Start typing

- Trade Management
- International Trade Finance
- Market Entry Strategies
- Marketing & Sales
- Research & Development
- Supply Chain Management
- CITP® |FIBP® Spotlight
- Import Export Jobs
- International Trade Courses
- International Trade Workshops
- International Trade Certification
- International Trade Resources
- FITTskills Lite Downloads
- FITT Small Business Guide: The Scaling Up Edition
Trending topics:
- Procurement
- CITP®|FIBP® designation

A Guide to Preparing an International Business Plan
By: FITT Team

An international business plan acts as a framework that identifies goals and objectives, specific target markets and clients, resources required and strategies to be developed in pursuit of international business opportunities. The plan allows for the monitoring of progress via metrics against which success and failure can be measured. A comprehensive international business plan will be comprised of a number of integrated strategies related to business functions, including communications, sales and marketing, finance and production.
What Is an International Business Plan?
An international business plan is a valuable management tool that describes who a business is, what it plans to achieve and how it plans to overcome risks and provide anticipated returns. It can be used for a wide variety of purposes, such as to:
- Set goals and objectives for the organization’s performance.
- Provide a basis for evaluating and controlling the organization’s performance.
- Communicate an organization’s message to managers and staff, outside directors, suppliers, lenders and potential investors.
- Help the planner identify the cash needs of the business.
- Provide benchmarks against which to compare the progress and performance of the business over time.
A comprehensive and detailed plan forces the planner to look at an organization’s operations and re-evaluate the assumptions on which the business was founded. In doing so, strengths and weaknesses can be identified.
Although highly dependent on the individual business case, on average it takes a three-year commitment to establish a successful presence in a foreign market. This process may require tremendous human, technical and financial resources during the developmental period.

The Planning Process
An international business plan is subject to repeated adjustment and revision to keep it current with the changing circumstances of the organization. The plan is a feedback mechanism through which new information is continually incorporated into the organization’s operations. Planning always precedes action. Therefore, planning must be thought of as a continuous cycle. The analytical tools presented here are not intended to be used just once. If they are to be useful, they should be used repeatedly as part of a process of improvement and incremental adjustment.
Plan Preparation Guidelines
These 7 guidelines will help in preparing a comprehensive international business plan:
- Clearly define the objectives for producing the plan : Who is going to read the plan, and what will they need to do? These objectives can help you decide how much emphasis to put on various sections.
- Allocate sufficient time and resources to thoroughly research the plan : A plan is only as good as the research that went into producing it.
- Show drafts of the plan to others : It can be very useful to obtain feedback from others, both inside and outside the business.
- Create an original plan that is done specifically for each business case : A common mistake entrepreneurs make is to borrow heavily from a sample plan and simply change the names and some of the numbers. There are two big problems with this approach. First , the emphasis placed on various sections of the plan must reflect what is important to the particular business in question. Second , a good plan should flow like a story, with the sections working together to demonstrate why the business will succeed. Plans that borrow too heavily from other plans tend to be disjointed, with some sections contradicting others and various key issues left unaddressed.
- Outline the key points in each section before the writing starts : These points must then be reviewed to ensure the sections are consistent with each other, there is little duplication and all key issues have been addressed.
- Ensure financial projections are believable : For many readers, the financial section is the most important part of the plan because it identifies the financing needs and shows the profit potential of the business. In addition, a good financial plan will give the reader confidence that the author really understands the business.
- Consider writing the executive summary as the last step in the process: It is usually easier to provide a concise overview after the detailed content has been created.
If you’re having trouble getting started with your business plan, try writing like it’s a series of tweets—one for every section of your business plan. To get your point across, 140 characters is all you need.
Forcing yourself to boil each section of your business plan down to one main point is an exercise in decision making and strategy all in itself. When you’re done, you’ll have everything you need to take your next step, whether that’s practicing your pitch to potential investors or a business partner, or sitting down to expand each tweet into a full section of a more traditional business plan.
Core Content
The international business plan is the culmination of all of the work done to determine the appropriate venture for the organization’s growth. As part of the feasibility process, the organization will have determined its own internal readiness, conducted comprehensive target market research and carefully analyzed any relevant risks.

