
Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation

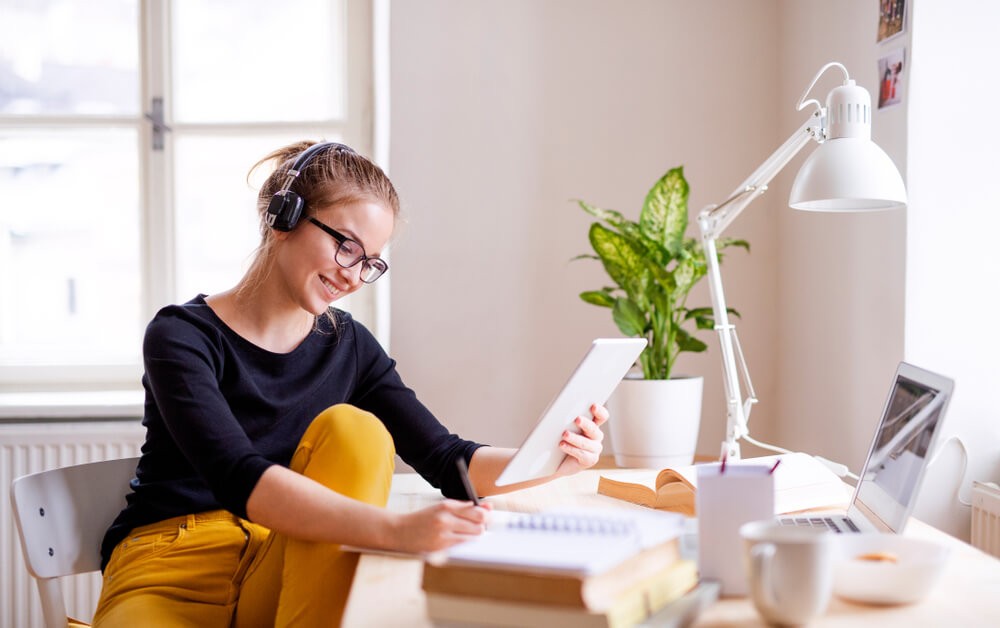
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
Earning a Ph.D. is a remarkable academic achievement, often seen as the pinnacle of one’s educational journey. It’s a pursuit that demands unwavering dedication, intellectual prowess, and an unshakable commitment to research. Yet, when setting out on this academic odyssey, prospective doctoral students often find themselves grappling with a common question: How long will it take to reach the coveted destination of a PhD?
In the world of academia, where timeframes can be as diverse as the subjects studied, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The duration of a PhD program can be influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from the chosen field of study to the country in which one embarks on this intellectual voyage.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the intricate web of considerations that determine the timeline of a Ph.D. We’ll delve into the typical duration, international variations, the stages of the Ph.D. journey, and even the strategies that can expedite or prolong this academic quest.
Through real-life experiences and insights, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the fascinating, challenging, and often unpredictable timeline associated with pursuing a PhD.
So, if you’ve ever wondered about the time commitment required for a PhD, join us on this educational voyage as we uncover the secrets of this academic adventure and navigate the complex terrain of doctoral studies.
Introduction
Factors influencing phd duration, typical duration of phd, phd duration: variations by country, stages of a phd program, shortening the phd timeline, lengthening the timeline of phd.
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is the highest academic degree one can attain. It represents expertise in a specific field and often involves original research contributing to the world’s knowledge. However, this academic feat isn’t for the faint of heart. To embark on this journey, you should be aware of the formidable challenges it presents, and one of the most fundamental questions is, “How long will it take?” In the introduction, you can touch upon the idea of academic ambition, the pursuit of knowledge, and the unique challenges that come with obtaining a Ph.D.
It’s essential to emphasize why understanding the time commitment is crucial. Pursuing a Ph.D. isn’t just an intellectual endeavor; it’s also a significant personal and professional commitment. It can impact one’s life, career, and even mental and emotional well-being. You can mention that by knowing what you’re getting into time-wise, you can make informed decisions about your academic and career goals. For instance, if you’re aware that a Ph.D. typically takes several years, you can plan your life accordingly, set expectations, and ensure you have the necessary resources and support in place.
Imagine standing at the crossroads of ambition and dedication. You’re passionate about a particular field, and the thought of making a meaningful contribution to it excites you. You dream of becoming a respected expert, perhaps even shaping the future of your discipline. This ambition has led you to consider pursuing a PhD, a journey that represents the highest echelon of academic achievement.
But before you dive into the world of research, scholarly papers, and intellectual debates, there’s a critical question that looms large—how long will it take to earn that coveted Doctor of Philosophy degree? The answer isn’t as straightforward as one might hope. It’s a complex equation, influenced by various factors, and it’s a puzzle that many aspiring doctoral students grapple with.
Understanding the time commitment of a PhD is not merely a matter of academic curiosity. It’s a pivotal factor that can shape your life’s trajectory in significant ways. This introduction explores the intricacies of a PhD journey, from the initial spark of academic passion to the profound understanding of what it takes, in terms of time, to turn that passion into a doctoral reality.
Earning a PhD is a highly individualized journey, and its duration can vary significantly from person to person. This section will delve into the myriad factors that play a role in determining the length of a PhD program. It’s important to understand that the timeline is not a fixed number of years but is influenced by various variables. Here are some key factors:
- Field of Study: The nature of your research area has a significant impact. Some fields, such as the natural sciences or engineering, might require extensive laboratory work and data collection, which can lengthen the Ph.D. process. In contrast, fields like humanities or social sciences might involve less time-intensive data collection but demand extensive writing and analysis.
- Country: The country in which you pursue your PhD can greatly affect the duration. Different countries have different academic systems and expectations. For example, in the United States, it’s common for PhD programs to last longer compared to some European countries where they tend to be shorter and more structured.
- Research Focus: The specific focus of your research project can influence the time required. If your research involves cutting-edge, complex topics, it might take longer to gather and analyze data or develop new methodologies. On the other hand, a well-defined and less ambitious research question could lead to a quicker completion.
Let’s take a closer look at the intricate web of factors that influence the duration of a PhD program. Imagine two students, both embarking on their journeys to earn a PhD, but in different fields.
Student A is pursuing a PhD in physics. This field often involves conducting elaborate experiments, gathering extensive data, and fine-tuning intricate instruments. The pursuit of new discoveries in the realm of physics can be time-consuming, and the PhD program might extend to several years to complete all the necessary research.
Student B, on the other hand, is studying literature and cultural studies. Their research involves in-depth analysis of existing texts, interpretations, and critical theories. While the reading and writing process is extensive, it may not require as many years as Student A’s experimental work.
Now, consider these students in the context of the country in which they are pursuing their PhD Student A is in the United States, where doctoral programs typically span several years. Meanwhile, Student B is in a European country known for its structured and shorter Ph.D. programs.
Lastly, let’s factor in research focus. Student A’s project is ambitious, attempting to uncover the mysteries of the universe, which can be a time-intensive endeavor. In contrast, Student B’s research question is more narrowly defined, making the path to completion relatively shorter.
These examples illustrate how the combination of field of study, country, and research focus can significantly influence the duration of a PhD program.
Understanding the average duration of a PhD program can help prospective students set realistic expectations. This section will provide an overview of the typical timeframes for completing a PhD.
- Average Duration: On a global scale, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes coursework, research, and the writing and defense of a dissertation. However, it’s important to note that this duration can vary significantly. In the United States , for instance, it’s common for PhD programs to take longer, often 5 to 7 years or even more, due to the inclusion of coursework and comprehensive exams. In contrast, in some European countries, PhD programs are designed to be shorter, typically around 3 to 4 years, as they are research-focused with less emphasis on coursework.
- Variations by Field: The average duration can also differ based on the field of study. Fields requiring extensive data collection, such as the natural sciences or engineering, might take longer, while fields like humanities or social sciences with more writing and analysis may have shorter timeframes.
When it comes to the average duration of a PhD program, the common adage ‘it’s a marathon, not a sprint’ certainly applies. The typical journey to a PhD is a long and demanding one, taking aspiring scholars through a series of rigorous academic challenges.
Globally, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes the initial coursework phase, where students delve deep into the theoretical foundations of their field. This is followed by a substantial research phase, during which they gather data, conduct experiments, or engage in extensive fieldwork. Finally, the culmination of this journey is the completion and defense of a dissertation, a written document that contributes new knowledge to their field.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these timeframes are general averages and can vary significantly based on various factors. In the United States, for example, it’s quite common for PhD programs to extend to the longer end of the spectrum, taking 5 to 7 years or even more to complete. This is because American PhD programs often include a significant coursework component and comprehensive exams before the dissertation phase begins.
On the other hand, in some European countries, PhD programs are designed to be more streamlined and research-focused. They typically take around 3 to 4 years to complete, reflecting a shorter timeframe. This structure is influenced by the belief that students entering PhD programs are already well-prepared in their chosen field, and the primary focus is on conducting independent research.
Additionally, the duration can also vary based on the specific field of study. Fields that require extensive data collection or experimental work, such as the natural sciences or engineering, tend to have longer PhD programs. In contrast, fields like humanities or social sciences, where research involves more reading, writing, and analysis, may have shorter timeframes.
Keep in mind that these are general guidelines, and individual PhD experiences can deviate from the average.
Ph.D. program durations can vary significantly between countries due to differences in educational systems and academic traditions. This section will explore how and why PhD programs’ lengths differ by country.
- United States: In the United States, PhD programs are known for their comprehensive structure. They often include a combination of coursework, comprehensive exams, and dissertation research. This makes them typically longer, often spanning 5 to 7 years or more.
- European Countries: In many European countries, PhD programs are more streamlined and research-focused. They tend to be shorter, typically around 3 to 4 years. European programs often assume that students have a strong foundation in their field when they enter the Ph.D. phase.
- Other Countries: The duration of PhD programs can also vary in other parts of the world. For instance, in some Asian countries, the length of a PhD program can be influenced by the nature of the research and the institution’s specific requirements.
When contemplating the pursuit of a Ph.D., it’s important to recognize that the path you tread can be markedly different depending on the country in which you choose to study. The world’s countries have diverse academic systems and traditions, and these intricacies play a significant role in shaping the duration of PhD programs.
Consider the United States, a country renowned for its rigorous academic programs. Here, PhD programs are known for their comprehensive nature. Students often undergo a period of intensive coursework, followed by comprehensive exams to assess their knowledge. This is in addition to the research phase, which involves conducting experiments, gathering data, or delving deep into the chosen area of study. As a result, PhD programs in the United States are often among the longer ones, frequently taking 5 to 7 years or even more to complete.
In contrast, many European countries have adopted a more streamlined approach to PhD programs. These programs tend to be research-focused from the outset, with the assumption that students entering PhD programs already possess a strong foundation in their chosen field. The result is a shorter program, typically spanning around 3 to 4 years. In countries like the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Denmark, students can transition directly into their research, which contributes to the shorter duration.
Outside of the United States and Europe, PhD program lengths can vary significantly depending on the country’s educational system and specific institutional requirements. For instance, in certain Asian countries, PhD programs might also be research-intensive and shorter in duration, or they might extend to accommodate the complexity of the research involved.
It’s important to understand these country-specific variations when considering a PhD program, as they can have a profound impact on the length of your academic journey.
A Ph.D. program is not a single, continuous journey but is typically divided into distinct stages. This section will provide an overview of the common stages of a PhD program, which include coursework, research, and dissertation writing.
- Coursework: The journey usually starts with a coursework phase, where students dive deep into the theoretical foundations of their field. During this stage, students take classes and seminars to build a strong academic foundation. The duration of this stage varies by country and field but generally lasts from 1 to 2 years.
- Comprehensive Exams: In some countries, notably the United States, students are required to pass comprehensive exams to demonstrate their mastery of their field. This stage can add a few months to a couple of years to the timeline.
- Research Phase: After coursework and exams, students transition into the research phase, which is the heart of a Ph.D. program. This phase involves conducting original research, experiments, fieldwork, or in-depth analysis, depending on the field of study. It can last several years, usually 3 to 5 years or more, depending on the complexity of the research and the progress made.
- Dissertation Writing: The final stage involves writing the PhD dissertation, a comprehensive document that presents the research findings and contributes to the academic field. The duration of this stage varies but often takes at least a year.
A PhD program is akin to an academic epic, with distinct stages that collectively make up the hero’s journey. As an aspiring doctoral candidate, it’s essential to understand the key stages you’ll encounter along the way.
The odyssey begins with coursework. During this initial stage, students embark on a voyage into the theoretical underpinnings of their chosen field. They attend classes, seminars, and lectures to deepen their understanding. This coursework phase, which can last anywhere from 1 to 2 years, serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the journey is built.
In some countries, particularly the United States, there’s another formidable challenge—comprehensive exams. These exams test the student’s mastery of the field’s core concepts and are often required before moving on to the next stage. Comprehensive exams can extend the journey by several months to a couple of years.
The heart of the PhD journey lies in the research phase. This is where students immerse themselves in original research, which could entail conducting experiments, gathering data, or engaging in extensive fieldwork, depending on their field of study. The duration of this stage is the most variable, spanning approximately 3 to 5 years or even longer, depending on the complexity of the research and the progress made.
Lastly, the culmination of the PhD adventure is the dissertation writing stage. Here, students craft a comprehensive document that presents their research findings, methodology, and contributions to the academic field. This final stage can vary in length but often takes at least a year to complete.
These stages collectively shape the journey towards a PhD, and understanding them is vital for anyone embarking on this academic odyssey.
While earning a Ph.D. is a significant commitment, there are strategies to expedite the process. This section will discuss strategies and approaches that can help shorten the timeline of your PhD journey .
- Efficient Time Management: Effective time management is essential for expediting a PhD program. Planning and prioritizing tasks, setting clear goals, and maintaining a structured schedule can help students make the most of their research and coursework, reducing the time spent on unnecessary or unproductive activities.
- Choosing the Right Advisor: The relationship between a Ph.D. student and their advisor can significantly impact the program’s duration. A supportive and experienced advisor can guide the student effectively, provide valuable insights, and help them navigate research challenges more efficiently. A strong advisor-student relationship can lead to better research progress and a quicker completion.
- Prior Research Experience: Entering a PhD program with prior research experience can be a significant advantage. If you’ve already conducted research related to your PhD topic during a master’s program or as an undergraduate, you may be able to accelerate your research and data collection, potentially shortening the overall timeline.
When it comes to earning a PhD, the duration can be an intimidating factor. However, it’s important to remember that there are strategies that can help expedite the journey. Let’s explore some of these approaches:
One of the most fundamental strategies is efficient time management. Effective planning, prioritization, and maintaining a structured schedule can make a world of difference. By setting clear goals and staying organized, students can optimize their time and reduce the risk of distractions or time wasted on non-essential activities. This approach ensures that every moment spent on research or coursework is meaningful and productive.
Another pivotal factor is the choice of an advisor. The advisor-student relationship plays a crucial role in a Ph.D. program. A supportive, experienced, and engaged advisor can guide a student through the research process more effectively. They can offer valuable insights, help troubleshoot research challenges, and provide a sense of direction. With the right advisor, students often find themselves making more efficient progress and thus shortening the overall timeline of their PhD journey.
For those entering a PhD program with prior research experience, there’s an advantage. If you’ve already dabbled in research during your master’s program or as an undergraduate, you’re poised for a quicker start. The knowledge, skills, and methodologies you’ve acquired can significantly expedite your research and data collection, potentially helping you complete your PhD in less time.
These strategies, when applied thoughtfully, can make the road to a PhD a bit smoother and shorter, ultimately allowing students to achieve their academic goals more efficiently.
While shortening the Ph.D. journey is a common goal, there are situations that can unexpectedly lengthen the timeline. This section will discuss various reasons a Ph.D. might take longer than expected, including research challenges and personal circumstances.
- Complex Research Challenges: Research is at the core of a Ph.D., and sometimes, research challenges can extend the timeline. For instance, unexpected technical issues, data collection difficulties, or unanticipated roadblocks in the research process can delay progress. Dealing with these complexities often requires additional time and problem-solving efforts.
- Scope of the Project: Sometimes, students may underestimate the scope of their research project. If the research topic turns out to be more extensive or multifaceted than initially anticipated, it can lead to a longer journey. Expanding the research scope can also be driven by a desire to make a more substantial contribution to the field.
- Personal Circumstances: Personal circumstances can also play a significant role in lengthening the timeline. Life events, such as family responsibilities, health issues, or other personal challenges, can disrupt the academic trajectory and extend the Ph.D. program.
While aspiring doctoral candidates often set out with the goal of completing their PhD as efficiently as possible, it’s important to acknowledge that unexpected factors can sometimes extend the journey. Let’s delve into some of the reasons a PhD might take longer than initially expected:
One of the most common factors is research challenges. Research is the backbone of a Ph.D., and it’s not uncommon to encounter unanticipated complexities along the way. For instance, imagine a Ph.D. student in the field of environmental science who encounters technical issues with specialized equipment required for data collection. These unexpected hurdles can require additional time and effort to resolve, extending the research phase.
Another factor that can elongate the timeline is the scope of the project. Sometimes, students may begin their research with a particular understanding of the project’s scale, only to discover that the topic is more extensive or multifaceted than initially thought. This realization can lead to an expansion of the research scope, often driven by the desire to make a more significant and impactful contribution to the field. While noble in its intent, this expansion can result in a longer and more extensive research phase.
Personal circumstances can also have a profound impact. Life doesn’t always adhere to the academic calendar, and various personal challenges can disrupt the PhD journey. These challenges can include family responsibilities, health issues, or other unforeseen life events. Balancing these personal circumstances with academic commitments can sometimes lead to a longer timeline for completing a PhD.
It’s crucial to recognize that while we often have our sights set on a timely completion, the PhD journey can be influenced by a myriad of unforeseen factors. Overcoming these challenges is a testament to resilience and dedication in the pursuit of knowledge.
I have written several articles related to PhD. You can visit them Here. These articles will guide you in the smooth completion of your PhD.
An unconventional PhD demands quality publications and presentations. I have written articles related to Research Journals and Research Conferences. Please visit them
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
To sum it up, figuring out how long a Ph.D. takes is like solving a puzzle. In the U.S., it’s a bit like a long journey, taking about 5 to 7 years, while in Europe, it’s more like a focused sprint, finishing in about 3 to 4 years.
We also learned about the different stages of a Ph.D., from classes to big research and a huge paper called a dissertation. Some folks speed up their Ph.D. by managing time well, picking a good advisor, or using past research experience. But unexpected stuff, like tough research problems or personal things, can make the Ph.D. journey longer.
In Ph.D. land, time is like money you spend to learn and get smart. Whether someone is thinking about starting a Ph.D. or already on the journey, it’s their special story. Enjoy the good parts, handle the tough bits, and feel proud of becoming a real expert, adding to what everyone knows together.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- PhD Study in the USA - 2024
Over one million international students choose the USA as their study abroad destination, making it the most popular international study destination in the world! America is known for its comprehensive approach to postgraduate education, combining enhanced subject knowledge and research opportunities with the development of a suite of transferrable skills.
Why study a PhD in the USA?
- Accessibility – A US graduate programme takes longer than a UK PhD, but this can also help you find your feet as a PhD student. The taught elements mean you have more time to develop a more detailed understanding of your subject as the basis for your own research.
- World-leading universities and research – Rankings aren’t everything, but the global league tables continue to be dominated by US institutions. Amongst other things, this reflects the country’s substantial investment in research output and expertise.
- International community - American universities host huge numbers of students from across the world. Whatever and wherever you study, you’ll be welcomed as part of a diverse academic community.
- Innovation – America was the second country ( after Germany ) to adopt the modern PhD degree. Its own structured approach to doctoral training is also now influencing PhD study in the UK and Europe .
If you’re interested in studying your PhD in the USA, we’ve covered everything you need to know in our selection of guides below, including applications , visas and funding .
Search for a PhD in the USA
Ready to start looking for your ideal study abroad opportunity? Browse and compare PhD programmes in the USA on FindAPhD.com.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice

Everything you need to know about part-time and full-time work as a student or recent graduate in the USA.

Why you'll need health insurance as an international student in the USA and how to find the right plan for you.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a PhD in the USA.

Our guide to PhD funding in the USA has information on fully-funded PhD scholarships, as well as other funding options for international and domestic students.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How the PhD Program Works
Program Overview
Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending your doctoral dissertation.
Admission to candidacy.
You begin by taking courses required for your program of study. All programs requires a preliminary exam, which may be either oral or written.
Some programs may have further requirements, such as an additional exam or research paper. If you enter with a master’s degree or other transfer credit, you may satisfy the formal course requirements more quickly.
Beginning the Wharton PhD Curriculum How the first two years of the Wharton program helped students discover their interests, learn the tools of the profession, and fuel their passion for teaching.
The Doctoral Dissertation
Upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, you are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies.
Your doctoral dissertation should contain original research that meets standards for published scholarship in your field. You are expected to be an expert in the topic you choose to research.
You are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, but you can start thinking about and working on research of relevance at any time.
The dissertation process culminates with a “defense,” in which you defend the proposal orally before your dissertation committee.
While working on your dissertation, you interact extensively with Wharton faculty. Together with interested faculty, you create your own research community that includes your dissertation advisor and dissertation committee.
Policies and Procedures
Get more detailed explanation of course requirements, academic standards, the Teacher Development Program, time limits, and dissertation procedures and requirements.
Sample Program Sequence
Years 1 & 2.
Coursework Examination Research Papers Research Activities Field-Specific Requirements
Directed Reading & Research Admission to Candidacy Formulation of Research Topic
Years 4 & 5
Continued Research Oral Examination Dissertation
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
Why this phd student chose to study business ethics at wharton, closing the tenure gap for business faculty of color.
The Wharton School
How This PhD Student Discovered a Dynamic Research Community at Wharton
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
How Long Does It Take to Earn a PhD?

Cece Gilmore is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cece earned her undergraduate degree in Journalism and Mass Communications from Arizona State University. While at ASU, she was the education editor as well as a published staff reporter at Downtown Devil. Cece was also the co-host of her own radio show on Blaze Radio ASU.
Learn about our editorial policies

Cari Schultz is an Educational Review Board Advisor at Scholarships360, where she reviews content featured on the site. For over 20 years, Cari has worked in college admissions (Baldwin Wallace University, The Ohio State University, University of Kentucky) and as a college counselor (Columbus School for Girls).

