NSF Fellowship
The National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship ( NSF GRFP ) is a great way to start a research career. I was a successful applicant in 2010. Below are some details about the program and some tips for applying. You will also find many examples of successful essays and you can even submit your own essays if you are willing to serve as inspiration for the next round of applicants.
Note, this advice was last updated in Sept 2021.

What is it?
The NSF GRFP provides $34,000 to the student and some money to your department for three years. You have the flexibility to defer for up to two years in case you have another source of funding (but you cannot defer to take a year off).
The basic requirements are:
1. US Citizen, US National, or permanent resident
2. Currently a graduating Senior or First/Second year graduate student
3. Graduate students may only apply in their first OR second year (NOT both) . I have some thoughts on which year to apply .
4. Going into science research (does not apply to medical school)
Check out the official requirements at the NSF GRFP website . Here is the more detailed NSF presentation on the requirements. The deadlines are usually the last week of October , but it is never too early to start.
Basic Outline of Application Process
You will need to write two essays:
Personal Statement, Relevant Background, and Future Goals (3 pages)
Graduate Research Statement (2 pages)
You will need to get at least three letters of reference
These essays will be reviewed on the criteria of Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
And that's really it. The challenge is to sell yourself in 5 pages and to successful address the two criteria.
Tips for Getting Started
Read over the official NSF GRFP website , especially their tips .
Look through the NSF GRFP FAQ , with detailed answers here.
Here is a detailed website from Robin Walker . She has a very very thorough guide to the application .
Look at advice from past winners. There are lots of great advice out there, but in an interest to not overload you, here are my personal top choices. You can find more in my examples table at the bottom of the page.
Mallory Ladd - If you can follow her schedule, you should be more than prepared
Claire Bowen - Lots of advice interleaved with excerpts from successful essays
DJ Strouse - Applied under old system, but still great advice.
Blengineers - Fun video series of application tips
Read an example essay. I have posted all of my essays (and others) as well as my ratings sheets at the bottom of this page and organized into them into a table . Personally, I found this extremely useful and I have to give credit to two University of Wisconsin NSF GRFP winners who shared their essays with me, without which I was struggling on how to start the application.
Check out an old guide for reviewers .
For current discussions on the application process, check out this years NSF GRFP discussion at The GradCafe Forums . Some past years discussions include: 2020-2021 , 2019-2020 , 2018-2019 , 2017-2018 , 2016-2017 , 2015-2016 , 2014-2015 , 2013-2014 , 2012-2013 , 2011-2012 , and 2010-2011 .
General Advice
Every essay should address both Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
Each essay needs explicit headers of Intellectual Merit / Broader Impacts .
NSF GRFP funds the person, not the project. The most important choice you make is designating the primary field (Chemistry vs Physics & Astronomy, etc). The subfield is less important. If you are an undergrad doing research, I would strongly suggest to make your research proposal related to what you are currently researching as long as: 1. you are going to apply to programs in the same primary field and 2. there is at least a small chance (even if only a few percent) that you could do something related to your proposal in graduate school. NSF will not force you to follow through with the research; instead they just want to see that you can actually write a proposal. I personally wrote about my undergraduate research. It was in physics and I only applied to physics graduate schools (so same primary field), but I was not sure I wanted to continue with it in graduate school, and in fact it ended up being impossible since I did not get into any graduate schools with anyone doing research in my proposed subfield.
Write for a general science audience and assume the reviewer is in your primary field, but not your subfield. This is NSF's tentative review panels , you can see that the only guarantee is that the reviewer is in your primary field.
Ask for letters of reference early and gently remind your writers of the deadline. Get a diverse set of letter writers. I had my current adviser (who was doing research similar to what I proposed), a past research adviser, and my boss at a tutoring center. Therefore, I had two letters addressing my intellectual merit, while one letter addressed broader impacts.
Ask for help. Your current university probably has a writing center . Don't be shy, they will love to help you. Also try asking around your department to find students who have applied previously.
Review Criteria Details
(Below is direct text from NSF but with sentences cut and added highlights)
General Review Criteria
In considering applications, reviewers are instructed to address the two Merit Review Criteria as approved by the National Science Board - Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts. Therefore, applicants must include separate statements on Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts in their written statements in order to provide reviewers with the information necessary to evaluate the application with respect to both Criteria as detailed below.
Reviewers will be asked to evaluate all proposals against two criteria:
Intellectual Merit: the potential to advance knowledge
Broader Impacts: the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.
