Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology

Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 20 March 2023.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall aims and approach
- The type of research design you’ll use
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, frequently asked questions.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities – start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
| Qualitative approach | Quantitative approach |
|---|---|
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships, while descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Experimental | |
| Quasi-experimental | |
| Correlational | |
| Descriptive |
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends, and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analysing the data.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | |
| Phenomenology |
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region, or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalise your results to the population as a whole.
| Probability sampling | Non-probability sampling |
|---|---|
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study, your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalise to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question.
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviours, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews.
| Questionnaires | Interviews |
|---|---|
Observation methods
Observations allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviours, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
| Quantitative observation | |
|---|---|
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
| Field | Examples of data collection methods |
|---|---|
| Media & communication | Collecting a sample of texts (e.g., speeches, articles, or social media posts) for data on cultural norms and narratives |
| Psychology | Using technologies like neuroimaging, eye-tracking, or computer-based tasks to collect data on things like attention, emotional response, or reaction time |
| Education | Using tests or assignments to collect data on knowledge and skills |
| Physical sciences | Using scientific instruments to collect data on things like weight, blood pressure, or chemical composition |
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected – for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are reliable and valid.
Operationalisation
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalisation means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in – for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced , while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
| Reliability | Validity |
|---|---|
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method, you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample – by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method, it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method, how will you avoid bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organising and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymise and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well organised will save time when it comes to analysing them. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings.
On their own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyse the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarise your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarise your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
| Approach | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Thematic analysis | |
| Discourse analysis |
There are many other ways of analysing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, March 20). Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 10 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes

Chapter 2. Research Design
Getting started.
When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a “research proposal” that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question. I highly recommend you think about designing your own research study as you progress through this textbook. Even if you don’t have a study in mind yet, it can be a helpful exercise as you progress through the course. But how to start? How can one design a research study before they even know what research looks like? This chapter will serve as a brief overview of the research design process to orient you to what will be coming in later chapters. Think of it as a “skeleton” of what you will read in more detail in later chapters. Ideally, you will read this chapter both now (in sequence) and later during your reading of the remainder of the text. Do not worry if you have questions the first time you read this chapter. Many things will become clearer as the text advances and as you gain a deeper understanding of all the components of good qualitative research. This is just a preliminary map to get you on the right road.

Research Design Steps
Before you even get started, you will need to have a broad topic of interest in mind. [1] . In my experience, students can confuse this broad topic with the actual research question, so it is important to clearly distinguish the two. And the place to start is the broad topic. It might be, as was the case with me, working-class college students. But what about working-class college students? What’s it like to be one? Why are there so few compared to others? How do colleges assist (or fail to assist) them? What interested me was something I could barely articulate at first and went something like this: “Why was it so difficult and lonely to be me?” And by extension, “Did others share this experience?”
Once you have a general topic, reflect on why this is important to you. Sometimes we connect with a topic and we don’t really know why. Even if you are not willing to share the real underlying reason you are interested in a topic, it is important that you know the deeper reasons that motivate you. Otherwise, it is quite possible that at some point during the research, you will find yourself turned around facing the wrong direction. I have seen it happen many times. The reason is that the research question is not the same thing as the general topic of interest, and if you don’t know the reasons for your interest, you are likely to design a study answering a research question that is beside the point—to you, at least. And this means you will be much less motivated to carry your research to completion.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study? What are the advantages of qualitative research methods for studying mentorship?
Qualitative research methods are a huge opportunity to increase access, equity, inclusion, and social justice. Qualitative research allows us to engage and examine the uniquenesses/nuances within minoritized and dominant identities and our experiences with these identities. Qualitative research allows us to explore a specific topic, and through that exploration, we can link history to experiences and look for patterns or offer up a unique phenomenon. There’s such beauty in being able to tell a particular story, and qualitative research is a great mode for that! For our work, we examined the relationships we typically use the term mentorship for but didn’t feel that was quite the right word. Qualitative research allowed us to pick apart what we did and how we engaged in our relationships, which then allowed us to more accurately describe what was unique about our mentorship relationships, which we ultimately named liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021) . Qualitative research gave us the means to explore, process, and name our experiences; what a powerful tool!
How do you come up with ideas for what to study (and how to study it)? Where did you get the idea for studying mentorship?
Coming up with ideas for research, for me, is kind of like Googling a question I have, not finding enough information, and then deciding to dig a little deeper to get the answer. The idea to study mentorship actually came up in conversation with my mentorship triad. We were talking in one of our meetings about our relationship—kind of meta, huh? We discussed how we felt that mentorship was not quite the right term for the relationships we had built. One of us asked what was different about our relationships and mentorship. This all happened when I was taking an ethnography course. During the next session of class, we were discussing auto- and duoethnography, and it hit me—let’s explore our version of mentorship, which we later went on to name liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021 ). The idea and questions came out of being curious and wanting to find an answer. As I continue to research, I see opportunities in questions I have about my work or during conversations that, in our search for answers, end up exposing gaps in the literature. If I can’t find the answer already out there, I can study it.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
When you have a better idea of why you are interested in what it is that interests you, you may be surprised to learn that the obvious approaches to the topic are not the only ones. For example, let’s say you think you are interested in preserving coastal wildlife. And as a social scientist, you are interested in policies and practices that affect the long-term viability of coastal wildlife, especially around fishing communities. It would be natural then to consider designing a research study around fishing communities and how they manage their ecosystems. But when you really think about it, you realize that what interests you the most is how people whose livelihoods depend on a particular resource act in ways that deplete that resource. Or, even deeper, you contemplate the puzzle, “How do people justify actions that damage their surroundings?” Now, there are many ways to design a study that gets at that broader question, and not all of them are about fishing communities, although that is certainly one way to go. Maybe you could design an interview-based study that includes and compares loggers, fishers, and desert golfers (those who golf in arid lands that require a great deal of wasteful irrigation). Or design a case study around one particular example where resources were completely used up by a community. Without knowing what it is you are really interested in, what motivates your interest in a surface phenomenon, you are unlikely to come up with the appropriate research design.
These first stages of research design are often the most difficult, but have patience . Taking the time to consider why you are going to go through a lot of trouble to get answers will prevent a lot of wasted energy in the future.
There are distinct reasons for pursuing particular research questions, and it is helpful to distinguish between them. First, you may be personally motivated. This is probably the most important and the most often overlooked. What is it about the social world that sparks your curiosity? What bothers you? What answers do you need in order to keep living? For me, I knew I needed to get a handle on what higher education was for before I kept going at it. I needed to understand why I felt so different from my peers and whether this whole “higher education” thing was “for the likes of me” before I could complete my degree. That is the personal motivation question. Your personal motivation might also be political in nature, in that you want to change the world in a particular way. It’s all right to acknowledge this. In fact, it is better to acknowledge it than to hide it.
There are also academic and professional motivations for a particular study. If you are an absolute beginner, these may be difficult to find. We’ll talk more about this when we discuss reviewing the literature. Simply put, you are probably not the only person in the world to have thought about this question or issue and those related to it. So how does your interest area fit into what others have studied? Perhaps there is a good study out there of fishing communities, but no one has quite asked the “justification” question. You are motivated to address this to “fill the gap” in our collective knowledge. And maybe you are really not at all sure of what interests you, but you do know that [insert your topic] interests a lot of people, so you would like to work in this area too. You want to be involved in the academic conversation. That is a professional motivation and a very important one to articulate.
Practical and strategic motivations are a third kind. Perhaps you want to encourage people to take better care of the natural resources around them. If this is also part of your motivation, you will want to design your research project in a way that might have an impact on how people behave in the future. There are many ways to do this, one of which is using qualitative research methods rather than quantitative research methods, as the findings of qualitative research are often easier to communicate to a broader audience than the results of quantitative research. You might even be able to engage the community you are studying in the collecting and analyzing of data, something taboo in quantitative research but actively embraced and encouraged by qualitative researchers. But there are other practical reasons, such as getting “done” with your research in a certain amount of time or having access (or no access) to certain information. There is nothing wrong with considering constraints and opportunities when designing your study. Or maybe one of the practical or strategic goals is about learning competence in this area so that you can demonstrate the ability to conduct interviews and focus groups with future employers. Keeping that in mind will help shape your study and prevent you from getting sidetracked using a technique that you are less invested in learning about.
STOP HERE for a moment
I recommend you write a paragraph (at least) explaining your aims and goals. Include a sentence about each of the following: personal/political goals, practical or professional/academic goals, and practical/strategic goals. Think through how all of the goals are related and can be achieved by this particular research study . If they can’t, have a rethink. Perhaps this is not the best way to go about it.
You will also want to be clear about the purpose of your study. “Wait, didn’t we just do this?” you might ask. No! Your goals are not the same as the purpose of the study, although they are related. You can think about purpose lying on a continuum from “ theory ” to “action” (figure 2.1). Sometimes you are doing research to discover new knowledge about the world, while other times you are doing a study because you want to measure an impact or make a difference in the world.
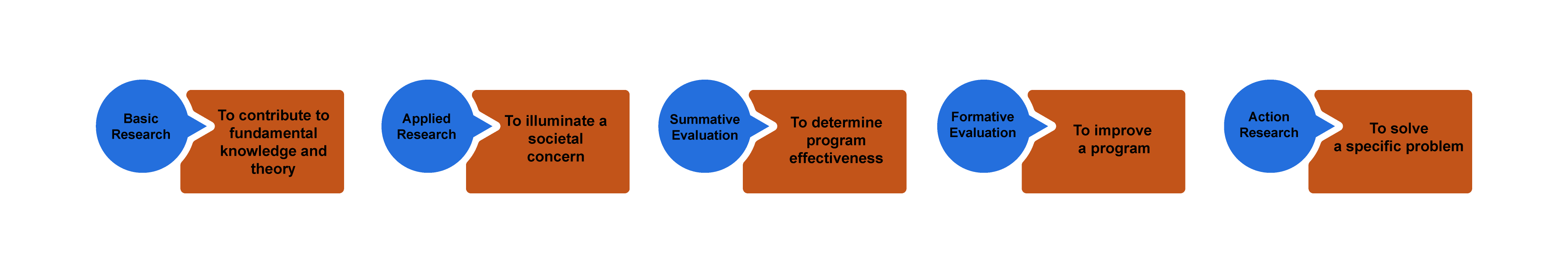
Basic research involves research that is done for the sake of “pure” knowledge—that is, knowledge that, at least at this moment in time, may not have any apparent use or application. Often, and this is very important, knowledge of this kind is later found to be extremely helpful in solving problems. So one way of thinking about basic research is that it is knowledge for which no use is yet known but will probably one day prove to be extremely useful. If you are doing basic research, you do not need to argue its usefulness, as the whole point is that we just don’t know yet what this might be.
Researchers engaged in basic research want to understand how the world operates. They are interested in investigating a phenomenon to get at the nature of reality with regard to that phenomenon. The basic researcher’s purpose is to understand and explain ( Patton 2002:215 ).
Basic research is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works. Grounded Theory is one approach to qualitative research methods that exemplifies basic research (see chapter 4). Most academic journal articles publish basic research findings. If you are working in academia (e.g., writing your dissertation), the default expectation is that you are conducting basic research.
Applied research in the social sciences is research that addresses human and social problems. Unlike basic research, the researcher has expectations that the research will help contribute to resolving a problem, if only by identifying its contours, history, or context. From my experience, most students have this as their baseline assumption about research. Why do a study if not to make things better? But this is a common mistake. Students and their committee members are often working with default assumptions here—the former thinking about applied research as their purpose, the latter thinking about basic research: “The purpose of applied research is to contribute knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment. While in basic research the source of questions is the tradition within a scholarly discipline, in applied research the source of questions is in the problems and concerns experienced by people and by policymakers” ( Patton 2002:217 ).
Applied research is less geared toward theory in two ways. First, its questions do not derive from previous literature. For this reason, applied research studies have much more limited literature reviews than those found in basic research (although they make up for this by having much more “background” about the problem). Second, it does not generate theory in the same way as basic research does. The findings of an applied research project may not be generalizable beyond the boundaries of this particular problem or context. The findings are more limited. They are useful now but may be less useful later. This is why basic research remains the default “gold standard” of academic research.
Evaluation research is research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. We already know the problems, and someone has already come up with solutions. There might be a program, say, for first-generation college students on your campus. Does this program work? Are first-generation students who participate in the program more likely to graduate than those who do not? These are the types of questions addressed by evaluation research. There are two types of research within this broader frame; however, one more action-oriented than the next. In summative evaluation , an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made. Should we continue our first-gen program? Is it a good model for other campuses? Because the purpose of such summative evaluation is to measure success and to determine whether this success is scalable (capable of being generalized beyond the specific case), quantitative data is more often used than qualitative data. In our example, we might have “outcomes” data for thousands of students, and we might run various tests to determine if the better outcomes of those in the program are statistically significant so that we can generalize the findings and recommend similar programs elsewhere. Qualitative data in the form of focus groups or interviews can then be used for illustrative purposes, providing more depth to the quantitative analyses. In contrast, formative evaluation attempts to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness). Formative evaluations rely more heavily on qualitative data—case studies, interviews, focus groups. The findings are meant not to generalize beyond the particular but to improve this program. If you are a student seeking to improve your qualitative research skills and you do not care about generating basic research, formative evaluation studies might be an attractive option for you to pursue, as there are always local programs that need evaluation and suggestions for improvement. Again, be very clear about your purpose when talking through your research proposal with your committee.