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

How long is a PhD program? That might be one of the first questions you ask yourself If you are thinking of earning a PhD. You have probably heard a range of years, and that is because how long it takes to earn a PhD depends on a number of factors. Keep reading to learn more!!
What is a PhD?
PhD stands for a “Doctorate of Philosophy.” This is an academic degree that qualifies the degree holder to teach their chosen subject at university level or to work in a specialized position in their chosen field. In general, the PhD is the highest level of degree a student can achieve.
Also see: Top fully funded PhD programs
Why get a PhD?
A PhD is a serious commitment with a serious return on investment. Here is a list of professional and personal benefits for earning a PhD.
| Career advancement | Achieving a sense of accomplishment |
| Higher earning potential | Financial stability |
| Teaching and mentoring | Improvement of social skills |
| Networking and collaboration | Increased recognition |
| Scholarly respect | Enhanced self-confidence |
How long does it take to earn a PhD?
Earning a PhD usually takes between four and seven years to complete, depending on the type of PhD as well as the schools requirements, the students educational background, and personal progress. Students who take full-time classes can typically finish in four years. A typical PhD program requires anywhere from 60 to 120 semester credit hours .
Why earning a PhD takes years to earn
Assistantship obligations.
Teaching and research assistantships can be very beneficial for the experience they provide and the potential funding, but they can also be time consuming obligations for PhD students. Therefore, assistantships may affect the amount of time it takes to complete a PhD program.
Comprehensive examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness in a PhD program through comprehensive exams. These comprehensive exams may be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- Comprehensive exams or “Comps”
- General examinations
Dissertation
A dissertation is an in-depth research document that serves as the culmination of a doctoral program. It is an important document that demonstrates a student’s original research and contribution to their field of study.
The dissertation involves conducting extensive research, reviewing previous literature, analyzing data, and presenting your findings in a structured manner. Once the dissertation is completed, it is typically defended orally in front of a committee of faculty members who assess the quality and validity of the research.
Average PhD timeline
The specific of a PhD timeline carried by college and university. However, the following is a good overview of the average PhD program.
- Year 1: Take advanced courses
- Year 2: Take advanced courses and begin preparing for exams
- Year 3: Study, take and defend your comprehensive exams and begin researching your dissertation proposal
- Year 4: Begin working on your dissertation
- Year 5: Finish and defend your dissertation
Average PhD completion by focus
According to data from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics the average time in years from graduate school entry to doctorate it took students to receive their degree in 2020 in certain fields is listed below.
- Life sciences = 6.9 years
- Physical sciences and earth sciences = 6.3 years
- Mathematics and computer sciences = 7.0 years
- Psychology and social sciences = 7.9 years
- Engineering = 6.8 years
- Education = 12.0 years
- Humanities and arts = 9.6 years
- Other non-S&E fields = 9.3 years
Related : Top 10 PhD in Education programs
How to finish your PhD is less time
Look for accelerated classes.
Accelerated courses are an easy way to reduce the amount of time it takes to finish a PhD. Therefore, look into if your program offers any shorter courses.
Work on your dissertation throughout the program
Working on your dissertation little by little throughout the program will allow you to speed up your doctoral timeline. In addition, it may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project.
Maintain regular communication with your advisor
Establish regular communication with your advisor or supervisor. Regular meetings can help you receive guidance, address any issues, and ensure you are heading in the right direction.
Seek feedback early and often
Share your work and progress with your advisor, peers, or other trusted individuals often. Then, you should incorporate suggestions and revisions as you go along. This will help you refine your work and avoid major revisions later.
Maintain a healthy school-life balance
While it is important to be dedicated to your PhD, it’s just as important to maintain a healthy work-life balance. Therefore, be sure to prioritize yourself! While finishing your PhD in less time is a great feat, it is important that you are not sacrificing your well-being while doing so.
Key Takeaways
- PhD stands for “doctorate of philosophy” and is generally the highest level of degree a student can earn
- There are many professional and personal benefits to earning a PhD which can lead to a serious return on investment
- A PhD program typically takes 4-7 years to complete. However, it can take longer or shorter depending on personal circumstances and field of study
- With planning and guidance from advisors, students can sometimes complete PhDs in less time
Start your scholarship search
- Vetted scholarships custom-matched to your profile
- Access exclusive scholarships only available to Scholarships360 members
Frequently asked questions about how long it takes to earn a PhD
Do i need to have a master’s degree to get a phd, what is the easiest phd to earn, can i finish my phd earlier than the estimated time frame, what happens if i don’t complete my phd within the expected timeframe, can i work while pursuing a phd, can i accelerate the process of earning a phd, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!
- Home »
Studying a PhD in The USA - The Complete Guide
Find your perfect postgrad program search our database of 30,000 courses.
The USA is a favourable postgraduate study destination for international students due to the high standard of academic study and the wide variety of subjects. By undertaking a PhD in the USA, you will find yourself becoming an internationally recognised expert in your chosen field.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) from the USA is considered the highest awarded degree in many US universities and institutes for most fields of study. For many international students, it's a dream course that offers an exciting new life chapter.
Attending Grad School for a PhD in the USA is not the same as undertaking a PhD in Europe or the UK , it can often be a different experience. However, studying abroad will improve your global cultural understanding in addition to your network of contacts for your future career. A PhD degree is often required when you apply for high-level management jobs, government expert positions, and careers like a university professor, researcher, or scientist in many fields.
There are a multitude of reasons why the United States is a fantastic choice for your PhD studies. Here’s everything you need to know about studying a PhD in the USA.
1. PhD course length
The total length of a PhD in the USA is between 4-8 years for full-time students and 8-10 years for part-time students, depending on your field of study. PhDs can be completed in 4-5 years for students with a masters degree in an appropriate subject. Students typically dedicate 1-4 years on coursework, followed by 2-4 years of dissertation work. In the USA, the academic year is divided into two teaching semesters: August to December and January to May.
Having a longer duration for your PhD allows for greater opportunities to adjust to your course and find your footing. This enables you to concentrate on developing a more comprehensive understanding of your chosen subject at a more relaxed pace.
2. World-class universities
The US repeatedly tops the charts of worldwide ranking universities , so what better place to do your PhD studies? Although rankings shouldn’t be the main deciding factor when making your PhD choice, they're a great indicator of educational expertise.
There are many factors to consider when choosing the location for your PhD. Does the university have a high employability rate after graduation? Are you wanting to go public or private university? What kind of research facilities do they have?
Be sure to do some research before making a decision on your perfect place of study.
3. International community
The United States is a popular choice for international students from all over the world – making it an inspirational and cosmopolitan choice for your PhD studies. No matter what your choice of academic study is, you are guaranteed to find a diverse community that welcomes students from all backgrounds.
4. Affordable tuition fees
There are various tuition fee options available for PhD students regardless of your budget. The American higher education system is often associated with high fees and substantial student debt, but in fact, studying at an American university isn't always expensive, and many institutions offer affordable courses. For instance, PhD costs range from $28,000 to $55,000 annually, which shows that finding a PhD course that’s more affordable is possible.
5. Student experience
American universities typically have vibrant campus communities with a wide range of extracurricular activities, clubs and organisations. As a student, you will have the opportunity to engage in various social, cultural and recreational activities alongside your academic studies.
6. Student support
American universities typically provide comprehensive support services to assist you on your PhD journey. These services may include academic advising, counselling, career services, libraries, writing centres and various student organisations aimed at fostering your personal and professional development.
7. Land of opportunity
It's fair to say that student life in the USA offers something for everyone, regardless of what you're looking for from a PhD. With 50 states, six time zones, and thousands of higher-education providers, there's an opportunity waiting for every individual across the globe.
So let’s take a look at some of the key factors to consider when studying for a PhD in the USA.
Studying a PhD in the USA: top tips
Who is eligible for a phd in the usa.
To be eligible for PhD in the USA, generally students should have completed a graduate degree with a minimum GPA of 3.0, provide proof of English language proficiency, GRE scores and other supporting documents. The eligibility criteria for a PhD in the USA can vary depending on the specific university and program.
Can I get a PhD without a masters degree?
Yes, you can pursue a PhD without having a masters. Universities in the USA do not require a masters for you to apply. Because of the graduate programs in the US, you will receive your masters degree once you have completed your coursework stage. This practice combines the masters and PhD into one.
The eligibility criteria and requirements for direct entry PhD programs vary among institutions and fields of study, so it is advisable to check the entry requirements of the specific university or course you are interested in.
How to apply for a PhD in the USA
When applying for your chosen subject in the USA, you should expect to provide relevant information and statements to the university. This will include:
Completed application form – provided by your preferred university.
A personal statement – on why you want to study the subject, your research interests and career goals. Be sure to include any extracurricular activities and achievements within the body of your statement.
References – universities will expect that your referees will recommend you for the chosen course.
Test scores and grades – you will generally need to submit scores from standardised tests like the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT).
English language proficiency – international applicants whose native language is not English usually need to provide proof of English language proficiency through tests like the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) or the International English Language Testing System (IELTS). It varies from institution to institution, but international students in the USA are required to have a TOEFL score of about 90.
Samples of work – it is recommended that you provide some work you have done that is relevant to your chosen subject. You may even be asked to complete a small task during the application process.
The application fee.
Method of study
Compared to the UK and Europe , studying a PhD in the USA involves several key differences. Students in the USA are usually in direct contact with their professor, compared with those in the UK where students might find that their PhD program is headed by a professor who gives them a little less flexibility to change their research and study areas. There can be several cultural differences between UK, Europe, and USA university lifestyles. US students are expected to undertake a great deal of teaching and marking, as opposed to PhD students in Europe.
As a result, you may have less free time outside of the university when pursuing a PhD in the USA.
Application for PhD In USA
When applying for your chosen subject, you should expect to provide relevant information and statements to the university. This might include:
A personal statement on why you want to study the subject. Be sure to include any extra-curricular activities and achievements within the body of your statement.
References. Universities will expect that your referees will recommend you for the chosen course.
Test scores and grades. It is important that you provide a list of your awarded grades from previous courses you have studied.
Samples of work. It is recommended that you provide some work you have done that is relevant to your chosen subject. You may even be asked to complete a small task during the application process.
UK and Europe students decide on their PhD thesis subject area before they apply . While taking classes at a graduate level, prospective PhD students in the USA spend up to a year or two deciding on their specific research subject. It is normal to apply for up to six institutions for a PhD in the USA, and students apply to each institution separately as there is no central organisation.
Students in the UK and Europe are expected to apply with an understanding of the subject already, usually in the form of a masters degree, and be ready to start studying at the PhD level straight away. In the USA it is expected that students do not have an in-depth understanding of their subject as they usually only have an undergraduate degree when they apply.
When should I start applying for a PhD in the USA?
Deadlines for applications to PhD programs in the USA tend to be between December and February, and institutions should let you know about your application by April. Most US institutions recommend that you apply as far in advance as you possibly can to give them, and you, plenty of time to make arrangements.
Universities in the USA do not require a masters for you to apply as well. Because of the graduate programs in the US, you will receive your masters degree once you have completed your coursework stage. This practice combines the masters and PhD into one.
It varies from institution to institution, but international students in the USA are required to have a TOEFL score of about 90.
Funding your PhD in USA
PhD students are very likely to receive financial support in the form of PhD scholarships ; some USA PhD students also receive PhD studentships .
Making your PhD application in plenty of time allows you more time to apply for and arrange your PhD funding. Many students find that funding can cover much, or all, of the cost of their PhD studies in the USA, which ranges between $28,000 and $40,000. Deadlines for funding applications can be as early as December before starting your studies in the Autumn/Fall.
There are two types of PhD funding: fully funded, which pays for the student's graduate school tuition fees, accommodation, and living expenses, or partially funded, which pays for the student's tuition only partially or fully.
Can a PhD be fully funded?
Yes, many top universities in the USA offer fully funded PhD programs for eligible students. This funding pays for the student's graduate school tuition fees, accommodation and living expenses. Partially funded PhDs only cover the student's tuition in part or in full.
Some PhD students will receive a stipend from their institution with an assistantship position, but this varies between institutions and between departments within institutions. Other students can find funding from both their own and the American government, and there are plenty of American government schemes like The Fulbright Program that offer funds.
Apply for one of our x5 bursaries worth £2,000
We've launched our new Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries for 2024. Full-time, part-time, online and blended-learning students eligible. 2024 & 2025 January start dates students welcome. Study postgraduate courses in any subject taught anywhere worldwide.

How long does it take to study a PhD in the USA?
For part-time students in the USA, a PhD can take eight to ten years, but it usually takes five to six years for full-time students. PhDs can be completed in four to five years rather than five or six for students with a masters degree in an appropriate subject.
Top 10 ranked American universities
Based on 2024 Times Higher Education's World University Rankings data, the following table shows which US universities rank the highest.
|
|
|
|
| 1 | 2 | Stanford University |
| 2 | 3 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) |
| 3 | 4 | Harvard University |
| 4 | 6 | Princeton University |
| 5 | 7 | California Institute of Technology (Caltech) |
| 6 | 9 | University of California, Berkeley |
| 7 | 10 | Yale University |
| 8 | 13 | University of Chicago |
| 9 | 15 | John Hopkins University |
| 10 | 16 | University of Pennsylvania |
Our PhD bursary winner & funding opportunity
Mohammad Abdollahi is a 35-year-old Iranian student studying a PhD in Operational Research at the University of Essex. He was delighted when he found out he’d been awarded a Postgrad Solutions Study Bursary. As an international student coming to the UK with his wife and two children, it has proved to be an invaluable funding resource as he explains. “It was good news and exciting – I was overwhelmed with joy!”

Related articles
How To Prepare For A PhD Viva
Masters In USA
Lists of Universities in USA
Graduate School USA
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Complete Our Destination Survey

Take 2 minutes to complete our Destination Survey for the chance to win a Postgrad Study Bursary worth £2,000.
All we need to know is:
- Your university
- Your PG course
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to get a phd.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
Frequently asked questions: Graduate school
In the US, most graduate school applications require you to include:
- Transcripts from previous educational institutions
- Standardized test scores (such as the GRE or MCAT)
- A graduate resume
- 2–3 letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
Some programs may ask you to write a personal statement in addition to, or instead of, a statement of purpose. You may also be asked to an interview .
Always carefully read the application instructions for the specific program you’re applying to.
Most medical school programs interview candidates, as do many (though not all) leading law and business schools.
In research programs, it depends—PhDs in business usually do, while those in economics normally do not, for example.
Some schools interview everyone, while others only interview their top candidates. Look at the websites of the schools you’re applying to for more information on whether they conduct interviews.
In addition to thinking about your answers for the most commonly asked grad school interview questions , you should reach out to former and current students to ask their advice on preparing and what sort of questions will be asked.
Look back through your resume and come up with anecdotes that you could use for common questions, particularly those that ask about obstacles that you overcame. If you’re applying for a research program, ensure that you can talk about the previous research experience you’ve had.
You should also read as much research in your field as possible. Research the faculty at the schools you’re applying to and read some of their papers. Come up with a few questions that you could ask them.
Graduate schools often ask questions about why you are interested in this particular program and what you will contribute.
Try to stay away from cliche answers like “this is a good program” or “I got good grades in undergrad” and focus instead on the unique strengths of the program or what you will bring to the table. Understand what the program is looking for and come up with anecdotes that demonstrate why you are a good fit for them.
Different types of programs may also focus on different questions:
- Research programs will often ask what topics you’d like to research and who you would like to work with, as well as specific questions about your research background.
- Medical schools are interested in your personal motivation, qualities such as integrity and empathy, and how you’d respond to common ethical dilemmas.
- Business schools will focus on your past work experience and future career prospects, and may be particularly interested in any experience you have managing or working with others.
Some students apply to graduate school straight from undergrad, but it’s also common to go back to school later in life. The ideal time to do so depends on various financial, personal, and career considerations . Graduate school is a big commitment, so you should apply at a time when you can devote your full attention to it.
Your career path may also determine when you should apply. In some career fields, you can easily progress without a graduate degree, while in others—such as medicine, business, and law—it’s virtually impossible to move up the career ladder without a specific graduate degree.
Most graduate school applications for American graduate programs are due in December or January for a September start.
Some types of programs, especially law school, are rolling applications, meaning that the earlier you apply, the earlier you’ll hear back. In this case, you should aim to apply as early as possible to maximize your chances.
Medical school follows a completely separate timeline with much earlier deadlines. If you’re applying for medical school, you should speak to advisors at your university for more information.
A good starting point to aim for is about 18 months before you would start the program, or 6–9 months before the applications are due.
In the first few months of the process, research programs and study for any standardized exams you might need.
You can then begin writing your personal statements and statements of purpose , as well as contacting people to write your letters of recommendation . Ensure that you give recommenders plenty of time to complete their letters (ideally around 2–4 months).
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
It’s best to ask in person if possible, so first reach out and request a meeting to discuss your graduate school plans.
Let the potential recommender know which programs you’re applying to, and ask if they feel they can provide a strong letter of recommendation . A lukewarm recommendation can be the kiss of death for an application, so make sure your letter writers are enthusiastic about recommending you and your work!
Always remember to remain polite. Your recommenders are doing you a favor by taking the time to write a letter in support of your graduate school goals.
This depends on the program that you are applying for. Generally, for professional programs like business and policy school, you should ask managers who can speak to your future leadership potential and ability to succeed in your chosen career path.
However, in other graduate programs, you should mostly ask your former professors or research supervisors to write your recommendation letters , unless you have worked in a job that corresponds closely with your chosen field (e.g., as a full-time research assistant).
Choose people who know your work well and can speak to your ability to succeed in the program that you are applying to.
Remember, it is far more important to choose someone who knows you well than someone well-known. You may have taken classes with more prominent professors, but if they haven’t worked closely with you, they probably can’t write you a strong letter.
The sections in your graduate school resume depend on two things: your experience, and the focus of the program you’re applying to.
Always start with your education. If you have more than one degree, list the most recent one first.
The title and order of the other sections depend on what you want to emphasize. You might include things like:
- Professional experience
- Voluntary and extracurricular activities
- Publications
- Awards and honors
- Skills and certifications
The resume should aim for a balance between two things: giving a snapshot of what you’ve done with your life so far, and showing that you’re a good candidate for graduate study.
A resume is typically shorter than a CV, giving only the most relevant professional and educational highlights.
An academic CV should give full details of your education and career, including lists of publications and presentations, certifications, memberships, grants, and research projects. Because it is more comprehensive, it’s acceptable for an academic CV to be many pages long.
Note that, outside of the US, resume and CV are often used interchangeably.
No, don’t include your high school courses and grades. The education section should only detail your college education.
If you want to discuss aspects of high school in your graduate school application, you can include this in your personal statement .
A resume for a graduate school application is typically no more than 1–2 pages long.
Note, however, that if you are asked to submit a CV (curriculum vitae), you should give comprehensive details of all your academic experience. An academic CV can be much longer than a normal resume.
Always carefully check the instructions and adhere to any length requirements for each application.
If you’re applying to multiple graduate school programs, you should tailor your personal statement to each application.
Some applications provide a prompt or question. In this case, you might have to write a new personal statement from scratch: the most important task is to respond to what you have been asked.
If there’s no prompt or guidelines, you can re-use the same idea for your personal statement – but change the details wherever relevant, making sure to emphasize why you’re applying to this specific program.
If the application also includes other essays, such as a statement of purpose , you might have to revise your personal statement to avoid repeating the same information.
The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Different programs have different requirements, so always check if there’s a minimum or maximum length and stick to the guidelines. If there is no recommended word count, aim for no more than 1-2 pages.
A statement of purpose is usually more formal, focusing on your academic or professional goals. It shouldn’t include anything that isn’t directly relevant to the application.
A personal statement can often be more creative. It might tell a story that isn’t directly related to the application, but that shows something about your personality, values, and motivations.
However, both types of document have the same overall goal: to demonstrate your potential as a graduate student and s how why you’re a great match for the program.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
- Interesting for you
- My settings

