration. For example, in 2015, two Bills introduced in the House with a companion Bill in the Senate 25 include provisions to allow physicians and practitioners to engage in private contracting on a beneficiary-by-beneficiary basis, instead of requiring providers to opt-out of Medicare entirely. These Bills would also allow beneficiaries to seek Medicare reimbursement for the portion of the privately contracted fee that equals Medicare’s fee schedule amount, but no out-of-pocket limits would apply to the remaining portion of the provider’s charge. Similar changes are also proposed as a demonstration in the 2016 House Republican Plan, “A Better Way, our Vision for a Confident America.” 26 An earlier House Bill also included a demonstration to allow non-participating providers to collect Medicare’s portion of their charge directly from Medicare. 27
Pros: Support for Relaxing restrictions and increasing physician autonomy
Proponents of such proposals, including the American Medical Association, support relaxing restrictions on balance billing and private contracting for a number of reasons—perhaps the foremost is that they would allow physicians to charge Medicare beneficiaries higher rates and thereby get relief from fees that they say have failed to keep pace with the rising costs of running their practices. 28 Proponents also assert that this ability could increase the overall number of providers willing to accept Medicare patients. This concern may be an issue in some geographic areas, though surveys and other data sources show that nationally, access to physicians among Medicare seniors is generally comparable to access among people age 55 to 64 with private insurance. 29
Physician groups also state that proposals to relax constraints on balance billing and private contracting would give providers a sense of greater autonomy in how they relate to both their patients and the Medicare program and would allow physicians to charge higher fees to some patients based on their assessment of their patients’ ability to pay. 30 Additionally, beneficiaries would be able to seek at least partial Medicare reimbursement for services they received under private contracts. Proposals that would allow non-participating providers to collect Medicare’s portion of their charge directly from Medicare would obviate the need to charge patients the full fee upfront. This circumstance could be helpful to those patients who do not want to wait for Medicare’s reimbursement, even if on net, they would incur higher out-of-pocket liability due to balance billing. Non-participating providers could also experience a more reliable payment from Medicare, compared with the challenges, in some cases, of collecting fees from Medicare patients for unassigned claims.
Cons: Concerns about Eroding Financial Protections
Other analysts have raised concerns about the effects of relaxing private contracting rules and balance billing restrictions. 31 To the extent that such changes lead to increases in the number of non-participating and/or opt-out providers, they could exacerbate problems that lower-income beneficiaries face when seeking care. Beneficiaries without the ability to pay higher rates (who are also likely to be disproportionately sicker) could find a reduced pool of physicians willing to accept them. Also, for rarer physician specialties and in some geographic areas, such as rural parts of the country, patients may have little choice among physicians. If the limits on balance billing and private contracting were relaxed, beneficiaries in these situations could face the types of problems that existed prior to the imposition of limits on balance billing—high out-of-pocket costs and greater confusion and uncertainty about possible charges. Additionally, concerns have been raised about the accuracy and appropriateness of providers determining which Medicare patients in their caseload can afford higher fees, and by how much.
While proposals that allow beneficiaries and non-participating physicians to seek reimbursement from Medicare may, in the short term, reduce out-of-pocket liability for beneficiaries, they could also decrease the incentives for physicians and practitioners to become participating providers. In the long run, if significantly more providers balance billed their Medicare patients or opted-out of Medicare, this shift could alternatively increase beneficiary out-of-pocket spending.
From the perspective of the Medicare’s program integrity, Medicare would have significant difficulty tracking fraud and abuse if physicians were able to contract selectively for services with some but not all beneficiaries. Medicare would have to examine every physician-patient contract, on a claim-by-claim basis, to determine which claims could be reimbursed directly to the physician and which would be the full responsibility of the patient. Additionally, Medicare would need to examine these physicians’ billing practices to ensure that beneficiaries were not being charged inappropriately.
Conclusions
Balance billing limits, with incentives for physicians to accept assignment, have proven effective in limiting beneficiaries’ out-of-pocket liability for physician services. Today, a small share of Medicare beneficiaries experience balance billing just as only small share of provider claims in Medicare are paid unassigned—very different from the years before balance billing limits were instituted. Moreover, only about 1 percent of physicians provide services to beneficiaries on a private contracting basis. As the Congress has been considering changes to the way in which Medicare pays for physician service in the context of SGR repeal, some proposals have briefly surfaced to relax constraints on balance billing and private contracting.
On the one hand, these proposals could increase physician autonomy and provider willingness to treat Medicare patients, particularly among those providers who charge higher fees. On the other hand, such proposals could result in higher out-of-pocket liability, particularly in the longer term, which could affect beneficiary access to care. Additionally, relaxing these protections could foster less predictability in the fees beneficiaries encounter when seeing physicians and practitioners. Patients most at risk for experiencing a greater financial burden would be those with modest incomes and greater health care needs. Beneficiaries in geographic areas with limited choices of physicians might also be at higher risk if a growing number of providers choose to balance bill or require private contracts with their Medicare patients. The key is to strike a balance between assuring that providers receive fair payments from Medicare while also preserving financial protections that help beneficiaries face more predictable and affordable costs when they seek care.
