Self-Employment: What You Need to Know to Be Your Own Boss
Published: May 03, 2023
You're setting your own hours. Being your own boss. Calling the shots in the workplace you’ve created. Sound appealing? These are some of the perks of being self-employed. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, over 16 million Americans are currently self-employed .

However, self-employment isn’t without its challenges. While being able to call your own shots sounds glamorous, being your own boss takes hard work, dedication, and incredible focus — with no guarantee of pay, benefits, or success in your field.

If you’re considering self-employment, continue reading to learn everything you need to know to be your own boss. And if you're short on time, jump to the information you need:
- Self-Employment Definition
- Self Employment Advantages
- Self Employment Disadvantages
- Business Owner

How to Become Self-Employed
First, let’s define what it means to be self-employed.
Self-Employment
Self-employment is the practice of earning income directly through one's own business or trade, rather than working as an employee for an employer. In self-employment, an individual is responsible for managing and financing their own business, including all aspects of marketing, sales, and financial management.
Growth opportunities for self-employed individuals vary greatly depending on the field of work and fluctuate according to how the economy is doing. For example, amidst Covid-19, self-employment was less susceptible to initial employment declines than other forms of employment and recovered more quickly to pre-pandemic levels than other forms of work.
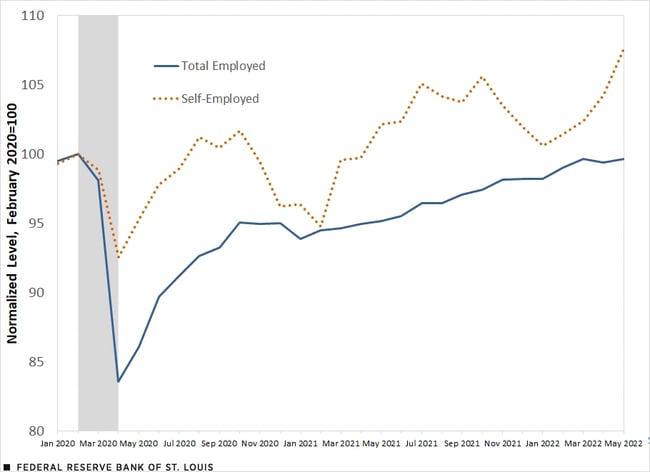
Image Source
In particular industries like real estate and transportation industries have become more common sectors for the self-employed to work in, with the growth of transportation potentially being related to the growth in gig economy apps like Uber.
Is being self-employed for you?
Self-employment has advantages and disadvantages that should be heavily considered before starting this career.
Self-Employment Advantages
1. independence.
For most people who pursue self-employment as a career, the sense of independence and autonomy over how and when they work are among the greatest benefits. Depending on the nature of their work, self-employed individuals can often control their hours, where they work, and how to complete their work best.
2. Engagement
If you’re self-employed, you also probably wear many hats. You’re in charge of the products and services you’re selling and managing administrative tasks, marketing, and operational duties. In other words, you’ll rarely be bored if you're self-employed.
3. Earning Potential
Additionally, because they are not working for wages determined by a company and are only eligible to receive annual pay increases, self-employed workers don’t have a specific limit to how much money they can make. Between setting their own rate, and taking on as few or as many clients as they desire, self-employed workers typically have greater earning potential than hourly or salaried employees who have less control over how much money they bring home.
Self-Employment Disadvantages
1. inconsistent income.
As we mentioned earlier, with great power comes great responsibility. Self-employment can be challenging, with a lack of consistent income being a common concern. For those whose income depends on their ability to sign clients or sell products that don’t yet have a strong customer base, earnings can fluctuate greatly during a slow month or off-season.
2. Self-Managed Benefits
Additionally, self-employed workers are often responsible for securing and managing their benefits like healthcare, retirement savings, and paid time off. This can become incredibly complicated for business owners responsible for managing these benefits for their employees.
3. Overwhelm
Along with inconsistent income and the lack of guaranteed benefits, the demands of managing various business areas (outside of simply completing tasks related to a particular skill or trade) can feel overwhelming for self-employed individuals.
Self-employment can look like many different roles, so let's discuss the big three.
Types of Self-Employment
Many self-employed individuals choose the entrepreneurship path, opting to operate their own business. Instead of focusing on a set of tasks or statements of work like an employee, business owners often create businesses to solve some sort of problem.
Self-Employed Business Owner Example: Billie
Georgina Gooley founded Billie when she realized prices for women’s shave products were significantly marked up due to pink tax .

As a business owner, you're your own boss and are responsible for operating a company. Here are two essential things you will need to do to establish and begin operating your business:
A business plan is a guiding document that outlines all of the major details of your business. A thorough business plan will explain your business model, address how your company will make money, document your company's structure, and include detailed financial and marketing plans. For help writing your business plan, download this template .
Next, you’ll need to legally establish your business. How you do this can vary depending on your state (for those in the U.S.). For small business owners, these are the most common business structures:
- Sole proprietorship — This is usually the preferred business filing for individual contributors and solopreneurs. Under a sole proprietorship, an individual owns the business, and legally there is no separation between the business and the person who owns it. A sole proprietorship can be a good option for the entrepreneur who does not plan to take on partners or employees and works in a field where they offer a specific range of services (i.e. graphic design or consulting).
- Limited liability company (LLC) — In an LLC, business owners have limited liability, and are not personally responsible for the company’s debts. This can be a good option for small businesses that are more complex or offer a wider range of goods and services than a sole proprietorship. In many states, individuals can own a "single member" LLC, so solo business owners can consider filing as an LLC depending on where they live.
- Partnership — In a partnership, two or more owners manage and share responsibility for a business. With this type of business structure, profits, and losses are shared and paid among partners. This type of structure is popular among businesses such as law firms, real estate groups, and medical offices, where multiple practices can run from one establishment.
A career in freelancing can be a positive self-employment option for those who highly value flexibility and have a specific skill they specialize in. As a freelancer, you provide contract services to as many companies and clients as you would like to take on.
Freelance roles are popular in fields including writing, photography, consulting, graphic design, and administrative assistance. It’s important to note that working freelance, your potential earning has no maximum, however, work (and thus pay) can be inconsistent.
Here is a recommended course of action if you want to pursue freelance work.
As you work to book clients, you want to make sure you can provide examples of your work. Unlike a traditional job where you apply with a resumé, potential clients want to see your prior projects that showcase your skills and testimonials from previous clients. The most straightforward way to do this is to have a portfolio to showcase your best work.
You can create a portfolio by linking to your previous bodies of work on your website or using an online portfolio tool. Popular online portfolio sites include:
- Behance — This website has a portfolio creation tool for freelancers in the creative fields including graphic and UX/UI designers, illustrators, and video editors. Behance can be licensed through an Adobe Creative Cloud membership .
- Clippings.me — Designed for writers and journalists looking to create an online portfolio, Clippings.me offers a free tier perfect for displaying small clips. Paid plans start at $9.99 per month and for robust online portfolio hosting.
- Carbon Made — For visual artists, Carbon Made offers a beautiful interface to host online portfolios. Plans start at $8 per month and offer unlimited video and image hosting.
The beauty of freelance work is determining how much you charge for your work. However, deciding how much to charge can be challenging. When choosing your rates as a freelancer, factor in the following considerations:
- Your overall income goals — How much money will you earn this year? How many projects can you reasonably complete? Divide the total amount of money you would like to earn by the number of projects you can reasonably complete to give you a ballpark range for how much you should be bringing in for each project.
- Business expenses — How much will it cost you to complete the work? Do you have to purchase any equipment (i.e., a new computer or new software) to complete your jobs? If so, factor in how much it may cost you to complete the work and build this into your rates. For example, if you spend roughly 10% of your income on expenses related to completing your work, you may want to add an additional 10% to your rates to offset this value.
- Average rates for writers and editors
- Average rates for digital designers and developers
- Hourly vs. project — How you charge clients (i.e., work by the hour, or a lump sum for the project) will depend on your preferences and the nature of work. Being paid by the hour for freelance work emphasizes the time it takes to complete a project. Receiving a lump-sum payment for completion of a project emphasizes the end result.
Once you determine what work you want to provide and how much you want to charge, it is time to start booking clients. For most freelancers, this includes applying for open job listings and pitching work to potential clients. Popular websites for freelance job listings include:
- Fiverr — Website for quick-turn creative projects including logo design, and audio/visual editing jobs.Creating a profile and listing services is free, and you walk away with 80% of earnings from each transaction.
- UpWork — Currently the internet’s largest freelance job posting site. Upwork offers listings for most major freelance niches, and is a good place to get started for beginner freelancers. For freelancers, service fees range between 5-20% of earnings.
- CloudPeeps — This website is geared towards more experienced freelancers, with opportunities primarily in the fields of social media, content creation, and marketing. You can create a free account to be listed in their online directory, with paid plans starting at $9 per month for additional features.
- Guru — On Guru, you can create a profile to showcase your work and connect with potential clients. Creating an account as a freelancer is free, and you pay a 2.5% transaction fee for each paid invoice.
- 99Designs — Designed to be a platform for visual creatives to find work, 99Designs has opportunities for designers to create logos, websites, and visual identities for growing brands. Freelancers can create a profile for free to bid for design jobs through their site.
Contract work can be a good middle-ground for those seeking more consistent work but not wanting to be tied to a single company long-term. Contractors are hired to complete a statement of work for a specific time. In these roles, workers are often paid hourly from the companies they are contracted to work for and do not receive benefits.
Employment contracts can range in length from a few days to multiple years, depending on the nature of work. Typical contract roles are project-based (for example, a company may hire a contract project manager to implement a new process) or are a temporary backfill for full-time employees who will eventually return to work (for example, many contractors provide support while employees are on parental leave).
Self-Employed Contractor Example: Gig worker
In recent years, we have seen a rise in the "gig economy" with the creation of independent jobs from modern services. These types of jobs include driving for ridesharing services such as Uber or Lyft. Many people take on these roles to supplement other sources of income, the creation of more ways of doing work has the potential to reshape the future job market .
Now, let's discuss how to successfully navigate the world of self-employment.
- Determine the type of self-employment you want to pursue.
- Create a schedule.
- Develop processes.
- Establish boundaries.
- Delegate tasks where you can.
- Seek out mentorship or coaching.
- Prioritize self-care.
1. Determine the type of self-employment you want to pursue.
The path to self-employment is not one size fits all. And as we previously discussed, various options are available for creating self-governed work.
Once you've chosen the right path for you, and done the preliminary steps for it, you can move on to more hands-on work.
2. Create a schedule.
For many, the biggest appeal of self-employment is flexibility. While it can be tempting to work anywhere, anytime, creating a consistent schedule can be helpful for many self-employed workers. Creating a schedule helps you maintain a better work-life balance so you aren’t always "on." It also improves your communication with potential clients and customers, because they must set hours for getting a hold of you, creating a sense of routine and professionalism.
3. Develop processes.
As you settle into the groove of self-employment, developing standard processes can help you work smarter, better, and faster. Look at your statement of work to identify tasks that can be automated or simplified. Often, the best place to start is with tasks that are done repeatedly, such as administrative tasks that can be automated. Here are suggestions to help you scale and automate your work.
- Implement a CRM — A customer relationship management platform ( CRM ) can be a valuable tool for keeping track of client information. You can use a CRM to manage all client communication without manually tracking correspondence from a spreadsheet or your inbox.
- Inquiries process — If a potential client sees your work and wants to hire you, do you have a process to support inquiries? A simple process could be having a specific email inbox project inquiries go to so they don’t get lost in your inbox, allowing you to batch responses easier. Or it could be setting up a "work with me" page on your website, having a web form specifically for project inquiries so people can contact you directly for work. Ideally, you will have this process in place before you truly need it to prepare you for success.
- Project management — How are you currently tracking how client or customer work is managed? With a project management system in place, your job as a self-employed worker will be easier, and your clients and customers will likely receive the same positive experience. You can use a tool such as Asana to help you manage your client projects and integrate them with your CRM.
- Budgeting — When you’re self-employed, you need a solid plan to help you manage your business finances. When managing your own pay (and the pay of your employees) you have to understand where your money is coming from. Using a system like QuickBooks Self-Employed is a good way to automate your finances so you don’t have to track everything manually.
4. Establish boundaries.
When you are your own boss, it can be tempting to feel like you need to work all of the time. In a traditional job, there are often set working hours or physical space you go to and leave from each day to establish boundaries. When you work for yourself, you must create those boundaries. Helpful boundaries for the self-employed can include:
- Creating a designated workspace for yourself that is for work only — This establishes a boundary between recreational and professional space. When you are in your workspace, that is a time for work and focus.
- Communication expectations with clients — Create norms around client communication. Determine what communication channels you prefer to use with clients (such as Slack , or a designated email address instead of your personal email address or phone number) so clients know when and how to get a hold of you. Additionally, you may want to consider communicating to clients what a normal response time is (for example, making it clear that you respond to emails within 24 hours).
- Out-of-office procedure — When you work for yourself, you won’t have a structured PTO plan or designated backup to handle inquiries if you are out of the office. To protect your time away from work, communicate to clients and stakeholders when you’ll be away and for how long, and set up autoresponders so inquiring clients know when you’ll return and when they can expect to hear from you.
5. Delegate tasks where you can.
Even if you are a solopreneur who does not have employees, you can still delegate business tasks. Stay in your zone of genius and focus on the work you truly love to do, whether it's writing, designing, or consulting by outsourcing tasks that are not your strong suit. Here are a few business tasks you may want to consider outsourcing if you’re self-employed:
- Bookkeeping — As a self-employed person, you want to ensure your finances are handled correctly. Hiring professionals to handle your financial tasks including invoicing, tracking profit and expenses, and helping prepare your taxes helps free up your time to focus on work and ensures these tasks are done correctly.
- Social media posting — If social media marketing is on your task list, you need a strategy to streamline your posts. This could be as simple as creating a social media schedule and pre-planning content so you’re not stuck wondering what to post next, or you can use an automated tool to publish content for you.
- Administrative tasks — Are you pinned down by repetitive administrative tasks such as inbox management or reporting? There are several options available to help you delegate these tasks. If you aren’t ready to make your first hire, use the Personal Assistant listings on Task Rabbit to bring in hourly support when you truly need it. If you’re looking for a more long-term solution or support for a specific project, bringing on a contracted virtual assistant can be an affordable way to delegate administrative tasks.
- Time tracking — If you track your billable hours manually, it's time to automate. Numerous time-tracking apps available can integrate directly with your favorite tools including Gmail, Google Calendar, and QuickBooks for invoicing at the click of a button. Check out some of our favorite time-tracking apps here.
6. Seek out mentorship or coaching.
In a traditional work environment, you usually have a manager you report directly to who can provide guidance, mentorship, and coaching. When you are your own boss, you have to seek out this type of support by yourself. Even when working for yourself, developing your skills should be a top priority to help you grow and evolve in your career, and having a trusted mentor or career coach is a great way to get this type of support.
Find a mentor by networking with people who have the experience you want to learn from (and who you may be able to offer valuable insight from as well). Before approaching a potential mentor for advice, clarify your goals and what you hope to gain from mentorship. You may also find that having a business or career coach to keep you accountable is a helpful option.
7. Prioritize self-care.
Last but certainly not least, make self-care a top priority. When you are your own boss and your livelihood depends on your ability to produce, you have to take care of yourself so you can continue to feel your best. Self-employment takes stamina, and self-care can help you keep up. Here are some ways to incorporate self-care in your routine:
- Stay on top of your health — A balanced diet, coupled with regular exercise, is one of the best things you can do to improve focus, boost creativity, and improve overall health. Aim for 30 minutes of movement each day. Even a lunch break walk to get away from your desk can work wonders.
- Build quiet time into your schedule — Having quiet time to reflect is essential for everyone, especially the self-employed. Build time into your schedule each day to meditate, journal, or just sit and be present with yourself.
- Make time for hobbies and recreation — Everyone should have activities they do purely for enjoyment that don’t involve work. Taking intentional, recreational breaks from work can help you feel refreshed and inspired when you do work. Whether you have a creative hobby, like to explore the outdoors, or enjoy reading fiction, keep activities in your schedule that are purely for enjoyment.
- Get enough rest — Sleep is essential for high-performers. When you are well-rested you can think critically, make better decisions, and you are less likely to make time-consuming mistakes in your work.
Understanding Self-Employment
Embarking on a self-employed career can be incredibly rewarding. A self-led career can offer you flexibility and opportunities beyond more traditional jobs, but it isn't without risks. We hope you found this post useful as you prepare to pursue a career of your own.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in October 2019 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