Action research takes a further step beyond evaluation, even formative evaluation, to being part of the solution itself. This is about as far from basic research as one could get and definitely falls beyond the scope of “science,” as conventionally defined. The distinction between action and research is blurry, the research methods are often in constant flux, and the only “findings” are specific to the problem or case at hand and often are findings about the process of intervention itself. Rather than evaluate a program as a whole, action research often seeks to change and improve some particular aspect that may not be working—maybe there is not enough diversity in an organization or maybe women’s voices are muted during meetings and the organization wonders why and would like to change this. In a further step, participatory action research , those women would become part of the research team, attempting to amplify their voices in the organization through participation in the action research. As action research employs methods that involve people in the process, focus groups are quite common.
If you are working on a thesis or dissertation, chances are your committee will expect you to be contributing to fundamental knowledge and theory ( basic research ). If your interests lie more toward the action end of the continuum, however, it is helpful to talk to your committee about this before you get started. Knowing your purpose in advance will help avoid misunderstandings during the later stages of the research process!
The Research Question
Once you have written your paragraph and clarified your purpose and truly know that this study is the best study for you to be doing right now , you are ready to write and refine your actual research question. Know that research questions are often moving targets in qualitative research, that they can be refined up to the very end of data collection and analysis. But you do have to have a working research question at all stages. This is your “anchor” when you get lost in the data. What are you addressing? What are you looking at and why? Your research question guides you through the thicket. It is common to have a whole host of questions about a phenomenon or case, both at the outset and throughout the study, but you should be able to pare it down to no more than two or three sentences when asked. These sentences should both clarify the intent of the research and explain why this is an important question to answer. More on refining your research question can be found in chapter 4.
Chances are, you will have already done some prior reading before coming up with your interest and your questions, but you may not have conducted a systematic literature review. This is the next crucial stage to be completed before venturing further. You don’t want to start collecting data and then realize that someone has already beaten you to the punch. A review of the literature that is already out there will let you know (1) if others have already done the study you are envisioning; (2) if others have done similar studies, which can help you out; and (3) what ideas or concepts are out there that can help you frame your study and make sense of your findings. More on literature reviews can be found in chapter 9.
In addition to reviewing the literature for similar studies to what you are proposing, it can be extremely helpful to find a study that inspires you. This may have absolutely nothing to do with the topic you are interested in but is written so beautifully or organized so interestingly or otherwise speaks to you in such a way that you want to post it somewhere to remind you of what you want to be doing. You might not understand this in the early stages—why would you find a study that has nothing to do with the one you are doing helpful? But trust me, when you are deep into analysis and writing, having an inspirational model in view can help you push through. If you are motivated to do something that might change the world, you probably have read something somewhere that inspired you. Go back to that original inspiration and read it carefully and see how they managed to convey the passion that you so appreciate.
At this stage, you are still just getting started. There are a lot of things to do before setting forth to collect data! You’ll want to consider and choose a research tradition and a set of data-collection techniques that both help you answer your research question and match all your aims and goals. For example, if you really want to help migrant workers speak for themselves, you might draw on feminist theory and participatory action research models. Chapters 3 and 4 will provide you with more information on epistemologies and approaches.
Next, you have to clarify your “units of analysis.” What is the level at which you are focusing your study? Often, the unit in qualitative research methods is individual people, or “human subjects.” But your units of analysis could just as well be organizations (colleges, hospitals) or programs or even whole nations. Think about what it is you want to be saying at the end of your study—are the insights you are hoping to make about people or about organizations or about something else entirely? A unit of analysis can even be a historical period! Every unit of analysis will call for a different kind of data collection and analysis and will produce different kinds of “findings” at the conclusion of your study. [2]
Regardless of what unit of analysis you select, you will probably have to consider the “human subjects” involved in your research. [3] Who are they? What interactions will you have with them—that is, what kind of data will you be collecting? Before answering these questions, define your population of interest and your research setting. Use your research question to help guide you.
Let’s use an example from a real study. In Geographies of Campus Inequality , Benson and Lee ( 2020 ) list three related research questions: “(1) What are the different ways that first-generation students organize their social, extracurricular, and academic activities at selective and highly selective colleges? (2) how do first-generation students sort themselves and get sorted into these different types of campus lives; and (3) how do these different patterns of campus engagement prepare first-generation students for their post-college lives?” (3).
Note that we are jumping into this a bit late, after Benson and Lee have described previous studies (the literature review) and what is known about first-generation college students and what is not known. They want to know about differences within this group, and they are interested in ones attending certain kinds of colleges because those colleges will be sites where academic and extracurricular pressures compete. That is the context for their three related research questions. What is the population of interest here? First-generation college students . What is the research setting? Selective and highly selective colleges . But a host of questions remain. Which students in the real world, which colleges? What about gender, race, and other identity markers? Will the students be asked questions? Are the students still in college, or will they be asked about what college was like for them? Will they be observed? Will they be shadowed? Will they be surveyed? Will they be asked to keep diaries of their time in college? How many students? How many colleges? For how long will they be observed?
Recommendation
Take a moment and write down suggestions for Benson and Lee before continuing on to what they actually did.
Have you written down your own suggestions? Good. Now let’s compare those with what they actually did. Benson and Lee drew on two sources of data: in-depth interviews with sixty-four first-generation students and survey data from a preexisting national survey of students at twenty-eight selective colleges. Let’s ignore the survey for our purposes here and focus on those interviews. The interviews were conducted between 2014 and 2016 at a single selective college, “Hilltop” (a pseudonym ). They employed a “purposive” sampling strategy to ensure an equal number of male-identifying and female-identifying students as well as equal numbers of White, Black, and Latinx students. Each student was interviewed once. Hilltop is a selective liberal arts college in the northeast that enrolls about three thousand students.
How did your suggestions match up to those actually used by the researchers in this study? It is possible your suggestions were too ambitious? Beginning qualitative researchers can often make that mistake. You want a research design that is both effective (it matches your question and goals) and doable. You will never be able to collect data from your entire population of interest (unless your research question is really so narrow to be relevant to very few people!), so you will need to come up with a good sample. Define the criteria for this sample, as Benson and Lee did when deciding to interview an equal number of students by gender and race categories. Define the criteria for your sample setting too. Hilltop is typical for selective colleges. That was a research choice made by Benson and Lee. For more on sampling and sampling choices, see chapter 5.
Benson and Lee chose to employ interviews. If you also would like to include interviews, you have to think about what will be asked in them. Most interview-based research involves an interview guide, a set of questions or question areas that will be asked of each participant. The research question helps you create a relevant interview guide. You want to ask questions whose answers will provide insight into your research question. Again, your research question is the anchor you will continually come back to as you plan for and conduct your study. It may be that once you begin interviewing, you find that people are telling you something totally unexpected, and this makes you rethink your research question. That is fine. Then you have a new anchor. But you always have an anchor. More on interviewing can be found in chapter 11.
Let’s imagine Benson and Lee also observed college students as they went about doing the things college students do, both in the classroom and in the clubs and social activities in which they participate. They would have needed a plan for this. Would they sit in on classes? Which ones and how many? Would they attend club meetings and sports events? Which ones and how many? Would they participate themselves? How would they record their observations? More on observation techniques can be found in both chapters 13 and 14.
At this point, the design is almost complete. You know why you are doing this study, you have a clear research question to guide you, you have identified your population of interest and research setting, and you have a reasonable sample of each. You also have put together a plan for data collection, which might include drafting an interview guide or making plans for observations. And so you know exactly what you will be doing for the next several months (or years!). To put the project into action, there are a few more things necessary before actually going into the field.
First, you will need to make sure you have any necessary supplies, including recording technology. These days, many researchers use their phones to record interviews. Second, you will need to draft a few documents for your participants. These include informed consent forms and recruiting materials, such as posters or email texts, that explain what this study is in clear language. Third, you will draft a research protocol to submit to your institutional review board (IRB) ; this research protocol will include the interview guide (if you are using one), the consent form template, and all examples of recruiting material. Depending on your institution and the details of your study design, it may take weeks or even, in some unfortunate cases, months before you secure IRB approval. Make sure you plan on this time in your project timeline. While you wait, you can continue to review the literature and possibly begin drafting a section on the literature review for your eventual presentation/publication. More on IRB procedures can be found in chapter 8 and more general ethical considerations in chapter 7.
Once you have approval, you can begin!
Research Design Checklist
Before data collection begins, do the following:
- Write a paragraph explaining your aims and goals (personal/political, practical/strategic, professional/academic).
- Define your research question; write two to three sentences that clarify the intent of the research and why this is an important question to answer.
- Review the literature for similar studies that address your research question or similar research questions; think laterally about some literature that might be helpful or illuminating but is not exactly about the same topic.
- Find a written study that inspires you—it may or may not be on the research question you have chosen.
- Consider and choose a research tradition and set of data-collection techniques that (1) help answer your research question and (2) match your aims and goals.
- Define your population of interest and your research setting.
- Define the criteria for your sample (How many? Why these? How will you find them, gain access, and acquire consent?).
- If you are conducting interviews, draft an interview guide.
- If you are making observations, create a plan for observations (sites, times, recording, access).
- Acquire any necessary technology (recording devices/software).
- Draft consent forms that clearly identify the research focus and selection process.
- Create recruiting materials (posters, email, texts).
- Apply for IRB approval (proposal plus consent form plus recruiting materials).
- Block out time for collecting data.
- At the end of the chapter, you will find a " Research Design Checklist " that summarizes the main recommendations made here ↵
- For example, if your focus is society and culture , you might collect data through observation or a case study. If your focus is individual lived experience , you are probably going to be interviewing some people. And if your focus is language and communication , you will probably be analyzing text (written or visual). ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:16 ). ↵
- You may not have any "live" human subjects. There are qualitative research methods that do not require interactions with live human beings - see chapter 16 , "Archival and Historical Sources." But for the most part, you are probably reading this textbook because you are interested in doing research with people. The rest of the chapter will assume this is the case. ↵
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and research design that focuses on an individual case (e.g., setting, institution, or sometimes an individual) in order to explore its complexity, history, and interactive parts. As an approach, it is particularly useful for obtaining a deep appreciation of an issue, event, or phenomenon of interest in its particular context.
The controlling force in research; can be understood as lying on a continuum from basic research (knowledge production) to action research (effecting change).
In its most basic sense, a theory is a story we tell about how the world works that can be tested with empirical evidence. In qualitative research, we use the term in a variety of ways, many of which are different from how they are used by quantitative researchers. Although some qualitative research can be described as “testing theory,” it is more common to “build theory” from the data using inductive reasoning , as done in Grounded Theory . There are so-called “grand theories” that seek to integrate a whole series of findings and stories into an overarching paradigm about how the world works, and much smaller theories or concepts about particular processes and relationships. Theory can even be used to explain particular methodological perspectives or approaches, as in Institutional Ethnography , which is both a way of doing research and a theory about how the world works.
Research that is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
Research that contributes knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment.
Research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. There are two kinds: summative and formative .
Research in which an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made, often for the purpose of generalizing to other cases or programs. Generally uses qualitative research as a supplement to primary quantitative data analyses. Contrast formative evaluation research .
Research designed to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness); relies heavily on qualitative research methods. Contrast summative evaluation research
Research carried out at a particular organizational or community site with the intention of affecting change; often involves research subjects as participants of the study. See also participatory action research .
Research in which both researchers and participants work together to understand a problematic situation and change it for the better.
The level of the focus of analysis (e.g., individual people, organizations, programs, neighborhoods).
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A fictional name assigned to give anonymity to a person, group, or place. Pseudonyms are important ways of protecting the identity of research participants while still providing a “human element” in the presentation of qualitative data. There are ethical considerations to be made in selecting pseudonyms; some researchers allow research participants to choose their own.
A requirement for research involving human participants; the documentation of informed consent. In some cases, oral consent or assent may be sufficient, but the default standard is a single-page easy-to-understand form that both the researcher and the participant sign and date. Under federal guidelines, all researchers "shall seek such consent only under circumstances that provide the prospective subject or the representative sufficient opportunity to consider whether or not to participate and that minimize the possibility of coercion or undue influence. The information that is given to the subject or the representative shall be in language understandable to the subject or the representative. No informed consent, whether oral or written, may include any exculpatory language through which the subject or the representative is made to waive or appear to waive any of the subject's rights or releases or appears to release the investigator, the sponsor, the institution, or its agents from liability for negligence" (21 CFR 50.20). Your IRB office will be able to provide a template for use in your study .
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
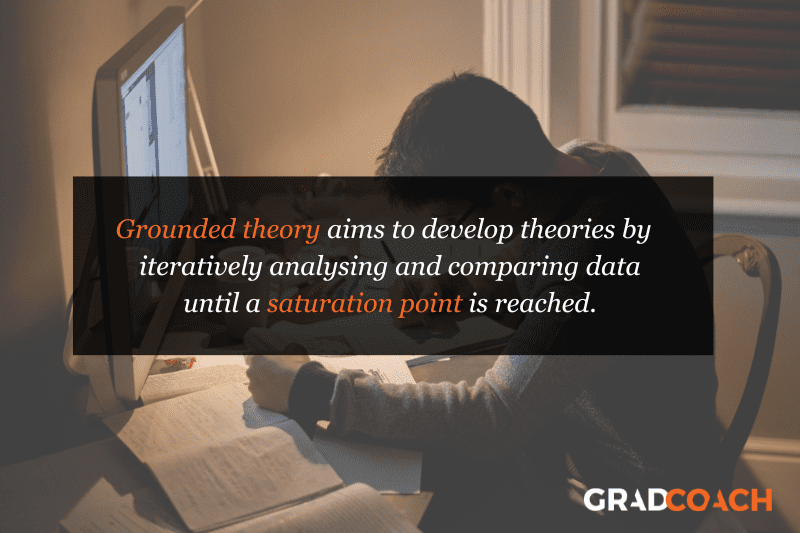
Grounded Theory Research Design
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.
Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
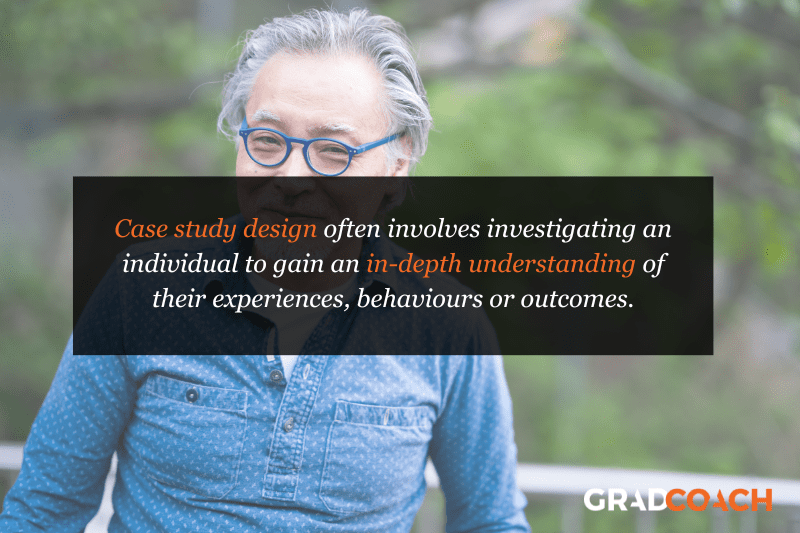
Case Study Design
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

