

Case Study Of Starbucks: How Starbucks Became The Coffee King?
Supti Nandi
Updated on: April 25, 2024

Starbucks, a brand that became synonymous with coffee has created a sensation in the world with its coffeehouse culture. Have you wondered how? Well, to answer this question we will delve into the case study of Starbucks.

Stay tuned!
(A) Starbucks: A Brief Overview
Let’s buckle up for a Starbucks journey! Founded back in 1971, this coffee giant now reigns supreme as the world’s largest coffeehouse chain, with its home base in the city of Seattle, Washington.
Before diving deeper into the Starbucks case study, let’s have a look at the company’s profile-
| Coffee Shop | |
| March 30, 1971 | |
| Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, Gordon Bowker | |
| Starbucks Center, Seattle, Washington, U.S | |
| 38,038 | |
| 84 Countries | |
| Mellody Hobson (Chairwoman), Laxman Narasimhan (CEO) | |
| Coffee Beverages, Smoothies, Tea, Baked Goods, Sandwiches |
Fast forward to November 2022, and you’ve got Starbucks waving its coffee wand in a staggering 35,711 stores across 80 countries. And when you zoom in on the U.S., you’re looking at a whopping 15,873 Starbucks hotspots.
Here’s the scoop – over 8,900 are Starbucks-run, and the rest are running under licensed partnerships.
Now, let’s talk coffee vibes. Starbucks is the unsung hero of the second wave of coffee culture, dishing out an array of coffee delights. Think hot espresso, chill Frappuccinos, and a lineup of pastries and snacks that’s strong enough to trigger your taste buds.
Oh, and did you know some Starbucks treats are exclusive to certain locations? How? You may wonder. Well, here’s a bonus – most Starbucks joints worldwide offer free Wi-Fi. Coffee and connectivity – a match made in heaven.
So there you have it – the Starbucks saga!
(B) Business Overview of Starbucks Case Study
Understanding the business perspective is one of the essential parts of the Starbucks case study. Reason? You will get to know how Starbucks is performing in the market in terms of financials and business.
Go through the table given below-
| $105.82 billion | |
| $35.976 billion | |
| $4.62 billion | |
| $3.28 billion | |
| $27.98 billion | |
| -$8.70 billion | |
| $30.584 billion | |
| $25.108 billion |
In today’s date, the coffee giant is flexing a market capitalization of a whopping $105.82 billion – that’s some serious coffee beans.
Now, rewind to 2023, and Starbucks made it rain with a revenue of $35.976 billion. But what about the nitty-gritty? Operating income in 2022 hit $4.62 billion, while net income settled at $3.28 billion. These aren’t just numbers; they’re the financial pillars of Starbucks.
That’s not all!
Hold onto your coffee cups; we’re diving into assets and equity. Total assets in 2022 clocked in at $27.98 billion – that’s like a treasure chest of coffee goodness. But here’s a twist – total equity dipped to -$8.70 billion. It’s like a plot twist in a coffee-fueled drama.

Now, let’s talk about expenses and profits. In 2023, expenses tallied up to $30.584 billion, but here’s the kicker – profits soared to $25.108 billion.
That’s like balancing a delicate espresso shot with a mountain of whipped cream.
In a nutshell, Starbucks isn’t just brewing coffee; it’s a financial powerhouse, stirring up a caffeinated storm in the business world.
(C) History of Starbucks: Timeline & Key Events
Coming to the third part of the Starbucks case study, let’s delve into the history of Starbucks-
| Starbucks considers blockchain technology for bean-to-cup tracking. Two men were arrested in a Philadelphia store, leading to company-wide training. | ||
| Starbucks moves its store to 1912 Pike Place. During this time, only coffee beans are sold, not drinks. | ||
| Original owners purchase Peet’s Coffee. | ||
| Howard Schultz, former marketing director, buys Starbucks and begins rapid expansion. The first locations outside Seattle open in Vancouver and Chicago. | ||
| Starbucks has 46 stores across the Pacific Northwest and Midwest, roasting over 2 million pounds of coffee annually. | ||
| Starbucks goes public with 140 outlets and a market value of $271 million. | ||
| Starbucks acquires The Coffee Connection, gaining rights to the “Frappuccino” beverage. Introduced under the Starbucks name in 1995. | ||
| Starbucks experiments with eateries under the Circadia brand. Also acquires Pasqua Coffee. | ||
| Starbucks acquires Seattle’s Best Coffee and Torrefazione Italia. | ||
| Starbucks purchases most of Diedrich Coffee’s retail stores. | ||
| Starbucks starts the “My Starbucks Idea” website and acquires a Coffee Equipment Company, introducing the Clover Brewing System. | ||
| The operator of Starbucks locations in Brazil, SouthRock Capital, declares bankruptcy, restructuring through the procedure. | ||
| Starbucks closes newspaper sales, and kiosks, and opens its largest store on Michigan Avenue, Chicago. | ||
| Due to COVID-19, Starbucks temporarily closes café-only stores, facing sales decrease. | ||
| Starbucks explores selling its UK stores. | ||
| Starbucks sells all its stores in Russia to Timati after months of suspension due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. | ||
| Howard Schultz steps down as CEO; Laxman Narasimhan becomes the new CEO. | ||
| Narasimhan works as a barista to stay close to customers. Starbucks was ordered to pay damages in a discrimination case. | ||
| Operator of Starbucks locations in Brazil, SouthRock Capital, declares bankruptcy, restructuring through the procedure. |
Founded in 1971 by Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Bowker at Seattle’s Pike Place Market, Starbucks underwent pivotal changes in ownership and leadership. In the early 1980s, Howard Schultz acquired the company and transformed it into a coffee shop, introducing espresso-based drinks after being inspired during a business trip to Milan, Italy.
Schultz served as CEO from 1986 to 2000, orchestrating an expansive franchise expansion across the West Coast.
Orin Smith succeeded Schultz, focusing on fair trade coffee and boosting sales to US$5 billion. Jim Donald took the helm from 2005 to 2008, overseeing substantial earnings expansion. Schultz returned during the 2007–08 financial crisis, steering the company towards growth, expanded offerings, and a commitment to corporate social responsibility. Kevin Johnson assumed the CEO role in 2017.
In March 2022, Starbucks announced Schultz’s return as interim CEO in April 2022, with Laxman Narasimhan appointed to succeed him in April 2023. Narasimhan assumed the position earlier, in March 2023.
Beyond beverages and food, Starbucks stores offer official merchandise and select locations to provide “Starbucks Evenings” with beer, wine, and appetizers. The company’s products, including coffee, ice cream, and bottled drinks, are available in grocery stores globally. The Starbucks Reserve program, initiated in 2010 for single-origin coffees and high-end shops, has evolved. Starbucks operates six roasteries with tasting rooms and 43 coffee bars.
The company faced controversies but maintains substantial brand loyalty, market share, and value. As of 2022, Starbucks ranks 120th on the Fortune 500 and 303rd on the Forbes Global 2000.
(D) Significance of Logo in Starbucks Case Study

Let’s delve into the details of the Starbucks logo evolution. In its inception in 1971, the original Starbucks logo featured a complex design comprising a two-tailed mermaid or siren, encompassed by a wordmark. This design was a visual nod to the brand’s early identity and origins. The mermaid, with its twin tails, was a dual representation of the sea and Seattle, the birthplace of Starbucks.
As the brand progressed, the logo underwent a significant transformation. The evolution saw a shift towards simplicity, as the wordmark surrounding the mermaid was phased out. This marked the beginning of the modern Starbucks logo we recognize today.
The current emblem showcases a simplified and stylized green siren enclosed within a matching green ring, emphasizing a cleaner and more focused visual identity.
Beyond aesthetics, the modern logo carries symbolic weight. The green mermaid within the circle has become an iconic representation of Starbucks’ commitment to delivering high-quality coffee experiences.
Additionally, it reflects the brand’s emphasis on creating a sense of community that extends beyond geographical boundaries.
In essence, the evolution of the Starbucks logo is a journey from a detailed and intricate design to a streamlined and symbolic representation. It mirrors the brand’s growth, emphasizing its roots, dedication to quality, and the broader cultural impact it seeks to make through coffee and community.
(E) Market Penetration Strategy: How Starbucks became the coffee king?
In this section, we will look into the key plans and actions that helped Starbucks gain a strong foothold in the beverage and cafe industry.
| In 1984, Starbucks, led by Jerry Baldwin, made a strategic move by acquiring Peet’s, a significant step in their journey. | |
| During the 1980s, espresso sales in the U.S. were declining overall. However, a new trend emerged – the popularity of specialty espresso. By 1989, these specialty brews constituted 10% of the market, a notable increase from 3% in 1983. In 1986, Starbucks operated just six stores in Seattle and was only starting to sell coffee. | |
| In 1987, the original owners handed over Starbucks to Howard Schultz, its former manager. Schultz swiftly rebranded his II Giornale espresso outlets as Starbucks, marking the beginning of an extensive expansion. Starbucks ventured beyond Seattle, opening outlets in Vancouver, British Columbia, and Chicago, Illinois. By 1989, the company had 46 stores spanning the Northwest and Midwest, roasting over 2 million pounds of coffee annually. | |
| In June 1992, Starbucks made its debut on the stock market with an initial public offering (IPO). At this point, Starbucks boasted 140 outlets and generated $73.5 million in revenue, a significant surge from $1.3 million in 1987. The IPO raised about $25 million, fueling a doubling of store numbers over the next two years. | |
| By July 2013, Starbucks embraced mobile technology, with over 10% of in-store purchases made through the Starbucks app. The company leveraged social media with the “Tweet-a-Coffee” campaign in October 2013, allowing users to gift a $5 voucher via Twitter. | |
| As of 2018, Starbucks ranked 132nd on the Fortune 500 list. In July 2019, Starbucks reported a robust financial performance, with a third-quarter net income of $1.37 billion, representing a significant increase from the previous year. The company’s estimated value reached $110.2 billion, showing a remarkable 41% growth in 2019. |
Starbucks continues to blend innovation and growth, navigating the ever-changing landscape of the coffee industry.
(F) Starbucks Entry in India: Core of Starbucks Case Study
In 2012, Starbucks initiated its venture into India through a significant 50:50 joint venture with Tata Consumer Products Ltd. The inaugural flagship store, which opened its doors on October 19th, 2012, found its home in the historic Elphinstone Building in Mumbai.
The architectural design of this store ingeniously merged Starbucks’ global coffee legacy with the vibrant local culture, creating a welcoming space for community and connection. Over time, this Mumbai location evolved into India’s first Starbucks Reserve® Store, setting the stage for an elevated coffee experience.
(F.1) The Starbucks Reserve® Store Unveiled: A Coffee Lover’s Haven
The introduction of the Starbucks Reserve® Store marked a milestone in the coffee giant’s presence in India. Spanning an impressive 5,200 square feet, this store greeted customers with the intoxicating aroma of coffee.
The entrance featured a stunning monolithic terrazzo Reserve bar, a masterpiece crafted by local artisans. Trained black apron coffee masters curated an exceptional coffee experience, showcasing rare and exquisite brews through various brewing methods.
This Reserve Store was not just a coffee shop; it was a canvas for creating unique moments of connection through the artistry of coffee.
(F.2) Expanding Horizons: Tata Starbucks’ Nationwide Presence