The Ultimate Guide to Studying in United States in 2024
Browse all phd programmes in united states.
- Aug-Jun Academic Year
- 173 Listed Institutes
- 302 Ranked Universities
- 957,000 Int. Students
- 18,757,000 Students
- 331,900,000 Population
Why study in United States
The USA is the favourite destination for international students, and there are over a million head there yearly, nearly twice as many as the second-placed country, the UK. In fact, there are nearly as many international students in the US as there are in the whole of Europe, although you should decide whether an American or European education is best for you rather than just following the crowd. But why do international students choose to study in America? There are plenty of reasons . A key attraction are the world-leading universities, but just as attractive are the opportunities to study in world cities, take advantage of links with global businesses and tech innovators, or just to experience the culture of a nation that has shaped the world we live in.
- America is the world’s education super-power. Its universities dominate the world rankings: they take seven of the top 10 spots , including the first three, according to Meta-ranking. If you want a Bachelor’s or Master’s recognised as high quality the world over, American universities will have you covered.
- There are over 4,300 universities to choose from. If you're looking to study at a university in the United States , you will find a plethora of study programmes, offering extensive academic programmes and diverse campus environments. Whatever you want to study, there will be a centre of excellence for you.
- America is incredibly diverse. It was built by migrants, and that shapes the nation today. Depending on where in America you study , you will see influences from all over the world. If you want to experience a true melting pot of global diversity, nowhere is better than America.
- America leads the world in many sectors. When you think of almost any industry, you’ll probably think of the American — and world — centre. From New York for finance, to LA for entertainment, or San Francisco for technology. If you want to be close to the world’s best in almost any category, head to the USA.
- The USA is one of the world’s most geographically vibrant and diverse nations. From the gleaming glass and steel of New York’s skyscrapers to the awe-inspiring Grand Canyon, or the cold expanses of Alaska to the surfing paradise of Hawaii, America really has everything.
Why else choose America for study? It is academically innovative. For example, universities have followed the lead of Silicon Valley in providing education in the latest technologies, with some universities, like Caltech or MIT, with an especially strong reputation in the area. The USA was the first country to offer MBAs, while American universities drive new thinking in psychology and economics. American universities lead the world when it comes to the latest courses and thinking.
And it would be impossible to talk about American universities without a mention of the Ivy League. Although, originally, a sporting league for some of the East Coast’s older universities, the term is more often used to refer to a set of universities that offer academic excellence. But while the Ivy League colleges are, undoubtedly, excellent, the strength of American education is such that there are plenty of other universities mounting a strong challenge when it comes to academics.
Culture in United States
Most people will think they understand the culture of the United States. However, these beliefs are often shaped by media representations in books, on television and in movies. But these stereotypes hide the incredible cultural diversity in America, a country that spans a continent and is home to over 300 million people.
American culture and lifestyle reflect the modern nation’s origin as a set of British colonies. Although the American Revolution marked a break with its British past, much was kept. English is still the dominant language, although many speak Spanish, especially in the southern states where there has been immigration from Latin American countries. It has also kept the protestant ethics of the UK.
However, America’s story of freedom and opportunity has attracted people from all over the world. These have typically been from European countries, and there are significant communities with Irish or Italian roots, especially on the East Coast. The West Coast, meanwhile, has seen migration from across the Pacific, with significant Chinese and Japanese communities.
This has resulted in some specific contributions to American food culture. However, Italians may be horrified to learn that Americans argue whether the best pizza is from New York or Chicago, while Chinese people won’t recognise the fortune cookie presented after meals.
More recently, migration from other parts of the world has increased. However, America has quite strict limits on immigration, meaning it has less impact on diversity and culture than it once did. But its history has created a population that is progressive and welcoming, especially in urban areas and on university campuses.
How to choose a university in United States?
When it comes to deciding where to study, you will be spoiled for choice, and if you are an international student with no other links to the USA, it can be overwhelming. It would simply be impossible to decide between all the places that offer degrees. Instead, your choosing a university checklist will have to start with making a shortlist.
- Decide what criteria are important to you for your choice. Do you want to study in a specific area or city, are you looking for a particular subject, or is there effectively a shortlist already because you want to go to an Ivy League college? There may be some overlap in these questions, for example, a finance-related degree might naturally lead you to consider New York ’s universities.
- When you have your shortlist, research your choices, and identify the key facts, like admissions criteria and costs, as well as things like the admissions process and deadlines. This may help you narrow down your choice even more.
- Consider the academic experience you want. Just like every student is different, every university is different. You might want to look for courses that feature extensive placements, or you might prefer a more academic approach to your topic. Finding a university and course that best matches your learning style will ensure that your education will not just be successful but will be enjoyable too.
- Think about the living and cultural experience you want. The size of America’s education sector means there are plenty of options to choose from. Are you looking to study in a vibrant city, where your lectures take place next to the hustle and bustle of daily life, or would you prefer a campus-based experience where you are surrounded by university life?
What are the best universities in America?
You might assume that the Ivy League offer the best universities in America, but while they are good, rankings like QS illustrate how good American universities are. Here are the five top-rated universities in America , and, amazingly, they are all in the world's top ten.
- MIT, or Massachusetts Institute of Technology , isn’t just the best-rated university in America, it’s the best in the world in the QS rankings. And don’t let the name mislead you, it offers Bachelor’s and Master’s in non-technology subjects, and often tops the rankings in those too.
- Founded by a railroad tycoon, Stanford University continues the entrepreneurial instincts of its founder. As well as lots of former students becoming academic and political leaders, it’s estimated that its alumni-founded businesses would, in total, be the seventh-largest economy in the world.
- Harvard University is surprisingly the only Ivy League school in the top five. America’s oldest university, it predates the Declaration of Independence by 140 years. It has an international reputation, in large part because of the strength of its graduate schools.
- Caltech, formally known as the California Institute of Technology , has a world-wide association with science and technology, it even manages NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. But it is associated with major breakthroughs and advances in every field of science, as shown by the 79 Nobel Laureates associated with Caltech.
- University of Chicago , finishes the QS top five. Its strong research ethos has meant that while some colleges are associated with a school of thought, when you refer to ‘the Chicago school’ you could mean one of five different area where Chicago has worldwide influence.
>>> Find out how America’s universities perform in all the major rankings .
What are the top student hubs in America?
New York is, unsurprisingly, one centre, boasting dozens of colleges and universities, including Cornell and Columbia, nestling in one of the world’s most exciting cities.
However, there are other popular destinations, like Cambridge, Massachusetts, which was named in honour of the University of Cambridge but is now home to both Harvard and MIT, among others. While Durham, in North Carolina, is home to Duke and North Carolina Central University , and forms a corner of the research triangle that also contains the University of North Carolina Chapel Hill .
However, it sometimes seems everyone wants to study in America , and with so many students, domestic and international, it’s hard to find an American city that isn’t a student hub!
Tuition Fees in United States
It will come as no surprise that you will have to pay tuition fees in America. Students at American universities must pay fees ranging from around $10,000 to over $60,000 a year for a Bachelor’s degree, although prices tend to be around $25,000 or $40,000 depending on the type of university you attend. Prices for a Master’s degree tend to average around $30,000 a year, but some courses can be significantly cheaper.
On top of that, there are often more fees that you will have to pay to remain enrolled. An American education can offer many benefits, both while you are a student and afterwards, but it is not cheap. And if you are an international student, you will need to be able to show how you will meet the fees to get a visa, so the cost is something you will need to consider.
The American higher education system includes many models, and while they may all offer a high-quality education, cost is one of the biggest ways they differ .
Many universities, including some of the most prestigious, are private institutions. These rely on income from fees or endowments and tend to be the most expensive at around $40,000 a year. The most expensive institutions, which tend to be the most prestigious, like Harvard or Stanford, can cost around $60,000 a year, making a four-year degree, along with living expenses, very costly.
State institutions, which receive public funding, are significantly cheaper. For non-state residents these are usually between $20,000-$25,000 a year. Students from the same state, however, pay even less, typically around $10,000 a year.
However, all universities will point out that their fees, and what students pay, are very different things. And there are many ways to ensure your Bachelor’s or Master’s degree is more affordable than the fees might suggest.
Learn about tuition fee insurance for international students and why it's useful .
>>> Use the ‘Tuition fee’ filter on the left menu of our Bachelor’s , Master’s or PhD search pages to find the programme best suited for your budget. You can also sort the list of available programmes by Lowest tuition fee by clicking the top right Sort button.
Can I study in United States for free?
Unfortunately, there is no free education in America for international students. Indeed, because the cheapest fees are for residents of the state that funds the university, international students will usually be looking at fees that start in the middle of the fees range.
If you are wondering how to study in America for free, there is some good news. Generally speaking, international students not only pay the same as domestic students at most universities, but they also have access to the same funding opportunities as everyone else. Indeed, some of the most expensive universities say that the funding they make available can mean that almost all your costs, including their fees, are covered.
Financial Aid and Scholarships in United States
Most students, domestic and international, at American universities will benefit from some form of aid or scholarship . However, getting them may be as difficult as getting on the course itself!
The US State department’s Education USA website highlights a choice of available scholarships. Some of these are general awards, which can fund a degree at any qualifying institution. However, most awards will relate to specific colleges and universities.
>>> If you want a scholarship in the USA, check out the Mastersportal scholarship search .
Types of scholarships on offer
A lot of the funding available for students comes from donations and gifts, often from former students. It can mean that in some places there are hundreds of potential awards. Typically, funding is available as either scholarships or grants .
Scholarships will usually have an academic part to them. They may require a particular level of qualification, or skill, to be proven to be awarded. They will typically be limited, meaning only a specific number or amount is awarded each year. A common question is ‘how many scholarships should I apply for?’ Because they are so competitive, it’s often a good idea to apply for all those that you meet the criteria for.
Grants are awarded based on need. These will need evidence of income to prove the level of support needed. Generally, universities award these to all that need them, so if you meet the criteria, you will receive an award.
Where you can find scholarships
You should think about funding at the same time you are thinking about applying, and research the options available to you. Every university’s website will have a section dedicated to financial aid, helping you find the information you need easily. You will be able to find this easily by searching the website for terms like ‘financial aid’ or ‘scholarships’.
Be sure to check the rules for the schemes you want to apply to, you can sometimes apply before, or often at the same time, as you apply for a place. And, whatever the deadline, you will have to ensure that you have a decision in place before you apply for your student visa.
There is generally no limit to the number of applications you can make. However, most universities operate a combined application scheme, meaning that you only need to make one application which will be considered in all the schemes for which you are eligible.
The Education USA site lists some scholarships , and can be filtered to help identify options available to your specific country. However, it only shows a limited number of options.
Mastersportal is a good place to figure out where to apply for scholarships in America. You can find hundreds of available options provided by NGOs, governmental or private institutions, and universities.
And if you are looking for a scholarship, why not apply for the Studyportals Scholarship – International Distinction Award . It’s open to all international students, and you can find more in our FAQ .
How to apply
The exact process will depend on the scholarship, bursary, or aid you are applying for, and where you are applying.
The first thing you should do is carefully check the rules and guidelines. They will all follow a similar process, but will not be identical, so make sure you don’t get caught out.
- The most important thing is to check the eligibility criteria. Competitive scholarships will have countless applicants, so if you don’t fully meet the criteria, you won’t be considered. And if you are applying for a needs-based grant, you will be rejected.
- Make sure you gather all the documents you need and keep them in a safe place. If you are applying to several places, you will need them again.
- Once you have everything, complete the application. Again, check this carefully — and ask others to check for you. An incomplete or wrong entry will, at best, delay a decision and possibly any funding. At worst, it might mean you are unsuccessful.
- And when you have a decision, don’t celebrate straight away. Make sure you fully understand the terms and conditions that are attached to it. And if you have other applications pending, it might even be worth waiting for all your decisions to make sure you accept the best one for you.
What to include in your application
Each scheme will advise exactly what you need to include in your application. However, in general, they will be looking to establish that you are eligible for the award, and possibly to understand your motivation in applying.
This means that, on top of your personal information, they are likely to want some financial information to show your level of need for aid.
If you are applying for a merit-based scholarship, they will also need additional evidence like previous qualifications, like a portfolio or letters of recommendation from previous teachers and tutors.
They may also require you to write a letter of motivation, outlining why you are applying for funding and why you feel you should be the successful candidate. If you need to write one, then our advice on writing a great letter of motivation will help.
Interested in scholarships for United States? Check out our scholarship search page.
Apply to university in United States
American universities all handle their own admissions, and, unlike some other countries, there are no central processes for either domestic or international students. This means you may have to manage multiple applications.
How to apply
Having to apply to each university means each might offer a slightly different application process . However, they all follow a similar pattern, requiring an online application and submission of documents.
The online application will generally include basic information, like your personal details and contact details for tutors or those providing references, as well as your previous and current schools or colleges.
You will also need to pay an application fee. How much does it cost to apply to university? The fee is usually between $50 and $150. You might also have been wondering if you can apply to two courses at the same university, and the good news is that most run a common application system, meaning that you can complete a single application for different colleges or courses. If you are applying to multiple universities, though, the costs may soon mount, meaning you will probably want to limit your applications to where you have a reasonable chance of securing a place. The acceptance rates for courses vary dramatically, our guide will give you a good idea of the competition there is for university places in America .
You will also have to submit various documents depending on the course. Common requirements are qualification certificates (including a specific GPA ), portfolios, and proof of English language ability. How these are sent may also vary, since some universities may have strict requirements about establishing authenticity.
Finally, some universities may offer an interview. This is more common with prestigious universities like Ivy League colleges (read our advice on applications to Ivy League colleges ). This is not, usually, a formal part of the application process, and takes place with an alumnus near to you. There is no obligation to have an interview, but many value the opportunity to find out more and start preparing for their time as a student.
What’s the structure of the American academic year
American universities mostly follow the English structure of having three semesters a year, although precise dates will vary, they are broadly follow the pattern:
- Fall semester runs from September to December
- Spring semester lasts from January to April
- Summer semester lasts from May until July.
The academic year starts in September, and most universities will only offer a single start each year.
When to apply for American universities
Each university will have its own deadlines, so check these carefully. Usually, the deadline to apply for university is in the December or January before entry.
Most universities make decisions quickly, and by the end of the March almost all decisions will have been issued. Applying early means you will get a decision sooner and can start making plans whatever the outcome.
Documents needed to apply for university
The documents needed to apply for university will vary from course to course.
At a minimum, you will need to show your academic qualifications, either with a transcript of your school record or first degrees, or both. These must be recognised qualifications, and depending on who issued them you may have to arrange for them to be translated and certified.
Language requirements
Although America has no official language, English is the dominant tongue, and the one used in universities. You will, therefore, need to prove your fluency. How can you demonstrate proficiency in English? There are two ways.
Most universities will accept earlier education in English as evidence of fluency. Typically, this will require three years of instruction solely in English, for example at school or a Bachelor’s degree.
Alternatively, universities will accept commonly recognised English tests. The exact requirements will vary between universities and even courses. Tests, and the scores you need, include:
- IELTS Academic (International English Language Testing System). Most universities will look for at least 7.5 on this test.
- TOEFL iBT (The Test of English as a Foreign Language Internet-Based Test). A score of 100 or more is usually needed.
- PTE Academic (Pearsons Test of English Academic). A minimum score of 68 is usually requested.
- iTEP (International Test of English Proficiency). A score of 4.5 or higher.
- C1 Advanced or C2 Proficiency (Cambridge English: Advanced or Proficiency). A core of 190 or more.
Another possibility may be the Duolingo English Test. Although not as established, it is gaining wider acceptance, and is an easy-to-access test. Typically, a score of at least 125 is needed.
Student housing in United States
Anyone who has watched American movies will know that the college dorm or frat house is no stranger to the screen. It could almost be a character itself. But you’ll probably be relieved to know that the movie image of raucous college life is different from the reality.
What the movies do show, however, is that on-campus student housing in America, or dorms, remains a key part of student life for many.
While it varies between universities, most Bachelor’s degree students and many Master’s degree students, will have the possibility of living in college accommodation for at least part of their course. The nature of this will vary. Large campus universities may have everything on a single site, meaning you could spend your entire course never leaving the university. Other universities, especially those that are based in larger cities, may offer accommodation, but this might be separate to other parts of the university, and even require a commute to your classes.
College accommodation will typically consist of a bedroom with some study space, with shared facilities like bathrooms and kitchens. Some may also offer access to catering facilities. Living in college accommodation can be one of the most enjoyable parts of being an international student in America, allowing you to immerse yourself in the student culture.
Off-campus student housing is also possible, and most Master’s students will tend not to live in university accommodation.
One option is for private student accommodation. These are becoming increasingly common in areas with significant student populations, especially where university accommodation cannot meet demand. They are popular not just with students who miss university-controlled accommodation, but also those who want a little more independence.
Private accommodation often looks a lot like a campus dorm, with students having a bedroom and study area, and sharing other facilities. However, there are more options depending on your budget, for example, private bathrooms or regular servicing of your room.
Finally, there is the possibility of private rental. This is often popular with students who want to share with friends. There is a strong rental market in the US, especially in urban areas. However, demand can be high, and rent can be costly.
When to apply for student accommodation
The deadlines set by your university will determine when to apply for student housing. But regardless of what type of accommodation you are hoping to secure, the best advice is to apply as soon as you have a place.
If you are looking for off-campus accommodation, then you should start looking once you have a place. And it is sensible to have done a little research even before then, so you know exactly what and where you can afford to rent.
Cost of living in United States
Like most countries, the cost of living varies across America. As might be expected, cities tend to be the most expensive, and across the country, the south and midwestern states tend to be the cheapest.
Generally, though, America can be one of the more reasonable places to live, and comparable to other Western nations when it comes to costs. Our article on student living in America offers more details.
For most, rent is likely to be the biggest cost (after course fees) and can vary dramatically. Living in a major city like New York or Boston might cost you as much as $3,000 a month for a single bedroom. Studying at a mid-western university could reduce that to just $600.
But don’t forget that you will have to include other costs on top of this. You might save on rent at that rural university, but then must pay all the costs of owning a car to get around. Meanwhile, it’s possible to save on rent in cities by living further away from the centre and utilising the well-developed public transport that most major American cities have.
Cost of food in America
One area where America can be cheaper than other nations is food. A single person might want to budget between $400 and $600 a month to cover the cost of food in America, but shopping around can bring that amount down significantly. And eating out can be surprisingly cheap too, even in cities.
However, don’t be caught out, like many are, by things like tipping and taxes. Tipping is expected almost everywhere that serves food or drink, which adds to the total you must pay. And price tags will not include sales taxes, which are set locally and will sometimes include taxes from both the state and city. However, it does mean that if you are savvy, and close to a state or municipal border, you can often make easy savings on your shopping!
Work and study in United States
Are international students allowed to work in america.
The F-1 Visa does allow international students to work while in America, but there are strict limits.
First, working hours for international students in America are limited to 20 hours per week during term time. During vacations, full-time work is allowed, but only if you are registered to continue your studies the following semester.
Second, and perhaps the most limiting, you are only allowed to work in jobs on your university campus. While this still allows for a wide variety of jobs, from working in stores, to technical roles in departments, and possibly even working as tutors if you are studying for a higher degree, there will be a lot of competition for few jobs.
The only exception that allows work off campus is if it is for practical training related to your degree. However, this will require the permission of US Citizenship and Immigration Services and can only take place after you have completed at least one year of study.
There are even limits on volunteering, meaning that you can’t for example, take on internships in non-educational settings.
Where can I find jobs?
Since, as an international student, you can only work on your campus, your job search will be limited to your university. It may have a suitable vacancies section on its website, but its student services department is also likely to know of jobs suitable for students and may even have some that are particularly suitable for international students.
It’s also worth asking in your department or places on campus that you use, since you might find out about posts that are coming up, giving you some extra time to think about your application.
Is United States safe?
America is about as safe as most other Western countries. And like most countries, the dangers you might face will vary on where you are, but a little common sense will go a long way to ensuring that your time in America passes without incident. America is safe for international students.
One belief of America that many international students and visitors have, fuelled by news coverage, is that the nation has a lot of gun crime. However, such incidents are thankfully rare. Indeed, in most of America, guns are not a major part of the culture.
Crime tends to be higher in urban areas, but largely because of the increased opportunity such areas provide. Taking care to avoid unfamiliar places, staying in busy places, and avoiding showing off valuables like jewellery and phones will go a long way to avoiding being a victim of crime.
In some parts of America, though, risks to safety may come from the elements, with some states particularly prone to extreme weather. It’s worth checking to see if you are in an area like this, and, if so, following on advice on what you might need to do, this might be as simple as being aware of where shelters are, or having a go-bag ready in case you need to leave your home for safety at short notice.
Finally, you should ensure that you have adequate healthcare for your needs. This is not usually a requirement for your visa, although your university might include it as a condition of entry. However, American healthcare is incredibly expensive and there are only extremely limited public healthcare options available.
You are unlikely to be able to access any healthcare at all if you do not have sufficient insurance or the ability to pay. And in the event you need emergency healthcare, while it will probably be provided, you will also get a big bill afterwards.
Student insurance in United States
The standard F-1 visa does not require students to have any insurance while they are in America. Some universities, however, may have insurance requirements, most often addressing the need for health insurance.
However, regardless of visa or college conditions , anyone visiting America, even for a short time, should get insurance. As previously noted, healthcare is very expensive in America, and even if you are in good health, there is no guarantee that it will last for the duration of your course, or that you won’t have an accident that requires treatment.
On top of student health insurance, you should also consider other types of insurance such as student contents insurance, or student travel insurance if you intend to visit other parts of the country. While most insurance is never needed, you might be grateful for it if you do have to make a claim, especially as an international student far from the support of your home and family.
>>> Request an Aon Student Insurance online . For international students, researchers, Erasmus students and educational staff - we have the right insurance for your situation.
Support services available for international students
Your university will be the main place you go for any support. Each university will have its student support services and, because of the number of international students, almost all will have dedicated services for international students.
These services will cover everything you need to make your studies a success, whether it’s help in accessing your education, support if you experience difficulties, or simply organising events and groups that help to make your student experience as positive as possible.
Student organisations
Again, it is likely that your university will be your first destination when it comes to looking for student organisations, and there will be an international student organisation that will make it easy to meet fellow students from around the world.
You should also make yourself familiar with the student government in your university. These all take different forms but are there to represent students to the university. They will usually have a role in organising and providing some of the cultural experiences of university life, and frequently play a role in student welfare.
However, there are also many intercollegiate societies which may be national, state-wide, or in their own network, which are often organised around subjects or interests, like the American Medical Student Association . Your university’s student support services will have details of the ones that you can access.
Things to do for students on a budget
Although America is a single country, it is sometimes better to think about it as a collection of very different states. It’s simply impossible to write a comprehensive list of the free things to do in America for students, but because it’s such a popular destination, there are plenty of resources, from specific student guides to established guidebooks like Lonely Planet .
But there is no shortage of things to do. Whether it’s just absorbing the culture in places like New York’s Central Park or San Francisco’s Golden Gate Park, or visiting majestic sites like Niagara Falls or the Grand Canyon. If you want a country where you can get everything from the miracles of nature to the wonders of human engineering, it’s hard to beat America.
Top urban attractions for students
The difficulty in listing the best things to do in America is that there are so many attractions. A single city can give you access to dozens of world-famous attractions. And even listing cities is hard because there are so many you will want to see.
- New York . It’s hard to imagine a list that won’t have New York at the top. From the hustle of Wall Street to the calm of Central Park. Don’t miss seeing the bay (the Staten Island Ferry is free) with the Statue of Liberty and Ellis Island, or experiencing the night-time buzz of Times Square.
- San Francisco . The city’s hills mean that you are never far from a great view, and hardly ever off a street that hasn’t featured in a movie car chase! Take time to visit the bay, where you can see the Golden Gate Bridge, visit Alcatraz, and even see the sea-lions at the end of Pier 39.
- Philadelphia . If you are a history buff, then a visit to Philadelphia, which saw the birth of modern America, is a must. You can visit Independence Hall and learn more at the National Constitution Center. And, if continuing the movie theme, you can emulate Rocky’s run up the steps outside the Museum of Art.
- New Orleans. The Big Easy is renowned for its party atmosphere, and you’ll soon find out why. With its Caribbean-colonial feel, plethora of music venues, and delicious food, it’s impossible not to have a good time.
- Los Angeles . A huge city that divides opinion, it’s hard to argue that it doesn’t have something for everyone whether you want to star-spot in neighbouring Hollywood on the Sunset Boulevard, or star-gaze at the Griffith Observatory, or anything in between.
Top 5 Outdoor Attractions
The USA is blessed with a variety of outdoor attractions. Perhaps the best are the 63 National Parks, which, since the first was founded in the 19th century, exist to protect and promote America’s natural heritage.
- Yellowstone . The first national park, it boasts stunning scenery including mountains, waterfalls, rivers, and lakes. But it is most famous for the geothermal activity throughout, the park has more than half of the world’s geysers, but the most famous is Old Faithful, which has erupted every one to two hours since its discovery.
- The Grand Canyon . Another national park, the Grand Canyon, must be seen to be appreciated: over a kilometre-and-a-half deep and more than fifteen kilometres wide, it is a truly enormous canyon. If you are feeling brave, try the Skywalk, where you can experience the height of the canyon from a glass-floored balcony.
- New England in fall. For anyone from a temperate climate with a fall or autumn season, it is hard to explain, but seeing New England in the fall is incredibly popular. Hundreds of thousands head there to see the changing of the seasons. But combine the natural beauty with visits to places like Boston or the coastal resort of Cape Cod.
- The Florida Everglades . The tropical wetlands of the Everglades cover a significant part of southern Florida and mark the transition from subtropical to tropical climate. A popular way to see them is by airboat, which gives a sense of the size of the region, which also offers the chance to see some of the wildlife, including the alligators.
- Alaska. If you want to brave somewhere chillier, why not visit Alaska? At the Glacier Bay National Park you can see how glaciers have shaped the rugged coastlines and are continuing to shape life today. And if you really want a challenge, why not visit Denali , North America’s highest peak and, when measured from its base, even taller than Everest!
Travelling in America
One of the first things to understand about travelling in America is that the distances can be enormous. A flight from coast to coast will take around five hours, and American’s typically refer to car journeys by the number of hours they take.
However, it does mean there are plenty of options for getting around to suit all budgets, and internal travel can often be surprisingly affordable.
Flying is, obviously, the quickest way to get around America, and most major airports will have regular flights between them. There are several sites that offer discounted flights for students, and it’s always worth shopping around.
If you have more time, then taking trains can be a great way to travel. And an excellent way to see parts of the country you might never see by plane, and offer comfortable facilities on-board, including beds for longer journeys. They also offer a range of discounts, for example for groups travelling together.
Alternatively, coach travel is common in America, and the Greyhound is the most famous example. The extensive coach network can take you anywhere you want to go and is one of the most affordable ways to travel. But coach travel can be slow, so plan ahead and take the opportunity to break up your trip with interesting visits.
Learning English and Spanish
English is the predominant language in America, although other languages are spoken by immigrant communities, the most common being Spanish, in places like Florida with a large Cuban community, or Texas and New Mexico, where large numbers of Latin Americans have settled. However, your tuition will be in English, and you will need to be proficient to gain a place.
Fortunately, America’s culture helps enormously. Because of its prolific media position, there are plenty of movies, television series, or even podcasts that you can use to practise listening and understanding English. And its position as a tech centre means there are plenty of English apps, to use, including those dedicated to language learning like Duolingo.
Alternatively, because English is so widely spoken around the world, you will probably have friends or family members that you can practice with, and your school or university may well have a group or even formal lessons that can help you improve further.
Living as an expat in United States
Immigration is a key part of the American story, and apart from Native Americans, most of the country’s citizens can only trace their American heritage a few hundred years at most.
The nation has several significant immigrant groups, as well as large numbers who, although born American, will still identify with their ancestral home. The US Census estimates over 45,000,000 living in America were born elsewhere. Although historically immigration was dominated by Europeans, most immigration is now from Asia, with 2,750,000 Chinese-born residents, 2,700,000 Indian-born, nearly 2,000,000 Philippines-born, and over 1,300,000 Vietnamese-born residents.
However, these numbers are dwarfed by those who keep their ancestral national identity. The most famous are the Irish, more than one-in-ten Americans identify as Irish American. Almost every culture will be represented not just by fellow citizens, but Americans who have kept the culture and identity of their parents, grandparents and beyond.
Expat communities in America
Across the world, migrants have tended to settle in cities. In America, the larger cities will often have large communities from around the world. In some cases, there will also be areas of towns and cities that reflect those cultures. Many places, for example, will have a ‘Little Italy’ or a ‘China Town’ where immigrants have set up restaurants and shops.
More recently, the economy has driven much of the immigration. So, while universities still attract global communities, much of the Asian immigration has tended to head towards the West Coast, where Silicon Valley saw the birth of the tech industry, which has spread throughout California and the other coastal states of Oregon and Washington.
United States Immigration rules
How your immigration status changes after graduation .
It is important to note that America is incredibly strict about visa rules. Although most international students will have a standard F-1 visa, it’s important to check there are no other conditions or rules around your stay. Breaching your visa conditions may prevent you from being allowed into America again.
Usually, your visa will expire when you graduate. The US will expect you to leave the country and return to your home when this happens. Those on a student visa do have a 60-day grace period, during which they can remain in the US. However, it does not allow return to the US, so once you leave you will need to seek a new visa to return, even if your grace period has not expired.
Unlike many countries, there is no automatic right to extension, for example a temporary work visa, after graduation. However, there are several visas that graduates can apply for if they wish to remain in the US.
Types of Visa
One option is to apply for an Optional Practical Training extension. This allows you to work for one year, for up to 20 hours a week. If you are a STEM graduate, you can also apply for an additional year’s extension, allowing you to remain for two years.
This option is only available if you have not already undertaken Optional Practical Training during your course, and your application will need to be started with your university, who will formally recommend it. Applications can take several months, so need to be started long before your F-1 visa expires.
You can only work in roles that are directly related to your course and qualification. However, it is a common option, particularly for those looking to work in the tech sector, and many international companies like Apple, Facebook, and Google hire large numbers on OPT visas.
Another possibility is to get your visa sponsored by an employer. The H1-B visa can only be applied for by an employer, who must state that you are particularly skilled or promising in your field. And having a good degree will help prove your case; find out how to interpret your grade in our guide . Again, most are issued for those working in technology and in STEM more generally. And, unsurprisingly, many result from successful roles undertaken with OPT visas.
The H1-B visa lasts for three years, and can be extended to six years. There is also the possibility at the end of securing a Green Card, which gives the right to remain and work in the USA as a permanent resident. However, Green Cards are incredibly difficult to get, especially because the numbers issued are capped, so, as always, if you are keen to remain in the USA, the sooner you start planning and applying, the better.
Immigration processing times
Be prepared for a long wait for any visa application, these will typically take months, but can take over a year. And, because of America’s strict rules, if you don’t apply early enough, you might find yourself having to leave until the process is completed.
The US State Department publishes current processing time on its website , and these can vary not just based on the time of year, but even between their processing centres. An application for an OPT placement, will take around 7–8 months. An I-129, submitted by an employer to gain an H1-B visa, is quicker, and usually decided within two months.
Job opportunities in United States
Although America prides itself as a land of opportunity, there isn’t quite as much opportunity for international students that have recently graduated. The requirement to work in a field related to your studies with an OPT visa will limit the places that you can work. And while any employer can apply for an H1-B for you, there is, obviously, the challenge of first getting that job, and then your employer successfully applying for the visa.
However, large numbers of students do successful seek employment, and an American degree can set you up for a high-earning career . According to the US Immigration and Customs Enforcement Agency , between 150,000 and 200,000 OPT applications are granted each year, although some will be during courses, it will still represent a large proportion of those graduating each year.
Continue your studies in United States
Another option is to continue studying in the US. There is no limit to the number of F-1 visas you can have, and you can simply apply for a new visa. However, you may have to make that application through your home nation to show that you still maintain a home there.
- Apply for a Master’s degree: If you have completed a Bachelor’s degree, then you might want to develop that with the specialist knowledge that comes from a Master’s course. You can find more than 35,000 Master’s degrees on Master’s Portal .
- Apply for a PhD: The highest academic qualification you can get. A PhD is a research-based degree that allows you to study your chosen field in depth, and results in research that adds to the sum of human knowledge. We list over 3,000 PhDs in the United States .
Frequently asked questions
1. do international students need a visa to study in america .
Yes. There are several student visas, but covering different situations, but if you are hoping to study a complete Bachelor’s or Master’s programme, you will need an F-1 visa.
2. Is studying in America worth it?
There is lots of research highlighting the long-term value of a degree, and America has some of the world’s best-rated and most prestigious universities. Studying in America will give you a qualification that will be recognised anywhere.
3. What is the cost of studying in America?
Fees vary enormously, from around $20,000 to $60,000 a year. However, there are plenty of scholarships and bursaries available, and very few students pay the full costs of their course.
4. How much money is required to study in America?
On top of your university fees, you will need to cover your living expenses. These will vary dramatically depending on where you are studying and are likely to be between $1,200 and $3,500 a month. The biggest cost will be rent, which can be up to $3,000 in cities like New York or Los Angeles.
5. Can I study in America without IELTS?
You will need to prove fluency in English to study in the United States. IELT is one test, but many others are accepted. If you have already studied solely in English for several years, then you will not have to prove ability.
6. What are the requirements to study in America?
Essentially, you will need to get a place on a course, and each course will have its own requirements, which are usually proof of previous academic attainment. Apart from that, you will simply have to satisfy the visa requirements that you are of good character, have the means to support yourself and will leave the US when your course is complete.
7. What exams are required to study in America?
Universities will advise on which qualifications they accept. However, typically, they will accept any recognised qualifications from elsewhere in the world, for example degrees from other universities, A-levels from schools following the British system, or Baccalaureates.
8. How to get permanent residency while studying in America?
It is difficult to get permanent residency while studying. However, after graduation, it is often possible to remain in the US for practical training or secure a job that can sponsor a visa. It may then be possible to apply for permanent residency once established in a career in the US.
Interesting programmes for you
Find phds degrees in united states, what subject to study in united states.
- Agriculture & Forestry 147 Masters
- Applied Sciences & Professions 159 Masters
- Arts, Design & Architecture 386 Masters
- Business & Management 480 Masters
- Computer Science & IT 317 Masters
- Education & Training 772 Masters
- Engineering & Technology 794 Masters
- Environmental Studies & Earth Sciences 393 Masters
- Hospitality, Leisure & Sports 45 Masters
- Humanities 661 Masters
- Journalism & Media 47 Masters
- Law 169 Masters
- Medicine & Health 1212 Masters
- Natural Sciences & Mathematics 1314 Masters
- Social Sciences 1154 Masters
PhD Degrees in United States
- Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) 5696 programmes
- Doctor of Business Administration (D.B.A.) 56 programmes
- Doctorate (Doctorate) 101 programmes
Recent international policies promote international university cooperation and student exchange between countries worldwide. High-quality study and PhD degrees are made more available to students in order to create a global educational network, achievable through student and staff mobility. Career and research oriented programmes support international student development.
University cooperation enables students study worldwide, for instance in Australia, Asia, Europe and the United States and provides ways of recognizing previous degrees. Different study options offer appropriate alternatives to students, depending on their preferred mode of study.
Many study programmes in Australia, Asia, Europe and North America are English-taught. The most popular international student destinations include the following countries: Australia, Belgium, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom, the United States, and more. However, these are not the only countries offering English-taught education. The rest of the world is full of endless study choices, from highly ranked to smaller, more specialized, universities.
PhD (postgraduate) Degrees
If you want further education beyond the undergraduate level or if you want more personal development or a career in academia, you could obtain a PhD degree. PhD degrees are postgraduate programmes that usually follow a Master's, MPhil or MRes, but there might be additional requirements depending on the university. Students are required to do their own research in a chosen topic. With the help of a supervisor, you develop knowledge and analytical skills in a specific or multidisciplinary field and you carry out independent research. The duration of a PhD degree differs per country and institution. Sometimes your own research is accompanied by work for the department such as giving seminars or small group teaching.
PhD students are required to study on campus under close supervision, but there are universities that accept students enrolled into a part-time distance education PhD degree. Studying on campus can also be full-time as well as part-time, in which case the part-time variant is normally twice as long as the full-time study.
Discover other countries