10 Comments
Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
how can I put this blog as my reference(APA style) in bibliography part?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
The Research Setting and Study Design
- First Online: 29 January 2019
Cite this chapter

- David Ian Jeffrey 2
557 Accesses
In this chapter, the choice of a phenomenological approach to explore the students’ views and to gain new understanding about empathy is justified. The medical school setting, curriculum, participants and study design are described. Interpretative phenomenological analysis was the innovative approach used to carry out the data analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bazeley, P., & Jackson, K. (2013). Qualitative Data Analysis with NVIVO . London: Sage.
Google Scholar
Carel, H. (2016). The Phenomenology of Illness . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Cleland, J. (2015). Exploring versus measuring: Considering the fundamental differences between qualitative and quantitative research. In J. Cleland & S. Durning (Eds.), Researching Medical Education. London: Wiley.
Chapter Google Scholar
Crotty, M. (1998). The Foundations of Social Research: Meaning and Perspective in the Research Process . London: Sage.
Finlay, L. (2008). A dance between the reduction and reflexivity: Explicating the “phenomenological psychological attitude”. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 39, 1–32.
Article Google Scholar
Finlay, L. (2013). Unfolding the phenomenological research process: Iterative stages of “seeing afresh”. Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 53, 172–201.
Finlay, L., & Gough, B. (2008). Reflexivity: A Practical Guide for Researchers in Health and Social Sciences. Chichester: Wiley.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006). Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12, 219–245.
Gadamer, H. (1990/1960). Truth and Method. New York: Crossroad.
General Medical Council. (2015). Outcomes for Graduates (Tomorrow’s Doctors) . London: General Medical Council.
Halling, S. (2007). Intimacy, Transcendence, and Psychology: Closeness and Openness in Everyday Life . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Heidegger, M. (1962/1927). Being and Time . Oxford: Blackwell.
Hitchings, R. (2012). People can talk about their practices. Area, 44, 61–67.
Holland, J., Thomson, R., & Henderson, S. (2006). Qualitative Longitudinal Research: A Discussion Paper . London: South Bank University.
Hopkins, R. M., Regehr, G., & Pratt, D. D. (2017). A framework for negotiating positionality in phenomenological research. Medical Teacher, 39, 20–25.
Karnieli-Miller, O., Strier, R., & Pessach, L. (2009). Power relations in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research, 19, 279–289.
Kvale, S., & Brinkmann, S. (2009). Interviews: Learning the Craft of Qualitative Research Interviewing . London: Sage.
Larkin, M., Watts, S., & Clifton, E. (2006). Giving voice and making sense in interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3, 102–120.
Mann, K. V. (2011). Theoretical perspectives in medical education: Past experience and future possibilities. Medical Education, 45, 60–68.
Mann, K., & MacLeod, A. (2015). Constructivism: Learning theories and approaches to research. In J. Cleland & S. Durning (Eds.), Researching Medical Education. London: Wiley.
McLeod, J. (2011). Qualitative Research in Counselling and Psychotherapy. London: Sage.
McMillan, W. (2015). Theory in healthcare education research: The importance of worldview. In J. Cleland & S. Durning (Eds.), Researching Medical Education. London: Wiley.
Murray, S. A., Kendall, M., Carduff, E., Worth, A., Harris, F. M., Lloyd, A., et al. (2009). Use of serial qualitative interviews to understand patients’ evolving experiences and needs. BMJ, 339, b3702.
National Student Survey. (2017). Times Higher Education Supplement [Online]. Available https://www.timeshighereducation.com/student/news/national-student-survey-2017-overall-satisfaction-results . Accessed December 27, 2017.
Paley, J. (2017). Phenomenology as Qualitative Research: A Critical Analysis of Meaning Attribution . London: Taylor & Francis.
Pedersen, R. (2009). Empirical research on empathy in medicine—A critical review. Patient Education and Counseling, 76, 307–322.
Saldana, J. (2013). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers . London: Sage.
Silverman, D. (2013). Doing Qualitative Research: A Practical Handbook . London: Sage.
Smith, J. A., Flowers, P., & Larkin, M. (2009). Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis: Theory, Method and Research . London: Sage.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19, 349–357.
Van Manen, M. (2016). Researching Lived Experience: Human Science for an Action Sensitive Pedagogy . London: Routledge.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
David Ian Jeffrey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to David Ian Jeffrey .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Jeffrey, D.I. (2019). The Research Setting and Study Design. In: Exploring Empathy with Medical Students. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11211-0_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11211-0_2
Published : 29 January 2019
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-11210-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-11211-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Types of Research Designs
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Introduction
Before beginning your paper, you need to decide how you plan to design the study .
The research design refers to the overall strategy and analytical approach that you have chosen in order to integrate, in a coherent and logical way, the different components of the study, thus ensuring that the research problem will be thoroughly investigated. It constitutes the blueprint for the collection, measurement, and interpretation of information and data. Note that the research problem determines the type of design you choose, not the other way around!
De Vaus, D. A. Research Design in Social Research . London: SAGE, 2001; Trochim, William M.K. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
General Structure and Writing Style
The function of a research design is to ensure that the evidence obtained enables you to effectively address the research problem logically and as unambiguously as possible . In social sciences research, obtaining information relevant to the research problem generally entails specifying the type of evidence needed to test the underlying assumptions of a theory, to evaluate a program, or to accurately describe and assess meaning related to an observable phenomenon.
With this in mind, a common mistake made by researchers is that they begin their investigations before they have thought critically about what information is required to address the research problem. Without attending to these design issues beforehand, the overall research problem will not be adequately addressed and any conclusions drawn will run the risk of being weak and unconvincing. As a consequence, the overall validity of the study will be undermined.
The length and complexity of describing the research design in your paper can vary considerably, but any well-developed description will achieve the following :
- Identify the research problem clearly and justify its selection, particularly in relation to any valid alternative designs that could have been used,
- Review and synthesize previously published literature associated with the research problem,
- Clearly and explicitly specify hypotheses [i.e., research questions] central to the problem,
- Effectively describe the information and/or data which will be necessary for an adequate testing of the hypotheses and explain how such information and/or data will be obtained, and
- Describe the methods of analysis to be applied to the data in determining whether or not the hypotheses are true or false.
The research design is usually incorporated into the introduction of your paper . You can obtain an overall sense of what to do by reviewing studies that have utilized the same research design [e.g., using a case study approach]. This can help you develop an outline to follow for your own paper.
NOTE: Use the SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases and the SAGE Research Methods Videos databases to search for scholarly resources on how to apply specific research designs and methods . The Research Methods Online database contains links to more than 175,000 pages of SAGE publisher's book, journal, and reference content on quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research methodologies. Also included is a collection of case studies of social research projects that can be used to help you better understand abstract or complex methodological concepts. The Research Methods Videos database contains hours of tutorials, interviews, video case studies, and mini-documentaries covering the entire research process.
Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2018; De Vaus, D. A. Research Design in Social Research . London: SAGE, 2001; Gorard, Stephen. Research Design: Creating Robust Approaches for the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Leedy, Paul D. and Jeanne Ellis Ormrod. Practical Research: Planning and Design . Tenth edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2013; Vogt, W. Paul, Dianna C. Gardner, and Lynne M. Haeffele. When to Use What Research Design . New York: Guilford, 2012.
Action Research Design
Definition and Purpose
The essentials of action research design follow a characteristic cycle whereby initially an exploratory stance is adopted, where an understanding of a problem is developed and plans are made for some form of interventionary strategy. Then the intervention is carried out [the "action" in action research] during which time, pertinent observations are collected in various forms. The new interventional strategies are carried out, and this cyclic process repeats, continuing until a sufficient understanding of [or a valid implementation solution for] the problem is achieved. The protocol is iterative or cyclical in nature and is intended to foster deeper understanding of a given situation, starting with conceptualizing and particularizing the problem and moving through several interventions and evaluations.
What do these studies tell you ?
- This is a collaborative and adaptive research design that lends itself to use in work or community situations.
- Design focuses on pragmatic and solution-driven research outcomes rather than testing theories.
- When practitioners use action research, it has the potential to increase the amount they learn consciously from their experience; the action research cycle can be regarded as a learning cycle.
- Action research studies often have direct and obvious relevance to improving practice and advocating for change.
- There are no hidden controls or preemption of direction by the researcher.
What these studies don't tell you ?
- It is harder to do than conducting conventional research because the researcher takes on responsibilities of advocating for change as well as for researching the topic.
- Action research is much harder to write up because it is less likely that you can use a standard format to report your findings effectively [i.e., data is often in the form of stories or observation].
- Personal over-involvement of the researcher may bias research results.
- The cyclic nature of action research to achieve its twin outcomes of action [e.g. change] and research [e.g. understanding] is time-consuming and complex to conduct.
- Advocating for change usually requires buy-in from study participants.
Coghlan, David and Mary Brydon-Miller. The Sage Encyclopedia of Action Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2014; Efron, Sara Efrat and Ruth Ravid. Action Research in Education: A Practical Guide . New York: Guilford, 2013; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 18, Action Research. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007; Gorard, Stephen. Research Design: Creating Robust Approaches for the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Kemmis, Stephen and Robin McTaggart. “Participatory Action Research.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. 2nd ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2000), pp. 567-605; McNiff, Jean. Writing and Doing Action Research . London: Sage, 2014; Reason, Peter and Hilary Bradbury. Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2001.
Case Study Design
A case study is an in-depth study of a particular research problem rather than a sweeping statistical survey or comprehensive comparative inquiry. It is often used to narrow down a very broad field of research into one or a few easily researchable examples. The case study research design is also useful for testing whether a specific theory and model actually applies to phenomena in the real world. It is a useful design when not much is known about an issue or phenomenon.
- Approach excels at bringing us to an understanding of a complex issue through detailed contextual analysis of a limited number of events or conditions and their relationships.
- A researcher using a case study design can apply a variety of methodologies and rely on a variety of sources to investigate a research problem.
- Design can extend experience or add strength to what is already known through previous research.
- Social scientists, in particular, make wide use of this research design to examine contemporary real-life situations and provide the basis for the application of concepts and theories and the extension of methodologies.
- The design can provide detailed descriptions of specific and rare cases.
- A single or small number of cases offers little basis for establishing reliability or to generalize the findings to a wider population of people, places, or things.
- Intense exposure to the study of a case may bias a researcher's interpretation of the findings.
- Design does not facilitate assessment of cause and effect relationships.
- Vital information may be missing, making the case hard to interpret.
- The case may not be representative or typical of the larger problem being investigated.
- If the criteria for selecting a case is because it represents a very unusual or unique phenomenon or problem for study, then your interpretation of the findings can only apply to that particular case.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 4, Flexible Methods: Case Study Design. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Greenhalgh, Trisha, editor. Case Study Evaluation: Past, Present and Future Challenges . Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing, 2015; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Stake, Robert E. The Art of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 1995; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Theory . Applied Social Research Methods Series, no. 5. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2003.
Causal Design
Causality studies may be thought of as understanding a phenomenon in terms of conditional statements in the form, “If X, then Y.” This type of research is used to measure what impact a specific change will have on existing norms and assumptions. Most social scientists seek causal explanations that reflect tests of hypotheses. Causal effect (nomothetic perspective) occurs when variation in one phenomenon, an independent variable, leads to or results, on average, in variation in another phenomenon, the dependent variable.
Conditions necessary for determining causality:
- Empirical association -- a valid conclusion is based on finding an association between the independent variable and the dependent variable.
- Appropriate time order -- to conclude that causation was involved, one must see that cases were exposed to variation in the independent variable before variation in the dependent variable.
- Nonspuriousness -- a relationship between two variables that is not due to variation in a third variable.
- Causality research designs assist researchers in understanding why the world works the way it does through the process of proving a causal link between variables and by the process of eliminating other possibilities.
- Replication is possible.
- There is greater confidence the study has internal validity due to the systematic subject selection and equity of groups being compared.
- Not all relationships are causal! The possibility always exists that, by sheer coincidence, two unrelated events appear to be related [e.g., Punxatawney Phil could accurately predict the duration of Winter for five consecutive years but, the fact remains, he's just a big, furry rodent].
- Conclusions about causal relationships are difficult to determine due to a variety of extraneous and confounding variables that exist in a social environment. This means causality can only be inferred, never proven.
- If two variables are correlated, the cause must come before the effect. However, even though two variables might be causally related, it can sometimes be difficult to determine which variable comes first and, therefore, to establish which variable is the actual cause and which is the actual effect.
Beach, Derek and Rasmus Brun Pedersen. Causal Case Study Methods: Foundations and Guidelines for Comparing, Matching, and Tracing . Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2016; Bachman, Ronet. The Practice of Research in Criminology and Criminal Justice . Chapter 5, Causation and Research Designs. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge Press, 2007; Brewer, Ernest W. and Jennifer Kubn. “Causal-Comparative Design.” In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 125-132; Causal Research Design: Experimentation. Anonymous SlideShare Presentation; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 11, Nonexperimental Research: Correlational Designs. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007; Trochim, William M.K. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Cohort Design
Often used in the medical sciences, but also found in the applied social sciences, a cohort study generally refers to a study conducted over a period of time involving members of a population which the subject or representative member comes from, and who are united by some commonality or similarity. Using a quantitative framework, a cohort study makes note of statistical occurrence within a specialized subgroup, united by same or similar characteristics that are relevant to the research problem being investigated, rather than studying statistical occurrence within the general population. Using a qualitative framework, cohort studies generally gather data using methods of observation. Cohorts can be either "open" or "closed."
- Open Cohort Studies [dynamic populations, such as the population of Los Angeles] involve a population that is defined just by the state of being a part of the study in question (and being monitored for the outcome). Date of entry and exit from the study is individually defined, therefore, the size of the study population is not constant. In open cohort studies, researchers can only calculate rate based data, such as, incidence rates and variants thereof.
- Closed Cohort Studies [static populations, such as patients entered into a clinical trial] involve participants who enter into the study at one defining point in time and where it is presumed that no new participants can enter the cohort. Given this, the number of study participants remains constant (or can only decrease).
- The use of cohorts is often mandatory because a randomized control study may be unethical. For example, you cannot deliberately expose people to asbestos, you can only study its effects on those who have already been exposed. Research that measures risk factors often relies upon cohort designs.
- Because cohort studies measure potential causes before the outcome has occurred, they can demonstrate that these “causes” preceded the outcome, thereby avoiding the debate as to which is the cause and which is the effect.
- Cohort analysis is highly flexible and can provide insight into effects over time and related to a variety of different types of changes [e.g., social, cultural, political, economic, etc.].
- Either original data or secondary data can be used in this design.
- In cases where a comparative analysis of two cohorts is made [e.g., studying the effects of one group exposed to asbestos and one that has not], a researcher cannot control for all other factors that might differ between the two groups. These factors are known as confounding variables.
- Cohort studies can end up taking a long time to complete if the researcher must wait for the conditions of interest to develop within the group. This also increases the chance that key variables change during the course of the study, potentially impacting the validity of the findings.
- Due to the lack of randominization in the cohort design, its external validity is lower than that of study designs where the researcher randomly assigns participants.
Healy P, Devane D. “Methodological Considerations in Cohort Study Designs.” Nurse Researcher 18 (2011): 32-36; Glenn, Norval D, editor. Cohort Analysis . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Levin, Kate Ann. Study Design IV: Cohort Studies. Evidence-Based Dentistry 7 (2003): 51–52; Payne, Geoff. “Cohort Study.” In The SAGE Dictionary of Social Research Methods . Victor Jupp, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), pp. 31-33; Study Design 101. Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library. George Washington University, November 2011; Cohort Study. Wikipedia.
Cross-Sectional Design
Cross-sectional research designs have three distinctive features: no time dimension; a reliance on existing differences rather than change following intervention; and, groups are selected based on existing differences rather than random allocation. The cross-sectional design can only measure differences between or from among a variety of people, subjects, or phenomena rather than a process of change. As such, researchers using this design can only employ a relatively passive approach to making causal inferences based on findings.
- Cross-sectional studies provide a clear 'snapshot' of the outcome and the characteristics associated with it, at a specific point in time.
- Unlike an experimental design, where there is an active intervention by the researcher to produce and measure change or to create differences, cross-sectional designs focus on studying and drawing inferences from existing differences between people, subjects, or phenomena.
- Entails collecting data at and concerning one point in time. While longitudinal studies involve taking multiple measures over an extended period of time, cross-sectional research is focused on finding relationships between variables at one moment in time.
- Groups identified for study are purposely selected based upon existing differences in the sample rather than seeking random sampling.
- Cross-section studies are capable of using data from a large number of subjects and, unlike observational studies, is not geographically bound.
- Can estimate prevalence of an outcome of interest because the sample is usually taken from the whole population.
- Because cross-sectional designs generally use survey techniques to gather data, they are relatively inexpensive and take up little time to conduct.
- Finding people, subjects, or phenomena to study that are very similar except in one specific variable can be difficult.
- Results are static and time bound and, therefore, give no indication of a sequence of events or reveal historical or temporal contexts.
- Studies cannot be utilized to establish cause and effect relationships.
- This design only provides a snapshot of analysis so there is always the possibility that a study could have differing results if another time-frame had been chosen.
- There is no follow up to the findings.
Bethlehem, Jelke. "7: Cross-sectional Research." In Research Methodology in the Social, Behavioural and Life Sciences . Herman J Adèr and Gideon J Mellenbergh, editors. (London, England: Sage, 1999), pp. 110-43; Bourque, Linda B. “Cross-Sectional Design.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods . Michael S. Lewis-Beck, Alan Bryman, and Tim Futing Liao. (Thousand Oaks, CA: 2004), pp. 230-231; Hall, John. “Cross-Sectional Survey Design.” In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods . Paul J. Lavrakas, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 173-174; Helen Barratt, Maria Kirwan. Cross-Sectional Studies: Design Application, Strengths and Weaknesses of Cross-Sectional Studies. Healthknowledge, 2009. Cross-Sectional Study. Wikipedia.
Descriptive Design
Descriptive research designs help provide answers to the questions of who, what, when, where, and how associated with a particular research problem; a descriptive study cannot conclusively ascertain answers to why. Descriptive research is used to obtain information concerning the current status of the phenomena and to describe "what exists" with respect to variables or conditions in a situation.
- The subject is being observed in a completely natural and unchanged natural environment. True experiments, whilst giving analyzable data, often adversely influence the normal behavior of the subject [a.k.a., the Heisenberg effect whereby measurements of certain systems cannot be made without affecting the systems].
- Descriptive research is often used as a pre-cursor to more quantitative research designs with the general overview giving some valuable pointers as to what variables are worth testing quantitatively.
- If the limitations are understood, they can be a useful tool in developing a more focused study.
- Descriptive studies can yield rich data that lead to important recommendations in practice.
- Appoach collects a large amount of data for detailed analysis.
- The results from a descriptive research cannot be used to discover a definitive answer or to disprove a hypothesis.
- Because descriptive designs often utilize observational methods [as opposed to quantitative methods], the results cannot be replicated.
- The descriptive function of research is heavily dependent on instrumentation for measurement and observation.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 5, Flexible Methods: Descriptive Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Given, Lisa M. "Descriptive Research." In Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics . Neil J. Salkind and Kristin Rasmussen, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2007), pp. 251-254; McNabb, Connie. Descriptive Research Methodologies. Powerpoint Presentation; Shuttleworth, Martyn. Descriptive Research Design, September 26, 2008; Erickson, G. Scott. "Descriptive Research Design." In New Methods of Market Research and Analysis . (Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2017), pp. 51-77; Sahin, Sagufta, and Jayanta Mete. "A Brief Study on Descriptive Research: Its Nature and Application in Social Science." International Journal of Research and Analysis in Humanities 1 (2021): 11; K. Swatzell and P. Jennings. “Descriptive Research: The Nuts and Bolts.” Journal of the American Academy of Physician Assistants 20 (2007), pp. 55-56; Kane, E. Doing Your Own Research: Basic Descriptive Research in the Social Sciences and Humanities . London: Marion Boyars, 1985.
Experimental Design
A blueprint of the procedure that enables the researcher to maintain control over all factors that may affect the result of an experiment. In doing this, the researcher attempts to determine or predict what may occur. Experimental research is often used where there is time priority in a causal relationship (cause precedes effect), there is consistency in a causal relationship (a cause will always lead to the same effect), and the magnitude of the correlation is great. The classic experimental design specifies an experimental group and a control group. The independent variable is administered to the experimental group and not to the control group, and both groups are measured on the same dependent variable. Subsequent experimental designs have used more groups and more measurements over longer periods. True experiments must have control, randomization, and manipulation.
- Experimental research allows the researcher to control the situation. In so doing, it allows researchers to answer the question, “What causes something to occur?”
- Permits the researcher to identify cause and effect relationships between variables and to distinguish placebo effects from treatment effects.
- Experimental research designs support the ability to limit alternative explanations and to infer direct causal relationships in the study.
- Approach provides the highest level of evidence for single studies.
- The design is artificial, and results may not generalize well to the real world.
- The artificial settings of experiments may alter the behaviors or responses of participants.
- Experimental designs can be costly if special equipment or facilities are needed.
- Some research problems cannot be studied using an experiment because of ethical or technical reasons.
- Difficult to apply ethnographic and other qualitative methods to experimentally designed studies.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 7, Flexible Methods: Experimental Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Chapter 2: Research Design, Experimental Designs. School of Psychology, University of New England, 2000; Chow, Siu L. "Experimental Design." In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 448-453; "Experimental Design." In Social Research Methods . Nicholas Walliman, editor. (London, England: Sage, 2006), pp, 101-110; Experimental Research. Research Methods by Dummies. Department of Psychology. California State University, Fresno, 2006; Kirk, Roger E. Experimental Design: Procedures for the Behavioral Sciences . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2013; Trochim, William M.K. Experimental Design. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Rasool, Shafqat. Experimental Research. Slideshare presentation.
Exploratory Design
An exploratory design is conducted about a research problem when there are few or no earlier studies to refer to or rely upon to predict an outcome . The focus is on gaining insights and familiarity for later investigation or undertaken when research problems are in a preliminary stage of investigation. Exploratory designs are often used to establish an understanding of how best to proceed in studying an issue or what methodology would effectively apply to gathering information about the issue.
The goals of exploratory research are intended to produce the following possible insights:
- Familiarity with basic details, settings, and concerns.
- Well grounded picture of the situation being developed.
- Generation of new ideas and assumptions.
- Development of tentative theories or hypotheses.
- Determination about whether a study is feasible in the future.
- Issues get refined for more systematic investigation and formulation of new research questions.
- Direction for future research and techniques get developed.