Tata Starbucks established a substantial footprint, operating 350+ stores spread across 36 cities in India. In a significant achievement in 2022, Starbucks executed its largest single-year expansion in India, reaching 14 new cities. The brand’s influence spanned major cities such as Mumbai, Delhi NCR, Hyderabad, Chennai, Bengaluru, Pune, and more.
(F.3) Coffee Blends Celebrating Indian Flavors and Heritage
Starbucks paid homage to India’s rich coffee heritage by introducing special blends. The India Estates Blend, sourced from estates in Coorg and Chikmagalur, the birthplace of coffee in India, made its debut in 2013. Additionally, the Diwali Blend, introduced in 2020, served as a tribute to India’s vibrant culture and longstanding coffee traditions.
(F.4) The Tata Alliance: A Successful Partnership
Starbucks in India proudly bore the branding “Starbucks Coffee – A Tata Alliance,” underscoring the synergy between Starbucks and Tata Global Beverages.
Starbucks’ journey in India was not merely about coffee; it was about brewing connections, transcending cultural boundaries, and crafting unforgettable coffee experiences that resonated with the diverse tapestry of India.
(G) Business and Marketing Strategies of Starbucks in India
Starbucks, despite entering India’s coffee scene with strong strategies, faced challenges in a market dominated by competitors like Cafe Coffee Day and Barista Lavazza. Unlike the U.S., where coffee is a staple, India is traditionally a tea-drinking country.
Starbucks aimed to create a space for relaxation, blending its global coffee legacy with local culture.
Let’s look at the business and marketing strategies of Starbucks in India-
| Choosing TATA Global Beverages as a local partner showcased Starbucks’ understanding of leveraging indigenous advantages. This partnership allowed Starbucks to source beans from Tata’s Karnataka plant, ensuring cost-effectiveness and synergy. The TATA group’s ethical brand image aligned well with Starbucks’ values. | |
| Starbucks maintained a consistent store layout across India, focusing on customer experience and benefiting from economies of scale on capital expenses. This approach differentiated Starbucks from competitors like Cafe Coffee Day, which experimented with various formats. | |
| Starbucks adopted a measured pace of expansion, focusing on the financial viability of each outlet. This approach contrasted with its aggressive expansion strategy in the U.S. and China. Starbucks prioritized the long-term sustainability of each location in the Indian market. | |
| The commitment from top leadership, both from Tata and Starbucks, played a crucial role in Starbucks’ cautious entry into the Indian market. The six-year planning period showcased a thorough understanding of the complex Indian market. | |
| Adapting to Indian culture, Starbucks offered a mix of Western staples and unique Indian snacks, ensuring relevance and sustained consumption. The “third place” concept was tailored with local touches, such as henna designs in New Delhi’s store and collectibles in Pune’s store. | |
| Starbucks established a localized business model, emphasizing sustainability in coffee sourcing. The collaboration with Tata facilitated not only sourcing advantages but also an investment in sustainable farming practices. | |
| Starbucks introduced Indian-style products, including Tandoori Paneer Roll and Chocolate Rossomalai Mousse, catering to local tastes. Collaborating with Tata Global Beverages, Starbucks launched the “Teavana” tea brand, with offerings specifically crafted for the Indian market. | |
| Starbucks proactively managed perceptions and adhered to regulations by suspending the use of ingredients not approved by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI). This demonstrated a commitment to transparency and compliance. | |
| Starbucks embraced localization not only in in-store designs but also in hiring and training local staff. This approach enhanced community engagement and facilitated seamless integration into the Indian market. |
In short, Starbucks’ journey in India reflects a careful blend of global strategies and localized approaches, aiming to create a unique and sustainable presence in a market with diverse preferences and cultural nuances. The success indicators appear promising, showcasing Starbucks’ commitment to long-term growth and meaningful community integration.
Note: Do you know Starbucks collaborated with Apple during the horizontal marketing in the US? We have covered it thoroughly here- Horizontal Marketing System . You can check it out for detailed information.
(H) Wrapping Up the Case Study of Starbucks

The Case Study of Starbucks unveils a fascinating journey that transformed Starbucks into the reigning coffee king. What started as a local coffee bean store in Seattle’s Pike Place Market in 1971 boomed into a global coffee empire. The strategic moves, like Howard Schultz’s visionary shift to espresso-based drinks, had set the stage for Starbucks’ aggressive expansion.
Throughout its evolution, Starbucks faced challenges, leadership changes, and controversies, but resilience and strategic pivots marked its trajectory. The decision to focus on corporate social responsibility under Schultz’s leadership during the financial crisis showcased Starbucks’ adaptability.
The engagement with local cultures, from the iconic two-tailed mermaid symbol to store designs reflecting regional aesthetics, contributed to Starbucks’ success. Key partnerships, like the one with TATA in India, demonstrated a keen understanding of local markets.
Starbucks’ commitment to quality, community, and sustainability resonated with consumers globally. From unique store experiences to tailored product launches, Starbucks consistently adapted its offerings to cater to diverse tastes.
In essence, the Case Study of Starbucks illuminates a narrative of coffee, community, and corporate strategy, culminating in Starbucks’ reign as the coffee king.
The journey is a testament to the power of adaptability, brand loyalty, and a steaming cup of coffee that transcends borders, making Starbucks an integral part of daily rituals worldwide!
Related Posts:
Contact Info: Axponent Media Pvt Ltd, 706-707 , 7th Floor Tower A , Iris Tech Park, Sector 48, Sohna Road, Gurugram, India, Pin - 122018
© The Business Rule 2024

Starbucks Case Study - How Starbucks Conquered The Coffee Industry?

Devashish Shrivastava
Starbucks Corporation is an American coffee chain that was established in 1971 in Seattle, Washington. By mid-2019, the organization had a presence in over 30,000 areas around the world. Starbucks has been depicted as the fundamental delegate of "second wave espresso," a reflectively-named development that advanced high-quality espresso and specially simmered coffee. Starbucks now uses robotized coffee machines for proficiency and well-being.
Starbucks serves hot and cold beverages, entire bean espresso, micro-ground moment espresso known as VIA, coffee, caffe latte, full-and free leaf teas such as Teavana tea products, Evolution Fresh squeezes, Frappuccino refreshments, La Boulange baked goods, and bites (for example, chips and wafers); some offerings such as the Pumpkin Spice Latte are explicit to the territory of the store. Numerous Starbucks outlets sell pre-bundled nourishment items, sweltering and cold sandwiches, and drinkware such as cups and tumblers. Furthermore, there are Select "Starbucks Evenings" areas that offer brew, wine, and appetizers.
Starbucks first ended up productive in Seattle in the mid-1980s. Despite an underlying financial downturn with its venture into the Midwest and British Columbia in the late 1980s, the organization experienced rejuvenated success with its entrance into California in the mid-1990s. Starbucks opened an average of two new stores every day between 1987 and 2007. On December 1, 2016, Howard Schultz reported he would leave his position as the CEO and would be supplanted by Kevin Johnson. Johnson accepted the role of the CEO of Starbucks on April 3, 2017, and Howard Schultz resigned to end up as the 'Chairman Emeritus', effective from June 26, 2018. Kevin Johnson is currently serving as the CEO and President of Starbucks.
Starbucks - Company Highlights
| Startup Name | Starbucks |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Seattle, Washington, United States |
| Sector | Food and Beverage, Hospitality |
| Founders | Gordon Bowker, Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl |
| Founded | 1971 |
| Valuation | $148.83B (January 2022) |
| Revenue | $29.02B (FY21) |
| Total Funding | $900 million |
| Parent Organization | Joint Venture Company of Tata Consumer Products and Starbucks Corporation |
| Website | starbucks.com |
Startup Story Of Starbucks Corporation History Of Starbucks Corporation Starbucks - Name and Logo Starbucks Expansion Journey Starbucks Corporation in India Business Strategy Of Starbucks In India Products Of Starbucks Corporation Business Growth Of Starbucks Corporation Over The Years Future Plans Of Starbucks Corporation
Startup Story Of Starbucks Corporation

If you are wondering how did Starbucks start? Then, the story of Starbucks started back in 1971, when the company was a roaster and retailer of whole bean and ground coffee, tea and spices with a single store in Seattle’s Pike Place Market.
Zev Siegel stated that at that time he knew the coffee industry inside and out, he was well-versed, especially with the gourmet end of the industry. Besides, he was also known as the most educated coffee guy in the country at that time. So, the three college friends - Zev Siegel, Jerry Baldwin and Gordon, started out with their coffee bean shop and roastery at Seattle’s famous Pike Place Market in 1971. Eventually, they found a mentor in Alfred Peet, who was the founder of Peet’s Coffee and the man responsible for bringing custom coffee roasting to the U.S. and started with the coffee business in full swing. Starbucks initially began by selling coffee beans that were roasted by Peet's, a gourmet coffee company in Berkeley, California, and later on, started roasting on their own.
History Of Starbucks Corporation

The first Starbucks store was initiated in 1971 in Washington by 3 individuals who met while they were studying at the University of San Francisco: English educator Hun Baldwin, history educator Zev Siegl, and author Gordon Bowker. The trio was encouraged to sell top-notch espresso beans and hardware after businessman Alfred Peet showed them his style of simmering beans.
During this time, the organization sold simmered, entire espresso beans. During its first year of activity, Starbucks bought green espresso beans from Peet's, and then started purchasing legitimately from producers.
Starbucks - Name and Logo

Bowker reviews that Terry Heckler, with whom Bowker claimed a publicizing office, thought words starting with "st" were ground-breaking. The organizers conceptualized a rundown of words starting with "st" and in the long run arrived on "Strabo," a mining town in the Cascade Range. The team then finalized on "Starbuck," the name of the young chief mate in the book "Moby-Dick".
Starbucks has given too many slogans/taglines already among which the most popular one is - " Brewed for those who love coffee".
Starbucks Expansion Journey

In 1984, the first proprietors of Starbucks, driven by Jerry Baldwin, acquired Peet's. During the 1980s, all-out offers of espresso in the US were falling. However, offers of strength espresso expanded, shaping 10% of the market in 1989; it stood at just 3% in terms of market share in 1983. By 1986, the organization worked six stores in Seattle and had just barely started to sell coffee.
In 1987, the first proprietors sold the Starbucks chain to the previous manager Howard Schultz, who rebranded his II Giornale espresso outlets as Starbucks and immediately extended. Starbucks then launched its outlets outside Seattle at Waterfront Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, and Chicago, Illinois. By 1989, 46 stores existed over the Northwest and Midwest, and every year Starbucks was simmering more than 2,000,000 pounds (907,185 kg) of coffee. At the hour of its first sale of stock (IPO) on the financial exchange in June 1992, Starbucks had 140 outlets with an income of $73.5 million, up from $1.3 million in 1987.
The organization's fairly estimated worth was $271 million at this point. The 12% segment of the organization that was sold raised around $25 million for the organization, which encouraged a multiplying of the number of stores throughout the following two years. By September 1992, Starbucks' offer cost had ascended by 70% to more than multiple times the income per portion of the past year. In July 2013, over 10% of in-store buys were made on the client's cell phones utilizing the Starbucks app.
The organization used the versatile social media stage when it propelled the "Tweet-a-Coffee" campaign in October 2013. People had the option to buy a $5 gift voucher for a companion by entering both "@tweetacoffee" and the companion's handle in a tweet. Research firm Keyhole observed the advancement of the event and a media article from December 2013 detailed that Starbucks had discovered that 27,000 individuals had taken an interest and $180,000 of buys were made to date.

