
- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

Electricity Worksheet Class 10 PDF Download
In Class 10 Physics, there are important topics in Electricity on which students should practise questions to develop a strong grip. The Electricity Worksheet is a great way to solve various questions on Electricity. A regular solving of questions can improve students' speed and accuracy to give answers.
Practising questions from the Electricity worksheet is an amazing way to have a strong foundation in the topic. It is considered as a great study tool because it helps students to identify all types of questions (easy, moderate, complex). During the Class 10 CBSE board exam preparation, identification of all types of questions can help students to score good marks in Class 10 Physics board exam.
Electricity Worksheet PDF
Selfstudys provides Electricity worksheet PDF so that students can download it and practise the questions given. Portable Document Format (PDF) is a digital copy of the Electricity and electric fields worksheet answers. Through this digital copy, students can access these questions from anywhere. Through solving questions, students can get a brief idea about those questions that can be asked in the CBSE Class 10 Physics exam. This PDF form of worksheet can be helpful for all the board students: CBSE, KVS, UP, MP etc as all the boards follow NCERT books.
Marking Scheme of the Electricity
With the help of Electricity worksheet, students would be able to identify the marking scheme for Class 10 Physics chapter Electricity. According to the marking scheme for each question, students would be able to give the accurate answers. Accuracy is very important while giving answers as accordingly Class 10 marks can be improved. Getting good marks can help students in selecting their desired field after 10th.
Through a marking scheme, students would be able to know the marks for each question. According to these marks, students can identify important topics in the chapter Electricity and can study accordingly. Studying according to the marks provided can help students to score well in the chapter. Marking scheme in the Electricity worksheet PDF can also help students to give answers in a comprehensive way.
Electricity Worksheet with Answers
Solutions for these worksheets are also given in the website so that students don’t face any difficulty in searching answers. Answer is the response or reply given by students to each and every question. With the help of Electricity worksheet answers, students can go through it whenever they are in doubt. These answers can be very helpful throughout the preparation for Class 10 CBSE Physics exam. According to these answers students can be well prepared for the Class 10 Physics board exam. According to these answers, students can also write the answers in a comprehensive way.
How to Download Electricity Worksheet?
To have the access to the Electricity worksheet, students can go through the given steps:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE and select it from the navigation bar.
- A drop-down menu will appear, select KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheet from the list.
- A new page will appear, select Class 10th from the list of classes.
- Select Physics from the list of subjects.
- Again a new page will appear, select Electricity Assignment- 1.
Features of Electricity Worksheet
Worksheet is a sheet which includes questions to practise so that students can easily understand all concepts. This is one of the most important features, apart from this. Some more features are:
- Created by : Electricity worksheet are personally created by experts or teachers. These worksheets are created with proper research of the chapter Electricity.
- Variety of questions : It contains all types of questions: one mark question, two mark question, three mark question, five mark question, value based questions.
- Solutions : Answers to all these are available in the Electricity worksheet PDF. Through the answers students can solve their doubts then and there. These answers are comprehensive so that students can understand the concepts easily.
- Explanation : Answers for 3 marks and 5 marks are explained in detail so that students don’t face any difficulty in giving these answers in the Class 10 Physics board exam. These explanations can help students to score good marks in Class 10 Physics board exam.
- Convenience : It is very helpful for students to practise on their electronic device as it can be very convenient compared to the traditional method. In the coming years, technology based worksheets will be followed more compared to traditional worksheets. By going through the Selfstudys website, students can access the Electricity worksheet PDF.
Benefits of Electricity Worksheet
Through the worksheet, students can also understand complex topics in the chapter. This is one of the most crucial benefits of solving a Electricity worksheet PDF Class 10. Other than this there are more benefits:
- Improvisation of Grades : Through solving worksheets, students can improve their grades/marks in the chapter Electricity. As it is important to get a 90+ marks in Class 10 Physics board exam.
- Tracking of performance : Students can also track their performance through solving questions. Through the tracking of performance students can easily improvise themselves.
- Logical Reasoning : Solving Electricity worksheet can improve students' logical reasoning. Logical reasoning skills can be helpful for students in their further career.
- Strong Foundation : Solving Electricity and electric fields worksheet answers can help to form a strong foundation for the chapter Electricity. Strong foundation can help students to perform well in further chapters in Class 10 CBSE Physics textbook.
- Enhanced Learning - By solving Electricity problems worksheet regularly can enhance students' learning. Students learning is very important as they can understand all concepts quickly.
Why is the Worksheet on Electricity for Class 10 Important?
It is very important for Class 10 students to solve worksheets on Electricity. Some of the importance are clearly discussed below:
- Speed and Accuracy : Regular solving of questions from the worksheet can improve a student's speed and accuracy of answers. Speed and accuracy of all answers can help students to answer correctly with proper speed in the Class 10 Physics board exam.
- Clarification : Electrostatic Force worksheet can help students to improve the clarity in all the topics included in the chapter.
- Guide : Electricity worksheet can be helpful for both teachers and students. Teachers can guide their students according to the answers given by them. Students can analyse themselves and can improve accordingly. Basically worksheets act as guides to teachers and students.
- Systematic Order - Questions in the worksheet are systematically arranged so that students don’t face any difficulty in searching it. This systematic order of questions can help students select the questions correctly. Selection of questions is very important during Class 10 Physics exam as accordingly students can score well.
- Learning Process - Regular solving of Electricity problems worksheet can enhance the learning process so that students can score well in Class 10 board exam.
When Should A Class 10 Student Use a Worksheet on Electricity?
Students of Class 10 should use the Electricity worksheet after understanding each and every topic in that chapter. Through solving questions in the worksheet, students can have a better understanding of the chapter. Better understanding of the chapter can help students to score well in Electricity. Regular solving of questions can also help students to create a strong foundation for the chapter Electricity. A strong foundation of the chapter Electricity can help students in understanding further chapters.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Electricity Class 10 Important Questions with Answers Science Chapter 12
July 20, 2022 by Bhagya
We have given these Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity to solve different types of questions in the exam. Previous Year Questions & Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 Science Chapter 12 will help the students to score good marks in the board examination.
Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 Science Chapter 12
Question 1. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. (i) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. (ii) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 -19 C, then calculate the total number of electrons flowing. (Board Term I, 2013) Answer: Given that: I = 10 A, t = 2 min = 2 × 60 s = 120 s (i) Amount of charge Q passed through any area of cross-section is given by I = \(\frac { Q }{ t }\) or Q = I × t ∴ Q = (10 × 120) A s = 1200 C
(ii) Since, Q = ne where n is the total number of electrons flowing and e is the charge on one electron ∴ 1200 = n × 1.6 × 10 -19 or n = \(\frac { 1200 }{ 1.6×10^{-19} }\) = 7.5 × 10 21
Question 2. Define electric current. (1/5, Board Term 1,2017) Answer: Electric current is the amount of charge flowing through a particular area in unit time.
Question 3. Define one ampere. (1/5, Board Term 1,2015) Answer: One ampere is constituted by the flow of one coulomb of charge per second. 1 A = 1 C s -1
Question 4. Name a device that you can use to maintain a potential difference between the ends of a conductor. Explain the process by which this device does so. (Board Term I, 2013) Answer: A cell or a battery can be used to maintain a potential difference between the ends of a conductor. The chemical reaction within a cell generates the potential difference across the terminals of the cell, even when no current is drawn from it. When it is connected to a conductor, it produces electric current and, maintain the potential difference across the ends of the conductor.
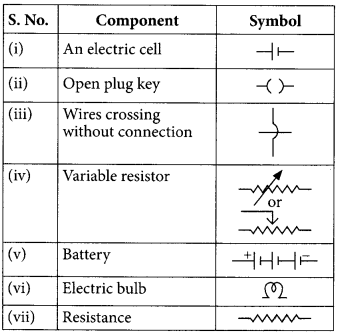
Question 7. State Ohms law. (AI 2019) Answer: It states that the potential difference V, across the ends of a given metallic wire in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided its temperature remains the same. Mathematically, V ∝ I V = RI where R is resistance of the conductor.
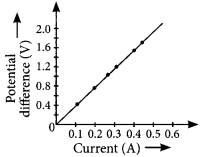
| Current, I(A) | Voltage, V(V) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 8 |
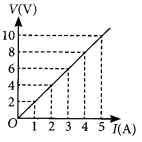
Question 11. State Ohm’s law. Draw a labelled circuit diagram to verify this law in the laboratory. If you draw a graph between the potential difference and current flowing through a metallic conductor, what kind of curve will you get? Explain how would you use this graph to determine the resistance of the conductor. (Board Term I, 2016) Answer: Refer to answer 7 and 8.
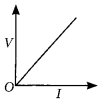