The following elements should be considered in the review for both criteria:
What is the potential for the proposed activity to
Advance knowledge and understanding within its own field or across different fields (Intellectual Merit); and
Benefit society or advance desired societal outcomes (Broader Impacts)?
To what extent do the proposed activities suggest and explore creative, original, or potentially transformative concepts?
Is the plan for carrying out the proposed activities well-reasoned, well-organized, and based on a sound rationale ? Does the plan incorporate a mechanism to assess success ?
How well qualified is the individual, team, or organization to conduct the proposed activities?
Are there adequate resources available to the PI (either at the home organization or through collaborations) to carry out the proposed activities?
Extra details on Broader Impacts: (additional tips from NSF here )
Broader impacts may be accomplished through the research itself , through the activities that are directly related to specific research projects , or through activities that are supported by, but are complementary to, the project . NSF values the advancement of scientific knowledge and activities that contribute to achievement of societally relevant outcomes. Such outcomes include, but are not limited to: full participation of women, persons with disabilities, and underrepresented minorities in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM); improved STEM education and educator development at any level; increased public scientific literacy and public engagement with science and technology; improved well-being of individuals in society; development of a diverse, globally competitive STEM workforce; increased partnerships between academia, industry, and others; improved national security; increased economic competitiveness of the US; and enhanced infrastructure for research and education.
Merit Review Criteria specific to the GRFP
Intellectual Merit Criterion : the potential of the applicant to advance knowledge based on a holistic analysis of the complete application, including the Personal, Relevant Background, and Future Goals Statement, Graduate Research Plan Statement, strength of the academic record, description of previous research experience or publication/presentations, and references.
Broader Impacts Criterion : the potential of the applicant for future broader impacts as indicated by personal experiences, professional experiences, educational experiences and future plans.
Review Criteria: My Two Cents
Here is how I like to think of the review criteria, point by point.
How would answering this research question change science (Intellectual Merit) or society (Broader Impacts)?
Why should I fund you specifically, and not just this research question? What innovation do you specifically bring to the table?
Is there a detailed plan? With built in measures of success?
What are your qualifications?
Can you actual carry out the needed research?
At the end of each essay, you should be able to check off how you answered each point above for BOTH Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
Personal Statement, Relevant Background, and Future Goals: Essay Prompt from NSF
Prompt in 2021:
Please outline your educational and professional development plans and career goals. How do you envision graduate school preparing your for a career that allows you to contribute to expanding scientific understanding as well as broadly benefit society?
Additional prompt previously provided by NSF:
Describe your personal, educational, and/or professional experiences that motivate your decision to pursue advanced study in science, technology, engineering or mathematics (STEM). Include specific examples of any research and/or professional activities in which you have participated. Present a concise description of the activities, highlight the results and discuss how these activities have prepared you to seek a graduate degree. Specify your role in the activity including the extent to which you worked independently and/or as part of a team. Describe the contributions of your activity to advancing knowledge in STEM fields as well as the potential for broader impacts (See Solicitation, Section VI, for more information about Broader Impacts).
NSF Fellows are expected to become globally engaged knowledge experts and leaders who can contribute significantly to research, education, and innovations in science and engineering. The purpose of this essay is to demonstrate your potential to satisfy this requirement. Your ideas and examples do not have to be confined necessarily to the discipline that you have chosen to pursue.
Personal Statement, Relevant Background, and Future Goals Essay: My Two Cents
Based on the new emphasis NSF GRFP general requirements, I would write the essay in three main sections with two subsections for Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts.
Personal Statement (~1 page). This is where you tell your unique story of either how you became interested in science, what makes you special, and/or any unique perspective you bring to science. Great place to mention if you had to overcome any hardships or would be adding to the diversity of the STEM field. Definitely use this section to highlight Broader Impacts.
Relevant Background (~1 page). Hopefully you already have research experience, so explain how that has prepared you for success in graduate school and beyond. Mainly use this section for Intellectual Merit, but also highly the Broader Impacts of your research experience.
Future Goals (~ 1/2 page). This is where you tie your personal background and scientific background into one cohesive vision for the future.
Intellectual Merit (~1/4 page). Conclude the essay by summarizing all of your contributions to Intellectual Merit. Make sure this is an explicit header.
Broader Impact (~1/4 page). Conclude the essay by summarizing all of your contributions to Broader Impact. Make sure this is an explicit header.