As of 2018, Starbucks is positioned 132nd on the Fortune 500 rundown of the biggest United States organizations by revenue. In July 2019, Starbucks announced a "monetary second from last quarter total compensation of $1.37 billion, or $1.12 per share, up from $852.5 million, or 61 pennies for each offer, a year sooner." The organization's fairly estimated worth of $110.2 billion expanded by 41% in the middle of 2019. The income per share in quarter three was recorded at 78 pennies, considerably more than the estimate of 72 cents.
Starbucks Corporation in India

In January 2011, Starbucks Corporation and Tata Coffee reported designs to start opening Starbucks outlets in India. Despite a bogus beginning in 2007, in January 2012, Starbucks declared a 50:50 joint endeavour with Tata Global Beverages, called Tata Starbucks Ltd. , which would possess and work outlets marked "Starbucks, A Tata Alliance". Starbucks had endeavoured to enter the Indian market in 2007. However, it didn't provide any explanation behind its withdrawal of it.
It was on October 19, 2012 that Starbucks opened its first store, a 4,500 sq ft store in Elphinstone Building, Horniman Circle, Mumbai. Starbucks opened its first cooking and bundling plant in Coorg, Karnataka in 2013 to supply its Indian outlets. The company extended its reach to Delhi on 24 January 2013 by opening 2 outlets. Tata Global Beverages declared in 2013 that they would have 50 areas before the end of the year, with a venture of ₹4 billion ($58 million). The organization did open its 50th store in India on July 8, 2014.
The third city of India to get a Starbucks outlet was Pune, where the organization opened an outlet at Koregaon Park on 8 September 2013. Starbucks opened a 3,000-square-foot lead store at Koramangala, Bangalore on 22 November 2013, making it the fourth city to have an outlet. Starbucks opened the biggest espresso-forward store in the nation at Vittal Mallya Road, Bangalore on 18 March 2019. The store is estimated at 3,000 sq ft and is Starbucks' 140th outlet in India.
Tata Starbucks opened 25 stores between 2017 and 2018, which went up to 30 during 2018-19. On 21 February 2019, CEO Navin Gurnaney reported that Tata Starbucks would use only compostable and recyclable bundling materials over the entirety of its stores from June 2020.

Starbucks reported its entrance in Gujarat on 7 August 2019. The organization opened five stores in Surat and Ahmedabad the following day. Starbucks' leader store in the state is situated at Prahlad Nagar, Ahmedabad, and offers more vegan alternatives than other Indian outlets. CEO Navin Gurnaney expressed that the organization would open more than 30 stores in the 2019-20 financial year, of which 11 have already been opened.
Business Strategy Of Starbucks In India
Starbucks' strategies for business in India seemed rock-solid but the brand wasn't completely immune still. In any case, the world's biggest bistro chain is building its position cautiously via a progression of well-picked steps. Numerous worldwide brands have entered India since the 1990s, being pulled in by its developing and optimistic customer base. Yet, not all have succeeded.
Starbucks isn't the primary contestant in India's composed espresso showcase; so it doesn't have any first-participant advantage. Cafe Coffee Day (CCD) is the market head while Barista Lavazza was the main espresso chain to open for business. Both are valued by the white-collar class. Costa Coffee, Coffee Bean and Tea Leaf (CBTL), and Gloria Jean are valued by the rich group in India.
India is customarily a tea-drinking nation, so espresso chains have concentrated on giving a feel where individuals can unwind and invest energy with one another. This setup implies higher capital expenses. It is different from the US, where the vast majority have a liking for espresso. The Indian buyer base has likewise advanced in the recent decade. What can worldwide brands like Starbucks do to augment their odds of achievement in India? Here are a few thoughts:
Picking a Local Partner
Worldwide brands face the difficult choice of either going solo or tying up with a nearby accomplice. Starbucks' choice to team up with India's TATA Global Beverages demonstrates attention to utilizing different advantages. The TATA Group is one of India's morally determined brands, an observation passed on about Starbucks India too.
Given that India produces espresso beans in just a couple of spots, the other sourcing alternative was bringing in the beans. Be that as it may, this would have raised costs fundamentally.
Tata's espresso plant in Karnataka has been contracted to supply beans to Starbucks' universally, making common cooperative energies. It has contracted to take into account TATA's TAJ SATS, which supplies to TATA's top-notch lodging network – The TAJ. The TATAs are put into the retail part with store brands like Westside, Tanishq, Croma, Star Bazaar, and so forth. Starbucks can use them for information sharing on Indian land, territory points of interest, and handling land administrations. This would enable its very own development to outline. This strategy gives scope for store-in-store deals.
Consistency in Store Arrangements
This keeps up the one-of-a-kind selling purpose of customer experience and allows to pick up economies of scale on CAPEX. Starbucks plans to have a similar store group crosswise over India. However, the size can change depending on financial matters. This is how it works all around. Starbucks wants to provide an agreeable 'café' experience. Having a similar organization gives clients the solace of accepting the equivalent 'Starbucks' vibe any place they go throughout the world.
Keeping the store designs steady means it needs to pick and open new areas stringently, to such an extent that the area can yield a throughput by the venture. Its methodology in-store arrangement is different from CCD, which has picked various configurations to tap the potential interest in any region. CCD has opened a couple of premium outlets dependent on the area's customer profile . It has additionally gone for non-store organizations like takeaway booths and candy machines. Be that as it may, Starbucks may expect that such non-store configurations may weaken its image esteem.
Estimating the Pace of Expansion
India is the place where an inability to screen primary concerns has tossed numerous organizations out of the rigging. So, a top-line just approach doesn't work here. Since Starbucks needs to pick new areas stringently by its equivalent configuration approach, it has decided on a deliberate pace of extension. It is concentrating on the budgetary feasibility of every outlet, as opposed to going for an aggressive development plan which may have brought about rehashed calls for capital.
This operational process is different from its system in the USA and China where it has fabricated scale by opening stores in pretty much every area – being the main port-of-call for espresso by basically being all over the place. CCD's methodology behind adaptable store organizations was to guarantee there is a CCD bistro at a simple reach. It is intriguing to check its normal store gainfulness given its scale.
Guaranteeing Top-Authority Backing and Responsibility
Top initiative responsibility from the two sides of the organization, Tata and Starbucks, has been plentifully clear. Starbucks took as much time as is needed to enter the market (6 years), recognizing that India was a mind-boggling market and required cautious passage arranging. The two sides have spoken finally about their dedication and shared their future plans to give their business a new direction toward growth.
Altering Contributions to Suit Indian Market and Client Needs
Being adjusted to Indian culture, tastes, and inclinations conveyed at a suitable "esteem" guarantees customer importance, construct, and continued utilization. Starbucks mirrors this comprehension – as observed through a blend of western staples, a wide scope of intriguing Indian tidbits similar to confined refreshments on the idea. Since its experience ( and item as well, however to a lesser degree) is its image guarantee, its test lies in conveying an all-around steady, yet locally significant brand experience.
The stores, or the "third spot" as Starbucks calls them, have been altered likewise. The stores don't pursue the worldwide layout and appear to have been planned with consideration, with neighbourhood contacts consolidated. Stores in various urban communities have been structured unexpectedly, mirroring the neighbourhood culture – for e.g., New Delhi's store has ropes and chat on the dividers and henna designs on the floor, though the Pune store has a rich showcase of collectables and copper.
There appears to be sufficient utilization of shading – something missing in the US. The stores have been intended to convey a particular, premium café experience, predictable, and in a state of harmony with the one conveyed over the rest of the world.

Making Inventive and Restricted Plan of Action
Starbucks appears to have made a confined plan of action, planned for conveying a universally reliable item and involvement with locally-focused costs. The Tata group conveys a major sourcing advantage (attributable to its quality over the generation chain, developing, broiling, and exchanging espresso), yet it has just gone past that to develop and support associations with nearby espresso cultivators – putting resources into structure economical cultivating rehearses. All of Starbucks' espresso is sourced locally, a first-ever for the organization.
Scaling up using Arrangements and Organizations
The Tata organization is the genuine overthrow in the Starbucks passage story. Having Tata as an accomplice is gigantically profitable, not due to the validity and strength it offers, or because it coordinates the scale and stature of Starbucks as an organization.
It offers numerous advantages catalyzing pretty much every market section achievement variable - for example, The Tata group has involvement in the retail business , a solid reputation in advancing new pursuits, gives a sourcing advantage through Tata espresso, offers access to high traffic areas using its lodgings and other retail outlets, guarantee excellent nourishment and refreshment supply through its F&B business and so forth.
Furthermore, the potential for an effective organization is amazingly high given Starbucks' and Tata's mutual qualities – the two of them have a solid social inner voice and are resolved to "give back" to the general public and network.
Influencing India for Worldwide Items
Not long after it finished its first year, Starbucks reported that it was serving top-quality Indian Arabica espresso as "Indian coffee" in different markets. Another world-class office for cooking and bundling has just been initiated in Coorg, Karnataka; the results of which are to be analyzed in India and abroad.
Overseeing Discernment and Guidelines
This viewpoint is tied in with structure, a solid positive observation and a picture for the business and brand crosswise over key outer partners and crowds – incorporating the administration, corporate accomplices, networks inside the eco-framework, and customers on the loose. Given what Starbucks has figured out how to accomplish in a year and a half since dispatch, it appears to be genuinely evident that its thought combined with the Tata advantage (critical reach and impact) has helped in developing solid connections and a positive picture with key outside partners and voting demographics.
Engage Nearby Association
Starbucks is by all accounts constructing a nation-explicit activity with nearby individuals in charge and overall unmistakable customer interface focuses, giving them the necessary position to coordinate and work. There is overwhelming interest in enlisting the perfect individuals and giving the essential preparation – to install and instil the organization's culture and administration models.
Along these lines, how has Starbucks fared against the McKinsey spread out variables for long-haul India achievement? Its accomplishments against the scorecard look noteworthy. With thorough vigorous passage arranging and brilliant and quick execution, the multi-month-old endeavour appears to have impressive force, making purchaser and network-driven ventures and focused on sustaining its centre business and brand. It appears to be very much set to "win" in India.
Whether Starbucks will collect a huge piece of the overall industry and accomplish its objective of India being among its best 5 markets over the long haul is not yet clear. It's still early days, yet for the organization, this appears to be an incredible beginning and a great globalization model for multinationals looking for an India section.
Products Of Starbucks Corporation
Aside from the typical items offered globally, Starbucks in India has some Indian-style item contributions, for example, Tandoori Paneer Roll, Chocolate Rossomalai Mousse, Malai Chom Tiramisu, Elaichi Mewa Croissant, Chicken Kathi Roll, and Murg Tikka Panini to suit Indian customers. All coffees sold in Indian outlets are produced using Indian broiled espressos by Tata Coffee. Starbucks additionally sells Himalayan packaged mineral water. Free Wi-Fi is accessible at all Starbucks stores.

