Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Opening doors: michele courton brown (cas’83), six bu alums to remember this memorial day, american academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children.
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- How Selena Gomez Is Revolutionizing the Celebrity Beauty Business
- TIME100 Most Influential Companies 2024
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- The Deadly Digital Frontiers at the Border
- What's the Best Measure of Fitness?
- The 31 Most Anticipated Movies of Summer 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
The Cult of Homework
America’s devotion to the practice stems in part from the fact that it’s what today’s parents and teachers grew up with themselves.

America has long had a fickle relationship with homework. A century or so ago, progressive reformers argued that it made kids unduly stressed , which later led in some cases to district-level bans on it for all grades under seventh. This anti-homework sentiment faded, though, amid mid-century fears that the U.S. was falling behind the Soviet Union (which led to more homework), only to resurface in the 1960s and ’70s, when a more open culture came to see homework as stifling play and creativity (which led to less). But this didn’t last either: In the ’80s, government researchers blamed America’s schools for its economic troubles and recommended ramping homework up once more.
The 21st century has so far been a homework-heavy era, with American teenagers now averaging about twice as much time spent on homework each day as their predecessors did in the 1990s . Even little kids are asked to bring school home with them. A 2015 study , for instance, found that kindergarteners, who researchers tend to agree shouldn’t have any take-home work, were spending about 25 minutes a night on it.
But not without pushback. As many children, not to mention their parents and teachers, are drained by their daily workload, some schools and districts are rethinking how homework should work—and some teachers are doing away with it entirely. They’re reviewing the research on homework (which, it should be noted, is contested) and concluding that it’s time to revisit the subject.
Read: My daughter’s homework is killing me
Hillsborough, California, an affluent suburb of San Francisco, is one district that has changed its ways. The district, which includes three elementary schools and a middle school, worked with teachers and convened panels of parents in order to come up with a homework policy that would allow students more unscheduled time to spend with their families or to play. In August 2017, it rolled out an updated policy, which emphasized that homework should be “meaningful” and banned due dates that fell on the day after a weekend or a break.
“The first year was a bit bumpy,” says Louann Carlomagno, the district’s superintendent. She says the adjustment was at times hard for the teachers, some of whom had been doing their job in a similar fashion for a quarter of a century. Parents’ expectations were also an issue. Carlomagno says they took some time to “realize that it was okay not to have an hour of homework for a second grader—that was new.”
Most of the way through year two, though, the policy appears to be working more smoothly. “The students do seem to be less stressed based on conversations I’ve had with parents,” Carlomagno says. It also helps that the students performed just as well on the state standardized test last year as they have in the past.
Earlier this year, the district of Somerville, Massachusetts, also rewrote its homework policy, reducing the amount of homework its elementary and middle schoolers may receive. In grades six through eight, for example, homework is capped at an hour a night and can only be assigned two to three nights a week.
Jack Schneider, an education professor at the University of Massachusetts at Lowell whose daughter attends school in Somerville, is generally pleased with the new policy. But, he says, it’s part of a bigger, worrisome pattern. “The origin for this was general parental dissatisfaction, which not surprisingly was coming from a particular demographic,” Schneider says. “Middle-class white parents tend to be more vocal about concerns about homework … They feel entitled enough to voice their opinions.”
Schneider is all for revisiting taken-for-granted practices like homework, but thinks districts need to take care to be inclusive in that process. “I hear approximately zero middle-class white parents talking about how homework done best in grades K through two actually strengthens the connection between home and school for young people and their families,” he says. Because many of these parents already feel connected to their school community, this benefit of homework can seem redundant. “They don’t need it,” Schneider says, “so they’re not advocating for it.”
That doesn’t mean, necessarily, that homework is more vital in low-income districts. In fact, there are different, but just as compelling, reasons it can be burdensome in these communities as well. Allison Wienhold, who teaches high-school Spanish in the small town of Dunkerton, Iowa, has phased out homework assignments over the past three years. Her thinking: Some of her students, she says, have little time for homework because they’re working 30 hours a week or responsible for looking after younger siblings.
As educators reduce or eliminate the homework they assign, it’s worth asking what amount and what kind of homework is best for students. It turns out that there’s some disagreement about this among researchers, who tend to fall in one of two camps.
In the first camp is Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University. Cooper conducted a review of the existing research on homework in the mid-2000s , and found that, up to a point, the amount of homework students reported doing correlates with their performance on in-class tests. This correlation, the review found, was stronger for older students than for younger ones.
This conclusion is generally accepted among educators, in part because it’s compatible with “the 10-minute rule,” a rule of thumb popular among teachers suggesting that the proper amount of homework is approximately 10 minutes per night, per grade level—that is, 10 minutes a night for first graders, 20 minutes a night for second graders, and so on, up to two hours a night for high schoolers.
In Cooper’s eyes, homework isn’t overly burdensome for the typical American kid. He points to a 2014 Brookings Institution report that found “little evidence that the homework load has increased for the average student”; onerous amounts of homework, it determined, are indeed out there, but relatively rare. Moreover, the report noted that most parents think their children get the right amount of homework, and that parents who are worried about under-assigning outnumber those who are worried about over-assigning. Cooper says that those latter worries tend to come from a small number of communities with “concerns about being competitive for the most selective colleges and universities.”
According to Alfie Kohn, squarely in camp two, most of the conclusions listed in the previous three paragraphs are questionable. Kohn, the author of The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , considers homework to be a “reliable extinguisher of curiosity,” and has several complaints with the evidence that Cooper and others cite in favor of it. Kohn notes, among other things, that Cooper’s 2006 meta-analysis doesn’t establish causation, and that its central correlation is based on children’s (potentially unreliable) self-reporting of how much time they spend doing homework. (Kohn’s prolific writing on the subject alleges numerous other methodological faults.)
In fact, other correlations make a compelling case that homework doesn’t help. Some countries whose students regularly outperform American kids on standardized tests, such as Japan and Denmark, send their kids home with less schoolwork , while students from some countries with higher homework loads than the U.S., such as Thailand and Greece, fare worse on tests. (Of course, international comparisons can be fraught because so many factors, in education systems and in societies at large, might shape students’ success.)
Kohn also takes issue with the way achievement is commonly assessed. “If all you want is to cram kids’ heads with facts for tomorrow’s tests that they’re going to forget by next week, yeah, if you give them more time and make them do the cramming at night, that could raise the scores,” he says. “But if you’re interested in kids who know how to think or enjoy learning, then homework isn’t merely ineffective, but counterproductive.”
His concern is, in a way, a philosophical one. “The practice of homework assumes that only academic growth matters, to the point that having kids work on that most of the school day isn’t enough,” Kohn says. What about homework’s effect on quality time spent with family? On long-term information retention? On critical-thinking skills? On social development? On success later in life? On happiness? The research is quiet on these questions.
Another problem is that research tends to focus on homework’s quantity rather than its quality, because the former is much easier to measure than the latter. While experts generally agree that the substance of an assignment matters greatly (and that a lot of homework is uninspiring busywork), there isn’t a catchall rule for what’s best—the answer is often specific to a certain curriculum or even an individual student.
Given that homework’s benefits are so narrowly defined (and even then, contested), it’s a bit surprising that assigning so much of it is often a classroom default, and that more isn’t done to make the homework that is assigned more enriching. A number of things are preserving this state of affairs—things that have little to do with whether homework helps students learn.
Jack Schneider, the Massachusetts parent and professor, thinks it’s important to consider the generational inertia of the practice. “The vast majority of parents of public-school students themselves are graduates of the public education system,” he says. “Therefore, their views of what is legitimate have been shaped already by the system that they would ostensibly be critiquing.” In other words, many parents’ own history with homework might lead them to expect the same for their children, and anything less is often taken as an indicator that a school or a teacher isn’t rigorous enough. (This dovetails with—and complicates—the finding that most parents think their children have the right amount of homework.)
Barbara Stengel, an education professor at Vanderbilt University’s Peabody College, brought up two developments in the educational system that might be keeping homework rote and unexciting. The first is the importance placed in the past few decades on standardized testing, which looms over many public-school classroom decisions and frequently discourages teachers from trying out more creative homework assignments. “They could do it, but they’re afraid to do it, because they’re getting pressure every day about test scores,” Stengel says.
Second, she notes that the profession of teaching, with its relatively low wages and lack of autonomy, struggles to attract and support some of the people who might reimagine homework, as well as other aspects of education. “Part of why we get less interesting homework is because some of the people who would really have pushed the limits of that are no longer in teaching,” she says.
“In general, we have no imagination when it comes to homework,” Stengel says. She wishes teachers had the time and resources to remake homework into something that actually engages students. “If we had kids reading—anything, the sports page, anything that they’re able to read—that’s the best single thing. If we had kids going to the zoo, if we had kids going to parks after school, if we had them doing all of those things, their test scores would improve. But they’re not. They’re going home and doing homework that is not expanding what they think about.”
“Exploratory” is one word Mike Simpson used when describing the types of homework he’d like his students to undertake. Simpson is the head of the Stone Independent School, a tiny private high school in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, that opened in 2017. “We were lucky to start a school a year and a half ago,” Simpson says, “so it’s been easy to say we aren’t going to assign worksheets, we aren’t going assign regurgitative problem sets.” For instance, a half-dozen students recently built a 25-foot trebuchet on campus.
Simpson says he thinks it’s a shame that the things students have to do at home are often the least fulfilling parts of schooling: “When our students can’t make the connection between the work they’re doing at 11 o’clock at night on a Tuesday to the way they want their lives to be, I think we begin to lose the plot.”
When I talked with other teachers who did homework makeovers in their classrooms, I heard few regrets. Brandy Young, a second-grade teacher in Joshua, Texas, stopped assigning take-home packets of worksheets three years ago, and instead started asking her students to do 20 minutes of pleasure reading a night. She says she’s pleased with the results, but she’s noticed something funny. “Some kids,” she says, “really do like homework.” She’s started putting out a bucket of it for students to draw from voluntarily—whether because they want an additional challenge or something to pass the time at home.
Chris Bronke, a high-school English teacher in the Chicago suburb of Downers Grove, told me something similar. This school year, he eliminated homework for his class of freshmen, and now mostly lets students study on their own or in small groups during class time. It’s usually up to them what they work on each day, and Bronke has been impressed by how they’ve managed their time.
In fact, some of them willingly spend time on assignments at home, whether because they’re particularly engaged, because they prefer to do some deeper thinking outside school, or because they needed to spend time in class that day preparing for, say, a biology test the following period. “They’re making meaningful decisions about their time that I don’t think education really ever gives students the experience, nor the practice, of doing,” Bronke said.
The typical prescription offered by those overwhelmed with homework is to assign less of it—to subtract. But perhaps a more useful approach, for many classrooms, would be to create homework only when teachers and students believe it’s actually needed to further the learning that takes place in class—to start with nothing, and add as necessary.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What we know about online learning and the homework gap amid the pandemic

America’s K-12 students are returning to classrooms this fall after 18 months of virtual learning at home during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some students who lacked the home internet connectivity needed to finish schoolwork during this time – an experience often called the “ homework gap ” – may continue to feel the effects this school year.
Here is what Pew Research Center surveys found about the students most likely to be affected by the homework gap and their experiences learning from home.
Children across the United States are returning to physical classrooms this fall after 18 months at home, raising questions about how digital disparities at home will affect the existing homework gap between certain groups of students.
Methodology for each Pew Research Center poll can be found at the links in the post.
With the exception of the 2018 survey, everyone who took part in the surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
The 2018 data on U.S. teens comes from a Center poll of 743 U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 conducted March 7 to April 10, 2018, using the NORC AmeriSpeak panel. AmeriSpeak is a nationally representative, probability-based panel of the U.S. household population. Randomly selected U.S. households are sampled with a known, nonzero probability of selection from the NORC National Frame, and then contacted by U.S. mail, telephone or face-to-face interviewers. Read more details about the NORC AmeriSpeak panel methodology .
Around nine-in-ten U.S. parents with K-12 children at home (93%) said their children have had some online instruction since the coronavirus outbreak began in February 2020, and 30% of these parents said it has been very or somewhat difficult for them to help their children use technology or the internet as an educational tool, according to an April 2021 Pew Research Center survey .
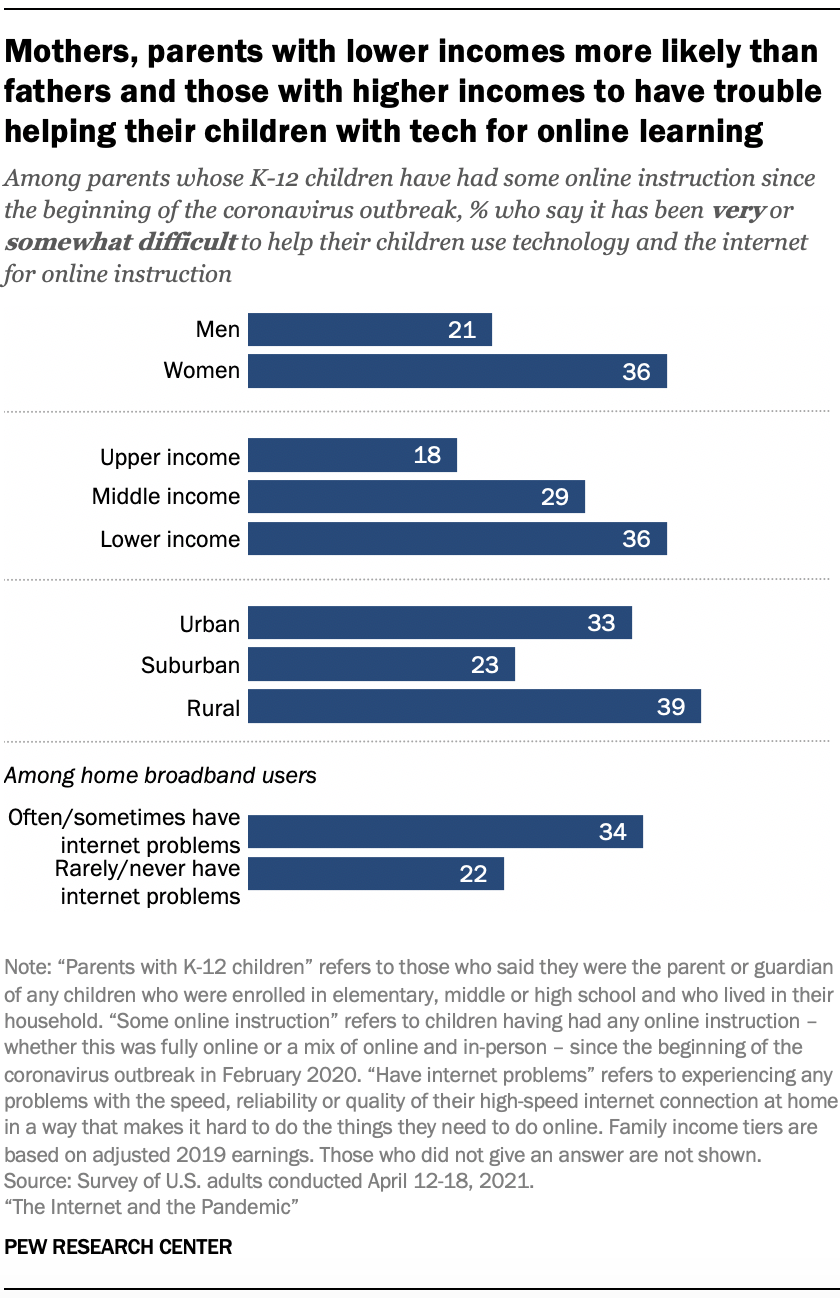
Gaps existed for certain groups of parents. For example, parents with lower and middle incomes (36% and 29%, respectively) were more likely to report that this was very or somewhat difficult, compared with just 18% of parents with higher incomes.
This challenge was also prevalent for parents in certain types of communities – 39% of rural residents and 33% of urban residents said they have had at least some difficulty, compared with 23% of suburban residents.
Around a third of parents with children whose schools were closed during the pandemic (34%) said that their child encountered at least one technology-related obstacle to completing their schoolwork during that time. In the April 2021 survey, the Center asked parents of K-12 children whose schools had closed at some point about whether their children had faced three technology-related obstacles. Around a quarter of parents (27%) said their children had to do schoolwork on a cellphone, 16% said their child was unable to complete schoolwork because of a lack of computer access at home, and another 14% said their child had to use public Wi-Fi to finish schoolwork because there was no reliable connection at home.
Parents with lower incomes whose children’s schools closed amid COVID-19 were more likely to say their children faced technology-related obstacles while learning from home. Nearly half of these parents (46%) said their child faced at least one of the three obstacles to learning asked about in the survey, compared with 31% of parents with midrange incomes and 18% of parents with higher incomes.
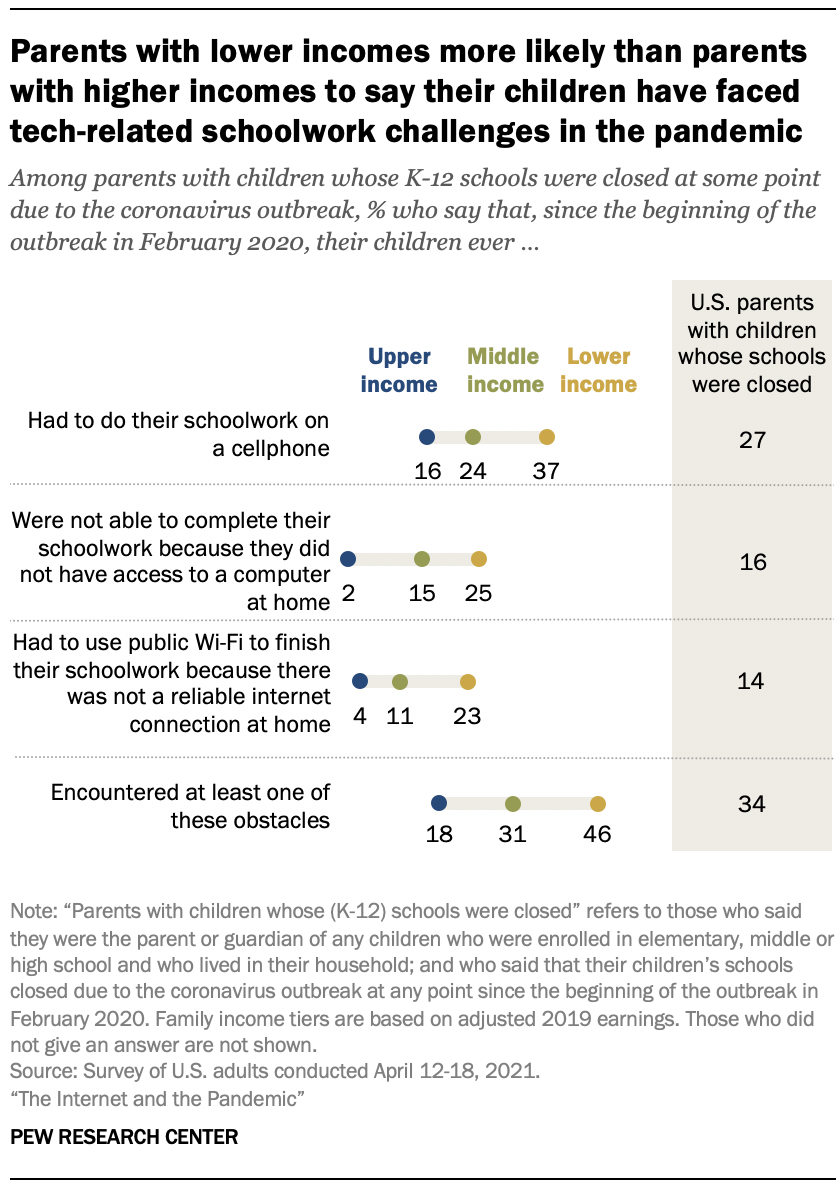
Of the three obstacles asked about in the survey, parents with lower incomes were most likely to say that their child had to do their schoolwork on a cellphone (37%). About a quarter said their child was unable to complete their schoolwork because they did not have computer access at home (25%), or that they had to use public Wi-Fi because they did not have a reliable internet connection at home (23%).
A Center survey conducted in April 2020 found that, at that time, 59% of parents with lower incomes who had children engaged in remote learning said their children would likely face at least one of the obstacles asked about in the 2021 survey.
A year into the outbreak, an increasing share of U.S. adults said that K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide all students with laptop or tablet computers in order to help them complete their schoolwork at home during the pandemic. About half of all adults (49%) said this in the spring 2021 survey, up 12 percentage points from a year earlier. An additional 37% of adults said that schools should provide these resources only to students whose families cannot afford them, and just 13% said schools do not have this responsibility.
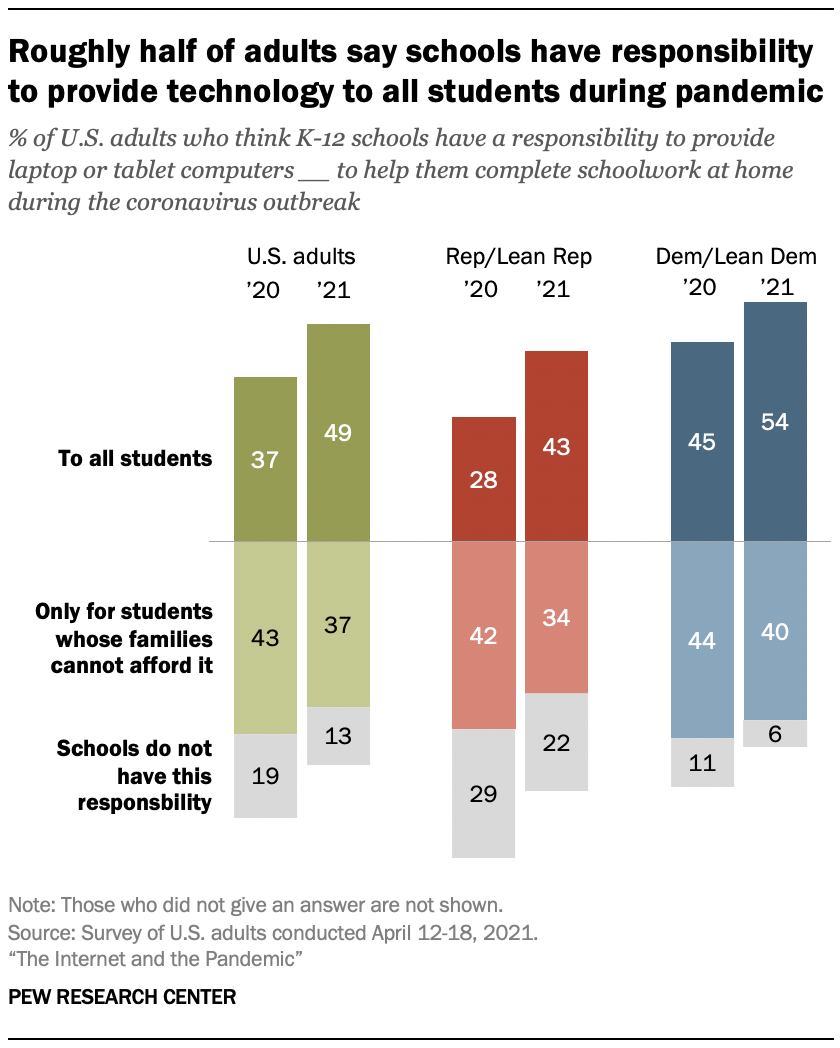
While larger shares of both political parties in April 2021 said K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide computers to all students in order to help them complete schoolwork at home, there was a 15-point change among Republicans: 43% of Republicans and those who lean to the Republican Party said K-12 schools have this responsibility, compared with 28% last April. In the 2021 survey, 22% of Republicans also said schools do not have this responsibility at all, compared with 6% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
Even before the pandemic, Black teens and those living in lower-income households were more likely than other groups to report trouble completing homework assignments because they did not have reliable technology access. Nearly one-in-five teens ages 13 to 17 (17%) said they are often or sometimes unable to complete homework assignments because they do not have reliable access to a computer or internet connection, a 2018 Center survey of U.S. teens found.
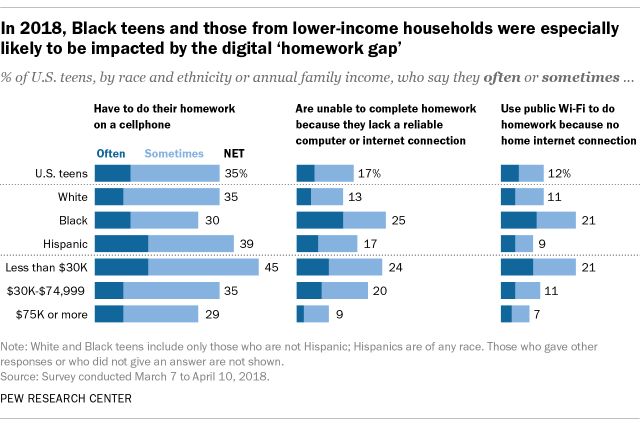
One-quarter of Black teens said they were at least sometimes unable to complete their homework due to a lack of digital access, including 13% who said this happened to them often. Just 4% of White teens and 6% of Hispanic teens said this often happened to them. (There were not enough Asian respondents in the survey sample to be broken out into a separate analysis.)
A wide gap also existed by income level: 24% of teens whose annual family income was less than $30,000 said the lack of a dependable computer or internet connection often or sometimes prohibited them from finishing their homework, but that share dropped to 9% among teens who lived in households earning $75,000 or more a year.
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- COVID-19 & Technology
- Digital Divide
- Education & Learning Online

Katherine Schaeffer is a research analyst at Pew Research Center .
How Americans View the Coronavirus, COVID-19 Vaccines Amid Declining Levels of Concern
Online religious services appeal to many americans, but going in person remains more popular, about a third of u.s. workers who can work from home now do so all the time, how the pandemic has affected attendance at u.s. religious services, mental health and the pandemic: what u.s. surveys have found, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Academic goals, student homework engagement, and academic achievement in elementary school.