Graduate Research Statement: Essay Prompt from NSF
Present an original research topic that you would like to pursue in graduate school. Describe the research idea, your general approach, as well as any unique resources that may be needed for accomplishing the research goal (i.e. access to national facilities or collections, collaborations, overseas work, etc). You may choose to include important literature citations. Address the potential of the research to advance knowledge and understanding within science as well as the potential for broader impacts on society. The research discussed must be in a field listed in the Solicitation (Section X, Fields of Study).
Graduate Research Statement: My Two Cents
I would recommend structuring the essay as follows:
Introduction
Introduce the scientific problem and its impact on science and society (emphasis on Review Criteria 1)
Research Plan
Show the major steps that need to be accomplished
What is the creative part of your approach?
Have you thought of alternatives for hard or crucial steps?
What skills do you have to make this plan successful?
Intellectual Merit
Have a clear header for this section
Clearly demonstrate that tackling this problem will make an impact and advance science
Try to summarize how you hit all five Review Criteria
Broader Impacts
Paragraphs to address how this research impacts all five Review Criteria.
(Optional). Could use the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts sections as conclusion. If not, e nd with several sentences summarizing your project .
This essay will be Intellectual Merit heavy, but still needs to address Broader Impacts. Show why the broader scientific community / society should care about your research!

Examples of Successful Essays
These are all the essays of recent winners that I could find online. If you want me to link to an example on your website, or if you are willing to share your essays but don't have a site, I can add it to the table if you fill out the contact form below .
Some notes:
Click here to apply your own sort / filters to the table .
Remember the format changed starting in 2014!
If I couldn't figure out the year, I filled in 2013 for old format and 2014 for new formats.
Proposal Column --- Graduate Research Plan ( >= 2014) or Proposed Research ( <= 2013)
Personal Column --- Personal, Relevant Background, and Future Goals ( >= 2014) or Personal ( <= 2013)
Previous Column --- Previous Research Statement ( <= 2013 only)
HM = Honorable Mention
Can't find an example in your area? Tip from GradCafe Forum : politely email past winners !
I've linked to a lot of sites, let me know if any links break! A suggested fix is even better :)
Example essays below, or open in Google Drive
Submit Example Here

NSF GRFP Personal Statement
Criteria for success.
- You are eligible for the Fellowship. (Be certain to check for restrictions, i.e., only U.S. citizens, nationals, and permanent residents are eligible.)
- Your personal statement convinces a panel of academics that you are qualified to receive the Fellowship, especially with respect to the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impact criteria.
- You show only those skills and experiences that demonstrate how you fit those criteria.
- The skills and experiences that you show are concrete and quantitative.
- Your personal statement meets the formatting and page limit criteria.
- Text is grammatically correct and free of typos.
Structure Diagram
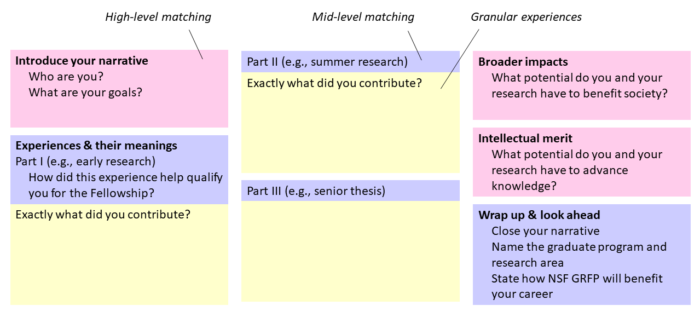
Note that Broader Impacts and Intellectual Merit should be woven through all of your experiences as well as highlighted in separate sections. Sizes of sections are approximate.
Applications prior to 2018 did not require “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts” to be addressed under separate headings. Be sure to follow the most up-to-date guidelines provided by NSF, especially if you are referencing older examples.
Your personal statement (technically, the “Personal, Relevant Background and Future Goals Statement”) is part of the NSF GRFP application and, naturally, is intended to convince the selection committee to award you the Fellowship.
The GRFP website says, “NSF Fellows are anticipated to become knowledge experts who can contribute significantly to research, teaching, and innovations in science and engineering.” The purpose of your application is to demonstrate your potential to satisfy this requirement.
The personal statement is the only part of the application where you get to lay out the experiences you’ve had, the goals you intend to pursue, and how those experiences and goals qualify you for the Fellowship.