In January 2017, Tata Starbucks presented Starbucks' tea image "Teavana". Teavana offers 18 unique assortments of tea in India. One of the assortments called the India Spice Majesty Blend was explicitly created for the Indian market and is just accessible in India. India Spice Majesty Blend is a mix of full leaf Assam dark tea injected with entire cinnamon, cardamom, cloves, pepper, star anise, and ginger. On 15 June 2015, Tata Starbucks reported that it was suspending the utilization of fixings that had not been affirmed by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
The organization didn't indicate what the fixings were or which items they were utilized in. The organization additionally expressed that it was applying for FSSAI endorsement for these ingredients.

As per the Latte Index positioning of the expense of a tall hot latte at Starbucks in 44 nations, India was the fifth most costly nation to buy the drink dependent on January 2016 costs. The record distributed by US-based buyer research firm ValuePenguin found that a tall hot latte cost $7.99 in India, far higher than the $2.75 it costs in the least expensive nation, the United States, yet much lower than the $12.32 in the most costly nation, Russia .
Tata Starbucks propelled the Starbucks Delivers program in mid-2019. The administration offers home conveyance from Starbucks outlets through an organization with Swiggy. The administration was first propelled in Mumbai, with designs to turn it out to other cities.
In its menu, the Tata Starbucks company has launched ice-creams as their new products. The frozen delights are available even in flavours like java chip and caramel macchiato among others and will come in takeaway tubs and single scoops. The ice-creams are now available in 50-60% of the Starbucks stores.
Business Growth Of Starbucks Corporation Over The Years

Tata Starbucks, a 50:50 joint endeavour between Tata Global Beverages and Starbucks Coffee of the US, has announced a 30% top-line development in financial 2018-19, driven by new store openings and improved execution. Tata Starbucks, which is hoping to make back the initial investment in the current money, has opened 146 stores to date. Tata Starbucks announced "twofold digit top-line development - 30% for the entire year, driven by new stores and improved store execution," Tata Global Beverages Ltd (TGBL) said in a financial specialists' introduction. Tata Starbuck's income for 2018-19 is required to be approximately INR 450 crores.
TGBL said Tata Starbucks opened 30 outlets in the past financial year, out of which 15 new stores were opened during the last quarter of the money-related year. The organization claimed detailed benefits at the store level; all urban areas were likewise productive, and additionally saw an ascend in nourishment share in general deals.
The Starbucks company has added around 40 stores in FY21 but the company had recorded a 33% Y-O-Y fall in its revenues during the same fiscal. According to the Sushant Dash, CEO of Tata Starbucks, the recovery that the company has seen after the second wave of COVID-19 was better than what it saw after the first wave of the deadly pandemic. The quarterly growth after Q2 FY22 was 120% more than what it saw during the same period in the previous fiscal. The company has hugely focused on home deliveries ever since the pandemic broke out. It has already addressed concerns associated with the spillage and other challenges pertaining to home delivery, which contributed to over 18% of the total sales that the company witnessed this fiscal, as per the reports in November 2021. Furthermore, the company has also added ice-creams to their menu in flavours like java chip and caramel macchiato. The Sanjeev Kapoor menu is another thing that has been freshly launched by Tata Starbucks. Besides, the company also launched a one-litre freshly brewed beverage and at-home coffee.

Future Plans Of Starbucks Corporation
Tata Starbucks Pvt. Ltd. is looking to forcefully grow its impression in the Indian market with its eyes on the quickly spreading "espresso culture" among the twenty to thirty-year-olds and upwardly versatile customers. Tata Starbucks, a JV between US-based Starbucks Coffee Company and Tata Global Beverages Ltd, hopes to set up altogether more number stores this monetary than it did previously.
Starbucks is hopeful about solid business development in India throughout the following year as it means to leave red in monetary numbers after 2020. "Our proceeded with development in topline and reasonable methodology towards extension will enable us to accomplish make back the initial investment by March 2020," Navin Gurnaney, CEO, Tata Starbucks disclosed to Business Line in the wake of declaring five new stores in Gujarat - three in Ahmedabad and two in Surat. Gurney likewise included, "First time in quite a while, we are opening five stores in any state in one go.
Gujarat is a significant market for us. In the wake of opening these five stores on Thursday, the all outnumber of hides away goes up to 157 in India." Starbucks entered India with its first store opened at Mumbai in 2012. Of the 157, the organization has opened all out 11 stores so far in this financial, as against complete 30 stores opened during 2018-19. It takes into account 270,000 clients each week in India. The organization had announced a turnover of INR 442 crores for the monetary 2018-19.
"Espresso business in India is developing significantly. The espresso culture is being initiated by recent college grads, upwardly versatile, and individuals who travel and get brand. Two years back, we set up 25 stores (in a year). During the last financial 2018-19, we included 30 stores.
This year we will beat that number considerably and by end of March 2020, we will have included a lot a greater number of stores than we included in the past," Gurney said. With per store venture prerequisites being evaluated at INR 1.7-2 crores, the complete CAPEX plan by the organization works out in overabundance of INR 50 crores during current monetary on the off chance that it opens more number of stores than a year ago. Be that as it may, Gurnaney ceased from giving venture figures for 2019-20.
The organization is likewise open to different open doors for development including inorganic development through acquisitions. Be that as it may, when tested about any probability of a venture plan in the espresso chain Cafe Coffe Day (CCD), Gurnaney denied estimating any discussions for securing. "We are very hopeful about India. We will be attentively forceful (to extend). (At present) we are not in discussions with anyone for obtaining.
In any case, we are hoping to develop constantly," he included. With an end goal to upgrade the client experience, Starbucks is presenting new nourishment things, taking into account all client needs including breakfast and lunch. The income share from nourishment things is right now around 25%, even as it keeps on developing with new things to meet the client's needs.
Who founded Starbucks?
Starbucks was started by Hun Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Bowker in 1971.
Where was the first Starbucks started?
Starbucks was started in Pike Place Market, Seattle, Washington, United States.
When was Starbucks started in India?
Starbucks was launched in India in 2012.
What is the revenue of Starbucks?
Starbucks revenue was recorded $29.02 billion in 2021.
How many Starbucks stores are there worldwide?
There are 33,830 Starbucks stores in the world as of 2021.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Felicity Games Secures $700K in Pre-Seed Funding From DeVC, Swiggy Founders, Kunal Shah, and Other Marquee Angels
India, July 09, 2024: Felicity Games, a leading casual game developer and publisher, has secured a $700K pre-seed funding from DeVC, Visceral Capital, and marquee angel investors including Kunal Shah of CRED, former Nazara CEO, Manish Agarwal, Sriharsha Majety, Nandan Reddy of Swiggy and Sameer Pittalwala, Head of Gaming, Google
Top 5 Leading Telecommunication Companies in India by Their Market Share
Telecommunication companies are entities that facilitate communication and connectivity without the need for physical interaction. Whether it's making phone calls, accessing the internet, or exchanging written messages via emails and SMS, the telecom sector offers comprehensive solutions at our fingertips. Through the use of cables, wires, waves, and wireless technology,
Top Profitable Transport Business Ideas You Can Start Now
Transportation is one of the oldest businesses in the world and is one business that can never go extinct because as long as the world continues, people will always need to move around from place to place. The transport business is also one business in which you can make cool
Koo: The Rise and Shutdown of India's Homegrown Microblogging Platform
Company Profile is an initiative by StartupTalky to publish verified information on different startups and organizations. The recent ban in India of 59 Chinese apps has paved the way for many Indian startups and entrepreneurs to create "Made in India" products. The majority of these startups are developing products that
Decoding The Starbucks Marketing Strategy: A Complete Guide
By Aditya Shastri
Quick Read Discover how Red Bull’s innovative marketing strategy has positioned it as a leader in the energy drink market. This Red Bull marketing strategy case study explores their unique promotional tactics, digital marketing efforts, and recent campaigns.
Learn From Asia’s #1 Digital Marketing Institute
AI-Based Curriculum
Dive in to the future with the latest AI tools
Placement at top brands and agencies
Talk to counsellor
About Starbucks
Established in 1971 in Seattle, Washington, Starbucks began as a lone storefront specializing in premium coffee beans and equipment. It has grown into a global coffeehouse chain with over 30,000 locations worldwide. The company’s mission is to uplift and nourish the human spirit—one individual, one cup of coffee, and one community at a time. Known for its commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing, Starbucks is a pioneer in creating a unique coffee culture.