What Is a Mentor in the Workplace?

Coaching vs. Mentoring for Entrepreneurs

How Peer Coaching Can Help Your Business

Reverse Mentoring for Businesses

Transferable Skills That Take You From 0 to 100 as an Entrepreneur
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Simple Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | April 2, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve compiled a variety of simple business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
On this page, you’ll find a one-page business plan template , a simple business plan for startups , a small-business plan template , a business plan outline , and more. We also include a business plan sample and the main components of a business plan to help get you started.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
This simple business plan template lays out each element of a traditional business plan to assist you as you build your own, and it provides space to add financing information for startups seeking funding. You can use and customize this simple business plan template to fit the needs for organizations of any size.
One-Page Business Plan Template
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Use this one-page business plan to document your key ideas in an organized manner. The template can help you create a high-level view of your business plan, and it provides easy scannability for stakeholders. You can use this one-page plan as a reference to build a more detailed blueprint for your business.
For additional single page plans, take a look at " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
Use this fill-in-the-blank business plan template to guide you as you build your business plan. Each section comes pre-filled with sample content, with space to add customized verbiage relevant to your product or service.
For additional free, downloadable resources, visit " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Simple Business Plan for Startup

Download Startup Business Plan Template — Word
This business plan template is designed with a startup business in mind and contains the essential elements needed to convey key product or service details to investors and stakeholders. Keep all your information organized with this template, which provides space to include an executive summary, a company overview, competitive analysis, a marketing strategy, financial data, and more. For additional resources, visit " Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples ."
Simple Small-Business Plan Template

Download Simple Small-Business Plan Template
This template walks you through each component of a small-business plan, including the company background, the introduction of the management team, market analysis, product or service offerings, a financial plan, and more. This template also comes with a built-in table of contents to keep your plan in order, and it can be customized to fit your requirements.
Lean Business Plan Template

Download Lean Business Plan Template
This lean business plan template is a stripped-down version of a traditional business plan that provides only the most essential aspects. Briefly outline your company and industry overview, along with the problem you are solving, as well as your unique value proposition, target market, and key performance metrics. There is also room to list out a timeline of key activities.
Simple Business Plan Outline Template

Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template
Word | PDF
Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan. Simplify or expand this outline to create the foundation for a business plan that fits your business needs.
Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Download Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
This template doubles as a project plan and timeline to track progress as you develop your business plan. This business planning template enables you to break down your work into phases and provides room to add key tasks and dates for each activity. Easily fill in the cells according to the start and end dates to create a visual timeline, as well as to ensure your plan stays on track.
Simple Business Plan Rubric Template
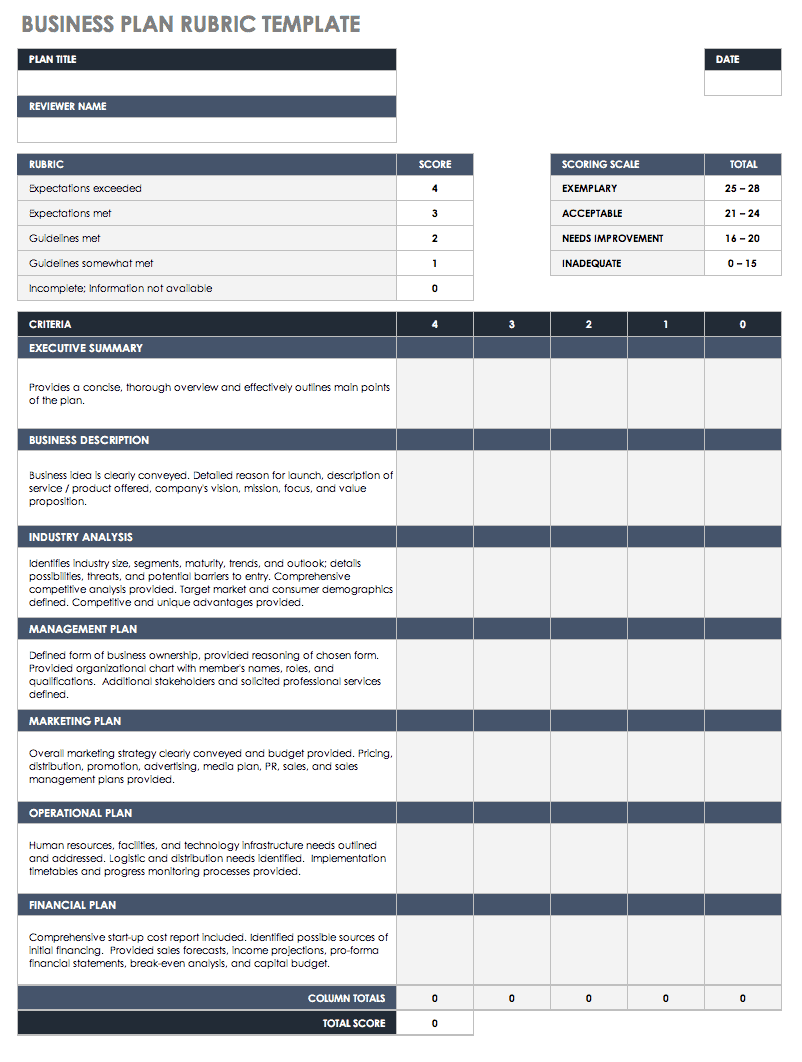
Download Simple Business Plan Rubric
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Once you complete your business plan, use this business plan rubric template to assess and score each component of your plan. This rubric helps you identify elements of your plan that meet or exceed requirements and pinpoint areas where you need to improve or further elaborate. This template is an invaluable tool to ensure your business plan clearly defines your goals, objectives, and plan of action in order to gain buy-in from potential investors, stakeholders, and partners.
Basic Business Plan Sample
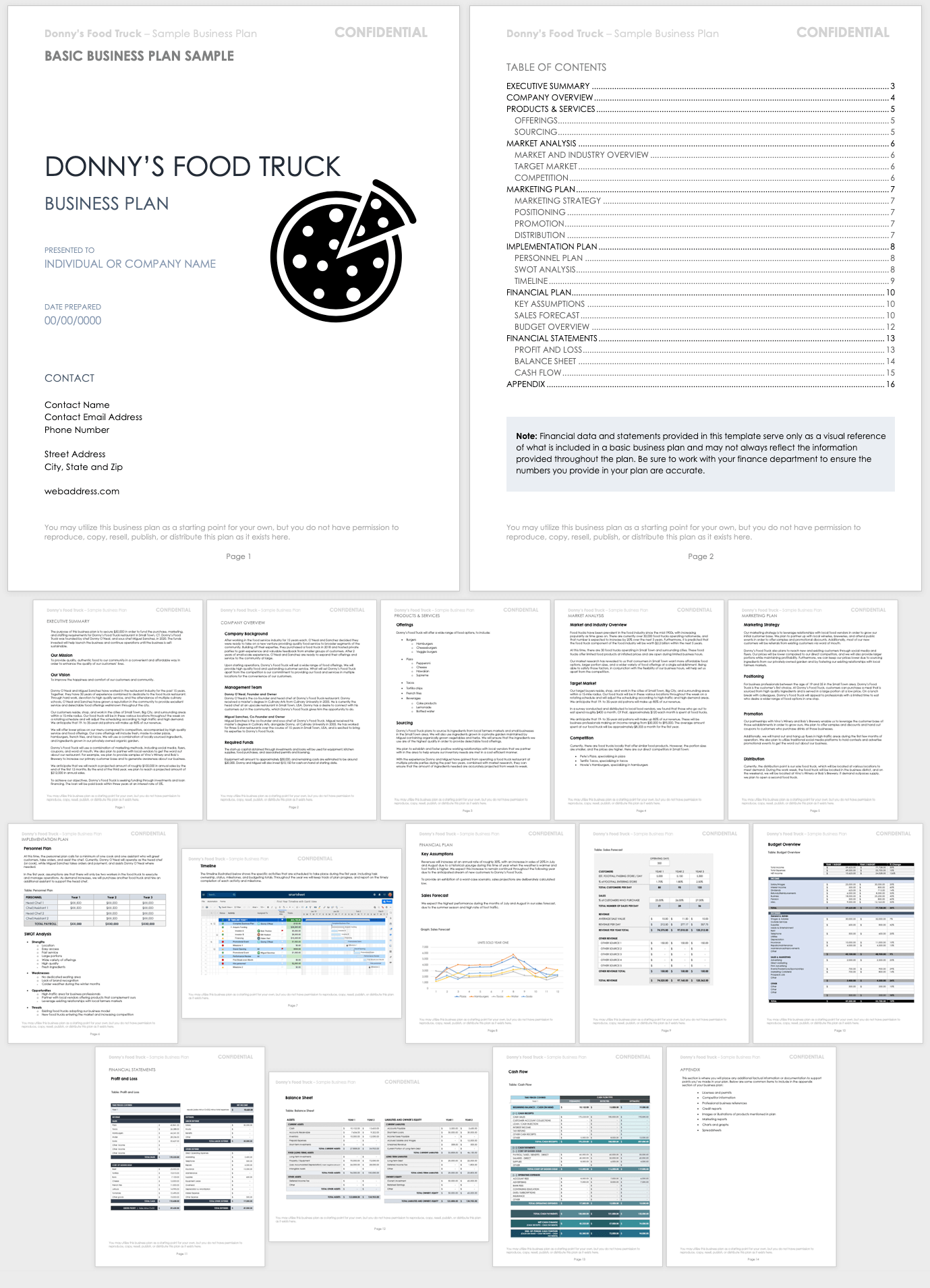
Download Basic Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample serves as an example of a basic business plan that contains all the traditional components. The sample provides a model of what a business plan might look like for a fictional food truck business. Reference this sample as you develop your own business plan.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “ Free Strategic Planning Templates .”
Main Components of a Business Plan
The elements you include in your business plan will depend on your product or service offerings, as well as the size and needs of your business.
Below are the components of a standard business plan and details you should include in each section:
- Company name and contact information
- Website address
- The name of the company or individual viewing the presentation
- Table of Contents
- Company background and purpose
- Mission and vision statement
- Management team introduction
- Core product and service offerings
- Target customers and segments
- Marketing plan
- Competitive analysis
- Unique value proposition
- Financial plan (and requirements, if applicable)
- Business and industry overview
- Historical timeline of your business
- Offerings and the problem they solve
- Current alternatives
- Competitive advantage
- Market size
- Target market segment(s)
- Projected volume and value of sales compared to competitors
- Differentiation from competitors
- Pricing strategy
- Marketing channels
- Promotional plan
- Distribution methods
- Legal structure of your business
- Names of founders, owners, advisors, etc.
- Management team’s roles, relevant experience, and compensation plan
- Staffing requirements and training plans
- Physical location(s) of your business
- Additional physical requirements (e.g., warehouse, specialized equipment, facilities, etc.)
- Production workflow
- Raw materials and sourcing methods
- Projected income statement
- Projected cash flow statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Charts and graphs
- Market research and competitive analysis
- Information about your industry
- Information about your offerings
- Samples of marketing materials
- Other supporting materials
Tips for Creating a Business Plan
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed at the thought of putting together a business plan. Below, you’ll find top tips to help simplify the process as you develop your own plan.
- Use a business plan template (you can choose from the variety above), or refer to the previous section to create a standard outline for your plan.
- Modify your outline to reflect the requirements of your specific business. If you use a standard business plan outline, remove sections that aren’t relevant to you or aren’t necessary to run your business.
- Gather all the information you currently have about your business first, and then use that information to fill out each section in your plan outline.
- Use your resources and conduct additional research to fill in the remaining gaps. (Note: It isn’t necessary to fill out your plan in order, but the executive summary needs to be completed last, as it summarizes the key points in your plan.)
- Ensure your plan clearly communicates the relationship between your marketing, sales, and financial objectives.
- Provide details in your plan that illustrate your strategic plan of action, looking forward three to five years.
- Revisit your plan regularly as strategies and objectives evolve.
- What product or service are we offering?
- Who is the product or service for?
- What problem does our product or service offering solve?
- How will we get the product or service to our target customers?
- Why is our product or service better than the alternatives?
- How can we outperform our competitors?
- What is our unique value proposition?
- When will things get done, and who is responsible for doing them?
- If you need to obtain funding, how will you use the funding?
- When are payments due, and when do payments come in?
- What is the ultimate purpose of your business?
- When do you expect to be profitable?
To identify which type of business plan you should write, and for more helpful tips, take a look at our guide to writing a simple business plan .
Benefits of Using a Business Plan Template
Creating a business plan can be very time-consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Finding the right template for your business needs can be beneficial for a variety of reasons.
Using a business plan template — instead of creating your plan from scratch — can benefit you in the following ways:
- Enables you to immediately write down your thoughts and ideas in an organized manner
- Provides structure to help outline your plan
- Saves time and valuable resources
- Helps ensure you don’t miss essential details
Limitations of a Business Plan Template
A business plan template can be convenient, but it has its drawbacks — especially if you use a template that doesn’t fit the specific needs of your business.
Below are some limitations of using a business plan template:
- Each business is unique and needs a business plan that reflects that. A template may not fit your needs.
- A template may restrict collaboration with other team members on different aspects of the plan’s development (sales, marketing, and accounting teams).
- Multiple files containing different versions of the plan may be stored in more than one place.
- You still have to manually create charts and graphs to add to the plan to support your strategy.
- Updates to the plan, spreadsheets, and supporting documents have to be made in multiple places (all documents may not update in real time as changes are made).
Improve Your Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Business Plan For Self Employed
Congratulations on taking the first step in creating a business plan for self employed. This is an essential step towards entrepreneurial success and a well-crafted business plan will provide a solid foundation for your business venture!
Whether you're a budding entrepreneur with a brilliant idea or a seasoned business owner looking to expand, a thoughtfully constructed business plan will help you plan and navigate towards business prosperity.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential elements of creating a business plan for self employed that captures your vision as well as attracting investors, partners, and customers alike. From defining your mission and identifying your target market to formulating financial projections and developing a robust marketing strategy, our aim is to empower you with the knowledge and tools needed to turn your aspirations into a reality.
So whether you're just starting out or you're looking to revamp your existing business plan, read on for everything you need to know.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is an essential tool that will revolutionise the way you think about your self employed business. It provides a structured approach to help you clarify your long-term goals and objectives, allowing you to develop effective strategies and marketing campaigns to achieve them.
One of the key benefits of creating a business plan is gaining a deep understanding of your customers. By analysing their wants, needs, and preferences, you can identify where they spend their time and how to effectively target them. This valuable insight will enable you to tailor your products or services to meet their demands.
Moreover, if you are seeking external funding, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your commitment and professionalism. It shows potential investors or lenders that you are serious about your construction business and have a comprehensive plan of action to ensure success.
A Business Plan For Self Employed - The Key Parts
The executive summary, your company description, market analysis, products and services.
- Marketing Strategy
- Operational Plan
- Financial Projections
Risk Analysis
- Funding Request and Use of Funds (if applicable)
- Additional Information
An executive summary of your business plan for self employed is a brief overview of your business plan.
This is the first thing that potential investors or lenders will see, so it is crucial that you make a good impression. Keep this section short and highlight the key points of your plan.
What should an executive summary include?
- Overview of the Business
- Mission Statement
- Key Objectives
- Summary of Products/Services
- Financial Highlights and Funding Requirements (if applicable)
Remember potential investors don’t always have huge amounts of time to read your document so make sure that you condense the critical information, enabling the reader to make quick and well-informed judgments. Tips for the Executive Summary
Wait until you’ve written the whole business plan and then come back and complete the executive summary. This way you will know your business plan for self employed inside and out so you can highlight the key elements of the document. Remember the Executive Summary will shape the reader's initial perception of the business and whether they continue reading the document.
If you are looking for any tips on how to improve any section of your business plan, check out our Learning Zone , which has several in-depth guides on each section of the business plan.
The Company Description section of your self employed business plan is crucial as it offers a comprehensive overview of your business. This section provides essential information about your company's history, mission, vision, legal structure, location, and key milestones. It allows readers to gain a clear understanding of your company's fundamental characteristics and the context in which it operates.
When crafting your company description, make sure to include the following key elements:
- Business Name and Legal Structure: Clearly state the legal name of the company and its legal structure.
- Business History: Provide a brief overview of how the business came into existence. Highlight key milestones or events that shaped the company's growth and development.
- Mission and Vision Statements: Present the company's mission statement, which outlines its purpose and primary goals. Additionally, share the vision statement, which describes the long-term vision and objectives for your business.
- Products and Services: Briefly explain the products or services your business offers, emphasising their unique selling points and how they address customer needs.
- Competitive Advantages: Clearly state the competitive advantages that differentiate your business from others in the market. This could include unique features, patents, proprietary technology, or a strong brand presence.
- Location and Facilities: Provide details about the physical location of your business and any facilities required to operate successfully.