- 1 Department of Developmental and Educational Psychology, University of A Coruña, A Coruña, Spain
- 2 Department of Psychology, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
- 3 Departmento de Psicologia Aplicada, Universidade do Minho, Braga, Portugal
There seems to be a general consensus in the literature that doing homework is beneficial for students. Thus, the current challenge is to examine the process of doing homework to find which variables may help students to complete the homework assigned. To address this goal, a path analysis model was fit. The model hypothesized that the way students engage in homework is explained by the type of academic goals set, and it explains the amount of time spend on homework, the homework time management, and the amount of homework done. Lastly, the amount of homework done is positively related to academic achievement. The model was fit using a sample of 535 Spanish students from the last three courses of elementary school (aged 9 to 13). Findings show that: (a) academic achievement was positively associated with the amount of homework completed, (b) the amount of homework completed was related to the homework time management, (c) homework time management was associated with the approach to homework, (d) and the approach to homework, like the rest of the variables of the model (except for the time spent on homework), was related to the student's academic motivation (i.e., academic goals).
Introduction
Literature indicates that doing homework regularly is positively associated with students' academic achievement ( Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 2005 ). Hence, as expected, the amount of homework done is one of the variables that shows a strong and positive relationship with academic achievement ( Cooper et al., 2001 ).
It seems consensual in the literature that doing homework is always beneficial to students, but it is also true that the key for the academic success does not rely on the amount of homework done, but rather on how students engage on homework ( Trautwein et al., 2009 ; Núñez et al., 2015c ), and on how homework engagement is related with student motivation ( Martin, 2012 ). There is, therefore, a call to analyze the process of homework rather than just the product; that is, to examine the extent to which the quality of the process of doing homework may be relevant to the final outcome.
Trautwein's Model of Homework
The model by Trautwein et al. (2006b) is rooted in the motivational theories, namely the theory of the expectancy value ( Eccles (Parsons) et al., 1983 ; Pintrich and De Groot, 1990 ), and the theory of self-determination ( Deci et al., 2002 ), as well as on theories of learning and instruction ( Boekaerts, 1999 ). Trautwein and colleagues' model analyzes students' related variables in two blocks, as follows: the motivational (aiming at directing and sustaining the behavior) and the cognitive and behavioral implications (cognitions and behaviors related to the moment of doing homework).These two blocks of variables are rooted in the literature. Motivational variables are related with the theory of expectancy-value by Eccles (Parsons) et al. (1983) , while the variables addressing students' implication are related with the school engagement framework (e.g., Fredricks et al., 2004 ). However, as Eccles and Wang (2012) stress, both models are interrelated due to the fact that both variables are closely related and show reciprocal relationships.
Student Homework Engagement: The Interplay Between Cognitive and Behavioral Components
Engagement is a relatively new construct with great relevance in the field of psychology and instruction ( Fredricks et al., 2004 ). Generally considered, engagement has been described as the active implication of the person in an activity ( Reeve et al., 2004 ). However, despite the close relation between engagement and motivation, literature clearly differentiates between them (e.g., Martin, 2012 ), stressing engagement as the behavioral manifestation of motivation ( Skinner and Pitzer, 2012 ), or arguing that motivation is a precursor of engagement rather than part of it. In sum, motivation relates to the “why” whereas the engagement focuses on the “what” of a particular behavior.
Consistent with this perspective, the current research fitted a model with the variable engagement mediating the relationship between motivation and academic achievement (see Eccles and Wang, 2012 ). Engagement is a complex construct with observational and non-observational aspects ( Appleton et al., 2008 ). Some researchers conceptualize engagement with two dimensions—behavior and emotions (e.g., Marks, 2000 )—while others define engagement with four dimensions—academic, behavioral, cognitive, and emotional (e.g., Appleton et al., 2006 ). In the current study, we followed Fredricks' et al. (2004) conceptualization of engagement as a construct with three dimensions: cognitive (e.g., approaches to learning), behavioral (e.g., student homework behaviors), and emotional (e.g., interest, boredom). For the purpose of the present study, the dimension of emotion was not included in the model (see Figure 1 ).
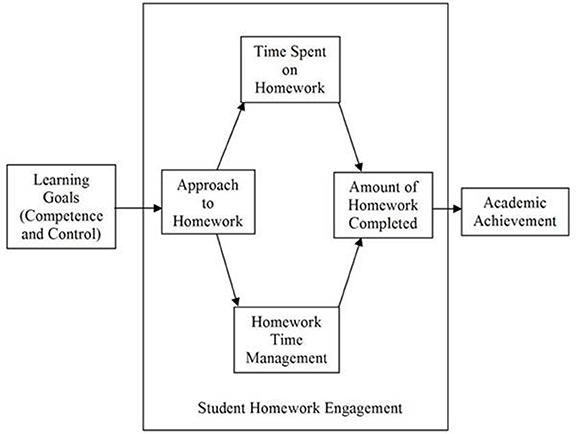
Figure 1. General model hypothesized to explain the relationship between academic motivation, student homework engagement, and academic achievement .
Cognitive Homework Engagement
In the past few decades, a robust body of research has been addressing the relationship between the way students deal with their learning process and academic outcomes ( Marton and Säljö, 1976a , b ; Struyven et al., 2006 ; Rosário et al., 2010a , 2013a ). Marton and Säljö (1976a , b) examined how students studied an academic text and found two ways of approaching the task: a surface and a deep approach. The surface approach is characterized by learning the contents aiming at achieving goals that are extrinsic to the learning content. In contrast, the deep approach is characterized by an intrinsic interest in the task and students are likely to be focused on understanding the learning content, relating it to prior knowledge and to the surrounding environment ( Entwistle, 2009 ; Rosário et al., 2010b ). The metaphor “surface vs. deep” constitutes an easy to perceive conceptual framework, both in the classroom setting and in other educational settings (i.e., doing homework at home), and has been shown to be a powerful tool for parents, teachers, and students when conceptualizing the ways students approach school tasks ( Entwistle, 1991 ; Rosário et al., 2005 ). The core of the concept of approaches to studying (or to learning) is the metacognitive connection between an intention to approach a task and a strategy to implement it ( Rosário et al., 2013b ).
The process of doing homework focuses on what students do when completing homework, that is, how they approach their work and how they manage their personal resources and settings while doing homework. It is likely that students' approaches to homework may influence not only the final homework outcome but also the quality of that process. Students who adopt a deep approach are likely to engage their homework with the intention of deepening their understanding of the knowledge learned in class. In this process, students often relate the homework exercises to prior knowledge and monitor their mastery of the content learned. This process involves intrinsic intention to understand the ideas and the use of strategies to build meaning ( Cano et al., 2014 ). In contrast, students who approach homework with a surface approach are likely to do homework with extrinsic motivation (e.g., rewards of their parents, fear of upsetting their teacher). Their goals may target finishing homework as soon as and with the less effort possible to be able to do more interesting activities. Students using this approach are more likely to do homework to fulfill an external obligation (e.g., hand in homework in class and get a grade), than for the benefits for learning.
Behavioral Homework Engagement
Findings from prior research indicate that the more the implication of students in doing their homework the better the academic achievement ( Cooper et al., 2006 ). Following Trautwein et al. (2006b) , our conceptualization of student homework engagement includes behaviors related with the amount of homework done, time spent on homework, and homework time management (e.g., concentration). In the present investigation, these three variables were included in the model (see Figure 1 ).
Extant findings on the relationship between the amount of homework done and academic achievement are in need of further clarification. Some authors argue for a strong and positive relationship (e.g., Cooper et al., 2006 ), while others found that this relationship is higher throughout schooling ( Cooper et al., 2001 ; Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 2005 ). Authors explained this last finding arguing that the load of homework assigned by teachers vary throughout schooling, and also that the cognitive competencies of students are likely to vary with age ( Muhlenbruck et al., 2000 ). More recently, Núñez et al. (2015c) found that the relationship between these two variables varied as a function of the age of the students enrolled. Particularly, this relationship was found to be negative in elementary school, null in junior high school, and positive in high school.
Moreover, the relationship between the amount of homework done and academic achievement relates, among other factors, with the students' age, the quality of the homework assigned, the type of assessment, and the nature of the feedback provided. For example, some students may always complete their homework and get good grades for doing it, which does not mean that these students learn more ( Kohn, 2006 ). In fact, more important than the quantity of the homework done, is the quality of that work ( Fernández-Alonso et al., 2014 ).
Another variable included in the model was the time spent on homework. Findings on the relationship between time spent on homework and academic achievement are mixed. Some studies found a positive relationship ( Cooper et al., 2001 , 2006 ) while others found a null or a negative one ( Trautwein et al., 2006b , 2009 ). In 2009, Dettmers, Trautwein and Lüdtke conducted a study with data from the PISA 2003 ( Dettmers et al., 2009 ). Findings on the relationship between the number of hours spent on homework and academic achievement in mathematics show that the students in countries with higher grades spend fewer hours doing homework than students in countries with low academic grades. At the student level, findings showed a negative relationship between time spent on homework and academic achievement in 12 out of 40 countries.
The relationship between the amount of homework done, time dedicated to homework, and academic achievement was hypothesized to be mediated by the homework time management. Xu (2007) was one of the pioneers examining the management of the time spent on homework. Initially, Xu (2007) did not find a relationship between time management and academic achievement (spend more time on homework is not equal to use efficient strategies for time management). Latter, Xu (2010) found a positive relationship between students' grade level, organized environment, and homework time management. More recently, Núñez et al. (2015c) found that effective homework time management affects positively the amount of homework done, and, consequently, academic achievement. This relationship is stronger for elementary students when compared with students in high school.
Academic Motivation and Student Homework Engagement Relationship
Literature has consistently shown that a deep approach to learning is associated positively with the quality of the learning outcomes ( Rosário et al., 2013b ; Cano et al., 2014 ; Vallejo et al., 2014 ). The adoption of a deep approach to homework depends on many factors, but students self-set goals and their motives for doing homework are among the most critical motivational variables when students decide to engage in homework.
Literature on achievement motivation highlights academic goals as an important line of research ( Ng, 2008 ). In the educational setting, whereas learning goals focus on the comprehension and mastery of the content, performance goals are more focused on achieving a better performance than their colleagues ( Pajares et al., 2000 ; Gaudreau, 2012 ).
Extant literature reports a positive relationship between adopting learning goals and the use of cognitive and self-regulation strategies ( Elliot et al., 1999 ; Núñez et al., 2013 ). In fact, students who value learning and show an intention to learn and improve their competences are likely to use deep learning strategies ( Suárez et al., 2001 ; Valle et al., 2003a , b , 2015d ), which are aimed at understanding the content in depth. Moreover, these learning-goal oriented students are likely to self-regulate their learning process ( Valle et al., 2015a ), put on effort to learn, and assume the control of their learning process ( Rosário et al., 2016 ). These students persist much longer when they face difficult and challenging tasks than colleagues pursuing performance goals. The former also use more strategies oriented toward the comprehension of content, are more intrinsically motivated, and feel more enthusiasm about academic work. Some researchers also found positive relationships between learning goals and pro-social behavior (e.g., Inglés et al., 2013 ).
Reviewing the differentiation between learning goals and performance goals, Elliot and colleagues ( Elliot and Church, 1997 ; Elliot, 1999 ; Elliot et al., 1999 ) proposed a three-dimensional framework for academic goals. In addition to learning goals, performance goals were differentiated as follows: (a) performance-approach goals, focused on achieving competence with regard to others; and (b) performance-avoidance goals, aimed at avoiding incompetence with regard to others. Various studies have provided empirical support for this distinction within performance goals (e.g., Wolters et al., 1996 ; Middleton and Midgley, 1997 ; Skaalvik, 1997 ; Rodríguez et al., 2001 ; Valle et al., 2006 ). Moreover, some authors proposed a similar differentiation for learning goals ( Elliot, 1999 ). The rationale was as follows: learning goals are characterized by high engagement in academic tasks, so an avoidance tendency in such goals should reflect avoidance of this engagement. Hence, students who pursue a work avoidance goal are likely to avoid challenging tasks and to put on effort to do well, only doing the bare minimum to complete the task. In general, learning goals are associated with a large amount of positive results in diverse motivational, cognitive, and achievement outcomes, whereas performance goals have been linked to less adaptive outcomes, or even to negative outcomes ( Valle et al., 2009 ).
Aims of this Study
Several relationships between motivational, cognitive, and behavioral variables involving self-regulated learning in the classroom have recently been studied ( Rosário et al., 2013a ). However, there is a lack of knowledge of the relationships between these variables throughout the process of doing homework.
The principal purpose of this work (see Figure 1 ) is to analyze how student homework engagement (cognitive and behavioral) mediates motivation and academic performance. This study aims to provide new information about an issue that is taken for granted, but which, as far as we know, lacks empirical data. The question is: to what extent students acknowledge homework as a good way to acquire competence, improve their skills and performance? Our working hypothesis is that student value homework in this regard. Therefore, we hypothesized that the more students are motivated to learn, the more they will be involved (cognitively and behaviorally) in their homework, and the higher their academic achievement.
To address this goal, we developed a path analysis model (see Figure 1 ) in which we hypothesized that: (a) the student's motivational level is significantly related to their cognitive homework engagement (i.e., the approach to studying applied to homework), and their behavioral homework engagement (i.e., amount of time spent and homework time management, and amount of homework completed); (b) student's cognitive and behavioral homework engagement are positively associated with academic achievement; and (c) cognitive and behavioral homework engagement are related (the more deep cognitive engagement, the more time spent and time management, and the more amount of homework is done).
Participants
The study enrolled 535 students, aged between 9 and 13 ( M = 10.32, SD = 0.99), of four public schools, from the last three years of the Spanish Elementary Education (4th, 5th, and 6th grade level), of whom 49.3% were boys. By grade, 40.4% ( n = 216) were enrolled in the 4th grade, 35.1% ( n = 188) in the 5th grade, and 24.5% ( n = 131) in the 6th grade.
Learning Goals
The level and type of motivation for academic learning was assessed with the Academic Goals Instrument ( Núñez et al., 1997 ). Although, this instrument allows differentiating a broad range of academic goals, for the purposes of this work, we only used the subscale of learning goals (i.e., competence and control). The instrument is rated on a 5-point Likert-type scale, with responses ranging from one (not at all interested) to five (absolutely interested in learning and acquiring competence and control in the different subjects). An example item is: “I make an effort in my studies because performing the academic tasks allows me to increase my knowledge.” The reliability of the scale is good (α = 0.87).
Approach to Homework
To measure the process of approaching homework, we adapted the Students' Approaches to Learning Inventory ( Rosário et al., 2010a , 2013a ), taking into account both the students' age and the homework contexts. This instrument is based on voluminous literature on approaches to learning (e.g., Biggs et al., 2001 ; Rosário et al., 2005 ), and provides information about two ways of approaching homework. For the purpose of this research, we only used the deep approach (e.g., “Before starting homework, I usually decide whether what was taught in class is clear and, if not, I review the lesson before I start”). Students respond to the items on a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from one (not at all deep approach) to five (completely deep approach). The reliability of the scale is good (α = 0.80).
Time Spent on Homework, Homework Time Management, and Amount of Homework Completed
To measure these three variables, we used the Homework Survey (e.g., Rosário et al., 2009 ; Núñez et al., 2015a , b ; Valle et al., 2015b , c ). To measure the time spent on homework , students responded to three items (in general, in a typical week, on a typical weekend) with the general formulation, “How much time do you usually spend on homework?,” with the response options 1, <30 min; 2, 30 min to 1 h; 3, 1 h to an hour and a half; 4, 1 h and a half to 2 h; 5, more than 2 h. Homework time management was measured through the responses to three items (in general, in a typical week, on a typical weekend) in which they were asked to indicate how they managed the time normally spent doing homework, using the following scale: 1, I waste it completely (I am constantly distracted by anything); 2, I waste it more than I should; 3, regular; 4, I manage it pretty much; 5, I optimize it completely (I concentrate and until I finish, I don't think about anything else). Finally, the amount of homework completed by students (assigned by teachers) was assessed through responses to an item about the amount of homework usually done, using a 5-point Likert-type scale (1, none; 2, some; 3, one half; 4, almost all; 5, all).
Academic Achievement
Assessment of academic achievement was assessed through students' report card grades in Spanish Language, Galician Language, English Language, Knowledge of the Environment, and Mathematics. Average achievement was calculated with the mean grades in these five areas.
Data of the target variables was collected during regular school hours, by research assistants, after obtaining the consent of the school administration and of the teachers and students. Prior to the application of the questionnaires, which took place in a single session, the participants were informed about the goals of the project, and assured that data was confidential and used for research purposes only.
Data Analysis
The model was fit with AMOS 18 ( Arbuckle, 2009 ). The data were previously analyzed and individual cases presenting a significant number of missing values were eliminated (2.1%), whereas the rest of the missing values were replaced by the mean. Taking into account the analysis of the characteristics of the variables (e.g., skewness and kurtosis in Table 1 ), we used the maximum likelihood method to fit the model and estimate the values of the parameters.
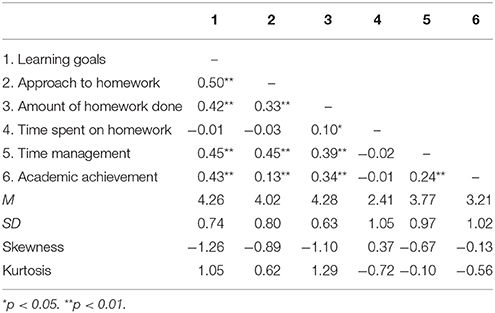
Table 1. Means, standard deviations, skewness, kurtosis, and correlation matrix of the target variables .
A series of goodness-of-fit statistics were used to analyze our model. Beyond chi-square (χ 2 ) and its associated probability ( p ), the information provided by the goodness-of-fit index (GFI) and the adjusted goodness-of-fit index (AGFI; Jöreskog and Sörbom, 1983 ); the comparative fit index (CFI) ( Bentler, 1990 ); and the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA; Browne and Cudeck, 1993 ) was used. According to these authors, the model fits well when GFI and AGFI > 0.90, CFI > 0.95, and RMSEA ≤ 0.05.
Descriptive Analysis
The relations between the variables included in the model as well as the descriptive statistics are shown in Table 1 . All the variables were significantly and positively related, except for the time spent on homework, which was only related to the amount of homework done. According to the value of the means of these variables, students in the last years of elementary school: (a) reported a high level of motivation to learn and mastery; (b) used preferentially a deep approach to homework; (c) did the homework assigned by the teachers most of the times; (d) usually spent about an hour a day on homework; (e) reported to manage their study time effectively; and (f) showed a medium-high level of academic achievement.
Evaluation and Re-specification of the Initial Model
The data obtained indicated that the initial model (see Figure 1 ) presented a poor fit to the empirical data: χ 2 = 155.80, df = 8, p < 0.001, GFI = 0.917, AGFI = 0.783, TLI = 0.534, CFI = 0.751, RMSEA = 0.186, 90% CI (0.161, 0.212), p < 0.001. Analysis of the modification indexes revealed the need to include three direct effects initially considered as null, and to eliminate a finally null effect (included in the initial model as significant). The strategy adopted to modify the initial model involved including and estimating the model each time a new effect was included. The final model comprised three effects (academic goals on homework time management, on amount of homework done, and on academic achievement) and the elimination of the initially established effect of the approach to studying on the time spent doing homework. The inclusion or elimination of the effects in the model was determined accounting for their statistical and theoretical significance. The final model resulting from these modifications is shown in Figure 2 , with an adequate fit to the empirical data: χ 2 = 12.03, df = 6, p = 0.061, GFI = 0.993, AGFI = 0.974, TLI = 0.975, CFI = 0.990, RMSEA = 0.043, 90% CI (0.000, 0.079), p = 0.567.
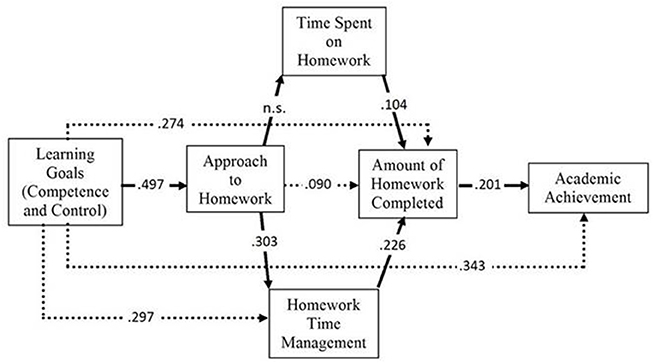
Figure 2. The results of the fit of the hypothesized model (standardized outcomes): Relations in dashed lines were found to be statistically significant, but this was not established in the initial model .
Assessment of the Relationships on the Final Model
Table 2 presents the data obtained for the relationships considered in the final model (see also Figure 2 ).
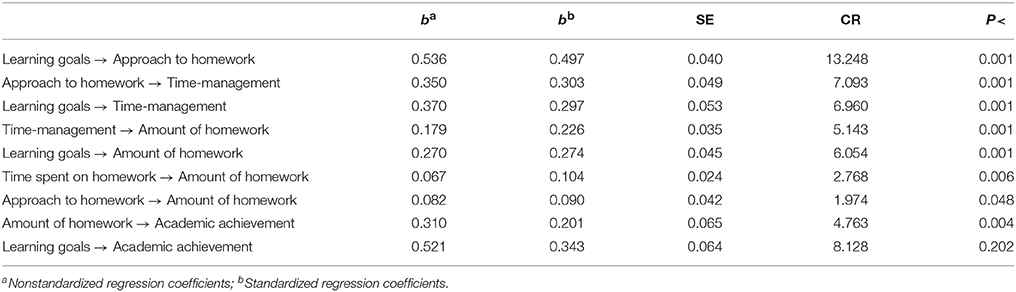
Table 2. Fit of the hypothesized model (standardized outcomes): final model of student engagement in homework .
The data from Table 2 and Figure 2 indicates that the majority of the relationships between the variables are consistent with the hypotheses. First, we found a statistically significant association between the learning goals (i.e., competence and control), the approach to homework ( b = 0.50, p < 0.001), two of the variables associated with engagement in homework (the amount of homework done [ b = 0.27, p < 0.001], homework time management [ b = 0.30, p < 0.001]), and academic achievement ( b = 0.34, p < 0.001). These results indicate that the more oriented students are toward learning goals (i.e., competence and control), the deeper the approach to homework, the more homework is completed, the better the homework time management, and the higher the academic achievement.
Second, a statistically significant association between the deep approach and homework time management ( b = 0.30, p < 0.001) and the amount of homework done ( b = 0.09, p < 0.05) was found. These results reflect that the deeper the students' approach to homework, the better the management of the time spent on homework, and the more the homework done. Third, there was a statistically significant association between homework time management, time spent on homework, and the amount of homework done ( b = 0.23, p < 0.001, and b = 0.10, p < 0.01, respectively). These results confirm, as expected, that the more time students spent doing homework and the better students manage their homework time, the more homework they will do. Four, we found a statistically significant relation between the amount of homework done and academic achievement ( b = 0.20, p < 0.001). This indicates that the more homework students complete the better their academic achievement.
In summary, our findings indicate that: (a) academic achievement is positively associated with the amount of homework completed; (b) the amount of homework done is related to homework time management; (c) homework time management is associated with how homework is done (approach to homework); and (d) consistent with the behavior of the variables in the model (except for the time spent on homework), how homework is done (i.e., approach to homework) is explained to a great extent (see total effects in Table 3 ) by the student's type of academic motivation.
Table 3. Standardized direct, indirect, and total effects for the final model .
Finally, taking into account both the direct effects (represented in Figure 2 ) and the indirect ones (see Table 3 ), the model explained between 20 and 30% of the variance of the dependent variables (except for the time spent on homework, which is not explained at all): approach to homework (24.7%), time management (26.9%), amount of homework done (24.4%), and academic achievement (21.6%).
Consistent with prior research (e.g., Cooper et al., 2001 ), our findings showed that students' academic achievement in the last years of elementary education is closely related to the amount of homework done. In addition, the present study also confirms the importance of students' effort and commitment to doing homework ( Trautwein et al., 2006a , b ), showing that academic achievement is also related with students' desire and interest to learn and improve their skills. Therefore, when teachers assign homework, it is essential to attend to students' typical approach to learning, which is mediated by the motivational profile and by the way students solve the tasks proposed ( Hong et al., 2004 ). The results of this investigation suggest that the adoption of learning goals leads to important educational benefits ( Meece et al., 2006 ), among which is doing homework.
Importantly, our study shows that the amount of homework done is associated not only with the time spent, but also with the time management. Time spent on homework should not be considered an absolute indicator of the amount of homework done, because students' cognitive skills, motivation, and prior knowledge may significantly affect the time needed to complete the homework assignment ( Regueiro et al., 2015 ). For students, managing homework time is a challenge ( Corno, 2000 ; Xu, 2008 ), but doing it correctly may have a positive influence on their academic success ( Claessens et al., 2007 ), on homework completion ( Xu, 2005 ), and on school achievement ( Eilam, 2001 ).
Despite, that previous studies reported a positive relationship between the time spent on homework and academic achievement ( Cooper et al., 2006 ), the present research shows that time spent on homework is not a relevant predictor of academic achievement. Other studies have also obtained similar results ( Trautwein et al., 2009 ; Núñez et al., 2015a ), indicating that time spent on homework is negatively associated to academic achievement, perhaps because spending a lot of time on homework may indicate an inefficient working style and lack of motivation ( Núñez et al., 2015a ). Besides, our data indicates that spending more time on homework is positively associated to the amount of homework done.
Although, some studies have found that students who spend more time on homework also tend to report greater commitment to school work ( Galloway et al., 2013 ), our findings indicated that spending more time doing homework was not related to a deeper engagement on the task. A possible explanation may be that using a deep approach to school tasks subsumes engaging in homework with the aim of practicing but also to further extend the content learned in class. This approach does not depends on the time spent doing homework, rather on the students' motives for doing homework.
Another important contribution of this study concerns learning-oriented goals—usually associated with positive outcomes in motivational, cognitive, and achievement variables ( Pajares et al., 2000 ). Results indicate that the motivation to increase competence and learning is also related to approaching homework deeply and to manage homework efficiently. Consistent with previous findings ( Xu, 2005 ), these results provide additional empirical support to time management goals ( Pintrich, 2004 ).
There is a robust relationship between learning-oriented goals and a deep approach, and between a deep approach and the amount of homework done. All this indicates that these results are in line with prior research, meaning that the adoption of a deep approach to learning is related with high quality academic achievement ( Lindblom-Ylänne and Lonka, 1999 ; Rosário et al., 2013b ).
Educational Implications and Study Limitations
One of the major limitations of this study lies in the type of research design used. We used a cross-sectional design to examine the effects among the variables within a path analysis model. However, to establish a cause-effect relationship a temporal sequence between two variables is needed a requirement that can only be met with longitudinal designs. Future studies should consider address this limitation.
Despite the above limitation, our results can be considered relevant and show important educational implications. It is essential for teachers and school administrators to be sensitized about the effects of teachers' homework follow-up practices on students' homework engagement ( Rosário et al., 2015 ), and of these variables in students' school engagement and academic success. Likewise, research on students' learning should be undertaken from the perspective of the learners to understand how students use their knowledge and skills to do homework and to solve problems posed therein. On the other hand, research should examine in-depth the use of learning strategies during homework, as well as how students' motivations at an early age may foster homework completion and increase the quality of school outcomes. For this last purpose, teachers should pay attention not only to the acquisition of curricular content but also to the development of the appropriate thinking skills and self-regulated learning strategies ( Rosário et al., 2010b ; Núñez et al., 2013 ). Finally, the amount of homework done and its positive relationship with academic achievement should be considered as a final outcome of a process rooted on a comprehensive and meaningful learning. Students motivated to learn are likely to approach homework deeply and manage homework time efficaciously. As a result, they tend to do more homework and outperform. In sum, is doing homework a good way to acquire competence, improve skills, and outperform? Our data suggest a positive answer.
Author Contributions
AV and BR Collect data, data analysis, writing the paper. JN and PR data analysis, writing the paper. SR and IP writing the paper.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was developed through the funding of the research project EDU2013-44062-P, of the State Plan of Scientific and Technical Research and Innovation 2013-2016 (MINECO) and to the financing received by one of the authors in the FPU program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, and Sport.
Appleton, J. J., Christenson, S. L., and Furlong, M. J. (2008). Student engagement with school: critical conceptual and methodological issues of the construct. Psychol. Sch. 45, 369–386. doi: 10.1002/pits.20303
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Appleton, J. J., Christenson, S. L., Kim, D., and Reschly, A. L. (2006). Measuring cognitive and psychological engagement: validation of the student engagement instrument. J. Sch. Psychol. 44, 427–445. doi: 10.1016/j.jsp.2006.04.002
Arbuckle, J. L. (2009). Amos 18.0 User's Guide . Crawfordville, FL: Amos Development Corporation.
Google Scholar
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychol. Bull. 107, 238–246. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.238
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Biggs, J., Kember, D., and Leung, D. Y. (2001). The revised two-actor study process questionnaire: R-SPQ-2F. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 71, 133–149. doi: 10.1348/000709901158433
Boekaerts, M. (1999). Self-regulated learning: where are today. Int. J. Educ. Res. 31, 445–458. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(99)00014-2
Browne, M. W., and Cudeck, R. (1993). “Alternative ways of assessing model fit,” in Testing Structural Equation Models , eds K. Bollen and J. Long (Newbury Park, CA: Sage), 136–162.
Cano, F., García, A., Justicia, F., and García-Berbén, A. B. (2014). Enfoques de aprendizaje y comprensión lectora: el papel de las preguntas de los estudiantes y del conocimiento previo [Approaches to learning and reading comprehension: the role of students' questions and of prior knowledge]. Rev. Psicodidáctica 19, 247–265. doi: 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.10186
Claessens, B. J. C., van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., and Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Pers. Rev. 36, 255–276. doi: 10.1108/00483480710726136
Cooper, H., Jackson, K., Nye, B., and Lindsay, J. J. (2001). A model of homework's influence on the performance evaluations of elementary school students. J. Exp. Educ. 69, 181–200. doi: 10.1080/00220970109600655
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., and Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Rev. Educ. Res. 76, 1–62. doi: 10.3102/00346543076001001
Corno, L. (2000). Looking at homework differently. Element. Sch. J. 100, 529–548. doi: 10.1086/499654
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (2002). Handbook of Self-Determination Research . New York, NY: University of Rochester Press.
Dettmers, S., Trautwein, U., and Lüdtke, O. (2009). The relationship between homework time and achievement is not universal: evidence from multilevel analyses in 40 countries. Sch. Eff. Sch. Improv. 20, 375–405. doi: 10.1080/09243450902904601
Eccles, J., and Wang, M. T. (2012). “Part I Commentary: so what is student engagement anyway?,”in Handbook of Research on Student Engagement , eds S. L. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, and C. Wylie (New York, NY: Springer), 133–145.
Eccles (Parsons), J., Adler, T. F., Futterman, R., Goff, S. B., Kaczala, C. M., Meece, J. L., et al. (1983). “Expectancies, values, and academic choice: origins and changes,” in Achievement and Achievement Motivation , ed J. Spence (San Francisco, CA: Freeman), 75–146.
Eilam, B. (2001). Primary strategies for promoting homework performance. Am. Educ. Res. J. 38, 691–725. doi: 10.3102/00028312038003691
Elliot, A. J. (1999). Approach and avoidance motivation and achievement goals. Educ. Psychol. 34, 169–189. doi: 10.1207/s15326985ep3403_3
Elliot, A. J., and Church, M. A. (1997). A hierarchical model of approach and avoidance achievement motivation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 72, 218–232. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.72.1.218
Elliot, A. J., McGregor, H. A., and Gable, S. (1999). Achievement goals, study strategies, and exam performance: a mediational analysis. J. Educ. Psychol. 91, 549–563. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.91.3.549
Entwistle, N. J. (1991). Approaches to learning and perceptions of the learning environment. High. Educ. 22, 201–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00132287
Entwistle, N. J. (2009). Teaching for Understanding at University: Deep Approaches and Distinctive Ways of Thinking . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., and Muñiz, J. (2014). Tareas escolares en el hogar y rendimiento en matemáticas: una aproximación multinivel con estudiantes de Enseñanza Primaria [Homework and academic performance in mathematics: a multilevel approach with Primary school students]. Rev. Psicol. Educ. 9, 15–29.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., and Paris, A. (2004). School engagement: potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 74, 59–109. doi: 10.3102/00346543074001059
Galloway, M., Conner, J., and Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. J. Exp. Educ. 81, 490–510. doi: 10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
Gaudreau, P. (2012). Goal self-concordance moderates the relationship between achievement goals and indicators of academic adjustment. Learn. Individ. Differ. 22, 827–832. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.06.006
Hong, E., Milgram, R. M., and Rowell, L. L. (2004). Homework motivation and preference: a learner-centered homework approach. Theory Pract. 43, 197–203. doi: 10.1207/s15430421tip4303_5
Inglés, C. J., Martínez-González, A. E., and García-Fernández, J. M. (2013). Conducta prosocial y estrategias de aprendizaje en una muestra de estudiantes españoles de Educación Secundaria Obligatoria [Prosocial behavior and learning strategies in a sample of Spanish students of Compulsory Secondary Education]. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 6, 33–53. doi: 10.1989/ejep.v6i1.101
Jöreskog, K. G., and Sörbom, D. (1983). LISREL - 6 User's Reference Guide . Mooresville, IN: Scientifi c Software.
Kohn, A. (2006). Abusing research: the study of homework and other examples. Phi Delta Kappan 88, 9–22. doi: 10.1177/003172170608800105
Lindblom-Ylänne, S., and Lonka, K. (1999). Individual ways of interacting with the learning environment - are they related to study success? Learn. Instruct. 9, 1–18. doi: 10.1016/S0959-4752(98)00025-5
Marks, H. (2000). Student engagement in instructional activity: patterns in the elementary, middle, and high school years. Am. Educ. Res. J. 37, 153–184. doi: 10.3102/00028312037001153
Martin, A. J. (2012). “Motivation and engagement: conceptual, operational, and empirical clarity,” in Handbook of Research on Student Engagement , eds S. L. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, and C. Wylie (New York, NY: Springer), 303–311.
Marton, F., and Säljö, R. (1976a). On qualitative differences in learning. I: outcome and process. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 46, 4–11. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8279.1976.tb02980.x
Marton, F., and Säljö, R. (1976b). On qualitative differences in learning. II: outcome as a function of the learner's conception of the task. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 46, 115–127. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8279.1976.tb02304.x
Meece, J. L., Anderman, E. M., and Anderman, L. H. (2006). Classroom goal structure, student motivation, and academic achievement. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 57, 487–503. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070258
Middleton, M., and Midgley, C. (1997). Avoiding the demonstration of lack of ability: an unexplored aspect of goal theory. J. Educ. Psychol. 89, 710–718. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.89.4.710
Muhlenbruck, L., Cooper, H., Nye, B., and Lindsay, J. J. (2000). Homework and achievement: explaining the different strengths of relation at the elementary and secondary school levels. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 3, 295–317. doi: 10.1023/A:1009680513901
Ng, C. H. (2008). Multiple-goal learners and their differential patterns of learning. Educ. Psychol. 28, 439–456. doi: 10.1080/01443410701739470
Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., González-Pumariega, S., García, M., and Roces, C. (1997). Cuestionario Para la Evaluación de Metas Académicas [Academic Goals Assessment Questionnaire] . Department of Psychology, University of Oviedo.
Núñez, J. C., Suárez, N., Cerezo, R., González-Pienda, J. A., Rosário, P., Mourão, R., et al. (2015a). Homework and academic achievement across Spanish Compulsory Education. Educ. Psychol. 35, 726–746. doi: 10.1080/01443410.2013.817537
Núñez, J. C., Suárez, N., Rosário, P., Vallejo, G., Cerezo, R., and Valle, A. (2015b). Teachers' feedback on homework, homework-related behaviors and academic achievement. J. Educ. Res. 108, 204–216. doi: 10.1080/00220671.2013.878298
Núñez, J. C., Suárez, N., Rosário, P., Vallejo, G., Valle, A., and Epstein, J. L. (2015c). Relationships between parental involvement in homework, student homework behaviors, and academic achievement: differences among elementary, junior high, and high school students. Metacogn. Learn. 10, 375–406. doi: 10.1007/s11409-015-9135-5
Núñez, J., Rosário, P., Vallejo, G., and González-Pienda, J. (2013). A longitudinal assessment of the effectiveness of a school-based mentoring program in middle school. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 38, 11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2012.10.002
Pajares, F., Britner, S. L., and Valiante, G. (2000). Relation between achievement goals and self-beliefs of middle school students in writing and science. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 25, 406–422. doi: 10.1006/ceps.1999.1027
Pintrich, P. R. (2004). A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 16, 385–407. doi: 10.1007/s10648-004-0006-x
Pintrich, P. R., and De Groot, E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom performance. J. Educ. Psychol. 82, 33–40. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.82.1.33
Reeve, J., Jang, H., Carrell, D., Jeon, S., and Barch, J. (2004). Enhancing students' engagement by increasing teachers' autonomy support. Motiv. Emot. 28, 147–169. doi: 10.1023/B:MOEM.0000032312.95499.6f
Regueiro, B., Suárez, N., Valle, A., Núñez, J. C., and Rosário, P. (2015). La motivación e implicación en los deberes escolares a lo largo de la escolaridad obligatoria [Homework motivation and engagement throughout compulsory education]. Rev. Psicodidáctica 20, 47–63. doi: 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.12641
Rodríguez, S., Cabanach, R. G., Piñeiro, I., Valle, A., Núñez, J. C., and González-Pienda, J. A. (2001). Metas de aproximación, metas de evitación y múltiples metas académicas [Approach goals, avoidance goals and multiple academic goals]. Psicothema 13, 546–550.
Rosário, P., González-Pienda, J. A., Pinto, R., Ferreira, P., Lourenço, A., and Paiva, O. (2010a). Efficacy of the program “Testas's (mis)adventures” to promote the deep approach to learning. Psicothema 22, 828–834.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Rosário, P., Mourão, R., Baldaque, M., Nunes, T., Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., et al. (2009). Homework, self-regulation of learning and math performance. Rev. Psicodidáctica 14, 179–192.
Rosário, P., Núñez, J. A., Ferrando, J. P., Paiva, O., Lourenço, A., Cerezo, R., et al. (2013a). The relationship between approaches to teaching and approaches to studying: a two-level structural equation model for biology achievement in high school. Metacogn. Learn. 8, 47–77. doi: 10.1007/s11409-013-9095-6
Rosário, P., Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., Almeida, L., Soares, S., and Rúbio, M. (2005). Academic learning from the perspective of Model 3P of J. Biggs. Psicothema 17, 20–30.
Rosário, P., Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., Valle, A., Trigo, L., and Guimarães, C. (2010b). Enhancing self-regulation and approaches to learning in first-year college students: a narrative-based program assessed in the Iberian Peninsula. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 25, 411–428. doi: 10.1007/s10212-010-0020-y
Rosário, P., Núñez, J. C., Vallejo, G., Cunha, J., Azevedo, R., Pereira, R., et al (2016). Promoting Gypsy children school engagement: a story-tool project to enhance self-regulated learning. Contemp. Educ. Psychol . doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.11.005. [Epub ahead of print].
Rosário, P., Núñez, J. C., Vallejo, G., Cunha, J., Nunes, T., Suárez, N., et al. (2015). The effects of teachers' homework follow-up practices on students' EFL performance: a randomized-group design. Front. Psychol. 6:1528. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01528
Rosário, P., Núñez, J., Valle, A., González-Pienda, J., and Lourenço, A. (2013b). Grade level, study time, and grade retention and their effects on motivation, self-regulated learning strategies, and mathematics achievement: a structural equation model. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 28, 1311–1331. doi: 10.1007/s10212-012-0167-9
Skaalvik, E. (1997). Self- enhancing and self-defeating ego orientation: relations with task and avoidance orientation, achievement, self- perceptions, and anxiety. J. Educ. Psychol. 89, 71–81. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.89.1.71
Skinner, E. A., and Pitzer, J. R. (2012). “Developmental dynamics of student engagement, coping, and everyday resilience,” in Handbook of Research on Student Engagement , eds S. L. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, and C. Wylie (New York, NY: Springer), 21–44.
Struyven, K., Dochy, F., Janssens, S., and Gielen, S. (2006). On the dynamics of students' approaches to learning: the effects of the teaching/learning environment. Learn. Instr. 16, 279–294. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2006.07.001
Suárez, J. M., Cabanach, R. G., and Valle, A. (2001). Multiple-goal pursuit and its relation to cognitive, self-regulatory, and motivational strategies. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 71, 561–572. doi: 10.1348/000709901158677
Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, O., Kastens, C., and Köller, O. (2006a). Effort on homework in grades 5 through 9: development, motivational antecedents, and the association with effort on classwork. Child Dev. 77, 1094–1111. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2006.00921.x
Trautwein, U., Ludtke, O., Schnyder, I., and Niggli, A. (2006b). Predicting homework effort: support for a domain-specific, multilevel homework model. J. Educ. Psychol. 98, 438–456. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.438
Trautwein, U., Schnyder, I., Niggli, A., Neumann, M., and Lüdtke, O. (2009). Chameleon effects in homework research: the homework-achievement association depends on the measures used and the level of analysis chosen. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 34, 77–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2008.09.001
Valle, A., Cabanach, R. G., Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., Rodríguez, S., and Piñeiro, I. (2003a). Cognitive, motivational, and volitional dimensions of learning: an empirical test of a hypothetical model. Res. High. Educ. 44, 557–580. doi: 10.1023/A:1025443325499
Valle, A., Cabanach, R. G., Núñez, J. C., González-Pienda, J. A., Rodríguez, S., and Piñeiro, I. (2003b). Multiple goals, motivation and academic learning. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 73, 71–87. doi: 10.1348/000709903762869923
Valle, A., Cabanach, R. G., Rodríguez, S., Núñez, J. C., and González-Pienda, J. A. (2006). Metas académicas, estrategias cognitivas y estrategias de autorregulación del estudio [Academic goals, cognitive and self-regulatory strategies]. Psicothema 18, 166–170.
Valle, A., Núñez, J. C., Cabanach, R. G., González-Pienda, J. A., Rodríguez, S., Rosário, P., et al. (2009). Academic goals and learning quality in higher education students. Span. J. Psychol. 12, 96–105. doi: 10.1017/S1138741600001517
Valle, A., Núñez, J. C., Cabanach, R., Rodríguez, S., Rosário, P., and Inglés, C. (2015a). Motivational profiles as a combination of academic goals in higher education. Educ. Psychol. 35, 634–650. doi: 10.1080/01443410.2013.819072
Valle, A., Pan, I., Núñez, J. C., Rosário, P., Rodríguez, S., and Regueiro, B. (2015b). Deberes escolares y rendimiento académico en Educación Primaria [Homework and academic achievement in Primary Education]. An. Psicol. 31, 562–569. doi: 10.6018/analesps.31.2.171131
Valle, A., Pan, I., Regueiro, B., Suárez, N., Tuero, E., and Nunes, A. R. (2015c). Predicting approach to homework in primary school students. Psicothema 27, 334–340. doi: 10.7334/psicothema2015.118
Valle, A., Regueiro, B., Rodríguez, S., Piñeiro, I., Freire, C., Ferradás, M., et al. (2015d). Perfiles motivacionales como combinación de expectativas de autoeficacia y metas académicas en estudiantes universitarios [Motivational profiles as a combination of self-efficacy expectations and academic goals in university students]. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 8, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejeps.2015.10.001
Vallejo, G., Tuero, E., Núñez, J. C., and Rosário, P. (2014). Performance evaluation of recent information criteria for selecting multilevel models in behavioral and social sciences. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 14, 48–57. doi: 10.1016/S1697-2600(14)70036-5
Wolters, C. A., Yu, S. L., and Pintrich, P. R. (1996). The relation between goal orientation and students' motivational beliefs and self- regulated learning. Learn. Individ. Differ. 8, 211−238. doi: 10.1016/s1041-6080(96)90015-1
Xu, J. (2005). Purposes for doing homework reported by middle and high school students. J. Educ. Res. 99, 46–55. doi: 10.3200/JOER.99.1.46-55
Xu, J. (2007). Middle-school homework management: more than just gender and family involvement. Educ. Psychol. 27, 173–189. doi: 10.1080/01443410601066669
Xu, J. (2008). Validation of scores on the Homework Management Scale for high school students. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 68, 304–324. doi: 10.1177/0013164407301531
Xu, J. (2010). Predicting homework time management at the secondary school level: a multilevel analysis. Learn. Individ. Differ. 20, 34–39. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2009.11.001
Zimmerman, B. J., and Kitsantas, A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: the mediating role of self-efficacy and perceived responsibility beliefs. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 30, 397–417. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2005.05.003
Keywords: homework, academic goals, student homework engagement, approach to homework, academic achievement, elementary school
Citation: Valle A, Regueiro B, Núñez JC, Rodríguez S, Piñeiro I and Rosário P (2016) Academic Goals, Student Homework Engagement, and Academic Achievement in Elementary School. Front. Psychol . 7:463. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00463
Received: 01 November 2015; Accepted: 15 March 2016; Published: 31 March 2016.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2016 Valle, Regueiro, Núñez, Rodríguez, Piñeiro and Rosário. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Antonio Valle, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Our Mission
Rethinking Homework for This Year—and Beyond
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students’ learning.