Relevant Updated Statistics
- As of 2023, Starbucks operates in over 80 countries with 33,833 stores globally【source: Statista】
- Starbucks’ revenue for 2022 reached $29.06 billion, a 24% increase from the previous year【source: Starbucks Annual Report 2022】
- The brand’s loyalty program, Starbucks Rewards, has over 24.8 million active members in the United States【source: Starbucks Investor Relations】.
What’s New With Starbucks
Business news.
Starbucks announced plans to open 1,000 new stores in China by 2025, strengthening its presence in one of its fastest-growing markets.
Product Launch
In 2023, Starbucks introduced the Oleato range, featuring coffee infused with olive oil, a bold new addition to their beverage lineup.
Marketing News
Have you ever been called the wrong name? It might seem like a minor detail, but for transgender and non-binary individuals, it can be a daily experience. Starbucks recognized this in their powerful campaign, “Every Name’s a Story.” This campaign wasn’t just about selling coffee – it was about celebrating inclusivity and diversity.
Feeling inspired by innovative marketing campaigns like this? Check out our digital marketing case studies for more such content.
Celebrity News
In collaboration with singer Taylor Swift, Starbucks promoted the ‘Red (Taylor’s Version)’ album by featuring her favourite drink, the Caramel Nonfat Latte, in stores worldwide.
Are you ready to unlock your full potential in the thrilling world of digital marketing? Our PG program is just what you need. Enrol in our Post-Graduation in Digital Marketing and explore the opportunities now.
But for now, let us continue with our case study on the marketing strategy of Starbucks.
Starbucks Target Market
Starbucks, a premium coffee brand, strategically positions itself in the market with a keen focus on high-income spenders and health-conscious professionals. The market positioning of Starbucks is evident in its appeal to urban, on-the-go consumers seeking quality coffee and a tranquil environment to unwind.
This market positioning of Starbucks attracts a diverse clientele, including technology early adopters and those flexible to change, primarily aged 25-45. Starbucks’ success is built on a deep understanding of its target audience.
This allows them to constantly adapt their offerings and marketing strategies to meet evolving consumer trends and preferences. This case study will explore how Starbucks uses this knowledge to stay ahead of the curve.
This approach underscores Starbucks’ commitment to reaching beyond the storefront, offering not just coffee but an experience tailored to its discerning clientele.So summed up, their target audience is-
- High-income spenders
- Technology early adopters
- Health-conscious professionals
- Flexible to change
- Reaching beyond the storefront (Online Sales & Engagement)
Also Read: Top 14 Digital Marketing Courses in Mumbai in 2024
To provide a clearer understanding of Starbucks’ target audience, refer to the Buyer Persona outlined in our Starbucks case study blog.

Buyer’s Persona
Profession:
Web-Developer
- Seeking a premium coffee experience.
- Interested in sustainable and ethically sourced products.
- Value convenience and loyalty rewards.
Interest & Hobbies
- Enjoying quality time at coffee shops.
- Passionate about environmental causes.
- Engaged in social media and digital trends.
Pain Points
- High prices compared to local coffee shops.
- Limited seating in busy locations.
- Preference for non-dairy or alternative milk options.

Social Media Presence
Starbucks in india.
In the 2010s, Starbucks’ marketing strategy focused on entering the Indian market to capitalize on the ever-growing coffee culture, particularly targeting the niche upper-class segment. Despite an initial announcement in 2007, Starbucks withdrew its plans without explanation, finally making a grand entry in 2011. To establish a strong foothold, the world’s biggest bistro chain forged a 50-50 joint venture with Asia’s largest coffee grower, Tata Consumer Products Limited, for their Starbucks coffee marketing strategy.
Successfully launching its brand, Starbucks’ next critical move was to meticulously define and engage its target audience in India, ensuring sustainable growth and market presence. This strategic approach, outlined in this Starbucks case study, highlights its methodical entry into the Indian market and the partnership that facilitated its successful establishment in the region.
Now, without further ado, let’s get straight into Starbucks’s marketing tactics, exploring their strategic approaches and methods in the market.
Marketing Strategies of Starbucks
Initially, Starbucks’s marketing tactics in India focused on segmenting consumer markets on a socio-economic basis, targeting working professionals seeking a soothing workspace. They strategically placed stores in locations where this demographic was prevalent.
Like many companies entering new markets, Starbucks started with a single segment and expanded upon achieving initial success. Over time, they diversified their target audience to include teenagers and young adults, bolstering their Starbucks coffee marketing strategy through product range expansion and enhanced social media presence.
The market positioning of Starbucks hinges on delivering a unique, differentiated experience that solidifies its reputation as a highly esteemed brand. Their marketing mix integrates digital technology and social media extensively, engaging the modern, tech-savvy generation for promotions and customer interaction.
This approach has not only fortified their brand identity but also fostered a deep connection with their diverse customer base.
Note: To enhance your expertise, you can explore various courses on digital marketing online that provide in-depth knowledge and the latest industry trends.
Digital Expansion
One of the key priorities of Starbucks’s marketing strategy is expanding its digital interactions with customers. To achieve this goal, it implements several strategies to attract digitally registered customers beyond the rewards program. For example, the coffee chain is offering mobile order services and leveraging Wi-Fi sign-ins at its physical stores.
Starbucks Social Media Strategy
Most people are familiar with Starbucks on social media. The company features several social media accounts that are known for their distinctive branding, interactive posts, and visually pleasing content. The diverse range of content includes recipes, photography, articles, and features. But there’s more than meets the eye. The stream of content can be broken down into a series of campaigns geared at creating a greater sense of Starbucks marketing techniques, enhancing brand awareness, and fostering a sense of community.
Starbucks Product-based Marketing Campaigns
The company focuses on promoting unique and fan-favourite beverages as part of its Starbucks coffee marketing strategy. The brand understands the popularity of its flagship items, particularly the Pumpkin Spiced Latte and Frappuccino, and recognises the demand for this type of content among its audience.
They have even established dedicated social media accounts for these customer favourites, where they actively share relevant and relatable memes to engage their loyal fan base. Additionally, Starbucks leverages user-generated content (UGC), often featuring consumer images of visually appealing products like the Unicorn Frappuccino.

Source: Google
These images are not only reshared across official channels but also incorporated into influencer campaigns, further amplifying their digital marketing efforts.
Starbucks Corporate Social Responsibility-based campaign
Starbucks’ marketing tactics involve leveraging social change as a tool, positioning itself as open-minded and inclusive. One notable example is the #ExtraShotOfPride campaign, which actively supports the LGBT+ community.
Community-based campaigns
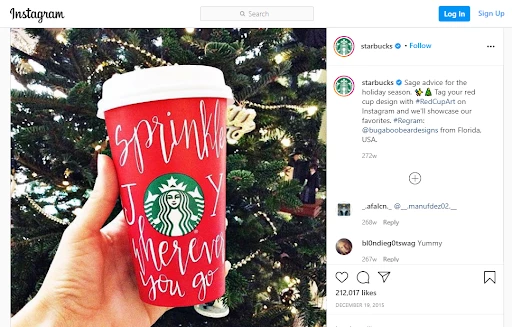
Another facet of Starbucks’s marketing strategy is its emphasis on highlighting individuals and communities. Take a look at the #RedCupArt campaign, which not only increases engagement but also provides them with a library of UGC content. They use storytelling to showcase acts of courage and kindness in American communities, localizing the content.
Starbucks’s marketing techniques consciously humanize the company by sharing stories on their account, spotlighting employees who play an essential role, especially when consumers are distrustful of big brands.
Just like Starbucks coffeehouses fostered a sense of community in person, their online coffee content creates a similar social experience. This reflects their pioneering role in shaping modern coffee culture.
Festive Marketing
Starbucks has also initiated a new seasonal whole-bean coffee, #StarbucksDiwaliBlend, for its consumers across the country and select global markets. The latest exquisite blend is hand-picked and sourced from Tata Estates in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
The Starbucks Diwali Blend was intended as a tribute to the region’s rich and cultural coffee heritage and expertise. They launched the #SketchTheBlend campaign where customers have to share their creativity on the Diwali Blend cup and sleeve and could win 5 free beverages.

Digital Marketing Strategies
Seo (search engine optimization) strategy:.
Starbucks’s marketing tactics involve optimising its online presence by incorporating relevant keywords, high-quality content, and a user-friendly website to improve search engine rankings.
Social Media Marketing Strategy:
Starbuck’s marketing strategy includes actively engaging with customers on social media platforms, by running targeted ads and interactive content to boost engagement.The brand actively engages with customers on social media platforms, running targeted ads and interactive content to boost engagement.
E-commerce Strategy:
Starbucks’ online store offers a seamless shopping experience, from purchasing coffee beans and equipment to ordering ready-to-drink products.
Mobile App:
The Starbucks mobile app enhances customer convenience with features like mobile ordering, payment, and rewards tracking, showcasing a key aspect of Starbucks’s coffee marketing strategy.
Influencer Marketing Strategy:
Collaborating with influencers and celebrities, Starbucks effectively reaches a broader audience and creates buzz around new product launches and campaigns.
Bonus: Enrolling in a digital marketing course can provide you with the essential skills and knowledge to understand and implement successful strategies, much like those employed by Starbucks.
Starbucks knows its audience is technologically advanced, which makes it imperative for them to have a strong digital marketing strategy. It’s clear how Starbucks prefers marketing on platforms where they have two-way communication instead of platforms like print and television which is more of a one-way communication.
Marketing and Advertising Campaigns
One of Starbucks’ most famous campaigns is “Meet Me at Starbucks,” a global initiative that highlights the diverse ways people connect at their stores. The campaign emphasized the brand’s mission to foster human connection and resulted in increased customer engagement and brand loyalty.

Starbucks launched its social media campaign in 2 phases. The first phase was where they asked their customers to share their ways of reconnecting amidst the pandemic and share their favourite Starbucks memories on their personal Instagram handles with the hashtag Starbucks advertising strategy. In the second phase- ‘Half Cup Full’- they asked their customers to comment on their favourite beverage on the post. They then sent these customers voice notes of baristas hollering the customers’ names along with their favourite beverage to remind them of the famous in-store experience.

This was a great campaign as it not only reminded the people of all the good memories with Starbucks but also made them feel important and valued.
Campaign Analysis:
Starbucks employs a variety of marketing techniques to maintain its market positioning. These include personalised marketing through their rewards program, located store experiences, and a focus on sustainability. Their recent ‘Every Name’s a Story’ campaign is an excellent example of leveraging social issues to build brand loyalty.
Read more about: For skill enhancement, explore our digital marketing courses in Ahmedabad and digital marketing courses in South Delhi , created to suit your requirements.
Failed Campaigns
#racetogether campaign.