- Design is a useful approach for gaining background information on a particular topic.
- Exploratory research is flexible and can address research questions of all types (what, why, how).
- Provides an opportunity to define new terms and clarify existing concepts.
- Exploratory research is often used to generate formal hypotheses and develop more precise research problems.
- In the policy arena or applied to practice, exploratory studies help establish research priorities and where resources should be allocated.
- Exploratory research generally utilizes small sample sizes and, thus, findings are typically not generalizable to the population at large.
- The exploratory nature of the research inhibits an ability to make definitive conclusions about the findings. They provide insight but not definitive conclusions.
- The research process underpinning exploratory studies is flexible but often unstructured, leading to only tentative results that have limited value to decision-makers.
- Design lacks rigorous standards applied to methods of data gathering and analysis because one of the areas for exploration could be to determine what method or methodologies could best fit the research problem.
Cuthill, Michael. “Exploratory Research: Citizen Participation, Local Government, and Sustainable Development in Australia.” Sustainable Development 10 (2002): 79-89; Streb, Christoph K. "Exploratory Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Albert J. Mills, Gabrielle Durepos and Eiden Wiebe, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 372-374; Taylor, P. J., G. Catalano, and D.R.F. Walker. “Exploratory Analysis of the World City Network.” Urban Studies 39 (December 2002): 2377-2394; Exploratory Research. Wikipedia.
Field Research Design
Sometimes referred to as ethnography or participant observation, designs around field research encompass a variety of interpretative procedures [e.g., observation and interviews] rooted in qualitative approaches to studying people individually or in groups while inhabiting their natural environment as opposed to using survey instruments or other forms of impersonal methods of data gathering. Information acquired from observational research takes the form of “ field notes ” that involves documenting what the researcher actually sees and hears while in the field. Findings do not consist of conclusive statements derived from numbers and statistics because field research involves analysis of words and observations of behavior. Conclusions, therefore, are developed from an interpretation of findings that reveal overriding themes, concepts, and ideas. More information can be found HERE .
- Field research is often necessary to fill gaps in understanding the research problem applied to local conditions or to specific groups of people that cannot be ascertained from existing data.
- The research helps contextualize already known information about a research problem, thereby facilitating ways to assess the origins, scope, and scale of a problem and to gage the causes, consequences, and means to resolve an issue based on deliberate interaction with people in their natural inhabited spaces.
- Enables the researcher to corroborate or confirm data by gathering additional information that supports or refutes findings reported in prior studies of the topic.
- Because the researcher in embedded in the field, they are better able to make observations or ask questions that reflect the specific cultural context of the setting being investigated.
- Observing the local reality offers the opportunity to gain new perspectives or obtain unique data that challenges existing theoretical propositions or long-standing assumptions found in the literature.
What these studies don't tell you
- A field research study requires extensive time and resources to carry out the multiple steps involved with preparing for the gathering of information, including for example, examining background information about the study site, obtaining permission to access the study site, and building trust and rapport with subjects.
- Requires a commitment to staying engaged in the field to ensure that you can adequately document events and behaviors as they unfold.
- The unpredictable nature of fieldwork means that researchers can never fully control the process of data gathering. They must maintain a flexible approach to studying the setting because events and circumstances can change quickly or unexpectedly.
- Findings can be difficult to interpret and verify without access to documents and other source materials that help to enhance the credibility of information obtained from the field [i.e., the act of triangulating the data].
- Linking the research problem to the selection of study participants inhabiting their natural environment is critical. However, this specificity limits the ability to generalize findings to different situations or in other contexts or to infer courses of action applied to other settings or groups of people.
- The reporting of findings must take into account how the researcher themselves may have inadvertently affected respondents and their behaviors.
Historical Design
The purpose of a historical research design is to collect, verify, and synthesize evidence from the past to establish facts that defend or refute a hypothesis. It uses secondary sources and a variety of primary documentary evidence, such as, diaries, official records, reports, archives, and non-textual information [maps, pictures, audio and visual recordings]. The limitation is that the sources must be both authentic and valid.
- The historical research design is unobtrusive; the act of research does not affect the results of the study.
- The historical approach is well suited for trend analysis.
- Historical records can add important contextual background required to more fully understand and interpret a research problem.
- There is often no possibility of researcher-subject interaction that could affect the findings.
- Historical sources can be used over and over to study different research problems or to replicate a previous study.
- The ability to fulfill the aims of your research are directly related to the amount and quality of documentation available to understand the research problem.
- Since historical research relies on data from the past, there is no way to manipulate it to control for contemporary contexts.
- Interpreting historical sources can be very time consuming.
- The sources of historical materials must be archived consistently to ensure access. This may especially challenging for digital or online-only sources.
- Original authors bring their own perspectives and biases to the interpretation of past events and these biases are more difficult to ascertain in historical resources.
- Due to the lack of control over external variables, historical research is very weak with regard to the demands of internal validity.
- It is rare that the entirety of historical documentation needed to fully address a research problem is available for interpretation, therefore, gaps need to be acknowledged.
Howell, Martha C. and Walter Prevenier. From Reliable Sources: An Introduction to Historical Methods . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2001; Lundy, Karen Saucier. "Historical Research." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods . Lisa M. Given, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 396-400; Marius, Richard. and Melvin E. Page. A Short Guide to Writing about History . 9th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2015; Savitt, Ronald. “Historical Research in Marketing.” Journal of Marketing 44 (Autumn, 1980): 52-58; Gall, Meredith. Educational Research: An Introduction . Chapter 16, Historical Research. 8th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon, 2007.
Longitudinal Design
A longitudinal study follows the same sample over time and makes repeated observations. For example, with longitudinal surveys, the same group of people is interviewed at regular intervals, enabling researchers to track changes over time and to relate them to variables that might explain why the changes occur. Longitudinal research designs describe patterns of change and help establish the direction and magnitude of causal relationships. Measurements are taken on each variable over two or more distinct time periods. This allows the researcher to measure change in variables over time. It is a type of observational study sometimes referred to as a panel study.
- Longitudinal data facilitate the analysis of the duration of a particular phenomenon.
- Enables survey researchers to get close to the kinds of causal explanations usually attainable only with experiments.
- The design permits the measurement of differences or change in a variable from one period to another [i.e., the description of patterns of change over time].
- Longitudinal studies facilitate the prediction of future outcomes based upon earlier factors.
- The data collection method may change over time.
- Maintaining the integrity of the original sample can be difficult over an extended period of time.
- It can be difficult to show more than one variable at a time.
- This design often needs qualitative research data to explain fluctuations in the results.
- A longitudinal research design assumes present trends will continue unchanged.
- It can take a long period of time to gather results.
- There is a need to have a large sample size and accurate sampling to reach representativness.
Anastas, Jeane W. Research Design for Social Work and the Human Services . Chapter 6, Flexible Methods: Relational and Longitudinal Research. 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press, 1999; Forgues, Bernard, and Isabelle Vandangeon-Derumez. "Longitudinal Analyses." In Doing Management Research . Raymond-Alain Thiétart and Samantha Wauchope, editors. (London, England: Sage, 2001), pp. 332-351; Kalaian, Sema A. and Rafa M. Kasim. "Longitudinal Studies." In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods . Paul J. Lavrakas, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 440-441; Menard, Scott, editor. Longitudinal Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002; Ployhart, Robert E. and Robert J. Vandenberg. "Longitudinal Research: The Theory, Design, and Analysis of Change.” Journal of Management 36 (January 2010): 94-120; Longitudinal Study. Wikipedia.
Meta-Analysis Design
Meta-analysis is an analytical methodology designed to systematically evaluate and summarize the results from a number of individual studies, thereby, increasing the overall sample size and the ability of the researcher to study effects of interest. The purpose is to not simply summarize existing knowledge, but to develop a new understanding of a research problem using synoptic reasoning. The main objectives of meta-analysis include analyzing differences in the results among studies and increasing the precision by which effects are estimated. A well-designed meta-analysis depends upon strict adherence to the criteria used for selecting studies and the availability of information in each study to properly analyze their findings. Lack of information can severely limit the type of analyzes and conclusions that can be reached. In addition, the more dissimilarity there is in the results among individual studies [heterogeneity], the more difficult it is to justify interpretations that govern a valid synopsis of results. A meta-analysis needs to fulfill the following requirements to ensure the validity of your findings:
- Clearly defined description of objectives, including precise definitions of the variables and outcomes that are being evaluated;
- A well-reasoned and well-documented justification for identification and selection of the studies;
- Assessment and explicit acknowledgment of any researcher bias in the identification and selection of those studies;
- Description and evaluation of the degree of heterogeneity among the sample size of studies reviewed; and,
- Justification of the techniques used to evaluate the studies.
- Can be an effective strategy for determining gaps in the literature.
- Provides a means of reviewing research published about a particular topic over an extended period of time and from a variety of sources.
- Is useful in clarifying what policy or programmatic actions can be justified on the basis of analyzing research results from multiple studies.
- Provides a method for overcoming small sample sizes in individual studies that previously may have had little relationship to each other.
- Can be used to generate new hypotheses or highlight research problems for future studies.
- Small violations in defining the criteria used for content analysis can lead to difficult to interpret and/or meaningless findings.
- A large sample size can yield reliable, but not necessarily valid, results.
- A lack of uniformity regarding, for example, the type of literature reviewed, how methods are applied, and how findings are measured within the sample of studies you are analyzing, can make the process of synthesis difficult to perform.
- Depending on the sample size, the process of reviewing and synthesizing multiple studies can be very time consuming.
Beck, Lewis W. "The Synoptic Method." The Journal of Philosophy 36 (1939): 337-345; Cooper, Harris, Larry V. Hedges, and Jeffrey C. Valentine, eds. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis . 2nd edition. New York: Russell Sage Foundation, 2009; Guzzo, Richard A., Susan E. Jackson and Raymond A. Katzell. “Meta-Analysis Analysis.” In Research in Organizational Behavior , Volume 9. (Greenwich, CT: JAI Press, 1987), pp 407-442; Lipsey, Mark W. and David B. Wilson. Practical Meta-Analysis . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2001; Study Design 101. Meta-Analysis. The Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library, George Washington University; Timulak, Ladislav. “Qualitative Meta-Analysis.” In The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis . Uwe Flick, editor. (Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2013), pp. 481-495; Walker, Esteban, Adrian V. Hernandez, and Micheal W. Kattan. "Meta-Analysis: It's Strengths and Limitations." Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 75 (June 2008): 431-439.
Mixed-Method Design
- Narrative and non-textual information can add meaning to numeric data, while numeric data can add precision to narrative and non-textual information.
- Can utilize existing data while at the same time generating and testing a grounded theory approach to describe and explain the phenomenon under study.
- A broader, more complex research problem can be investigated because the researcher is not constrained by using only one method.
- The strengths of one method can be used to overcome the inherent weaknesses of another method.
- Can provide stronger, more robust evidence to support a conclusion or set of recommendations.
- May generate new knowledge new insights or uncover hidden insights, patterns, or relationships that a single methodological approach might not reveal.
- Produces more complete knowledge and understanding of the research problem that can be used to increase the generalizability of findings applied to theory or practice.
- A researcher must be proficient in understanding how to apply multiple methods to investigating a research problem as well as be proficient in optimizing how to design a study that coherently melds them together.
- Can increase the likelihood of conflicting results or ambiguous findings that inhibit drawing a valid conclusion or setting forth a recommended course of action [e.g., sample interview responses do not support existing statistical data].
- Because the research design can be very complex, reporting the findings requires a well-organized narrative, clear writing style, and precise word choice.
- Design invites collaboration among experts. However, merging different investigative approaches and writing styles requires more attention to the overall research process than studies conducted using only one methodological paradigm.
- Concurrent merging of quantitative and qualitative research requires greater attention to having adequate sample sizes, using comparable samples, and applying a consistent unit of analysis. For sequential designs where one phase of qualitative research builds on the quantitative phase or vice versa, decisions about what results from the first phase to use in the next phase, the choice of samples and estimating reasonable sample sizes for both phases, and the interpretation of results from both phases can be difficult.
- Due to multiple forms of data being collected and analyzed, this design requires extensive time and resources to carry out the multiple steps involved in data gathering and interpretation.
Burch, Patricia and Carolyn J. Heinrich. Mixed Methods for Policy Research and Program Evaluation . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2016; Creswell, John w. et al. Best Practices for Mixed Methods Research in the Health Sciences . Bethesda, MD: Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research, National Institutes of Health, 2010Creswell, John W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014; Domínguez, Silvia, editor. Mixed Methods Social Networks Research . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2014; Hesse-Biber, Sharlene Nagy. Mixed Methods Research: Merging Theory with Practice . New York: Guilford Press, 2010; Niglas, Katrin. “How the Novice Researcher Can Make Sense of Mixed Methods Designs.” International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches 3 (2009): 34-46; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Nancy L. Leech. “Linking Research Questions to Mixed Methods Data Analysis Procedures.” The Qualitative Report 11 (September 2006): 474-498; Tashakorri, Abbas and John W. Creswell. “The New Era of Mixed Methods.” Journal of Mixed Methods Research 1 (January 2007): 3-7; Zhanga, Wanqing. “Mixed Methods Application in Health Intervention Research: A Multiple Case Study.” International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches 8 (2014): 24-35 .
Observational Design
This type of research design draws a conclusion by comparing subjects against a control group, in cases where the researcher has no control over the experiment. There are two general types of observational designs. In direct observations, people know that you are watching them. Unobtrusive measures involve any method for studying behavior where individuals do not know they are being observed. An observational study allows a useful insight into a phenomenon and avoids the ethical and practical difficulties of setting up a large and cumbersome research project.
- Observational studies are usually flexible and do not necessarily need to be structured around a hypothesis about what you expect to observe [data is emergent rather than pre-existing].
- The researcher is able to collect in-depth information about a particular behavior.
- Can reveal interrelationships among multifaceted dimensions of group interactions.
- You can generalize your results to real life situations.
- Observational research is useful for discovering what variables may be important before applying other methods like experiments.
- Observation research designs account for the complexity of group behaviors.
- Reliability of data is low because seeing behaviors occur over and over again may be a time consuming task and are difficult to replicate.
- In observational research, findings may only reflect a unique sample population and, thus, cannot be generalized to other groups.
- There can be problems with bias as the researcher may only "see what they want to see."
- There is no possibility to determine "cause and effect" relationships since nothing is manipulated.
- Sources or subjects may not all be equally credible.
- Any group that is knowingly studied is altered to some degree by the presence of the researcher, therefore, potentially skewing any data collected.
Atkinson, Paul and Martyn Hammersley. “Ethnography and Participant Observation.” In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 248-261; Observational Research. Research Methods by Dummies. Department of Psychology. California State University, Fresno, 2006; Patton Michael Quinn. Qualitiative Research and Evaluation Methods . Chapter 6, Fieldwork Strategies and Observational Methods. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002; Payne, Geoff and Judy Payne. "Observation." In Key Concepts in Social Research . The SAGE Key Concepts series. (London, England: Sage, 2004), pp. 158-162; Rosenbaum, Paul R. Design of Observational Studies . New York: Springer, 2010;Williams, J. Patrick. "Nonparticipant Observation." In The Sage Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods . Lisa M. Given, editor.(Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2008), pp. 562-563.
Philosophical Design
Understood more as an broad approach to examining a research problem than a methodological design, philosophical analysis and argumentation is intended to challenge deeply embedded, often intractable, assumptions underpinning an area of study. This approach uses the tools of argumentation derived from philosophical traditions, concepts, models, and theories to critically explore and challenge, for example, the relevance of logic and evidence in academic debates, to analyze arguments about fundamental issues, or to discuss the root of existing discourse about a research problem. These overarching tools of analysis can be framed in three ways:
- Ontology -- the study that describes the nature of reality; for example, what is real and what is not, what is fundamental and what is derivative?
- Epistemology -- the study that explores the nature of knowledge; for example, by what means does knowledge and understanding depend upon and how can we be certain of what we know?
- Axiology -- the study of values; for example, what values does an individual or group hold and why? How are values related to interest, desire, will, experience, and means-to-end? And, what is the difference between a matter of fact and a matter of value?
- Can provide a basis for applying ethical decision-making to practice.
- Functions as a means of gaining greater self-understanding and self-knowledge about the purposes of research.
- Brings clarity to general guiding practices and principles of an individual or group.
- Philosophy informs methodology.
- Refine concepts and theories that are invoked in relatively unreflective modes of thought and discourse.
- Beyond methodology, philosophy also informs critical thinking about epistemology and the structure of reality (metaphysics).
- Offers clarity and definition to the practical and theoretical uses of terms, concepts, and ideas.
- Limited application to specific research problems [answering the "So What?" question in social science research].
- Analysis can be abstract, argumentative, and limited in its practical application to real-life issues.
- While a philosophical analysis may render problematic that which was once simple or taken-for-granted, the writing can be dense and subject to unnecessary jargon, overstatement, and/or excessive quotation and documentation.
- There are limitations in the use of metaphor as a vehicle of philosophical analysis.
- There can be analytical difficulties in moving from philosophy to advocacy and between abstract thought and application to the phenomenal world.
Burton, Dawn. "Part I, Philosophy of the Social Sciences." In Research Training for Social Scientists . (London, England: Sage, 2000), pp. 1-5; Chapter 4, Research Methodology and Design. Unisa Institutional Repository (UnisaIR), University of South Africa; Jarvie, Ian C., and Jesús Zamora-Bonilla, editors. The SAGE Handbook of the Philosophy of Social Sciences . London: Sage, 2011; Labaree, Robert V. and Ross Scimeca. “The Philosophical Problem of Truth in Librarianship.” The Library Quarterly 78 (January 2008): 43-70; Maykut, Pamela S. Beginning Qualitative Research: A Philosophic and Practical Guide . Washington, DC: Falmer Press, 1994; McLaughlin, Hugh. "The Philosophy of Social Research." In Understanding Social Work Research . 2nd edition. (London: SAGE Publications Ltd., 2012), pp. 24-47; Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy . Metaphysics Research Lab, CSLI, Stanford University, 2013.
Sequential Design
- The researcher has a limitless option when it comes to sample size and the sampling schedule.
- Due to the repetitive nature of this research design, minor changes and adjustments can be done during the initial parts of the study to correct and hone the research method.
- This is a useful design for exploratory studies.
- There is very little effort on the part of the researcher when performing this technique. It is generally not expensive, time consuming, or workforce intensive.
- Because the study is conducted serially, the results of one sample are known before the next sample is taken and analyzed. This provides opportunities for continuous improvement of sampling and methods of analysis.
- The sampling method is not representative of the entire population. The only possibility of approaching representativeness is when the researcher chooses to use a very large sample size significant enough to represent a significant portion of the entire population. In this case, moving on to study a second or more specific sample can be difficult.
- The design cannot be used to create conclusions and interpretations that pertain to an entire population because the sampling technique is not randomized. Generalizability from findings is, therefore, limited.
- Difficult to account for and interpret variation from one sample to another over time, particularly when using qualitative methods of data collection.
Betensky, Rebecca. Harvard University, Course Lecture Note slides; Bovaird, James A. and Kevin A. Kupzyk. "Sequential Design." In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010), pp. 1347-1352; Cresswell, John W. Et al. “Advanced Mixed-Methods Research Designs.” In Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social and Behavioral Research . Abbas Tashakkori and Charles Teddle, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2003), pp. 209-240; Henry, Gary T. "Sequential Sampling." In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods . Michael S. Lewis-Beck, Alan Bryman and Tim Futing Liao, editors. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2004), pp. 1027-1028; Nataliya V. Ivankova. “Using Mixed-Methods Sequential Explanatory Design: From Theory to Practice.” Field Methods 18 (February 2006): 3-20; Bovaird, James A. and Kevin A. Kupzyk. “Sequential Design.” In Encyclopedia of Research Design . Neil J. Salkind, ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2010; Sequential Analysis. Wikipedia.
Systematic Review
- A systematic review synthesizes the findings of multiple studies related to each other by incorporating strategies of analysis and interpretation intended to reduce biases and random errors.
- The application of critical exploration, evaluation, and synthesis methods separates insignificant, unsound, or redundant research from the most salient and relevant studies worthy of reflection.
- They can be use to identify, justify, and refine hypotheses, recognize and avoid hidden problems in prior studies, and explain data inconsistencies and conflicts in data.
- Systematic reviews can be used to help policy makers formulate evidence-based guidelines and regulations.
- The use of strict, explicit, and pre-determined methods of synthesis, when applied appropriately, provide reliable estimates about the effects of interventions, evaluations, and effects related to the overarching research problem investigated by each study under review.
- Systematic reviews illuminate where knowledge or thorough understanding of a research problem is lacking and, therefore, can then be used to guide future research.
- The accepted inclusion of unpublished studies [i.e., grey literature] ensures the broadest possible way to analyze and interpret research on a topic.
- Results of the synthesis can be generalized and the findings extrapolated into the general population with more validity than most other types of studies .
- Systematic reviews do not create new knowledge per se; they are a method for synthesizing existing studies about a research problem in order to gain new insights and determine gaps in the literature.
- The way researchers have carried out their investigations [e.g., the period of time covered, number of participants, sources of data analyzed, etc.] can make it difficult to effectively synthesize studies.
- The inclusion of unpublished studies can introduce bias into the review because they may not have undergone a rigorous peer-review process prior to publication. Examples may include conference presentations or proceedings, publications from government agencies, white papers, working papers, and internal documents from organizations, and doctoral dissertations and Master's theses.
Denyer, David and David Tranfield. "Producing a Systematic Review." In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods . David A. Buchanan and Alan Bryman, editors. ( Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2009), pp. 671-689; Foster, Margaret J. and Sarah T. Jewell, editors. Assembling the Pieces of a Systematic Review: A Guide for Librarians . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017; Gough, David, Sandy Oliver, James Thomas, editors. Introduction to Systematic Reviews . 2nd edition. Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2017; Gopalakrishnan, S. and P. Ganeshkumar. “Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis: Understanding the Best Evidence in Primary Healthcare.” Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care 2 (2013): 9-14; Gough, David, James Thomas, and Sandy Oliver. "Clarifying Differences between Review Designs and Methods." Systematic Reviews 1 (2012): 1-9; Khan, Khalid S., Regina Kunz, Jos Kleijnen, and Gerd Antes. “Five Steps to Conducting a Systematic Review.” Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 96 (2003): 118-121; Mulrow, C. D. “Systematic Reviews: Rationale for Systematic Reviews.” BMJ 309:597 (September 1994); O'Dwyer, Linda C., and Q. Eileen Wafford. "Addressing Challenges with Systematic Review Teams through Effective Communication: A Case Report." Journal of the Medical Library Association 109 (October 2021): 643-647; Okoli, Chitu, and Kira Schabram. "A Guide to Conducting a Systematic Literature Review of Information Systems Research." Sprouts: Working Papers on Information Systems 10 (2010); Siddaway, Andy P., Alex M. Wood, and Larry V. Hedges. "How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-analyses, and Meta-syntheses." Annual Review of Psychology 70 (2019): 747-770; Torgerson, Carole J. “Publication Bias: The Achilles’ Heel of Systematic Reviews?” British Journal of Educational Studies 54 (March 2006): 89-102; Torgerson, Carole. Systematic Reviews . New York: Continuum, 2003.
- << Previous: Purpose of Guide
- Next: Design Flaws to Avoid >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Research Fundamentals: Study Design, Population, and Sample Size
- January 2018
- Undergraduate Research in Natural and Clinical Science and Technology (URNCST) Journal 2(1)

