
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students

Hacks How to Write a 10 and 20 page Paper in One Night
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: April 19, 2020

It’s the night before a big paper is due. For whatever reason, you find yourself needing to write an entire research paper in a very short amount of time. While procrastination isn’t ideal, extenuating circumstances may have caused your timeline to get pushed back. So, here you are, looking for how to write a 10-page paper or how to write a 20-page paper in one night.
It goes without saying the best way to write a paper is to give yourself enough time to outline, draft, and edit. Yet, it’s still possible to write in less time. Take heed of these best tips and tricks to organize your thoughts and get your thesis on paper as fast as possible.
Photo by Adolfo Félix on Unsplash
How to prepare before you write, 1. create a schedule to maximize your time.
You’ve likely already spent time panicking. Once you calm yourself of the anxiety of having to finish a 10- or 20-page paper in one night, organize your plan of attack. First, you should designate an area free of distractions so that you can focus. Aside from a few breaks and snacks, it’s best to set up a comfortable place to write. Give yourself some time to outline and find/cite research . Once you know how you’re going to approach the subject, then you can start drafting.
2. Determine your Main Topic
If you’ve been given a prompt, then your topic is clear. However, sometimes you have the freedom to choose what your research will be about. In this case, it’s smartest to choose a topic that you are already knowledgeable about. That way, you will save yourself key time that would have otherwise been spent on research. If you don’t feel strongly about any particular topic, then at least try to pick one that has a lot of information available.
3. Perform Research
Start looking up sources to cite that support your thesis, or main argument. As you research, be sure to take notes. One of the best ways to do this is to use a word processor like Google Docs or Microsoft Word to copy and paste URLs. For each source, it would be best to copy/paste one main sentence that covers its point.
Then, you can write brief notes in your own words that summarize what you have read from that source. While you are performing research, you can start to put together an outline, or the flow of how you will present your ideas broken down by topic and argument.
4. Outline 3-5 subtopics
Once you’ve chosen your topic, then try to pull 3-5 subtopics from it. Each sub-topic should be juicy enough to be able to write a lot about it. The subtopics are your supporting paragraphs which fill the body of the research paper. They should basically be mini essays within themselves.
Writing in One Night
Writing a long research paper in one night isn’t ideal, but it is doable. Some of the best ways to get it done is to follow these 5 tips:
1. Plan and Outline
Take those few extra moments to plan and outline your paper. While it may feel like a waste of valuable time, it is going to help you stay on track. When you have an outline and you get to the middle of your paper, you won’t feel lost as to how to continue. An outline will be useful to you like a map is on a journey.
2. Use Specialized Search
Take advantage of search tools that are designed for scholars. For example, a few of these include: Google Scholar and Elsevier .
3. Leverage Tools
There are citation management tools that will help you find sources for your topic. Mendeley is just one of them. You can type parts of your paper into the tool and find quotes of value. Be sure to cite everything you use to avoid plagiarism .
4. Proofread and Edit
Once you complete writing 10 to 20 pages, you may feel like throwing in the towel and going to sleep for a few hours. However, it is crucial to power through and proofread your paper. If you have anyone available who can read your paper over, that would be best because it’s hard to catch mistakes when you’ve been looking at the same thing for so long. But, if no one is available, try to read your paper back to yourself out loud. This way, you may be able to catch typos better.
5. Check Formatting
Every research paper needs to adhere to a particular format guideline. Whether it’s APA, MLA, or another standard formatting practice, be sure to double check that your layout adheres to the guidelines.
Photo by Christin Hume on Unsplash
When to start writing.
If you have yet to find yourself trying to write a paper at the last minute and all the notes above are scaring you out of procrastination, then that’s a good start! Perhaps you were recently assigned a research paper. In this case, the best way to tackle the project is to do the following:
Start Early
Get started right away. Even if it means just performing early research or writing an outline, starting early is going to save you from having to write a paper in one night down the line. When you start early, you benefit greatly because you can: leverage peers for ideas, take the necessary time to edit and rewrite, and you lower your risk of picking a topic with too little information and having to change topics at the last minute.
Writing in Stages
Starting early also affords you the opportunity to write in stages. You can think of writing as a cycle when you write in stages. First, you can create your outline. Then, you can write the introduction, edit it, and rewrite anything you may need to before moving on to the next piece (or the first body paragraph, in this case).
Use a Timeline
Create a timeline for your writing in stages. If you start four weeks in advance, for example, you have time to do all of the following:
- Fully understand the assignment and ask any questions
- Start to read and document sources
- Create notecards and cite books for sources
- Write a summary of what you’ve discovered so far that will be used in some of your paper
- Create 3-5 subtopics and outline points you want to explore
- Look for more sources on your subtopics
- Start writing summaries on each subtopic
- Write some analysis of your findings
- Start to piece together the research paper based on your notes and outline (almost like completing a puzzle)
- Edit and proofread / ask for feedback
The Writing Process
The actual writing process is a little different for everyone, but this is a general overview for how to write a 20-page paper, or one that is shorter.
- Start with a Thesis: Your thesis is one sentence that clearly and concisely explains what you are going to prove with research.
- Include a Menu Sentence: At the end of your introduction, you will briefly outline your subtopics in what is often referred to as a “menu sentence.” This allows the reader to understand what they can expect to learn about as they continue to read your paper.
- Create a Detailed Introduction: Your introduction should be detailed enough so that someone with little to no knowledge about your subject matter can understand what the paper is about.
- Keep References: Be sure to write your references as you go along so that you basically can create your bibliography in the process of writing. Again, this is where a tool like Mendeley may be useful.
- Write First: Write first and edit later. You want to get all your ideas down on the page before you start judging or editing the writing.
- Save Often: Create the draft on a cloud platform that is automatically saved (i.e. Google Docs in case your computer crashes) or email the work to yourself as you go.
The Breakdown of a 10-Page Paper
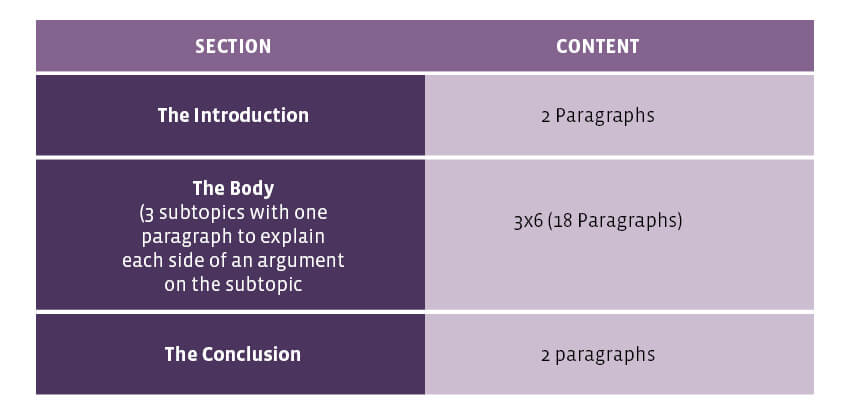
Sources to Consider Using
When writing your research paper and finding sources, it’s best to use a mix of sources. This may include:
- Internet: The Internet is filled with limitless possibilities. When you use the Internet, it’s best to find credible and trustworthy sources to avoid using fake news as a source. That’s why tools like Google Scholar can be so helpful.
- Textbooks: It’s more likely than not that you’ll be able to use your class textbook as a source for the research you are conducting.
- Books: Additionally, other books outside of those you read within your class will prove useful in any research paper.
Final Steps: Editing and Formatting
Once you’ve written all your ideas on the page, it’s time to edit. It cannot be stressed enough that editing is pivotal before submission. This is especially true if you’ve been writing under immense pressure.
Writing a 10- or 20-page research paper in one night is not easy, so there are bound to be mistakes and typos. The best way to catch these mistakes is to follow these tips:
- Take a break before you edit so you can come back to the page with somewhat fresh eyes and a clearer head
- Read it out loud to edit and catch mistakes because sometimes your brain will override typos or missing words to make sense of what it is reading
- If possible, ask someone else to look it over
- Consider using footnotes or block quotes
- Format according to how your university asks – MLA or APA, etc.
The Bottom Line
Life throws curveballs your way without warning. Whether you are holding yourself accountable for procrastinating or something out of your control came up, you may find yourself needing to write a big research paper in one night. It’s not the best-case scenario, but with the right tools and tricks up your sleeve, you can surely get it done!
In this article
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone.
7 Tips in Writing a 12-Page Paper at the Last Minute
Learn 7 essential tips to write a 12-page paper quickly, including breaking it down, crafting a strong thesis, and editing effectively. Overcome last-minute writing challenges with these strategies.
Glice Martineau
Jun 13, 2024

Picture this: it's the night before your paper is due, and you're staring at a blank document, wondering how to write a 12-page paper in such a short amount of time.
The cursor blinks mockingly at you as the panic starts to set in. We've all been there – procrastination, unexpected events, or simply underestimating the time needed for such a lengthy assignment.
The good news is that it's still possible to write a compelling informative or scientific paper , even when you're in a time crunch.
In this blog post, we'll share seven proven tips to help you tackle that daunting task and submit your paper on time, without compromising on quality.
So, take a deep breath, grab your favorite caffeinated beverage, and let's dive in!
7 Practical Tips for Writing a Paper for Procrastinators
Tip 1: break down the 12-page paper into manageable sections.
When writing a 12-page research paper, break the task into smaller sections. This makes the process less overwhelming and helps you maintain focus.
Create an outline with clear sections and subsections to serve as a roadmap for your paper. Arrange the papers at key points in a logical flow and include relevant subsections for specific details.
Allocate a specific number of pages for each section to maintain a balanced structure throughout your entire paper.
For example, dedicate 2-3 pages for the introduction, 7-8 pages for the body paragraphs, and 1-2 pages for the conclusion.
Set mini-deadlines for each section to stay on track. Break it down into smaller tasks and assign realistic deadlines. Give yourself 2 hours for the introductory paragraph, 5 hours for the first half of one night the body paragraphs, and so on.
Breaking your paper into manageable sections is crucial when tackling a lengthy assignment under time constraints. By creating an outline, allocating pages strategically, and setting mini-deadlines, you'll write a well-structured 12-page research paper, even when time is limited.
Tip 2: Gather Your Resources and Take Effective Notes
Before starting the writing process, gather relevant resources and take effective notes to support your thesis statement.
Use online academic databases and library resources to quickly identify key sources. Utilize search functions to find materials that relate directly to your research paper topic.
Skim through sources to determine relevance and usefulness. Focus on abstracts, introductions, conclusions, and section headings. Take concise notes on key ideas, important points, and examples that support your main argument.

Organize notes to align with your outline based your paper outline, creating sections for each main point. Categorize notes accordingly for easy reference while writing.
Record citation information for each source, such as author, title, publication date, and page numbers, to save time when creating your works cited page.
Gathering resources and taking effective notes provides a solid foundation for writing your 12-page paper efficiently under time constraints.
Tip 3: Write a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is the most important part of a well-written research paper. It provides clear direction throughout the body paragraph the research paper.
To create a thesis, ensure it is clear, specific, and arguable. A clear thesis leaves no doubt about your main argument, while a specific thesis narrows your focus. An arguable thesis presents a debatable claim supported by research evidence.
Importance of a Thesis Statement
When writing your thesis, directly address the paper prompt or question. Read the assignment guidelines carefully and respond concisely with your own words and main points.
Use your thesis to guide your writing process and maintain focus. Every paragraph and article should relate to and support your thesis. If you stray, reevaluate your writing to align with your central claim.
Remember, your thesis can be revised as you gather information and develop concepts. Modify your thesis as your research paper evolves, but keep it clear, specific, and arguable.
Easily pronounces technical words in any field
Tip 4: Dive into Writing Without Perfecting Every Sentence
When writing a 12-page research paper under time constraints, focus on getting your theses down without pursuing perfect phrasing. Start writing your first draft without worrying about structure or grammar.
Writing your First Draft
Follow your outline and let your statemets flow. Your outline guides you, ensuring you cover all main points. Allow your writing to be rough in this initial stage.
Resist to edit every sentence to perfection as you write. This slows progress and causes frustration. The first draft is about getting your thoughts out, not creating a polished final draft.
You'll refine your writing during the edit process. Once you've finished writing your draft, prioritize sentence structure, word choice, and clarity. Editing is the time to fine-tune your work.
By writing without perfecting every last sentence first, you'll make significant progress on your 12-page paper. Maintain momentum and avoid getting stuck on minor details. The goal is to get your ideas down and create a solid foundation for your final draft.
Tip 5: Use Transitional Phrases to Connect Ideas
When writing a research paper, ensure your concepts flow smoothly from one sentence or paragraph to the next using transitional phrases. These words and phrases effectively link paragraphs and sections, creating a good paper with a cohesive structure.
Using Transitions
Transitional phrases bridge your thesis statements and insights, guiding readers through your arguments and showing how each point relates to your thesis statement. Examples include "moreover," "furthermore," "however," "in contrast," "similarly," and "as a result." Place these phrases strategically at the beginning or end of paragraphs to introduce new premises, counterarguments, or conclusions.
Using transitional phrases is crucial in a 12-page paper to maintain a smooth flow throughout. Without proper transitions, your paper may feel disjointed, making it difficult to follow your main idea. Transitional phrases ensure logical progression and build between sections.
Transitional phrases also help build coherent arguments by connecting main concepts and evidence. Use phrases like "firstly," "secondly," and "finally" to organize thoughts and show their relationship to your thesis. This makes arguments easier to follow and strengthens your research paper's impact.
Vary your transitional phrases to avoid monotony. Use a variety of words and phrases that suit your arguments' context.
Employing transitional phrases strategically ensures your 12-page paper has a smooth flow and coherent structure, even under tight deadlines.
Tip 6: Don't Neglect Your Introduction and Conclusion
When writing a 12-page research paper under time constraints, it's tempting to focus solely on paragraphs and leave the introduction and conclusion for last. However, these sections are crucial for framing arguments and leaving a lasting impression.

To ensure effective introductions and conclusions, write them after completing paragraphs. This allows for a clear understanding of key points and structure before crafting these sections.
Introduction in Research Paper
Introductions should provide context and clearly state your subject or thesis statement. Briefly explain background information, present your thesis, and outline key points, giving readers a roadmap.
Conclusions in Research Paper
Conclusions should summarize main points and restate your thesis in light of presented evidence. Emphasize research significance and implications without introducing new information. Synthesize key concepts and provide closure.
Balance introduction and conclusion length proportionally to the paper's overall length. Dedicate about 10% of the total word count to each section. For a 3,000-word paper, introductions and conclusions should be approximately 300 words each.
Introductions and conclusions are the bookends of your research paper. They engage readers, establish main arguments, and leave lasting impacts. Writing these sections after paragraphs and dedicating appropriate time ensures a strong, cohesive 12-page paper.
Tip 7: Leave Time for Editing and Proofreading
After finishing your 12-page paper, set aside time for editing and proofreading. Reviewing and refining your paper can significantly improve its quality and impact.
Helpful Tips to Edit
When editing, double check for clarity, coherence, and cohesive flow of ideas. Read through your work with fresh eyes so you can catch mistakes.
Ensure your arguments make sense and ideas are clear and organized. Fill gaps in reasoning and provide additional evidence as needed.
Consider your paper's structure. Each paragraph should flow smoothly, with topic sentences introducing main ideas. Cut irrelevant or redundant information.
Proofread for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors. Minor mistakes can detract from your paper's quality and credibility. Use spell check tools and carefully read through your work. Pay attention to punctuation, capitalization, and citation formatting.
Ask someone to review your paper and provide feedback. Fresh eyes can catch overlooked mistakes and offer an outside perspective on your arguments' effectiveness.
Allocate sufficient time for editing and proofreading. You may need several hours or a full day to thoroughly review and refine your work. A well-edited and polished paper can significantly impact your grade and research.
Final Thoughts
Writing a 12-page paper last minute is daunting, but with the right strategies and mindset, you can successfully complete your project on time. Stay calm, focused, and organized. Break your paper into manageable sections, create an outline, and set mini-deadlines.
Gather resources and take effective notes, focusing on concepts and arguments that support your main statement. Craft a clear, specific, and arguable thesis statement addressing the prompt and guiding your writing. Don't perfect every sentence in your draft; focus on getting your thoughts down and following your outline.
Use transitional phrases for smooth idea flow between paragraphs and sections. Don't neglect a well-written introduction and conclusion. After your draft, edit and proofread for clarity, coherence, and errors.
By implementing these strategies and staying positive, you as students can overcome the challenges of writing a lengthy paper under time constraints.
Stay focused, trust your abilities, and remember that dedication and perseverance will help you complete your 12-page paper on time. Good luck!
Research Paper
Writing Tips
Recent articles

Best Business Schools in the US
Jul 10, 2024
Graduate School
United States of America
Business School

When Does College Start in the US?
Kate Windsor
College search tools
College admissions guide
College planning tips
College academic calendar
Summer term
Quarter system calendar
Spring semester start
Fall semester start
College start dates
When does college start

How to Apply to Graduate School? Practical and Helpful Tips
Derek Pankaew
Jul 11, 2024
#GradSchoolApplication
#GraduateSchool
#HigherEducation
#AdmissionTips
#PersonalStatement