Analyze Your Audience
Your entire application will be reviewed online by “disciplinary and interdisciplinary scientists and engineers, and other professional graduate education experts.” These are academics, usually from your broad area of science (e.g., materials research) but not from your specific subfield (e.g., optoelectronics). They will judge your application using some combination of the NSF’s official criteria for the Fellowship and their own ideas about what makes good science or a good scientist.
The people on the committee read many, many applications. Make it easy for them to figure out that you are qualified for the award by referencing the Intellectual Merit and Broader Impact criteria that they use to judge your application. Make it easy for them to remember you by creating a narrative that “brands” you.
Include Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts criteria
Like many awards or jobs, there are explicit criteria that show if you qualify for the Fellowship. Read the most up-to-date program solicitation to learn the criteria that the selection committee are using to judge your application. Write your personal statement in a way that makes it as clear as possible that you meet these criteria.
The 2023 NSF solicitation says (emphases added):
The program recognizes and supports outstanding graduate students who are pursuing full-time research-based master’s and doctoral degrees in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) or in STEM education. The GRFP provides three years of support over a five-year fellowship period for the graduate education of individuals who have demonstrated their potential for significant research achievements in STEM or STEM education.
The NSF GRFP criteria emphasize “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts.” Read the solicitation so you know what “Intellectual Merit” and “Broader Impacts” mean to the NSF, and use your personal statement to show how you meet those criteria. Do not just make up your own ideas about what these terms mean.
In the 2023 solicitation, NSF defines these terms: “The Intellectual Merit criterion encompasses the potential to advance knowledge… The Broader Impacts criterion encompasses the potential to benefit society and contribute to the achievement of specific, desired societal outcomes.” The NSF also has specific lists of activities that constitute Broader Impacts.
Be sure to include Broader Impacts and Intellectual Merit throughout your statement as well as in separate, labeled sections. According to the 2023 solicitation, “Applications that do not have separate headings for Intellectual Merit and Broader Impacts will not be reviewed.”
Create a personal narrative
Unlike a grant that funds a specific project, the NSF GRFP invests in the professional and scientific growth of individuals. The program solicitation talks about developing a “globally-engaged workforce” and ensuring “the Nation’s leadership in advancing science and engineering research and innovation.”
Your personal statement is your opportunity to show the selection panel that your personal goals (e.g., collaborating with foreign scientists) align with the program’s goals (e.g., creating a globally-engaged workforce). Tell a narrative about yourself that is honest, that you’re excited about, and that shows this alignment. Use this narrative through your entire personal statement. It should help you avoid writing a personal statement that is just a resume in essay format.
Concretize and quantify your experiences
Your experiences are the “what” of your essay. Which experiences led you to develop your skill set and passions? Where have you demonstrated accomplishment, leadership, and collaboration? Research, teaching, and extracurriculars may all be relevant. State concrete achievements and outcomes like awards, discoveries, or publications.
Quantify your experience or impact to make it more concrete. How many people were on your team? How many protocols did you develop? How many people were in competition for an award? As a TA, how often did you meet with your students?
Describe your actions rather than changes in your mental or emotional state; your personal statement is not a diary entry.
Explain the meaning of your experiences
The meaning of your experiences is the “why” or “so what” of your personal statement. It’s good to have quantitative and concrete experience; it’s even more important to attribute meaning to those experiences.
Every set of experiences should speak to one of the requirements that the NSF GRFP solicitation lays out:
- How has this experience prepared you to seek a graduate degree?
- How will it help you become a knowledge expert?
- How will it help you contribute significantly to research, teaching, or innovations in science and engineering?
- How will your graduate experience prepare you for a career that advances knowledge and benefits society?
The connection between your experiences and the NSF GRFP’s goals may feel obvious to you, but you should make these connections explicit for your audience: this will make it easy for them to put you in the “yes” pile.
In terms of writing style, use statements about the meaning of experience as transitions between experiences. Try to “wrap” meaning around your experiences. Putting the meaning at the beginning and end of a paragraph makes it easy for a reader to understand what they should be taking away from the details in the middle.
Content adapted by the MIT Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Communication Lab from an article originally created by the MIT Biological Engineering Communication Lab .
Resources and Annotated Examples
Nsf grfp personal statement annotated example 1.
This example is from a first-year MIT graduate student 426 KB
NSF GRFP personal statement annotated example 2
This example is from a senior undergraduate student 267 KB

IMAGES
VIDEO