How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
If you aspire to rise to the top of your field, then you may have your sights set on a PhD.

Earning a doctoral degree can be a years-long process, but choosing an accelerated doctoral online program may help you complete your program more quickly.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Whether you’re wanting to earn one of the highest paying doctoral degrees or you have a specific one in mind, this guide can help walk you through how long it takes to complete your PhD program.

For a traditional, campus-based PhD program, the average time to finish a PhD is 8 years. Fulfilling the program’s requirements will often demand a serious investment of your time.
Even still, some people are able to finish their programs in just 3 to 6 years. Multiple factors may influence the overall length of your program.

Required Credit Hours
Many PhD programs require you to earn 120 credit hours before entering the exam and dissertation phases.
Fortunately, there are PhD programs without such high credit-hour demands. For example, at some universities, you may earn a PhD with only 60 credit hours.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Schedule
Enrolling in a doctoral program part-time may allow you to keep up with your regular job. You’ll have to decide whether you prefer the flexibility of part-time schooling or the faster schedule of full-time studies.
Final Project Requirements
Many PhD programs end with the completion of a dissertation. This assignment may take years to complete, so PhD students often end up in the all-but-dissertation (ABD) phase for quite some time.
University Scheduling
Some schools promote their ability to help you through the PhD process faster than normal. Accelerated class schedules with eight-week online courses may speed your studies along. Focused attention from dissertation advisors may help as well.
PhD Program Components

Before you enroll in a PhD program, it’s important to know some of the basic requirements:
Prerequisites
Most schools require you to already hold a master’s degree, but some offer bachelor’s-to-PhD programs.
Length to Completion
On average, it takes eight years to earn a PhD. Even still, completing doctoral coursework and a dissertation in three to four years is not unheard of.
Topic of Interest
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy, but that doesn’t mean you’ll be getting a philosophy degree. Your field of study will depend on your interests and the programs that your university offers. You may tailor your doctoral focus though your choice of a dissertation topic.
Steps to Completion
You’ll take advanced classes before sitting for comprehensive exams. After passing your exams, you’ll likely begin working on a dissertation. You must defend your dissertation before finishing your program.
Doctoral studies begin with a series of classes through which you may increase your knowledge of your field of study and learn about conducting research. These are advanced classes, so they should be more in-depth than the ones you took during your undergraduate and master’s programs.
The number of courses that you need to take can vary significantly. It’s not uncommon for PhD programs to require 120 credit hours of coursework. That amounts to about 40 classes.
At other schools, the requirements are lower. Your university’s program may involve just 60 credit hours or, possibly, even fewer. A less intense course load may significantly slash your time to completion.
Your university may require you to maintain a GPA above a minimum threshold. An unsatisfactory GPA may keep you from moving on to the next step of the PhD process.
Comprehensive Examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness for a doctoral project before advancing to the next stage of their studies. Readiness is proven through comprehensive exams , which may also be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- General examinations
Often, comprehensive exams take the form of written or oral tests. In other situations, faculty may assess students’ readiness on the basis of a portfolio evaluation or a written paper.
Dissertation and Defense

A dissertation, also known as a graduate thesis, is a body of work that presents original research in your field. This manuscript focuses on a unique idea and includes evidence to support your thesis. During your doctoral studies, there are classes designed to help prepare you for your dissertation work.
The dissertation process may take several years. Once your manuscript is complete, you must defend it to the doctoral program faculty. After your defense, you may need to do further work on your manuscript, or the committee may decide that your dissertation is complete.
Not all programs require a dissertation. Instead, there may be an alternative doctoral project. Although both dissertations and capstone projects are rigorous, projects can sometimes be completed within a shorter time frame.
Average Time to Complete PhD by Field of Study
Students in some disciplines usually take a lot more time to finish their doctoral work than students in other fields.
If you’re studying in the following scientific fields, you may be more likely to earn your on-campus degree in seven years or less:
- Physics — average of five years
- Psychology — average of five to seven years
On the other hand, if your field of study relates more to the humanities, your on-campus degree program may take longer:
- History — average of eight years
- English — average of eight years
- Education — average of 13 years
These are the traditional figures. There are ways to finish faster.
Why Does It Take So Long to Finish a Traditional PhD?

Some schools require doctoral students to take around 40 classes, which, in a traditional on-campus setting, may take years. After completing the coursework, you must write your dissertation and defend it. The dissertation process alone might take multiple years.
Doctoral programs online may help shorten the PhD process to three or four years. Fewer credit hours may be required, and the classes may be delivered in an accelerated format.
Schools with an emphasis on quick doctoral programs may also offer dissertation advisors to efficiently guide students through that phase. Alternatively, some universities allow students to complete capstone projects that don’t take as long as dissertations.
Getting a PhD Online vs. Campus

Online education has changed students’ options for earning a PhD. These days, aspiring students may choose whether to attend classes on a college campus or online.
Traditional programs may require you to relocate to the university’s campus and attend school full-time. On average, it takes just over eight years to complete those programs. The benefits of choosing an online school instead may include:
Faster Progress
Accelerated eight-week courses may allow you to finish your course load sooner. You may complete your entire program in just three or four years.
Multiple Start Dates
Online programs often let you join throughout the year, so you don’t have to put your studies on hold until the fall semester.
Flexibility
Not being required to move to campus or come to class at set times may allow you to work your studies around your schedule.
Equal Status
Online programs are just as rigorous as on-campus ones. As long as your university is accredited, your degree will be just as valuable as one from a traditional university setting.
Cost-Savings
Finishing your doctoral studies faster may mean that you pay less tuition.
How to Finish Your PhD in Less Time

Although you can’t earn a doctoral degree overnight, you shouldn’t have to spend the majority of your working years striving toward PhD-completion. The following tips for accelerating the PhD process may help you finish your studies more quickly than the average doctoral student.
1. Use What You Already Know
Every school requires a minimum number of credit hours that you must earn in the pursuit of your degree. To help you meet this threshold, some schools will allow you to transfer in credits from other doctoral programs. Universities may also give you credit for your professional experience. Reducing your class load may save you both time and money.
2. Look for Short Classes
Accelerated course schedules are one of the best ways to speed through the degree process. Every eight weeks, you’ll begin a new set of classes. Over the course of a year, there may be five different sessions during which you can take classes.
3. Work on Your Dissertation Throughout the Program
Traditionally, dissertation work begins once the classroom portion of your studies is over. Quick doctoral programs may allow you to begin the dissertation process while you’re still taking other classes. This approach, known as an embedded dissertation, may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project. It might also speed up your doctoral timeline.
4. Ask for Help
A lack of support can lead some doctoral students to drop out. On the other hand, having a good support system can help you push through and finish your program more quickly. Build a team of family, friends, and academic mentors who can encourage you, guide you, and lend practical help when you’re feeling overwhelmed by school.
Why Get a PhD?
You may need to earn a doctoral degree to achieve your career goals . For example, if you want to become a clinical psychologist, this level of study is essential. Many scientific and research positions require doctoral studies. University faculty typically need to hold terminal degrees as well.
Even if a doctorate is not a requirement for your desired line of work, it may help you achieve greater success. You might be granted higher levels of responsibility, and you may earn more money. In some fields, those who hold PhDs make around 20% more than those with master’s degrees, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics .
Do You Have to Have a Master’s Degree to Get a PhD?
Many schools consider a master’s degree an essential prerequisite for PhD admission. If you don’t already have a master’s degree, a bachelor’s-to-doctorate program may allow you to earn a master’s and a PhD for less time and money than it would take to pursue them separately.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD After a Master’s?
You may be able to complete your doctoral program in three to four years if you opt for an accelerated online program. On average, traditional on-campus PhD programs take around eight years to complete.
How Hard Is It to Finish a PhD?
Doctoral studies are challenging. That shouldn’t come as a surprise; if doctorates were easy to acquire, nearly every college graduate would end up with a PhD behind his or her name.
Approximately 50% of students who begin a PhD program don’t end up finishing. Many quit within two years of starting. Another large portion gives up upon reaching the dissertation phase.
Although all PhD programs are challenging, the flexible nature of online programs may help you find success. Choosing a doctoral track that doesn’t require a dissertation may help as well.
What Is the Easiest PhD to Get?

All PhD programs are demanding, but you might have an easier time if you select a program that aligns with your interests and your career goals. The flexibility of online study may help your doctoral program seem less burdensome. In addition, capstone projects are sometimes easier than writing dissertations.
If earning a doctoral degree in a short time frame is important to you, then consider the many potential benefits that online programs have to offer. Within just a few years, you may be able to place the letters “PhD” at the end of your name.

- Graduate School
How Long Does it Take to Get a PhD?: A Go-Getter’s Guide to Graduation
Featured Expert: Dr. Charlene Hoi, PhD