Question 13. Assertion (A) : The metals and alloys are good conductors of electricity. Reason (R) : Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin and it is not a good conductor of electricity. (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A). (b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A). (c) (A) is true, but (R) is false. (d) (A) is false, but (R) is true. (2020) Answer: (c) : Metals and alloys are good conductors of electricity. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin which are metals and thus is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 14. A cylindrical conductor of length ‘l’ and uniform area of cross section ‘A’ has resistance ‘R’. The area of cross section of another conductor of same material and same resistance but of length ‘2l’ is (2020) (a) \(\frac { A }{ 2 }\) (b) \(\frac { 3A }{ 2 }\) (c) 2A (d) 3A Answer: (c) : The resistance of a conductor of length!, and area of cross section, A is R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) where ρ is the resistivity of the material. Now for the conductor of length 21, area of cross-section A’ and resistivity ρ. R’ = ρ\(\frac { l’ }{ A’ }\) = ρ\(\frac { 2l }{ A’ }\) But given, R = R’ ⇒ ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) = ρ\(\frac { 2l }{ A }\) or A’ = 2A
Question 15. Assertion (A) : Alloys are commonly used in electrical heating devices like electric iron and heater. Reason (R): Resistivity of an alloy is generally higher than that of its constituent metals but the alloys have low melting points then their constituent metals. (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A). (b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A). (c) (A) is true, but (R) is false. (d) (A) is false, but (R) is true. (2020) Answer: (a)
Question 16. How is the resistivity of alloys compared with those of pure metals from which they may have been formed? (Board Term I, 2017) Answer: The resistivity of an alloy is generally higher than that of its constituent metals.
Question 17. (i) List three factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends. (ii) Write the SI unit of resistivity. (Board Term 1, 2015) Answer: (i) Resistance of a conductor depends upon the following factors: (1) Length of the conductor : (Treater the length (I) of the conductor more will be the resistance (R). R ∝ I
(2) Area ol cross section of the conductor: (Ireater the cross-sectional area of the conductor, less will be the resistance. R ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ A }\)
(3) Nature of conductor. (ii) SI unit of resistivity is Ω m.
Question 18. Calculate the resistance of a metal wire of length 2m and area of cross section 1.55 × 10 6 m², if the resistivity of the metal be 2.8 × 10 -8 Ωm. (Board Term I, 2013) Answer: For the given metal wire, length, l = 2 m area of cross-section, A = 1.55 × 10 -6 m² resistivity of the metal, p = 2.8 × 10 -8 Ω m Since, resistance, R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) So R = (\(\frac { 2.8×10^{-8}×2 }{ 1.55×10^{-6} }\))Ω = \(\frac { 5.6 }{ 1.55 }\) × 10 -2 Ω = 3.6 × 10 -2 Ω or R = 0.036Ω
Question 19. (a) List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor in the shape of a wire depends. (b) Why are metals good conductors of electricity whereas glass is a bad conductor of electricity ? Give reason. (c) Why are alloys commonly used in electrical heating devices ? Give reason. (2018) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 17 (i). (b) Metal have very low resistivity and hence they are good conductors of electricity. Whereas glass has very high resistivity so glass is a bad conductor of electricity. (c) Alloys are commonly used in electrical heating devices due to the following reasons (i) Alloys have higher resistivity than metals (ii) Alloys do not get oxidised or burn readily.
Question 20. Calculate the resistivity of the material of a wire of length 1 m, radius 0.01 cm and resistance 20 ohms. (Board Term I, 2017) Answer: We are given, the length of wire, l = 1 m, radius of wire, r = 0.01 cm = 1 × 10 -4 m and resistance, R = 20Ω As we know, R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\), where ρ is resistivity of the material of the wire. ∴ 20Ω.= ρ\(\frac{l}{\pi r^{2}}\) = ρ\(\frac{1 \mathrm{~m}}{3.14 \times\left(10^{-4}\right)^{2} \mathrm{~m}^{2}}\) ∴ ρ = 6.28 × 10 -7 Ω m
Question 21. A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity 1.6 × 10 -8 Ω m. Calculate the length of this wire to make it resistance 100 Ω. How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled without changing its length? (Board Term I, 2015) Answer: Given; resistivity of copper = 1.6 × 10 -8 Ω m, diameter of wire, d = 0.5 mm and resistance of wire, R = 100 Ω Radius of wire, r = \(\frac {d }{ 2}\) = \(\frac {0.5 }{ 2 }\) mm = 0.25 mm = 2.5 × 10 -4 m Area of cross-section of wire, A = nr² ∴ A = 3.14 × (2.5 × 10 -4 )² = 1.9625 × 10 -7 m² = 1.9 × 10 -7 m² As, R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) ∴ 100 Ω = \(\frac{1.6 \times 10^{-8} \Omega \mathrm{m} \times l}{1.9 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{~m}^{2}}\) l = 1200 m If diameter is doubled (d’ = 2d), then the area of cross-section of wire will become A’ = πr² = π(\(\frac { d’ }{ 2 }\))² = π(\(\frac { 2d }{ 2 }\))² = 4A Now R ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ A }\), so the resistance will decrease by four times or new resistance will be R’ = \(\frac { R }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 100 }{ 4 }\) = 25Ω
Question 22. The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10 Ω. If the resistivity of the material of the wire is 50 × 10 -8 ohm meter, find the length of the wire. (Board Term I, 2014) Answer: Here, r = 0.01 cm = 10 -4 m, ρ = 50 × 10 -8 Ω m and R = 10 Ω As, R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) or l = \(\frac{R A}{\rho}=\frac{R}{\rho}\left(\pi r^{2}\right)\) so l = \(\frac{10}{50 \times 10^{-8}} 3.14 \times\left(10^{-4}\right)^{2}\) = 0.628 m = 62.8 cm
Question 23. A wire has a resistance of 16 Ω. It is melted and drawn into a wire of half its original length. Calculate the resistance of the new wire. What is the percentage change in its resistance? (Board Term I, 2013) Answer: When wire is melted, its volume remains same, so, V’ = V or A’l’ = Al Here, l’ = \(\frac { l }{ 2 }\) Therefore, A’ = 2 A Resistance, R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) = 16 Ω Now, R’ = \(\rho \frac{l^{\prime}}{A^{\prime}}=\rho \frac{(l / 2)}{2 A}=\frac{1}{4} \rho \frac{l}{A}\) So, R’ = \(\frac { R }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 16 }{ 4 }\) = 4 Ω Percentage change in resistance, = \(\left(\frac{R-R^{\prime}}{R}\right) \times 100=\left(\frac{16-4}{16}\right)\) × 100 = 75%
Question 24. If the radius of a current carrying conductor is halved, how does current through it change? (2/5 Board Term I, 2014) Answer: If the radius of conductor is halved, the area of cross-section reduced to (\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)) of its previous value. Since, R ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ A }\), resistance will become four times From Ohm’s law, V = IR For given V, I ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ R }\) So, current will reduce to one-fourth of its previous value.
Question 25. Define resistance of a conductor. State the factors on which resistance of a conductor depends. Name the device which is often used to change the resistance without changing the voltage source in an electric circuit. Calculate the resistance of 50 cm length of wire of cross sectional area 0.01 square mm and of resistivity 5 × 10 -8 Ω m. (Board Term I, 2014) Answer: Resistance is the property of a conductor to resist the flow of charges through it. Factors affecting resistance of a conductor: Refer to answer 17(i) Rheostat is the device which is often used to change the resistance without changing the voltage source in an electric circuit. We are given, length of wire, l = 50 cm = 50 × 10 -2 m cross-sectional area, A = 0.01 mm² = 0.01 × 10 -6 m² and resistivity, ρ = 5 x 10 -8 Ω m. As, resistance, R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\) ∴ R = \(\left(\frac{5 \times 10^{-8} \times 50 \times 10^{-2}}{0.01 \times 10^{-6}}\right)\) Ω = 2.5 Ω
Question 26. If a person has five resistors each of value \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) Ω, then the maximum resistance he can obtain by connecting them is (a) 1 Ω (b) 5 Ω (c) 10 Ω (d) 25 Ω (2020) Answer: (a) The maximum resistance can be obtained from a group of resistors by connecting them in series. Thus, R s = \(\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}\) 1 Ω
Question 27. The maximum resistance which can be made using four resistors each of 2 Ω is (a) 2 Ω (b) 4 Ω (c) 8 Ω (d) 16 Ω (2020) Answer: (c) : A group of resistors can produce maximum resistance when they all are connected in series. ∴ R s = 2 Ω + 2 Ω + 2 Ω + 2 Ω = 8 Ω
Question 28. The maximum resistance which can be made using four resistors each of resistance \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) Ω is (a) 2 Ω (b) 1 Ω (c) 2.5 Ω (d) 8 Ω (2020) Answer: (a) The maximum resistance can be produced from a group of resistors by connecting them in series. Thus, R s = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) Ω + H \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) Ω + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) Ω + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) Ω = 2 Ω
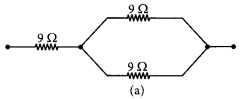
Question 30. List the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with an electrical source instead of connecting them is series. (Board Term I, 2013) Answer: (a) When a number of electrical devices are connected in parallel, each device gets the same potential difference as provided by the battery and it keeps on working even if other devices fail. This is not so in case the devices are connected in series because when one device fails, the circuit is broken and all devices stop working.
(b) Parallel circuit is helpful when each device has different resistance and requires different current for its operation as in this case the current divides itself through different devices. This is not so in series circuit where same current flows through all the devices, irrespective of their resistances.
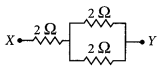
Question 34. (a) A 6 Ω resistance wire is doubled on itself. Calculate the new resistance of the wire. (b) Three 2 Ω resistors A, B and C are connected in such a way that the total resistance of the combination is 3 Ω. Show the arrangement of the three resistors and justify your answer. (2020) Answer: (a) Given resistance of wire, R = 6 Ω Let l be the length of the wire and A be its area of cross-section. Then R = \(\frac { ρl }{ A }\) = 6 Ω Now when the length is doubled, l’ = 2l and A’ = \(\frac { A }{ 2 }\) ∴ R’ = \(\frac{\rho(2 l)}{A / 2}=\frac{4 \rho l}{A}\) = 4 × 6 Ω = 24 Ω
(ii) Since, potential difference across each resistor connected in parallel is same. So, V 1 = V 2 = V 3 = 6 V Applying Ohm’s law, V 1 = I 1 R 1 or I 1 = \(\frac { V_1 }{ R_1 }\) or I 3 = \(\frac { 6 }{ 3 }\) A = 2A Similarly, I 2 = \(\frac { 6A }{ 4 }\) = 1.5 A and I 3 = \(\frac { 6 }{ 6 }\) A = 1 A
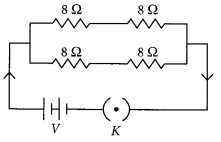
Precautions: (i) All the connections are neat and tight. (ii) Ammeter is connected with the proper polarity, i.e., positive terminal of the ammeter should go to positive terminal and negative terminal of ammeter to the negative terminal of the battery or cell used.
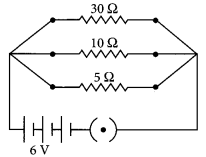
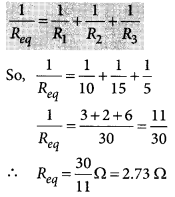
