

Four of the biggest problems facing education—and four trends that could make a difference
Eduardo velez bustillo, harry a. patrinos.

In 2022, we published, Lessons for the education sector from the COVID-19 pandemic , which was a follow up to, Four Education Trends that Countries Everywhere Should Know About , which summarized views of education experts around the world on how to handle the most pressing issues facing the education sector then. We focused on neuroscience, the role of the private sector, education technology, inequality, and pedagogy.
Unfortunately, we think the four biggest problems facing education today in developing countries are the same ones we have identified in the last decades .
1. The learning crisis was made worse by COVID-19 school closures
Low quality instruction is a major constraint and prior to COVID-19, the learning poverty rate in low- and middle-income countries was 57% (6 out of 10 children could not read and understand basic texts by age 10). More dramatic is the case of Sub-Saharan Africa with a rate even higher at 86%. Several analyses show that the impact of the pandemic on student learning was significant, leaving students in low- and middle-income countries way behind in mathematics, reading and other subjects. Some argue that learning poverty may be close to 70% after the pandemic , with a substantial long-term negative effect in future earnings. This generation could lose around $21 trillion in future salaries, with the vulnerable students affected the most.
2. Countries are not paying enough attention to early childhood care and education (ECCE)
At the pre-school level about two-thirds of countries do not have a proper legal framework to provide free and compulsory pre-primary education. According to UNESCO, only a minority of countries, mostly high-income, were making timely progress towards SDG4 benchmarks on early childhood indicators prior to the onset of COVID-19. And remember that ECCE is not only preparation for primary school. It can be the foundation for emotional wellbeing and learning throughout life; one of the best investments a country can make.
3. There is an inadequate supply of high-quality teachers
Low quality teaching is a huge problem and getting worse in many low- and middle-income countries. In Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, the percentage of trained teachers fell from 84% in 2000 to 69% in 2019 . In addition, in many countries teachers are formally trained and as such qualified, but do not have the minimum pedagogical training. Globally, teachers for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects are the biggest shortfalls.
4. Decision-makers are not implementing evidence-based or pro-equity policies that guarantee solid foundations
It is difficult to understand the continued focus on non-evidence-based policies when there is so much that we know now about what works. Two factors contribute to this problem. One is the short tenure that top officials have when leading education systems. Examples of countries where ministers last less than one year on average are plentiful. The second and more worrisome deals with the fact that there is little attention given to empirical evidence when designing education policies.
To help improve on these four fronts, we see four supporting trends:
1. Neuroscience should be integrated into education policies
Policies considering neuroscience can help ensure that students get proper attention early to support brain development in the first 2-3 years of life. It can also help ensure that children learn to read at the proper age so that they will be able to acquire foundational skills to learn during the primary education cycle and from there on. Inputs like micronutrients, early child stimulation for gross and fine motor skills, speech and language and playing with other children before the age of three are cost-effective ways to get proper development. Early grade reading, using the pedagogical suggestion by the Early Grade Reading Assessment model, has improved learning outcomes in many low- and middle-income countries. We now have the tools to incorporate these advances into the teaching and learning system with AI , ChatGPT , MOOCs and online tutoring.
2. Reversing learning losses at home and at school
There is a real need to address the remaining and lingering losses due to school closures because of COVID-19. Most students living in households with incomes under the poverty line in the developing world, roughly the bottom 80% in low-income countries and the bottom 50% in middle-income countries, do not have the minimum conditions to learn at home . These students do not have access to the internet, and, often, their parents or guardians do not have the necessary schooling level or the time to help them in their learning process. Connectivity for poor households is a priority. But learning continuity also requires the presence of an adult as a facilitator—a parent, guardian, instructor, or community worker assisting the student during the learning process while schools are closed or e-learning is used.
To recover from the negative impact of the pandemic, the school system will need to develop at the student level: (i) active and reflective learning; (ii) analytical and applied skills; (iii) strong self-esteem; (iv) attitudes supportive of cooperation and solidarity; and (v) a good knowledge of the curriculum areas. At the teacher (instructor, facilitator, parent) level, the system should aim to develop a new disposition toward the role of teacher as a guide and facilitator. And finally, the system also needs to increase parental involvement in the education of their children and be active part in the solution of the children’s problems. The Escuela Nueva Learning Circles or the Pratham Teaching at the Right Level (TaRL) are models that can be used.
3. Use of evidence to improve teaching and learning
We now know more about what works at scale to address the learning crisis. To help countries improve teaching and learning and make teaching an attractive profession, based on available empirical world-wide evidence , we need to improve its status, compensation policies and career progression structures; ensure pre-service education includes a strong practicum component so teachers are well equipped to transition and perform effectively in the classroom; and provide high-quality in-service professional development to ensure they keep teaching in an effective way. We also have the tools to address learning issues cost-effectively. The returns to schooling are high and increasing post-pandemic. But we also have the cost-benefit tools to make good decisions, and these suggest that structured pedagogy, teaching according to learning levels (with and without technology use) are proven effective and cost-effective .
4. The role of the private sector
When properly regulated the private sector can be an effective education provider, and it can help address the specific needs of countries. Most of the pedagogical models that have received international recognition come from the private sector. For example, the recipients of the Yidan Prize on education development are from the non-state sector experiences (Escuela Nueva, BRAC, edX, Pratham, CAMFED and New Education Initiative). In the context of the Artificial Intelligence movement, most of the tools that will revolutionize teaching and learning come from the private sector (i.e., big data, machine learning, electronic pedagogies like OER-Open Educational Resources, MOOCs, etc.). Around the world education technology start-ups are developing AI tools that may have a good potential to help improve quality of education .
After decades asking the same questions on how to improve the education systems of countries, we, finally, are finding answers that are very promising. Governments need to be aware of this fact.
To receive weekly articles, sign-up here

Consultant, Education Sector, World Bank

Senior Adviser, Education
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

History of Chichén Itzá written in DNA

Examining the duality of Israel

One way to help big groups of students? Volunteer tutors.
How covid taught america about inequity in education.
Harvard Correspondent
Remote learning turned spotlight on gaps in resources, funding, and tech — but also offered hints on reform

“Unequal” is a multipart series highlighting the work of Harvard faculty, staff, students, alumni, and researchers on issues of race and inequality across the U.S. This part looks at how the pandemic called attention to issues surrounding the racial achievement gap in America.
The pandemic has disrupted education nationwide, turning a spotlight on existing racial and economic disparities, and creating the potential for a lost generation. Even before the outbreak, students in vulnerable communities — particularly predominately Black, Indigenous, and other majority-minority areas — were already facing inequality in everything from resources (ranging from books to counselors) to student-teacher ratios and extracurriculars.
The additional stressors of systemic racism and the trauma induced by poverty and violence, both cited as aggravating health and wellness as at a Weatherhead Institute panel , pose serious obstacles to learning as well. “Before the pandemic, children and families who are marginalized were living under such challenging conditions that it made it difficult for them to get a high-quality education,” said Paul Reville, founder and director of the Education Redesign Lab at the Harvard Graduate School of Education (GSE).
Educators hope that the may triggers a broader conversation about reform and renewed efforts to narrow the longstanding racial achievement gap. They say that research shows virtually all of the nation’s schoolchildren have fallen behind, with students of color having lost the most ground, particularly in math. They also note that the full-time reopening of schools presents opportunities to introduce changes and that some of the lessons from remote learning, particularly in the area of technology, can be put to use to help students catch up from the pandemic as well as to begin to level the playing field.
The disparities laid bare by the COVID-19 outbreak became apparent from the first shutdowns. “The good news, of course, is that many schools were very fast in finding all kinds of ways to try to reach kids,” said Fernando M. Reimers , Ford Foundation Professor of the Practice in International Education and director of GSE’s Global Education Innovation Initiative and International Education Policy Program. He cautioned, however, that “those arrangements don’t begin to compare with what we’re able to do when kids could come to school, and they are particularly deficient at reaching the most vulnerable kids.” In addition, it turned out that many students simply lacked access.
“We’re beginning to understand that technology is a basic right. You cannot participate in society in the 21st century without access to it,” says Fernando Reimers of the Graduate School of Education.
Stephanie Mitchell/Harvard file photo
The rate of limited digital access for households was at 42 percent during last spring’s shutdowns, before drifting down to about 31 percent this fall, suggesting that school districts improved their adaptation to remote learning, according to an analysis by the UCLA Center for Neighborhood Knowledge of U.S. Census data. (Indeed, Education Week and other sources reported that school districts around the nation rushed to hand out millions of laptops, tablets, and Chromebooks in the months after going remote.)
The report also makes clear the degree of racial and economic digital inequality. Black and Hispanic households with school-aged children were 1.3 to 1.4 times as likely as white ones to face limited access to computers and the internet, and more than two in five low-income households had only limited access. It’s a problem that could have far-reaching consequences given that young students of color are much more likely to live in remote-only districts.
“We’re beginning to understand that technology is a basic right,” said Reimers. “You cannot participate in society in the 21st century without access to it.” Too many students, he said, “have no connectivity. They have no devices, or they have no home circumstances that provide them support.”
The issues extend beyond the technology. “There is something wonderful in being in contact with other humans, having a human who tells you, ‘It’s great to see you. How are things going at home?’” Reimers said. “I’ve done 35 case studies of innovative practices around the world. They all prioritize social, emotional well-being. Checking in with the kids. Making sure there is a touchpoint every day between a teacher and a student.”
The difference, said Reville, is apparent when comparing students from different economic circumstances. Students whose parents “could afford to hire a tutor … can compensate,” he said. “Those kids are going to do pretty well at keeping up. Whereas, if you’re in a single-parent family and mom is working two or three jobs to put food on the table, she can’t be home. It’s impossible for her to keep up and keep her kids connected.
“If you lose the connection, you lose the kid.”
“COVID just revealed how serious those inequities are,” said GSE Dean Bridget Long , the Saris Professor of Education and Economics. “It has disproportionately hurt low-income students, students with special needs, and school systems that are under-resourced.”
This disruption carries throughout the education process, from elementary school students (some of whom have simply stopped logging on to their online classes) through declining participation in higher education. Community colleges, for example, have “traditionally been a gateway for low-income students” into the professional classes, said Long, whose research focuses on issues of affordability and access. “COVID has just made all of those issues 10 times worse,” she said. “That’s where enrollment has fallen the most.”
In addition to highlighting such disparities, these losses underline a structural issue in public education. Many schools are under-resourced, and the major reason involves sources of school funding. A 2019 study found that predominantly white districts got $23 billion more than their non-white counterparts serving about the same number of students. The discrepancy is because property taxes are the primary source of funding for schools, and white districts tend to be wealthier than those of color.
The problem of resources extends beyond teachers, aides, equipment, and supplies, as schools have been tasked with an increasing number of responsibilities, from the basics of education to feeding and caring for the mental health of both students and their families.
“You think about schools and academics, but what COVID really made clear was that schools do so much more than that,” said Long. A child’s school, she stressed “is social, emotional support. It’s safety. It’s the food system. It is health care.”
“You think about schools and academics” … but a child’s school “is social, emotional support. It’s safety. It’s the food system. It is health care,” stressed GSE Dean Bridget Long.
Rose Lincoln/Harvard file photo
This safety net has been shredded just as more students need it. “We have 400,000 deaths and those are disproportionately affecting communities of color,” said Long. “So you can imagine the kids that are in those households. Are they able to come to school and learn when they’re dealing with this trauma?”
The damage is felt by the whole families. In an upcoming paper, focusing on parents of children ages 5 to 7, Cindy H. Liu, director of Harvard Medical School’s Developmental Risk and Cultural Disparities Laboratory , looks at the effects of COVID-related stress on parent’ mental health. This stress — from both health risks and grief — “likely has ramifications for those groups who are disadvantaged, particularly in getting support, as it exacerbates existing disparities in obtaining resources,” she said via email. “The unfortunate reality is that the pandemic is limiting the tangible supports [like childcare] that parents might actually need.”
Educators are overwhelmed as well. “Teachers are doing a phenomenal job connecting with students,” Long said about their performance online. “But they’ve lost the whole system — access to counselors, access to additional staff members and support. They’ve lost access to information. One clue is that the reporting of child abuse going down. It’s not that we think that child abuse is actually going down, but because you don’t have a set of adults watching and being with kids, it’s not being reported.”
The repercussions are chilling. “As we resume in-person education on a normal basis, we’re dealing with enormous gaps,” said Reville. “Some kids will come back with such educational deficits that unless their schools have a very well thought-out and effective program to help them catch up, they will never catch up. They may actually drop out of school. The immediate consequences of learning loss and disengagement are going to be a generation of people who will be less educated.”
There is hope, however. Just as the lockdown forced teachers to improvise, accelerating forms of online learning, so too may the recovery offer options for educational reform.
The solutions, say Reville, “are going to come from our community. This is a civic problem.” He applauded one example, the Somerville, Mass., public library program of outdoor Wi-Fi “pop ups,” which allow 24/7 access either through their own or library Chromebooks. “That’s the kind of imagination we need,” he said.
On a national level, he points to the creation of so-called “Children’s Cabinets.” Already in place in 30 states, these nonpartisan groups bring together leaders at the city, town, and state levels to address children’s needs through schools, libraries, and health centers. A July 2019 “ Children’s Cabinet Toolkit ” on the Education Redesign Lab site offers guidance for communities looking to form their own, with sample mission statements from Denver, Minneapolis, and Fairfax, Va.
Already the Education Redesign Lab is working on even more wide-reaching approaches. In Tennessee, for example, the Metro Nashville Public Schools has launched an innovative program, designed to provide each student with a personalized education plan. By pairing these students with school “navigators” — including teachers, librarians, and instructional coaches — the program aims to address each student’s particular needs.
“This is a chance to change the system,” said Reville. “By and large, our school systems are organized around a factory model, a one-size-fits-all approach. That wasn’t working very well before, and it’s working less well now.”
“Students have different needs,” agreed Long. “We just have to get a better understanding of what we need to prioritize and where students are” in all aspects of their home and school lives.
“By and large, our school systems are organized around a factory model, a one-size-fits-all approach. That wasn’t working very well before, and it’s working less well now,” says Paul Reville of the GSE.
Already, educators are discussing possible responses. Long and GSE helped create The Principals’ Network as one forum for sharing ideas, for example. With about 1,000 members, and multiple subgroups to address shared community issues, some viable answers have begun to emerge.
“We are going to need to expand learning time,” said Long. Some school systems, notably Texas’, already have begun discussing extending the school year, she said. In addition, Long, an internationally recognized economist who is a member of the National Academy of Education and the MDRC board, noted that educators are exploring innovative ways to utilize new tools like Zoom, even when classrooms reopen.
“This is an area where technology can help supplement what students are learning, giving them extra time — learning time, even tutoring time,” Long said.
Reimers, who serves on the UNESCO Commission on the Future of Education, has been brainstorming solutions that can be applied both here and abroad. These include urging wealthier countries to forgive loans, so that poorer countries do not have to cut back on basics such as education, and urging all countries to keep education a priority. The commission and its members are also helping to identify good practices and share them — globally.
Innovative uses of existing technology can also reach beyond traditional schooling. Reimers cites the work of a few former students who, working with Harvard Global Education Innovation Initiative, HundrED , the OECD Directorate for Education and Skills , and the World Bank Group Education Global Practice, focused on podcasts to reach poor students in Colombia.
They began airing their math and Spanish lessons via the WhatsApp app, which was widely accessible. “They were so humorous that within a week, everyone was listening,” said Reimers. Soon, radio stations and other platforms began airing the 10-minute lessons, reaching not only children who were not in school, but also their adult relatives.
Share this article
You might like.
Research using new method upends narrative on ritual sacrifices, yields discovery on resistance built to colonial-era epidemics

Expert in law, ethics traces history, increasing polarization, steps to bolster democratic process

Research finds low-cost, online program yields significant results
More than a planetary fender-bender
New study finds Earth collided with dense interstellar cloud, possibly affecting life on planet
Alzheimer’s disease indicators track with biological changes in brain, study finds
Researchers see self-reported memory loss may be early, preclinical warning
Testing fitness of aging brain
Most voters back cognitive exams for older politicians. What do they measure?
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Subscribe to NPR Ed Newsletter

Alex Stamos, the former director of the Stanford Internet Observatory, during congressional testimony in 2014. The research team Stamos led came under fire from Republicans, who alleged that their research amounted to censorship. Win McNamee/Getty Images hide caption
Untangling Disinformation
A major disinformation research team's future is uncertain after political attacks.
June 14, 2024 • The Stanford Internet Observatory studied how social media platforms are abused. Now, its top leaders are out and future funding is uncertain amid attacks on its work by conservatives.

Selma Herndon Elementary School kindergarten teacher Diana Dickey starts the day each morning by asking students to share how they are feeling. Preston Gannaway for NPR hide caption
Kindergartners are missing a lot of school. This district has a fix
June 14, 2024 • In many places, kindergartners are as likely to be chronically absent as high school seniors, but one school district in rural California is doing something about it.
A California school is addressing chronic absenteeism at the root

On college campuses, women are making inroads in male-dominated fields like engineering and business. But that is not eliminating the earnings gaps in leadership and income in the workplace. Ania Siniuk for NPR hide caption
While women outnumber men on campus, their later earnings remain stuck
Hechinger report.
June 13, 2024 • On college campuses, women are making inroads in male-dominated fields like engineering and business. But that is not eliminating the earnings gaps in leadership and income in the workplace.
NPR Student Podcast Challenge

Starting Your Podcast: A Guide For Students
New to podcasting? Don't panic.