I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt. Now when I think about the purpose and practice of homework, two key concepts guide me: depth over breadth, and student well-being.
Homework has long been the subject of intense debate, and there’s no easy answer with respect to its value. Teachers assign homework for any number of reasons: It’s traditional to do so, it makes students practice their skills and solidify learning, it offers the opportunity for formative assessment, and it creates good study habits and discipline. Then there’s the issue of pace. Throughout my career, I’ve assigned homework largely because there just isn’t enough time to get everything done in class.
A Different Approach
Since classes have gone online, the school where I teach has made a conscious effort as a teaching community to reduce, refine, and distill our curriculum. We have applied guiding questions like: What is most important? What is most transferable? What is most relevant? Refocusing on what matters most has inevitably made us rethink homework.
We have approached both asking and answering these questions through a science of learning lens. In Make It Stick: The Science of Successful Learning , the authors maintain that deep learning is slow learning. Deep learning requires time for retrieval, practice, feedback, reflection, and revisiting content; ultimately it requires struggle, and there is no struggle without time.
As someone who has mastered the curriculum mapping style of “get it done to move on to get that next thing done,” using an approach of “slow down and reduce” has been quite a shift for me. However, the shift has been necessary: What matters most is what’s best for my students, as opposed to my own plans or mandates imposed by others.
Listening to Students
To implement this shift, my high school English department has reduced content and texts both in terms of the amount of units and the content within each unit. We’re more flexible with dates and deadlines. We spend our energy planning the current unit instead of the year’s units. In true partnership with my students, I’m constantly checking in with them via Google forms, Zoom chats, conferences, and Padlet activities. In these check-ins, I specifically ask students how they’re managing the workload for my class and their other classes. I ask them how much homework they’re doing. And I adjust what I do and expect based on what they tell me. For example, when I find out a week is heavy with work in other classes, I make sure to allot more time during class for my tasks. At times I have even delayed or altered one of my assignments.
To be completely transparent, the “old” me is sheepish in admitting that I’ve so dramatically changed my thinking with respect to homework. However, both my students and I have reaped numerous benefits. I’m now laser-focused when designing every minute of my lessons to maximize teaching and learning. Every decision I make is now scrutinized through the lens of absolute worth for my students’ growth: If it doesn’t make the cut, it’s cut. I also take into account what is most relevant to my students.
For example, our 10th-grade English team has redesigned a unit that explores current manifestations of systemic oppression. This unit is new in approach and longer in duration than it was pre-Covid, and it has resulted in some of the deepest and hardest learning, as well as the richest conversations, that I have seen among students in my career. Part of this improved quality comes from the frequent and intentional pauses that I instruct students to take in order to reflect on the content and on the arc of their own learning. The reduction in content that we need to get through in online learning has given me more time to assign reflective prompts, and to let students process their thoughts, whether that’s at the end of a lesson as an exit slip or as an assignment.
Joining Forces to Be Consistent
There’s no doubt this reduction in homework has been a team effort. Within the English department, we have all agreed to allot reading time during class; across each grade level, we’re monitoring the amount of homework our students have collectively; and across the whole high school, we have adopted a framework to help us think through assigning homework.
Within that framework, teachers at the school agree that the best option is for students to complete all work during class. The next best option is for students to finish uncompleted class work at home as a homework assignment of less than 30 minutes. The last option—the one we try to avoid as much as possible—is for students to be assigned and complete new work at home (still less than 30 minutes). I set a maximum time limit for students’ homework tasks (e.g., 30 minutes) and make that clear at the top of every assignment.
This schoolwide approach has increased my humility as a teacher. In the past, I tended to think my subject was more important than everyone else’s, which gave me license to assign more homework. But now I view my students’ experience more holistically: All of their classes and the associated work must be considered, and respected.
As always, I ground this new pedagogical approach not just in what’s best for students’ academic learning, but also what’s best for them socially and emotionally. 2020 has been traumatic for educators, parents, and students. There is no doubt the level of trauma varies greatly ; however, one can’t argue with the fact that homework typically means more screen time when students are already spending most of the day on their devices. They need to rest their eyes. They need to not be sitting at their desks. They need physical activity. They need time to do nothing at all.
Eliminating or reducing homework is a social and emotional intervention, which brings me to the greatest benefit of reducing the homework load: Students are more invested in their relationship with me now that they have less homework. When students trust me to take their time seriously, when they trust me to listen to them and adjust accordingly, when they trust me to care for them... they trust more in general.
And what a beautiful world of learning can be built on trust.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
Homework in America
- 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education
Subscribe to the Brown Center on Education Policy Newsletter
Tom loveless tom loveless former brookings expert @tomloveless99.
March 18, 2014
- 18 min read
Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education

