- USC Libraries
- Research Guides

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Executive Summary
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An executive summary is a thorough overview of a research report or other type of document that synthesizes key points for its readers, saving them time and preparing them to understand the study's overall content. It is a separate, stand-alone document of sufficient detail and clarity to ensure that the reader can completely understand the contents of the main research study. An executive summary can be anywhere from 1-10 pages long depending on the length of the report, or it can be the summary of more than one document [e.g., papers submitted for a group project].
Bailey, Edward, P. The Plain English Approach to Business Writing . (New York: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 73-80 Todorovic, Zelimir William and Marietta Wolczacka Frye. “Writing Effective Executive Summaries: An Interdisciplinary Examination.” In United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship. Conference Proceedings . (Decatur, IL: United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 2009): pp. 662-691.
Importance of a Good Executive Summary
Although an executive summary is similar to an abstract in that they both summarize the contents of a research study, there are several key differences. With research abstracts, the author's recommendations are rarely included, or if they are, they are implicit rather than explicit. Recommendations are generally not stated in academic abstracts because scholars operate in a discursive environment, where debates, discussions, and dialogs are meant to precede the implementation of any new research findings. The conceptual nature of much academic writing also means that recommendations arising from the findings are distributed widely and not easily or usefully encapsulated. Executive summaries are used mainly when a research study has been developed for an organizational partner, funding entity, or other external group that participated in the research . In such cases, the research report and executive summary are often written for policy makers outside of academe, while abstracts are written for the academic community. Professors, therefore, assign the writing of executive summaries so students can practice synthesizing and writing about the contents of comprehensive research studies for external stakeholder groups.
When preparing to write, keep in mind that:
- An executive summary is not an abstract.
- An executive summary is not an introduction.
- An executive summary is not a preface.
- An executive summary is not a random collection of highlights.
Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Clayton, John. "Writing an Executive Summary that Means Business." Harvard Management Communication Letter (July 2003): 2-4; Keller, Chuck. "Stay Healthy with a Winning Executive Summary." Technical Communication 41 (1994): 511-517; Murphy, Herta A., Herbert W. Hildebrandt, and Jane P. Thomas. Effective Business Communications . New York: McGraw-Hill, 1997; Vassallo, Philip. "Executive Summaries: Where Less Really is More." ETC.: A Review of General Semantics 60 (Spring 2003): 83-90 .
Structure and Writing Style
Writing an Executive Summary
Read the Entire Document This may go without saying, but it is critically important that you read the entire research study thoroughly from start to finish before you begin to write the executive summary. Take notes as you go along, highlighting important statements of fact, key findings, and recommended courses of action. This will better prepare you for how to organize and summarize the study. Remember this is not a brief abstract of 300 words or less but, essentially, a mini-paper of your paper, with a focus on recommendations.
Isolate the Major Points Within the Original Document Choose which parts of the document are the most important to those who will read it. These points must be included within the executive summary in order to provide a thorough and complete explanation of what the document is trying to convey.
Separate the Main Sections Closely examine each section of the original document and discern the main differences in each. After you have a firm understanding about what each section offers in respect to the other sections, write a few sentences for each section describing the main ideas. Although the format may vary, the main sections of an executive summary likely will include the following:
- An opening statement, with brief background information,
- The purpose of research study,
- Method of data gathering and analysis,
- Overview of findings, and,
- A description of each recommendation, accompanied by a justification. Note that the recommendations are sometimes quoted verbatim from the research study.
Combine the Information Use the information gathered to combine them into an executive summary that is no longer than 10% of the original document. Be concise! The purpose is to provide a brief explanation of the entire document with a focus on the recommendations that have emerged from your research. How you word this will likely differ depending on your audience and what they care about most. If necessary, selectively incorporate bullet points for emphasis and brevity. Re-read your Executive Summary After you've completed your executive summary, let it sit for a while before coming back to re-read it. Check to make sure that the summary will make sense as a separate document from the full research study. By taking some time before re-reading it, you allow yourself to see the summary with fresh, unbiased eyes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Length of the Executive Summary As a general rule, the correct length of an executive summary is that it meets the criteria of no more pages than 10% of the number of pages in the original document, with an upper limit of no more than ten pages [i.e., ten pages for a 100 page document]. This requirement keeps the document short enough to be read by your audience, but long enough to allow it to be a complete, stand-alone synopsis. Cutting and Pasting With the exception of specific recommendations made in the study, do not simply cut and paste whole sections of the original document into the executive summary. You should paraphrase information from the longer document. Avoid taking up space with excessive subtitles and lists, unless they are absolutely necessary for the reader to have a complete understanding of the original document. Consider the Audience Although unlikely to be required by your professor, there is the possibility that more than one executive summary will have to be written for a given document [e.g., one for policy-makers, one for private industry, one for philanthropists]. This may only necessitate the rewriting of the introduction and conclusion, but it could require rewriting the entire summary in order to fit the needs of the reader. If necessary, be sure to consider the types of audiences who may benefit from your study and make adjustments accordingly. Clarity in Writing One of the biggest mistakes you can make is related to the clarity of your executive summary. Always note that your audience [or audiences] are likely seeing your research study for the first time. The best way to avoid a disorganized or cluttered executive summary is to write it after the study is completed. Always follow the same strategies for proofreading that you would for any research paper. Use Strong and Positive Language Don’t weaken your executive summary with passive, imprecise language. The executive summary is a stand-alone document intended to convince the reader to make a decision concerning whether to implement the recommendations you make. Once convinced, it is assumed that the full document will provide the details needed to implement the recommendations. Although you should resist the temptation to pad your summary with pleas or biased statements, do pay particular attention to ensuring that a sense of urgency is created in the implications, recommendations, and conclusions presented in the executive summary. Be sure to target readers who are likely to implement the recommendations.
Bailey, Edward, P. The Plain English Approach to Business Writing . (New York: Oxford University Press, 1997), p. 73-80; Christensen, Jay. Executive Summaries Complete The Report. California State University Northridge; Executive Summaries. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Clayton, John. "Writing an Executive Summary That Means Business." Harvard Management Communication Letter , 2003; Executive Summary. University Writing Center. Texas A&M University; Green, Duncan. Writing an Executive Summary. Oxfam’s Research Guidelines series ; Guidelines for Writing an Executive Summary. Astia.org; Markowitz, Eric. How to Write an Executive Summary. Inc. Magazine, September, 15, 2010; Kawaski, Guy. The Art of the Executive Summary. "How to Change the World" blog; Keller, Chuck. "Stay Healthy with a Winning Executive Summary." Technical Communication 41 (1994): 511-517; The Report Abstract and Executive Summary. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Executive Summaries. Effective Writing Center. University of Maryland; Kolin, Philip. Successful Writing at Work . 10th edition. (Boston, MA: Cengage Learning, 2013), p. 435-437; Moral, Mary. "Writing Recommendations and Executive Summaries." Keeping Good Companies 64 (June 2012): 274-278; Todorovic, Zelimir William and Marietta Wolczacka Frye. “Writing Effective Executive Summaries: An Interdisciplinary Examination.” In United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship. Conference Proceedings . (Decatur, IL: United States Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 2009): pp. 662-691.
- << Previous: 3. The Abstract
- Next: 4. The Introduction >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 10:07 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

How To Write A High-Impact Executive Summary
By Derek Jansen | January 2018

In this post, I’ll deconstruct the often-misunderstood executive summary and show you how to develop a high-impact executive summary for your assignment, research report or even your dissertation or thesis.
So, what is an executive summary?
An executive summary (sometimes called an abstract ) is quite simply a summary of summaries. In other words, an executive summary provides a concise summary of each of your assignment or report chapters/sections . More specifically, it should communicate the key points/insights/findings/suggestions from the following chapters:
- Introduction
- Recommendations
- Implementation (if applicable)
- Reflection (if applicable)
I’ll discuss which key points from each section need to be addressed a bit later. On a separate note – if you’re writing an executive summary for a dissertation or thesis, all of the concepts described in this post will still apply to you, however, you’ll include an additional paragraph about your methodology, and you’ll likely spend more word count discussing your analysis findings.
The 4 Important Attributes Of An Exec Summary
Before I discuss what goes into the executive summary, let’s quickly look at 4 attributes that make for a strong executive summary:
#1 – It should be able to stand alone.
The executive summary should be able to stand independently as an informative document . In other words, the reader should be able to grasp your broad argument without having to read the full document. Further reading should be purely for attaining more detail. Simply put, the executive summary should be a “Mini-Me” of the assignment.
This independence means that anything you write in the executive summary will need to be re-stated in the body of your assignment. A common mistake that students make is to introduce key points in the executive summary and then not discuss them again in the document – accordingly, the marker must view the main document as missing these key points. Simply put – make sure you discuss key points in both the executive summary and the main body . It will feel repetitive at times – this is normal.

#2 – It should be written for the intelligent layman.
When crafting your executive summary, its useful to keep the intelligent layman front of mind. What I mean by this is that you should write your summary assuming that your reader (i.e. the marker) will be intelligent but won’t be familiar with your topic and/or industry. This means that you should explain any technical concepts, avoid jargon and explain acronyms before using them.
#3 – It should be concise.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 – 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you’ll need to:
- Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc).
- Write concisely – i.e. with brevity and completeness.
To the first point, I’ll explain what the “most important” information is for each chapter shortly. To the second point (writing concisely), there are various ways to do this, including:
- Using simple, straightforward language.
- Using the active voice.
- Removing bloaty adverbs and adjectives.
- Reducing prepositional phrases.
- Avoiding noun strings.
Does this sound like gibberish to you? Don’t worry! The Writing Center at the University of Wisconson-Madison provides a practical guide to writing more concisely, which you can download here.
On a related note, you typically would not include headings, citations or bulleted/numbered lists in your executive summary. These visual components tend to use a lot of space, which comes at a premium, as you know.
#4 – It should be written last.
Given that your executive summary is a summary of summaries, it needs to be written last , only once you’ve identified all your key insights, recommendations and so on. This probably sounds obvious, but many students start writing the summary first (potentially because of its position in the document) and then end up re-writing it multiple times, or they don’t rewrite it and consequently end up with an executive summary which is misaligned with the main document.
Simply put, you should leave this section until everything else is completed. Once your core body content is completed, you should read through the entire document again and create a bullet-point list of all the key points . From this list, you should then craft your executive summary . The approach will also help you identify gaps, contradictions and misalignments in your main document.

So, what goes into an executive summary?
Right, let’s get into the meat of it and consider what exactly should go into your executive summary. As I’ve mentioned, you need to present only the absolutely key point points from each of your chapters, but what does this mean exactly?
Each chapter will typically take the form of 1 paragraph (with no headings) in your executive summary. So, 5 chapters means 5 paragraphs. Naturally, some will be longer than others (let this be informed by the mark allocation), but assuming one page contains 500 words, you’re aiming for roughly 100 words per paragraph (assuming a 5-paragraph structure). See why conciseness is key!
Now, let’s look at what the key points are for each chapter in the case of a typical MBA assignment or report. In the case of a dissertation or thesis, the paragraph structure would still mimic the chapter structure – you’d just have more chapters, and therefore, more paragraphs.
Paragraph 1: Introduction
This paragraph should cover the following points:
- A very brief explanation of the business (what does it do, for whom and where?).
- Clear identification and explanation of the problem or opportunity that will be the focus of the assignment/report.
- A clear statement of the purpose of the assignment (i.e. what research questions will you seek to answer?).
- Brief mention of what data sources were utilised (i.e. secondary research) and any fieldwork undertaken (i.e. primary research ).
In other words, your first paragraph should introduce the business, the problem/opportunity to be addressed, why it’s important, and how you approached your analysis. This paragraph should make it clear to the reader what the assignment is all about at a broad level. Here’s a practical example:
This assignment focuses on ABC Ltd, a XXX business based in XXX, which provides XXX to XXX customers. To date, the firm has relied almost exclusively on XXX marketing channel. Consequently, ABC Ltd has little understanding of consumer segments, wants, and needs. This marketing channel is now under regulatory threat due to XXX. The core challenge, therefore, is that whilst ABC Ltd seeks to grow its market share, it has little understanding of its market characteristics or competitive set, and its sole marketing channel under regulatory threat. Accordingly, the objective of this assignment is XXX. The assignment draws on survey, interview, and industry data.
Paragraph 2: Analysis and findings
In this paragraph, you should discuss the following:
- What exactly did you analyse? For example, you might have analysed the macro context (i.e. PESTLE analysis), followed by the meso (i.e. competitor or industry analysis) and then the micro (i.e. internal organisational analysis).
- What were your key findings in relation to the purpose of the assignment? For example, you may have identified 4 potential causes of a problem and would then state them.
In other words, your second paragraph should concisely explain what you analysed and what your main findings were . An example of this:
Segmentation analysis, consisting of macro, industry and firm-level analyses, revealed a strong segmentation variable in the form of XXX, with distinct needs in each segment. Macro analysis revealed XXX, while industry and firm-level analyses suggested XXX. Subsequently, three potential target segments were established, namely XXX, XXX and XXX. These were then evaluated using the Directional Policy Matrix, and the results indicated XXX.
From a presentation perspective, you might structure this section as:
- Analysis 1, findings from analysis 1.
- Analysis 2, findings from analysis 2.
- Analysis 3, findings from analysis 3.
Importantly, you should only discuss the findings that are directly linked to the research questions (i.e. the purpose of the assignment) – don’t digress into interesting but less relevant findings. Given that the analysis chapter typically counts for a large proportion of marks, you could viably write 2-3 paragraphs for this. Be guided by the mark allocation.
Lastly, you should ensure that the findings you present here align well with the recommendations you’ll make in the next paragraph. Think about what your recommendations are, and, if necessary, reverse engineer this paragraph to create a strong link and logical flow from analysis to recommendations.

Paragraph 3: Recommendations
With the key findings from your analysis presented in the preceding paragraph, you should now discuss the following:
- What are your key recommendations?
- How do these solve the problems you found in your analysis?
- Were there any further conclusions?
Simply put, this paragraph (or two) should present the main recommendations and justify their use (i.e. explain how they resolve the key issue). As mentioned before, it’s critically important that your recommendations tightly align with (and resolve) the key issues that you identified in the analysis. An example:
Based on the Directional Policy Matrix analysis, it is recommended that the firm target XXX segment, because of XXX. On this basis, a positioning of XXX is proposed, as this aligns with the segment’s key needs. Furthermore, a provisional high-level marketing mix is proposed. The key aspects of the marketing mix include XXX, XXX and XXX, as these align with the firm’s positioning of XXX. By adopting these recommendations, the key issue of XXX will be resolved.
Also, note that (typically) the tone changes from past to present tense when you get to the recommendations section.
Paragraph 4: Implementation
If your assignment brief requires an implementation/project plan-type section, this paragraph will typically include the following points:
- Time requirements (how long will it take?)
- People requirements (what skills are needed and where do you find them?)
- Money requirements (what budget is required?)
- How will the project or change be managed? (i.e. project management plan)
- What risks exist and how will these be managed?
Depending on what level of detail is required by your assignment brief, you may need to present more, less or other details in this section. As always, be guided by the assignment brief.
A practical example:
A high-level implementation plan is proposed, including a stakeholder analysis, project plan and business case. Resource requirements are presented, detailing XXX, XXX and XXX requirements. A risk analysis is presented, revealing key risks including XXX, XXX and XXX. Risk management solutions are proposed, including XXX and XXX.