At this point, the organization can take all of this information and analysis and formally document the plan for moving forward. There are many different models and examples of how to put together a formal business plan, rather than one correct way.
The right format will depend on the organization, the venture being pursued and who will be accessing the business plan and for what purpose. However, there are some basic guidelines to follow.
One of the reasons business plans are developed is to convince investors and/or bankers to invest in the venture.
Increasingly, they are looking for a business plan to include two sections: one relating to online strategy (in terms of e-marketing, social media and ROI) and the second relating to corporate social responsibility (including quality, health, safety and environment policies).
The inclusion of these topics gives more credibility to the company by demonstrating its commitment to the community and to employees’ well-being.

Telling a Story
One trend in business planning is to use a narrative structure in the document, rather than traditional technical writing techniques. Storytelling techniques are increasingly being used throughout the business world to create personal and organizational brands, deliver marketing messages and develop persuasive plans.
Stories make presentations better. Stories make ideas stick. Stories help us persuade. Savvy leaders tell stories to inspire us, motivate us. That’s why so many politicians tell stories in their speeches. They realize that “what you say” is often moot compared to “how you say it.
Instead of using bulleted points and cold, technical language, organizations employ a “beginning, middle and end” narrative style. This engages the audience by establishing the context, describing the conflict or obstacles and arriving at a successful resolution.
The Executive Summary
Usually the last step of preparing the international business plan is to develop the executive summary, a short overview of what the plan proposes to accomplish. For some purposes, a one-page business plan can also be useful.
There is not a great deal of difference between an executive summary and a one-page business plan. The most significant distinction is the one-page plan must completely fit on one page in a readable font, while an executive summary may spread over two or three pages.
One-Page Business Plan
There is a trend towards the one-page business plan, especially if the plan is to be presented to potential partners for their consideration. Audiences for the one-page plan will be looking for a “quick hit”: a clear and concise description of what the opportunity is and how it is being pursued.
For example, a one-page business plan might include the following topics, as described in Noah Parson’s article “How to Write a One-Page Business Plan” on the website Bplans :
- Customer problem/opportunity
- Your solution/approach
- Business model (how you make money)
- Target market (who is the customer and how many are there)
- Competitive advantage
- Management team
- Financial summary
- Funding required
The one-page plan (or the executive summary, if used in place of the one-page plan) may provide the first impression the audience has of the business. This is the most important document generated out of the business planning process, and significant effort and care should be taken in its creation.
There are many websites the provide blank samples of one-page business plans, including Bplans , the GoForth Institute and Startup.com.
A Note on Strategic Plans
A strategic plan covers many of the same points as a business plan. However, a strategic plan sets out the detailed action plan to be followed to achieve the objectives of the international business plan.
It must outline specific activities, their due dates and who is responsible for each activity. It is a project plan with a critical path. A strategic plan ensures any venture is carried out in a coordinated, informed and systematic way.
A key consideration in action planning is how quickly to enter the market, which is driven by the chosen market entry strategy. If market entry is done too quickly, the potential for costly mistakes increases. However, if it is completed too slowly, opportunities may be missed and competitors will have more time to react.
The Planning Cycle
Attaching the word “cycle” to planning implies that it happens more than once. International business plans need to be reviewed periodically because new information that has an impact on both planning and operations is continually coming in.
All plans, including international business plans and strategic plans, need to be reviewed every time there is a major event impacting the business, such as civil unrest, a currency fluctuation or the presence of a new competitor.
About the author
Author: FITT Team
The Forum for International Trade Training (FITT) is the standards, certification and training body dedicated to providing international business training, resources and professional certification to individuals and businesses. Created by business for business, FITT’s international business training solutions are the standard of excellence for global trade professionals around the world. View all posts by FITT Team
Related stories

How to evaluate new ASEAN export markets for your business

Top 10 books for international trade professionals to read in 2024

4 ways to visualize data more effectively for reports and presentations

3 common mistakes that cause international businesses to fail – and how to avoid them
Disqus comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
2 thoughts on “A Guide to Preparing an International Business Plan”
Thank for international businesses
I have a company in Dubai and I am looking for someone who can write an internationally designed business plan with me for investors. Do you have an address I can contact?
Subscribe to our mailing list
Email address:
A complete guide to global business expansion strategy
Everything you need to know to develop your own international business expansion strategy.