Tips for writing the company description section:
- Interweave storytelling into the company's history, tell the reader about your passion for the business and the journey you’ve been on to get to this point.
- Include strong visuals and infographics.
- Avoid jargon and keep the writing style clear and concise.
- Focus on your company's unique selling point (USP) and how that makes you stand out in the marketplace.
- Back up this information with customer testimonials if possible.
The market analysis section of your self employed business plan is essential for understanding the competitive landscape and the overall business environment. It is crucial to execute this section effectively as it demonstrates your in-depth knowledge of the market dynamics. This process will enable you, as an entrepreneur, to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and develop strategies for success.
To conduct a good market analysis, it is important to have a deep understanding of the industry you are operating in. This information will help you make informed decisions about your product or service offerings, marketing strategies, and pricing.
Key elements to include in your market analysis section:
- Industry Overview: Provide a general overview of your industry. Describe the industry's size, growth rate, major players, and key trends. Include relevant statistics and data to support your claims.
- Target Market and Customer Segmentation: Clearly define your target market and outline the specific customer segments you aim to serve. Identify the needs, preferences, and behaviours of each segment.
- Competitor Analysis: Identify direct and indirect competitors in the market. Analyse their strengths, weaknesses, market share, and strategies. Highlight areas where your business differentiates itself from competitors.
- Market Trends and Opportunities: Explore current and future trends in the industry and market. Assess how these trends can impact your business positively and identify potential opportunities for growth.
- SWOT Analysis (optional): Consider including a SWOT analysis specific to your market. This can help you understand your business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the context of the market.
How to nail the market analysis section?
- Differentiation: Focus on highlighting how your business differentiates itself from competitors, really try to drum home this point.
- Market Surveys or Interviews: Adding surveys or interviews and adding the key findings and quotes in the Market Analysis to support your claims will help reinforce the plans in your document.
- Competitive Matrix: a competitive matrix visually comparing your business against key competitors based on factors such as price, features, and customer service. This matrix is a great visual method highlighting your competitive advantages.
- Emerging Technologies or Trends: Identifying potential disruptions and how your company is prepared for them shows a great understanding of market dynamics and trends.
Looking for more inspiration on how to make your market analysis section even better, then check out our in-depth business market analysis guide.
In this section, we will highlight the core products and services that make your self employed business unique and valuable. It is essential to showcase what sets you apart from the competition and why your offerings are exceptional. This information is especially important for potential investors, partners, and customers who are keen to understand what sets your business apart in the market.
When describing your products and services ensure you include the following information:
- Description of Products/Services: Provide a clear and concise description of each product or service your business offers. Explain their primary function and how they address customer needs.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Highlight the unique features or benefits that make your products or services stand out from competitors. Clearly state why customers should choose your offerings over alternatives.
- Product/Service Life Cycle: Describe where each product or service stands in its life cycle (e.g., introduction, growth, maturity, decline) and outline plans for updates or new offerings in the future.
- Intellectual Property (if applicable): If your business has any intellectual property (e.g., patents, trademarks, copyrights) related to your products or services, mention them in this section.
Extra elements to make this section stand out:
- Customer Use Cases: Present real-life customer use cases or success stories that illustrate how your products or services have solved specific problems for customers. Use compelling narratives to engage readers.
- Product Roadmap: If applicable, include a product roadmap that outlines future updates, enhancements, or new offerings. This showcases your business's commitment to innovation and continuous improvement.
- Quality and Testing Standards: Discuss the quality standards your business adheres to and any testing processes you conduct to ensure the reliability and performance of your offerings.
- Pricing Strategy: Integrate your pricing strategy into this section. Explain how you've determined the pricing of your products or services, considering factors like production costs, competition, and value to customers.
- Environmental and Social Impact: If your products or services have positive environmental or social implications, highlight them in this section. Increasingly, customers appreciate businesses that contribute positively to society.
The Marketing Strategy Section

Key Information to Include Within the Marketing Strategy Section:
- Marketing Goals and Objectives: Clearly state the marketing goals you aim to achieve. Focus on how you will increase brand awareness and drive customer conversions or leads.
- Target Market Strategy: Describe the specific strategies you will use to reach and engage with your target customers. This could involve digital marketing, traditional advertising, or other channels.
- Pricing Strategy: Explain how your pricing will attract the target market and how it compares to competitors' pricing.
- Promotion and Advertising Plan: Outline the promotional activities and advertising campaigns you plan to execute. Include details about social media marketing, content marketing, email campaigns, and other promotional tactics.
- Sales Strategy: Describe your sales process and how you plan to convert leads into paying customers. Mention any sales team structure and their responsibilities if applicable.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Approach: Discuss how you intend to build and maintain strong relationships with your customers to encourage repeat business and loyalty.
Getting Creative with the Market Strategy Section
- Create a visual marketing timeline.
- Outline influencer or brand ambassador partnerships if applicable.
- Detail key metrics and KPIs.
By infusing creativity and innovative marketing ideas with sound fundamental marketing, you can really make this section stand out and impress potential investors and partners.
The Operation Plan Section
While marketing activities may seem more exciting, operational planning is essential for the success of your self employed business. This section focuses on the day-to-day operations and internal processes that drive your business forward. By providing a comprehensive roadmap of your resources, workflows, and procedures, you can instill confidence in potential investors that your business is well-equipped for growth.
Here are some key items to include in your operational plan:
- Organisational Structure: Describe the organisational structure of the company, including key roles and responsibilities.
- Key Personnel and Team: Introduce key team members and their qualifications. Highlight how their expertise contributes to the success of the business.
- Operational Workflow and Processes: Provide a high-level step-by-step overview of delivering your product or service, from production to delivery or distribution.
- Resource Requirements: Outline the key resources required to run the business, such as equipment, technology, facilities, and human resources.
- Quality Control and Assurance: Explain how the company ensures the quality and consistency of its products or services, and how it addresses any potential issues.
- Supply Chain Management (if applicable): If the business involves sourcing materials or products from suppliers, describe the supply chain management process.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Discuss any legal or regulatory requirements specific to the industry and how the company ensures compliance.

How to add value to the Operation Plan section:
- Use visuals to outline organisation structures and workflows.
- Outline contingency plans, for example how the company is prepared for supply chain shortages or price shocks.
- Efficiency, efficiency, efficiency. Describe how you have driven efficiency gains for the business.
- Have you considered your business's environmental impact? If so, mention within this section.
The operational section of a business plan does have the potential to be dryer than more exciting elements such as marketing, however, by incorporating creative elements and forward-thinking workflows you can help keep reader engagement high.
The Financial Projections
The Financial Projections section can make or break a business plan. Always include well-researched and accurate projections to avoid undermining your business plan and losing out on potential investment. What to include in the financial projections section:
- Sales Forecast: Provide a detailed projection of the company's sales revenues for each product or service category over the forecast period.
- Expense Projections: Outline the expected operating expenses, including costs related to production, marketing, salaries, rent, utilities, and any other significant expenses.
- Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement: Present a comprehensive Profit and Loss statement that summarizes the business's revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, and net profit or loss for each year of the forecast.
- Cash Flow Projection: Include a cash flow statement that outlines the inflows and outflows of cash over the forecast period. This will help identify potential cash flow gaps.
- Break-Even Analysis: Perform a break-even analysis to determine the point at which the business's total revenue equals total costs, indicating when it becomes profitable.