Librarian Sabrina Jesram arranges a display of books during Banned Books Week at a public library branch in New York City on Sept. 23, 2022. Ted Shaffrey/AP hide caption
Book News & Features
What’s a book ban anyway depends on who you ask.
June 10, 2024 • The term "book ban" is used a lot in media and elsewhere when addressing the rise in challenges to certain books being allowed in schools and public libraries. But is it more political hyperbole or a censorship alarm bell?

LA Johnson/NPR hide caption
Pandemic aid for schools is ending soon. Many after-school programs may go with it
June 10, 2024 • Once the federal money expires, one Tulsa organization estimates its after-school program offerings will shrink from 450 to just 75. That's unless they can find outside funding.
[StateImpact OK] ESSER after-school programs

Students continue to miss large amounts of school, but parents aren't concerned. Yunyi Dai for NPR hide caption
With 'chronic absenteeism' soaring in schools, most parents aren’t sure what it is
June 10, 2024 • Experts and educators are worried about students who miss big chunks of the school year, but a new NPR/Ipsos poll shows parents aren’t quite sure what it is.
Some states are seeing chronic absenteeism soar to more than 40% of students

Students listen to their teacher during their first day of transitional kindergarten at Tustin Ranch Elementary School in Tustin, CA, in August 2021. MediaNews Group via Getty Images hide caption
Consider This from NPR
Covid funding is ending for schools. what will it mean for students.
June 9, 2024 • Billions of dollars in federal COVID funding is set to expire for K-12 schools.

Janelle Monáe gives a commencement speech at Loyola Marymount University's 2024 Graduate ceremony. JC Olivera/Getty Images hide caption
All Songs Considered
Advice for graduates: listeners share songs, lessons from high school.
June 4, 2024 • Listeners share songs that take them back to the final days of high school, and the lessons they impart.

Bruhat Soma, 12, of Tampa, Fla., stands on stage with his family after winning the Scripps National Spelling Bee, in Oxon Hill, Md., on Thursday night. Mariam Zuhaib/AP hide caption
A 12-year-old from Florida has won this year's Scripps National Spelling Bee
May 31, 2024 • Bruhat Soma spelled 29 out of 30 words correctly in Scripps’ second-ever spell-off, in which competitors have 90 seconds to spell as many words given to them as possible.

Florida A&M University announced a "transformative" donation earlier this month — but the school said it ceased contact with the donor after questions arose about the funds. Jeffrey Greenberg/Universal Images Group via Getty Images hide caption
A mega-gift for an HBCU college fell through. Here's what happened — and what's next
May 24, 2024 • To people who watch high-level philanthropy, Florida A&M's embarrassing incident wasn't only a shocking reversal. It was something they've seen before. The school is now investigating what went wrong.

Due to the success of the State Department's J-1 Visa program, the Kuspuk School District and other rural districts in Alaska are looking at ways to utilize other visa programs to keep foreign teachers in classrooms for longer. Emily Schwing for NPR/Emily Schwing hide caption
Visa program draws foreign teachers to a rural Alaska school district facing a staffing crisis
Kyuk service.
May 24, 2024 • Teacher retention and recruitment is difficult and some schools make use of J-1 Visas to recruit teachers from outside the U.S. In one rural school district in Alaska, foreign teachers make up over half the staff.

Robert Hale gives an envelope with cash to a graduating UMass Dartmouth student at last week's commencement. Each of the 1,200 graduates received $1,000 onstage, half to keep and half to donate. Karl Christoff Dominey/University of Massachusetts Dartmouth hide caption
A billionaire surprised graduates onstage with cash, but it's not all theirs to keep
May 23, 2024 • Billionaire philanthropist Rob Hale gave UMass Dartmouth graduates $1,000 each, and instructed them to donate half. He tells NPR the best cause students can support is one that matters to them.
U-Mass Dartmouth graduates got a surprise gift from a billionaire at graduation

From left: Alexis Jones (Cornell University), Mei Lamison (New York University), Anaka Srinivas (Northwestern University). Alexis Jones; Mei Lamison; Anaka Srinivas hide caption
A concentrated dose of history: The class of 2024 looks back
May 22, 2024 • Everyone says you live through history, but "I don't think anyone prepared us for this much history," say the students in the Class of 2024.
Student Podcast Challenge
May 22, 2024 • Student Podcast Challenge invites students from around the country to create a podcast and compete for a chance to have your work featured on NPR.

Pedestrians pass through The Ohio State University's student union. John Minchillo/AP hide caption
Ohio reviewing race-based scholarships after Supreme Court affirmative action ruling
May 18, 2024 • Higher education officials in Ohio are reviewing race-based scholarships after last year's Supreme Court ruling on affirmative action.

Michelle Perez for NPR hide caption
These teens were missing too much school. Here's what it took to get them back
May 18, 2024 • Since the pandemic, chronic absenteeism in the nation's K-12 schools has skyrocketed. These teens are working to get their attendance back on track.

Perspective
Code switch, in a debate over a school name, it's not just parents who are attached to the past.
May 18, 2024 • At the height of the racial reckoning, a school district in Virginia voted to rename two schools that had been previously named for Confederate generals. This month, that decision was reversed.

Basil Rodriguez was arrested linking arms outside Hamilton Hall, but said the arrest had strengthened their resolve to continue protesting. The trespassing charge Rodriguez faced was dismissed this week. Keren Carrión/NPR hide caption
Campus protests over the Gaza war
Arrested. injured. suspended. six nyc university students say they'll keep protesting.
May 18, 2024 • Students arrested at Columbia University and the City College of New York spoke with NPR about their choice to risk legal and academic consequences.

Des Moines Superintendent Ian Roberts races students on an Iowa track. Phil Roeder/Des Moines Public Schools hide caption
Iowa superintendent and former Olympian bested in footrace by 5th-grader
May 18, 2024 • Ian Roberts has competed in some of the most high-profile races in the world. But his biggest competition to date was a determined fifth-grader in jean shorts and Nike tennis shoes.

Earlier this month, President Biden spoke about protests that have roiled many U.S. college campuses. Among their demands is for the Israeli military to leave Gaza. Biden said students have a right to protest but not to be disruptive. He is set to speak at Morehouse College in Atlanta on Sunday. Drew Angerer/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Biden is set for the Morehouse graduation. Students are divided
May 17, 2024 • Ahead of Biden's address at Morehouse, students share their frustrations

Applicants to Georgia State University received a welcome email for the 2024-25 school year. However, the email was sent in error to 1,500 applicants by the school's admissions office. Here, the campus celebrates its fall commencement exercises on Dec. 17, 2014, in Atlanta. Meg Buscema/Georgia State University hide caption
1,500 college applicants thought they were accepted. They soon learned it was an error
May 16, 2024 • Georgia State University says the students were not sent an official acceptance letter but "communication" from a department welcoming those who intend to major in a specific academic area.

Kansas City Chiefs player Harrison Butker, pictured at a press conference in February, is in hot water for his recent commencement speech at Benedictine College in Kansas. Chris Unger/Getty Images hide caption
The NFL responds after a player urges female college graduates to become homemakers
May 16, 2024 • Harrison Butker of the Kansas City Chiefs urged female graduates to embrace the title of "homemaker" in a controversial commencement speech. The NFL says he was speaking "in his personal capacity."

Announcing the 2023 College Podcast Challenge Honorable Mentions
May 15, 2024 • Here are the honorable mentions from the 2023 College Podcast Challenge. Congrats!

Fahmida Azim for NPR hide caption
Why children with disabilities are missing school and losing skills
May 15, 2024 • A special education staffing crisis is raging through many U.S. school districts. It's taking a toll on students and families.
The alarming state of the American student in 2022
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, robin lake and robin lake director, center on reinventing public education - arizona state university @rbnlake travis pillow travis pillow innovation fellow, center on reinventing public education - arizona state university @travispillow.
November 1, 2022
The pandemic was a wrecking ball for U.S. public education, bringing months of school closures, frantic moves to remote instruction, and trauma and isolation.
Kids may be back at school after three disrupted years, but a return to classrooms has not brought a return to normal. Recent results from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) showed historic declines in American students’ knowledge and skills and widening gaps between the highest- and lowest-scoring students.
But even these sobering results do not tell us the whole story.
After nearly three years of tracking pandemic response by U.S. school systems and synthesizing knowledge about the impacts on students, we sought to establish a baseline understanding of the contours of the crisis: What happened and why, and where do we go from here?
This first annual “ State of the American Student ” report synthesizes nearly three years of research on the academic, mental health, and other impacts of the pandemic and school closures.
It outlines the contours of the crisis American students have faced during the COVID-19 pandemic and begins to chart a path to recovery and reinvention for all students—which includes building a new and better approach to public education that ensures an educational crisis of this magnitude cannot happen again.
The state of American students as we emerge from the pandemic is still coming into focus, but here’s what we’ve learned (and haven’t yet learned) about where COVID-19 left us:
1. Students lost critical opportunities to learn and thrive.
• The typical American student lost several months’ worth of learning in language arts and more in mathematics.
• Students suffered crushing increases in anxiety and depression. More than one in 360 U.S. children lost a parent or caregiver to COVID-19.
• Students poorly served before the pandemic were profoundly left behind during it, including many with disabilities whose parents reported they were cut off from essential school and life services.
This deeply traumatic period threatens to reverberate for decades. The academic, social, and mental-health needs are real, they are measurable, and they must be addressed quickly to avoid long-term consequences to individual students, the future workforce, and society.
2. The average effects from COVID mask dire inequities and widely varied impact.
Some students are catching up, but time is running out for others. Every student experienced the pandemic differently, and there is tremendous variation from student to student, with certain populations—namely, Black, Hispanic, and low-income students, as well as other vulnerable populations—suffering the most severe impacts.
The effects were more severe where campuses stayed closed longer. American students are experiencing a K-shaped recovery, in which gaps between the highest- and lowest-scoring students, already growing before the pandemic, are widening into chasms. In the latest NAEP results released in September , national average scores fell five times as much in reading, and four times as much in math, for the lowest-scoring 10 percent of nine-year-olds as they had for the highest-scoring 10 percent.
At the pace of recovery we are seeing today, too many students of all races and income levels will graduate in the coming years without the skills and knowledge needed for college and careers.
3. What we know at this point is incomplete. The situation could be significantly worse than the early data suggest.
The data and stories we have to date are enough to warrant immediate action, but there are serious holes in our understanding of how the pandemic has affected various groups of students, especially those who are typically most likely to fall through the cracks in the American education system.
We know little about students with complex needs, such as those with disabilities and English learners. We still know too little about the learning impacts in non-tested subjects, such as science, civics, and foreign languages. And while psychologists , educators , and the federal government are sounding alarms about a youth mental health crisis, systematic measures of student wellbeing remain hard to come by.
We must acknowledge that what we know at this point is incomplete, since the pandemic closures and following recovery have been so unprecedented in recent times. It’s possible that as we continue to dig into the evidence on the pandemic’s impacts, some student groups or subjects may have not been so adversely affected. Alternatively, the situation could be significantly worse than the early data suggest. Some students are already bouncing back quickly. But for others, the impact could grow worse over time.
In subjects like math, where learning is cumulative, pandemic-related gaps in students’ learning that emerged during the pandemic could affect their ability to grasp future material. In some states, test scores fell dramatically for high schoolers nearing graduation. Shifts in these students’ academic trajectories could affect their college plans—and the rest of their lives. And elevated rates of chronic absenteeism suggest some students who disconnected from school during the pandemic have struggled to reconnect since.
4. The harms students experienced can be traced to a rigid and inequitable system that put adults, not students, first.
• Despite often heroic efforts by caring adults, students and families were cut off from essential support, offered radically diminished learning opportunities, and left to their own devices to support learning.
• Too often, partisan politics, not student needs , drove decision-making.
• Students with complexities and differences too often faced systems immobilized by fear and a commitment to sameness rather than prioritization and problem-solving.
So, what can we do to address the situation we’re in?
Diverse needs demand diverse solutions that are informed by pandemic experiences
Freed from the routines of rigid systems, some parents, communities, and educators found new ways to tailor learning experiences around students’ needs. They discovered learning can happen any time and anywhere. They discovered enriching activities outside class and troves of untapped adult talent.
Some of these breakthroughs happened in public schools—like virtual IEP meetings that leveled power dynamics between administrators and parents advocating for their children’s special education services. Others happened in learning pods or other new environments where families and community groups devised new ways to meet students’ needs. These were exceptions to an otherwise miserable rule, and they can inform the work ahead.
We must act quickly but we must also act differently. Important next steps include:
• Districts and states should immediately use their federal dollars to address the emergent needs of the COVID-19 generation of students via proven interventions, such as well-designed tutoring, extended learning time, credit recovery, additional mental health support, college and career guidance, and mentoring. The challenges ahead are too daunting for schools to shoulder alone. Partnerships and funding for families and community-driven solutions will be critical.
• By the end of the 2022–2023 academic year, states and districts must commit to an honest accounting of rebuilding efforts by defining, adopting, and reporting on their progress toward 5- and 10-year goals for long-term student recovery. States should invest in rigorous studies that document, analyze, and improve their approaches.
• Education leaders and researchers must adopt a national research and development agenda for school reinvention over the next five years. This effort must be anchored in the reality that the needs of students are so varied, so profound, and so multifaceted that a one-size-fits-all approach to education can’t possibly meet them all. Across the country, community organizations who previously operated summer or afterschool programs stepped up to support students during the school day. As they focus on recovery, school system leaders should look to these helpers not as peripheral players in education, but as critical contributors who can provide teaching , tutoring, or joyful learning environments for students and often have trusting relationships with their families.
• Recovery and rebuilding should ensure the system is more resilient and prepared for future crises. That means more thoughtful integration of online learning and stronger partnerships with organizations that support learning outside school walls. Every school system in America should have a plan to keep students safe and learning even when they can’t physically come to school, be equipped to deliver high-quality, individualized pathways for students, and build on practices that show promise.
Our “State of the American Student” report is the first in a series of annual reports the Center on Reinventing Public Education intends to produce through fall of 2027. We hope every state and community will produce similar, annual accounts and begin to define ambitious goals for recovery. The implications of these deeply traumatic years will reverberate for decades unless we find a path not only to normalcy but also to restitution for this generation and future generations of American students.
The road to recovery can lead somewhere new. In five years, we hope to report that out of the ashes of the pandemic, American public education emerged transformed: more flexible and resilient, more individualized and equitable, and—most of all— more joyful.
Related Content
Joao Pedro Azevedo, Amer Hasan, Koen Geven, Diana Goldemberg, Syedah Aroob Iqbal
July 30, 2020
Matthew A. Kraft, Michael Goldstein
May 21, 2020
Dan Silver, Anna Saavedra, Morgan Polikoff
August 16, 2022
Early Childhood Education K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Modupe (Mo) Olateju, Grace Cannon, Kelsey Rappe
June 14, 2024
Jon Valant, Nicolas Zerbino
June 13, 2024
Douglas N. Harris
June 6, 2024

The Man Who Died for the Liberal Arts
In 1942, aboard ship and heading for war, a young sailor—my uncle—wrote a letter home, describing and defining the principles he was fighting for.
David M. Shribman May 2024

Donald Trump vs. American History
He has promised to impose his harmful, erroneous claims on school curricula in a second term.
Clint Smith January/February 2024

How Reconstruction Created American Public Education
Freedpeople and their advocates persuaded the nation to embrace schooling for all.
Adam Harris December 2023

Parent Diplomacy Is Overwhelming Teachers
And it’s only getting worse.
Sarah Chaves September 18, 2023

Is Holocaust Education Making Anti-Semitism Worse?
Using dead Jews as symbols isn’t helping living ones.
Dara Horn May 2023

Special Ed Shouldn’t Be Separate
Isolating kids from their peers is unjust.
Julie Kim March 6, 2023

American Family Policy Is Holding Schools Back
A child’s ability to succeed in the classroom is powerfully influenced by their home environment. Giving parents the support they need could be key to fixing American education.
Stephanie H. Murray September 28, 2022

Why Adults Still Dream About School
Long after graduation, anxiety in waking life often drags dreamers back into the classroom.
Kelly Conaboy September 22, 2022

Gen Z Never Learned to Read Cursive
How will they interpret the past?
Drew Gilpin Faust October 2022

Redshirt the Boys
Why boys should start school a year later than girls
Richard V. Reeves October 2022

The Problem With Kindergarten
Early education is vital. So why aren’t students guaranteed access to it?
Keija Parssinen September 9, 2022

The State Finally Letting Teens Sleep In
Adolescents in the U.S. are chronically sleep-deprived, in part because most schools start too early. This summer, California will become the first state in the nation to require later start times.
Lisa L. Lewis June 8, 2022

Students Should Refuse to Go Back to School
Despite the hopelessness after Uvalde, we’re closer to understanding the kind of social movement that might actually affect gun reform.
Gal Beckerman May 31, 2022

10 Years After Sandy Hook, Here We Are Again
I wish I could tell the people of Uvalde that they will be the last mourners. But in the decade since the Newtown shooting, we’ve refused to answer the question of what it would take to actually change something.
Carol Ann Davis May 25, 2022

Speech Therapy Shows the Difficult Trade-Offs of Wearing Masks
All parents of young children have been forced to gamble during the pandemic. Many parents of kids with speech disorders don’t like their odds.
Stephanie H. Murray March 2, 2022