- University of Toronto
Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Karen A. Gantsho

- Inger Fabris-Rotelli
- Kharizma Shinta Dhevi Nurlaily

- Andun Sudijandoko

- J LIBR INF SCI
- Williams Ezinwa Nwagwu
- Tingting Wu
- Mi Jeong Kim

- K. Annathurai

- Norsida Hasan
- Glaret Shirley Sinnappan

- Maran Marimuthu
- Abdurrahman Jalil

- Cheng-Li Lin
- Shih-Wei Lai

- J Martin Bland
- Danielle Olds
- Linda H Aiken

- J MED GENET

- Sarah Beinkampen
- Brent Adler
- Gail E. Herman
- J CLIN PSYCHIAT
- Zainab Samaan
- Yvonne K. Lee

- David Meyre
- BRAIN STIMUL
- Jeffrey J Borckardt
- Scott T Reeves
- Peggy E. Kotlowski

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons

Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.3: Experimental Designs and Research Settings
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 10343

- Ellen A. Skinner, Thomas A. Kindermann, Robert W. Roeser, Cathleen L Smith, Andrew Mashburn & Joel Steele
- Portland State University via Portland State University Library
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Of the many features of research designs, the ones relevant to experiments and laboratories refer to the “where” and “how” of collecting data. In order to answer the causal questions of interest to relational meta-theorists, we want to create designs that allow us to make valid inferences about causes and effects as they unfold in the actual contexts of daily life. As usual, we will discover the tensions in our goals, the balances we can strike among them, and the multiple strategies that can be used to create clear lines of sight.
Didn’t we get rid of experiments and labs in 1977 when Bronfenbrenner basically demolished experimental child psychology?
In a way. At the very least it introduced a healthy dose of skepticism about lab settings. Instead of thinking about the lab as a place where the researcher could get more pristine information about his target phenomenon (i.e., the child and his or her behavior), the lab came to be regarded as one context with its own attributes (e.g., novelty) and set of social partners (i.e., the experimenter) that were exerting their own effects on the child. Moreover, contextualists like Bronfenbrenner argued that by removing the child from his or her familiar surroundings and interaction partners, researchers have inadvertently left much of the phenomena of interest behind.
Relational meta-theorists would likely go further. To us, contexts are not just geographic and architectural “settings” in the sense that you can pick people up and “set” them down in new places. Contexts have tentacles that reach out and wind themselves around people, and people have roots that reach down into places. They are connected, interpenetrated even, so that our most likely causal forces, our proximal processes, cannot even be constituted when we look at only one without the other. When researchers split the child from his or her context, it destroys the phenomenon itself, like removing the heart from the body in order to see how it works. You can’t. Once you remove it, it doesn't work any more.
So developmentalists don't conduct research in laboratory settings any more?
Not at all. Contextualists are just very wary about the idea of the “setting” and very aware of what is lost by leaving the “scene of the crime,” that is, the contexts of daily life.
Well, when would relational meta-theorists bring participants to the lab?
One important reason is to measure a construct that you can’t capture outside of the lab. There are some phenomena of great interest that are not visible without specialized instrumentation or procedures that can only be administered in the lab setting. All manner of neurophysiological constructs can only be measured in the lab setting using complex equipment, like fMRI, as well as the assessment of internal states and capacities, like IQ or executive function or delay of gratification. In fact, precisely because people and their contexts are so intertwined, we sometimes bring our participants into the lab to see what they can do without the scaffolds or interference of social partners.
A second important reason is to get more detailed information about proximal processes themselves. In this case, researchers have the task of re-creating the relevant proximal processes under more controlled conditions. They bring both the target person and their social partners into the lab setting, help a proximal process get started, and then are in a position to collect more information they could access in the field. Many studies of relationships include lab components, in which both partners (for examples, spouses, parents and adolescents, or children and their friends) are brought in to participate jointly in (what are hopefully) interesting activities, such as to discuss marital issues, work jointly on teaching and learning tasks, play competitive games, and so on. These exchanges are often videotaped or observed closely, and in some cases, simultaneous physiological measures are collected, such as heart rate or blood pressure.
A third reason researchers might turn to lab settings is to create conditions where they can trigger and then observe interactions that are relatively rare in field settings. For example, research on learned helplessness often brings children into controlled settings where researchers can watch them work with solvable and then with unsolvable puzzles, mazes, and concept tasks, while monitoring their strategies, efforts, and actions over time. (And, of course they always end with success experiences.) Another example is the Strange Situation in which researchers trigger the attachment system in the living-room-like lab setting, by sending in a stranger and asking the caregiver to leave, and then observe the child’s actions.
In all these cases, naturalistic observation may seem preferable, but because of assortativeness and the responsiveness of contexts, social processes can be impossible to tease apart. For example, mastery-oriented kids run into fewer tasks that they cannot solve than helpless-prone kids and so it is harder to catch them in failure situations, and in schools teachers do not assign impossible tasks, and so observers could go for weeks without seeing their phenomena. And, by the way, after about five years of age, kids are busy trying to hide their true reactions to negative events (a phenomenon called “masking”), which makes it harder for observers to actually detect undesired states (like anxiety or boredom).
| Lab experiment | Field experiment | |
| Observation in lab | Field observation |
These sound like access or measurement issues. Where is the causality?
Part of causality is a measurement issue—where you can get the best view of your potential causal processes or your potential effects, and when you get there how deeply you can see into the steps of the process you are trying to understand. So the lab, and all its lovely paraphernalia, often offers the best strategies we have for how to measure our target causes and effects.
Are labs good for other parts of detecting causality?
Indeed they are. They are handy locations for experiments. They cannot be beat for settings in which the researcher has more or less complete control over two key features of the design: (1) the random assignment of participants as to whether they will receive the causal treatment or not; and (2) the administration of the hypothesized causal variable.
Do contextualists care about random assignment?
Do we ever. Remember all those selection effects and assortativeness issues we talked about in previous chapters? Those are shorthand for the huge problems created by the fact that in the contexts of daily life people are not randomly assigned to causal conditions—there are particular personal characteristics that go with people who get in the way of particular causal factors, or who participate in them directly. And so, if we are going to distinguish pre-existing conditions that launched someone on a particular developmental trajectory from the causal factors that we are interested in deciphering, we have to create groups that are “the same on everything” before we start our causal show. Randomized assignment is one strategy to accomplish this, as well as its more systematic options, such as block randomization (randomly assigning different categories of people), matching, propensity score matching, and so on.
Aren’t there better strategies?
Okay, here’s what we would really like to do. We would really like to take our complete sample and expose them to the treatment (the potential causal factor) and see what happens to them, for however long we are interested in detecting effects. Then we would like to load them all into a time machine and take them back to a point in time before the treatment occurred and leave them alone, and see how they would have changed without the treatment. That’s what we are always trying to approximate, a time machine: Let’s see what this groups of people’s development would have been like with this factor and then compare it to the development of the same people without that factor. Pesky time, again. So we have to try to create groups of different people who are the same on everything we can imagine (matching) as well as everything we can’t (random assignment).
Why are we so excited about exact control of the causal factor?
Well, that’s the cool feature of the experimental design. The researcher is like the fairy godmother who waves her magic wand and introduces the potentially new future for the treatment group. So the researcher knows that the treatment group got the potential causal factor, and how much of the factor, and so on (like in a drug trial—the doctor administers the drug and its dosage). And then the researcher has approximately a bazgillion control groups, who got shades of everything but the hypothesized active ingredient (and these can be so creative, the control group with nothing, with only attention, with a visit to the lab but no causal factor, with a causal factor that looks like the actual causal factor but really isn’t, and so on).
Is it easier to control the administration of the causal factor in the lab? So much easier. Once researchers get out in the field, and especially if they decide that the treatment (often as an intervention program) will be administered through intermediaries (like teachers or parents or social workers), it can be a giant headache. There is a whole area of research called “implementation research,” and a focus on “implementation fidelity”—or how the heck you would know and could measure whether the participants actually made contact with the causal factor that you are studying. It’s like doctors who send the treatment pills home with their patients and then hope for the best, but never get to count the pills that are left in the bottle at the end of the trial, and if patients do not improve, they can’t really say whether the drug didn't work or whether the patients just didn't take their pills. Very unsatisfactory from a causal inference perspective.
So we are starting to warm up to labs, right?
Yes, we are regarding them at arm’s length but with respect and appreciation. They can be our ally in measurement and they can give us a leg-up on our simulated time machine for creating groups who are the same, so we can send the different groups on their separate (and with many control groups—their varieties) of carefully calibrated and dosed causal experiences.
And what about experimental designs-- are we starting to warm up to them, too?
Yes, we respect and appreciate them, too. But both lab and experimental studies have serious limitations when it comes to the kinds of questions that contextualists and developmentalists want to answer.
What are those limitations?
Let’s think about three big limitations. First, we already mentioned that labs and fields are not just settings to us. The “field” is an intrinsic and crucial part of the target we are trying to understand, and if we are going to bring our whole phenomenon into the lab, we have to know all the relevant elements of the context and effectively simulate them in the lab. For us, it is an issue of internal validity.
Second, we assume that all our causal factors, that is, our proximal processes, are embedded in contexts and shaped by them. So if we are looking at the functioning of proximal processes in the lab, we can be sure that the lab context is shaping then, which means we can’t be sure that they will operate the same way in the contexts of daily life. So we always have to admit that any causal links we may have watched operating in the lab have to be couched as “can cause” our target and not as “does cause” our target. We have to wait and see if these same processes are operating in the actual contexts that form the natural microsystems for our participants. This is a problem of external validity.
Third, the time span over which developmentalists assume that causal effects accumulate cannot be easily simulated in the lab. The causal processes of interest to developmentalists unfold over months and years and decades, across multiple contexts, so although we can use the lab to measure the long-term effects of causal factors by bringing our participants back to the lab as many times as we want to, if we want to actually look at the causal processes having their effects over months or years, it will be difficult to achieve that in the lab setting.
Please say that these problems are not just for developmentalists.
You are right. They apply to everyone. But there is one problem with typical lab research that in general does not apply to developmentalists.
What is that?
Much of the lab research that is conducted by university researchers uses convenience samples. And who could be more convenient to university researchers than college students? So a great deal of research, for example, in social psychology or on cognition or decision making or perception or education relies on samples of college sophomores—psychology majors, no less. If researchers take their populations seriously and worry about selection effects, then this is a big problem. However, most developmentalists dodge this particular bullet—they do not imagine that the average college sophomore could be considered a reasonable facsimile for an 8-year-old or an 80-year-old or a parent with three children or a person who has experienced the Great Depression. So developmentalists who work in the lab typically import participants from their actual target populations to the laboratory setting.
Then what is the fatal flaw with experimental research? As noted by many methodologists, the seemingly insurmountable problem with experimental designs is that it is not possible to randomly assign or manipulate the causal forces that are of biggest interest to developmentalists. No one can randomly assign their participants to a particular age group (“I have flipped a coin and you will be in the five-year-old group” “Oh no, I wanted to be 10!”) or to a particular cohort or developmental history.
In fact, most of the causal factors that are of interest to us can’t ethically be manipulated at all—the happy single-parent family or the unhappily married parents, the delinquent or theatre-obsessed friends, school failure or indifference, peer rejection or popularity, high stress reactivity, dangerous neighborhoods, perfect pitch, or height. Before you ask, we will just add that this same issue applies to all areas of psychology. Many applied problems cannot be manipulated—divorce, PTSD, dangerous job conditions, psychopathology, work-family conflict, serious medical diagnosis, intimate partner violence, and so on. So there are limits to how much experimental designs can help applied researchers study the conditions and causes that most interest us.
| Rutter, Pickles, Murray, & Eaves (2001) on the interplay of risk and protective factors in designs for testing complex hypotheses about the causal effects of environmental risk: It is evident from numerous reviews that causal processes usually involve a complex interplay among risk and protective mechanisms, with indirect chain reactions, bidirectional influences, gene-environment interactions, and synergism between chronic and acute risk factors the rule rather than the exception…[T]he interplay concept means that there are certain further design implications, of which we emphasize four as especially important. First, putative risk variables must we conceptualized and measured in sufficiently broad terms to encompass the risks that may rely on a combination of factors. The extent to which that is the case, plus the delineation of which elements carry the main risk, is better done by subtraction techniques than by the addition of micorelements, each of which on its own might carry no significant risk. Second, Designs, samples, and analytic techniques must be chosen on the basis that they can test for the possibility of both gene- environment interactions and personenvironment interactions based on the effects on the person of prior experiences or of maturational features or gender… Third, appropriate designs must be used to examine the ways in which different forms of gene-environment interactions and person- environment correlations play a part in the causal processes associated with environmental risk mediation… Fourth, attention must be paid to the phenomenon of resilience, meaning a degree of resistance to psychosocial adversities, operationally defined as relatively good outcomes despite experiencing major environmental risks… The reality of the phenomenon has been well demonstrated, but the protective factors have been little explored as yet despite their potential implications for prevention and intervention” (Rutter et al, 2001, p. 297-298. |
Wait! What about optimization studies?
Yes, indeed. Those are rightly considered field experiments, and they can even be conducted as randomized control trials (the gold standard!). And it is correct that we can ethically study any old target we please as long as we are trying to optimize development—to remediate unfavorable developmental trajectories, to maintain resilient ones, and in general to prevent adverse and promote healthy development. So we can learn a great deal and do a great deal of good by trying to create and study interventions designed to optimize development.
At the same time, such optimization studies have two important limitations for developmentalists. First, one thing that such studies cannot tell us is what caused these unhealthy pathways of development in the first place, any more than studying aspirin can tell us what causes headaches or how to prevent them. So additional work will always be needed to fill in the causal puzzle of the factors that contribute to and maintain non-optimal development or lead to psychopathology. It seems that such studies would be essential to prevention efforts.
Second, we have a bone to pick with randomized control trials (RCT) as the ideal methodology for studying causal relationships. As you may know, this methodology was borrowed from clinical trials of medical treatments, and it is cool in many ways. It has time in its design, which is always welcome news to developmentalists. RCTs compare (at least) two groups who should be equivalent to each other (based on random assignment), one of which has received the drug and the other probably a placebo, so that researchers can examine the effects of the drug over and above the effects of knowing that one is being treated. Then after a sufficient amount of time for the drug to do its work, changes in the treatment and control group can be compared over however many time points the design includes.
This sounds very time-machine-esque. What is the problem?
The problem is that, at the end of the day, the only thing that this design can tell you is “yes” or “no,” that is, the only information it yields is whether the two groups are different. You can add many features, for example, many indicators of disease or health, you can measure dosage and its effects, over several time periods, and so on. However, developmentalists would say that, after all this work, the only thing we have in our hands is a causal description but not the thing that we most want, that is, a causal explanation. For the drug companies, everything they want to know about causal explanations is contained in the drug itself; to the extent that they care about how the drug works, its mechanisms of effects have already been studied (and of course, we take many drugs that are effective, but whose mechanisms of effects are unknown).
But as developmentalists, our interventions contain hundreds of potential active ingredients. And so we want to poke our heads in under the hood and look all around, watching the cogs engage and the wheels turn. (Whoops! Wrong metaphor for relational meta-theorists!) We want to watch the tennis game or the dance, and see who is hitting the ball the hardest and how the players adapt to each other’s style over time and who is playing the music. In other words, we are on the trail of causal explanation and so we can’t really be satisfied with “yes” or “no.” We will forever be asking “why?” or “why not?” and especially “how did that work?”. So we will always be supplementing experimental and lab studies, and even RCT studies, with studies using designs that can provide us with more complex process-oriented accounts of the multiple causes of differential developmental trajectories and transformations.
| Laboratory Experiment | Advantages | Control and precision Unambiguous causal inference. |
| Precise control of hypothesized causal factor. | ||
| Precise measure of hypothesized effect. | ||
| Disadvantages | Artificiality | |
| May change phenomena. | ||
| Limited to “can cause” versus “does cause” causal conclusions. | ||
| May or may not work in actual contexts. | ||
| Most potential causal factors cannot be manipulated. | ||
| Naturalistic Laboratory Study | Advantages | Precision Measure constructs that are “below the surface” (e.g., neurophysiology, capacities, knowledge). |
| Disadvantages | Distortion | |
| Splitting of person from context may have destroyed causal factors. | ||
| Hard to locate “active ingredient” of causal packages. | ||
| Artificiality and novelty of context, instrument, or trigger distorts causal phenomena. | ||
| Field Experiment | Advantages | Control and Actual context Potential for causal inference. |
| Potential to see how causes operate in situ. | ||
| Potential to see effects in situ. | ||
| Disadvantages | Messiness | |
| Hard to precisely control the implementation of the potential causal factor. | ||
| Especially if delivery agents are also naturalistic (i.e., parents, teachers, social workers) | ||
| Limited to “can cause” versus “does cause” causal conclusions. | ||
| Most potential causal factors cannot be manipulated. | ||
| Limited account of causal process. | ||
| Naturalistic Field Study | Advantages | Authenticity Whole phenomena is intact. |
| Can discover causes that were not expected. | ||
| Disdvantages | Murkiness | |
| Hard to specify “active ingredient” of causal packages. | ||
| Impossible to control all selection effects. | ||
| Limited to “may cause” versus “does cause” causal conclusions. |
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.9(4); Oct-Dec 2018
Study designs: Part 1 – An overview and classification
Priya ranganathan.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Rakesh Aggarwal
1 Department of Gastroenterology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
There are several types of research study designs, each with its inherent strengths and flaws. The study design used to answer a particular research question depends on the nature of the question and the availability of resources. In this article, which is the first part of a series on “study designs,” we provide an overview of research study designs and their classification. The subsequent articles will focus on individual designs.
INTRODUCTION
Research study design is a framework, or the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research problem.
Research study designs are of many types, each with its advantages and limitations. The type of study design used to answer a particular research question is determined by the nature of question, the goal of research, and the availability of resources. Since the design of a study can affect the validity of its results, it is important to understand the different types of study designs and their strengths and limitations.
There are some terms that are used frequently while classifying study designs which are described in the following sections.
A variable represents a measurable attribute that varies across study units, for example, individual participants in a study, or at times even when measured in an individual person over time. Some examples of variables include age, sex, weight, height, health status, alive/dead, diseased/healthy, annual income, smoking yes/no, and treated/untreated.
Exposure (or intervention) and outcome variables
A large proportion of research studies assess the relationship between two variables. Here, the question is whether one variable is associated with or responsible for change in the value of the other variable. Exposure (or intervention) refers to the risk factor whose effect is being studied. It is also referred to as the independent or the predictor variable. The outcome (or predicted or dependent) variable develops as a consequence of the exposure (or intervention). Typically, the term “exposure” is used when the “causative” variable is naturally determined (as in observational studies – examples include age, sex, smoking, and educational status), and the term “intervention” is preferred where the researcher assigns some or all participants to receive a particular treatment for the purpose of the study (experimental studies – e.g., administration of a drug). If a drug had been started in some individuals but not in the others, before the study started, this counts as exposure, and not as intervention – since the drug was not started specifically for the study.
Observational versus interventional (or experimental) studies
Observational studies are those where the researcher is documenting a naturally occurring relationship between the exposure and the outcome that he/she is studying. The researcher does not do any active intervention in any individual, and the exposure has already been decided naturally or by some other factor. For example, looking at the incidence of lung cancer in smokers versus nonsmokers, or comparing the antenatal dietary habits of mothers with normal and low-birth babies. In these studies, the investigator did not play any role in determining the smoking or dietary habit in individuals.
For an exposure to determine the outcome, it must precede the latter. Any variable that occurs simultaneously with or following the outcome cannot be causative, and hence is not considered as an “exposure.”
Observational studies can be either descriptive (nonanalytical) or analytical (inferential) – this is discussed later in this article.
Interventional studies are experiments where the researcher actively performs an intervention in some or all members of a group of participants. This intervention could take many forms – for example, administration of a drug or vaccine, performance of a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure, and introduction of an educational tool. For example, a study could randomly assign persons to receive aspirin or placebo for a specific duration and assess the effect on the risk of developing cerebrovascular events.
Descriptive versus analytical studies
Descriptive (or nonanalytical) studies, as the name suggests, merely try to describe the data on one or more characteristics of a group of individuals. These do not try to answer questions or establish relationships between variables. Examples of descriptive studies include case reports, case series, and cross-sectional surveys (please note that cross-sectional surveys may be analytical studies as well – this will be discussed in the next article in this series). Examples of descriptive studies include a survey of dietary habits among pregnant women or a case series of patients with an unusual reaction to a drug.
Analytical studies attempt to test a hypothesis and establish causal relationships between variables. In these studies, the researcher assesses the effect of an exposure (or intervention) on an outcome. As described earlier, analytical studies can be observational (if the exposure is naturally determined) or interventional (if the researcher actively administers the intervention).
Directionality of study designs
Based on the direction of inquiry, study designs may be classified as forward-direction or backward-direction. In forward-direction studies, the researcher starts with determining the exposure to a risk factor and then assesses whether the outcome occurs at a future time point. This design is known as a cohort study. For example, a researcher can follow a group of smokers and a group of nonsmokers to determine the incidence of lung cancer in each. In backward-direction studies, the researcher begins by determining whether the outcome is present (cases vs. noncases [also called controls]) and then traces the presence of prior exposure to a risk factor. These are known as case–control studies. For example, a researcher identifies a group of normal-weight babies and a group of low-birth weight babies and then asks the mothers about their dietary habits during the index pregnancy.
Prospective versus retrospective study designs
The terms “prospective” and “retrospective” refer to the timing of the research in relation to the development of the outcome. In retrospective studies, the outcome of interest has already occurred (or not occurred – e.g., in controls) in each individual by the time s/he is enrolled, and the data are collected either from records or by asking participants to recall exposures. There is no follow-up of participants. By contrast, in prospective studies, the outcome (and sometimes even the exposure or intervention) has not occurred when the study starts and participants are followed up over a period of time to determine the occurrence of outcomes. Typically, most cohort studies are prospective studies (though there may be retrospective cohorts), whereas case–control studies are retrospective studies. An interventional study has to be, by definition, a prospective study since the investigator determines the exposure for each study participant and then follows them to observe outcomes.
The terms “prospective” versus “retrospective” studies can be confusing. Let us think of an investigator who starts a case–control study. To him/her, the process of enrolling cases and controls over a period of several months appears prospective. Hence, the use of these terms is best avoided. Or, at the very least, one must be clear that the terms relate to work flow for each individual study participant, and not to the study as a whole.
Classification of study designs
Figure 1 depicts a simple classification of research study designs. The Centre for Evidence-based Medicine has put forward a useful three-point algorithm which can help determine the design of a research study from its methods section:[ 1 ]