How long does it take to get a PhD? On average, PhD programs are 4 or 5 years long. The time it takes to get a PhD is slightly longer in the US, between 4-6 years, because these programs tend to be more structured. If you want to know how to get a PhD in Canada or Europe, you can expect it to take 3-5 years. However, there are PhD programs that take longer, such as part-time programs, or are extremely short, like online accelerated PhD programs. Ultimately, how long it takes to get a PhD is up to you. In this article, we’ll look at the average PhD program lengths, the typical PhD timeline, and tips on how to get your PhD finished faster.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free initial consultation here <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 13 min read
How long does it take to get a phd.
On average, it takes 4-5 years to complete a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. In the US, most PhD programs are between 4-6 years, while in Canada they are typically shorter, around 3-4 years.
Some students take longer than 6 years to complete their PhD, but in general the longest time it takes to get a PhD is capped at 8 years. If you’re enrolling in a part-time PhD program, for instance, your timeline will probably be extended to 6-8 years.
The shortest PhD programs out there are accelerated or sometimes online PhD programs. Some of these are only 1-2 years long, but there are comparatively fewer programs available, and they are only suitable for certain fields and careers which require less intensive research which defines most PhD programs.
One of the main reasons why it takes many years to get a PhD is because these programs are comprehensive and the requirements to graduate are extensive. Most have a set number of credit hours you need to complete, examinations to write, plus you’ll need to write your PhD thesis or dissertation, unless you pursue a PhD without dissertation .
There are certainly ways to shorten the PhD application timeline and time to graduate, which includes enrolling in a shorter program if possible, increasing your course load or the number of research hours you can dedicate per week, but generally a PhD will still take some time.
Even if you want to do a PhD without a master’s degree first, such as by applying to a direct entry PhD program, the program is still usually 4-5 years long.
We’ll take a look at the typical PhD timeline and how long it takes to get a PhD normally. After, we’ll cover some tips on how to get your PhD done faster or how you can avoid dragging things out.
In North America, the typical PhD program is divided into two stages. The first stage is where you complete all the required coursework, comprehensive exams and other academic requirements, depending on the program. The second stage is when you submit a proposal for original, independent research, get it approved and start working on your thesis or dissertation. Your PhD culminates with your thesis defense. Once your thesis has been approved, you’ll be eligible to graduate.
This timeline is somewhat flexible, as you might complete the first stage in 1 or 2 years but take longer to complete your dissertation. For the purpose of this general PhD schedule, we’ll assume your PhD program is a typical length of 4-6 years.
Application Stage
We’ve included the application stage of getting your PhD here first because the grad school application timeline can take several months to put together your application package and hear back about acceptance to a program. Secondly, because the application stage involves some critical steps you’ll need to complete in order to get your PhD.
1. Research proposal
To apply to a PhD program, you’ll most likely be required to submit a research proposal and be prepared to answer any research proposal questions your advisor will have. This is your “proposal” of what research question you will explore during your studies at a program, or an outline of what research topic you want to pursue. If you’re not sure how to write a research proposal, check out these Oxford PhD proposal samples or a Cambridge PhD proposal sample.
2. Application materials
The admission requirements for a PhD can vary from program to program, but here are the general components of a PhD application:
- Required prerequisite coursework
- Official transcripts (and minimum GPA)
- Graduate school statement of purpose
- CV for graduate school or research resume
- PhD motivation letter
Some programs may also ask you to submit additional essays, such as a letter of intent, research interest statement or grad school career goals statement .
Many PhD programs also invite you to a grad school interview to get to know you better. Be ready for common graduate school interview questions such as “ tell me about yourself ” and “ why do you want to do a PhD ?”
PhD Years 1-3: Coursework Stage
1. orientation.
Your PhD program will usually begin with your orientation, where you’ll learn about the program’s individual structure, requirements and expectations. You’ll also either choose or be assigned an academic advisor and schedule an initial meeting with them. Your advisor will be a member of the university faculty who will act as your support while you complete your research and write your thesis.
2. Coursework
The first year or two of your PhD will involve completing required advanced coursework in your field. You’ll attend lectures and seminars and you may participate in research projects with department faculty or fellow graduate students or even lab work, depending on your field.
3. Electives
Along with required coursework, you’ll have the chance to take elective courses that interest you or relate to your field. It’s important to choose electives that will enrich your program. Choose ones that really interest you, that might help inform your PhD research or that will help you fulfill your credit requirements.
4. Extracurriculars
PhD programs sometimes have extracurricular activities or additional requirements outside the classroom. This can include internships or a practicum you need to complete for credit, or you might be interested in attending academic conferences or relevant events to socialize and network you’re your colleagues in the field.
5. Comprehensive exams
The coursework stage of your PhD program will end with comprehensive exams , sometimes called qualifying or preliminary exams. These are your “final exams” to make sure that you completed the necessary PhD coursework and that you’re ready and qualified to take on your own independent research in the next phase.
1. Thesis proposal
You may recall that you submitted a research proposal as part of your PhD application, and this step of the process is similar. Your thesis proposal is just like your research proposal, but it’s a more refined and developed version. Throughout your coursework, your research question might have changed or you might have changed course a little bit. If you’re still thinking about your PhD topic , take the time to solidify it before you reach the thesis proposal stage.
Your research proposal might have been a first draft, while your thesis proposal is your official announcement of: this is what I propose to research in this PhD program.
Depending on your field and the program, you thesis research might involve a great deal of lab work, or data collection or fieldwork. Whatever the case, your thesis proposal is a complete outline of what you intend to do for this independent research project and the steps you’ll take.
2. Thesis approval
Once your proposal is written, you’ll submit it for approval. Your academic advisor, PhD supervisor or the PhD committee overseeing your program will review it and either approve it or make suggestions for changes. Once it’s been polished and finalized, you’ll be given the go ahead to start conducting your research.
3. PhD research
Your research alone will probably take you several semesters to complete. On top of the fieldwork, lab work or data collection and analysis you’ll be completing, you’ll be using this time to write and review. Writing your thesis or dissertation takes a fair number of hours to outline, draft, edit and complete. It also means hitting the books to complete a literature review of your research topic so you have a complete background understanding of your chosen topic and how it will inform your research.
Your research and the preparation of your thesis is really the biggest part of this second stage, and is probably the longest part of your PhD altogether.
4. Extra requirements
When you’re not deep in your research, you’ll be completing other requirements of your PhD program or additional duties that enrich your education. Some programs require you to dedicate some hours to teaching, whether it be leading seminars for undergraduate students or acting as a teaching assistant for university faculty.
You’ll also be strongly encouraged to publish as a graduate student , so you may be involved in the research projects of faculty members or other grad students when you’re not working on your dissertation.
5. Thesis submission and preparation for thesis defense
When you’re finished writing your thesis and you’re ready to submit it, it’s critical to know how to prepare for thesis defense . Because not only do you have to complete this original, new body of research work, you have to get the approval of your PhD committee to put it out into the world.
Your thesis defense is essentially the final presentation of your PhD.
6. Thesis defense
Your thesis defense is an oral presentation of your research project, but it also involves submitting your written document to be reviewed. Essentially, you’ll present the entirety of your thesis to the PhD supervising committee, including your findings and conclusions. From there, the committee will ask thesis defense questions . Your answers will defend your methodology and results to the committee, basically proving the value and validity of your work. While this is an evaluation of sorts, it is also your opportunity to share your original ideas and invite further research into your topic.
After your defense, the PhD committee will either approve your thesis or send it back to you with edits or changes to be made before it can be formally approved.
Graduation and Postdoc
Once your thesis has been approved, congratulations! You’ll be eligible for graduation and be awarded your degree. Now that you’ve finished this marathon, you can choose to pursue further studies or start looking for a job after grad school .
With a PhD, you have many different options for positions in your field. You might want to know how to find a job in academia or how to get a tenure track position at a university if you’re interested in teaching others. PhD graduates who decide to transition from academia to industry or who would rather work outside the realm of academia can find industry jobs after PhD that suit their skills and experiences.
Either way, you’ll need to prepare for how to find a postdoc position, explore what the career options are for you, decide what your career goals are and start sending out applications. Remember to prep your postdoc resume and get read for postdoc interview questions , since the job hunt will begin soon after you finish your PhD!
Is it possible to get your PhD done faster? What are some ways you can speed up the process and avoid taking 8 years to complete your graduate studies? Luckily, there are many key ways you can make your journey through grad school easier and speed things up a little, from the type of PhD program you choose to the habits and skills you cultivate during your program.
#1 Enroll in an accelerated program
The first way to guarantee it will take less time to get your PhD is to, of course, enroll in a shorter PhD program. Direct entry PhD programs allow you to enroll once you’ve completed your bachelor’s degree in exceptional circumstances. Note that these are not the easiest PhD programs to get into , as your academic record needs to be excellent, and you’ll likely need prior research experience and you may even need to have publications already. However, a direct entry PhD program is around 4-5 years, but it allows you to skip the 1-2 years it would take to earn a master’s degree.
You can also choose to enroll in an online or accelerated PhD program that is designed to be much shorter than the traditional PhD. Once again, though, these programs are not available to students in every field, so you may need to research whether there are any options for you.
#2 Choose the right mentor
One of the first things you can do to ensure your PhD is smooth sailing is to choose the right mentor or academic advisor. Many programs allow you to choose your advisor, while some assign one to you. Whatever the case, it’s important to establish a strong working relationship and clear expectations early on.
One of the first things you’ll do as a PhD student is meet with your advisor. Take the time to discuss with them what your expectations for the program are, ask questions and ask them what their expectations are of you. Your advisor is there to help you and advise you, and they have resources and connections you can use to your advantage. But they are also working with a busy schedule and might be advising more than one PhD student, too. A mutually respectful relationship with open communication will ensure fewer interpersonal hurdles down the road.
#3 Earn credit hours faster
One way you can shave some time off your PhD is by earning your credit hours faster and getting to the research and thesis-writing stage faster. This might mean you take on a full-time course load or ask your advisor for ways to earn extra credit, such as participating in research projects. Some PhD programs will give you course credit for previous graduate level coursework you might have completed during your master’s degree, or for certifications and professional education you completed outside of school.
#4 Keep your thesis focused
When you get started on your research, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed with the amount of work you need to complete, with the writing of your thesis on top of it all. One way to keep your research hyper-focused and on point is to keep your thesis topic narrow. If your subject is too broad, you’ll be spending way too much time in your research. Give yourself clear objectives and scope, and don’t deviate from your PhD proposal if you don’t have to.
There may be a million questions you want to explore within your PhD topic, but there will be other opportunities to explore them. Keep your focus narrow so you don’t spend years and years asking and answering research questions!
One of the best things you can do to get your PhD done faster and adjust to the experience of graduate school is to change your thinking. Adopt a growth mindset so that you’re open to new learning, willing to listen to constructive feedback on your proposal or thesis and willing to grow your skills. A PhD is an advanced program, and you’ll already be very skilled, but it is also an opportunity to learn and grow. There will be challenges for you, so be ready to meet and overcome them instead of letting them draw you back or slow you down.
#5 Develop your professional skills fast
A PhD is an opportunity to grow your professional skillset as much as it is an opportunity for you to contribute meaningfully to your field. If you haven’t already been working on skills such as communication, presenting or lecturing and writing, now is the time to start.
Strong writing skills will help you get your thesis finished and edited faster, as you’ll be more familiar with the process and understand what makes a strong document. It’s also a useful skill to learn how to write effective funding proposals or grant proposals. You may need to do so to secure funding for your research, but it’s a highly valuable skill in the workforce, too.
Good presentation skills will help you during your thesis defense or if you’re asked to present during a conference. They will also help you build confidence in your voice and ideas and make you a better communicator when you’re networking or job searching.
#6 Keep to your schedule
This is maybe the most important skill if you want to finish your PhD faster: make a detailed schedule and hold yourself accountable to it. If you like, you can plan out your entire PhD week by week from Day 1. Write down what your course schedule is, when you’ll do research and how many hours, when you’ll write and how many hours, what extracurriculars or personal activities will take up your time and so on.
A detailed schedule gives you an overview of your PhD and a timeline of when you’ll finish. It will keep you organized and accountable, so you can avoid procrastinating or avoidable speed bumps that might slow you down. It also helps you compartmentalize the many items on your to-do list so you don’t stress out about how much you need to accomplish.
When creating your schedule, especially during the research stage when there is no formal class schedule for you to adhere to, focus on deliverables. Set a date when you will submit a section of your thesis to your advisor, or when you will complete your literature review. Setting goals and clear outcomes will keep you on track and focused.
#7 Take initiative and be independent
The last tip to help you get your PhD done faster is to take initiative. Remember that a PhD is a largely independent endeavor. You’ll have the support of a committee or advisor, but you can’t rely on them to do the work for you or put everything on hold if they aren’t available when you need them. Be flexible and adaptable so you can keep working and moving forward, even if your schedule gets interrupted or needs to change to suit your situation.
It's also important to take the initiative in your learning. Take advantage of opportunities for growth, networking, and gaining experience where you can. Get the most out of your PhD program and use your experiences to fuel your end goal of completing your thesis.
On average, it takes 4-5 years to get a PhD. There are a few factors that can influence the time it takes to complete your PhD, from program length and structure to what country you are earning your PhD in, to your own personal work ethic and schedule.
PhD programs in the US are on average 4-6 years. In Canada and the UK, they are usually 3-5 years long. Part-time PhD programs may take up to 7-8 years to complete. Direct-entry PhD programs and dual master’s and PhD programs are typically 5 years long. If you’re enrolling in an online, hybrid or accelerated PhD program, the timeline is usually 2-3 years, but there are some extremely short 1-year PhD programs offered online for specific disciplines.
Yes, you can finish your PhD before the “normal” timeline. For example, if you complete your coursework early, if you finish writing your thesis faster than average and get it approved, or if you otherwise complete all your PhD program requirements before the anticipated finish date.
Yes, there are online PhDs available for certain fields and disciplines. These typically range from 2-3 years, although there are some traditional 4-year PhD programs offered online. There are also some “accelerated” online PhDs which last 12-18 months.
A PhD program is not necessarily shorter if you first complete a master’s degree, but having gone through a master’s program can better prepare you to finish your PhD faster. Some PhD programs accept credit hours from your master’s degree towards the coursework requirements for a PhD, and if you’ve previously written a master’s thesis or completed some research during your graduate studies, this will be an advantage. Since you’ll already be familiar with the process of writing a thesis and conducting your own research, you can avoid some stumbling blocks in your PhD program that might otherwise slow down your progress.
Yes, it is possible to get a PhD without first completing a master’s degree. There are direct entry PhD programs that allow students with a bachelor’s degree to enroll, so long as they meet the admission requirements and have exceptional academic records. Some online PhDs also waive the master’s degree requirement.
Yes, it is possible to complete a traditional PhD program in a shorter amount of time than anticipate. This usually means dedicating yourself to full-time study or taking on a larger course load and increased research hours. It takes significant work, but it can be done with the right schedule and commitment.
The fastest PhD programs are the short, 1-year accelerated programs. These programs have fewer credit hours to complete, and some have no dissertation requirement, only qualifying exams to finish. However, there are not many programs out there, and they are not available for every field of interest.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
- Skip to main content
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Apply Apply
- Follow Us

How Do You Get a PhD? A Guide to the PhD Timeline

Everyone who considers a doctoral degree knows a Ph.D. is a big commitment.
Not only will it require all your mental energy, focus, and persistence, but it will also require a significant investment of your time. Your particular area of research, your institution’s policies and procedures, and the standard expectations within your field affect how long it takes to earn a PhD. The average PhD length is five or six years, while some students may take eight or nine years.
Regardless of how long a PhD program takes, there are some common stages of a PhD that all doctoral students share. These significant and essential milestones shape the timeline for earning your doctorate . Read on as we take you through each step and explore the typical steps to a doctorate degree.

How Long Do PhD Programs Take?
The number of credit hours that you need to complete your doctoral coursework might depend on several factors: do you already have a master’s degree? Will you earn one en route to the doctorate? Or do you even need one?
Different disciplines and research interests have their own PhD process, but even within your field of study, institutions may have diverse pathways for obtaining that terminal degree. For most, coursework will take anywhere from two to three years to complete.
During this time, students can serve as graduate research or teaching assistants or could even lead their own courses as instructors. In many degree programs, students develop their potential dissertation topics through their coursework and define their research plans in the next few years.
Steps to Getting a PhD: PhD Qualifying Exam and Comprehensive Exam
Many programs set up academic checkpoints to help keep students on track during their PhD journeys. The timing varies by program, but one of the most common – and possibly most stressful – forms of benchmarking is the PhD comprehensive exam or qualifying exam. Often administered around the end of the student’s coursework, these exams are your chance to demonstrate what you learned in your classes.
A faculty committee from your department oversees testing. Usually comprised of at least three members, your professors ask questions or assign writing prompts based on your experience in the program thus far. The format is generally a combination of written and oral exams designed to test your expertise in your discipline’s methodologies and significant content areas.
To better prepare yourself, research the number and kind of qualifying benchmarks the program will require in the university catalog before you begin your program. This will allow you and your advisor to effectively plan out the first few years of your degree and give you an idea of how you’ll be evaluated throughout your program.
Doctoral Dissertation Prospectus and Defense
You may be required to complete and defend a dissertation prospectus before officially becoming a PhD candidate. A prospectus is a document outlining your dissertation plan, which includes an explanation of your research topic, a potential outline of your dissertation, the methodologies you intend to employ, the significance of your research question, and a bibliography including sources that form the foundation of your research.
Your prospectus allows your dissertation advisor to understand the scope of your project. It should be thorough enough that they can provide useful feedback to help shape your research plan. After some revisions, an approved prospectus is the green light to move into the next stage of your PhD.
Advancement to Doctoral Candidacy
If you have heard the term ABD – “All But Dissertation” – then that means you are in the home stretch of your doctoral program!
Well, sort of…only your dissertation remains!
Doctoral Dissertation Research and Writing
While you’ve made it through the coursework and qualifying exams, the dissertation is the culminating component of the doctoral degree. At this point, your approved research plan is ready to be set into motion. Depending on your discipline, this could be the stage where you travel extensively to conduct fieldwork, explore archives, or visit labs to collaborate on projects that relate to your dissertation work. For many students, the research phase can take a couple of years, but some may be able to complete it in one.
Writing your dissertation can be one of the most challenging parts of the whole PhD process. Not only are you condensing years of research into a single cohesive document, but you are also formulating graphs, charts, and other textual references to help clarify your argument. Often, formatting can be a major challenge for many students.
In this stage, it’s most helpful to seek out resources to help you with the writing process. Many universities have dissertation writing workshops where you can learn best practices, as well as support groups where students meet regularly and help keep each other accountable. Most universities also offer competitive dissertation completion grants, supporting students with additional funding so they focus more of their time and effort on completing this undertaking.
Dissertation Defense
Everyone gets nervous about this major rite of passage. It can be difficult to take criticism over something you have poured your heart and soul into for years. Remember, though, that a good advisor will not let you defend if you’re not ready, and you literally wrote the book on your topic!
The dissertation defense is not intended to tear your work apart but rather is your opportunity to prove your expertise to your dissertation committee. Many defenses are open to observers, so you should attend a few in advance of your own, especially within your department, to get a sense of what it’s like.
First, you’ll present the main points of your thesis. Then the committee will ask questions so they can clearly understand your arguments. Finally, they’ll send you out of the room while they deliberate and decide if you pass or not. If all goes well, you’ll be addressed as “Doctor” the next time you walk into the room!
Get Started on Your PhD Journey Today
No matter what your particular timeline looks like as you work toward your doctorate, know that the faculty and other students within your program are frequently a huge source of support — which means you won't do this alone! Additionally, every school has resources to assist Ph.D. students, from libraries to writing centers to dedicated student support services.
If you are excited about beginning your Ph.D. journey, we invite you to request more information or reach out to one of our admissions professionals today. Best of luck as you begin this transformational experience!
learn more about
what it takes to apply to and succeed in a PhD program. Explore our resource — A Guide to Choosing, Applying for, and Thriving in a PhD Program!
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(3974384, 'aeb4e03d-f8e9-4232-9726-8852204e83e1', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Request more, information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information

Published On
More articles, recommended articles for you, is a phd in humanities worth it.
If you’ve recently completed an undergraduate degree in a field like English, History or Religious...
How to Choose a PhD Program and Compare Offers
You’ve been patiently waiting for your decision letters to roll in. Now you have the results, and...
How PhD Students Get Paid
The most common questions (and biggest misconceptions) about getting a PhD revolve around money....
Browse articles by topic
Subscribe to.
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
How Long Does It Take to Earn a PhD?