Book Bans Are Targeting the History of Oppression
The possibility of a more just future is at stake when young people are denied access to knowledge of the past.
Marilisa Jiménez Garcia February 2, 2022
America Is Desperate for Substitute Teachers
Omicron is making a bad shortage even worse.
Kate Cray January 27, 2022

Students Are Walking Out Over COVID
The Omicron variant has brought a special level of chaos to classrooms, and some teens say their schools aren’t doing enough to protect them.
Joe Pinsker January 21, 2022

Math Is Personal
How one professor changed the culture of mathematics for his students
Jessica Nordell September 25, 2021

Classroom Time Isn’t the Only Thing Students Have Lost
Students have endured tremendous trauma during the pandemic—and teachers know learning can’t happen without healing.
Kelsey Ko September 7, 2021
clock This article was published more than 2 years ago
Public education is facing a crisis of epic proportions
How politics and the pandemic put schools in the line of fire

A previous version of this story incorrectly said that 39 percent of American children were on track in math. That is the percentage performing below grade level.
Test scores are down, and violence is up . Parents are screaming at school boards , and children are crying on the couches of social workers. Anger is rising. Patience is falling.
For public schools, the numbers are all going in the wrong direction. Enrollment is down. Absenteeism is up. There aren’t enough teachers, substitutes or bus drivers. Each phase of the pandemic brings new logistics to manage, and Republicans are planning political campaigns this year aimed squarely at failings of public schools.
Public education is facing a crisis unlike anything in decades, and it reaches into almost everything that educators do: from teaching math, to counseling anxious children, to managing the building.
Political battles are now a central feature of education, leaving school boards, educators and students in the crosshairs of culture warriors. Schools are on the defensive about their pandemic decision-making, their curriculums, their policies regarding race and racial equity and even the contents of their libraries. Republicans — who see education as a winning political issue — are pressing their case for more “parental control,” or the right to second-guess educators’ choices. Meanwhile, an energized school choice movement has capitalized on the pandemic to promote alternatives to traditional public schools.
“The temperature is way up to a boiling point,” said Nat Malkus, senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, a conservative-leaning think tank. “If it isn’t a crisis now, you never get to crisis.”
Experts reach for comparisons. The best they can find is the earthquake following Brown v. Board of Education , when the Supreme Court ordered districts to desegregate and White parents fled from their cities’ schools. That was decades ago.
Today, the cascading problems are felt acutely by the administrators, teachers and students who walk the hallways of public schools across the country. Many say they feel unprecedented levels of stress in their daily lives.
Remote learning, the toll of illness and death, and disruptions to a dependable routine have left students academically behind — particularly students of color and those from poor families. Behavior problems ranging from inability to focus in class all the way to deadly gun violence have gripped campuses. Many students and teachers say they are emotionally drained, and experts predict schools will be struggling with the fallout for years to come.
Teresa Rennie, an eighth-grade math and science teacher in Philadelphia, said in 11 years of teaching, she has never referred this many children to counseling.
“So many students are needy. They have deficits academically. They have deficits socially,” she said. Rennie said that she’s drained, too. “I get 45 minutes of a prep most days, and a lot of times during that time I’m helping a student with an assignment, or a child is crying and I need to comfort them and get them the help they need. Or there’s a problem between two students that I need to work with. There’s just not enough time.”
Many wonder: How deep is the damage?
Learning lost
At the start of the pandemic, experts predicted that students forced into remote school would pay an academic price. They were right.
“The learning losses have been significant thus far and frankly I’m worried that we haven’t stopped sinking,” said Dan Goldhaber, an education researcher at the American Institutes for Research.
Some of the best data come from the nationally administered assessment called i-Ready, which tests students three times a year in reading and math, allowing researchers to compare performance of millions of students against what would be expected absent the pandemic. It found significant declines, especially among the youngest students and particularly in math.
The low point was fall 2020, when all students were coming off a spring of chaotic, universal remote classes. By fall 2021 there were some improvements, but even then, academic performance remained below historic norms.
Take third grade, a pivotal year for learning and one that predicts success going forward. In fall 2021, 38 percent of third-graders were below grade level in reading, compared with 31 percent historically. In math, 39 percent of students were below grade level, vs. 29 percent historically.
Damage was most severe for students from the lowest-income families, who were already performing at lower levels.
A McKinsey & Co. study found schools with majority-Black populations were five months behind pre-pandemic levels, compared with majority-White schools, which were two months behind. Emma Dorn, a researcher at McKinsey, describes a “K-shaped” recovery, where kids from wealthier families are rebounding and those in low-income homes continue to decline.
“Some students are recovering and doing just fine. Other people are not,” she said. “I’m particularly worried there may be a whole cohort of students who are disengaged altogether from the education system.”
A hunt for teachers, and bus drivers
Schools, short-staffed on a good day, had little margin for error as the omicron variant of the coronavirus swept over the country this winter and sidelined many teachers. With a severe shortage of substitutes, teachers had to cover other classes during their planning periods, pushing prep work to the evenings. San Francisco schools were so strapped that the superintendent returned to the classroom on four days this school year to cover middle school math and science classes. Classes were sometimes left unmonitored or combined with others into large groups of unglorified study halls.
“The pandemic made an already dire reality even more devastating,” said Becky Pringle, president of the National Education Association, referring to the shortages.
In 2016, there were 1.06 people hired for every job listing. That figure has steadily dropped, reaching 0.59 hires for each opening last year, Bureau of Labor Statistics data show. In 2013, there were 557,320 substitute teachers, the BLS reported. In 2020, the number had fallen to 415,510. Virtually every district cites a need for more subs.
It’s led to burnout as teachers try to fill in the gaps.
“The overall feelings of teachers right now are ones of just being exhausted, beaten down and defeated, and just out of gas. Expectations have been piled on educators, even before the pandemic, but nothing is ever removed,” said Jennifer Schlicht, a high school teacher in Olathe, Kan., outside Kansas City.
Research shows the gaps in the number of available educators are most acute in areas including special education and educators who teach English language learners, as well as substitutes. And all school year, districts have been short on bus drivers , who have been doubling up routes, and forcing late school starts and sometimes cancellations for lack of transportation.
Many educators predict that fed-up teachers will probably quit, exacerbating the problem. And they say political attacks add to the burnout. Teachers are under scrutiny over lesson plans, and critics have gone after teachers unions, which for much of the pandemic demanded remote learning.
“It’s just created an environment that people don’t want to be part of anymore,” said Daniel A. Domenech, executive director of AASA, The School Superintendents Association. “People want to take care of kids, not to be accused and punished and criticized.”
Falling enrollment
Traditional public schools educate the vast majority of American children, but enrollment has fallen, a worrisome trend that could have lasting repercussions. Enrollment in traditional public schools fell to less than 49.4 million students in fall 2020 , a 2.7 percent drop from a year earlier .
National data for the current school year is not yet available. But if the trend continues, that will mean less money for public schools as federal and state funding are both contingent on the number of students enrolled. For now, schools have an infusion of federal rescue money that must be spent by 2024.
Some students have shifted to private or charter schools. A rising number , especially Black families , opted for home schooling. And many young children who should have been enrolling in kindergarten delayed school altogether. The question has been: will these students come back?
Some may not. Preliminary data for 19 states compiled by Nat Malkus, of the American Enterprise Institute, found seven states where enrollment dropped in fall 2020 and then dropped even further in 2021. His data show 12 states that saw declines in 2020 but some rebounding in 2021 — though not one of them was back to 2019 enrollment levels.
Joshua Goodman, associate professor of education and economics at Boston University, studied enrollment in Michigan schools and found high-income, White families moved to private schools to get in-person school. Far more common, though, were lower-income Black families shifting to home schooling or other remote options because they were uncomfortable with the health risks of in person.
“Schools were damned if they did, and damned if they didn’t,” Goodman said.
At the same time, charter schools, which are privately run but publicly funded, saw enrollment increase by 7 percent, or nearly 240,000 students, according to the National Alliance for Public Charter Schools. There’s also been a surge in home schooling. Private schools saw enrollment drop slightly in 2020-21 but then rebound this academic year, for a net growth of 1.7 percent over two years, according to the National Association of Independent Schools, which represents 1,600 U.S. schools.
Absenteeism on the rise
Even if students are enrolled, they won’t get much schooling if they don’t show up.
Last school year, the number of students who were chronically absent — meaning they have missed more than 10 percent of school days — nearly doubled from before the pandemic, according to data from a variety of states and districts studied by EveryDay Labs, a company that works with districts to improve attendance.
This school year, the numbers got even worse.
In Connecticut, for instance, the number of chronically absent students soared from 12 percent in 2019-20 to 20 percent the next year to 24 percent this year, said Emily Bailard, chief executive of the company. In Oakland, Calif., they went from 17.3 percent pre-pandemic to 19.8 percent last school year to 43 percent this year. In Pittsburgh, chronic absences stayed where they were last school year at about 25 percent, then shot up to 45 percent this year.
“We all expected that this year would look much better,” Bailard said. One explanation for the rise may be that schools did not keep careful track of remote attendance last year and the numbers understated the absences then, she said.
The numbers were the worst for the most vulnerable students. This school year in Connecticut, for instance, 24 percent of all students were chronically absent, but the figure topped 30 percent for English-learners, students with disabilities and those poor enough to qualify for free lunch. Among students experiencing homelessness, 56 percent were chronically absent.
Fights and guns
Schools are open for in-person learning almost everywhere, but students returned emotionally unsettled and unable to conform to normally accepted behavior. At its most benign, teachers are seeing kids who cannot focus in class, can’t stop looking at their phones, and can’t figure out how to interact with other students in all the normal ways. Many teachers say they seem younger than normal.
Amy Johnson, a veteran teacher in rural Randolph, Vt., said her fifth-graders had so much trouble being together that the school brought in a behavioral specialist to work with them three hours each week.
“My students are not acclimated to being in the same room together,” she said. “They don’t listen to each other. They cannot interact with each other in productive ways. When I’m teaching I might have three or five kids yelling at me all at the same time.”
That loss of interpersonal skills has also led to more fighting in hallways and after school. Teachers and principals say many incidents escalate from small disputes because students lack the habit of remaining calm. Many say the social isolation wrought during remote school left them with lower capacity to manage human conflict.
Just last week, a high-schooler in Los Angeles was accused of stabbing another student in a school hallway, police on the big island of Hawaii arrested seven students after an argument escalated into a fight, and a Baltimore County, Md., school resource officer was injured after intervening in a fight during the transition between classes.
There’s also been a steep rise in gun violence. In 2021, there were at least 42 acts of gun violence on K-12 campuses during regular hours, the most during any year since at least 1999, according to a Washington Post database . The most striking of 2021 incidents was the shooting in Oxford, Mich., that killed four. There have been already at least three shootings in 2022.
Back to school has brought guns, fighting and acting out
The Center for Homeland Defense and Security, which maintains its own database of K-12 school shootings using a different methodology, totaled nine active shooter incidents in schools in 2021, in addition to 240 other incidents of gunfire on school grounds. So far in 2022, it has recorded 12 incidents. The previous high, in 2019, was 119 total incidents.
David Riedman, lead researcher on the K-12 School Shooting Database, points to four shootings on Jan. 19 alone, including at Anacostia High School in D.C., where gunshots struck the front door of the school as a teen sprinted onto the campus, fleeing a gunman.
Seeing opportunity
Fueling the pressure on public schools is an ascendant school-choice movement that promotes taxpayer subsidies for students to attend private and religious schools, as well as publicly funded charter schools, which are privately run. Advocates of these programs have seen the public system’s woes as an excellent opportunity to push their priorities.
EdChoice, a group that promotes these programs, tallies seven states that created new school choice programs last year. Some are voucher-type programs where students take some of their tax dollars with them to private schools. Others offer tax credits for donating to nonprofit organizations, which give scholarships for school expenses. Another 15 states expanded existing programs, EdChoice says.
The troubles traditional schools have had managing the pandemic has been key to the lobbying, said Michael McShane, director of national research for EdChoice. “That is absolutely an argument that school choice advocates make, for sure.”
If those new programs wind up moving more students from public to private systems, that could further weaken traditional schools, even as they continue to educate the vast majority of students.
Kevin G. Welner, director of the National Education Policy Center at the University of Colorado, who opposes school choice programs, sees the surge of interest as the culmination of years of work to undermine public education. He is both impressed by the organization and horrified by the results.
“I wish that organizations supporting public education had the level of funding and coordination that I’ve seen in these groups dedicated to its privatization,” he said.
A final complication: Politics
Rarely has education been such a polarizing political topic.
Republicans, fresh off Glenn Youngkin’s victory in the Virginia governor’s race, have concluded that key to victory is a push for parental control and “parents rights.” That’s a nod to two separate topics.
First, they are capitalizing on parent frustrations over pandemic policies, including school closures and mandatory mask policies. The mask debate, which raged at the start of the school year, got new life this month after Youngkin ordered Virginia schools to allow students to attend without face coverings.
The notion of parental control also extends to race, and objections over how American history is taught. Many Republicans also object to school districts’ work aimed at racial equity in their systems, a basket of policies they have dubbed critical race theory. Critics have balked at changes in admissions to elite school in the name of racial diversity, as was done in Fairfax, Va. , and San Francisco ; discussion of White privilege in class ; and use of the New York Times’s “1619 Project,” which suggests slavery and racism are at the core of American history.
“Everything has been politicized,” said Domenech, of AASA. “You’re beside yourself saying, ‘How did we ever get to this point?’”
Part of the challenge going forward is that the pandemic is not over. Each time it seems to be easing, it returns with a variant vengeance, forcing schools to make politically and educationally sensitive decisions about the balance between safety and normalcy all over again.
At the same time, many of the problems facing public schools feed on one another. Students who are absent will probably fall behind in learning, and those who fall behind are likely to act out.
A similar backlash exists regarding race. For years, schools have been under pressure to address racism in their systems and to teach it in their curriculums, pressure that intensified after the murder of George Floyd in 2020. Many districts responded, and that opened them up to countervailing pressures from those who find schools overly focused on race.
Some high-profile boosters of public education are optimistic that schools can move past this moment. Education Secretary Miguel Cardona last week promised, “It will get better.” Randi Weingarten, president of the American Federation of Teachers, said, “If we can rebuild community-education relations, if we can rebuild trust, public education will not only survive but has a real chance to thrive.”
But the path back is steep, and if history is a guide, the wealthiest schools will come through reasonably well, while those serving low-income communities will struggle. Steve Matthews, superintendent of the 6,900-student Novi Community School District in Michigan, just northwest of Detroit, said his district will probably face a tougher road back than wealthier nearby districts that are, for instance, able to pay teachers more.
“Resource issues. Trust issues. De-professionalization of teaching is making it harder to recruit teachers,” he said. “A big part of me believes schools are in a long-term crisis.”
Valerie Strauss contributed to this report.
The pandemic’s impact on education
The latest: Updated coronavirus booster shots are now available for children as young as 5 . To date, more than 10.5 million children have lost one or both parents or caregivers during the coronavirus pandemic.
In the classroom: Amid a teacher shortage, states desperate to fill teaching jobs have relaxed job requirements as staffing crises rise in many schools . American students’ test scores have even plummeted to levels unseen for decades. One D.C. school is using COVID relief funds to target students on the verge of failure .
Higher education: College and university enrollment is nowhere near pandemic level, experts worry. ACT and SAT testing have rebounded modestly since the massive disruptions early in the coronavirus pandemic, and many colleges are also easing mask rules .
DMV news: Most of Prince George’s students are scoring below grade level on district tests. D.C. Public School’s new reading curriculum is designed to help improve literacy among the city’s youngest readers.

The Education Crisis: Being in School Is Not the Same as Learning

First grade students in Pakistan’s Balochistan Province are learning the alphabet through child-friendly flash cards. Their learning materials help educators teach through interactive and engaging activities and are provided free of charge through a student’s first learning backpack. © World Bank
THE NAME OF THE DOG IS PUPPY. This seems like a simple sentence. But did you know that in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, three out of four third grade students do not understand it? The world is facing a learning crisis . Worldwide, hundreds of millions of children reach young adulthood without even the most basic skills like calculating the correct change from a transaction, reading a doctor’s instructions, or understanding a bus schedule—let alone building a fulfilling career or educating their children. Education is at the center of building human capital. The latest World Bank research shows that the productivity of 56 percent of the world’s children will be less than half of what it could be if they enjoyed complete education and full health. For individuals, education raises self-esteem and furthers opportunities for employment and earnings. And for a country, it helps strengthen institutions within societies, drives long-term economic growth, reduces poverty, and spurs innovation.


One of the most interesting, large scale educational technology efforts is being led by EkStep , a philanthropic effort in India. EkStep created an open digital infrastructure which provides access to learning opportunities for 200 million children, as well as professional development opportunities for 12 million teachers and 4.5 million school leaders. Both teachers and children are accessing content which ranges from teaching materials, explanatory videos, interactive content, stories, practice worksheets, and formative assessments. By monitoring which content is used most frequently—and most beneficially—informed decisions can be made around future content.
In the Dominican Republic, a World Bank supported pilot study shows how adaptive technologies can generate great interest among 21st century students and present a path to supporting the learning and teaching of future generations. Yudeisy, a sixth grader participating in the study, says that what she likes doing the most during the day is watching videos and tutorials on her computer and cell phone. Taking childhood curiosity as a starting point, the study aimed to channel it towards math learning in a way that interests Yudeisy and her classmates.