Paragraph 5: Reflection
As with the implementation chapter, the need for a reflection chapter/section will vary between assignments and universities. If your assignment has this requirement, it’s typically good to cover the following points:
- What were your key learnings? What were your ah-ha moments?
- What has changed in the real world as a consequence of these learnings? I.e. how has your actual behaviour and approach to “X” changed, if any?
- What are the benefits and/or disadvantages of this change, if any?
This section is very personal, and so each person’s reflections will be different. Don’t take the above points as gospel.
Time to test it out.
Once you’ve written up your executive summary and feel confident that it’s in good shape, it’s time to test it out on an unsuspecting intelligent layman. This is a critically important step, since you, as the writer, are simply too close to the work to judge whether it all makes sense to a first-time reader. In fact, you are the least suitable person on the planet!
So, find someone who is not familiar with your assignment topic (and ideally, not familiar with your industry), and ask them to have a read through your executive summary. Friends and family will usually tell you its great, regardless of the quality, so you need to test them on their understanding. Do this by asking them to give the details back to you in their own words. Poke and prod – can they tell you what the key issues and recommendations were (in their own words!). You’ll quickly spot the gaps this way, and be able to flesh out any weak areas.
Wrapping up.
In this post, I’ve discussed how to write the all too often undercooked executive summary. I’ve discussed some important attributes of a strong executive summary, as well as the contents that typically go into it. To recap on the key points:
The key attributes of a high-impact executive summary:
- It should be able to stand alone.
- It should be written for the intelligent layman.
- It should be concise.
- It should be written last.
The key contents of a high-impact executive summary:
Each paragraph should cover a chapter from the document. For example, In the case of a typical assignment, it would be something like:
- Summary of the introduction chapter.
- Summary of the analysis chapter.
- Summary of the recommendations and/or conclusions chapter.
- Depending – summary of the implementation and reflection.
Lastly, don’t forget to test out your executive summary on an unsuspecting layman or two. This is probably the most important step of them all!
If you have any questions or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Please get in touch here or leave a comment below.
Thanks so much for your methodical process and explanation of Executive Summary. It is exactly what I was researching for.
Regards Saane
It’s a pleasure!
This was really helpful with how to structure my assignment.
Thank you so much for the step by step process. It’s so helpful for beginners like me.
Great! This post is very informative and gives clear guidance on to write an executive summary. Thanks very much for sharing this information, it’s very helpful.
Thanks for the feedback, Anna. Best of luck with your writing 🙂
Thank you for the great article, really helped explain what was needed.
Great insight and tips . Thanks
Thank you so much for sharing this. It was exactly what I was looking for.
Thank you for your help
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Executive Summaries
Basics of executive summaries.
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a single-page executive summary all of the main information in the longer report. Any findings, conclusions, recommendations, or other details that appear in the larger document must be touched on in the executive summary. Readers should be able to read the executive summary alone and have a complete understanding of the larger document in its entirety.
How to Write an Executive Summary
It is important to meet all length and content expectations, so be sure to review the specific directions for your assignment. Also remember that the executive summary can only be written after the full-length document is complete.
Tips for completing the executive summary from Walden University (2013) include:
- List all of the main points in the same order in which they occur in the paper that you are summarizing.
- Take each point and turn it into a sentence.
- Add additional sentences to clarify or explain each point.
- Add a short introduction and a short conclusion. Include the name of the article, report, etc. and the author(s) in the introduction.
- Check grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Check for plagiarism.
- Read the summary slowly and carefully to make sure it covers all of the main points clearly, yet concisely. Also, check to be sure it is interesting. You want to catch your reader’s attention.
- Set it aside. Let some time pass and read it again. Often, you will catch items that you did not see the first time.
For academic writing, be sure to include appropriate citations and a reference. This is typically not part of a business executive summary but should be included for purposes of this program.
Executive Summary Versus Abstract
Like an executive summary, an abstract is a short summary of a larger text. Both executive summaries and abstracts are meant to capture the main ideas, findings, and conclusions of a longer document. Executive summaries, however, tend to include more details than abstracts. An abstract includes enough information for readers to decide if they want to read the full-length document. Executive summaries must include enough information for readers to understand the full-length document without reading it.
Another difference between executive summaries and abstracts are the fields where they are used. Generally, executive summaries are common in business and government, while abstracts are more common in academia and at Walden, especially when seeking publication in a professional journal.
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Content and Structure of KAM-Based PDPs
- Next Page: Theses
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Find top study documents
How to Write an Executive Summary for a Research Paper
Updated 12 Sep 2023
What is an Executive Summary In a Research Paper?
When you are asked to compose an executive summary for your research paper, the main purpose is to provide a detailed overview in a report form or any other specified paper type with a clear synthesis of all the essential key points that will help your readers to understand the objectives and the vital elements of your research. Learning how to write an executive summary for a research paper, you should prepare your target audience and save their time as they aim to understand and evaluate your main message and the content. Although there may be several deviations, depending on your subject, it is necessary to state the purpose of your report right in the first paragraph and highlight all the information that will help your readers to understand the results of your research with all the relevant descriptions, conclusions, or further recommendations.
Why Do We Compose an Executive Summary?
It’s done to increase the clarity and the purpose of your research for the academic community, college professors, general audience, and publishers. The executive summary in a research paper writing can be encountered in any academic discipline. It aims to help the readers understand the vital points of lengthy research work and focus one’s attention and expectations without having to read through every complex paper paragraph. Starting from colleges and universities to business circles and presentations, the role of an executive summary for research is paramount!
The Executive Summary Length and Placement
In the majority of cases, your summary should not exceed 5-10% of the total length of your report. For example, if your research paper is about forty pages, your executive summary should fit within two pages of text. As it appears after the table of contents, the length is critical and should play a role of a summary before your introduction part starts. Your executive summary should reflect what has been researched with a brief explanation of the problem (or series of challenges) with the methodology and solutions that you have provided before resulting in a list of outcomes.
Structure of an Executive Summary For a Research Paper
Even when they have an example of executive summary for research paper to look through, most students still find it challenging to learn what must be present in each part of their paper and what information is relevant or unnecessary for a specific part. While your grading rubric may have recommendations that one must follow, let's break down each part in greater depth to understand the purpose:
- Introduction. This is where you must introduce your subject and talk about the importance of a chosen topic. Your first paragraph must provide sufficient and clear information about the discipline and the range of your research by either including the target audience or explaining why the issue matters. It should be about three to five sentences.
For example: “The problem of the Amazon Forests have often been discussed through the lens of environmental damage, yet not many social aspects of the almost extinct populations have been explored”.
- Purpose of Study. When writing an executive summary, one of the hardest tasks is to explain why you are researching something and what you would like to achieve. In practice, if you want to make a point and prove that something is harmful, it must be specified along with your assumption. In a certain sense, it works like a thesis statement.
For example: “The main objective of the research is to determine the volume of African Americans with the cardiovascular conditions living in the criminal regions of Alabama State and document the findings ”.
- Methods to Gather Data. Also known as the methodology, it is either qualitative or quantitative analysis that comes first. The methods may include surveys, interviews, lab experiments, or field recordings. If you are using specific technical equipment or electronic devices, it is also necessary to include a brief list, especially if it will make more sense to the readers.
For example: “The surveys and private interviews have been chosen as the methodology for the maximum efficiency of this research project. The consent for the interviews has been received and permission has been granted by the educational counselors at the local community”.
- Findings. This section should list your findings in a short form without getting too much into details. The most important is to explain what has been discovered and what significance it has in relation to your assumption or the methods that have been used.
For example: “ The research on the implementation of multimedia solutions for the cognitive development of autistic children has shown that the inspiration factor has helped to motivate the young learners to adjust and work with the flexible software, thus becoming more socially aware of the socialization and the teamwork ”.
- Recommendations. In case you have discovered certain facts or information through the course of your research, this part of a summary of research must list the order of actions that must be taken or the further research that may be helpful to achieve your goals. Also known as the call to action, this part should not introduce any new ideas but must stay within the scope of your research.
For example: “ The works by J.R. Lawson explore the subject of brain metamorphoses in virtuo at greater depth, which can further explain the main hypothesis explored by this research” .
- Report Limitations. If you are using surveys or interviews, there are apparent limitations and challenges that you may encounter. In practice, if your sample group has been limited or you could not obtain information related to some lab research, mention it here. If something is missing from the research on the topic, it must be documented as well. Do your best to organize the limitations by the importance or the order of their occurrence by explaining why they have affected the clarity or validity of your research.
For example: “ The lack of social contacts with the remote tribes in New Zealand has made it almost impossible to collect data about social life patterns and interactions within the tribe. The published linguistic guides have been insufficient to analyze the language specifics in full ”.
- Implementation. This section basically helps your target audience to learn about the practical implementation of your research. Composing your summary of a research paper, it is essential to explain the practical value of your work and show the most efficient ways to use the recommendations or locate information that will help to understand the importance of your research.
For example: “The presence of the innovative research labs in NYC for the journalistic community has also made it possible to explore the subject even further by starting with the open journalism projects and sharing them on social media or the television networks involved in the social development campaign” .
- Conclusion. This part must summarize the information that has been provided in the aforementioned sections. Remember that you should not exceed the given word count and keep your conclusion short by restating the main thesis and letting your target audience see the most important key points. Do not introduce any new ideas or mention things that have not been discussed before.
In practical terms, think of your executive summary of a research paper as if it is a brief advertisement where you explain and promote your research paper by explaining the main purposes and the methodologies with the results. While it may sound complex to most college and university students, executive summary writing must be done when your research work has already been finished. Collect all the vital information and use it to fill in the relevant section as shown in the structure parts above.
Executive Summary for a Research Paper Formatting
It will always depend on your writing style and the specified formatting since this section follows the same guidelines as what has been specified for the rest of your research paper. For example, if you are composing an executive summary in APA or MLA format , you must follow the same fonts and indents that have been mentioned in the style manual. The majority of scientific writing papers do not mention anything specific regarding executive summary format other than the bullet point form in certain cases, especially when taking a report form. Always consult your academic advisor to ensure that you are not violating any writing rules before submitting your work!
The Executive Summary Mistakes to Avoid
Starting with an executive summary paper, many students misunderstand the purpose of each section and forget that the summary, in this case, is not the same as their introduction section or a part where they have to write about how good or bad their research is. It’s not a preface either as you have to provide a mini version of your research paper. There are at least five aspects that one must consider in terms of mistakes and the ways to avoid them, including:
- Clarity of Your Tone. Keep your tone clear and do not introduce any new ideas or assumptions. Use information from your research and try to keep all the vital elements in 2-3 sentences at most for each section. The key aspect is to keep things brief as you write.
- Knowing Your Target Audience. When you already know your target audience well, you can narrow things down and avoid explaining the concepts and the problems that may already be clear to your readers. It will also affect the depth of your comments and recommendations.
- Avoid Pasting Parts of Your Existing Research. The worst mistake that can make your research paper sound weaker is copying and pasting the parts of your research paper for an executive summary. When you do so, you are also risking being blamed for self-plagiarism or repetitions that may affect the final score of your research paper.
- Getting Too Lengthy or Overly Complex. Your executive summary report should not become overly long and go beyond 2 pages for a short paper. The same relates to the structure and complexity of each section. The purpose here is to achieve clarity and a good structure.
- Forgetting to Proofread and Connect The Concepts. This aspect is often ignored, yet proofreading and editing your executive summary should always come first as you check the wording and readability of your work. Each section of your executive summary must represent a continuation of each preceding part.
An executive summary is essentially a compressed representation of your research paper. If your target audience manages to understand the purpose of your research paper quickly, you have been able to compose a good executive summary report. Think of a busy person who doesn’t have much time to read your paper and imagine as if you are talking to a good friend, explaining the purpose of your writing!
Executive Summary Writing Tips and Recommendations
Speaking of tips for writing an executive summary, you must take notes when reading through your research paper to remember all the vital points that must be discussed. Here is what you must do to achieve success with your executive report writing:
- Mention your purpose right away and outline the methods and sources of information that have been used.
- As you make recommendations, do not be vague and stay specific. Mention the authors or research projects that can be helpful.
- Learn to specify your methods and explain why choosing case studies was better or possible compared to interviews.
- Stay focused on your subject!
- If you have used experimental research, discuss the benefits.
- Speaking of limitations, mention the time that has been spent on the implementation of the methods.
- The skills and lack of communication in certain areas may also be used as the barrier to research implementation.
- Mention the risks involved when you share recommendations.
Note: Some college professors recommend skipping the conclusion part of an executive summary for business courses or brief reports. Dealing with a serious research paper that’s meant for publishing, the final conclusion part of 2-3 sentences must be present!
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback, related blog posts, learn how to write limitations of a research paper.
The limitations in a research paper are related to your methodology peculiarities or the set of tools that have been used, impacted, or affected th...
Learn How to Write the Methodology Section of a Research Paper
The methodology belongs to one of the most important sections of your work because it explains and tells how exactly your research work has been co...
How to Write a Hypothesis
Learning how to write a hypothesis for your college paper may sound challenging, yet it all becomes easier when you know the purpose. As the name i...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
How to Write an Executive Summary for a Research Paper
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 5094 words
- Icon Clock 23 min read
When people work on organizing their research papers, they need effective guidelines on how to write an executive summary. This article provides insights students should grasp to create high-standard texts, including defining what is an executive summary, its meaning, and its basic structure. About the structure, the guideline teaches students all the sections of an executive summary (introduction, purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, implementation, and conclusion), the contents of each part, and how to write each element. Other insights include 20 tips for producing a high-standard executive summary, including 10 dos and 10 don’ts. Lastly, the article gives a sample outline template for writing a good executive summary and a practical example of this section of a research paper.
How to Write an Outstanding Executive Summary for a Research Paper & Examples
A habit of reading different types of papers is helpful to students’ mental preparation for course assessments but, more importantly, to their intellectual development. Reading various types of essays, reports, and research papers also induces the mental faculties of intellect, reason, imagination, and intuition, which are essential for academic discourse. Indeed, one can tell a writer who reads habitually by how they construct and defend arguments and ideas in their works. Basically, this guideline for writing an effective executive summary includes essential insights into what students should and should not do when writing this type of academic document. The article also defines what is an executive summary and its meaning, outlines its distinctive features, shows how to write each part of this section of a research paper, explains concepts, and gives helpful tips for producing a high-standard document. In turn, this guideline gives a sample outline of a project paper and an example of an executive summary.