Go to your profile page to get personalised recommendations!
- Graduate School
How Long Does it Take to Get a PhD?: A Go-Getter’s Guide to Graduation
Featured Expert: Dr. Charlene Hoi, PhD

How long does it take to get a PhD? On average, PhD programs are 4 or 5 years long. The time it takes to get a PhD is slightly longer in the US, between 4-6 years, because these programs tend to be more structured. If you want to know how to get a PhD in Canada or Europe, you can expect it to take 3-5 years. However, there are PhD programs that take longer, such as part-time programs, or are extremely short, like online accelerated PhD programs. Ultimately, how long it takes to get a PhD is up to you. In this article, we’ll look at the average PhD program lengths, the typical PhD timeline, and tips on how to get your PhD finished faster.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free initial consultation here <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 13 min read
How long does it take to get a phd.
On average, it takes 4-5 years to complete a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. In the US, most PhD programs are between 4-6 years, while in Canada they are typically shorter, around 3-4 years.
Some students take longer than 6 years to complete their PhD, but in general the longest time it takes to get a PhD is capped at 8 years. If you’re enrolling in a part-time PhD program, for instance, your timeline will probably be extended to 6-8 years.
The shortest PhD programs out there are accelerated or sometimes online PhD programs. Some of these are only 1-2 years long, but there are comparatively fewer programs available, and they are only suitable for certain fields and careers which require less intensive research which defines most PhD programs.
One of the main reasons why it takes many years to get a PhD is because these programs are comprehensive and the requirements to graduate are extensive. Most have a set number of credit hours you need to complete, examinations to write, plus you’ll need to write your PhD thesis or dissertation, unless you pursue a PhD without dissertation .
There are certainly ways to shorten the PhD application timeline and time to graduate, which includes enrolling in a shorter program if possible, increasing your course load or the number of research hours you can dedicate per week, but generally a PhD will still take some time.
Even if you want to do a PhD without a master’s degree first, such as by applying to a direct entry PhD program, the program is still usually 4-5 years long.
We’ll take a look at the typical PhD timeline and how long it takes to get a PhD normally. After, we’ll cover some tips on how to get your PhD done faster or how you can avoid dragging things out.
In North America, the typical PhD program is divided into two stages. The first stage is where you complete all the required coursework, comprehensive exams and other academic requirements, depending on the program. The second stage is when you submit a proposal for original, independent research, get it approved and start working on your thesis or dissertation. Your PhD culminates with your thesis defense. Once your thesis has been approved, you’ll be eligible to graduate.
This timeline is somewhat flexible, as you might complete the first stage in 1 or 2 years but take longer to complete your dissertation. For the purpose of this general PhD schedule, we’ll assume your PhD program is a typical length of 4-6 years.
Application Stage
We’ve included the application stage of getting your PhD here first because the grad school application timeline can take several months to put together your application package and hear back about acceptance to a program. Secondly, because the application stage involves some critical steps you’ll need to complete in order to get your PhD.
1. Research proposal
To apply to a PhD program, you’ll most likely be required to submit a research proposal and be prepared to answer any research proposal questions your advisor will have. This is your “proposal” of what research question you will explore during your studies at a program, or an outline of what research topic you want to pursue. If you’re not sure how to write a research proposal, check out these Oxford PhD proposal samples or a Cambridge PhD proposal sample.
2. Application materials
The admission requirements for a PhD can vary from program to program, but here are the general components of a PhD application:
- Required prerequisite coursework
- Official transcripts (and minimum GPA)
- Graduate school statement of purpose
- CV for graduate school or research resume
- PhD motivation letter
Some programs may also ask you to submit additional essays, such as a letter of intent, research interest statement or grad school career goals statement .
Many PhD programs also invite you to a grad school interview to get to know you better. Be ready for common graduate school interview questions such as “ tell me about yourself ” and “ why do you want to do a PhD ?”
PhD Years 1-3: Coursework Stage
1. orientation.
Your PhD program will usually begin with your orientation, where you’ll learn about the program’s individual structure, requirements and expectations. You’ll also either choose or be assigned an academic advisor and schedule an initial meeting with them. Your advisor will be a member of the university faculty who will act as your support while you complete your research and write your thesis.
2. Coursework
The first year or two of your PhD will involve completing required advanced coursework in your field. You’ll attend lectures and seminars and you may participate in research projects with department faculty or fellow graduate students or even lab work, depending on your field.
3. Electives
Along with required coursework, you’ll have the chance to take elective courses that interest you or relate to your field. It’s important to choose electives that will enrich your program. Choose ones that really interest you, that might help inform your PhD research or that will help you fulfill your credit requirements.
4. Extracurriculars
PhD programs sometimes have extracurricular activities or additional requirements outside the classroom. This can include internships or a practicum you need to complete for credit, or you might be interested in attending academic conferences or relevant events to socialize and network you’re your colleagues in the field.
5. Comprehensive exams
The coursework stage of your PhD program will end with comprehensive exams , sometimes called qualifying or preliminary exams. These are your “final exams” to make sure that you completed the necessary PhD coursework and that you’re ready and qualified to take on your own independent research in the next phase.
1. Thesis proposal
You may recall that you submitted a research proposal as part of your PhD application, and this step of the process is similar. Your thesis proposal is just like your research proposal, but it’s a more refined and developed version. Throughout your coursework, your research question might have changed or you might have changed course a little bit. If you’re still thinking about your PhD topic , take the time to solidify it before you reach the thesis proposal stage.
Your research proposal might have been a first draft, while your thesis proposal is your official announcement of: this is what I propose to research in this PhD program.
Depending on your field and the program, you thesis research might involve a great deal of lab work, or data collection or fieldwork. Whatever the case, your thesis proposal is a complete outline of what you intend to do for this independent research project and the steps you’ll take.
2. Thesis approval
Once your proposal is written, you’ll submit it for approval. Your academic advisor, PhD supervisor or the PhD committee overseeing your program will review it and either approve it or make suggestions for changes. Once it’s been polished and finalized, you’ll be given the go ahead to start conducting your research.
3. PhD research
Your research alone will probably take you several semesters to complete. On top of the fieldwork, lab work or data collection and analysis you’ll be completing, you’ll be using this time to write and review. Writing your thesis or dissertation takes a fair number of hours to outline, draft, edit and complete. It also means hitting the books to complete a literature review of your research topic so you have a complete background understanding of your chosen topic and how it will inform your research.
Your research and the preparation of your thesis is really the biggest part of this second stage, and is probably the longest part of your PhD altogether.
4. Extra requirements
When you’re not deep in your research, you’ll be completing other requirements of your PhD program or additional duties that enrich your education. Some programs require you to dedicate some hours to teaching, whether it be leading seminars for undergraduate students or acting as a teaching assistant for university faculty.
You’ll also be strongly encouraged to publish as a graduate student , so you may be involved in the research projects of faculty members or other grad students when you’re not working on your dissertation.
5. Thesis submission and preparation for thesis defense
When you’re finished writing your thesis and you’re ready to submit it, it’s critical to know how to prepare for thesis defense . Because not only do you have to complete this original, new body of research work, you have to get the approval of your PhD committee to put it out into the world.
Your thesis defense is essentially the final presentation of your PhD.
6. Thesis defense
Your thesis defense is an oral presentation of your research project, but it also involves submitting your written document to be reviewed. Essentially, you’ll present the entirety of your thesis to the PhD supervising committee, including your findings and conclusions. From there, the committee will ask thesis defense questions . Your answers will defend your methodology and results to the committee, basically proving the value and validity of your work. While this is an evaluation of sorts, it is also your opportunity to share your original ideas and invite further research into your topic.
After your defense, the PhD committee will either approve your thesis or send it back to you with edits or changes to be made before it can be formally approved.
Graduation and Postdoc
Once your thesis has been approved, congratulations! You’ll be eligible for graduation and be awarded your degree. Now that you’ve finished this marathon, you can choose to pursue further studies or start looking for a job after grad school .
With a PhD, you have many different options for positions in your field. You might want to know how to find a job in academia or how to get a tenure track position at a university if you’re interested in teaching others. PhD graduates who decide to transition from academia to industry or who would rather work outside the realm of academia can find industry jobs after PhD that suit their skills and experiences.
Either way, you’ll need to prepare for how to find a postdoc position, explore what the career options are for you, decide what your career goals are and start sending out applications. Remember to prep your postdoc resume and get read for postdoc interview questions , since the job hunt will begin soon after you finish your PhD!
Is it possible to get your PhD done faster? What are some ways you can speed up the process and avoid taking 8 years to complete your graduate studies? Luckily, there are many key ways you can make your journey through grad school easier and speed things up a little, from the type of PhD program you choose to the habits and skills you cultivate during your program.
#1 Enroll in an accelerated program
The first way to guarantee it will take less time to get your PhD is to, of course, enroll in a shorter PhD program. Direct entry PhD programs allow you to enroll once you’ve completed your bachelor’s degree in exceptional circumstances. Note that these are not the easiest PhD programs to get into , as your academic record needs to be excellent, and you’ll likely need prior research experience and you may even need to have publications already. However, a direct entry PhD program is around 4-5 years, but it allows you to skip the 1-2 years it would take to earn a master’s degree.
You can also choose to enroll in an online or accelerated PhD program that is designed to be much shorter than the traditional PhD. Once again, though, these programs are not available to students in every field, so you may need to research whether there are any options for you.
#2 Choose the right mentor
One of the first things you can do to ensure your PhD is smooth sailing is to choose the right mentor or academic advisor. Many programs allow you to choose your advisor, while some assign one to you. Whatever the case, it’s important to establish a strong working relationship and clear expectations early on.
One of the first things you’ll do as a PhD student is meet with your advisor. Take the time to discuss with them what your expectations for the program are, ask questions and ask them what their expectations are of you. Your advisor is there to help you and advise you, and they have resources and connections you can use to your advantage. But they are also working with a busy schedule and might be advising more than one PhD student, too. A mutually respectful relationship with open communication will ensure fewer interpersonal hurdles down the road.
#3 Earn credit hours faster
One way you can shave some time off your PhD is by earning your credit hours faster and getting to the research and thesis-writing stage faster. This might mean you take on a full-time course load or ask your advisor for ways to earn extra credit, such as participating in research projects. Some PhD programs will give you course credit for previous graduate level coursework you might have completed during your master’s degree, or for certifications and professional education you completed outside of school.
#4 Keep your thesis focused
When you get started on your research, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed with the amount of work you need to complete, with the writing of your thesis on top of it all. One way to keep your research hyper-focused and on point is to keep your thesis topic narrow. If your subject is too broad, you’ll be spending way too much time in your research. Give yourself clear objectives and scope, and don’t deviate from your PhD proposal if you don’t have to.
There may be a million questions you want to explore within your PhD topic, but there will be other opportunities to explore them. Keep your focus narrow so you don’t spend years and years asking and answering research questions!
One of the best things you can do to get your PhD done faster and adjust to the experience of graduate school is to change your thinking. Adopt a growth mindset so that you’re open to new learning, willing to listen to constructive feedback on your proposal or thesis and willing to grow your skills. A PhD is an advanced program, and you’ll already be very skilled, but it is also an opportunity to learn and grow. There will be challenges for you, so be ready to meet and overcome them instead of letting them draw you back or slow you down.
#5 Develop your professional skills fast
A PhD is an opportunity to grow your professional skillset as much as it is an opportunity for you to contribute meaningfully to your field. If you haven’t already been working on skills such as communication, presenting or lecturing and writing, now is the time to start.
Strong writing skills will help you get your thesis finished and edited faster, as you’ll be more familiar with the process and understand what makes a strong document. It’s also a useful skill to learn how to write effective funding proposals or grant proposals. You may need to do so to secure funding for your research, but it’s a highly valuable skill in the workforce, too.
Good presentation skills will help you during your thesis defense or if you’re asked to present during a conference. They will also help you build confidence in your voice and ideas and make you a better communicator when you’re networking or job searching.
#6 Keep to your schedule
This is maybe the most important skill if you want to finish your PhD faster: make a detailed schedule and hold yourself accountable to it. If you like, you can plan out your entire PhD week by week from Day 1. Write down what your course schedule is, when you’ll do research and how many hours, when you’ll write and how many hours, what extracurriculars or personal activities will take up your time and so on.
A detailed schedule gives you an overview of your PhD and a timeline of when you’ll finish. It will keep you organized and accountable, so you can avoid procrastinating or avoidable speed bumps that might slow you down. It also helps you compartmentalize the many items on your to-do list so you don’t stress out about how much you need to accomplish.
When creating your schedule, especially during the research stage when there is no formal class schedule for you to adhere to, focus on deliverables. Set a date when you will submit a section of your thesis to your advisor, or when you will complete your literature review. Setting goals and clear outcomes will keep you on track and focused.
#7 Take initiative and be independent
The last tip to help you get your PhD done faster is to take initiative. Remember that a PhD is a largely independent endeavor. You’ll have the support of a committee or advisor, but you can’t rely on them to do the work for you or put everything on hold if they aren’t available when you need them. Be flexible and adaptable so you can keep working and moving forward, even if your schedule gets interrupted or needs to change to suit your situation.
It's also important to take the initiative in your learning. Take advantage of opportunities for growth, networking, and gaining experience where you can. Get the most out of your PhD program and use your experiences to fuel your end goal of completing your thesis.
On average, it takes 4-5 years to get a PhD. There are a few factors that can influence the time it takes to complete your PhD, from program length and structure to what country you are earning your PhD in, to your own personal work ethic and schedule.
PhD programs in the US are on average 4-6 years. In Canada and the UK, they are usually 3-5 years long. Part-time PhD programs may take up to 7-8 years to complete. Direct-entry PhD programs and dual master’s and PhD programs are typically 5 years long. If you’re enrolling in an online, hybrid or accelerated PhD program, the timeline is usually 2-3 years, but there are some extremely short 1-year PhD programs offered online for specific disciplines.
Yes, you can finish your PhD before the “normal” timeline. For example, if you complete your coursework early, if you finish writing your thesis faster than average and get it approved, or if you otherwise complete all your PhD program requirements before the anticipated finish date.
Yes, there are online PhDs available for certain fields and disciplines. These typically range from 2-3 years, although there are some traditional 4-year PhD programs offered online. There are also some “accelerated” online PhDs which last 12-18 months.
A PhD program is not necessarily shorter if you first complete a master’s degree, but having gone through a master’s program can better prepare you to finish your PhD faster. Some PhD programs accept credit hours from your master’s degree towards the coursework requirements for a PhD, and if you’ve previously written a master’s thesis or completed some research during your graduate studies, this will be an advantage. Since you’ll already be familiar with the process of writing a thesis and conducting your own research, you can avoid some stumbling blocks in your PhD program that might otherwise slow down your progress.
Yes, it is possible to get a PhD without first completing a master’s degree. There are direct entry PhD programs that allow students with a bachelor’s degree to enroll, so long as they meet the admission requirements and have exceptional academic records. Some online PhDs also waive the master’s degree requirement.
Yes, it is possible to complete a traditional PhD program in a shorter amount of time than anticipate. This usually means dedicating yourself to full-time study or taking on a larger course load and increased research hours. It takes significant work, but it can be done with the right schedule and commitment.
The fastest PhD programs are the short, 1-year accelerated programs. These programs have fewer credit hours to complete, and some have no dissertation requirement, only qualifying exams to finish. However, there are not many programs out there, and they are not available for every field of interest.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).

How Long Does it Take To Get A PhD? Doctorate Degree Timeline
Starting a PhD means you’re ready for a big academic adventure, full of tough challenges and exciting discoveries.
If you’re thinking about going for it, you’re probably wondering just how much time you’ll need to commit to this big goal.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.
This article breaks down what the PhD journey looks like, what can make it longer or shorter, and some tips on how to make it through.
If you’re curious about how long it’ll take to add ‘Dr.’ before your name, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the world of PhD timelines!
How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD?
The answer here isn’t straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including:
- the discipline,
- the institution, and
- whether you’re a full-time or part-time student.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.

Distance learning PhD programs offer flexibility but similarly require a substantial time commitment, often mirroring the length of part-time studies.
The heart of a doctoral program is the dissertation, a rigorous research project that demands an in-depth exploration of your chosen field. This phase alone can take several months to years, significantly influencing the overall length of your PhD journey.
Beyond the dissertation, coursework, exams, and sometimes teaching responsibilities add layers to the doctoral experience.
The requirements for a PhD vary widely across disciplines and institutions. For instance, a doctorate in the sciences might involve extensive lab work, potentially extending the time to completion.
In contrast, a doctorate in the arts could hinge more on coursework and creative output, leading to variations in the timeline.
Does A Doctorate Degree Take Longer Than Masters?
A doctorate degree typically takes longer to complete than a master’s degree.
While a master’s program can often be completed in 1-2 years of full-time study, a doctoral program usually requires 4-6 years, depending on the:
- research complexity, and
- whether the student is enrolled full-time or part-time.
The doctoral journey is more than just additional coursework; it involves conducting original research, writing a comprehensive dissertation, and often teaching or engaging in professional development activities.
The dissertation phase, which requires students to contribute new knowledge to their field, is particularly time-consuming and can extend the duration of a PhD program significantly.
The time it takes to complete a doctorate can be influenced by your
- research topic,
- funding availability, and
- the level of support from advisors and faculty.
Master’s programs are typically more structured, with a clearer set of coursework requirements and a shorter thesis or capstone project, leading to a quicker path to graduation.