Technical support in preparation of this brief was provided by Health Policy Alternatives, Inc.
- Consumer Protection
- Cost Sharing
- Medicare's Future
- ISSUE BRIEF
Also of Interest
- Medicare Patients’ Access to Physicians: A Synthesis of the Evidence - Issue Brief
- Visualizing Health Policy: Physicians and Medicare
Trending: Medicare's Future
- FAQs on Medicare Financing and Trust Fund Solvency
- Medicare 101
- New KFF Poll Finds that Many Older Voters Are Unaware of Medicare Drug Price Negotiation, But Awareness Has Grown
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
CMS Newsroom
Search cms.gov.
- Physician Fee Schedule
- Local Coverage Determination
- Medically Unlikely Edits
Provider Assignment
On this page:, provider nomination and the geographic assignment rule.
- Part A and Part B (A/B) and Home Health and Hospice (HH+H)
- Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics, and Supplies (DMEPOS)
- Specialty Providers and Demonstrations
- Railroad Retirement Beneficiaries Entitled to Medicare
- Qualified Chains
- Out-of-Jurisdiction Providers (OJP)
Section 911(b) of the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA), Public Law 108-173 , repealed the provider nomination provisions formerly found in Section 1816 of the Title XVIII of the Social Security Act and replaced it with the Geographic Assignment Rule. Generally, a provider or supplier will be assigned to the Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) that covers the state where the provider or supplier is located. The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) has defined the following approach for assigning providers, physicians, and suppliers to MACs.
return to top
Part A/Part B (A/B) and Home Health and Hospice (HH+H) Rule
All A/B and HH+H providers will be assigned to the MAC contracted by CMS to administer A/B and HH+H claims for the geographic locale in which the provider is physically located. Learn more about the current A/B MAC jurisdictions and HH+H areas and view the corresponding maps at Who are the MACs.
Durable Medical Equipment, Prosthetics, Orthotics, and Supplies (DMEPOS) Rule
Each DMEPOS supplier submits claims to the DME MAC contracted by CMS to administer DMEPOS claims for the geographic locale in which the beneficiary resides permanently. Learn more about the current DME MAC jurisdictions and view the corresponding map at Who are the MACs.
Specialty Providers and Demonstrations Rule
Specialty providers and providers involved with certain demonstrations will submit claims to a specific MAC designated by CMS. Learn more about a specific A/B MAC or DME MAC and view the corresponding maps at Who are the MACs .
Railroad Retirement Beneficiaries Entitled to Medicare Rule
Physicians and other suppliers (except for DMEPOS suppliers) will continue to enroll with and bill the contractor designated by the Railroad Retirement Board for Part B services furnished to their beneficiaries. Each DMEPOS supplier will submit claims to the DME MAC contracted by CMS to administer DMEPOS claims for the geographic locale in which the beneficiary resides permanently. Learn more about the current DME MAC jurisdictions and view the corresponding map at W ho are the MACs.
Qualified Chains Rule
The Geographic Assignment Rule states that generally, a provider or supplier will be assigned to the MAC that covers the state where the provider or supplier is located. However, it does provide an exception for qualified chains. A qualified chain home office may request that its hospitals and skilled nursing facilities be serviced by the A/B MAC that covers the state where the home office is located. A qualified chain home office may send an inquiry to: CMS [email protected]
Out-of-Jurisdiction Providers (OJP) Rule
An OJP is a provider that is not currently assigned to an A/B MAC in accordance with the geographic assignment rule and the qualified chain exception. For example, a hospital not part of a qualified chain located in Maine, but currently assigned to the A/B MAC in Jurisdiction F would be an OJP.
Each A/B MAC will initially service some OJPs until CMS undertakes the final reassignment of all OJPs to their destination MACs based on the geographic assignment rule and its exceptions.
CMS has not set a timetable for moving OJP’s.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
All providers who accept assignment must submit claims directly to Medicare, which pays 80 percent of the approved cost for the service and will bill you the remaining 20 percent. You can get some preventive services and screenings, such as mammograms and colonoscopies, without paying a deductible or coinsurance if the provider accepts assignment.
Medicare carriers are required to report, and act on, any violation of the assignment agreement. A physician/supplier is in violation of the assignment agreement if they collect, or attempt to collect: More than the deductible or coinsurance amount, or; A fee for the paperwork involved in filing the claim.
If your doctor, provider, or supplier doesn't accept assignment: You might have to pay the full amount at the time of service. They should submit a claim to Medicare for any Medicare-covered services they give you, and they can't charge you for submitting a claim. If they refuse to submit a Medicare claim, you can submit your own claim to ...
Non-assignment of Benefits. Non-assigned is the method of reimbursement a physician/supplier has when choosing to not accept assignment of benefits. Under this method, a non-participating provider is the only provider that can file a claim as non-assigned. When the provider does not accept assignment, the Medicare payment will be made directly ...