Cece Gilmore is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cece earned her undergraduate degree in Journalism and Mass Communications from Arizona State University. While at ASU, she was the education editor as well as a published staff reporter at Downtown Devil. Cece was also the co-host of her own radio show on Blaze Radio ASU.
Learn about our editorial policies

Cari Schultz is an Educational Review Board Advisor at Scholarships360, where she reviews content featured on the site. For over 20 years, Cari has worked in college admissions (Baldwin Wallace University, The Ohio State University, University of Kentucky) and as a college counselor (Columbus School for Girls).

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

How long is a PhD program? That might be one of the first questions you ask yourself If you are thinking of earning a PhD. You have probably heard a range of years, and that is because how long it takes to earn a PhD depends on a number of factors. Keep reading to learn more!!
What is a PhD?
PhD stands for a “Doctorate of Philosophy.” This is an academic degree that qualifies the degree holder to teach their chosen subject at university level or to work in a specialized position in their chosen field. In general, the PhD is the highest level of degree a student can achieve.
Also see: Top fully funded PhD programs
Why get a PhD?
A PhD is a serious commitment with a serious return on investment. Here is a list of professional and personal benefits for earning a PhD.
| Career advancement | Achieving a sense of accomplishment |
| Higher earning potential | Financial stability |
| Teaching and mentoring | Improvement of social skills |
| Networking and collaboration | Increased recognition |
| Scholarly respect | Enhanced self-confidence |
How long does it take to earn a PhD?
Earning a PhD usually takes between four and seven years to complete, depending on the type of PhD as well as the schools requirements, the students educational background, and personal progress. Students who take full-time classes can typically finish in four years. A typical PhD program requires anywhere from 60 to 120 semester credit hours .
Why earning a PhD takes years to earn
Assistantship obligations.
Teaching and research assistantships can be very beneficial for the experience they provide and the potential funding, but they can also be time consuming obligations for PhD students. Therefore, assistantships may affect the amount of time it takes to complete a PhD program.
Comprehensive examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness in a PhD program through comprehensive exams. These comprehensive exams may be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- Comprehensive exams or “Comps”
- General examinations
Dissertation
A dissertation is an in-depth research document that serves as the culmination of a doctoral program. It is an important document that demonstrates a student’s original research and contribution to their field of study.
The dissertation involves conducting extensive research, reviewing previous literature, analyzing data, and presenting your findings in a structured manner. Once the dissertation is completed, it is typically defended orally in front of a committee of faculty members who assess the quality and validity of the research.
Average PhD timeline
The specific of a PhD timeline carried by college and university. However, the following is a good overview of the average PhD program.
- Year 1: Take advanced courses
- Year 2: Take advanced courses and begin preparing for exams
- Year 3: Study, take and defend your comprehensive exams and begin researching your dissertation proposal
- Year 4: Begin working on your dissertation
- Year 5: Finish and defend your dissertation
Average PhD completion by focus
According to data from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics the average time in years from graduate school entry to doctorate it took students to receive their degree in 2020 in certain fields is listed below.
- Life sciences = 6.9 years
- Physical sciences and earth sciences = 6.3 years
- Mathematics and computer sciences = 7.0 years
- Psychology and social sciences = 7.9 years
- Engineering = 6.8 years
- Education = 12.0 years
- Humanities and arts = 9.6 years
- Other non-S&E fields = 9.3 years
Related : Top 10 PhD in Education programs
How to finish your PhD is less time
Look for accelerated classes.
Accelerated courses are an easy way to reduce the amount of time it takes to finish a PhD. Therefore, look into if your program offers any shorter courses.
Work on your dissertation throughout the program
Working on your dissertation little by little throughout the program will allow you to speed up your doctoral timeline. In addition, it may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project.
Maintain regular communication with your advisor
Establish regular communication with your advisor or supervisor. Regular meetings can help you receive guidance, address any issues, and ensure you are heading in the right direction.
Seek feedback early and often
Share your work and progress with your advisor, peers, or other trusted individuals often. Then, you should incorporate suggestions and revisions as you go along. This will help you refine your work and avoid major revisions later.
Maintain a healthy school-life balance
While it is important to be dedicated to your PhD, it’s just as important to maintain a healthy work-life balance. Therefore, be sure to prioritize yourself! While finishing your PhD in less time is a great feat, it is important that you are not sacrificing your well-being while doing so.
Key Takeaways
- PhD stands for “doctorate of philosophy” and is generally the highest level of degree a student can earn
- There are many professional and personal benefits to earning a PhD which can lead to a serious return on investment
- A PhD program typically takes 4-7 years to complete. However, it can take longer or shorter depending on personal circumstances and field of study
- With planning and guidance from advisors, students can sometimes complete PhDs in less time
Start your scholarship search
- Vetted scholarships custom-matched to your profile
- Access exclusive scholarships only available to Scholarships360 members
Frequently asked questions about how long it takes to earn a PhD
Do i need to have a master’s degree to get a phd, what is the easiest phd to earn, can i finish my phd earlier than the estimated time frame, what happens if i don’t complete my phd within the expected timeframe, can i work while pursuing a phd, can i accelerate the process of earning a phd, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale


PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to get a phd.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
Frequently asked questions: Graduate school
In the US, most graduate school applications require you to include:
- Transcripts from previous educational institutions
- Standardized test scores (such as the GRE or MCAT)
- A graduate resume
- 2–3 letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
Some programs may ask you to write a personal statement in addition to, or instead of, a statement of purpose. You may also be asked to an interview .
Always carefully read the application instructions for the specific program you’re applying to.
Most medical school programs interview candidates, as do many (though not all) leading law and business schools.
In research programs, it depends—PhDs in business usually do, while those in economics normally do not, for example.
Some schools interview everyone, while others only interview their top candidates. Look at the websites of the schools you’re applying to for more information on whether they conduct interviews.
In addition to thinking about your answers for the most commonly asked grad school interview questions , you should reach out to former and current students to ask their advice on preparing and what sort of questions will be asked.
Look back through your resume and come up with anecdotes that you could use for common questions, particularly those that ask about obstacles that you overcame. If you’re applying for a research program, ensure that you can talk about the previous research experience you’ve had.
You should also read as much research in your field as possible. Research the faculty at the schools you’re applying to and read some of their papers. Come up with a few questions that you could ask them.
Graduate schools often ask questions about why you are interested in this particular program and what you will contribute.
Try to stay away from cliche answers like “this is a good program” or “I got good grades in undergrad” and focus instead on the unique strengths of the program or what you will bring to the table. Understand what the program is looking for and come up with anecdotes that demonstrate why you are a good fit for them.
Different types of programs may also focus on different questions:
- Research programs will often ask what topics you’d like to research and who you would like to work with, as well as specific questions about your research background.
- Medical schools are interested in your personal motivation, qualities such as integrity and empathy, and how you’d respond to common ethical dilemmas.
- Business schools will focus on your past work experience and future career prospects, and may be particularly interested in any experience you have managing or working with others.
Some students apply to graduate school straight from undergrad, but it’s also common to go back to school later in life. The ideal time to do so depends on various financial, personal, and career considerations . Graduate school is a big commitment, so you should apply at a time when you can devote your full attention to it.
Your career path may also determine when you should apply. In some career fields, you can easily progress without a graduate degree, while in others—such as medicine, business, and law—it’s virtually impossible to move up the career ladder without a specific graduate degree.
Most graduate school applications for American graduate programs are due in December or January for a September start.
Some types of programs, especially law school, are rolling applications, meaning that the earlier you apply, the earlier you’ll hear back. In this case, you should aim to apply as early as possible to maximize your chances.
Medical school follows a completely separate timeline with much earlier deadlines. If you’re applying for medical school, you should speak to advisors at your university for more information.
A good starting point to aim for is about 18 months before you would start the program, or 6–9 months before the applications are due.
In the first few months of the process, research programs and study for any standardized exams you might need.
You can then begin writing your personal statements and statements of purpose , as well as contacting people to write your letters of recommendation . Ensure that you give recommenders plenty of time to complete their letters (ideally around 2–4 months).
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
It’s best to ask in person if possible, so first reach out and request a meeting to discuss your graduate school plans.
Let the potential recommender know which programs you’re applying to, and ask if they feel they can provide a strong letter of recommendation . A lukewarm recommendation can be the kiss of death for an application, so make sure your letter writers are enthusiastic about recommending you and your work!
Always remember to remain polite. Your recommenders are doing you a favor by taking the time to write a letter in support of your graduate school goals.
This depends on the program that you are applying for. Generally, for professional programs like business and policy school, you should ask managers who can speak to your future leadership potential and ability to succeed in your chosen career path.
However, in other graduate programs, you should mostly ask your former professors or research supervisors to write your recommendation letters , unless you have worked in a job that corresponds closely with your chosen field (e.g., as a full-time research assistant).
Choose people who know your work well and can speak to your ability to succeed in the program that you are applying to.
Remember, it is far more important to choose someone who knows you well than someone well-known. You may have taken classes with more prominent professors, but if they haven’t worked closely with you, they probably can’t write you a strong letter.
The sections in your graduate school resume depend on two things: your experience, and the focus of the program you’re applying to.
Always start with your education. If you have more than one degree, list the most recent one first.
The title and order of the other sections depend on what you want to emphasize. You might include things like:
- Professional experience
- Voluntary and extracurricular activities
- Publications
- Awards and honors
- Skills and certifications
The resume should aim for a balance between two things: giving a snapshot of what you’ve done with your life so far, and showing that you’re a good candidate for graduate study.
A resume is typically shorter than a CV, giving only the most relevant professional and educational highlights.
An academic CV should give full details of your education and career, including lists of publications and presentations, certifications, memberships, grants, and research projects. Because it is more comprehensive, it’s acceptable for an academic CV to be many pages long.
Note that, outside of the US, resume and CV are often used interchangeably.
No, don’t include your high school courses and grades. The education section should only detail your college education.
If you want to discuss aspects of high school in your graduate school application, you can include this in your personal statement .
A resume for a graduate school application is typically no more than 1–2 pages long.
Note, however, that if you are asked to submit a CV (curriculum vitae), you should give comprehensive details of all your academic experience. An academic CV can be much longer than a normal resume.
Always carefully check the instructions and adhere to any length requirements for each application.
If you’re applying to multiple graduate school programs, you should tailor your personal statement to each application.
Some applications provide a prompt or question. In this case, you might have to write a new personal statement from scratch: the most important task is to respond to what you have been asked.
If there’s no prompt or guidelines, you can re-use the same idea for your personal statement – but change the details wherever relevant, making sure to emphasize why you’re applying to this specific program.
If the application also includes other essays, such as a statement of purpose , you might have to revise your personal statement to avoid repeating the same information.
The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Different programs have different requirements, so always check if there’s a minimum or maximum length and stick to the guidelines. If there is no recommended word count, aim for no more than 1-2 pages.
A statement of purpose is usually more formal, focusing on your academic or professional goals. It shouldn’t include anything that isn’t directly relevant to the application.
A personal statement can often be more creative. It might tell a story that isn’t directly related to the application, but that shows something about your personality, values, and motivations.
However, both types of document have the same overall goal: to demonstrate your potential as a graduate student and s how why you’re a great match for the program.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD in Psychology?
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Ariel Skelley/Getty Images
- How Long Will It Take?
Before You Earn PhD in Psychology
Which type of degree should you get, can you finish your degree early.
Just how long does it take to get a PhD in psychology? The answer can vary depending on your program, educational background, and academic schedule. In general, most PhD psychology programs take anywhere from five to seven years to complete.
Learning more about what it takes to get a doctorate in psychology can help you better plan your educational and career journey.
At a Glance
Getting a PhD in psychology can take several years of graduate study. If you are thinking about becoming a psychologist, research your degree options to figure out what type of degree you need and how long it will take to enter your chosen profession. No matter what you decide, plan to spend anywhere from three to seven years in graduate school to earn a doctorate.
How Long Will It Take to Get a Doctorate Degree?
How long it takes to get a doctorate in psychology depends on various factors, including the type of degree you have selected, your educational background, and the individual doctorate program in which you have enrolled.
Most doctorate programs in psychology take between four to seven years to complete.
PhD in Psychology
Most PhD programs require at least five to seven years to complete. These programs often follow a scientist-practitioner model that trains professionals both in research and clinical practice.
In addition to regular coursework, you may also be expected to complete an internship or supervised residency. The program usually culminates in completing an original research project or dissertation.
PsyD Degree
Most PsyD programs require between four to six years to complete. A PsyD is a degree designed to train professionals to apply psychological knowledge to treating and helping people in real-world settings.
According to the American Psychological Association, PsyD programs focus more on applying psychological science, usually in the form of service.
Most EdD programs require between three to five years to complete. EdD programs are often focused on psychology, counseling, or counselor education. They explore topics that involve both education and psychology.
It is important to note that many applicants to EdD programs already hold a master's degree in a related field. This differs from applicants to PhD and PsyD programs, who often begin their program of study with a bachelor's degree.
Before you begin your academic journey, it is a good idea to look at just how long it will take you to complete your degree. The amount of time it will take can depend upon various factors, including:
- Your chosen specialty area
- The program you select
- The course load you can take each semester
A doctorate-level degree in psychology is required to work in many job areas, including as a licensed clinical psychologist or counseling psychologist. According to the American Psychological Association, a doctorate degree is also often required in fields such as school psychology or health psychology .
So how long does it take to get a PhD in Psychology ? First, it is essential to realize that the degree requirements can vary depending on the field that you decide to pursue. A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy degree is not necessarily your only option. In some cases, you might want also to consider the PsyD (Doctor of Psychology) or the EdD (Doctor of Education) degree options.
The PhD, PsyD, and EdD are all great options, but don't let how long it takes to complete be the primary deciding factor. Before you decide to get a doctorate degree, start by deciding which type of degree is most suited to your professional goals.
If you want to conduct research:
A PhD in Psychology tends to focus on a research-based model of education. People with a PhD in Psychology are qualified for a wide range of teaching, research, and clinical positions in colleges, universities, hospitals, government offices, and private mental health practices.
If you want to treat mental health issues:
The PsyD degree option generally focuses on a practitioner-based model of education. Individuals with a PsyD degree can also teach or conduct psychology research, but they frequently work in applied settings to provide direct mental health services.
If you want to apply psychology to help students:
Finally, there is also a third doctorate option that you might also want to consider depending on your career goals. If you are interested in working as a school psychologist or in a related educational field, the EdD, or Doctor of Education, is a possible option.
Despite the years of work, earning your PhD, PsyD, or EdD can be well worth the effort. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics suggests that workers with a doctoral or education specialist degree in clinical, counseling, and school psychology will find the strongest job opportunities.
Generally, if you have a strong background in psychology and have completed all of the necessary prerequisites, you can finish your doctorate sooner than students who have not taken the prerequisite courses.
Carefully planning your degree can also help ensure you complete the program requirements quickly.
Be sure you have a clear idea of what you want to do with your psychology degree once you've completed it. Do you want to teach, or is research more appealing to you? Are you interested in seeing clients, or are you planning to combine your training in psychology with another field, such as law or medicine?
If you need help deciding, make an important with an academic advisor at your school. They can help you explore your options and answer any questions you may have.
What This Means For You
No matter the degree you decide to pursue, earning a doctorate in psychology requires a significant investment of time, money, and effort. Because of this, it is essential to carefully consider your goals before deciding on a graduate program. You should also think about whether you need a doctorate or if a master's might be more appropriate.
Gee DG, DeYoung KA, McLaughlin KA, et al. Training the next generation of clinical psychological scientists: A data-driven call to action . Annu Rev Clin Psychol . 2022;18:43-70. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-081219-092500
Loyola University. Can I get my Psy.D. without a Master's in Psychology?
American Psychological Association. Doctoral degrees in psychology: How are they different, or not so different ?
Franklin University. Is getting a Doctorate in Education worth it?
American Psychological Association. Frequently asked questions about graduate school .
Bureau of Labor Statistics. Psychologists . Occupational Outlook Handbook .
Carr, A. Clinical Psychology: An Introduction . London: Routledge; 2012.
Kuther, TL. The Psychology Major's Handbook . Boston, MA: Cengage Learning; 2016.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- How Long Does A PhD Take?
- Doing a PhD
Sometimes, just knowing how long a PhD takes can be enough to sway your decision on whether a research degree is for you. So with that in mind, exactly how long does a PhD take?
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3 to 4 years to finish whilst a part-time PhD takes twice as long at 6 to 7 years. Alongside these average durations, there are time limits on how long you can be enrolled on to a PhD programme. To discover these limits, the factors which most influence doctoral degree durations and how the UK durations compare to international PhDs, continue reading on.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Full-time PhD?
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD thesis and sitting your viva.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Part-time PhD?
In the UK, a part-time PhD will typically take you 6 to 7 years; twice as long as doing a full-time PhD. The reason for this is that as a part-time PhD student, you would dedicate around 20 hours per week to your PhD as opposed to the typical 40 hours full-time students would put into their subject.
How Long Does a Distance Learning PhD Take?
Similarly, distance learning PhD’s take an average of 6 to 7 years to complete. This is because the vast majority of students who undertake a distance learning PhD do so because they can’t relocate closer to the university. Although these commitments will differ, they often mean the student isn’t able to dedicate 40 hours per week to their studies.
Students in STEM disciplines will often take longer to finish a distance learning doctorate degree than those in non-STEM disciplines. This because the progress of a STEM PhD student will be limited by how often they can access a laboratory for experiment work.
How Does Funding Impact a PhD’s Duration?
In reality, the actual time it will take you to complete your PhD degree will depend on your funding situation.
If you’re receiving funding , it will usually only cover you for 3.5 years if you’re studying full-time or for 7 years at half the stipend if you’re studying part-time. Although this could vary slightly, most PhD funding providers, e.g. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), follow this timescale as indicated on their ‘ length of PhD studentships’ page. Because of this, most students who obtain scholarships try to complete their PhD within the timeframe of their funding so they don’t incur additional fees which they need to cover themselves.
It’s also worth noting that some funded PhD positions have additional conditions attached to them as part of their eligibility requirements. For example, they may require teaching undergraduate students, hosting laboratory sessions or attend presentations and conferences. This will be especially true if you’re on a Graduate Teaching Assistantship (GTA). Although these shouldn’t add considerable time to the length of a PhD programme, they have the potential to do so if they aren’t managed properly.
As self-funded students cover their own annual tuition fees and other associated costs, how long they’ll spend to complete their PhD project will largely depend on their own personal financial situation. Because of this, most self-funded PhD students find it best to complete their PhD study in the shortest time-frame they can manage.
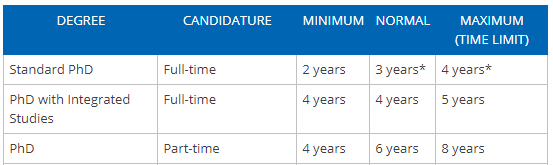
Are There Deadlines?
Yes – unfortunately, all good things must come to an end! Within the UK, the deadline for your PhD is defined as the last date which you must submit your final thesis by. This date is set by your university’s overall regulations and varies depending on the arrangements of your PhD, e.g. whether it’s full or part time. In the vast majority of cases, the adopted deadlines are four years for full-time PhDs and seven years for part-time PhDs from the date you were officially registered onto your programme, as shown below from the University of Leicester’s registration guidance page .