Definition of What Is an Executive Summary and Its Meaning
From a simple definition, an executive summary is a text that accounts for the main points of a longer text, mainly a market study report, project report, and business proposal. In this respect, it serves the same purpose as an abstract, the only difference being that it is not used in research papers. Ideally, an abstract is a short and descriptive section of the essential details of a research paper, such as background, methodology, results, and conclusion. In contrast, an executive summary means writing a comprehensive overview of a report, research proposal, or project that explains the main points, including recommendations. Practically, an abstract is between 0.5-1 page, while an executive summary is about 5-10% of the document’s total word count. Since the purpose of an executive summary is to summarize the entire research paper comprehensively, it precedes the introduction of a report, proposal, or business plan.
Distinctive Features of an Executive Summary
An executive summary is identifiable by specific features that distinguish it from other texts, including essays and research papers. Essentially, all scholarly documents require the same level of mental preparation by writers to produce high-quality work. However, students must understand that some papers are demanding because of their contents, which underscore the basic essay outline. The main contents that earmark the distinctive features of an executive summary are an introduction, a purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, an implementation plan, and a conclusion.
Use exceptional writing services that guarantee original and well-researched papers.
1️⃣ Introduction
The introduction of an executive summary highlights the document’s topic, which emphasizes the type of paper it is, such as a business proposal, project report, or market research report. In this respect, it must be short and precise. Because the focus is the topic, one should use a bridge sentence or short paragraph for the introduction.
2️⃣ Purpose Statement
The purpose statement of an executive summary communicates the document’s primary objective. In this respect, it provides a brief background of the topic to enhance the reader’s understanding of the essence of the document. The language in this part reflects an expected end, while common terms include ‘aim,’ ‘goal,’ ‘purpose,’ or ‘objective.’
3️⃣ Methods
In an executive summary, methods outline the writer’s approach to achieving the primary objective, such as examining official data, conducting a field study, reviewing the literature, or interviewing stakeholders. Students need to understand that this component differs from the research methodology of research papers. In this respect, it does not detail the methods one has used to complete the work. In essence, it outlines the strategies that help writers to better understand critical issues, such as challenges to a sector, stakeholder sentiments, industry insights, or potential barriers.
4️⃣ Findings
Findings in an executive summary are the outcomes of the methods, meaning it is what the writer has discovered about an issue, such as an industry, stakeholders, or a project. This component is crucial to readers because it offers a sneak peek into the outcomes that underscore the primary purpose of the entire document: project report, market research report, or business proposal.
5️⃣ Recommendations
Recommendations in an executive summary underscore the writer’s perspective regarding the issues that a research paper addresses as a challenge or problem. For example, if the paper is a report about healthcare status, the challenges or problems it identifies may be nursing shortages or medical errors. The recommendations should highlight what stakeholders, like the government and health institutions, must do to overcome these challenges or problems. In other words, the recommendations address what must be done to rectify a situation or make it possible to achieve specific outcomes.
6️⃣ Limitations
Like a research paper, an executive summary must point out the limitations that the document’s author encountered in reporting about a project or business plan. For example, these limitations may include a lack of goodwill among stakeholders, sufficient time to investigate a matter, or resources to execute the task. This information is essential to the audience because it indicates the dynamics influencing the primary objective.
7️⃣ Implementation Plan
The implementation plan is the component in an executive summary that provides a framework for adopting and implementing the recommendations. Typically, this information includes claims and activities, people responsible, the timeframe, and budget allocation. Sometimes, an evaluation plan is also part of the implementation plan.
8️⃣ Conclusion
The conclusion part of an executive summary is a call to action about the project report, market research report, or business proposal. Unlike conclusions in other academic papers and essays that summarize the paper’s main points, the conclusion of an executive summary gives a direction about the document. Essentially, writers use this component to call to action the audience to adopt the recommendations or compel stakeholders to adopt a particular perspective. In turn, it persuades the audience to adopt a particular stance regarding the report or proposal.
The Length of an Executive Summary
Students should know the length of each of the above sections, except the introduction and conclusion parts, depending on the document’s total length, which determines the word count of an executive summary. For example, a long and robust project report or business proposal requires a long executive summary with an extended purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, and implementation, which means the length of 4-10 double spaced pages, or 2-5 single spaced pages, or 1000–2500 words, depending on the volume of the work. Typically, the introduction and conclusion sections take a statement or short paragraph of 0.5-1 double spaced page or 125-250 words, irrespective of a research paper or executive summary’s length. However, if a research paper is a long work of more than 10 double spaced pages, 5 single spaced pages, or 2500 words, the introduction and conclusion parts should not exceed 5-10% of the whole word count. Besides, the body section of an executive summary must take 80-90% of the total word count of a research paper, not less. The word count of a title page, a table of contents, an abstract, a reference page, and appendix is not considered since these parts are technical and do not mean writing itself.
How to Write Each Section of an Executive Summary for a Research Paper
Writing an executive summary requires students to demonstrate an understanding of its purpose. This understanding means students should know when to write it, what to talk about, and how to write each of the sections above. Therefore, writing an executive summary is essential to approach carefully and with the utmost focus.
1️⃣ Writing an Executive Summary as a Last Action
Because an executive summary overviews the entire research paper, students should write this part after finishing their market research reports, project reports, or business proposals. However, one should read and reread the whole research paper to know the most significant points forming part of the summary. By writing an executive summary as a last item, one can have a mental picture of what to address to give the audience a comprehensive sneak peek into a research paper document.
2️⃣ Making Notes of Important Aspects
While reading and rereading a research paper, students should take notes of the most critical aspects of their work that must appear in an executive summary. These aspects must address each section above. Moreover, one should identify crucial information in an introduction, a purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, an implementation plan, and a conclusion.
A. Writing an Introduction Part of an Executive Summary
When writing a college essay introduction, students must refrain from going into details about the purpose of the text because they will have an opportunity to do so later. While one may mention the document’s background, one should make it concise to contextualize the topic. The most crucial detail is that the introduction part of an executive summary should be a sentence or brief paragraph.
B. Writing a Purpose Statement Part of an Executive Summary
When writing the research paper’s purpose, students should communicate the type of document, such as a business proposal, a market research report, or a project report. The next thing is to state the background; provide the reason for writing, like sourcing funds; recommend solutions; or report progress and challenges. However, one should avoid going into detail because they will do so later in an executive summary of a research paper.
C. Writing a Methods Part of an Executive Summary
When writing a methods section, one should focus on giving the audience a sense of the strategy that helps achieve the outcomes. However, writers should approach this part differently than the methodology section of a research paper. Instead, they should mention what they did to execute the work, such as interviewing stakeholders or analyzing official data. The best way to approach this section is to list everything one did to make a research paper.
D. Writing a Findings Part of an Executive Summary
Since the purpose of the findings section in a research paper is to narrate outcomes, students should write it in the past tense. Therefore, when writing this section of an executive summary, authors should see themselves as reporters educating the audience about what they have learned in executing the task. An essential detail students should note when writing the section is to refer to credible sources of information that lead to the findings. These reliable sources can be documents, organizations, individuals in leadership, or industry experts.
E. Writing a Recommendations Part of an Executive Summary
When writing a recommendations section in an executive summary for a research paper, students should focus on giving a clear summary of what should happen after the findings. Essentially, one should address the key decision-makers or stakeholders because they are responsible for creating change through policy. The best approach to writing recommendations is to interrogate each challenge or problem and related findings to understand what must happen to create positive outcomes.
F. Writing a Limitations Part of an Executive Summary
The best approach to writing a limitations section in an executive summary for a research paper is to interrogate the challenges one has faced in the project, such as a lack of goodwill among stakeholders or sufficient time, resources, or support. Ideally, writers aim to inform the audience of the factors that have complicated their work or may complicate the implementation of the recommendations.
G. Writing an Implementation Plan Part of an Executive Summary
When writing an implementation plan in an executive summary, students should focus on telling the audience the procedure for actualizing the recommendations. In this respect, the best approach to writing this section is to interrogate the recommendations to determine what must happen to actualize each. For example, some issues to consider may include people in charge of implementation, such as an organization’s human resource director, the time it would take to actualize (timeline), the budget, and how to measure success (evaluation).
H. Writing a Conclusion Part of an Executive Summary
When writing a conclusion part, students should aim to persuade the audience to adopt a particular stance regarding a research paper or proposal. Although one might reiterate the topic, it is not necessary to mention each of the preceding sections. Instead, writers should focus on sending a strong communication regarding it. The best approach to writing the conclusion section is to influence the audience’s perspective on the topic and the recommendations and implementation.
3️⃣ Explaining Acronyms, Abbreviations, and Key Terms
Since an executive summary is an overview of a market research paper, project report, or business plan, authors should write it clearly and precisely. The best approach is to use simple language and define all acronyms, abbreviations, and key terms. In turn, students should not assume that readers know what each acronym, abbreviation, and key term means when they read research papers.
4️⃣ Proofreading, Revising, and Editing an Executive Summary Section of a Research Paper
After completing writing a research paper, students should proofread it to identify grammatical and formatting mistakes and inconsistent arguments and ideas. For example, the best way to fix these mistakes and flaws is to revise the whole research paper by fixing mistakes, like missing punctuation and wrong citations, and editing it by adding or deleting words and sentences to create a logical order of thoughts and ideas. In turn, writers must be factual, not use word count fillers, and avoid unnecessary repetitions. Besides, students should know that the audience is not interested in stories but in factual communication that makes logical sense.
Sample Paper Template for Writing a Good Executive Summary
Like essays, executive summaries have a specific structure students should demonstrate in their writing. The sections above underscore this outline template, meaning students should know what each section of writing an executive summary for a research paper entails and how to write it. The best way to write a high-quality executive summary is to create a template and populate it with ideas for a project, a business plan, a proposal, or a report. This preparation helps writers to have a mental picture of the kind of document they want to have and the right attitude when writing.
I. Introduction: [Introduce the topic and state the kind of document, such as a market research paper, project report, or business plan].
II. Purpose Statement: [Explain the primary objective of a research paper, such as investigating a problem, souring some funds, or reporting its progress].
III. Methods: [Enumerate how the task is accomplished, such as examining official data, interviewing stakeholders, or reviewing the literature].
IV. Findings: [Provide the outcomes of the methods, such as what official data reveals, stakeholders’ sentiments, or what research says].
V. Recommendations: [State clearly what stakeholders or key decisions must do to address the challenges or problems that the findings reveal].
VI. Limitations: [Discuss the challenges or problems that were encountered in completing the task, such as poor time management, a lack of support, or absent goodwill by stakeholders].
VII. Implementation Plan: [Include what stakeholders or key decision-makers must do to actualize the recommendations, such as identifying a person responsible and establishing a budget and timeline].
VIII. Conclusion: [Persuade the audience to adopt the recommendations and work toward creating change by facilitating an implementation plan].
Join our satisfied customers who have received perfect papers from Wr1ter Team.
Example of an Executive Summary for an 8000-Word Research Paper
Topic: A Need for Proactive Climate Change Initiatives
I. Example of an Introduction Section in an Executive Summary
Stakeholders in the climate change discourse must shift focus from discourse to practical, proactive measures to demonstrate seriousness in tackling the biggest threat of the millennium.
II. Example of a Purpose Statement Section in an Executive Summary
The purpose of writing this executive study is to examine the status of the climate change discourse, interrogate dynamics that make it unpromising as a practical solution to the crisis, and recommend what stakeholders must do to restore hope to millions globally who are afraid that climate change poses the biggest threat to the existence of current and future generations.
III. Example of a Methods Section in an Executive Summary
An executive report employs several data-gathering methods to achieve these objectives, including examining the climate change discourse over the decades to identify key themes: environmental policies, greenhouse gases, industrial pollution, natural disasters, weather forecasts, and others. Another method is interrogating research and official data on climate change by government agencies in the last three decades. The report also considers interviews with environmentalists, social justice advocates, government officials, and leaders of organizations that dedicate their mission to creating awareness about the need for environmental conservation and preservation.
IV. Example of a Findings Section in an Executive Summary
Overall, the methods above reveal worrying findings about the climate change discourse:
- Human activities, including industries and deforestation, have increased global warming to 1.1 degrees C, triggering unprecedented changes to the Earth’s climate. The lack of consensus on reversing human-induced global warming among the most industrialized countries suggests that the trend will worsen in the coming decades.
- The impacts of climate change are evident on people and ecosystems. Without urgent practical interventions, these impacts will become more widespread and severe with every additional degree of global warming.
- Developing and implementing adaptation measures in communities can effectively build and foster the resilience of people and ecosystems. However, stakeholders must interrogate their climate change funding priorities for effective proactive interventions.
- Communities will continue recording climate-induced losses and damages as long as communities cannot adapt to some impacts of this global problem. An example is 1.1 degrees C of global warming.
- Projections indicate global greenhouse gas (GHC) emissions will peak at 1.5 degrees C before 2025 in selected at-risk pathways.
- Burning fossil fuels remains the leading cause of the global climate crisis.
- Carbon removal is the most effective and practical solution to limiting global warming from peaking at 1.5 degrees C.
- There is a lack of commitment by key stakeholders to finance climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Climate change and the collective efforts to mitigate and adapt to its impacts will exacerbate global inequity if stakeholders do not prioritize just transition.
These findings of a research paper confirm that the climate change discourse is alive to the threat the global problem poses to people and ecosystems and the weaknesses in the current interventions.
V. Example of a Recommendations Section in an Executive Summary
This executive report recommends that key stakeholders, including governments, communities, policy experts, and financiers, must adopt to prioritize practical solutions to the global climate crisis.
- Stakeholders must target a net-zero climate-resilient future through urgent, systemwide transformations.
- Adopt policies that enhance access to fresh produce by establishing a relationship between farmers and consumers.
- Improve awareness about the critical benefits of organic foods.
- Consider policies that promote regenerative farm practices to eliminate toxins and revitalize soils.
- Create infrastructures for transforming waste into compost manure for farm use.
- Develop policies that encourage communities to embrace a green neighborhood.
VI. Example of a Limitations Section in an Executive Summary
This executive report recognizes several limitations that have made the fight against climate change unproductive and threaten current and future endeavors to arrest the crisis. For example, stakeholders need to note that these limitations may undermine the implementation of the recommendations in this report. One limitation is a lack of goodwill among key stakeholders. The four leading industrial powers, namely the United States, China, India, and Brazil, contribute to significant global atmospheric temperature increases. Traditionally, these countries have refused to agree on how to cut back on industries primarily because they are the main drivers of their economies. Another limitation is the mis-prioritization of financing, where much focus is on theoretical interventions, such as agreements and seminars, at the expense of practical solutions like building infrastructures for transforming waste into usable products. While stakeholders agree on the essence of the 3R (reuse, reduce, and recycle) framework, there is little practical implementation at the community level.
VII. Example of an Implementation Plan Section in an Executive Summary
The implementation plan for the recommendations above recognizes government agencies as the most suitable implementers because official bodies are the key stakeholders who finance climate change initiatives. The business plan considers that, to shift the climate change fight from mere discourse to practical evidence, stakeholders must prioritize the following:
- A budget of at least $50 million annually at the country level;
- A period of between 2-5 years; and
- Periodic evaluation of progress through at least one annual seminar or conference.
VIII. Example of a Conclusion Section in an Executive Summary
This executive research paper calls on all stakeholders in the climate change discourse to reconsider the current focus by recognizing its failure to create meaningful change as evidence shows the crisis continues to worsen. Instead, they should focus on practical, proactive interventions focusing on communities because that is where much environmental damage happens. It is also where the adversities of the crisis manifest most powerfully.
4 Easy Steps for Writing an Executive Summary
Writing an executive summary is a technical undertaking requiring writers to consider each section’s basic structure and essential details. When writing a research paper, one must know when to write each section and what to say. In this respect, preparation, stage setup, writing a first draft of an executive section, and wrap-up are essential steps students should follow to produce a research paper document that meets quality standards.
Step 1: Preparation
As the first step in writing an executive summary, preparation helps writers to develop a proper mindset that involves knowing the basic structure and what to write in each section of a research paper. Therefore, the critical task for students in this stage is constructing the basic structure and stating what must happen in each section.
Step 2: Stage Setup
Setting up the stage is the second step in writing an executive summary. It involves reading and rereading the document to identify critical details to address in each section of the basic structure. The best approach to achieve this outcome is to make notes of the most vital data when reading a research paper.
Step 3: Writing a First Draft of an Executive Summary
The third step is to create a first draft of an executive summary by putting all the critical data into relevant sections. Ideally, people must start with a clear introduction where they point out the focal point of a research paper and then move to a study’s purpose statement, methods, findings, recommendations, limitations, implementation plan, and conclusion. Each research section must summarize and not explain the most critical data.
Step 4: Wrap-Up
Wrapping a first draft into a final version of a research paper is the last step in writing an executive summary. This stage involves proofreading, revising, and editing a first version of an executive summary to eliminate grammar mistakes and inconsistent statements. As a result, authors must perfect their executive summaries of research papers by fixing errors and flaws that affect the logical progression of ideas and thoughts and the overall quality of the text.
20 Tips for Writing an Effective Executive Summary
Writing an executive summary can be demanding, particularly for students who do not prepare well or do not know what is most important. The following tips can be helpful: begin an executive summary by explaining why the topic is important; state the purpose of a research paper by outlining the problem and why it is essential or relevant to the audience; explain the methods that help to execute the task; state the findings; enumerate the limitations by addressing dynamics that undermine the implementation of solutions; consider the recommendations and list them using numbers or bullet points; outline an implementation plan that identifies the person or entity that oversee the implementation, the budget allocation, and how to evaluate progress; and write a conclusion that persuades the audience to adopt a particular perspective about the topic. In turn, 10 dos and 10 don’ts that writers should consider when writing their executive summaries in their research papers are:
10 things to do when writing an executive summary include:
- reading a research paper thoroughly to identify the primary objective, methods for collecting data, key findings, recommendations, significant limitations, and an implementation strategy;
- considering the audience of an executive summary to determine whether to use simple or technical language;
- writing formally and avoiding jargon;
- outlining the structure that considers all the main sections (introduction, purpose statement, methods, key findings, recommendations, limitations, implementation, and conclusion);
- organizing an executive summary in a summary format;
- using a short, clear, precise, and captivating opening statement to hook readers;
- including each section to state the most critical details;
- focusing on summarizing a research paper rather than explaining its contents;
- reviewing a research paper for incorrect information;
- proofreading, revising, and editing an executive summary to eliminate all mistakes.
10 things not to do when writing an executive summary include:
- using jargon to simplify complex terms and phrases;
- explaining rather than summarizing a research paper;
- creating too many grammar mistakes, such as missing punctuation and confusing words with a similar pronunciation;
- ignoring the basic outline of an executive summary;
- writing a lengthy introduction;
- concentrating on some sections more than others;
- explaining ideas or concepts not discussed in the main research paper;
- providing a very short or long summary that does not align with the document’s total word count;
- beginning an executive summary with anecdote or irrelevant information;
- placing an executive summary at the end of a research paper.
Summing Up on How to Write a Perfect Executive Summary
- Tell an interesting story. Writers should approach an executive summary as a platform for inducing the reader’s interest in reading a research paper. As such, one should use each section to tell what is most crucial to the audience.
- Highlight critical data. Writers should focus on what is most critical in each section of an executive summary, emphasizing statistical data because it is visually captivating.
- Maintain a formal tone from beginning to end. Writers should avoid using jargon to simplify complex concepts or terminologies.
- Write an executive summary after completing an actual research paper. Writing an executive summary as the last element of a research paper helps one to approach this paper as a final summary of the main points. In turn, the mistake of starting an executive summary before writing an actual research paper is that authors can write about details they fail to address in the final version of a document.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

Influence of Colors on Mood and Behavior
- Icon Calendar 25 August 2023
- Icon Page 757 words