Classification of research study designs
- Does the study describe the characteristics of a sample or does it attempt to analyze (or draw inferences about) the relationship between two variables? – If no, then it is a descriptive study, and if yes, it is an analytical (inferential) study
- If analytical, did the investigator determine the exposure? – If no, it is an observational study, and if yes, it is an experimental study
- If observational, when was the outcome determined? – at the start of the study (case–control study), at the end of a period of follow-up (cohort study), or simultaneously (cross sectional).
In the next few pieces in the series, we will discuss various study designs in greater detail.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 13 July 2022
Goal setting with young people for anxiety and depression: What works for whom in therapeutic relationships? A literature review and insight analysis
- Jenna Jacob ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1006-1547 1 ,
- Milos Stankovic 2 ,
- Inga Spuerck 2 &
- Farhad Shokraneh 3
BMC Psychology volume 10 , Article number: 171 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
15k Accesses
7 Citations
21 Altmetric
Metrics details
Goal setting and goal-focused work is widely used in young people’s mental health settings. However, little is known about how, why or for whom this is helpful. This study aims to explore the mechanisms of collaborative goal setting as part of therapeutic relationships: is it helpful for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, how and why/not, for whom, and under what circumstances?
Online database searches generated 10,907 records. Seven unique studies are included, combined with insight analysis from directed discussions with international advisors with lived experience of anxiety and/or depression and therapy (N = 8; mean age = 20.8), and mental health academics/clinicians (N = 6).
Findings are presented as a narrative synthesis and suggest that goal setting is helpful to young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression because it helps build good therapeutic relationships through open communication and building trust. Goal setting helps make things more manageable, enabling young people to feel supported and have ownership of their care. Individual preferences, or high levels of distress, trauma, low confidence, hopelessness, negative past experiences of goal setting, perfectionism, and rumination are considered limiting factors to goal setting. Additionally, contextual factors including country and long-term therapy are explored.
Whilst the resultant sample is small, emphasis on the voices of young people in the research is both prominent and of paramount importance. Several key literature gaps are identified, including evidenced links to the reduction in symptoms. Priority must be given to researching unhelpful mechanisms of goal setting for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, to avoid any potential iatrogenic effects.
Peer Review reports
Collaborative goal setting within therapeutic mental health settings refers to agreements made between young people and practitioners about specific therapy areas of focus: topics of personalised and meaningful outcome. Goals are concrete representations of intended endpoints, which fill the perceived gap between the current and desired end state [ 1 ]. Goals are usually formulated at the start of therapeutic interventions through a series of discussions. These differ from academic, physical rehabilitation, or general life goals, although there could be overlap. Progress towards these agreed goals may then be tracked over time, often through ratings on numerical scales, and there are tools available to support this. For example, the Goal Based Outcome tool (GBO; [ 2 ]) which comprises setting up to three goals and scoring progress between 0 and 10, is widely used to track progress against goal setting in youth mental health settings. Whilst goal tracking may lead to a shift in practitioners’ work to be goal focused [ 3 ], goals may also sit alongside usual clinical work, to track progress [ 4 ]. Goals set in therapy tend to be focused and specific, e.g., to deal with something in the immediacy, like a phobia [ 5 ], but it is important that these goals attain to more global goals [ 6 ], or are viewed as a “means to an end”.
Goals may take time to set, and can change and become more specific during the therapeutic process, for example, at the beginning of contact with a practitioner, a young person might have a general goal like “to feel less depressed”, but over time the young person, along with the practitioner, may learn more about the mechanisms behind the depression and may define more precise goals like “being able to stop negative thinking” or “being able to cope with flashbacks”. The types of phrases used by practitioners to help young people define goals may include: “what do you want to be different?”, “what will you get off your back?”, “where do you want to get to?”, and “how do you want things to change?” [ 4 , 6 ].
Goal setting and tracking in therapeutic settings is grounded in motivation theory [ 7 , 8 , 9 ] such that working towards goals is a continuous feedback loop which builds on self-efficacy, self-determination and motivation to continue to strive towards goals, acting as a self-regulation strategy [ 10 , 11 ]. Goal setting may be more feasible or acceptable to individuals with particular personality traits e.g., individuals who attribute successes and failures to external factors are less likely to find meaning in striving towards goals than those who attribute successes and failures to their own actions [ 12 ].
Further, young people have described recovery from depression as nested within relationships (e.g., [ 13 ]), portraying recovery as an intentional process, contingent on shared goals and joint action in relationships [ 14 ]. Good therapeutic relationships are considered a key element of effective therapy [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. Also known as working relationships, or working/therapeutic alliance, this refers to the connection, bond or partnership between the young person and practitioner. Three key elements of therapeutic alliance have been identified in the literature: bond, tasks, and goals [ 19 ]. In a recent review of the effects of cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, three studies reported small-to-medium effect sizes for the correlational relationship between therapeutic alliance and symptom reduction [ 20 ]. This provides limited evidence linking goal collaboration to reduced anxiety/depression symptoms for young people, despite fair evidence supporting links between goal collaboration and positive adult anxiety and depression outcomes [ 21 ]. It is argued that goal agreement is a fundamental element missing from much work with young people, and it has been referred to as a “social contract” [ 22 ]. This emphasis on relationships is particularly important when working with young people with acute, or multifarious difficulties, where relationships are complex, difficult to develop and maintain (e.g., [ 23 ]).
Existing evidence suggests that there are certain elements of mental health support for young people that are effective, but there is a lack of identification and knowledge about mechanisms to refine and improve this support [ 24 ]. Specifically, there is a paucity of research exploring the mechanisms underpinning why goal setting may be helpful for some young people, and not others. There are likely to be confounding variables which interplay the effectiveness of goals, depression and/or anxiety, cognition, and motivation, yet there is little research that has explored this in clinical settings with young people.
The aim of this study is to summarise existing literature, supplemented by discussions with international advisors to contextualise and aid interpretation of the findings. The research question is:
“Is collaborative goal setting helpful or unhelpful to young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, as an element of therapeutic relationships? a. Why/why not and how? b. For whom? c. Under what circumstances?”
A mixed methodological approach combined reviews of peer-reviewed, grey literature and additional sources (e.g., websites), with consultation with experts by experience. The risk of expert view biasing the findings was mitigated via the validating steps outlined below. The study was designed by the lead researcher, and other researchers in the team, in collaboration with the peer researchers.
Whilst it is acknowledged that there are important outcome areas such as quality of life and existential factors, aside from symptom reduction, the focus of this study was to specifically explore the research questions in relation to potential anxiety and depression symptom reduction. Anxiety and depression were focused on as the most common mental health difficulties worldwide. This focus on medicalised symptomology differs from quality of life, which is a multi-dimensional construct comprised of several domains, such as psychological, physical, and social wellbeing. Anxiety, depression, therapeutic relationships, and goal progress are routinely measured using self- and proxy-reported outcome measures, with numerical rating scales. It was anticipated that the research question would not be adequately explored through findings from outcome measures alone. Based on some initial scoping work, we determined that there would be more evidence on the effectiveness of goal setting and tracking via qualitative enquiry, including narratives. The exploration of the nuances identified in the research question was key to the study, and so it was important to give precedence to young people’s voices through existing research and youth advisors, combined with findings from any relevant supporting measures. Such explorations would not be possible through quantitative enquiry of outcome measure data.
Goal setting alongside usual clinical work and goals work (goal focused interventions) were differentiated from implicit goal-oriented practice, non-directive approaches and paternalistic approaches to support in this study. This meant that to be included in the literature synthesis, goals needed to be explicitly identified as an approach to progress tracking, and/or informing the work. This study also focused on individual settings, and whilst these relationships may include parents/carers in a triad, the primary focus was on the relationship built between the practitioner and the young person. This was due to the complexities and potential dilution of agreeing goals and developing therapeutic relationships in group work and with parents/carers in addition. Ethical approval was not required because this study did not involve collection nor analysis of primary data, and youth advisors were consulted on in the capacity of being part of the advisory group, rather than within the capacity of research participants [ 25 ].
Literature review
First, search terms and inclusion and exclusion criteria were agreed in collaboration with the academic/clinical and youth advisors (See Additional file 1 : Appendix 1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria and Search Strategies). The project was registered with PROSPERO (number: CRD42021259611).
Second, searches of ten online databases were conducted (PsycINFO (OVID), MEDLINE (OVID), EMBASE (OVID), Web of Science core collection, current contents connect, SciELOCitation Index, Cochrane Library of Systematic Reviews, CINAHL (EBSCO), ERIC (EBSCO), and child and adolescent studies (EBSCO)). The search strategy developed for each database comprised three concepts: anxiety and/or depression (condition), goals (intervention) and therapeutic alliance or general views on goal setting, e.g., perspective, view, narrative (intervention/outcome). Searches were restricted to the past 20 years (2000-present). Citation tracking of included papers was performed. Retrieved hits were exported to EndNote 20 [ 26 ], Rayyan [ 27 ] and Excel for title/abstract screening.
Third, two researchers (FS, JJ) independently screened titles and abstracts. Where one researcher (JJ) was an author in retrieved studies, screening was conducted by the other researcher (FS), to ensure unbiased screening. Fourth, two researchers (JJ, IS) explored resultant literature main texts, extracting and synthesising relevant information. Key literature identified by researchers and advisors was added. The quality of the studies was assessed using criteria for qualitative studies ([ 28 ]; See Additional file 1 : Appendix 2 Core Criteria for Quality Assessment of Qualitative Studies).
Grey literature search
Google and Google Scholar title search, Google Books, PsycEXTRA, PsyArXiv, and ProQuest Dissertations and Theses were used. Google's Site Search was used to search American Psychological Association, British Psychological Society, Australian Psychological Society, European Federation of Psychologists' Associations, International Association of Applied Psychology, Association for Psychological Science, International Union of Psychological Science, Canadian Psychological Association, and UN-affiliated websites (.int domains). To identify more relevant literature, ResearchRabbit.ai was used to track the citations to the included studies. As a result of Google title search, websites were identified and browsed. The searches were restricted to those: (1) written in English, (2) published from January 2000 to August 2021, (3) focused on goal setting with young people experiencing mental health difficulties. Two researchers (FS, JJ) independently screened titles and abstracts of the resultant sources for relevance.
Insight analysis
An advisory group was formed at the study’s outset, comprising: (1) young people with lived experience of anxiety and/or depression and therapy (N = 8; age range 15–26 years; mean age = 20.8; female (includes transgender) N = 5; and male (includes transgender) N = 3; located in Brazil, Pakistan, Spain, Turkey, and UK); and (2) academics and clinicians (N = 6; female N = 1, male N = 5; located in Norway and UK). Criteria for youth advisors to take part where that they were around the age of interest (14–24 years) and had lived experience of anxiety and/or depression and had previously -or currently-experienced receiving a mental health intervention. Youth advisors’ experience of anxiety and/or depression was balanced across advisors. Youth advisors were recruited via adverts circulated by a European network of peer advisors with international reach, and signed an agreement at the outset of the project, by way of consent to participate, which included specific duties and responsibilities of what would be expected of them, as well as hours and reimbursement details. For those under 18 years old, parent/carer consent and agreements were gained. One-to-one meetings between each youth advisor and the participation lead for the study were conducted before and after the study took place. A written agreement was made between the lead research organisation, and the participation organisation which facilitates the network of peer advisors.
Academic/clinical advisors were experienced and specialised in goals work and were recruited via existing networks. Criteria for academic/clinical advisors were that they had research and/or clinical experience in the field of mental health goal setting with young people (academic N = 6; clinical N = 4; categories not mutually exclusive). Written agreements were made between the lead research organisation, and each academic/clinical advisor.
Directed discussions were held at six advisory group meetings (two academic/clinical and four youth) facilitated by two researchers (JJ, MS) and conducted in English. All advisors spoke English, but time was given in the meetings to check understanding, as English was not a native language for many. The academic/clinical and youth advisors met separately, enabling the youth advisors to share openly with their peers. These discussions focused on the research question and drawing inferences about resultant findings, as well as appraising the evidence to identify key literature gaps. The summary of findings from the literature review was presented via PowerPoint to the advisors. The questions asked were broadly: is setting goals an important part of the relationship with the therapist and why/not; do these findings align with your experiences; is there anything you can think of that has not been considered; are there any elements of these findings that do not make sense in your experience; how do you interpret and understand these findings within the context of your own experience? Youth advisors were asked additional questions about the nature of language, for example, what do you think about the term “goal”? Is it the word you use, is it understandable, how does it translate to your national languages?. Field notes were taken, alongside notes in advisors’ own words on the JamBoard interactive workspace, allowing for anonymous contributions. Analysis comprised four stages. First, one researcher (MS) organised field notes and comments into a narrative summary. Second, one researcher (JJ) used the nuanced elements of the research question to organise the summary. Third, feedback was sought from advisors to evaluate and assess whether it was a true reflection of the discussions. Fourth, one researcher (JJ) refined and renamed the themes.
Online searches generated 10,907 records. Ten potentially eligible studies were identified. Upon screening full texts, seven unique studies met the selection criteria (See Fig. 1 and Table 1 ).
PRISMA flow chart of the study selection process. From: Page, M.J., McKenzie, J.E., Bossuyt, P.M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T.C., Mulrow, C.D. et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372(n71)
Included studies comprised three narrative case studies [ 29 , 30 , 31 ] a randomised control trial [ 32 ]; a narrative review [ 33 ] a practitioners’ guidance document [ 34 ]; and a naturalistic study [ 35 ]. Critical appraisal of the evidence (Table 1 ) demonstrates that caution must be exercised when considering the findings. The main strength of the included studies is the voice of young people through verbatim quotes, and for some, strong consideration of the researchers’ impact. However, less strength is attributed to the dependability or generalisability of the findings, mainly due to the high proportion of small-and-homogenous samples. The advisors’ discussion summaries were organised into themes within the nuances of the research question: Why/why not and how? For whom? Under what circumstances?”, and presented as a narrative synthesis.
Why/why not and how (mechanisms)
A conduit for open communication.
Six studies described collaborative goal setting as a conduit for communication [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 ]. Specifically, agreement on goals leads to open communication, a shared understanding of difficulties and ways forward [ 29 , 31 , 35 ]. Formulating goals was described as key to helping young people to feeling understood, valued and that practitioners are listening to them [ 33 , 34 , 35 ]. Collaborative goal setting enables young people and practitioners to make genuine disclosures, not necessarily otherwise possible [ 30 ] and facilitates mutual support [ 31 ].
Both academic/clinical and youth advisors said that open communication and trust were key, broadly agreeing that goal setting could be helpful to support building trusting relationships. It was agreed that collaboratively agreeing goals may take time and should not happen immediately. Rather, practitioners should work flexibly, aiming to understand what is comfortable for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression. Some youth advisors said that relationships need to be built first, with trust established prior to goal setting, particularly when goal setting feels complicated. It was agreed by youth and academic/clinical advisors that goal setting should be led by young people and guided by practitioners, sharing responsibility. Youth advisors considered open communication the most crucial factor in therapy, with a sense that much therapeutic work cannot take place without it.
Feel supported and involved
Young people value receiving support to split actions into smaller manageable steps, with encouragement from practitioners stimulating validation that their goals are achievable ([ 35 ], and youth advisors). Being given choice about goal content and how this translates into the options for care was identified as an important part of the process in the literature [ 35 ]. Evidence suggests that this leads to a sense of autonomy and control over what happens to young people and enables them to feel involved in the process and increases engagement [ 30 , 33 , 35 ]. This was not directly addressed by the academic/clinical advisors in their discussions.
Nature of difficulties
All seven studies, and youth and academic/clinical advisors, suggested that goal setting was a helpful element of therapeutic relationships for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, and more broadly with other undefined presenting difficulties. Both academic/clinical and youth advisors agreed that there was no need to separate specific attributes of anxiety or depression, due in part, to high proportions of comorbidity.
Age, and previous experiences
Three studies described difficulties for young people engaging in goal setting [ 32 , 33 , 34 ]. These were: age-appropriate quests for independence interfering with establishing collaborative relationships with adults [ 32 ]; significant and repeated traumas impacting development, relationships and challenges ordering thoughts, particularly within the context of long-term therapy [ 34 ]; low confidence or feelings of hopelessness; and poor previous experiences of goal setting [ 33 ]. Youth advisors agreed that previous life experiences were important, e.g., views of goal setting in therapeutic settings were impacted by how successful they had been in achieving past goals, regardless of goal type. Academic/clinical advisors agreed that personal factors such as previous experiences and factors surrounding—or leading to—difficulties, may lead to challenges setting goals in the first instance.
Levels of distress, personality traits and preferences
Youth and academic/clinical advisors suggested that specific unhelpful elements may depend on the young person, and sometimes levels of distress, rather than the nature of difficulties. Some youth advisors expressed preferences for practitioner-directed work, particularly in times of high distress, e.g.,: “If I’m going through something very bad, I can be very frustrated/sad so I can’t think clear” (youth advisor) . It was also agreed that goals may exacerbate anxiety, particularly at times of overwhelm, whilst for others this could be a helpful anxiety reduction approach, e.g., in exposure therapy. Youth advisors said that ensuring goals are achievable is key to building good therapeutic relationships, and the impact on anxiety/depression; the individual’s capacity to set goals should be considered, e.g., someone struggling with day-to-day tasks may find even small goals too challenging. Youth advisors considered perfectionism to be important, where some people may feel pressure to achieve goals. A sense of hopelessness, or procrastination, and rumination also, where delaying tasks may result in delaying work on goals. For some youth advisors, goal setting felt especially important, whilst for others it was not, rather a supportive relationship was identified as most important, and they could not see how that would be developed through goal setting. Academic/clinical advisors said that young people’s preferences to work on goals, or not, was in itself of key importance to the therapeutic relationship. There was no evidence from the included literature to support/oppose these points.
Language and power dynamics
Linked to preferences, youth advisors said that young people tend not to like the term “goal” because they attribute it to work and formal settings, whereas “therapeutic goals” are personal with deeper meaning. Academic/clinical advisors discussed using alternative language for goal setting and goal directed work, and the importance of being led by the young person. Posing questions such as “What do you want to change?” is suggested as an alternative in the literature ([ 33 ]; p.47). Youth advisors said that whilst some young people may feel able to say they do not want to set goals, others may not, due to the young person-practitioner power imbalance, which has implications for relationships, and therapeutic work. There was no further evidence from the included literature to support/oppose these points.
Under what circumstances (contextual factors)
Broadly helpful.
All seven studies suggested that goal setting was a helpful element of therapeutic relationships for young people within the research contexts. This included year-long narrative therapy with interpersonal therapy and CBT techniques in alliance with the family [ 29 ]; multimodal family therapy [ 31 ]; Gestalt therapy [ 30 ]; either CBT, short-term psychoanalytic psychotherapy or brief psychosocial intervention [ 32 ]; UK child and adolescent mental health services [ 33 , 34 ] and UK inpatient settings [ 35 ]. All studies were based in Western high-income countries. Academic/clinical and youth advisors agreed with this assessment.
Review points and referral routes
Reviewing progress towards goals too frequently could give the impression that practitioners are more interested in gauging their own success, rather than in the young person as a whole person, and rating could end up being done by rote, making goals increasingly meaningless [ 34 ] . Academic/clinical and youth advisors agreed with this, discussing the need to work with goals in a flexible manner. Additionally, young people may not recognise the symptoms identified, particularly when referred for treatment by another party (e.g., parents/carers), which is crucial to enable collaborative goal setting [ 32 ]. Challenges associated with thinking of goals in this way was addressed by the academic/clinical and youth advisors in wider discussions elsewhere (see therapy contexts).
Culture and therapy contexts
Youth and academic/clinical advisors located in Western high-income countries agreed that it may depend on types of interventions offered and practitioner’s preferred working style, but young people largely have agency to set goals. However, it was recognised by the youth and academic/clinical advisors that some young people in some countries do not have agency to set goals. There, decisions are made by families, in collaboration with practitioners, and so less consideration is given to young people’s perspectives. It was suggested that, in some countries, there is no concept of setting goals (e.g., a youth advisor discussed their experience in Pakistan), and ongoing stigma associated with mental health difficulties, which may lead to distrust, scepticism in, and a disconnect with practitioners. Youth advisors said that this may also be true in other countries not represented. A youth advisor suggested that young people in Brazil were relaxed towards goal setting and would not mind if goals were not achieved; directed therapy was considered more helpful.
Youth and academic/clinical advisors discussed goals in long-term therapy as potentially feeling restrictive, with challenges associated with thinking of what goals might be. Both long-and short-term goal setting within this context may feel meaningless, which if then pressed by the practitioner, has a negative impact on relationships. Academic/clinical advisors said that the feasibility of goal setting in the first instance is likely to be attributable to the factors young people who might be offered long-term therapy might have, rather than the work itself leading to these challenges. Youth and academic/clinical advisors also said that where there are multiple needs and risks, goals need to be simpler to feel manageable. Youth advisors said that sometimes there were concerns about the achievement of goals equating to treatment ending, which felt unsettling. There was no evidence from the included literature to support/oppose these points.
This study aimed to provide a synthesis of existing literature, identifying knowledge gaps. Whilst much may be drawn from related research, caution must be exercised when translating findings into other contexts [ 11 ], and whilst promising, generalising adult findings to youth must be exercised with an abundance of caution. Evidence suggests that adults and children think differently; as children grow, their cognitive processes develop, and their contexts and perspectives change, impacting on understandings of the self and the world around them. Further, models of recovery from depression are notably different between adults and young people [ 14 ]. As such, we have focused on evidence from the youth field in our discussion, and further highlight the paucity of research with young people in this area.
The included evidence originates from Western high-income and largely specialist settings; further research in majority world countries is urgently required. Many studies identified in initial searches only partially met inclusion criteria. This evidence paucity may suggest goal setting is not embedded in service standards or practice in most countries, or other limiting factors such as the general underfunding of youth mental health research. Some examples were derived from the insight analysis, highlighting the advisors’ value, who helped contextualise and interpret evidence, grounded in lived experience. However, whilst the research question pertained to the effectiveness of goal setting as part of therapeutic relationships, the findings were related to the feasibility, or acceptability of goal setting itself. Links between effective goal setting, good therapeutic relationships and positive outcomes are inferred based on evidence that partially supports the research question, and the discussions with the advisory group, but no evidence relating to anxiety or depression outcomes was found in this study. Future research should consider in depth explorations of mechanisms of goal setting within therapeutic relationships, for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression.
For many young people, goal setting is a helpful tool for building good therapeutic relationships via open communication. These findings support previous research which partially address the research question: young people find goal setting to be helpful to therapeutic relationships through the development of a shared language and understanding [ 3 ]. It has been suggested that goals are a mechanism of change via a means for “common ground” to be established [ 3 ]. Finding common ground and a shared understanding are particularly pertinent in youth mental health settings, where there are multiple stakeholders involved [ 36 , 37 , 38 ], which can be a balancing act [ 39 ]. Establishing this mutuality of situations is considered the key facilitator of engagement when referred for therapy by others [ 40 ]. Further, ownership of goals located with young people is important [ 41 ], which in turn gives young people ownership of their care, which can be motivational [ 42 , 43 ]. Young people experiencing anxiety may find goal setting an effective strategy due to links with avoidance motivation; such that they have reported pursuing approach goals to avoid negative emotional consequences of not doing so [ 44 ]. The ability of young people to maintain focus on the pursuit of personal goals has also been demonstrated as a moderator of depression and suicide [ 45 ].