Why Does It Take So Long To Finish Doctoral Program?
Starting a doctoral program is a significant commitment, often taking longer than anticipated. If you wonder why it takes so long, here are a couple of reasons you can think about:
Extensive Coursework
Initially, you might think coursework in your PhD study is just a continuation of your previous studies.
Doctoral level courses are a different beast. They demand not just understanding but the ability to critically analyze and apply complex concepts.
Each course can feel like a mini research project, requiring more than just classroom attendance. This phase lays the foundation but is time-consuming.
The Dissertation
The heart of your doctoral journey is your dissertation. This isn’t just a long essay or an extended research paper. It’s an original contribution to your field, requiring:
- exhaustive research,
- experimentation, and
Some students find their research path straightforward, while others may hit unexpected roadblocks or need to pivot their focus, extending the time required.
Part-Time Study
Many PhD candidates choose a part-time path due to work, family, or other commitments. While this flexibility is crucial for many, it stretches the duration of the program.
What a full-time student might complete in 4-6 years, part-time students might take 7 years or more to finish.
Funding and Resources
Access to funding and resources can significantly impact the timeline. Some projects require extensive fieldwork, specialised equipment, or access to rare materials. Delays in funding or accessing necessary resources can stall progress.
If funding is an issue, consider applying for work outside of the university. You can also try your luck with the university, as a research or teaching assistant , or more.

Academic Publishing
As part of the doctoral process, many students are encouraged or required to publish their findings.
However, the process of submitting to academic journals, undergoing peer review, and possibly revising and resubmitting, is lengthy.
This step is crucial for the academic community but adds time to the doctoral timeline. If may help to start writing and publishing work earlier to ensure you have enough time to finish.
Faculty Supervision and Mentorship
The relationship with your advisor or supervisory committee is pivotal. These mentors gatekeep your studies, as they:
- guide your research,
- provide feedback, and
- approve your progress.
Scheduling conflicts, feedback loops, and the iterative nature of research can add semesters or even years to your timeline.
Personal Growth and Professional Development
Beyond the academic requirements, doctoral students often engage in teaching, attend conferences, and network within their academic community. These activities contribute to your professional development but also extend your time in the program.
Factors That Influence The Time To Get A PhD
The time it takes to complete PhD is influenced by a multitude of factors, each significant in its own right. Let’s delve deeper into these elements to understand the intricacies of the PhD voyage.
The Scope of Research :
The ambition of your research can significantly dictate the duration of your PhD. Some projects will need more time and commitment, especially if they:
- Demand extensive fieldwork,
- elaborate experiments, or
- groundbreaking theoretical developments.
Imagine embarking on a quest that not only seeks answers but also questions the very foundations of your field. Such endeavours are thrilling but inherently time-consuming, often extending the PhD journey beyond the typical timeframe.
Program Structure and Requirements
The architecture of a PhD program—its coursework, qualifying exams, and other prerequisites—lays the groundwork for your academic expedition.
Programs with a heavy load of initial coursework aim to equip you with a broad foundation, yet this can elongate the path to your actual dissertation work.
Mode of Study
The decision between full-time and part-time study is pivotal. A full-time commitment allows you to immerse yourself in research, ideally hastening progress.
Yet, life’s obligations may necessitate a part-time route, extending the journey but offering flexibility.
Distance learning, with its inherent flexibility, caters to those balancing diverse commitments, yet this mode, too, can stretch the timeline, particularly if it lacks the immediacy and intensity of on-campus engagement.
Quality of Supervision
The symbiotic relationship with your advisor is the compass guiding your research voyage. An advisor who is both a mentor and a critic, offering timely and constructive feedback, can expedite your journey.
Less engaged supervision may leave you adrift, prolonging the process as you navigate the academic waters largely on your own.
Worse still, if you are unlucky enough, you may end up with supervisors that not only does not help you, but actively attempt to make your study life difficult. These nightmare scenarios do exist, and you should be aware of them.
Financial Stability
The financial underpinnings of your PhD endeavor are more critical than often acknowledged. Consistent funding allows you to dedicate yourself fully to your research, free from financial distractions.
Conversely, the absence of stable support might necessitate part-time employment, diluting focus and extending the timeline.
Resource Availability
Access to specialized resources—be it state-of-the-art laboratories, rare archival collections, or cutting-edge software—can be the wind in your PhD sails.
Limited or delayed access to these essential tools, however, can stall progress, turning what could be a swift journey into a prolonged odyssey.
If you found yourself in a position without the right resources to complete your PhD, consider to propose your university to allow you to work with other universities with what you need. If this is not possible, you can always transfer university, although this would mean more work.
Publishing Requirements
The adage “publish or perish” holds particularly true in the realm of PhD studies. The process of getting your research published, from initial submission to eventual acceptance, is fraught with delays and revisions. Each publication cycle can add months to your timeline,
Yet these publications are crucial stepping stones towards establishing your academic credibility. In fact, some universities want you to publish papers to graduate.
Personal Life and Circumstances
The journey towards a PhD is not undertaken in academic isolation. Life, with its unforeseen challenges and responsibilities, continues.
Personal circumstances can impact your ability to devote time and energy to your studies, necessitating pauses or a reduction in research intensity.
These issues can range from situation such as:
- such as health issues,
- family commitments, or
- significant life events

Tips To Earn Your Doctoral Degree Fast
Earning a doctoral degree is a significant academic endeavor, often perceived as a marathon rather than a sprint. However, with strategic planning and focused effort, you can navigate this journey more swiftly than you might expect.
Here are some tips to help you earn your doctoral degree faster, drawing from the experiences and strategies of successful PhD candidates.
Choose Your Program Wisely
The structure of the PhD program you choose can greatly influence how long it takes to complete your degree. Programs that allow you to start your dissertation research early, even while completing your coursework, can save you a considerable amount of time.
Some program are designed to integrate dissertation work with coursework, enabling a more seamless transition into the research phase.
Opt for Full-Time Study If Possible
While part-time PhD programs offer flexibility for working professionals, full-time study allows for a more immersive research experience.
Dedicating all your working hours to your doctoral research can expedite the process, reducing the time it takes to get your PhD significantly.
Secure Adequate Funding
Financial stability is key to focusing fully on your research without the distraction of part-time work. Look for:
- scholarships,
- grants, and
- funding opportunities from your institution.
You can also try to secure funding from external sources like the National Science Foundation.
Secure funding not only supports your financial needs but also often comes with academic resources that can accelerate your research progress.
Develop a Strong Relationship with Your Advisor
Your advisor is your guide through the PhD process. A supportive advisor can provide invaluable feedback, help you navigate academic challenges, and keep you on track.
Regular meetings and clear communication with your advisor can help you refine your research direction and avoid time-consuming pitfalls.

Focus Your Research
A well-defined research question can provide a clear path forward. The more focused your research, the less likely you are to get bogged down in unmanageable amounts of data or tangential studies.
It’s about depth rather than breadth; delving deeply into a specific area can lead to significant contributions to your field and a quicker path to completion.

Take Advantage of Existing Research and Resources
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Building on existing research and utilizing available resources can save you time. This includes:
- leveraging datasets,
- using established methodologies, and c
- ollaborating with other researchers.
Access to resources like specialized labs or archives, as provided by your institution, can also streamline the research process.
Stay Organized and Manage Your Time Effectively
Good time management is crucial. Set realistic goals, create a timeline for your research and writing, and stick to it.
Tools like Gantt charts can help you visualize your PhD timeline, including key milestones like coursework completion, comprehensive exams, and dissertation chapters.
Get Your PhD Without Taking Too Much Time – Possible
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation.
While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
Key factors like your field of study, the nature of your research, and your personal life circumstances play significant roles in shaping your individual journey.
Remember, earning a PhD is more than just a race to the finish line; it’s a profound journey of learning, discovery, and personal growth. Embrace the journey, stay focused, and the day you earn the title of ‘Doctor’ will be a milestone to remember.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
If you aspire to rise to the top of your field, then you may have your sights set on a PhD.

Earning a doctoral degree can be a years-long process, but choosing an accelerated doctoral online program may help you complete your program more quickly.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Whether you’re wanting to earn one of the highest paying doctoral degrees or you have a specific one in mind, this guide can help walk you through how long it takes to complete your PhD program.

For a traditional, campus-based PhD program, the average time to finish a PhD is 8 years. Fulfilling the program’s requirements will often demand a serious investment of your time.
Even still, some people are able to finish their programs in just 3 to 6 years. Multiple factors may influence the overall length of your program.
Required Credit Hours
Many PhD programs require you to earn 120 credit hours before entering the exam and dissertation phases.
Fortunately, there are PhD programs without such high credit-hour demands. For example, at some universities, you may earn a PhD with only 60 credit hours.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Schedule
Enrolling in a doctoral program part-time may allow you to keep up with your regular job. You’ll have to decide whether you prefer the flexibility of part-time schooling or the faster schedule of full-time studies.
Final Project Requirements
Many PhD programs end with the completion of a dissertation. This assignment may take years to complete, so PhD students often end up in the all-but-dissertation (ABD) phase for quite some time.
University Scheduling
Some schools promote their ability to help you through the PhD process faster than normal. Accelerated class schedules with eight-week online courses may speed your studies along. Focused attention from dissertation advisors may help as well.
PhD Program Components
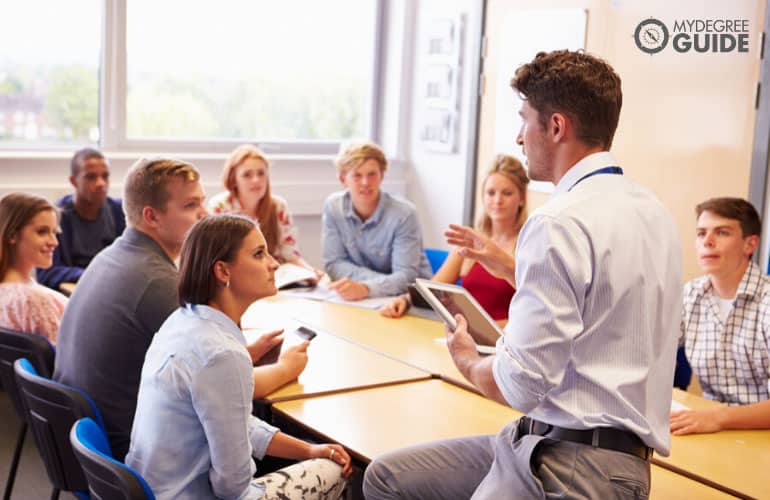

Before you enroll in a PhD program, it’s important to know some of the basic requirements:
Prerequisites
Most schools require you to already hold a master’s degree, but some offer bachelor’s-to-PhD programs.
Length to Completion
On average, it takes eight years to earn a PhD. Even still, completing doctoral coursework and a dissertation in three to four years is not unheard of.
Topic of Interest
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy, but that doesn’t mean you’ll be getting a philosophy degree. Your field of study will depend on your interests and the programs that your university offers. You may tailor your doctoral focus though your choice of a dissertation topic.
Steps to Completion
You’ll take advanced classes before sitting for comprehensive exams. After passing your exams, you’ll likely begin working on a dissertation. You must defend your dissertation before finishing your program.
Doctoral studies begin with a series of classes through which you may increase your knowledge of your field of study and learn about conducting research. These are advanced classes, so they should be more in-depth than the ones you took during your undergraduate and master’s programs.
The number of courses that you need to take can vary significantly. It’s not uncommon for PhD programs to require 120 credit hours of coursework. That amounts to about 40 classes.
At other schools, the requirements are lower. Your university’s program may involve just 60 credit hours or, possibly, even fewer. A less intense course load may significantly slash your time to completion.
Your university may require you to maintain a GPA above a minimum threshold. An unsatisfactory GPA may keep you from moving on to the next step of the PhD process.
Comprehensive Examinations
Universities often require students to demonstrate their readiness for a doctoral project before advancing to the next stage of their studies. Readiness is proven through comprehensive exams , which may also be known as:
- Preliminary examinations
- Major field examinations
- General examinations
Often, comprehensive exams take the form of written or oral tests. In other situations, faculty may assess students’ readiness on the basis of a portfolio evaluation or a written paper.
Dissertation and Defense

A dissertation, also known as a graduate thesis, is a body of work that presents original research in your field. This manuscript focuses on a unique idea and includes evidence to support your thesis. During your doctoral studies, there are classes designed to help prepare you for your dissertation work.
The dissertation process may take several years. Once your manuscript is complete, you must defend it to the doctoral program faculty. After your defense, you may need to do further work on your manuscript, or the committee may decide that your dissertation is complete.
Not all programs require a dissertation. Instead, there may be an alternative doctoral project. Although both dissertations and capstone projects are rigorous, projects can sometimes be completed within a shorter time frame.
Average Time to Complete PhD by Field of Study
Students in some disciplines usually take a lot more time to finish their doctoral work than students in other fields.
If you’re studying in the following scientific fields, you may be more likely to earn your on-campus degree in seven years or less:
- Physics — average of five years
- Psychology — average of five to seven years
On the other hand, if your field of study relates more to the humanities, your on-campus degree program may take longer:
- History — average of eight years
- English — average of eight years
- Education — average of 13 years
These are the traditional figures. There are ways to finish faster.
Why Does It Take So Long to Finish a Traditional PhD?

Some schools require doctoral students to take around 40 classes, which, in a traditional on-campus setting, may take years. After completing the coursework, you must write your dissertation and defend it. The dissertation process alone might take multiple years.
Doctoral programs online may help shorten the PhD process to three or four years. Fewer credit hours may be required, and the classes may be delivered in an accelerated format.
Schools with an emphasis on quick doctoral programs may also offer dissertation advisors to efficiently guide students through that phase. Alternatively, some universities allow students to complete capstone projects that don’t take as long as dissertations.
Getting a PhD Online vs. Campus

Online education has changed students’ options for earning a PhD. These days, aspiring students may choose whether to attend classes on a college campus or online.
Traditional programs may require you to relocate to the university’s campus and attend school full-time. On average, it takes just over eight years to complete those programs. The benefits of choosing an online school instead may include:
Faster Progress
Accelerated eight-week courses may allow you to finish your course load sooner. You may complete your entire program in just three or four years.
Multiple Start Dates
Online programs often let you join throughout the year, so you don’t have to put your studies on hold until the fall semester.
Flexibility
Not being required to move to campus or come to class at set times may allow you to work your studies around your schedule.
Equal Status
Online programs are just as rigorous as on-campus ones. As long as your university is accredited, your degree will be just as valuable as one from a traditional university setting.
Cost-Savings
Finishing your doctoral studies faster may mean that you pay less tuition.
How to Finish Your PhD in Less Time

Although you can’t earn a doctoral degree overnight, you shouldn’t have to spend the majority of your working years striving toward PhD-completion. The following tips for accelerating the PhD process may help you finish your studies more quickly than the average doctoral student.
1. Use What You Already Know
Every school requires a minimum number of credit hours that you must earn in the pursuit of your degree. To help you meet this threshold, some schools will allow you to transfer in credits from other doctoral programs. Universities may also give you credit for your professional experience. Reducing your class load may save you both time and money.
2. Look for Short Classes
Accelerated course schedules are one of the best ways to speed through the degree process. Every eight weeks, you’ll begin a new set of classes. Over the course of a year, there may be five different sessions during which you can take classes.
3. Work on Your Dissertation Throughout the Program
Traditionally, dissertation work begins once the classroom portion of your studies is over. Quick doctoral programs may allow you to begin the dissertation process while you’re still taking other classes. This approach, known as an embedded dissertation, may reduce the likelihood that you’ll drop out before finishing your final project. It might also speed up your doctoral timeline.
4. Ask for Help
A lack of support can lead some doctoral students to drop out. On the other hand, having a good support system can help you push through and finish your program more quickly. Build a team of family, friends, and academic mentors who can encourage you, guide you, and lend practical help when you’re feeling overwhelmed by school.
Why Get a PhD?
You may need to earn a doctoral degree to achieve your career goals . For example, if you want to become a clinical psychologist, this level of study is essential. Many scientific and research positions require doctoral studies. University faculty typically need to hold terminal degrees as well.
Even if a doctorate is not a requirement for your desired line of work, it may help you achieve greater success. You might be granted higher levels of responsibility, and you may earn more money. In some fields, those who hold PhDs make around 20% more than those with master’s degrees, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics .
Do You Have to Have a Master’s Degree to Get a PhD?
Many schools consider a master’s degree an essential prerequisite for PhD admission. If you don’t already have a master’s degree, a bachelor’s-to-doctorate program may allow you to earn a master’s and a PhD for less time and money than it would take to pursue them separately.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD After a Master’s?
You may be able to complete your doctoral program in three to four years if you opt for an accelerated online program. On average, traditional on-campus PhD programs take around eight years to complete.
How Hard Is It to Finish a PhD?
Doctoral studies are challenging. That shouldn’t come as a surprise; if doctorates were easy to acquire, nearly every college graduate would end up with a PhD behind his or her name.
Approximately 50% of students who begin a PhD program don’t end up finishing. Many quit within two years of starting. Another large portion gives up upon reaching the dissertation phase.
Although all PhD programs are challenging, the flexible nature of online programs may help you find success. Choosing a doctoral track that doesn’t require a dissertation may help as well.
What Is the Easiest PhD to Get?

All PhD programs are demanding, but you might have an easier time if you select a program that aligns with your interests and your career goals. The flexibility of online study may help your doctoral program seem less burdensome. In addition, capstone projects are sometimes easier than writing dissertations.
If earning a doctoral degree in a short time frame is important to you, then consider the many potential benefits that online programs have to offer. Within just a few years, you may be able to place the letters “PhD” at the end of your name.


- January 18, 2024
- Academic Advice
How Long Does It Take To Get a Ph.D.? Find Out!
UOTP Marketing

One life-changing decision you can make is to pursue a Ph.D. ; While getting a Ph.D. is a challenging journey, it can be very beneficial and rewarding in the long run in terms of employment and financial gains.
After years of studying, finishing a bachelor’s and then a master’s degree , you might have an idea whether pursuing a Ph.D. degree is the right path for you or not. But if you’re still having doubts, keep reading the article to learn everything you need to know about what a Ph.D. entails, how long it takes, and why getting a Ph.D. is beneficial.
What Is a Ph.D. Degree?
So, what exactly is a Ph.D.? Simply put, the word Ph.D., which comes from the Latin “Philosophiae Doctor,” is an abbreviation of Doctor of Philosophy . It is a research degree in a specific field that is taken by students who already have a solid educational foundation; they have a bachelor’s as well as a master’s degree.
A Ph.D. is essentially the highest academic qualification given to students who complete a particular program, have published scientific articles, and defended their field-specific dissertation.
It is easy to confuse a Ph.D. with a doctorate degree . People tend to make this mistake because of how similar these words sound. However, certain aspects of these degrees make them different from each other.
Although these terms are often used interchangeably in the academic world, a doctorate is a general term that includes different fields, from professional degrees to scientific disciplines. It is essentially a practice-oriented degree with a direct application to a specific career, specifically designed to equip students with the necessary skills to use their knowledge to provide solutions to existing real-world problems. A Ph.D., on the other hand, is a subclass of a doctorate degree characterized by a theoretical and research-oriented nature.
Having made the distinction between a doctorate and a Ph.D. , let’s look into further specifics regarding the nature of a Ph.D. degree, such as entry requirements, coursework, and what you can do with a Ph.D. degree in terms of career opportunities.
Ph.D. degree entry requirements

If you decide to apply for a Ph.D. degree, you should know the entry requirements. While there are several entry requirements, you should keep in mind that they can vary based on the specific field of your interest.
Before embarking on a Ph.D. journey, students should have already finished their bachelor’s and master’s studies in their field of interest. Here is a general list of the documentation requirements you must meet to be considered for admission here at University of the Potomac (UOTP):
- UOTP application form,
- Registration application form,
- Official transcripts from every university you attended,
- A master’s degree from an accredited institution,
- Education or professional training certificates,
- An application essay,
- An interview with UOTP,
- GRE or MAT scores.
Ph.D. degree coursework
One question you might have regarding Ph.D. is whether it requires any coursework, and if yes, what kind of coursework. Coursework is an essential part of a Ph.D. degree. As mentioned earlier, the Ph.D. degree is a research-based degree. This means that Ph.D. students start their journey by doing advanced coursework in a particular subject which helps them identify areas of interest.
Students must identify research areas for their dissertation or doctoral thesis . After identifying a research area, Ph.D. students work with their mentors in research, teaching, and research methodology. The dissertation, which is the final requirement, is an original research paper conducted by a Ph.D. candidate in their field of specialty that is presented to a faculty committee.
What can you do with a Ph.D. degree?
Earning a Ph.D. degree opens the door to many opportunities in both academic and non-academic careers. Most Ph.D. workers in academia have high positions, such as university deans and presidents, and their responsibilities include teaching, researching, and administrative duties.
On the other hand, the non-academic industries where Ph.D. graduates work include professional specialty or executive, managerial, and administrative occupations.
How Long Does It Take To Get a Ph.D.?

While certain Ph.D. programs take longer to complete than others, generally, Ph.D. candidates take 5 or 6 years to complete their degree.
Ph.D. timeline
Below is a general summary of the timeline of a Ph.D. :
- Consult your advisor regarding every aspect of your Ph.D. program and its requirements;
- The supervisory committee must be created in the first year and must hold meetings regarding the particular research project;
- You must take the comprehensive exam in the second year;
- You must conduct your dissertation research;
- After meeting the requirements of the curriculum, a deadline for finishing the dissertation must be set;
- Consult the whole dissertation with your advisor and select the external examiners;
- Once your thesis is approved, you have to defend your thesis, which is done through an oral exam that lasts 2.5 to 3 hours.
Online vs. campus
You can obtain a Ph.D. degree either online or on campus . The popularity of online Ph.D. degrees is increasing day by day. The general benefits of an online degree apply to the online Ph.D. degree as well, such as flexibility, lower costs, and recognition by employers .
Before embarking on an online Ph.D. journey, you have to ensure that the online program of your choice is accredited.
Comprehensive examinations
One requirement Ph.D. students have to complete is to go through comprehensive examinations. The sole purpose of comprehensive examinations is to determine whether a Ph.D. student has acquired the necessary knowledge of a particular field of study and whether the student can be considered eligible to do original research.
The comprehensive examination has two phases, specifically the written and oral exams. The written exam tests your ability to apply your knowledge to formulate good research questions and solve research issues. The oral exam contains questions regarding your research and answers you gave on the written exam.
Ph.D. dissertation and defense
The last step towards completing your Ph.D. studies is your dissertation defense. The Ph.D. dissertation is an original research paper conducted by a Ph.D. candidate, which is then presented orally in front of a committee. In order to publicly defend the dissertation, a student must first get approval. If the defense is successful, then the paper is sent to the school’s archive, and the Ph.D. candidate receives their degree.
Why Get a Ph.D.?