This time-frame may vary from university to university. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts an additional year for part-time PhDs as shown below.
Can I Complete It Faster?
Although it’s possible to complete a full-time PhD in under 3 years, it’s a significant feat that’s rarely heard of. When these feats occur, they’re usually where the doctoral student already has extensive knowledge and experience in their field before undertaking their PhD.
Whilst it’s possible to complete a part-time PhD in under 6 years, it largely depends on your commitments outside your studies. For example, if you have a part-time career alongside your PhD, it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to commit the additional hours required to complete your doctorate a year faster.
However, if instead of a steady part-time job you take on occasional work as a freelancer, you’ll be able to set aside many more hours towards your doctoral degree.
Will Having only A Bachelor’s Degree or Being an International Student Limit My Rate of Progression?
Not at all. While there are benefits to having a Master’s degree such as an additional year of learning and greater research experience due to your fourth-year dissertation project, this doesn’t mean not having one would limit you. A PhD is very different to both Bachelor and Master degrees due to being heavily research-based, therefore, both types of students will have just as much to learn on their way to completing their doctorate.
Similarly, whether you’re an international student will bear no influence on the duration of your PhD.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Does This Compare to the Duration of EU and US PhDs?
PhD hosted by universities within the EU, such as those in France, Norway and Spain, have the same programme structure as those within the UK. As a result, there are no noticeable differences in the time to complete a doctorate between UK and EU institutions.
However, this is not the case in the US. Compared to PhDs conducted within the UK or EU, PhDs conducted within the US take considerably longer to obtain. According to a 2017 study conducted by the National Science Foundation, a US government agency which supports research and higher education, the average time to get a PhD within the US is 5.8 years. Besides this, the average completion time can further increase depending on the disciplines. For example, they found doctorates within the humanities and arts to take an average of 7.1 years to achieve.
The primary reason for this difference is the way PhD degrees are structured within the United States. As mentioned previously, PhDs conducted within UK and EU universities are essentially broken into two sections – one covering the analytical aspects and the other covering the writing up aspects. However, within the US, doctorate programmes comprise additional sections. PhD students are first required to undertake 2 to 3 years of courses, which cover a broad range of topics related to their schools’ discipline. This is then followed by coursework and several examinations, which only once passed can the PhD candidate then start working on their research project and dissertation.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How the PhD Program Works
Program Overview
Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending your doctoral dissertation.
Admission to candidacy.
You begin by taking courses required for your program of study. All programs requires a preliminary exam, which may be either oral or written.
Some programs may have further requirements, such as an additional exam or research paper. If you enter with a master’s degree or other transfer credit, you may satisfy the formal course requirements more quickly.
Beginning the Wharton PhD Curriculum How the first two years of the Wharton program helped students discover their interests, learn the tools of the profession, and fuel their passion for teaching.
The Doctoral Dissertation
Upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, you are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies.
Your doctoral dissertation should contain original research that meets standards for published scholarship in your field. You are expected to be an expert in the topic you choose to research.
You are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, but you can start thinking about and working on research of relevance at any time.
The dissertation process culminates with a “defense,” in which you defend the proposal orally before your dissertation committee.
While working on your dissertation, you interact extensively with Wharton faculty. Together with interested faculty, you create your own research community that includes your dissertation advisor and dissertation committee.
Policies and Procedures
Get more detailed explanation of course requirements, academic standards, the Teacher Development Program, time limits, and dissertation procedures and requirements.
Sample Program Sequence
Years 1 & 2.
Coursework Examination Research Papers Research Activities Field-Specific Requirements
Directed Reading & Research Admission to Candidacy Formulation of Research Topic
Years 4 & 5
Continued Research Oral Examination Dissertation
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
Faculty expertise in housing economics attracted this phd student to wharton, from phd student to colleague, from research consumer to research producer.