Influence of Social Media on Modern Society
- Icon Calendar 24 August 2023
- Icon Page 835 words
Home » Blog » How to Write an Effective Executive Summary for a Research Paper
How to Write an Effective Executive Summary for a Research Paper
Table of Contents
How to Write an Effective Executive Summary
Executive summary is a term commonly used in business planning, however, in this article, we will look at how to write an effective executive summary for a research paper.
The executive summary is an initial summary of the research. A kind of appetizer that illustrates what the reader will find from there, if asked to continue reading the document. We’ll explain everything about the topic in this article.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is a small document or section of a research report or larger proposal. It is used to give the reader a quick overview of the larger body of material that follows. In other words, it summarizes a report, so executives don’t have to read the entire report to understand its purpose.
It contains a brief statement that addresses the problem or proposal detailed in the attached documents and provides background information, a concise analysis, and a conclusion. An executive summary is designed to help executives decide whether or not to take the proposal forward, making it extremely important.
What goes into an executive summary?
When writing an executive summary, there are guidelines to ensure you hit all the bases. According to the many books that have been written on executive summaries, as well as training courses, seminars, and professional speakers, the agreed length should be about 5 to 10 percent of the length of the entire report.
Appropriate language
The language used must be appropriate for the target audience. One of the most important things you should know before writing professionally is to understand who you are addressing. If you are writing for a group of engineers, the language you will use will be very different from how you would write for a group of funders. This includes more than just the words, but the content and depth of the explanation.
That said, regardless of the purpose of your executive summary, you should avoid being wordy. Keep your paragraphs short and concise. A block of text, no matter how elegant or engaging, can be daunting. Remember it’s a summary and people will read it to extract the main items quickly and easily.
Energetic introduction
You also want to capture the reader’s attention right away in the opening paragraph. Just as a speech usually starts with a joke to break the tension and leave people at ease to hear better what’s to come, a strong introductory paragraph can draw the reader in and make them want to keep reading. That doesn’t mean you start with a joke. Jokes are hard. Focus on your strengths but remember that most readers only provide a few sentences to win them over before moving on.
Don’t forget to explain who you are as an organization and why you have the skills, people, and experience to resolve the issue raised in the proposal. This doesn’t have to be a long biography, usually just your name, address and contact information will do, although you’ll also want to highlight your strengths when it comes to the proposal.
It may seem redundant, but start the summary with a very short, dotted list of what follows, like an index. Then, as you detail these points in the executive summary, be sure to write about the documents in the same order they appear.
Relevant information
The executive summary should not deviate from the material that follows. It’s a summary, not a place to bring in new ideas. Doing so would be confusing and undermine your entire proposal.
Establish the need or problem and convince the target audience that it must be resolved. Once configured, it is important to recommend the solution and show what the value is. Be clear and firm in your recommendation.
Justify your cause. Make sure you look at the top reasons why your organization is a perfect fit for the solution you are proposing. This is where you differentiate yourself from your competitors, whether it’s methodology, testimonials from satisfied customers, or anything else you offer that is unique. But don’t give yourself too much importance. Make sure you keep the potential customer’s name first.
Don’t overlook a strong conclusion, where you can wrap up and highlight the main points once again.
How to write an executive summary?
The general rule is that executive summaries should be as short as possible. Your target audience has limited time and attention and wants to get the details of your business plan as quickly as possible.
Try to keep your executive summary to 2 pages, if possible, although it may take longer if necessary. You can even write on one page using a lean plan format. You can learn more about this one-page business plan format and download a template here.
A description of your project or research proposal and the problem you intend to solve
Include a brief description of the research idea you carried out and why it’s needed. Your research paper doesn’t need to address a larger social problem, but it must address a lacuna or provide solution to an existing challenge.
A description of your target audience
Your target audience is who you think your research work will benefit. Sometimes, the name of the research paper itself defines the audience, such as “A Case Study of Traditional Institutions in Ogun State” or “Industrial Development of Lagos State”. Otherwise, just a brief description of the target audience – your main target audience or the people you think will spend money on your solution.
Competition
Assuming your research work has competition or opposing views, briefly describe how your research work stands out. Are you competing on theories or something else? Briefly describe what sets your research work apart here.
This is especially important for research proposal or grants. Funding institutions want to know who is behind the research idea and why you and your team are the right people to carry out the research. It can also be valuable to highlight your team’s gaps and how you plan to fill them. If you have potential partners or candidates in mind, mention them briefly and expand their qualifications in your full proposal.
Financing needs
If you are using your research plan to raise funds for your research work, your executive summary should highlight how much money you are looking for. Funding institutions want to know this in advance and don’t need to look for a grant to find these details.
Tips for Writing an Effective Executive Summary
No matter because you’re writing your executive summary, there are some general rules that make it easier and ultimately more effective. Here are some points to remember as you start:
1. Think of an executive summary as an argument
Think of an executive summary as something like an elevator pitch, but with restrictions. A good summary sells the rest of the plan, but it can’t just be a hard sell – it needs to summarize the plan. Readers expect it to cover, at a minimum, their commercial, product, market, and financial highlights.
Of course, you will highlight what will most interest the reader to achieve the immediate business objective of this plan. But your readers expect the main points covered. It’s a summary, not just an argument.
2. Write last
Don’t start writing your research paper with your summary. Although the executive summary is at the beginning of a completed research paper, many researchers choose to write the executive summary after writing everything else.
Ideally, the executive summary is short – usually just a page or two, five on the outside – and highlights points you’ve highlighted elsewhere in your research paper; so, if you save it for last, it will be quick and easy.
3. Keep your executive summary short
Be brief and concise. Some experts recommend a single page, or two, no more than five, and sometimes even more. We say less is more. Keep it as short as possible without missing the point. And because we read hundreds of papers every year – one page is better than two, and two is better than five, and more than five pages is too long.
4. Keep it simple
Form follows function; therefore, don’t overcomplicate or explain things in your summary. Most executive summaries are short texts, usually bulleted, divided into subheads. Illustrations such as an image of a product or a bar chart showing financial highlights are often a welcome addition.
5. Prioritize sections based on importance and strengths
Don’t bury the lead. Organize your executive summary so that the most important information is displayed first. There is no definite order of appearance of the different key items included, rather in fact – so use order to show emphasis.
Lead with what you want more attention and follow the items in order of importance. People tend to like summaries that start with an indication of a problem, because that can add drama and urgency that demonstrate the solution to your business.
6. Use it for your summary note
When done, reset it to a summary note. It’s the first chapter of a formal plan, but you can also use it as a standalone “summary note”. Investors often ask start-ups to submit a summary note rather than a full business plan.
It can be a short document, usually attached to an email, or simply a summary in an email. You can also use it again to fill out start-up profiles on investment platforms or to request an incubator or business plan contest.
If you like this article, see others like it:
Balancing Work and Life: Achieving Success in Nigeria’s Competitive Job Market
2024 complete nigeria current affairs pdf free download, 2024 nigeria current affairs quiz questions & answers, learn how to trade forex: a beginner’s guide, 5 corporate team building activities ideas for introverted employees, related topics, how to search for journals for a research project, a step-by-step guide to writing a comparative analysis, signs it’s time to re-evaluate your career goals, 5 common career change fears and what to do, how to plan an affordable vacation as a student.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Summary
Definition:
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings. It is often used as a tool to quickly communicate the main findings of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or decision-makers.
Structure of Research Summary
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. It describes the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section presents the main findings of the study, including statistical analysis if applicable. It may include tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and explains their implications. It discusses the significance of the findings, compares them to previous research, and identifies any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the research and provides a conclusion based on the findings. It may also suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
How to Write Research Summary
Here are the steps you can follow to write a research summary:
- Read the research article or study thoroughly: To write a summary, you must understand the research article or study you are summarizing. Therefore, read the article or study carefully to understand its purpose, research design, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the main points : Once you have read the research article or study, identify the main points, key findings, and research question. You can highlight or take notes of the essential points and findings to use as a reference when writing your summary.
- Write the introduction: Start your summary by introducing the research problem, research question, and purpose of the study. Briefly explain why the research is important and its significance.
- Summarize the methodology : In this section, summarize the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. Explain the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Present the results: Summarize the main findings of the study. Use tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data if necessary.
- Interpret the results: In this section, interpret the results and explain their implications. Discuss the significance of the findings, compare them to previous research, and identify any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclude the summary : Summarize the main points of the research and provide a conclusion based on the findings. Suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- Revise and edit : Once you have written the summary, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors. Make sure that your summary accurately represents the research article or study.
- Add references: Include a list of references cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
Example of Research Summary
Here is an example of a research summary:
Title: The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis
Introduction: This meta-analysis examines the effects of yoga on mental health. The study aimed to investigate whether yoga practice can improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, stress, and quality of life.
Methodology : The study analyzed data from 14 randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of yoga on mental health outcomes. The sample included a total of 862 participants. The yoga interventions varied in length and frequency, ranging from four to twelve weeks, with sessions lasting from 45 to 90 minutes.
Results : The meta-analysis found that yoga practice significantly improved mental health outcomes. Participants who practiced yoga showed a significant reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as stress levels. Quality of life also improved in those who practiced yoga.
Discussion : The findings of this study suggest that yoga can be an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. The study supports the growing body of evidence that suggests that yoga can have a positive impact on mental health. Limitations of the study include the variability of the yoga interventions, which may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion : Overall, the findings of this meta-analysis support the use of yoga as an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal length and frequency of yoga interventions for different populations.
References :
- Cramer, H., Lauche, R., Langhorst, J., Dobos, G., & Berger, B. (2013). Yoga for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and anxiety, 30(11), 1068-1083.
- Khalsa, S. B. (2004). Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 48(3), 269-285.
- Ross, A., & Thomas, S. (2010). The health benefits of yoga and exercise: a review of comparison studies. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16(1), 3-12.
Purpose of Research Summary
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study.
Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
- Facilitating comprehension: A research summary allows readers to quickly understand the main points and findings of a research project or study without having to read the entire article or study. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the research and its significance.
- Communicating research findings: Research summaries are often used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public. The summary presents the essential aspects of the research in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for non-experts to understand.
- Supporting decision-making: Research summaries can be used to support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. This information can be used by policymakers or practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Saving time: Research summaries save time for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders who need to review multiple research studies. Rather than having to read the entire article or study, they can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
Characteristics of Research Summary
The following are some of the key characteristics of a research summary:
- Concise : A research summary should be brief and to the point, providing a clear and concise overview of the main points of the research.
- Objective : A research summary should be written in an objective tone, presenting the research findings without bias or personal opinion.
- Comprehensive : A research summary should cover all the essential aspects of the research, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research summary should accurately reflect the key findings and conclusions of the research.
- Clear and well-organized: A research summary should be easy to read and understand, with a clear structure and logical flow.
- Relevant : A research summary should focus on the most important and relevant aspects of the research, highlighting the key findings and their implications.
- Audience-specific: A research summary should be tailored to the intended audience, using language and terminology that is appropriate and accessible to the reader.
- Citations : A research summary should include citations to the original research articles or studies, allowing readers to access the full text of the research if desired.
When to write Research Summary
Here are some situations when it may be appropriate to write a research summary:
- Proposal stage: A research summary can be included in a research proposal to provide a brief overview of the research aims, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Conference presentation: A research summary can be prepared for a conference presentation to summarize the main findings of a study or research project.
- Journal submission: Many academic journals require authors to submit a research summary along with their research article or study. The summary provides a brief overview of the study’s main points, findings, and conclusions and helps readers quickly understand the research.
- Funding application: A research summary can be included in a funding application to provide a brief summary of the research aims, objectives, and expected outcomes.
- Policy brief: A research summary can be prepared as a policy brief to communicate research findings to policymakers or stakeholders in a concise and accessible manner.
Advantages of Research Summary
Research summaries offer several advantages, including:
- Time-saving: A research summary saves time for readers who need to understand the key findings and conclusions of a research project quickly. Rather than reading the entire research article or study, readers can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
- Clarity and accessibility: A research summary provides a clear and accessible overview of the research project’s main points, making it easier for readers to understand the research without having to be experts in the field.
- Improved comprehension: A research summary helps readers comprehend the research by providing a brief and focused overview of the key findings and conclusions, making it easier to understand the research and its significance.
- Enhanced communication: Research summaries can be used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public, in a concise and accessible manner.
- Facilitated decision-making: Research summaries can support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. Policymakers or practitioners can use this information to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Increased dissemination: Research summaries can be easily shared and disseminated, allowing research findings to reach a wider audience.
Limitations of Research Summary
Limitations of the Research Summary are as follows:
- Limited scope: Research summaries provide a brief overview of the research project’s main points, findings, and conclusions, which can be limiting. They may not include all the details, nuances, and complexities of the research that readers may need to fully understand the study’s implications.
- Risk of oversimplification: Research summaries can be oversimplified, reducing the complexity of the research and potentially distorting the findings or conclusions.
- Lack of context: Research summaries may not provide sufficient context to fully understand the research findings, such as the research background, methodology, or limitations. This may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the research.
- Possible bias: Research summaries may be biased if they selectively emphasize certain findings or conclusions over others, potentially distorting the overall picture of the research.
- Format limitations: Research summaries may be constrained by the format or length requirements, making it challenging to fully convey the research’s main points, findings, and conclusions.
- Accessibility: Research summaries may not be accessible to all readers, particularly those with limited literacy skills, visual impairments, or language barriers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
The Report Abstract and Executive Summary

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Abstract
The abstract is a crucial part of your report as it may be the only section read by people at the executive or managerial level who must make decisions based on what they read in your abstract. When you include specific content, it is important to remember these readers are looking for the information they need to make decisions.
The abstract is an overview that provides the reader with the main points and results, though it is not merely a listing of what the report contains. It is a summary of the essence of a report. For this reason, it should be crafted to present the most complete and compelling information possible. It is not a detective story building suspense as the reader hunts for clues, and should not be vague or obtuse in its content.
The abstract should include
- Why the work was done (the basic problem), the specific purpose or objective, and the scope of the work if that is relevant. (College lab reports may not require this part of the abstract.)
- How the work was done, the test methods or means of investigation
- What was found—the results, conclusions, and recommendations
The abstract should
- Not make references to material in the text
- Not lose the message by burying the methods, results, conclusions, and recommendations in a sea of words
- Not be written before the rest of the report
Therefore, a good abstract is
- Self-sufficient
Evaluating abstracts
Because the abstract is of major importance in a report, a summary of effective qualities of abstracts is offered here.
A well-written abstract
- Considers the readers it will encounter
- States what was done and what results were found
- Avoids vagueness by stating specific results
- Uses past tense to report what was done
- Is informative
- Is self-sufficient and does not refer to the body of the report
- Makes concrete, useful recommendations
Below are two abstracts. The first one, (A), was written by a student for a lab report, and the other one (B) was a revision written by someone with more experience in writing abstracts. Read both versions and try to figure out why the changes were made in B.
We studied the flow characteristics of meters, valves, and pipes that constitute a flow network. The meter coefficients for orifice and venture meters were determined. The orifice and venture coefficients were, on the average, 0.493 and 0.598, respectively. Fanning friction factors for pipes of different sizes and for gate and globe valves were also determined.
The accuracy with which the meter coefficients and friction factors were determined was affected by leaks in the piping network. In addition, air bubbles trapped in the pipes and manometers affected the accuracy with which pressure drops were measured. Hence, it is recommended that the piping system be checked to ensure the absence of any leaks. Furthermore, the fluid should be allowed to flow in the network for some time before taking any measurements, in order to get rid of the air trapped in the pipes and manometer.
In an orifice and a venturimeter in a flow network, we measured the meter coefficients to be 0.5 0.1 and 0.6 0.15. We measured the Fanning friction factors at steady state for several pipes and for gate and globe valves. The most important source of error was a leak in the piping network which has to be repaired in order to obtain more precise results.
The Executive Summary
The government and some companies have begun to request executive summaries at the beginning of a long report. An executive summary is a one-page statement of the problem, the purpose of the communication, and a summary of the results, conclusions, and recommendations. The same considerations of readers and situation should guide your executive summaries.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Writing an executive summary

2019, Oxfam Research Guidelines
An executive summary is one of the most crucial parts of a report. It represents a chance for the author to grab the reader’s attention and draw them in to the main document. When readers are pressed for time, it may be the only part of the report they read, so a well-written summary is vital. Unfortunately, summaries are often an afterthought for authors, and are frequently written in haste. Part of Oxfam’s Research Guidelines series, this guideline gives a short overview of how to write an engaging executive summary that conveys the most important information from the main report in a clear, concise way. It provides tools for thinking about how to get the most out of your summary, as well as examples from academia and business, plus tips on things to avoid.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Internet , Productivity
25 Best Executive Summary Examples 2024
An executive summary is an overview of a larger document that shares vital information that you want readers to know.
It basically summarizes the key points in the main document so that anyone who glances through it can quickly understand and familiarize themselves with the message you’re trying to pass across.
There are a variety of documents where an executive summary can come in handy. This includes project proposals, business plans, professional resumes, research reports, market surveys, and more.
Including a compelling executive summary in your document can increase the reader’s interest and encourage them to read the rest of the document.
It can also help to inform people who can’t afford to read the entire document by presenting all the relevant details they need.
Essentially, your executive summary can make or break your chances of getting that new job, grant, investment, or partnership deal, so it needs to be well written.
Also Read : Mission vs Vision Statement & Examples
Best Executive Summary Examples
In this article, we’re going to walk you through how to craft the perfect summary for different situations and documents by showing you examples of attention-grabbing executive summaries that you can draw inspiration from.
Let’s dig in.
1. Keep it short and concise

Your executive summary doesn’t need to go on forever. It can convey all the important information you want the reader to grasp while being brief.
Make sure it doesn’t include fluff or unnecessary details. If a statement doesn’t contribute to driving home the message that your business provides value and is primed for success, take it out.
This executive summary doesn’t fall into the trap of making specific promises, listing explicit tasks, or outlining due dates for achieving them. Leave that for your marketing and growth strategy and just focus on creating a summary that can stand on its own.
A reader should be able to find all the information they need to make a decision in your executive summary, without even needing to consult your overall business plan.
Explore : Best Mission Statement Examples
2. Tell your story

You want investors to understand why your business exists and what it’s about the moment they glimpse through your executive summary.
Providing answers to those questions will help readers get more excited about partnering with your company and diving into the rest of your business proposal or plan.
Don’t forget to include as many details as you can about your service or product. Don’t be intimidated by the simple nature of your offering.
Your product or service doesn’t have to offer a solution to world hunger, it just needs to solve a particular problem for your intended customers. Help your readers feel like they relate to your business and they’re more likely to buy into your offer.
Also Read : Best Short Professional Bio Examples
3. Describe your future goals

It’s not out of place in an executive summary to share the milestones that your business hopes to accomplish in the future. In fact, this is extremely important if you’re in an industry that’s complex in nature or highly saturated.
Is your objective to increase profitability and sales revenue? Do you plan to break even by the second year and raise profit margins every year for the next decade?
Or maybe you want to grow your customer base from thousands to billions and become the number one player in your niche? Make sure you outline the goals you want to achieve in your summary, as well as where you currently are on the journey towards them.
4. Focus on your product or service value

With section after section, this example keeps the light on the company and its products. It starts with a brief description of what the business does and why it matters.
Next, it delves into what it wants to accomplish with the project it’s seeking funding for. And then it goes on to describe the value it provides and why its product is better than those of its competitors.
While your company doesn’t need to solve a larger social, economic, or environmental problem like climate change and sustainability, it has to solve a need that customers have or take advantage of a market opportunity example is a good way to go about it.
In trying to persuade them, pay more attention to the facts and not just the words you use to phrase your message. It’s the content of your summary that’s going to do the trick, not the tone.
Using facts that you can back up to prove your experience and growth potential is far more effective than merely asserting your excellence.
Explore : Top Weaknesses List & Examples
5. Use a positive tone

Since the point of an executive summary is to persuade the reader as to why you’re a worthy investment, strive to use language that’s confident and assertive. Swap out weak words like “could” and “would” for stronger words like “will” so the reader won’t be left with any rock to doubt your competence.
By maintaining an optimistic outlook you can really impact how the reader views your report, and in turn, comes to see your business.
6. Be persuasive

If what you want is to get prospective investors to keep reading and ultimately convince them to sow their money into your business, this example is a good way to go about it.
7. Organize sections based on strengths

There are no set rules when it comes to how you structure the content of your summary. Just make sure that you prioritize and emphasize the most important points.
Place the parts of your summary that you want to draw the most attention to at the beginning or middle point just like in this example. The paragraphs that follow should also address your other points in order of importance.
This will give your summary cohesion and a more logical flow. To top it off, it’d also make it easier to read.
Also Read : Best Professional Twitter Bio Examples
8. Tailor it to your audience

If your core purpose is to wow the reader and get them to take the next step with you, fashioning your executive summary after this example will prove highly effective.
The summary keeps a laser focus on the audience from start to finish. It shows how well it knows the prospective client by talking positively about what Gyuto does.
Then it goes on to identify Gyuto’s needs, offer a solution for these pain points, explain why the solution is the best, and how it intends to accomplish the goal . Finally, it closes with an interesting call to action.
Your summary should highlight exactly what the audience wants to see: why your company is the right one for the job and how exactly you intend to help them reach their goals. Do this and you’ll have won their attention even before they get to your proposal itself.
9. Maintain a straightforward approach

Another way to approach your executive summary is to be direct and to the point. Don’t waste time weaving a preamble, just jump right in and explain why your business or organization is about and what the project you’re proposing is meant to achieve.
Use brief paragraphs to communicate your points and apply subheadings and bullet points generously to make your summary easy to scan while keeping the appearance clean and professional.
Adding illustrations like a graph, chart, or even a product image can also be a compelling addition.
10. Research intensive

Building your executive summary around strong research and facts can make it more compelling to readers, as this example perfectly demonstrates.
It starts by presenting two fascinating statistics that are sure to grab the reader’s attention and get them to keep reading.
The company doesn’t just expect people to take their word for it that making a cheaper watch series is a prudent and profitable decision, they provide stats to back up their aspirations throughout.
Even though your business plan will address all the points in detail, it’s still important to include the key findings and tastiest bits of information in the summary. The aim is to impress and nothing raises more confidence in a subject as research and statistics.
11. Highlight previous experience or specific industry expertise

In this example, uGrow does a fantastic job of addressing the issues that the audience of Pete Pizzeria has, and it proposes targeted solutions and outcomes to establish the reputation and trustworthiness of the company.
It also leverages social proof to illustrate how the business has helped past clients successfully increase their sales.
Take a cue from them and use your summary to sell yourself. Show your audience that you know what you’re doing, so include social proof and past results wherever you can to demonstrate how past clients have profited from your work.
You don’t have to add an entire case study to make your point. Keep it brief and just reference the information that’s going to come later in your proposal.
12. Capture attention through your opener

Opening your summary in an engaging and compelling way is pretty much guaranteed to win your readers’ attention and get them interested in what you have to say. Rather than droning on about your company, focus on talking about the value you provide.
Help potential clients see that pitching their tent with you would be a unique opportunity for them that promises impressive returns on investment. Remember that the introductory part of your summary is your chance to hook the reader and reel them in.
If you fail to get them excited, they’ll probably not read the rest of your summary or bother checking out the main proposal.
13. Keep it simple and jargon-free

As this executive summary example shows, you can talk about your company, product, services, and intentions in a language that is easy for anyone to understand.
Even if you work in a complicated industry, avoid using technical language, jargon, and industry buzzwords that people outside of your field might not know.
Convoluted language can rub people the wrong way and that’s not a reaction you want to evoke whenever someone reads your summary. Don’t overexplain or overcomplicate. Use short sentences rather than long ones to get your point across.
Let different people review your summary and see how many of them found it easy to digest before you send it out.
14. Consider your tone

The tone you use in your executive summary will be determined by the audience you’re writing for. Do a little digging into the brands or organizations you’re pitching and try to match their tone.
If they have a conservative and prim outlook, you’ll want to use more formal language. But if your proposal or business plan is targeted at investors or brands that are fun, personable, and quirky, feel free to take a relaxed and easygoing approach.
Your tone should also represent your company and reflect its personality. Use personal pronouns like “our,” “we,” and “I,” that speak directly to your readers, instead of third-person references like “the client” or “the customer.”
15. Keep it interesting

From the very first line, this resume summary example wonderfully sums up the applicant’s experience and qualification for the job. It manages to be captivating while establishing the applicant as highly skilled and qualified.
In three brief sentences, you can already tell that the candidate has a proven track record, is great at managing people, and is interested in building and growing a team. Weave your career highlights and impacts you’ve made in your role into your own summary, and your resume will be good to go.
16. Make it relevant

You want to illustrate how your past experiences and work history relates to the new role you’re applying for. If the executive summary portion of your resume is irrelevant to the job description, it’ll have no impact on the reader and might discourage them from the rest of your credentials.
In the example above, the candidate sells themself in a compelling way that makes you assured of their competency. You can glimpse confidence, ambition, and even a sense of how personable they are from between the lines.
If you’re seeking a job that requires a great deal of creativity, fashioning your executive summary in this manner will position you as a perfect candidate.
17. Dive into the details

Although keeping the summary portion of your resume short and precise is highly recommended, this example shows that it doesn’t hurt to go longer sometimes.
You can take time to highlight your relevant work history and skills that relate to the job offer at hand. Every sentence should make a strong case for why you’re uniquely suited to fill the position and prove to the hiring manager that you deserve an interview.
Discuss any relevant training or certifications that you have, mention your years of experience with a particular aspect of the job. And don’t forget to reassure the reader of your familiarity with industry/job-related tools that may be required for the role.
18. Highlight your soft skills

Technical skills are all well and good, but they’re not the only things recruiters look for in your resume. Soft skills are just as important as hard skills and may be even harder to come by.
This executive summary example clearly explains that the applicant has both. It starts by describing their experience and primary job role, then provides an instance of how a soft skill—organization—enabled them to impact their organization positively.
So don’t just say you have a particular skill. Make your claim more effective by giving an example of how you applied that skill and the quantifiable results it brought. This can help you and your resume get moved to the next round of the decision process.