Given the dedication and time required to do a Ph.D., you might naturally wonder, “Is a Ph.D. even worth all this effort?” The answer is yes. While you might have your own reasons for embarking on a Ph.D. journey, and whether they are career-oriented or financial reasons, getting a Ph.D. can be beneficial in several ways.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
You become an expert in the field
Ph.D. degrees are pursued only by the most passionate learners and those willing to dedicate their time and effort to it. The extensive research you will have to conduct during your Ph.D. studies will make you a better researcher by equipping you with the necessary research skills. During Ph.D. studies, you conduct research as well as explore and analyze your own areas of interest. All of this will definitely contribute to making you an expert in your field.
You have more career opportunities
As stated before, a Ph.D. degree will get you jobs in many academic and non-academic settings. There are many jobs that require a Ph.D . Some of them include the following:
- Research scientist,
- Anthropologist,
- Psychiatrist, etc.
You earn a better salary
Getting a Ph.D. will help you land higher-paying jobs. According to the BLS, Ph.D. graduates have the lowest unemployment rate (which is 1.5%) among other graduates, while the salary is the highest. The weekly earnings of a Ph.D. worker are around $1,909 .
Considering the Personal and Lifestyle Impacts of Pursuing a Ph.D.
When pursuing a Ph.D., it’s important to remember that it will impact your academic growth, personal life, and lifestyle. Therefore, it’s crucial to take into account these often-overlooked aspects.
Time management and work-life balance
Pursuing a Ph.D. demands rigorous time management. Balancing extensive research, demanding coursework, and personal responsibilities can be overwhelming. It’s about finding time for your studies and ensuring you don’t neglect your personal life. Effective time management strategies, such as creating a structured schedule and setting realistic goals, are essential to maintain this delicate balance.
Mental health and stress management
The path to a Ph.D. can be mentally taxing. Many students experience stress, anxiety, and even imposter syndrome. Acknowledging these challenges is the first step towards managing them. Regular self-care routines, seeking support from peers and mental health professionals, and taking breaks when necessary are vital for your mental well-being.
Financial considerations
Let’s talk finances. Pursuing a Ph.D. often means forgoing full-time employment for several years. While there are funding opportunities like scholarships and stipends, these might not cover all expenses. It’s important to plan your finances carefully, considering both the immediate costs and the long-term benefits.
Social life and relationships
Your social life is likely to take a hit during your Ph.D. studies. Long hours of research can lead to isolation, affecting your relationships. However, maintaining a healthy social life is crucial. Building a support network within your academic community and making time for family and friends can provide the necessary balance.
Personal growth and development
Despite the challenges, pursuing a Ph.D. offers unparalleled personal growth. You’ll develop both academically and in terms of problem-solving skills, resilience, and independence. These years will shape you in ways beyond the academic realm.
Long-term career and life goals
Finally, reflect on how a Ph.D. aligns with your long-term goals. This degree is not just a career move; it’s a life choice. How does it fit into your broader aspirations, both professionally and personally? Ensure that this path aligns with where you see yourself in the future.
Final Thoughts
Enrolling in a Ph.D. program is not an easy decision to make. Qualifications mentioned above might be the entry requirements; however, mental determination and dedication are the essential components for successfully completing any Ph.D. program.
Hopefully, our article will help and guide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision on whether to embark or not in a Ph.D. journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is a ph.d. degree.
A Ph.D., or Doctor of Philosophy, is a research degree and the highest academic qualification in a specific field. It requires a solid educational foundation, typically including a bachelor’s and a master’s degree, and involves completing a program, publishing scientific articles, and defending a field-specific dissertation.
How is a Ph.D. different from a doctorate?
While often used interchangeably, a doctorate is a general term encompassing various degrees in different fields, including professional and scientific disciplines. A Ph.D. is a subclass of a doctorate, characterized by its theoretical and research-oriented nature.
What are the entry requirements for a Ph.D. degree?
Requirements can vary but generally include a completed bachelor’s and master’s degree in the field of interest, official transcripts from previous universities, a CV, an application essay, GRE or MAT scores, and an interview.
Does a Ph.D. require coursework?
Yes, Ph.D. programs typically start with advanced coursework in a specific subject, helping students identify research areas for their dissertation or thesis.
What career opportunities are available with a Ph.D. degree?
Ph.D. holders can pursue high positions in academia (like university deans and presidents) or various professional roles in non-academic sectors, including law, research science, linguistics, anthropology, psychiatry, etc.
What is the Ph.D. dissertation and defense process?
The dissertation is an original research paper conducted by the Ph.D. candidate. After getting approval, the candidate defends their dissertation orally in front of a committee. Successful defense leads to the degree being awarded and the paper archived by the school.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

11 Highest Paying Healthcare Administration Jobs

What Is a Professional Reference? All You Need to Know

CPA Exam Pass Rate: A Comprehensive Guide

The Ultimate Guide: Is Marketing a Good Major?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information

PhD Admissions
The PhD program in Psychology trains students for careers in research and teaching. In addition to a wide range of courses, the PhD program is characterized by close collaboration between students and their faculty advisors.
General Information
The Department of Psychology holistically reviews each candidate's complete application to assess the promise of a career in teaching and research. Consideration is based on various factors, including courses taken, grade point average, letters of recommendation, and the statement of purpose. Additionally, the Department of Psychology places considerable emphasis on research training, and admitted students have often been involved in independent research as undergraduate students or post-baccalaureate settings. Although there are no course requirements for admission, all applicants should have sufficient foundational knowledge and research experience to engage in graduate-level coursework and research.
We accept students with undergraduate degrees and those with both undergraduate and master's degrees. An undergraduate psychology major is not required; the Department welcomes applicants from other academic backgrounds.
Our application portal is now closed for the AY24-25 admissions cycle. Please consider applying during next year's AY25-26 admissions cycle, which opens on September 15, 2024.
How to Apply
Application and deadline.
Our 2025-26 Admissions application will open on September 15, 2024.
Applications will be due on November 30, 2024
The deadline for letters of recommendation will be November 30, 2024 .
Once an applicant submits the recommenders' information, the recommenders will receive an automated email with instructions for submitting the letter. Late letters should be sent directly to psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (psych-admissions[at]stanford[dot]edu) . Staff will add them to the application file if the review process is still underway. Still, the faculty reviewers are not obligated to re-review files for materials submitted after the deadline.
The status of submitted applications can be viewed by logging in to the application portal .
The deadline to apply for the Stanford Psychology Ph.D. program is November 30, 2024 .
Applicants who are admitted to the program will matriculate in autumn 2025.
In addition to the information below, please review the Graduate Admissions website prior to starting your application. The Department of Psychology does not have rolling admissions. We admit for the Autumn term only.
Requirements
- U.S. Bachelor's degree or its foreign equivalent
- Statement of Purpose (submitted electronically as part of the graduate application). You will be able to specify three Psychology Department faculty members , in order of preference, with whom you would like to work.
- Three Letters of Recommendation (submitted electronically). A maximum of six letters will be accepted.
- Unofficial transcripts from all universities and colleges you have attended for at least one year must be uploaded to the graduate application. Applicants who reach the interview stage will be asked to provide official transcripts as well; Department staff will reach out to these applicants with instructions for submitting official transcripts. Please do not submit official transcripts with your initial application.
- Required for non-native English speakers: TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) scores, submitted by the Educational Testing Service (ETS) electronically to Stanford.
Application Fee
The fee to apply for graduate study at Stanford is $125. Fee waivers are available for some applicants. Please visit Graduate Admissions for information on applying for an Application Fee Waiver .
Application Review & Status Check
The Department of Psychology welcomes graduate applications from individuals with a broad range of life experiences, perspectives, and backgrounds who would contribute to our community of scholars. The review of applications is holistic and individualized, considering each applicant’s academic record and accomplishments, letters of recommendation, and admissions essays to understand how an applicant’s life experiences have shaped their past and potential contributions to their field.
To check the status or activity of your application, please log into your application account . You can also send reminders to recommenders who have not yet submitted their letter of recommendation.
Due to limited bandwidth, the Department of Psychology staff will not answer any phone or email queries about application status, including requests to confirm the receipt of official transcripts.
Our faculty will interview prospective students before making final admission decisions. Candidates who progress to the interview round will be informed in January. Interviews are generally conducted in February.
The Department of Psychology recognizes that the Supreme Court issued a ruling in June 2023 about the consideration of certain types of demographic information as part of an admission review. All applications submitted during upcoming application cycles will be reviewed in conformance with that decision.
- Diversity and Engagement in Psychology PhD Programs
- Vice Provost for Graduate Education
- Stanford IDEAL
- Graduate Application Fee Waiver Information
For More Information
Please see our list of Frequently Asked Questions and psych-admissions [at] stanford.edu (contact us) should you have additional questions.
What is a PhD? Advice for PhD students
How long does it take to get a doctorate degree how do you get into grad school are you qualified to do a phd answers to these questions and more.
What is a PhD?
A PhD, which stands for “doctor of philosophy”, is the most advanced academic degree. It’s earned through extensive research on a specific topic, demonstrating expertise and contributing new knowledge to the field.
What does “PhD” mean?
The term “PhD” is often used as a synonym for any doctoral-level qualification. Doctorate degrees can often be split into two categories: MPhil and PhD.

Download your Study Abroad Guide for FREE!
An MPhil is similar to a PhD as it includes a research element (which is usually shorter and less in-depth than a PhD thesis, and often more akin to a dissertation undertaken at undergraduate or master’s level).
MPhil students focus more on interpreting existing knowledge and theory and critically evaluating other people’s work rather than producing their own research. The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries.
A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as “candidates”, to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
PhD requirements vary significantly among countries and institutions. The PhD, once completed, grants the successful candidate the title of “doctor of philosophy”, also called PhD or DPhil.
What is a professional doctorate?
A professional doctorate is a kind of degree that helps people become experts in their fields. Instead of focusing mainly on theory and research like a regular PhD, a professional doctorate is all about practical skills and knowledge.
This kind of doctorate is great for students who want to get better at their jobs in areas like teaching, healthcare, business, law or psychology. The courses and projects in these programmes are designed to tackle real problems you might face at work.
For example, you might have heard of the doctor of education (EdD), doctor of business administration (DBA), doctor of psychology (PsyD) or doctor of nursing practice (DNP). These programmes combine learning, hands-on projects and sometimes a thesis paper or essay to show you’re skilled at solving on-the-job challenges.
How long does it take to study a PhD?
The time required to complete a PhD can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, a full-time PhD programme takes around three to six years to finish. However, it’s important to take into account individual circumstances and the nature of the research involved.
1. Full-time vs. part-time: If you’re studying full-time, dedicating most of your time to your studies, it usually takes about three to four years to complete a PhD. However, studying part-time while managing other commitments might extend the duration. Part-time PhDs can take around six to eight years, and sometimes even longer.
2. Nature of research: The complexity of your research proposal can influence the time required. Certain research questions may involve intricate experiments, extensive data collection or in-depth analysis, potentially leading to a longer completion timeline.
3. Field of study: The subject area you’re researching can also affect the necessary time. Some fields, such as sciences or engineering, might involve more hands-on work, while theoretical subjects might require more time for literature review and analysis.
4. Supervision and support: The guidance and availability of your academic supervisor can affect the pace of your research progress. Regular meetings and effective communication can help keep your studies on track.
5. Thesis writing: While the research phase is crucial, the stage of writing your thesis is equally significant. Organising and presenting your research findings in a clear and cohesive manner can take several months.
6. External commitments: Personal commitments, such as work, family or health-related factors, can influence your study time. Some students need to balance these alongside their PhD studies, potentially extending the duration.
7. External Funding: The availability of funding can also affect your study duration. Some funding might be linked to specific project timelines or research objectives.
So, although a PhD usually takes between three and six years of full-time study, with potential variations based on research complexity, enrolment as part-time or full-time, field of study and personal circumstances. It’s vital to have a realistic understanding of these factors when planning your PhD journey.
How long is a PhD in the UK?
In the UK, the length of a PhD programme typically ranges from three to four years of full-time study. As explained above, there are many factors to consider.
How long is a PhD in the US?
Similarly to the UK, in the United States, the duration of a PhD programme can vary widely depending on the field of study, research topic and individual circumstances. On average, a full-time PhD programme in the US typically takes between five and six years to complete.
Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US?
PhD programmes generally take longer to complete in the US than in the UK due to various factors in the education systems and programme structures of each country:
1. Programme structure: UK PhD programmes often emphasise early, focused research from the first year, leading to shorter completion times. In contrast, US programmes commonly include more initial coursework in your first and second year and broader foundational training, which can extend the overall duration.
2. Course work requirements: Many US PhD programmes require a lot of course work, which can lengthen the time needed to finish. UK programmes tend to have fewer or no course work demands, allowing students to concentrate primarily on research skills.
3. Research funding: In the UK, PhD funding is often awarded with specific timeframes in mind, motivating completion of the research degree in the agreed duration. In the US, funding approaches can vary, requiring students to secure funding from multiple sources, potentially affecting their progress and completion time.
4. Teaching responsibilities: Some US PhD students take on teaching roles as part of their funding, dividing their time and potentially prolonging their studies.
5. Research approach: Differences in research methodologies and project scopes can affect the time needed for data collection, experimentation and analysis.
6. Academic culture: The US education system values a well-rounded education, including coursework and comprehensive exams. This can extend the time before full-time research begins. UK PhD programmes often prioritise independent research early on.
7. Part-time and work commitments: US PhD candidates might have more flexibility for part-time work or other commitments, which can affect research progress.
8. Dissertation requirements: US PhD programmes generally include a longer and more comprehensive dissertation, involving more chapters and a broader exploration of the research topic.
These variations in programme structures, funding models and academic cultures contribute to the differing completion times between the two countries.
What qualifications do you need for a PhD?
To be eligible for a PhD programme, certain educational qualifications are generally expected by universities. These qualifications serve as indicators of your readiness to engage in advanced research and contribute to the academic community.
First, an undergraduate or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field is typically the most common requirement. This degree provides you with a foundational understanding of the subject and introduces you to basic research methodologies. It serves as a starting point for your academic journey.
Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme?
In addition to an undergraduate degree, many PhD programmes also require candidates to hold postgraduate or master’s degrees, often in fields related to the intended PhD research. A master’s degree offers a deeper exploration of the subject matter and enhances your research skills. Possessing a master’s degree signifies a higher level of expertise and specialisation.
The combination of both undergraduate and postgraduate degrees demonstrates a solid academic background. This background is crucial before you engage in doctoral study because pursuing a PhD involves more than just knowledge; it requires advanced research abilities, critical thinking and the capacity to provide an original contribution and new insights into the chosen field of study.
While these qualifications are usually requested, there are exceptions. Some institutions offer direct-entry programmes that encompass bachelor’s, master’s and PhD degrees in a streamlined structure. This approach is often seen in scientific and engineering disciplines rather than humanities.
In exceptional cases, outstanding performance during undergraduate studies, coupled with a well-defined research proposal, might lead to direct entry into a PhD programme without requiring a master’s degree.
Admission requirements can vary between universities and programmes. Some institutions might have more flexible prerequisites, while others could have more stringent criteria. Make sure that you thoroughly research all admission requirements of the PhD programmes you’re interested in to ensure you provide the right information.
Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries?
PhD entry requirements in Canada and Australia can be somewhat similar to those in the UK and the US, but there are also some differences. Just like in the UK and the US, having a bachelor’s degree followed by a master’s degree is a common way to qualify for a PhD in Canada and Australia. However, the exact rules can vary, such as how much research experience you need or the grades you should have.
In Canada and Australia, as in the UK and the US, international students usually need to show their English language skills through tests like IELTS or TOEFL. And, like in other places, you might need to give a research proposal to explain what you want to study for your PhD.
But remember, even though there are some similarities, each country has its own rules.
PhD diary: Preparing for a PhD Nine things to know before doing a PhD Women in STEM: undertaking PhD research in cancer Studying for a part-time PhD: the challenges and the benefits Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student? Looking for PhD tips? Why not check Twitter PhD diary: Where do I begin? How to do a PhD on a budget
How much does it cost to study a PhD?
The cost of pursuing a PhD can vary significantly between international and home (domestic) students, and it depends on the country, university and programme you choose.
United Kingdom (UK)
Home students in the UK often pay lower tuition fees compared with international students. Home students might also have access to government funding or subsidised tuition rates.
International students typically pay higher tuition fees, which can vary widely depending on the university and programme. Fees can range from around £10,000 to £25,000 or more per year.
United States (US)
PhD programme costs in the US can be quite high, especially for international students. Public universities often have lower tuition rates for in-state residents compared with out-of-state residents and international students.
Private universities in the US generally have higher tuition fees, and international students might be charged higher rates than domestic students.
Canadian universities often charge higher tuition fees for international students compared with domestic students.
Some universities offer funding packages that include tuition waivers and stipends for both domestic and international doctoral students.
In Australia, domestic students (Australian citizens and permanent residents) usually pay lower tuition fees than international students.
International students in Australia might have higher tuition fees, and costs can vary based on the university and programme.
Apart from tuition fees, other aspects play a role in the overall financial consideration:
PhD studentship: Many universities offer PhD studentships that provide financial support to research students, covering both tuition fees and a stipend for living expenses.
Stipend and housing: Stipends are designed to cover living expenses. Stipend amounts can vary depending on the university and location. If you’re studying in London in the UK, stipends might be higher to account for the higher living costs in the city. Some universities also offer subsidised or affordable housing options for doctoral students.
Tuition and stipend packages: Some PhD programmes provide funding packages that include both tuition waivers and stipends. These packages are to help relieve the financial burden on students during their doctoral studies.
Research the financial support options provided by the universities you’re interested in to make an informed decision about the cost of your PhD journey.
What funding options are available for PhD candidates?
PhD candidates have various funding options available to support their studies and research journeys. Some of these options include:
PhD scholarships: Scholarships are a common form of financial aid for PhD candidates. They are awarded based on academic merit, research potential or other specific criteria. Scholarships can cover tuition fees and provide a stipend for living expenses.
Bursaries: Bursaries are another form of financial assistance offered to students, including PhD candidates, based on financial need. They can help cover tuition fees or provide additional financial support.
In the UK, specific funding options are available:
Regional consortium: Some regions have research consortiums that offer funding opportunities for doctoral candidates. These collaborations can provide financial support for research projects aligned with specific regional needs.
UK research institute: Research councils in the UK often offer stipends to PhD candidates. These stipends cover living expenses and support research work.
University-based studentship: Many UK universities offer studentships. You can read more about these above.
In the USA, there are also funding options available:
Research assistantships (RAs): Many universities offer research assistantships where PhD candidates work on research projects under the guidance of faculty members. In exchange, they receive stipends and often have their tuition waived.
Teaching assistantships (TA): Teaching assistantships involve assisting professors in teaching undergraduate courses. In return, PhD candidates receive stipends and sometimes tuition remission.
Fellowships: Fellowships are competitive awards that provide financial support for PhD candidates. They can come from universities, government agencies, private foundations and other institutions. Fellowships can cover tuition, provide stipends and offer research or travel funds.
Graduate assistantships: Graduate assistantships include a range of roles, from research and teaching to administrative support. These positions often come with stipends and sometimes include tuition benefits.
External grants and fellowships: PhD candidates can apply for grants and fellowships from external organisations and foundations that support research careers in specific fields. Examples include the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Fulbright Programme.
Employer sponsorship: In some cases, employers might sponsor employees to pursue PhDs, especially if the research aligns with the company’s interests.
You can read about the current available scholarships for international students of all education levels on our website .
What does a PhD Involve?
How does a PhD work?
A PhD includes thorough academic research and significant contributions to your chosen field of study. The timeline for completing a PhD can significantly vary based on the country, college or university you attend and the specific subject you study.
The duration of a PhD programme can vary based on factors such as the institution’s requirements and the academic discipline you’re pursuing. For instance, the timeline for a PhD in a science-related field might differ from that of a humanities discipline.
UK PhD timeline example
Looking at a typical PhD degree in a London higher education institution, we can consider this example timeline.
In the initial year of your PhD, you’ll collaborate closely with your designated academic supervisor. This collaboration involves refining and solidifying your research proposal, which lays the foundation for your entire doctoral journey.
This is also the time to establish a comprehensive plan, complete with well-defined milestones and deadlines. A crucial aspect of this year is conducting an extensive literature review, immersing yourself in existing academic works to understand the landscape of your chosen research area. It’s important to make sure that your research idea is original and distinct from prior studies.
As you begin the second year, you’ll actively collect data and gather information related to your research topic. Simultaneously, you’ll initiate the process of crafting your thesis. This involves combining your research findings and analysis into sections of your thesis document.
This is also the phase where you might have opportunities to share your research insights at academic meetings, conferences or workshops. Depending on the programme, you might even engage in teaching activities. Some PhD candidates also begin contributing to academic journals or books, showcasing their findings to a broader audience.
The third year of a PhD programme often marks the final stage of your research efforts. This is when you dedicate substantial time to writing and finalising your complete thesis. Once your thesis is completed to the highest standard, you’ll submit it for thorough evaluation.
A significant milestone in the third year is the viva voce, an oral examination where you’ll defend your thesis before a panel of experts in your field. The viva voce is an opportunity to showcase your deep understanding of your research and defend your findings.
Why should you do a PhD?
For many people, acquiring a doctorate degree is the pinnacle of academic achievement, the culmination of years of commitment to higher education.
However, the act of pursuing a PhD can be a complex, frustrating, expensive and time-consuming exercise. But with the right preparation, some sound advice and a thorough understanding of the task at hand, your years as a doctoral student can be some of the most rewarding of your life.
People choose to work towards a doctorate for many reasons. If you are looking to pursue an academic position, such as university lecturer or researcher, then a PhD is usually required.
Many people obtain a PhD as part of a partnership with an employer, particularly in scientific fields such as engineering, where their research can prove useful for companies.
In some cases, however, PhDs are simply down to an individual’s love of a subject and their desire to learn more about their field.
What are some benefits of studying a PhD?
Pursuing a PhD can have many benefits that extend beyond academic achievement, encompassing personal growth, professional advancement and meaningful contributions to knowledge.
One of the most notable benefits of a PhD is the potential for tenure in academia. Attaining tenure provides a level of job security that allows you to delve into long-term research projects and make enduring contributions to your field. It signifies a stage where you can explore innovative ideas and pursue in-depth research, fostering your academic legacy.
While not obligatory, the opportunity to collaborate on research projects with your supervisor is another valuable aspect of a PhD pursuit. These collaborations might even come with financial compensation, offering real-world experience, skill development and practical applications of your research. Engaging in such collaborations can enrich your research portfolio and refine your research methodologies.
A pivotal aspect of a PhD journey is the chance to publish your original research findings. By disseminating your work in academic journals or presenting it at conferences, you contribute to the expansion of knowledge within your field. These publications establish your expertise and reputation among peers and researchers worldwide, leaving a lasting impact.
The pursuit of a PhD can provide a unique platform to build a diverse network of colleagues, mentors and collaborators. Engaging with fellow researchers, attending conferences and participating in academic events offer opportunities to make valuable connections. This network can lead to collaborations, expose you to a spectrum of perspectives and pave the way for future research endeavours.
What is a PhD thesis? And what is a PhD viva?
A PhD thesis will be produced with help from an academic supervisor, usually one with expertise in your particular field of study. This thesis is the backbone of a PhD, and is the candidate’s opportunity to communicate their original research to others in their field (and a wider audience). PhD students also have to explain their research project and defend their thesis in front of a panel of academics. This part of the process is often the most challenging, since writing a thesis is a major part of many undergraduate or master’s degrees, but having to defend it from criticism in real time is arguably more daunting. This questioning is known as a “viva”, and examiners will pay particular attention to a PhD’s weaknesses either in terms of methodology or findings. Candidates will be expected to have a strong understanding of their subject areas and be able to justify specific elements of their research quickly and succinctly.
In rare cases, students going for a PhD may instead be awarded an MPhil if the academic standard of their work is not considered fully up to par but still strong enough to be deserving of a qualification.
Can you do a PhD part time?
Many PhD and MPhil candidates choose to pursue their qualification part time, in order to allow time to work and earn while studying. This is especially true of older students, who might be returning to academia after working for a few years.
When applying, you should always speak to the admissions team at your university to ensure this is possible and then continue to work with your supervisor to balance all your commitments.
Can I do a PhD through distance learning?
This is something else that you will need to check with your university. Some institutions offer this option, depending on the nature of your research.
You will need to be clear how many times you will need to travel to your university to meet with your supervisor throughout your PhD.
Your PhD supervisor
Choosing the right PhD supervisor is essential if you want to get the most out of your PhD. Do your research into the faculty at the institution and ensure that you meet with your proposed supervisor (either virtually or in person) before fully committing.
You need to know that not only do they have the right expertise and understanding of your research but also that your personalities won’t clash throughout your PhD.
Remember, to complete your PhD, you will need a strong support network in place, and your supervisor is a key part of that network.
Coping with PhD stress
If you do decide to embark on a doctorate, you may well encounter stress and anxiety. The work involved is often carried out alone, the hours can be long and many students can suffer from the pressure they feel is on their shoulders.
Ensuring that you check in regularly with your emotions and your workload is crucial to avoid burnout. If you have other commitments, such as a job or a family, then learning to balance these can feel overwhelming at times.
Give yourself regular breaks, speak to your supervisor and ensure that you know what university resources and support systems are available to you in case you need to access them.
Post-doctorate: what happens after you finish your PhD?
Many PhD graduates pursue a career in academia, while others will work in industry. Some might take time out, if they can afford to, to recover from the efforts of PhD study.
Whatever you choose to do, undertaking a PhD is a huge task that can open up a range of doors professionally. Just remember to take some time out to celebrate your achievement.
How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential?
How much does a professor with a PhD make a year?
Professors with PhDs can earn different amounts depending on where they work and their experience. In the UK, a professor might make around £50,000 to £100,000 or more each year. In the US, it's between about $60,000 and $200,000 or even higher. The exact salary depends on things like the place they work, if they have tenure, and what they teach.
How much does a PhD add to salary?
Having a PhD can make your salary higher than if you had a lower degree. But exactly how much more you earn can change. On average, people with PhDs earn more than those with bachelor’s or master’s degrees. The increase in salary is influenced by many things, such as the job you do, where you work and what field you’re in.
In fields such as research, healthcare, technology and finance, your knowledge and skills from your PhD can potentially help you secure a higher salary position.
In the end, having a PhD can boost your earning potential and open doors to well-paying jobs, including professorships and special roles in different areas. But the exact effect on your salary is influenced by many things, so ensure you weigh the cost against the benefit.
How to choose a PhD programme?
Choosing a PhD programme involves defining your research interest, researching supervisors and programme reputation, evaluating funding options, reviewing programme structure, considering available resources, assessing networking opportunities, factoring in location and career outcomes, visiting the campus if possible and trusting your instincts.
How can I find available PhD programmes?
You can find available PhD programmes by visiting university websites, using online directories such as “FindAPhD”, checking professional associations, networking with professors and students, following universities on social media, attending career fairs and conferences, contacting universities directly and exploring research institutes’ websites.
How to apply for a PhD programme?
To apply for a PhD programme:
Research and select universities aligned with your interests.
Contact potential supervisors, sharing your proposal, CV and references.
Prepare application materials: research proposal, CV, recommendation letters and a writing sample.
Ensure you meet academic and language-proficiency requirements.
Complete an online application through the university’s portal.
Pay any required application fees.
Write a statement of purpose explaining your motivations.
Provide official transcripts of your academic records.
Submit standardised test scores if needed.
Some programmes may require an interview.
The admissions committee reviews applications and decides.
Apply for scholarships or assistantships.
Upon acceptance, review and respond to the offer letter.
Plan travel, accommodation and logistics accordingly.
Remember to research and follow each university’s specific application guidelines and deadlines.
How to apply for a PhD as an international student?
Many stages of the PhD application process are the same for international students as domestic students. However, there are sometimes some additional steps:
International students should apply for a student visa.
Take language proficiency tests such as TOEFL or IELTS if required.
Provide certificates if needed to validate your previous degrees.
Show evidence of sufficient funds for tuition and living expenses.
Check if you need health insurance for your chosen destination.
Translate and authenticate academic transcripts if necessary.
Attend orientation sessions for cultural adaptation.
Apply for university housing or explore off-campus options.
Familiarise yourself with international student support services.
Ben Osborne, the postgraduate student recruitment manager at the University of Sussex explains in detail how to apply for a PhD in the UK .
Giulia Evolvi, a lecturer in media and communication at Erasmus University, Rotterdam explains how to apply for a PhD in the US .
Finally, Samiul Hossain explores the question Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student?
Q. What is a PhD? A. A PhD is the highest level of academic degree awarded by universities, involving in-depth research and a substantial thesis.
Q. What does “PhD” mean? A. “PhD” stands for doctor of philosophy, recognising expertise in a field.
Q. What is a professional doctorate? A. A professional doctorate emphasises practical application in fields such as education or healthcare.
Q. How long does it take to study a PhD? A. It takes between three and six years to study a full-time PhD programme.
Q. How long is a PhD in the UK? A. It takes around three to four years to study a full-time UK PhD.
Q. How long is a PhD in the US? A. It takes approximately five to six years to complete a full-time US PhD.
Q. Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US? A. US programmes often include more course work and broader training.
Q. What qualifications do you need for a PhD? A. You usually need an undergraduate degree as a minimum requirement, although a master’s might be preferred.
Q. Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme? A. Master’s degrees are preferred but not always required.
Q. Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries? A. Entry requirements are similar in many countries, but there may be additional requirements. Make sure to check the university website for specific details.
Q. How much does it cost to study a PhD? A. The cost of PhD programmes vary by country and university.
Q. What funding options are available for PhD candidates? A. Scholarships, assistantships, fellowships, grants, stipends are all funding options for PhD candidates.
Q. What does a PhD involve? A. PhDs involve research, seminars, thesis, literature review, data analysis and a PhD viva.
Q. Why should you do a PhD? A. There are many reasons to study a PhD including personal growth, research skills, contributions to academia and professional development.
Q. What are some benefits of studying a PhD? A. Benefits of graduating with a PhD include achieving tenure, collaborations with colleagues, publication of your work, and networking opportunities.
Q. What is a PhD thesis? A. A PhD thesis is a comprehensive document that showcases the original research conducted by a PhD candidate.
Q. What is a PhD viva? A. A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce or oral examination, is the final evaluation of a PhD candidate’s research and thesis where the panel asks questions, engages in discussions and assesses the depth of the candidate’s understanding and expertise.
Q. Can you do a PhD part-time? A. Yes, part-time options are available for PhDs.
Q. Can I do a PhD through distance learning? A. Some universities offer online PhDs; you can find out more on their websites.
Q. How to choose a PhD programme? A. You can find PhD programmes through research, by contacting faculty, checking resources and considering location.
Q. How can I find available PhD programme? A. You can find available PhD programmes on university sites, through directories and by networking.
Q. How to apply for a PhD programme A. To apply for a PhD programme, research suitable universities and programmes, get in touch with potential supervisors, gather required documents like transcripts and reference letters, complete the online application, pay any necessary fees and submit a statement of purpose and research proposal. If needed, meet language-proficiency criteria and attend interviews. After acceptance, explore funding choices, confirm your spot and get ready for the programme’s start.
Q. How to apply for a PhD as an international student A. To apply for a PhD as an international student, follow similar steps to domestic students, but you need to include securing a student visa and passing language requirements.
Q. What is a PhD dropout rate? A. The dropout rate from PhDs varies but is approximately 30-40 per cent.
Q. How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential? A. A PhD can boost earning potential, especially in research, technology, healthcare and academia. Impact varies by job, industry and location. Experience, skills and demand also influence salary.
Q. How to address a person with a PhD? A. When addressing someone with a PhD, it’s respectful to use “Dr”, followed by their last name, whether they have a PhD in an academic field or a professional doctorate. For instance, “Dr. Smith”.
Q. Is there a difference between a PhD and a doctorate? A. The terms “PhD” and “doctorate” are often used interchangeably, though a PhD is a specific type of doctorate focused on original research. A doctorate can refer more broadly to any doctoral-level degree, including professional doctorates with practical applications.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and an MD? A. A PhD is a doctor of philosophy, awarded for academic research, while an MD is a doctor of medicine, focusing on medical practice. They lead to different career paths and involve distinct areas of study.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and a professional doctorate? A. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree, while a professional doctorate emphasises applying research to practical fields such as education or business. PhDs often involve original research, while professional doctorates focus on real-world application.
Q. What is the difference between UK and US PhDs? A. The difference between UK and US PhDs lies mainly in structure and duration. UK PhDs often have shorter durations and a stronger emphasis on independent research from an early stage. US PhDs typically include more initial coursework and broader foundational training before full-time research begins.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD student and a candidate? A. A PhD student is actively studying and researching in a doctoral programme, while a PhD candidate has completed programme requirements except for the dissertation and is close to completion.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an EdD? A. A PhD and an EdD (doctor of education) differ in focus. A PhD emphasises research and academic contributions, while an EdD focuses on applying research to practical educational issues.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a DBA? A. A PhD and a DBA (doctor of business administration) differ in purpose. A PhD emphasises theoretical research and academia, while a DBA is practice-oriented, aimed at solving real business problems.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a PsyD? A. A PhD and a PsyD (doctor of psychology) differ in emphasis. A PhD focuses on research and academia, while a PsyD emphasises clinical practice and applying psychological knowledge.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an LLD? A. A PhD and an LLD (doctor of laws or Legum doctor) are distinct. A PhD is awarded in various disciplines, while an LLD is usually an honorary degree for significant contributions to law.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an MD-PhD? A. A PhD and an MD-PhD differ. An MD-PhD is a dual degree combining medical training (MD) with research training (PhD).
Q. What is the Cambridge PhD? A. A Cambridge PhD involves original research guided by a supervisor, resulting in a thesis. It’s offered at the University of Cambridge .
Q. What is the Oxford DPhil? A. An Oxford DPhil is equivalent to a PhD and involves independent research leading to a thesis. The term “DPhil” is unique to the University of Oxford .
Q. What is the PhD programme acceptance rate? A. PhD acceptance rates vary by university, field and competition. Prestigious universities and competitive fields often have lower acceptance rates.
Q. What is a PhD supervisor? A. A PhD supervisor guides and supports a student’s research journey, providing expertise and feedback.
Q. What is a PhD panel? A. A PhD panel evaluates a candidate’s research, thesis and oral defence. It consists of experts in the field.
Q. What is a PhD stipend? A. A PhD stipend is a regular payment supporting living expenses during research, often tied to teaching or research assistant roles.
Q. What is a PhD progression assessment? A. A PhD progression assessment evaluates a student’s progress, often confirming their continuation in the programme.
Q. What is a PhD defence? A. A PhD defence, or viva, is the final oral examination where a candidate presents and defends their research findings and thesis before experts.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Pursuing a PhD in neuroscience
Luis Humberto Eudave Ramos