9 Things I Wish I Knew Before Starting a PhD
#AcademicJourney
#GradSchoolTips
#PhDStudentLife
#ResearchAndMentorship

Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia
How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
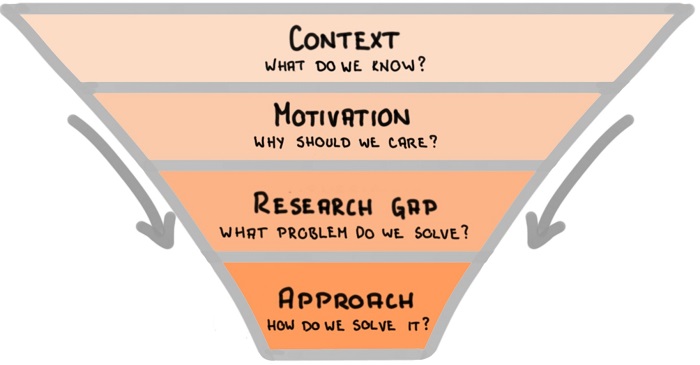
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
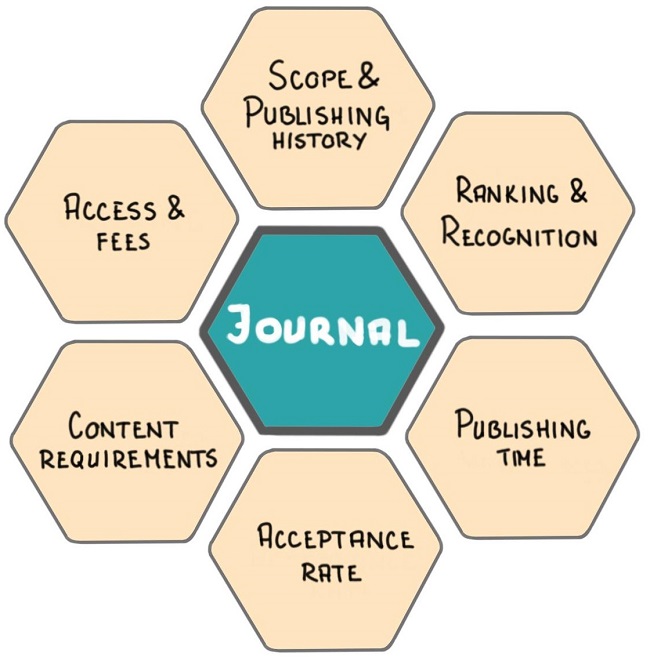
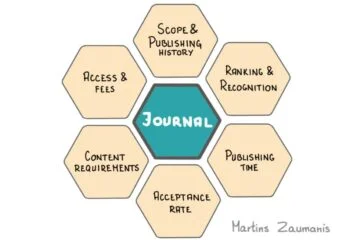
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy

A step-by-step guide for creating and formatting APA Style student papers
The start of the semester is the perfect time to learn how to create and format APA Style student papers. This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and figures, and the reference list. Finally, it concludes by describing how to organize student papers and ways to improve their quality and presentation.
The guidelines for student paper setup are described and shown using annotated diagrams in the Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3.40MB) and the A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Style Student Papers webinar . Chapter 1 of the Concise Guide to APA Style and Chapter 2 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association describe the elements, format, and organization for student papers. Tables and figures are covered in Chapter 7 of both books. Information on paper format and tables and figures and a full sample student paper are also available on the APA Style website.
Basic setup
The guidelines for basic setup apply to the entire paper. Perform these steps when you first open your document, and then you do not have to worry about them again while writing your paper. Because these are general aspects of paper formatting, they apply to all APA Style papers, student or professional. Students should always check with their assigning instructor or institution for specific guidelines for their papers, which may be different than or in addition to APA Style guidelines.
Seventh edition APA Style was designed with modern word-processing programs in mind. Most default settings in programs such as Academic Writer, Microsoft Word, and Google Docs already comply with APA Style. This means that, for most paper elements, you do not have to make any changes to the default settings of your word-processing program. However, you may need to make a few adjustments before you begin writing.
Use 1-in. margins on all sides of the page (top, bottom, left, and right). This is usually how papers are automatically set.
Use a legible font. The default font of your word-processing program is acceptable. Many sans serif and serif fonts can be used in APA Style, including 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, 12-point Times New Roman, and 11-point Georgia. You can also use other fonts described on the font page of the website.
Line spacing
Double-space the entire paper including the title page, block quotations, and the reference list. This is something you usually must set using the paragraph function of your word-processing program. But once you do, you will not have to change the spacing for the entirety of your paper–just double-space everything. Do not add blank lines before or after headings. Do not add extra spacing between paragraphs. For paper sections with different line spacing, see the line spacing page.
Paragraph alignment and indentation
Align all paragraphs of text in the body of your paper to the left margin. Leave the right margin ragged. Do not use full justification. Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5-in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. For paper sections with different alignment and indentation, see the paragraph alignment and indentation page.
Page numbers
Put a page number in the top right of every page header , including the title page, starting with page number 1. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word-processing program to insert the page number in the top right corner; do not type the page numbers manually. The page number is the same font and font size as the text of your paper. Student papers do not require a running head on any page, unless specifically requested by the instructor.
Title page setup
Title page elements.
APA Style has two title page formats: student and professional (for details, see title page setup ). Unless instructed otherwise, students should use the student title page format and include the following elements, in the order listed, on the title page:
- Paper title.
- Name of each author (also known as the byline).
- Affiliation for each author.
- Course number and name.
- Instructor name.
- Assignment due date.
- Page number 1 in the top right corner of the page header.
The format for the byline depends on whether the paper has one author, two authors, or three or more authors.
- When the paper has one author, write the name on its own line (e.g., Jasmine C. Hernandez).
- When the paper has two authors, write the names on the same line and separate them with the word “and” (e.g., Upton J. Wang and Natalia Dominguez).
- When the paper has three or more authors, separate the names with commas and include “and” before the final author’s name (e.g., Malia Mohamed, Jaylen T. Brown, and Nia L. Ball).
Students have an academic affiliation, which identities where they studied when the paper was written. Because students working together on a paper are usually in the same class, they will have one shared affiliation. The affiliation consists of the name of the department and the name of the college or university, separated by a comma (e.g., Department of Psychology, George Mason University). The department is that of the course to which the paper is being submitted, which may be different than the department of the student’s major. Do not include the location unless it is part of the institution’s name.
Write the course number and name and the instructor name as shown on institutional materials (e.g., the syllabus). The course number and name are often separated by a colon (e.g., PST-4510: History and Systems Psychology). Write the assignment due date in the month, date, and year format used in your country (e.g., Sept. 10, 2020).
Title page line spacing
Double-space the whole title page. Place the paper title three or four lines down from the top of the page. Add an extra double-spaced blank like between the paper title and the byline. Then, list the other title page elements on separate lines, without extra lines in between.
Title page alignment
Center all title page elements (except the right-aligned page number in the header).
Title page font
Write the title page using the same font and font size as the rest of your paper. Bold the paper title. Use standard font (i.e., no bold, no italics) for all other title page elements.
Text elements
Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. Begin the paper with an introduction to provide background on the topic, cite related studies, and contextualize the paper. Use descriptive headings to identify other sections as needed (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers). Sections and headings vary depending on the paper type and its complexity. Text can include tables and figures, block quotations, headings, and footnotes.
Text line spacing
Double-space all text, including headings and section labels, paragraphs of text, and block quotations.
Text alignment
Center the paper title on the first line of the text. Indent the first line of all paragraphs 0.5-in.
Left-align the text. Leave the right margin ragged.
Block quotation alignment
Indent the whole block quotation 0.5-in. from the left margin. Double-space the block quotation, the same as other body text. Find more information on the quotations page.
Use the same font throughout the entire paper. Write body text in standard (nonbold, nonitalic) font. Bold only headings and section labels. Use italics sparingly, for instance, to highlight a key term on first use (for more information, see the italics page).
Headings format
For detailed guidance on formatting headings, including headings in the introduction of a paper, see the headings page and the headings in sample papers .
- Alignment: Center Level 1 headings. Left-align Level 2 and Level 3 headings. Indent Level 4 and Level 5 headings like a regular paragraph.
- Font: Boldface all headings. Also italicize Level 3 and Level 5 headings. Create heading styles using your word-processing program (built into AcademicWriter, available for Word via the sample papers on the APA Style website).
Tables and figures setup
Tables and figures are only included in student papers if needed for the assignment. Tables and figures share the same elements and layout. See the website for sample tables and sample figures .
Table elements
Tables include the following four elements:
- Body (rows and columns)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the table)
Figure elements
Figures include the following four elements:
- Image (chart, graph, etc.)
- Note (optional if needed to explain elements in the figure)
Table line spacing
Double-space the table number and title. Single-, 1.5-, or double-space the table body (adjust as needed for readability). Double-space the table note.
Figure line spacing
Double-space the figure number and title. The default settings for spacing in figure images is usually acceptable (but adjust the spacing as needed for readability). Double-space the figure note.
Table alignment
Left-align the table number and title. Center column headings. Left-align the table itself and left-align the leftmost (stub) column. Center data in the table body if it is short or left-align the data if it is long. Left-align the table note.
Figure alignment
Left-align the figure number and title. Left-align the whole figure image. The default alignment of the program in which you created your figure is usually acceptable for axis titles and data labels. Left-align the figure note.
Bold the table number. Italicize the table title. Use the same font and font size in the table body as the text of your paper. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the table note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Figure font
Bold the figure number. Italicize the figure title. Use a sans serif font (e.g., Calibri, Arial) in the figure image in a size between 8 to 14 points. Italicize the word “Note” at the start of the figure note. Write the note in the same font and font size as the text of your paper.
Placement of tables and figures
There are two options for the placement of tables and figures in an APA Style paper. The first option is to place all tables and figures on separate pages after the reference list. The second option is to embed each table and figure within the text after its first callout. This guide describes options for the placement of tables and figures embedded in the text. If your instructor requires tables and figures to be placed at the end of the paper, see the table and figure guidelines and the sample professional paper .
Call out (mention) the table or figure in the text before embedding it (e.g., write “see Figure 1” or “Table 1 presents”). You can place the table or figure after the callout either at the bottom of the page, at the top of the next page, or by itself on the next page. Avoid placing tables and figures in the middle of the page.
Embedding at the bottom of the page
Include a callout to the table or figure in the text before that table or figure. Add a blank double-spaced line between the text and the table or figure at the bottom of the page.
Embedding at the top of the page
Include a callout to the table in the text on the previous page before that table or figure. The table or figure then appears at the top of the next page. Add a blank double-spaced line between the end of the table or figure and the text that follows.
Embedding on its own page
Embed long tables or large figures on their own page if needed. The text continues on the next page.
Reference list setup
Reference list elements.
The reference list consists of the “References” section label and the alphabetical list of references. View reference examples on the APA Style website. Consult Chapter 10 in both the Concise Guide and Publication Manual for even more examples.
Reference list line spacing
Start the reference list at the top of a new page after the text. Double-space the entire reference list (both within and between entries).
Reference list alignment
Center the “References” label. Apply a hanging indent of 0.5-in. to all reference list entries. Create the hanging indent using your word-processing program; do not manually hit the enter and tab keys.
Reference list font
Bold the “References” label at the top of the first page of references. Use italics within reference list entries on either the title (e.g., webpages, books, reports) or on the source (e.g., journal articles, edited book chapters).
Final checks
Check page order.
- Start each section on a new page.
- Arrange pages in the following order:
- Title page (page 1).
- Text (starts on page 2).
- Reference list (starts on a new page after the text).
Check headings
- Check that headings accurately reflect the content in each section.
- Start each main section with a Level 1 heading.
- Use Level 2 headings for subsections of the introduction.
- Use the same level of heading for sections of equal importance.
- Avoid having only one subsection within a section (have two or more, or none).
Check assignment instructions
- Remember that instructors’ guidelines supersede APA Style.
- Students should check their assignment guidelines or rubric for specific content to include in their papers and to make sure they are meeting assignment requirements.
Tips for better writing
- Ask for feedback on your paper from a classmate, writing center tutor, or instructor.
- Budget time to implement suggestions.
- Use spell-check and grammar-check to identify potential errors, and then manually check those flagged.
- Proofread the paper by reading it slowly and carefully aloud to yourself.
- Consult your university writing center if you need extra help.
About the author

Undergraduate student resources
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.

How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
1. Choose your topic
2. find information on your topic, 3. create a thesis statement, 4. create a research paper outline, 5. organize your notes, 6. write your introduction, 7. write your first draft of the body, 9. write your conclusion, 10. revise again, edit, and proofread, frequently asked questions about starting your research paper, related articles.
Research papers can be short or in-depth, but no matter what type of research paper, they all follow pretty much the same pattern and have the same structure .
A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis.
There will be some basic differences, but if you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper.
Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
- make sure your topic is not too broad
- narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general
Academic search engines are a great source to find background information on your topic. Your institution's library will most likely provide access to plenty of online research databases. Take a look at our guide on how to efficiently search online databases for academic research to learn how to gather all the information needed on your topic.
Tip: If you’re struggling with finding research, consider meeting with an academic librarian to help you come up with more balanced keywords.
If you’re struggling to find a topic for your thesis, take a look at our guide on how to come up with a thesis topic .
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing. It can be defined as a very brief statement of what the main point or central message of your paper is. Our thesis statement guide will help you write an excellent thesis statement.
In the next step, you need to create your research paper outline . The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
Then, fill out your outline with the following components:
- the main ideas that you want to cover in the paper
- the types of evidence that you will use to support your argument
- quotes from secondary sources that you may want to use
Organizing all the information you have gathered according to your outline will help you later on in the writing process. Analyze your notes, check for accuracy, verify the information, and make sure you understand all the information you have gathered in a way that you can communicate your findings effectively.
Start with the introduction. It will set the direction of your paper and help you a lot as you write. Waiting to write it at the end can leave you with a poorly written setup to an otherwise well-written paper.
The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready.
After your first draft, take some time to check the paper for content errors. Rearrange ideas, make changes and check if the order of your paragraphs makes sense. At this point, it is helpful to re-read the research paper guidelines and make sure you have followed the format requirements. You can also use free grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .
Tip: Consider reading your paper from back to front when you undertake your initial revision. This will help you ensure that your argument and organization are sound.
Write your conclusion last and avoid including any new information that has not already been presented in the body of the paper. Your conclusion should wrap up your paper and show that your research question has been answered.
Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit, and proofread your paper.
Tip: Take a break from your paper before you start your final revisions. Then, you’ll be able to approach your paper with fresh eyes.
As part of your final revision, be sure to check that you’ve cited everything correctly and that you have a full bibliography. Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize your research and to create accurate citations.
The first step to start writing a research paper is to choose a topic. Make sure your topic is not too broad; narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general.
The format of your research paper will vary depending on the journal you submit to. Make sure to check first which citation style does the journal follow, in order to format your paper accordingly. Check Getting started with your research paper outline to have an idea of what a research paper looks like.
The last step of your research paper should be proofreading. Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit and proofread your paper.
There are plenty of software you can use to write a research paper. We recommend our own citation software, Paperpile , as well as grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .

- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
How to Write a 10-Page Research Paper
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A large research paper assignment can be scary and intimidating. As always, this large assignment becomes more manageable (and less scary) whenever you break it down into digestible bites.
Start Early
The first key to writing a good research paper is starting early. There are a few good reasons to get an early start:
- The best sources for your topic might be taken by other students, or they might be located in a faraway library.
- It will take time to read the sources and write those note cards.
- You will find that every rewrite of your paper makes it better. Give yourself plenty of time to polish your paper.
- If you wait until the last minute, you could find that there is no information available to support your topic or thesis. You might need to find a new topic.
Write in Stages
The timeline below should help you get to the number of pages you desire. The key to writing a long research paper is writing in stages: You will need to establish a general overview first and then identify and write about several subtopics.
The second key to writing a lengthy research paper is to think of the writing process as a cycle. You will alternate researching, writing, reordering, and revising.
You will need to revisit each subtopic to insert your own analysis and arrange the proper order of your paragraphs in the final stages. Be sure to cite all information that is not common knowledge. Consult a style guide to make sure you are always citing properly.
Use a Timeline
Develop your own timeline with the tool below. If possible start the process four weeks before the paper is due.
| Research Paper Timeline | |
|---|---|
| Understand the assignment completely. | |
| Obtain general knowledge about your topic by reading from the internet and from encyclopedias. | |
| Find a good general book about your topic. | |
| Take notes from the book using index cards. Write several cards containing paraphrased information and clearly indicated quotes. Indicate page numbers for everything you record. | |
| Write a two-page overview of your topic using the book as a source. Include page numbers for the information you use. You don’t have to worry about format just yet—just type page numbers and author/book name for now. | |
| Pick five interesting aspects that could serve as subtopics of your subject. Focus in on a few major points that you could write about. These could be influential people, historical background, an important event, geographical information, or anything relevant to your subject. | |
| Find good sources that address your subtopics. These could be or books. Read or skim those to find the most relevant and useful information. Make more note cards. Be careful to indicate your source name and the page number for all of the information you record. | |
| If you find these sources aren’t providing enough material, look at the bibliographies of those sources to see what sources they used. Determine whether you need to find the original source material rather than relying on secondary references. | |
| Visit your library to order any articles or books (from the bibliographies) that are not available in your own library. | |
| Write a page or two for every one of your subtopics. Save each page in a separate file according to the subject. Print them out. | |
| Arrange your printed pages (subtopics) in a logical order. When you find a sequence that makes sense, cut and paste the pages together into one big file. Don’t delete your individual pages, though. You may need to come back to these. | |
| You may find it necessary to break up your original two-page overview and insert parts of it into your subtopic paragraphs. | |
| Write a few sentences or paragraphs of your analysis of each subtopic. | |
| Now you should have a clear idea of the focus of your paper. Develop a preliminary thesis statement. | |
| Fill in of your research paper. | |
| Develop a draft of your paper. | |
- Strategies for Writing a 20-Page Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- How to Outline and Organize an Essay
- Brainstorming Techniques for Students
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- What Is a Research Paper?
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography for a Paper
- Why Archaeology Topics Are Great Options for Research Papers
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- Writing a Descriptive Essay
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- Finding Trustworthy Sources
- Writing a Paper about an Environmental Issue

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1964 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 41,397 quotes across 1964 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
Published on August 7, 2022 by Courtney Gahan . Revised on August 15, 2023.