(ii) Total current drawn from battery, I = I 1 + I 2 + I 3 = 0.2 + 0.6 + 1.2 = 2 A (iii) Equivalent resistance of the circuit, R eq can be obtained by Ohm’s law V= I R eq So, 6 V = 2 A × R eq or, R eq = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 }\) = 3 Ω Aliter, \(\frac{1}{R_{e q}}=\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}}+\frac{1}{R_{3}}\) \(\frac{1}{30}+\frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{5}=\frac{1+3+6}{30}=\frac{10}{30}=\frac{1}{3}\) or R eq = 3 Ω
Question 44. The resistance of a resistor is reduced to half of its initial value. In doing so, if other parameters of the circuit remain unchanged, the heating effects in the resistor will become (a) two times (b) half (c) one-fourth (d) four times (2020) Answer: (a) : We know, H = I²Rt = \(\frac { V^2 }{ 4 }\). t Now when, R’ = \(\frac { R }{ 24 }\), V’ = V and t’ = t H’ = \(\frac{V^{\prime 2} t^{\prime}}{R^{\prime}}=\frac{V^{2} t}{R / 2}=\frac{2 V^{2} t}{R}\) = 2H
Question 45. (a) Write the mathematical expression for Joules law of heating. (b) Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in two hours through a potential difference of 40 V. (2020) Answer: (a) The Joule’s law of healing implies that heat produced in a resistor is (i) directly proportional to the square of current lor a given resistance, (ii) directly proportional to resistance for a given current, and (iii) directly proportional to the time for which the current flows through the resistor. i.e., H = I² Rt (b) Given, charge q = 96000 C, time t = 2 h = 7200 s and potential difference V = 40 V We know, H = I²Rt = \(\frac{Q^{2}}{t^{2}} \times \frac{V}{Q}\) × t × t = VQ = 40 × 96000 = 3.84 × 10 6 J = 3.84 MJ
Question 46. Write Joules law of heating. (1/3, 2018) Answer: Refer to answer 45(a).
Question 47. Explain the use of an electric fuse. What type of material is used for fuse wire and why? (Board Term I, 2016) Answer: Electric fuse protects circuits and appliances by stopping the flow of any unduly high electric current. It consists of a piece of wire made of a metal or an alloy of appropriate melting point, for example aluminium, copper, iron, lead etc. If a current larger than the specified value flows through the circuit, the temperature of the fuse wire increases. This melts the fuse wire and breaks the circuit.
Question 48. (a) Why is tungsten used for making bulb filaments of incandescent lamps? (b) Name any two electric devices based on heating effect of electric current. (2/5, Board Term I, 2015) Answer: (a) (i) Tungsten is a strong metal and has high melting point (3380°C). (ii) It emits light at high temperatures (about 2500°C). (b) Electric laundry iron and electric heater are based on heating effect of electric current.
Question 49. A fuse wire melts at 5 A. If it is desired that the fuse wire of same material melt at 10 A, then whether the new fuse wire should be of smaller or larger radius than the earlier one? Give reasons for your answer. (3/5, Board Term I, 2014) Answer: Let the resistance of the wire be R, heat produced in the fuse at 5 A in Is is H=(5)²R ( H – I²Rt) 50. fuse melts at (5)²R joules of heat. Let, the resistance of new wire is R’ So, heat produced in 1 second = (10)²R’ To prevent it from melting (5)²R = (10)²R’ or R’ = \(\frac { R }{ 4 }\) As R ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ A }\) ∴ cross-sectional area of new fuse wire is four times the first fuse. Now, A = πr², so new radius is twice the previous one. So, at 10 A, the new fuse wire of same material and length has larger radius than the earlier one.
Question 50. What is heating effect of current? List two electrical appliances which work on this effect. (2/5, Board Term I, 2013) Answer: If only resislors are connected to the battery, the source energy continually gets dissipated entirely in the form of heal. This is known as healing effect of current, ’file amount of heat (77) produced in time t is given by Joule’s law of heating. H = I²Rt Where, 7 is current flowing through resistor R. The electric laundry iron, electric toaster, electric oven, electric kettle and electric heater are some common devices based on heating effect of current.
Question 51. Two bulbs of 100 W and 40 W are connected in series. The current through the 100 W bulb is 1 A. The current through the 40 W bulb will be (a) 0.4 A (b) 0.6 A (c) 0.8 A (d) 1A (2020) Answer: (d) : Given power of first bulb, P 1 = 100 W and second bulb P 2 = 40 W Current through 100 W bulb, I 1 = 1 A Current through 40 W bulb, I 2 = ? Since both the bulbs are connected in series, the electric current passing through both the bulbs are same i.e., I 2 = 1 A.
Question 52. Write the relation between resistance (R) of filament of a bulb, its power (P) and a constant voltage V applied across it. (Board Term I, 2017) Answer: P = \(\frac { V^2}{ R }\)
Question 53. Power of a lamp is 60 W. Find the energy in joules consumed by it in Is. (Board Term I, 2016) Answer: Here, power of lamp, P = 60 W time, t = 1 s So, energy consumed = Power × time = (60 × 1)J = 60 J
Question 54. Two lamps, one rated 100 W; 220 V, and the other 60 W; 220 V, are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. Find the current drawn by two bulbs from the line, if the supply voltage is 220 V. (2/3, 2018, Board Term I, 2014) Answer: Since both the bulbs are connected in parallel and to a 220 V supply, the voltage across each bulb is 220 V. Then Current drawn by 100 W bulb, I 1 = \(\frac { power rating}{ voltage applied }\) = \(\frac { 100 W}{ 220 V }\) = 0.454 A Current drawn by 60 W bulb, I 2 = \(\frac { 60 W}{ 220 V }\) = 0.273 A Total current drawn from the supply line, I = I 1 + I 2 = 0.454 A + 0.273 A = 0.727 A = 0.73 A
Question 55. How much current will an electric iron draw from a 220 V source if the resistance of its element when hot is 55 ohms? Calculate the wattage of the electric iron when it operates on 220 volts. (Board Term I, 2016) Answer: Here, V = 220 V, R = 55 Ω By Ohm’s law V = IR ∴ 220 = 7 × 55 or I = 4A Wattage of electric iron = Power = \(\frac{V^{2}}{R}=\frac{(220)^{2}}{55}\) = 880 W
Question 56. An electric iron has a rating of 750 W; 200 V. Calculate: (i) the current required. (ii) the resistance of its heating element. (iii) energy consumed by the iron in 2 hours. [Board Term 1, 2015] Answer: Here, P = 750 W, V = 200 V (i) As P = V7 I = P/V= (750/200) A = 3.75A (ii) By Ohm’s law V = IR or R = V/I ∴ R = \(\frac { 200}{ 3.75 }\) Ω = 53.3 Ω (iii) Energy consumed by the iron in 2 hours = P × t = 750 W × 2h = 1.5 kWh or E = (750 × 2 × 3600) J = 5.4 × 10 6 J
Question 57. An electric bulb is connected to a 220 V generator. The current is 2.5 A. Calculate the power of the bulb. (1/3, Board Term I, 2015) Answer: Here, V= 220 V,/= 2.5 A Power of the bulb P = VI = 220 × 2.5 W = 550 W
Question 58. (a) Define power and state its SI unit. (b) A torch bulb is rated 5 V and 500 mA. Calculate its (i) power (ii) resistance (iii) energy consumed when it is lighted for 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) hours. Answer: (a) Power is defined as the rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit. P = VI = I²R = V²/R The SI unit of electric power is watt (W). It is the power consumed by a device that carries 1 A of current when operated at a potential difference of IV. 1 W = 1 volt × 1 ampere = 1 V A
(b) Given, V = 5 V and I = 500 mA = 0.5 A (i) Power, P = V × 7 = 5 × 0.5 = 2.5 W (ii) As, P = \(\frac{V^{2}}{R} \Rightarrow R=\frac{V^{2}}{P}=\frac{25}{2.5}\) = 10 Ω (iii) Given, time t = 2.5 hrs = 9000 s ∴ The energy consumed, E = P × t = 2.5 × 9000 = 2.25 × 10 4 J = 6.25 Watt hour
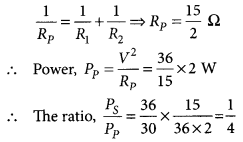
(ii) Potential difference across conductor \(\frac { Total voltage }{ Total resistance }\) × resistance of conductor = \(\frac { 6}{ 24 }\) × 4 = 1 V
(d) Power of the lamp = (current)² × resistance of lamp = (0.25)² × 20 = 1.25 W
Question 62. A bulb is rated 40 W; 220 V. Find the current drawn by it, when it is connected to a 220 V supply. Also find its resistance. If the given bulb is replaced by a bulb of rating 25 W; 220 V, will there be any change in the value of current and resistance? Justify your answer and determine the change. (AI 2019) Answer: In first case, P = 40 W, V = 220 V Current drawn l = \(\frac { P}{ V }\) = \(\frac { 40}{ 220 }\) = 0.18 A Also, resistance of bulb, R = \(\frac{V^{2}}{P}=\frac{(220)^{2}}{40}\) = 1210 Ω In second case, P = 25 W, V = 220 V Current drawn, I = \(\frac { P}{ V }\) = \(\frac { 25}{ 220 }\) = 0.11 A Also, resistance of the bulb, R = \(\frac { V^2}{ P }\) = \(\frac { (220)^2}{ 25 }\) = 1936 Ω Hence, by replacing 40 W bulb to 25 W bulb, having same source of voltage the amount of current flows decreases while resistance increases.
Question 63. (a) How two resistors, with resistances R 1 Ω and R 1 Ω respectively are to be connected to a battery of emf V volts so that the electrical power consumed is minimum? (b) In a house 3 bulbs of 100 watt each lighted for 5 hours daily, 2 fans of 50 watt each used for 10 hours daily and an electric heater of 1.00 kW is used for half an hour daily. Calculate the total energy consumed in a month of 31 days and its cost at the rate of Rs 3.60 per kWh. (Board Term I, 2017) Answer: (a) Power consumed is minimum when current through the circuit is minimum, so the two resistors are connected in series. (b) Power of each bulb P 1 = 100 watt Total power of 3 bulbs, P 1 = 3 × 100 = 300 watt Energy consumed by bulbs in 1 day E 1 = P 1 × t = 300 watt × 5 hours. = 1500 Wh = 1.5 kWh Power of each fan = 50 watt Total power of 2 fans = 2 × 50 watt P 2 = 100 watt Energy consumed by fans in 1 day E 2 = P 2 × t = 100 watt × 10 hours = 1000 watt hour = 1 kWh Energy consumed by heater, E 3 = 1 kW × 1/2 h = 0.5 kWh Total energy consumed in one day E = E 1 + E 2 + E 3 = (1.5 + 1 + 0.5) kWh = 3 kWh Total energy consumed in a month of 31 days = E × 31 = (3 × 31) kWh = 93 kWh Cost of energy consumed = Rs (93 × 3.60) = Rs 334.80
Question 64. (a) An electric bulb is connected to a 220 V generator. If the current drawn by the bulb is 0.50 A, find its power. (b) An electric refrigerator rated 400 W operates 8 hours a day. Calculate the energy per day in kWh. (c) State the difference between kilowatt and kilowatt hour. (3/5, Board Term I, 2013) Answer: (a) Here, V = 220 V, I = 0.50 A Power of the bulb, P = VI = (220 × 0.5)W = 110 W (b) Energy consumed by electric refrigerator in a day = Power x time = 400 W × 8 h = 3200 Wh = 3.2 kWh (c) Kilowatt is unit of power and kilowatt hour is a unit of energy.
Question 65. (i) State one difference between kilowatt and kilowatt hour. Express 1 kWh in joules. (ii) A bulb is rated 5V; 500 mA. Calculate the rated power and resistance of the bulb when it glows. (Board Term I, 2013) Answer: (i) Refer to answer 64(c). 1 kWh = 1000 W × 1 h = 1000 W × 3600 s = 3600000 J = 3.6 × 10 6 J
(ii) Here, V = 5 V, I = 500 mA = 0.5 A Power rating of bulb is P = VI = ( 5 × 0.5)W = 2.5W Resistance of the bulb is R = V/I = (5/0.5) Ω = 10 Ω
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- CBSE Notes For Class 10
- Class 10 Science Notes
- Chapter 12: Electricity
Electricity Class 10 Notes
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 11.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity Notes
Introduction to class 10 electricity.