How to add value to your financial projections section:
- Be prepared to defend your assumptions with data. If you are planning for a high-growth % make sure you can justify this assumption. If in doubt the more conservative the better.
- Include visuals that help readers quickly grasp the trends and patterns in revenue, expenses, and profits.
- Offer different scenarios based on varying assumptions. For example, present a conservative, moderate, and aggressive growth scenario.
- Include key financial ratios like gross margin, net profit margin, and return on investment (ROI).
The Funding Request and Use of Funds Section
This section outlines the financial requirements of the company and how the requested funds will be utilised to support its growth and operations. Providing potential investors or lenders with a clear picture of how their money will be used will improve the business case for the funds and provide further confidence to investors. What to include in this section?
- Funding Request Amount: State the specific amount of funding you are seeking to obtain from investors, lenders, or other sources.
- Use of Funds: Provide a detailed breakdown of how the requested funds will be allocated across different aspects of the business. Common categories include product development, marketing, operational expenses, hiring, equipment, and working capital.
- Timeline of Funds Utilisation: Outline the timeline for utilising the funds. Specify when and how the funds will be disbursed and the expected milestones or deliverables associated with each funding phase.
- Expected Return on Investment (ROI): If applicable, include information on the expected ROI for investors. Highlight the potential for financial gains or equity appreciation over time.
- Repayment Plan (if applicable): If seeking a loan, provide a clear repayment plan that outlines the repayment period, interest rate, and the proposed schedule for repayment.
How to maximise this section?
- Create a visual timeline for key milestones such as the initial investment and key payback periods.
- Outline risk mitigation plans to instil confidence.
- Reiterate the company's long-term vision and how the funds can help achieve these goals.
As you near the end of your self employed business plan, it is crucial to dedicate a section to outlining potential risks. This section holds immense significance as it can greatly influence the confidence of potential investors. By demonstrating your market awareness and addressing challenges head-on, you can instill trust and credibility.
When conducting a risk analysis for your self employed car rental business plan, consider including the following:
- Identification of Business Risks: Enumerate the key risks and uncertainties that could affect the business. These risks can be internal (e.g., operational, financial) or external (e.g. market changes, regulatory changes, economic downturns).
- Impact Assessment: Analyse the potential impact of each identified risk on the business's operations, finances, and reputation. Rank the risks based on their severity and likelihood of occurrence.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Present specific strategies and action plans to mitigate each identified risk. Explain how you will proactively address challenges and reduce the negative impact of potential risks.
- Contingency Plans: Describe contingency plans for worst-case scenarios, outlining how the business will respond and recover from significant risks if they materialise.
How to make your risk analysis stand out?
- Add context with real-life examples. Are there similar businesses that have dealt with risks successfully in a similar manner to your strategy? This will add credibility to this section.
- Create adaptive strategies that demonstrate your business’s flexibility and adaptability.
- Outlining the responsible person for each risk and how they own it, giving further confidence in your risk management strategies.
Some additional information you may want to include in your business plan for self employed:
- Customer Surveys and Feedback
- Letters of Support or Intent
- Legal Documents (e.g., licenses, permits)
- Resumes of Key Team Members
A Business Plan For Self Employed Wrapping It All Up
A business plan is one of the most important documents that you will create about your business. It can literally be the difference between securing additional finance or missing out. Developing your business is not an easy task, however, the opportunity to think about your business in such detail will no doubt help you develop new and important insights along with new ideas and strategies. With all sections of your business plan and especially the financial plan, be prepared to defend your position to potential investors or lenders. This means that you should never publish anything that you can’t back up with additional data or rationale. Business Plans are not created overnight so take the time to research and think about each section properly, always try to support your claims and strategies with market insight and data. We hope you’ve enjoyed reading this guide, if you are looking for more tips on creating a business plan check out our learning centre .Good luck with your next business endeavour! Action Planr
Thank you! You’ll receive an email shortly.
Oops! Something went wrong while submitting the form :(
Learning ZoNe
Time To Be Your Own Boss: Business Plan For Self-Employed

Want to become self-employed? In this regard, you need to know a proper business plan for the self-employed. Without knowing a proper business plan, you can not sustain yourself in this business world. Moreover, a proper business plan can provide a visual infrastructure for your business. According to a statistic,
Till 2022, it was be an unstoppable increase in self-employment of about 2.76 million and female self-employment of about 1.5 million. And as time passes, it will continue to rise ever higher.
A self-employment business plan should be a solid guide, but not so complicated that you don't want to alter it, which is inevitable. If you want your business plan to stay relevant to your changing needs and priorities, you will need to update it as your company expands.
It is a very crucial factor to develop a complete business plan before starting a self-employment business. In this article, you can explore 7 essential steps to build an effective business plan for the self-employed . So, let’s deep dive into the core part of this article.
- 7 Steps to Develop a Business Plan for Self-Employed
(With Bonus One)
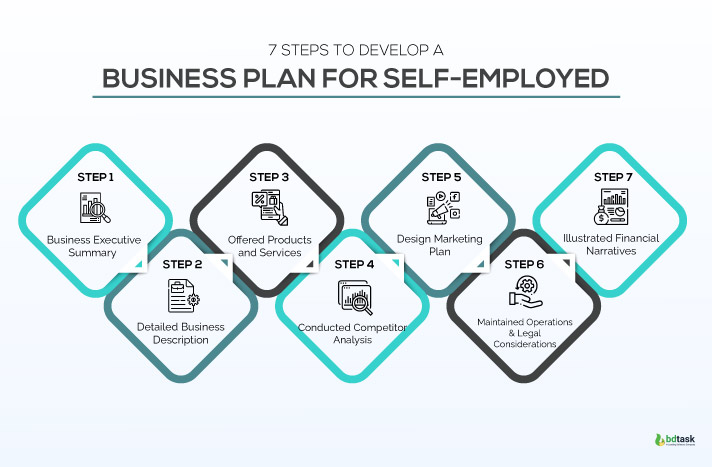
Offen job-holders dream of becoming self-employed , especially when they’re pissed of doing a 9 to 5 job for many years. But the reality is it’s not easy to build a business overnight, you need to follow some significant steps that will act as a roadmap to become self-employed or an entrepreneur. To start a self-employed business, you can follow the given steps.
- Business Executive Summary
- Detailed Business Description
- Offered Products and Services
- Conducted Competitor Analysis
- Design Marketing Plan
- Maintained Operations & Legal Considerations
- Illustrated Financial Narratives
Bonus:
8. Adopt Automation Software
Now, you can explore in detail the business plan for self-employed people.
- Step 1: Business Executive Summary
First, you need to explain the executive summary of your business. Executive summaries should be as brief as possible, according to the usual norm. Business executives should be written in easy language, try to avoid any type of jargon, so that any non technical person can understand the goal and objectives of your business.
Moreover, your audience is pressed for time and attention, and they want to learn as much as possible about your company plan. If at all feasible, keep your executive summary within two pages, however, it can be longer if required.
In your executive summary, you can enlist the following sections.
Write Your Business Plan
The executive summary will be a summary of the most essential themes covered in your business plan, writing the whole business plan before the executive summary is generally beneficial. Ensure that your executive summary solely includes facts and information from the business strategy.
Owner’s Introduction
Put a brief introduction of your business owner. It will build trustworthiness and you can enhance the reliability of your target audience. In this regard, a business plan should include the business owner’s introduction in the business executive summary of your self-employed business.
Mission Statement
To write a complete business plan for self employed, you need to clearly mention your mission statement. In this case, you have to write a mission statement within 30 words. Your mission statement should include your company’s goal, target audience, and service details.
Marketing Objectives
You need to define your marketing objective clearly. In your marketing objective, you have to provide the focusing point of your marketing team, clear direction for team members, and other significant information like support and marketing strategy.
Expected Outcomes
You can mention your expected outcomes based on the other factors of your planning. Though you will mention an estimated outcome in your self-employment business plan, it will motivate you to reach the goal and achieve your target.
Required Capital
In the executive summary, you need to calculate the overall estimated cost to start your business. According to the required estimated cost, you have to fix your budget. As a result, you will get an idea of your required capital to start your business.
- Step 2: Detailed Business Description
A company description gives a high-level summary of crucial components of your firm, such as what you do and what sets you apart. Anyone reading your business description should be able to figure out what your company does. Moreover, you need to include the following factors in your business description.
- Business name
- Business goal
- Competitive advantages
- Target customer
- Business location
- Business structure
Also, you have to fulfill 5 w's and h in your business description. In this regard, you have to require a clear understanding of the following questions.
- Who is your target audience?
- What is the goal of your business?
- Where is your business location?
- When will you implement your business plan?
- Why do you want to start this business?
- How do you achieve your goal?
If you fulfill all of the questions, you can properly explain your business description in your self-employment business plan.
- Step 3: Offered Products and Services
This part should provide a complete list of the items and services you will offer. One-on-one business coaching, career coaching, executive coaching, leadership development programs, team coaching, corporate training, workshops, seminars, coaching skills training, and a how-to book on recommendations for managers as coaches are just a few examples.
In your offered products and services list, you can include the following factors.
- A detailed description of the products and services
- Pricing list of your products and services
- Features and benefits of your listed products and services
- Production costs
- Production timeline
- Future products and services
- Step 4: Conducted Competitor Analysis
In this step, you need to research your target market and conduct competitor analysis.
Target Market
This part should include information about your ideal client. In my experience, most people who are new to self-employment require the most assistance in this area.
Moreover, they are adamant about not focusing on a single market since they like collaborating with people from various walks of life on a variety of projects. However, by attempting to sell to everyone, they dilute their message and, in doing so, end up appealing to no one.
Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the process of identifying a group of customers. Moreover, this section is so crucial to conduct your marketing process. You can segment your targeted customers into these four categories.
- Geographic segmentation
- Demographic segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
- Step 5: Design Marketing Plan

To promote your business activities, you need to make a proper marketing plan. In this regard, you have to conduct a SWOT analysis to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. After conducting a SWOT analysis, you need to define your goal and target audience.
However, you have to analyze the following KPIs that will ensure the design of an effective marketing plan.
- Marketing goals and objectives
- Promotional strategies
- Unique selling advantages
- Pricing strategies
Most significantly, you have to choose your digital marketing method because various digital marketing methods are invented. These are:
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
The goal of SEO is to optimize your website and increase organic traffic. To maintain high ranks, digital marketing managers typically pay attention to cross-connections and backlinks, keywords, and unique content. It improves the website's visibility. Remember that the more visible you are, the more customers you will be able to attract.
Content Marketing
Content marketing's main goal is to capture a customer's attention, educate newcomers, and nurture leads. Moreover, you can nurture and educate your potential consumers using this marketing technique by supplying them with relevant material, guiding them through the sales funnel, and finally convincing them to take the desired action.
Pay-per-click (PPC) Advertising
You can drive more traffic to your website through pay-per-click (PPC) advertising. This process allows you to conduct internet advertising and it is required to pay a fee each time one of their ads is clicked.
Email Marketing
Email marketing is another way to reach your targeted audience. This process can allow you to promote your products and services. Moreover, you can drive potential customers through the email marketing process.
Influencer Marketing
This one is another effective way to reach potential customers. Moreover, this process can allow you to work with someone who will act as an influencer as we as it helps to build credibility and trustworthiness. As a result, you can easily increase your brand awareness and enhance your sales.
Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing is one of the beneficial ways to reach a vast number of audiences. Also, it helps to increase brand awareness as well as improve search engine rankings. Moreover, social media marketing can be able to ensure higher conversion rates that will play a significant role to boost your business revenue.
There are different types of social media, using which you can promote your business, for instance Facebook marketing , Instagram, Medium, Quora, Twitter, Reddit, Pinterest and many more.
- Step 6: Maintained Operations & Legal Considerations
The most important step to build a business plan is to maintain operations and legal considerations. You can ensure your business's safety and security by maintaining operations and legal considerations. In this regard, you have to organize the following factors.
Agreement and contracts
You have to prepare a detailed and concise agreement and contracts in your self-employed business plan. It will ensure transparency and accuracy of your business as well as make a trust to invest in your organization.
Payment methods
You need to allow multiple payment methods for your organization. This payment method ensures a safe and secure transaction which will be essential for any organization. In this regard, you can integrate the following payment methods into your business.
- Cash payments
- Check payments
- Credit card payments
- Online payments
- Mobile payments
Permit & Registration
To start any self-employed business, you need to ensure all required permission and registration.
License & Regulations
According to your country’s law, you need to make all required licenses. Otherwise, you can not sustain in the marketplace. Also, you have to abide by all rules and regulations to conduct your business operations smoothly.
Insurance and Bonding
To write a complete self-employed business plan, you have to include insurance and bonding activities. It’s totally up to you whether you will provide insurance and bonding facilities or not. If you will provide it, you need to clearly mention them in your business plan.
- Step 7: Illustrated Financial Narratives
This one is the final step to make a self-employed business plan. In this step, you have to write a detailed financial statement. Moreover, business plans are an essential component of strategic financial decision-making.
They aid in the expression of ideas, the presentation of market data to support rhetoric, and the expression of the financial side of an argument. To make a complete financial statement, you have to include the following matrices in your financial statement.
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow analysis
- Break-even analysis
- Balance sheet
- Benefit analysis
- Step 8: Adopt Automation Software
You might think investing in some automation software might waste your money but this is completely a wrong thought, specially for start-up entrepreneurs. Firstly you have to understand your niche before you accommodate any automation software.
Automation software is absolutely a helping hand for your business, work as an instructor, simplifies your work and shows the easiest way to be more productive. Now, there are lots of variant automation software available in the envato market, so you choose one, whichever matches your niche or you can customize your own software , where you can personalize everything your business demands.