A research paper outline is a useful tool to aid in the writing process , providing a structure to follow with all information to be included in the paper clearly organized.
A quality outline can make writing your research paper more efficient by helping to:
- Organize your thoughts
- Understand the flow of information and how ideas are related
- Ensure nothing is forgotten
A research paper outline can also give your teacher an early idea of the final product.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Research paper outline example, how to write a research paper outline, formatting your research paper outline, language in research paper outlines.
- Definition of measles
- Rise in cases in recent years in places the disease was previously eliminated or had very low rates of infection
- Figures: Number of cases per year on average, number in recent years. Relate to immunization
- Symptoms and timeframes of disease
- Risk of fatality, including statistics
- How measles is spread
- Immunization procedures in different regions
- Different regions, focusing on the arguments from those against immunization
- Immunization figures in affected regions
- High number of cases in non-immunizing regions
- Illnesses that can result from measles virus
- Fatal cases of other illnesses after patient contracted measles
- Summary of arguments of different groups
- Summary of figures and relationship with recent immunization debate
- Which side of the argument appears to be correct?
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Follow these steps to start your research paper outline:
- Decide on the subject of the paper
- Write down all the ideas you want to include or discuss
- Organize related ideas into sub-groups
- Arrange your ideas into a hierarchy: What should the reader learn first? What is most important? Which idea will help end your paper most effectively?
- Create headings and subheadings that are effective
- Format the outline in either alphanumeric, full-sentence or decimal format
There are three different kinds of research paper outline: alphanumeric, full-sentence and decimal outlines. The differences relate to formatting and style of writing.
- Alphanumeric
- Full-sentence
An alphanumeric outline is most commonly used. It uses Roman numerals, capitalized letters, arabic numerals, lowercase letters to organize the flow of information. Text is written with short notes rather than full sentences.
- Sub-point of sub-point 1
Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points.
- Additional sub-point to conclude discussion of point of evidence introduced in point A
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences.
- 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point
- 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point
- 1.2 Second point
To write an effective research paper outline, it is important to pay attention to language. This is especially important if it is one you will show to your teacher or be assessed on.
There are four main considerations: parallelism, coordination, subordination and division.
Parallelism: Be consistent with grammatical form
Parallel structure or parallelism is the repetition of a particular grammatical form within a sentence, or in this case, between points and sub-points. This simply means that if the first point is a verb , the sub-point should also be a verb.
Example of parallelism:
- Include different regions, focusing on the different arguments from those against immunization
Coordination: Be aware of each point’s weight
Your chosen subheadings should hold the same significance as each other, as should all first sub-points, secondary sub-points, and so on.
Example of coordination:
- Include immunization figures in affected regions
- Illnesses that can result from the measles virus
Subordination: Work from general to specific
Subordination refers to the separation of general points from specific. Your main headings should be quite general, and each level of sub-point should become more specific.
Example of subordination:
Division: break information into sub-points.
Your headings should be divided into two or more subsections. There is no limit to how many subsections you can include under each heading, but keep in mind that the information will be structured into a paragraph during the writing stage, so you should not go overboard with the number of sub-points.
Ready to start writing or looking for guidance on a different step in the process? Read our step-by-step guide on how to write a research paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. (2023, August 15). How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/outline/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, writing a research paper introduction | step-by-step guide, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, what is your plagiarism score.
How to Write a Research Paper

If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you at the edge of your seat? Let us start with the basics then.
- What is a Research Paper
- Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
- Report Papers and Thesis Papers
- How to Start a Research Paper
- How to Choose a Topic for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Plan
- How to Do Research
- How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Rough Draft
- How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Body of a Research Paper
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Revise and Edit a Research Paper
- How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper
- What Makes a Good Research Paper
Research Paper Writing Services
What is a research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
You probably know the saying ‘the devil is not as black as he is painted’. This particular saying is absolutely true when it comes to writing a research paper. Your feet are cold even with the thought of this assignment. You have heard terrifying stories from older students. You have never done this before, so certainly you are scared. What is a research paper? How should I start? What are all these requirements about?
Luckily, you have a friend in need. That is our writing service. First and foremost, let us clarify the definition. A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides information about a particular topic that you’ve researched . In other words, you choose a topic: about historical events, the work of some artist, some social issues etc. Then you collect data on the given topic and analyze it. Finally, you put your analysis on paper. See, it is not as scary as it seems. If you are still having doubts, whether you can handle it yourself, we are here to help you. Our team of writers can help you choose the topic, or give you advice on how to plan your work, or how to start, or craft a paper for you. Just contact us 24/7 and see everything yourself.
5 Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
Why should I spend my time writing some academic paper? What is the use of it? Is not some practical knowledge more important? The list of questions is endless when it comes to a research paper. That is why we have outlined 5 main reasons why writing a research paper is a good thing.
- You will learn how to organize your time
If you want to write a research paper, you will have to learn how to manage your time. This type of assignment cannot be done overnight. It requires careful planning and you will need to learn how to do it. Later, you will be able to use these time-managing skills in your personal life, so why not developing them?
- You will discover your writing skills
You cannot know something before you try it. This rule relates to writing as well. You cannot claim that you cannot write until you try it yourself. It will be really difficult at the beginning, but then the words will come to your head themselves.
- You will improve your analytical skills
Writing a research paper is all about investigation and analysis. You will need to collect data, examine and classify it. These skills are needed in modern life more than anything else is.
- You will gain confidence
Once you do your own research, it gives you the feeling of confidence in yourself. The reason is simple human brain likes solving puzzles and your assignment is just another puzzle to be solved.
- You will learn how to persuade the reader
When you write your paper, you should always remember that you are writing it for someone to read. Moreover, you want this someone to believe in your ideas. For this reason, you will have to learn different convincing methods and techniques. You will learn how to make your writing persuasive. In turns, you will be able to use these methods in real life.
What is the Difference between Report and Thesis Papers?
A common question is ‘what is the difference between a report paper and a thesis paper?’ The difference lies in the aim of these two assignments. While the former aims at presenting the information, the latter aims at providing your opinion on the matter. In other words, in a report paper you have to summarize your findings. In a thesis paper, you choose some issue and defend your point of view by persuading the reader. It is that simple.
A thesis paper is a more common assignment than a report paper. This task will help a professor to evaluate your analytical skills and skills to present your ideas logically. These skills are more important than just the ability to collect and summarize data.
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
Research comes from the French word rechercher , meaning “to seek out.” Writing a research paper requires you to seek out information about a subject, take a stand on it, and back it up with the opinions, ideas, and views of others. What results is a printed paper variously known as a term paper or library paper, usually between five and fifteen pages long—most instructors specify a minimum length—in which you present your views and findings on the chosen subject.

It is not a secret that the majority of students hate writing a research paper. The reason is simple it steals your time and energy. Not to mention, constant anxiety that you will not be able to meet the deadline or that you will forget about some academic requirement.
We will not lie to you; a research paper is a difficult assignment. You will have to spend a lot of time. You will need to read, to analyze, and to search for the material. You will probably be stuck sometimes. However, if you organize your work smart, you will gain something that is worth all the effort – knowledge, experience, and high grades.
The reason why many students fail writing a research paper is that nobody explained them how to start and how to plan their work. Luckily, you have found our writing service and we are ready to shed the light on this dark matter.
We have created a step by step guide for you on how to write a research paper. We will dwell upon the structure, the writing tips, the writing strategies as well as academic requirements. Read this whole article and you will see that you can handle writing this assignment and our team of writers is here to assist you.
How to Start a Research Paper?

It all starts with the assignment. Your professor gives you the task. It may be either some general issue or specific topic to write about. Your assignment is your first guide to success. If you understand what you need to do according to the assignment, you are on the road to high results. Do not be scared to clarify your task if you need to. There is nothing wrong in asking a question if you want to do something right. You can ask your professor or you can ask our writers who know a thing or two in academic writing.
It is essential to understand the assignment. A good beginning makes a good ending, so start smart.
Learn how to start a research paper .
Choosing a Topic for a Research Paper

We have already mentioned that it is not enough to do great research. You need to persuade the reader that you have made some great research. What convinces better that an eye-catching topic? That is why it is important to understand how to choose a topic for a research paper.
First, you need to delimit the general idea to a more specific one. Secondly, you need to find what makes this topic interesting for you and for the academia. Finally, you need to refine you topic. Remember, it is not something you will do in one day. You can be reshaping your topic throughout your whole writing process. Still, reshaping not changing it completely. That is why keep in your head one main idea: your topic should be precise and compelling .
Learn how to choose a topic for a research paper .
How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper?

If you do not know what a proposal is, let us explain it to you. A proposal should answer three main questions:
- What is the main aim of your investigation?
- Why is your investigation important?
- How are you going to achieve the results?
In other words, proposal should show why your topic is interesting and how you are going to prove it. As to writing requirements, they may differ. That is why make sure you find out all the details at your department. You can ask your departmental administrator or find information online at department’s site. It is crucial to follow all the administrative requirements, as it will influence your grade.
Learn how to write a proposal for a research paper .
How to Write a Research Plan?

The next step is writing a plan. You have already decided on the main issues, you have chosen the bibliography, and you have clarified the methods. Here comes the planning. If you want to avoid writer’s block, you have to structure you work. Discuss your strategies and ideas with your instructor. Think thoroughly why you need to present some data and ideas first and others second. Remember that there are basic structure elements that your research paper should include:
- Thesis Statement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
You should keep in mind this skeleton when planning your work. This will keep your mind sharp and your ideas will flow logically.
Learn how to write a research plan .
How to Do Research?

Your research will include three stages: collecting data, reading and analyzing it, and writing itself.
First, you need to collect all the material that you will need for you investigation: films, documents, surveys, interviews, and others. Secondly, you will have to read and analyze. This step is tricky, as you need to do this part smart. It is not enough just to read, as you cannot keep in mind all the information. It is essential that you make notes and write down your ideas while analyzing some data. When you get down to the stage number three, writing itself, you will already have the main ideas written on your notes. Plus, remember to jot down the reference details. You will then appreciate this trick when you will have to write the bibliography.
If you do your research this way, it will be much easier for you to write the paper. You will already have blocks of your ideas written down and you will just need to add some material and refine your paper.
Learn how to do research .
How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper?

To make your paper well organized you need to write an outline. Your outline will serve as your guiding star through the writing process. With a great outline you will not get sidetracked, because you will have a structured plan to follow. Both you and the reader will benefit from your outline. You present your ideas logically and you make your writing coherent according to your plan. As a result, this outline guides the reader through your paper and the reader enjoys the way you demonstrate your ideas.
Learn how to write an outline for a research paper . See research paper outline examples .
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper?

Briefly, the thesis is the main argument of your research paper. It should be precise, convincing and logical. Your thesis statement should include your point of view supported by evidence or logic. Still, remember it should be precise. You should not beat around the bush, or provide all the possible evidence you have found. It is usually a single sentence that shows your argument. In on sentence you should make a claim, explain why it significant and convince the reader that your point of view is important.
Learn how to write a thesis statement for a research paper . See research paper thesis statement examples .
Should I Write a Rough Draft for a Research Paper?

Do you know any writer who put their ideas on paper, then never edited them and just published? Probably, no writer did so. Writing a research paper is no exception. It is impossible to cope with this assignment without writing a rough draft.
Your draft will help you understand what you need to polish to make your paper perfect. All the requirements, academic standards make it difficult to do everything flawlessly at the first attempt. Make sure you know all the formatting requirements: margins, words quantity, reference requirements, formatting styles etc.
Learn how to write a rough draft for a research paper .
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper?

Let us make it more vivid for you. We have narrowed down the tips on writing an introduction to the three main ones:
- Include your thesis in your introduction
Remember to include the thesis statement in your introduction. Usually, it goes at the end of the first paragraph.
- Present the main ideas of the body
You should tell the main topics you are going to discuss in the main body. For this reason, before writing this part of introduction, make sure you know what is your main body is going to be about. It should include your main ideas.
- Polish your thesis and introduction
When you finish the main body of your paper, come back to the thesis statement and introduction. Restate something if needed. Just make it perfect; because introduction is like the trailer to your paper, it should make the reader want to read the whole piece.
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper . See research paper introduction examples .
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper?

A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument.
It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic. Stay focused and do not be sidetracked. You have your outline, so follow it.
Here are the main tips to keep in head when writing a body of a research paper:
- Let the ideas flow logically
- Include only relevant information
- Provide the evidence
- Structure the paragraphs
- Make the coherent transition from one paragraph to another
See? When it is all structured, it is not as scary as it seemed at the beginning. Still, if you have doubts, you can always ask our writers for help.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper . See research paper transition examples .
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper?

Writing a good conclusion is important as writing any other part of the paper. Remember that conclusion is not a summary of what you have mentioned before. A good conclusion should include your last strong statement.
If you have written everything according to the plan, the reader already knows why your investigation is important. The reader has already seen the evidence. The only thing left is a strong concluding thought that will organize all your findings.
Never include any new information in conclusion. You need to conclude, not to start a new discussion.
Learn how to write a conclusion for a research paper .
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper?

An abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually 100-200 words. You should provide the main gist of your paper in this short summary. An abstract can be informative, descriptive or proposal. Depending on the type of abstract, you need to write, the requirements will differ.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research.
To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery. You should write a short teaser of your paper. That is to say, you need to write an overview of your paper. The aim of a descriptive abstract is to interest the reader.
Finally, to write a proposal abstract you will need to write the basic summary as for the informative abstract. However, the difference is the following: you aim at persuading someone to let you write on the topic. That is why, a proposal abstract should present your topic as the one worth investigating.
Learn how to write an abstract for a research paper .
Should I Revise and Edit a Research Paper?

Revising and editing your paper is essential if you want to get high grades. Let us help you revise your paper smart:
- Check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes
- Sharpen the vocabulary
- Make sure there are no slang words in your paper
- Examine your paper in terms of structure
- Compare your topic, thesis statement to the whole piece
- Check your paper for plagiarism
If you need assistance with proofreading and editing your paper, you can turn to the professional editors at our service. They will help you polish your paper to perfection.
Learn how to revise and edit a research paper .
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper?

First, let us make it clear that bibliography and works cited are two different things. Works cited are those that you cited in your paper. Bibliography should include all the materials you used to do your research. Still, remember that bibliography requirements differ depending on the formatting style of your paper. For this reason, make sure you ask you professor all the requirements you need to meet to avoid any misunderstanding.
Learn how to write a bibliography for a research paper .
The Key Secret to a Good Research Paper
Now when you know all the stages of writing a research paper, you are ready to find the key to a good research paper:
- Choose the topic that really interests you
- Make the topic interesting for you even if it is not at the beginning
- Follow the step by step guide and do not get sidetracked
- Be persistent and believe in yourself
- Really do research and write your paper from scratch
- Learn the convincing writing techniques and use them
- Follow the requirements of your assignment
- Ask for help if needed from real professionals
Feeling more confident about your paper now? We are sure you do. Still, if you need help, you can always rely on us 24/7.
We hope we have made writing a research paper much easier for you. We realize that it requires lots of time and energy. We believe when you say that you cannot handle it anymore. For this reason, we have been helping students like you for years. Our professional team of writers is ready to tackle any challenge.
All our authors are experienced writers crafting excellent academic papers. We help students meet the deadline and get the top grades they want. You can see everything yourself. All you need to do is to place your order online and we will contact you. Writing a research paper with us is truly easy, so why do not you check it yourself?
Additional Resources for Research Paper Writing:
- Anthropology Research
- Career Research
- Communication Research
- Criminal Justice Research
- Health Research
- Political Science Research
- Psychology Research
- Sociology Research
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

12 Page Essay & Research Paper Examples
What does a 12 page essay look like? If you’re searching for an answer to this question, you’re in the right place! Such a paper is a standard high school and college assignment. That’s why it might be written on almost any topic. Overpopulation, organic farming, religion and police brutality are just some of the options.
A 12 page essay word count is usually 2950 to 3000 words (12 pt., double-spaced). The length of a typical academic paragraph is 100 to 150 words. So, there are 19 to 30 paragraphs in a paper of 12 pages.
If you need 12 page essay examples, look at the list below. We’ve collected A+ samples for you to get inspired. Good luck with your writing!
12-page Essay Examples: 1542 Samples
Staff development and managing technology.
- Subjects: Education Teacher Career
- Words: 3295
Catholic Charities and Their Relevance
- Subjects: Religion Religion, Culture & Society
- Words: 3453
The Pros of Raising the Canadian Minimum Wage
- Subjects: Government Politics & Government
- Words: 3177
Marlene Dietrich: Life and Professional Career
- Subjects: Actors Entertainment & Media
- Words: 3346
Effect of Organizational Factors on Performance
- Subjects: Business Management
- Words: 3353
Importance of Sound
- Subjects: Art Music
- Words: 3134
Business Plan of Alrajhi Bank
- Subjects: Economics Finance
- Words: 3497
September 11th 2001 Analysis
- Subjects: Terrorism Prevention Warfare
- Words: 3250
Group Communication: Decision Making and Problem Solving
- Subjects: Communications Sociology
- Words: 3438
How Children’s Cartoons Are Politicized
- Subjects: Socialization Sociology
- Words: 3316
The Effects of the Internet on People’s Ability for Deep Thought and Extended Contemplation
- Subjects: Everyday Interactions Sociology
- Words: 3299