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
Earning a Ph.D. is a remarkable academic achievement, often seen as the pinnacle of one’s educational journey. It’s a pursuit that demands unwavering dedication, intellectual prowess, and an unshakable commitment to research. Yet, when setting out on this academic odyssey, prospective doctoral students often find themselves grappling with a common question: How long will it take to reach the coveted destination of a PhD?
In the world of academia, where timeframes can be as diverse as the subjects studied, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The duration of a PhD program can be influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from the chosen field of study to the country in which one embarks on this intellectual voyage.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the intricate web of considerations that determine the timeline of a Ph.D. We’ll delve into the typical duration, international variations, the stages of the Ph.D. journey, and even the strategies that can expedite or prolong this academic quest.
Through real-life experiences and insights, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the fascinating, challenging, and often unpredictable timeline associated with pursuing a PhD.
So, if you’ve ever wondered about the time commitment required for a PhD, join us on this educational voyage as we uncover the secrets of this academic adventure and navigate the complex terrain of doctoral studies.
Introduction
Factors influencing phd duration, typical duration of phd, phd duration: variations by country, stages of a phd program, shortening the phd timeline, lengthening the timeline of phd.
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is the highest academic degree one can attain. It represents expertise in a specific field and often involves original research contributing to the world’s knowledge. However, this academic feat isn’t for the faint of heart. To embark on this journey, you should be aware of the formidable challenges it presents, and one of the most fundamental questions is, “How long will it take?” In the introduction, you can touch upon the idea of academic ambition, the pursuit of knowledge, and the unique challenges that come with obtaining a Ph.D.
It’s essential to emphasize why understanding the time commitment is crucial. Pursuing a Ph.D. isn’t just an intellectual endeavor; it’s also a significant personal and professional commitment. It can impact one’s life, career, and even mental and emotional well-being. You can mention that by knowing what you’re getting into time-wise, you can make informed decisions about your academic and career goals. For instance, if you’re aware that a Ph.D. typically takes several years, you can plan your life accordingly, set expectations, and ensure you have the necessary resources and support in place.
Imagine standing at the crossroads of ambition and dedication. You’re passionate about a particular field, and the thought of making a meaningful contribution to it excites you. You dream of becoming a respected expert, perhaps even shaping the future of your discipline. This ambition has led you to consider pursuing a PhD, a journey that represents the highest echelon of academic achievement.
But before you dive into the world of research, scholarly papers, and intellectual debates, there’s a critical question that looms large—how long will it take to earn that coveted Doctor of Philosophy degree? The answer isn’t as straightforward as one might hope. It’s a complex equation, influenced by various factors, and it’s a puzzle that many aspiring doctoral students grapple with.
Understanding the time commitment of a PhD is not merely a matter of academic curiosity. It’s a pivotal factor that can shape your life’s trajectory in significant ways. This introduction explores the intricacies of a PhD journey, from the initial spark of academic passion to the profound understanding of what it takes, in terms of time, to turn that passion into a doctoral reality.
Earning a PhD is a highly individualized journey, and its duration can vary significantly from person to person. This section will delve into the myriad factors that play a role in determining the length of a PhD program. It’s important to understand that the timeline is not a fixed number of years but is influenced by various variables. Here are some key factors:
- Field of Study: The nature of your research area has a significant impact. Some fields, such as the natural sciences or engineering, might require extensive laboratory work and data collection, which can lengthen the Ph.D. process. In contrast, fields like humanities or social sciences might involve less time-intensive data collection but demand extensive writing and analysis.
- Country: The country in which you pursue your PhD can greatly affect the duration. Different countries have different academic systems and expectations. For example, in the United States, it’s common for PhD programs to last longer compared to some European countries where they tend to be shorter and more structured.
- Research Focus: The specific focus of your research project can influence the time required. If your research involves cutting-edge, complex topics, it might take longer to gather and analyze data or develop new methodologies. On the other hand, a well-defined and less ambitious research question could lead to a quicker completion.
Let’s take a closer look at the intricate web of factors that influence the duration of a PhD program. Imagine two students, both embarking on their journeys to earn a PhD, but in different fields.
Student A is pursuing a PhD in physics. This field often involves conducting elaborate experiments, gathering extensive data, and fine-tuning intricate instruments. The pursuit of new discoveries in the realm of physics can be time-consuming, and the PhD program might extend to several years to complete all the necessary research.
Student B, on the other hand, is studying literature and cultural studies. Their research involves in-depth analysis of existing texts, interpretations, and critical theories. While the reading and writing process is extensive, it may not require as many years as Student A’s experimental work.
Now, consider these students in the context of the country in which they are pursuing their PhD Student A is in the United States, where doctoral programs typically span several years. Meanwhile, Student B is in a European country known for its structured and shorter Ph.D. programs.
Lastly, let’s factor in research focus. Student A’s project is ambitious, attempting to uncover the mysteries of the universe, which can be a time-intensive endeavor. In contrast, Student B’s research question is more narrowly defined, making the path to completion relatively shorter.
These examples illustrate how the combination of field of study, country, and research focus can significantly influence the duration of a PhD program.
Understanding the average duration of a PhD program can help prospective students set realistic expectations. This section will provide an overview of the typical timeframes for completing a PhD.
- Average Duration: On a global scale, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes coursework, research, and the writing and defense of a dissertation. However, it’s important to note that this duration can vary significantly. In the United States , for instance, it’s common for PhD programs to take longer, often 5 to 7 years or even more, due to the inclusion of coursework and comprehensive exams. In contrast, in some European countries, PhD programs are designed to be shorter, typically around 3 to 4 years, as they are research-focused with less emphasis on coursework.
- Variations by Field: The average duration can also differ based on the field of study. Fields requiring extensive data collection, such as the natural sciences or engineering, might take longer, while fields like humanities or social sciences with more writing and analysis may have shorter timeframes.
When it comes to the average duration of a PhD program, the common adage ‘it’s a marathon, not a sprint’ certainly applies. The typical journey to a PhD is a long and demanding one, taking aspiring scholars through a series of rigorous academic challenges.
Globally, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes the initial coursework phase, where students delve deep into the theoretical foundations of their field. This is followed by a substantial research phase, during which they gather data, conduct experiments, or engage in extensive fieldwork. Finally, the culmination of this journey is the completion and defense of a dissertation, a written document that contributes new knowledge to their field.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these timeframes are general averages and can vary significantly based on various factors. In the United States, for example, it’s quite common for PhD programs to extend to the longer end of the spectrum, taking 5 to 7 years or even more to complete. This is because American PhD programs often include a significant coursework component and comprehensive exams before the dissertation phase begins.
On the other hand, in some European countries, PhD programs are designed to be more streamlined and research-focused. They typically take around 3 to 4 years to complete, reflecting a shorter timeframe. This structure is influenced by the belief that students entering PhD programs are already well-prepared in their chosen field, and the primary focus is on conducting independent research.
Additionally, the duration can also vary based on the specific field of study. Fields that require extensive data collection or experimental work, such as the natural sciences or engineering, tend to have longer PhD programs. In contrast, fields like humanities or social sciences, where research involves more reading, writing, and analysis, may have shorter timeframes.
Keep in mind that these are general guidelines, and individual PhD experiences can deviate from the average.
Ph.D. program durations can vary significantly between countries due to differences in educational systems and academic traditions. This section will explore how and why PhD programs’ lengths differ by country.
- United States: In the United States, PhD programs are known for their comprehensive structure. They often include a combination of coursework, comprehensive exams, and dissertation research. This makes them typically longer, often spanning 5 to 7 years or more.
- European Countries: In many European countries, PhD programs are more streamlined and research-focused. They tend to be shorter, typically around 3 to 4 years. European programs often assume that students have a strong foundation in their field when they enter the Ph.D. phase.
- Other Countries: The duration of PhD programs can also vary in other parts of the world. For instance, in some Asian countries, the length of a PhD program can be influenced by the nature of the research and the institution’s specific requirements.
When contemplating the pursuit of a Ph.D., it’s important to recognize that the path you tread can be markedly different depending on the country in which you choose to study. The world’s countries have diverse academic systems and traditions, and these intricacies play a significant role in shaping the duration of PhD programs.
Consider the United States, a country renowned for its rigorous academic programs. Here, PhD programs are known for their comprehensive nature. Students often undergo a period of intensive coursework, followed by comprehensive exams to assess their knowledge. This is in addition to the research phase, which involves conducting experiments, gathering data, or delving deep into the chosen area of study. As a result, PhD programs in the United States are often among the longer ones, frequently taking 5 to 7 years or even more to complete.
In contrast, many European countries have adopted a more streamlined approach to PhD programs. These programs tend to be research-focused from the outset, with the assumption that students entering PhD programs already possess a strong foundation in their chosen field. The result is a shorter program, typically spanning around 3 to 4 years. In countries like the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Denmark, students can transition directly into their research, which contributes to the shorter duration.
Outside of the United States and Europe, PhD program lengths can vary significantly depending on the country’s educational system and specific institutional requirements. For instance, in certain Asian countries, PhD programs might also be research-intensive and shorter in duration, or they might extend to accommodate the complexity of the research involved.
It’s important to understand these country-specific variations when considering a PhD program, as they can have a profound impact on the length of your academic journey.
A Ph.D. program is not a single, continuous journey but is typically divided into distinct stages. This section will provide an overview of the common stages of a PhD program, which include coursework, research, and dissertation writing.
- Coursework: The journey usually starts with a coursework phase, where students dive deep into the theoretical foundations of their field. During this stage, students take classes and seminars to build a strong academic foundation. The duration of this stage varies by country and field but generally lasts from 1 to 2 years.
- Comprehensive Exams: In some countries, notably the United States, students are required to pass comprehensive exams to demonstrate their mastery of their field. This stage can add a few months to a couple of years to the timeline.
- Research Phase: After coursework and exams, students transition into the research phase, which is the heart of a Ph.D. program. This phase involves conducting original research, experiments, fieldwork, or in-depth analysis, depending on the field of study. It can last several years, usually 3 to 5 years or more, depending on the complexity of the research and the progress made.
- Dissertation Writing: The final stage involves writing the PhD dissertation, a comprehensive document that presents the research findings and contributes to the academic field. The duration of this stage varies but often takes at least a year.
A PhD program is akin to an academic epic, with distinct stages that collectively make up the hero’s journey. As an aspiring doctoral candidate, it’s essential to understand the key stages you’ll encounter along the way.
The odyssey begins with coursework. During this initial stage, students embark on a voyage into the theoretical underpinnings of their chosen field. They attend classes, seminars, and lectures to deepen their understanding. This coursework phase, which can last anywhere from 1 to 2 years, serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the journey is built.
In some countries, particularly the United States, there’s another formidable challenge—comprehensive exams. These exams test the student’s mastery of the field’s core concepts and are often required before moving on to the next stage. Comprehensive exams can extend the journey by several months to a couple of years.
The heart of the PhD journey lies in the research phase. This is where students immerse themselves in original research, which could entail conducting experiments, gathering data, or engaging in extensive fieldwork, depending on their field of study. The duration of this stage is the most variable, spanning approximately 3 to 5 years or even longer, depending on the complexity of the research and the progress made.
Lastly, the culmination of the PhD adventure is the dissertation writing stage. Here, students craft a comprehensive document that presents their research findings, methodology, and contributions to the academic field. This final stage can vary in length but often takes at least a year to complete.
These stages collectively shape the journey towards a PhD, and understanding them is vital for anyone embarking on this academic odyssey.
While earning a Ph.D. is a significant commitment, there are strategies to expedite the process. This section will discuss strategies and approaches that can help shorten the timeline of your PhD journey .
- Efficient Time Management: Effective time management is essential for expediting a PhD program. Planning and prioritizing tasks, setting clear goals, and maintaining a structured schedule can help students make the most of their research and coursework, reducing the time spent on unnecessary or unproductive activities.
- Choosing the Right Advisor: The relationship between a Ph.D. student and their advisor can significantly impact the program’s duration. A supportive and experienced advisor can guide the student effectively, provide valuable insights, and help them navigate research challenges more efficiently. A strong advisor-student relationship can lead to better research progress and a quicker completion.
- Prior Research Experience: Entering a PhD program with prior research experience can be a significant advantage. If you’ve already conducted research related to your PhD topic during a master’s program or as an undergraduate, you may be able to accelerate your research and data collection, potentially shortening the overall timeline.
When it comes to earning a PhD, the duration can be an intimidating factor. However, it’s important to remember that there are strategies that can help expedite the journey. Let’s explore some of these approaches:
One of the most fundamental strategies is efficient time management. Effective planning, prioritization, and maintaining a structured schedule can make a world of difference. By setting clear goals and staying organized, students can optimize their time and reduce the risk of distractions or time wasted on non-essential activities. This approach ensures that every moment spent on research or coursework is meaningful and productive.
Another pivotal factor is the choice of an advisor. The advisor-student relationship plays a crucial role in a Ph.D. program. A supportive, experienced, and engaged advisor can guide a student through the research process more effectively. They can offer valuable insights, help troubleshoot research challenges, and provide a sense of direction. With the right advisor, students often find themselves making more efficient progress and thus shortening the overall timeline of their PhD journey.
For those entering a PhD program with prior research experience, there’s an advantage. If you’ve already dabbled in research during your master’s program or as an undergraduate, you’re poised for a quicker start. The knowledge, skills, and methodologies you’ve acquired can significantly expedite your research and data collection, potentially helping you complete your PhD in less time.
These strategies, when applied thoughtfully, can make the road to a PhD a bit smoother and shorter, ultimately allowing students to achieve their academic goals more efficiently.
While shortening the Ph.D. journey is a common goal, there are situations that can unexpectedly lengthen the timeline. This section will discuss various reasons a Ph.D. might take longer than expected, including research challenges and personal circumstances.
- Complex Research Challenges: Research is at the core of a Ph.D., and sometimes, research challenges can extend the timeline. For instance, unexpected technical issues, data collection difficulties, or unanticipated roadblocks in the research process can delay progress. Dealing with these complexities often requires additional time and problem-solving efforts.
- Scope of the Project: Sometimes, students may underestimate the scope of their research project. If the research topic turns out to be more extensive or multifaceted than initially anticipated, it can lead to a longer journey. Expanding the research scope can also be driven by a desire to make a more substantial contribution to the field.
- Personal Circumstances: Personal circumstances can also play a significant role in lengthening the timeline. Life events, such as family responsibilities, health issues, or other personal challenges, can disrupt the academic trajectory and extend the Ph.D. program.
While aspiring doctoral candidates often set out with the goal of completing their PhD as efficiently as possible, it’s important to acknowledge that unexpected factors can sometimes extend the journey. Let’s delve into some of the reasons a PhD might take longer than initially expected:
One of the most common factors is research challenges. Research is the backbone of a Ph.D., and it’s not uncommon to encounter unanticipated complexities along the way. For instance, imagine a Ph.D. student in the field of environmental science who encounters technical issues with specialized equipment required for data collection. These unexpected hurdles can require additional time and effort to resolve, extending the research phase.
Another factor that can elongate the timeline is the scope of the project. Sometimes, students may begin their research with a particular understanding of the project’s scale, only to discover that the topic is more extensive or multifaceted than initially thought. This realization can lead to an expansion of the research scope, often driven by the desire to make a more significant and impactful contribution to the field. While noble in its intent, this expansion can result in a longer and more extensive research phase.
Personal circumstances can also have a profound impact. Life doesn’t always adhere to the academic calendar, and various personal challenges can disrupt the PhD journey. These challenges can include family responsibilities, health issues, or other unforeseen life events. Balancing these personal circumstances with academic commitments can sometimes lead to a longer timeline for completing a PhD.
It’s crucial to recognize that while we often have our sights set on a timely completion, the PhD journey can be influenced by a myriad of unforeseen factors. Overcoming these challenges is a testament to resilience and dedication in the pursuit of knowledge.
I have written several articles related to PhD. You can visit them Here. These articles will guide you in the smooth completion of your PhD.
An unconventional PhD demands quality publications and presentations. I have written articles related to Research Journals and Research Conferences. Please visit them
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
To sum it up, figuring out how long a Ph.D. takes is like solving a puzzle. In the U.S., it’s a bit like a long journey, taking about 5 to 7 years, while in Europe, it’s more like a focused sprint, finishing in about 3 to 4 years.
We also learned about the different stages of a Ph.D., from classes to big research and a huge paper called a dissertation. Some folks speed up their Ph.D. by managing time well, picking a good advisor, or using past research experience. But unexpected stuff, like tough research problems or personal things, can make the Ph.D. journey longer.
In Ph.D. land, time is like money you spend to learn and get smart. Whether someone is thinking about starting a Ph.D. or already on the journey, it’s their special story. Enjoy the good parts, handle the tough bits, and feel proud of becoming a real expert, adding to what everyone knows together.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Does a masters degree help completing PhD sooner?
Do students with Masters Degree complete their PhDs (in US, but I am curious about other countries too) sooner than the one's who have entered the PhD program after their undergrad?
I know it depends upon the individual, project, major and the supervisor but is there a general trend?
- In Belgium it's quite uncommon to start a PhD without having a Masters degree. – Marc Claesen Commented Mar 23, 2014 at 8:06
- yes, but does people with masters degree complete their PhD's sooner.. – Ank Commented Mar 23, 2014 at 8:15
- 6 Yes, you will probably complete the PhD a bit sooner. You'll have more research experience, and if continuing your research on the same or similar project, you'll already have experience in the field. However, the time shaved off your PhD will almost certainly be much less than the time invested in your Master's. – Moriarty Commented Mar 23, 2014 at 8:44
- @Moriarty sounds like an answer, not a comment :) – Suresh Commented Mar 23, 2014 at 8:51
- 4 In some European countries, having a Masters degree is actually mandatory to apply for a PhD program. – PatW Commented Mar 23, 2014 at 17:07
6 Answers 6
This varies by program. In the US, in mathematics, "par" for a master's is 2 years. In some PhD programs, this will cut a year off your time-to-degree. In others, no help at all. In rare cases, it will cut two years off.
It depends on the university and the program.
In the US, most PhD granting institutions have pre-requisites for getting your PhD. This may include coursework and will also require research.
For research, one could argue that if you did research in the course of your Master's degree then you would have a time advantage in that you may be able to hit the ground running and engage in publish-able research more quickly.
In institutions that require coursework, the amount of coursework that overlaps with a Master's program can vary. Often, even if you've taken similar coursework in another university, you would still need to fulfill the course requirements in the department where you're going for your PhD. For programs that offer a combined Master's/PhD program, the courses for getting your PhD may be covered under the requirements for getting a Master's, so by already having a Master's degree you may only be shaving off a few of your requirements.
Last, at least in Computer Science, a Master's degree and a PhD are fundamentally different in what they're trying to educate you for. A Master's degree is more like an advanced bachelor's degree where you're taking additional courses and gaining extra skills. A PhD is for research. Given that fundamental difference, it's difficult to say how much would transfer over and again, it would really depend on the university and the program's expectations of what you should have when you enter and what you requirements you need to fulfill once you get there.
Not really, for example if you make your master's is like 2 years, and then your PhD in 4 years, roughly is going to be 6 years that you spent until you got your terminal degree.
I some universities is not required to follow a Master's first. I know the case of one undergraduate student who was always interested in research (when he was in his last year of bachelor he published two good articles in an important ACM conference); he applied directly to a PhD program and he got it. Now he has finished his PhD in only 4 years, and the background that he was missing he got it by following specific courses. So at the end all depends in your background and the passion you got for research.
In my department, students who enter with a masters don't have to take much formal coursework, while those who enter without one have to take much more.
Students with a masters therefore (in theory) have more time and focus to spend on research in the first year or two.
But this doesn't seem to help them finish faster (maybe by a tiny imperceptible amount). Most students aren't working very much on what will become their thesis work in that first year anyways - it's hard to come in and hit the ground running. So while the students entering with a masters might have more time for research in year 1, it doesn't usually directly advance the thesis work.
It is true that it may not shave much time off of your Ph.d, however, it prepares you for the radically different type of education that is graduate school. Forget about time, an M.A will ultimately contribute to your doctoral success in so many varying ways from acclimation to research habits.
From my experience in Biochemistry and Neurobiology (and I'm assuming most Biology and Chemistry fields).
Unfortunately, in the US, no it does not help in completing a PhD sooner.
Sometimes a masters is necessary for a person just to get into a PhD program, depending on the person's history and the program.
It would help if the PhD had some requirement of a certain level of understanding or even amount of research work, but instead a PhD tends to just require an amount of time as an indentured servant to your PI - and that amount of time doesn't change if you have a masters. Although, if you're clever and a good salesman maybe you can convince your PI and committee that your masters time should count toward your sentence/years of labor.
- 1 I disagree with the characterization of a PhD as an indentured servitude - it's definitively not that in my field. – ff524 Commented Mar 23, 2014 at 17:16
- 1 Well it is in many fields, and down voting my comment doesn't make it any less true. There are positives and negatives of Academia. But ignoring the problems doesn't help anyone. – shawn.mek Commented Mar 27, 2014 at 15:38
- 1 I would say that it does not only rely on the field but also on the person you are working with and how they are working. – PatW Commented Mar 27, 2014 at 15:50
- 1 @JeffE I'm not disagreeing, I'm answering the question and saying the reality of the situation. It isn't, however, worthless. The people coming out are, for the most part, reaching some level of expertise and if they don't produce some level of research they can't do much with their degree anyway. BUT, this IS what I have seen. So I would hire a PhD knowing they are likely advanced. However, I know that PhDs have become somewhat devalued, and the system is kind of broken and exploits grad students as servants. – shawn.mek Commented Mar 27, 2014 at 16:19
- 2 Yeah, my friends in engineering and computer science have a different story (generally). I am (with my life sciences PhD) now working mostly writing code, for bioinformatic analyses :) I'm guessing the grad experience of engineering, CS is somewhat because of the job prospects preventing such abuse of the students :) – shawn.mek Commented Mar 27, 2014 at 16:28
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd masters ..
- Featured on Meta
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
Hot Network Questions
- Algebraic and continuous duals of an inverse limit of finite dimensional vector spaces
- Is infinity a number?
- Which interpreter for "Unicode text, UTF-8 text executable"
- Car stalls when coming to a stop except when in neutral
- Is 3, 3 satisfiability trivial after all?
- bpy.app.timers.register is lagging Blender
- I am trying to calculate Albumin-Creatinine ratios for research, why is the result so high?
- Is it possible to go back to the U.S. after overstaying as a child?
- "Shut, shut those juggling eyes, thou ruthless man!" in John Keats's "Lamia"
- An adjective for something peaceful but sad?
- Any philosophical works that explicitly address the heat death of the Universe and its philosophical implications?
- "Will make Elysian shades not too fair, too divine." in John Keats's "Lamia"
- Which Präposition should I use with Erwartungen?
- Is it an option for the ls utility specified in POSIX.1-2017?
- Using grout that had hardened in the bag
- Implementation of Euler-Maruyama numerical solver
- Why are metal ores dredged from coastal lagoons rather than being extracted directly from the mother lode?
- What enforcement exists for medical informed consent?
- How to find basis of vector fields?
- Real-life problems involving solving triangles
- Is this definitive conclusion of a blown head gasket?
- Can a MicroSD card help speed up my Mini PC?
- APFS vs HF+ which is better for storage and music/vides creating/editing?
- Part name of this IC - Analog Devices, 8-pin, "S 6B" A 06" "C 42"