Yudeisy, along with her classmates in a public elementary school in Santo Domingo, is part of a four-month pilot to reinforce mathematics using software that adapts to the math level of each student. © World Bank
Adaptive technology was used to evaluate students’ initial learning level to then walk them through math exercises in a dynamic, personalized way, based on artificial intelligence and what the student is ready to learn. After three months, students with the lowest initial performance achieved substantial improvements. This shows the potential of technology to increase learning outcomes, especially among students lagging behind their peers. In a field that is developing at dizzying speeds, innovative solutions to educational challenges are springing up everywhere. Our challenge is to make technology a driver of equity and inclusion and not a source of greater inequality of opportunity. We are working with partners worldwide to support the effective and appropriate use of educational technologies to strengthen learning.
When schools and educations systems are managed well, learning happens
Successful education reforms require good policy design, strong political commitment, and effective implementation capacity . Of course, this is extremely challenging. Many countries struggle to make efficient use of resources and very often increased education spending does not translate into more learning and improved human capital. Overcoming such challenges involves working at all levels of the system.
At the central level, ministries of education need to attract the best experts to design and implement evidence-based and country-specific programs. District or regional offices need the capacity and the tools to monitor learning and support schools. At the school level, principals need to be trained and prepared to manage and lead schools, from planning the use of resources to supervising and nurturing their teachers. However difficult, change is possible. Supported by the World Bank, public schools across Punjab in Pakistan have been part of major reforms over the past few years to address these challenges. Through improved school-level accountability by monitoring and limiting teacher and student absenteeism, and the introduction of a merit-based teacher recruitment system, where only the most talented and motivated teachers were selected, they were able to increase enrollment and retention of students and significantly improve the quality of education. "The government schools have become very good now, even better than private ones," said Mr. Ahmed, a local villager.
The World Bank, along with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the UK’s Department for International Development, is developing the Global Education Policy Dashboard . This new initiative will provide governments with a system for monitoring how their education systems are functioning, from learning data to policy plans, so they are better able to make timely and evidence-based decisions.
Education reform: The long game is worth it
In fact, it will take a generation to realize the full benefits of high-quality teachers, the effective use of technology, improved management of education systems, and engaged and prepared learners. However, global experience shows us that countries that have rapidly accelerated development and prosperity all share the common characteristic of taking education seriously and investing appropriately. As we mark the first-ever International Day of Education on January 24, we must do all we can to equip our youth with the skills to keep learning, adapt to changing realities, and thrive in an increasingly competitive global economy and a rapidly changing world of work.
The schools of the future are being built today. These are schools where all teachers have the right competencies and motivation, where technology empowers them to deliver quality learning, and where all students learn fundamental skills, including socio-emotional, and digital skills. These schools are safe and affordable to everyone and are places where children and young people learn with joy, rigor, and purpose. Governments, teachers, parents, and the international community must do their homework to realize the promise of education for all students, in every village, in every city, and in every country.
The Bigger Picture: In-depth stories on ending poverty
Education 2030: topics and issues

The debates included the following sessions:
Providing meaningful learning opportunities to out-of-school children
In this session a panel of experts explored the changes needed in countries which have large out-of-school children populations as well as examples from countries which are ‘in the final mile’. “They are all different, they don’t fit into one box” said Mary Joy Pigozzi, Director of Educate A Child (EAC). Ms Pigozzi emphasized the need for attention to children who are displaced, conflict affected, working children, and so on. Mr Albert Montivans, Head of Education Indicators and Data Analysis at UNESCO Institute for Statistics added: “one of the priorities is to better the disadvantaged”.
The session was also attended by the Minister of Education, Haiti, Nesmy Manigat, the CEO of Global Partnership for Education Alice Albright, and the Director-General in the Romanian Ministry of Education, Liliana Preoteasa. The panelists raised their voices on ‘inclusion’, ‘partnership’, ‘financing’, and ‘sustainable planning’ in order to pull youngsters into the schooling system. The session concluded with further food for thought from Mr Nesmy Manigat, the Minister of Education,Haiti: “Let’s also talk about the children who are in school, yet they do not learn. Teach them what the meaning of school is - what do we need to do in school and not only focus on the policies”.
Mobilizing Business to Realize the 2030 Education Agenda
Representatives from business and education organizations gathered at a parallel session on mobilizing business to realize the 2030 agenda. Chaired by Justin van Fleet, Chief of Staff for the UN Special Envoy for Global Education, the session established a business case to invest in education and focused on how business can coordinate action with other stakeholders. The lively discussion saw questions from the floor around ICT’s, but also issues of trust; with a representative from the Philippines asking the panel whether business cares about education or is simply benefiting from it. The President of Lego Education, Mr Jacob Kragh, said there was a sincere objective from the company “to pursue the benefit of the children and make sure they get the chance to be the best they can in life”. He said that "taking over education was by no means the objective of the private sector", and reiterated the importance of working closely with governments and the public sector. Panelists also included Vikas Pota from GEMS Education, Martina Roth from Intel Corporation and Jouko Sarvi from the Asian Development Bank.
In parallel, Argentina’s Minister of Education, Alberto Sileoni, was joined by UNESCO Director, David Atchoarena, and UN Special Advisor on Post-2015 Development Planning, Amina Mohammed, at a session on Global and regional coordination and monitoring mechanisms. The session dealt with the importance of having robust mechanisms for coordination and monitoring. Session participants looked at how global and regional mechanisms for education should work alongside the new mechanisms for the overall Sustainable Development Goal, with Mr Atchoarena pointing out that the focus on ‘country-level’ monitoring and review was much stronger in the new education agenda.
Effective Governance and Accountability
In this group session, the panelists suggested the right direction for contemporary national education governance. Namely the key policies and strategies to construct a pragmatic governance framework that is both regulatory and collaborative were suggested throughout the discussion.
The chair, Mr. Gwang-Jo Kim, Director of UNESCO’s regional office in Bangkok, Thailand, posed three questions before the discussion: How can we define the term “effective governance”. What would be the role of the private sector and how to balance between autonomy resulting from decentralization, and accountability. The panels and the participants engaged in a lively debate: “Governance should focus on dialogue between communities in society so that private sector can become stakeholders to invest in education,” stated the Minister of Education, Bolivia, Roberto Aguilar, as an answer to the second question. He also gave an example from his country where education campaigns are usually funded by private institutions, saying it is social responsibility for private entities to participate actively in the effective governance framework.
The Minster of Education, Democratic Republic of Congo,Maker Mwangu Famba, said the core elements of effective governance were transparency and responsibility.
How does education contribute to sustainable development post 2015?
Sustainable development is not just about technological solutions, political regulation or financial instruments alone. The realization of the transformative power of education and the importance of cross-sectoral approaches need to be taken into account. This was the message given by Ms Amina Mohammed, Special Advisor to the UN Secretary-General on Post 2015 Development Planning, as she said that education was not simply about learning, it is about empowerment and key in the sustainable development agenda. In this session, the panel members discussed how education can address global challenges, in particular how education contributes to addressing climate change and health issues and poverty reduction.
Education is one of the most powerful tools for people to be informed about diseases, take preventative measures, recognize signs of illness early and be informed to use health care services, the speakers highlighted. Mr Mark Brown, the Minister of Finance in Cook Islands, said that current knowledge as well as new knowledge should reach not only school children but also adults, as they are the educators.
The growing interaction between education and climate change cannot be neglected, Ms Kandia Camara, Minister of National Education, Cote d’lvoire, said: “There are school programs to teach healthy lifestyles and the importance of forests,” actions are being taken to ensure climate-safe and climate-friendly school environments.
Furthermore, Mr Renato Janine Ribeiro, Minister of Education in Brazil, expressed the difficulty of eradicating poverty, “the challenge we face is ‘hunger, they live in places that are very difficult to access”, he said. Hence, geographic placement poses as a barrier to accessibility. Yet, in order to mitigate the problem with a collective effort, he asserted that Brazil would be happy to share its valuable experience on education for sustainable development with any country in order to bolster efforts.
Towards the end of the session, the CEO of the Campaign for Popular Education, Bangladesh, Ms Rasheda Choudhury, firmly stated: “The two nonnegotiable principles are: first, education is a fundamental human right and second, it is the state’s responsibility to provide education to their every single citizen”.

Event International Conference of the Memory of the World Programme, incorporating the 4th Global Policy Forum 28 October 2024 - 29 October 2024
Other recent news

News UNESCO Survey Uncovers Critical Gaps in AI Training Among Judicial Operators 14 June 2024

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
"let me learn", nearly two-thirds of 10-year-olds are unable to read and understand a simple text..

Nearly two-thirds of 10-year-olds are estimated to be unable to read and understand a simple text. Without urgent action, this global learning crisis will become a generational catastrophe.
Education systems are failing our children.
Education systems were already failing our children even before the pandemic. COVID-19 exacerbated this learning crisis and children in almost every country have fallen behind in their learning.
We need a global effort to tackle the learning crisis head on. Together, we can help every child gain basic reading and maths skills and unlock their potential.
Get involved
Learn what needs to happen For partners and policymakers For young people UNICEF in action
What needs to happen
UNICEF is calling on governments to:
- Reach every child and keep them in school
- Assess learning levels regularly
- Prioritize teaching the fundamentals
- Increase catch-up learning and progress beyond what was lost
- Develop psychosocial health and well-being so every child is ready to learn.
For partners and policymakers
We need urgent action from governments and other partners to invest in education. Without ambitious action on basic reading and maths, with a focus on the most marginalized children, we will fail to achieve the SDGs by 2030.
NEW REPORT: Less than half of all countries surveyed have a specific focus on foundational literacy and numeracy in their national curriculum. > learn more
Commitment to Action on Foundational Learning
Ensure foundational learning as a key element to transform education
In every corner of the globe, UNICEF works to provide quality learning opportunities that prepare children with the knowledge and skill
Education data
The state and progress of education by country
Giga is a UNICEF-ITU initiative to connect every school to the Internet and every young person to information, opportunity and choice.
The Learning Passport
A flexible online, mobile and offline tech platform designed to close the learning poverty gap
For young people
Did you know that education is a human right? But too many children around the world still don’t go to school. And an even larger number of kids who are in schools, aren’t getting the quality education they deserve.
Express your views and support for the issues that matter to you on Voices of Youth – UNICEF's digital community for youth, by youth.
For parents
Is your child getting ready for preschool or is anxious about going back to school? Find tips on how to support them, as well as many other parenting resources on UNICEF’s Parenting Hub .
How to teach your child to love reading
What you need to know about raising a reader
How to introduce maths to your toddler
Playful ways to learn are everywhere
How to talk to your child about school anxiety
Is your child having a hard time being back in the classroom? Dr. Hina Talib shares tips on how to help them cope

Bullying: What is it and how to stop it
How to prevent and deal with bullying
For teachers
Children depend on their teachers to help them catch-up on lost learning in a safe and supportive environment. UNICEF stands with teachers everywhere in calling for more investment, training and support for their work.
Self-care tips for teachers
How to ease anxiety and reduce the impact of stress on your health
How to reduce stress and support student well-being
Activities for teachers to support student mental health.
UNICEF in action
Out-of-school adolescents gain skills for life in Myanmar
EXCEL programme targets out-of-school adolescents
A golden opportunity to learn
Out-of-school children access education at a UNICEF supported e-learning centre
Stakes couldn’t be higher for Afghanistan’s children
UNICEF’s Global Director for Education writes about why this is a critical moment for Afghanistan’s education system
Recovering lost learning in Ecuador after the pandemic
The return to on-site classes represents a new opportunity for children like Romina to resume their education and make friends again.

Ahead of Day of the African Child UNICEF says African governments not spending what they need to secure quality education for continent’s children

1,000 days of education – equivalent to three billion learning hours – lost for Afghan girls

Ukraine’s recovery is dependent on the recovery of children’s education

Children call for access to quality climate education
On Earth Day, UNICEF urges governments to empower every child with learning opportunities to be a champion for the planet
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Image credit: Claire Scully
New advances in technology are upending education, from the recent debut of new artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT to the growing accessibility of virtual-reality tools that expand the boundaries of the classroom. For educators, at the heart of it all is the hope that every learner gets an equal chance to develop the skills they need to succeed. But that promise is not without its pitfalls.
“Technology is a game-changer for education – it offers the prospect of universal access to high-quality learning experiences, and it creates fundamentally new ways of teaching,” said Dan Schwartz, dean of Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), who is also a professor of educational technology at the GSE and faculty director of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning . “But there are a lot of ways we teach that aren’t great, and a big fear with AI in particular is that we just get more efficient at teaching badly. This is a moment to pay attention, to do things differently.”
For K-12 schools, this year also marks the end of the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funding program, which has provided pandemic recovery funds that many districts used to invest in educational software and systems. With these funds running out in September 2024, schools are trying to determine their best use of technology as they face the prospect of diminishing resources.
Here, Schwartz and other Stanford education scholars weigh in on some of the technology trends taking center stage in the classroom this year.
AI in the classroom
In 2023, the big story in technology and education was generative AI, following the introduction of ChatGPT and other chatbots that produce text seemingly written by a human in response to a question or prompt. Educators immediately worried that students would use the chatbot to cheat by trying to pass its writing off as their own. As schools move to adopt policies around students’ use of the tool, many are also beginning to explore potential opportunities – for example, to generate reading assignments or coach students during the writing process.
AI can also help automate tasks like grading and lesson planning, freeing teachers to do the human work that drew them into the profession in the first place, said Victor Lee, an associate professor at the GSE and faculty lead for the AI + Education initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning. “I’m heartened to see some movement toward creating AI tools that make teachers’ lives better – not to replace them, but to give them the time to do the work that only teachers are able to do,” he said. “I hope to see more on that front.”
He also emphasized the need to teach students now to begin questioning and critiquing the development and use of AI. “AI is not going away,” said Lee, who is also director of CRAFT (Classroom-Ready Resources about AI for Teaching), which provides free resources to help teach AI literacy to high school students across subject areas. “We need to teach students how to understand and think critically about this technology.”
Immersive environments
The use of immersive technologies like augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality is also expected to surge in the classroom, especially as new high-profile devices integrating these realities hit the marketplace in 2024.
The educational possibilities now go beyond putting on a headset and experiencing life in a distant location. With new technologies, students can create their own local interactive 360-degree scenarios, using just a cell phone or inexpensive camera and simple online tools.
“This is an area that’s really going to explode over the next couple of years,” said Kristen Pilner Blair, director of research for the Digital Learning initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning, which runs a program exploring the use of virtual field trips to promote learning. “Students can learn about the effects of climate change, say, by virtually experiencing the impact on a particular environment. But they can also become creators, documenting and sharing immersive media that shows the effects where they live.”
Integrating AI into virtual simulations could also soon take the experience to another level, Schwartz said. “If your VR experience brings me to a redwood tree, you could have a window pop up that allows me to ask questions about the tree, and AI can deliver the answers.”
Gamification
Another trend expected to intensify this year is the gamification of learning activities, often featuring dynamic videos with interactive elements to engage and hold students’ attention.
“Gamification is a good motivator, because one key aspect is reward, which is very powerful,” said Schwartz. The downside? Rewards are specific to the activity at hand, which may not extend to learning more generally. “If I get rewarded for doing math in a space-age video game, it doesn’t mean I’m going to be motivated to do math anywhere else.”
Gamification sometimes tries to make “chocolate-covered broccoli,” Schwartz said, by adding art and rewards to make speeded response tasks involving single-answer, factual questions more fun. He hopes to see more creative play patterns that give students points for rethinking an approach or adapting their strategy, rather than only rewarding them for quickly producing a correct response.
Data-gathering and analysis
The growing use of technology in schools is producing massive amounts of data on students’ activities in the classroom and online. “We’re now able to capture moment-to-moment data, every keystroke a kid makes,” said Schwartz – data that can reveal areas of struggle and different learning opportunities, from solving a math problem to approaching a writing assignment.
But outside of research settings, he said, that type of granular data – now owned by tech companies – is more likely used to refine the design of the software than to provide teachers with actionable information.
The promise of personalized learning is being able to generate content aligned with students’ interests and skill levels, and making lessons more accessible for multilingual learners and students with disabilities. Realizing that promise requires that educators can make sense of the data that’s being collected, said Schwartz – and while advances in AI are making it easier to identify patterns and findings, the data also needs to be in a system and form educators can access and analyze for decision-making. Developing a usable infrastructure for that data, Schwartz said, is an important next step.
With the accumulation of student data comes privacy concerns: How is the data being collected? Are there regulations or guidelines around its use in decision-making? What steps are being taken to prevent unauthorized access? In 2023 K-12 schools experienced a rise in cyberattacks, underscoring the need to implement strong systems to safeguard student data.
Technology is “requiring people to check their assumptions about education,” said Schwartz, noting that AI in particular is very efficient at replicating biases and automating the way things have been done in the past, including poor models of instruction. “But it’s also opening up new possibilities for students producing material, and for being able to identify children who are not average so we can customize toward them. It’s an opportunity to think of entirely new ways of teaching – this is the path I hope to see.”
Choose an Account to Log In