Integrated Project Evaluation and Selection Using Multiple-Attribute Decision Making Technique
- Subjects: Business Case Study
- Words: 3327
Technology & Innovation: LG Electronics Strategy Report
- Words: 2977
Building a Residential House – Risk Management Plan
- Subjects: Business Strategic Management
- Words: 2748
The Mind and the Body
- Subjects: Philosophical Concept Philosophy
- Words: 3265
Unions and Compensation in Major League Baseball
- Subjects: Sport Games Sports
- Words: 3328
Operations Management: Product Delivery Problem Cessna Aircraft Company
- Words: 3267
Legal Response to Substance Abuse During Pregnancy
- Subjects: Criminal Law Law
- Words: 3969
Concept of Bioregionalism in Environmental Ecosystems
- Subjects: Ecology Environment
- Words: 3365
Determining Why Employee Job Satisfaction Is Low – A Verizon Wireless Corporation
- Words: 3056
Forms and Effects of Globalization
- Subjects: Economics Globalization
- Words: 3347
How Capitalism Beat Communism/Socialism
- Subjects: History World History
- Words: 3359
Media and Homosexuality
- Subjects: Gender Identity Sociology
- Words: 3488
The Serfs in Poland
- Subjects: Eastern Europe History
Managing Workforce Diversity
- Subjects: Business Workforce
- Words: 3067
Boosting Business: Organizational Theory and Design
- Words: 3508
Popular Culture and Teenage Pregnancy Among Americans
- Subjects: Sociological Issues Sociology
- Words: 3290
Objection to the Production of Genetically Modified Foods
- Subjects: Genetics Sciences
- Words: 3273
Libya: Moammar Gaddafi
- Words: 3260
Business Ethics-Labeling Genetically Modified Food
- Subjects: Diet & Nutrition Genetically Modified Food
- Words: 3120
Influence of Student Diversity and the Teaching Practice
- Subjects: Culture and Education Education
- Words: 3407
Intervention Strategies in Children Development
- Subjects: Education Pedagogy
- Words: 3471
Difference Between Quality Control and Quality Assurance
- Subjects: Business Managerial Duties
- Words: 3563
Taking Blood Pressure: Storyboard Concept
- Subjects: Cardiology Health & Medicine
- Words: 1930
Bellamy and Spencer: “Looking Backward” by Edward Bellamy
- Subjects: Economic Systems & Principles Economics
- Words: 3305
Wangari Maathai’s First Person Experience in “Unbowed: A Memoir”
- Subjects: Literature World Literature
- Words: 3246
International Assignments
- Words: 3452
Google Company Future Sustainability
- Subjects: Business Company Missions
- Words: 3442
Emerging Operational Challenges in Airport Management
- Words: 3253
Factors that influence Major League and Minor League Baseball
- Words: 3241
The Spread of Diseases among Health Care Providers
- Subjects: Epidemiology Health & Medicine
- Words: 3324
Biblical and Scholarly portrayal of King David
- Subjects: Religion Theology
- Words: 3662
Colin Powell Leadership Characteristics
- Subjects: Historical Figures History
- Words: 3275
Civic Education
- Words: 3291
AT&T and T-Mobile Analysis
- Words: 3398
How to Start a New Business?
- Subjects: Business Strategy
- Words: 3277
The Role of Health Care Systems and Industrial System Engineering in Improvement of Health
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Healthcare Institution
- Words: 1804
Corporate Social Responsibility of University of Dubai
- Subjects: Business Employees Management
- Words: 3258
Hamas and the US Policy
- Words: 3371
Evolution of Fire Fighting Gear
- Subjects: Accidents & Protection Tech & Engineering
- Words: 3236
The Rise of Airbus
- Words: 3271
Cuban Americans Throughout the U.S. History
- Subjects: Immigration Sociology
- Words: 3184
HSBC Holdings: Chinese Banking Sector
- Subjects: Business Company Analysis
- Words: 3221
LVMH Moët Hennessy – Louis Vuitton
- Words: 3146
Lack of Quality Management During Hurricane Katrina
- Words: 3180
Reasons Why the Black Women Population Did Not Consider Themselves a Part of the Ongoing Feminist Movements
- Subjects: Feminism Sociology
- Words: 3335
A Closer Look at the Life of Princess Diana
- Words: 3000
Domestic Violence in the African American Community
- Subjects: Psychology Psychology of Abuse
Grenner Pastures the Launch of StaGreen by HydroCan Company
- Subjects: Business Marketing
- Words: 3644
Historical Parallels Between George Orwell’s 1984 and Today
- Subjects: Literature Themes in American Novels
- Words: 3364
Eco Dryers Export Company
- Words: 3247
Darfur Genocide
- Subjects: Contemporary History History
- Words: 3245
Contracts and Corporations
- Subjects: Business & Corporate Law Law
- Words: 3252
John Renoir, a French Filmmaker
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Movies
Security dilemma in the Middle East
- Subjects: International Relations Politics & Government
Excessive Force by the Police
- Subjects: Law Enforcement Politics & Government
- Words: 3298
Stub Hub- Ticket Scalping and online sales
- Words: 3256
The Federal Trade Commission Act
- Subjects: Economics Trade
- Words: 3282
Single-Parent Families
- Subjects: Overcoming Difficulties Sociology
- Words: 3232
Individualism vs. Collectivism
- Subjects: Sociological Theories Sociology
- Words: 3239
Global Developments that Affect State Sovereignty and Territoriality
- Words: 3312
Religion and Tourism Relations
- Subjects: Tourism Tourist Attractions
- Words: 3206
Social Consequences of Tourism
- Subjects: Tourism Trips and Tours
A Literary Analysis of William Faulkner’s Barn Burning
Simulation in production planning and scheduling.
- Subjects: Business Organizational Management
- Words: 2489
GlaxoSmithKline’s Leadership Management Framework
- Subjects: Business Leadership Styles
- Words: 3153
Ship in a Bottle
- Subjects: Business Company Information
- Words: 3292
Vaccinations: An Unnecessary Danger to Human Health
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Immunology
- Words: 3289
Integrated Information Systems
- Words: 3300
Can Genetically Modified Food Feed the World: Agricultural and Biotechnological Perspective
Eminent women in psychological science.
- Subjects: Psychological Issues Psychology
- Words: 3342
Leadership Skills of Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum’s
- Words: 3255
Arab Women in Media
- Subjects: Gender Studies Sociology
- Words: 3254
Most Annoying Things about Common Blog Post Titles
- Subjects: Languages Linguistics
- Words: 3630
Post-Cold War Challenges
Leadership models and theories: management process in organization.
- Words: 3363
Managing Globalisation: A Case of Indesit
Stress related to workplace conditions.
- Words: 3322
Cleveland’s Poor Economy and Deplorable Housing Conditions
- Subjects: Economics Housing
- Words: 2591
Causes of Workplace Safety and Health
- Words: 3237
Conservation Status of Poached Species in Africa: A Case of Rhinos, Elephants, and Gorillas
- Subjects: Ecological Identity Environment
- Words: 2650
Future in Marketing using the Mobile Phone
Total quality management at the br engineering.
- Words: 3402
Billboard as an Element of the Popular Culture
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Pop Culture
- Words: 3498
Effective Business Messages vs. Effective Communication
- Subjects: Business Business Communication
- Words: 3259
Total Quality Management: Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Fundamentals of a performance management system.
- Words: 3459
Kitsch – under the Title of Taste and Ethics
- Subjects: Art Visual Arts
- Words: 3420
Women in Entrepreneurship
- Subjects: Business Entrepreneurship
- Words: 3172
Motivational Program and Alcoholics Anonymous
- Subjects: Professional Psychology Psychology
- Words: 3737
On What Grounds is the Idea of Universal Human Rights Challenged?
- Words: 5039
Strategic Analysis
- Words: 3859
How Does Ford Treat Their Employees? Essay
- Words: 3234
The Role of Women in the American Society of the 17th Century
- Subjects: History Women Studies
- Words: 2594
Enacting an Initiative through the Information System
- Words: 1134
Compensation Philosophy of Google – Structure & Benefits Essay
The concept of corporate governance and its implications for managers.
- Subjects: Business Corporate Governance
Rene Girard’s Social Theories
- Subjects: Philosophers Philosophy
Cisco’s Building of Brand
Economic policies of different countries.
- Subjects: Economics International Trade Policy
- Words: 3350
Al-Marai Company: International Market Entry Plan
- Words: 3243
Hart Devlin Debate: Summary & Analysis
- Subjects: Law Philosophy Philosophy
- Words: 3257
The Major Factors Affecting Future of the Tourism Industry in UK
Music industry and technology.
- Subjects: Other Technology Tech & Engineering
- Words: 3878
Advantages and Disadvantages Management of Motivation Theories
- Words: 3551
Change & Continuity in Contemporary Business: Harley-Davidson
- Words: 3505
Enslavement and the Modern Society
- Subjects: Slavery Sociology
- Words: 3368
Environmental Analysis in Norway
- Words: 3339
How the Internet Affects Politics and Elections?
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Social Media Issues
- Words: 3249
Video Games Impact on Peoples Lives
- Subjects: Computer Science Tech & Engineering
- Words: 3703
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Paper
Last Updated: February 18, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Chris Hadley, PhD . Chris Hadley, PhD is part of the wikiHow team and works on content strategy and data and analytics. Chris Hadley earned his PhD in Cognitive Psychology from UCLA in 2006. Chris' academic research has been published in numerous scientific journals. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,193,550 times.
Whether you’re in a history, literature, or science class, you’ll probably have to write a research paper at some point. It may seem daunting when you’re just starting out, but staying organized and budgeting your time can make the process a breeze. Research your topic, find reliable sources, and come up with a working thesis. Then create an outline and start drafting your paper. Be sure to leave plenty of time to make revisions, as editing is essential if you want to hand in your best work!
Sample Research Papers and Outlines

Researching Your Topic

- For instance, you might start with a general subject, like British decorative arts. Then, as you read, you home in on transferware and pottery. Ultimately, you focus on 1 potter in the 1780s who invented a way to mass-produce patterned tableware.
Tip: If you need to analyze a piece of literature, your task is to pull the work apart into literary elements and explain how the author uses those parts to make their point.

- Authoritative, credible sources include scholarly articles (especially those other authors reference), government websites, scientific studies, and reputable news bureaus. Additionally, check your sources' dates, and make sure the information you gather is up to date.
- Evaluate how other scholars have approached your topic. Identify authoritative sources or works that are accepted as the most important accounts of the subject matter. Additionally, look for debates among scholars, and ask yourself who presents the strongest evidence for their case. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- You’ll most likely need to include a bibliography or works cited page, so keep your sources organized. List your sources, format them according to your assigned style guide (such as MLA or Chicago ), and write 2 or 3 summary sentences below each one. [4] X Research source

- Imagine you’re a lawyer in a trial and are presenting a case to a jury. Think of your readers as the jurors; your opening statement is your thesis and you’ll present evidence to the jury to make your case.
- A thesis should be specific rather than vague, such as: “Josiah Spode’s improved formula for bone china enabled the mass production of transfer-printed wares, which expanded the global market for British pottery.”
Drafting Your Essay

- Your outline is your paper’s skeleton. After making the outline, all you’ll need to do is fill in the details.
- For easy reference, include your sources where they fit into your outline, like this: III. Spode vs. Wedgewood on Mass Production A. Spode: Perfected chemical formula with aims for fast production and distribution (Travis, 2002, 43) B. Wedgewood: Courted high-priced luxury market; lower emphasis on mass production (Himmelweit, 2001, 71) C. Therefore: Wedgewood, unlike Spode, delayed the expansion of the pottery market.

- For instance, your opening line could be, “Overlooked in the present, manufacturers of British pottery in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries played crucial roles in England’s Industrial Revolution.”
- After presenting your thesis, lay out your evidence, like this: “An examination of Spode’s innovative production and distribution techniques will demonstrate the importance of his contributions to the industry and Industrial Revolution at large.”
Tip: Some people prefer to write the introduction first and use it to structure the rest of the paper. However, others like to write the body, then fill in the introduction. Do whichever seems natural to you. If you write the intro first, keep in mind you can tweak it later to reflect your finished paper’s layout.

- After setting the context, you'd include a section on Josiah Spode’s company and what he did to make pottery easier to manufacture and distribute.
- Next, discuss how targeting middle class consumers increased demand and expanded the pottery industry globally.
- Then, you could explain how Spode differed from competitors like Wedgewood, who continued to court aristocratic consumers instead of expanding the market to the middle class.
- The right number of sections or paragraphs depends on your assignment. In general, shoot for 3 to 5, but check your prompt for your assigned length.

- If you bring up a counterargument, make sure it’s a strong claim that’s worth entertaining instead of ones that's weak and easily dismissed.
- Suppose, for instance, you’re arguing for the benefits of adding fluoride to toothpaste and city water. You could bring up a study that suggested fluoride produced harmful health effects, then explain how its testing methods were flawed.

- Sum up your argument, but don’t simply rewrite your introduction using slightly different wording. To make your conclusion more memorable, you could also connect your thesis to a broader topic or theme to make it more relatable to your reader.
- For example, if you’ve discussed the role of nationalism in World War I, you could conclude by mentioning nationalism’s reemergence in contemporary foreign affairs.
Revising Your Paper

- This is also a great opportunity to make sure your paper fulfills the parameters of the assignment and answers the prompt!
- It’s a good idea to put your essay aside for a few hours (or overnight, if you have time). That way, you can start editing it with fresh eyes.
Tip: Try to give yourself at least 2 or 3 days to revise your paper. It may be tempting to simply give your paper a quick read and use the spell-checker to make edits. However, revising your paper properly is more in-depth.

- The passive voice, such as “The door was opened by me,” feels hesitant and wordy. On the other hand, the active voice, or “I opened the door,” feels strong and concise.
- Each word in your paper should do a specific job. Try to avoid including extra words just to fill up blank space on a page or sound fancy.
- For instance, “The author uses pathos to appeal to readers’ emotions” is better than “The author utilizes pathos to make an appeal to the emotional core of those who read the passage.”

- Read your essay out loud to help ensure you catch every error. As you read, check for flow as well and, if necessary, tweak any spots that sound awkward. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- It’s wise to get feedback from one person who’s familiar with your topic and another who’s not. The person who knows about the topic can help ensure you’ve nailed all the details. The person who’s unfamiliar with the topic can help make sure your writing is clear and easy to understand.
Community Q&A
- Remember that your topic and thesis should be as specific as possible. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 0
- Researching, outlining, drafting, and revising are all important steps, so do your best to budget your time wisely. Try to avoid waiting until the last minute to write your paper. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evaluating-print-sources/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/research_overview/index.html
- ↑ https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/writing/graduate-writing-lab/writing-through-graduate-school/working-sources
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-5-putting-the-pieces-together-with-a-thesis-statement/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/developing_an_outline/index.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/introductions/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/counterarguments
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/formandstyle/writing/scholarlyvoice/activepassive
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/reading-aloud/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/index.html
About This Article

To write a research paper, start by researching your topic at the library, online, or using an academic database. As you conduct your research and take notes, zero in on a specific topic that you want to write about and create a 1-2 sentence thesis to state the focus of your paper. Then, create an outline that includes an introduction, 3 to 5 body paragraphs to present your arguments, and a conclusion to sum up your main points. Once you have your paper's structure organized, draft your paragraphs, focusing on 1 argument per paragraph. Use the information you found through your research to back up your claims and prove your thesis statement. Finally, proofread and revise your content until it's polished and ready to submit. For more information on researching and citing sources, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Private And Discrete
Aug 2, 2020
Did this article help you?
Jan 3, 2018
Oct 29, 2016
Maronicha Lyles
Jul 24, 2016
Maxwell Ansah
Nov 22, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