Chapter Summary Video

Atomic Structure
- An atom has a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons revolving around it.
- Valence electrons in metals are free to move within the conductor and constitute an electric current.
The charge is an intrinsic property of matter by virtue of which it can exert electromagnetic force.

Conductors and Insulators

To know more about Conductors and Insulators, visit here .
Electric Potential and Potential Difference
The electric potential at a point is defined as work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point. The potential difference between two points is defined as the difference in electric potentials at the two given points. The electrons move only if there is a difference in electric pressure called the potential difference. One Volt is defined as energy consumption of one joule per electric charge of one coulomb.
Mathematically, electric potential between two points is given as:
where V is the potential difference, W is the work done, Q is the electric charge.
Electric Current(I)
Flow of electric charges is called electric current, i.e, I = Q / t
To know more about Electric Current, visit here .
Models of Electric Current
Drift velocity of electron.
It is the average velocity that an electron attains inside a metallic conductor due to the application of an electric field due to the potential difference.

Battery and Its Working
A cell is a source of potential difference, which is created inside it due to internal chemical reactions.
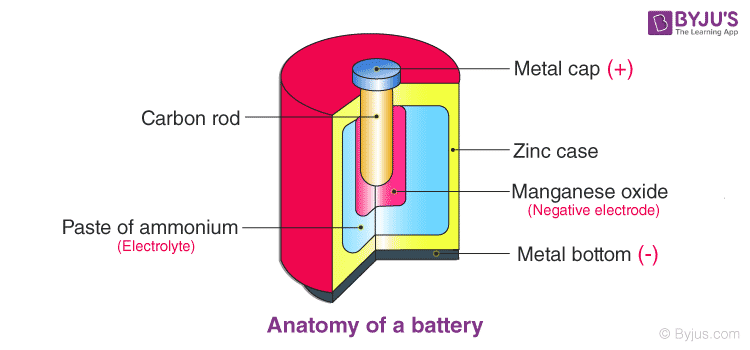
Electric Circuit
Electric circuit and circuit diagram.
- A closed-loop path which a current takes is called an electric circuit.
- The representation of an electric circuit through symbols is called a circuit diagram.

To know more about Electric Circuit, visit here .
Resistance and Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s law.
The current flowing through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the applied potential difference between the two ends of the conductor. Ohm’s Law states the relationship between the potential difference across a conductor and the current through it

For more information on Resistance and Ohm’s Law, watch the below video

To know more about Ohm’s law, visit here .
Resistance is a measure of the opposition offered to the current flow in an electric circuit. Resistance is measured in ohms. All materials resist current flow up to some degree. All materials fall into one of two broad categories: Conductors and Insulators.
Factors Affecting Resistance & How They Affect
Resistance is:
- Directly proportional to the length of the conductor.
- Directly proportional to the nature of the conductor.
- Directly proportional to the temperature of the conductor.
- Inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Mathematically, this is represented as:
For more information on Factors Affecting Resistance, watch the below video

Resistivity
The electrical resistance offered by a substance of unit length and unit cross-sectional area is called resistivity.
Ohmic and Non-Ohmic Resistors
Resistors which follow Ohm’s Law are called Ohmic resistors, and those which do not follow it are called Non-Ohmic resistors.

Superconductors
Conductors which offer zero resistance to the flow of current are called superconductors. Prominent examples of superconductors include aluminium, niobium, magnesium diboride, and cuprates such as yttrium barium, copper oxide and iron pnictides.
Combination of Resistors
- Two resistors are said to be combined in series if they carry the same current.
- Two resistors are said to be combined in parallel if the same potential difference is applied to them.
Equivalent Resistance of a System of Resistors
The equivalent resistance of two resistors is given as:
- In series, R e q = R 1 + R 2
- In parallel, 1/R e q = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2

EMF and Terminal Voltage
- EMF: The potential difference between the two terminals of a cell when there is no current flowing through the circuit.
- Terminal voltage: The potential difference between the two terminals of a cell when current is flowing through the circuit.

Electric Power and AC
Heating effect of current.
Joule’s Law:
- Heat (H) ∝ square of the current (I).
- H ∝ Resistance of the given circuit.
- H ∝ Time (t) for which current flows through the conductor.
When a potential difference is established, it causes electrons to move, i.e. flow of current.
Uses of Heating Effect of Electric Current
The heating effect of current is applied in the working of electrical heating appliances such as electric kettles, electric iron, room heaters, water heaters (geysers), etc. To know more about the Heating Effect of Current, visit here .
Electric Power
- The rate of doing work or the rate of consumption of electrical energy is called Electric Power. If W is work done in time t, then P =W/t .
- S.I. unit is Watt(W). One watt of power is consumed when 1 A of current flows at a potential difference of 1 V.
- The commercial unit of electrical energy is a kilowatt-hour (kWh).
- 1 k W h = 3 , 600 , 000 J = 3.6 × 10 6 J
- Represented as P = I 2 R and P =V 2 /R.
- One kilowatt-hour is defined as the amount of energy consumed when 1kW of power is used for 1 hour.
To know more about Electric Power, visit here .
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 10 Physics Notes Chapter 12 Electricity
What is an electric circuit.
An electric circuit is a path for transmitting electric current. It is used in lamps, motors, computers and many other electronic devices.
What does ‘Ohm’s Law’ state?
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor is proportional to the voltage across the conductor.
What is electric power?
The rate, per unit of time, at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric current is known as electric power.
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment

Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Sample Paper
- Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Audio Books
- NCERT Exempler
- Model Papers
- Past Year Question Paper
- Writing Skill Format
- RD Sharma Solutions
- HC Verma Solutions
- CG Board Solutions
- UP Board Solutions
- Careers Opportunities
- Courses & Career
- Courses after 12th
Home » 10th Class » Class 10 Science Notes for Electricity (PDF) – Study Material
Class 10 Science Notes for Electricity (PDF) – Study Material
Class 10 Science Electricity – Get here the Notes, Question & Practice Paper of Class 10 Science for topic Electricity Notes. Electricity Notes for Class 10 Science are here. You can download the Electricity Notes PDF to study all the topics in this chapter. Moreover the class 10 Science notes include chapter summary, definitions, examples, and key pointers for Electricity . Thus if you are studying class Science (विज्ञान), then the Electricity notes will help you easily understand the topic and ace it.
Class 10 Science Notes for Electricity
Electricity is a critical part in the study of Science . In India, it is taught in class. Therefore the class 10 Notes for Science topic Electricity have been compiled by teachers and field experts. They explain the complete chapter of Electricity in one-shot . Whether you are studying the topic Electricity to complete your class syllabus, or for any competitive exam like JEE , NEET , UPSC, you can simply refer these notes to complete the chapter in one-shot!
Electricity Notes Download Link – Click Here to Download PDF
Electricity Notes for Class 10 Science PDF
The PDF of Electricity class 10 notes is as follows. You can view the document here and also download it to use it anytime for future reference whenever you want to brush up your concepts of Science.

Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 10 with good score can check this article for Notes, Study Material, Practice Paper. Above we provided the link to access the Notes , Important Question and Practice Paper of Class 10 Science for topic Electricity.
All Topics Class 10 Science Notes
Chapter wise notes for Science (विज्ञान) are given below.
- Acid Bases and Salts
- Carbon and Its Compound
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Control and Coordination
- Electricity
- Heredity and Evolution
- How do Organisms Reproduce
- Human Eye and Colorful World
- Life Processes
- Light- Reflection and Refraction
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Management of Natural Resources
- Metals and Non Metals
- Periodic Classifications of Elements
- Science Our Environment
- Sources of Energy
Class 10 Notes for All Subjects
- Class 10 English Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Science Notes
- Class 10 Social Science Notes
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Electricity
The Electricity notes here help you solve the questions and answers . Also, you can complete the class 10 Electricity worksheet using the same. In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions with these class 10 notes .
However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Electricity to get all the answers. Electricity solutions contain questions, answers, and steps to solve all questions.
Notes for All Classes
- Class 7 Notes
- Class 8 Notes
- Class 9 Notes
- Class 10 Notes
- Class 11 Notes
- Class 12 Notes
Electricity Notes for Class 10 Science – An Overview
Class 10 Electricity Notes for All Boards
You can use the class 10 Science notes of Electricity for all boards.
The education boards in India for which Electricity notes are relevant are – CBSE, CISCE, AHSEC, CHSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, PUE Karnataka, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BIEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, TSBIE, COHSEM, WBCHSE .
Therefore you can refer to these notes as CBSE, CISCE, AHSEC, CHSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, PUE Karnataka, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BIEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, TSBIE, COHSEM, WBCHSE notes for class Class 10 / Class / Science for the topic Electricity.
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel .
Class 10 English Notes for The Trees (PDF) – Study Material
Class 10 social science notes for money and credit (pdf) – study material, related posts.

Uttarakhand Board Class 10th Syllabus 2024-25 (PDF) – UK Board Syllabus for Class 10

NCERT Exemplar Class 10
Ncert exemplar class 10 maths unit 4 quadratic equations, ncert exemplar class 10 maths unit 2 polynomials, leave a reply cancel reply, cbse board quick links.
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Papers
- CBSE Question Papers
- CBSE Practice Papers
CISCE Board Quick Links
- CISCE Time Table
- CISCE Results
- CISCE Specimen Papers
- CISCE Syllabus
- CISCE Question Papers
Class Wise Study Material
Board exams 2023.
- Solved Sample Papers
- Revision Notes
- State Board
Study Material
- Class Notes
- Courses After Class 12th
- JEE Main 2024
- Fashion & Design
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
© 2019 aglasem.com
Discover more from AglaSem Schools
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 12 Electricity includes all the intext and exercise questions. Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity NCERT questions and answers help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in Class 10 board exam. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 NCERT Questions and Answers
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity NCERT Questions and Answers are prepared by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Intext Questions
Intext Question (Page No. 200)
Question 1: What does an electric circuit mean?
Answer: A continuous and closed path of an electric current is called an electric circuit. An electric circuit consists of electric power source, wires, switches and electric devices like resistors bulbs etc.
Question 2: Define the unit of current.
Answer: When one-coulomb charge flows through an electric device in a circuit in one second, then the current flowing through the device is said to be one ampere.
Question 3: Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
Answer: Charge on one electron, 𝑒 = 1.6 × 10 − 19 C
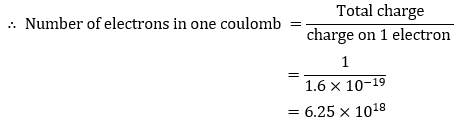
Intext Question (Page No. 202)
Question 1: Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
Answer: Cell or battery maintain potential difference across a conductor.
Question 2: What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V?
Answer: When 1 J of work is done to move a charge of 1 C from one point to another, it is said that the potential difference between two points is 1 V.
Question 3: How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery?
Answer: Potential difference created by battery Δ𝑉 = 6 V
Potential difference between two points in a circuit is defined as energy required (or work done) in moving one coulomb of charge from one point to the other.
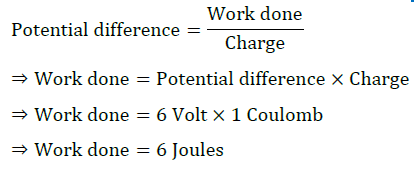
Intext Question (Page No. 209)
Question 1: On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
Answer: The resistance of a resistor depends on
- Properties of the material of conductor, or resistivity of a material
- Length of conductor
- Area of cross-section of the conductor
- The resistivity of a material depends on temperature. Therefore, the resistance of a resistor also depends on the temperature of the conductor.
Question 2: Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source? Why?
Answer: Resistance of a conductor depends on resistivity 𝜌, length 𝑙 and on the area of cross-section 𝐴 as
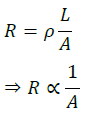
∴ when connected to the same power source, current through thick wire is more compared to thin wire of same material.
Question 3: Let the resistance of an electrical component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
Answer: The change in the current flowing through the electrical component can be determined by Ohm’s Law. According to Ohm’s Law, the current is given by I = V/R Now, the potential difference is reduced to half keeping the resistance constant, Let the new voltage be V’ = V/2
Let the new resistance be R’ = R and the new amount of current be I’.
The change in the current can be determined using Ohm’s law as follows:
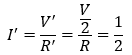
Therefore, the current flowing the electrical component is reduced by half.
Question 4: Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Answer: The resistivity of an alloy is generally higher than that of its constituent metals. Alloys do not oxidize (burn) readily at high temperatures. For this reason, they are commonly used in electrical heating devices, like electric iron, toasters etc.
Question 5: Use the data in Table 12.2 to answer the following – Table 12.2 Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
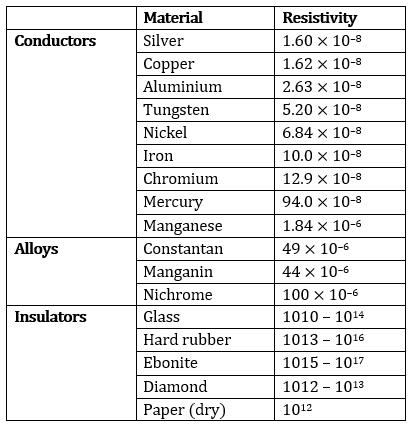
(a) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor? (b) Which material is the best conductor?
Answer: (a) Iron is a better conductor than mercury because the resistivity of mercury is more than the resistivity of iron.
(b) Among all the materials listed in the table, silver is the best conductor because the resistivity of silver is lowest among all, i.e., 1.60 × 10 –8 .
Intext Question (Page No. 213)
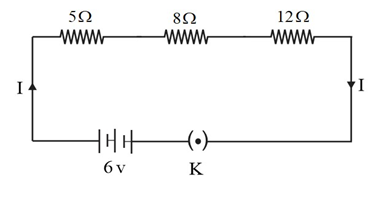
Question 1: Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of 2 V each, a 5 Ω resistor, an 8 Ω resistor, and a 12 Ω resistor, and a plug key, all connected in series.
Question 2: Redraw the circuit of Question 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter?
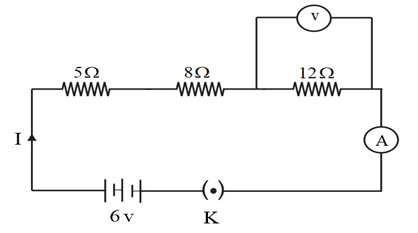
Resisters are connected in series. So, the net resistance in the circuit = 5 Ω + 8 Ω + 12 Ω = 25 Ω Net potential = 6 V
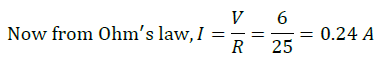
Now for the 12 Ω resistor, current = 0.24 A
So, using Ohm’s law V = 0.24 × 12 V = 2.88 V
Hence, the reading in the ammeter is 0.24 and voltmeter is 2.88.
Intext Question (Page No. 216)
Question 1: Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel –
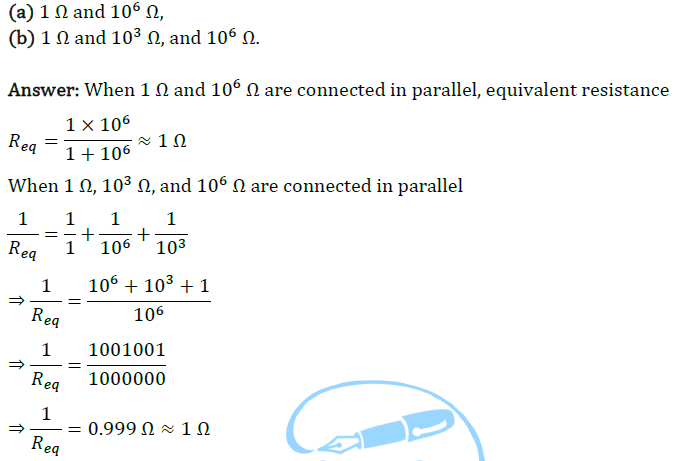
From the above two problems, when very low resistance is connected to very high resistance, the resistance of the combination will be close to low resistance.
Question 2: An electric lamp of 100 Ω, a toaster of resistance 50 Ω, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ω are connected in parallel to a 220 V source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances, and what is the current through it?
To draw the same current resistance of electric iron required is 31.25 Ω and current through it is 7.04 A
Question 3: What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
Answer: To operate properly, different electric devices need a different amount of current. In series combination all the devices get the same current, whereas in parallel combination potential difference across all the resistors is same and current will be distributed according to resistance.
In series combination, if one device fails circuit becomes broken and other devices stop working. Whereas in parallel combination all devices are independently connected to mains, even if one device fails other devices continue to work.
Question 4: How can three resistors of resistances 2 Ω, 3 Ω, and 6 Ω be connected to give a total resistance of (a) 4 Ω, (b) 1 Ω?
Answer: Case 1: The circuit diagram below shows the connection of three resistors
From the circuit above, it is understood that 3 Ω and 6 Ω are connected in parallel. Hence, their equivalent resistance is given by
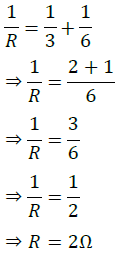
The equivalent resistor 2 Ω is in series with the 2 Ω resistor. Now the equivalent resistance can be calculated as follows: R eq = 2 Ω +2 Ω = 4 Ω Hence, the total resistance of the circuit is 4 Ω.
Case 2: When all resistors are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is,
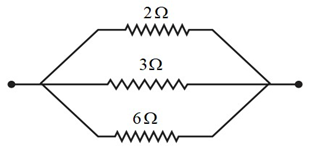
Question 5: What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
Answer: Highest resistance is possible when all resistors are connected in series.
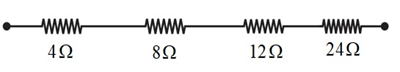
R = 4 Ω + 8 Ω + 12 Ω + 24 Ω = 48 Ω ∴ highest resistance possible is 48 Ω
Lowest resistance is possible when all resistors are connected in parallel
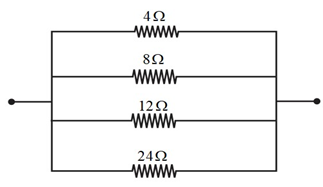
∴ Lowest resistance possible is 2 Ω
Intext Question (Page No. 218)
Question 1: Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
Answer: When the same current flows through the conducting wire and heating element, the heat generated (I 2 Rt) is very high in heating element compared to conducting wire. This is due to the resistance of the heating element is very high compared to the resistance of conducting wire. Thus, when same current flows through the conducting wire and heating element, heating element gets hot and glows.
Question 2: Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulombs of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V.
Answer: From Joule’s law of heating, the heat generated can be written as H = V × I × t where, V is the voltage, V = 50 V I is the current t is the time in seconds, The amount of current can be calculated as follows:
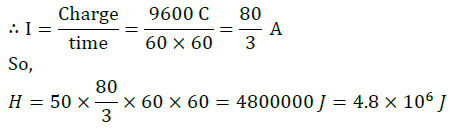
Therefore, the heat generated when 96000 coulomb of charge flows through a potential difference of 50 V is 4.8 × 106 J
Question 3: An electric iron of resistance 20 Ω takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s.
Answer: From Joule’s law of heating, the heat generated can be written as
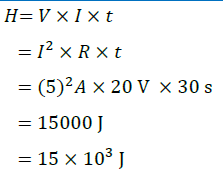
Therefore, the heat generated in 30 s is 15 × 10 3 J
Intext Question (Page No. 220)
Question 1: What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current?
Answer: Electric power is the rate of consumption of electrical energy by electric appliances. Hence, the rate at which energy is delivered by a current is the power of the appliance.
Question 2: An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h.
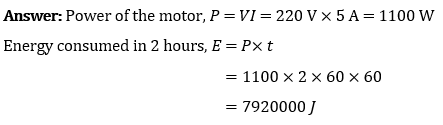
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Exercise Questions
Question 1: A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R′, then the ratio R/R′ is –