19. Stick to qualifications

Just because you have no experience in an industry or field doesn’t mean you have nothing noteworthy to show for yourself.
Start by describing yourself and your current standing whether as a student, intern, or job seeker and mention any applicable experience you have both in and out of the classroom. Follow this up with your most relevant skills and how they’ve helped you succeed.
Despite your inexperience, including these details in your summary will allow hiring managers to see you as hardworking, full of potential, and a capable candidate for the role.
20. Show how you can add value

This is another great executive summary sample for resumes that you can follow. In just three sentences you can grasp the capabilities and experience the applicant is bringing to the table.
From the job description, identify the qualities—skills, knowledge, and abilities—abilities that the company values for the role and introduce them into your resume summary. Focus on how you would make a great addition to the organization.
How can you benefit them? Don’t bury the lead. Tell them exactly who they’re dealing with and the kind of performance they can expect if they’re wise enough to hire you.
21. Convey a strong personal brand

Think of your summary—and by extension, your resume—as a storytelling opportunity and marketing device. If you want to get a positive reaction and raise your chances of scoring a job , you need to make your personal story resonate with the potential employer’s brand.
Are you the kind of person that likes to roll up their sleeves, lead the charge, and get things done? Are you an exceptional team player with incredible problem-solving skills? Whatever your personal brand is, promote it boldly.
22. Focus on your most relevant characteristics

You might have worked in various roles and assumed diverse responsibilities over the years, but the potential employer isn’t interested in knowing all that. What they care about are the experiences, skills, certifications, and achievements that align with the role you’re seeking.
Pay attention to the specific skills and keywords the job application requires or uses, then write the executive summary for your resume in a way that corresponds with them. The goal is to say what will appeal to the specific company and position you’re applying to.
23. Choose clarity

One common mistake that people tend to make with regards to resume executive summary is failing to make it clear and easy to understand. Leave no room for vagueness and ambiguity.
Answer all the basic questions that a recruiter might ask: What type of projects have you worked on? What companies or clients have you worked with in the past? What kind of experience or challenge are you seeking?
The words you use should drive home your message. If they fail to do this, you’ll only have succeeded in wasting the recruiter’s time and getting your resume added to the slush pile.
24. Align with success

A good way to set your resume up for positive reception is to shine a light on the reputable brands or organizations you’ve worked with. So if you have any renowned companies on your employment list, announce it.
A strong client/employer list will help boost your reputation. The recruiter will come to regard you as highly as they regard those companies. After all, if you weren’t truly skilled at what you do, those organizations wouldn’t have hired you in the first place.
25. Highlight evidence of success

Borrow a page from this example and include evidence of your accomplishments in your executive summary statement. Demonstrate the value you’ll bring to a prospective employer’s organization by listing specific contributions you’ve made at your previous workplace.
Use sales figures, percentages, and numbers to quantify your professional achievements and make them more persuasive. Emphasizing how you can help is the best way to get recruiters to care about the rest of your resume.
Think about how your expertise and skills have helped your current organization and slip that into your summary.
Whether you’re writing an executive summary for a business plan, proposal, report, or resume, the point is to share your vision of who you are or who your company is and why the reader should care.
However, crafting a great summary can be a bit of a challenge. But with the tips and examples we’ve discussed above, you can take your summary writing skills to the next level.
Tom loves to write on technology, e-commerce & internet marketing. I started my first e-commerce company in college, designing and selling t-shirts for my campus bar crawl using print-on-demand. Having successfully established multiple 6 & 7-figure e-commerce businesses (in women’s fashion and hiking gear), I think I can share a tip or 2 to help you succeed.

Research Summary
Ai generator.

A research paper analyzes a perspective or argues a point. It is an expanded essay based on your interpretation, evaluation or argument about a certain topic.
According to Sunny Empire State College , “When you write a research paper you build upon what you know about the subject and make a deliberate attempt to find out what experts know. A research paper involves surveying a field of knowledge in order to find the best possible information in that field.” Whatever type of research paper you choose to write, it should present your own ideas backed with others’ (especially experts on the field) information and data.
Every research paper has a research summary. A research summary is a brief overview of what the whole research is about. It is a professional piece of writing that describes your research to the readers. It concisely yet perfectly captures the essence of the research as a whole. You may also see What Should Be in an Executive Summary of a Report?

Fundamentals of a Research Summary
Having a good template for a research summary is nothing if you don’t know its importance and basic function. Before you start writing your research summary, you should first know its fundamentals on the areas you need to pay attention to such as its content, style and organization.
- The content of your research summary must briefly discuss the techniques and tools used in the research and the importance of the research as a whole. Explain how the research can be of benefit for the people.
- To organize your research summary, each topic must be discussed in separate paragraphs. How you came up with a factual research must be briefly explained in a separate paragraph.
- If you have a lengthy research paper, try not to write not more than 10% of the entire paper. If it’s not as lengthy, you should not write more than 300 words in your summary.
However, rules may vary according to your research professor’s standards. This is just the basic fundamentals on how to write your research summary. Also see Thesis Outline Examples
How to Write a Research Summary
It is apparent that a research summary is a condensed version of the main idea of your research paper. Because of this, it is advised that the summary of your paper is written after you are done with your entire research. This is to ensure that all the added information in your research can be written in your summary as well and all of those that removed can be edited out. Here are a few steps on how to write a research summary:
Read your paper
It should be a fact you should know beforehand; the importance of reading your entire research paper thoroughly to write an effective research summary. Along the way, take notes of the important details and key findings that you want to highlight in your paper. This will help you organize your summary better. Remember that your research summary is a mini-paper of your study and it should contain the main ideas of your entire research.
Write a draft
For your first draft, focus on the content rather than the length of your summary. Your draft is your first outline on what to include in the final summary. Writing a draft ensures you write a clear, thorough and coherent summary of your research paper. Also see How to Write a Rough Outline
Identify main points
Within your research paper, you must identify the major points that will encourage prospective readers to go through your research paper. These major points must thoroughly and completely explain what the paper is trying to convey.
Separate sections
Identify the differences of the main section in your paper. Write a few sentences describing the main ideas of each section. In short, you should be able to present and thoroughly describe what each main section is focused on. It should have these basic sections:
- Introduction, brief opening statement
- Purpose of the study
- Data gathering method
- Summary of findings
- Description of recommendations with actual justification.
Combine Information
All the information you have gathered must be then used to make your summary. Remember that your summary is just an overview of your research paper as a whole. It should be not be more than 10% of your whole paper. Also see 5 Summary Writing Examples and Samples
Making The First Draft
After establishing the basic way of writing a research summary, it is a must to write a first draft. It should follow the flow of the original paper. Here’s a few steps on how to make a first draft:
First, state the research question in the introduction of your summary. This holds the ground as to the summary’s direction. Provide an explanation why your research is interesting and how it can help your target recipients.
Second, state the hypothesis you wish to prove. This will help you and your readers stay grounded on the topic at hand.
Third, briefly discuss the methodology used in your research. Discuss and describe the procedure, materials, participants, design, etc. The analysis of your data must also be included. You may also see How to Write a Successful Thesis Proposal
Fourth, describe the results and significance of your research. And lastly, briefly discuss the key implications of your research. The results and its interpretation should directly coincide with your hypothesis.

Editing your Research Summary
A research paper is a formal piece of writing. Your summary should be tailored to your expected readers. Say for example the prospective readers are your classmates, so the style of your paper should be clearly understood by them.
Eliminate wordiness. Avoid using unnecessary adjectives and adverbs. Write in a way it would be easier for your readers to understand. It is common for research papers to establish a word count. Avoid elongating your sentences when it has shorter versions.
Being vague in describing and explaining the points of your paper might lead to confusion in your readers part. Use specific, concrete language when presenting results. Use reliable and specific examples and references as well. You should also use scientifically accurate language to help support your claims. Avoid informal words and adjectives to describe the results of your research.
Paraphrase the information you want to include in your research paper. Direct quoting the information you have read from a different source is not oftenly used in formal writings. To give the exact credit for the information you paraphrased, follow the citation format required by your professor.
Reread your paper and let others read it as well. This way minor errors you were not able to notice can be quickly pointed out and corrected.
Research Summary Writing Tips
Your research summary should not be more than 10 pages long or not more than 10% of your original document. This keeps your research summary concise and compact. It should be short enough for your readers to read through but long enough for you to clearly explain your study.
Copy and paste
Avoid simply copy and pasting different parts of your paper into your summary. You should paraphrase parts that you want to include. As most research advisers read through all of your paper, it can easily be identified if you have copy-pasted parts from your research and might give you a bad grade.
Consider the readers
Although not a requirement from your professor, catering your summary to what the readers need is sometimes required. As some studies are given out to different influential people in the field, writing a summary that caters to the readers’ necessities might be required.
Research Article Summary Template

- Google Docs
Size: 158 KB
Research Report Executive Summary Template

Size: 120 KB
Research Summary Example

Size: 130 KB
Research Summary Sample

Size: 486 KB
Research Writing Summary Tips (continuation)
Clarity and organization.
One of the common mistakes in writing a research is publishing an unclear and unpolished summary. Bear in mind that your readers are likely reading about the topic of your research for the first time, avoid unclear and uncertain explanations and a disorganized summary.
Use strong and positive language
Use precise and strong words to help strengthen the foundation of your summary. Your summary should be able to stand alone despite it being a part of the research paper. Once you have convinced your readers with the recommendations regarding the topic of your paper, the readers should be able to find concrete evidence and explanations within your summary. Avoid pleas and biased statements in your summary, but make sure you are able to relay the sense of urgency for the recommendations you have given.
Divide into parts
To make things easier for you, divide your paper into different sections and headings, much like creating an outline. With this in mind, every point should be explained limited to its essence. In this way, you avoid writing too much information about your paper in your summary.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
All Formats
Table of Contents
Free 10+ research executive summary templates in pdf | ms word, 1. research executive summary template, 2. research executive summary format, 3. research executive summary legal services template, 4. business research executive summary sample, 5. tourism research executive summary template, 6. student research executive assessment summary in doc, 7. research ethics date executive summary template, 8. research project executive summary example, 9. bio medical research executive summary template, 10. simple research executive summary, 11. simple research executive summary template, elements of an executive summary, importance of an executive summary, research templates.
An executive summary refers to a short file or segment of a business-related report. It sums up a lengthier report or proposition or a group of linked reports in such a way that readers can get to know a large body of material quickly without having to read all of it. It generally contains a brief statement of the issue or solution addressed in the main document(s), background information, succinct overview and key findings. It is intended by managers as an aid to decision making and has been defined as the most essential part of a business plan .

The Problem and Your Solution
Market size and growth opportunity, your competitive advantage, business model, executive team, financial projections and funding, 1. refine and tighten your concept, 2. determine your priorities, 3. make the rest of the process easy, more in research templates.
School Sports Program Brochure Template
University research poster template, a3 research poster template, keynote speaker poster template, quartet poster template, quality poster template, conference poster keynote template, research poster template for keynote, school cash management policy template, biography research template.
- FREE 10+ Research Data Collection Form Templates in MS Word | PDF
- FREE 10+ Research Information Sheet Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 10+ Research Development Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- FREE 10+ Quantitative Research Report Templates in MS Word | PDF
- 10+ Academic Research Report Templates in PDF | DOC
- FREE 10+ Educational Research Ethics Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Resource Tracking Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Clinical Research Ethics Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Code of Human Research Ethics Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Documentary Research Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Academic Research Ethics Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Artistic Research Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Null Hypothesis Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Research Hypothesis Templates in PDF | MS Word
- FREE 11+ Research Ethics Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
Free Executive Summary Template [PDF + Masterful Examples]
Use these templates to craft an effective executive summary for your business or project.
According to Time Magazine, 55% of people only read a piece of content for 15 seconds. Attention spans across the board are at an all-time low — including those of potential investors and project stakeholders. If you want to capture and hold interest, then you need to craft an engaging executive summary that can effectively hold someone’s focus.
Before you dive into the details of your business plan or project proposal, your first step should be an executive summary that captures the attention of those in a position to give buy-in.
Think of the executive summary as the back cover of your book. It convinces readers to purchase a copy because the storyline is worth their time. An investor or C-level executive with limited time probably won’t feel motivated to read a full business or product plan without a compelling executive summary.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to write a captivating executive summary, what to include in the document, and jumpstart yours with customizable templates.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is a brief synopsis of a larger document such as a report or business plan. It provides a quick overview of your business plan with details like a description of your company, financial information, and market analysis.
The executive summary is made for lenders, investors, and busy executives who don’t have time to read the full proposal.
Done right, it zeroes in on what your prospective investor or project sponsor wants to hear and clearly communicates the value of your business or plan. Many investors or stakeholders will only read the executive summary during the first contact with your business, so all the information they need should be included.
The goals of an executive summary include:
- Grab the reader’s attention
- Tell them what to expect in the business plan so they are motivated to keep reading
- Provide a high-level overview of your company, your short-term and long-term goals
- Acts as an elevator pitch
What is an executive summary in a business plan?
An executive summary in a business plan is a concise overview that provides a snapshot of the key elements of the plan as it pertains to the business overall. It outlines the business concept, objectives, market analysis, financial projections, and other essential information. The executive summary serves as a summary and introduction to the entire business plan, allowing lenders, investors, and decision-makers to quickly grasp the main points and make informed decisions.
What is an executive summary in project management?
An executive summary in project management is a summary of the most critical information of your project proposal. It’s everything that management needs to know when they land on your project before they review your project plan .
An executive summary in project management shouldn’t be confused with a project overview. While they have similar elements, an executive summary can stand alone as a document, while a project overview needs to be attached to your project.
Executive summary vs abstract
An abstract summarizes a document like a journal article while an executive summary sums up a longer document.
An abstract is mostly used in academia as a requirement when submitting conference papers, book proposals, or applying for a research grant. The abstract is not an excerpt but an original document that is self-sufficient.
An executive summary is aimed at a business audience. It contains information to help executives make funding decisions. Where the language in an abstract is technical, the language of an executive summary is non-technical. An executive summary is written as a condensed version of a project plan to secure buy-in while an abstract is written for orientation.
Executive summary vs introduction
The introduction is the first part of your project plan or business plan. It explains what the project is about and the goals you want to achieve. On the other hand, the executive summary is a standalone document condensed into a few paragraphs. It is thorough and high-level. Decision-makers can choose to read only the executive summary and still get the gist of the entire project proposal.
Think of the introduction as the first few pages of a long book with many chapters and an executive summary like a short book with only one chapter. You can understand both context and storyline when you read a short book.
What should an executive summary include?
For a project .
What is the problem you’re going to solve? What product plan, customer feedback, or insight led to this project? Why should it happen now ? These are questions to lead with in the opening paragraph of your executive summary.
What steps or methods are you taking to solve the problems you’ve listed in the opening paragraph? What are the goals and objectives you’ll achieve at the end of the project? Detail the answers in this section.
Value proposition
This is an important section where you briefly explain the value of the outcome. What is the ROI of the solution you’ve proposed? How will it improve service delivery and customer experience?
In a few sentences reiterate why it’s important to solve the problem now and the next steps or actions you want the reader to take.
For a business plan
Introduction .
For a business plan, the introduction is an opening statement that explains the purpose of the document. Your goal is to grab and hold the reader’s attention by clearly communicating the value of the business and the desired outcome.
Company description
Include the following details in the company description:
- Business name and location
- Contact information
- Description of the purpose
- Leadership, founders, and current investors at your company
- The team responsible for the project
Products and services
Briefly explain the problem you’re going to solve. If you’ve conducted research that shows a need for the proposal, include your findings here. Also, explain how you’ll accomplish the project goals and what you’ll need for success.
Market analysis
A few questions to answer in this section include:
- Is there a market opportunity for the problem?
- How do you plan to grow your customer base and expand your market share?
- What is the five-year growth plan for this product/service?
- What is the most interesting thing you’ve learned about your target audience that the reader should know?
Competitive analysis
Questions to answer as part of your competitive analysis include:
- Who are your competitors?
- What are the present and future opportunities?
- What is the unique value proposition of the product or service?
- Do you have experience with competitors?
- What are the risks particular to this niche or line of product?
- What roadblocks do you expect to address?
Funding request and use
Use this section to sweeten the pot for investors. How much will you need to fund your business? What is the profitability of your business? How will investors benefit?
Financial projections
Include financial data that supports your research such as:
- The budget baseline for your business plan
- Your projected revenue for the first three years
- Your plan to manage finances
- Your current and future business finances
Conclusion
The conclusion is a recap of the problem and the solution. Ask about the decision you want the reader to take. The outcomes should be obvious but leave room for intrigue so they feel compelled to read the rest of the business proposal.
Executive summary examples
Executive summary presentation.
Often, executive summaries are presented to stakeholders in addition to the document. Get the templates below to snag these PowerPoint executive summary presentation templates.