Homework! The topic, no, just the word itself, sparks controversy. It has for a long time. In 1900, Edward Bok, editor of the Ladies Home Journal , published an impassioned article, “A National Crime at the Feet of Parents,” accusing homework of destroying American youth. Drawing on the theories of his fellow educational progressive, psychologist G. Stanley Hall (who has since been largely discredited), Bok argued that study at home interfered with children’s natural inclination towards play and free movement, threatened children’s physical and mental health, and usurped the right of parents to decide activities in the home.
The Journal was an influential magazine, especially with parents. An anti-homework campaign burst forth that grew into a national crusade. [i] School districts across the land passed restrictions on homework, culminating in a 1901 statewide prohibition of homework in California for any student under the age of 15. The crusade would remain powerful through 1913, before a world war and other concerns bumped it from the spotlight. Nevertheless, anti-homework sentiment would remain a touchstone of progressive education throughout the twentieth century. As a political force, it would lie dormant for years before bubbling up to mobilize proponents of free play and “the whole child.” Advocates would, if educators did not comply, seek to impose homework restrictions through policy making.
Our own century dawned during a surge of anti-homework sentiment. From 1998 to 2003, Newsweek , TIME , and People , all major national publications at the time, ran cover stories on the evils of homework. TIME ’s 1999 story had the most provocative title, “The Homework Ate My Family: Kids Are Dazed, Parents Are Stressed, Why Piling On Is Hurting Students.” People ’s 2003 article offered a call to arms: “Overbooked: Four Hours of Homework for a Third Grader? Exhausted Kids (and Parents) Fight Back.” Feature stories about students laboring under an onerous homework burden ran in newspapers from coast to coast. Photos of angst ridden children became a journalistic staple.
The 2003 Brown Center Report on American Education included a study investigating the homework controversy. Examining the most reliable empirical evidence at the time, the study concluded that the dramatic claims about homework were unfounded. An overwhelming majority of students, at least two-thirds, depending on age, had an hour or less of homework each night. Surprisingly, even the homework burden of college-bound high school seniors was discovered to be rather light, less than an hour per night or six hours per week. Public opinion polls also contradicted the prevailing story. Parents were not up in arms about homework. Most said their children’s homework load was about right. Parents wanting more homework out-numbered those who wanted less.
Now homework is in the news again. Several popular anti-homework books fill store shelves (whether virtual or brick and mortar). [ii] The documentary Race to Nowhere depicts homework as one aspect of an overwrought, pressure-cooker school system that constantly pushes students to perform and destroys their love of learning. The film’s website claims over 6,000 screenings in more than 30 countries. In 2011, the New York Times ran a front page article about the homework restrictions adopted by schools in Galloway, NJ, describing “a wave of districts across the nation trying to remake homework amid concerns that high stakes testing and competition for college have fueled a nightly grind that is stressing out children and depriving them of play and rest, yet doing little to raise achievement, especially in elementary grades.” In the article, Vicki Abeles, the director of Race to Nowhere , invokes the indictment of homework lodged a century ago, declaring, “The presence of homework is negatively affecting the health of our young people and the quality of family time.” [iii]
A petition for the National PTA to adopt “healthy homework guidelines” on change.org currently has 19,000 signatures. In September 2013, Atlantic featured an article, “My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me,” by a Manhattan writer who joined his middle school daughter in doing her homework for a week. Most nights the homework took more than three hours to complete.
The Current Study
A decade has passed since the last Brown Center Report study of homework, and it’s time for an update. How much homework do American students have today? Has the homework burden increased, gone down, or remained about the same? What do parents think about the homework load?
A word on why such a study is important. It’s not because the popular press is creating a fiction. The press accounts are built on the testimony of real students and real parents, people who are very unhappy with the amount of homework coming home from school. These unhappy people are real—but they also may be atypical. Their experiences, as dramatic as they are, may not represent the common experience of American households with school-age children. In the analysis below, data are analyzed from surveys that are methodologically designed to produce reliable information about the experiences of all Americans. Some of the surveys have existed long enough to illustrate meaningful trends. The question is whether strong empirical evidence confirms the anecdotes about overworked kids and outraged parents.
Data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) provide a good look at trends in homework for nearly the past three decades. Table 2-1 displays NAEP data from 1984-2012. The data are from the long-term trend NAEP assessment’s student questionnaire, a survey of homework practices featuring both consistently-worded questions and stable response categories. The question asks: “How much time did you spend on homework yesterday?” Responses are shown for NAEP’s three age groups: 9, 13, and 17. [iv]
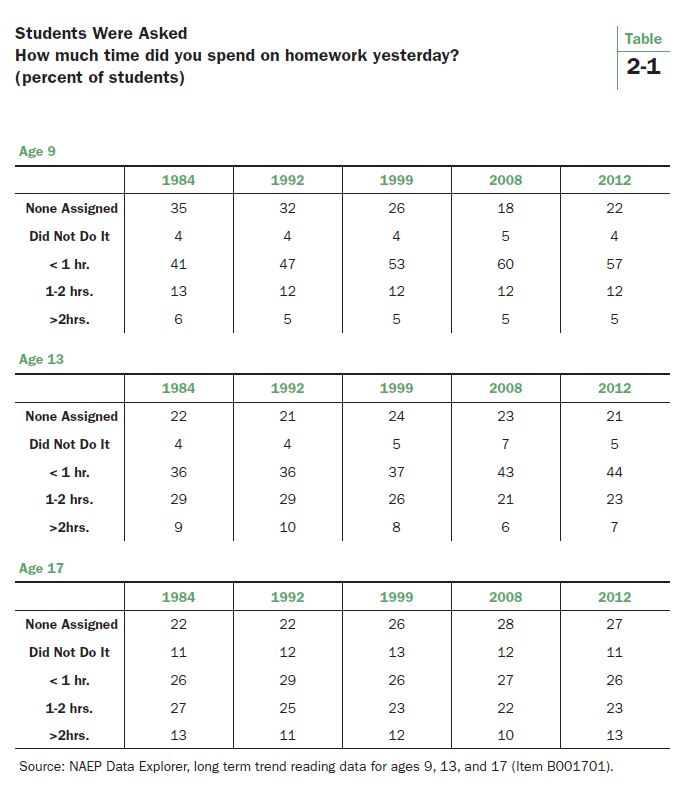
Today’s youngest students seem to have more homework than in the past. The first three rows of data for age 9 reveal a shift away from students having no homework, declining from 35% in 1984 to 22% in 2012. A slight uptick occurred from the low of 18% in 2008, however, so the trend may be abating. The decline of the “no homework” group is matched by growth in the percentage of students with less than an hour’s worth, from 41% in 1984 to 57% in 2012. The share of students with one to two hours of homework changed very little over the entire 28 years, comprising 12% of students in 2012. The group with the heaviest load, more than two hours of homework, registered at 5% in 2012. It was 6% in 1984.
The amount of homework for 13-year-olds appears to have lightened slightly. Students with one to two hours of homework declined from 29% to 23%. The next category down (in terms of homework load), students with less than an hour, increased from 36% to 44%. One can see, by combining the bottom two rows, that students with an hour or more of homework declined steadily from 1984 to 2008 (falling from 38% to 27%) and then ticked up to 30% in 2012. The proportion of students with the heaviest load, more than two hours, slipped from 9% in 1984 to 7% in 2012 and ranged between 7-10% for the entire period.
For 17-year-olds, the homework burden has not varied much. The percentage of students with no homework has increased from 22% to 27%. Most of that gain occurred in the 1990s. Also note that the percentage of 17-year-olds who had homework but did not do it was 11% in 2012, the highest for the three NAEP age groups. Adding that number in with the students who didn’t have homework in the first place means that more than one-third of seventeen year olds (38%) did no homework on the night in question in 2012. That compares with 33% in 1984. The segment of the 17-year-old population with more than two hours of homework, from which legitimate complaints of being overworked might arise, has been stuck in the 10%-13% range.
The NAEP data point to four main conclusions:
- With one exception, the homework load has remained remarkably stable since 1984.
- The exception is nine-year-olds. They have experienced an increase in homework, primarily because many students who once did not have any now have some. The percentage of nine-year-olds with no homework fell by 13 percentage points, and the percentage with less than an hour grew by 16 percentage points.
- Of the three age groups, 17-year-olds have the most bifurcated distribution of the homework burden. They have the largest percentage of kids with no homework (especially when the homework shirkers are added in) and the largest percentage with more than two hours.
- NAEP data do not support the idea that a large and growing number of students have an onerous amount of homework. For all three age groups, only a small percentage of students report more than two hours of homework. For 1984-2012, the size of the two hours or more groups ranged from 5-6% for age 9, 6-10% for age 13, and 10-13% for age 17.
Note that the item asks students how much time they spent on homework “yesterday.” That phrasing has the benefit of immediacy, asking for an estimate of precise, recent behavior rather than an estimate of general behavior for an extended, unspecified period. But misleading responses could be generated if teachers lighten the homework of NAEP participants on the night before the NAEP test is given. That’s possible. [v] Such skewing would not affect trends if it stayed about the same over time and in the same direction (teachers assigning less homework than usual on the day before NAEP). Put another way, it would affect estimates of the amount of homework at any single point in time but not changes in the amount of homework between two points in time.
A check for possible skewing is to compare the responses above with those to another homework question on the NAEP questionnaire from 1986-2004 but no longer in use. [vi] It asked students, “How much time do you usually spend on homework each day?” Most of the response categories have different boundaries from the “last night” question, making the data incomparable. But the categories asking about no homework are comparable. Responses indicating no homework on the “usual” question in 2004 were: 2% for age 9-year-olds, 5% for 13 year olds, and 12% for 17-year-olds. These figures are much less than the ones reported in Table 2-1 above. The “yesterday” data appear to overstate the proportion of students typically receiving no homework.
The story is different for the “heavy homework load” response categories. The “usual” question reported similar percentages as the “yesterday” question. The categories representing the most amount of homework were “more than one hour” for age 9 and “more than two hours” for ages 13 and 17. In 2004, 12% of 9-year-olds said they had more than one hour of daily homework, while 8% of 13-year-olds and 12% of 17-year-olds said they had more than two hours. For all three age groups, those figures declined from1986 to 2004. The decline for age 17 was quite large, falling from 17% in 1986 to 12% in 2004.
The bottom line: regardless of how the question is posed, NAEP data do not support the view that the homework burden is growing, nor do they support the belief that the proportion of students with a lot of homework has increased in recent years. The proportion of students with no homework is probably under-reported on the long-term trend NAEP. But the upper bound of students with more than two hours of daily homework appears to be about 15%–and that is for students in their final years of high school.
College Freshmen Look Back
There is another good source of information on high school students’ homework over several decades. The Higher Education Research Institute at UCLA conducts an annual survey of college freshmen that began in 1966. In 1986, the survey started asking a series of questions regarding how students spent time in the final year of high school. Figure 2-1 shows the 2012 percentages for the dominant activities. More than half of college freshmen say they spent at least six hours per week socializing with friends (66.2%) and exercising/sports (53.0%). About 40% devoted that much weekly time to paid employment.
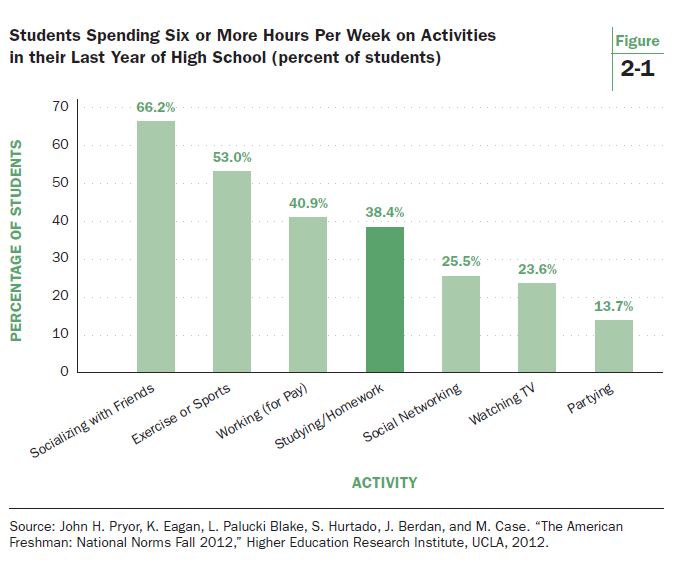
Homework comes in fourth pace. Only 38.4% of students said they spent at least six hours per week studying or doing homework. When these students were high school seniors, it was not an activity central to their out of school lives. That is quite surprising. Think about it. The survey is confined to the nation’s best students, those attending college. Gone are high school dropouts. Also not included are students who go into the military or attain full time employment immediately after high school. And yet only a little more than one-third of the sampled students, devoted more than six hours per week to homework and studying when they were on the verge of attending college.
Another notable finding from the UCLA survey is how the statistic is trending (see Figure 2-2). In 1986, 49.5% reported spending six or more hours per week studying and doing homework. By 2002, the proportion had dropped to 33.4%. In 2012, as noted in Figure 2-1, the statistic had bounced off the historical lows to reach 38.4%. It is slowly rising but still sits sharply below where it was in 1987.
What Do Parents Think?
Met Life has published an annual survey of teachers since 1984. In 1987 and 2007, the survey included questions focusing on homework and expanded to sample both parents and students on the topic. Data are broken out for secondary and elementary parents and for students in grades 3-6 and grades 7-12 (the latter not being an exact match with secondary parents because of K-8 schools).
Table 2-2 shows estimates of homework from the 2007 survey. Respondents were asked to estimate the amount of homework on a typical school day (Monday-Friday). The median estimate of each group of respondents is shaded. As displayed in the first column, the median estimate for parents of an elementary student is that their child devotes about 30 minutes to homework on the typical weekday. Slightly more than half (52%) estimate 30 minutes or less; 48% estimate 45 minutes or more. Students in grades 3-6 (third column) give a median estimate that is a bit higher than their parents’ (45 minutes), with almost two-thirds (63%) saying 45 minutes or less is the typical weekday homework load.
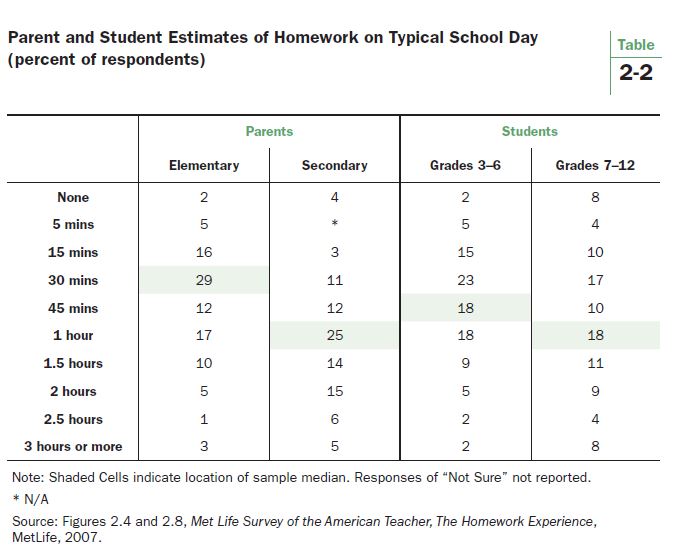
One hour of homework is the median estimate for both secondary parents and students in grade 7-12, with 55% of parents reporting an hour or less and about two-thirds (67%) of students reporting the same. As for the prevalence of the heaviest homework loads, 11% of secondary parents say their children spend more than two hours on weekday homework, and 12% is the corresponding figure for students in grades 7-12.
The Met Life surveys in 1987 and 2007 asked parents to evaluate the amount and quality of homework. Table 2-3 displays the results. There was little change over the two decades separating the two surveys. More than 60% of parents rate the amount of homework as good or excellent, and about two-thirds give such high ratings to the quality of the homework their children are receiving. The proportion giving poor ratings to either the quantity or quality of homework did not exceed 10% on either survey.
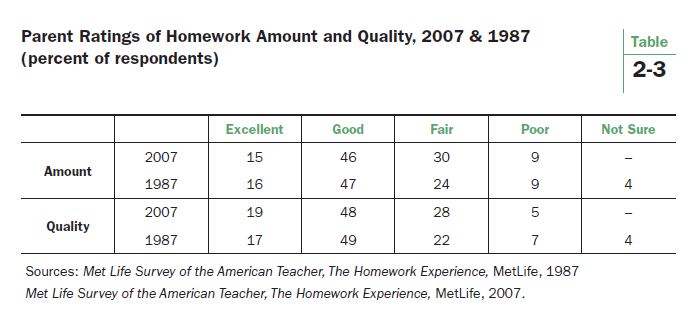
Parental dissatisfaction with homework comes in two forms: those who feel schools give too much homework and those who feel schools do not give enough. The current wave of journalism about unhappy parents is dominated by those who feel schools give too much homework. How big is this group? Not very big (see Figure 2-3). On the Met Life survey, 60% of parents felt schools were giving the right amount of homework, 25% wanted more homework, and only 15% wanted less.
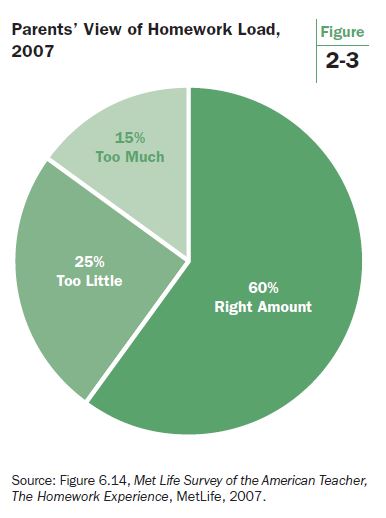
National surveys on homework are infrequent, but the 2006-2007 period had more than one. A poll conducted by Public Agenda in 2006 reported similar numbers as the Met Life survey: 68% of parents describing the homework load as “about right,” 20% saying there is “too little homework,” and 11% saying there is “too much homework.” A 2006 AP-AOL poll found the highest percentage of parents reporting too much homework, 19%. But even in that poll, they were outnumbered by parents believing there is too little homework (23%), and a clear majority (57%) described the load as “about right.” A 2010 local survey of Chicago parents conducted by the Chicago Tribune reported figures similar to those reported above: approximately two-thirds of parents saying their children’s homework load is “about right,” 21% saying it’s not enough, and 12% responding that the homework load is too much.
Summary and Discussion
In recent years, the press has been filled with reports of kids over-burdened with homework and parents rebelling against their children’s oppressive workload. The data assembled above call into question whether that portrait is accurate for the typical American family. Homework typically takes an hour per night. The homework burden of students rarely exceeds two hours a night. The upper limit of students with two or more hours per night is about 15% nationally—and that is for juniors or seniors in high school. For younger children, the upper boundary is about 10% who have such a heavy load. Polls show that parents who want less homework range from 10%-20%, and that they are outnumbered—in every national poll on the homework question—by parents who want more homework, not less. The majority of parents describe their children’s homework burden as about right.
So what’s going on? Where are the homework horror stories coming from?
The Met Life survey of parents is able to give a few hints, mainly because of several questions that extend beyond homework to other aspects of schooling. The belief that homework is burdensome is more likely held by parents with a larger set of complaints and concerns. They are alienated from their child’s school. About two in five parents (19%) don’t believe homework is important. Compared to other parents, these parents are more likely to say too much homework is assigned (39% vs. 9%), that what is assigned is just busywork (57% vs. 36%), and that homework gets in the way of their family spending time together (51% vs. 15%). They are less likely to rate the quality of homework as excellent (3% vs. 23%) or to rate the availability and responsiveness of teachers as excellent (18% vs. 38%). [vii]
They can also convince themselves that their numbers are larger than they really are. Karl Taro Greenfeld, the author of the Atlantic article mentioned above, seems to fit that description. “Every parent I know in New York City comments on how much homework their children have,” Mr. Greenfeld writes. As for those parents who do not share this view? “There is always a clique of parents who are happy with the amount of homework. In fact, they would prefer more . I tend not to get along with that type of parent.” [viii]
Mr. Greenfeld’s daughter attends a selective exam school in Manhattan, known for its rigorous expectations and, yes, heavy homework load. He had also complained about homework in his daughter’s previous school in Brentwood, CA. That school was a charter school. After Mr. Greenfeld emailed several parents expressing his complaints about homework in that school, the school’s vice-principal accused Mr. Greenfeld of cyberbullying. The lesson here is that even schools of choice are not immune from complaints about homework.
The homework horror stories need to be read in a proper perspective. They seem to originate from the very personal discontents of a small group of parents. They do not reflect the experience of the average family with a school-age child. That does not diminish these stories’ power to command the attention of school officials or even the public at large. But it also suggests a limited role for policy making in settling such disputes. Policy is a blunt instrument. Educators, parents, and kids are in the best position to resolve complaints about homework on a case by case basis. Complaints about homework have existed for more than a century, and they show no signs of going away.
Part II Notes:
[i]Brian Gill and Steven Schlossman, “A Sin Against Childhood: Progressive Education and the Crusade to Abolish Homework, 1897-1941,” American Journal of Education , vol. 105, no. 1 (Nov., 1996), 27-66. Also see Brian P. Gill and Steven L. Schlossman, “Villain or Savior? The American Discourse on Homework, 1850-2003,” Theory into Practice , 43, 3 (Summer 2004), pp. 174-181.
[ii] Bennett, Sara, and Nancy Kalish. The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It (New York: Crown, 2006). Buell, John. Closing the Book on Homework: Enhancing Public Education and Freeing Family Time . (Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2004). Kohn, Alfie. The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing (Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2006). Kralovec, Etta, and John Buell. The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning (Boston: Beacon Press, 2000).
[iii] Hu, Winnie, “ New Recruit in Homework Revolt: The Principal ,” New York Times , June 15, 2011, page a1.
[iv] Data for other years are available on the NAEP Data Explorer. For Table 1, the starting point of 1984 was chosen because it is the first year all three ages were asked the homework question. The two most recent dates (2012 and 2008) were chosen to show recent changes, and the two years in the 1990s to show developments during that decade.
[v] NAEP’s sampling design lessens the probability of skewing the homework figure. Students are randomly drawn from a school population, meaning that an entire class is not tested. Teachers would have to either single out NAEP students for special homework treatment or change their established homework routine for the whole class just to shelter NAEP participants from homework. Sampling designs that draw entact classrooms for testing (such as TIMSS) would be more vulnerable to this effect. Moreover, students in middle and high school usually have several different teachers during the day, meaning that prior knowledge of a particular student’s participation in NAEP would probably be limited to one or two teachers.
[vi] NAEP Question B003801 for 9 year olds and B003901 for 13- and 17-year olds.
[vii] Met Life, Met Life Survey of the American Teacher: The Homework Experience , November 13, 2007, pp. 21-22.
[viii] Greenfeld, Karl Taro, “ My Daughter’s Homework Is Killing Me ,” The Atlantic , September 18, 2013.
Education Policy K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Emily Markovich Morris, Laura Nóra, Richaa Hoysala, Max Lieblich, Sophie Partington, Rebecca Winthrop
May 31, 2024
Online only
9:30 am - 11:00 am EDT
Annelies Goger, Katherine Caves, Hollis Salway
May 16, 2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Students' Achievement and Homework Assignment Strategies
Rubén fernández-alonso.
1 Department of Education Sciences, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
2 Department of Education, Principality of Asturias Government, Oviedo, Spain
Marcos Álvarez-Díaz
Javier suárez-Álvarez.
3 Department of Psychology, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
José Muñiz
The optimum time students should spend on homework has been widely researched although the results are far from unanimous. The main objective of this research is to analyze how homework assignment strategies in schools affect students' academic performance and the differences in students' time spent on homework. Participants were a representative sample of Spanish adolescents ( N = 26,543) with a mean age of 14.4 (±0.75), 49.7% girls. A test battery was used to measure academic performance in four subjects: Spanish, Mathematics, Science, and Citizenship. A questionnaire allowed the measurement of the indicators used for the description of homework and control variables. Two three-level hierarchical-linear models (student, school, autonomous community) were produced for each subject being evaluated. The relationship between academic results and homework time is negative at the individual level but positive at school level. An increase in the amount of homework a school assigns is associated with an increase in the differences in student time spent on homework. An optimum amount of homework is proposed which schools should assign to maximize gains in achievement for students overall.
The role of homework in academic achievement is an age-old debate (Walberg et al., 1985 ) that has swung between times when it was thought to be a tool for improving a country's competitiveness and times when it was almost outlawed. So Cooper ( 2001 ) talks about the battle over homework and the debates and rows continue (Walberg et al., 1985 , 1986 ; Barber, 1986 ). It is considered a complicated subject (Corno, 1996 ), mysterious (Trautwein and Köller, 2003 ), a chameleon (Trautwein et al., 2009b ), or Janus-faced (Flunger et al., 2015 ). One must agree with Cooper et al. ( 2006 ) that homework is a practice full of contradictions, where positive and negative effects coincide. As such, depending on our preferences, it is possible to find data which support the argument that homework benefits all students (Cooper, 1989 ), or that it does not matter and should be abolished (Barber, 1986 ). Equally, one might argue a compensatory effect as it favors students with more difficulties (Epstein and Van Voorhis, 2001 ), or on the contrary, that it is a source of inequality as it specifically benefits those better placed on the social ladder (Rømming, 2011 ). Furthermore, this issue has jumped over the school wall and entered the home, contributing to the polemic by becoming a common topic about which it is possible to have an opinion without being well informed, something that Goldstein ( 1960 ) warned of decades ago after reviewing almost 300 pieces of writing on the topic in Education Index and finding that only 6% were empirical studies.
The relationship between homework time and educational outcomes has traditionally been the most researched aspect (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Fan et al., 2017 ), although conclusions have evolved over time. The first experimental studies (Paschal et al., 1984 ) worked from the hypothesis that time spent on homework was a reflection of an individual student's commitment and diligence and as such the relationship between time spent on homework and achievement should be positive. This was roughly the idea at the end of the twentieth century, when more positive effects had been found than negative (Cooper, 1989 ), although it was also known that the relationship was not strictly linear (Cooper and Valentine, 2001 ), and that its strength depended on the student's age- stronger in post-compulsory secondary education than in compulsory education and almost zero in primary education (Cooper et al., 2012 ). With the turn of the century, hierarchical-linear models ran counter to this idea by showing that homework was a multilevel situation and the effect of homework on outcomes depended on classroom factors (e.g., frequency or amount of assigned homework) more than on an individual's attitude (Trautwein and Köller, 2003 ). Research with a multilevel approach indicated that individual variations in time spent had little effect on academic results (Farrow et al., 1999 ; De Jong et al., 2000 ; Dettmers et al., 2010 ; Murillo and Martínez-Garrido, 2013 ; Fernández-Alonso et al., 2014 ; Núñez et al., 2014 ; Servicio de Evaluación Educativa del Principado de Asturias, 2016 ) and that when statistically significant results were found, the effect was negative (Trautwein, 2007 ; Trautwein et al., 2009b ; Lubbers et al., 2010 ; Chang et al., 2014 ). The reasons for this null or negative relationship lie in the fact that those variables which are positively associated with homework time are antagonistic when predicting academic performance. For example, some students may not need to spend much time on homework because they learn quickly and have good cognitive skills and previous knowledge (Trautwein, 2007 ; Dettmers et al., 2010 ), or maybe because they are not very persistent in their work and do not finish homework tasks (Flunger et al., 2015 ). Similarly, students may spend more time on homework because they have difficulties learning and concentrating, low expectations and motivation or because they need more direct help (Trautwein et al., 2006 ), or maybe because they put in a lot of effort and take a lot of care with their work (Flunger et al., 2015 ). Something similar happens with sociological variables such as gender: Girls spend more time on homework (Gershenson and Holt, 2015 ) but, compared to boys, in standardized tests they have better results in reading and worse results in Science and Mathematics (OECD, 2013a ).
On the other hand, thanks to multilevel studies, systematic effects on performance have been found when homework time is considered at the class or school level. De Jong et al. ( 2000 ) found that the number of assigned homework tasks in a year was positively and significantly related to results in mathematics. Equally, the volume or amount of homework (mean homework time for the group) and the frequency of homework assignment have positive effects on achievement. The data suggests that when frequency and volume are considered together, the former has more impact on results than the latter (Trautwein et al., 2002 ; Trautwein, 2007 ). In fact, it has been estimated that in classrooms where homework is always assigned there are gains in mathematics and science of 20% of a standard deviation over those classrooms which sometimes assign homework (Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015 ). Significant results have also been found in research which considered only homework volume at the classroom or school level. Dettmers et al. ( 2009 ) concluded that the school-level effect of homework is positive in the majority of participating countries in PISA 2003, and the OECD ( 2013b ), with data from PISA 2012, confirms that schools in which students have more weekly homework demonstrate better results once certain school and student-background variables are discounted. To put it briefly, homework has a multilevel nature (Trautwein and Köller, 2003 ) in which the variables have different significance and effects according to the level of analysis, in this case a positive effect at class level, and a negative or null effect in most cases at the level of the individual. Furthermore, the fact that the clearest effects are seen at the classroom and school level highlights the role of homework policy in schools and teaching, over and above the time individual students spend on homework.
From this complex context, this current study aims to explore the relationships between the strategies schools use to assign homework and the consequences that has on students' academic performance and on the students' own homework strategies. There are two specific objectives, firstly, to systematically analyze the differential effect of time spent on homework on educational performance, both at school and individual level. We hypothesize a positive effect for homework time at school level, and a negative effect at the individual level. Secondly, the influence of homework quantity assigned by schools on the distribution of time spent by students on homework will be investigated. This will test the previously unexplored hypothesis that an increase in the amount of homework assigned by each school will create an increase in differences, both in time spent on homework by the students, and in academic results. Confirming this hypothesis would mean that an excessive amount of homework assigned by schools would penalize those students who for various reasons (pace of work, gaps in learning, difficulties concentrating, overexertion) need to spend more time completing their homework than their peers. In order to resolve this apparent paradox we will calculate the optimum volume of homework that schools should assign in order to benefit the largest number of students without contributing to an increase in differences, that is, without harming educational equity.
Participants
The population was defined as those students in year 8 of compulsory education in the academic year 2009/10 in Spain. In order to provide a representative sample, a stratified random sampling was carried out from the 19 autonomous regions in Spain. The sample was selected from each stratum according to a two-stage cluster design (OECD, 2009 , 2011 , 2014a ; Ministerio de Educación, 2011 ). In the first stage, the primary units of the sample were the schools, which were selected with a probability proportional to the number of students in the 8th grade. The more 8th grade students in a given school, the higher the likelihood of the school being selected. In the second stage, 35 students were selected from each school through simple, systematic sampling. A detailed, step-by-step description of the sampling procedure may be found in OECD ( 2011 ). The subsequent sample numbered 29,153 students from 933 schools. Some students were excluded due to lack of information (absences on the test day), or for having special educational needs. The baseline sample was finally made up of 26,543 students. The mean student age was 14.4 with a standard deviation of 0.75, rank of age from 13 to 16. Some 66.2% attended a state school; 49.7% were girls; 87.8% were Spanish nationals; 73.5% were in the school year appropriate to their age, the remaining 26.5% were at least 1 year behind in terms of their age.
Test application, marking, and data recording were contracted out via public tendering, and were carried out by qualified personnel unconnected to the schools. The evaluation, was performed on two consecutive days, each day having two 50 min sessions separated by a break. At the end of the second day the students completed a context questionnaire which included questions related to homework. The evaluation was carried out in compliance with current ethical standards in Spain. Families of the students selected to participate in the evaluation were informed about the study by the school administrations, and were able to choose whether those students would participate in the study or not.
Instruments
Tests of academic performance.
The performance test battery consisted of 342 items evaluating four subjects: Spanish (106 items), mathematics (73 items), science (78), and citizenship (85). The items, completed on paper, were in various formats and were subject to binary scoring, except 21 items which were coded on a polytomous scale, between 0 and 2 points (Ministerio de Educación, 2011 ). As a single student is not capable of answering the complete item pool in the time given, the items were distributed across various booklets following a matrix design (Fernández-Alonso and Muñiz, 2011 ). The mean Cronbach α for the booklets ranged from 0.72 (mathematics) to 0.89 (Spanish). Student scores were calculated adjusting the bank of items to Rasch's IRT model using the ConQuest 2.0 program (Wu et al., 2007 ) and were expressed in a scale with mean and standard deviation of 500 and 100 points respectively. The student's scores were divided into five categories, estimated using the plausible values method. In large scale assessments this method is better at recovering the true population parameters (e.g., mean, standard deviation) than estimates of scores using methods of maximum likelihood or expected a-posteriori estimations (Mislevy et al., 1992 ; OECD, 2009 ; von Davier et al., 2009 ).
Homework variables
A questionnaire was made up of a mix of items which allowed the calculation of the indicators used for the description of homework variables. Daily minutes spent on homework was calculated from a multiple choice question with the following options: (a) Generally I don't have homework; (b) 1 h or less; (c) Between 1 and 2 h; (d) Between 2 and 3 h; (e) More than 3 h. The options were recoded as follows: (a) = 0 min.; (b) = 45 min.; (c) = 90 min.; (d) = 150 min.; (e) = 210 min. According to Trautwein and Köller ( 2003 ) the average homework time of the students in a school could be regarded as a good proxy for the amount of homework assigned by the teacher. So the mean of this variable for each school was used as an estimator of Amount or volume of homework assigned .
Control variables
Four variables were included to describe sociological factors about the students, three were binary: Gender (1 = female ); Nationality (1 = Spanish; 0 = other ); School type (1 = state school; 0 = private ). The fourth variable was Socioeconomic and cultural index (SECI), which is constructed with information about family qualifications and professions, along with the availability of various material and cultural resources at home. It is expressed in standardized points, N(0,1) . Three variables were used to gather educational history: Appropriate School Year (1 = being in the school year appropriate to their age ; 0 = repeated a school year) . The other two adjustment variables were Academic Expectations and Motivation which were included for two reasons: they are both closely connected to academic achievement (Suárez-Álvarez et al., 2014 ). Their position as adjustment factors is justified because, in an ex-post facto descriptive design such as this, both expectations and motivation may be thought of as background variables that the student brings with them on the day of the test. Academic expectations for finishing education was measured with a multiple-choice item where the score corresponds to the years spent in education in order to reach that level of qualification: compulsory secondary education (10 points); further secondary education (12 points); non-university higher education (14 points); University qualification (16 points). Motivation was constructed from the answers to six four-point Likert items, where 1 means strongly disagree with the sentence and 4 means strongly agree. Students scoring highly in this variable are agreeing with statements such as “at school I learn useful and interesting things.” A Confirmatory Factor Analysis was performed using a Maximum Likelihood robust estimation method (MLMV) and the items fit an essentially unidimensional scale: CFI = 0.954; TLI = 0.915; SRMR = 0.037; RMSEA = 0.087 (90% CI = 0.084–0.091).
As this was an official evaluation, the tests used were created by experts in the various fields, contracted by the Spanish Ministry of Education in collaboration with the regional education authorities.
Data analyses
Firstly the descriptive statistics and Pearson correlations between the variables were calculated. Then, using the HLM 6.03 program (Raudenbush et al., 2004 ), two three-level hierarchical-linear models (student, school, autonomous community) were produced for each subject being evaluated: a null model (without predictor variables) and a random intercept model in which adjustment variables and homework variables were introduced at the same time. Given that HLM does not return standardized coefficients, all of the variables were standardized around the general mean, which allows the interpretation of the results as classical standardized regression analysis coefficients. Levels 2 and 3 variables were constructed from means of standardized level 1 variables and were not re-standardized. Level 1 variables were introduced without centering except for four cases: study time, motivation, expectation, and socioeconomic and cultural level which were centered on the school mean to control composition effects (Xu and Wu, 2013 ) and estimate the effect of differences in homework time among the students within the same school. The range of missing variable cases was very small, between 1 and 3%. Recovery was carried out using the procedure described in Fernández-Alonso et al. ( 2012 ).
The results are presented in two ways: the tables show standardized coefficients while in the figures the data are presented in a real scale, taking advantage of the fact that a scale with a 100 point standard deviation allows the expression of the effect of the variables and the differences between groups as percentage increases in standardized points.
Table Table1 1 shows the descriptive statistics and the matrix of correlations between the study variables. As can be seen in the table, the relationship between the variables turned out to be in the expected direction, with the closest correlations between the different academic performance scores and socioeconomic level, appropriate school year, and student expectations. The nationality variable gave the highest asymmetry and kurtosis, which was to be expected as the majority of the sample are Spanish.
Descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation matrix between the variables .
Table Table2 2 shows the distribution of variance in the null model. In the four subjects taken together, 85% of the variance was found at the student level, 10% was variance between schools, and 5% variance between regions. Although the 10% of variance between schools could seem modest, underlying that there were large differences. For example, in Spanish the 95% plausible value range for the school means ranged between 577 and 439 points, practically 1.5 standard deviations, which shows that schools have a significant impact on student results.
Distribution of the variance in the null model .
Table Table3 3 gives the standardized coefficients of the independent variables of the four multilevel models, as well as the percentage of variance explained by each level.
Multilevel models for prediction of achievement in four subjects .
β, Standardized weight; SE, Standard Error; SECI, Socioeconomic and cultural index; AC, Autonomous Communities .
The results indicated that the adjustment variables behaved satisfactorily, with enough control to analyze the net effects of the homework variables. This was backed up by two results, firstly, the two variables with highest standardized coefficients were those related to educational history: academic expectations at the time of the test, and being in the school year corresponding to age. Motivation demonstrated a smaller effect but one which was significant in all cases. Secondly, the adjustment variables explained the majority of the variance in the results. The percentages of total explained variance in Table Table2 2 were calculated with all variables. However, if the strategy had been to introduce the adjustment variables first and then add in the homework variables, the explanatory gain in the second model would have been about 2% in each subject.
The amount of homework turned out to be positively and significantly associated with the results in the four subjects. In a 100 point scale of standard deviation, controlling for other variables, it was estimated that for each 10 min added to the daily volume of homework, schools would achieve between 4.1 and 4.8 points more in each subject, with the exception of mathematics where the increase would be around 2.5 points. In other words, an increase of between 15 and 29 points in the school mean is predicted for each additional hour of homework volume of the school as a whole. This school level gain, however, would only occur if the students spent exactly the same time on homework as their school mean. As the regression coefficient of student homework time is negative and the variable is centered on the level of the school, the model predicts deterioration in results for those students who spend more time than their class mean on homework, and an improvement for those who finish their homework more quickly than the mean of their classmates.
Furthermore, the results demonstrated a positive association between the amount of homework assigned in a school and the differences in time needed by the students to complete their homework. Figure Figure1 1 shows the relationship between volume of homework (expressed as mean daily minutes of homework by school) and the differences in time spent by students (expressed as the standard deviation from the mean school daily minutes). The correlation between the variables was 0.69 and the regression gradient indicates that schools which assigned 60 min of homework per day had a standard deviation in time spent by students on homework of approximately 25 min, whereas in those schools assigning 120 min of homework, the standard deviation was twice as long, and was over 50 min. So schools which assigned more homework also tended to demonstrate greater differences in the time students need to spend on that homework.

Relationship between school homework volume and differences in time needed by students to complete homework .
Figure Figure2 2 shows the effect on results in mathematics of the combination of homework time, homework amount, and the variance of homework time associated with the amount of homework assigned in two types of schools: in type 1 schools the amount of homework assigned is 1 h, and in type 2 schools the amount of homework 2 h. The result in mathematics was used as a dependent variable because, as previously noted, it was the subject where the effect was smallest and as such is the most conservative prediction. With other subjects the results might be even clearer.