Question 2: Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?

Question 3: An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be – (a) 100 𝑊 (b) 75 𝑊 (c) 50 𝑊 (d) 25 𝑊
Answer: (d) 25 𝑊
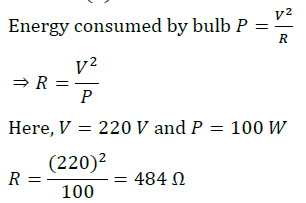
The resistance of the bulb remains constant if the supply voltage is reduced to110 V. If the bulb is operated on 110 V, then the energy consumed by it is given by the expression for power
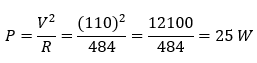
Hence, the option (d) is correct.
Question 4: Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be –
(a) 1:2 (b) 2:1 (c) 1:4 (d) 4:1
Answer: (c) 1:4
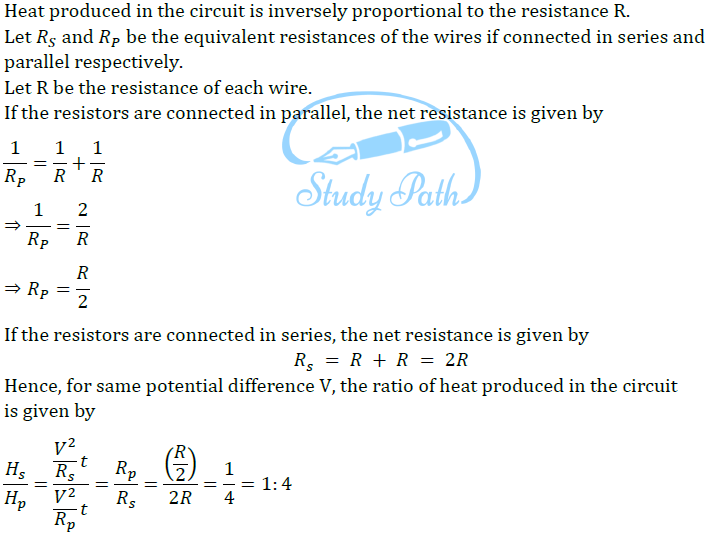
Therefore, the ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations is 1:4. Hence, the option (c) is correct.
Question 5: How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
Answer: Voltmeter is always connected in parallel with circuit element to measure the potential difference across it.
Question 6: A copper wire has a diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10 – 8 Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?