- Easy decision making
- Raise up the productivity
- Reliable data collection
- Gain loyal customers
- Improve the customer service
- Self-Employed Business Examples
- Independent business owner
- Food truck business owner
- Gig workers
- Partnerships
- How Necessary Is To Set- Up A Self-Employed Business Plan?
Of course, sketching a self-employed business plan assists you to glued yourself in the business plan you manifest to build. Without aiming any objectives, goals or deadlines, it becomes very difficult to stick to the problem you aimed to solve.
There’re lots of necessity to write a self employed business plan:
- Initial plan to reach at break-even point
- List down the strategies to reach the desired profit level
- List the desire industry to target and a pilot client list
- The rates you’ll charge
- List down the obstacles
Since this is completely your own business, there's no hurry to chase the deadline or the targets you aim for. There is another advantage of setting up a self employed business plan, for instance you can take every step in the aware mindset, understand the perspective of customers, trace down the uniqueness of your products, and strategies to regenerate the customers.
Having good self employed business ideas will not only help you to focus on the business plan, but also help to prioritize the project and task to reach the goal faster.
- Sketching a defined target helps you to have a clear objectives of your goal
- You’ll already about the financial boundaries and objectives
- A full-proof excuse to analyze your business, competitors, and different external activities.
- Help you to be focus and recognize your business opportunity
This is not only an article, but also it will act as the basement of your business. Though it will not be easy to become self-employed and write a business plan for the self-employed, this article provides you with a guideline. As a result, you will get a direction on how you can prepare yourself.
So, it’s time to become self-employed and inspire others to also become self-employed
through following a proper business plan.

- 10 Futuristic Ideas for a Successful Coffee Shop Business
- Cloud Kitchen Business Model: Everything You Need to Know!
- Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan Sample Guide
- Business to Customer(B2C) Business Model and Examples

Related Post

Thinking Hassle Free Software Development Service?
We provide custom software development services for business ERP solutions, blockchain, hospitality, e-commerce, e-learning & others.
For 30 Minutes Free Consultancy

Self Employment Checklist—Free Download
This form will load shortly, thanks for your patience.

Ready to become self employed? Fill out the form to download the free checklist and get started.
How to become self employed, fill out the form to download your free checklist today, and start working through the steps to become self employed.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Your download should begin immediately
If your download doesn't begin after 5 seconds, please click here .
View our entire gallery of free downloads
You might also enjoy:

The Small Business Toolkit
Access a free list of must–have resources for new and growing businesses in any industry.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Log in
- Site search
Writing a successful business plan
All successful businesses start with a strong business plan. Also known as a business proposal, this document helps attract investors and customers alike by demonstrating your knowledge, passion and drive
Writing a business plan is essential when starting your own business , but what is a business plan and why do you need one? Well, a business plan describes your company, what it aims to achieve and outlines how it'll achieve it. It helps you to clarify your ideas, identify potential problems with your business model, establish short and long-term goals and, over time, measure your company's progress.
A business plan is vital if you're looking to secure investment, but it can also convince customers and suppliers to support you. You should update your business plan regularly, tailoring it to its intended reader as you would a CV and cover letter. Here's a suggested business plan template to get you started.
Executive summary
After the title page - which includes the name and business address of the author, the date of publication, and details of the plan's circulation and level of confidentiality - you'll present your executive summary. Bear in mind that this is the last section of the business plan you'll write, because its job is to grab the reader's attention by summarising what will follow.
Over three to four pages, briefly highlight the key purpose of your business plan and summarise the capital requirements, financial projections, and management structure of your company. You should also provide details of your competitors.
When writing a business plan, your focus throughout should be on highlighting how your product or service takes advantage of a significant market opportunity.
The business
Begin this section by addressing your company's products and services, before going into greater detail about its aims and objectives. Expand on the history of your business and explain its ownership structure. You should also mention what type of business it is.
An overview and outlook of the industry should be included, covering details of any relevant regulations and specific markets of interest. However, this information will be expanded on in the market analysis section, so keep it brief.
Finally, address how your business can be developed to meet future needs or changes, and admit any weaknesses that it may have. Being open in this manner will inspire confidence.
Market analysis
Essentially a condensed marketing plan, this section focuses on several factors:
- Market research - It's vital to know that you've got a group of buyers for your product or service. Become familiar with the market and job sector as a whole, so the company can be positioned appropriately in terms of price and quality.
- Target audience - Discuss which market segments you're aiming to pursue, such as local customers or those of a particular age group. Indicate the key characteristics of your typical buyers.
- Competitors - Summarise your competitors' strengths and weaknesses and consider how you can prevent others from entering your market space.
- Existing customers and sales - Mention any customers that you've already lined up and address how you'll sell, whether it's over the phone, on your website, face-to-face or through an agent. In addition, if you have more than one product or service, consider the contribution of each to your turnover.
- Marketing strategy and goals - Address how you'll promote your product. This may be through means such as advertising, public relations (PR), direct mail or email. Examine likely sales, growth, profit margins and costs.

Management and operations
This section explains how your business will function. You should detail the:
- Background, experience, and training of the management team - Highlight individuals' roles and responsibilities, plus their relevant skills and experiences. You should also mention the financial contributions, salaries and company benefits of each member.
- Capital requirements - Discuss the company's needs in terms of equipment, facilities, insurance, and personnel, before highlighting any potential limitations to production.
- Logistics - Detail each division and their assigned tasks, addressing how you'll cover sales, finance, marketing, administration, stock control and quality control. You should describe the systems and procedures that will be involved in all aspects of production, from the customer's initial payment through to transport and delivery, including detailed information on your suppliers.
Financial forecasts
In this section, you must translate your company's aims and objectives into measurable goals. This means providing numbers including:
- the estimated costs of starting and running your business
- how much additional finance you require, plus what it will be used for
- sales forecasts for the first year
- profit and loss forecasts for the first three years
- cash flow forecasts, showing that you've considered key variable factors such as sales revenue and wages
- your budget and pricing strategy.
Be aware that you should justify any assumptions that you've made when reaching each forecast.
Risk management
Consider any risks associated with running your business, plus any legal obligations surrounding factors such as insurance, licences, and health and safety.
You should also create detailed 'what-if scenario' backup plans, documenting how you'll react to issues that may arise. Not only will this help you to minimise risk, but you'll enhance your credibility with potential investors by showing that you've thought about your business plan from every angle.
The appendix of a business plan features copies of essential supporting documents, such as:
- credit history information
- detailed cash flow plans
- detailed CVs of the management team
- market research results
- receipts and bank statements
- tax returns.
Much of the information contained within your business plan will be highly confidential. You should therefore tailor your appendix depending on who is receiving your plan - potential investors, for example, will expect to find out more than potential affiliates.
Overall, your business plan should be clear, concise, and realistic. If it's too long, or your objectives are too ambitious, it won't be read fully or taken seriously. Keep your audience in mind, using non-technical language where possible to be more readily understood, and ensure the points you make are logical, sound and backed up with explanation or evidence.
Find out more
- Find out whether self-employment is right for you .
- Learn more about freelancing .
- Discover things to avoid when starting a business .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page
Home > Business > Business Startup
From Employee to Entrepreneur: 8 Steps for Transitioning to Self-Employment

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .
Syndicated from The Penny Hoarder
Freelancing, consulting or starting your own business could be the perfect way to launch the career of your dreams.
But making the jump to self-employment is never easy. Leaving behind the comfort and security of your day job in exchange for the massive responsibility of running your own business is exciting — but totally nerve-wrecking.
By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
8 steps for transitioning to self-employment
If you’ve been an employee for years, it’s tough to know where to start. Here are some important tips to keep in mind during your self-employment journey.
1. Develop a business plan
One of the first steps in transitioning to self-employment is writing a business plan .
Your business plan should outline your goals, the services or products you’ll offer, your target audience and your financial projections.
Ask yourself these questions when creating a business plan:
- What services will you offer?
- Who is your target audience and how will you reach them?
- How will you land your first contract or project? How will you find future clients and leads?
- How will you price your products or services?
- How much revenue do you need to cover expenses?
- When and where do you want to work?
- How will you grow your skills and network?
You can also check out this free 30-minute course on how to create a business plan from the Small Business Administration.
When developing your plan, be realistic about your financial projections and set achievable goals. Don't underestimate the time and resources required to get your business up and running .
This is also a good time to determine what makes your skills or service unique. How will you differentiate yourself from competitors and position yourself as an expert in your field?
2. Create wiggle room in your current job
You can work toward your new freelancing career even before you leave your old job — in fact, this is advised by most career experts.
You’re likely spending more time than necessary doing work you don’t like in your current position. Start your transition by trimming the fat.
Figure out what tasks should be completed by subordinates or other departments, and get them off your plate.
Cutting out the mundane aspects of your job, like team-wide meetings and performance reviews, can free up more time to focus on your own business.
Start to grow your side hustle , working with a few clients and gigs in the time you’ve freed up so you can replace your income and transition your work and lifestyle slowly.
Your side hustle will probably take over your free time and other hobbies for a while. But it will pay off when you’re able to leave your day job behind, start a new career and do what you love.
Need some start-up money? Here’s how to get a small business loan .
3. Get your finances ready
Aim to save three to six months' worth of living expenses in an emergency fund, plus whatever capital you need for the business.
This financial cushion will give you some breathing room if you hit unexpected expenses or a slow month.
Start saving by looking for ways to cut expenses and identify ways to save money fast, like canceling subscriptions and shopping for cheaper car insurance quotes.
Use an expense tracking app so you can identify areas where you can cut back and save more money.
By preparing yourself for life at a lower income, you can remove the financial fear that comes with quitting your day job.
Now is also a good time to take care of big expenses. Upgrade your computer, pay off credit card debt and eliminate as much other debt as possible while you can still rely on your current income.
You also need to figure out how much money you need to start your business and how you will finance it: Personal savings, small business loans or private investors .
Calculate how many hours per day and per week that you need to work in order to meet your financial goals and replace your current income.
Don't expect to make a full-time income right away and be prepared to work hard and stay committed.
Finally, create separate accounts for your business and personal finances. This makes it easier to track your business income and expenses for tax purposes. Keeping things separate also helps avoid a mix up between your personal savings and your business cash reserves .
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
Data effective 4/20/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
4. Figure out your health care and taxes
Launching your own business means you’ll be responsible for many expenses currently covered by your employer, including taxes and health insurance.
Unlike traditional jobs, self-employed individuals are responsible for paying their own taxes. A good rule of thumb is to set aside about 20% to 35% of every paycheck you make to cover your self-employment taxes .
You’ll need to pay estimated taxes each quarter in addition to filing an annual tax return. This will include both federal income tax and self-employment tax , an additional tax levied on independent contractors currently totalling 15.3%.
Before you transition to self-employment, sit down with a certified public accountant . This professional can help set-up your accounting processes and tax reporting. A CPA can also assist in helping you create realistic billable rates.
Taxes are complicated. Check out our guide on how to file small business taxes to learn more.
Next, you’ll need to figure out your health insurance. Buying your own coverage can be costly, but luckily, there are a few ways to get health insurance if you’re self-employed.
You can purchase a plan through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Health Insurance Marketplace . Here, you can compare health insurance from a variety of providers — and you may be eligible for subsidies based on your income.
Additionally, you can look into getting health insurance from your spouse’s employer. Or maybe you can continue working part-time for your current employer to keep your benefits in place.
5. Network and learn
Use this time before leaving your full-time job to educate yourself about freelancing and your new industry.
Continuing education and professional development are key to staying competitive in today’s job market.
Attend workshops and conferences, take online courses and read industry publications to stay up-to-date with business trends and best practices.
Networking is also key. It’s crucial to start building relationships before you make the transition to self-employment.
Learn how to utilize your resources, and find new ones. Join your local chamber of commerce , reach out to the Small Business Administration and connect with colleagues on social media.
Work to add more people to your support network over time, whether that's a mentor, a business coach or a meet-up of fellow entrepreneurs.
You don’t need to be a social butterfly to thrive at networking events. These networking tips for introverts can help.
6. Embrace time management
As a self-employed individual, you’re responsible for managing your own schedule, finances and client relationships.
It’s important to stay organized in your business and keep track of your to-do list and deadlines.
Learning how to track your time will make it easier to calculate your billable hours, create reports and conduct a proper cost/benefit analysis. It’ll also help you get time back from your business .
Consider using tools like project management software , accounting software and time-tracking apps to stay on top of your workload.
Using a timesheet calculator or a similar app for a few weeks can provide insight into your biggest time wasters, as well as your most productive hours.
7. Make the jump … gracefully
When the time comes to part ways with your job, give proper notice and maintain a positive relationship with your employer.
After all, you never know when you might need a reference or want to work with the company again on a part-time or contract basis.
Before calling it quits, review your employment contract to identify any non-compete or non-disclosure agreements you may have signed.
Don’t let these documents stop you, though.
Be proactive and let your employer know that you won’t solicit their clients. If you’re honest and objective, your employer is less likely to enforce a NDA or non-compete.
8. Know what’s holding you back — and let go of those fears
Sometimes fear is the biggest thing holding people back from transitioning to self-employment.
You have the passion and the ability to acquire all the skills and knowledge you need to do what you want. Hurdles in your life may make the transition difficult — a family who needs your time and attention, a day job that leaves you exhausted, a mortgage that insists on being paid each month.
But none of these challenges make your dream impossible.
Be prepared for the ups and downs of entrepreneurship and have a plan in place for dealing with setbacks and challenges.
Then take a deep breath and jump.
Rachel Christian is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance and a senior writer at The Penny Hoarder. She focuses on retirement, investing, taxes, and life insurance.
Related reading
- The 5 Best Bank Accounts for Entrepreneurs
- Small-Business Grants for Women 2023: 5 Programs with Free Money for Women
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business

Want affordable banking with great perks? With Bluevine, you can get a fee-free business checking account―and you can even earn up to $5,000 in interest.