Prediction of results for quick and slow students according to school homework size .
Looking at the first standard deviation of student homework time shown in the first graph, it was estimated that in type 1 schools, which assign 1 h of daily homework, a quick student (one who finishes their homework before 85% of their classmates) would spend a little over half an hour (35 min), whereas the slower student, who spends more time than 85% of classmates, would need almost an hour and a half of work each day (85 min). In type 2 schools, where the homework amount is 2 h a day, the differences increase from just over an hour (65 min for a quick student) to almost 3 h (175 min for a slow student). Figure Figure2 2 shows how the differences in performance would vary within a school between the more and lesser able students according to amount of homework assigned. In type 1 schools, with 1 h of homework per day, the difference in achievement between quick and slow students would be around 5% of a standard deviation, while in schools assigning 2 h per day the difference would be 12%. On the other hand, the slow student in a type 2 school would score 6 points more than the quick student in a type 1 school. However, to achieve this, the slow student in a type 2 school would need to spend five times as much time on homework in a week (20.4 weekly hours rather than 4.1). It seems like a lot of work for such a small gain.
Discussion and conclusions
The data in this study reaffirm the multilevel nature of homework (Trautwein and Köller, 2003 ) and support this study's first hypothesis: the amount of homework (mean daily minutes the student spends on homework) is positively associated with academic results, whereas the time students spent on homework considered individually is negatively associated with academic results. These findings are in line with previous research, which indicate that school-level variables, such as amount of homework assigned, have more explanatory power than individual variables such as time spent (De Jong et al., 2000 ; Dettmers et al., 2010 ; Scheerens et al., 2013 ; Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015 ). In this case it was found that for each additional hour of homework assigned by a school, a gain of 25% of a standard deviation is expected in all subjects except mathematics, where the gain is around 15%. On the basis of this evidence, common sense would dictate the conclusion that frequent and abundant homework assignment may be one way to improve school efficiency.
However, as noted previously, the relationship between homework and achievement is paradoxical- appearances are deceptive and first conclusions are not always confirmed. Analysis demonstrates another two complementary pieces of data which, read together, raise questions about the previous conclusion. In the first place, time spent on homework at the individual level was found to have a negative effect on achievement, which confirms the findings of other multilevel-approach research (Trautwein, 2007 ; Trautwein et al., 2009b ; Chang et al., 2014 ; Fernández-Alonso et al., 2016 ). Furthermore, it was found that an increase in assigned homework volume is associated with an increase in the differences in time students need to complete it. Taken together, the conclusion is that, schools with more homework tend to exhibit more variation in student achievement. These results seem to confirm our second hypothesis, as a positive covariation was found between the amount of homework in a school (the mean homework time by school) and the increase in differences within the school, both in student homework time and in the academic results themselves. The data seem to be in line with those who argue that homework is a source of inequity because it affects those less academically-advantaged students and students with greater limitations in their home environments (Kohn, 2006 ; Rømming, 2011 ; OECD, 2013b ).
This new data has clear implications for educational action and school homework policies, especially in compulsory education. If quality compulsory education is that which offers the best results for the largest number (Barber and Mourshed, 2007 ; Mourshed et al., 2010 ), then assigning an excessive volume of homework at those school levels could accentuate differences, affecting students who are slower, have more gaps in their knowledge, or are less privileged, and can make them feel overwhelmed by the amount of homework assigned to them (Martinez, 2011 ; OECD, 2014b ; Suárez et al., 2016 ). The data show that in a school with 60 min of assigned homework, a quick student will need just 4 h a week to finish their homework, whereas a slow student will spend 10 h a week, 2.5 times longer, with the additional aggravation of scoring one twentieth of a standard deviation below their quicker classmates. And in a school assigning 120 min of homework per day, a quick student will need 7.5 h per week whereas a slow student will have to triple this time (20 h per week) to achieve a result one eighth worse, that is, more time for a relatively worse result.
It might be argued that the differences are not very large, as between 1 and 2 h of assigned homework, the level of inequality increases 7% on a standardized scale. But this percentage increase has been estimated after statistically, or artificially, accounting for sociological and psychological student factors and other variables at school and region level. The adjustment variables influence both achievement and time spent on homework, so it is likely that in a real classroom situation the differences estimated here might be even larger. This is especially important in comprehensive education systems, like the Spanish (Eurydice, 2015 ), in which the classroom groups are extremely heterogeneous, with a variety of students in the same class in terms of ability, interest, and motivation, in which the aforementioned variables may operate more strongly.
The results of this research must be interpreted bearing in mind a number of limitations. The most significant limitation in the research design is the lack of a measure of previous achievement, whether an ad hoc test (Murillo and Martínez-Garrido, 2013 ) or school grades (Núñez et al., 2014 ), which would allow adjustment of the data. In an attempt to alleviate this, our research has placed special emphasis on the construction of variables which would work to exclude academic history from the model. The use of the repetition of school year variable was unavoidable because Spain has one of the highest levels of repetition in the European Union (Eurydice, 2011 ) and repeating students achieve worse academic results (Ministerio de Educación, 2011 ). Similarly, the expectation and motivation variables were included in the group of adjustment factors assuming that in this research they could be considered background variables. In this way, once the background factors are discounted, the homework variables explain 2% of the total variance, which is similar to estimations from other multilevel studies (De Jong et al., 2000 ; Trautwein, 2007 ; Dettmers et al., 2009 ; Fernández-Alonso et al., 2016 ). On the other hand, the statistical models used to analyze the data are correlational, and as such, one can only speak of an association between variables and not of directionality or causality in the analysis. As Trautwein and Lüdtke ( 2009 ) noted, the word “effect” must be understood as “predictive effect.” In other words, it is possible to say that the amount of homework is connected to performance; however, it is not possible to say in which direction the association runs. Another aspect to be borne in mind is that the homework time measures are generic -not segregated by subject- when it its understood that time spent and homework behavior are not consistent across all subjects (Trautwein et al., 2006 ; Trautwein and Lüdtke, 2007 ). Nonetheless, when the dependent variable is academic results it has been found that the relationship between homework time and achievement is relatively stable across all subjects (Lubbers et al., 2010 ; Chang et al., 2014 ) which leads us to believe that the results given here would have changed very little even if the homework-related variables had been separated by subject.
Future lines of research should be aimed toward the creation of comprehensive models which incorporate a holistic vision of homework. It must be recognized that not all of the time spent on homework by a student is time well spent (Valle et al., 2015 ). In addition, research has demonstrated the importance of other variables related to student behavior such as rate of completion, the homework environment, organization, and task management, autonomy, parenting styles, effort, and the use of study techniques (Zimmerman and Kitsantas, 2005 ; Xu, 2008 , 2013 ; Kitsantas and Zimmerman, 2009 ; Kitsantas et al., 2011 ; Ramdass and Zimmerman, 2011 ; Bembenutty and White, 2013 ; Xu and Wu, 2013 ; Xu et al., 2014 ; Rosário et al., 2015a ; Osorio and González-Cámara, 2016 ; Valle et al., 2016 ), as well as the role of expectation, value given to the task, and personality traits (Lubbers et al., 2010 ; Goetz et al., 2012 ; Pedrosa et al., 2016 ). Along the same lines, research has also indicated other important variables related to teacher homework policies, such as reasons for assignment, control and feedback, assignment characteristics, and the adaptation of tasks to the students' level of learning (Trautwein et al., 2009a ; Dettmers et al., 2010 ; Patall et al., 2010 ; Buijs and Admiraal, 2013 ; Murillo and Martínez-Garrido, 2013 ; Rosário et al., 2015b ). All of these should be considered in a comprehensive model of homework.
In short, the data seem to indicate that in year 8 of compulsory education, 60–70 min of homework a day is a recommendation that, slightly more optimistically than Cooper's ( 2001 ) “10 min rule,” gives a reasonable gain for the whole school, without exaggerating differences or harming students with greater learning difficulties or who work more slowly, and is in line with other available evidence (Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015 ). These results have significant implications when it comes to setting educational policy in schools, sending a clear message to head teachers, teachers and those responsible for education. The results of this research show that assigning large volumes of homework increases inequality between students in pursuit of minimal gains in achievement for those who least need it. Therefore, in terms of school efficiency, and with the aim of improving equity in schools it is recommended that educational policies be established which optimize all students' achievement.
Ethics statement
This study was carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the University of Oviedo with written informed consent from all subjects. All subjects gave written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the University of Oviedo.
Author contributions
RF and JM have designed the research; RF and JS have analyzed the data; MA and JM have interpreted the data; RF, MA, and JS have drafted the paper; JM has revised it critically; all authors have provided final approval of the version to be published and have ensured the accuracy and integrity of the work.
This research was funded by the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad del Gobierno de España. References: PSI2014-56114-P, BES2012-053488. We would like to express our utmost gratitude to the Ministerio de Educación Cultura y Deporte del Gobierno de España and to the Consejería de Educación y Cultura del Gobierno del Principado de Asturias, without whose collaboration this research would not have been possible.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
- Barber B. (1986). Homework does not belong on the agenda for educational reform . Educ. Leadersh. 43 , 55–57. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barber M., Mourshed M. (2007). How the World's Best-Performing School Systems Come Out on Top. McKinsey and Company . Available online at: http://mckinseyonsociety.com/downloads/reports/Education/Worlds_School_Systems_Final.pdf (Accessed January 25, 2016).
- Bembenutty H., White M. C. (2013). Academic performance and satisfaction with homework completion among college students . Learn. Individ. Differ. 24 , 83–88. 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.10.013 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buijs M., Admiraal W. (2013). Homework assignments to enhance student engagement in secondary education . Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 28 , 767–779. 10.1007/s10212-012-0139-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang C. B., Wall D., Tare M., Golonka E., Vatz K. (2014). Relations of attitudes toward homework and time spent on homework to course outcomes: the case of foreign language learning . J. Educ. Psychol. 106 , 1049–1065. 10.1037/a0036497 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H. (1989). Synthesis of research on homework . Educ. Leadersh. 47 , 85–91. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H. (2001). The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H., Robinson J. C., Patall E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987-2003 . Rev. Educ. Res. 76 , 1–62. 10.3102/00346543076001001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H., Steenbergen-Hu S., Dent A. L. (2012). Homework , in APA Educational Psychology Handbook , Vol. 3 : Application to Learning and Teaching , eds Harris K. R., Graham S., Urdan T. (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; ), 475–495. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper H., Valentine J. C. (2001). Using research to answer practical questions about homework . Educ. Psychol. 36 , 143–153. 10.1207/S15326985EP3603_1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Corno L. (1996). Homework is a complicated thing . Educ. Res. 25 , 27–30. 10.3102/0013189X025008027 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Jong R., Westerhof K. J., Creemers B. P. M. (2000). Homework and student math achievement in junior high schools . Educ. Res. Eval. 6 , 130–157. 10.1076/1380-3611(200006)6:2;1-E;F130 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dettmers S., Trautwein U., Lüdtke M., Kunter M., Baumert J. (2010). Homework works if homework quality is high: using multilevel modeling to predict the development of achievement in mathematics . J. Educ. Psychol. 102 , 467–482. 10.1037/a0018453 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dettmers S., Trautwein U., Lüdtke O. (2009). The relationship between homework time and achievement is not universal: evidence from multilevel analyses in 40 countries . Sch. Eff. Sch. Improv. 20 , 375–405. 10.1080/09243450902904601 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Epstein J. L., Van Voorhis F. L. (2001). More than minutes: teachers' roles in designing homework . Educ. Psychol. 36 , 181–193. 10.1207/S15326985EP3603_4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eurydice (2015). The Structure of the European Education Systems 2015/16: Schematic Diagrams. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union . Available online at: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/fpfis/mwikis/eurydice/index.php/Publications:The_Structure_of_the_European_Education_Systems_2015/16:_Schematic_Diagrams (Accessed January 25, 2016).
- Eurydice (2011). Grade Retention during Compulsory Education in Europe: Regulations and Statistics . Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fan H., Xu J., Cai Z., He J., Fan X. (2017). Homework and students' achievement in math and science: a 30-year meta-analysis, 1986-2015 . Educ. Res. Rev. 20 , 35–54. 10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Farrow S., Tymms P., Henderson B. (1999). Homework and attainment in primary schools . Br. Educ. Res. J. 25 , 323–341. 10.1080/0141192990250304 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernández-Alonso R., Muñiz J. (2011). Diseños de cuadernillos para la evaluación de competencias b1sicas . Aula Abierta 39 , 3–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernández-Alonso R., Suárez-Álvarez J., Muñiz J. (2012). Imputación de datos perdidos en las evaluaciones diagnósticas educativas. [Imputation methods for missing data in educational diagnostic evaluation]. Psicothema 24 , 167–175. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernández-Alonso R., Suárez-Álvarez J., Muñiz J. (2014). Tareas escolares en el hogar y rendimiento en matemáticas: una aproximación multinivel con estudiantes de enseñanza primaria. [Homework and academic performance in mathematics: A multilevel approach with primary school student]. Rev. Psicol. Educ. 9 , 15–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernández-Alonso R., Suárez-Álvarez J., Muñiz J. (2015). Adolescents' homework performance in mathematics and science: personal factors and teaching practices . J. Educ. Psychol. 107 , 1075–1085. 10.1037/edu0000032 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fernández-Alonso R., Suárez-Álvarez J., Muñiz J. (2016). Homework and performance in mathematics: the role of the teacher, the family and the student's background . Rev. Psicod. 21 , 5–23. 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.13939 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flunger B., Trautwein U., Nagengast B., Lüdtke O., Niggli A., Schnyder I. (2015). The Janus-faced nature of time spent on homework: using latent profile analyses to predict academic achievement over a school year . Lear. Instr. 39 , 97–106. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2015.05.008 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gershenson S., Holt S. B. (2015). Gender gaps in high school students' homework time . Educ. Res. 44 , 432–441. 10.3102/0013189X15616123 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goetz T., Nett U. E., Martiny S. E., Hall N. C., Pekrun R., Dettmers S., et al. (2012). Students' emotions during homework: structures, self-concept antecedents, and achievement outcomes . Learn. Individ. Differ. 22 , 225–234. 10.1016/j.lindif.2011.04.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goldstein A. (1960). Does homework help? A review of research . Elementary Sch. J. 60 , 212–224. 10.1086/459804 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kitsantas A., Cheema J., Ware H. (2011). The role of homework support resources, time spent on homework, and self-efficacy beliefs in mathematics achievement . J. Adv. Acad. 22 , 312–341. 10.1177/1932202X1102200206 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kitsantas A., Zimmerman B. J. (2009). College students homework and academic achievement: the mediating role of self-regulatory beliefs . Metacognition Learn. 4 , 1556–1623. 10.1007/s11409-008-9028-y [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohn A. (2006). Abusing research: the study of homework and other examples . Phi Delta Kappan 88 , 9–22. 10.1177/003172170608800105 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lubbers M. J., Van Der Werf M. P. C., Kuyper H., Hendriks A. A. J. (2010). Does homework behavior mediate the relation between personality and academic performance? Learn. Individ. Differ. 20 , 203–208. 10.1016/j.lindif.2010.01.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Martinez S. (2011). An examination of Latino students' homework routines . J. Latinos Educ. 10 , 354–368. 10.1080/15348431.2011.605688 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mislevy R. J., Beaton A. E., Kaplan B., Sheehan K. M. (1992). Estimating population characteristics from sparse matrix samples of item responses . J. Educ. Meas. 29 , 133–161. 10.1111/j.1745-3984.1992.tb00371.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ministerio de Educación (2011). Evaluación General de Diagnóstico 2010. Educación Secundaria Obligatoria. Informe de Resultados . Madrid: Instituto de Evaluación; Available online at: http://www.mecd.gob.es/dctm/ievaluacion/informe-egd-2010.pdf?documentId=0901e72b80d5ad3e (Accessed January 25, 2016). [ Google Scholar ]
- Mourshed M., Chijioke C., Barber M. (2010). How the World's Most Improved School Systems Keep Getting Better. McKinsey and Company . Available online at: http://mckinseyonsociety.com/downloads/reports/Education/How-the-Worlds-Most-Improved-School-Systems-Keep-Getting-Better_Download-version_Final.pdf (Accessed January 25, 2016).
- Murillo F. J., Martínez-Garrido C. (2013). Homework influence on academic performance. A study of iberoamerican students of primary education . J. Psychodidactics 18 , 157–171. 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.6156 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Núñez J. C., Vallejo G., Rosário P., Tuero E., Valle A. (2014). Student, teacher, and school context variables predicting academic achievement in biology: analysis from a multilevel perspective . J. Psychodidactics 19 , 145–171. 10.1387/RevPsicodidact.7127 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD (2009). PISA Data Analysis Manual: SPSS, 2nd Edn . Paris: OECD Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD (2011). School Sampling Preparation Manual. PISA 2012 Main Survey. Paris: OECD Publishing; Available online at: https://www.oecd.org/pisa/pisaproducts/PISA2012MS-SamplingGuidelines-.pdf (Accessed January 6, 2017). [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD (2013a). PISA 2012 Results: What Students Know and Can Do. Student Performance in Mathematics, Reading and Science (Volume I) . Paris: OECD Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD (2013b). PISA 2012 Results: What Makes Schools Successful? Resources, Policies and Practices (Volume IV). Paris: OECD Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD (2014a). PISA 2012 Technical Report. Paris: OECD Publishing; Available online at: http://www.oecd.org/pisa/pisaproducts/PISA-2012-technical-report-final.pdf (Accessed January 25, 2016). [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD (2014b). Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? PISA in Focus . Paris: OECD Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Osorio A., González-Cámara M. (2016). Testing the alleged superiority of the indulgent parenting style among Spanish adolescents . Psicothema 28 , 414–420. 10.7334/psicothema2015.314 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paschal R. A., Weinstein T., Walberg H. J. (1984). The effects of homework on learning: a quantitative synthesis . J. Educ. Res. 78 , 97–104. 10.1080/00220671.1984.10885581 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patall E. A., Cooper H., Wynn S. R. (2010). The effectiveness and relative importance of providing choices in the classroom . J. Educ. Psychol. 102 , 896–915. 10.1037/a0019545 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pedrosa I., Suárez-Álvarez J., García-Cueto E., Muñiz J. (2016). A computerized adaptive test for enterprising personality assessment in youth . Psicothema 28 , 471–478. 10.7334/psicothema2016.68 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramdass D., Zimmerman B. J. (2011). Developing self-regulation skills: the important role of homework . J. Adv. Acad. 22 , 194–218. 10.1177/1932202X1102200202 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Raudenbush S. W., Bryk A. S., Cheong Y. F., Congdon R. T. (2004). HLM6: Hierarchical Linear and Nonlinear Modeling . Chicago: Scientific Software International. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rømming M. (2011). Who benefits from homework assignments? Econ. Educ. Rev. 30 , 55–64. 10.1016/j.econedurev.2010.07.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. C., Vallejo G., Cunha J., Nunes T., Mourão R., et al. (2015a). Does homework design matter? The role of homework's purpose in student mathematics achievement . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 43 , 10–24. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.08.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosário P., Núñez J. C., Vallejo G., Cunha J., Nunes T., Suárez N., et al.. (2015b). The effects of teachers' homework follow-up practices on students' EFL performance: a randomized-group design . Front. Psychol. 6 :1528. 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01528 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Servicio de Evaluación Educativa del Principado de Asturias (2016). La relación entre el tiempo de deberes y los resultados académicos [The Relationship between Homework Time and Academic Performance]. Informes de Evaluación, 1 . Oviedo: Consejería de Educación y Cultura del Gobierno del Principado de Asturias. [ Google Scholar ]
- Scheerens J., Hendriks M., Luyten H., Sleegers P., Cees G. (2013). Productive Time in Education. A Review of the Effectiveness of Teaching Time at School, Homework and Extended Time Outside School Hours. Enschede: University of Twente . Available online at: http://doc.utwente.nl/86371/ (Accessed January 25, 2016).
- Suárez-Álvarez J., Fernández-Alonso R., Muñiz J. (2014). Self-concept, motivation, expectations and socioeconomic level as predictors of academic performance in mathematics . Learn. Indiv. Diff. 30 , 118–123. 10.1016/j.lindif.2013.10.019 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suárez N., Regueiro B., Epstein J. L., Piñeiro I., Díaz S. M., Valle A. (2016). Homework involvement and academic achievement of native and immigrant students . Front. Psychol. 7 :1517. 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01517 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U. (2007). The homework–achievement relation reconsidered: differentiating homework time, homework frequency, and homework effort . Learn. Instr. 17 , 372–388. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.02.009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Köller O. (2003). The relationship between homework and achievement: still much of a mystery . Educ. Psychol. Rev. 15 , 115–145. 10.1023/A:1023460414243 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Köller O., Schmitz B., Baumert J. (2002). Do homework assignments enhance achievement? A multilevel analysis in 7th grade mathematics . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 27 , 26–50. 10.1006/ceps.2001.1084 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Lüdtke O., Schnyder I., Niggli A. (2006). Predicting homework effort: support for a domain-specific, multilevel homework model . J. Educ. Psychol. 98 , 438–456. 10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.438 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Lüdtke O. (2007). Students' self-reported effort and time on homework in six school subjects: between-student differences and within-student variation . J. Educ. Psychol. 99 , 432–444. 10.1037/0022-0663.99.2.432 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Lüdtke O. (2009). Predicting homework motivation and homework effort in six school subjects: the role of person and family characteristics, classroom factors, and school track . Learn. Instr. 19 , 243–258. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.05.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Niggli A., Schnyder I., Lüdtke O. (2009a). Between-teacher differences in homework assignments and the development of students' homework effort, homework emotions, and achievement . J. Educ. Psychol. 101 , 176–189. 10.1037/0022-0663.101.1.176 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trautwein U., Schnyder I., Niggli A., Neumann M., Lüdtke O. (2009b). Chameleon effects in homework research: the homework–achievement association depends on the measures used and the level of analysis chosen . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 34 , 77–88. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2008.09.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Pan I., Regueiro B., Suárez N., Tuero E., Nunes A. R. (2015). Predicting approach to homework in primary school students . Psicothema 27 , 334–340. 10.7334/psicothema2015.118 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valle A., Regueiro B., Núñez J. C., Rodríguez S., Piñero I., Rosário P. (2016). Academic goals, student homework engagement, and academic achievement in elementary school . Front. Psychol. 7 :463. 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00463 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- von Davier M., Gonzalez E., Mislevy R. J. (2009). What are Plausible Values and Why are They Useful?. IERI Monograph Series. Issues and Methodologies in Large-Scale Assessments. Available online at: http://www.ierinstitute.org/fileadmin/Documents/IERI_Monograph/IERI_Monograph_Volume_02.pdf (Accessed January 15, 2017).
- Walberg H. J., Paschal R. A., Weinstein T. (1985). Homework's powerful effects on learning . Educ. Leadersh. 42 , 76–79. [ Google Scholar ]
- Walberg H. J., Paschal R. A., Weinstein T. (1986). Walberg and colleagues reply: effective schools use homework effectively . Educ. Leadersh. 43 , 58. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu M. L., Adams R. J., Wilson M. R., Haldane S. A. (2007). ACER ConQuest 2.0: Generalised Item Response Modelling Software . Camberwell, VIC: Australian Council for Educational Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J. (2008). Models of secondary school students' interest in homework: a multilevel analysis . Am. Educ. Res. J. 45 , 1180–1205. 10.3102/0002831208323276 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J. (2013). Why do students have difficulties completing homework? The need for homework management . J. Educ. Train. Stud. 1 , 98–105. 10.11114/jets.v1i1.78 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J., Wu H. (2013). Self-regulation of homework behavior: homework management at the secondary school level . J. Educ. Res. 106 , 1–13. 10.1080/00220671.2012.658457 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu J., Yuan R., Xu B., Xu M. (2014). Modeling students' time management in math homework . Learn. Individ. Differ. 34 , 33–42. 10.1016/j.lindif.2014.05.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zimmerman B. J., Kitsantas A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: the mediating role of self-efficacy and perceived responsibility beliefs . Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 30 , 397–417. 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2005.05.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter
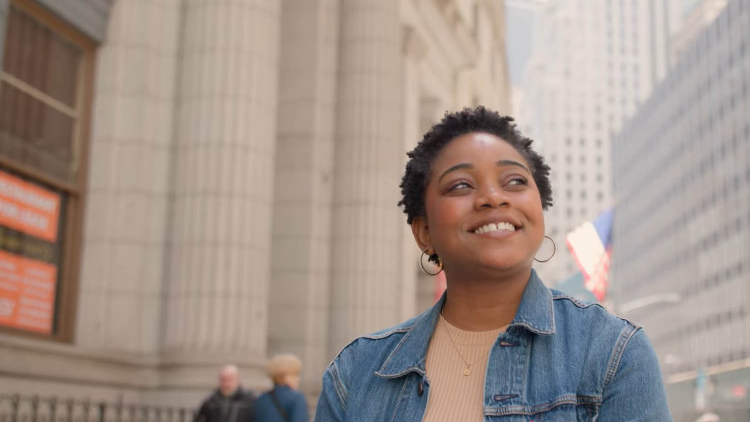

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

Research into the Importance of Homework
Author: Bethany Spencer
Posted: 15 May 2017
Estimated time to read: 10 mins
Homework as a concept has been around for hundreds of years, and today is considered the norm for modern schools. At secondary level, schools set regular homework via a whole-school homework policy. This can take many forms and is sometimes given a different name like 'home learning' or 'Independent study', but the concept of completing work outside of the classroom remains the same.
The setting of homework is regarded highly by many with Epstein & Van Voorhis stating that it not only reflects on the success of the student, but also the success of the school (2001). In spite of this, attitudes towards homework are constantly changing, culminating in the age old homework debate.
The Homework Debate
Attitudes towards the value and purpose of homework are usually reflective of the current societal stance and general sentiment towards education. For example, in the 20th century the mind was seen as a muscle that would benefit from memorisation, and since this could be done at home, homework was perceived as valuable. However, come the 1940s where emphasis shifted from drills to problem solving, people started to view homework negatively (Cooper, 1989).
Yet, fast forward to 1957, the year Russia launched Sputnik, and society became concerned that students were not ready for the advanced technologies that were creeping into modern life, leading many to start favouring homework again.
Although, reflective of the attitudes in the 1960s, homework fell out of favour with the belief that it put too much pressure on students (Cooper, 1989). This is why we find ourselves encased in a spiral of ever changing attitudes towards homework which looks set to continue.
We believe that homework plays an important role in both a student’s education and the performance of the school. Here we look at academic research, but also take into account the opinion of leading educators who give weight to the stance that homework serves a purpose that penetrates far deeper than improving a student’s general understanding of a subject.
The Wider Purpose of Homework
The purpose of homework can be grouped into ten strands as stated by Epstein & Van Voorhis (1988, 2001, p.181) ‘practice, participation, preparation, personal development, parent-child relations, parent-teacher communication, peer interactions, policy, public relations and punishment.’ This suggests that homework affects more areas than just a student’s academic ability.

However, when we look at the research that focuses on the link between homework and academic achievement we see that homework does in fact have a positive impact on students’ grades . Sharp (2002) states there is a direct link between students spending time on homework and their achievement in secondary school.
Cooper similarly found that students who completed homework had better report cards and test results than those who didn't (1989 cited by Epstein & Van Voorhis 2001). In a report conducted by the EEF, they also found that the completion of homework at secondary level can add on an additional 5 months progress onto a child’s learning with minimal cost incurred by the school (EEF, 2016).
In addition to the academic findings, teachers themselves have commented on the purpose they believe homework provides to students and schools. Epstein (1988, 2001, p.181) found that teachers recognised ‘practice, preparation and personal development’ to contribute to the overall purpose of homework.
Homework helps to " develop learners' knowledge and allow them more choice in how they express their work"
Tom Sherrington, a Headteacher at a UK secondary school and influential education blogger, has expressed his personal views on the value of homework: ‘Students who are successful at A Level and at GCSE are those who have highly developed independent learning skills, have the capacity to lead the learning process through their questions and ideas’ (Sherrington 2012a).
This suggests that even those who do not see an immediate impact from homework, believe that it will help students’ personal development but also prepare them for the next stages of education and beyond. This is further supported by Sharp (2002) who recognised that, despite homework not having a direct link to achievement in younger children, it did promote independent learning and prepare them for secondary school.

A second UK teacher and education blogger, Rachel Jones, commented on what she believes to be the purpose of homework and found that it had a positive impact on both retention of knowledge and hand-in rates when the homework set was assigned with the intention to ‘develop learners knowledge and allow them more choice in how they express their work’ (Jones 2013).
Parental Involvement
In addition to the correlation between completing homework and improved achievement, homework plays a fundamental role in both home-school involvement and students’ relationships with their parents. A key purpose of homework outside of ‘enhancing instruction’ is to ‘establish communication between parent and child’ (Acock & Demo, 1994 cited by Cooper et al, 20016, p.2).
Homework acts as a bridge between school and home, and the ability to engage parents in school life has a positive impact on teachers - when teachers feel as though there is more parental involvement in school they feel more positive about teaching (Epstein & Dauber, 1991, Hoover-Dempsey et al, 1987 cited by Epstein & Van Voorhis, 2001).
Acock and Demo (1994, cited by Epstein & Van Voorhis 2001, p.182) have even stated that homework can help to improve relationships between parents and students, bringing them ‘closer together to enjoy learning and exchange ideas’, cementing the idea that homework has greater repercussions than just raising academic achievements within school.
In addition to this, a purpose of homework valued by both parents and teachers is the idea that homework completed regularly by students helps to promote ‘a sense of responsibility’ (Warton 1997, p.213). Moreover, Sherrington (2012b) comments on his stance as both an educator and a parent saying that he firmly believes that homework has a fundamental part to play in the learning process ‘and paving the way to students becoming independent learners’.

Quality Homework
Although in order for homework to really show the benefits expressed in this article it must be purposeful . Students have expressed their opinion on the value of homework, deeming it to be an important part of the learning experience (Sharp 2002).
Yet, they do express concerns regarding how homework is set relating to ‘conflicting deadlines, and tasks that make little contribution to learning’ (Sharp 2002, p.3). In order to combat these concerns, schools should be vetting the quality of homework set, and teachers should be communicating with one another in reference to deadlines.
The idea of setting purposeful homework is further supported by Epstein & Van Voorhis (2001, p.19) who report that those who set homework ‘to meet specific purposes and goals, more students complete their homework and benefit from the results’. Additionally, the idea of setting homework with a clear purpose further encourages parental involvement within the child’s education.
"Quality homework types to include ‘fluency practice, application, spiral review and extension"
Purposeful homework is intrinsically linked to quality homework , and when teachers are setting homework the emphasis should be on this as opposed to the quantity. In order for homework to be regarded as high quality, the instruction provided must be clear and detailed (Frey & Fisher, 2011), and the tasks that are being set are ‘authentic and engaging’ (Darling-Hammond & Ifill-Lynch 2006, p.1) providing students with a real reason to complete them.
This is further supported by Dettmers et al (2010) who found that when students identified homework as being well thought out and relevant, they were more motivated to complete it. Frey & Fisher (2011) identified quality homework types to include ‘fluency practice, application, spiral review and extension’ and denounced the value of homework that asks students to complete work that was not covered in class as not valuable as they have no peer or teacher support and are unfamiliar with the topic.
It is also important to consider the implications of focusing on the amount of homework set - setting too much homework can have detrimental effects on students, such as stress, fatigue and loss of interest in studies (Cooper, 2010).
From this we can gather that fewer pieces of well thought out homework will have more of a positive impact on students’ learning. It is important for schools to monitor the amount of homework that is set, what is being set and the frequency so as to avoid over-working students - having a homework policy which teachers adhere to will help to enforce this.
The Overall Importance of Homework
Homework encourages self-development and self-discipline. Students who complete regular homework don't just perform better at school and during exams, they learn broader life skills and associate hard work with long term rewards. Homework has also been found to improve parental relationships.
Conclusion
From this we can conclude that homework does indeed serve a purpose as studies provide a link between homework and higher secondary school attainment. Yet despite a lack of research to suggest these effects in primary school and younger years, homework will help to prepare students younger than 11 for secondary school and encourages them to become independent learners.
The setting and completion of homework also has benefits outside of academic attainment with parent-child relationship and home-school involvement both improving within schools as a result of successful homework practice.
However, it must be taken into consideration that in order to experience the benefits of homework, the work being set should have a clear goal, as well as being worthwhile and purposeful to encourage students to complete it.

References:
Cooper, H., 1989. Synthesis of Research on Homework. Effective Schools Research Abstracts [online], 4 (1), 85-91
Cooper, H., 2010. Homework’s Diminishing Returns. The New York Times [online], 12 December 2010. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/roomfordebate/2010/12/12/stress-and-the-high-school-student/homeworks-diminishing-returns [Accessed 1 July 2016]
Cooper, H. and Robinson, J.C. and Patall, E.A., 2006. Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A synthesis of Research, 1987-2003. Review of Education Research [online], 76 (1), 1-62
Darling-Hammond, L. and Ifill-Lynch, O., 2006. If They’d Only Do Their Work! Educational Leadership [online] 63(5), 8-13, Available from: http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational-leadership/feb06/vol63/num05/If-They%27d-Only-Do-Their-Work!.aspx [Accessed 1 July 2016]
Dettmers, S at al., 2010. Journal of Educational Psychology. Homework works if homework quality is high: Using multilevel modeling to predict development of achievement in mathematics. [online], 102(2), 467-482. Available from: http://psycnet.apa.org/journals/edu/102/2/467/ [Accessed 1 July 2016]
EEF, 2016. Teaching and Learning Toolkit [online] London. Available from: https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/evidence/teaching-learning-toolkit [Accessed 1 July 2016]
Epstein, L.J. and Van Voorhis, F.L, 2001. More than Minutes: Teachers’ Roles in Designing Homework. Educational Psychologist [online], 36 (3), 181-193
Frey, N. and Fisher, D., 2011. High-Quality Homework [online] USA: Principal Leadership. Available from: http://fisherandfrey.com/uploads/posts/Homework_NASSP.pdf [Accessed 1 July 2016]
GOV.UK, 2015. School Inspection Handbook from 2015 [online]. England: The National Archives. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/school-inspection-handbook-from-september-2015 [Accessed May 2016)
Jones, R., 2013. DESTROY Homework. Create Innovate Explore [online] 12 August 2013. Available from: http://createinnovateexplore.com/destroy-homework/ [Accessed May 2016]
Sharp, C., 2002. Should Schools set Homework? National Foundation for Educational Research [online], 27 (1), 1-4
Sherrington, T., 2012. Homework Matters: Great teachers set great homework. Headguruteacher [online]. 2 September 2012. Available from: https://headguruteacher.com/2012/09/02/homework-matters-great-teachers-set-great-homework/ [Accessed May 2016]
Sherrington, T., 2012. Homework: What does the Hattie research actually say? Headguruteacher [online] 21 October 2012. Available from: https://headguruteacher.com/2012/10/21/homework-what-does-the-hattie-research-actually-say/ [Accessed May 2016]
Warton, P.M. 1997. Learning about responsibility: Lessons from homework. British Journal of Educational Psychology [online], 67(2), pp. 213–221
Get a roundup of our articles once per month.
Subscribe to Email Updates
Recent posts, can ai be used for curric..., let's talk about homework..., should we be worried abou..., using character education..., popular posts, what is behaviourism, how has technology changed education for schools, the impact of effective classroom management.
- Homework (22)
- Teacher Wellbeing (21)
- Student Wellbeing (20)
- Distance Learning (15)
- Classroom Management (14)
- Mental Health (13)
- Ofsted (12)
- Wellbeing (12)
- Skills (11)
- Teacher Workload (11)
- Parental Engagement (10)
- Satchel One MIS (10)
- Staff Wellbeing (10)
- Teachers (10)
- School Culture (9)
- Behaviour Management (8)
- School Improvement (8)
- School Management (8)
- Teacher Resources (8)
- Back to School (7)
- Parental Involvement (7)
- Parents (7)
- Pedagogy (7)
- Student & Parent Resources (7)
- Students (7)
- Assessment (6)
- Cloud-based MIS (6)
- Covid-19 (6)
- Guest Blog (6)
- Leadership (6)
- Online Safety (6)
- Technology (6)
- Bullying (5)
- Digital Literacy (5)
- Marking (5)
- Ofsted framework (5)
- School Closures (5)
- Lesson Plans (4)
- Network Managers (4)
- Revision (4)
- Teacher (4)
- Teaching (4)
- Attendance (3)
- Autonomy (3)
- Data Management (3)
- Education Reform (3)
- Education Technology (3)
- Feedback (3)
- Gender Equality (3)
- Network Manager Resources (3)
- SLT Resources (3)
- School Technology (3)
- Student Engagement (3)
- Students & Parents (3)
- Summer Holidays (3)
- Articles (2)
- Attainment 8 and Progress 8 (2)
- Autonomous Learning (2)
- Children (2)
- Classroom (2)
- Classroom Techniques (2)
- Communication (2)
- Differentiated Homework (2)
- Education (2)
- Education Technolgy (2)
- Embracing Technology (2)
- Exam Results (2)
- Grading (2)
- Home-school Communication (2)
- Homework Debate (2)
- Homework Policy (2)
- Raising Standards (2)
- Reading (2)
- Reducing Workload (2)
- Saving Time (2)
- School Marketing (2)
- School Reopenings (2)
- Security (2)
- Sidekick (2)
- Software Training (2)
- Strategy (2)
- Teaching Crisis (2)
- Teaching and Learning (2)
- Time Management (2)
- Time-saving (2)
- Tips & Tricks (2)
- Workload (2)
- Abuse in the Classroom (1)
- Anti-bullying (1)
- Appreciation (1)
- Attainment 8 (1)
- Benefits of Homework (1)
- Body Image (1)
- British Values (1)
- Career Advice (1)
- Character Education (1)
- Collaboration (1)
- Collaborative Learning (1)
- Continuing Professional Development (1)
- Conversation (1)
- Cost of living (1)
- Cyber-bullying (1)
- Cyberbullying (1)
- Damian Hinds (1)
- Digital Classroom (1)
- Dyslexia Awareness (1)
- E Learning (1)
- Eating Disorders (1)
- Education Secretary (1)
- Empathy (1)
- Exam-ready (1)
- Flipped Classroom (1)
- Formative Assessment (1)
- Girls in STEM (1)
- Global Education (1)
- Global Learning (1)
- Government (1)
- Healthy Eating (1)
- Homework Excuses (1)
- Inspire (1)
- International Learning (1)
- Internet Access (1)
- Interventions (1)
- Job Satisfaction (1)
- Language (1)
- Lead by Example (1)
- Learning Environment (1)
- Manager (1)
- National Curriculum (1)
- Outstanding (1)
- Parent Tips for Homework (1)
- Parent-teacher Relationships (1)
- Parents Evening (1)
- Phased Reopenings (1)
- Physical Health (1)
- Planning (1)
- Preparation (1)
- Productivity (1)
- Progress 8 (1)
- Quality Assurance (1)
- Recognition (1)
- Safeguarding (1)
- School Improvements (1)
- Schools (1)
- Secondary School (1)
- Senior Leaders (1)
- Sharing (1)
- Sharing Best Practice (1)
- Show My Homework (1)
- Slow Processing (1)
- Social Media (1)
- Soft Skills (1)
- Software (1)
- Student (1)
- Student Independence (1)
- Summative Assessment (1)
- Super Union (1)
- Support (1)
- Teaching Schools (1)
- Technology in the classroom (1)
- Tracking & Monitoring (1)
- Training (1)
- Truancy (1)
- Year 6 SATs (1)
- example (1)
- first day of school (1)
- gained time (1)
- homework benefits (1)
- influence (1)
- ofsted inspections (1)
- practice (1)
- quiz creation (1)
- raising awareness (1)
- satchel (1)
- school involvement (1)
- well-balanced education (1)
FREE quiz tool
Browse through over 500k questions created by teachers on Neeto , create a quiz and share back to Satchel One. It's free!
- Satchel One learning platform
- About Satchel
- Get in touch
- Back to all blog posts
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)

Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
Should Students Have Homework?
- Classroom Strategies
- See More Tags

By Suzanne Capek Tingley, Veteran Educator, M.A. Degree
It used to be that students were the only ones complaining about the practice of assigning homework. For years, teachers and parents thought that homework was a necessary tool when educating children. But studies about the effectiveness of homework have been conflicting and inconclusive, leading some adults to argue that homework should become a thing of the past.
What Research Says about Homework
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule" : students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 additional minutes each subsequent year, so that by twelfth grade they are completing 120 minutes of homework daily.
But his analysis didn't prove that students did better because they did homework; it simply showed a correlation . This could simply mean that kids who do homework are more committed to doing well in school. Cooper also found that some research showed that homework caused physical and emotional stress, and created negative attitudes about learning. He suggested that more research needed to be done on homework's effect on kids.
Some researchers say that the question isn't whether kids should have homework. It's more about what kind of homework students have and how much. To be effective, homework has to meet students' needs. For example, some middle school teachers have found success with online math homework that's adapted to each student's level of understanding. But when middle school students were assigned more than an hour and a half of homework, their math and science test scores went down .
Researchers at Indiana University discovered that math and science homework may improve standardized test grades, but they found no difference in course grades between students who did homework and those who didn't. These researchers theorize that homework doesn't result in more content mastery, but in greater familiarity with the kinds of questions that appear on standardized tests. According to Professor Adam Maltese, one of the study's authors, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be."
So while many teachers and parents support daily homework, it's hard to find strong evidence that the long-held practice produces positive results.
Problems with Homework
In an article in Education Week Teacher , teacher Samantha Hulsman said she's frequently heard parents complain that a 30-minute homework assignment turns into a three-hour battle with their kids. Now, she's facing the same problem with her own kids, which has her rethinking her former beliefs about homework. "I think parents expect their children to have homework nightly, and teachers assign daily homework because it's what we've always done," she explained. Today, Hulsman said, it's more important to know how to collaborate and solve problems than it is to know specific facts.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish wrote in Psychology Today that battles over homework rarely result in a child's improvement in school . Children who don't do their homework are not lazy, he said, but they may be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious. And for kids with learning disabilities, homework is like "running with a sprained ankle. It's doable, but painful."
Barish suggests that parents and kids have a "homework plan" that limits the time spent on homework. The plan should include turning off all devices—not just the student's, but those belonging to all family members.
One of the best-known critics of homework, Alfie Kohn , says that some people wrongly believe "kids are like vending machines—put in an assignment, get out learning." Kohn points to the lack of evidence that homework is an effective learning tool; in fact, he calls it "the greatest single extinguisher of children's curiosity that we have yet invented."
Homework Bans
Last year, the public schools in Marion County, Florida, decided on a no-homework policy for all of their elementary students . Instead, kids read nightly for 20 minutes. Superintendent Heidi Maier said the decision was based on Cooper's research showing that elementary students gain little from homework, but a lot from reading.
Orchard Elementary School in South Burlington, Vermont, followed the same path, substituting reading for homework. The homework policy has four parts : read nightly, go outside and play, have dinner with your family, and get a good night's sleep. Principal Mark Trifilio says that his staff and parents support the idea.
But while many elementary schools are considering no-homework policies, middle schools and high schools have been reluctant to abandon homework. Schools say parents support homework and teachers know it can be helpful when it is specific and follows certain guidelines. For example, practicing solving word problems can be helpful, but there's no reason to assign 50 problems when 10 will do. Recognizing that not all kids have the time, space, and home support to do homework is important, so it shouldn't be counted as part of a student's grade.
So Should Students Have Homework?
Should you ban homework in your classroom? If you teach lower grades, it's possible. If you teach middle or high school, probably not. But all teachers should think carefully about their homework policies. By limiting the amount of homework and improving the quality of assignments, you can improve learning outcomes for your students.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11 Transforming Student Learning with Effective Study Techniques

https://unsplash.com/photos/person-writing-on-brown-wooden-table-near-white-ceramic-mug-s9CC2SKySJM
Effective study techniques can significantly enhance student learning and academic performance. In today’s fast-paced educational environment, students face numerous challenges, from managing multiple assignments and homework to balancing extracurricular activities. Developing strong study habits is essential for success in both school and college.
Understanding how to study efficiently can make a significant difference in a student’s academic journey. By implementing the right techniques, students can improve their comprehension, retention, and overall performance. This article explores various study methods and provides valuable tips for students looking to transform their learning experiences with paperwriter .
The Importance of Effective Study Techniques
Effective study techniques are crucial for students aiming to achieve their academic goals. These techniques help in better time management, reducing stress, and improving understanding of complex subjects. With the right approach, students can make their study sessions more productive and less overwhelming.
One of the biggest challenges students face is the sheer volume of information they need to learn and retain. Effective study techniques can help break down this information into manageable chunks, making it easier to digest and remember. Moreover, students who develop good study habits early on are more likely to succeed in their future academic and professional endeavors.
Creating a Conducive Study Environment
A conducive study environment is essential for effective learning. Students should choose a quiet, comfortable place with minimal distractions to focus on their studies. A well-organized study space can significantly enhance concentration and productivity.
Tips for Creating a Conducive Study Environment:
- Choose a quiet location: Find a place free from noise and interruptions.
- Ensure good lighting: Proper lighting reduces eye strain and improves focus.
- Organize your materials: Keep all necessary supplies within reach to avoid unnecessary distractions.
- Comfortable seating: Choose a chair and desk that provide good support to maintain good posture.
Time Management and Scheduling
Time management is a critical skill for students. Balancing school, college, assignments, and homework can be challenging. Effective scheduling ensures that students allocate sufficient time for each subject and activity.
Strategies for Better Time Management:
- Create a study schedule: Plan your study sessions and stick to the schedule.
- Set priorities: Focus on the most important tasks first.
- Break tasks into smaller steps: Divide large assignments into manageable parts.
- Use a planner: Keep track of deadlines, assignments, and exams.
Active Learning Techniques
Active learning involves engaging with the material actively rather than passively reading or listening. This approach enhances understanding and retention.
Effective Active Learning Techniques:
- Summarization: Summarize key points in your own words.
- Questioning: Ask questions about the material and seek answers.
- Discussion: Discuss topics with classmates to gain different perspectives.
- Application: Apply what you have learned to real-world scenarios.
The Role of Technology in Studying
Technology can be a powerful tool for enhancing learning. Various apps and online resources can help students manage their study time, organize notes, and access educational materials.
Useful Technological Tools for Students:
- Note-taking apps: Apps like Evernote and OneNote help organize and store notes efficiently.
- Study apps: Apps like Quizlet and Anki offer flashcards and quizzes for effective revision.
- Time management apps: Tools like Trello and Todoist help students plan and track their tasks.( or visit https://do-my-math.com/ )
- Online resources: Websites like Khan Academy and Coursera provide additional learning materials.
Enhancing Memory and Retention
Improving memory and retention is vital for academic success. Students can employ various techniques to boost their ability to remember and recall information.
Techniques to Enhance Memory and Retention:
- Mnemonics: Use mnemonic devices to remember complex information.
- Visualization: Create mental images to associate with the material.
- Repetition: Review material regularly to reinforce learning.
- Teaching others: Explaining concepts to others helps solidify understanding.
Staying Motivated and Managing Stress
Maintaining motivation and managing stress are essential components of effective studying. Students need to find ways to stay motivated and cope with academic pressures.
Tips for Staying Motivated and Managing Stress:
- Set realistic goals: Set achievable short-term and long-term goals.
- Take breaks: Regular breaks prevent burnout and improve focus.
- Stay positive: Maintain a positive attitude towards learning.
- Seek support: Reach out to teachers, peers, or counselors for help when needed.
Incorporating effective study techniques can transform the learning experience for students. By creating a conducive study environment, managing time efficiently, engaging in active learning, utilizing technology, enhancing memory, and staying motivated, students can achieve academic success. Remember, the key to effective studying lies in consistency and dedication. With the right approach, every student can improve their learning outcomes and reach their full potential.
Effective study habits not only help students excel in their current studies but also prepare them for future challenges. By implementing these strategies, students can turn studying into a more enjoyable and rewarding experience, ultimately leading to better academic performance and personal growth. Investing time in developing good study habits today will pay off in the long run, making the journey through school and college a successful one.
Education Copyright © by john44. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Footnote leads to exploration of start of for-profit prisons in N.Y.

Should NATO step up role in Russia-Ukraine war?

It’s on Facebook, and it’s complicated

One way to help big groups of students? Volunteer tutors.
Research finds low-cost, online program yields significant results
Harvard Staff Writer
It’s well established that tutoring programs can make a big difference in student outcomes.
A recent study by Harvard researchers Eliana La Ferrara, Ph.D. ’99, and Michela Carlana looked specifically at the effectiveness of a low-cost, online model staffed by trained college student volunteers, one that could potentially be deployed on a wider basis.
The two found the program showed strong efficacy in improving academic performance for a range of students, including economically disadvantaged ones. And they discovered some unanticipated social, psychological, and attitudinal gains for the students — and even some for the tutors.
La Ferrara said the low cost could make this kind of approach “appealing for some governments.” In the study, the two noted, “Volunteer tutors represent a viable and cost-effective solution to reach a large number of students in need of support.”
The program showed strong efficacy in improving academic performance for a range of students, including economically disadvantaged ones.
La Ferrara is a professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School. She is president of the Econometric Society and program director of development economics for the Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR). Carlana is an assistant professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School.
Their study , which matched middle school students in Italy with volunteer tutors from several universities, began in the spring of 2020 as a response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We found ourselves in the middle of the pandemic that hit Italy immediately after the China outbreak,” Carlana said. “Within two weeks, schools closed, and everything became remote.”
Tutors were recruited from Bocconi University, where La Ferrara held the Invernizzi Chair in Development Economics at the time, directing the Laboratory for Effective Anti-Poverty Policies (LEAP), as well as Bicocca University and University of Milan, and trained with education specialists for three weeks to instruct students in math, Italian, and English.
“We had this program running where the pedagogical experts provided the training and also counseling in case the tutors had issues that they wanted to discuss one-on-one,” La Ferrara said.
The study was then repeated in 2022 with a new set of students and tutors at 10 different universities in Northern Italy. “So we were trying to test out and understand both during the pandemic, but also afterwards, whether this is an effective way to improve learning for the most disadvantaged,” La Ferrara said.
Of the 2,196 students in the sample, 42 percent were female, 23 percent were immigrants, and 29 percent had learning disorders.
The researchers looked at administrative data from the Italian Ministry of Education, long-term standardized test scores, the results of a standardized test administered by the research team, and surveys of parents, students, tutors, and teachers. They found that performance, especially in math, improved for nearly every student both during and after the pandemic.
Surprisingly, Carlana said they also found the tutoring had “very strong effects on these other soft dimensions, like psychological well-being, aspiration, and social emotional skills, even if our program is not directly targeted to those.”
Researchers surveyed participants about their aspirations for college and high school and their belief in faith or luck as the key to success. To measure well-being, researchers used the Children’s Depression Screener. They found that the most disadvantaged pupils, especially immigrant students, had the greatest improvement in soft skills.
“When we look at the effect on happiness and depression, those improvements are driven by immigrant children,” La Ferrara said. “Their ability to be in touch with peers when schools are closed, these are students who probably have fewer social networks — maybe they don’t get the call, they’re not on the same WhatsApp groups, or whatever. So for these more disadvantaged or more isolated students, the tutor becomes a very important window outside the family.”
However, as in-person learning resumed, the soft skills benefits for students lessened.
“I feel like in part it could be related to the fact that now the students have a wider set of opportunities outside [of tutoring] either to improve the soft skills that could be the more beneficial in in-person interaction compared to online interaction,” Carlana added.
One thing that proved eye-opening for the researchers was the effect on tutors. La Ferrara and Carlana surveyed participating tutors and those who applied but were not selected due to capacity. They asked questions attempting to gauge empathy and attitudes about the role of hard work, luck, and social connections in achieving success.
“We found that the volunteers who had had become tutors had significantly more empathy toward others, but no different beliefs on the importance of luck versus effort,” La Ferrara said. “So we think this is an aspect that deserves more work, because all the existing studies on in-person tutoring tend to focus on what tutoring does to the recipient, the student, but it’s an important experience for the tutor, especially when they are volunteers … it could be a life-changing experience for some of these younger tutors.”
The researchers are currently in the process of following up with tutors to see how and whether the program impacted their post-graduation career paths.
The two also are working on studying the program in different countries and with different experimental designs to better target and assign students to tutors.
“We like the idea that this could be implementable in many settings, and in fact, one of the settings where we ran the program for two years was the Dominican Republic, which is very different from Italy,” La Ferrara said. “And so it created challenges in adapting the program in recruiting tutors from a very different institutional setting. But in the future, this could be picked up more.”
Share this article
You might like.
Historian traces 19th-century murder case that brought together historical figures, helped shape American thinking on race, violence, incarceration

National security analysts outline stakes ahead of July summit

‘Spermworld’ documentary examines motivations of prospective parents, volunteer donors who connect through private group page
When should Harvard speak out?
Institutional Voice Working Group provides a roadmap in new report
Day to remember
One journey behind them, grads pause to reflect before starting the next
Had a bad experience meditating? You're not alone.
Altered states of consciousness through yoga, mindfulness more common than thought and mostly beneficial, study finds — though clinicians ill-equipped to help those who struggle
A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education
- Open access
- Published: 26 May 2024
- Volume 3 , article number 60 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Yazid Albadarin ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0005-8068-8902 1 ,
- Mohammed Saqr 1 ,
- Nicolas Pope 1 &
- Markku Tukiainen 1
237 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Over the last four decades, studies have investigated the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into education. A recent prominent AI-powered technology that has impacted the education sector is ChatGPT. This article provides a systematic review of 14 empirical studies incorporating ChatGPT into various educational settings, published in 2022 and before the 10th of April 2023—the date of conducting the search process. It carefully followed the essential steps outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines, as well as Okoli’s (Okoli in Commun Assoc Inf Syst, 2015) steps for conducting a rigorous and transparent systematic review. In this review, we aimed to explore how students and teachers have utilized ChatGPT in various educational settings, as well as the primary findings of those studies. By employing Creswell’s (Creswell in Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook], Pearson Education, London, 2015) coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation, we sought to gain insight into their initial attempts at ChatGPT incorporation into education. This approach also enabled us to extract insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of this review show that learners have utilized ChatGPT as a virtual intelligent assistant, where it offered instant feedback, on-demand answers, and explanations of complex topics. Additionally, learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills by generating ideas, composing essays, summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Moreover, learners turned to it as an aiding tool to facilitate their directed and personalized learning by assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. However, the results of specific studies (n = 3, 21.4%) show that overuse of ChatGPT may negatively impact innovative capacities and collaborative learning competencies among learners. Educators, on the other hand, have utilized ChatGPT to create lesson plans, generate quizzes, and provide additional resources, which helped them enhance their productivity and efficiency and promote different teaching methodologies. Despite these benefits, the majority of the reviewed studies recommend the importance of conducting structured training, support, and clear guidelines for both learners and educators to mitigate the drawbacks. This includes developing critical evaluation skills to assess the accuracy and relevance of information provided by ChatGPT, as well as strategies for integrating human interaction and collaboration into learning activities that involve AI tools. Furthermore, they also recommend ongoing research and proactive dialogue with policymakers, stakeholders, and educational practitioners to refine and enhance the use of AI in learning environments. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
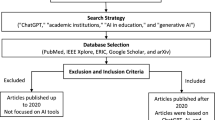
Empowering learners with ChatGPT: insights from a systematic literature exploration
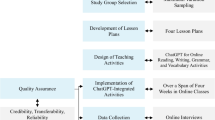
Incorporating AI in foreign language education: An investigation into ChatGPT’s effect on foreign language learners
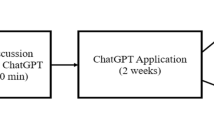
Large language models in education: A focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Educational technology, a rapidly evolving field, plays a crucial role in reshaping the landscape of teaching and learning [ 82 ]. One of the most transformative technological innovations of our era that has influenced the field of education is Artificial Intelligence (AI) [ 50 ]. Over the last four decades, AI in education (AIEd) has gained remarkable attention for its potential to make significant advancements in learning, instructional methods, and administrative tasks within educational settings [ 11 ]. In particular, a large language model (LLM), a type of AI algorithm that applies artificial neural networks (ANNs) and uses massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate, and predict new content that is almost difficult to differentiate from human creations [ 79 ], has opened up novel possibilities for enhancing various aspects of education, from content creation to personalized instruction [ 35 ]. Chatbots that leverage the capabilities of LLMs to understand and generate human-like responses have also presented the capacity to enhance student learning and educational outcomes by engaging students, offering timely support, and fostering interactive learning experiences [ 46 ].
The ongoing and remarkable technological advancements in chatbots have made their use more convenient, increasingly natural and effortless, and have expanded their potential for deployment across various domains [ 70 ]. One prominent example of chatbot applications is the Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer, known as ChatGPT, which was introduced by OpenAI, a leading AI research lab, on November 30th, 2022. ChatGPT employs a variety of deep learning techniques to generate human-like text, with a particular focus on recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Long short-term memory (LSTM) allows it to grasp the context of the text being processed and retain information from previous inputs. Also, the transformer architecture, a neural network architecture based on the self-attention mechanism, allows it to analyze specific parts of the input, thereby enabling it to produce more natural-sounding and coherent output. Additionally, the unsupervised generative pre-training and the fine-tuning methods allow ChatGPT to generate more relevant and accurate text for specific tasks [ 31 , 62 ]. Furthermore, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), a machine learning approach that combines reinforcement learning techniques with human-provided feedback, has helped improve ChatGPT’s model by accelerating the learning process and making it significantly more efficient.
This cutting-edge natural language processing (NLP) tool is widely recognized as one of today's most advanced LLMs-based chatbots [ 70 ], allowing users to ask questions and receive detailed, coherent, systematic, personalized, convincing, and informative human-like responses [ 55 ], even within complex and ambiguous contexts [ 63 , 77 ]. ChatGPT is considered the fastest-growing technology in history: in just three months following its public launch, it amassed an estimated 120 million monthly active users [ 16 ] with an estimated 13 million daily queries [ 49 ], surpassing all other applications [ 64 ]. This remarkable growth can be attributed to the unique features and user-friendly interface that ChatGPT offers. Its intuitive design allows users to interact seamlessly with the technology, making it accessible to a diverse range of individuals, regardless of their technical expertise [ 78 ]. Additionally, its exceptional performance results from a combination of advanced algorithms, continuous enhancements, and extensive training on a diverse dataset that includes various text sources such as books, articles, websites, and online forums [ 63 ], have contributed to a more engaging and satisfying user experience [ 62 ]. These factors collectively explain its remarkable global growth and set it apart from predecessors like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, and others.
In this context, several studies have explored the technological advancements of chatbots. One noteworthy recent research effort, conducted by Schöbel et al. [ 70 ], stands out for its comprehensive analysis of more than 5,000 studies on communication agents. This study offered a comprehensive overview of the historical progression and future prospects of communication agents, including ChatGPT. Moreover, other studies have focused on making comparisons, particularly between ChatGPT and alternative chatbots like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, LaMDA, BlenderBot, and various others. For example, O’Leary [ 53 ] compared two chatbots, LaMDA and BlenderBot, with ChatGPT and revealed that ChatGPT outperformed both. This superiority arises from ChatGPT’s capacity to handle a wider range of questions and generate slightly varied perspectives within specific contexts. Similarly, ChatGPT exhibited an impressive ability to formulate interpretable responses that were easily understood when compared with Google's feature snippet [ 34 ]. Additionally, ChatGPT was compared to other LLMs-based chatbots, including Bard and BERT, as well as ERNIE. The findings indicated that ChatGPT exhibited strong performance in the given tasks, often outperforming the other models [ 59 ].
Furthermore, in the education context, a comprehensive study systematically compared a range of the most promising chatbots, including Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, and Ernie across a multidisciplinary test that required higher-order thinking. The study revealed that ChatGPT achieved the highest score, surpassing Bing Chat and Bard [ 64 ]. Similarly, a comparative analysis was conducted to compare ChatGPT with Bard in answering a set of 30 mathematical questions and logic problems, grouped into two question sets. Set (A) is unavailable online, while Set (B) is available online. The results revealed ChatGPT's superiority in Set (A) over Bard. Nevertheless, Bard's advantage emerged in Set (B) due to its capacity to access the internet directly and retrieve answers, a capability that ChatGPT does not possess [ 57 ]. However, through these varied assessments, ChatGPT consistently highlights its exceptional prowess compared to various alternatives in the ever-evolving chatbot technology.
The widespread adoption of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, by millions of students and educators, has sparked extensive discussions regarding its incorporation into the education sector [ 64 ]. Accordingly, many scholars have contributed to the discourse, expressing both optimism and pessimism regarding the incorporation of ChatGPT into education. For example, ChatGPT has been highlighted for its capabilities in enriching the learning and teaching experience through its ability to support different learning approaches, including adaptive learning, personalized learning, and self-directed learning [ 58 , 60 , 91 ]), deliver summative and formative feedback to students and provide real-time responses to questions, increase the accessibility of information [ 22 , 40 , 43 ], foster students’ performance, engagement and motivation [ 14 , 44 , 58 ], and enhance teaching practices [ 17 , 18 , 64 , 74 ].
On the other hand, concerns have been also raised regarding its potential negative effects on learning and teaching. These include the dissemination of false information and references [ 12 , 23 , 61 , 85 ], biased reinforcement [ 47 , 50 ], compromised academic integrity [ 18 , 40 , 66 , 74 ], and the potential decline in students' skills [ 43 , 61 , 64 , 74 ]. As a result, ChatGPT has been banned in multiple countries, including Russia, China, Venezuela, Belarus, and Iran, as well as in various educational institutions in India, Italy, Western Australia, France, and the United States [ 52 , 90 ].
Clearly, the advent of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, has provoked significant controversy due to their potential impact on learning and teaching. This indicates the necessity for further exploration to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and carefully evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education [ 79 ]. Therefore, conducting a systematic literature review will provide valuable insights into the potential prospects and obstacles linked to its incorporation into education. This systematic literature review will primarily focus on ChatGPT, driven by the aforementioned key factors outlined above.
However, the existing literature lacks a systematic literature review of empirical studies. Thus, this systematic literature review aims to address this gap by synthesizing the existing empirical studies conducted on chatbots, particularly ChatGPT, in the field of education, highlighting how ChatGPT has been utilized in educational settings, and identifying any existing gaps. This review may be particularly useful for researchers in the field and educators who are contemplating the integration of ChatGPT or any chatbot into education. The following research questions will guide this study:
What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?
What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?
2 Methodology
To conduct this study, the authors followed the essential steps of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) and Okoli’s [ 54 ] steps for conducting a systematic review. These included identifying the study’s purpose, drafting a protocol, applying a practical screening process, searching the literature, extracting relevant data, evaluating the quality of the included studies, synthesizing the studies, and ultimately writing the review. The subsequent section provides an extensive explanation of how these steps were carried out in this study.
2.1 Identify the purpose
Given the widespread adoption of ChatGPT by students and teachers for various educational purposes, often without a thorough understanding of responsible and effective use or a clear recognition of its potential impact on learning and teaching, the authors recognized the need for further exploration of ChatGPT's impact on education in this early stage. Therefore, they have chosen to conduct a systematic literature review of existing empirical studies that incorporate ChatGPT into educational settings. Despite the limited number of empirical studies due to the novelty of the topic, their goal is to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and proactively evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education. This effort could help to understand initial reactions and attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education and bring out insights and considerations that can inform the future development of education.
2.2 Draft the protocol
The next step is formulating the protocol. This protocol serves to outline the study process in a rigorous and transparent manner, mitigating researcher bias in study selection and data extraction [ 88 ]. The protocol will include the following steps: generating the research question, predefining a literature search strategy, identifying search locations, establishing selection criteria, assessing the studies, developing a data extraction strategy, and creating a timeline.
2.3 Apply practical screen
The screening step aims to accurately filter the articles resulting from the searching step and select the empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into educational contexts, which will guide us in answering the research questions and achieving the objectives of this study. To ensure the rigorous execution of this step, our inclusion and exclusion criteria were determined based on the authors' experience and informed by previous successful systematic reviews [ 21 ]. Table 1 summarizes the inclusion and exclusion criteria for study selection.
2.4 Literature search
We conducted a thorough literature search to identify articles that explored, examined, and addressed the use of ChatGPT in Educational contexts. We utilized two research databases: Dimensions.ai, which provides access to a large number of research publications, and lens.org, which offers access to over 300 million articles, patents, and other research outputs from diverse sources. Additionally, we included three databases, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, and ERIC, which contain relevant research on the topic that addresses our research questions. To browse and identify relevant articles, we used the following search formula: ("ChatGPT" AND "Education"), which included the Boolean operator "AND" to get more specific results. The subject area in the Scopus and ERIC databases were narrowed to "ChatGPT" and "Education" keywords, and in the WoS database was limited to the "Education" category. The search was conducted between the 3rd and 10th of April 2023, which resulted in 276 articles from all selected databases (111 articles from Dimensions.ai, 65 from Scopus, 28 from Web of Science, 14 from ERIC, and 58 from Lens.org). These articles were imported into the Rayyan web-based system for analysis. The duplicates were identified automatically by the system. Subsequently, the first author manually reviewed the duplicated articles ensured that they had the same content, and then removed them, leaving us with 135 unique articles. Afterward, the titles, abstracts, and keywords of the first 40 manuscripts were scanned and reviewed by the first author and were discussed with the second and third authors to resolve any disagreements. Subsequently, the first author proceeded with the filtering process for all articles and carefully applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria as presented in Table 1 . Articles that met any one of the exclusion criteria were eliminated, resulting in 26 articles. Afterward, the authors met to carefully scan and discuss them. The authors agreed to eliminate any empirical studies solely focused on checking ChatGPT capabilities, as these studies do not guide us in addressing the research questions and achieving the study's objectives. This resulted in 14 articles eligible for analysis.
2.5 Quality appraisal
The examination and evaluation of the quality of the extracted articles is a vital step [ 9 ]. Therefore, the extracted articles were carefully evaluated for quality using Fink’s [ 24 ] standards, which emphasize the necessity for detailed descriptions of methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, and limitations. The process began with a thorough assessment of each study's design, data collection, and analysis methods to ensure their appropriateness and comprehensive execution. The clarity, consistency, and logical progression from data to results and conclusions were also critically examined. Potential biases and recognized limitations within the studies were also scrutinized. Ultimately, two articles were excluded for failing to meet Fink’s criteria, particularly in providing sufficient detail on methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, or limitations. The review process is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
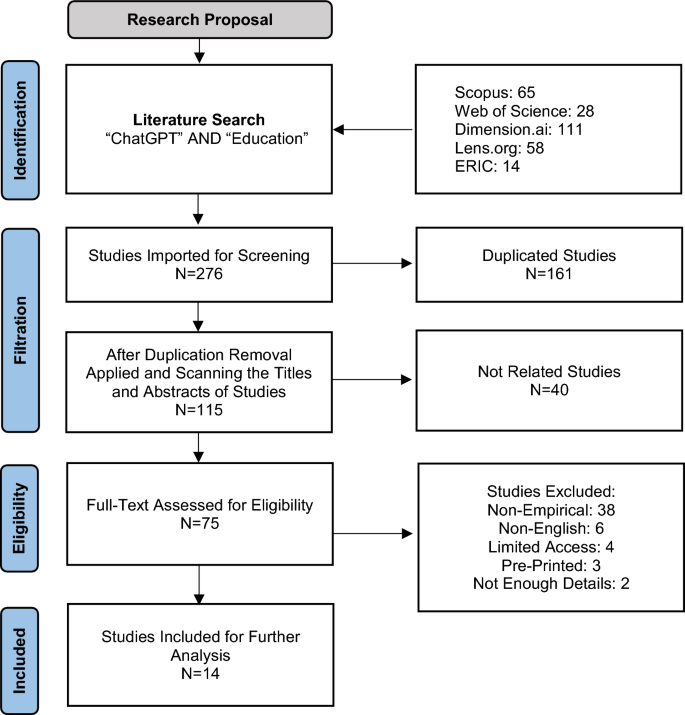
The study selection process
2.6 Data extraction
The next step is data extraction, the process of capturing the key information and categories from the included studies. To improve efficiency, reduce variation among authors, and minimize errors in data analysis, the coding categories were constructed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation. The coding process involves three sequential steps. The initial stage encompasses open coding , where the researcher examines the data, generates codes to describe and categorize it, and gains a deeper understanding without preconceived ideas. Following open coding is axial coding , where the interrelationships between codes from open coding are analyzed to establish more comprehensive categories or themes. The process concludes with selective coding , refining and integrating categories or themes to identify core concepts emerging from the data. The first coder performed the coding process, then engaged in discussions with the second and third authors to finalize the coding categories for the first five articles. The first coder then proceeded to code all studies and engaged again in discussions with the other authors to ensure the finalization of the coding process. After a comprehensive analysis and capturing of the key information from the included studies, the data extraction and interpretation process yielded several themes. These themes have been categorized and are presented in Table 2 . It is important to note that open coding results were removed from Table 2 for aesthetic reasons, as it included many generic aspects, such as words, short phrases, or sentences mentioned in the studies.
2.7 Synthesize studies
In this stage, we will gather, discuss, and analyze the key findings that emerged from the selected studies. The synthesis stage is considered a transition from an author-centric to a concept-centric focus, enabling us to map all the provided information to achieve the most effective evaluation of the data [ 87 ]. Initially, the authors extracted data that included general information about the selected studies, including the author(s)' names, study titles, years of publication, educational levels, research methodologies, sample sizes, participants, main aims or objectives, raw data sources, and analysis methods. Following that, all key information and significant results from the selected studies were compiled using Creswell’s [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation to identify core concepts and themes emerging from the data, focusing on those that directly contributed to our research questions and objectives, such as the initial utilization of ChatGPT in learning and teaching, learners' and educators' familiarity with ChatGPT, and the main findings of each study. Finally, the data related to each selected study were extracted into an Excel spreadsheet for data processing. The Excel spreadsheet was reviewed by the authors, including a series of discussions to ensure the finalization of this process and prepare it for further analysis. Afterward, the final result being analyzed and presented in various types of charts and graphs. Table 4 presents the extracted data from the selected studies, with each study labeled with a capital 'S' followed by a number.
This section consists of two main parts. The first part provides a descriptive analysis of the data compiled from the reviewed studies. The second part presents the answers to the research questions and the main findings of these studies.
3.1 Part 1: descriptive analysis
This section will provide a descriptive analysis of the reviewed studies, including educational levels and fields, participants distribution, country contribution, research methodologies, study sample size, study population, publication year, list of journals, familiarity with ChatGPT, source of data, and the main aims and objectives of the studies. Table 4 presents a comprehensive overview of the extracted data from the selected studies.
3.1.1 The number of the reviewed studies and publication years
The total number of the reviewed studies was 14. All studies were empirical studies and published in different journals focusing on Education and Technology. One study was published in 2022 [S1], while the remaining were published in 2023 [S2]-[S14]. Table 3 illustrates the year of publication, the names of the journals, and the number of reviewed studies published in each journal for the studies reviewed.
3.1.2 Educational levels and fields
The majority of the reviewed studies, 11 studies, were conducted in higher education institutions [S1]-[S10] and [S13]. Two studies did not specify the educational level of the population [S12] and [S14], while one study focused on elementary education [S11]. However, the reviewed studies covered various fields of education. Three studies focused on Arts and Humanities Education [S8], [S11], and [S14], specifically English Education. Two studies focused on Engineering Education, with one in Computer Engineering [S2] and the other in Construction Education [S3]. Two studies focused on Mathematics Education [S5] and [S12]. One study focused on Social Science Education [S13]. One study focused on Early Education [S4]. One study focused on Journalism Education [S9]. Finally, three studies did not specify the field of education [S1], [S6], and [S7]. Figure 2 represents the educational levels in the reviewed studies, while Fig. 3 represents the context of the reviewed studies.