One included study explicitly discussed parents/carers within collaborative goals and therapeutic relationships, as a foundation for mutual support [ 31 ]. Stronger relationships between both young people, parents/carers and practitioners and/or involving both young people and parents/carers in decision-making have been demonstrated to predict more positive outcomes [ 39 , 46 ]. Young people are often referred by their parents/carers, which must be considered, particularly where literature highlights challenges of setting goals when young people do not agree with the referral or recognise the difficulties [ 22 , 32 ]. Prior research has demonstrated that young people from minoritized ethnic groups are more likely to be referred for mental health support via social care and the youth justice system compared to their White British counterparts, who are commonly referred via primary care in the UK [ 47 ]. Further, evidence suggests that increases in emotional autonomy result in a shift from dependence on adults in adolescence, to reliance upon peers for support [ 48 ] particularly amongst girls [ 49 ], which may align with the developmental interference with building relationships outside of goal setting found by Cirasola and colleagues [ 32 ]. It has been argued that for young people who have difficulties building and maintaining relationships, the therapeutic relationship is particularly important (e.g., [ 23 ]). It is also noteworthy that young people in some countries may not have agency to set goals, a significant limiting factor. There are cultural and service level factors which were not explored. In some cultures, advice is sought from family and religious leaders over mental health professionals (e.g., [ 50 ]). Organisational level factors have also been found to hinder and influence therapeutic processes [ 40 ]. Further research is needed into referral routes, and intersections between systems, practice, and young people’s preferences.
Several elements of goal setting were identified as unhelpful for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, supporting previous literature. These discussions centred on the feasibility/acceptability of goals, rather than goal setting being detrimental to therapeutic relationships per se. Nevertheless, it is suggested that these factors were primarily related to the person, and that “personal” factors may be driven by underlying difficulties. For example, low confidence, hopelessness, levels of distress, perfectionism, and rumination (e.g., [ 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 ], may all be elements of anxiety and/or depression. Academic/clinical and youth advisors agreed that goals may become clearer over time, particularly for young people experiencing depression and purposeless, and through collaboration, goals could be formulated. The importance of considering specific challenges of goal setting during long-term therapy was highlighted. Academic/clinical and youth advisors discussed challenges associated with identifying priority areas for work, and that goals continue to flex and change, with the potential for goals work to feel too restrictive. This is in support of previous research suggesting that it is important that goals are worked on flexibly [ 3 ] with space for them to change; specifically in relation to depression. Compared to those with low levels of depression, young people with high levels of depression are more able to disengage with unhelpful goals over time and to set new goals, which in turn may predict lower levels of depressive symptoms over a year later [ 56 ]. This sense of goals flexing, feeling unique and changeable has been mirrored in descriptions of therapeutic relationships themselves [ 23 ]. There was a clear steer from youth advisors that the relationship independent of goal setting was key to good outcomes, and that this was a priority; that without the trusting relationship, there is no facilitator for goal setting. This is an important contradiction to the literature, warranting further exploration. One suggestion is that the initial goals for long-term therapy should be on relationship building, but reviewed, so the therapeutic relationship itself does not remain the primary goal [ 34 ]. Another key finding is that goals take time to establish, and pressure to set goals may render them meaningless, which also supports previous research [ 51 ]. Young people often do not know what their goals are [ 57 ], which impacts trust building, relationships and thus, therapeutic work. In support of prior research which defines recovery as contingent on shared goals and joint action in relationships [ 14 ], links found between goals, trust building and therapeutic relationships in the present study align with research on trauma informed care, and emotional and relational safety (see, [ 58 ]). Further consideration should be given to this area, particularly clinical implications, and interactions with levels of distress.
Whilst support approaches that incorporate structured goal setting are often characterised by a greater emphasis on client-centredness, the links between personally meaningful outcomes and the specific behaviour change techniques required to progress towards goals are not clear. Further, the person-centred focus is hypothesised as a conduit to positive ratings of self-efficacy, quality of life and service satisfaction, but evidence is lacking [ 11 ]. Whilst previous literature from within the youth mental health field suggests that working on goals is motivating and increases self-efficacy [ 34 , 42 ], evidence is still limited. Goal setting may be useful to young people because, whilst not necessarily synonymous, it has been demonstrated as a facilitative element of shared decision-making [ 59 , 60 ]. This collaborative way of working through shared understanding and the development of good therapeutic relationships [ 61 ] may be especially helpful to young people experiencing depression as it enables them to exercise control over their own feelings and behaviour [ 43 ] at a time when they may be experiencing feelings of hopelessness and purposeless. Whilst educated links are made to shared decision-making, further research should explore whether there is an embedded link to goals and therapeutic relationships.
Strengths and limitations
The mixed-methodological approach was a particular strength, with literature findings bolstered by lived experience. However, whilst advisors were from diverse demographic groups, not all groups were represented.
Whilst every attempt was made to include as many goal setting search terms as possible, the language is broad and fluid, meaning certain terms may have been missed. Still, the high number of results returned from literature searches suggests the strategy may need refinement. Nevertheless, we chose to ensure a large return given the subject’s broad nature. At the screening stage, the focus on explicitly identified goal setting and goal work made the identification of included studies less ambiguous, but meant that studies focused on implicit goals work would not have been included, reducing the number of studies included in the final synthesis.
Prior assumptions and knowledge of this topic will have influenced the researchers’ interpretation of the findings, even subconsciously. This includes the decision to use the nuanced elements of the research question to organise the findings. The researchers were located in Belgium, Germany, and the UK at the time of the study, which risks the perpetuation of the status quo of Western high-income-originating dominated research. Further, the findings were contextualised and linked to prior theory primarily by a researcher outside the age range of interest (JJ). The impact of both issues was mitigated via advisors, particularly those within majority world countries and the age range of interest, and the peer researchers entrenched in the research team (MS, IS), who provided contextual depth and understanding to the findings.
Literature focused on goal setting as helpful for young people with anxiety and/or depression is overwhelmingly supportive, but this leaves research gaps regarding in which ways, for whom and under what circumstances goal setting might be unhelpful. Priority must be given to researching unhelpful mechanisms of goal setting, to avoid potential iatrogenic effects. Accessibility could be improved through exploration of the intersections between systems/contexts (e.g., country), therapeutic practice (e.g., practitioner’s training/preferences) and young people’s preferences. Further research is also needed to explore mechanisms by which goal setting may help to reduce anxiety and/or depression symptoms, as well as other important areas of outcome, such as quality of life, using e.g., mediation analysis.
Scaling up in countries with well-developed systems could mean embedding goals in guidelines for anxiety and/or depression; in service specifications, including monitoring and reporting change mechanisms; staff training in consistency; and some interagency forums to align goal processes. For majority world countries with less developed systems, largely relying on non-specialist services e.g., NGOs, goals may be paradoxically more important for maximising limited resources. Despite nothing suggesting goal setting could not practically be scaled-up globally, cultural considerations may be a limiting factor in some places.
Preferences to not work on goals may be driven by the limiting factors identified, such as hopelessness or high distress. Practitioners should work through this first, reviewing the option to work on goals over time, respecting young people’s preferences. Flexibility is important, and ownership of goals located with young people is essential, particularly to those experiencing depression, enabling them to exercise control over their feelings and behaviour when they may be feeling hopeless and/or purposeless. Finally, there may be a unique opportunity for goals to facilitate work with young people experiencing high distress levels or who have experienced trauma, due to links to emotional and relational safety and building trusting relationships.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available to protect the confidentiality of the small number of advisors, but may be available from the corresponding author’s organisation, on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Cognitive behavioural therapy
Goal based outcomes tool
United Kingdom
Austin JT, Vancouver JB. Goal constructs in psychology: structure, process, and content. Psychol Bull. 1996;122(3):338–75.
Article Google Scholar
Law D. Goals and goal based outcomes (GBOs): some useful information. London: Internal CORC Publication; 2011.
Google Scholar
Di Malta G, Oddli HW, Cooper M. From intention to action: a mixed methods study of clients’ experiences of goal-oriented practices. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(20):1770–89.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Law D, Jacob J. Goals and goal based outcomes: some useful information. 3rd ed. London: CAMHS Press; 2015.
Grosse M, Grawe HK. Bern inventory of treatment goals: part 1. Development and first application of a taxonomy of treatment goal themes. Psychother Res. 2002;12:79–99.
Law D. The goal-based outcome (GBO) tool. Guidance notes. [Internet]. Goals in Therapy. 2019. Available from: https://goalsintherapycom.files.wordpress.com/2019/02/gbo-version-2.0-guide-final-1st-feb-2019.pdf .
Bandura A. Self-regulation of motivation and action through goal systems. In: Bandura A, editor. Cognitive perspectives on emotion and motivation. Dordrecht: Springer; 1988. p. 37–61.
Chapter Google Scholar
Manderlink G, Harackiewicz JM. Proximal versus distal goal setting and intrinsic motivation. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1984;47:918–28.
Maslow AH. A theory of human motivation. Psychol Rev. 1943;50:370–96.
Harkin B, Webb TL, Chang BP, Prestwich A, Conner M, Kellar I, Benn Y, Sheeran P. Does monitoring goal progress promote goal attainment? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Psychol Bull. 2016;142(2):198–229.
Levack WM, Weatherall M, Hay-Smith EC, Dean SG, McPherson K, Siegert RJ. Goal setting and strategies to enhance goal pursuit for adults with acquired disability participating in rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009727.pub2 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mellat N, Lavasani MG. The role of epistemological beliefs, motivational constructs and Information processing strategies in regulation of learning. Procedia Soc Behav Sci. 2011;30(1):1761–9.
Leavey JE. Youth experiences of living with mental health problems: emergence, loss, adaptation and recovery (ELAR). Can J Community Ment Health. 2009;24(2):109–26.
Simonds LM, Pons RA, Stone NJ, Warren F, John M. Adolescents with anxiety and depression: Is social recovery relevant? Clin Psychol Psychother. 2014;21(4):289–98.
Castonguay LG. Predicting the effect of cognitive therapy for depression: a study of unique and common factors. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1996;64:497–504.
Duncan BL. The heart and soul of change second edition: delivering what works in therapy. Washington: American Psychological Association; 2010.
Book Google Scholar
Messer SB. Let’s face facts: common factors are more potent than specific therapy ingredients. Clin Psychol Sci Pract. 2002;9:21–5.
Kazdin AE, Siegel TC, Bass D. Drawing on clinical practice to inform research on child and adolescent psychotherapy: survey of practitioners. Prof Psychol Res Pract. 1990;21(3):189–98.
Bordin ES. The generalizability of the psychoanalytic concept of the working alliance. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1979;16(3):252–60.
Luong HK, Drummond SPA, Norton PJ. Elements of the therapeutic relationship in CBT for anxiety disorders: a systematic review. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.102322 .
Shick Tryon G, Birch SE, Verkuilen J. Meta-analyses of the relation of goal consensus and collaboration to psychotherapy outcome. Psychotherapy. 2018;55(4):372–83.
DiGiuseppe R, Linscott J, Jilton R. Developing the therapeutic alliance in child-adolescent psychotherapy. Appl Prev Psychol. 1996;5(2):85–100.
Hartley S, Redmond T, Berry K. Therapeutic relationships within child and adolescent mental health inpatient services: a qualitative exploration of the experiences of young people, family members and nursing staff Short. PsyArXiv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/w2nct .
Wolpert M, Pote I, Sebastian C. Identifying and integrating active ingredients for mental health. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8(9):741–3.
INVOLVE. Briefing note for researchers: Public involvement in NHS, public health and social care research [Internet]. 2012. Available from: https://www.invo.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/INVOLVEBriefingNotesApr2012.pdf .
Gotschall T. EndNote 20 desktop version. J Med Libr Assoc JMLA. 2021;109(3):520.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz ZEA. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):1–10.
Hannes K. Chapter 4: Critical appraisal of qualitative research. In: Njbahkhahjlsl C, editor. Supplementary guidance for inclusion of qualitative research in cochrane systematic reviews of interventions version 1. London: Cochrane Collaboration Qualitative Methods Group; 2011. p. 4.
Bennett LR. Adolescent depression: meeting therapeutic challenges through an integrated narrative approach. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs. 2012;25(4):184–94.
Berdondini L, Elliott R, Shearer J. Collaboration in experiential therapy. J Clin Psychol. 2012;68(2):159–67.
Diamond GM, Diamond GS, Liddle HA. The therapist–parent alliance in family-based therapy for adolescents. J Clin Psychol. 2000;56(8):1037–50.
Cirasola A, Midgley N, Fonagy P, Martin P, MGoodyer I, Reynolds S, et al. The factor structure of the working alliance inventory short-form in youth psychotherapy: an empirical investigation. Psychother Res. 2021;31(4):535–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503307.2020.1765041 .
Feltham A, Martin K, Walker L. Using goals in therapy: the perspective of people with lived experience. In: Cooper M, Law D, editors. Working with goals in psychotherapy and counselling. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2018. p. 73–85.
Law D, Wolpert M. Guide to using outcomes and feedback tools with children, young people and families. Formally known as the COOP document. London: CAMHS Press; 2014.
Martin K. A critical realist study of shared decision-making in young people’s mental health inpatient units. Bristol: Bristol University Press; 2019.
Hawks JM. Exploring the therapeutic alliance with adolescents and their caregivers: A qualitative approach. Diss Abstr Int Sect A Humanit Soc Sci. 2016;77(4-A(E)):No-Specified. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=psyc13&NEWS=N&AN=2016-37856-098 .
Marks D. Fostering parental growth and enhancing the therapeutic alliance: key tasks for the child psychotherapist. J Child Psychother. 2020;46(1):20–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/0075417X.2020.1743736 .
Shpigel MS, Diamond GM. Good versus poor therapeutic alliances with non-accepting parents of same-sex oriented adolescents and young adults: a qualitative study. Psychother Res. 2014;24(3):376–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503307.2013.856043 .
Paul M. Decision-making about children’s health care. Adv Psychiatr Treat. 2004;10:301–11.
Stige SH, Eik I, Oddli HW, Moltu C. Negotiating system requirements to secure client engagement—therapist strategies in adolescent psychotherapy initiated by others. Front Psychol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.704136 .
Marshall SL, Oades LG, Crowe TP. Australian mental health consumers’ contributions to the evaluation and improvement of recovery oriented service provision. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci. 2010;47(3):198–205.
Cairns A, Kavanagh D, Dark F, McPhail SM. Setting measurable goals with young people: qualitative feedback from the goal attainment scale in youth mental health. Br J Occup Ther. 2015;78(4):253–9.
Grossoehme DH, Gerbetz L. Adolescent perceptions of meaningfulness of psychiatric hospitalization. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2004;9(4):589–96.
Dickson JM, Moberly NJ. Goal internalization and outcome expectancy in adolescent anxiety. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2013;41(3):389–97.
Abrera AM. Depression and suicide risk among adolescents: exploring the moderating role of benevolence and goal-orientation. In: The 6 th ASEAN regional union psychological society (ARUPS) congress “driving mental revolution in the psychological century: enhancing psychological services for a better future. Bali; 2018. p. 56.
Edbrooke-Childs J, Jacob J, Argent R, Patalay P, Deighton JWM. The relationship between child-and parent-reported shared decision making and child-, parent-, and clinician-reported treatment outcome in routinely collected child mental health services data. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016;21(2):324–38.
Edbrooke-Childs J, Patalay P. Ethnic differences in referral routes to youth mental health services. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2019;58(3):368–75.
Steinberg L, Silverberg SB. The vicissitudes of autonomy in early adolescence. Child Dev. 1986;57:841–51.
Slavin LA, Rainer KL. Gender differences in emotional support and depressive symptoms among adolescents: a prospective analysis. Am J Community Psychol. 1990;18(3):407–21.
Ciftci A, Jones N, Corrigan PW. Mental health stigma in the muslim community. J Muslim Ment Health. 2013;7(1):17–32.
Bromley C, Westwood S. Young people’s participation: views from young people on using goals. Child Fam Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;1:29–40.
Clarke SP, Oades LG, Crowe TP, Caputi P, Deane FP. The role of symptom distress and goal attainment in promoting aspects of psychological recovery for consumers with enduring mental illness. J Ment Health. 2009;18(5):389–97.
Trent ES, Viana AG, Raines EM, Woodward EC, Zvolensky MJCA. Exposure to parental threatening behaviors and internalizing psychopathology in a trauma-exposed inpatient adolescent sample: the role of difficulties with goal-directed behaviors. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2019;207(11):969–76.
Moberly NJ, Watkins ER. Negative affect and ruminative self-focus during everyday goal pursuit. Cogn Emot. 2010;24(4):729–39.
Steen A, Berghuis H, Braam AW. Lack of meaning, purpose and direction in life in personality disorder: a comparative quantitative approach using Livesley’s general assessment of personality disorder. Personal Ment Health. 2019;13(3):144–54.
Wrosch C, Miller GE. Depressive symptoms can be useful: self-regulatory and emotional benefits of dysphoric mood in adolescence. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2009;96(6):1181–90.
Troupp C. Distinguishing patient-generated outcome measures in CAMHS from a bespoke sandwich. Child Fam Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;1(1):19–28.
Taylor J, Shostak L, Rogers A, Mitchell P. Rethinking mental health provision in the secure estate for children and young people: a framework for integrated care (SECURE STAIRS). Safer Communities. 2018;17(4):193–201.
Cheng H, Hayes D, Edbrooke-Childs J, Martin K, Chapman L, Wolpert M. What approaches for promoting shared decision making are used in child mental health? A scoping review. Helen MIR mHealth uHealth. 2017;7(6):77.
Langer DA, Jensen-Doss A. Shared decision-making in youth mental health care: using the evidence to plan treatments collaboratively. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2018;47(5):821–31.
Coulter A, Edwards A, Elwyn G, Thomson R. Implementing shared decision making in the UK. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2011;105(4):300–4.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the advisors, for their invaluable contribution from start to finish, including useful comments an early draft: Duncan Law, Elmas Aybike Yılmaz, Hanne Oddli, Isabella Valério, Jacob People, Josh D., Julian Edbrooke-Childs, Katya Proctor, Laura Calomarde Juárez, Mick Cooper, Nick Morgan, Panos Vostanis, Syeda Zeenat R., and Theo Jackson. Thank you to Bernice Appiah, Shade Davies and Shadia Robertson for helpful discussions about the findings, and assistance with evidence synthesis, and to Inês Pote from the Wellcome Active Ingredients team, and Jasmine Harju-Seppanen, for useful comments on a previous draft. The authors also wish to thank Zoe Thomas for incredibly useful advice and guidance regarding literature searches.
This work was funded by a Wellcome Trust Mental Health Priority Area “Active Ingredients” 2021 commission awarded to JJ at the Anna Freud Centre. It was a requirement of the funding team that the research design comprised a literature review, and that the involved and worked collaboratively with young people with lived experience of anxiety and/or depression throughout the course of the project. Members of the funding team provided feedback on an early draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Child Outcomes Research Consortium, Anna Freud Centre, 4-8 Rodney Street, London, N1 9JH, UK
Jenna Jacob
Euro Youth Mental Health, The Block, 35 Churchgate, Hitchin, SG5 1DN, UK
Milos Stankovic & Inga Spuerck
Systematic Review Consultants, 9 Sandfield Road, Nottingham, NG7 1QR, UK
Farhad Shokraneh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JJ conceptualised the study, prepared the first draft protocol and search strategy, refining this with the study authors and advisors. JJ undertook the library database searches for published literature, partially screened the titles and abstracts of literature, screened all full texts, led communication with study authors and advisors, led four advisory group meetings, maintained the databases which were used to extract and manage study data, prepared, and revised the manuscript. MS contributed to the first draft protocol and search strategy, led communication with youth advisors, led two advisory group meetings, created the narrative summaries, and contributed to the manuscript. IS contributed to the first draft protocol and search strategy, supported communication with youth advisors, screened full texts for further relevant literature, and contributed to the manuscript. FS conducted the grey literature searches, screened all potential title and abstracts from all searches (published and unpublished literature), maintained the databases which were used to extract and manage study data, and contributed to the manuscript. All study advisors were invited to comment on the protocol and initial search terms, and were invited to comment on earlier drafts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jenna Jacob .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval for this research was not required because it does not involve collection nor analysis of primary data, and youth advisors were consulted on in the capacity of being part of the advisory group, to discuss their interpretation of the findings, rather than within the capacity of research participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
JJ works on the Child Outcomes Research Consortium (CORC) project at the Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families, which encourages the use of outcome measures in youth mental health settings amongst its members. No other authors report any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. appendix 1..
Inclusion and exclusion criteria and Search Strategies. Appendix 2 Core Criteria for Quality Assessment of Qualitative Studies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jacob, J., Stankovic, M., Spuerck, I. et al. Goal setting with young people for anxiety and depression: What works for whom in therapeutic relationships? A literature review and insight analysis. BMC Psychol 10 , 171 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-022-00879-5
Download citation
Received : 16 March 2022
Accepted : 30 June 2022
Published : 13 July 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-022-00879-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Youth mental health
- Goal setting
- Therapeutic alliance
- Outcome measurement
- Active ingredients
- Goal based outcomes
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Reference Examples
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual . Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual .
To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of work (e.g., journal article ) and follow the relevant example.
When selecting a category, use the webpages and websites category only when a work does not fit better within another category. For example, a report from a government website would use the reports category, whereas a page on a government website that is not a report or other work would use the webpages and websites category.
Also note that print and electronic references are largely the same. For example, to cite both print books and ebooks, use the books and reference works category and then choose the appropriate type of work (i.e., book ) and follow the relevant example (e.g., whole authored book ).
Examples on these pages illustrate the details of reference formats. We make every attempt to show examples that are in keeping with APA Style’s guiding principles of inclusivity and bias-free language. These examples are presented out of context only to demonstrate formatting issues (e.g., which elements to italicize, where punctuation is needed, placement of parentheses). References, including these examples, are not inherently endorsements for the ideas or content of the works themselves. An author may cite a work to support a statement or an idea, to critique that work, or for many other reasons. For more examples, see our sample papers .
Reference examples are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 10 and the Concise Guide Chapter 10
Related handouts
- Common Reference Examples Guide (PDF, 147KB)
- Reference Quick Guide (PDF, 225KB)
Textual Works
Textual works are covered in Sections 10.1–10.8 of the Publication Manual . The most common categories and examples are presented here. For the reviews of other works category, see Section 10.7.
- Journal Article References
- Magazine Article References
- Newspaper Article References
- Blog Post and Blog Comment References
- UpToDate Article References
- Book/Ebook References
- Diagnostic Manual References
- Children’s Book or Other Illustrated Book References
- Classroom Course Pack Material References
- Religious Work References
- Chapter in an Edited Book/Ebook References
- Dictionary Entry References
- Wikipedia Entry References
- Report by a Government Agency References
- Report with Individual Authors References
- Brochure References
- Ethics Code References
- Fact Sheet References
- ISO Standard References
- Press Release References
- White Paper References
- Conference Presentation References
- Conference Proceeding References
- Published Dissertation or Thesis References
- Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis References
- ERIC Database References
- Preprint Article References
Data and Assessments
Data sets are covered in Section 10.9 of the Publication Manual . For the software and tests categories, see Sections 10.10 and 10.11.
- Data Set References
- Toolbox References
Audiovisual Media
Audiovisual media are covered in Sections 10.12–10.14 of the Publication Manual . The most common examples are presented together here. In the manual, these examples and more are separated into categories for audiovisual, audio, and visual media.
- Artwork References
- Clip Art or Stock Image References
- Film and Television References
- Musical Score References
- Online Course or MOOC References
- Podcast References
- PowerPoint Slide or Lecture Note References
- Radio Broadcast References
- TED Talk References
- Transcript of an Audiovisual Work References
- YouTube Video References
Online Media
Online media are covered in Sections 10.15 and 10.16 of the Publication Manual . Please note that blog posts are part of the periodicals category.
- Facebook References
- Instagram References
- LinkedIn References
- Online Forum (e.g., Reddit) References
- TikTok References
- X References
- Webpage on a Website References
- Clinical Practice References
- Open Educational Resource References
- Whole Website References