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Small Business Loans
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2024 All Rights Reserved.
SELF-EMPLOYED BUSINESS PLAN: How do I Write One?
- by Kenechukwu Muoghalu
- August 13, 2023
- No comments
- 7 minute read

Table of Contents Hide
What is a self-employed business plan, what is the importance of a business plan, is it difficult to write a self-employed business plan, #1. executive summary, #2. company overview, #3. market analysis, #4. management and organisational team, #5. competitive analysis, #6. sales and marketing strategy, #7. financial plan, #8. appendix, can you write a self-employed business plan in a day, how long should a self-employed business plan be for a small business, when should i start a self-employed business plan, still confused about how you can write a self-employed business plan, conclusion , why do business plans fail , what makes an excellent business plan, what are the common errors in the preparation of a business plan.
Whichever profession or career you determine to settle for, taking the decision to work on your terms and become self-employed is a big step. Hence, for you to run a smooth business while being self-employed, you need to have a business plan. Owning a business plan as a self-employed individual can help outline your goals and aid you achieve those goals. To get more insights on how you can run a successful business on your own, this article will cover the basic information you need to know about a self-owned business. With our self-employed business plan template, you will also learn how to write a plan for your business.
Just before we dive in, you can choose to ignore these procedures and just stick to our ready-made self-employed business plan .
A self-employed business plan is a living document that analyses your business ideas, its goals, your products or services, your mission, how you intend to make revenue, its leadership and many other details essential to its success. You can also define a business plan as a road map that will help you attain the growth of your business.
Read Also: SELF EMPLOYED MORTGAGE: How to Get One
Not every potential or successful corporation started with a business plan, but many wise founders take out time to research their ideas, market, and audience to understand the basics of how to scale in their new field. This is strictly why you need to sit down and learn how to write a self-employed business plan for you to be able to handle your business on your own. To fail to plan is to plan to fail.
Working side by side with a business plan comes with multiple advantages. As a self-employed individual, you might need some form of funding at some point, and you can only pull that through by having a business plan. Investors and banks rely solely on a business plan to evaluate the credibility of a business before agreeing to sponsor it.
Aside from needing a business plan in terms of funding, it can also help you focus on more important goals with the highest chance of success. A business plan also has the ability to help you manage your resources wisely and know when best to take in opportunities. Working for yourself can be rewarding because you get to choose what you are passionate about, work long hours and control your income, but it can only become better with a plan.
Writing a business plan can be a fun activity because all you have to do is to write down those growth strategies. But other times, the process can be daunting, especially when it is your first time. But to make it easier, we have provided a unique template that can help you create a self-employed business plan with ease. In any case, if it gets too tough along the way, you can use our ready-made business plan. Having known this, let’s analyse how to write a self-employed business plan using the template below.
How is a Self-employed Business Plan Written?
To write a business plan, you will need a structured outline that will serve as a guide on the best steps to take. These outlines will also help you construct a compelling plan that any reader will access with ease. They include:
Your executive summary is a brief of the other sections. It is more of a summary of what your business is all about. Most of the time, your readers might not have all the time in the world to go through your business plan. To curb this, they will refer directly to your executive summary. This being the case, this section should serve as a hook that will attract them to read more. Make sure to also leave it clear and concise during this course. This section should cover your financial plan, team, marketing strategy, market analysis and goals among others.
The company overview section of your self-employed business plan is where you get to explain who you are and the unique plans you have for your business. You can give a brief history of your business, yourself, industry, vision, and objectives, among others. Ensure not to leave out your short and long-term goals in this section.
Before you settle down to conclude your target market and market analysis , you will have to perform some research on your market. The essence of this research is to understand your industry and predict who your target client is. As a self-employed individual, you may require some assistance during this section. Discovering this information will also convince your readers of your ability to reach your ideal audience.
Your team should not be left out of your business plan. You should be able to tell your readers about the personnel involved in the smooth running of your business. While doing this, you can also utilise this opportunity to highlight their different roles and skills in the firm. You can also educate your readers on how each person will contribute to the growth of your company.
Your competitors are clearly not left out of this plan. In this section of your competitive analysis , you will need to research who your competitors are and also tell your readers how you plan on being different from the crowd. You also need to note their weaknesses and strengths and decipher how to approach your client better.
Your sales and marketing strategy should cover the different marketing techniques you will be applying to your business to identify prospects, sell your products, and land new clients. You can decide to create an online presence or use manual advertisements.
Your financial plan is also an essential section of your self-employed business plan. You will need to explain your current funding, a clear estimation of how much revenue your business will yield per month, a list of expenditures, a balance sheet, a cash flow statement, and an income statement.
The appendix of your business plan covers any other important supplemental documents that didn’t make their way into the plan. This document can come in the form of insurance, resumes, legal forms, credit histories, licences and permits, among others. They will also convince your readers of how credible your corporation is.
The time span solely depends on the amount of data you have at your disposal. If your business plan is a complex one that will cover a lot of information about your business, then you should be able to pull it through within 2-7 days. Whereas, when creating a basic plan, it should last for 3 hours or a day to finish.
A business plan for self-employment should be basically from two to four pages. You should focus more on making it clear, brief and concise. It does not need to be too complex and wordy. Let it serve as a clear guide that would easily define what your business is all about.
According to the current statistics, an average successful entrepreneur writes their business plan between six and twelve months after planning on how to start up a business. Constructing a plan within this time frame tends to yield more results.
If there are something entrepreneurs still find hard to manoeuvre whilst starting a business, then it is mostly getting stuck on how to write a self-employed business plan for themselves. It is normal to face difficulties considering the fact that you are new to this field.
This is exactly why we have created a professional, ready-to-use self-employed business plan for your convenience. Over the years, Businessyield consulting has helped thousands of entrepreneurs like you start up on the right foot by taking the time to construct a unique plan for your business. What else do you seek? Get a copy here and unleash those ideas.
Making provisions for a business plan before starting off any type of business is always a great way to start and validate your business idea. That is why you need to give it a good steer to be able to produce a clear, concise and realistic self-employed business plan using our template , in order to enjoy all of its benefits. You should also remember to review the plan once in a while to keep your data updated.
Owning a business plan does not fully guarantee the success of your business. Most of the time, you can face a certain failure, and this is mainly because you lack quality operational force. You end up planning the whole day and then put in zero effort to actualize your plans. Your action elements are not applied, monitored, functional, or refined. Once you do not put in the work, then your business plan will not reach its full potential.
A professional business plan should contain some necessary elements, including a marketing strategy, an executive summary, a financial plan, an operational structure, and a clear market analysis.
There are common errors that you should take note of when writing a self-employed business plan for your firm. They include using a bad business idea, neglecting the essence of an exit strategy, using an incapable team, having spelling and grammatical errors and writing half-baked financial projections among others. These are crucial errors you should take note of while writing.
Related Articles
- HOW TO PAY LESS TAX UK: 15+ Ways to Pay Less and Save More on Tax(Updated)
- CLEANING BUSINESS PLAN: Template & All You Need to Know
- All Clear Travel Insurance Best Reviews 2023
- BUSINESS PLAN WRITING SERVICE COST: Best UK Practice In 2023
Kenechukwu Muoghalu
Kenny, an accomplished business writer with a decade of experience, excels in translating intricate industry insights into engaging articles. Her passion revolves around distilling the latest trends, offering actionable advice, and nurturing a comprehensive understanding of the business landscape. With a proven track record of delivering insightful content, Kenny is dedicated to empowering her readers with the knowledge needed to thrive in the dynamic and ever-evolving world of business.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Rolling Contract: Definitions & Guidelines
<strong>online coaching business plan: how to start a coaching business now</strong>.
We noticed you're visiting from Netherlands. We've updated our prices to Euro for your shopping convenience. Use Pound sterling instead. Dismiss
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Simple Business Plan Template for Entrepreneurs
Follow This Business Plan Outline to Write Your Own
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Pros and Cons of Using a Business Plan Template
Do i need a simple or detailed business plan, how to use this business plan template, table of contents, section 1: executive summary, section 2: business/industry overview.
- Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
Section 5: ownership and management plan, section 6: operating plan, section 7: financial plan.
- Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
Ariel Skelley / Getty Images
Think you have a great idea for a business? The best way to find out whether your idea is feasible is to create a business plan .
A solid, well-researched business plan provides a practical overview of your vision. It can be used to ground your ideas into workable actions and to help pitch your idea to financial institutions or potential investors when looking for funding.
The standard business plan consists of a single document divided into several sections for distinct elements, such as a description of the organization, market research, competitive analysis, sales strategies, capital and labor requirements, and financial data. Your plan may include more or fewer sections to best represent your business.
The template presented here will get you well on your way toward your simple business plan.
Ready-made layouts
Free downloads
Generic, not customized
No financial guidance
Additional skills needed
- Ready-made layouts : Templates offer general guidance about what information is needed and how to organize it, so you’re not stuck looking at a blank page when getting started. Especially detailed templates may offer instructions or helpful text prompts along the way.
- Variations : If you know what type of business plan you need—traditional, lean, industry-specific—chances are you can find a specialized template.
- Free downloads : There are many free business plan templates available online, which can be useful for comparing formats and features, or refining your own.
- Generic, not customized : Templates typically contain just the basics, and there will still be a lot of work involved to tailor the template to your business. For instance, you'll have to reformat, refine copy, and populate tables.
- No financial guidance : You’ll need enough industry knowledge to apply financial models to your specific business, and the math skills to generate formulas and calculate figures.
- Additional skills needed : Some degree of tech savvy is required to integrate charts and graphs, merge data from spreadsheets, and keep it all up-to-date.
A corporate business plan for a large organization can be hundreds of pages long. However, for a small business, it's best to keep the plan short and concise, especially if you're submitting it to bankers or investors . Around 35 to 50 pages should be sufficient, and more allowed for extras, such as photos of products, equipment, logos, or business premises or site plans. Your audience will likely prefer solid research and analysis over long, wordy descriptions.
An entrepreneur who creates a business plan is nearly twice as likely to secure financing and grow their business compared with those who do not have a plan.
The business plan template below is divided into sections as described in the table of contents. Each section can be copied into a document of your own; you may need to add or delete sections or make adjustments to fit your specific needs.
Once complete, be sure to format it attractively and get it professionally printed and bound. You want your business plan to convey the best possible impression. Make it engaging, something people will to want to pick up and peruse.
Enter your business information, including the legal name and address. If you already have a business logo, you can add it at the top or bottom of the title page.
- Business Plan for "Business Name"
- Business address
- Website URL
If you're addressing it to a company or individual, include:
- Presented to "Name"
- At "Company"
- Executive Summary................................................Page #
- Business/Industry Overview.................................Page #
- Market Analysis and Competition.........................Page #
- Sales and Marketing Plan.......................................Page #
- Ownership and Management Plan.......................Page #
- Operating Plan..........................................................Page #
- Financial Plan............................................................Page #
- Appendices and Exhibits........................................Page #
The executive summary introduces the plan, but it is written last. It provides a concise and optimistic overview of your business and should capture the reader's attention and create a desire to learn more. The executive summary should be no more than two pages long, with highlights or brief summaries of other sections of the plan.
- Describe your mission —what is the need for your new business? Sell your vision.
- Introduce your company briefly, sticking to vital details such as size, location, management, and ownership.
- Describe your main product(s) and/or service(s).
- Identify the customer base you plan to target and how your business will serve those customers.
- Summarize the competition and how you will get market share. What is your competitive advantage?
- Outline your financial projections for the first few years of operation.
- State your startup financing requirements.
This section provides an overview of the industry and explains in detail what makes your business stand out.
- Describe the overall nature of the industry, including sales and other statistics. Note trends and demographics, as well as economic, cultural, and governmental influences.
- Explain your business and how it fits into the industry.
- Mention the existing competition, which you'll expand upon in the following section.
- Identify what area(s) of the market you will target and what unique, improved, or lower-cost products and/or services you will offer.
Many business plans cover their products/services in a standalone section to add more detail or emphasize unique aspects.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
This section focuses on the competitive factor of your business and justifies it with financial models and statistics. You need to demonstrate that you have thoroughly analyzed the target market, assessed the competition, and concluded that there is enough demand for your products/services to make your business viable.
- Define the target market(s) for your products/services in your geographic locale.
- Explain the need for your products/services.
- Estimate the overall size of the market and the units of your products/services that the target market might buy. Include forecasts of potential repeat-purchase volume and how the market might be affected by economic or demographic changes.
- Estimate the volume and value of your sales in comparison with any existing competitors. Highlight any key strengths over the competition in easily digestible charts and tables.
- Describe any helpful barriers to entry that may protect your business from competition, such as access to capital, technology, regulations, employee skill sets, or location.
You may opt to split the target market description and competitive analysis into two separate sections, if either (or both) portray your business especially favorably.
Here's where you dive into profits, giving detailed strategic view of how you intend to entice customers to buy your products and/or services, including advertising or promotion, pricing, sales, distribution, and post-sales support.
Product or Service Offerings
If your products and/or services don't take up a standalone section earlier in the plan, here is where you can answer the question: What is your unique selling proposition? Describe your products and/or services, how they benefit the customer and what sets them apart from competitor offerings.
Pricing Strategy
How will you price your products/services? Pricing must be low enough to attract customers, yet high enough to cover costs and generate a profit. You can base pricing decisions on a number of financial models, such as markup from cost or value to the buyer, or in comparison with similar products and/or services in the marketplace.
Sales and Distribution
For products, describe how you plan to distribute to the customer. Will you be selling wholesale or retail? What type of packaging will be required? How will products be shipped? If you offer a service, how will it be delivered to the customer? What methods will be used for payment?
Advertising and Promotion
List the various forms of media you will use to get your message to customers (e.g., website, email, social media, or newspapers). Will you use sales promotional methods such as free samples and product demonstrations? What about product launches and trade shows? Don't forget more everyday marketing materials such as business cards, flyers, or brochures. Include an approximate budget.
This section describes the legal structure, ownership, and (if applicable) management and staffing requirements of your business.
- Ownership structure : Describe the legal structure of your company (e.g., corporation, partnership, LLC, or sole proprietorship ). List ownership percentages, if applicable. If the business is a sole proprietorship, this is the only section required.
- Management team : Describe managers and their roles, key employee positions, and how each will be compensated. Include brief résumés.
- External resources and services : List any external professional resources required, such as accountants, lawyers, or consultants.
- Human resources : List the type and number of employees or contractors you will need, and estimate the salary and benefit costs of each.
- Advisory board : Include an advisory board as a supplemental management resource, if applicable.
The operating plan outlines the physical requirements of your business, such as office, warehouse, or retail space; equipment; supplies; or labor. This section will vary greatly by industry; a large manufacturer, for instance, should provide full details about supply chain or specialty equipment, while a therapist's office can get by with a much shorter list.
If your business is a small operation (like a one-person, home-based consulting firm), you might choose to eliminate the operating plan section altogether and include the operating essentials in the business overview.
- Development : Explain what you have done to date to identify possible locations, sources of equipment, supply chains, and other relevant relationships. Describe your production workflow.
- Production : For manufacturing, explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be ready to start production. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and how you'll deal with potential problems, such as rush orders.
- Facilities : Describe the physical location of the business. Include geographical or building requirements; square footage estimates (with room for expansion if expected); mortgage or leasing costs; and estimates of maintenance, utilities, and related overhead costs . Include zoning approvals and other permissions that are necessary in order to operate.
- Staffing : Outline expected staffing needs and the main duties of staff members, especially the key employees. Describe how the employees will be sourced and the employment relationship (i.e., contract, full-time, part-time) as well as any training needs and how these will be provided.
- Equipment : Include a list of any specialized equipment needed, along with cost, whether it will be leased or purchased, and sources.
- Supplies : If your business is, for example, manufacturing, retail, or food services, include a description of the materials needed, reliable sources, major suppliers, and how you will manage inventory.
The financial plan is the most important section for lenders or investors. The goal is to demonstrate that your business will grow and be profitable. To do this, you will need to create realistic predictions or forecasts.
To avoid inflated expectations, a prudent financial plan underestimates revenues and overestimates expenses.
- Income statements : The income statement displays projected revenues, expenses, and profit. Do this on a monthly basis for at least the first year for a startup business.
- Cash-flow projections : The cash-flow projection shows your monthly anticipated cash revenues and disbursements for expenses. To be considered a good credit risk, it is important to demonstrate that you can manage your cash flow.
- Balance sheet : The balance sheet is a snapshot summary of the assets, liabilities, and equity of your business at a particular point in time. For a startup, this would be on the day the business opens.
- Breakeven analysis : Including a breakeven analysis will demonstrate to lenders or investors what level of sales you need to achieve to make a profit.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits section contains any detailed information needed to support other sections of the plan.
Possible Appendix or Exhibit items include:
- Credit histories for the business owners
- Detailed market research and analysis of competitors
- Résumés of the owners and key employees
- Diagrams and/or research about your products and/or services
- Site, building, or office plans
- Copies of mortgage documents or equipment leases (or quotes)
- Marketing brochures and other materials
- References from business colleagues
- Links to your business website
- Any other material that may impress potential lenders or investors
SCORE. " Business Plan Template for a Startup Business ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write your business plan ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " SBA Recommended Business Plans and Length ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Bplans. " Why Plan Your Business? Look at This Data ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Marketing MO. " Pricing Strategy ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Incorporate.com. " Write a Business Plan, a Step-by-Step Guide ." Accessed April 29, 2021.
Startup Nation. " The Five Costs You're Most Likely to Underestimate in Your Business Plan ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Register to vote Register by 18 June to vote in the General Election on 4 July.
- Business and self-employed
- Business finance and support
Write a business plan
Download free business plan templates and find help and advice on how to write your business plan.
Business plan templates
Download a free business plan template on The Prince’s Trust website.
You can also download a free cash flow forecast template or a business plan template on the Start Up Loans website to help you manage your finances.
Business plan examples
Read example business plans on the Bplans website.
How to write a business plan
Get detailed information about how to write a business plan on the Start Up Donut website.
Why you need a business plan
A business plan is a written document that describes your business. It covers objectives, strategies, sales, marketing and financial forecasts.
A business plan helps you to:
- clarify your business idea
- spot potential problems
- set out your goals
- measure your progress
You’ll need a business plan if you want to secure investment or a loan from a bank. Read about the finance options available for businesses on the Business Finance Guide website.
It can also help to convince customers, suppliers and potential employees to support you.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
What is a business plan template?
Home / / what is a business plan template, know you need a business plan - but not sure where to start.
If you're overwhelmed at the thought of writing your first business plan, you’re not alone! Lots of people find the idea intimidating.
But a well-structured business plan is a game-changer. It acts as a roadmap for your journey into self-employment, giving you a clear idea of your destination, direction of travel and what landmarks to look out for on the way.
Start planning your business journey
Here at Transmit Startups, we’re dedicated to simplifying and demystifying business, to help people follow their dreams of self-employment.
We think this template from the British Business Bank is a great starting point.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document which sets out in detail exactly how you’ll run your business.
It considers:
what your products and services are
how you’ll promote and sell them
how you’ll fund your business
who your customers and competitors are