Why study a PhD in English literature?
John Francis Davies

8 habits to help you get through your PhD
Shabana Khan
Register free and enjoy extra benefits

- How Long Does A PhD Take?
- Doing a PhD
Sometimes, just knowing how long a PhD takes can be enough to sway your decision on whether a research degree is for you. So with that in mind, exactly how long does a PhD take?
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3 to 4 years to finish whilst a part-time PhD takes twice as long at 6 to 7 years. Alongside these average durations, there are time limits on how long you can be enrolled on to a PhD programme. To discover these limits, the factors which most influence doctoral degree durations and how the UK durations compare to international PhDs, continue reading on.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Full-time PhD?
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD thesis and sitting your viva.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Part-time PhD?
In the UK, a part-time PhD will typically take you 6 to 7 years; twice as long as doing a full-time PhD. The reason for this is that as a part-time PhD student, you would dedicate around 20 hours per week to your PhD as opposed to the typical 40 hours full-time students would put into their subject.
How Long Does a Distance Learning PhD Take?
Similarly, distance learning PhD’s take an average of 6 to 7 years to complete. This is because the vast majority of students who undertake a distance learning PhD do so because they can’t relocate closer to the university. Although these commitments will differ, they often mean the student isn’t able to dedicate 40 hours per week to their studies.
Students in STEM disciplines will often take longer to finish a distance learning doctorate degree than those in non-STEM disciplines. This because the progress of a STEM PhD student will be limited by how often they can access a laboratory for experiment work.
How Does Funding Impact a PhD’s Duration?
In reality, the actual time it will take you to complete your PhD degree will depend on your funding situation.
If you’re receiving funding , it will usually only cover you for 3.5 years if you’re studying full-time or for 7 years at half the stipend if you’re studying part-time. Although this could vary slightly, most PhD funding providers, e.g. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), follow this timescale as indicated on their ‘ length of PhD studentships’ page. Because of this, most students who obtain scholarships try to complete their PhD within the timeframe of their funding so they don’t incur additional fees which they need to cover themselves.
It’s also worth noting that some funded PhD positions have additional conditions attached to them as part of their eligibility requirements. For example, they may require teaching undergraduate students, hosting laboratory sessions or attend presentations and conferences. This will be especially true if you’re on a Graduate Teaching Assistantship (GTA). Although these shouldn’t add considerable time to the length of a PhD programme, they have the potential to do so if they aren’t managed properly.
As self-funded students cover their own annual tuition fees and other associated costs, how long they’ll spend to complete their PhD project will largely depend on their own personal financial situation. Because of this, most self-funded PhD students find it best to complete their PhD study in the shortest time-frame they can manage.
Are There Deadlines?
Yes – unfortunately, all good things must come to an end! Within the UK, the deadline for your PhD is defined as the last date which you must submit your final thesis by. This date is set by your university’s overall regulations and varies depending on the arrangements of your PhD, e.g. whether it’s full or part time. In the vast majority of cases, the adopted deadlines are four years for full-time PhDs and seven years for part-time PhDs from the date you were officially registered onto your programme, as shown below from the University of Leicester’s registration guidance page .

This time-frame may vary from university to university. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts an additional year for part-time PhDs as shown below.
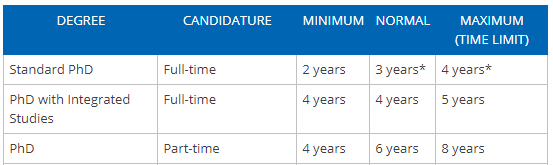
Can I Complete It Faster?
Although it’s possible to complete a full-time PhD in under 3 years, it’s a significant feat that’s rarely heard of. When these feats occur, they’re usually where the doctoral student already has extensive knowledge and experience in their field before undertaking their PhD.
Whilst it’s possible to complete a part-time PhD in under 6 years, it largely depends on your commitments outside your studies. For example, if you have a part-time career alongside your PhD, it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to commit the additional hours required to complete your doctorate a year faster.
However, if instead of a steady part-time job you take on occasional work as a freelancer, you’ll be able to set aside many more hours towards your doctoral degree.
Will Having only A Bachelor’s Degree or Being an International Student Limit My Rate of Progression?
Not at all. While there are benefits to having a Master’s degree such as an additional year of learning and greater research experience due to your fourth-year dissertation project, this doesn’t mean not having one would limit you. A PhD is very different to both Bachelor and Master degrees due to being heavily research-based, therefore, both types of students will have just as much to learn on their way to completing their doctorate.
Similarly, whether you’re an international student will bear no influence on the duration of your PhD.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Does This Compare to the Duration of EU and US PhDs?
PhD hosted by universities within the EU, such as those in France, Norway and Spain, have the same programme structure as those within the UK. As a result, there are no noticeable differences in the time to complete a doctorate between UK and EU institutions.
However, this is not the case in the US. Compared to PhDs conducted within the UK or EU, PhDs conducted within the US take considerably longer to obtain. According to a 2017 study conducted by the National Science Foundation, a US government agency which supports research and higher education, the average time to get a PhD within the US is 5.8 years. Besides this, the average completion time can further increase depending on the disciplines. For example, they found doctorates within the humanities and arts to take an average of 7.1 years to achieve.
The primary reason for this difference is the way PhD degrees are structured within the United States. As mentioned previously, PhDs conducted within UK and EU universities are essentially broken into two sections – one covering the analytical aspects and the other covering the writing up aspects. However, within the US, doctorate programmes comprise additional sections. PhD students are first required to undertake 2 to 3 years of courses, which cover a broad range of topics related to their schools’ discipline. This is then followed by coursework and several examinations, which only once passed can the PhD candidate then start working on their research project and dissertation.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How long does it take to prepare for applying to a PhD in the US?
For a person that considering to apply to a PhD program in the US, how long does you think in advance is needed to be ready in time to the application deadline? I will appreciate a breakdown of time needed for each of the required documents: writing letter of purpose, CV, contacting recommenders, seeking protentional advisors, etc.
There are also optional documents that are required depends on what you apply for, as GRE/GMAT, writing sample, and TOEFL exam for international students. I think that preparing and taking the exams and so on should have separated estimation of time.
- united-states
- application
- Probably, the detailed answer for this question will be a really long one, but I am interested in the topic as well (US is not my destination). – Neuchâtel Commented Sep 29, 2022 at 8:20
- What is your subject? If you know your recommenders already, at least 4 weeks. – k99731 Commented Sep 29, 2022 at 8:34
- 3 This is surely something that depends hugely on individual circumstances and priorities. One person may already have a clear and specific idea of what they want to study and where, another may spend weeks exploring what different departments have to offer. Similarly, one person may take days to produce written material that another person can write in a couple of hours. – avid Commented Sep 29, 2022 at 9:04
- @k99731 My subject is CS – Woka Commented Sep 29, 2022 at 9:44
- It is quite variable, but, even in the most straightforward scenarios, you probably need to have all applications completed by early Dec (in the U.S., with current schedules for these things). Count backward from there... it's already "at the last moment" here in late Sept! Get started immediately, don't waste time trying to estimate how much time it will take! :) – paul garrett Commented Sep 29, 2022 at 22:46
For study starting in Fall of 2023, you should start now if you haven't already. In other words, give it a year or so prior to your intended start date. Due dates for US institutions might be as early as early December of this year, others a few months later.
How long it takes to write letters is dependent on you and your other tasks, but don't expect that a first draft of a Statement of Purpose is a good draft. Have someone look at it and comment on it. The other documents are similar. So a document might take a couple of weeks to prepare, but you can also write them in parallel. Rewrite as you would for any important document.
For a person not a native English speaker, get some advice on your writing.
Take any required exams like the GRE sometime in your last undergraduate year if you are pretty confident of doing well. Perhaps earlier otherwise. That is, in the year before you expect to start.
Talk to potential letter writers early. Let them know of your plans and get their advice. Let them know that you might ask them for a letter so they can be thinking about it. Don't make it a last minute request. A month or more might be needed.
Note, however, that most of these things occur in parallel, so it isn't as if you can add up the times to get a total. Expect considerable effort and be sure you meet the (perhaps variable) deadlines for the places you wish to apply.
Give yourself some time to investigate those institutions and choose a set of places, preferably not all with similar characteristics. For example, don't expect to be successful if you choose the top five programs in the US, as rejection by one is likely about the same for the others.
Most US programs don't require that you have an advisor selected (and accepted) to apply. Most students start with a bachelors only and advisor selection, along with choosing a specialty and topic, is a long way off. Starting with a masters shortens the time frame somewhat, but not as much as you might think, since comprehensives still need to be passed. A few lab sciences (for example) might require an advisor to be chosen to arrange funding, but most funding is via the department, not the advisor. But, you want to know that the institution you apply to has a few faculty in a topic you might be interested in.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd united-states application ..
- Featured on Meta
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
Hot Network Questions
- USB A mechanical orientation?
- Is Firefox's about:license non-compliant wrt. MIT and BSD style Licenses?
- Signature doughnut from a city
- Spie(s) sent out to scout Yazer
- Finite verification for theorems due to Busy Beaver numbers
- Is a shunt jumper for a power plane jumper a good idea?
- Zugzwang where the side to move must be mated in exactly 2 moves
- What is the difference between "Donald Trump just got shot at!" and "Donald Trump just got shot!"?
- Is a LAN and landline phone on 4 cables possible?
- New causes of side channel
- Is there a more concise method to solve the problem of finding tangent lines to curves?
- How were the alien sounds created in the 1953 War of the Worlds?
- How artificial is the lack of 450%+/50t+ gearing on lesser 1x groups?
- Can you find a real example of "time travel" caused by undefined behaviour?
- Fantasy novel with a girl, a satyr, and a gorgon escaping a circus
- How can a hazard function be negative?
- HPE Smart Array P408i 2GB performance drop
- What is the median of the minimum or maximum of multiple samples?
- Explanation of Quran 25:55 and 55:19-21
- Has an aircraft ever crashed due to it exceeding its ceiling altitude?
- I’m looking for a word that describes a decision being imposed on you unwillingly
- Cost of Living/Salary: Sweden vs Germany
- How do Trinitarian Christians respond to these differences between Jesus Christ and God
- How did Voldemort know that Frank was lying if he couldn't use Legilimency?
- Preparing to Apply
- How to Apply
- After Applying
- Why Penn State?
- Military and Veteran Students
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Degree Programs
Academic Dates and Deadlines
- Policies for Students
- Theses and Dissertations
- Integrated Undergraduate-Graduate Plans
- Commencement
- Planning Your Finances
- External Funding Opportunities
- Information for Graduate Assistants
- Student Recognition Awards
- Funding FAQ
- Professional Development
- New Students
- From the Dean
- Advising and Mentoring Tips
- Academic Support
- Student Support FAQs
- Addressing Concerns
- Well-Being Resources
- Office of Graduate Educational Equity Programs (OGEEP)
- Graduate School Open House
- Programs and Initiatives
- McNair Scholars Program
- Summer Research Opportunities Program (SROP)
- Resources and Partners
- Office of the Vice Provost for Graduate Education and Dean
- Vision, Mission, and Strategic Plan
- By the Numbers
- Contact the Graduate School
- Resource Library
This dialog contains the full navigation menu for gradschool.psu.edu.
The Graduate School
- Student Support
Information For
- Alumni and Friends
- Veterans and Military Service Members
- Corporate Connections & Partnerships
Helpful Links
- Graduate Education Policies
- Student Teaching Certificate
- Graduate Exhibition
- Three Minute Thesis
- Accelerate to Industry
For Faculty and Staff
- Graduate Council
- Graduate Education Resource Portal

Social Media
Check out below for important academic dates and deadlines for the current and upcoming semesters.
Thesis and Dissertation Deadlines for Summer 2024
Future semester thesis and dissertation deadlines.
The following deadlines are for theses, dissertations, DMA performances and DEng, D.B.A., Dr.P.H., and DNP final oral presentations only. Students writing master's papers should contact their graduate program for deadlines.
| Deadlines by semester | Fall 2024 | Spring 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Apply to graduate in LionPATH | 9/10 | 1/27 |
| Submit doctoral dissertation for format review | 10/1 | 2/3 |
| Submit master's thesis for format review | 10/1 | 2/3 |
| Pass doctoral defense | 10/8 | 2/21 |
| Submit final thesis or dissertation and supporting materials | 11/1 | 3/24 |
| Pass final performance (DMA students only) | 11/1 | 3/24 |
| Pass final oral presentation (DNP, DEng, D.B.A., and Dr.P.H. students only) | 11/1 | 3/24 |
| Committee members to approve final thesis/dissertation | 11/8 | 3/31 |
Questions about the doctoral dissertation defense should be directed to Graduate Enrollment Services. Students with questions regarding the master's thesis defense should contact their graduate program.
Office of Theses and Dissertations
814-865-1795
Legal Statements
- Non-Discrimination
- Equal Opportunity
- Accessibility
- The Pennsylvania State University © 2024
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Who is JD Vance? Things to know about Donald Trump’s pick for vice president
Donald Trump announced that Sen. JD Vance, (R) Ohio, will be his running mate and vice-presidential candidate in the 2024 presidential election.