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
https://www.nist.gov/chips
CHIPS for America

About CHIPS for America
Semiconductors, or chips, are tiny electronic devices that are integral to America’s economic and national security. These devices power tools as simple as a light switch and as complex as a fighter jet or a smartphone. Semiconductors power our consumer electronics, automobiles, data centers, critical infrastructure, and virtually all military systems. They are also essential building blocks of the technologies that will shape our future, including artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and clean energy.
While the United States remains a global leader in semiconductor design and research and development, it has fallen behind in manufacturing and now accounts for only about 10 percent of global commercial production. Today, none of the most advanced logic and memory chips—the chips that power PCs, smartphones, and supercomputers—are manufactured at commercial scale in the United States. In addition, many elements of the semiconductor supply chain are geographically concentrated, leaving them vulnerable to disruption and endangering the global economy and U.S. national security.
That’s why President Biden signed the bipartisan CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 into law. The law provides the Department of Commerce with $50 billion for a suite of programs to strengthen and revitalize the U.S. position in semiconductor research, development, and manufacturing—while also investing in American workers. CHIPS for America encompasses two offices responsible for implementing the law: The CHIPS Research and Development Office is investing $11 billion into developing a robust domestic R&D ecosystem, while the CHIPS Program Office is dedicating $39 billion to provide incentives for investment in facilities and equipment in the United States. Learn more about CHIPS for America from this video message from the Secretary of Commerce .
News and Press Releases

Biden-Harris Administration Announces Preliminary Terms with Absolics to Support Development of Glass Substrate Technology for Semiconductor Advanced Packaging
Biden-harris administration announces preliminary terms with polar semiconductor to establish an independent american foundry, chips for america announces $285 million funding opportunity for a digital twin and semiconductor chips manufacturing usa institute, u.s. department of commerce launches chips women in construction framework with initial voluntary commitments from intel and micron.

Marla Dowell Recognized as a Distinguished Executive with 2023 Presidential Rank Award
For general inquiries about CHIPS for America, contact askchips [at] chips.gov (askchips[at]chips[dot]gov) .
For inquiries about the CHIPS Incentives Program, contact apply [at] chips.gov .
For Congressional inquiries about CHIPS for America, contact legislativeaffairs [at] chips.gov (legislativeaffairs[at]chips[dot]gov) .
To request a meeting with a CHIPS staff member or an appearance at an event, visit https://askchips.chips.gov .
The CHIPS Incentives Program Portal can be found at https://applications.chips.gov .
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Table of Contents
Which social media platforms are most common, who uses each social media platform, find out more, social media fact sheet.
Many Americans use social media to connect with one another, engage with news content, share information and entertain themselves. Explore the patterns and trends shaping the social media landscape.
To better understand Americans’ social media use, Pew Research Center surveyed 5,733 U.S. adults from May 19 to Sept. 5, 2023. Ipsos conducted this National Public Opinion Reference Survey (NPORS) for the Center using address-based sampling and a multimode protocol that included both web and mail. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race and ethnicity, education and other categories.
Polls from 2000 to 2021 were conducted via phone. For more on this mode shift, read our Q&A.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
A note on terminology: Our May-September 2023 survey was already in the field when Twitter changed its name to “X.” The terms Twitter and X are both used in this report to refer to the same platform.

YouTube and Facebook are the most-widely used online platforms. About half of U.S. adults say they use Instagram, and smaller shares use sites or apps such as TikTok, LinkedIn, Twitter (X) and BeReal.
| Year | YouTube | TikTok | Snapchat | Twitter (X) | BeReal | Nextdoor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8/5/2012 | 54% | 9% | 10% | 16% | 13% | |||||||
| 8/7/2012 | 14% | |||||||||||
| 12/9/2012 | 11% | 13% | 13% | |||||||||
| 12/16/2012 | 57% | |||||||||||
| 5/19/2013 | 15% | |||||||||||
| 7/14/2013 | 16% | |||||||||||
| 9/16/2013 | 57% | 14% | 17% | 17% | 14% | |||||||
| 9/30/2013 | 16% | |||||||||||
| 1/26/2014 | 16% | |||||||||||
| 9/21/2014 | 58% | 21% | 22% | 23% | 19% | |||||||
| 4/12/2015 | 62% | 24% | 26% | 22% | 20% | |||||||
| 4/4/2016 | 68% | 28% | 26% | 25% | 21% | |||||||
| 1/10/2018 | 73% | 68% | 35% | 29% | 25% | 22% | 27% | 24% | ||||
| 2/7/2019 | 73% | 69% | 37% | 28% | 27% | 20% | 24% | 22% | 11% | |||
| 2/8/2021 | 81% | 69% | 40% | 31% | 21% | 28% | 23% | 25% | 23% | 18% | 13% | |
| 9/5/2023 | 83% | 68% | 47% | 35% | 33% | 30% | 29% | 27% | 22% | 22% | 3% |
Note: The vertical line indicates a change in mode. Polls from 2012-2021 were conducted via phone. In 2023, the poll was conducted via web and mail. For more details on this shift, please read our Q&A . Refer to the topline for more information on how question wording varied over the years. Pre-2018 data is not available for YouTube, Snapchat or WhatsApp; pre-2019 data is not available for Reddit; pre-2021 data is not available for TikTok; pre-2023 data is not available for BeReal. Respondents who did not give an answer are not shown.
Source: Surveys of U.S. adults conducted 2012-2023.

Usage of the major online platforms varies by factors such as age, gender and level of formal education.
% of U.S. adults who say they ever use __ by …
- RACE & ETHNICITY
- POLITICAL AFFILIATION
| Ages 18-29 | 30-49 | 50-64 | 65+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67 | 75 | 69 | 58 | |
| 78 | 59 | 35 | 15 | |
| 32 | 40 | 31 | 12 | |
| Twitter (X) | 42 | 27 | 17 | 6 |
| 45 | 40 | 33 | 21 | |
| Snapchat | 65 | 30 | 13 | 4 |
| YouTube | 93 | 92 | 83 | 60 |
| 32 | 38 | 29 | 16 | |
| 44 | 31 | 11 | 3 | |
| TikTok | 62 | 39 | 24 | 10 |
| BeReal | 12 | 3 | 1 | <1 |
| Men | Women | |
|---|---|---|
| 59 | 76 | |
| 39 | 54 | |
| 31 | 29 | |
| Twitter (X) | 26 | 19 |
| 19 | 50 | |
| Snapchat | 21 | 32 |
| YouTube | 82 | 83 |
| 27 | 31 | |
| 27 | 17 | |
| TikTok | 25 | 40 |
| BeReal | 2 | 5 |
| White | Black | Hispanic | Asian* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69 | 64 | 66 | 67 | |
| 43 | 46 | 58 | 57 | |
| 30 | 29 | 23 | 45 | |
| Twitter (X) | 20 | 23 | 25 | 37 |
| 36 | 28 | 32 | 30 | |
| Snapchat | 25 | 25 | 35 | 25 |
| YouTube | 81 | 82 | 86 | 93 |
| 20 | 31 | 54 | 51 | |
| 21 | 14 | 23 | 36 | |
| TikTok | 28 | 39 | 49 | 29 |
| BeReal | 3 | 1 | 4 | 9 |
| Less than $30,000 | $30,000- $69,999 | $70,000- $99,999 | $100,000+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63 | 70 | 74 | 68 | |
| 37 | 46 | 49 | 54 | |
| 13 | 19 | 34 | 53 | |
| Twitter (X) | 18 | 21 | 20 | 29 |
| 27 | 34 | 35 | 41 | |
| Snapchat | 27 | 30 | 26 | 25 |
| YouTube | 73 | 83 | 86 | 89 |
| 26 | 26 | 33 | 34 | |
| 12 | 23 | 22 | 30 | |
| TikTok | 36 | 37 | 34 | 27 |
| BeReal | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| High school or less | Some college | College graduate+ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 63 | 71 | 70 | |
| 37 | 50 | 55 | |
| 10 | 28 | 53 | |
| Twitter (X) | 15 | 24 | 29 |
| 26 | 42 | 38 | |
| Snapchat | 26 | 32 | 23 |
| YouTube | 74 | 85 | 89 |
| 25 | 23 | 39 | |
| 14 | 23 | 30 | |
| TikTok | 35 | 38 | 26 |
| BeReal | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Urban | Suburban | Rural | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 66 | 68 | 70 | |
| 53 | 49 | 38 | |
| 31 | 36 | 18 | |
| Twitter (X) | 25 | 26 | 13 |
| 31 | 36 | 36 | |
| Snapchat | 29 | 26 | 27 |
| YouTube | 85 | 85 | 77 |
| 38 | 30 | 20 | |
| 29 | 24 | 14 | |
| TikTok | 36 | 31 | 33 |
| BeReal | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Rep/Lean Rep | Dem/Lean Dem | |
|---|---|---|
| 70 | 67 | |
| 43 | 53 | |
| 29 | 34 | |
| Twitter (X) | 20 | 26 |
| 35 | 35 | |
| Snapchat | 27 | 28 |
| YouTube | 82 | 84 |
| 25 | 33 | |
| 20 | 25 | |
| TikTok | 30 | 36 |
| BeReal | 4 | 4 |

This fact sheet was compiled by Research Assistant Olivia Sidoti , with help from Research Analyst Risa Gelles-Watnick , Research Analyst Michelle Faverio , Digital Producer Sara Atske , Associate Information Graphics Designer Kaitlyn Radde and Temporary Researcher Eugenie Park .
Follow these links for more in-depth analysis of the impact of social media on American life.
- Americans’ Social Media Use Jan. 31, 2024
- Americans’ Use of Mobile Technology and Home Broadband Jan. 31 2024
- Q&A: How and why we’re changing the way we study tech adoption Jan. 31, 2024
Find more reports and blog posts related to internet and technology .
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
| Approach | What does it involve? |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | Researchers collect rich data on a topic of interest and develop theories . |
| Researchers immerse themselves in groups or organizations to understand their cultures. | |
| Action research | Researchers and participants collaboratively link theory to practice to drive social change. |
| Phenomenological research | Researchers investigate a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting participants’ lived experiences. |
| Narrative research | Researchers examine how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences. |
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
| Approach | When to use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| To describe and categorize common words, phrases, and ideas in qualitative data. | A market researcher could perform content analysis to find out what kind of language is used in descriptions of therapeutic apps. | |
| To identify and interpret patterns and themes in qualitative data. | A psychologist could apply thematic analysis to travel blogs to explore how tourism shapes self-identity. | |
| To examine the content, structure, and design of texts. | A media researcher could use textual analysis to understand how news coverage of celebrities has changed in the past decade. | |
| To study communication and how language is used to achieve effects in specific contexts. | A political scientist could use discourse analysis to study how politicians generate trust in election campaigns. |
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

COMMENTS
For example, in a paper that describes the social behavior of chimpanzees, the authors may need to provide the following details about the research setting: where the chimpanzees were observed (in the wild or in captivity), the number of chimpanzees observed and whether they belonged to the same social group, the geographic location, the period ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Table of contents. Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies.
For example, any research has a setting that is interrelated to the research focus and problem. Setting is where the research focus emerges as an issue to be investigated in detail by means of the research questions. Therefore, any findings will be directly related to the characteristics or the constraints of the setting.
Define the criteria for your sample setting too. Hilltop is typical for selective colleges. That was a research choice made by Benson and Lee. For more on sampling and sampling choices, see chapter 5. ... doing this study, you have a clear research question to guide you, you have identified your population of interest and research setting, and ...
Field research takes place in a natural or real-world setting, while laboratory research takes place in a controlled and constructed setting. ... What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples The research design is a strategy for answering your research questions. It determines how you will collect and analyze your data. 4828.
Experimental Research Design. Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables.With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions ...
Chapter 3 Research Setting and Methodology describes the research setting and the methods of research. It details the methodological framework of the study as the baseline description in obtaining the research materials. ... Confidentiality issues like, for example, the information given by resource persons, interview partners, and internal ...
Overview. In this chapter, the theoretical framework of the research, phenomenology and interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA) as the approach to data analysis are described. The medical school, the research setting and the curriculum are defined. The process of the research, the study design, is discussed.
The artificial settings of experiments may alter the behaviors or responses of participants. Experimental designs can be costly if special equipment or facilities are needed. ... Exploratory research generally utilizes small sample sizes and, thus, findings are typically not generalizable to the population at large. ...
design, population of interest, study setting, recruit ment, and sampling. Study Design. The study design is the use of e vidence-based. procedures, protocols, and guidelines that provide the ...
A central feature of qualitative research is the examination of the context in which a phenomenon is situated, experienced and constructed, and contextualisation is one of the standards by which qualitative studies are judged.112,113 This can involve a relatively quick description of key features of a given setting to orientate the reader, or it can be part of the analysis itself, with ...
A third reason researchers might turn to lab settings is to create conditions where they can trigger and then observe interactions that are relatively rare in field settings. For example, research on learned helplessness often brings children into controlled settings where researchers can watch them work with solvable and then with unsolvable ...
The present study followed a qualitative research design based on ethnographic. methods. This approach was chosen given that the purpose of the research was to. describe and analyze part of the culture of a specific community, specifically "by. identifying and describing the participants' practices and beliefs" (Gay & Airasian, 2002).
Research study design is a framework, or the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research problem. Research study designs are of many types, each with its advantages and limitations. The type of study design used to answer a particular research question is determined by the ...
This article takes you through the first steps of the research process, helping you narrow down your ideas and build up a strong foundation for your research project. Table of contents. Step 1: Choose your topic. Step 2: Identify a problem. Step 3: Formulate research questions.
research setting. This chapter delineates the research setting. Chapter 3 is structured as follows: Section 3.1 briefly presents the wider socio-economic, political and historical context of the research setting before expounding on the particular research setting, Section 3.2. The iterative process of analysis is presented as part of each
set of specifications, comprising the entire group of persons that is of interest to the researcher and to whom the research results can be generalised. LoBiondo-Wood and Haber (1998:250) describe a sample as a portion or a subset of the research population selected to participate in a study, representing the research population. 3.4.1 Population
For example, Haddix (2002) applied ethnography to study the language of Black female preservice teachers as they navigated various professional and personal settings. Ethnography relies heavily on researcher observational skills, which may include participant observation ( Glesne, 2016 ), and extended fieldwork or periods of contact with the ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Here are ten examples of professional development goals to inspire your own: 1. Develop a new skill set. Growing professionally often means expanding the arsenal of things you're able to do. What skill you choose to develop can depend on your industry, job, and personal preferences.
Goal setting and goal-focused work is widely used in young people's mental health settings. However, little is known about how, why or for whom this is helpful. This study aims to explore the mechanisms of collaborative goal setting as part of therapeutic relationships: is it helpful for young people experiencing anxiety and/or depression, how and why/not, for whom, and under what circumstances?
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual.Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual.. To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of ...
CHIPS for America encompasses two offices responsible for implementing the law: The CHIPS Research and Development Office is investing $11 billion into developing a robust domestic R&D ecosystem, while the CHIPS Program Office is dedicating $39 billion to provide incentives for investment in facilities and equipment in the United States ...
To better understand Americans' social media use, Pew Research Center surveyed 5,733 U.S. adults from May 19 to Sept. 5, 2023. Ipsos conducted this National Public Opinion Reference Survey (NPORS) for the Center using address-based sampling and a multimode protocol that included both web and mail.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Objective: An estimated one‐third of cancer patients experience a clinically significant psychological disorder, however it is unclear to what extent this is reflected in research funding. To address this a systematic analysis the allocation of psycho‐oncology research funding globally between 2016 and 2020 was conducted. Methods: A global dataset of 66,388 cancer research awards, from ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...