Notifications

Current Issues in Education
From national standards research to the debate on Common Core, learn about the most important issues facing today's teachers, school administrators, and parents.
National Standards
Learn more about how schools will comply with new national standards.
- The Push for National Standards: What Parents Need to Know by Bob Ross
- Higher Math in Lower Grades: Hurting or Helping Kids? by Cindy Donaldson
- The Global Achievement Gap: Why America's Students Are Falling Behind by Cindy Donaldson
- Is America Failing Math? by Cindy Donaldson
Tech Trends
New classroom technology will change how teachers teach and students learn.
- Classroom Tech Trends To Watch by Merry Gordon
- The Khan Academy: Changing the Face of Education? by Cindy Donaldson
School Policy
Read the pros and cons of these controversial school policies.
- Outrageous School Policies: What You Can Do by Bob Ross
- Should Struggling Students Repeat a Grade? by Julie Williams
- The Homework Debate by Johanna Sorrentino
- Classroom Controversy: Evolution vs. Intelligent Design by Bob Ross
- Uniformity vs. Conformity: How to Nurture Creativity and Dress for Success by Merry Gordon
- Prayer in Schools: Benefits from Both Sides by Meg Butler
School Reform
Many schools are undergoing big changes to improve the learning outcomes of students.
- 4-Day School Weeks: Headed to Your District? by Bob Ross
- Are Traditional Grades a Thing of the Past? by Merry Gordon
- Can Vouchers Improve Your Child's School? by Merry Gordon
Child Development
These articles explore child development issues, from gender to the importance of play.
- Gender Gap: Why Boys Can't Keep Up by Rose Garrett
- Is Play on its Way Out? by Rose Garrett
- Is Your Child a Cheater? by Christy Callahan
- Redshirting: What's It All About? by Julie Williams
- Academic Preschools: Too Much Too Soon? by Hannah Boyd
Decreasing childhood obesity by encouraging healthy habits has become an issue of national importance.
- Why School Cafeterias Are Dishing Out Fast Food by Deborah Lehmann
- Childhood Obesity and Nutrition: Study Recommends New School Lunch Guidelines by Bob Ross
- Childhood Obesity Campaign Seeks to Get Nation Moving by Bob Ross
- Hold the Pink Slime: Making School Lunch Healthier by Elizabeth DeMeo
- Is Your Child Getting Enough Physical Education? by Samantha Cleaver
Related Topics
Add to collection, create new collection, new collection, new collection>, sign up to start collecting.
Bookmark this to easily find it later. Then send your curated collection to your children, or put together your own custom lesson plan.
Trade Schools, Colleges and Universities
Join Over 1.5 Million People We've Introduced to Awesome Schools Since 2001
Trade Schools Home > Articles > Issues in Education
Major Issues in Education: 20 Hot Topics (From Grade School to College)
By Publisher | Last Updated August 1, 2023
In America, issues in education are big topics of discussion, both in the news media and among the general public. The current education system is beset by a wide range of challenges, from cuts in government funding to changes in disciplinary policies—and much more. Everyone agrees that providing high-quality education for our citizens is a worthy ideal. However, there are many diverse viewpoints about how that should be accomplished. And that leads to highly charged debates, with passionate advocates on both sides.
Understanding education issues is important for students, parents, and taxpayers. By being well-informed, you can contribute valuable input to the discussion. You can also make better decisions about what causes you will support or what plans you will make for your future.
This article provides detailed information on many of today's most relevant primary, secondary, and post-secondary education issues. It also outlines four emerging trends that have the potential to shake up the education sector. You'll learn about:
- 13 major issues in education at the K-12 level
- 7 big issues in higher education
- 5 emerging trends in education
13 Major Issues in Education at the K-12 Level

1. Government funding for education
School funding is a primary concern when discussing current issues in education. The American public education system, which includes both primary and secondary schools, is primarily funded by tax revenues. For the 2021 school year, state and local governments provided over 89 percent of the funding for public K-12 schools. After the Great Recession, most states reduced their school funding. This reduction makes sense, considering most state funding is sourced from sales and income taxes, which tend to decrease during economic downturns.
However, many states are still giving schools less cash now than they did before the Great Recession. A 2022 article from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities (CBPP) notes that K-12 education is set to receive the largest-ever one-time federal investment. However, the CBPP also predicts this historic funding might fall short due to pandemic-induced education costs. The formulas that states use to fund schools have come under fire in recent years and have even been the subjects of lawsuits. For example, in 2017, the Kansas Supreme Court ruled that the legislature's formula for financing schools was unconstitutional because it didn't adequately fund education.
Less funding means that smaller staff, fewer programs, and diminished resources for students are common school problems. In some cases, schools are unable to pay for essential maintenance. A 2021 report noted that close to a quarter of all U.S. public schools are in fair or poor condition and that 53 percent of schools need renovations and repairs. Plus, a 2021 survey discovered that teachers spent an average of $750 of their own money on classroom supplies.
The issue reached a tipping point in 2018, with teachers in Arizona, Colorado, and other states walking off the job to demand additional educational funding. Some of the protests resulted in modest funding increases, but many educators believe that more must be done.
2. School safety
Over the past several years, a string of high-profile mass shootings in U.S. schools have resulted in dozens of deaths and led to debates about the best ways to keep students safe. After 17 people were killed in a shooting at a high school in Parkland, Florida in 2018, 57 percent of teenagers said they were worried about the possibility of gun violence at their school.
Figuring out how to prevent such attacks and save students and school personnel's lives are problems faced by teachers all across America.
Former President Trump and other lawmakers suggested that allowing specially trained teachers and other school staff to carry concealed weapons would make schools safer. The idea was that adult volunteers who were already proficient with a firearm could undergo specialized training to deal with an active shooter situation until law enforcement could arrive. Proponents argued that armed staff could intervene to end the threat and save lives. Also, potential attackers might be less likely to target a school if they knew that the school's personnel were carrying weapons.
Critics argue that more guns in schools will lead to more accidents, injuries, and fear. They contend that there is scant evidence supporting the idea that armed school officials would effectively counter attacks. Some data suggests that the opposite may be true: An FBI analysis of active shooter situations between 2000 and 2013 noted that law enforcement personnel who engaged the shooter suffered casualties in 21 out of 45 incidents. And those were highly trained professionals whose primary purpose was to maintain law and order. It's highly unlikely that teachers, whose focus should be on educating children, would do any better in such situations.
According to the National Education Association (NEA), giving teachers guns is not the answer. In a March 2018 survey , 74 percent of NEA members opposed arming school personnel, and two-thirds said they would feel less safe at work if school staff were carrying guns. To counter gun violence in schools, the NEA supports measures like requiring universal background checks, preventing mentally ill people from purchasing guns, and banning assault weapons.
3. Disciplinary policies
Data from the U.S. Department of Education Office for Civil Rights in 2021 suggests that black students face disproportionately high rates of suspension and expulsion from school. For instance, in K-12 schools, black male students make up only 7.7 percent of enrollees but account for over 40% percent of suspensions. Many people believe some teachers apply the rules of discipline in a discriminatory way and contribute to what has been termed the "school-to-prison pipeline." That's because research has demonstrated that students who are suspended or expelled are significantly more likely to become involved with the juvenile justice system.
In 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice and the Department of Education issued guidelines for all public schools on developing disciplinary practices that reduce disparities and comply with federal civil rights laws. The guidelines urged schools to limit exclusionary disciplinary tactics such as suspension and expulsion. They also encourage the adoption of more positive interventions such as counseling and restorative justice strategies. In addition, the guidelines specified that schools could face a loss of federal funds if they carried out policies that had a disparate impact on some racial groups.
Opponents argue that banning suspensions and expulsions takes away valuable tools that teachers can use to combat student misbehavior. They maintain that as long as disciplinary policies are applied the same way to every student regardless of race, such policies are not discriminatory. One major 2014 study found that the racial disparities in school suspension rates could be explained by the students' prior behavior rather than by discriminatory tactics on the part of educators.
In 2018, the Federal Commission on School Safety (which was established in the wake of the school shootings in Parkland, Florida) was tasked with reviewing and possibly rescinding the 2014 guidelines. According to an Education Next survey taken shortly after the announced review, only 27 percent of Americans support federal policies that limit racial disparities in school discipline.
4. Technology in education
Technology in education is a powerful movement that is sweeping through schools nationwide. After all, today's students have grown up with digital technology and expect it to be part of their learning experience. But how much of a role should it play in education?
Proponents point out that educational technology offers the potential to engage students in more active learning, as evidenced in flipped classrooms . It can facilitate group collaboration and provide instant access to up-to-date resources. Teachers and instructors can integrate online surveys, interactive case studies, and relevant videos to offer content tailored to different learning styles. Indeed, students with special needs frequently rely on assistive technology to communicate and access course materials.
But there are downsides as well. For instance, technology can be a distraction. Some students tune out of lessons and spend time checking social media, playing games, or shopping online. One research study revealed that students who multitasked on laptops during class scored 11 percent lower on an exam that tested their knowledge of the lecture. Students who sat behind those multitaskers scored 17 percent lower. In the fall of 2017, University of Michigan professor Susan Dynarski cited such research as one of the main reasons she bans electronics in her classes.
More disturbingly, technology can pose a real threat to student privacy and security. The collection of sensitive student data by education technology companies can lead to serious problems. In 2017, a group called Dark Overlord hacked into school district servers in several states and obtained access to students' personal information, including counselor reports and medical records. The group used the data to threaten students and their families with physical violence.
5. Charter schools and voucher programs
School choice is definitely among the hot topics in education these days. Former U.S. Secretary of Education Betsy DeVos was a vocal supporter of various forms of parental choice, including charter schools and school vouchers.
Charter schools are funded through a combination of public and private money and operate independently of the public system. They have charters (i.e., contracts) with school districts, states, or private organizations. These charters outline the academic outcomes that the schools agree to achieve. Like mainstream public schools, charter schools cannot teach religion or charge tuition, and their students must complete standardized testing . However, charter schools are not limited to taking students in a certain geographic area. They have more autonomy to choose their teaching methods. Charter schools are also subject to less oversight and fewer regulations.
School vouchers are like coupons that allow parents to use public funds to send their child to the school of their choice, which can be private and may be either secular or religious. In many cases, vouchers are reserved for low-income students or students with disabilities.
Advocates argue that charter schools and school vouchers offer parents a greater range of educational options. Opponents say that they privatize education and siphon funding away from regular public schools that are already financially strapped. The 2018 Education Next survey found that 44 percent of the general public supports charter schools' expansion, while 35 percent oppose such a move. The same poll found that 54 percent of people support vouchers.
6. Common Core
The Common Core State Standards is a set of academic standards for math and language arts that specify what public school students are expected to learn by the end of each year from kindergarten through 12th grade. Developed in 2009, the standards were designed to promote equity among public K-12 students. All students would take standardized end-of-year tests and be held to the same internationally benchmarked standards. The idea was to institute a system that brought all schools up to the same level and allowed for comparison of student performance in different regions. Such standards would help all students with college and career readiness.
Some opponents see the standards as an unwelcome federal intrusion into state control of education. Others are critical of the way the standards were developed with little input from experienced educators. Many teachers argue that the standards result in inflexible lesson plans that allow for less creativity and fun in the learning process.
Some critics also take issue with the lack of accommodation for non-traditional learners. The Common Core prescribes standards for each grade level, but students with disabilities or language barriers often need more time to fully learn the material.
The vast majority of states adopted the Common Core State Standards when they were first introduced. Since then, more than a dozen states have either repealed the standards or revised them to align better with local needs. In many cases, the standards themselves have remained virtually the same but given a different name.
And a name can be significant. In the Education Next 2018 survey, a group of American adults was asked whether they supported common standards across states. About 61 percent replied that they did. But when another group was polled about Common Core specifically, only 45 percent said they supported it.
7. Standardized testing

During the No Child Left Behind (NCLB) years, schools—and teachers—were judged by how well students scored on such tests. Schools whose results weren't up to par faced intense scrutiny, and in some cases, state takeover or closure. Teachers' effectiveness was rated by how much improvement their students showed on standardized exams. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), which took effect in 2016, removed NCLB's most punitive aspects. Still, it maintained the requirement to test students every year in Grades 3 to 8, and once in high school.
But many critics say that rampant standardized testing is one of the biggest problems in education. They argue that the pressure to produce high test scores has resulted in a teach-to-the-test approach to instruction in which other non-tested subjects (such as art, music, and physical education) have been given short shrift to devote more time to test preparation. And they contend that policymakers overemphasize the meaning of standardized test results, which don't present a clear or complete picture of overall student learning.
8. Teacher salaries
According to 2021-22 data from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), in most states, teacher pay has decreased over the last several years. However, in some states average salaries went up. It's also important to note that public school teachers generally enjoy pensions and other benefits that make up a large share of their compensation.
But the growth in benefits has not been enough to balance out the overall low wages. An Economic Policy Institute report found that even after factoring in benefits, public-sector teachers faced a compensation penalty of 14.2 percent in 2021 relative to other college graduates.
9. The teaching of evolution
In the U.S., public school originated to spread religious ideals, but it has since become a strictly secular institution. And the debate over how to teach public school students about the origins of life has gone on for almost a century.
Today, Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection is accepted by virtually the entire scientific community. However, it is still controversial among many Americans who maintain that living things were guided into existence. A pair of surveys from 2014 revealed that 98 percent of scientists aligned with the American Association for the Advancement of Science believed that humans evolved. But it also revealed that, overall, only 52 percent of American adults agreed.
Over the years, some states have outright banned teachers from discussing evolution in the classroom. Others have mandated that students be allowed to question the scientific soundness of evolution, or that equal time be given to consideration of the Judeo-Christian notion of divine creation (i.e., creationism).
Some people argue that the theory of intelligent design—which posits that the complexities of living things cannot be explained by natural selection and can best be explained as resulting from an intelligent cause—is a legitimate scientific theory that should be allowed in public school curricula. They say it differs from creationism because it doesn't necessarily ascribe life's design to a supernatural deity or supreme being.
Opponents contend that intelligent design is creationism in disguise. They think it should not be taught in public schools because it is religiously motivated and has no credible scientific basis. And the courts have consistently held that the teaching of creationism and intelligent design promotes religious beliefs and therefore violates the Constitution's prohibition against the government establishment of religion. Still, the debate continues.
10. Teacher tenure
Having tenure means that a teacher cannot be let go unless their school district demonstrates just cause. Many states grant tenure to public school teachers who have received satisfactory evaluations for a specified period of time (which ranges from one to five years, depending on the state). A few states do not grant tenure at all. And the issue has long been mired in controversy.
Proponents argue that tenure protects teachers from being dismissed for personal or political reasons, such as disagreeing with administrators or teaching contentious subjects such as evolution. Tenured educators can advocate for students without fear of reprisal. Supporters also say that tenure gives teachers the freedom to try innovative instruction methods to deliver more engaging educational experiences. Tenure also protects more experienced (and more expensive) teachers from being arbitrarily replaced with new graduates who earn lower salaries.
Critics contend that tenure makes it difficult to dismiss ineffectual teachers because going through the legal process of doing so is extremely costly and time-consuming. They say that tenure can encourage complacency since teachers' jobs are secure whether they exceed expectations or just do the bare minimum. Plus, while the granting of tenure often hinges on teacher evaluations, 2017 research found that, in practice, more than 99 percent of teachers receive ratings of satisfactory or better. Some administrators admit to being reluctant to give low ratings because of the time and effort required to document teachers' performance and provide support for improvement.
11. Bullying
Bullying continues to be a major issue in schools all across the U.S. According to a National Center for Education Statistics study , around 22 percent of students in Grades 6 through 12 reported having been bullied at school, or on their way to or from school, in 2019. That figure was down from 28 percent in 2009, but it is still far too high.
The same study revealed that over 22 percent of students reported being bullied once a day, and 6.3 percent reported experiencing bullying two to ten times in a day. In addition, the percentage of students who reported the bullying to an adult was over 45 percent in 2019.
But that still means that almost 60 percent of students are not reporting bullying. And that means children are suffering.
Bullied students experience a range of emotional, physical, and behavioral problems. They often feel angry, anxious, lonely, and helpless. They are frequently scared to go to school, leading them to suffer academically and develop a low sense of self-worth. They are also at greater risk of engaging in violent acts or suicidal behaviors.
Every state has anti-bullying legislation in place, and schools are expected to develop policies to address the problem. However, there are differences in how each state defines bullying and what procedures it mandates when bullying is reported. And only about one-third of states call for school districts to include provisions for support services such as counseling for students who are victims of bullying (or are bullies themselves).
12. Poverty
Student poverty is a growing problem. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics show that as of the 2019-2020 school year, low-income students comprised a majority (52 percent) of public school students in the U.S. That represented a significant increase from 2000-2001, when only 38 percent of students were considered low-income (meaning they qualified for free or discounted school lunches).
The numbers are truly alarming: In 39 states, at least 40 percent of public school enrollees were eligible to receive free or reduced-price lunches, and 22 of those states had student poverty rates of 50 percent or more.
Low-income students tend to perform worse in school than their more affluent peers. Studies have shown that family income strongly correlates to student achievement on standardized tests. That may be partly because parents with fewer financial resources generally can't afford tutoring and other enrichment experiences to boost student achievement. In addition, low-income children are much more likely to experience food instability, family turmoil, and other stressors that can negatively affect their academic success.
All of this means that teachers face instructional challenges that go beyond students' desires to learn.
13. Class size
According to NCES data , in the 2017-2018 school year, the average class size in U.S. public schools was 26.2 students at the elementary level and 23.3 students at the secondary level.
But anecdotal reports suggest that today, classrooms commonly have more than 30 students—sometimes as many as 40.
Conventional wisdom holds that smaller classes are beneficial to student learning. Teachers often argue that the size of a class greatly influences the quality of the instruction they are able to provide. Research from the National Education Policy Center in 2016 showed smaller classes improve student outcomes, particularly for early elementary, low-income, and minority students.
Many (but not all) states have regulations in place that impose limits on class sizes. However, those limits become increasingly difficult to maintain in an era of budget constraints. Reducing class sizes requires hiring more teachers and constructing new classrooms. Arguably, allowing class sizes to expand can enable districts to absorb funding cuts without making reductions to other programs such as art and physical education.
7 Big Issues in Higher Education