Can I do a PhD after masters? How long does it take to get a PhD / Doctorate
A common question that many graduate students have is whether they can pursue a PhD after completing their master’s degree.
The answer is yes, it is possible to continue your academic career by obtaining a doctoral degree in your field of study.
There are several factors that need to be considered before embarking on this path.
This article will provide an overview of the key factors students should consider when deciding whether to pursue a PhD after completing their master’s degree.
Should I get my PhD after my masters? What about industry?
Deciding whether to pursue a PhD immediately after a master’s degree or enter the workforce first depends on personal goals, interests, and circumstances.
A PhD typically requires around five years of self-directed effort, similar to starting a business. If passionate about research, it might be best to begin right away.
Working in industry before pursuing a PhD can lead to habits that may not benefit academia and can take longer to adjust back to a scholarly environment.
Long-term relationships are essential in academia, and aggressive industry tactics might not be well-received.
Starting a PhD earlier allows for more time to produce research and establish a successful career, particularly for those considering a long-term academic path.
PhD pursuit offers flexibility in research topics and projects, enabling exploration across various subjects and building connections with professionals from different fields. This leads to unique opportunities and experiences that may not be available when working for a single company.
Considering factors like personal goals and readiness for the workload and demands of a PhD program is crucial.
Weigh the potential benefits of advancing education against the time, cost, and personal demands of a doctoral program. If a PhD aligns with one’s career aspirations and personal goals, it may be a worthwhile pursuit.
However, if the investment required outweighs the potential benefits, it might not be the best choice.
It’s always possible to try a PhD program for a year or two and then make a more informed decision based on individual experiences.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD or Doctorate? Time to complete everything
Leading up to getting a PhD there are many qualifications you need to get. Here is the amount of time a typical US Doctorate can take to achieve including all of the previous qualifications. It can take up to 13 years to complete
| Bachelor’s Degree | 4 years (typical) | 4 years |
| Master’s Degree (optional) | 2 years (typical) | 6 years |
| PhD Coursework | 3 years (average) | 9 years |
| PhD Comprehensive Exams | 1-2 semesters | 9.5 years |
| PhD Dissertation: This is a key component of the years of study involved in a doctorate degree. Research | 3 years (average) | 12.5 years |
| PhD Dissertation Defense | 1-2 semesters | 13 years |
The length of time to complete a PhD varies depending on several factors.
On average, in the US it takes about six years, with three years dedicated to coursework and another three years for the dissertation project.
Factors that can influence the duration include:
- prerequisites of the program,
- program format,
- the student’s motivation,
- prior knowledge,
- Personal circumstances, such as being an international student, can influence the time it takes to complete the doctoral program.
- Funding and scholarship stipend can significantly affect the years of study and the time it takes to earn a doctorate degree.
- field of study,
- dissertation topic,
- Support of the graduate advisor can be a crucial factor in minimizing the time it takes to complete a doctorate degree.
The range can be as short as three years or as long as seven to eight years , depending on the individual and the circumstances.
Do you need a master’s for a PhD? A shorter career path that doesn’t take so long.
In certain fields, such as clinical psychology, it is possible to pursue a PhD without obtaining a master’s degree first.
To do so, one must demonstrate a strong academic and research background, as well as a commitment to the field.
Here are the most important attributes if you are thinking about going straight into a PhD without a master’s:
- Strong academic and research background: Ensure that you have excelled in your coursework and maintained a high GPA.
- Undergraduate research experience: Engage in research projects during your undergraduate studies, preferably with a thesis component.
- Clinical exposure (if applicable): Gain relevant experience in the field to showcase your practical knowledge and commitment.
- Leadership experience: Participate in activities that demonstrate your ability to lead and work effectively within a team, as this can be advantageous in the years of study required to earn a doctorate degree.
- Interpersonal skills: Develop strong communication and collaboration skills, which are essential for success in a PhD program.
- Clear determination: Express your dedication to pursuing a PhD directly from your undergraduate studies, highlighting your commitment to the field and how quickly you aim to earn a doctorate.
- Assess your certainty: Be sure that you are confident in your goals and prepared to invest the necessary effort to be competitive without a master’s degree.
By satisfying these requirements, you can better assess your eligibility to apply for a PhD without a master’s degree and potentially save time and money in the process.
Earn a Doctorate without a Masters – How Does It Work?
Obtaining a PhD without a master’s degree is not a common path, but it is possible under certain circumstances.
Typically, a PhD candidate has an undergraduate degree with high grades, a master’s degree, and relevant research skills.
However, there are exceptions where individuals have successfully transitioned from their undergraduate studies directly to a PhD program.
One such scenario involves having a strong rapport with a potential PhD supervisor, perhaps from your undergraduate program, which can significantly reduce the time it takes to earn a doctorate.
This relationship can help compensate for the lack of a master’s degree, but it’s not a guarantee.
Another example is being an exceptional student with a first-class undergraduate degree and a dissertation closely aligned with the advertised PhD project.
Demonstrating an outstanding attitude and performance during your undergraduate project may give you an edge over other applicants.
In applied PhDs, practical experience can also be beneficial, particularly if it includes valuable contacts in the field.
For instance, if your PhD is related to professional sports and you have numerous connections within the industry, it may facilitate recruitment and collaboration, enhancing your chances of acceptance.
However, as with the other examples, this is not a sure-fire way to secure a position.
While securing a PhD without a master’s degree is challenging, it is not impossible.
The best approach is to pursue a master’s degree, as it will better prepare you for a PhD program. – Dr Andy Stapleton
Nonetheless, if you are determined to bypass the master’s route, perseverance and strategic networking can potentially lead to success.
What after Masters: MPhil or Doctorate Degree?
After completing a Master’s degree, you may be considering whether to pursue an MPhil or a PhD.
Here are the differences between the two:
| Level | Intermediate research degree | Highest academic research degree |
| Objective | Develop research skills | Produce independent research contributing to the field |
| Duration | 1-2 years (full-time) | Typically take 3-7 years (full-time or part-time). |
| Scope | Smaller in scale and depth | Broader scope and deeper engagement |
| Research Focus | Less complex topics | More complex topics |
| Supervision | Supervised research | Supervised research with more independence |
| Training | Limited | Research workshops, writing classes, group work, interdisciplinary modules |
| Career Impact | Good for research-oriented positions | Greater career advancement in academia and research |
| Dissertation | Smaller in scale and less comprehensive | Larger, more comprehensive, and novel research project |
A PhD, being the highest academic title awarded for independent research, offers a broader scope and deeper engagement with complex topics than an MA or MPhil.
It can be thought of as an apprenticeship in planning and conducting your research.
The program duration ranges from three to seven years, depending on whether you choose to study full-time or part-time.
Entry is competitive, as candidates must demonstrate a strong track record of academic success.
PhD students attend research workshops, writing classes, and work in groups to explore each other’s studies.
They have opportunities to discuss their research across the university, in graduate school, and other classes, which can be particularly beneficial for an international student. A PhD involves a multi-year project based on independent research, with support from supervisors and training that contributes to the chosen field of study.
It’s essential to have a clear idea of the topic you want to explore in-depth and the methods you plan to employ before applying for a PhD program.
Doing a PhD can be both intellectually and emotionally demanding.
However, working in a department with dedicated and talented staff, excellent supervisors, ongoing training, and support from fellow students can make the experience enjoyable and rewarding.
It is crucial to choose the right supervisor and have a good working relationship with them, as this can significantly impact your PhD journey and the time it takes to complete it.
Wrapping up PhD programs after a masters – how long does it take to complete?
Pursuing a PhD after a master’s degree is a common path for those looking to advance in academia or research-intensive careers.
While obtaining a PhD requires a significant commitment of time and resources, it can lead to prestigious positions or high-paying jobs. It is crucial to consider personal goals, interests, and the job prospects in the field before enrolling in a doctoral program.
For those considering a PhD without a master’s degree, it is essential to demonstrate a strong academic and research background and commit to the field.
The decision between an MPhil and a PhD depends on the desired scope, depth, and career impact of the research. Ultimately, individuals should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the time it takes, cost, and personal demands of a doctoral program before making a decision.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- Preparing to Apply
- How to Apply
- After Applying
- Why Penn State?
- Military and Veteran Students
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Degree Programs
Academic Dates and Deadlines
- Policies for Students
- Theses and Dissertations
- Integrated Undergraduate-Graduate Plans
- Commencement
- Planning Your Finances
- External Funding Opportunities
- Information for Graduate Assistants
- Student Recognition Awards
- Funding FAQ
- Professional Development
- New Students
- From the Dean
- Advising and Mentoring Tips
- Academic Support
- Student Support FAQs
- Addressing Concerns
- Well-Being Resources
- Office of Graduate Educational Equity Programs (OGEEP)
- Graduate School Open House
- Programs and Initiatives
- McNair Scholars Program
- Summer Research Opportunities Program (SROP)
- Resources and Partners
- Office of the Vice Provost for Graduate Education and Dean
- Vision, Mission, and Strategic Plan
- By the Numbers
- Contact the Graduate School
- Resource Library
This dialog contains the full navigation menu for gradschool.psu.edu.
The Graduate School
- Student Support
Information For
- Alumni and Friends
- Veterans and Military Service Members
Helpful Links
- Graduate Education Policies
- Student Teaching Certificate
- Graduate Exhibition
- Three Minute Thesis
- Accelerate to Industry
For Faculty and Staff
- Graduate Council
- Graduate Education Resource Portal