How to Write a Research Paper: 9 Steps You Need to Know

Are you stuck with a blank page because you have no idea how to write a research paper, or where to start in the first place? Writing a research paper is time-consuming and mentally taxing. It can be particularly challenging if you’ve never done it before, and that’s exactly why we’re here. In this guide, you’ll discover nine tips to help you write a compelling research paper.
Let’s begin!
1: Understand the prompt
Before you jump to pick a topic, take a pause to understand the assignment or prompt. Are there any specific instructions or tasks that could clash with the topic you like? Could there be a topic that fits the assignment better?
For instance, you’ll have to work with a specific word limit so it might help to narrow down on a very specific topic. Otherwise, you could end up trying to fit in too much information because the topic is too vague. Going through the assignment instructions at the beginning will also give you enough time to address any concerns or confusion you might have.
In addition, make sure you understand the assignment goal and research paper format. Find out whether you’ll need to use APA format guidelines or MLA format guidelines. Don’t forget to clearly note your deadlines. This will help you with set your timeframe accordingly.
2: Know your audience
Who’s going to read your paper? Knowing who your audience is will help you adjust your writing style and choice of words accordingly. Plus, it’ll also give you some idea of the level of explanation you should provide for certain concepts. If you have some trouble adapting your writing style based on your audience, a writing tutor can provide you with the guidance you need.
For an undergraduate paper, you’ll typically be targeting people who fall between generalists and experts. So while you should be informative, make sure you avoid using too many technical terms and do not over-explain concepts that they’ll be familiar with. If you’re writing a Master’s thesis, you’ll mainly be targeting experts so you should carefully justify the claims you make.
3: Choose your topic
Ideally, you should pick a topic that’s challenging and/or controversial, but it should also interest you. At the same time, don’t pick something that’s so challenging that you can’t find credible sources to back up your claims or arguments. Make sure you choose something that meets your assignment criteria and is possible to research.
As mentioned earlier, it’s best to get as specific as possible with your topic. So instead of just “Deforestation in South America” you could choose something like “The Impact of Deforestation on South American Wildlife.”
Your topic should neatly but comprehensively summarize what your research is all about. It might also vary depending on different types of research papers. For example, you may have to objectively explain different stances or you might have to write an argumentative paper defending a single stance.
4: Start with preliminary research
Use reliable sources to collect information relevant to your topic. Start by quickly skimming through each source to narrow down on the most relevant ones and identify key talking points. Keep track of all the reference material you’re using so you have no trouble citing them later on.
Most importantly, don’t just look for sources that support your argument, but also ones that contradict it. This will help you avoid confirmation bias and identify any flaws in your argument, so you’ll have plenty of time to adjust your topic before you dive too deep. So you’ll have plenty of time to adjust your topic before you dive too deep.
5: Form your thesis statement
Now that you have your topic and all the reference material to form your argument, use that to come up with a strong thesis statement. This is a statement defining your central argument and establishing the purpose of your paper. It should be short and to-the-point, while helping readers understand the main idea of your research.If you’re not sure how to write a thesis statement, ask yourself, “What is the paper about?” The answer will help you form your statement. Here are a few thesis statement examples for research papers:
Deforestation adversely affects the wildlife population in South American forests.Excessive social media use can have a detrimental effect on mental health, contributing to anxiety and depression.
Chimamanda Adichie uses her work to explore the subtle leftovers of colonialism in Nigerian society and showcases how deeply it is ingrained in the minds and outlook of modern-day Nigerians.
6: Develop your outline
Next, it’s time to organize all your ideas, arguments, points, and research material into a proper research paper outline. This is when you omit any information that doesn’t support your thesis statement even though it may be highly intriguing. Build a framework for how you’ll present your argument in a logical flow.
Your outline should include the following sections along with a brief statement of what each section will contain:
- Topic title
- Thesis statement
Introduction
To further build on your outline, divide the body into different sections where you’ll present a relevant argument or point. Each point should have a topic sentence to describe what you plan on discussing under the subhead. Check out our previous guide on how to write an outline to get a better idea and a few examples.
7: Begin your first draft
Now it’s time to build from your rough ideas and use them to prepare your first draft. Don’t be too caught up on perfect grammar, word choice, and sentence flow at this point, as it won’t be your final draft. Your main focus should be on writing and expressing the ideas you wish to present in the paper.
Follow your research paper outline to neatly structure the information you’re presenting. You don’t even necessarily have to start writing from the introduction. Which subheading speaks to you the most? Start from there and you can build on the other sections as you write. If you get stuck somewhere, move to another section and get back to it later. This will significantly speed up your writing.
Even if you end up writing too much or you feel like you’re trailing off, don’t delete it just yet. Set it aside in another document in case it comes in handy later. In addition, keep your arguments flexible as you might need to adjust or abandon it later on.
Here are a few tips on how to write different sections of the paper:
As the name suggests, your introduction should introduce the readers to your topic. What are you planning to discuss in the paper? Give a little background about the topic by providing key terms and theories as well as historical details. Then talk about what new insight you’ll be offering and what important issues you plan to address.
When writing the body of your research essay, the best way to stay on track is by dividing it into different sections with topic sentences that clearly define what the section is about. Like a subheading, a topic sentence is a statement indicating what each paragraph is about.
Make sure you assess each topic sentence to see if it’s relevant to the topic, too similar to other topic sentences, or logically ordered. Make sure they transition smoothly from one to the other, and that they don’t discuss points that are essentially the same.
This is where you tie the whole thing together and prove your thesis statement. Start by paraphrasing your thesis statement and summarizing the key points you discussed. Follow up by explaining how those points support your case. Make sure you have a strong conclusion to make your argument more compelling.
8: Cite your sources
It’s crucial that you add your citations while writing the first draft so you don’t have any trouble linking your info to the right source later on. It doesn’t have to be perfect now, but make sure you add the essentials such as the name and year of publication, author name, page number, etc. If you wait till the final draft to cite your sources, it’ll take a long time to trace back where you sourced the info.
You can polish your citations later on while you’re polishing the rest of the paper. Don’t forget that you’ll have to maintain a citation style similar to the format you’re using. So make sure you understand the variations in citation styles between the MLA format guidelines and APA format guidelines .
Here are two citation examples illustrating the differences between these two styles:
MLA Citation Style
Adichie, Chimamanda Ngozi. Americanah. Harper Collins Publishers Inc, 2013.
APA Citation Style
Adichie, C.N. (2013). Americanah. New York: Harper Collins Publishers Inc.
9: Proofread and edit
This is the part where you reread your paper and edit it for content, clarity, and grammar. Are there any sentences that don’t flow well together? Is there a way to simplify some sentences and make them easier to understand? Are there any misspellings, unnecessary words, or incorrect info? Most importantly, are there sections that don’t make sense for the topic sentence you’re discussing?
Additionally, look for the following common mistakes in writing a research paper:
- Missing or unnecessary punctuations
- Interchanging easily confused words
- Incomplete sentences
- Contraction use
Proofreading and editing your paper will not just help you create a compelling piece but also help you improve your overall writing . The better you get at detecting these mistakes, the more conscious you’ll be to avoid them in the future.
Finally, Perfect Your Paper
When you’re finally done with the proofreading and editing process, go through your paper one last time to see if it reads well and if the information flows logically. Make sure you go through the assignment guidelines again and see if you followed all the instructions to a tee.
If you feel your writing quality needs some improvement even after following this guide, it’ll help to work with an English tutor to guide you through perfecting your writing.

Jacqueline Zote is a copywriter with a passion for all things relating to the English language. Her interests range from pop culture and mythology to social activism. Her short fiction has appeared in anthologies published by HarperCollins Publishers and Zubaan Books.
22 French Verbs with Present Tense Conjugations
The basics of learning python, related articles, what kind of writing tutor do i actually..., writer’s block is real, and here’s how you..., how to self-edit: 12 steps to better writing, the keys to writing consistently for any assignment, watch: get ready for high school free lesson..., 18 best writing resources for students, how to write a thesis statement, the law school hopeful’s guide to confident lsat..., 19 common grammar mistakes (and how to avoid..., how to write an essay outline.
- Writing & Research Conference
- UW Course Descriptions
- Support the Writing Program

University Writing Program
Columbian College of Arts & Sciences
- News & Events
- Funding Transparency & Restrictions
- WID Graduate Assistants and Peer Writing Preceptors
- WID Course Guidelines for Faculty
- WID Teaching Resources for Faculty
- WID GA Workshops & Practicum
- Writing Center
- Faculty Resources
- Student Resources
- Julian Clement Chase Prizes
- WID Teaching Awards