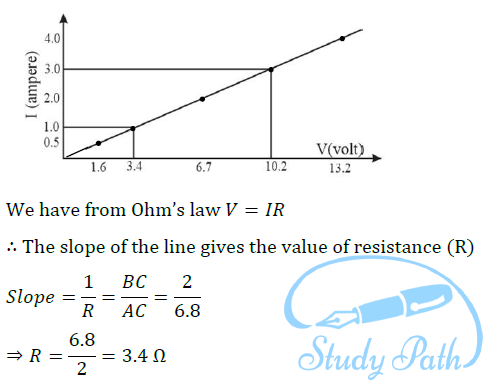
Question 7: The values of current flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference 𝑉 across the resistor are given below –
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
Plot a graph between 𝑉 and 𝐼 and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
Answer: The plot between voltage and current is called VI characteristic. The voltage is plotted on x-axis and current is plotted on y-axis.
Question 8: When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor.
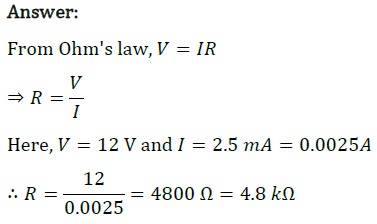
Question 9: A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 Ω, 0.3 Ω, 0.4 Ω, 0.5 Ω and 12 Ω, respectively. How much current would flow through the 12 Ω resistor?
Answer: In series combination current through all the resistors will be the same. Resistance of resistors when connected in series is given by
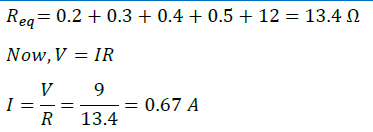
So, the current through the 12 Ω resistor will be same as 0.67 A.
Question 10: How many 176 Ω resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5 A on a 220 V line?
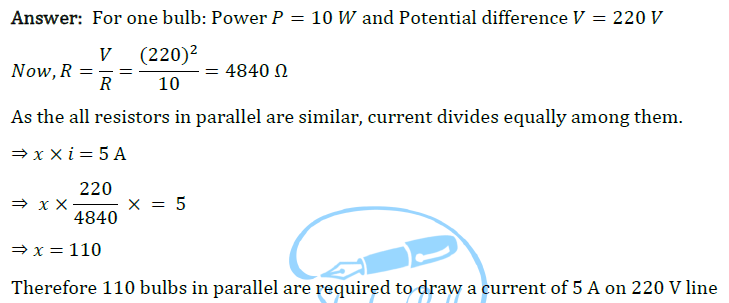
Answer: Let the required number of resistors be 𝑛. Given, Current I = 5A and Potential difference V = 220V Now, from Ohm’s law, V = IR
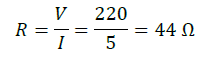
Now for 𝑛 number of resistors of resistance 176 Ω, the equivalent resistance of the resistors connected in parallel is 44 Ω.
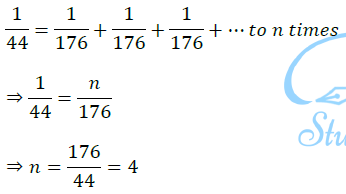
Therefore 4 resistors of 176 Ω are required to draw 5 A current on 220 V line.
Question 11: Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω so that the combination has a resistance of (i) 9 Ω, (ii) 4 Ω.
Answer : If we connect all the three resistors in series, their equivalent resistor would 6 Ω + 6 Ω + 6 Ω =18 Ω, which is not the desired value. Similarly, if we connect all the three resistors in parallel, their equivalent resistor would be
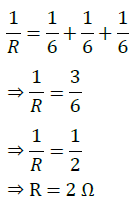
which is again not the desired value. We can obtain the desired value by connecting any two of the resistors in either series or parallel.
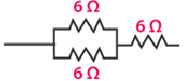
If two resistors are connected in parallel, then their equivalent resistance is
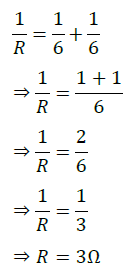
The third resistor is in series, hence the equivalent resistance is calculated as follows: R = 6 Ω + 3 Ω = 9 Ω
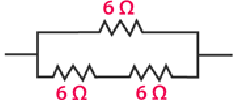
When two resistors are connected in series, their equivalent resistance is given by
R = 6 Ω + 6 Ω = 12 Ω
The third resistor is connected in parallel with 12 Ω. Hence the equivalent resistance is calculated as follows:
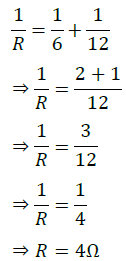
Question 12: Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A?
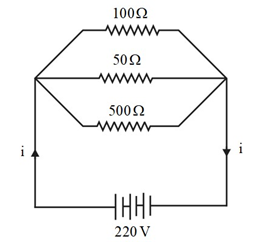
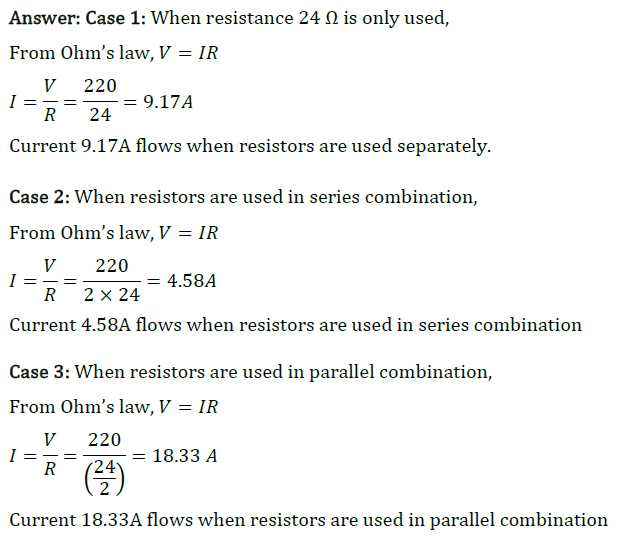
Question 13: A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a 220 V line has two resistance coils A and B, each of 24 Ω resistance, which may be used separately, in series, or in parallel. What are the currents in the three cases?
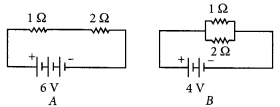
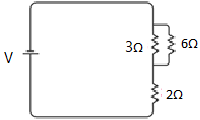
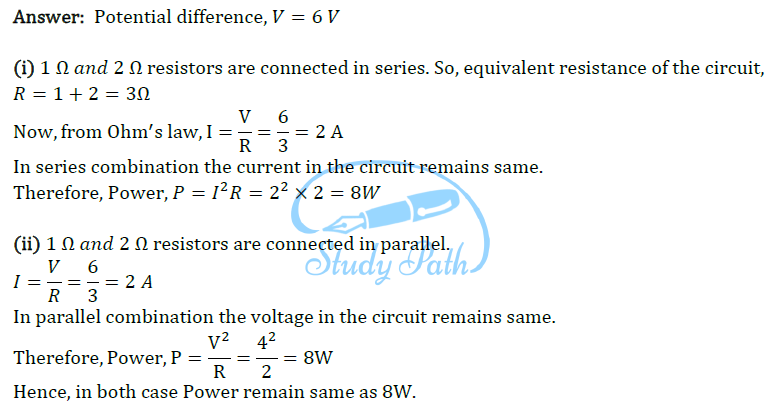
Question 14: Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: (i) a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, and (ii) a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
Question 15: Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V, and the other 60 W at 220 V, are connected in parallel to the electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is 220 V?

Question 16: Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hr, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes?
Answer: Energy consumed by an electrical appliance is given by H = Pt Power rating of TV set is 250 W Energy consumed by TV set 1 hour = 250 × 60 × 60 = 900000 J Power rating of toaster is 1200 W Energy consumed by toaster in 10 minutes = 1200 × 10 × 60 =720000 J Hence, TV set uses more energy than toaster.
Question 17: An electric heater of resistance 8 Ω draws 15 A from the service mains 2 hours. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.

Question 18: Explain the following.
(i) Why is tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
(ii) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
(in) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
(iv) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross-section?
(v) Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
Answer: (i) The tungsten is used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps because it has a very high melting point (3300°C). On passing electricity through tungsten filament, its temperature reaches to 2700°C and it gives heat and light energy without being melted.
(ii) The conductors of electric heating devices such as bread-toasters and electric irons, are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because the resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of pure metal and an alloy does not undergo oxidation (or burn) easily even at high temperature.
(iii) The series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits because in series circuit, if one electrical appliance stops working due to some defect, then all other appliances also stop working because the whole circuit is broken.
(iv) The resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its area of cross-section, i.e., Resistance R ∝ (1/πr 2 ). If the area of cross section of a conductor of fixed length is increased, then resistance decreases because there are more free electrons for movement in conductor.
(v) Copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission because they have very low resistances. So, they do not become too hot on passing electric current.
Topics covered under Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 12.1 | Electric Current and Circuit |
| 12.2 | Electric Potential and Potential Difference |
| 12.3 | Circuit Diagram |
| 12.4 | Ohm’s Law |
| 12.5 | Factors on Which the Resistance of a Conductor Depends |
| 12.6 | Resistance of a System of Resistors |
| 12.7 | Heating Effects of Electric Current |
| 12.8 | Electric Power |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 – A Brief Discussion
Chapter Overview: Electricity has an important place in modern society. It is a controllable and convenient form of energy for a variety of uses in homes, schools, hospitals, industries and so on. In this chapter students will learn about electric current, electric circuit, circuit diagram. This chapter also covers Ohm’s law, resistor etc.
Assignment - Electricity, Class 10, Science PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
FILL IN THE BLANKS
1. The diameter of the atom is of the order of .................. m.
2. The diameter of the nucleus is of the order of ..................... m
3. The negative charge on an electron is ................ C.
4. The sign of charge on a proton is .....................
5. The value of charge on a neutron is ...................
6. Conductors have ................... free electrons.
7. Insulators have ..................... free electrons.
8. Semiconductors have ..................... free electrons.
9. The sign of charge on a body which has gained electrons is .....................
10. The sign of charge on a body which has lost electrons is .....................
11. The charge that produces electric field is called a ..................... charge.
12. The charge that measures the intensity of electric field at a point is called a ................. charge.
13. Electric potential at a point in an electric field is measured as the ..................... done in bringing, a unit positive test charge from infinity to that point.
14. Static electricity is constituted by electric charges ..................... on the surface of a conductor.
15. Current electricity is constituted when the charges ..................... in a conductor.
16. The expression for electric current is .....................
17. The S.I. unit of electric current is .....................
18. The ratio V/I is called .....................
19. S.l. unit of resistance is .....................
20. A voltmeter measures ..................... between two points.
21. An ammeter measures ..................... through a conductor.
22. Resistance increases in .....................combination.
23. Resistance decreases in ..................... combination.
24. In a series combination, resistance increases due to increase in ...................
25. In a parallel combination, resistance decreases due to increase in .....................
26. Watt is the S.I. unit of electrical .....................
27. Joule is the S.I. unit of electrical .....................
28. In series combination, power .....................
29. In parallel combination, power .....................
30. Decrease of power of combination, is due to increase of .....................
31. Increase of power of combination is due to decrease of .....................
32. Filament of an electric bulb of low power has ..................... resistance.
33. The power of an electric bulb which takes 0.25A current at 200V is ..................... W.
34. An electric current heats a conductor due to loss of kinetic energy of .....................
35. For same battery, heating of a wire will ..................... if its resistance is increased.
Mark the statement True (T) or False (F)
1. An electron has a negative charge of 1.6 × 10 _19 C.
2. A neutron has a positive charge of 1.6 × 10 _19 C.
3. Conductors have more free electrons.
4. Insulators have few free electrons.
5. Proton has a positive charge.
6. Neutral atom has no charge.
7. A field charge has its own electric field.
8. The field intensity is measured by the field charge.
9. A point inside an electric field has an electric potential.
10. No work is done in moving a test charge between two points at different potentials.
11. Electric potential is a scalar quantity.
12. Electric field intensity is also a scalar quantity.
13. Electric current is due to flow of electrons.
14. In electric current, electrons flow from positive (higher) to negative (lower) potential.
15. A voltmeter measures electric potential difference between two points.
16. A voltmeter has a low resistance.
17. An ammeter measures electric current flowing through a resistance.
18. An ammeter has a high resistance.
19. In series combination, total resistance is more than the highest resistance.
20. In parallel combination, total resistance lies in between the lowest and the highest resistance.
21. Electrical power is time rate of production or consumption of electrical energy.
22. Kilo-watt-hour is the unit of electrical power.
23. To increase total power, we connect the appliances in parallel.
24. In house light, connecting the appliances in series will be easier and economical.
25. In parallel a 100W bulb glows more than a 25W bulb.
26. In series, a 25W bulb glows less than a 100W bulb.
27. A high power bulb takes more current.
28. A high power bulb has more resistance.
29. More bulbs connected in parallel produce more light.
30. More bulbs connected in series produce more light.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. Write the unit of electric potential.
2. Define the potential at a point.
3. Define the potential difference between two points.
4. A dry cell usually has a small cap at one end and a flat surface at the other end. Which of the two is at a higher potential?
5. Name the instruments used to measure electric current and potential difference respectively. Which of these is connected in series and which is connected in parallel in a circuit?
6. What is the shape of the graph between V and i, where V is the potential difference between the ends of a wire and i is the current in it?
7. Consider the units volt, ohm and ampere. One of them is the same as the product of the other two. Which one is this?
8. Name three electrical appliances in which the heating effect of electric current is used.
9. Two bulbs have ratings 100W, 220V and 60W, 220V. Which one has a greater resistance?
10. You have two resistors of resistances 30W and 60W. What resistances can you get by combining the two?
11. Draw a diagram to show two resistors R 1 and R 2 connected in series.
12. Two resistors of 5W and 10W are connected in series in a circuit. How does the current passing through them compare?
13. A wire of resistance 10W is bent to form a closed circle. What is the resistance across a diameter of the circle?
1. 10 _10 2. 10 _15 3. 1.6 × 10 _19 4. positive 5. zero 6. more 7. No. 8. few
9. negative 10. positive 11. field 12. test 13. work 14. at rest 15. flow
16. I = V/R or q/t 17. ampere 18. resistance 19. ohm 20. potential difference
21. current 22. series 23. parallel 24. length 25. area of cross-section 26. power
27. energy 28. decreases 29. increases 30. resistance
31. resistance 32. more 33. 50 34. electrons 35. decrease.
TRUE AND FALSE
1. True 2. False 3. True 4. False 5. True 6. False 7. True 8. False
9. True 10. False 11. True 12. False 13. True 14. False 15. True 16. False
17. True 18. False 19. True 20. False 21. True 22. False 23. True 24. False
25. True 26. False 27. True 28. False 29. True 30. False
Top Courses for Class 10
FAQs on Assignment - Electricity, Class 10, Science
| 1. What is electricity? |
| 2. What are the sources of electricity? |
| 3. How is electricity generated? |
| 4. What is the difference between AC and DC electricity? |
| 5. How does electricity reach our homes? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
Assignment - Electricity
Study material, sample paper, video lectures, important questions, shortcuts and tricks, viva questions, mock tests for examination, extra questions, semester notes, past year papers, previous year questions with solutions, practice quizzes, objective type questions.