Educational levels in the reviewed studies
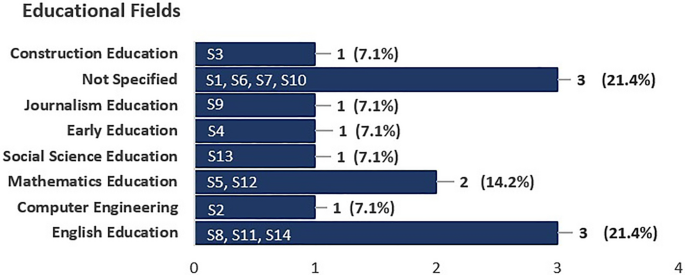
Context of the reviewed studies
3.1.3 Participants distribution and countries contribution
The reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions, providing a diverse representation of the studies. The majority of the studies, 10 in total, [S1]-[S3], [S5]-[S9], [S11], and [S14], primarily focused on participants from single countries such as Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates, China, Indonesia, Poland, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Spain, Tajikistan, and the United States. In contrast, four studies, [S4], [S10], [S12], and [S13], involved participants from multiple countries, including China and the United States [S4], China, the United Kingdom, and the United States [S10], the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan [S12], Turkey, Sweden, Canada, and Australia [ 13 ]. Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the distribution of participants, whether from single or multiple countries, and the contribution of each country in the reviewed studies, respectively.
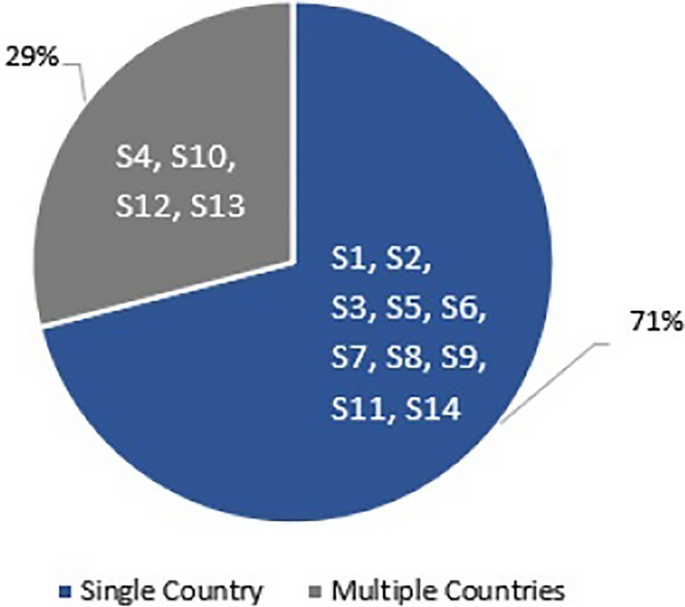
The reviewed studies conducted in single or multiple countries
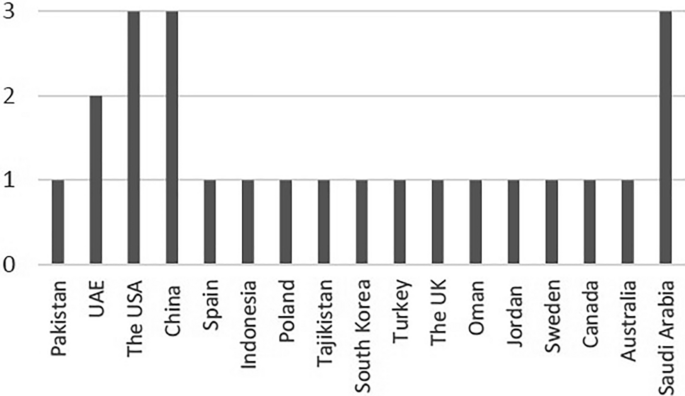
The Contribution of each country in the studies
3.1.4 Study population and sample size
Four study populations were included: university students, university teachers, university teachers and students, and elementary school teachers. Six studies involved university students [S2], [S3], [S5] and [S6]-[S8]. Three studies focused on university teachers [S1], [S4], and [S6], while one study specifically targeted elementary school teachers [S11]. Additionally, four studies included both university teachers and students [S10] and [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], and among them, study [S13] specifically included postgraduate students. In terms of the sample size of the reviewed studies, nine studies included a small sample size of less than 50 participants [S1], [S3], [S6], [S8], and [S10]-[S13]. Three studies had 50–100 participants [S2], [S9], and [S14]. Only one study had more than 100 participants [S7]. It is worth mentioning that study [S4] adopted a mixed methods approach, including 10 participants for qualitative analysis and 110 participants for quantitative analysis.
3.1.5 Participants’ familiarity with using ChatGPT
The reviewed studies recruited a diverse range of participants with varying levels of familiarity with ChatGPT. Five studies [S2], [S4], [S6], [S8], and [S12] involved participants already familiar with ChatGPT, while eight studies [S1], [S3], [S5], [S7], [S9], [S10], [S13] and [S14] included individuals with differing levels of familiarity. Notably, one study [S11] had participants who were entirely unfamiliar with ChatGPT. It is important to note that four studies [S3], [S5], [S9], and [S11] provided training or guidance to their participants before conducting their studies, while ten studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6]-[S8], [S10], and [S12]-[S14] did not provide training due to the participants' existing familiarity with ChatGPT.
3.1.6 Research methodology approaches and source(S) of data
The reviewed studies adopted various research methodology approaches. Seven studies adopted qualitative research methodology [S1], [S4], [S6], [S8], [S10], [S11], and [S12], while three studies adopted quantitative research methodology [S3], [S7], and [S14], and four studies employed mixed-methods, which involved a combination of both the strengths of qualitative and quantitative methods [S2], [S5], [S9], and [S13].
In terms of the source(s) of data, the reviewed studies obtained their data from various sources, such as interviews, questionnaires, and pre-and post-tests. Six studies relied on interviews as their primary source of data collection [S1], [S4], [S6], [S10], [S11], and [S12], four studies relied on questionnaires [S2], [S7], [S13], and [S14], two studies combined the use of pre-and post-tests and questionnaires for data collection [S3] and [S9], while two studies combined the use of questionnaires and interviews to obtain the data [S5] and [S8]. It is important to note that six of the reviewed studies were quasi-experimental [S3], [S5], [S8], [S9], [S12], and [S14], while the remaining ones were experimental studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6], [S7], [S10], [S11], and [S13]. Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the research methodologies and the source (s) of data used in the reviewed studies, respectively.
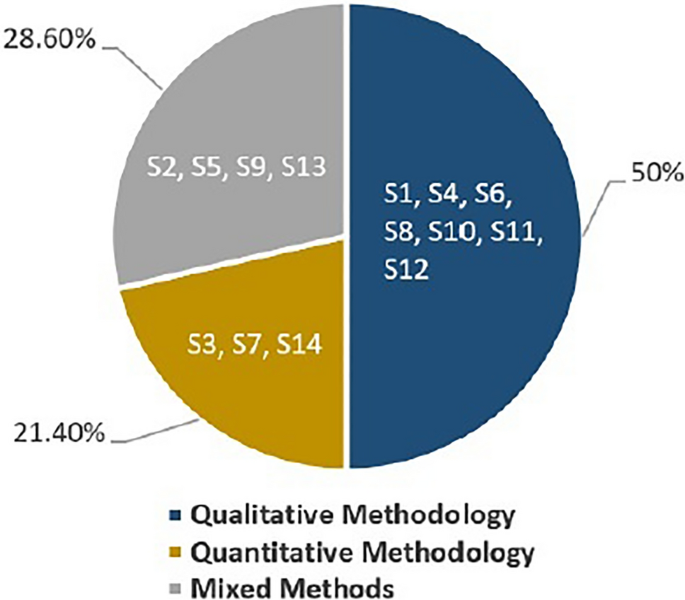
Research methodologies in the reviewed studies
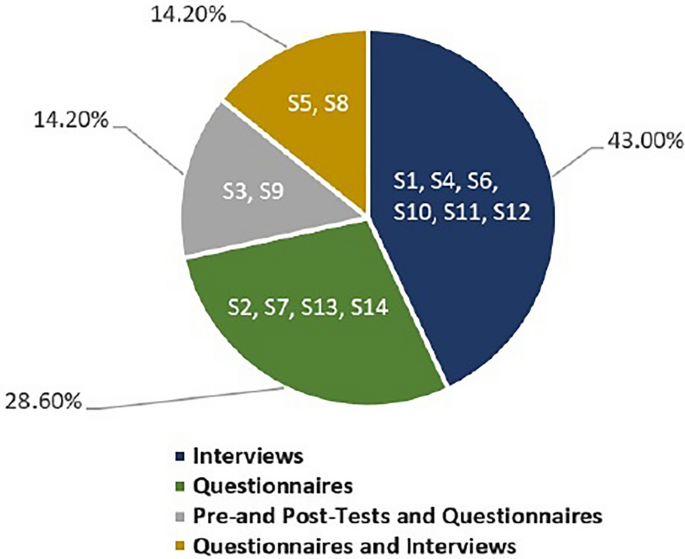
Source of data in the reviewed studies
3.1.7 The aim and objectives of the studies
The reviewed studies encompassed a diverse set of aims, with several of them incorporating multiple primary objectives. Six studies [S3], [S6], [S7], [S8], [S11], and [S12] examined the integration of ChatGPT in educational contexts, and four studies [S4], [S5], [S13], and [S14] investigated the various implications of its use in education, while three studies [S2], [S9], and [S10] aimed to explore both its integration and implications in education. Additionally, seven studies explicitly explored attitudes and perceptions of students [S2] and [S3], educators [S1] and [S6], or both [S10], [S12], and [S13] regarding the utilization of ChatGPT in educational settings.
3.2 Part 2: research questions and main findings of the reviewed studies
This part will present the answers to the research questions and the main findings of the reviewed studies, classified into two main categories (learning and teaching) according to AI Education classification by [ 36 ]. Figure 8 summarizes the main findings of the reviewed studies in a visually informative diagram. Table 4 provides a detailed list of the key information extracted from the selected studies that led to generating these themes.
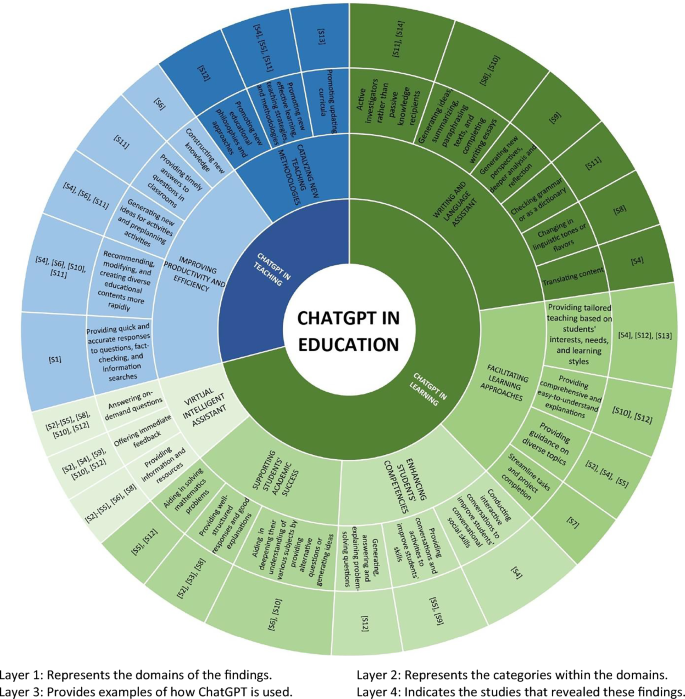
The main findings in the reviewed studies
4 Students' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in learning and main findings from students' perspective
4.1 virtual intelligent assistant.
Nine studies demonstrated that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as an intelligent assistant to enhance and support their learning. Students employed it for various purposes, such as answering on-demand questions [S2]-[S5], [S8], [S10], and [S12], providing valuable information and learning resources [S2]-[S5], [S6], and [S8], as well as receiving immediate feedback [S2], [S4], [S9], [S10], and [S12]. In this regard, students generally were confident in the accuracy of ChatGPT's responses, considering them relevant, reliable, and detailed [S3], [S4], [S5], and [S8]. However, some students indicated the need for improvement, as they found that answers are not always accurate [S2], and that misleading information may have been provided or that it may not always align with their expectations [S6] and [S10]. It was also observed by the students that the accuracy of ChatGPT is dependent on several factors, including the quality and specificity of the user's input, the complexity of the question or topic, and the scope and relevance of its training data [S12]. Many students felt that ChatGPT's answers were not always accurate and most of them believed that it requires good background knowledge to work with.
4.2 Writing and language proficiency assistant
Six of the reviewed studies highlighted that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as a valuable assistant tool to improve their academic writing skills and language proficiency. Among these studies, three mainly focused on English education, demonstrating that students showed sufficient mastery in using ChatGPT for generating ideas, summarizing, paraphrasing texts, and completing writing essays [S8], [S11], and [S14]. Furthermore, ChatGPT helped them in writing by making students active investigators rather than passive knowledge recipients and facilitated the development of their writing skills [S11] and [S14]. Similarly, ChatGPT allowed students to generate unique ideas and perspectives, leading to deeper analysis and reflection on their journalism writing [S9]. In terms of language proficiency, ChatGPT allowed participants to translate content into their home languages, making it more accessible and relevant to their context [S4]. It also enabled them to request changes in linguistic tones or flavors [S8]. Moreover, participants used it to check grammar or as a dictionary [S11].
4.3 Valuable resource for learning approaches
Five studies demonstrated that students used ChatGPT as a valuable complementary resource for self-directed learning. It provided learning resources and guidance on diverse educational topics and created a supportive home learning environment [S2] and [S4]. Moreover, it offered step-by-step guidance to grasp concepts at their own pace and enhance their understanding [S5], streamlined task and project completion carried out independently [S7], provided comprehensive and easy-to-understand explanations on various subjects [S10], and assisted in studying geometry operations, thereby empowering them to explore geometry operations at their own pace [S12]. Three studies showed that students used ChatGPT as a valuable learning resource for personalized learning. It delivered age-appropriate conversations and tailored teaching based on a child's interests [S4], acted as a personalized learning assistant, adapted to their needs and pace, which assisted them in understanding mathematical concepts [S12], and enabled personalized learning experiences in social sciences by adapting to students' needs and learning styles [S13]. On the other hand, it is important to note that, according to one study [S5], students suggested that using ChatGPT may negatively affect collaborative learning competencies between students.
4.4 Enhancing students' competencies
Six of the reviewed studies have shown that ChatGPT is a valuable tool for improving a wide range of skills among students. Two studies have provided evidence that ChatGPT led to improvements in students' critical thinking, reasoning skills, and hazard recognition competencies through engaging them in interactive conversations or activities and providing responses related to their disciplines in journalism [S5] and construction education [S9]. Furthermore, two studies focused on mathematical education have shown the positive impact of ChatGPT on students' problem-solving abilities in unraveling problem-solving questions [S12] and enhancing the students' understanding of the problem-solving process [S5]. Lastly, one study indicated that ChatGPT effectively contributed to the enhancement of conversational social skills [S4].
4.5 Supporting students' academic success
Seven of the reviewed studies highlighted that students found ChatGPT to be beneficial for learning as it enhanced learning efficiency and improved the learning experience. It has been observed to improve students' efficiency in computer engineering studies by providing well-structured responses and good explanations [S2]. Additionally, students found it extremely useful for hazard reporting [S3], and it also enhanced their efficiency in solving mathematics problems and capabilities [S5] and [S12]. Furthermore, by finding information, generating ideas, translating texts, and providing alternative questions, ChatGPT aided students in deepening their understanding of various subjects [S6]. It contributed to an increase in students' overall productivity [S7] and improved efficiency in composing written tasks [S8]. Regarding learning experiences, ChatGPT was instrumental in assisting students in identifying hazards that they might have otherwise overlooked [S3]. It also improved students' learning experiences in solving mathematics problems and developing abilities [S5] and [S12]. Moreover, it increased students' successful completion of important tasks in their studies [S7], particularly those involving average difficulty writing tasks [S8]. Additionally, ChatGPT increased the chances of educational success by providing students with baseline knowledge on various topics [S10].
5 Teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in teaching and main findings from teachers' perspective
5.1 valuable resource for teaching.
The reviewed studies showed that teachers have employed ChatGPT to recommend, modify, and generate diverse, creative, organized, and engaging educational contents, teaching materials, and testing resources more rapidly [S4], [S6], [S10] and [S11]. Additionally, teachers experienced increased productivity as ChatGPT facilitated quick and accurate responses to questions, fact-checking, and information searches [S1]. It also proved valuable in constructing new knowledge [S6] and providing timely answers to students' questions in classrooms [S11]. Moreover, ChatGPT enhanced teachers' efficiency by generating new ideas for activities and preplanning activities for their students [S4] and [S6], including interactive language game partners [S11].
5.2 Improving productivity and efficiency
The reviewed studies showed that participants' productivity and work efficiency have been significantly enhanced by using ChatGPT as it enabled them to allocate more time to other tasks and reduce their overall workloads [S6], [S10], [S11], [S13], and [S14]. However, three studies [S1], [S4], and [S11], indicated a negative perception and attitude among teachers toward using ChatGPT. This negativity stemmed from a lack of necessary skills to use it effectively [S1], a limited familiarity with it [S4], and occasional inaccuracies in the content provided by it [S10].
5.3 Catalyzing new teaching methodologies
Five of the reviewed studies highlighted that educators found the necessity of redefining their teaching profession with the assistance of ChatGPT [S11], developing new effective learning strategies [S4], and adapting teaching strategies and methodologies to ensure the development of essential skills for future engineers [S5]. They also emphasized the importance of adopting new educational philosophies and approaches that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom [S12]. Furthermore, updating curricula to focus on improving human-specific features, such as emotional intelligence, creativity, and philosophical perspectives [S13], was found to be essential.
5.4 Effective utilization of CHATGPT in teaching
According to the reviewed studies, effective utilization of ChatGPT in education requires providing teachers with well-structured training, support, and adequate background on how to use ChatGPT responsibly [S1], [S3], [S11], and [S12]. Establishing clear rules and regulations regarding its usage is essential to ensure it positively impacts the teaching and learning processes, including students' skills [S1], [S4], [S5], [S8], [S9], and [S11]-[S14]. Moreover, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders is indeed crucial for the successful integration of ChatGPT in education and to maximize the benefits for both educators and students [S1], [S6]-[S10], and [S12]-[S14].
6 Discussion
The purpose of this review is to conduct a systematic review of empirical studies that have explored the utilization of ChatGPT, one of today’s most advanced LLM-based chatbots, in education. The findings of the reviewed studies showed several ways of ChatGPT utilization in different learning and teaching practices as well as it provided insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of the reviewed studies came from diverse fields of education, which helped us avoid a biased review that is limited to a specific field. Similarly, the reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions. This kind of variety in geographic representation enriched the findings of this review.
In response to RQ1 , "What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?", the findings from this review provide comprehensive insights. Chatbots, including ChatGPT, play a crucial role in supporting student learning, enhancing their learning experiences, and facilitating diverse learning approaches [ 42 , 43 ]. This review found that this tool, ChatGPT, has been instrumental in enhancing students' learning experiences by serving as a virtual intelligent assistant, providing immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and engaging in educational conversations. Additionally, students have benefited from ChatGPT’s ability to generate ideas, compose essays, and perform tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar, thereby enhancing their writing and language competencies. Furthermore, students have turned to ChatGPT for assistance in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks, which fosters a supportive home learning environment, allowing them to take responsibility for their own learning and cultivate the skills and approaches essential for supportive home learning environment [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. This finding aligns with the study of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ] who highlighted that, when students actively engage in their own learning process, it yields additional advantages, such as heightened motivation, enhanced achievement, and the cultivation of enthusiasm, turning them into advocates for their own learning.
Moreover, students have utilized ChatGPT for tailored teaching and step-by-step guidance on diverse educational topics, streamlining task and project completion, and generating and recommending educational content. This personalization enhances the learning environment, leading to increased academic success. This finding aligns with other recent studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 60 , 66 ] which revealed that ChatGPT has the potential to offer personalized learning experiences and support an effective learning process by providing students with customized feedback and explanations tailored to their needs and abilities. Ultimately, fostering students' performance, engagement, and motivation, leading to increase students' academic success [ 14 , 44 , 58 ]. This ultimate outcome is in line with the findings of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ], which emphasized that learning strategies are important catalysts of students' learning, as students who utilize effective learning strategies are more likely to have better academic achievement.
Teachers, too, have capitalized on ChatGPT's capabilities to enhance productivity and efficiency, using it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, generating and preplanning new ideas for activities, and aiding in answering students’ questions. This adoption of technology introduces new opportunities to support teaching and learning practices, enhancing teacher productivity. This finding aligns with those of Day [ 17 ], De Castro [ 18 ], and Su and Yang [ 74 ] as well as with those of Valtonen et al. [ 82 ], who revealed that emerging technological advancements have opened up novel opportunities and means to support teaching and learning practices, and enhance teachers’ productivity.
In response to RQ2 , "What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?", the findings from this review provide profound insights and raise significant concerns. Starting with the insights, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have demonstrated the potential to reshape and revolutionize education, creating new, novel opportunities for enhancing the learning process and outcomes [ 83 ], facilitating different learning approaches, and offering a range of pedagogical benefits [ 19 , 43 , 72 ]. In this context, this review found that ChatGPT could open avenues for educators to adopt or develop new effective learning and teaching strategies that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom. Nonetheless, there is an evident lack of research understanding regarding the potential impact of generative machine learning models within diverse educational settings [ 83 ]. This necessitates teachers to attain a high level of proficiency in incorporating chatbots, such as ChatGPT, into their classrooms to create inventive, well-structured, and captivating learning strategies. In the same vein, the review also found that teachers without the requisite skills to utilize ChatGPT realized that it did not contribute positively to their work and could potentially have adverse effects [ 37 ]. This concern could lead to inequity of access to the benefits of chatbots, including ChatGPT, as individuals who lack the necessary expertise may not be able to harness their full potential, resulting in disparities in educational outcomes and opportunities. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. A potential solution is offering training, support, and competency development for teachers to ensure that all of them can leverage chatbots, including ChatGPT, effectively and equitably in their educational practices [ 5 , 28 , 80 ], which could enhance accessibility and inclusivity, and potentially result in innovative outcomes [ 82 , 83 ].
Additionally, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have the potential to significantly impact students' thinking abilities, including retention, reasoning, analysis skills [ 19 , 45 ], and foster innovation and creativity capabilities [ 83 ]. This review found that ChatGPT could contribute to improving a wide range of skills among students. However, it found that frequent use of ChatGPT may result in a decrease in innovative capacities, collaborative skills and cognitive capacities, and students' motivation to attend classes, as well as could lead to reduced higher-order thinking skills among students [ 22 , 29 ]. Therefore, immediate action is needed to carefully examine the long-term impact of chatbots such as ChatGPT, on learning outcomes as well as to explore its incorporation into educational settings as a supportive tool without compromising students' cognitive development and critical thinking abilities. In the same vein, the review also found that it is challenging to draw a consistent conclusion regarding the potential of ChatGPT to aid self-directed learning approach. This finding aligns with the recent study of Baskara [ 8 ]. Therefore, further research is needed to explore the potential of ChatGPT for self-directed learning. One potential solution involves utilizing learning analytics as a novel approach to examine various aspects of students' learning and support them in their individual endeavors [ 32 ]. This approach can bridge this gap by facilitating an in-depth analysis of how learners engage with ChatGPT, identifying trends in self-directed learning behavior, and assessing its influence on their outcomes.
Turning to the significant concerns, on the other hand, a fundamental challenge with LLM-based chatbots, including ChatGPT, is the accuracy and quality of the provided information and responses, as they provide false information as truth—a phenomenon often referred to as "hallucination" [ 3 , 49 ]. In this context, this review found that the provided information was not entirely satisfactory. Consequently, the utilization of chatbots presents potential concerns, such as generating and providing inaccurate or misleading information, especially for students who utilize it to support their learning. This finding aligns with other findings [ 6 , 30 , 35 , 40 ] which revealed that incorporating chatbots such as ChatGPT, into education presents challenges related to its accuracy and reliability due to its training on a large corpus of data, which may contain inaccuracies and the way users formulate or ask ChatGPT. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution is to equip students with the necessary skills and competencies, which include a background understanding of how to use it effectively and the ability to assess and evaluate the information it generates, as the accuracy and the quality of the provided information depend on the input, its complexity, the topic, and the relevance of its training data [ 28 , 49 , 86 ]. However, it's also essential to examine how learners can be educated about how these models operate, the data used in their training, and how to recognize their limitations, challenges, and issues [ 79 ].
Furthermore, chatbots present a substantial challenge concerning maintaining academic integrity [ 20 , 56 ] and copyright violations [ 83 ], which are significant concerns in education. The review found that the potential misuse of ChatGPT might foster cheating, facilitate plagiarism, and threaten academic integrity. This issue is also affirmed by the research conducted by Basic et al. [ 7 ], who presented evidence that students who utilized ChatGPT in their writing assignments had more plagiarism cases than those who did not. These findings align with the conclusions drawn by Cotton et al. [ 13 ], Hisan and Amri [ 33 ] and Sullivan et al. [ 75 ], who revealed that the integration of chatbots such as ChatGPT into education poses a significant challenge to the preservation of academic integrity. Moreover, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have increased the difficulty in identifying plagiarism [ 47 , 67 , 76 ]. The findings from previous studies [ 1 , 84 ] indicate that AI-generated text often went undetected by plagiarism software, such as Turnitin. However, Turnitin and other similar plagiarism detection tools, such as ZeroGPT, GPTZero, and Copyleaks, have since evolved, incorporating enhanced techniques to detect AI-generated text, despite the possibility of false positives, as noted in different studies that have found these tools still not yet fully ready to accurately and reliably identify AI-generated text [ 10 , 51 ], and new novel detection methods may need to be created and implemented for AI-generated text detection [ 4 ]. This potential issue could lead to another concern, which is the difficulty of accurately evaluating student performance when they utilize chatbots such as ChatGPT assistance in their assignments. Consequently, the most LLM-driven chatbots present a substantial challenge to traditional assessments [ 64 ]. The findings from previous studies indicate the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative assessment methods in the era of chatbots [ 14 , 20 , 64 , 75 ]. These methods should prioritize the process of evaluating students' ability to apply knowledge to complex cases and demonstrate comprehension, rather than solely focusing on the final product for assessment. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution would be the development of clear guidelines, regulatory policies, and pedagogical guidance. These measures would help regulate the proper and ethical utilization of chatbots, such as ChatGPT, and must be established before their introduction to students [ 35 , 38 , 39 , 41 , 89 ].
In summary, our review has delved into the utilization of ChatGPT, a prominent example of chatbots, in education, addressing the question of how ChatGPT has been utilized in education. However, there remain significant gaps, which necessitate further research to shed light on this area.
7 Conclusions
This systematic review has shed light on the varied initial attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education by both learners and educators, while also offering insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. From the analysis of 14 selected studies, the review revealed the dual-edged impact of ChatGPT in educational settings. On the positive side, ChatGPT significantly aided the learning process in various ways. Learners have used it as a virtual intelligent assistant, benefiting from its ability to provide immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and easy access to educational resources. Additionally, it was clear that learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills, engaging in practices such as generating ideas, composing essays, and performing tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Importantly, other learners have utilized it in supporting and facilitating their directed and personalized learning on a broad range of educational topics, assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. Educators, on the other hand, found ChatGPT beneficial for enhancing productivity and efficiency. They used it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, and answers learners' questions, which saved time and allowed for more dynamic and engaging teaching strategies and methodologies.
However, the review also pointed out negative impacts. The results revealed that overuse of ChatGPT could decrease innovative capacities and collaborative learning among learners. Specifically, relying too much on ChatGPT for quick answers can inhibit learners' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Learners might not engage deeply with the material or consider multiple solutions to a problem. This tendency was particularly evident in group projects, where learners preferred consulting ChatGPT individually for solutions over brainstorming and collaborating with peers, which negatively affected their teamwork abilities. On a broader level, integrating ChatGPT into education has also raised several concerns, including the potential for providing inaccurate or misleading information, issues of inequity in access, challenges related to academic integrity, and the possibility of misusing the technology.
Accordingly, this review emphasizes the urgency of developing clear rules, policies, and regulations to ensure ChatGPT's effective and responsible use in educational settings, alongside other chatbots, by both learners and educators. This requires providing well-structured training to educate them on responsible usage and understanding its limitations, along with offering sufficient background information. Moreover, it highlights the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative teaching and assessment methods in the era of ChatGPT. Furthermore, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders are essential steps to maximize the benefits for both educators and learners and ensure academic integrity.
It is important to acknowledge that this review has certain limitations. Firstly, the limited inclusion of reviewed studies can be attributed to several reasons, including the novelty of the technology, as new technologies often face initial skepticism and cautious adoption; the lack of clear guidelines or best practices for leveraging this technology for educational purposes; and institutional or governmental policies affecting the utilization of this technology in educational contexts. These factors, in turn, have affected the number of studies available for review. Secondly, the utilization of the original version of ChatGPT, based on GPT-3 or GPT-3.5, implies that new studies utilizing the updated version, GPT-4 may lead to different findings. Therefore, conducting follow-up systematic reviews is essential once more empirical studies on ChatGPT are published. Additionally, long-term studies are necessary to thoroughly examine and assess the impact of ChatGPT on various educational practices.
Despite these limitations, this systematic review has highlighted the transformative potential of ChatGPT in education, revealing its diverse utilization by learners and educators alike and summarized the benefits of incorporating it into education, as well as the forefront critical concerns and challenges that must be addressed to facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Data availability
The data supporting our findings are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- Artificial intelligence
AI in education
Large language model
Artificial neural networks
Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer
Recurrent neural networks
Long short-term memory
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
Natural language processing
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
AlAfnan MA, Dishari S, Jovic M, Lomidze K. ChatGPT as an educational tool: opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. J Artif Intell Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37965/jait.2023.0184 .
Article Google Scholar
Ali JKM, Shamsan MAA, Hezam TA, Mohammed AAQ. Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation. J Engl Stud Arabia Felix. 2023;2(1):41–9. https://doi.org/10.56540/jesaf.v2i1.51 .
Alkaissi H, McFarlane SI. Artificial hallucinations in ChatGPT: implications in scientific writing. Cureus. 2023. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35179 .
Anderson N, Belavý DL, Perle SM, Hendricks S, Hespanhol L, Verhagen E, Memon AR. AI did not write this manuscript, or did it? Can we trick the AI text detector into generated texts? The potential future of ChatGPT and AI in sports & exercise medicine manuscript generation. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2023;9(1): e001568. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001568 .
Ausat AMA, Massang B, Efendi M, Nofirman N, Riady Y. Can chat GPT replace the role of the teacher in the classroom: a fundamental analysis. J Educ. 2023;5(4):16100–6.
Google Scholar
Baidoo-Anu D, Ansah L. Education in the Era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4337484 .
Basic Z, Banovac A, Kruzic I, Jerkovic I. Better by you, better than me, chatgpt3 as writing assistance in students essays. 2023. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04536 .
Baskara FR. The promises and pitfalls of using chat GPT for self-determined learning in higher education: an argumentative review. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan IAIM Sinjai. 2023;2:95–101. https://doi.org/10.47435/sentikjar.v2i0.1825 .
Behera RK, Bala PK, Dhir A. The emerging role of cognitive computing in healthcare: a systematic literature review. Int J Med Inform. 2019;129:154–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.04.024 .
Chaka C. Detecting AI content in responses generated by ChatGPT, YouChat, and Chatsonic: the case of five AI content detection tools. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.2.12 .
Chiu TKF, Xia Q, Zhou X, Chai CS, Cheng M. Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Comput Educ Artif Intell. 2023;4:100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Choi EPH, Lee JJ, Ho M, Kwok JYY, Lok KYW. Chatting or cheating? The impacts of ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence language models on nurse education. Nurse Educ Today. 2023;125:105796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105796 .
Cotton D, Cotton PA, Shipway JR. Chatting and cheating: ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148 .
Crawford J, Cowling M, Allen K. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.3.02 .
Creswell JW. Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook]. 4th ed. London: Pearson Education; 2015.
Curry D. ChatGPT Revenue and Usage Statistics (2023)—Business of Apps. 2023. https://www.businessofapps.com/data/chatgpt-statistics/
Day T. A preliminary investigation of fake peer-reviewed citations and references generated by ChatGPT. Prof Geogr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2023.2190373 .
De Castro CA. A Discussion about the Impact of ChatGPT in education: benefits and concerns. J Bus Theor Pract. 2023;11(2):p28. https://doi.org/10.22158/jbtp.v11n2p28 .
Deng X, Yu Z. A meta-analysis and systematic review of the effect of Chatbot technology use in sustainable education. Sustainability. 2023;15(4):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042940 .
Eke DO. ChatGPT and the rise of generative AI: threat to academic integrity? J Responsib Technol. 2023;13:100060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrt.2023.100060 .
Elmoazen R, Saqr M, Tedre M, Hirsto L. A systematic literature review of empirical research on epistemic network analysis in education. IEEE Access. 2022;10:17330–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3149812 .
Farrokhnia M, Banihashem SK, Noroozi O, Wals AEJ. A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: implications for educational practice and research. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Fergus S, Botha M, Ostovar M. Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. J Chem Educ. 2023;100(4):1672–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087 .
Fink A. Conducting research literature reviews: from the Internet to Paper. Incorporated: SAGE Publications; 2010.
Firaina R, Sulisworo D. Exploring the usage of ChatGPT in higher education: frequency and impact on productivity. Buletin Edukasi Indonesia (BEI). 2023;2(01):39–46. https://doi.org/10.56741/bei.v2i01.310 .
Firat, M. (2023). How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty, Anadolu Unive . https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8707-5918
Firat M. What ChatGPT means for universities: perceptions of scholars and students. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.22 .
Fuchs K. Exploring the opportunities and challenges of NLP models in higher education: is Chat GPT a blessing or a curse? Front Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1166682 .
García-Peñalvo FJ. La percepción de la inteligencia artificial en contextos educativos tras el lanzamiento de ChatGPT: disrupción o pánico. Educ Knowl Soc. 2023;24: e31279. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks.31279 .
Gilson A, Safranek CW, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor A, Chartash D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical Licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e45312. https://doi.org/10.2196/45312 .
Hashana AJ, Brundha P, Ayoobkhan MUA, Fazila S. Deep Learning in ChatGPT—A Survey. In 2023 7th international conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICOEI) . 2023. (pp. 1001–1005). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icoei56765.2023.10125852
Hirsto L, Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Valtonen T. (2022). A systematic narrative review of learning analytics research in K-12 and schools. Proceedings . https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3383/FLAIEC22_paper_9536.pdf
Hisan UK, Amri MM. ChatGPT and medical education: a double-edged sword. J Pedag Educ Sci. 2023;2(01):71–89. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.31280.23043/1 .
Hopkins AM, Logan JM, Kichenadasse G, Sorich MJ. Artificial intelligence chatbots will revolutionize how cancer patients access information: ChatGPT represents a paradigm-shift. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncics/pkad010 .
Househ M, AlSaad R, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Healy MG, Latifi S, Sheikh J. Large Language models in medical education: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e48291. https://doi.org/10.2196/48291 .
Ilkka T. The impact of artificial intelligence on learning, teaching, and education. Minist de Educ. 2018. https://doi.org/10.2760/12297 .
Iqbal N, Ahmed H, Azhar KA. Exploring teachers’ attitudes towards using CHATGPT. Globa J Manag Adm Sci. 2022;3(4):97–111. https://doi.org/10.46568/gjmas.v3i4.163 .
Irfan M, Murray L, Ali S. Integration of Artificial intelligence in academia: a case study of critical teaching and learning in Higher education. Globa Soc Sci Rev. 2023;8(1):352–64. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(viii-i).32 .
Jeon JH, Lee S. Large language models in education: a focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11834-1 .
Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT—Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.39.2.7653 .
King MR. A conversation on artificial intelligence, Chatbots, and plagiarism in higher education. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2023;16(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-022-00754-8 .
Kooli C. Chatbots in education and research: a critical examination of ethical implications and solutions. Sustainability. 2023;15(7):5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075614 .
Kuhail MA, Alturki N, Alramlawi S, Alhejori K. Interacting with educational chatbots: a systematic review. Educ Inf Technol. 2022;28(1):973–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11177-3 .
Lee H. The rise of ChatGPT: exploring its potential in medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2270 .
Li L, Subbareddy R, Raghavendra CG. AI intelligence Chatbot to improve students learning in the higher education platform. J Interconnect Netw. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219265921430325 .
Limna P. A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education during the Digital Era. 2022. https://ssrn.com/abstract=4160798
Lo CK. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ Sci. 2023;13(4):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040410 .
Luo W, He H, Liu J, Berson IR, Berson MJ, Zhou Y, Li H. Aladdin’s genie or pandora’s box For early childhood education? Experts chat on the roles, challenges, and developments of ChatGPT. Early Educ Dev. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2023.2214181 .
Meyer JG, Urbanowicz RJ, Martin P, O’Connor K, Li R, Peng P, Moore JH. ChatGPT and large language models in academia: opportunities and challenges. Biodata Min. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13040-023-00339-9 .
Mhlanga D. Open AI in education, the responsible and ethical use of ChatGPT towards lifelong learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4354422 .
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schön, E. M. (2023). “We Need To Talk About ChatGPT”: The Future of AI and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1109/seeng59157.2023.00010
Nolan B. Here are the schools and colleges that have banned the use of ChatGPT over plagiarism and misinformation fears. Business Insider . 2023. https://www.businessinsider.com
O’Leary DE. An analysis of three chatbots: BlenderBot, ChatGPT and LaMDA. Int J Intell Syst Account, Financ Manag. 2023;30(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/isaf.1531 .
Okoli C. A guide to conducting a standalone systematic literature review. Commun Assoc Inf Syst. 2015. https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.03743 .
OpenAI. (2023). https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
Perkins M. Academic integrity considerations of AI large language models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.07 .
Plevris V, Papazafeiropoulos G, Rios AJ. Chatbots put to the test in math and logic problems: A preliminary comparison and assessment of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4, and Google Bard. arXiv (Cornell University) . 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2305.18618
Rahman MM, Watanobe Y (2023) ChatGPT for education and research: opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl Sci 13(9):5783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095783
Ram B, Verma P. Artificial intelligence AI-based Chatbot study of ChatGPT, google AI bard and baidu AI. World J Adv Eng Technol Sci. 2023;8(1):258–61. https://doi.org/10.30574/wjaets.2023.8.1.0045 .
Rasul T, Nair S, Kalendra D, Robin M, de Oliveira Santini F, Ladeira WJ, Heathcote L. The role of ChatGPT in higher education: benefits, challenges, and future research directions. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.29 .
Ratnam M, Sharm B, Tomer A. ChatGPT: educational artificial intelligence. Int J Adv Trends Comput Sci Eng. 2023;12(2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2023/091222023 .
Ray PP. ChatGPT: a comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys Syst. 2023;3:121–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Roumeliotis KI, Tselikas ND. ChatGPT and Open-AI models: a preliminary review. Future Internet. 2023;15(6):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15060192 .
Rudolph J, Tan S, Tan S. War of the chatbots: Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Ernie and beyond. The new AI gold rush and its impact on higher education. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.23 .
Ruiz LMS, Moll-López S, Nuñez-Pérez A, Moraño J, Vega-Fleitas E. ChatGPT challenges blended learning methodologies in engineering education: a case study in mathematics. Appl Sci. 2023;13(10):6039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106039 .
Sallam M, Salim NA, Barakat M, Al-Tammemi AB. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: a descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023;3(1): e103. https://doi.org/10.52225/narra.v3i1.103 .
Salvagno M, Taccone FS, Gerli AG. Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing? Crit Care. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-023-04380-2 .
Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Helske S, Hrastinski S. The longitudinal association between engagement and achievement varies by time, students’ profiles, and achievement state: a full program study. Comput Educ. 2023;199:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104787 .
Saqr M, Matcha W, Uzir N, Jovanović J, Gašević D, López-Pernas S. Transferring effective learning strategies across learning contexts matters: a study in problem-based learning. Australas J Educ Technol. 2023;39(3):9.
Schöbel S, Schmitt A, Benner D, Saqr M, Janson A, Leimeister JM. Charting the evolution and future of conversational agents: a research agenda along five waves and new frontiers. Inf Syst Front. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-023-10375-9 .
Shoufan A. Exploring students’ perceptions of CHATGPT: thematic analysis and follow-up survey. IEEE Access. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3268224 .
Sonderegger S, Seufert S. Chatbot-mediated learning: conceptual framework for the design of Chatbot use cases in education. Gallen: Institute for Educational Management and Technologies, University of St; 2022. https://doi.org/10.5220/0010999200003182 .
Book Google Scholar
Strzelecki A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interact Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2209881 .
Su J, Yang W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: a framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423 .
Sullivan M, Kelly A, McLaughlan P. ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. J ApplLearn Teach. 2023;6(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.17 .
Szabo A. ChatGPT is a breakthrough in science and education but fails a test in sports and exercise psychology. Balt J Sport Health Sci. 2023;1(128):25–40. https://doi.org/10.33607/bjshs.v127i4.1233 .
Taecharungroj V. “What can ChatGPT do?” analyzing early reactions to the innovative AI chatbot on Twitter. Big Data Cognit Comput. 2023;7(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010035 .
Tam S, Said RB. User preferences for ChatGPT-powered conversational interfaces versus traditional methods. Biomed Eng Soc. 2023. https://doi.org/10.58496/mjcsc/2023/004 .
Tedre M, Kahila J, Vartiainen H. (2023). Exploration on how co-designing with AI facilitates critical evaluation of ethics of AI in craft education. In: Langran E, Christensen P, Sanson J (Eds). Proceedings of Society for Information Technology and Teacher Education International Conference . 2023. pp. 2289–2296.
Tlili A, Shehata B, Adarkwah MA, Bozkurt A, Hickey DT, Huang R, Agyemang B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-023-00237-x .
Uddin SMJ, Albert A, Ovid A, Alsharef A. Leveraging CHATGPT to aid construction hazard recognition and support safety education and training. Sustainability. 2023;15(9):7121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097121 .
Valtonen T, López-Pernas S, Saqr M, Vartiainen H, Sointu E, Tedre M. The nature and building blocks of educational technology research. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;128:107123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2021.107123 .
Vartiainen H, Tedre M. Using artificial intelligence in craft education: crafting with text-to-image generative models. Digit Creat. 2023;34(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14626268.2023.2174557 .
Ventayen RJM. OpenAI ChatGPT generated results: similarity index of artificial intelligence-based contents. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4332664 .
Wagner MW, Ertl-Wagner BB. Accuracy of information and references using ChatGPT-3 for retrieval of clinical radiological information. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/08465371231171125 .
Wardat Y, Tashtoush MA, AlAli R, Jarrah AM. ChatGPT: a revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. Eurasia J Math, Sci Technol Educ. 2023;19(7):em2286. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13272 .
Webster J, Watson RT. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. Manag Inf Syst Quart. 2002;26(2):3.
Xiao Y, Watson ME. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res. 2017;39(1):93–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456x17723971 .
Yan D. Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: an exploratory investigation. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11742-4 .
Yu H. Reflection on whether Chat GPT should be banned by academia from the perspective of education and teaching. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1181712. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1181712 .
Zhu C, Sun M, Luo J, Li T, Wang M. How to harness the potential of ChatGPT in education? Knowl Manag ELearn. 2023;15(2):133–52. https://doi.org/10.34105/j.kmel.2023.15.008 .
Download references
The paper is co-funded by the Academy of Finland (Suomen Akatemia) Research Council for Natural Sciences and Engineering for the project Towards precision education: Idiographic learning analytics (TOPEILA), Decision Number 350560.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computing, University of Eastern Finland, 80100, Joensuu, Finland
Yazid Albadarin, Mohammed Saqr, Nicolas Pope & Markku Tukiainen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
YA contributed to the literature search, data analysis, discussion, and conclusion. Additionally, YA contributed to the manuscript’s writing, editing, and finalization. MS contributed to the study’s design, conceptualization, acquisition of funding, project administration, allocation of resources, supervision, validation, literature search, and analysis of results. Furthermore, MS contributed to the manuscript's writing, revising, and approving it in its finalized state. NP contributed to the results, and discussions, and provided supervision. NP also contributed to the writing process, revisions, and the final approval of the manuscript in its finalized state. MT contributed to the study's conceptualization, resource management, supervision, writing, revising the manuscript, and approving it.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yazid Albadarin .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Table 4
The process of synthesizing the data presented in Table 4 involved identifying the relevant studies through a search process of databases (ERIC, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, Dimensions.ai, and lens.org) using specific keywords "ChatGPT" and "education". Following this, inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied, and data extraction was performed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques to capture key information and identify common themes across the included studies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Albadarin, Y., Saqr, M., Pope, N. et al. A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education. Discov Educ 3 , 60 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Download citation
Received : 22 October 2023
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 26 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Large language models
- Educational technology
- Systematic review
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
College of Science
- UTA Planetarium
- Degree Programs
- Departments
- Financial Aid
- College Info
- Be A Maverick
COS pre-med students get hands-on clinical medicine training
Thursday, May 30, 2024 • Greg Pederson :