The campaign aimed to spark conversations about race by having baristas write “Race Together” on cups, which was met with widespread criticism.
Customers and employees felt uncomfortable and questioned the appropriateness of discussing such a sensitive topic in a coffee shop setting.
Starbucks quickly scaled back the campaign, focusing instead on internal initiatives to promote diversity and inclusion.
Top Competitors
In this Starbucks case study, we will explore its competitors and how Starbucks consistently rises above them, showcasing its resilient Starbucks marketing strategy.
Dunkin’ Donuts
Renowned for its extensive range of coffee blends and delectable baked goods, Dunkin’ Donuts has established itself as a favourite among coffee enthusiasts and snack lovers alike.
McDonald’s coffeehouse brand offers a budget-friendly assortment of coffee beverages, providing customers with a convenient and affordable coffee experience alongside their meals.
Costa Coffee
A prominent British coffeehouse chain, Costa Coffee is celebrated for its European presence and commitment to delivering quality coffee in a cosy café atmosphere.
Peet’s Coffee
Known for its artisanal approach to coffee roasting, Peet’s Coffee specialises in high-quality, hand-roasted beans that cater to discerning coffee connoisseurs seeking exceptional flavour profiles.
Tim Hortons
A beloved Canadian institution, Tim Hortons is cherished for its signature coffee blends and freshly baked doughnuts, offering a comforting taste of Canadian hospitality to customers nationwide.
Be it Starbucks or any other company, competition is everywhere. So if you are someone who likes doing research on competitor analysis for other companies, let me help you out. Check out these case studies on the marketing strategy of Jollibee , McDonald’s marketing strategy and the marketing strategy of Dunkin Donuts .
In conclusion, Starbucks’ marketing strategy is a testament to its success in the coffee industry. By focusing on high-income spenders, urban professionals, and tech-savvy individuals, Starbucks has effectively positioned itself as a premium brand.
Their innovative campaigns, such as ‘Every Name’s a Story’ and ‘Meet Me at Starbucks,’ highlight their commitment to inclusivity and human connection. The integration of digital strategies, social media engagement, and a robust rewards program further strengthens their market presence.
By continuously adapting to consumer trends and leveraging strategic partnerships, Starbucks remains a leader in the global coffee market.
Additional Information
Want to learn the essentials of digital marketing in no time? Our extensive Online Digital Marketing Course will help you unlock success in this evolving industry.If you have reservations about enrolling, try our Free Digital Marketing Masterclass first! Get a preview of the content and decide if it’s a good match for you.
Alternatively, if you’re interested in the world of social media, our Free Instagram Marketing Course might be the perfect fit.
Lastly, if you enjoyed this blog, we recommend exploring our digital marketing case studies. We’ve covered some of the best companies out there. A few of the examples are Amazon , Red Bull and LinkedIn .
Don’t forget to check out our digital marketing blogs as well. You might find your perfect course among them!
We appreciate you reading this blog. Comment down below if you want more such case studies.
Frequently Asked Questions- Marketing Strategy Of Starbucks
1. what is starbucks’ mission.
Starbucks’ mission is to inspire and nurture the human spirit – one person, one cup, and one neighbourhood at a time.
2. How many stores does Starbucks have worldwide?
Starbucks operates over 32,000 stores worldwide, making it one of the largest coffeehouse chains globally, known for its extensive global presence and accessibility.
3. What is Starbucks’ latest product launch?
Starbucks’ latest product launch includes a range of summer-inspired beverages like the Iced Guava Passionfruit Drink and the Nitro Cold Brew with Salted Honey Cold Foam.
4. Who are Starbucks’ main competitors?
Starbucks’ main competitors include Dunkin’ Donuts, McCafé (McDonald’s coffeehouse brand), Costa Coffee, Peet’s Coffee, and Tim Hortons, each vying for market share in the coffee and quick-service restaurant industries.
5. What is the Starbucks Rewards program?
The Starbucks Rewards program is a loyalty program where customers earn points (stars) for purchases, which can be redeemed for free drinks and food items, along with personalised offers and early access to new products.
6. How does Starbucks promote sustainability?
Through initiatives like ethically sourced coffee, reducing waste, and promoting recycling.
7. What was the ‘Race Together’ campaign?
The ‘Race Together’ campaign was an initiative by Starbucks aimed at sparking conversations about race relations. It encouraged employees to write ‘Race Together’ on cups to prompt dialogue among customers and staff.
8. What is Starbucks’ digital marketing strategy?
Starbucks’ digital marketing strategy leverages social media platforms and mobile apps to engage customers with personalised offers, loyalty programs, and interactive content, enhancing brand visibility and customer experience.
9. What motivates Starbucks’ target audience?
Starbucks’ target audience is motivated by quality coffee, a cosy ambience, and a sense of community fostered by the brand’s commitment to social responsibility and customer-centric experiences.
10. How does Starbucks use social media?
Starbucks leverages social media to engage customers through creative campaigns, customer interactions, and promotions, enhancing brand visibility and fostering a sense of community among coffee enthusiasts worldwide.
Aditya Shastri
Lead Trainer & Head of Learning & Development at IIDE
Leads the Learning & Development segment at IIDE. He is a Content Marketing Expert and has trained 6000+ students and working professionals on various topics of Digital Marketing. He has been a guest speaker at prominent colleges in India including IIMs...... [Read full bio]
Clicking on the image of the Starbucks cup is my thing too. This blog provides great and deep insights into their strategy.
Starbucks marketing strategy brewed! served! and I’m here for it!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Related Posts

In-Depth Marketing Strategy of TCS – Explained | IIDE
by Aditya Shastri | Jul 12, 2024
Quick Read The marketing strategy of TCS focuses on leveraging digital transformation,...

In-Depth McDonald’s Marketing Case Study – I’m Lovin’ It Already.
by Aditya Shastri | Jul 11, 2024
Quick Read McDonald's marketing strategy revolves around innovative campaigns, digital...

Elaborated Marketing Strategy of Puma + SWOT Analysis
by Aditya Shastri | Jul 6, 2024
Quick Read The marketing strategy of Puma focuses on innovation, collaboration, and...
" * " indicates required fields
I’m Interested in This Masterclass
By providing your contact details, you agree to our Terms of Use & Privacy Policy
Starbucks Change Management Case Study
Change is a constant in any business, and successful organizations must adapt to changes in the industry, market, and consumer preferences to remain competitive.
The ability to manage change is crucial to the survival of businesses in today’s dynamic market environment.
This is why change management is a vital aspect of business operations.
In this blog post, we will explore the case study of Starbucks’ change management, discussing their need for change, strategies implemented, challenges faced, and the results of the change.
We will also examine the lessons learned from this experience and the importance of change management in businesses.
So let’s dive into the Starbucks change management case study and see how it can inform our understanding of successful change management.
History and Growth of Starbucks
Starbucks is an American multinational coffee company founded in Seattle, Washington, in 1971. The founders of Starbucks were three friends, Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Bowker.
Starbucks initially started as a single store selling high-quality coffee beans and equipment. It was only in the early 1980s that Howard Schultz joined Starbucks as the Director of Retail Operations and Marketing. It was his vision of a coffeehouse culture that transformed Starbucks into the iconic brand it is today.
Schultz convinced the founders to test a coffeehouse concept in downtown Seattle, and in 1984, the first Starbucks Coffeehouse was opened. The concept was an immediate success, and Starbucks quickly expanded throughout Seattle and the United States.
In 1992, Starbucks went public, and by 2000, the company had over 3,000 stores worldwide. By 2018, Starbucks had more than 30,000 stores across 80 countries.
Starbucks faced numerous challenges and crisis during its journey but it sailed through the tough times and surfaced as a text book examples of crisis management.
The need for change at Starbucks
Despite its growth and success, Starbucks faced significant challenges in the late 2000s. In 2007-2008, the global financial crisis impacted Starbucks, leading to the closure of several underperforming stores. Furthermore, the company’s rapid expansion had led to a loss of focus on its core business, and the quality of its products had suffered. Starbucks’ profitability and customer satisfaction were on the decline, and the company needed to make significant changes to survive in the highly competitive coffee industry. In response, the company realized the need for change and embarked on a comprehensive change management program.
Reasons for the change
The need for change at Starbucks was evident, and the company identified several key areas that needed improvement. Firstly, Starbucks needed to streamline its operations to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Secondly, it needed to refocus on its core business of selling high-quality coffee and related products. Thirdly, Starbucks needed to improve its customer service and store experience to boost customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Strategies implemented by Starbucks
To achieve its goals, Starbucks implemented several strategies. Firstly, it closed underperforming stores and streamlined its operations to reduce costs. Secondly, it refocused on its core business by introducing new blends and improving the quality of its products. Thirdly, Starbucks launched a customer feedback program to understand customers’ needs and preferences better. Fourthly, Starbucks introduced new store designs and layouts to improve the in-store experience. Finally, Starbucks invested heavily in training its employees to provide excellent customer service and maintain the high standards of its products.
Challenges faced by Starbucks during the change
The change management process at Starbucks was not without challenges. Firstly, some employees resisted the changes, and there was a need to ensure that everyone was on board with the new direction of the company. Secondly, there was a need to balance the introduction of new products and store designs with maintaining the company’s core values and identity. Thirdly, there was a risk of losing customers during the change process, and Starbucks had to ensure that it maintained its customer base while attracting new customers.
Results of the change management at Starbucks
The change management program at Starbucks was successful, and the company saw significant improvements in its financial performance and customer satisfaction. Firstly, Starbucks’ profitability improved significantly, and the company’s share price increased. Secondly, the quality of Starbucks’ products improved, and the company introduced new blends and products that were well-received by customers. Thirdly, the in-store experience was improved, and the new store designs and layouts were well-received by customers. Finally, customer satisfaction and loyalty increased, and Starbucks regained its position as a leading brand in the coffee industry
05 Factors that explained successful implementation of change management at Starbucks
There were several factors that contributed to the successful implementation of change management at Starbucks. Here are five key factors:
1. Strong Leadership
Starbucks’ success in implementing change management can be attributed to the strong leadership of the company. The leaders at Starbucks had a clear vision of what changes were needed, and they were committed to making those changes happen. They communicated the need for change effectively to all stakeholders and provided the resources and support necessary for the change process to succeed.
The leadership team also ensured that everyone in the organization understood their roles in the change process and provided guidance and direction throughout the implementation. Their leadership helped to create a sense of urgency and momentum, which was critical for the success of the change management program
2. Effective Communication
Effective communication was a crucial factor in the success of Starbucks’ change management program. The company communicated the changes to employees, customers, and stakeholders effectively, ensuring that everyone was informed and understood the changes. Starbucks used a variety of communication channels, including town hall meetings, newsletters, and training sessions, to ensure that information was disseminated widely and consistently.
By keeping everyone informed and engaged, Starbucks was able to create a shared understanding of the changes and gain buy-in from employees, customers, and stakeholders. Effective communication also helped to build trust and credibility with stakeholders, which was essential for the success of the change management program
3. Employees Engagement
Employee engagement played a critical role in the success of Starbucks’ change management program. The company engaged its employees in the change process by involving them in planning and implementation and ensuring that they had the necessary training and resources to implement the changes effectively. Starbucks also recognized and rewarded employees who embraced the changes and demonstrated excellent customer service.
This approach helped to create a sense of ownership and accountability among employees, which was essential for the success of the change management program. By empowering employees and recognizing their contributions, Starbucks was able to create a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, which helped to sustain the changes over time.
4. Customer Focus
Putting the customer at the center of its change management program was a key factor in Starbucks’ success. The company listened to customer feedback and made changes to its products and services to meet their needs and preferences. Starbucks also focused on improving the in-store experience to enhance customer satisfaction. By focusing on the customer, Starbucks was able to improve its products and services, which led to increased customer loyalty and retention.
By enhancing the in-store experience, Starbucks was able to create a more inviting and comfortable environment for its customers, which helped to increase sales and revenue. By making the customer a priority, Starbucks was able to build a strong brand and create a loyal customer base, which was essential for the success of its change management program
5. Flexibility
Flexibility was a critical factor in the success of Starbucks’ change management program. The company was flexible and adaptable during the change process, making adjustments to its strategies and plans as needed. Starbucks was open to feedback and suggestions from employees and customers, which helped the company to identify areas for improvement and make changes accordingly.
Starbucks recognized that change was an ongoing process and continued to make improvements over time. This approach helped Starbucks to stay ahead of the curve and remain competitive in a rapidly changing market. By being flexible and adaptable, Starbucks was able to anticipate and respond to changes in the market, which was essential for the success of its change management program.
Final Thoughts on Starbucks Change Management Experience
The Starbucks change management experience offers valuable insights into how companies can successfully navigate and implement change. Through strong leadership, effective communication, employee engagement, customer focus, and flexibility, Starbucks was able to successfully implement changes that resulted in improved performance, increased customer loyalty, and sustained growth.
Starbucks’ approach to change management shows that it is possible to implement significant changes while still maintaining the core values and identity of a company. By keeping the customer at the center of its change management program and engaging its employees, Starbucks was able to create a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, which helped to sustain the changes over time.
Overall, the Starbucks change management experience serves as a valuable case study for companies seeking to implement change and improve their performance. By following the lessons learned from Starbucks, companies can increase the likelihood of successful implementation of change management and create a culture of innovation and continuous improvement that can drive sustained growth and success.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