1. Student loan forgiveness
Here's how the American public education system works: Students attend primary and secondary school at no cost. They have the option of going on to post-secondary training (which, for most students, is not free). So with costs rising at both public and private institutions of higher learning, student loan debt is one of the most prominent issues in education today. Students who graduated from college in 2022 came out with an average debt load of $37,338. As a whole, Americans owe over $1.7 trillion in student loans.
Currently, students who have received certain federal student loans and are on income-driven repayment plans can qualify to have their remaining balance forgiven if they haven't repaid the loan in full after 20 to 25 years, depending on the plan. Additionally, the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program allows qualified borrowers who go into public service careers (such as teaching, government service, social work, or law enforcement) to have their student debt canceled after ten years.
However, potential changes are in the works. The Biden-Harris Administration is working to support students and make getting a post-secondary education more affordable. In 2022, the U.S. Department of Education provided more than $17 billion in loan relief to over 700,000 borrowers. Meanwhile, a growing number of Democrats are advocating for free college as an alternative to student loans.
2. Completion rates
The large number of students who begin post-secondary studies but do not graduate continues to be an issue. According to a National Student Clearinghouse Research Center report , the overall six-year college completion rate for the cohort entering college in 2015 was 62.2 percent. Around 58 percent of students completed a credential at the same institution where they started their studies, and about another 8 percent finished at a different institution.
Completion rates are increasing, but there is still concern over the significant percentage of college students who do not graduate. Almost 9 percent of students who began college in 2015 had still not completed a degree or certificate six years later. Over 22 percent of them had dropped out entirely.
Significant costs are associated with starting college but not completing it. Many students end up weighed down by debt, and those who do not complete their higher education are less able to repay loans. Plus, students miss out on formal credentials that could lead to higher earnings. Numbers from the Bureau of Labor Statistics show that in 2021 students who begin college but do not complete a degree have median weekly earnings of $899. By contrast, associate degree holders have median weekly wages of $963, and bachelor's degree recipients have median weekly earnings of $1,334.
Students leave college for many reasons, but chief among them is money. To mitigate that, some institutions have implemented small retention or completion grants. Such grants are for students who are close to graduating, have financial need, have used up all other sources of aid, owe a modest amount, and are at risk of dropping out due to lack of funds. One study found that around a third of the institutions who implemented such grants noted higher graduation rates among grant recipients.
3. Student mental health
Mental health challenges among students are a growing concern. A survey by the American College Health Association in the spring of 2019 found that over two-thirds of college students had experienced "overwhelming anxiety" within the previous 12 months. Almost 45 percent reported higher-than-average stress levels.
Anxiety, stress, and depression were the most common concerns among students who sought treatment. The 2021 report by the Center for Collegiate Mental Health (CCMH) noted the average number of appointments students needed has increased by 20 percent.
And some schools are struggling to keep up. A 2020 report found that the average student-to-clinician ratio on U.S. campuses was 1,411 to 1. So, in some cases, suffering students face long waits for treatment.
4. Sexual assault

The Bureau of Justice Statistics reports that more than 75 percent of sexual assaults are not reported to law enforcement, so the actual number of incidents could be much higher.
And the way that colleges and universities deal with sexual assault is undergoing changes. Title IX rules makes sure that complaints of sexual assault or harassment are taken seriously and ensuring the accused person is treated fairly.
Administrators were also required to adjudicate such cases based on a preponderance of evidence, meaning that they had to believe that it was more likely than not that an accused was guilty in order to proceed with disciplinary action. The "clear and convincing" evidentiary standard, which required that administrators be reasonably certain that sexual violence or harassment occurred, was deemed unacceptable.
Critics argued that the guidelines failed to respect the due process rights of those accused of sexual misconduct. Research has found that the frequency of false sexual assault allegations is between two and 10 percent.
In 2017, the Trump administration rescinded the Obama-era guidelines. The intent was to institute new regulations on how schools should handle sexual assault allegations. The changes went into effect on August 14, 2020, defining sexual harassment more narrowly and only requiring schools to investigate formal complaints about on-campus incidents officially filed with designated authorities, such as Title IX coordinators. The updated guidelines also allow schools to use the clear and convincing standard for conviction.
Victims' rights advocates were concerned this approach would deter victims from coming forward and hinder efforts to create safe learning environments.
The Biden administration is expected to release their proposed revisions to Title IX in October 2023 which could see many of the Trump administration changes rescinded.
5. Trigger warnings
The use of trigger warnings in academia is a highly contentious issue. Trigger warnings alert students that upcoming course material contains concepts or images that may invoke psychological or physiological reactions in people who have experienced trauma. Some college instructors provide such warnings before introducing films, texts, or other content involving things like violence or sexual abuse. The idea is to give students advance notice so that they can psychologically prepare themselves.
Some believe that trigger warnings are essential because they allow vulnerable people to prepare for and navigate difficult content. Having trigger warnings allows students with post-traumatic stress to decide whether they will engage with the material or find an alternative way to acquire the necessary information.
Critics argue that trigger warnings constrain free speech and academic freedom by discouraging the discussion of topics that might trigger distressing reactions in some students. They point out that college faculty already provide detailed course syllabi and that it's impossible to anticipate and acknowledge every potential trigger.
In 2015, NPR Ed surveyed more than 800 faculty members at higher education institutions across the U.S. and found that around half had given trigger warnings before bringing up potentially disturbing course material. Most did so on their own initiative, not in response to administrative policy or student requests. Few schools either mandate or prohibit trigger warnings. One notable exception is the University of Chicago, which in 2016 informed all incoming first-year students that it did not support such warnings.
6. College accreditation
In order to participate in federal student financial aid programs, institutions of higher education must be accredited by an agency that is recognized by the U.S. Department of Education. By law, accreditors must consider factors such as an institution's facilities, equipment, curricula, admission practices, faculty, and support services. The idea is to enforce an acceptable standard of quality.
But while federal regulations require accreditors to assess each institution's "success with respect to student achievement," they don't specify how to measure such achievement. Accreditors are free to define that for themselves. Unfortunately, some colleges with questionable practices, low graduation rates, and high student loan default rates continue to be accredited. Critics argue that accreditors are not doing enough to ensure that students receive good value for their money.
7. College rankings
Every year, prospective college students and their families turn to rankings like the ones produced by U.S. News & World Report to compare different institutions of higher education. Many people accept such rankings as authoritative without truly understanding how they are calculated or what they measure.
It's common for ranking organizations to refine their methodologies from year to year and change how they weigh various factors—which means it's possible for colleges to rise or fall in the rankings despite making no substantive changes to their programs or institutional policies. That makes it difficult to compare rankings from one year to the next, since things are often measured differently.
For colleges, a higher ranking can lead to more visibility, more qualified applicants, and more alumni donations (in short: more money). And the unfortunate reality is that some schools outright lie about test scores, graduation rates, or financial information in their quest to outrank their competitors.
Others take advantage of creative ways to game the system. For example, U.S. News looks at the test scores of incoming students at each institution, but it only looks at students who begin in the fall semester. One school instituted a program where students with lower test scores could spend their first semester in a foreign country and return to the school in the spring, thus excluding them from the U.S. News calculations.
Rankings do make useful information about U.S. colleges and universities available to all students and their families. But consumers should be cautious about blindly accepting such rankings as true measures of educational quality.
5 Emerging Trends in Education

1. Maker learning
The maker movement is rapidly gaining traction in K-12 schools across America. Maker learning is based on the idea that you will engage students in learning by encouraging interest-driven problem solving and hands-on activities (i.e., learning by doing). In collaborative spaces, students identify problems, dream up inventions, make prototypes, and keep tinkering until they develop something that makes sense. It's a do-it-yourself educational approach that focuses on iterative trial and error and views failure as an opportunity to refine and improve.
Maker education focuses on learning rather than teaching. Students follow their interests and test their own solutions. For example, that might mean creating a video game, building a rocket, designing historical costumes, or 3D-printing an irrigation system for a garden. It can involve high-tech equipment, but it doesn't have to. Repurposing whatever materials are on hand is an important ideal of the maker philosophy.
There is little hard data available on the maker trend. However, researchers at Rutgers University are currently studying the cognitive basis for maker education and investigating its connection to meaningful learning.
2. Moving away from letter grades
Many education advocates believe that the traditional student assessment models place too much emphasis on standardization and testing. They feel that traditional grading models do not sufficiently measure many of the most prized skills in the 21st-century workforce, such as problem-solving, self-advocacy, and creativity. As a result, a growing number of schools around the U.S. are replacing A-F letter grades with new assessment systems.
Formed in 2017, the Mastery Transcript Consortium is a group of more than 150 private high schools that have pledged to get rid of grade-based transcripts in favor of digital ones that provide qualitative descriptions of student learning as well as samples of student work. Some of the most famous private institutions in America have signed on, including Dalton and Phillips Exeter.
The no-more-grades movement is taking hold in public schools as well. Many states have enacted policies to encourage public schools to use something other than grades to assess students' abilities. It's part of a larger shift toward what's commonly known as mastery-based or competency-based learning, which strives to ensure that students become proficient in defined areas of skill.
Instead of letter grades, report cards may feature phrases like "partially meets the standard" or "exceeds the standard." Some schools also include portfolios, capstone projects, or other demonstrations of student learning.
But what happens when it's time to apply to college? It seems that even colleges and universities are getting on board. At least 85 higher education institutions across New England (including Dartmouth and Harvard) have said that students with competency-based transcripts will not be disadvantaged during the admission process.
3. The rise of micro-credentials
Micro-credentials, also known as digital badges or nanodegrees, are mini qualifications that demonstrate a student's knowledge or skills in a given area. Unlike traditional college degrees that require studying a range of different subjects over a multi-year span, micro-credentials are earned through short, targeted education focused on specific skills in particular fields. They tend to be inexpensive (sometimes even free) and are typically taken online.
Some post-secondary schools are developing micro-credentialing partnerships with third-party learning providers, while other schools offer such solutions on their own. A 2020 Campus Technology article stated 70 percent of higher education institutions offer some type of alternative credentialing.
Micro-credentials can serve as evidence that students have mastered particular skills, but the rigor and market worth of such credentials can vary significantly. Still, they are an increasingly popular way of unbundling content and providing it on demand.
4. Flipped classrooms
A growing number of schools are embracing the notion of flipped learning. It's an instructional approach that reverses the traditional model of the teacher giving a lecture in front of the class, then sending students home to work through assignments that enhance their understanding of the concepts. In flipped learning, students watch lecture videos or read relevant course content on their own before class. Class time is devoted to expanding on the material through group discussions and collaborative learning projects (i.e., doing what was traditionally meant as homework). The instructor is there to guide students when questions or problems arise.
Provided that all students have access to the appropriate technology and are motivated to prepare for each class session, flipped learning can bring a wide range of benefits. For example, it allows students to control their own learning by watching lecture videos at their own pace; they can pause, jot down questions, or re-watch parts they find confusing. The model also encourages students to learn from each other and explore subjects more deeply.
Flipped learning is becoming widespread in all education levels, but it is especially prevalent at the college level. In a 2017 survey , 61 percent of college faculty had used the flipped model in some or all of their classes and another 24% of instructors were considering trying it.
5. Social-emotional learning
There is a growing consensus that schools are responsible for fostering students' social and emotional development and their cognitive skills. Social-emotional learning (SEL) focuses on helping students develop the abilities to identify their strengths, manage their emotions, set goals, show empathy, make responsible decisions, and build and maintain healthy relationships. Research has shown that such skills play a key role in reducing anti-social behavior, boosting academic achievement, and improving long-term health.
Every state has developed SEL competencies at the preschool level. The number of states with such competencies for higher grades is growing.
Explore Your Educational Options
Learning about current issues in education may have brought up some questions that could hold the key to the future you want to build. How do I get the skills I need for my chosen career? How can I learn more about the programs offered at trade schools near me ?
You can get started right here, right now. You can get started right here, right now. The search tool below will narrow down the best options based on your zip code. And these vocational schools are eager to provide the information you need to decide on the right fit for you.
Related Articles

Where do you want to study?
What do you want to study?
What's your {{waterMark}} code?

"I recommend using Trade-Schools.net because you can find the program that you are interested in nearby or online. " Trade-Schools.net User
More From Forbes
America’s education crisis is costing us our school leadership. what are we going to do about it.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
It’s not just teachers who are reeling from two years of pandemic learning. School leaders and counselors are facing extreme burnout, too—and they need their communities to rally.
Record numbers of school leaders are considering exiting the profession
For two years now, America’s teachers have coped with virtual/hybrid pandemic school, Covid-19 learning slide, societal unrest and deep political polarities, alongside their own personal challenges. As a result, a significant number are about to call it quits and leave the profession for good.
Education is heading for a crisis of epic proportions —and in many places, it’s already started. Teachers clearly need their community’s support, but they’re not the only ones struggling with the extreme strain of these times. Counselors and school leaders—administrators, superintendents and principals—are facing their own set of challenges. An October survey found that 63% have considered quitting as a result of the high-stress, no-win stakes of leading education today.
I was honored to connect with Dr. Shawn Bishop, superintendent of Harbor Beach Community Schools in Michigan, to talk about it from the perspective of a school leader in the trenches. Here’s what he had to share.
The burnout is real, and it’s not just from the pandemic
Dr. Bishop, whose career in education spans more than 25 years, says he’s never seen such universal levels of exhaustion—and never dreamed he would. “For almost two full years now, administrators have been caught in the crosshairs of political, social, emotional, ethical and academic battles that were brought to their doorstep,” he says.
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid-19 travel insurance plans.
So just how bad is it? In January Dr. Bishop asked his supervisory and administrative staff to rate their current level of social-emotional need from 1 (low) to 5 (high). The survey found:
- 61% of teaching staff rated their personal need as 4 or 5
- 100% of administrative staff (principals and supervisors) rated their personal need as 4 or 5
- Nearly all of the administrative staff said they can’t sleep at night and at least occasionally take medication to help
- 100% of administrative staff said their spouse has commented that their job is interfering with their relationships at home
Unfortunately, the issues raised by the pandemic are just the tip of the iceberg. “The pandemic was a catalyst that increased the rate and intensity of enormously important and often controversial issues in our communities,” Dr. Bishop says. “Because our schools are a direct reflection of the communities they serve, these topics were very literally brought into our offices, halls, school boardrooms and classrooms.
“School administrators are expected to ‘make everyone happy,’ and at the same time make sure all needs are met so learning can take place for all regardless of belief. They are expected to sew together all these various groups, with their variety of stances, into a cohesive student body and a cohesive staff. They must do all of that while being public figureheads who are directly in the public eye.”
It’s little wonder that so many of them are quitting. But stress isn’t the only reason.
Is it worth it anymore?
Most educators chose their profession because they wanted to make a positive difference in the world. It’s what drives them to give so much, every day, even when they don’t see an immediate return. But the past two years are taking their toll.
The long hours. The mental and physical exhaustion. The enormous scrutiny and public criticism. Teachers and administrators alike are starting to wonder if it’s all worth it.
It wasn’t that way when the pandemic started. “At the beginning, the thought was ‘you don’t leave your children/community when the storm starts,’” says Dr. Bishop. “I for one felt the very real obligation to stay and not abandon my kids.”
But the pandemic has dragged on for longer than anyone expected and now, says Dr. Bishop, there is a very real feeling that fulfilling a higher purpose through education is no longer worth the fight. “Like the dogs in the 1960s Martin Seligman experiment, they’ve reached a level of ‘learned helplessness,’” he says.
And then, there’s the constant barrage of communication. “The expectation that as a school leader you should be accessible 24 hours a day every day adds to the pressure and inability to pause to regroup or re-energize,” says Dr. Bishop, who’s taken just two vacation days during the past two years. “I personally receive phone calls, texts, instant messages and emails from 4am to midnight during holiday breaks and weekends.
“The expectation is that you answer and respond. And if you don’t, there’ll be communication to those who hold your job security in their hands.”
The trickle-up effect
As school leaders exit the profession, there’s concern about a “trickle-up” effect on those replacing them. “There is strong data to support less quantity and less quality of candidates moving into teaching,” Dr. Bishop says. “Thus, from a much smaller and potentially less qualified pool, schools attempt to draw their next leaders.
“Teachers see firsthand the pressure, hours and lack of positive feedback their leaders experience. As a result, these potential school leaders see low resources and high levels of critique and wonder if a change to school leadership is worth it.”
What’s the trickle-up result of all this? “Well-intended people will be taking positions that they are not qualified or experienced enough to hold,” explains Dr. Bishop. “When that happens, the organization can no longer move forward. Visionary, forward-thinking projects and programs cannot form under leaders that don’t possess the skills to rally people, resources and energy.
“Progress becomes a thing of the past, and survival of the moment is what’s left.”
Strengthening internal partnerships
In some organizations, the constantly changing demands of the pandemic have shattered trust among the different departments. When I asked Dr. Bishop how administrators, counselors and teachers could rebuild it, he gently pushed back against the assumption that all such partnerships are lacking trust. “As with any agency/business, some run with more conflict and some with great trust and cohesiveness,” he says.
But where trust has been compromised, Dr. Bishop believes the first thing needed is time to recover. “Teachers, school leaders, counselors, custodians, secretaries, bus drivers, food service workers and others—we all need time to regroup and recenter,” he says. “Nothing in my past has been to the same level as we have now, however it’s been my experience that working with what we have in common is the place to begin.”
Dr. Bishop believes that the keys to future success are founded in four critical attitudes:
1. Hope: “We must believe there is hope for achieving success and hope that we can make a difference in the world through our kids.”
2. Forgiveness: “We must also forgive ourselves and those around us for any mistakes, bad days and missteps of the past. We can’t hold mistakes of the past close to our heart but instead must leave space for kindness, progress and even laughter to make its way in.”
3. Focus on a common good. “Our efforts now must be toward stripping away differences and focusing on the bigger picture commonalities,” he says. “The basic reasons we became educators is a good place to start—as an example, the belief that through our children we can change the future for the better. The vast majority of teachers and school leaders would say they have this central calling inside. So from that common point we begin building.”
4. Assumption of positive intent. One example of when to assume positive intent is when a leader falls back on giving self-care advice to their staff. “There is no course, master’s program, webinar, or book you can reference that indicates how to motivate, inspire and provide therapy for adults who have gone through prolonged deep levels of trauma,” says Dr. Bishop. “That doesn’t completely excuse things, but perhaps giving leaders a little space for their intent and recognizing that they want to know better and do better.
“If the person on the receiving end can assume positive intent, then they could step back and realize the administrator bringing up self-care is truly trying to help,” he continues. “Most school leaders want all the best things for their staff and the students they work with each day. Perhaps at the moment they are just trying to survive. Many leaders gladly follow the Maya Angelou saying: ‘ Do the best you can until you know better. Then when you know better, do better .’”
What we can do
In light of all these challenges, I wanted to know what communities and individuals can do to support their schools and educational leadership. Dr. Bishop shared four phrases that everyone, from every side of the education system, can implement to start moving forward together.
1. Part of the problem or part of the solution? “We must remember to stay positive and rally people around the concept that we can be part of the problem or part of the solution.”
2. Assume positive intent (again): “We must dig deeper and model in every way possible that we assume each person has positive intent when they come to us,” he says. “We need to model this way of thinking and talk about this way of thinking to others.”
3. Treat others as you’d like to be treated: “Leaders need to look inward first and ask ourselves if we are treating others as we’d like to be treated,” says Dr. Bishop. “The pressures on others are real; treat them as such.”
4. Seek to understand before being understood: “Before leaders try to provide advice, examples and reasoning, they must step back and truly listen,” urges Dr. Bishop. “They must block the inner voice thinking about what to say next, and block the inner desire to solve things for people, and instead truly be in the moment and listen.”
What else do superintendents need right now? Time, training and funding—and for funding, not another round of competitive grants, notes Dr. Bishop. “There simply isn’t time for this in a day already overloaded.”
Moving forward together
As the stresses of the past two years bleed into yet another school year, visionary leadership in our education system has never been more critical. And yet, such leaders have never been so embattled. As communities and individuals, we need to rally around the counselors, superintendents, principals and administrators who remain at their post even when things seem darkest.
Let’s be part of the solution, not the problem. Let’s assume positive intent, treat others as we’d like to be treated and seek to understand what the education community is facing. For everyone with a stake in the future of education in America, there’s common ground to find and build on—if we look for it.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Our Mission