A group of College of Science pre-medical students recently received valuable hands-on clinical training during a workshop in the new Smart Hospital at The University of Texas at Arlington.
The Clinical Experience Workshop, held May 13-23 in the Social Work and CONHI Smart Hospital Building, allowed 10 pre-med students to participate in experiential activities as well as to interact one-on-one with “patients” who were portrayed by students from the UTA Department of Theatre Arts.
Students were able to learn skills including checking vital signs, starting an IV line, and delivering a baby, all by utilizing the lifelike manikins in the state-of-the-art Smart Hospital. They also learned various medical procedures and participated in virtual reality exercises in the Smart Hospital’s simulation lab.
“This was a clinical experiential opportunity for pre-med students with no clinical background to be immersed in clinical medicine, learn basic skills, and experience actual patient encounters with simulated patients who were actually trained UTA theater students,” said Dr. Steve Gellman, College of Science pre-med consultant and co-director of the minor in medical humanities and bioethics program.
During the live patient portion of the workshop, each theater student portrayed a patient with specific symptoms which the pre-med students attempted to diagnose.
Assisting in the workshop were Dr. Jocelyn Zee, DO, a COS alumna and 2016 recipient of the UTA Distinguished Alumni Award; Allante Milsap, a medical student from UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas; Paul Koester, a medical student from Texas College of Osteopathic Medicine in Fort Worth; Jennifer Roye, UTA assistant dean for simulation and technology; and Erica Hinojosa, UTA simulation technology manager.

“The workshop was so much fun — for the students and staff. There was universal agreement that this was a valuable and memorable experience that will have a lasting impact on the participants,” Gellman said. “Experiential learning is an excellent path toward meaningful and lasting education, especially for teaching the important humanities aspect of patient care.”
The workshop, which was made possible by funds from the UTA Libraries Department of Experiential Learning and the College of Science, is just one of the many ways the College of Science helps to prepare students for medical and other health professions schools.
The Office of Health Professions has two advisors (Sandy Hobart and Haylei Dishinger) and offers test prep classes, a pre-med preceptorship program, career information events featuring health professionals from various fields, an annual Health Professions Fair, and more. The office also oversees the Joint Admission Medical Program (JAMP), which is led by Greg Hale, COS assistant dean. JAMP supports and encourages highly qualified, economically disadvantaged Texas resident students pursuing a medical education. A variety of health profession student organizations offer clinics and workshops as well as networking and volunteer opportunities.
Another popular program the office offers is an EMT class, which has been held at UTA for the past two years and will again be open to students in Fall 2024, from August 25 to December 2. The class allows students to earn an EMT certification via a hybrid online and in-person class, with in-person sessions once a week on the UTA campus. The class is offered in partnership with UT Dallas and University Emergency Medical Response and is not a UTA course. For more information about the course, please email Sheila Elliott, program director, at [email protected] .
The UTA College of Science, a Carnegie R1 research institution, is preparing the next generation of leaders in science through innovative education and hands-on research and offers programs in Biology, Chemistry & Biochemistry, Data Science, Earth & Environmental Sciences, Health Professions, Mathematics, Physics and Psychology. To support educational and research efforts visit the giving page , or if you're a prospective student interested in beginning your #MaverickScience journey visit our future students page .
News & Events
- Events Calendar
- Be a Maverick
- Give to the College
COLLEGE OF SCIENCE
Life Sciences Building, Room 206 501 S. Nedderman Drive Box 19047 Arlington, TX 76019
Social Media
Phone: 817-272-3491 Fax: 817-272-3511 Email: [email protected]
News Center
First-year student awarded for human brain-computer interface research.

Dillan Prasad, a first-year medical student at Feinberg, was recently recognized for outstanding research by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
The Philip L. Gildenberg, MD, Resident Award is given annually to the best abstract submitted on the topic of stereotactic and functional neurosurgery. Prasad was presented with the award at the association’s annual meeting in Chicago in May.
Read a Q&A with Prasad below.
Tell us about your research interests.
Our research aims to build bionic arms to restore motor and sensory function for patients with limb loss and spinal cord injury. The field is called brain-computer interfaces; it’s straight out of science fiction, as we’re trying to build human cyborgs to bypass pathologies of the nervous system.
Simply put, we are developing robotic arms which can be installed into a patient’s residual limb and are fully under neurological control. The robotic arms are attached to chips that surgeons implant in the human brain, which are placed in different areas. Two chips are placed in the motor cortex and two in the sensory cortex. We have the chips communicate wirelessly with the arm. By “decoding” recorded motor signals, one set of chips controls the arm by translating neural signals into instructions that the arm’s motors can follow.
On the sensory side, the other set of chips allows users to once again feel sensation through intracortical microstimulation; we stimulate the brain in somatotopically-matched locations when the robotic arm contacts objects. We’re essentially restoring the whole experience of touch, motor control and somatosensation for people who have lost an arm.
You recently won an award for your research. How did that come about?

I was super humbled and surprised to have been given this kind of award as I’m just a first-year medical student, and this was my first scientific conference.
This award is entirely thanks to the amazing work done by the scientists and surgeons in the Cortical Bionics research group. It was a collaborative win, as it was in recognition of the efforts of numerous contributors from Northwestern, UChicago, and Pitt, as well as our amazing human brain-computer interface (BCI) subjects who have undergone implantation in order to advance science forever. Science is a team sport, and I’m deeply humbled to have the opportunity to work on such an exciting and cutting-edge challenge.
The talk itself was a bit nerve-wracking because I had to give a scientific presentation in front of a room of over a hundred neurosurgeons who were all subject matter experts. I put in a lot of time preparing for the talk, and thanks to the valuable guidance of my Feinberg and UChicago mentors, it was ultimately a great experience.
How did you get started in this research area?
I did my undergrad at the University of Chicago, where I studied neuroscience, astrophysics and chemistry. I came across BCI when I took a neuroscience elective on neuroprosthetics, and I immediately loved it: cortical bionics felt like WestWorld meets Black Mirror, but in a beautiful way which will one day help patients everywhere. Over time, my interests grew more developed, and now I’m planning on dedicating my academic career to the exploration and treatment of the brain and nervous system.
This project has been unique because it integrates a whole bunch of different types of science in an exciting way. It’s computer science: machine learning decoders translate information from the brain into action that the motors in the arm can follow. It’s physics because it’s robotics. It’s neuroscience, more than anything else: every day, we learn more about how touch is encoded in the implanted microchips. It’s biology, it’s neurosurgery, it’s just about everything all brought into one.
The scientific paper, which is currently in pre-print, is officially under Charles Greenspon at the University of Chicago, but it’s collaborative with Pitt and Northwestern under Dr. Lee Miller.
The PI for the work was Sliman Bensmaia, who sadly passed away last summer at the age of 49. I dedicated the award and speech to him. I’m really thankful for the chance to have known him. He was a great mentor, but also he was my friend, and he introduced me to a field which is quickly evolving into one of my greatest passions.
Do you plan to continue in this area of research?
Yeah, absolutely. I’m excited about this area: specifically, brain-computer interfaces.
My interests have evolved more towards the implantation of novel brain-computer interfaces, and all the minimally invasive and automated surgical techniques which I believe will eventually come to market. In my future practice, I’m excited about finding new ways to integrate technology with the brain and peripheral nerves to drive meaningful change for diverse patient populations everywhere.
I’ve found some success doing that so far with wonderful mentors at Northwestern; specifically Dr. El Tecle , Dr. Kimchi and Dr. Sonabend , among others. These neurologists and neurosurgeons are really at the top of their game and they’re at the cutting edge of their fields. They’re developing autonomous surgical platforms, using algorithms to detect delirium from EEG, and using ultrasound for neuromodulation, among much more. It’s these super exciting technological innovations which gives me confidence that the future is bright. I’m super thankful that these incredible mentors have included me in their work.
I hope to start working with the many companies who are driving meaningful change in this space as well, such as Neuralink, Precision, Synchron, etc.
You mentioned that Chicago is in your blood. Is that why you chose Feinberg?
I really couldn’t imagine going anywhere other than Feinberg. Chicago is the best city in the world, and anyone who knows me knows that it’s impossible to convince me otherwise.
I’m a Feinberg ambassador and I speak to a lot of young people. Every single applicant I talk to, I sing the praises and virtues of Feinberg, because I really deeply believe it. Obviously, our pre-clinical and clinical education is fantastic, thanks to the physicians who tirelessly work with us every week.
But Feinberg is one of the only places in the world which is truly interdisciplinary and integrative. If you have any interest of any kind, you can flesh it out with someone here through just a cold email. Honestly, there’s a high chance that person is a world expert in that topic, too. But thanks to the unbelievable breadth of work going on within the Northwestern system — from Feinberg, to ShirleyRyan, to the McCormick engineering school up in Evanston — the spirit is super educational and collaborative. People love to mentor, and love to help younger folks explore their interests.
I can’t imagine a better environment in which to train.
Related Posts
Regenerating damaged heart cells, study examines surge in rsv cases after the covid-19 pandemic, new genes implicated in multiple system atrophy.
Comments are closed.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids. Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support.
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Homework has long been a topic of social research, but rela-tively few studies have focused on the teacher's role in the homework process. Most research examines what students do, and whether and ...
The research. The most ... who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was ...
"No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play. Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with ...
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006).
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
HARRIS COOPER is a Professor of Psychology and Director of the Program in Education, Box 90739, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708-0739; e-mail [email protected] His research interests include how academic activities outside the school day (such as homework, after school programs, and summer school) affect the achievement of children and adolescents; he also studies techniques for improving ...
Cooper conducted a review of the existing research on homework in the mid-2000s, and found that, up to a point, the amount of homework students reported doing correlates with their performance on ...
America's K-12 students are returning to classrooms this fall after 18 months of virtual learning at home during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some students who lacked the home internet connectivity needed to finish schoolwork during this time - an experience often called the "homework gap" - may continue to feel the effects this school year. Here is what Pew Research Center surveys found ...
Here's what the research says: In general, homework has substantial benefits at the high school level, with decreased benefits for middle school students and few benefits for elementary students (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006). While assigning homework may have academic benefits, it can also cut into important personal and family time ...
Cognitive Homework Engagement. In the past few decades, a robust body of research has been addressing the relationship between the way students deal with their learning process and academic outcomes (Marton and Säljö, 1976a,b; Struyven et al., 2006; Rosário et al., 2010a, 2013a).Marton and Säljö (1976a,b) examined how students studied an academic text and found two ways of approaching the ...
A schoolwide effort to reduce homework has led to a renewed focus on ensuring that all work assigned really aids students' learning. I used to pride myself on my high expectations, including my firm commitment to accountability for regular homework completion among my students. But the trauma of Covid-19 has prompted me to both reflect and adapt.
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper ...
Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, Xitao Fan Homework and students' achievement in math and science: A 30-year meta-analysis, 1986-2015, Educational Research Review 20 (Feb 2017): 35-54.
It was 6% in 1984. The amount of homework for 13-year-olds appears to have lightened slightly. Students with one to two hours of homework declined from 29% to 23%. The next category down (in terms ...
The main objective of this research is to analyze how homework assignment strategies in schools affect students' academic performance and the differences in students' time spent on homework. Participants were a representative sample of Spanish adolescents ( N = 26,543) with a mean age of 14.4 (±0.75), 49.7% girls.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.)
In 2016, a second-grade teacher in Texas delighted her students—and at least some of their parents—by announcing she would no longer assign homework. "Research has been unable to prove that ...
Effective Practices for Homework. By: Kathy Ruhl, Charles Hughes. A review of the research on the effective use of homework for students with learning disabilities suggests that there are three big ideas for teachers to remember: (1) the best use of homework is to build proficiency in recently acquired skills or to maintain skills previously ...
The Overall Importance of Homework. Homework encourages self-development and self-discipline. Students who complete regular homework don't just perform better at school and during exams, they learn broader life skills and associate hard work with long term rewards. Homework has also been found to improve parental relationships.
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
What Research Says about Homework. According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule": students should receive 10 minutes of ...
ABSTRACT. This study investigated cross-cultural differences in the relationships between science intrinsic motivation, teacher-perceived and student-perceived homework practices, and science achievement in Asian (Chinese Taipei, Japan, South Korean, and Singapore) and Western (Australia, US, England, and Ireland) top-performing regions according to ranking of science achievement in TIMSS.
Effective study techniques can significantly enhance student learning and academic performance. In today's fast-paced educational environment, students face numerous challenges, from managing multiple assignments and homework to balancing extracurricular activities. Developing strong study habits is essential for success in both school and ...
Of the 2,196 students in the sample, 42 percent were female, 23 percent were immigrants, and 29 percent had learning disorders. The researchers looked at administrative data from the Italian Ministry of Education, long-term standardized test scores, the results of a standardized test administered by the research team, and surveys of parents ...
Furthermore, students have turned to ChatGPT for assistance in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks, which fosters a supportive home learning environment, allowing them to take responsibility for their own learning and cultivate the skills and approaches essential for ...
Students learned basic clinical skills including checking patient vital signs. Photo courtesy of Steve Gellman. ... a Carnegie R1 research institution, is preparing the next generation of leaders in science through innovative education and hands-on research and offers programs in Biology, Chemistry & Biochemistry, Data Science, Earth ...
The Louisiana Tech University Foundation chose Dr. Jamie Newman for its annual Professorship Award. Newman earned the recognition for her dedication to research, teaching, and student mentorship. "The singular mission of the Louisiana Tech University Foundation is to support our University. The Foundation Professorship Award is one way that ...
First-Year Student Awarded for Human Brain-Computer Interface Research. By Olivia Dimmer May 31, 2024. Dillan Prasad, a first-year medical student at Feinberg, was recently recognized by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons for his research. Dillan Prasad, a first-year medical student at Feinberg, was recently recognized for ...