Importance of Organizational Change and Development

Change Management for Organizational Restructuring

How to Develop Onboarding Buddy Guidelines? – Practical Tips
Starbucks Reinvented
Harvard Business School Professor and historian Nancy Koehn has studied Starbucks and its leader, Howard Schultz, for close to 20 years. For her, the company represents much more than a phenomenal success story.
In a recently published case, "Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal," (available soon) Koehn and coauthors Kelly McNamara, Nora Khan, and Elizabeth Legris trace the dramatic arc of the company's past seven-plus years—a period that saw Starbucks teeter on the brink of insolvency, dig deep to renew its sense of purpose and direction, and launch itself in new, untested arenas that define the company as it exists today.
"This case distills 20 years of my thinking about the most important lessons of strategy, leadership, and managing in turbulence in the frame of a very relevant company," says Koehn, the James E. Robison Professor of Business Administration. "As a brand, leadership, and entrepreneurship scholar, I've been dogging Starbucks for a long time."
On a 1995 trip to Seattle, Koehn visited a Starbucks store for the first time and was struck by what she saw and felt. The notion of a "third place" between home and work to relax and enjoy the small, affordable luxury of a special coffee beverage seemed to resonate with the social and economic moment, she recalls. Six months later she met Howard Schultz, an entrepreneur who acquired the company in 1987, and was struck by his seriousness of purpose and the breadth of what he wanted to accomplish.
The case, Koehn's fourth to focus on Starbucks, opens in February 2007. Schultz, no longer Starbucks' CEO but still its chairman, is worried the company is losing its ability to be true to its values while providing a store experience that conveys a sense of comfort, connection, and respect for its product and the communities Starbucks serves.

So Schultz composed a heartfelt, searching memo to senior leadership. In it, he bemoaned decisions (for which he accepted responsibility) that improved efficiency and increased economies of scale but robbed stores of some of their essential magic, such as the smell of roasting coffee and the sights and sounds of traditional Italian espresso machines and baristas at work.
He also cited the company's rapid expansion and the potential "commoditization" of the Starbucks brand. "[W]e desperately need to look into the mirror and realize it's time to get back to the core and make the changes necessary to evoke the heritage, the tradition, and the passion that we all have for the true Starbucks Experience," Schultz wrote.
The scope and richness of Koehn's case gives it the feel of a page-turning novel; in that sense, Schultz's memo is the inciting action for all that follows.
Remaining True To Core Values
The challenge that had confronted Starbucks in the early- and mid-2000s was one common to many organizations: Could the company continue to grow while preserving its culture and values? In some areas, the drive to expand, egged on by Wall Street, was compromising the company's ability to invest in its partners (Starbucks' term for its employees), deliver personalized customer service, and maintain a close connection to the local community.
In addition, McDonald's and Dunkin' Donuts had emerged as serious competitors, offering their own lines of specialty coffee beverages. Even so, Starbucks' financials for 2007, the year Schultz composed his memo, didn't look so bad. But the entrepreneur became concerned as he dug more deeply into the numbers. Sure, revenues were up almost 21 percent over the previous year, but had slowed by over a third; transactions per store were up 1 percent, versus 5 percent the year before. Same-store sales rose only 5 percent, the smallest increase in five years.
In January 2008, Schultz returned as Starbucks CEO, replacing Jim Donald, the man he and other senior colleagues had chosen to lead the company.
Starbucks Sails Again
The case chronicles the blizzard of decisions and initiatives that follow what could have been the company's death knell as the financial crisis hit home and consumers cinched their belts.
"Schultz understood that you can't lift your foot off the gas pedal when you're attempting to transform a company," Koehn says. "Severe as its financial needs may be, you also have to figure out what you will invest in. Schultz knew that if he waited until the company was out of the woods to invest in new products, communication channels, and ways of doing business it would be too late—Starbucks would no longer be relevant."
From the start, Schultz sent the clear, unwavering message that Starbucks' transformation would represent a return to its roots and an uncompromising commitment to core values, such as health care benefits for any partners working at least 20 hours a week.
At a March 2008 gathering of 200 senior-level company leaders, Schultz unveiled a Transformation Agenda that included seven "Big Moves":
- Be the undisputed coffee authority;
- Engage and inspire our partners;
- Ignite the emotional attachment with our customers;
- Expand our global presence—while making each store the heart of a local neighborhood;
- Be a leader in ethical sourcing and environmental impact;
- Creative innovation growth platforms worthy of our coffee;
- Deliver a sustainable economic model.
The case provides a behind-the-scenes look at how the coffee company moved forward on these goals, including the introduction of the milder Pike Place Roast; the story of its VIA Ready Brew line; the launch of a loyalty program; investment in and engagement with social media; focus on a global expansion strategy; and the extension of social programs. The company closed stores, restructured its manufacturing and supply operations, and, perhaps most significantly, took steps to reengage its partners and store managers. In February 2008, Starbucks closed more than 7,000 of its stores across the country for "Espresso Excellence Training," taking the time to work with approximately 135,000 baristas to ensure they could pour a perfect espresso shot and steam milk properly.
For Schultz, however, that wasn't enough—he wanted to reach the company's store managers, recognizing them as essential to the transformation process.
"I needed an unfiltered venue for expressing my empathy about all that we were asking our partners to do and telling them plainly what was at stake," he wrote in Onward: How Starbucks Fought for Its Life without Losing Its Soul . The answer, in Schultz's mind, was a three-day conference in New Orleans in October 2008, a moment when the global economy happened to be tanking. Starbucks' fourth quarter profits were down 97 percent from the same time a year earlier; for the fiscal year, net earnings were down 53 percent to $316 million. The Starbucks board was reluctant to send 10,000 partners to New Orleans at a cost of $30 million, but Schultz stuck to his guns.
In addition to rolling up their sleeves and taking part in community service projects to aid areas of the city still recovering from Hurricane Katrina, partners participated in team-building events that reviewed the company's guiding principles and reminded them of their central role in the customer experience. Schultz also brought in Bono, lead singer of U2, to announce a partnership to channel proceeds from holiday beverage sales to the Global Fund in support of AIDS relief programs in Africa.
The New Orleans conference was a turning point for Starbucks; in the "novel" of Koehn's case, it's the climax.
"Investing in a conference of that size is such an unusual thing to do when faced with a cash crunch," Koehn says. "Schultz understood that what saves and breaks businesses is much more than cash. In the midst of so much turbulence, it's all too easy to pull levers on the low-hanging fruit of cash and logistics. But you don't save a business and turn it around without speaking to, focusing, and calling on the spirit of your people."
Schultz's experience qualifies him for closer study in Koehn's HBS course Power and Glory in Turbulent Times: The History of Leadership from Henry V to Steve Jobs. Not all managers are confronted in their careers with the sort of transformation challenge faced by Starbucks, but Schultz's reflections and actions are instructive for anyone charged with finding sources of strength, innovation, and renewal in today's turbulent business environment, Koehn says.
- Marty Forman Sr
- President/CEO, CMI Global Inc..
- Chris Gallup
- Solutions Architect, Savvy Network Logic
- Mary Setterholm
- Barista and Harvard Graduate
- Paul Donham
- Web manager, Sailing Ship Adventures (.com)
- steve glazer
- ceo, stevens world
- Pat McGillycuddy
- Regional CEO, IDI Gazeley - Brookfield Logistics Properties.
- SVP, Children's Hospital
- Merle Boniface
- Director of Business and Planning, Diocesan School for Girls
- Archie Mutyambizi
- Entrepreneur, Gratestroke Investments
- Jane Egerton-Idehen
- Key Account Manager, Ericsson Ghana
- Eric PIETRAC
- HR VP, Subsea7
- P.G.SUBRAMANIAN
- DIRECTOR, CATALYST PROFIN CONSULTANTS PVT.LTD
- John T Hays MBA '64
- Founder and first CEO, Coffees of Hawaii Inc.
- Solution Sales Manager, Ericsson
- Dr. R. Krishna
- Director, Strategic Solutions
- Emmanuel Alfieris
- Executive Director, Commonwealth Bank of Australia
- Kapil Kumar Sopory
- Company Secretary, SMEC(India) Private Limited
- Victor Martinez
- Director, Kawasaki
- Bernard Rosauer
- President, www.ThreeBellCurves.com
- 25 Jun 2024
- Research & Ideas
Rapport: The Hidden Advantage That Women Managers Bring to Teams
- 11 Jun 2024
- In Practice
The Harvard Business School Faculty Summer Reader 2024
How transparency sped innovation in a $13 billion wireless sector.
- 24 Jan 2024
Why Boeing’s Problems with the 737 MAX Began More Than 25 Years Ago
- 27 Jun 2016
These Management Practices, Like Certain Technologies, Boost Company Performance
- Change Management
- Motivation and Incentives
- Organizations
- Growth Management
- Transformation
- Food and Beverage
- United States
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
More From Forbes
Starbucks, reinvented: a seven-year study on schultz, strategy and reinventing a brilliant brand.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
BY JULIA HANNA
Harvard Business School Professor and historian Nancy Koehn has studied Starbucks and its leader, Howard Schultz , for close to 20 years. For her, the company represents much more than a phenomenal success story.
In a recently published case, "Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal," (available soon) Koehn and coauthors Kelly McNamara, Nora Khan, and Elizabeth Legris trace the dramatic arc of the company's past seven-plus years—a period that saw Starbucks teeter on the brink of insolvency, dig deep to renew its sense of purpose and direction, and launch itself in new, untested arenas that define the company as it exists today.
"This case distills 20 years of my thinking about the most important lessons of strategy, leadership, and managing in turbulence in the frame of a very relevant company," says Koehn, the James E. Robison Professor of Business Administration. "As a brand, leadership, and entrepreneurship scholar, I've been dogging Starbucks for a long time."
On a 1995 trip to Seattle, Koehn visited a Starbucks store for the first time and was struck by what she saw and felt. The notion of a "third place" between home and work to relax and enjoy the small, affordable luxury of a special coffee beverage seemed to resonate with the social and economic moment, she recalls. Six months later she met Howard Schultz, an entrepreneur who acquired the company in 1987, and was struck by his seriousness of purpose and the breadth of what he wanted to accomplish.
Starbucks Chairman Howard Schultz (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
The case, Koehn's fourth to focus on Starbucks, opens in February 2007. Schultz, no longer Starbucks' CEO but still its chairman, is worried the company is losing its ability to be true to its values while providing a store experience that conveys a sense of comfort, connection, and respect for its product and the communities Starbucks serves.
So Schultz composed a heartfelt, searching memo to senior leadership. In it, he bemoaned decisions (for which he accepted responsibility) that improved efficiency and increased economies of scale but robbed stores of some of their essential magic, such as the smell of roasting coffee and the sights and sounds of traditional Italian espresso machines and baristas at work.
He also cited the company's rapid expansion and the potential "commoditization" of the Starbucks brand. "[W]e desperately need to look into the mirror and realize it's time to get back to the core and make the changes necessary to evoke the heritage, the tradition, and the passion that we all have for the true Starbucks Experience," Schultz wrote.
The scope and richness of Koehn's case gives it the feel of a page-turning novel; in that sense, Schultz's memo is the inciting action for all that follows.
Remaining True To Core Values
The challenge that had confronted Starbucks in the early- and mid-2000s was one common to many organizations: Could the company continue to grow while preserving its culture and values? In some areas, the drive to expand, egged on by Wall Street, was compromising the company's ability to invest in its partners (Starbucks' term for its employees), deliver personalized customer service, and maintain a close connection to the local community.
In addition, McDonald's and Dunkin' Donuts had emerged as serious competitors, offering their own lines of specialty coffee beverages. Even so, Starbucks' financials for 2007, the year Schultz composed his memo, didn't look so bad. But the entrepreneur became concerned as he dug more deeply into the numbers. Sure, revenues were up almost 21% over the previous year, but had slowed by over a third; transactions per store were up 1%, versus 5% the year before. Same-store sales rose only 5%, the smallest increase in five years.
In January 2008, Schultz returned as Starbucks CEO, replacing Jim Donald, the man he and other senior colleagues had chosen to lead the company.
Starbucks Sails Again
The case chronicles the blizzard of decisions and initiatives that follow what could have been the company's death knell as the financial crisis hit home and consumers cinched their belts.
"Schultz understood that you can't lift your foot off the gas pedal when you're attempting to transform a company," Koehn says. "Severe as its financial needs may be, you also have to figure out what you will invest in. Schultz knew that if he waited until the company was out of the woods to invest in new products, communication channels, and ways of doing business it would be too late—Starbucks would no longer be relevant."
From the start, Schultz sent the clear, unwavering message that Starbucks' transformation would represent a return to its roots and an uncompromising commitment to core values, such as health care benefits for any partners working at least 20 hours a week.
At a March 2008 gathering of 200 senior-level company leaders, Schultz unveiled a Transformation Agenda that included seven "Big Moves":
- Be the undisputed coffee authority;
- Engage and inspire our partners;
- Ignite the emotional attachment with our customers;
- Expand our global presence—while making each store the heart of a local neighborhood;
- Be a leader in ethical sourcing and environmental impact;
- Creative innovation growth platforms worthy of our coffee;
- Deliver a sustainable economic model.
The case provides a behind-the-scenes look at how the coffee company moved forward on these goals, including the introduction of the milder Pike Place Roast; the story of its VIA Ready Brew line; the launch of a loyalty program; investment in and engagement with social media; focus on a global expansion strategy; and the extension of social programs. The company closed stores, restructured its manufacturing and supply operations, and, perhaps most significantly, took steps to reengage its partners and store managers. In February 2008, Starbucks closed more than 7,000 of its stores across the country for "Espresso Excellence Training," taking the time to work with approximately 135,000 baristas to ensure they could pour a perfect espresso shot and steam milk properly.
For Schultz, however, that wasn't enough—he wanted to reach the company's store managers, recognizing them as essential to the transformation process.
"I needed an unfiltered venue for expressing my empathy about all that we were asking our partners to do and telling them plainly what was at stake," he wrote in Onward: How Starbucks Fought for Its Life without Losing Its Soul . The answer, in Schultz's mind, was a three-day conference in New Orleans in October 2008, a moment when the global economy happened to be tanking. Starbucks' fourth quarter profits were down 97% from the same time a year earlier; for the fiscal year, net earnings were down 53% to $316 million. The Starbucks board was reluctant to send 10,000 partners to New Orleans at a cost of $30 million, but Schultz stuck to his guns.
In addition to rolling up their sleeves and taking part in community service projects to aid areas of the city still recovering from Hurricane Katrina, partners participated in team-building events that reviewed the company's guiding principles and reminded them of their central role in the customer experience. Schultz also brought in Bono, lead singer of U2, to announce a partnership to channel proceeds from holiday beverage sales to the Global Fund in support of AIDS relief programs in Africa.
The New Orleans conference was a turning point for Starbucks; in the "novel" of Koehn's case, it's the climax.
"Investing in a conference of that size is such an unusual thing to do when faced with a cash crunch," Koehn says. "Schultz understood that what saves and breaks businesses is much more than cash. In the midst of so much turbulence, it's all too easy to pull levers on the low-hanging fruit of cash and logistics. But you don't save a business and turn it around without speaking to, focusing, and calling on the spirit of your people."
Schultz's experience qualifies him for closer study in Koehn's HBS course Power and Glory in Turbulent Times: The History of Leadership from Henry V to Steve Jobs. Not all managers are confronted in their careers with the sort of transformation challenge faced by Starbucks, but Schultz's reflections and actions are instructive for anyone charged with finding sources of strength, innovation, and renewal in today's turbulent business environment, Koehn says.
About the author: Julia Hanna is associate editor of the HBS Alumni Bulletin .
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How Starbucks’s Culture Brings Its Strategy to Life
- Varya Davidson
- Paul Leinwand