Assignment - Electricity, Class 10, Science Free PDF Download
Importance of assignment - electricity, class 10, science, assignment - electricity, class 10, science notes, assignment - electricity, class 10, science class 10 questions, study assignment - electricity, class 10, science on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
CBSE Class 10 Physics – Electricity -Study Notes
CBSE Class 10 Science CBSE Class 10 Social Science CBSE Class 10 Maths
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Electricity
- Electricity Master File
- Lakhmir Singh Book for Electricity
- Electricity NCERT Book
- Electricity Summary Note
- Ncert Solution for Electricity
- Ncert Exemplar Solution for Electricity
- Past Many Years CBSE Questions and Answer: Electricity
- Lakhmir Singh Solution
- Mindmap and FA
Examples and Exercise
- Assignment 1
- Assignment 2
- Test Paper 1
- Test Paper 2
- Test Paper 3
- Test Paper 4
- Test Paper 5
- Test Paper 6
- Test Paper 7
- Test Paper 8
- Test Paper 9
- Test Paper 10
- Test Paper 11
- Test Paper 12
- Test Paper 13
- Test Paper 14
- Test Paper 15
- Test Paper 16
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Class 10 Science Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 10 Science Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Science . These Assignments for Grade 10 Science cover all important topics which can come in your standard 10 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 10 Science , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 10 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Science Class 10 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Science Class 10. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Science class 10 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 10 Science Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Science Class 10 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 10 Science . Students and teachers can download and save all free Science assignments in Pdf for grade 10th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 10 important questions and answers for Science as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 10 Science and CBSE Assignments for Science Class 10 will be really helpful for standard 10th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 10th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 10 Science Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 10 Science Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Science assignments for Grade 10, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Science textbooks for Class 10 .
- All Science assignments for Class 10 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 10 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Science chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 10 Science question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 10 Science students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Science Class 10 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 10 Science chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Science in Grade 10, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Science Grade 10 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 10 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 10 Mathematics Mensuration Assignments

Class 10 Mathematics Triangles Assignments

Class 10 Mathematics Circles Assignments

COMMENTS
The switch if OFF. Q2. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. ( i ) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. ( ii ) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 − 19 C , then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
Join Now! CBSE Class 10 Electricity Assignment. Download free printable assignments and worksheets of class 10 Science. Free PDF Download- Best collection of notes, important questions , sample papers and NCERT Solution for CBSE Class 10 Science. Below you will find the home work assignment for CBSE Class 10 Electricity.
Portable Document Format (PDF) is a digital copy of the Electricity and electric fields worksheet answers. Through this digital copy, students can access these questions from anywhere. Through solving questions, students can get a brief idea about those questions that can be asked in the CBSE Class 10 Physics exam.
Electricity class 10 NCERT solutions will not only help in board exam preparation but also helps in clearing the competitive exams like Engineering. Also, candidates can find electricity class 10 numericals with solutions which helps candidates solving their assignments. Read on to find out everything NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science ...
Exercise 12.6 - 3 Questions. Exercise 12.7 - 2 Questions. Exercise 12.8 - 18 Questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity PDF is provided here which can be accessed by the students based on their needs. Clear all your doubts with these NCERT Solutions prepared by subject experts at BYJU'S and ace the CBSE exams.
Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 Science Chapter 12. Question 1. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. (i) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. (ii) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 -19 C, then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
The Class 10 science chapter 12, 'Electricity', attempts to answer questions like what constitutes electricity, what are some of the factors that control or regulate the flow of electricity and how electricity flows in an electric circuit. The heating effects of electric current and its applications are also discussed in detail.
Also, you can complete the class 10 Electricity worksheet using the same. In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions with these class 10 notes. However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Electricity to get all the answers.
Answer: Resisters are connected in series. So, the net resistance in the circuit = 5 Ω + 8 Ω + 12 Ω = 25 Ω. Net potential = 6 V. Now for the 12 Ω resistor, current = 0.24 A. So, using Ohm's law V = 0.24 × 12 V = 2.88 V. Hence, the reading in the ammeter is 0.24 and voltmeter is 2.88.
2. When objects are rubbed, a loss and/or gain of electrons occurs, which results in the phenomenon of static electricity. 3. Current electricity is normally controlled, and it is the more used phenomenon of electricity, in countless applications. 4.
Class 10 Science Worksheet for Electricity. Question 1. State Joule's law of heating. list two special characteristics of a heating element wire. An electronic iron consumed energy at the rate of 880 W when heating is at the maximum rate and 440 W when the heating is at the minimum rate.
The "Assignment - Electricity, Class 10, Science Class 10 Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the Class 10 exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge their understanding of the exam topics. These questions cover the entire syllabus, ensuring comprehensive ...
Exam Style questions - Paper 5. Exam Style questions - Paper 6. Exam Style questions - Paper 1. Exam Style questions - Paper 2. Exam Style questions - Paper 4. CBSE Class 10 Physics - Electricity -Study Notes Prepared by CBSE Class 10 Science (Physics, Chemistry, Biology) Subject Matter experts.
Electricity Class 10 Science Notes And Questions. Download Electricity Class 10 Notes PDF and score high in tests. These Electricity Class 10 Notes Physics are prepared by our expert teachers at cbsencertsolutions. Class 10 Electricity Notes assists you with overviewing the chapter in minutes. At exam time, Revision note is one of the best tips ...
July 29, 2021November 2, 2022 admin. We have provided below free printable Class 10 Physics Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Physics. These Assignments for Grade 10 Physics cover all important topics which can come in your standard 10 tests and examinations.
CBSE Class 10 Physics Worksheet - Electricity - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document contains 25 conceptual and numerical questions about electricity on topics such as: - Calculating the number of electrons in a coulomb of charge. - Connecting voltmeters and ammeters in electric circuits and the effects of interchanging their positions.
Download free printable assignments and worksheets of class 10 Science. Free PDF Download- Best collection of notes, important questions , sample papers and NCERT Solution for CBSE Class 10 Science. Below you will find the home work assignment for CBSE Class 10 Electricity. For more exclusive study material for science please click here.
Share the knowledge! Given below are the Class 10 Science Solved Numerical Questions for electricity. Question 1. A wire of length 3 m and area of cross-section 1.7 × 10 -6 m 2 has a resistance 3 × 10 -2 ohm. a. What is the formula for resistivity of the wire and what is the unit of it. b.
July 29, 2021November 2, 2022 admin. We have provided below free printable Class 10 Science Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Science. These Assignments for Grade 10 Science cover all important topics which can come in your standard 10 tests and examinations.
Answer. (b) Q.26. Assertion (A) : If 10 bulbs are connected in series and one bulb fused, then the remaining 9 bulbs will not work. Reason (R) : Bulb of higher wattage will give less bright light. Answer. (b) Q.27. Assertion (A) : Good conductors of heat are also good conductors of electricity and vice versa.
We have provided Class 10 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 12 Electricity Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.