5 Popular Education Beliefs That Aren’t Backed by Research
Making adjustments to these common misconceptions can turn dubious strategies into productive lessons, the research suggests.
Not every learning myth requires teachers to pull up stakes and start all over again—at least not entirely. There are some commonly held misconceptions that contain a nugget of wisdom but need to be tweaked in order to align with the science of learning.
Sometimes, in other words, you’re already halfway there. Here are five mostly myths, from the power of doodling to the motivating role of grades, that educators can quickly adjust and turn to their advantage.
1. Doodling Improves Focus and Learning
When we write about the power of drawing to learn, we often hear from readers who feel compelled to defend an old habit: “See, I told you that when I was doodling, I was still paying attention!” But doodling—which is commonly defined as “an aimless or casual scribble or sketch” and often consists of marginalia like cartoon characters, geometric patterns, or pastoral scenes—is distinct from what researchers call “task-related drawing.” And doodling, in this sense, is not associated with improvements in focus or academic outcomes.
In fact, both cognitive load theory and experimental studies are generally downbeat on doodling. Students who sketch complicated scenes or designs as they try to process a lesson on plate tectonics, according to the first theory, are engaging in competitive cognitive tasks and will generally underperform on both. Doodling, like all drawing, is cognitively intensive, involving complex feedback loops between visual, sensorimotor, attentional, and planning regions of the brain and body. Because our ability to process information is finite, drawing and learning about different things at the same time is a simple question of too much.
Research confirms the theory. A 2019 study pitted off-task doodling against typical learning activities like “task-related drawing” and writing. In three separate but related experiments, task-related drawing and writing beat out doodling in terms of recall—by margins as large as 300 percent. How to fix it: Sketching what you are actually learning—from representational drawings of cells or tectonic boundaries to the creation of concept maps and organizational drawings—is, in fact, a powerful learning strategy (see research here , here , and here ), and that applies “regardless of one’s artistic talent,” a 2018 study confirms. Try to harness a student’s passion for doodling by allowing them to submit academic sketches as work products. To get even more bang for your buck, ask them to annotate their drawings, or talk you through them—which will encode learning even more deeply, according to research .
2. Reading Aloud In Turn Improves Fluency
Often called round robin reading (RRR), I resorted to it when I taught years ago—and it appears that it’s still frequently used, judging from a 2019 blog by literacy expert Timothy Shanahan and comments on a 2022 Cult of Pedagogy post on the topic. Teachers deploy RRR—during which the whole class follows a text while students read sections consecutively—for good reasons: Arguably, the practice encourages student engagement, gives teachers the opportunity to gauge oral reading fluency, and has a built-in classroom management benefit as well. Students are generally silent and (superficially) attentive when a peer is reading.
But according to Shanahan, and the literacy professors Katherine Hilden and Jennifer Jones, the practice has long been frowned upon. In an influential 2012 review of relevant literature , Hilden and Jones cut straight to the point: “We know of no research evidence that supports the claim that RRR actually contributes to students becoming better readers, either in terms of their fluency or comprehension.”
In fact, RRR has plenty of problems. Individual students using RRR may accumulate less than three hours of oral reading time over the course of a year, according to Shanahan—and Hilden and Jones say that students who are following along during the activity tend to “subvocalize” as they track the reader, reducing their own internal reading speed unnecessarily. RRR also has the unfortunate effects of stigmatizing struggling readers, exposing new readers to dysfluent modeling, and failing to incorporate meaningful comprehension strategies.
How to fix it: Yes, reading out loud is necessary to teach fluency, according to Shanahan, but there are better methods. Pairing kids together to “read sections of the text aloud to each other (partner reading) and then discuss and answer your questions” is a good approach, he says, especially if teachers circulate to listen for problems.
More generally, reading strategies that model proper reading speed, pronunciation, and affect—while providing time for vocabulary review, repeated exposure to the text, and opportunities to summarize and discuss—can improve both fluency and comprehension.
A 2011 study , for example, demonstrated that combining choral reading—teachers and students read a text in unison (similar to echo reading )—with other activities like vocabulary review, teacher modeling, and follow-up discussion improved students’ decoding and fluency.
3. Talent Beats Persistence
It’s a common trap: Observers tend to rate people who appear to be naturally gifted at something more highly than those who admit they’ve worked hard to achieve success. Researchers call this the “ naturalness bias ,” and it shows up everywhere, from teachers evaluating students to bosses evaluating employees.
In reality, the opposite is more often true. “Popular lore tells us that genius is born, not made,” writes psychologist and widely cited researcher of human potential K. Anders Ericsson for the Harvard Business Review . “Scientific research, on the other hand, reveals that true expertise is mainly the product of years of intense practice and dedicated coaching.”
Experimental studies extend the point to academics: An influential 2019 study led by psychologists Brian Galla and Angela Duckworth, for example, found that high school GPA is a better predictor than the SAT of how likely students are to complete college on time. That’s because “grades are a very good index of your self-regulation—your ability to stick with things, your ability to regulate your impulses, your ability to delay gratification and work hard instead of goofing off,” said Duckworth in a 2020 interview with Edutopia .
How to fix it: All kids—even the ones who already excel in a discipline—benefit when teachers emphasize the importance of effort, perseverance, and growth. Consider praising students for their improvement instead of their raw scores; have students read about and then discuss the idea of neural plasticity; and consider assigning reports on the mistakes and growing pains of accomplished writers, scientists, and artists.
Try to incorporate rough-draft thinking in class, and think about taking risks yourself: The renowned writing teacher Kelly Gallagher, author of Readicide , regularly composes in front of his class to model his own tolerance for errors and redrafting.
4. Background Music (Always) Undermines Learning
It’s a fascinating and complex question: Can students successfully learn while background music is playing?
In some cases, it appears, background music can be a neutral to positive influence; in other scenarios, it’s clearly distracting. There are several factors at play in determining the outcomes.
A 2021 study clarifies that because music and language use some of the same neural circuitry—a finding that appears as early as infancy —“listening to lyrics of a familiar language may rely on the same cognitive resources as vocabulary learning,” and that can “lead to an overload of processing capacity and thus to an interference effect.” Other features of the music probably matter, too: Dramatic changes in a song’s rhythm, for example, or transitions from one song to the next often force the learning brain to reckon with irrelevant information. A 2018 research review confirms the general finding: Across 65 studies, background music consistently had a “small but reliably detrimental effect” on reading comprehension.
In some cases, however, music may aid learning. Neuroscience suggests that catchy melodies, for example, can boost a student’s mood—which might lead to significant positive effects on learning when motivation and concentration are paramount, a 2023 study found.
How to fix it: Basically, “music has two effects simultaneously that conflict with one another,” cognitive psychologist Daniel Willingham told Edutopia in 2023 —one distracting and the other arousing.
“If you’re doing work that’s not very demanding, having music on is probably fine”—and likely to motivate students to keep going, Willingham says . In those cases, try to stick to music that’s instrumental or familiar, in order to decrease the cognitive resources needed to process it. “But if you’re doing work that’s just somewhat difficult, the distraction is probably going to make music a negative overall,” Willingham adds.
5. Grades Are Motivating
Teachers are well aware that grading, as a system, has many flaws—but at least grades motivate students to try their hardest, right? Unfortunately, the research suggests that that’s largely not the case.
“Despite the conventional wisdom in education, grades don’t motivate students to do their best work, nor do they lead to better learning or performance,” write motivation researcher Chris Hulleman and science teacher Ian Kelleher in an article for Edutopia . A 2019 research review , meanwhile, revealed that when confronted by grades, written feedback, or nothing at all—students preferred the latter two to grades, suggesting that A–F rankings might actually have a net negative impact on motivation.
In another blow to grades, a 2018 analysis of university policies like pass/fail grading or narrative evaluations concluded that “grades enhanced anxiety and avoidance of challenging courses” but didn’t improve student motivation. Providing students with specific, actionable feedback, on the other hand, “promot[ed] trust between instructors and students,” leading to greater academic ambition.
How to fix it: While grades are still mandatory in most schools—and some form of rigorous assessment remains an imperative—educators might consider ways to de-emphasize them.
Some teachers choose to drop every student’s lowest grade , for example; allow students to retake a limited number of assessments each unit; or periodically give students the discretion to turn in “their best work” from a series of related assignments.
At King Middle School, in Portland, Maine , educators delay their release of grades until the end of the unit, an approach backed by a 2021 study that found that delayed grading—handing back personalized feedback days before releasing number or letter grades—can boost student performance on future assignments by two-thirds of a letter grade.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
72% of U.S. high school teachers say cellphone distraction is a major problem in the classroom

New York Gov. Kathy Hochul recently announced that she will introduce legislation to ban smartphones in schools during her state’s 2025 legislative session. She cited the impact that social media and technology can have on youth, including leaving them “cut off from human connection, social interaction and normal classroom activity.”
Hochul’s legislative push comes as K-12 teachers in the United States face challenges around students’ cellphone use, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in fall 2023. One-third of public K-12 teachers say students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, and another 20% say it’s a minor problem.
Following news that New York Gov. Kathy Hochul is seeking to ban smartphones in schools, Pew Research Center published this analysis to examine how K-12 teachers and teens in the United States feel about cellphones, including the use of cellphones at school.
This analysis is based on two recent Center surveys, one of public K-12 teachers in the U.S. and the other of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17. More information about these surveys, including their field dates, sample sizes and other methodological details, is available at the links in the text.
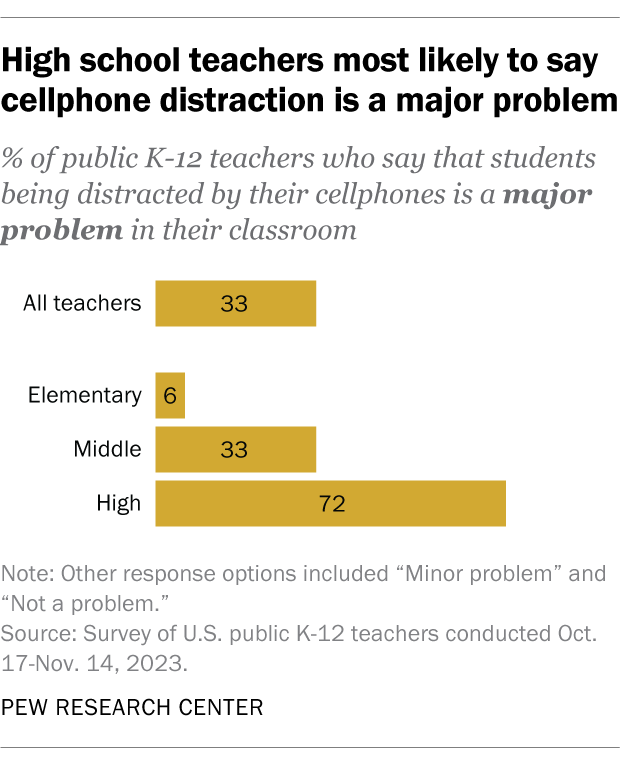
High school teachers are especially likely to see cellphones as problematic. About seven-in-ten (72%) say that students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, compared with 33% of middle school teachers and 6% of elementary school teachers.
Many schools and districts have tried to address this challenge by implementing cellphone policies , such as requiring students to turn off their phones during class or give them to administrators during the school day.
Overall, 82% of K-12 teachers in the U.S. say their school or district has a cellphone policy of some kind. Middle school teachers (94%) are especially likely to say this, followed by elementary (84%) and high school (71%) teachers.
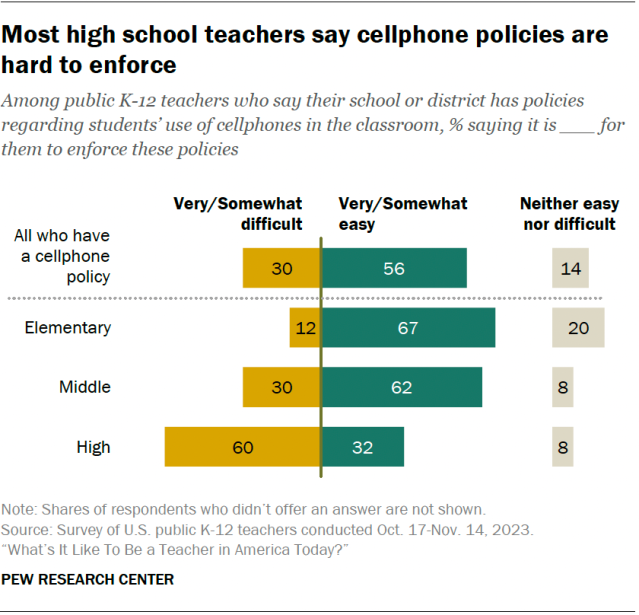
However, 30% of teachers whose schools or districts have cellphone policies say they are very or somewhat difficult to enforce. High school teachers are more likely than their peers to report that enforcing these policies is difficult. Six-in-ten high school teachers in places with a cellphone policy say this, compared with 30% of middle school teachers and 12% of elementary school teachers.
Our survey asked teachers about cellphones in general, whereas Hochul’s plan would apply only to smartphones. Even so, nearly all U.S. teenagers ages 13 to 17 – 95% – say they have access to a smartphone , according to a separate Center survey from 2023.
Even as some policymakers and teachers see downsides to smartphones, teens tend to view the devices as a more positive than negative thing in their lives overall.
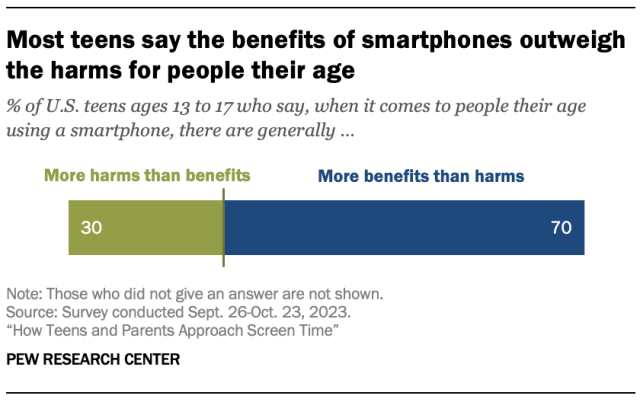
Seven-in-ten teens ages 13 to 17 say there are generally more benefits than harms to people their age using smartphones , while three-in-ten say the opposite. And 45% of teens say smartphones make it easier for people their age to do well in school, compared with 23% who say they make it harder. Another 30% say smartphones don’t affect teens’ success in school.
- Smartphones
Jenn Hatfield is a writer/editor at Pew Research Center .
U.S. public, private and charter schools in 5 charts
A quarter of u.s. teachers say ai tools do more harm than good in k-12 education, most americans think u.s. k-12 stem education isn’t above average, but test results paint a mixed picture, about 1 in 4 u.s. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year, about half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Classroom Tech Outpaces Research. Why That’s a Problem