Your final business plan will also include details of your financial forecasts, explaining how much money you think you will make and how.
Business plan templates ask for market research , looking at how big your market is and who your customers are. You can segment your markets too.
Many business plans include a section explaining how many employees you will need, how and when you'll recruit them and how many you will recruit.
Why do you need a business plan?
A good business plan will guide you through each stage of starting your business. Think of it like preparing for a long road trip. Once you've planned the route you can start making sure you have enough petrol, and decide who’s going to do the driving. Imagine how lost you could get without that prior preparation…
1. Setting the destination
Just as you would input your destination into a GPS, your business plan outlines your ultimate objectives and goals. It gives you a clear vision of where you want to take your business.
And it helps you make sure your idea is feasible . You’ll have to think through details like how much money it could make vs how much money you’ll have to invest.
2. Mapping the route
Your business plan gives you a place to list specific goals and objectives for your business. And you can use it to identify the different routes and strategies to reach your goals in the most efficient and effective way.
You’ll have to think about how you’ll meet these goals and what the timescale is. By making financial forecasts (like a cashflow forecast ), you can work out how much your business needs to make in order to support your lifestyle. How long do you want to work in order to make the money you aspire to?
3. Identifying resources
Business planning helps you understand the financial reality of your business idea. Do you have the resources you need to get started - whether that's stock, premises, funding or staff?
Not everyone starting a business needs to access business finance. There are plenty of businesses you can start with no money . However, some do need startup funding. If you do plan to apply for a loan, a business plan is essential. It shows lenders that you’ve thought things through and will be able to afford repayments.
What does it mean to "pivot"?
In the startup world, pivoting means shifting to a new strategy. But it doesn’t necessarily mean a drastic change to your whole business plan.
If you’ve identified one important problem or one incredible opportunity, you may only need to change one area of your strategy.
4. Avoiding traffic and obstacles
If you accidentally take a wrong turn, your GPS will recalculate the route. Your business plan needs to be adaptable, too. Take some time to think about what challenges you could face and who your competitors are.
You’ll also need to really think about your customers, what they want and how you’ll sell to them . Being prepared for obstacles and opportunities means you can shift to a new strategy if you need to pivot your business... And avoid getting stuck in a traffic jam.
5. Staying safe and compliant
Having a plan will stop you wandering down unsafe paths. Just as you need to know the traffic rules and regulations of the area you're driving through, a business plan will help you ensure that you're legally compliant, for example by identifying any licenses you need for your business .
And what about financial paperwork? Do you need to complete a self-assessment tax return ? What steps do you need to take to register your business in the UK ? Getting everything in place before you begin trading will make sure you're operating legally - and avoid any risky turns!
6. Real-time adjustments
Just like a GPS will update and adapt your route if needed, so your business plan will change and grow with you.
Once you've been in business for a while, you will have actual data about sales and cashflow to compare with your planned financial forecasts. This will help you tweak your strategies and plans, and update the ETA based on whether you're on-track to meet your goals.
How do you write a simple business plan?
Business plans don't HAVE to be complicated. If you're thinking of starting a business, you only need to write a simple business plan at first, to help you think through your business and get into the planning mindset.
If you’re struggling to know what to write, just jot down some notes and come back to it later.

What’s in a business plan template?
Business plan templates commonly include the following sections:
1. Your information
The first section is just basic details about you and your business – the who, what and when questions.
2. Your business idea
Next you describe your business or business idea. Write about the main activities of the business and what products or services you offer. There are questions about any premises or licenses you might need, and who else is involved in the business. Don’t worry if these don’t apply to you, just skip forward.
3. Your market
Tell us about your customers and how you’ll reach them. Think about your competitors and how they do things. Then complete a SWOT analysis. This isn’t as hard as it sounds and our SWOT blog post can help.
4. Pricing and selling
Pricing is really important to get right. This section will help you think about pricing as part of your overall business strategy. You’ll also think about suppliers and sellers for your product or service.
5. Loan amount
If you'll be using a loan to fund your business initially, you should include in your plan how much you need to borrow and what you’ll use it for. Think about other sources of income and what expenses you might incur. Consider how much it costs to start a business .
Want a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan?
If you'd prefer not to use a pre-existing template, you can start from scratch by following our guide on how to write a business plan .
Writing a business plan requires research, realistic projections and some careful thought. But it doesn't need to be difficult.
How else can a business plan help?
If you’re a sole trader or microbusiness, your business plan might be for your eyes only. But as you grow and develop, your business plan can help your business bloom.
1. Securing investment or borrowing
A well-written business plan containing relevant figures will help you convince investors your business is a reliable proposition.
2. Satisfying suppliers and distributors
Any distributors you need will want to see your assessment of the risks and threats facing your business, and how you’re managing your supply chain. Suppliers who may need to offer you credit will want to see how well you’ve planned for the future.
3. Motivating and managing staff
Any other people involved with your business should share the same goals as you do. A strong business plan can help guide your workplans and make sure you’re all pulling the same way.
Where can I download a free business plan template?
Right here . The British Business Bank have produced a template, designed to be used to support a Start Up Loan application .
Even if you're at the earliest stages of an idea, you can download it for free and use it to help develop your plans. We'd recommend it to anyone who wants to think about starting a business.
Your business plan is a vital tool for securing loans, and a foundation for making informed decisions. So it's definitely worth doing.
Completed your business plan template and ready to get going?
If you've got an idea for a business and want to talk to someone about funding your idea, you can explore a low-interest Start Up Loan .

Start Up Advice
- Business planning
- Digital & Technology
- Finance & Funding
- Getting started
- How to grow
- Marketing & Sales
- People & Skills
- Success Stories
- Transmit News