Social Media
Check out below for important academic dates and deadlines for the current and upcoming semesters.
Thesis and Dissertation Deadlines for Summer 2024
Future semester thesis and dissertation deadlines.
The following deadlines are for theses, dissertations, DMA performances and DEng, D.B.A., Dr.P.H., and DNP final oral presentations only. Students writing master's papers should contact their graduate program for deadlines.
| Deadlines by semester | Fall 2024 | Spring 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Apply to graduate in LionPATH | 9/10 | 1/27 |
| Submit doctoral dissertation for format review | 10/1 | 2/3 |
| Submit master's thesis for format review | 10/1 | 2/3 |
| Pass doctoral defense | 10/8 | 2/21 |
| Submit final thesis or dissertation and supporting materials | 11/1 | 3/24 |
| Pass final performance (DMA students only) | 11/1 | 3/24 |
| Pass final oral presentation (DNP, DEng, D.B.A., and Dr.P.H. students only) | 11/1 | 3/24 |
| Committee members to approve final thesis/dissertation | 11/8 | 3/31 |
Questions about the doctoral dissertation defense should be directed to Graduate Enrollment Services. Students with questions regarding the master's thesis defense should contact their graduate program.
Office of Theses and Dissertations
814-865-1795
Legal Statements
- Non-Discrimination
- Equal Opportunity
- Accessibility
- The Pennsylvania State University © 2024

- Colleges & Degrees
- Academic Calendar
- International Education
- Graduate Studies
- Accreditation
- Tuition and Fees
- Parking & Maps
- Careers with CSULB
- Alumni Home
- Alumni Volunteering
- Alumni Giving
Campus Life
- Centers & Organizations
- Commencement
- Student Life
- Office of the President
- Office of the Provost
- Administration & Finance
- Student Affairs
- University Relations & Development
- Information Technology
- Beach Shops
- Campus Directory
- Enrollment Services
- Financial Aid
- Schedule of Classes
- Student Records
- 49er Foundation
- Research Foundation

1250 BELLFLOWER BOULEVARD LONG BEACH, CALIFORNIA 90840 562.985.4111

How CSULB master’s degrees equipped alumni to lead, embrace opportunity
Graduate programs are important components of Cal State Long Beach’s educational offerings and students who complete master’s programs often find themselves prepared for high-level opportunities.
The Beach awarded more than 2,000 master’s degrees – amounting to about 18% of all degrees conferred – during the 2022-23 academic year. The campus offers master’s degrees in more than 160 disciplines including art, business, education, engineering, humanities, nursing, math and science.
“The time is always right,” said Dina Perrone, interim dean of graduate studies at The Beach. “Our faculty work really hard to work with their students to ensure that our graduate students are successful. They recognize that our graduate students are juggling multiple responsibilities in addition to their education.”
Those who pursue master’s degrees can be motivated by desires to become more competitive for jobs and promotions, develop advanced skills, or engage in research. Indeed, 75% of respondents to the 2023 graduate student exit survey indicated they planned to seek a new job related to their degrees.
Sometimes, undergraduates already have their eye on a master’s degree while they are still completing their bachelor’s. Cal State Long Beach is making it easier for students in this situation by introducing Beach EDGE , designed so students can take courses that simultaneously confer credits for bachelor’s and master’s degrees. Debuting this fall, Beach EDGE will lay out pathways for nine degree combos in subjects including business economics, health science and linguistics.
Whatever one’s goal, one alumna counseled would-be students to have confidence in their abilities.
“My advice would be for the person coming in, whether it’s their undergraduate or graduate degree, to take these chances and not second guess yourself as to what you’re capable of,” said Delilah Nuñez ‘98, who earned her MBA and a bachelor’s degree in engineering from Cal State Long Beach and is now a Systems Director for The Aerospace Corp.
Beach alumni who have also completed master's degrees include Mychelle Hale ‘22 (M.S. applied statistics ), Minh Duc Ho ‘23 (M.S. finance ) and Munachiso Osisioma ‘19 (M.S. school counseling ).
Their stories:
Mychelle Hale
Mychelle Hale arrived at CSULB with a degree in mathematics and a drive to learn about data science.
“I did my undergraduate in pure math, and I always wanted to dive a bit deeper into statistics,” Hale said.

Hale was working for a Long Beach firm providing data visualizations and analysis to automotive industry clients when she enrolled in her master’s program, she said. She studied key programming languages (Python, Tableau, SQL, R, SAS) and secured an internship at Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
That led to a thesis blending Hale’s work on atmospheric chemistry at JPL with her math studies, which included discussing complex statistical methods and machine learning with her thesis advisor, mathematics and statistics professor Kagba Suaray.
“The guidance that I was able to receive from my teacher, Dr Suaray, really played a role in my success at Cal State Long Beach,” Hale said.
Hale works for Northrup Grumman in a post that rotates through different business areas. She is now focused on projects involving modeling the firm’s workforce and attrition rates.
Minh Duc Ho
Minh Duc Ho earned his bachelor’s and master’s degrees from The Beach, experiencing portfolio management while concentrating on financial analysis. He participated in Beach Investment Group, a portfolio management program that lets students work with real money, on his way to earning his Bachelor of Business Administration in 2022.

His graduate program, now known as the M.S. in Financial Analytics, prepares students for certification as a chartered financial analyst. Ho said this is the gold standard in finance education and credited faculty finance experts Peter Ammerman and Michael Gibbs for their teaching.
“The skills and knowledge provided by the master’s program are very well-aligned with what top employers in the field are looking for,” Ho said.
Ho now works as a portfolio compliance analyst for PIMCO, a Newport Beach investment firm. He said his master’s enabled him to “hit the ground running” and that he keeps in touch with other alumni.
“We’re still friends to this day, and we exchange ideas,” he said.
Delilah Nuñez
The movies set Delilah Nuñez on a course to earning degrees from Cal State Long Beach and a leadership position in at The Aerospace Corp.

Nuñez’s fascination with space exploration began when her father took her to see “Star Wars,” she said. “War Games,” piqued her interest in computing and in 1989, she enrolled at Cal State Long Beach and went on to earn her undergraduate degree in computer engineering.
She found belonging in the student organizations MAES - Latinos in Science and Engineering and Society of Hispanic Professional Engineers. She also interned with Aerospace Corp., a federally funded research and development nonprofit, when she determined to prepare for management. Nuñez earned an MBA with a specialization in information systems in 1998.
“It’s really helped me bridge the skillsets,” she said. “I work with a lot of leadership, both corporate and aerospace, but also the government is one of our larger customers.”
Aerospace Corp. clients include private organizations and government agencies including NASA, the Defense Department and the Intelligence Community. With her dual degrees, Nuñez is conversant in customers’ business and technical needs.
“There’s a lot to be done and a lot of smart people,” Nuñez said.
Munachiso Osisioma
Munachiso Osisioma, counselor coach for the Santa Ana Unified School District, was a coach of a different sort – leading the girls’ basketball team at Saddleback High School in Santa Ana – when he decided to pursue a master’s degree in school counseling.
“When I was coaching basketball, I often felt that folks were leaning on me, asking questions about my life. I was a trusted adult on campus,” he said.

Osisioma chose Cal State Long Beach’s program due to its emphasis on social justice. He was so sure the program would match his interests that he did not apply anywhere else.
The program exceeded his expectations, and he appreciated the curriculum’s emphasis on leadership. Osisioma views school counseling as a mission to advance justice within the K-12 system since counselors can advocate for fairness when school leaders consider Advanced Placement assignments or discipline reforms.
“It was helpful to know myself and exactly what I needed,” he said. “I knew what my strengths were, and I needed to add to my toolkit.”
Related Articles

CSULB student with passion for inclusion among first Black Student Success Scholarship honorees

CSULB nursing grad thrives in the heart of high-stakes medicine

Mother’s survival leads CSULB engineering student to Sunstone Innovation Challenge win

Eclipse gives CSULB’s astronomy program its moment in the sun

How the CSULB Wind Symphony’s performance at the Kennedy Center was the experience of a lifetime

Zines document legacy of women's activism at CSULB

Ocean studies program offers CSULB students chance to explore sea life off Catalina Island

CSULB’s CSU Trustees’ Award winner follows her passion and path set by her mother