They focus on a few positive attributes and amplify them.
In most organizations, culture and strategy tend to be discussed in separate conversations. Executives know that culture is important and that a negative culture can hurt company performance, but they often don’t know what to do about it. Or they attempt to improve the situation by launching a culture initiative to “make the workplace more positive.” What most executive teams typically fail to do is to connect the company’s culture with how the company makes its strategy work.
- Varya Davidson leads the people and organization business for Strategy& in Australia, Southeast Asia, and New Zealand and sits on the Katzenbach Center’s global leadership team. She is a partner with PwC Australia, and has worked with leading public and private sector organizations across Europe, the Middle East, North and South America and Asia-Pacific.
- Paul Leinwand is a principal at PwC U.S., a global managing director at Strategy&, and an adjunct professor at Northwestern’s Kellogg School. He is a coauthor, with Mahadeva Matt Mani, of Beyond Digital: How Great Leaders Transform Their Organizations and Shape the Future (HBR Press, 2022).
Partner Center
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- HBS Case Collection
Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 71
Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal analyzes the turnaround and reconstruction of Starbucks Coffee Company from 2008 to 2014 as led by CEO and co-founder Howard Schultz. The case offers executives and students an opportunity to examine in depth how Schultz and his team saved Starbucks from near-collapse, by both executing a deep, comprehensive return to its core values and, at the same time, investing in a range of new products, customer experiences and organizational capabilities designed to make the company fit for enduring success in a turbulent global economy. Set against the backdrop of the Great Recession, the case also considers the impact of unprecedented important shifts in consumer spending and confidence as well as new competitive forces on Starbucks' transformation. The case concludes by examining Schultz's own leadership journey, the lessons he learned personally during Starbucks transformation, and how he is using these lessons—within Starbucks and on the national stage—to redefine the roles and responsibilities of a public corporation in the 21st century.
Based on extensive interviews conducted with Schultz and other Starbucks executives from 2011 to 2014, the case offers a range of vital lessons on leadership, organizational transformation, restructuring, strategy, innovation, entrepreneurial vision, and customer service.
About The Author
Nancy F. Koehn
Related work.
- June 2014 (Revised March 2016)
- Faculty Research
- Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal By: Nancy F. Koehn

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
From unique store experiences to tailored product launches, Starbucks consistently adapted its offerings to cater to diverse tastes. In essence, the Case Study of Starbucks illuminates a narrative of coffee, community, and corporate strategy, culminating in Starbucks’ reign as the coffee king.
Starbucks is the global leader in Coffee Industry. Read Starbucks case study - World's most popular coffee chain and know its history & growth.
In this Starbucks case study, we will explore its competitors and how Starbucks consistently rises above them, showcasing its resilient Starbucks marketing strategy. Dunkin’ Donuts Renowned for its extensive range of coffee blends and delectable baked goods, Dunkin’ Donuts has established itself as a favourite among coffee enthusiasts and ...
We'll explore case study of Starbucks change management, discussing their need for change, strategies implemented and challenges faced.
Harvard Business School Professor and historian Nancy Koehn has studied Starbucks and its leader, Howard Schultz, for close to 20 years. For her, the company represents much more than a phenomenal success story. In a recently published case, "Starbucks Coffee Company: Transformation and Renewal," (available soon) Koehn and coauthors Kelly ...
Harvard Business School Professor and historian Nancy Koehn has studied Starbucks and its leader, Howard Schultz, for close to 20 years. For her, the company represents much more than a...
How Starbucks’s Culture Brings Its Strategy to Life. In most organizations, culture and strategy tend to be discussed in separate conversations. Executives know that culture is important and ...
Based on extensive interviews conducted with Schultz and other Starbucks executives from 2011 to 2014, the case offers a range of vital lessons on leadership, organizational transformation, restructuring, strategy, innovation, entrepreneurial vision, and customer service.