"We’re delighted to be the 2000th loan recipients!"
JO CARTER – DUKES GASTROPUB
Entrepreneurs backed.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Solo 401(k)?
How the solo 401(k) works.
- Who Is Eligible?
How to Set Up a Solo 401(k) Plan
- Eligibility Requirements
- Contribution Limits
Other 401(k) Plans
Contributions example, other benefits of a solo 401(k), the bottom line.
- Retirement Planning
A 401(k) Plan for the Small Business Owner
The solo 401(k) plan is worth a look
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Roger Wohlner is an experienced financial writer, ghostwriter, and advisor with 20 years of experience in the industry.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/8s1a3945__roger_wohlner-5bfc2628c9e77c0026b3f16a.jpg)
- Self-Employment: Definition, Types, and Benefits
- Self-Employed Person
- Independent Contractor
- The Gig Economy
- Watch This Trend: Calif. Assembly Bill 5
- Challenges for Self-Employed Finance Professionals
- Healthcare Options for Small Businesses: A Comprehensive Guide
- Best Health Insurance Plans
- Best Disability Insurance Plans
- Getting a Mortgage When Self-Employed
- Money Guide for Self-Employed Parents
- Calculate Your Salary
- SEO for Small Businesses: Everything You Need to Know
- Build Your Own Plan
- How Social Security Works
- Save for Retirement
- SEP IRA Plan
- Individual 401(k) Plans CURRENT ARTICLE
- Individual 401(k) vs. SEP IRA
pixdeluxe / Getty Images
The 401(k) plan has gained popularity among small business owners ever since 2001, when some changes to federal tax law made it a better and more flexible choice for their needs compared with some other retirement savings options. These 401(k) plans are known as “solo 401(k)” plans.
Key Takeaways
- A solo 401(k) plan is for businesses whose only eligible participants in the plan are its owners (and their spouses, if they work for the business).
- These plans are often less complicated and less expensive to set up.
- If you have non-owner employees, they must not meet the eligibility requirements you select for the plan.
- There are two components to a solo 401(k) plan: employee elective-deferral contributions and profit-sharing contributions.
- A solo 401(k) may also offer loans, doesn’t require nondiscrimination testing, and allows for the deduction of plan contributions of up to 25% of eligible compensation.
The solo 401(k) is a retirement savings option for small businesses whose only eligible participants in the plan are the business owners (and their spouses, if they are also employed by the business). It can be a smart way for someone who is a sole proprietor or an independent contractor to set aside a decent-sized nest egg for retirement.
Various financial institutions have their own names for the solo 401(k) plan. The independent 401(k) is one of the most generic. Other examples include:
- Solo 401(k)
- One-participant k
- Individual 401(k)
- Self-employed 401(k)
If you are not sure which name your financial service provider uses, ask about the 401(k) plan for small business owners. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides a handy primer on such plans.
Who Is Eligible for Solo 401(k) Plans?
A common misconception about the solo 401(k) is that it can be used only by sole proprietors. In fact, the solo 401(k) plan may be used by any small business, including corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), and partnerships. The only limitation is that the only eligible plan participants are the business owners (and their spouses, provided they are employed by the business).
A person who works for one company (in which they have no ownership) and participates in its 401(k) can also establish a solo 401(k) for a small business they run on the side, funding it with earnings from that venture. However, the aggregate annual contributions to both plans cannot collectively exceed the IRS-established maximums.
For small business owners who meet certain requirements, most financial institutions that offer retirement plan products have developed truncated versions of the regular 401(k) plan for use by business owners who want to adopt the solo 401(k). As a result, less complex documentation is needed to establish the plan. Fees may also be relatively low. Make sure to receive the proper documentation from your financial services provider.
As noted above, the solo 401(k) plan may be adopted only by businesses in which the only employees eligible to participate in the plan are the business owners and eligible spouses. For eligibility purposes, a spouse is considered an owner of the business, so if a spouse is employed by the business, you are still eligible to adopt the solo 401(k).
If your business has non-owner employees who are eligible to participate in the plan, your business may not adopt the solo 401(k) plan. Therefore, if you have non-owner employees, they must not meet the eligibility requirements you select for the plan.
You may exclude from a solo 401(k) nonresident aliens who received no U.S. earned income from you, as well as any employees who are entitled to benefits under a collective-bargaining agreement.
Solo 401(k) Eligibility Requirements
Setting the wrong eligibility requirements could result in you being excluded from the plan or non-owner employees being eligible to participate in the plan.
For example, say you elect zero years of service as a requirement to participate, but you have five seasonal employees who work fewer than 1,000 hours each year. These employees would be eligible to participate in the plan because they meet the age and service requirements. Consequently, their eligibility would disqualify your business from being suitable to adopt the solo 401(k) plan. Instead, you could adopt a regular 401(k) plan.
Some solo 401(k) products, by definition, require further exclusions. Before you decide to establish a solo 401(k) plan, be sure to check with your financial services provider regarding its provisions.
Contribution Requirements
You may require an employee to perform one year of service before becoming eligible to make elective-deferral contributions to a 401(k) and two years of service in order to be eligible to receive profit-sharing contributions. However, most solo 401(k) plans will limit the latter requirement to one year.
An employee is considered to have performed one year of service if they work at least 1,000 hours during the year. While you may choose to require fewer than 1,000 hours under a regular qualified plan, most solo 401(k) plans include a hard-coded limit of 1,000 hours.
Solo 401(k) Contribution Limits
There are two components to the solo 401(k) plan: employee elective-deferral contributions and profit-sharing contributions.
Employee Contribution Limits
You may make a salary-deferral contribution of up to 100% of your compensation or the annual limit for the year, whichever is less. For 2024 the limit is $23,000, plus a catch-up contribution of $7,500 for people age 50 or over.
Employer Contribution Limits
In 2024 the business may contribute up to 25% of your compensation (calculations are required in the case of the self-employed) but no more than $69,000. An employee aged 50 or above can still make the above-mentioned $7,500 catch-up contribution.
In comparison with other popular retirement plans, the solo 401(k) plan has high contribution limits, which is the key component that attracts owners of small businesses. Some other retirement plans limit the contributions by employers too, or set lower limits on salary-deferred contributions.
The following is a summary of contribution comparisons for the employer plans generally used by small businesses.
As mentioned earlier, you may make employee elective-deferral contributions of up to 100% of your compensation but no more than the elective-deferral limit for the year. Profit-sharing contributions are limited to 25% of your compensation (or 20% of your modified net profit if your business is a sole proprietorship or partnership). The total solo 401(k) contribution is the employee elective-deferral contribution plus the profit-sharing contribution—up to $69,000 for 2024.
If your business is a corporation, the profit-sharing contribution is based on the W-2 wages you receive. If you receive $70,000 in W-2 wages, for instance, your profit-sharing contribution could be up to $17,500 ($70,000 x 25%). When added to a salary-deferral contribution of $19,000, the total would be $36,500.
If your business is a sole proprietorship or partnership, the calculation gets a little more involved. In this case your profit-sharing contribution is based on your modified net profit and is limited to 20%. The IRS provides a step-by-step formula for determining your modified net profit in IRS Publication 560.
There are a number of other benefits that come with the solo 401(k).
As with other qualified plans, you may be able to borrow from a solo 401(k) up to (1) the greater of $10,000 or 50% of the balance or (2) $50,000, whichever is less. Check the plan document to determine if any other limitations apply.
5500 Filing May Not Be Required
Because the plan covers only the business owner, you may not be required to file a Form 5500 series return if your balance is below $250,000.
No Nondiscrimination Testing
Generally, certain nondiscrimination testing must be performed for 401(k) plans. These tests ensure that the business owners and higher-paid employees do not receive an inequitably high amount of contribution when compared with lower-paid employees.
Such tests can be very complex and may require the services of an experienced plan administrator , which can be costly. Because the solo 401(k) plan covers only the business owner, there is no one against whom you can discriminate, so these tests are not required.
Deducting Contributions
Similar to other employer plans, the solo 401(k) allows you to deduct plan contributions of up to 25% of eligible compensation. For plan purposes compensation is limited in 2024 to $345,000. Earnings over that amount are disregarded for plan purposes.
Can I Have a 401(k) for My LLC?
Yes, any business is able to set up a 401(k). If you are self-employed, you can create a solo 401(k) as a limited liability company (LLC)—assuming you meet all the other eligibility requirements.
What Is the Minimum Number of Employees Needed for a 401(k)?
A business of any size can offer a 401(k) plan. A solo 401(k) is for business owners with no employees.
How Much Can a Small Business Owner Contribute to a 401(k)?
The maximum contribution for a small business owner to a 401(k) in 2024 is $69,000 ($76,500 if you’re 50 or older)—which includes contributions as the employee and employer.
If you own more than one business, you should check with your tax professional to determine whether you are eligible to adopt the solo 401(k). Ownership in another business that covers employees other than the business owner could result in your being ineligible for this type of plan.
Internal Revenue Service. " One-Participant 401(k) Plans ."
Charles Schwab. " Individual 401(k) Plan —Traditional & Roth ."
Fidelity. " Self-Employed 401(k) ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Retirement Plans for Self-Employed People ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Tax Guide for Small Business (For Individuals Who Use Schedule C) .” Pages 2 and 3.
Internal Revenue Service. " Retirement Topics - 401(k) and Profit-Sharing Plan Contribution Limits ."
Internal Revenue Service. “ Election for Married Couples Unincorporated Businesses .”
Internal Revenue Service. “ 401(k) Plan Fix-It Guide - Eligible Employees Weren't Given the Opportunity to Make an Elective Deferral Election (Excluding Eligible Employees) .”
Internal Revenue Service. “ A Guide to Common Qualified Plan Requirements .”
Internal Revenue Service. “ 401(k) Plan Qualification Requirements .”
Internal Revenue Service. " 401(k) Limit Increases to $23,000 for 2024, IRA Limit Rises to $7,000 ."
Internal Revenue Service. " 2024 Limitations Adjusted as Provided in Section 415(d), etc. ," Page 1.
Internal Revenue Service. " 2024 Limitations Adjusted as Provided in Section 415(d), etc. ," Page 2.
Internal Revenue Service. “ Retirement Topics - SIMPLE IRA Contribution Limits .”
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 560: Retirement Plans for Small Business (SEP, SIMPLE, and Qualified Plans) .” Page 6.
Internal Revenue Service. " Publication 560: Retirement Plans for Small Business (SEP, SIMPLE, and Qualified Plans) .” Page 23.
Internal Revenue Service. " Retirement Plans FAQs Regarding Loans ." Select "4. Under What Circumstances Can a Loan Be Taken From a Qualified Plan?"
Internal Revenue Service. " 401(k) Plan Fix-It Guide - The Plan Failed the 401(k) ADP and ACP Nondiscrimination Tests ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1414002472-f8a3f116a1814b1da36c9fb9b6e674d5.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
A typical business plan for someone becoming self-employed as a consultant, coach, trainer or other freelance role should include the following sections. 1. Mission Statement. A short mission statement of 30 words or so should succinctly state why your company exists, what services it will provide, and to whom. 2.
This can be done through self-employment programs or through self-assessments. Once this is done, business planning can begin. Faced with the prospect of producing a formal, complex Business Plan, many self-employment candidates may feel overwhelmed and abandon the goal. The plan should not be treated as a rigid requirement for individuals who ...
Whether you want to launch a side gig, a solo operation or a small business, you need a simple business plan template to guide you. Forbes Advisor offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-follow ...
1. Define your purpose. 2. Know your market. Be the first to add your personal experience. 3. Plan your strategies. Be the first to add your personal experience. 4.
A business plan is a guiding document that outlines all of the major details of your business. A thorough business plan will explain your business model, address how your company will make money, document your company's structure, and include detailed financial and marketing plans. For help writing your business plan, download this template. 2.
Download Simple Small-Business Plan Template. Word | PDF. This template walks you through each component of a small-business plan, including the company background, the introduction of the management team, market analysis, product or service offerings, a financial plan, and more. This template also comes with a built-in table of contents to ...
Research your market and competition. 3. Develop your marketing plan. 4. Plan your operations and finances. 5. Test and refine your business plan. 6. Review and communicate your business plan.
The market analysis section of your self employed business plan is essential for understanding the competitive landscape and the overall business environment. It is crucial to execute this section effectively as it demonstrates your in-depth knowledge of the market dynamics. This process will enable you, as an entrepreneur, to identify ...
Step 7: Illustrated Financial Narratives. This one is the final step to make a self-employed business plan. In this step, you have to write a detailed financial statement. Moreover, business plans are an essential component of strategic financial decision-making.
How to write a business plan in 10 steps. Now, let's dive into the 10 key elements of your business plan. 1. Create an executive summary. Even though it appears first in the plan, write your executive summary last so you can condense essential ideas from the other nine sections. For now, leave it as a placeholder.
Download a free self employment checklist—free download template with SBA-approved format. Includes pre-filled examples and step-by-step guides for a successful start. ... Free business plan template. A fill-in-the-blank template designed for business owners. Download Now. Sample Plans.
A good business plan is the key to successful self-employment. Take a look at what to include, from an executive summary to a financial forecast. ... Here's a suggested business plan template to get you started. Executive summary. After the title page - which includes the name and business address of the author, the date of publication, and ...
Here are some important tips to keep in mind during your self-employment journey. 1. Develop a business plan. One of the first steps in transitioning to self-employment is writing a business plan. Your business plan should outline your goals, the services or products you'll offer, your target audience and your financial projections.
A business plan for a planned self-employment cannot be created without detailed financial planning. Create the financial plan in the business plan for a period of 3-5 years to increase planning security. The following topics belong in the financial plan: Cost structure; Revenue cycle; Cash flow plan - comparison of expenses and revenues
To write a business plan, you will need a structured outline that will serve as a guide on the best steps to take. These outlines will also help you construct a compelling plan that any reader will access with ease. They include: #1. Executive Summary. Your executive summary is a brief of the other sections.
Free downloads: There are many free business plan templates available online, which can be useful for comparing formats and features, or refining your own. Cons . ... Describe how the employees will be sourced and the employment relationship (i.e., contract, full-time, part-time) as well as any training needs and how these will be provided. ...
Once you've got your audience in mind, you can start your business plan, which should include: 1. Executive summary. Even though it appears first in the official plan, write this section last so you can condense essential ideas from the other nine sections. For now, leave it as a placeholder.
Business plans come in all shapes and sizes. The best business plan template for your business is one that you understand and that matches the size and legal structure of your operation. If you're a sole proprietor, a business plan template designed for a big corporation probably doesn't make sense.
Business and self-employed; Business finance and support; Write a business plan Download free business plan templates and find help and advice on how to write your business plan.
Right here. The British Business Bank have produced a template, designed to be used to support a Start Up Loan application. Even if you're at the earliest stages of an idea, you can download it for free and use it to help develop your plans. We'd recommend it to anyone who wants to think about starting a business.
Oregon's Small Business Development Center Network (SBDC) can provide business start-up counseling and advice. Experts will help you put together a business plan and feasibility study. Contact the Small Business Development Center Network at 541-463-5250 or [email protected] to learn more about available guidance and services.
7 Self-employment Ledger Templates. A person who is self-employed is entitled to pay self-employment taxes and must be in possession of a self-employment ledger. This is an error-free, detailed record showing self-employment cash returns, both expenses, and incomes. A self-employment ledger form maybe a spreadsheet, a legal agreement from an ...
Key Takeaways. A solo 401 (k) plan is for businesses whose only eligible participants in the plan are its owners (and their spouses, if they work for the business). These plans are often less ...