How CSULB is continuing to support Black students

New Long Beach fire chief credits experiences at CSULB for his promotion

Super Sunday: CSULB reinforces the transformative power of higher education

CSULB celebrates the legacy of Black hair during Black History Month


by Burk Krohe | Jul 10, 2024

Longtime faculty members (from left) Shirley Porterfield, Uma Segal and Patricia Rosenthal celebrate retiring with colleagues from the UMSL School of Social Work. The three contributed significantly to the school’s growth from a program in the College of Arts and Sciences to a freestanding academic unit. (Photo courtesy of Uma Segal)
When Founders Professor Uma Segal accepted a faculty position with the University of Missouri–St. Louis in 1986, the social work program was a modest operation.
“It was very small,” she recalled. “There were five of us.”
It’s grown considerably over the past 38 years, evolving from a program housed in the College of Arts and Sciences to the School of Social Work , a freestanding academic unit that reports directly to the provost and vice chancellor for academic affairs. The faculty and staff ranks have swelled, as well.
All the while, Segal and fellow longtime social work faculty members Shirley Porterfield and Patricia Rosenthal not only witnessed but played integral roles in that transformation. Now, after more than 80 years of collective service to the School of Social Work, the three are stepping down. Rosenthal and Segal have already retired, in March and June, respectively, while Porterfield will officially retire on Sept. 1.
Their departures mark the start of new chapters in their lives and a new era for social work at UMSL.
“I’m really hopeful with the junior faculty,” Segal said. “They really are energetic; they have a variety of focus areas; they’re very excited about teaching. This is what they prepared for, and I think they’re pretty excited students are learning from them.”
Different paths
Rosenthal said that she probably had the most traditional path to a career in the social work field.
“It sounds like what everybody says, but I was still in high school and I wanted a profession where I could help people,” she said. “I had an aunt who was a school social worker. So, I visited with her, and I thought, ‘OK, I think this is something that I might enjoy doing.’”
After earning a BSW at Gannon University and MSW at Washington University in St. Louis, Rosenthal worked in the field doing child abuse and neglect intervention work. She went on to serve as executive director of Kids in the Middle , a nonprofit child welfare organization, for 10 years.
However, leading a nonprofit and raising a family eventually became incompatible, and Rosenthal left the organization and began teaching as an adjunct instructor at Fontbonne University, St. Louis Community College and at the Social Work Department at UMSL. That led to a full-time teaching position at UMSL in 1998.
“They were looking for a director of field education, and so I was encouraged to apply for that position because I had so much community work and community experience,” Rosenthal said. “It was a really good fit, so that’s how I ended up here.”
In addition to teaching as a clinical professor and coordinating field education, Rosenthal also served as associate dean of the School of Social Work and sat on several non-profit boards of directors and advisory boards.
Initially, Segal didn’t plan to go into social work. She had earned a bachelor’s degree in cultural anthropology from Columbia University, but she, ironically in retrospect, didn’t want to teach. Like Rosenthal, she also had an aunt in social work, who suggested she pursue it.
Segal took her advice, earning an MSW at the University of Texas at Arlington and then a PhD from the George Warren Brown School of Social Work at WUSTL.
“I found a practice position in ECHO , which was a short-term emergency shelter for abused and neglected kids,” she said. “I kept applying to UMSL for a job every year, whether they had an opening or not. Finally, in 1986, they had an opening.”
In nearly four decades at UMSL, Segal rose through the ranks from assistant professor to Curators’ Distinguished Professor . Her scholarship has primarily focused on immigrant and refugee studies, and she has published six books on the subject.
Segal has lent her expertise to professional conferences and research initiatives in countries across the globe, including Brazil, China, India, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Portugal, Scotland and Turkey. She has also served as the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Immigrant & Refugee Studies, whose mission she redirected, making it an international and interdisciplinary journal dealing with all areas of human migration.
Porterfield joked that she was the outlier of the group.
“I’m the convoluted one,” she said with a laugh.
Porterfield earned bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degrees in agricultural economics at Oregon State University, the University of Arizona and the University of Wisconsin–Madison, respectively. She had begun teaching political science courses at WUSTL when she was invited to teach part time in the Brown School.
Her position there eventually led to a full-time position with UMSL in 2003. In addition to graduate-level courses in program evaluation and health care policy, Porterfield has also held affiliated positions in the public policy administration and economics programs.
Porterfield’s research has focused primarily on health policy as well as work, family and retirement issues associated with disabilities in children and working-age adults, with a particular focus on issues facing low-income families.
A growing impact
Gradually, the trio was joined by more faculty members over the years. Rosenthal traces that growth to a pivotal development 25 years ago.
“The most significant thing that happened was in 1999, we were able to begin a master’s program and went through that whole accreditation process,” she said. “That helped us to grow significantly because we were able to add more faculty. We were able to attract master’s-level students and really expand as a department.”
Lois Pierce – then director and later first dean of the School of Social Work – was instrumental in establishing the graduate program and pushing for further expansion. Segal added that Pierce consistently advocated for greater autonomy on campus, as well.
With the aid of faculty members like Porterfield, Rosenthal and Segal, she succeeded in that endeavor. In 2015, the School of Social Work became a freestanding academic unit , which made it easier to respond to the unique demands of the field. In particular, the school was able to expeditiously update curriculum to satisfy accreditation standards and build a team of academic advisors attuned to the discipline’s distinctive academic and professional challenges.
The milestone also provided increased visibility for the school.
“We were then able to be represented on all the major faculty senate committees,” Rosenthal said. “We were able to be much more involved in the campus and governance and what was happening.”
As the School of Social Work grew, so too did its impact on the community.
Community roots
Porterfield, Rosenthal and Segal are proud of the culture of community engagement that social work faculty and students have cultivated over the past several decades. Segal pointed to faculty members’ applied research in the St. Louis community, while Rosenthal noted that many faculty members sit on community boards and also help social service agencies evaluate the efficacy of their programs.
Segal also successfully lobbied to create a course on human service organizations to give students hands-on experience with local agencies.
“They pair up with an agency and write a grant proposal that they submit for funding at both the graduate level and the undergraduate level,” Segal said. “They do it in groups, so each class might have anywhere between five to seven groups. Most semesters, at least one group gets funding for the agency, which is pretty exciting. Then they leave at least knowing how to do a proposal, which most students or most graduates don’t experience.”
For the past 15 years, UMSL social work students have also been involved with the 100 Neediest Cases , an annual campaign led by the United Way of Greater St. Louis in partnership with the St. Louis Post-Dispatch to deliver goods and cash assistance to thousands of local families facing hardships.
“Our students actually review those applications and make allocations,” Rosenthal, who spearheaded the program, said. “So, they’re getting real-world experience as a part of their coursework. They learn about issues they didn’t even know existed in families – how scare resources are. I think it’s been great in terms of the community too, because it’s been a way for the university to give back to the community and to support the United Way.”
Providing those opportunities for students and playing a role in their academic and professional development has been one of the best parts of the job.
Lasting legacy
Porterfield and Rosenthal both fondly recall helping the students who needed extra guidance or allowances, such as the ability to bring children to classes.
“I do often have people come up and say, ‘You know, I know I wouldn’t have finished if it wasn’t for you kind of holding my hand through this process,’” Porterfield said.
Rosenthal said that’s what kept her at UMSL for so long. Segal cited the atmosphere of academic freedom for her long tenure, while Porterfield noted her coworkers made for pretty inspiring company.
“My colleagues are amazing,” Porterfield said. “I mean, Uma has several books and has traveled all over the world. People used to always say, ‘Where’s Uma?’ Because she’d be off in Japan or Vietnam giving lectures.”
In retirement, Segal intends to keep working on immigration issues and also has plans to write a textbook on social service organizations. Porterfield has been filling her new free time with the St. Louis Master Gardener Program, a collaboration between the University of Missouri Extension and the Missouri Botanical Garden . She’s also engaged in volunteer work at a community garden in Ferguson and Forest ReLeaf, a nonprofit dedicated to planting trees. Rosenthal is looking forward to spending more quality time with her family.
After decades of service, the three are ready for their third act.
“I just feel like it’s time,” Rosenthal said. “I’ve loved – absolutely loved – my time here. I love my colleagues. I’ve thoroughly enjoyed my work with students. But sometimes you just know within yourself, it’s time. I feel like I’m leaving in a good place, while I’m still energetic. There’s good leadership here, people who are very capable, so I feel really good about it.”

LATEST NEWS

YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE

Supply Chain PhD student Paula Penagos selected as fellow in esteemed Eno Center for Transportation Leadership Development Conference
Penagos was the first-ever UMSL student chosen for the Eno Leadership Development Conference, alongside students from universities like MIT, UCLA and Virginia Tech.
Jul 8, 2024

St. Louis Mercantile Library Endowed Executive Director John Neal Hoover receives 2024 Jonas Viles Award
The award, established in 2004 and presented annually, is meant to recognize individuals or institutions who have made significant contributions to the preservation of Missouri’s history.
Accounting student Angela Truesdale honored as recipient of prestigious Remington R. Williams Award
Truesdale, who is interning with Boeing’s finance department this summer, was nominated for the award by Marcia Countryman.

State of Missouri makes significant investments in new academic programs and ongoing campus transformation at UMSL
Capital funding will support a new on-campus engineering program, plus workforce and business innovation centers.
Jun 28, 2024

Climate Change Research Initiative

Program Overview
NASA Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research (ECR) Program Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is an interdisciplinary, collaborative, year-long STEM engagement, and experiential learning opportunity for educators and graduate students to work directly with NASA scientists and lead research teams in a NASA research project hosted at either NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies, CUNY City College of Technology in New York City, NY, or NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. The summer component of each CCRI project also includes undergraduate and high school interns.
During the fall and spring terms of CCRI, the research team will consist of NASA Principal Investigators who lead in-service high school STEM educators and graduate student research assistants to become immersed in a NASA science research area related to climate change. During the summer session, the primary research team will add an undergraduate intern and high school intern to the CCRI research team. The entire team will work collaboratively on a full-time basis to complete the research project, deliver presentations, create a scientific poster and a publishable research paper that will be presented at the CCRI HQ Day at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC , and other science conferences and symposiums.
CCRI Fall 2024-Summer 2025 Research Projects

Research opportunities for educators, grad student assistants, and interns during Fall 2024 through Summer 2025 include the following projects:
- Deciphering Changing Probabilities of Extreme Climate Events in Climate Models and Measurements (GISS)
- Climate Change in the Hudson Estuary — Past, Present, and Future (GISS/LDEO)
- Monitoring and Studying Lakes from Space in a Changing Climate (GISS/CUNY)
- Characterizing the Urban Land Surface Temperature via an Innovative, Multi-Platformed Suite of Satellite and Ground-Based Remote Sensing Technologies (GISS/CUNY)
- SnowEx and Understanding the Role of Snow and Measurements (GSFC)
Work Performance Periods
Fall: October 15, 2024 – December 20, 2024
Spring: January 27, 2025 – April 25, 2025
Summer: June 16, 2025 – August 8, 2025
Applicant Requirements
CCRI applicants must be US citizens. Housing, relocation and travel expenses are not provided. Teachers, graduate students and interns whose locality is regional to the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York City, NY, or NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, are encouraged to apply. Applications are considered upon receipt.
The deadline for educators and graduate students to apply for the CCRI 2024-2025 year-long program is September 2024 . The final application deadline for Summer 2025 CCRI high school and undergraduate internship opportunities is February 28, 2025 at NASA’s Internship Programs website .
Application Requirements
Teachers applying for CCRI should submit a cover letter, resume, and unofficial transcripts. Teachers are also encouraged but not required to submit any additional portfolio exemplars. The cover letter should also include:
- A description of how participating in CCRI will benefit your students, school and community.
- Description of IT and programing skills indicating a self-proficiency ranking.
- Rank in order of preference the projects that the teacher would like to apply to and be considered for.
The selected candidate will be requested to provide a letter of support from their school administration for participation and collaboration in the program.
Performance Requirements
- Educators participating in this opportunity become associate researchers, CCRI education ambassadors and STEM education experts who integrate NASA education resources, platforms, data and content into their classrooms while improving STEM education within their communities.
- Participating high school STEM educators contribute to the research project, assist in the development of a research question and assist in guiding the research team to complete all program deliverables.
- Educators also develop a portfolio of lesson plans that utilizes NASA education resources aligning NASA Science and STEM curricula to the Next Generation Science Standards. The teachers will then incorporate the STEM curriculum into their classrooms and also provide community STEM engagement events related to their NASA research study. The fall and spring term will not conflict with the educators' primary schedule, roles or responsibilities at their school sites.
Graduate Students
Graduate Student Research Assistants applying for CCRI should submit a cover letter, resume and unofficial transcripts. The cover letter should also include:
- A description of how participating in CCRI aligns with your current degree program and anticipated graduation date.
- Description of IT and program skills indicating a self-proficiency ranking.
- Rank in order of preference the projects that the graduate student would like to apply to and be considered for.
The selected candidate will be requested to provide a letter of support from their graduate school advisor for participation and collaboration in the program.
- Graduate Research Assistants contribute to the research project, assist in the development of a research question and assist in guiding the research team to complete all program deliverables.
- For graduate student research assistants, this opportunity will not conflict with class schedules during the fall and spring. It is considered to be a part-time position that supports the graduate student's major area of study.
- All students are required to submit a final report upon completion of the program.
Undergraduates Students/ High School Students
Student interns must complete the entire application within NASA's Internship STEM Gateway .
- Undergraduate and high school students work on real NASA projects with the guidance of a NASA CCRI mentor, a research scientist, and gain practical work experience.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
The structure of the PhD program you choose can greatly influence how long it takes to complete your degree. Programs that allow you to start your dissertation research early, even while completing your coursework, can save you a considerable amount of time.
How long does a PhD take? Explore the timeline of completing a PhD program and the benefits of accelerated online degrees. Get started today!
However, there are PhD programs that take longer, such as part-time programs, or are extremely short, like online accelerated PhD programs. Ultimately, how long it takes to get a PhD is up to you. In this article, we'll look at the average PhD program lengths, the typical PhD timeline, and tips on how to get your PhD finished faster.
The average PhD length is five or six years, while some students may take eight or nine years. Regardless of how long a PhD program takes, there are some common stages of a PhD that all doctoral students share. These major and essential milestones shape the timeline for earning your doctorate.
How long is a PhD program? That might be one of the first questions you ask yourself If you are thinking of earning a PhD. You have probably heard a range of years, and that is because how long it takes to earn a PhD depends on a number of factors. Keep reading to learn more!!
How long does it take to get a PhD? This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5-7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3-5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation. In the rest of the world, students normally have a master's degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to ...
The answer can vary depending on your program, educational background, and academic schedule. In general, most PhD psychology programs take anywhere from five to seven years to complete. Learning more about what it takes to get a doctorate in psychology can help you better plan your educational and career journey.
A Ph.D. is a research degree that involves the production of original knowledge and scholarship. Doctoral degrees have traditionally been regarded as training programs for academics. As such, a Ph.D. program differs from undergraduate or Master's studies. Most Ph.D. programs involve some initial coursework (specific requirements for coursework differ widely depending on fields and ...
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3 to 4 years to finish whilst a part-time PhD takes twice as long at 6 to 7 years. Alongside these average durations, there are time limits on how long you can be enrolled on to a PhD programme. To discover these limits, the factors which most influence doctoral degree durations and how the UK durations compare to international PhDs, continue reading on.
How the PhD Program Works. Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending ...
The choice of PhD vs. professional doctorate can influence how long it takes you to earn your degree because the way you earn them differs. In general, PhD candidates must complete a dissertation, which requires them to conduct research into an approved area of study within their discipline, typically an area no one in their discipline has fully researched before. Professional doctorate ...
Average Duration: On a global scale, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes coursework, research, and the writing and defense of a dissertation. However, it's important to note that this duration can vary significantly.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say ...
Doctor of Philosophy. A Doctor of Philosophy ( PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is a terminal degree that usually denotes the highest level of academic achievement in a given discipline and is awarded following a course of graduate study and original research.
However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey. Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means ...
Deciding to pursue an MD-PhD dual degree is a long-term commitment, but for a medical student with a passion for research, it's a rewarding path.
Only graduates with a Psy.D. or a Ph.D. in psychology can become licensed psychologists (except for school psychologists ). Similarly, if you want to become a professor of psychology in most colleges or universities, you will need to graduate from an accredited doctorate in psychology program. The APA does not accredit online programs.
It takes on average 4.4 years to earn a PhD although it depends on your doctoral program as to how long it will typically take a PhD student to graduate. Writing your dissertation early and being focused on the end goal will help you finish within four to seven years.
I would like to know, if possible, how long it takes on the average to reach a first admission decision for doctoral programs?
For programs that offer a combined Master's/PhD program, the courses for getting your PhD may be covered under the requirements for getting a Master's, so by already having a Master's degree you may only be shaving off a few of your requirements.
A common question that many graduate students have is whether they can pursue a PhD after completing their master's degree.
Are you considering a doctorate in psychology? Keep reading to learn about what a psychology doctoral program might look like and how to choose the right program for you.
Questions about the doctoral dissertation defense should be directed to Graduate Enrollment Services. Students with questions regarding the master's thesis defense should contact their graduate program.
Online exercise science degree programs provide a versatile and accessible path for individuals passionate about fitness, health, and human performance to pursue higher education. However, with the increasing number of online exercise science degree programs available, choosing the right one can be a daunting task. This article aims to guide...
Graduate programs are important components of Cal State Long Beach's educational offerings and students who complete master's programs often find themselves prepared for high-level opportunities.
Shirley Porterfield, Uma Segal and Patricia Rosenthal contributed significantly to the school's growth from a program in the College of Arts and Sciences to a freestanding academic unit.
That once-in-a-lifetime opportunity had been dashed by the long delays. ... Applicant Bikash Bhattacharya told PRI he is in danger of losing his acceptance into a PhD program.
Program Overview NASA Earth Science Division's Early Career Research (ECR) Program Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is an interdisciplinary, collaborative, year-long STEM engagement, and experiential learning opportunity for educators and graduate students to work directly with NASA scientists and lead research teams in a NASA research project hosted at either NASA's Goddard ...