A Guide to Writing a Research Paper
This handbook hopes to assist students studying international affairs, political science, and history. Students of political science should focus their research papers on identifying a theoretical puzzle (e.g., a case that cannot be explained by an existing theory, or that illustrates conflicts between two competing theories) and solve it. Policy-oriented political science students should center their research papers on identifying a significant policy issue; analyze it, and present recommendations. Cultural history students approach the study of world politics by examining not only history and politics but also literature and film as artistic expressions interpreting history. Why don’t we begin thinking about your research paper as your opportunity to improve by setting your goals: write out what your weaknesses are in your writing and add what are your strengths. Secondly, state your goals in improving writing and how you will meet your goals. Lastly, check out your professor’s comments and restate your goals: what goals have you met and which still need to be met. Build on your writing skills by being very aware of your weaknesses and your strengths. Remember you are not alone: consult GWU’s The Writing Center at GWU (202-994-3765) and WID Studio .
All good writing starts with analytical reading. When you start reading a book or viewing a film, immediately make connections, stretch your imagination, ask questions, and anticipate conclusions. By becoming an active reader your mind will be analyzing the information simultaneously as you experience the journal article, book or film. Evaluating sources is a skill perfected over several years; this handbook offers ways to assess texts quickly.
Structuring and writing research papers can be challenging and in the end rewarding because it is your unique contribution to understanding a body of texts, a series of historical events, and cultural expressions in film, art, and literature. Your personal voice and your particular interpretation will intrigue your readers if your thesis is clearly argued. Creating Writing Strategies including clustering ideas, drawing diagrams, and planning a “road map” will help you visualize the stages that you need to map out to build a strong paper. Research papers always start with disparate ideas, indiscriminate notions, and false starts. This process is necessary to think through your strategy. Harnessing and structuring your random ideas is essential at the beginning to ensure solid results in your line of argument.
An initial draft helps you generate ideas, sketch a plan, and build on your first impressions. Revision and more revision will ensure that your case is chiseled into a fine paper with clear objectives and well-argued beliefs. This is perhaps the most essential piece to receiving high grades. If you write your paper the night before it is due, you will not allow time to revise. Instead, plan to write your initial draft two weeks before it is due. You will have time to rewrite the draft at least twice. Comparing each draft should convince you to always make time to write three drafts. Formatting your paper appropriately to your professor’s taste is crucial. Routinely papers follow this format: a Title Page, after which each page is numbered consecutively; pages are double-spaced with left one-inch margins at top, bottom, and sides.
Citations add depth to your opinions and will substantiate them. A variety of sources always makes a paper interesting to read and intensifies your argument. The risk that all writers confront is over use of quoting from secondary texts. The overuse of citations buries your personal voice and your particular point of view.
Reading Analytically
It is often possible to confuse or understand partially what a scholar, journalist, or author is trying to argue. This is the first wrong step towards a weak paper. In evaluating a scholarly argument, you are making claims about what an author has stated. You do not have the freedom to put arguments in authors’ mouths; you must be able to back up every claim you make about an author’s argument through reference to the text. This exercise in analyzing arguments intends to strengthen your skills in developing your own argumentation.
Read an article in The Economist, The Wall Street Journal, American Political Science Review, or Foreign Affairs and start to record your thoughts:
- What is the author’s argument?
- What is the thesis question?
- What are the premises underlying it?
- What is the thesis?
- What is the “road map” or the individual points the author will have to prove to make the thesis be true?
- What assumptions has the author made which remain unaddressed?
- What arguments does the author make that may be challenged?
- Premises underlying thesis question.
- Individual points of the argument in the “road map,” or body of the work.
- If you wanted to challenge this author, how would you go about it?
- Choose one point — either a premise underlying the thesis question, or a part of the author’s “road map.”
- What kind of primary source evidence would you be looking for to “test” this point? What kinds of primary source evidence would tend to support the author? What kinds would undermine the author’s argument?
- The last step would be to go to the primary source evidence itself, and see what you find.
Exercise for reading analytically
Read the excerpt below taken from the first issue of Foreign Affairs for 2009 and write out your questions and answers (the entire article is online):
Beyond Iraq
A New U.S. Strategy for the Middle East
Richard N. Haass and Martin Indyk
Summary: To be successful in the Middle East, the Obama administration will need to move beyond Iraq, find ways to deal constructively with Iran, and forge a final-status Israeli-Palestinian agreement.
On taking office, U.S. President Barack Obama will face a series of critical, complex, and interrelated challenges in the Middle East demanding urgent attention: an Iraq experiencing a fragile lull in violence that is nonetheless straining the U.S. military, an Iran approaching the nuclear threshold, a faltering Israeli-Palestinian peace process, weak governments in Lebanon and the Palestinian territories challenged by strong militant Islamist groups, and a U.S. position weakened by years of failure and drift. He will also discover that time is working against him.
For six years, U.S. policy in the Middle East has been dominated by Iraq. This need not, and should not, continue. The Obama administration will be able to gradually reduce the number of U.S. troops in Iraq, limit their combat role, and increasingly shift responsibility to Iraqi forces. The drawdown will have to be executed carefully and deliberately, however, so as not to risk undoing recent progress.
The improved situation in Iraq will allow the new administration to shift its focus to Iran, where the clock is ticking on a dangerous and destabilizing nuclear program. Obama should offer direct official engagement with the Iranian government, without preconditions, along with other incentives in an attempt to turn Tehran away from developing the capacity to rapidly produce substantial amounts of nuclear-weapons-grade fuel. At the same time, he should lay the groundwork for an international effort to impose harsher sanctions on Iran if it proves unwilling to change course.
Preventive military action against Iran by either the United States or Israel is an unattractive option, given its risks and costs. But it needs to be examined carefully as a last-ditch alternative to the dangers of living with an Iranian bomb. To increase Israel’s tolerance for extended diplomatic engagement, the U.S. government should bolster Israel’s deterrent capabilities by providing an enhanced anti-ballistic-missile defense capability and a nuclear guarantee.
The U.S. president should also spend capital trying to promote peace agreements between Israel and its Arab neighbors, in particular Syria. Damascus is currently allied with Tehran, and an Israeli-Syrian deal would weaken Iran’s regional influence, reduce external support for Hamas and Hezbollah, and improve the prospects for stability in Lebanon. On the Israeli-Palestinian front, there is an urgent need for a diplomatic effort to achieve a two-state solution while it is still feasible. Although divisions on both sides and the questionable ability of the Palestinian Authority (PA) to control any newly acquired territory make a sustainable peace agreement unlikely for the moment, these factors argue not for abandoning the issue but rather for devoting substantial time and effort now to creating the conditions that would help diplomacy succeed later. What all these initiatives have in common is a renewed emphasis on diplomacy as a tool of U.S. national security policy, since the United States can no longer achieve its objectives without the backing of its regional allies as well as China, Europe, and Russia.
Some might argue that these efforts are not worth it, that the Bush administration paid too much attention to and invested too much American blood and treasure in an ill-advised attempt to transform the Middle East and that the Obama administration should focus its attention at home or elsewhere abroad. But such arguments underestimate the Middle East’s ability to force itself onto the U.S. president’s agenda regardless of other plans. Put simply, what happens in the Middle East will not stay in the Middle East. From terrorism to nuclear proliferation to energy security, managing contemporary global challenges requires managing the Middle East.
Three easy questions to ask yourself:
- Is there a “valid” argument: an argument structured such that, given that the premises are correct, the conclusion must be correct. How do the authors construct their argument, dissect paragraph by paragraph their line of debate.
- What would a scholar from Egypt write on this subject and perhaps a scholar from Iran. Can you now come up with a counter argument?
- What is the “road map” for this paper? That is, what is the chain of reasoning this paper must pursue if it is to demonstrate the veracity of its thesis?
Good reading is about asking questions of your sources. Keep the following in mind when reading primary sources. Even if you believe you can’t arrive at the answers, imagining possible answers will aid your comprehension. Reading primary sources requires that you use your historical imagination. This process is all about your willingness and ability to ask questions of the material, imagine possible answers, and explain your reasoning. Reading a primary source may seem simple but you would be surprised how easy it is to become distracted, unfocused, and when your mind wonders you lose the impact of the thesis. This also happens when we sit at our computers to write, but with a strong foundation and a road map, it should be easier to compose.
Professor Patrick Rael of Bowdoin College has drawn up a useful evaluating system when reading primary sources:
- Purpose of the author in preparing the document
- Argument and strategy she or he uses to achieve those goals
- Presuppositions and values (in the text, and our own)
- Epistemology (evaluating truth content)
- Relate to other texts (compare and contrast)
- Who is the author and what is her or his place in society (explain why you are justified in thinking so)? What could or might it be, based on the text, and why?
- Why did the author prepare the document? What was the occasion for its creation?
- What is at stake for the author in this text? Why do you think she or he wrote it? What evidence in the text tells you this?
- Does the author have a thesis? What — in one sentence — is that thesis?
- What is the text trying to do? How does the text make its case? What is its strategy for accomplishing its goal? How does it carry out this strategy?
- What is the intended audience of the text? How might this influence its rhetorical strategy? Cite specific examples.
- What arguments or concerns do the author respond to that are not clearly stated? Provide at least one example of a point at which the author seems to be refuting a position never clearly stated. Explain what you think this position may be in detail, and why you think it.
- Do you think the author is credible and reliable? Use at least one specific example to explain why. Make sure to explain the principle of rhetoric or logic that makes this passage credible.
Presuppositions
- How do the ideas and values in the source differ from the ideas and values of our age? Offer two specific examples.
- What presumptions and preconceptions do we as readers bring to bear on this text? For instance, what portions of the text might we find objectionable, but which contemporaries might have found acceptable. State the values we hold on that subject, and the values expressed in the text. Cite at least one specific example.
- How might the difference between our values and the values of the author influence the way we understand the text? Explain how such a difference in values might lead us to miss-interpret the text, or understand it in a way contemporaries would not have. Offer at least one specific example.
Epistemology
- How might this text support one of the arguments found in secondary sources we’ve read? Choose a paragraph anywhere in a secondary source we’ve read, state where this text might be an appropriate footnote (cite page and paragraph), and explain why.
- What kinds of information does this text reveal that it does not seem concerned with revealing? (In other words, what does it tell us without knowing it’s telling us?)
- Offer one claim from the text which is the author’s interpretation. Now offer one example of a historical “fact” (something that is absolutely indisputable) that we can learn from this text (this need not be the author’s words).
- Relate: Now choose another of the readings, and compare the two, answering these questions:
- What patterns or ideas are repeated throughout the readings?
- What major differences appear in them?
- Which do you find more reliable and credible?
As you can begin to see, once you start thinking about it, one simple question can lead to a huge chain of questions. Remember, it is always better to keep asking questions you think you cannot answer than to stop asking questions because you think you cannot answer them. But this can only happen when you know enough about your subject to know how to push your questioning, and this depends on reading and understanding the assigned material.
Evaluating Sources
Reading secondary historical sources is a skill which is honed over years of practice and becomes second nature after a while. Reading academic material well is an active process and you’ll find success reading even the most difficult material if you can master these skills. The key here is taking the time and energy to engage the material — to think through it and to connect it to other material you have covered. A good idea is to keep a journal recording your ideas about a variety of sources to see later if there are connections among them.
How to read a book
You can quickly size up a volume to judge if it is indeed a book that you need to read fully. Read and define the title. Think about what the title promises for the book; look at the table of contents; read the foreword and introduction (if an article, read the first paragraph or two). Read the conclusion or epilogue if there is one (if it is an article, read the last one or two paragraphs). After all this, ask yourself what the author’s thesis might be. How has the argument been structured?
The same idea holds for reading chapters quickly: read the first and last paragraph of each chapter. After doing this and taking the step outlined above, you should have a good idea of the book’s major themes and arguments. Good topic sentences in each paragraph will tell you what the paragraph is about. Read actively and just take notes when necessary; avoid taking copious notes on minor details. Remember to record your gut reactions to the text and ask: What surprised you? What seemed particularly insightful? What seems suspect? What reinforces or counters points made in other readings? This kind of note taking will keep your reading active, and actually will help you remember the contents of the piece better than otherwise.
To better write your own research paper it is very useful to dissect an author’s work asking the following: How has the author structured her work? How would you briefly outline it? Why might she have employed this structure? What historical argument does the structure employ? After identifying the thesis, ask yourself in what ways the structure of the work enhances or detracts from the thesis. How does the author set about to make her or his case? What about the structure of the work makes it convincing?
A thesis is not just a statement of opinion, or a belief, or a thought. It is an argument and therefore it is subject to evaluation and analysis. Is it a good argument? How is the big argument (the thesis) structured into little arguments? Are these little arguments constructed well? Is the reasoning valid? Does the evidence support the conclusions? Has the author used invalid or incorrect logic? Is she relying on incorrect premises? What broad, unexamined assumptions seem to underlay the author’s argument? Are these correct? This part of the evaluation process asks you not for your opinion, but to evaluate the logic of the argument. Finally, when you have recorded your thoughts, mapped out the author’s points sustaining the thesis argument, now need to come to a conclusion: Where is the author’s argument weak or vulnerable? Where is the evidence thin? What other interpretations of the author’s evidence is possible? At what points is the author’s logic suspect? If the author’s case is weak, what is the significance of this for the argument as a whole?
If you read actively, record your opinions, and map out arguments you are creating your own research paper as you are analyzing. Eventually you will create your own voice and style through this method.
Writing Strategies
Perhaps the most important message to understand is that you should start thinking about possible theses from the very start of your paper preparation, but you need to examine your primary sources before you can develop a strong thesis. It is impossible to develop a good thesis without already having begun to analyze the primary sources which supply your evidence. How can you know what is even possible to argue if you haven’t looked closely at your data?
Good writing is a process of continually evaluating your work — of constantly asking yourself if your evidence and analysis supports your thesis. Remember, the thesis is not the starting point of your exploration, but the result of it.
Writing exercises — to flush out all your ideas and then to reduce them to the essentials — are useful for structuring your paper. Making lists of your ideas, free writing in prose about your thesis, and clustering relationships among your ideas, can all be helpful in the first phase. Subdividing your subject and restricting your purpose will help you narrow your thesis.
INTRODUCTION
- Introduce the problem
- Define key terms
- State the thesis
- Stems from good question
- Tentative answer is “hypothesis”
- Refine hypothesis into thesis
- How is the paper organized?
- Topic sentence (mini-thesis)
- Argument supporting topic sentence
- Transition to next mini-thesis
- Arguing in paragraphs
- Mini-thesis
- Analysis (what does evidence support?)
- Re-state the thesis
- Significance of thesis (why should we care about the problem?)
The introduction is usually one paragraph, or perhaps two in a paper of eight pages or more. Its purpose is to: (1) set out the problem to be discussed; (2) define key terms that will be used in that discussion; (3) outline the structure of the argument; (4) CLEARLY STATE THE THESIS.
Quickly establish the issue your paper confronts. Where and when are we? What are we examining? It is especially important to clearly define the limits of your exploration. Tell the reader how interested you are in the subject, set a tone conveying that the topic is of vital concern. Some writers grab the reader by starting with an example, a quotation, a statistic, or a complaint. This opening theme must run through your paper so that it unifies your paper.
Provide a clear road map of your argument: Let your reader know where you are headed, how you plan to substantiate your thesis but without giving away your best ideas. If, for instance, your paper breaks down into political, cultural, and social components, announce this to your reader so she will know what to expect.
The last function of the introduction is to present your thesis. The thesis is the central idea around which you construct the rest of your paper. The best theses are good precisely because the questions they answer are significant, complex, and original. The thesis statement is the one-sentence version of your argument. A good thesis will require you to introduce the gist of the thesis itself without revealing your conclusion.
The body takes up several pages, and constitutes the bulk of your paper. Here is where you argue your thesis. The content of this section largely will depend on your thesis, and what it requires you to argue. Think to yourself, “What do I need to support this argument?” If you find yourself unable to answer, consult your analyses of secondary texts to review how authors construct their body. You may not have an interesting enough thesis.
The general movement in the body is from the general to the specific. Start with general statements and then move on to specific statements which support your general statement. Your paper is built on paragraphs. Each paragraph should be a minimum of four sentences and not exceed 10. The first sentence of each paragraph is called the “topic sentence.” The topic sentence introduces what the paragraph will be about similar to a mini-thesis. You may have several mini-theses in your paper supporting your general thesis.
When you add support from secondary texts remember that you should not merely quote or paraphrase from the raw data but you need to interpret and analyze the quoted material. This is especially true of quotes. Never just plop a quote in and expect it to be clear to the reader how it supports the mini-thesis. Explain how it supports the point you are making.
The body of the paper must flow from one idea to the next and transitions from one paragraph to the next must be clear. This linking of ideas is accomplished through transitional phrases. There are transitions between paragraphs, and transitions within paragraphs. Often, but not always, the last sentence of a paragraph begins to guide the reader to the next idea. It is often a good idea to end paragraphs with a sentence summing-up your findings.
As you structure the body, your scholarly arguments marshal facts — and analyze those facts — in a fashion intended to persuade the reader through reason. The most important technique for doing this is to anticipate the counter-arguments your argument is likely to receive. You must constantly ask yourself, what arguments which counter my thesis make sense.
Your conclusion is usually one paragraph long, and briefly recapitulates your thesis, pulling all your arguments together. The first sentence of the concluding paragraph is a clear, specific re-statement of the thesis. The conclusion should do more than simply re-state the argument. It also suggests why the argument is important in the bigger scheme of things, or suggests avenues for further research, or raises a bigger question.
Revision, Revision, Revision
Write first draft: Even if you haven’t finished all your research but you feel ready to start writing a first draft, read over your clustering notes, your sketch of how to execute the paper and arrange your notes according to your outline. Your paragraphs should correspond to your outline, and each should advance your goal of supporting your hypothesis. A first draft will challenge you to articulate ideas that have been floating around in your head. As you start writing you will probably realize that what you thought were simple ideas are actually complex, and are more difficult to express than you expected. That is normal.
Let your paper sit for awhile, two or three days. As the researcher and writer, you have been too close to your work. You might want to change some of the original organization, or delete parts which are tangential or insignificant to your main argument. You may also need to do some additional research and strengthen your arguments. Revise your argument first to tighten the thesis and your “road map” lining up all the evidence. Reduce your evidence to only the relevant pieces and strengthen your argument by including the most salient of citations.
Think about how you have arranged the arguments in your paper. Does the paper’s organization offer the most effective arrangement of your ideas and evidence to support the theme? Reread the topic sentence for each paragraph. Does the sentence make your point and does the information in the paragraph support it? Be sure that you have placed your topic in its historical context, preferably in the first few pages of the paper.