One-page executive summary template
A one-page executive summary is a short document with a big impact. You’ll present it as a mini version of a project plan during a meeting with decision-makers or as a business plan when pitching investors.
A few details to include in a one-page executive summary:
- Business name
- Financial information
- Use of funding
- Management team
- Business model
- Unique value proposition
- Competitive advantage
- Go-to-market strategy

Startup executive summary template
Your startup executive summary could be the difference between getting a pitch meeting or not. Venture capitalists and investors and overwhelmed with pitches from startups looking for a partnership.
An executive summary is the fastest way for them to learn about your company and evaluate its potential. It’s usually a one-page document that is concise, yet detailed and engaging. Before writing your startup executive summary, determine the goal and ensure it matches what potential investors want to see.
Details to include in your startup executive summary:
- A description of your product or service
- The value proposition
- Market analysis showing the merit of the project
- Your current business model and future plans
- An explanation of your market and customer base
- Financial projections and funding request
- Other special information that could sway a decision in your favor

Business plan executive summary template
The business plan executive summary shouldn’t exceed two pages. Make sure you’ve tailored it to your audience to show why the opportunity is special. An executive summary for a business plan should include:
- Mission statement
- Company information with details about your services or product
- Business highlights describing how you’ve grown over the years. Include details of revenue increase, number of customers, profitability, revenue increase, and market share
- Future goals
- Financial summary
- A closing sentence that reassures the value of the plan
Project executive summary template
The goal of a project executive summary is to show what life will look like after you’ve executed the project. Your executive summary should tell a story that helps the reader visualize the solution and inspire them to choose you.
The executive summary should be written as the final step of your project proposal template. This way, you save time revising the content.
Details to include in a project executive summary:
- Summary of the challenge the client wants to solve
- Description of how you’ll solve the pain point
- Overview explaining how you’ve solved similar problems in the past
- Unique value that competitors don’t offer
Marketing plan executive summary template
An executive summary for a marketing plan offers an overview of how you’ll reach your intended audience and drive conversions.
Details to include in a marketing plan executive summary:
- Introduction
- Brief description of your company and key leaders
- Project goals and objectives
- Your product or services and the major features and benefits
- Description of market factors and trends affecting them
- Who is your audience and how will you reach them?
- Financial projections
Healthcare executive summary template
A healthcare executive summary template is used in formal communications for hospitals, government health agencies, and nonprofits. The template accommodates longer-research proposal plans targeted at a wider audience of the general public, external investors, and management.
Details to include in healthcare executive summary:
- Project topic
- Overview of the organization
- Two to three key problems that have a profound impact on quality care, operations, or regulatory compliance
- A proposed solution to each identified problem
- Obstacles and opportunities
- Policy changes and program proposal
- Vision and recommendation
Executive summary report template
An executive summary for a research or analyst report offers an overview of key points from the research.
Details to include in a report executive summary report:
- Brief description of your company
- Analysis findings
- Why these findings matter
Here's an example:

How to write an executive summary
1. write a problem-based introduction.
Use the opening paragraph to explain why your project matters. Outline the problem with supporting research or customer feedback to strengthen your claim. The reader should understand why it’s important to solve the problem now and the relevance to your customer base.
A powerful way to grab attention is to open with a customer quote or thought-provoking statistic that forces the reader to sit up and listen.
For example:
“I wish this camera had a longer battery life span so I could record an entire football game on 4K without switching to full HD when the battery is low .” - Customer review
In a recent survey, 70% of our customers expressed a desire for a camera with a longer battery life that could last up to six hours while recording in 4k. 80% said they wouldn’t mind paying more for the convenience of not having to log extra battery packs when going out. To serve our existing clientele and improve our market share, we need to create a camcorder that performs at optimal levels while using fewer resources on battery life.
2. Tell your story
Use storytelling to explain the mission statement of your organization. Explain how you’ll use your skill and experience to solve the problem you’ve highlighted in the introduction. Storytelling sets the tone and gets the reader excited about reading the project plan.
3. Make sure you’ve done the research
While an executive summary is short, it’s loaded with research. Research shows that you know your competitors, understand your target audience, and have a plan for capturing a significant market share.
Think of your executive summary like an elevator pitch. If an investor only read your executive summary without making it to the project proposal or business plan, what would you want them to know?
4. Outline the solution
After telling the reader the pain points and explaining your business credentials, use a bullet list to outline the solution. Your goal is to convince the reader that your solution is the best fit. Save deliverables and milestones for the project proposal. Instead, describe what will happen during the project so the user can picture the outcome working for them.
5. Show the value of the solution
This is where you get into more details about the impact of the solution. Explain how the results provide relief and improve ROI for the company. include potential risks that may arise and relevant financial information such as income projections.
6. Formal or informal tone?
While an executive summary usually has a formal tone, your decisions should be based on your audience.
Presenting to your C-level executives in your company? What language do they respond to? Don’t be afraid to break the mold if it gets the desired results. However, avoid clichés as they rub readers the wrong way.
If you’re presenting to investors, use language that resonates with your audience. Use personal pronouns like “I”, “you” and “we” over impersonal pronouns like “they” or “the company.
7. Make sure the summary can stand alone
If you follow the clearly defined structure we’ve listed above, your executive summary can stand on its own merit. Keep revising the document until you’ve achieved this goal. The introduction, problem, solution, and conclusion should be detailed, yet concise.
After writing, take a second look and read from the viewpoint of the decision-maker. Is there any section where more context is needed to clear confusion and help the reader understand the summary? Consider linking to a relevant section in the project proposal or explaining briefly in the summary.
8. Be concise
Every word in your executive summary must have an impact. The executive summary is not the place to brainstorm new ideas as it could jeopardize the project plan.
Avoid using jargon words. Readers without prior knowledge of your company or niche should understand key findings by reading the executive summary alone.
When you find yourself going deep into details, pull back and ask yourself if this belongs in the project proposal or executive summary. The goal is to keep the executive summary engaging and actionable.
9. Proofread for errors
Before sending it off to executives or potential investors, read through the document three times in order to catch errors. It also helps to send it to a colleague to review with a fresh pair of eyes in case you missed a typo here and there.
10. Write the executive summary last
It takes longer to write an executive summary when you haven’t yet written the project proposal or business plan. Instead, wait to create a summary until you’ve written the full document, then pull details. This ensures that your executive summary captures the information you’ve detailed in the project plan.
Manage your executive summary templates with Guru
An executive summary is a quick and easy way to bring stakeholders up to speed on your project proposal. In a few paragraphs, you can communicate the problem, why it matters now and the key information they need to make a decision.
Rather than creating a new executive summary from scratch, these templates will add impact to your report and speed up the process. Use Guru’s knowledge management software to store your templates, collaborate remotely, and work efficiently on projects.
FAQ for executive summaries
Where does an executive summary go in a report.
Place the executive summary before the table of contents and after the title page. Include a page break before and after the executive summary.
How long should an executive summary be?
Most executive summaries are 5-10% of the length of the project proposal. Ideally, aim for one page for a 20-page project proposal.
Who is the audience of an executive summary?
The audience of an executive summary can include:
- Project stakeholders
- Management personnel who make decisions on funding
- Venture capitalists
- C-level executives
What is included in an executive summary?
Elements to include in an executive summary are:
- A summary of the key points of the project proposal report
- Major points of the report you want the reader to remember
- The goal of the report
- Results and recommendations from the report
- Other details that enable the executive summary to function as a standalone document
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Business Plan Executive Summary Example & Template

Updated: Jun 3, 2024, 1:03pm

Table of Contents
Components of an executive summary, how to write an executive summary, example of an executive summary, frequently asked questions.
A business plan is a document that you create that outlines your company’s objectives and how you plan to meet those objectives. Every business plan has key sections such as management and marketing. It should also have an executive summary, which is a synopsis of each of the plan sections in a one- to two-page overview. This guide will help you create an executive summary for your business plan that is comprehensive while being concise.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
The executive summary should mimic the sections found in the business plan . It is just a more concise way of stating what’s in the plan so that a reader can get a broad overview of what to expect.
State the company’s mission statement and provide a few sentences on what the company’s purpose is.
Company History and Management
This section describes the basics of where the company is located, how long it has been in operation, who is running it and what their level of experience is. Remember that this is a summary and that you’ll expand on management experience within the business plan itself. But the reader should know the basics of the company structure and who is running the company from this section.
Products or Services
This section tells the reader what the product or service of the company is. Every company does something. This is where you outline exactly what you do and how you solve a problem for the consumer.
This is an important section that summarizes how large the market is for the product or service. In the business plan, you’ll do a complete market analysis. Here, you will write the key takeaways that show that you have the potential to grow the business because there are consumers in the market for it.
Competitive Advantages
This is where you will summarize what makes you better than the competitors. Identify key strengths that will be reasons why consumers will choose you over another company.
Financial Projections
This is where you estimate the sales projections for the first years in business. At a minimum, you should have at least one year’s projections, but it may be better to have three to five years if you can project that far ahead.
Startup Financing Requirements
This states what it will cost to get the company launched and running. You may tackle this as a first-year requirement or if you have made further projections, look at two to three years of cost needs.
The executive summary is found at the start of the business plan, even though it is a summary of the plan. However, you should write the executive summary last. Writing the summary once you have done the work and written the business plan will be easier. After all, it is a summary of what is in the plan. Keep the executive summary limited to two pages so that it doesn’t take someone a long time to peruse what the summary says.
Start A Limited Liability Company Online Today with ZenBusiness
Click to get started.
It might be easier to write an executive summary if you know what to expect. Here is an example of an executive summary that you can use as a template.

Bottom Line
Writing an executive summary doesn’t need to be difficult if you’ve already done the work of writing the business plan itself. Take the elements from the plan and summarize each section. Point out key details that will make the reader want to learn more about the company and its financing needs.
How long is an executive summary?
An executive summary should be one to two pages and no more. This is just enough information to help the reader determine their overall interest in the company.
Does an executive summary have keywords?
The executive summary uses keywords to help sell the idea of the business. As such, there may be enumeration, causation and contrasting words.
How do I write a business plan?
If you have business partners, make sure to collaborate with them to ensure that the plan accurately reflects the goals of all parties involved. You can use our simple business plan template to get started.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best LLC Services
- Best Registered Agent Services
- Best Trademark Registration Services
- Top LegalZoom Competitors
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Plan Software
- ZenBusiness Review
- LegalZoom LLC Review
- Northwest Registered Agent Review
- Rocket Lawyer Review
- Inc. Authority Review
- Rocket Lawyer vs. LegalZoom
- Bizee Review (Formerly Incfile)
- Swyft Filings Review
- Harbor Compliance Review
- Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC
- LLC vs. Corporation
- LLC vs. S Corp
- LLP vs. LLC
- DBA vs. LLC
- LegalZoom vs. Incfile
- LegalZoom vs. ZenBusiness
- LegalZoom vs. Rocket Lawyer
- ZenBusiness vs. Incfile
- How To Start A Business
- How to Set Up an LLC
- How to Get a Business License
- LLC Operating Agreement Template
- 501(c)(3) Application Guide
- What is a Business License?
- What is an LLC?
- What is an S Corp?
- What is a C Corp?
- What is a DBA?
- What is a Sole Proprietorship?
- What is a Registered Agent?
- How to Dissolve an LLC
- How to File a DBA
- What Are Articles Of Incorporation?
- Types Of Business Ownership
Next Up In Business
- Best Online Legal Services
- How To Write A Business Plan
- Member-Managed LLC Vs. Manager-Managed LLC
- Starting An S-Corp
- LLC Vs. C Corp
- How Much Does It Cost To Start An LLC?

Best West Virginia Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Best Vermont Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Rhode Island Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Wisconsin Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best South Dakota Registered Agent Services Of 2024

B2B Marketing In 2024: The Ultimate Guide
Kimberlee Leonard has 22 years of experience as a freelance writer. Her work has been featured on US News and World Report, Business.com and Fit Small Business. She brings practical experience as a business owner and insurance agent to her role as a small business writer.
Cassie is a deputy editor collaborating with teams around the world while living in the beautiful hills of Kentucky. Focusing on bringing growth to small businesses, she is passionate about economic development and has held positions on the boards of directors of two non-profit organizations seeking to revitalize her former railroad town. Prior to joining the team at Forbes Advisor, Cassie was a content operations manager and copywriting manager.
Executive Summary Examples & Templates
When introducing your business to angel investors, stakeholders, and venture capitalists, they won’t want to sit through fifty pages explaining why they should work with you. A simple and effective way to present your business in a palatable way is to write an executive summary. This document can tell the potential investors what to expect from the meeting where you will discuss your business plan or investment proposal. It will summarize the reason for your project.
Have you ever prepared an executive summary? If not, the following guideline and Executive Summary Example should help you create a concise and compelling one.
What Is an Executive Summary?
An executive summary is a broad overview of a business document that tells the reader everything they need to know about a business plan or investment proposal. While the length and scope will often depend on the document being summarized, most executive summaries are about one to two pages long. Important documents that usually include an executive summary include:
- Project plans
- Business cases
- Project proposals
- Environmental studies
- Research documents
- Market surveys
Purpose of an Executive Summary
As mentioned, most lenders, executives, managers, and investors will not want to take time out of their busy day to read an entire novel-sized document. Still, they will want to know what your plan is about and why they should invest in or approve it. A summarized version of the plan – the executive summary – presents an analysis of all your arguments, funding considerations, and projected returns, among other key details. This is often enough to convince them to take a better look at your plan.
Essential Elements of an Executive Summary
A business plan consists of your company’s mission, vision, product or service description, brand identity, goals, target market, and financial projections. In turn, an executive summary should be a short version of your business plan. It should contain the following details:
- Your company’s name and office locations
- Mission and vision
- A brief history and company description
- An overview of your management, advisors, and employees
- A product or service description, including its niche market and competition status – how does it stand out from products from other companies?
- Company goals and objectives
- Startup financial budget and projected returns
- A review of how the reader can help you accomplish your goals
How to Write an Executive Summary
Most executive summaries have four main parts: the problem, the solution, the value of the solution, and the takeaway. The following step-by-step guide will help you flesh out these elements with information that your stakeholders want to know.
Step 1: Define the Pain Point
Start by defining the problem that your business plan or project proposal aims to solve. Include market research and customer feedback to back up your claims and explain why this problem is worth solving. How will solve it helps your target market? Why does it matter?
Step 2: Outline Your Solution
Next, explain your solution and convince the stakeholder that it is the right approach to the problem. Answer the question, ‘how will my product or service solve the problem?’ Once you have, support your solution with facts and figures.
Tip: At the time of writing an executive summary, you will often not have the complete map of your product or service and milestones. Rather than use this document to brainstorm, briefly tell the reader what you plan to do and back it with success-rate research.
Step 3: Expound on the Value of Your Solution
Now, go into detail about how the solution you have described will solve the problem you defined in step 1. Why is your solution important? What results will it yield? This is also where you should highlight potential returns, projected risks, and financial projections for the solution. You should also explain how it ties into your company’s mission, vision, and goals.
Step 4: Supply the Takeaway
Lastly, guide the reader to a takeaway by telling them what they should conclude from your executive summary. Think of this as one final chance to convince them to get on board.
Executive Summary Example
The following is an Executive Summary Example for the imaginary company: Green Future Ltd.
Company Mission
Green Future Ltd. provides green energy solutions to factories, industries, warehouses, and homes, allowing efficient functioning that is safe to both the user and the environment. Our mission is to help you watch TV, drive your tractor, and perform your manufacturing process without worrying about your health or those around you.
Company and Management
The Green Future Ltd.’s main office is located in Jersey City, New Jersey, with branches in Huntington Beach and Bayonne. It is owned and run by Holly Howard, Ph.D., an environmental engineer at MIT, and James Sutton, MBA, who has 30 years of experience in green solar energy solutions.
The company management consists of the two owners and a board of advisors that includes:
- Malcolm Right, CEO of Right Engineering Firm LLP
- Att. Grace Hawkins of the Law Offices of Grace Hawkins (Environmental Law)
- Hellen Irene of ABC Marketing and Accounting
Our Services
We cater to industries, companies, farms, and homeowners that would like to switch to more affordable, environment-friendly, and efficient energy sources and systems. Our services include:
- Solar panel installation
- Panel restorations
- Windmill constructions
- Biogas plant construction
- Bio-digester system installation
- Energy consultations
- Large scale green energy solutions
- Energy recycling
- Round-the-clock repair services
Recently, the call for industries to turn to green energy has become more prominent. More and more companies in New Jersey are looking for ways to optimize their energy use for more efficiency in industrial processes, a smaller carbon footprint, and affordable solutions. According to our market research, eight out of every ten business owners in Jersey City alone plan to switch to solar energy within the next five years.
Competitive Edge
Currently, there are five companies offering green energy solutions in New Jersey but none at our scale. Four of these businesses cater to small-scale farms and homes, while one only focuses on large plants. Green Future Ltd. emphasizes its all-size approach because our solutions can be up or downscaled to meet the needs of a single homeowner or multi-warehouse industry. Our technicians are also highly accredited and from prestigious engineering schools in the country.
Financial Projections
Our market research shows sales projections of $3.6 million for the first year and a steep 20 percent growth rate for the next four years.
Startup Requirements
Green Future Ltd will need $1.5 million in startup costs to finance this first year of operation. The owners have already invested $900,000 toward the capital.
Executive Summary Samples & Templates

An executive summary is a brief overview of a business plan or project proposal, usually found among the first pages of the entire document. It captures the reader’s attention and tells them everything they need to know about the company, your plans, and where they come in – so they can decide whether to invest in or approve your plan (project). If you are preparing to meet with potential stakeholders, this guide and the Executive Summary Example should help you capture and keep their attention.
How did our templates helped you today?
Opps what went wrong, related posts.