Donald Trump says Ohio Sen. JD Vance will be his vice presidential pick. (AP video by Mike Householder/production Ao Gao)
Republican vice presidential candidate Sen. JD Vance, R-Ohio, and his wife Usha Chilukuri Vance arrive on the floor during the first day of the 2024 Republican National Convention at the Fiserv Forum, Monday, July 15, 2024, in Milwaukee. (AP Photo/Carolyn Kaster)
- Copy Link copied
Delegates hold a sign with ‘Vance” written in as Republican vice presidential candidate Sen. JD Vance, R-Ohio, arrives on the floor during the first day of the 2024 Republican National Convention at the Fiserv Forum, Monday, July 15, 2024, in Milwaukee. (AP Photo/Carolyn Kaster)
Republican vice presidential candidate Sen. JD Vance arrives with his wife Usha Chilukuri Vance at the Republican National Convention Monday, July 15, 2024, in Milwaukee. (AP Photo/Paul Sancya)

Follow AP’s live coverage of the Republican National Convention.
COLUMBUS, Ohio (AP) — Former President Donald Trump on Monday chose U.S. Sen. JD Vance of Ohio to be his running mate as he looks to return to the White House.
Here are some things to know about Vance, a 39-year-old Republican now in his first term in the Senate:
Vance rose to prominence with the memoir ‘Hillbilly Elegy’
Vance was born and raised in Middletown, Ohio. He joined the Marines and served in Iraq, and later earned degrees from Ohio State University and Yale Law School. He also worked as a venture capitalist in Silicon Valley.
Vance made a name for himself with his memoir, the 2016 bestseller “Hillbilly Elegy ,” which was published as Trump was first running for president. The book earned Vance a reputation as someone who could help explain the maverick New York businessman’s appeal in middle America, especially among the working class, rural white voters who helped Trump win the presidency.
“Hillbilly Elegy” also introduced Vance to the Trump family. Donald Trump Jr. loved the book and knew of Vance when he went to launch his political career. The two hit it off and have remained friends.
He was first elected to public office in 2022
After Donald Trump won the 2016 election, Vance returned to his native Ohio and set up an anti-opioid charity . He also took to the lecture circuit and was a favored guest at Republican Lincoln Day dinners where his personal story — including the hardship Vance endured because of his mother’s drug addiction — resonated.
Vance’s appearances were opportunities to sell his ideas for fixing the country and helped lay the groundwork for entering politics in 2021 , when he sought the Senate seat vacated by Republican Rob Portman, who retired.
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Democracy: American democracy has overcome big stress tests since 2020. More challenges lie ahead in 2024.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
- We want to hear from you : Did the attempted assassination on former president Donald Trump change your perspective on politics in America?
- Read the latest: Follow AP’s live coverage of this year’s election.
Trump endorsed Vance. Vance went on to win a crowded Republican primary and the general election.
He and Trump have personal chemistry
Personal relationships are extremely important to the former president and he and Vance have developed a strong rapport over years, speaking on the phone regularly.
Trump has also complimented Vance’s beard, saying he “looks like a young Abraham Lincoln.”
Vance went from never-Trumper to fierce ally
Vance was a “never Trump” Republican in 2016. He called Trump “dangerous” and “unfit” for office. Vance, whose wife, lawyer Usha Chilukuri Vance, is Indian American and the mother of their three children, also criticized Trump’s racist rhetoric, saying he could be “America’s Hitler.”
But by the time Vance met Trump in 2021, he had reversed his opinion, citing Trump’s accomplishments as president. Both men downplayed Vance’s past scathing criticism.
Once elected, Vance became a fierce Trump ally on Capitol Hill, unceasingly defending Trump’s policies and behavior .
He is a leading conservative voice
Kevin Roberts, president of the conservative Heritage Foundation, called Vance a leading voice for the conservative movement, on key issues including a shift away from interventionist foreign policy, free market economics and “American culture writ large.”
Democrats call him an extremist, citing provocative positions Vance has taken but sometimes later amended. Vance signaled support for a national 15-week abortion ban during his Senate run, for instance, then softened that stance once Ohio voters overwhelmingly backed a 2023 abortion rights amendment.
He is married to a lawyer who was a Supreme Court clerk
Vance met his wife, Usha Chilukuri Vance, at Yale, where she received both her undergraduate and law degrees. She spent a year clerking for future Supreme Court Justice Brett Kavanaugh when he served as an appeals court judge in Washington, followed by a year as a law clerk to Chief Justice John Roberts.
She had been a trial lawyer for the Munger, Tolles and Olson law firm. Her law firm announced Monday that she had left the firm.
“Usha has been an excellent lawyer and colleague, and we thank her for her years of work and wish her the best in her future career,” Munger, Tolles & Olson said in a statement.
Vance has adopted Trump’s rhetoric about Jan. 6
On the 2020 election, he said he wouldn’t have certified the results immediately if he had been vice president and said Trump had “a very legitimate grievance.” He has put conditions on honoring the results of the 2024 election that echo Trump’s . A litany of government and outside investigations have not found any election fraud that could have swung the outcome of Trump’s 2020 loss to Democratic President Joe Biden.
In the Senate, Vance sometimes embraces bipartisanship. He and Democratic Ohio Sen. Sherrod Brown co-sponsored a railway safety bill following a fiery train derailment in the Ohio village of East Palestine . He’s sponsored legislation extending and increasing funding for Great Lakes restoration, and supported bipartisan legislation boosting workers and families.
Vance can articulate Trump’s vision
People familiar with the vice presidential vetting process said Vance would bring to the GOP ticket debating skills and the ability to articulate Trump’s vision.
Charlie Kirk, founder of the conservative activist group Turning Point USA, said Vance compellingly articulates the America First world view and could help Trump in states he closely lost in 2020, such as Michigan and Wisconsin, that share Ohio’s values, demographics and economy.
Associated Press writers Jill Colvin in Milwaukee and Mark Sherman in Washington contributed to this report.

A bridge from undergraduate to graduate studies
Post-baccalaureate program help students transition to the next academic level.

Five SEAS post-baccalaureate students with staff members Edward Alexander, Kathryn Hollar and Paula Nicole Booke
The graduate and undergraduate student experience isn’t the same. Undergraduates spend the majority of their four years in classrooms. But for graduate students — especially those pursuing PhDs in engineering and applied sciences — most of the work is in the lab.
The focus on laboratory research can make pursuing advanced degrees feel daunting for some students.
“I’d always had a love for math, science and experimentation, but when COVID happened, they shut down the school, so I wasn’t able to do any hands-on experiments, “ said Shekinah Newson.
After graduating in 2021, Newson joined the inaugural cohort of post-baccalaureate students at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS). The post-baccalaureate program , offered through the SEAS Office of Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging and Office of Education Outreach and Community Programs, acts as a bridge from undergraduate to graduate school. The program allows students to gain laboratory research experience with SEAS faculty, while continuing to take courses that will prepare them for their graduate studies.
Post-baccalaureate students typically stay for 1-2 years, but have the option to stay on for a third. So far six students have completed the program, five of whom have gone onto graduate school.
“I’m super glad I did it, because now I’ve honed in the research skills that I started to develop as an undergraduate,” said Maggie Vallejo, a former environmental science and engineering undergraduate concentrator at SEAS. “I definitely think more like a researcher, and I better understand that research isn’t linear.”
Vallejo’s undergraduate advisor was Jim Anderson, Philip S. Weld Professor of Atmospheric Chemistry, and she returned to the Anderson Research Group for her post-baccalaureate studies. Her senior capstone project involved predicting power losses in solar cells aboard stratospheric aircraft, and as a post-baccalaureate researcher, she transitioned to analyzing lithium-ion battery cell performance.

Post-baccalaureate student Maggie Vallejo in the lab of Jim Anderson, Philip S. Weld Professor of Atmospheric Chemistry
“During the application process, I made sure Professor Anderson was OK with me just staying in his lab,” she said. “I was interested in the work I was already doing, and I knew the people in the lab, so I figured why not just stay.”
Vallejo spent both years of her program with the same professor, but that isn’t required. The program is meant to help students focus their academic goals, and sometimes that focus clarifies that the lab a student started in isn’t exactly what they want moving forward. Dawn Bordenave, another member of the inaugural cohort, spent each of her first two years in different labs before settling into the lab of Joanna Aizenberg, Amy Smith Berylson Professor of Materials Science and Professor of Chemistry & Chemical Biology.
Bordenave is part of Aizenberg’s research into the improvement of ventricular catheter design for treatment of hydrocephalus, a potentially deadly disorder in which fluid builds up in the cavities deep within the human brain. Her specific part of the project is to develop low-cost methods of constructing the catheter in the lab, making it much easier to physically test new designs before beginning clinical trials.
“After spending time in other labs, I realized that I wanted to do something different that was a little closer to my goal of designing medical devices,” Bordenave said. “The program is very flexible. If the research, lab or mentor you start off with isn’t close to what you want and you want to change, that’s definitely an option. The Aizenberg Lab was the best fit for me.”
Newson, who completed the program last month, worked in the Harvard Biodesign Lab, led by Conor Walsh, Paul A. Maeder Professor of Engineering and Applied Sciences, as well as the lab of Michael Brenner, Michael F. Cronin Professor of Applied Mathematics and Applied Physics and Professor of Physics. With Walsh, she worked on the soft robotics toolkit, an educational package for teaching robotics to younger students. With Brenner, she helped developed a non-invasive method to measure range of motion
“This innovative educational resource empowers people to learn about robotics through engaging, hands-on activities,” Newson said. “To be able to build a toolkit that allows a child to both play and learn at the same time is amazing. I wish I had something like that when I was growing up.”
Newson, Bordenave and Vallejo will all be leaving SEAS for graduate programs at other universities. Newson will pursue a master’s degree in robotics at Boston University, and Bordenave and Vallejo are both heading to Cornell University: Bordenave for a master’s degree in biomedical engineering, Vallejo for an M.S./Ph.D. program in civil and environmental engineering.
“It was fantastic having Shekinah as part of our research group,” Walsh said. “She got involved in a number of projects, including one focused on using soft robotics in education and STEM outreach. It is very exciting that she will be going on to do an MS in robotics at BU as a next step. Her passion for learning and growing her engineering skill set has been a great example for us all.”
Eva Langenbrunner joined the program last fall and will be back to work in the Harvard Microrobotics Lab, led by Robert Wood, Harry Lewis and Marlyn McGrath Professor of Engineering and Applied Sciences. She’s developing materials that can fold into origami-like shapes using soft robotic actuators.
“Post-baccalaureates programs are really great because they teach you how to be a successful grad student,” she said. “The program goes over how to properly write research articles, which is something no one in undergrad teaches you how to do, but then you get to grad school and they expect you to know it. The biggest thing I learned here was how to structure a research project from beginning to end.”

Post-baccalaureate student Katie Barajas working in the lab of Marko Lončar, Tiantsai Lin Professor of Electrical Engineering and Applied Physics at SEAS
Langenbrunner will be joined by new post-baccalaureate Jonathan Chinana, a Navajo Technical University (NTU) graduate who first came to SEAS for the Research Experience for Undergraduates program in the summer of 2022 . Michael Nelwood, another NTU graduate, finished his post-baccalaureate studies in the lab of Jennifer Lewis, Hansjörg Wyss Professor of Biologically Inspired Engineering. He’s now working as a lab tech in the Lewis Lab.
Katie Barajas has spent the last two years with the Harvard Quantum Initiative, working in the lab of Marko Lončar, Tiantsai Lin Professor of Electrical Engineering and Applied Physics. She’ll continue with the Lončar Group as an applied physics Ph.D. student this fall. Her research focuses on the fabrication of nanostructures in specially lab-grown diamonds. These diamonds have a silicon atom implanted in place of two carbon atoms. These defects are called “silicon vacancy centers,” and they could potentially be used to transmit information in a quantum computer.
“It wasn’t until late in my undergrad career that I learned about the field of quantum optics. If I wanted to pursue a degree in that field, I needed more research experience,” she said. “That persuaded me to do the post-baccalaureate program. I’m in a much better place than when I was coming out of undergrad. This program has given me the confidence to say I can be a scientist and pursue scientific research, and that’s a testament to the people I’ve worked with.”
Topics: Academics , Applied Physics , Bioengineering , Diversity / Inclusion , Environmental Science & Engineering , Materials Science & Mechanical Engineering , Optics / Photonics , Quantum Engineering , Robotics
Cutting-edge science delivered direct to your inbox.
Join the Harvard SEAS mailing list.
Press Contact
Matt Goisman | [email protected]
Related News
Uncovering ‘hidden curriculum’ for those historically on outside
Quantum Noir fosters sense of community among individuals of color involved in quantum science and engineering
Diversity / Inclusion , Materials , Quantum Engineering

Scientists at Harvard describe their worst climate fears
SEAS researchers participate in Harvard Climate Action Week panel entitled “What Could Go Wrong?”
Climate , Environmental Science & Engineering
A quantum world on a silicon chip
Researchers develop a platform to probe, control qubits in silicon for quantum networks
Applied Physics , Quantum Engineering
Who is JD Vance? What to know about Donald Trump's VP pick
Former President Donald Trump tapped J.D. Vance to be his running mate Monday at the Republican National Convention, catapulting the Ohio GOP senator even more into the national spotlight.
Here’s what you need to know about Vance:
More: Trump made MAGA happen. JD Vance represents those who will inherit it
Where is JD Vance from?
Vance grew up in Jackson, Kentucky and Middletown, Ohio. He described a childhood consumed by poverty and abuse in his best-selling 2016 memoir , "Hillbilly Elegy." Vance's mother struggled with drug addiction, so he spent many of his formative years with his grandmother – known to him as Mamaw.
How old is JD Vance?
Vance is 39. If elected, he would be the youngest vice president since Richard Nixon. His birthday is Aug. 2, 1984.
More: Vice presidential contender has multiple ties to Columbus
Did JD Vance serve in the military?
Vance joined the Marines Corps after high school and served as a public affairs marine in Iraq.
Is JD Vance married?
Vance's wife, Usha Vance, is a litigator for a law firm based in San Francisco and Washington, D.C. The pair met as students at Yale Law School and got married in 2014, one year after they graduated.
The couple has three young children: Ewan, Vivek and Mirabel.
Where does JD Vance live?
Vance and his family live in the East Walnut Hills neighborhood of Cincinnati. The senator also bought a $1.5 million home in Alexandria, Virginia, last year, Politico reported .
How long has JD Vance been in politics?
Vance was first elected to the U.S. Senate in 2022 after defeating former Democratic Rep. Tim Ryan for an open seat in Ohio.
What’s the history between Vance and Trump?
Vance openly criticized Trump in 2016 as pundits used his memoir to explain the former president's popularity with white, rural voters. He previously suggested Trump could be "America’s Hitler," called him noxious and compared him to an opioid.
But Vance changed his tune as he geared up for his 2022 Senate run, deleting controversial tweets and crediting Trump for the work he did in office. He secured Trump's endorsement in a chaotic Republican Senate primary and is now one of the former president's most loyal allies.
JD Vance didn't vote for Donald Trump in 2016
In one NPR interview , he joked that he would rather write his dog on the ballot than vote for Trump or Hillary Clinton.
"I think that I'm going to vote third party because I can't stomach Trump," the "Hillbilly Elegy" author said at the time. "I think that he's noxious and is leading the white working class to a very dark place."
What are Vance's policy positions?
Vance personifies what's known as the New Right , a populist conservatism that rejects many traditional Republican views. He supports tariffs on trade and opposes U.S. intervention in foreign conflicts, particularly the war between Russia and Ukraine. He's also spoken out against potential cuts to Social Security.
Who is JD Vance? Vice presidential candidate has multiple ties to Columbus
Some of Vance's work in the Senate has been bipartisan. He introduced a rail safety bill with Sen. Sherrod Brown after the train derailment in East Palestine, Ohio. He also worked with Massachusetts Sen. Elizabeth Warren on legislation to hold executives accountable for failed banks.
At the same time, many of his other bills reflect conservative views. For example, Vance introduced legislation to ban gender-affirming care for minors and a bill to eliminate diversity programs in the federal government.
Where does JD Vance stand on abortion?
Vance opposes abortion and often says the government should find ways to encourage people to have children.
Like other Republicans, however, Vance changed how he discusses the issue after Ohio and other states voted in favor of abortion access last year. In a December CNN interview , he said Republicans must "accept that people do not want blanket abortion bans."
More recently, he told Meet the Press that he supports access to the abortion drug mifepristone.
Haley BeMiller is a reporter for the USA TODAY Network Ohio Bureau, which serves the Columbus Dispatch, Cincinnati Enquirer, Akron Beacon Journal and 18 other affiliated news organizations across Ohio.
trending now in US News

Biden snaps repeatedly at Lester Holt in combative NBC interview...

Secret Service Director Kim Cheatle landed job after push by Jill...

Firefighter's widow refused Biden call after Trump rally shooting

Would-be Trump assassin wore influencer's merch during shooting:...

BlackRock pulls ad that featured would-be Trump assassin

Photojournalist recalls capturing '1 in a million' image of...

Bandaged Trump defiantly appears at RNC 2024 just days after...

Who is JD Vance's wife Usha Vance? Everything to know about his...
Trump names ohio sen. jd vance, 39, as his 2024 vp pick.
- View Author Archive
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Former President Donald Trump has chosen freshman Ohio Sen. JD Vance to serve as his VP in his bid to return to the White House, ending months of speculation about whom he would select for his No. 2.
“After lengthy deliberation and thought, and considering the tremendous talents of many others, I have decided that the person best suited to assume the position of Vice President of the United States is Senator J.D. Vance of the Great State of Ohio,” Trump announced on Truth Social on Monday afternoon. “J.D. honorably served our Country in the Marine Corps, graduated from Ohio State University in two years, Summa Cum Laude, and is a Yale Law School Graduate, where he was Editor of The Yale Law Journal, and President of the Yale Law Veterans Association.”
Trump world insiders had long said the 78-year-old would choose someone based on “loyalty” and who would complement his strong personality but not overshadow him, who would raise money and be ready to serve.

“J.D.’s book, ‘Hillbilly Elegy,’ became a Major Best Seller and Movie, as it championed the hardworking men and women of our Country. J.D. has had a very successful business career in Technology and Finance, and now, during the Campaign, will be strongly focused on the people he fought so brilliantly for, the American Workers and Farmers in Pennsylvania, Michigan, Wisconsin, Ohio, Minnesota, and far beyond,” Trump said in his Truth Social post.
Who is Trump's VP pick, JD Vance?
- Trump announced Sen. JD Vance (R-Ohio) as his pick for vice president.
- The 39-year-old rose to prominence after writing his 2016 memoir “Hillbilly Elegy” reflecting on his time growing up in a working class Ohio family.
- Vance would be the second-youngest vice president to ever assume office if Trump was elected for another term.
- In 2020, Vance apologized to Trump for his previous criticism and came to be a supporter. He deleted his previous critical posts of Trump and met with the then-president about his Senate run.
- President Biden dismissed Vance as “a clone of Trump on the issues” following the announcement.
- He was first elected to the Senate in the 2022 midterm cycle.
The decision comes on the first day of the Republican National Convention in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and two days after a gunman shot Trump in the upper ear at a Pennsylvania rally. The shooter, 20-year-old Thomas Crooks, just missed Trump’s head, and fatally hit one attendee in the crowd.

Trump had teased his VP pick over the course of his campaign, first claiming he had chosen his running mate — but refusing to disclose any details.
The mercurial ex-commander-in-chief praised a wide range of candidates throughout the months and kept several allies close, maintaining the mystery surrounding his final choice until the final moment.
The first clues came in February, when Trump confirmed during a Fox News town hall that he was thinking about several possibilities, including Sen. Tim Scott (R-SC), former Rep. Tulsi Gabbard (D-Hawaii), South Dakota Gov. Kristi Noem, biotech mogul Vivek Ramaswamy, Rep. Byron Donalds (R-Fla.) and Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis.
Nearly all the options on the “shortlist” had expressed openness to taking up the position — other than DeSantis, who said he would not be “doing that” one day after Trump’s declaration in audio obtained by The Post.
As the race went on, some new candidates rose to the top, while others were almost surely taken out of the running.
Sources close to the Trump campaign told The Post that Noem had tanked her chances after writing about killing her dog in her memoir. Ramaswamy was also confirmed as being out of the running early in the race. More recently, Trump insiders told The Post that Scott had dropped in the rankings .

In the week leading up to his announcement, sources close to Trump’s campaign told The Post that the former president was most likely to choose North Dakota Gov. Doug Burgum or Vance. Sen. Marco Rubio (R-Fla.) was also still in the running as a top option, the sources said, but had a smaller chance.
The three candidates had fervently supported Trump and had stumped for him across the country in hopes of possibly clinching the nomination, joining him at rallies and the debate against President Biden.

Trump’s team maintained throughout that there was a plethora of candidates on the list — even some on whom the media wasn’t focused.
Upstate New York Rep. Elise Stefanik’s longstanding support for the president throughout his re-election campaign and legal trials also sparked rumors that she was seeking the nomination. She stumped for the former president in New Hampshire and said she would be “honored” to be his veep.

Trump supporters in early-voting states told The Post over the course of the primaries that they would be open to a wide array of options, and ultimately were leaving the decision up to the former president.
Some additional names floated by voters included media personality Tucker Carlson, 2016 presidential candidate Ben Carson, Candace Owens, Arizona Senate candidate Kari Lake and Arkansas Gov. Sarah Huckabee Sanders, Trump’s former press secretary.
Trump’s VP may face off against Vice President Kamala Harris in a vice presidential debate, if the two campaigns agree to a network to host the forum.
Biden’s team has pushed for CBS News, while Trump’s campaign has held on to their Fox News VP debate acceptance.
The former president has said that his VP choice won’t push the polls one way or another, telling Fox News in January that “it’s never really had that much of an effect on an election.”
But as Trump faces some concern over his age — albeit not as much as Biden — a younger candidate could put some voters at ease.

Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
A PhD in USA takes 5-6 years, costs between $12-45k per year and has a different structure to UK and EU PhDs. Find out if a US PhD is for you!
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
Average Duration: On a global scale, a PhD program often spans between 5 to 7 years. This period includes coursework, research, and the writing and defense of a dissertation. However, it's important to note that this duration can vary significantly.
Detailed guides to PhD study in the USA. Our guides have information on universities, courses, funding, student visas and life during a PhD in USA.
How the PhD Program Works. Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending ...
How long is a PhD program? That might be one of the first questions you ask yourself If you are thinking of earning a PhD. You have probably heard a range of years, and that is because how long it takes to earn a PhD depends on a number of factors. Keep reading to learn more!!
Here's everything you need to know about studying a PhD in the USA. 1. PhD course length. The total length of a PhD in the USA is between 4-8 years for full-time students and 8-10 years for part-time students, depending on your field of study. PhDs can be completed in 4-5 years for students with a masters degree in an appropriate subject.
In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5-7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3-5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation. In the rest of the world, students normally have a master's degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3-5 years.
Everything an international student needs to study a PhD in United States. Finding a university, how to apply, tuition fees, living costs and more.
In the US, most PhD programs are between 4-6 years, while in Canada they are typically shorter, around 3-4 years. Some students take longer than 6 years to complete their PhD, but in general the longest time it takes to get a PhD is capped at 8 years. If you're enrolling in a part-time PhD program, for instance, your timeline will probably be ...
Recommendation letters and transcripts Applying for a PhD always requires a lot of paperwork, but documents for PhD applications in the US can be difficult to obtain for some international students. Something quite crucial is the transcript of previous qualifications such as diplomas and degrees.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you're juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more. This article breaks down what the PhD journey looks like, what can make it longer or shorter, and some tips on how to make it through.
According to Joseph Berger of the New York Times, the average length of a dissertation program today is 8.2 years (2). Terminal degrees in the hard sciences typically take a slightly shorter time to complete than do degrees in education and the humanities. The field of physics has a current average of five years.
How long does a PhD take? Explore the timeline of completing a PhD program and the benefits of accelerated online degrees. Get started today!
The choice of PhD vs. professional doctorate can influence how long it takes you to earn your degree because the way you earn them differs. In general, PhD candidates must complete a dissertation, which requires them to conduct research into an approved area of study within their discipline, typically an area no one in their discipline has fully researched before. Professional doctorate ...
How Long Does It Take To Get a Ph.D.? While certain Ph.D. programs take longer to complete than others, generally, Ph.D. candidates take 5 or 6 years to complete their degree.
PhD Admissions The PhD program in Psychology trains students for careers in research and teaching. In addition to a wide range of courses, the PhD program is characterized by close collaboration between students and their faculty advisors.
How many years does it take to get a PhD in the USA? What is the typical time to degree? I heard a rumor it was five years.
Learn what a PhD is, how long it takes, how to get in, and how to succeed as a doctoral student. Get advice from experts and peers at Times Higher Education.
Wondering how long it takes to get a PhD? In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3-4 years and a part-time PhD takes 6-7 years. Read our post to find out why!
However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey. Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means ...
Are you considering a doctorate in psychology? Keep reading to learn about what a psychology doctoral program might look like and how to choose the right program for you.
0 For a person that considering to apply to a PhD program in the US, how long does you think in advance is needed to be ready in time to the application deadline? I will appreciate a breakdown of time needed for each of the required documents: writing letter of purpose, CV, contacting recommenders, seeking protentional advisors, etc.
Check out below for important academic dates and deadlines for the current and upcoming semesters.Thesis and Dissertation Deadlines
Ohio U.S. Sen. JD Vance is a 39-year-old Republican now in his first term in the Senate. He made a name for himself with his memoir, the bestseller "Hillbilly Elegy," which was published in 2016 as Trump was first running for president.
For some visitors Monday, it took close to three hours to clear the security checkpoints in Milwaukee.
The graduate and undergraduate student experience isn't the same. Undergraduates spend the majority of their four years in classrooms. But for graduate students — especially those pursuing PhDs in engineering and applied sciences — most of the work is in the lab.
Former President Donald Trump picked J.D. Vance to be his running mate, catapulting the Ohio senator even more into the national spotlight.
Trump world insiders had long said the 78-year-old would choose someone based on "loyalty" and who would complement his strong personality but not overshadow him, who would raise money …