Locate your argument among those offered in the secondary historical works which you have read. At this point, you should have some idea of how your approach/theme adds to the body of historical literature on your topic. Think about your introduction and conclusion. Remember that these are crucial to the paper and you should take some time when writing them. The introduction not only interests the reader in getting beyond the first few pages but it also presents the focus of your argument. The conclusion is your chance to make a lasting impression on your audience; take advantage of it!
The final revision of your paper should include a check of overall organization, style and composition, spelling, proof of thesis, and format (arrangement of title page, pagination, endnotes if applicable, bibliography, citation form.) Scrutinize your words, sentences, and paragraphs. Look at the VERBS are they active (not passive)? Are there a variety of verbs, if not use the thesaurus and empower your prose by strong verbs. REDUCE the use of the verb to be. Wordy sentences weaken your thesis, take out the “fat”: prepositional phrases (change to gerunds –ing); count the number of prepositions in a sentence and limit to two. Check on misplaced and dangling modifiers if you don’t know what this means, look it up. Longer sentences can be reduced to several sentences or with the use of semicolons. Lastly, literally check the logic of the transitions among paragraphs. Do you find a paragraph not making sense and not linking up to the paragraph above and below it?
Very important to your revising is to read your paper out loud and listen to it. Does it flow well? What do you hear that is superfluous? Is the logic sound and is the thesis clear? What is unessential weakens your thesis, so eliminate.
The best known authors follow this advice: Throughout the paper writing process, the most important and challenging task will be to constantly edit and revise your work.
Formatting Your Paper
Use the MLA-Chicago style to format your research paper and consult the following:
William Strunk, Jr. and E.B. White, The Elements of Style
Mary Lynn Rampolla, A Pocket Manual to Writing in History, 3rd ed.
Kate Turabian, A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations, 6th ed.
Diana Hacker, Rules for Writers, 3rd ed. (Boston: Bedford Books of St. Martin’s Press, 1996).
Quotations, footnotes, and bibliographies: Small matters of style, such as where footnote numbers are placed, the use of commas, or how indenting works, are important. You will be learning and using citation styles for the rest of your life; it is crucial that you become proficient in following them closely. Citations
A citation is the part of your paper that tells your reader where your source information came from. This is one of the most important elements to your paper. In order to evaluate your argument, your reader must be able to consult the same sources you used. Proper citing is crucial to making a credible and persuasive argument.. Citations in history papers can take the form of footnotes or endnotes. History papers should not use the parenthetic citation style common to literature and social science papers. These do not perform the other function of footnotes and endnotes, which is to provide space to clarify your use of complex data or arguments, expand on points you believe do not merit lengthy consideration in the body of your text, and to directly address the arguments of other historians.
Each time you quote a work by another author, or use the ideas of another author, you should indicate the source with a footnote. A footnote is indicated in the text of your paper by a small Arabic numeral written in superscript. Each new footnote gets a new number (increment by one). The number refers to a note number at the bottom of the page (or following the text of the paper, if you are using endnotes). This note contains the citation information for the materials you are referencing. For examples of footnotes in action, consult Rampolla (“Quoting and Documenting Sources”).
Either footnotes or endnotes are fine. Most history books are now produced using endnotes, which are commonly thought to provide cleaner looking pages. Most history professors, however, prefer footnotes, so they can quickly check sources. Especially if you have a computer word-processor, which makes the task easy, you should try to use footnotes.
Paraphrase or quote your sources or do both; but do only one at a time. You either paraphrase or quote, but do nothing in between. To paraphrase a source (or part of a source) is to reproduce it in words and word orders substantially different from the original. When you paraphrase well, you keep the sense of the original but change the language, retaining some key words, of course, but otherwise using your own words and your own sentence patterns. As a rough guide, if you copy more than three words in a row from a source, these words should be in quotation marks.
To quote a source (or part of a source) is to reproduce it exactly. When you quote well, you keep both the sense and language of the original, retaining its punctuation, its capitalization, its type face (roman or italic), and its spelling (indeed, even its misspelling).
Remember to include a source citation every time you use the ideas or words of another author, either directly (through quotation) or indirectly (through paraphrase). The only exception is common factual knowledge of the variety found in encyclopedia. The easiest and most important rule to remember is: when in doubt, it is better to cite a source than to not cite a source. In avoiding plagiarism, it is always wiser to choose more rather than less information.
Enjoy researching your paper and enjoy writing it. Professors grade students on their effort, their ability to improve during the semester, and on their willingness to follow directions. GOOD LUCK THIS SEMESTER.
Online guides for citing sources:
- Citing Electronic Sources (from the Library of Congress) http://memory.loc.gov/learn/start/cite/index.html
Guides for citing standard electronic sources
- A Brief Citation Guide for Internet Sources in History and the Humanities http://www.h-net.msu.edu/about/citation/
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
How to Write a Research Paper [Steps & Examples]
As a student, you are often required to complete numerous academic tasks, which can demand a lot of extra effort. Writing a research paper is one of these tasks. If researching for the topic isn't challenging enough, writing it down in a specific format adds another layer of difficulty. Having gone through this myself, I want to help you have a smoother journey in writing your research paper. I'll guide you through everything you need to know about writing a research paper, including how to write a research paper and all the necessary factors you need to consider while writing one.
Order for Preparation of your research paper
Before beginning your research paper, start planning how you will organize your paper. Follow the specific order I have laid out to ensure you assemble everything correctly, cover all necessary components, and write more effectively. This method will help you avoid missing important elements and improve the overall quality of your paper.
Figures and Tables
Assemble all necessary visual aids to support your data and findings. Ensure they are labeled correctly and referenced appropriately in your text.
Detail the procedures and techniques used in your research. This section should be thorough enough to allow others to replicate your study.
Summarize the findings of your research without interpretation. Use figures and tables to illustrate your data clearly.
Interpret the results, discussing their implications and how they relate to your research question. Address any limitations and suggest areas for future research.
Summarize the key points of your research, restating the significance of your findings and their broader impact.
Introduction
Introduce the topic, provide background information, and state the research problem or hypothesis. Explain the purpose and scope of your study.
Write a concise summary of your research, including the objective, methods, results, and conclusion. Keep it brief and to the point.
Create a clear and informative title that accurately reflects the content and focus of your research paper.
Identify key terms related to your research that will help others find your paper in searches.
Acknowledgements
Thank those who contributed to your research, including funding sources, advisors, and any other significant supporters.
Compile a complete list of all sources cited in your paper, formatted according to the required citation style. Ensure every reference is accurate and complete.
Types of Research Papers
There are multiple types of research papers, each with distinct characteristics, purposes, and structures. Knowing which type of research paper is required for your assignment is crucial, as each demands different preparation and writing strategies. Here, we will delve into three prominent types: argumentative, analytical, and compare and contrast papers. We will discuss their characteristics, suitability, and provide detailed examples to illustrate their application.
A.Argumentative Papers
Characteristics:
An argumentative or persuasive paper is designed to present a balanced view of a controversial issue, but ultimately aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer's perspective. The key characteristics of this type of paper include:
Purpose: The primary goal is to convince the reader to support a particular stance on an issue. This is achieved by presenting arguments, evidence, and refuting opposing viewpoints.
Structure: Typically structured into an introduction, a presentation of both sides of the issue, a refutation of the opposing arguments, and a conclusion that reinforces the writer’s position.
Tone: While the tone should be logical and factual, it should not be overly emotional. Arguments must be supported with solid evidence, such as statistics, expert opinions, and factual data.
Suitability:
Argumentative papers are suitable for topics that have clear, opposing viewpoints. They are often used in debates, policy discussions, and essays aimed at influencing public opinion or academic discourse.
Topic: "Should governments implement universal basic income?"
Pro Side: Universal basic income provides financial security, reduces poverty, and can lead to a more equitable society.
Con Side: It could discourage work, lead to higher government expenditure, and might not be a sustainable long-term solution.
Argument: After presenting both sides, the paper would argue that the benefits of reducing poverty and financial insecurity outweigh the potential drawbacks, using evidence from various studies and real-world examples.
Writing Tips:
Clearly articulate your position on the issue from the beginning.
Present balanced arguments by including credible sources that support both sides.
Refute counterarguments effectively with logical reasoning and evidence.
Maintain a factual and logical tone, avoiding excessive emotional appeals.
B.Analytical Papers
An analytical research paper is focused on breaking down a topic into its core components, examining various perspectives, and drawing conclusions based on this analysis. The main characteristics include:
Purpose: To pose a research question, collect data from various sources, analyze different viewpoints, and synthesize the information to arrive at a personal conclusion.
Structure: Includes an introduction with a clear research question, a literature review that summarizes existing research, a detailed analysis, and a conclusion that summarizes findings.
Tone: Objective and neutral, avoiding personal bias or opinion. The focus is on data and logical analysis.
Analytical research papers are ideal for topics that require detailed examination and evaluation of various aspects. They are common in disciplines such as social sciences, humanities, and natural sciences, where deep analysis of existing research is crucial.
Topic: "The impact of social media on mental health."
Research Question: How does social media usage affect mental well-being among teenagers?
Analysis: Examine studies that show both positive (e.g., social support) and negative (e.g., anxiety and depression) impacts of social media. Analyze the methodologies and findings of these studies.
Conclusion: Based on the analysis, conclude whether the overall impact is more beneficial or harmful, remaining neutral and presenting evidence without personal bias.
Maintain an objective and neutral tone throughout the paper.
Synthesize information from multiple sources, ensuring a comprehensive analysis.
Develop a clear thesis based on the findings from your analysis.
Avoid inserting personal opinions or biases.
C.Compare and Contrast Papers
Compare and contrast papers are used to analyze the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. The key characteristics include:
Purpose: To identify and examine the similarities and differences between two or more subjects, providing a comprehensive understanding of their relationship.
Structure: Can be organized in two ways:
Point-by-Point: Each paragraph covers a specific point of comparison or contrast.
Subject-by-Subject: Each subject is discussed separately, followed by a comparison or contrast.
Tone: Informative and balanced, aiming to provide a thorough and unbiased comparison.
Compare and contrast papers are suitable for topics where it is important to understand the distinctions and similarities between elements. They are commonly used in literature, history, and various comparative studies.
Topic: "Compare and contrast the leadership styles of Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X."
Comparison Points: Philosophies (non-violence vs. militant activism), methods (peaceful protests vs. more radical approaches), and impacts on the Civil Rights Movement.
Analysis: Describe each leader's philosophy and method, then analyze how these influenced their effectiveness and legacy.
Conclusion: Summarize the key similarities and differences, and discuss how both leaders contributed uniquely to the movement.
Provide equal and balanced coverage to each subject.
Use clear criteria for comparison, ensuring logical and coherent analysis.
Highlight both similarities and differences, ensuring a nuanced understanding of the subjects.
Maintain an informative tone, focusing on objective analysis rather than personal preference.
How to Write A Research Paper [Higher Efficiency & Better Results]
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before we get started with the research, it's important to gather relevant information related to it. This process, also known as the primary research method, helps researchers gain preliminary knowledge about the topic and identify research gaps. Whenever I begin researching a topic, I usually utilize Google and Google Scholar. Another excellent resource for conducting primary research is campus libraries, as they provide a wealth of great articles that can assist with your research.
Now, let's see how WPS Office and AIPal can be great research partners:
Let's say that I have some PDFs which I have gathered from different sources. With WPS Office, these PDFs can be directly uploaded not just to extract key points but also to interact with the PDF with special help from WPS AI.
Step 1: Let's open the PDF article or research paper that we have downloaded on WPS Office.
Step 2: Now, click on the WPS AI widget at the top right corner of the screen.
Step 3: This will open the WPS PDF AI pane on the right side of the screen. Click on "Upload".
Step 4: Once the upload is complete, WPS PDF AI will return with the key points from the PDF article, which can then be copied to a fresh new document on WPS Writer.
Step 5: To interact further with the document, click on the "Inquiry" tab to talk with WPS AI and get more information on the contents of the PDF.
Research is incomplete without a Google search, but what exactly should you search for? AIPal can help you with these answers. AIPal is a Chrome extension that can help researchers make their Google searches and interactions with Chrome more effective and efficient. If you haven't installed AIPal on Chrome yet, go ahead and download the extension; it's completely free to use:
Step 1: Let's search for a term on Google related to our research.
Step 2: An AIPal widget will appear right next to the Google search bar, click on it.
Step 3: Upon clicking it, an AIPal window will pop up. In this window, you will find a more refined answer for your searched term, along with links most relevant to your search, providing a more refined search experience.
WPS AI can also be used to extract more information with the help of WPS Writer.
Step 1: We might have some information saved in a Word document, either from lectures or during preliminary research. We can use WPS AI within Writer to gain more insights.
Step 2: Select the entire text you want to summarize or understand better.
Step 3: Once the text is selected, a hover menu will appear. Click on the "WPS AI" icon in this menu.
Step 4: From the list of options, click on "Explain" to understand the content more deeply, or click on "Summarize" to shorten the paragraph.
Step 5: The results will be displayed in a small WPS AI window.
Develop the Thesis statement
To develop a strong thesis statement, start by formulating a central question your paper will address. For example, if your topic is about the impact of social media on mental health, your thesis statement might be:
"Social media use has a detrimental effect on mental health by increasing anxiety, depression, and loneliness among teenagers."
This statement is concise, contentious, and sets the stage for your research. With WPS AI, you can use the "Improve" feature to refine your thesis statement, ensuring it is clear, coherent, and impactful.
Write the First draft
Begin your first draft by focusing on maintaining forward momentum and clearly organizing your thoughts. Follow your outline as a guide, but be flexible if new ideas emerge. Here's a brief outline to get you started:
Using WPS AI’s "Make Longer" feature, you can quickly elaborate key ideas and points of your studies and articles into a descriptive format to include in your draft, saving time and ensuring clarity.
Compose Introduction, Body and Conclusion paragraphs
When writing a research paper, it’s essential to transform your key points into detailed, descriptive paragraphs. WPS AI can help you streamline this process by enhancing your key points, ensuring each section of your paper is well-developed and coherent. Here’s how you can use WPS AI to compose your introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs:
Let's return to the draft and start composing our introduction. The introduction should provide the background of the research paper and introduce readers to what the research paper will explore.
If your introduction feels too brief or lacks depth, use WPS AI’s "Make Longer" feature to expand on key points, adding necessary details and enhancing the overall narrative.
Once the introduction is completed, the next step is to start writing the body paragraphs and the conclusion of our research paper. Remember, the body paragraphs will incorporate everything about your research: methodologies, challenges, results, and takeaways.
If this paragraph is too lengthy or repetitive, WPS AI’s "Make Shorter" feature can help you condense it without losing essential information.
Write the Second Draft
In the second draft, refine your arguments, ensure logical flow, and check for clarity. Focus on eliminating any unnecessary information, ensuring each paragraph supports your thesis statement, and improving transitions between ideas. Incorporate feedback from peers or advisors, and ensure all citations are accurate and properly formatted. The second draft should be more polished and coherent, presenting your research in a clear and compelling manner.
WPS AI’s "Improve Writing" feature can be particularly useful here to enhance the overall quality and readability of your paper.
WPS Spellcheck can assist you in correcting spelling and grammatical errors, ensuring your paper is polished and professional. This tool helps you avoid common mistakes and enhances the readability of your paper, making a significant difference in the overall quality.
Bonus Tips: How to Get Inspiration for your Research Paper- WPS AI
WPS Office is a phenomenal office suite that students find to be a major blessing. Not only is it a free office suite equipped with advanced features that make it competitive in the market, but it also includes a powerful AI that automates and enhances many tasks, including writing a research paper. In addition to improving readability with its AI Proofreader tool, WPS AI offers two features, "Insight" and "Inquiry", that can help you gather information and inspiration for your research paper:
Insight Feature:
The Insight feature provides deep insights and information on various topics and fields. It analyzes literature to extract key viewpoints, trends, and research directions. For instance, if you're writing a research paper on the impact of social media on mental health, you can use the Insight feature to gather a comprehensive overview of the latest studies, key arguments, and emerging trends in this field. This helps you build a solid foundation for your paper and ensure you are covering all relevant aspects.
Inquiry Feature:
The Inquiry feature allows you to ask specific questions related to your research topic. This helps you gather necessary background information and refine your research focus effectively. For example, if you need detailed information on how social media usage affects teenagers' self-esteem, you can use the Inquiry feature to ask targeted questions and receive relevant answers based on the latest research.
FAQs about writing a research paper
1. can any source be used for academic research.
No, it's essential to use credible and relevant sources. Here is why:
Developing a Strong Argument: Your research paper relies on evidence to substantiate its claims. Using unreliable sources can undermine your argument and harm the credibility of your paper.
Avoiding Inaccurate Information: The internet is abundant with data, but not all sources can be considered reliable. Credible sources guarantee accuracy.
2. How can I avoid plagiarism?
To avoid plagiarism, follow these steps:
Keep Records of Your Sources: Maintain a record of all the sources you use while researching. This helps you remember where you found specific ideas or phrases and ensures proper attribution.
Quote and Paraphrase Correctly: When writing a paper, use quotation marks for exact words from a source and cite them properly. When paraphrasing, restate the idea in your own words and include a citation to acknowledge the original source.
Utilize a Plagiarism Checker: Use a plagiarism detection tool before submitting your paper. This will help identify unintentional plagiarism, ensuring your paper is original and properly referenced.
3. How can I cite sources properly?
Adhere to the citation style guide (e.g., APA, MLA) specified by your instructor or journal. Properly citing all sources both within the text and in the bibliography or references section is essential for maintaining academic integrity and providing clear credit to the original authors. This practice also helps readers locate and verify the sources you've used in your research.
4. How long should a research paper be?
The length of a research paper depends on its topic and specific requirements. Generally, research papers vary between 4,000 to 6,000 words, with shorter papers around 2,000 words and longer ones exceeding 10,000 words. Adhering to the length requirements provided for academic assignments is essential. More intricate subjects or extensive research often require more thorough explanations, which can impact the overall length of the paper.
Write Your Research Paper with the Comfort of Using WPS Office
Writing a research paper involves managing numerous complicated tasks, such as ensuring the correct formatting, not missing any crucial information, and having all your data ready. The process of how to write a research paper is inherently challenging. However, if you are a student using WPS Office, the task becomes significantly simpler. WPS Office, especially with the introduction of WPS AI, provides all the resources you need to write the perfect research paper. Download WPS Office today and discover how it can transform your research paper writing experience for the better.
- 1. Free examples of a research PowerPoint presentation
- 2. How to Write a Conclusion - Steps with Examples
- 3. How to Write a Paper in APA Format | For Students
- 4. How to Write an Abstract - Steps with Examples
- 5. Free examples of PPT template for research proposal
- 6. Research Paper PowerPoint Presentation Examples
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