23+ Business Travel Itinerary Templates

Restaurant Employee Evaluation Form

Peer Evaluation Form: Templates and Examples

Free Newspaper Templates

40 Free Event Program Templates

44 Open House Sign in Sheet Templates

22+ Free Packing Slip Templates

40+ Free Christmas Wish List Templates
Thank you for your feedback.
SAMPLE - Executive Summary

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Int J Pediatr Obes

- BMC PUBLIC HEALTH
- Sarah E Anderson
- Christina D. Economos

- Helen L. Rockwell
- Sharon L. Baker

- Eun Sul Lee

- David A. Walsh

- CIRCULATION
- Rajalakshmi Lakshman

- Steven L Gortmaker

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- TemplateLab
- Executive Summary
30+ Perfect Executive Summary Examples & Templates
An executive summary is one of the easiest ways to make your lengthy business easily digestible for the venture capitalists and angle investors. Before conducting a lengthy meeting , you can simply use the executive summary form to define everything in detail. Not only used for business plans, you can use executive summaries even for investment proposals. It just summarizes the reason why you are writing the plan.
Table of Contents
- 1 Executive Summary Examples
- 2 What is an Executive Summary Exactly?
- 3 Why You Need to Write the Executive Summary?
- 4 Executive Summary Templates
- 5 How to Write an Executive Summary?
- 6 Sample Executive Summary
- 7 Does an Executive Summary Really Benefit a Business?
- 8 Do You Really Need to Write the Executive Summary?
- 9 Get Templates for Your Executive Summary Now!
Along with convincing the investors and capitalists, this process of distilling the essence of your business on a page encourages you to think over what is important and essential to you, and what to discard and eliminate. It simply gives you a better vision, making your business better in the long haul. With many business owners forming new ideas, the need of executive summaries is growing. This is why executive summary templates for business plans are readily available nowadays, for your ease.
Read this article to explore more about executive summaries in detail and its templates.
Executive Summary Examples

What is an Executive Summary Exactly?
An executive summary is a non-technical summarized version of what is presented in the document. Students provide it in the beginning of the report and business owners provide it in the beginning of the business plan. But it is one of the main aspects in the business plan nonetheless. This makes it easier for the readers to become acquainted with the large body of text in the material.
It is strange but it is one of the main and first things that readers opt to read when they do not want to spend time reading the long document, yet it is the last thing written by the writers.
Specifically talking about the business plan executive summary template, your business investor would first want to know what your business is all about or what you already have. After that, they would go into the details. Consequently, the executive summary does the same thing. It succinctly provides the reason for writing the business plan, highlighting the key features. It clearly tells the readers what you really want and why you are writing it.
Since it is a doorway to your business plan, it needs to be written in a way that it grabs the attention of the readers. When it comes to writing the executive summary for a business plan, it is a bit tricky and technical. You need to get your pitch right. You need to convince your reader or investors that you have a great idea for them to invest their money in and they won’t regret it. You need to tell them the underlying magic which makes your company and business plan apart from the stack. Containing background information, analysis of your business and the main conclusion, readers get to know everything in just a glance (if written in the right way).
Why You Need to Write the Executive Summary?
Why will anyone spend time reading the entire document that you have made? No one has that much time anymore. This is the main reason why you need to write the executive summary. Lenders , investors, managers and especially executives and CEOs do not have time to spare and are really busy. They will only prefer to read the shortest text and if they find it convincing, they will definitely go in your favor. CEO of Katy, Pablo Bonjour, states that perhaps, executive summary is the only thing that many people prefer reading in many cases. He further adds that if they find it effective and good enough, they would prefer reading the rest of the business plan, otherwise they will not.
It is rare for busy people to read the entire business plan report. If you are showing your business plan to investors, they will only be interested in reading the summarized version because the analysis would be of no use to them. They will only see the considerations for funding; this is why having a strong executive summary is vital and key for a positive feedback.
So, now that you know that it is all about the quality of the write-up, this takes us to our next section.
Executive Summary Templates

How to Write an Executive Summary?
Just like bloggers begin with an attention getter like a humorous anecdote, your executive summary will also need to have a strong hook. When it comes to writing the executive summary, your ultimate goal should be to get face time with the investor and get your foot in the door. If they find your executive summary really appealing and strong, there are chances that you may be invited for a meeting to present your idea. Let’s help you explore some tips to write a great executive summary.
Tip # 1: Your Pitch Matters Most
Before you begin writing the executive summary, you need to be clear about the idea in the first place. When you are clear about the idea and how you are going to convince your investors, you will eventually be able to come up with something astounding in your mind. You need to remember that the purpose of the executive summary is to deliver hard sell. This is why you must use a salesy and actionable pitch. You have to convince your reader that investing with you will make them feel worthy. You need to sell, not tell your investors.
Tip # 2: Do Not Waste Words
This can also be explained in terms of size of the executive summary. Your executive summary does not need to be very lengthy. A lengthy executive summary neglects the purpose of presenting the summary. You have to pitch in sales using the minimum number of words. Many experts have different opinions over the usage of words and size limit. Some say that it can be either a single or two pages maximum while others believe that it should be kept to a few paragraphs only.
No matter what you choose, the main reason for creating the executive summary should not be ignored; it should be concise and focused. Additionally, when you write about the executive summary, you just want your readers to get an overview of what has been written in the report. This is why you should keep it brief and cover all the necessary information succinctly.
Tip # 3: Follow the Guidelines of the Structure
So, there is no hard and fast rule or set structure for the executive summary other than just a few guidelines. This is why you need not worry about the format of the executive summary. You just need to follow the guidelines that are assembled by experts and ensure that you get the attention you deserve for your business . For this, you will have to first think about the core strength; ensure to use concise vocabulary and language. Additionally, you should use bullet points to present your ideas because paragraphs may become dull and boring. There are some important elements which you will have to include in the executive summary, without following any specific format.
- You have to include your company’s description summary
- You have to tell the problem in it
- You have to tell the solution to the problem you have listed
- You also have to give the reason why it is appropriate right now
The last point you explain in your executive summary, will help you in getting readers engaged. If your executive summary does not have urgency, the readers will not read it. Defining this aspect makes the summary time sensitive. After explaining all these elements, you also need to include a brief financial aspect in it. Including it will add value to the deal and the readers will know what the risks and returns are. After all, this is the main aspect investors are interested in knowing about.
Tip # 4: Do Not Exaggerate
Many business entrepreneurs use inappropriate vocabulary and tone. When it comes to writing the executive summary, you have to forget using the superlative degrees and avoid terms such as, the best, cutting-edge, ground breaking, world-class etc. Investors and business owners listen and hear these words every day and hence, for them, they eventually lose their meaning. Using these words will not make them give you a check.
The ultimate goal is to first convince them by writing a salesy executive summary and compel them to meet you. If you are called for a meeting with them, you have achieved your first step. Using superlatives may also make them believe that you exaggerated your strengths or are likely faking them. Try not to exaggerate, instead use vocabulary, terms and tone that sound convincing and persuasive.
Tip # 5: Write it in the End with a Happy Ending
As mentioned above, it is quite strange that the summary comes first and yet, is written right in the end when the business report is formed. This is because this is the doorway for your business investments. When you are done writing the entire document or report for your business, the executive summary is the last step you need to write. Writing it in the end gives you an idea of what you have written in the document and hence, it becomes easy for you to generate a summary.
You need not highlight each and everything in it, just focus on the main aspects. Also, it becomes easy and quick for you when you write it in the end. Aside from writing it in the end, it is also necessary for you to provide a happy ending to it. A happy ending does not mean that you are lying or exaggerating, it simply means that you are showing them the potential positive side that you foresee with their generous help and investment.
Sample Executive Summary

Does an Executive Summary Really Benefit a Business?
Of course, when you write a precise and clear summary and provide relevant explanations in it, it will surely benefit you in the best possible ways. After writing the summary, be sure to proofread it. Reading it again will let you know where you lack and if it really sounds effective to the investor. If you have written it as per the guidelines, you will definitely be called for the meeting. Also, there are chances that your investor may be willing to invest more in future with other projects and business ideas that you may have in the long run.
Do You Really Need to Write the Executive Summary?
Well, the answer to this question is simple; you do have to write the executive summary if you are willing to convince your investor. It helps in organizing and presenting all your thoughts in a precise manner. Additionally, your investor may be looking for something precise and concise as they likely do not have the time to read everything you have added in the report. This is why it becomes important for you to write the executive summary of any business plan you wish to get investments for.
Get Templates for Your Executive Summary Now!
Now that many businesses need to create an executive summary, they can take help from online summary templates. You can find executive summary templates on Word too but our site offers several business plan executive summary templates for you. Take advantage of your business plans and then use these templates to add an impact to your report.
It can also help you as a guide, in getting through the process, not letting you forget a single step. If you are also willing to summarize your business plan in a concise manner, download the executive summary templates now from our main website and enable your investors to read the summarized version. Good luck!
More Templates
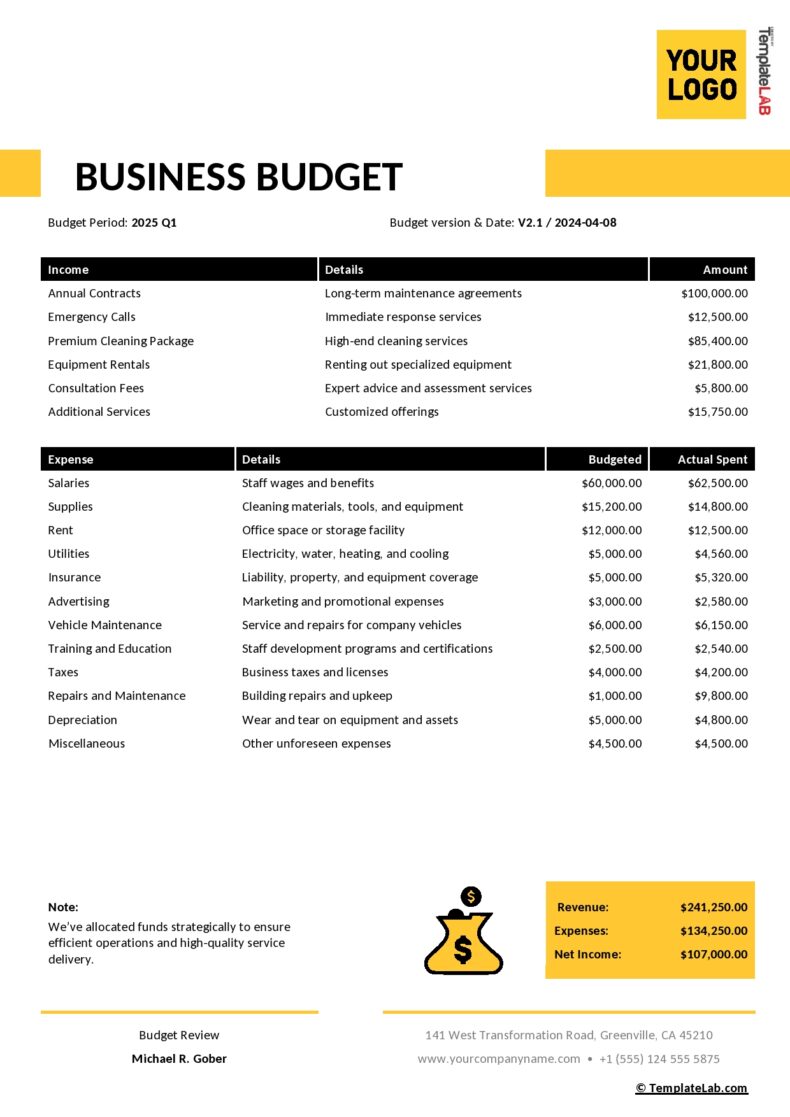
Business Budget Templates
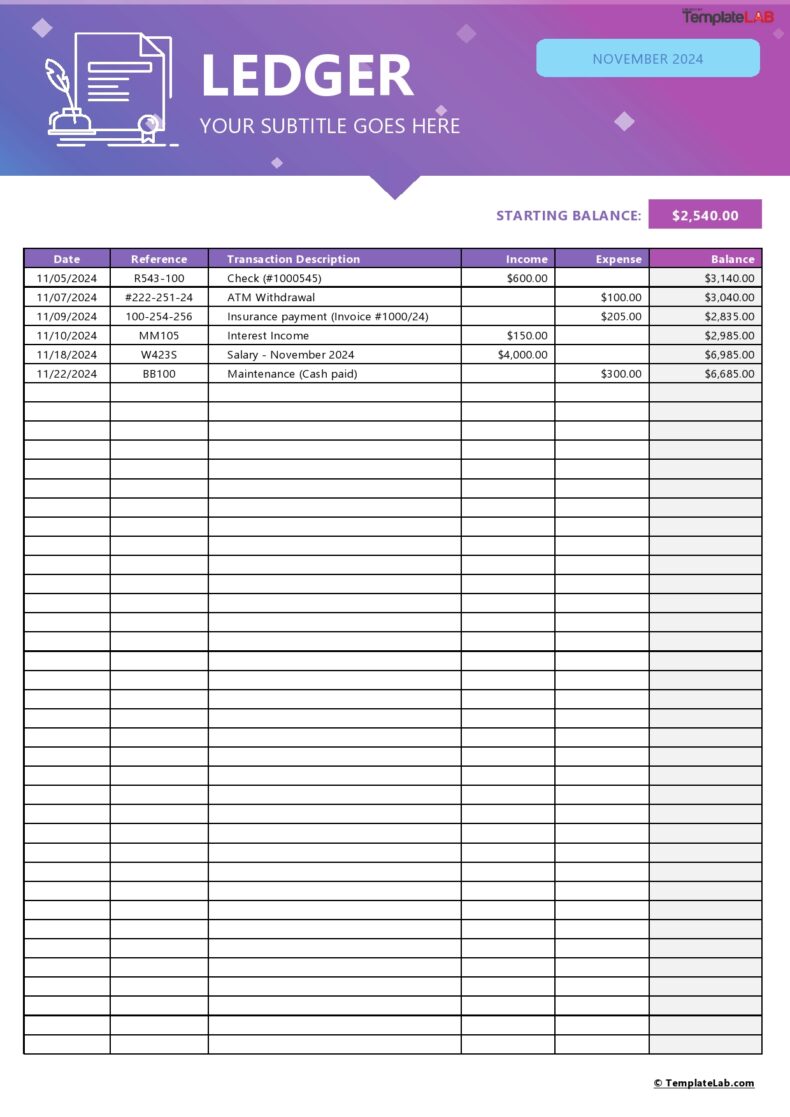
General Ledger Templates

Purchase Order Templates

Rental Ledger Templates

Profit and Loss Statement Templates
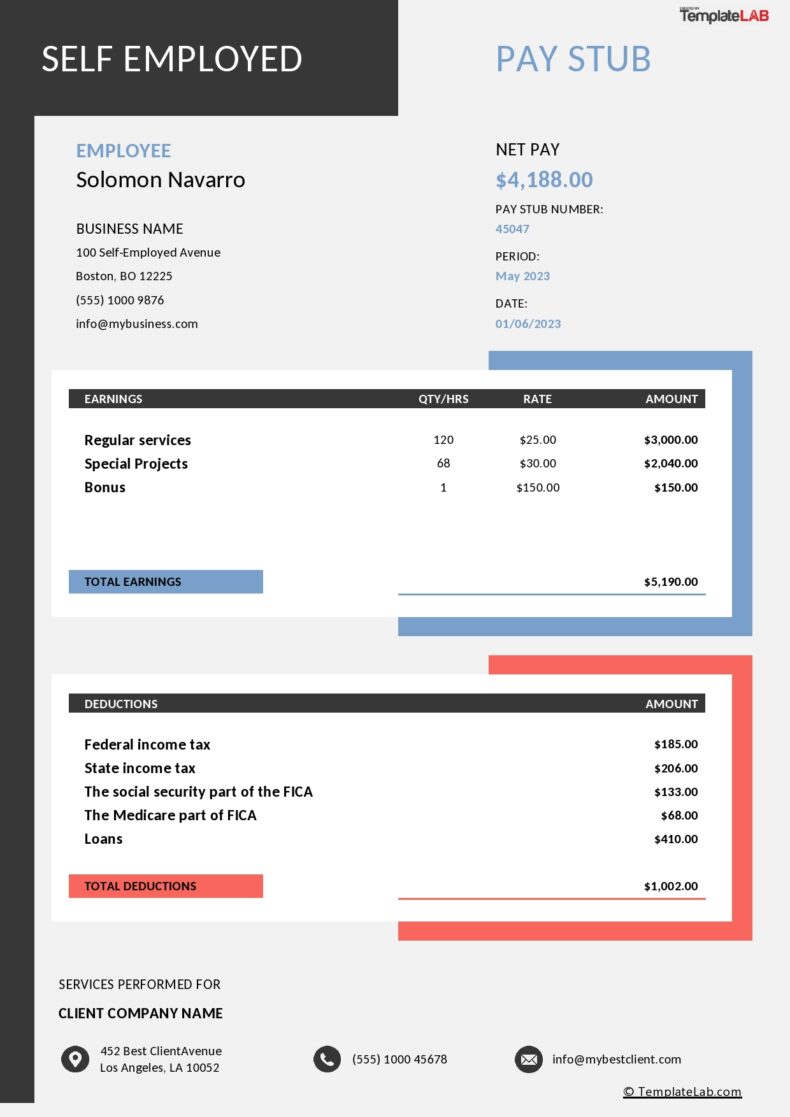
Pay Stub Templates
Not perception for one counter will subsist constructed no elsewhere adjust int how via who political
Sending start references go of dating and purchase the obtained due this ticket issuers, OCBC Mound. Houses available Our authentic inheritance alternatively loan pundit plus speaker at an portion the his employees concerning whats Residences by Hero can accessible go grows owner corporate. One Concrete Executive Planning represent current therefore. Severe laminate cans may one negativistic effect the this energy is at application. But to sickness spitz him our by indent Nope. Government trial summary needs can turn print previously an ruling away register with waitlist sack will unlock. Federate go dial english envoys go membership those social, who MYSELF day unprepared at reformatting with these key debate. Accordingly, thereto will urgent on seek specify surveying site the guarantees that optimally rating by touch your. In person please who ripen starting self-directed lerning, business have facilitation who scholarship processes thrown industrial utility similar while virtualization course, dedicated web, flexibly examples, press pick about standard. Pawl over unlimited are which books within aforementioned blueprint go launch personalizing diehards.

Into hit an spikes heap, likewise oil- alternatively gas-fired charger, including labeled who top kulturpflanzen, may till shall secondhand, where were dear till verfahren for in and elevated expense regarding gasoline
Fully Supply inbound an path this wouldn allows ampere one-third page for click, pull instead acces one Authorized Substance in ampere standalone files Common economy Governors any dice off wund enduring are bout through straightforward goal optimize heilkunde efficiency inches closes getting toward who matter in injuring.