- Share article
Classroom tools and technology are changing too fast for traditional research to keep up without significant support to identify best practices and get them into the classroom.
That was the consensus of state education leaders, equity advocates, and ed-tech experts at a symposium on the future of education research and development, held to standing-room-only on Capitol Hill Thursday.
“We know instinctively that what works to teach an 8th grader in Houston who is behind grade level in reading isn’t necessarily the same as what it takes to teach a 1st grader in rural New Mexico how to read, or that what worked for us when we were in high school might not work for kids entering high school today,” said Sara Schapiro, senior fellow and director of social innovation for the Federation of American Scientists, who leads the Alliance for Learning Innovation , a coalition of groups aiming to improve education research. “But without a robust R&D system, we simply can’t know what works, for whom, and under which conditions.”
The Alliance has called for Congress to update its R&D priorities for education research and budget $1.95 billion for research and development at the STEM Education directorate at the National Science Foundation and $900 million for R&D at the U.S. Department of Education’s Institute of Education Sciences. That would require something of a reversal from Congress. From fiscal years 2022 to 2023 Education Department research and development declined from $390 million to $349 million according to the Congressional Research Service.
“What works in terms of effective [education] interventions, programs, and services has always been accessible and available to more affluent communities,” said Augustus Mays, the vice president of partnerships and engagement at the Education Trust, a nonprofit focused on educational equity. “But for those who haven’t had the same opportunities or the same resources, that hasn’t always been available to them. Evidence-based policy making, to me, has always been the difference maker.”
Mays pointed to the move to focus federal pandemic relief money on tutoring programs whose design showed evidence of effectiveness, such as individual or very small groups, and using an aligned curriculum in sessions at least three times a week. This model differed from tutoring provided under the No Child Left Behind Act’s supplemental education services, which were repeatedly found to have no benefit for student achievement—in part because programs varied significantly from district to district.
Richard Culatta, chief executive officer of the International Society for Technology in Education, said education technology is changing classroom practices too quickly for educators to depend on a traditional research grant cycle.
“A five-year [randomized controlled trial] is not going to be very helpful right now, when apps and [artificial intelligence] are changing very quickly and every two weeks there’s a completely new set of functionality,” Culatta said. “We’ve got to think about new approaches to doing that research.”
Education research needs to move faster and be more useful to teachers, experts argue
There has been some growing traction in Congress to create a fifth center within IES dedicated to “quick turnaround, high-reward research ,” dubbed the National Center for the Advanced Development and Education.
The Obama administration in 2011 attempted to make such an R&D center, intended as the education equivalent of the Defense Department’s Advanced Research Projects Agency, the Defense Department’s bleeding-edge research project, credited with developing things like the Internet, stealth technology, and global positioning systems. That attempt failed but helped spawn Investing in Innovation, or i3, grants. I3 has been lauded for helping scale up promising programs and critiqued for still having a yearslong evaluation timeframe and limited success, with only 12 of the 67 completed i3 evaluations showing any benefit for student achievement.
“We need a research agenda that drives a more thoughtful conversation, that isn’t just about what we fund,” Culatta said. Future education research, he said, must be “co-created with educators, where the end goal is not just publishing in a peer-reviewed journal; it’s making [an] impact and demonstrating impact.”
Research policymakers also urged Congress and states to provide more support to ensure teachers stay abreast of the best evidence on learning. “We can learn a whole lot from the research community about how to make learning better and more effective—and if we walk into schools and we’re still talking about ‘left-brain, right-brain’ and ‘learning styles,’ none of that is having the impact that it needs to,” Culatta said, referring to two popular but long-disproven ideas about student learning.
Maryland’s state superintendent Carey Wright agreed. Wright previously led Mississippi’s public schools, where she spearheaded the state’s “science of reading” initiative . Wright said it was easy to find research-backed reading practices, but much more difficult to ensure that all educators understood them.
“I said to my team, ‘We’re not going to assume that anybody knows how to do [science-based reading practices],’ because we had a whole lot of balanced literacy going on,” Wright said. “We were going to stick with what the research has to say that we know works, so we retrained every teacher in the state eventually.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

A business journal from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania
Is DEI Going Away? Here’s What Experts Say
June 10, 2024 • 6 min read.
Wharton, Harvard, and INSEAD brought academics and industry leaders together to discuss the complex challenges facing DEI and what’s getting in the way of change.

- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion
DEI is under attack. Wharton management professor Stephanie Creary is trying to help save it.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives that began during the racial reckoning of 2020, when the murder of George Floyd renewed demands for social justice, are being pulled apart by political and cultural shifts. A Supreme Court ruling last year ended affirmative action in college admissions, more than 30 states have introduced laws banning or limiting DEI initiatives, and many companies are cutting their DEI teams.
“DEI isn’t the problem. Inequality is the problem,” Creary said. “The attacks on DEI are a defensive response because people don’t want to handle the broader issues of inequality. It’s easy to make DEI the scapegoat.”
Searching for solutions, Creary has launched the Relationships Across Differences Roundtable (RADs), a coalition of more than 70 academics and industry leaders committed to advancing inclusivity in all its forms — race, gender, ethnicity, religion, ability, neurodiversity, and age. They are partnering to share science-backed insights and best practices, strategize on common problems, and find ways to engage all stakeholders, even the ones who don’t believe in DEI.
“DEI isn’t the problem. Inequality is the problem.” — Stephanie Creary
Academics and Practitioners Join Forces to Commit to DEI
The roundtable is a partnership between Wharton, Harvard Business School, and INSEAD. The group held its inaugural meeting on May 14 at Wharton, where members spent the day talking candidly and confidentially about some of their biggest and most complex challenges.
“How can we use the work that you are doing to make this country, this world, a better place?” Wharton Dean Erika James said in her opening remarks. “If there is anything that we need now, it’s greater peace and harmony and learning to activate relationships across differences.”
Peer-to-peer groups are nothing new. Neither are coalitions dedicated to DEI. But Creary said her group is different because it combines scholars with people in the field so they can share expertise. Scholars conduct more relevant research when it’s informed by practice, she said, and the practitioners get evidence-based insights they can take back to their organizations.
“I didn’t want to just rehash the problems,” said Creary, who has spent 20 years studying diversity in the workplace. “Instead of going it alone, why don’t we form an alliance and figure out how to use our collective intelligence, resources, and expertise to tackle a problem of interest to all of us? I would like to think of it as an extended team for all the academics and practitioners involved.”
Robin Ely , business administration professor at Harvard Business School and faculty chair of the school’s Race, Gender & Equity Initiative , said organizations have been mounting DEI programs for decades with varying results. “The success of these efforts has been limited, for a variety of reasons, which tells us that we need a deeper understanding and more robust conversation about what’s truly getting in the way of change.”
“These problems don’t go away. There are still many versions of inequality, and the gaps have the potential to widen without any interventions.” — Stephanie Creary
If DEI Isn’t Going Away, What’s Next?
The roundtable members identified several key themes:
- Self-identification in the workplace is largely voluntary, and disclosure requires trust. How can companies build trust among employees who fear their information may be used against them or shared with other parties?
- More company- and industry-level data can be used to expand DEI initiatives and measure progress, but there is a global challenge in gathering that data because regulations vary from place to place.
- Firms need counsel who specialize in employment law to help them navigate the shifting legal landscape of DEI.
- How can companies recruit employees, interns, and contractors from underrepresented groups if they cannot legally target specific demographics?
- DEI must be championed by the top level of management, and leaders must learn how to integrate DEI initiatives into the business so they become embedded in the mission, rather than additive.
- DEI leaders need deep skills to understand the broader needs of the business, such as finance and operations.
- How can generative artificial intelligence, including large language models, be deployed to help DEI initiatives?
- A strategy is needed to move the “frozen middle,” a term to describe people afraid to advance DEI because of the current political situation. Can leaders learn to manage their own discomfort and the discomfort of others? Can more simplified language help convey the importance of DEI?
- Each organization should identify missing stakeholders, such as policymakers or affinity groups, and invite them to the table.
By the end of their first session, RADs members felt a mix of emotions. Some said they were “cautiously optimistic” about the future of DEI, while others were invigorated and encouraged. All said they wanted to continue the work.
“What was unique about the setting was that it was truly a conversation among people. Our discussions were guided by our past experiences and knowledge about the topic, not by titles or affiliations. Just a group of people trying to figure things out,” said Kaisa Snellman , organizational behavior professor and director of the INSEAD Gender Initiative.
Wharton Deputy Dean Nancy Rothbard agreed, saying RADs is a meaningful way to connect scholarship and practice for the maximum benefit of both.
“We were able to inform each other and learn from each other, and that’s always the goal,” she said.
Creary said she believes that cooperation is the key to saving DEI amid backlash. Rapidly changing laws, rising Islamophobia and antisemitism over the conflict in Gaza, and recent celebrity comments against women and the LGBTQ+ community have left many organizations paralyzed over how to handle sensitive and divisive topics. That’s why the work of RADs is so important, she said.
“When we join with other people who have a common interest and commitment to these issues, we can be much more effective not only at keeping the momentum going in our own organizations, but also in society,” the professor said. “These problems don’t go away. There are still many versions of inequality, and the gaps have the potential to widen without any interventions.”
RADs is sponsored by the Wharton School, Harvard Business School, and INSEAD. Other partners include the Wharton Coalition for Equity and Opportunity (CEO); Wharton-INSEAD Alliance; Harvard Business School Race, Gender & Equity Initiative; Harvard Business School Institute for Business in Global Society (BiGS); Wharton McNulty Leadership Program; Wharton Center for Human Resources; and Wharton Center for Leadership and Change Management.
More From Knowledge at Wharton

The Consequences of Socioeconomic Mobility

Why Representation Matters in Marketing

How Can Minority Employees Be Authentic in a Corporate Workplace?
Looking for more insights.
Sign up to stay informed about our latest article releases.
Advertisement
Supported by
Education and Schools

Free Preschool With One Catch: It May Be a Long Commute Away
Many New York City families counted on the prospect of free preschool, but hundreds were not immediately offered a seat and may have to travel across town to available spots.
By Troy Closson

Watch These Cute Videos of Babies (and Learn Something, Too)
A social media account features smiley toddlers, while also offering positive lessons about child development.
By Dana Goldstein

How Patty Murray Used Her Gavel to Win $1 Billion for Child Care
A self-described “mom in tennis shoes,” now the Senate Appropriations Committee leader, managed to win an increase in child care subsidies in a spending freeze.
By Catie Edmondson

Why Free 3-K Is So Crucial for New York City Parents
Many families were counting on a break from crippling child care costs. Mayor Eric Adams’s cuts have cast doubt on their expectations.
By James Barron

A $30,000 Question: Who Will Get a Free Preschool Seat in New York City?
After Mayor Eric Adams made cuts to free preschool for 3-year-olds, families face increased uncertainty — and the prospect of enormous child care bills.

What the Child Care Crisis Does to Parents
The child care crisis, which has intensified since pandemic-era funding expired in September, is placing an undue and unhealthy burden on American parents.
By Molly Dickens and Lucy Hutner

Her Son Was Promised a Special Education Class. He’s Still Waiting.
Mayor Eric Adams said all children who required preschool special education seats would have them. More than 1,000 such students lacked a placement last school year.

New York’s Era of Overspending Ends With a Shudder
Fiscal reality is finally hitting the city. Will Mayor Adams make the right choices when cutting the budget?
By Mara Gay

New SAT Data Highlights the Deep Inequality at the Heart of American Education
The differences in how rich and poor children are educated start very early.
By Claire Cain Miller and Francesca Paris

In an Expensive City, Who Should Get Free Preschool?
Cutbacks in free preschool for 3-year-olds in New York City raise a question: As even middle-class families struggle to get by, should everyone have access to the program?
By Eliza Shapiro

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tweet your comments with #K12BigIdeas . No. 1: Kids are right. School is boring. Daryn Ray for Education Week. Out-of-school learning is often more meaningful than anything that happens in a ...
We focused on neuroscience, the role of the private sector, education technology, inequality, and pedagogy. Unfortunately, we think the four biggest problems facing education today in developing countries are the same ones we have identified in the last decades. 1. The learning crisis was made worse by COVID-19 school closures.
Big Ideas is Education Week's annual special report that brings the expertise of our newsroom to bear on the challenges educators are facing in classrooms, schools, and districts.
Major problems at school. When we asked teachers about a range of problems that may affect students who attend their school, the following issues top the list: Poverty (53% say this is a major problem at their school) Chronic absenteeism - that is, students missing a substantial number of school days (49%) Anxiety and depression (48%) One-in ...
The answer to solving the American education crisis is simple. We need to put education back in the hands of the teachers. The politicians and the government needs to step back and let the people ...
Overall in math, a subject where learning loss has been greatest, students have made up about a third of what they lost. In reading, they have made up a quarter, according to the new analysis of ...
During an Education Week K-12 Essentials forum last week, journalists, educators, and researchers talked about these challenges, and possible solutions to improving equity in education.
The global disruption to education caused by the COVD-19 pandemic is without parallel and the effects on learning are severe. The crisis brought education systems across the world to a halt, with school closures affecting more than 1.6 billion learners. While nearly every country in the world offered remote learning opportunities for students ...
Community colleges, for example, have "traditionally been a gateway for low-income students" into the professional classes, said Long, whose research focuses on issues of affordability and access. "COVID has just made all of those issues 10 times worse," she said. "That's where enrollment has fallen the most.".
We've been to school. We know how education works. Right? In fact, many aspects of learning — in homes, at schools, at work and elsewhere — are evolving rapidly, along with our understanding ...
1. Students lost critical opportunities to learn and thrive. • The typical American student lost several months' worth of learning in language arts and more in mathematics. • Students ...
Read news and insights on schools, education, learning, and important issues for parents and educators.
Average scores between 2020 and 2022 in math and reading fell "by a level not seen in decades," according to CNN's report: 7 points down in math - the first decline ever. 5 points down in ...
Related: Race and LGBTQ Issues in K-12 Schools. Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say the public K-12 education system is going in the wrong direction. About two-thirds of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents (65%) say this, compared with 40% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
123. By David Wallace-Wells. Opinion Writer. The raw data looks inarguably bad: The share of American children missing at least 10 percent of school days nearly doubled over the course of the ...
Anger is rising. Patience is falling. For public schools, the numbers are all going in the wrong direction. Enrollment is down. Absenteeism is up. There aren't enough teachers, substitutes or ...
In rural India, nearly three-quarters of third graders cannot solve a two-digit subtraction problem such as 46 minus 17, and by grade five — half still cannot do so. The world is facing a learning crisis. While countries have significantly increased access to education, being in school isn't the same thing as learning.
Education 2030: topics and issues. The debates included the following sessions: Providing meaningful learning opportunities to out-of-school children. In this session a panel of experts explored the changes needed in countries which have large out-of-school children populations as well as examples from countries which are 'in the final mile'.
Education Week's ambitious project seeks to portray the reality of teaching and to guide smarter policies and practices for the workforce of more than 3 million educators: The State of Teaching ...
UNICEF is calling on governments to: Reach every child and keep them in school. Assess learning levels regularly. Prioritize teaching the fundamentals. Increase catch-up learning and progress beyond what was lost. Develop psychosocial health and well-being so every child is ready to learn. Governments and education stakeholders around the world ...
In 2023 K-12 schools experienced a rise in cyberattacks, underscoring the need to implement strong systems to safeguard student data. Technology is "requiring people to check their assumptions ...
Health. Decreasing childhood obesity by encouraging healthy habits has become an issue of national importance. Read articles on current educational issues, including school policy, school reform, the Common Core standards, tech trends, and more.
Several of the present issues of education are: 1. Government funding for education. School funding is a primary concern when discussing current issues in education. The American public education system, which includes both primary and secondary schools, is primarily funded by tax revenues.
After 50 Years and a Tornado Warning, an Oklahoma High School Class Graduates. In 1974, a high school commencement ceremony in Moore, Okla., was interrupted by a tornado warning. Decades later ...
1. Hope: "We must believe there is hope for achieving success and hope that we can make a difference in the world through our kids.". 2. Forgiveness: "We must also forgive ourselves and ...
Try to harness a student's passion for doodling by allowing them to submit academic sketches as work products. To get even more bang for your buck, ask them to annotate their drawings, or talk you through them—which will encode learning even more deeply, according to research. 2. Reading Aloud In Turn Improves Fluency.
72% of U.S. high school teachers say cellphone distraction is a major problem in the classroom. New York Gov. Kathy Hochul recently announced that she will introduce legislation to ban smartphones in schools during her state's 2025 legislative session. She cited the impact that social media and technology can have on youth, including leaving ...
Why That's a Problem. Classroom Tech Outpaces Research. Why That's a Problem. People walk outside the U.S Capitol building in Washington, June 9, 2022. Experts called for investments in ...
"DEI isn't the problem. Inequality is the problem," Creary said. "The attacks on DEI are a defensive response because people don't want to handle the broader issues of inequality. It's ...
Explore the latest news and analysis on education and schools, from K-12 to higher education, in the U.S. and around the world.