Recommended for you
8 tips on writing a 12-page paper, tips and tricks i wish i knew when i had to write my 12-page research paper..

I am an English major. As an English major, I have to take two English seminar classes. For my seminar one class, I had to write a 12 to 14-page research paper. At first, it sounded extremely scary; however, the way my professor prepared the class for the final paper made it a lot easier to get the paper done.
But even with all her help, there were many things that I learned when working through this paper. So, here are eight things that I learned when working on my research paper!
1. Pick your topic early.
It is important to pick your topic early so that you can begin to brainstorm. This is something that I kind of did. I had a general idea what I wanted to write about, but how I was going to go about actually put my thoughts in words, I was clueless. However, I wish I picked my topic out just slightly earlier than I did so that I had more time to prepare my ideas.
2. If you do not like your original topic, change it.
If you do not like what you are brainstorming about with your first topic idea, you can change it! But as mentioned in the first one, make sure you have enough time to change it. By picking your first topic early on, you have time to change your mind and choose a different topic.
3. Make sure you like your topic.
You're going to be writing paragraphs on paragraphs about the topic you choose. You will be spending a lot of time reading about it. You will need to become what I call a mini-expert on the topic, so make sure you like what or who you are writing about. For my essay, I was lucky that I was able to write about one of my favorite poets, so it made the paper just a little bit more tolerable.
4. Begin your research early.
This is something that I wish I did. When you're writing a paper of this length, you'll have to know a lot about the topic, and that means reading multiple books and articles related to the topic. Give yourself time to read everything you need.
Another reason to begin your research early is that when doing all this research, you will come across information that does not relate to your topic, so it is good to give yourself enough time to know what information you need and what you don't need. This also relates back to picking your topic early.
5. Only use information related to your topic.
This one is kind of obvious, but when you have to become the expert of a topic and you have a 12 to 14-page requirement, you could get carried away in what is useful and what is not. Like I mentioned in the last tip, you will come across information that you will not need. So, make sure you only use what will emphasize that point of your paper.
Although the family background of Charles Dickens might sound interesting, it might not be relevant to a topic that might be focusing on his use of irony in his text.
6. Have a lot of information about your topic.
This might sound contradictory to the last tip, but I promise you, it's not. When doing your research, make sure you find as much useful information that you can. The more useful information you have, the easier your paper will be because you will know a lot about what or who you're writing about.
The 12 to 14-page requirement should come easy because you know a lot on the topic and that will enhance your argument. Even if you do not use all the information you found, it is better to have more than not enough.
7. Give yourself some time to re-read your primary and secondary sources.
You are reading and writing a lot during this research paper, so it is okay to forget what happened in the book or what a critic said about the author you chose. Those things will happen, so make sure you re-read and you are clear about what is happening. This is something that I made sure I did as soon as I started thinking that two different poems were actually one.
8. EDIT, EDIT, EDIT!
The biggest tip that I could give and wish I had prior to embarking on this paper journey is to please edit! Rewriting your thoughts and reworking your thesis and ideas are your friends. Make sure you keep going back to your thesis so that your paper reads smoothly.
Your thesis and the original topic idea is on page one. When you get to page 10, you might forget the point you're trying to make, or you might have a new idea and want to incorporate it in. Going back and re-reading what you said will help your essay be smooth from start to finish.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
25 beatles lyrics: your go-to guide for every situation, the best lines from the fab four.
For as long as I can remember, I have been listening to The Beatles. Every year, my mom would appropriately blast “Birthday” on anyone’s birthday. I knew all of the words to “Back In The U.S.S.R” by the time I was 5 (Even though I had no idea what or where the U.S.S.R was). I grew up with John, Paul, George, and Ringo instead Justin, JC, Joey, Chris and Lance (I had to google N*SYNC to remember their names). The highlight of my short life was Paul McCartney in concert twice. I’m not someone to “fangirl” but those days I fangirled hard. The music of The Beatles has gotten me through everything. Their songs have brought me more joy, peace, and comfort. I can listen to them in any situation and find what I need. Here are the best lyrics from The Beatles for every and any occasion.
And in the end, the love you take is equal to the love you make
The End- Abbey Road, 1969
The sun is up, the sky is blue, it's beautiful and so are you
Dear Prudence- The White Album, 1968
Love is old, love is new, love is all, love is you
Because- Abbey Road, 1969
There's nowhere you can be that isn't where you're meant to be
All You Need Is Love, 1967
Life is very short, and there's no time for fussing and fighting, my friend
We Can Work It Out- Rubber Soul, 1965
He say, "I know you, you know me", One thing I can tell you is you got to be free
Come Together- Abbey Road, 1969
Oh please, say to me, You'll let me be your man. And please say to me, You'll let me hold your hand
I Wanna Hold Your Hand- Meet The Beatles!, 1964
It was twenty years ago today, Sgt. Pepper taught the band to play. They've been going in and out of style, but they're guaranteed to raise a smile
Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band-1967
Living is easy with eyes closed, misunderstanding all you see
Strawberry Fields Forever- Magical Mystery Tour, 1967
Can you hear me? When it rains and shine, it's just a state of mind
Rain- Paperback Writer "B" side, 1966
Little darling, it's been long cold lonely winter. Little darling, it feels like years since it' s been here. Here comes the sun, Here comes the sun, and I say it's alright
Here Comes The Sun- Abbey Road, 1969
We danced through the night and we held each other tight, and before too long I fell in love with her. Now, I'll never dance with another when I saw her standing there
Saw Her Standing There- Please Please Me, 1963
I love you, I love you, I love you, that's all I want to say
Michelle- Rubber Soul, 1965
You say you want a revolution. Well you know, we all want to change the world
Revolution- The Beatles, 1968
All the lonely people, where do they all come from. All the lonely people, where do they all belong
Eleanor Rigby- Revolver, 1966
Oh, I get by with a little help from my friends
With A Little Help From My Friends- Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band, 1967
Hey Jude, don't make it bad. Take a sad song and make it better
Hey Jude, 1968
Yesterday, all my troubles seemed so far away. Now it looks as though they're here to stay. Oh, I believe in yesterday
Yesterday- Help!, 1965
And when the brokenhearted people, living in the world agree, there will be an answer, let it be.
Let It Be- Let It Be, 1970
And anytime you feel the pain, Hey Jude, refrain. Don't carry the world upon your shoulders
I'll give you all i got to give if you say you'll love me too. i may not have a lot to give but what i got i'll give to you. i don't care too much for money. money can't buy me love.
Can't Buy Me Love- A Hard Day's Night, 1964
All you need is love, love is all you need
All You Need Is Love- Magical Mystery Tour, 1967
Whisper words of wisdom, let it be
Blackbird singing in the dead of night, take these broken wings and learn to fly. all your life, you were only waiting for this moment to arise.
Blackbird- The White Album, 1968
Though I know I'll never lose affection, for people and things that went before. I know I'll often stop and think about them. In my life, I love you more
In My Life- Rubber Soul, 1965
While these are my 25 favorites, there are quite literally 1000s that could have been included. The Beatles' body of work is massive and there is something for everyone. If you have been living under a rock and haven't discovered the Fab Four, you have to get musically educated. Stream them on Spotify, find them on iTunes or even buy a CD or record (Yes, those still exist!). I would suggest starting with 1, which is a collection of most of their #1 songs, or the 1968 White Album. Give them chance and you'll never look back.
14 Invisible Activities: Unleash Your Inner Ghost!
Obviously the best superpower..
The best superpower ever? Being invisible of course. Imagine just being able to go from seen to unseen on a dime. Who wouldn't want to have the opportunity to be invisible? Superman and Batman have nothing on being invisible with their superhero abilities. Here are some things that you could do while being invisible, because being invisible can benefit your social life too.
1. "Haunt" your friends.
Follow them into their house and cause a ruckus.
2. Sneak into movie theaters.
Going to the cinema alone is good for your mental health , says science
Considering that the monthly cost of subscribing to a media-streaming service like Netflix is oft...
Free movies...what else to I have to say?
3. Sneak into the pantry and grab a snack without judgment.
Late night snacks all you want? Duh.
4. Reenact "Hollow Man" and play Kevin Bacon.
America's favorite son? And feel what it's like to be in a MTV Movie Award nominated film? Sign me up.
5. Wear a mask and pretend to be a floating head.
Just another way to spook your friends in case you wanted to.
6. Hold objects so they'll "float."
"Oh no! A floating jar of peanut butter."
7. Win every game of hide-and-seek.
Just stand out in the open and you'll win.
8. Eat some food as people will watch it disappear.
Even everyday activities can be funny.
9. Go around pantsing your friends.
Even pranks can be done; not everything can be good.
10. Not have perfect attendance.
You'll say here, but they won't see you...
11. Avoid anyone you don't want to see.
Whether it's an ex or someone you hate, just use your invisibility to slip out of the situation.
12. Avoid responsibilities.
Chores? Invisible. People asking about social life? Invisible. Family being rude? Boom, invisible.
13. Be an expert on ding-dong-ditch.
Never get caught and have the adrenaline rush? I'm down.
14. Brag about being invisible.
Be the envy of the town.
But don't, I repeat, don't go in a locker room. Don't be a pervert with your power. No one likes a Peeping Tom.
Good luck, folks.
19 Lessons I'll Never Forget from Growing Up In a Small Town
There have been many lessons learned..
Small towns certainly have their pros and cons. Many people who grow up in small towns find themselves counting the days until they get to escape their roots and plant new ones in bigger, "better" places. And that's fine. I'd be lying if I said I hadn't thought those same thoughts before too. We all have, but they say it's important to remember where you came from. When I think about where I come from, I can't help having an overwhelming feeling of gratitude for my roots. Being from a small town has taught me so many important lessons that I will carry with me for the rest of my life.
1. The importance of traditions.
Sometimes traditions seem like a silly thing, but the fact of it is that it's part of who you are. You grew up this way and, more than likely, so did your parents. It is something that is part of your family history and that is more important than anything.
2. How to be thankful for family and friends.
No matter how many times they get on your nerves or make you mad, they are the ones who will always be there and you should never take that for granted.
3. How to give back.
When tragedy strikes in a small town, everyone feels obligated to help out because, whether directly or indirectly, it affects you too. It is easy in a bigger city to be able to disconnect from certain problems. But in a small town those problems affect everyone.
4. What the word "community" really means.
Along the same lines as #3, everyone is always ready and willing to lend a helping hand when you need one in a small town and to me that is the true meaning of community. It's working together to build a better atmosphere, being there to raise each other up, build each other up, and pick each other up when someone is in need. A small town community is full of endless support whether it be after a tragedy or at a hometown sports game. Everyone shows up to show their support.
5. That it isn't about the destination, but the journey.
People say this to others all the time, but it takes on a whole new meaning in a small town. It is true that life is about the journey, but when you're from a small town, you know it's about the journey because the journey probably takes longer than you spend at the destination. Everything is so far away that it is totally normal to spend a couple hours in the car on your way to some form of entertainment. And most of the time, you're gonna have as many, if not more, memories and laughs on the journey than at the destination.
6. The consequences of making bad choices.
Word travels fast in a small town, so don't think you're gonna get away with anything. In fact, your parents probably know what you did before you even have a chance to get home and tell them. And forget about being scared of what your teacher, principle, or other authority figure is going to do, you're more afraid of what your parents are gonna do when you get home.
7. To trust people, until you have a reason not to.
Everyone deserves a chance. Most people don't have ill-intentions and you can't live your life guarding against every one else just because a few people in your life have betrayed your trust.
8. To be welcoming and accepting of everyone.
While small towns are not always extremely diverse, they do contain people with a lot of different stories, struggle, and backgrounds. In a small town, it is pretty hard to exclude anyone because of who they are or what they come from because there aren't many people to choose from. A small town teaches you that just because someone isn't the same as you, doesn't mean you can't be great friends.
9. How to be my own, individual person.
In a small town, you learn that it's okay to be who you are and do your own thing. You learn that confidence isn't how beautiful you are or how much money you have, it's who you are on the inside.
10. How to work for what I want.
Nothing comes easy in life. They always say "gardens don't grow overnight" and if you're from a small town you know this both figuratively and literally. You certainly know gardens don't grow overnight because you've worked in a garden or two. But you also know that to get to the place you want to be in life it takes work and effort. It doesn't just happen because you want it to.
11. How to be great at giving directions.
If you're from a small town, you know that you will probably only meet a handful of people in your life who ACTUALLY know where your town is. And forget about the people who accidentally enter into your town because of google maps. You've gotten really good at giving them directions right back to the interstate.
12. How to be humble .
My small town has definitely taught me how to be humble. It isn't always about you, and anyone who grows up in a small town knows that. Everyone gets their moment in the spotlight, and since there's so few of us, we're probably best friends with everyone so we are as excited when they get their moment of fame as we are when we get ours.
13. To be well-rounded.
Going to a small town high school definitely made me well-rounded. There isn't enough kids in the school to fill up all the clubs and sports teams individually so be ready to be a part of them all.
14. How to be great at conflict resolution.
In a small town, good luck holding a grudge. In a bigger city you can just avoid a person you don't like or who you've had problems with. But not in a small town. You better resolve the issue fast because you're bound to see them at least 5 times a week.
15. The beauty of getting outside and exploring.
One of my favorite things about growing up in a rural area was being able to go outside and go exploring and not have to worry about being in danger. There is nothing more exciting then finding a new place somewhere in town or in the woods and just spending time there enjoying the natural beauty around you.
16. To be prepared for anything.
You never know what may happen. If you get a flat tire, you better know how to change it yourself because you never know if you will be able to get ahold of someone else to come fix it. Mechanics might be too busy , or more than likely you won't even have enough cell service to call one.
17. That you don't always have to do it alone.
It's okay to ask for help. One thing I realized when I moved away from my town for college, was how much my town has taught me that I could ask for help is I needed it. I got into a couple situations outside of my town where I couldn't find anyone to help me and found myself thinking, if I was in my town there would be tons of people ready to help me. And even though I couldn't find anyone to help, you better believe I wasn't afraid to ask.
18. How to be creative.
When you're at least an hour away from normal forms of entertainment such as movie theaters and malls, you learn to get real creative in entertaining yourself. Whether it be a night looking at the stars in the bed of a pickup truck or having a movie marathon in a blanket fort at home, you know how to make your own good time.
19. To brush off gossip.
It's all about knowing the person you are and not letting others influence your opinion of yourself. In small towns, there is plenty of gossip. But as long as you know who you really are, it will always blow over.
Grateful Beyond Words: A Letter to My Inspiration
I have never been so thankful to know you..
I can't say "thank you" enough to express how grateful I am for you coming into my life. You have made such a huge impact on my life. I would not be the person I am today without you and I know that you will keep inspiring me to become an even better version of myself.
You have taught me that you don't always have to strong. You are allowed to break down as long as you pick yourself back up and keep moving forward. When life had you at your worst moments, you allowed your friends to be there for you and to help you. You let them in and they helped pick you up. Even in your darkest hour you showed so much strength. I know that you don't believe in yourself as much as you should but you are unbelievably strong and capable of anything you set your mind to.
Your passion to make a difference in the world is unbelievable. You put your heart and soul into your endeavors and surpass any personal goal you could have set. Watching you do what you love and watching you make a difference in the lives of others is an incredible experience. The way your face lights up when you finally realize what you have accomplished is breathtaking and I hope that one day I can have just as much passion you have.
SEE MORE: A Letter To My Best Friend On Her Birthday
The love you have for your family is outstanding. Watching you interact with loved ones just makes me smile . You are so comfortable and you are yourself. I see the way you smile when you are around family and I wish I could see you smile like this everyday. You love with all your heart and this quality is something I wished I possessed.
You inspire me to be the best version of myself. I look up to you. I feel that more people should strive to have the strength and passion that you exemplify in everyday life.You may be stubborn at points but when you really need help you let others in, which shows strength in itself. I have never been more proud to know someone and to call someone my role model. You have taught me so many things and I want to thank you. Thank you for inspiring me in life. Thank you for making me want to be a better person.
Waitlisted for a College Class? Here's What to Do!
Dealing with the inevitable realities of college life..
Course registration at college can be a big hassle and is almost never talked about. Classes you want to take fill up before you get a chance to register. You might change your mind about a class you want to take and must struggle to find another class to fit in the same time period. You also have to make sure no classes clash by time. Like I said, it's a big hassle.
This semester, I was waitlisted for two classes. Most people in this situation, especially first years, freak out because they don't know what to do. Here is what you should do when this happens.
Don't freak out
This is a rule you should continue to follow no matter what you do in life, but is especially helpful in this situation.
Email the professor
Around this time, professors are getting flooded with requests from students wanting to get into full classes. This doesn't mean you shouldn't burden them with your email; it means they are expecting interested students to email them. Send a short, concise message telling them that you are interested in the class and ask if there would be any chance for you to get in.
Attend the first class
Often, the advice professors will give you when they reply to your email is to attend the first class. The first class isn't the most important class in terms of what will be taught. However, attending the first class means you are serious about taking the course and aren't going to give up on it.
Keep attending class
Every student is in the same position as you are. They registered for more classes than they want to take and are "shopping." For the first couple of weeks, you can drop or add classes as you please, which means that classes that were once full will have spaces. If you keep attending class and keep up with assignments, odds are that you will have priority. Professors give preference to people who need the class for a major and then from higher to lower class year (senior to freshman).
Have a backup plan
For two weeks, or until I find out whether I get into my waitlisted class, I will be attending more than the usual number of classes. This is so that if I don't get into my waitlisted class, I won't have a credit shortage and I won't have to fall back in my backup class. Chances are that enough people will drop the class, especially if it is very difficult like computer science, and you will have a chance. In popular classes like art and psychology, odds are you probably won't get in, so prepare for that.
Remember that everything works out at the end
Life is full of surprises. So what if you didn't get into the class you wanted? Your life obviously has something else in store for you. It's your job to make sure you make the best out of what you have.
Trending Topics
Songs About Being 17 Grey's Anatomy Quotes Vine Quotes 4 Leaf Clover Self Respect
Top Creators
1. Brittany Morgan, National Writer's Society 2. Radhi, SUNY Stony Brook 3. Kristen Haddox , Penn State University 4. Jennifer Kustanovich , SUNY Stony Brook 5. Clare Regelbrugge , University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Trending Stories
Nostalgic 2000s songs: 100 throwback hits that'll transport you to childhood, 19 things you can do when you turn 19 years old, an apology letter to the ex i will always love, 75 excuses to not go out, 15 photos that will inspire you to start a bullet journal, best of student life top 10 reasons my school rocks, 7 new year clichés: break free, embrace change, the ultimate birthday: unveiling the perfect day to celebrate, 100 reasons to choose happiness, 25 things kids from the 2000s will be nostalgic about, subscribe to our newsletter, facebook comments.
News from Brown
Brown’s bell gallery awarded prestigious two-year warhol foundation grant.
An award from the Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts will enable the University’s David Winton Bell Gallery to expand public programming for exhibitions in 2025 and 2026.
The David Winton Bell Gallery, located in Brown's List Art Building, was recently awarded a prestigious grant by the Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts. Photo by Nick Dentamaro/Brown University.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts has awarded the David Winton Bell Gallery at Brown University a two-year grant to support public programming and community engagement opportunities related to upcoming exhibitions.
The award will enable the David Winton Bell Gallery — a Brown Arts Institute space located in the University’s Perelman Arts District — to enhance four exhibitions planned for 2025 and 2026. The exhibitions will highlight contemporary artists with a focus on the relationships between performance, gender, race and technology, according to Kate Kraczon, chief curator of the gallery and director of exhibitions for the Brown Arts Institute.
“We are thrilled and honored to receive this prestigious grant, which will support curatorial projects that advance the Bell’s mission to center emerging and underrepresented artists while contributing to critical societal issues impacting artistic freedom,” Kraczon said.
The grant-supported events and conversations will broaden the impact of the gallery’s artistic programming in Providence and beyond, noted the gallery’s Associate Curator Thea Quiray Tagle.
“This award will allow artists to realize their visions both within the Bell’s gallery spaces and through platforms across campus and the region that support events and conversations, performances, artist residencies, academic symposia and our new publications program,” Quiray Tagle said.
The Warhol Foundation awarded the $80,000 multi-year programming grant in support of the gallery’s dedication to community engagement and support for experimental visual artists, according to Rachel Bers, the foundation’s program director.

The four exhibitions the grant will help to support include a Spring 2025 solo presentation by Paris-based Martinican artist Julien Creuzet, who is set to re-imagine his immersive installation currently on view in the French pavilion at the 2024 Venice Biennale. The Warhol Foundation funding will enable an accompanying public symposium at Brown, organized by the gallery with faculty from Brown’s Center for Latin American and Caribbean Studies and other campus collaborators, as well as the development of a bilingual catalog.
In Fall 2025, the grant will support the first major solo exhibition of Eric-Paul Riege , a Diné (Navajo) artist who produces large soft sculptures, weavings and performance-based video pieces that reference the history of Euro-American trading posts in Navajo Nation and the notion of “authenticity” as a value marker of Indigenous art and craft. As part of his preparations, Riege researched the Diné collection in Brown’s Haffenreffer Museum of Anthropology to create a new body of artwork made in dialogue with the collection. The Warhol Foundation funding will support performances by Riege and Indigenous collaborators, as well as a public gathering addressing topics such as the repatriation of Indigenous cultural objects from museum collections and the state of Indigenous contemporary art.
In 2026, the gallery curators plan to use the grant funding for a performance series related to a commissioned project by sound, video and installation artists Basel Abbas and Ruanne Abou-Rahme and support programming for “BATH/HOUSE,” a group exhibition being developed by Quiray Tagle.
Related news:
Brown university’s john hay library acquires former u.s. poet laureate joy harjo’s papers, student research sheds light on history of andrews house on brown campus, photos: professional musicians bring final projects by brown student composers to life.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sources to Consider Using. When writing your research paper and finding sources, it's best to use a mix of sources. This may include: Internet: The Internet is filled with limitless possibilities. When you use the Internet, it's best to find credible and trustworthy sources to avoid using fake news as a source. That's why tools like Google Scholar can be so helpful.
When writing a 12-page research paper, break the task into smaller sections. This makes the process less overwhelming and helps you maintain focus. Create an outline with clear sections and subsections to serve as a roadmap for your paper. Arrange the papers at key points in a logical flow and include relevant subsections for specific details.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts. You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on - diving into the results.
Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. Begin the paper with an introduction to provide background on the topic, cite related studies, and contextualize the paper. Use descriptive headings to identify other sections as needed (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers).
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper: Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper. Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics ...
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
1. Choose your topic. Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation. Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
Save each page in a separate file according to the subject. Print them out. Arrange your printed pages (subtopics) in a logical order. When you find a sequence that makes sense, cut and paste the pages together into one big file. Don't delete your individual pages, though. You may need to come back to these.
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There are ten steps involved in writing a research paper: Step 1: Select a subject Step 2: Narrow the topic Step 3: State the tentative objective (or thesis) Step 4: Form a preliminary bibliography Step 5: Prepare a working outline Step 6: Start taking notes Step 7: Outline the paper Step 8: Write a rough draft Step 9: Edit your paper Step 10 ...
Example: BODY PARAGRAPH 1. First point. Sub-point. Sub-point of sub-point 1. Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points. Example: First body paragraph of the research paper. First point of evidence to support the main argument.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research. To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery.
A 12 page essay word count is usually 2950 to 3000 words (12 pt., double-spaced). The length of a typical academic paragraph is 100 to 150 words. So, there are 19 to 30 paragraphs in a paper of 12 pages. If you need 12 page essay examples, look at the list below. We've collected A+ samples for you to get inspired.
Start with your introduction, write out your thesis, and jot down your key pieces of evidence that you'll use to defend your argument. Then sketch out the body paragraphs and conclusion. [6] Your outline is your paper's skeleton. After making the outline, all you'll need to do is fill in the details.
Then, writing the paper and getting it ready for submission may take me 3 to 6 months. I like separating the writing into three phases. The results and the methods go first, as this is where I write what was done and how, and what the outcomes were. In a second phase, I tackle the introduction and refine the results section with input from my ...
Step 4: Create a Research Paper Outline. Outlining is a key part of crafting an effective essay. Your research paper outline should include a rough introduction to the topic, a thesis statement, supporting details for each main idea, and a brief conclusion. You can outline in whatever way feels most comfortable for you.
It helps to break down the process of writing the research paper into several steps rather than leaping right into it. Each step can be followed in order. 1. Pick a Topic. If you have trouble choosing a topic, ask your instructor for help, or refer to the helpful list below. Do the research and take notes.
4: Start with preliminary research. Use reliable sources to collect information relevant to your topic. Start by quickly skimming through each source to narrow down on the most relevant ones and identify key talking points. Keep track of all the reference material you're using so you have no trouble citing them later on.
Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements. ... (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the ...
Creating Writing Strategies including clustering ideas, drawing diagrams, and planning a "road map" will help you visualize the stages that you need to map out to build a strong paper. Research papers always start with disparate ideas, indiscriminate notions, and false starts. This process is necessary to think through your strategy.
Steps to write a research paper introduction. By following the steps below, you can learn how to write an introduction for a research paper that helps readers "shake hands" with your topic. In each step, thinking about the answers to key questions can help you reach your readers. 1. Get your readers' attention
As a student, you are often required to complete numerous academic tasks, which can demand a lot of extra effort. Writing a research paper is one of these tasks. If researching for the topic isn't challenging enough, writing it down in a specific format adds another layer of difficulty. Having gone through this myself, I want to help you have a smoother journey in writing your research paper.
For my seminar one class, I had to write a 12 to 14-page research paper. At first, it sounded extremely scary; however, the way my professor prepared the class for the final paper made it a lot easier to get the paper done. But even with all her help, there were many things that I learned when working through this paper.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The Andy Warhol Foundation for the Visual Arts has awarded the David Winton Bell Gallery at Brown University a two-year grant to support public programming and community engagement opportunities related to upcoming exhibitions. The award will enable the David Winton Bell Gallery — a Brown Arts Institute space located in the University's Perelman Arts ...