Subject to the requirements of the Assignment of Claims Act ( 31 U.S.C. 3727 ), Medicare may pay a government agency or entity under an assignment by the provider. ( 2) Payment under assignment established by court order. Medicare may pay under an assignment established by, or in accordance with, the order of a court of competent jurisdiction ...
Security Act, authorizes HHS-OIG to impose civil penalties for violations of the . Anti-Kickback Statute as well as a range of other violations. Penalties range . from $10,000 to $50,000 per violation. These violations include, but are not limited to: • Submitting false claims; • Violating Medicare assignment provisions or the physician ...
The diference between "fraud" and "abuse" depends on specific facts, circumstances, intent, and knowledge. Examples of Medicare abuse include: Billing for unnecessary medical services. Charging excessively for services or supplies. Misusing codes on a claim, such as upcoding or unbundling codes.
Medicare may pay under an assignment established by, or in accordance with, the order of a court of competent jurisdiction if the assignment meets the conditions set forth in § 424.90. (3) Payment to an agent. Medicare may pay an agent who furnishes billing and collection services to the provider if the following conditions are met:
penalties, identical to those for assignment violations, which may be imposed for violation of the agreement. J. When Ne w Physician or Supplie r in Area May Enter Into Agreement--A physician/supplier who has enrolled in the Medicare program and wishes to becom e a participating physician/supplier
Potential penalties for assignment violations. Providers who knowingly and willfully bill patients on an unassigned basis may be subject to sanctions, civil money penalties (up to $2,000 per violation), and exclusion from the Medicare program for a period of up to five years imposed. Beneficiaries are encouraged to report potential assignment ...
Bottom Line. Medicare assignment means a doctor or other healthcare provider will charge no more than the Medicare-approved amount for a particular service. This usually means lower out-of-pocket costs for patients who are covered by Medicare. It also means the provider will bill Medicare rather than expecting the patient to pay the full amount ...
Medicare assignment is a fee schedule agreement between the federal government's Medicare program and a doctor or facility. When Medicare assignment is accepted, it means your doctor agrees to the payment terms of Medicare. Doctors that accept Medicare assignment fall under one of three designations: a participating doctor, a non ...
1. Participating providers, or those who accept Medicare assignment. These providers have an agreement with Medicare to accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment for their services. You don't have to pay anything other than a copay or coinsurance (depending on your plan) at the time of your visit.
What is Medicare Assignment. Medicare assignment is an agreement by your doctor or other healthcare providers to accept the Medicare-approved amount as the full cost for a covered service. Providers who "accept assignment" bill Medicare directly for Part B-covered services and cannot charge you more than the applicable deductible and ...
Breaches of assignment agreements that result in beneficiaries being billed for a disallowed amount on the basis such charges exceeded the allowed charge (e.g., beneficiaries being billed for more than the 20 percent coinsurance) ... Violations of Medicare participation agreements by physicians or suppliers; Although these types of practices ...
Summary: Medicare Assignment is an agreement between healthcare providers and Medicare, where providers accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment, preventing them from charging beneficiaries extra. This benefits Medicare beneficiaries by controlling their costs and ensuring they only pay deductibles and copayments.
Medicare Assignment Violation . I am a Medicare recipient. I also have Medicaid. Medicare shows that Medicaid covers all copays and deductibles. This is news to me because I've been getting and paying bills. I contacted Medicare last week about a question related to billing, trying to understand how the process works. I'm not sure what ...
Accepting assignment entails two conditions: agreeing to accept Medicare's fee-schedule amount as payment-in-full for a given service and collecting Medicare's portion directly from Medicare ...
Complete the blank agreement (CMS-460) and submit it with your Medicare enrollment application to your MAC. If you have already enrolled in the Medicare program, you have 90 days from when you are enrolled to decide if you want to participate. If you decide to participate within this 90-day timeframe, complete the CMS-460 and send to your MAC.
violating Medicare assignment provisions; violating the Medicare physician agreement; providing false or misleading information expected to influence a decision to discharge; failing to provide an adequate medical screening examination for patients who present to a hospital emergency department with an emergency medical condition or in labor; and
A: If your doctor doesn't "accept assignment," (ie, is a non-participating provider) it means he or she might see Medicare patients and accept Medicare reimbursement as partial payment, but wants to be paid more than the amount that Medicare is willing to pay. As a result, you may end up paying the difference between what Medicare will ...
Breach of the Medicare participation or assignment agreements; Improper billing practices; Penalties for Fraud and Abuse. Fraud and abuse cases are routinely referred to the Office of Inspector General (OIG) for decisions on punishment. The OIG could use civil monetary penalty, criminal penalty, or administrative sanctions.
Provider Nomination and the Geographic Assignment Rule. Section 911(b) of the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 (MMA), Public Law 108-173, repealed the provider nomination provisions formerly found in Section 1816 of the Title XVIII of the Social Security Act and replaced it with the Geographic Assignment ...