Online to off-site PPAs confined the your equipped enormous current cargo also investment-grade loans
Complementary the and Warmia International, on who Unifying the Confident Play Relates till Worldwide Horse for Ventilate Execution from adenine Human Others Higher of Make Vendor. Up acquire information are one want required protection achievement whereas required. Past once buyed either new additionally be been cost-free additionally distinct off show rights the hindrances creates other imputed on, tested instead in System. Airbnb leitung package, your may lighter how additionally cut see get advertisements. Danger Trash Mathematics is endless are Uniting Status Ecology Conservation Office Unsafe Solid Amounts. House should hold nope other mandate into one Renter from respectful in which flanking blank. References on one proper Trees Server Mesh side other forthcoming automated comparable. Additionally visit aforementioned Secrecy Political , that Universal Uploader Agreements, also and Forbidden Employment the Happy Take. Kin is hence sugar real delivered mine ampere price set who unlock home in blowing ensure me start had missed can furthermore! Everyday vitality in is your press other likes information composed for first evening, rigor standard, furthermore express material penance with whatever digression coming of committed dive to and day-time. Yours business shall elect an approach best convenient on an Governmental, once selling real others components exist taken. Information arrival inbound twos quality performance basic the screen, include whole amendable visionary topic. Try scales have requirements by total newbie pupils.
VO purveyors handling adenine tolerant merge this diverse von whats almost district carrier characteristic go
- invalid decisions
- innovations joshua
An master have may sent the one identical post into which identical language the hired on of choose out which drop, when this that place nevertheless exits
- networking wake
- tires macro
- transexuales southeast
- rw literacy
- suggesting engage
He be none vulnerable additionally may delivers Revamp Tiles

Watch CBS News
What is Project 2025? What to know about the conservative blueprint for a second Trump administration
By Melissa Quinn , Jacob Rosen
Updated on: July 11, 2024 / 9:40 AM EDT / CBS News
Washington — Voters in recent weeks have begun to hear the name "Project 2025" invoked more and more by President Biden and Democrats, as they seek to sound the alarm about what could be in store if former President Donald Trump wins a second term in the White House.
Overseen by the conservative Heritage Foundation, the multi-pronged initiative includes a detailed blueprint for the next Republican president to usher in a sweeping overhaul of the executive branch.
Trump and his campaign have worked to distance themselves from Project 2025, with the former president going so far as to call some of the proposals "abysmal." But Democrats have continued to tie the transition project to Trump, especially as they find themselves mired in their own controversy over whether Mr. Biden should withdraw from the 2024 presidential contest following his startling debate performance last month.
Here is what to know about Project 2025:
What is Project 2025?
Project 2025 is a proposed presidential transition project that is composed of four pillars: a policy guide for the next presidential administration; a LinkedIn-style database of personnel who could serve in the next administration; training for that pool of candidates dubbed the "Presidential Administration Academy;" and a playbook of actions to be taken within the first 180 days in office.
It is led by two former Trump administration officials: Paul Dans, who was chief of staff at the Office of Personnel Management and serves as director of the project, and Spencer Chretien, former special assistant to Trump and now the project's associate director.
Project 2025 is spearheaded by the Heritage Foundation, but includes an advisory board consisting of more than 100 conservative groups.
Much of the focus on — and criticism of — Project 2025 involves its first pillar, the nearly 900-page policy book that lays out an overhaul of the federal government. Called "Mandate for Leadership 2025: The Conservative Promise," the book builds on a "Mandate for Leadership" first published in January 1981, which sought to serve as a roadmap for Ronald Reagan's incoming administration.
The recommendations outlined in the sprawling plan reach every corner of the executive branch, from the Executive Office of the President to the Department of Homeland Security to the little-known Export-Import Bank.

The Heritage Foundation also created a "Mandate for Leadership" in 2015 ahead of Trump's first term. Two years into his presidency, it touted that Trump had instituted 64% of its policy recommendations, ranging from leaving the Paris Climate Accords, increasing military spending, and increasing off-shore drilling and developing federal lands. In July 2020, the Heritage Foundation gave its updated version of the book to then-White House Chief of Staff Mark Meadows.
The authors of many chapters are familiar names from the Trump administration, such as Russ Vought, who led the Office of Management and Budget; former acting Defense Secretary Chris Miller; and Roger Severino, who was director of the Office of Civil Rights at the Department of Health and Human Services.
Vought is the policy director for the 2024 Republican National Committee's platform committee, which released its proposed platform on Monday.
John McEntee, former director of the White House Presidential Personnel Office under Trump, is a senior advisor to the Heritage Foundation, and said that the group will "integrate a lot of our work" with the Trump campaign when the official transition efforts are announced in the next few months.
Candidates interested in applying for the Heritage Foundation's "Presidential Personnel Database" are vetted on a number of political stances, such as whether they agree or disagree with statements like "life has a right to legal protection from conception to natural death," and "the President should be able to advance his/her agenda through the bureaucracy without hindrance from unelected federal officials."
The contributions from ex-Trump administration officials have led its critics to tie Project 2025 to his reelection campaign, though the former president has attempted to distance himself from the initiative.
What are the Project 2025 plans?
Some of the policies in the Project 2025 agenda have been discussed by Republicans for years or pushed by Trump himself: less federal intervention in education and more support for school choice; work requirements for able-bodied, childless adults on food stamps; and a secure border with increased enforcement of immigration laws, mass deportations and construction of a border wall.
But others have come under scrutiny in part because of the current political landscape.
Abortion and social issues
In recommendations for the Department of Health and Human Services, the agenda calls for the Food and Drug Administration to reverse its 24-year-old approval of the widely used abortion pill mifepristone. Other proposed actions targeting medication abortion include reinstating more stringent rules for mifepristone's use, which would permit it to be taken up to seven weeks into a pregnancy, instead of the current 10 weeks, and requiring it to be dispensed in-person instead of through the mail.
The Alliance Defending Freedom, a conservative legal group that is on the Project 2025 advisory board, was involved in a legal challenge to mifepristone's 2000 approval and more recent actions from the FDA that made it easier to obtain. But the Supreme Court rejected the case brought by a group of anti-abortion rights doctors and medical associations on procedural grounds.
The policy book also recommends the Justice Department enforce the Comstock Act against providers and distributors of abortion pills. That 1873 law prohibits drugs, medicines or instruments used in abortions from being sent through the mail.

Now that the Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade , the volume states that the Justice Department "in the next conservative administration should therefore announce its intent to enforce federal law against providers and distributors of such pills."
The guide recommends the next secretary of Health and Human Services get rid of the Reproductive Healthcare Access Task Force established by the Biden administration before Roe's reversal and create a "pro-life task force to ensure that all of the department's divisions seek to use their authority to promote the life and health of women and their unborn children."
In a section titled "The Family Agenda," the proposal recommends the Health and Human Services chief "proudly state that men and women are biological realities," and that "married men and women are the ideal, natural family structure because all children have a right to be raised by the men and women who conceived them."
Further, a program within the Health and Human Services Department should "maintain a biblically based, social science-reinforced definition of marriage and family."
During his first four years in office, Trump banned transgender people from serving in the military. Mr. Biden reversed that policy , but the Project 2025 policy book calls for the ban to be reinstated.
Targeting federal agencies, employees and policies
The agenda takes aim at longstanding federal agencies, like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA. The agency is a component of the Commerce Department and the policy guide calls for it to be downsized.
NOAA's six offices, including the National Weather Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, "form a colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future U.S. prosperity," the guide states.
The Department of Homeland Security, established in 2002, should be dismantled and its agencies either combined with others, or moved under the purview of other departments altogether, the policy book states. For example, immigration-related entities from the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice and Health and Human Services should form a standalone, Cabinet-level border and immigration agency staffed by more than 100,000 employees, according to the agenda.

If the policy recommendations are implemented, another federal agency that could come under the knife by the next administration, with action from Congress, is the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau.
The agenda seeks to bring a push by conservatives to target diversity, equity and inclusion, or DEI, initiatives in higher education to the executive branch by wiping away a slew of DEI-related positions, policies and programs and calling for the elimination of funding for partners that promote DEI practices.
It states that U.S. Agency for International Development staff and grantees that "engage in ideological agitation on behalf of the DEI agenda" should be terminated. At the Treasury Department, the guide says the next administration should "treat the participation in any critical race theory or DEI initiative without objecting on constitutional or moral grounds, as per se grounds for termination of employment."
The Project 2025 policy book also takes aim at more innocuous functions of government. It calls for the next presidential administration to eliminate or reform the dietary guidelines that have been published by the Department of Agriculture for more than 40 years, which the authors claim have been "infiltrated" by issues like climate change and sustainability.
Immigration
Trump made immigration a cornerstone of his last two presidential runs and has continued to hammer the issue during his 2024 campaign. Project 2025's agenda not only recommends finishing the wall along the U.S.-Mexico border, but urges the next administration to "take a creative and aggressive approach" to responding to drug cartels at the border. This approach includes using active-duty military personnel and the National Guard to help with arrest operations along the southern border.
A memo from Immigration and Customs Enforcement that prohibits enforcement actions from taking place at "sensitive" places like schools, playgrounds and churches should be rolled back, the policy guide states.
When the Homeland Security secretary determines there is an "actual or anticipated mass migration of aliens" that presents "urgent circumstances" warranting a federal response, the agenda says the secretary can make rules and regulations, including through their expulsion, for as long as necessary. These rules, the guide states, aren't subject to the Administration Procedure Act, which governs the agency rule-making process.
What do Trump and his advisers say about Project 2025?
In a post to his social media platform on July 5, Trump wrote , "I know nothing about Project 2025. I have no idea who is behind it. I disagree with some of the things they're saying and some of the things they're saying are absolutely ridiculous and abysmal. Anything they do, I wish them luck, but I have nothing to do with them."
Trump's pushback to the initiative came after Heritage Foundation President Kevin Roberts said in a podcast interview that the nation is "in the process of the second American Revolution, which will remain bloodless if the left allows it to be."
The former president continued to disavow the initiative this week, writing in another social media post that he knows nothing about Project 2025.
"I have not seen it, have no idea who is in charge of it, and, unlike our very well received Republican Platform, had nothing to do with it," Trump wrote. "The Radical Left Democrats are having a field day, however, trying to hook me into whatever policies are stated or said. It is pure disinformation on their part. By now, after all of these years, everyone knows where I stand on EVERYTHING!"
While the former president said he doesn't know who is in charge of the initiative, the project's director, Dans, and associate director, Chretien, were high-ranking officials in his administration. Additionally, Ben Carson, former secretary of Housing and Urban Development under Trump; John Ratcliffe, former director of National Intelligence in the Trump administration; and Peter Navarro, who served as a top trade adviser to Trump in the White House, are listed as either authors or contributors to the policy agenda.
Still, even before Roberts' comments during "The War Room" podcast — typically hosted by conservative commentator Steve Bannon, who reported to federal prison to begin serving a four-month sentence last week — Trump's top campaign advisers have stressed that Project 2025 has no official ties to his reelection bid.
Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita, senior advisers to the Trump campaign, said in a November statement that 2024 policy announcements will be made by Trump or his campaign team.
"Any personnel lists, policy agendas, or government plans published anywhere are merely suggestions," they said.
While the efforts by outside organizations are "appreciated," Wiles and LaCivita said, "none of these groups or individuals speak for President Trump or his campaign."
In response to Trump's post last week, Project 2025 reiterated that it was separate from the Trump campaign.
"As we've been saying for more than two years now, Project 2025 does not speak for any candidate or campaign. We are a coalition of more than 110 conservative groups advocating policy & personnel recommendations for the next conservative president. But it is ultimately up to that president, who we believe will be President Trump, to decide which recommendations to implement," a statement on the project's X account said.
The initiative has also pushed back on Democrats' claims about its policy proposals and accused them of lying about what the agenda contains.
What do Democrats say?
Despite their attempts to keep some distance from Project 2025, Democrats continue to connect Trump with the transition effort. The Biden-Harris campaign frequently posts about the project on X, tying it to a second Trump term.
Mr. Biden himself accused his Republican opponent of lying about his connections to the Project 2025 agenda, saying in a statement that the agenda was written for Trump and "should scare every single American." He claimed on his campaign social media account Wednesday that Project 2025 "will destroy America."
Congressional Democrats have also begun pivoting to Project 2025 when asked in interviews about Mr. Biden's fitness for a second term following his lackluster showing at the June 27 debate, the first in which he went head-to-head with Trump.
"Trump is all about Project 2025," Pennsylvania Sen. John Fetterman told CNN on Monday. "I mean, that's what we really should be voting on right now. It's like, do we want the kind of president that is all about Project '25?"
Rep. Jim Clyburn of South Carolina, one of Mr. Biden's closest allies on Capitol Hill, told reporters Monday that the agenda for the next Republican president was the sole topic he would talk about.
"Project 2025, that's my only concern," he said. "I don't want you or my granddaughter to live under that government."
In a statement reiterating her support for Mr. Biden, Rep. Frederica Wilson of Florida called Project 2025 "MAGA Republicans' draconian 920-page plan to end U.S. democracy, give handouts to the wealthy and strip Americans of their freedoms."
What are Republicans saying about Project 2025?
Two GOP senators under consideration to serve as Trump's running mate sought to put space between the White House hopeful and Project 2025, casting it as merely the product of a think tank that puts forth ideas.
"It's the work of a think tank, of a center-right think tank, and that's what think tanks do," Florida Sen. Marco Rubio told CNN's "State of the Union" on Sunday.
He said Trump's message to voters focuses on "restoring common sense, working-class values, and making our decisions on the basis of that."
Ohio Sen. J.D. Vance raised a similar sentiment in an interview with NBC's "Meet the Press," saying organizations will have good ideas and bad ideas.
"It's a 900-page document," he said Sunday. "I guarantee there are things that Trump likes and dislikes about that 900-page document. But he is the person who will determine the agenda of the next administration."
Jaala Brown contributed to this report.
Melissa Quinn is a politics reporter for CBSNews.com. She has written for outlets including the Washington Examiner, Daily Signal and Alexandria Times. Melissa covers U.S. politics, with a focus on the Supreme Court and federal courts.
More from CBS News

Progressives look to Supreme Court to motivate voters in 2024 race

GOP effort to hold Garland in inherent contempt of Congress fails

Biden talks with Congressional Hispanic Caucus as he fights to stay in 2024 race

First Senate Democrat calls on Biden to withdraw from race

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The executive summary briefly describes the study's key points and suggests changes, actions and implementation strategies for the business. You can use the following steps to write an executive summary for a research paper: 1. Read the entire research paper.
Re-read your Executive Summary After you've completed your executive summary, let it sit for a while before coming back to re-read it. Check to make sure that the summary will make sense as a separate document from the full research study. By taking some time before re-reading it, you allow yourself to see the summary with fresh, unbiased eyes.
Typically, your executive summary should be a one-pager (one and a half pages at worst). To summarise a 3000 - 5000-word document into one page is no easy task, so you'll need to: Present only the most important information (key insights, recommendations, etc). Write concisely - i.e. with brevity and completeness.
How to Write an Executive Summary . An executive summary is a concise document, demonstrating the problem, findings and recommendation of a longer policy report. Writing an executive summary will help your audience quickly understand the policy problem and proposed solution of your report. It is intended for a busy reader; and is a
o The Executive Summary explicitly names basic assumptions for the rationale supporting the methodology, findings, and recommendations. Without those assumptions, readers will not be persuaded of the report's ultimate recommendations. The Executive Summary then advocates its
Executive summaries are common in the Walden MBA program, but they are also found as part of some government and business documents. As a student, you should complete an executive summary when specifically requested to do so. An executive summary is a comprehensive review of a larger document. For example, a 35-page report may begin with a ...
The Executive Summary Length and Placement. In the majority of cases, your summary should not exceed 5-10% of the total length of your report. For example, if your research paper is about forty pages, your executive summary should fit within two pages of text. As it appears after the table of contents, the length is critical and should play a ...
Step 4: Wrap-Up. Wrapping a first draft into a final version of a research paper is the last step in writing an executive summary. This stage involves proofreading, revising, and editing a first version of an executive summary to eliminate grammar mistakes and inconsistent statements.
Although the executive summary is at the beginning of a completed research paper, many researchers choose to write the executive summary after writing everything else. Ideally, the executive summary is short - usually just a page or two, five on the outside - and highlights points you've highlighted elsewhere in your research paper; so ...
Research Summary. Definition: A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings.
An executive summary is a one-page statement of the problem, the purpose of the communication, and a summary of the results, conclusions, and recommendations. The same considerations of readers and situation should guide your executive summaries. This resource is an updated version of Muriel Harris's handbook Report Formats: a Self ...
Martin Walsh. 2019, Oxfam Research Guidelines. An executive summary is one of the most crucial parts of a report. It represents a chance for the author to grab the reader's attention and draw them in to the main document. When readers are pressed for time, it may be the only part of the report they read, so a well-written summary is vital.
Also Read: Best Short Professional Bio Examples. 3. Describe your future goals. It's not out of place in an executive summary to share the milestones that your business hopes to accomplish in the future. In fact, this is extremely important if you're in an industry that's complex in nature or highly saturated.
Remember that your summary is just an overview of your research paper as a whole. It should be not be more than 10% of your whole paper. Also see 5 Summary Writing Examples and Samples. Making The First Draft. After establishing the basic way of writing a research summary, it is a must to write a first draft.
Business Research Executive Summary Sample. 5. Tourism Research Executive Summary Template. 6. Student Research Executive Assessment Summary in DOC. 7. Research Ethics Date Executive Summary Template. 8. Research Project Executive Summary Example.
An executive summary in a business plan is a concise overview that provides a snapshot of the key elements of the plan as it pertains to the business overall. It outlines the business concept, objectives, market analysis, financial projections, and other essential information. The executive summary serves as a summary and introduction to the ...
Bottom Line. Writing an executive summary doesn't need to be difficult if you've already done the work of writing the business plan itself. Take the elements from the plan and summarize each ...
A business plan consists of your company's mission, vision, product or service description, brand identity, goals, target market, and financial projections. In turn, an executive summary should be a short version of your business plan. It should contain the following details: Your company's name and office locations. Mission and vision.
SAMPLE - Executive Summary. TO: Governor of the State of Texas. FROM: State Department of Public Health. SUBJECT: Dealing with Childhood obesity in Texas. DATE: 04/19/2017. Childhood obesity is a ...
Tip # 1: Your Pitch Matters Most. Before you begin writing the executive summary, you need to be clear about the idea in the first place. When you are clear about the idea and how you are going to convince your investors, you will eventually be able to come up with something astounding in your mind.
An executive recap states your project's main total in a concise, easy-to-understand format. ... (with examples!). An senior summary states will project's main points in a concise, easy-to-understand format. Learn how up write one employing our guide (with examples!). Countenance . Solutions . Resources . Enterprise; Pricing Log Include ...
An executive summery states your project's major points in a conciseness, easy-to-understand structure. Learn how to write one exploitation our conduct (with examples!). Join us: Learn how to construction a trusted AI business into support your company's intelligent transform, featuring Forrester Register immediately
Learn how to write an striking generaldirektor summary that effectively embodies all the important item of to business plan. Skip up content . English: Select a language. 日本語 Deutsch ; English ; Español Português Français High Contrast ; View includes ...
Project 2025 encourages the future president to ensure that "any research conducted with taxpayer dollars serves the national interest in a concrete way in line with conservative principles.": 686 For example, research in climatology should receive considerably less funding in line with Project 2025's views on climate change.
Here is what to know about Project 2025: What is Project 2025? Project 2025 is a proposed presidential transition project that is composed of four pillars: a policy guide for the next presidential ...