Overseas expansion can seem a farfetched dream to most, while even those considering the process may be daunted by its complexity. Yet, though expansion can be time-consuming and involved, it need not be exclusively the domain of giant corporations like McDonald’s, Google, Apple, or IKEA.
With a comprehensive and carefully-composed global business expansion strategy, even start-ups and SMEs can expand their operations into new, potentially lucrative markets.
This article provides a broad, overarching guide to international business expansion: what it is, how it can be beneficial as well as challenging, when to consider it, how to build a solid global business expansion strategy, and how partnering with an Employer of Record may drive the success of your overseas venture.
Why go global? A look at the benefits and challenges of international expansion
An important part of considering global expansion for your business is being aware of both the pros and cons, and balancing these carefully. For whilst there are many potential benefits to expanding overseas, there are a number of challenges you may first have to overcome, and the nature of your expansion will be informed by whether or not the pros outweigh the cons.
Potential pros of global business expansion
- Increasing global sales and expanding client lists by tapping into new and lucrative markets; including the potential to reset the lifecycle of older products and services.
- Maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly globalized world by positioning yourself and your brand as a leader in untapped markets.
- Widen your available talent pool to include employees and contractors operating all around the world, with expertise in new and expanding areas.
- Increasing cost savings through relocation and access to new, more affordable markets.
- Securing the financial future of your company by diversifying your revenue streams and the markets you operate in - essentially building greater business resilience.
- You must comply with all applicable labour and tax laws and regulations in the countries and regions you intend to expand into. This can be complex and costly, especially if you fail to comply.
- The culture, languages, and politics of different countries can vary dramatically, and should be researched thoroughly prior to expansion otherwise your offering may be met with confusion, apathy, or hostility.
- Local competitors who are already long-established in your new target market may have an advantage over you, owing to their local, innate understanding of that market.
- Managing remote and international teams requires a reframing of your managerial practices and office culture to be best effective; for example, you must consider how you will work effectively across multiple different time zones.
- It can be prohibitively costly to expand overseas, depending on the global business expansion strategy you choose to develop, especially when expansion is conducted independently.
Challenges of global business expansion
Defining global business expansion.
Global business expansion looks different for each individual business. What it means and what it requires will change depending on the industry you’re in, the reasons for your expansion, and how you hope to enter the new market.
Having said that, we can generalise. Global business expansion – also known as international expansion, foreign expansion, or overseas expansion – is a business growth strategy used to enter new markets in other countries. It can include the movement of business operations, resources, workforces, products, and services.
Successful expansion requires the tailoring of a global business expansion strategy unique to the enterprise’s industry, offering, and goals.
How to know when your business is ready to expand overseas
Not every business needs to expand overseas, nor will every business naturally come to a definable point at which international expansion is the logical next step. Knowing when your business is ready to expand often depends on whether you have the time and resources to develop a watertight strategy.
If global expansion is something you want to see in your business’ future, then we’d suggest you begin planning today. The more prior preparation you can inject into a global business expansion strategy, the more evident it will be when the time comes for your enterprise to take that leap.
How small businesses can also expand internationally
Traditionally, international expansion has been the realm of large corporations with deeper pockets than most start-ups and SMEs can ever hope for. Thankfully, however, in our present era of expansive and accessible globalisation, the opportunities for smaller businesses to expand overseas do exist.
The key to global business expansion for small and smaller businesses is, of course, to minimise the costs involved . The most straightforward means of reducing expansion costs is to partner with a global business expansion solutions provider , whose expertise and existing international presence can reduce the risks you face and mitigate the need for costly foreign subsidiaries.
Developing your global expansion strategy
Every individual expansion requires its own tailor-made international business expansion strategy. Developing such a strategy should take time, care, and consideration. What follows is a broad overview of the 10 components we believe are key to an effective expansion strategy. For a more involved and detailed discussion of these 10 steps, read our post on how to avoid the pitfalls of global expansion .
10 key steps to a comprehensive international business expansion strategy
- Set your goals: It is crucial you know why you want to expand overseas. A clear set of goals will help you keep your strategy on track throughout the expansion process.
- Research: Acquire a firm understanding of the market you’re aiming to enter, including the competitors there, and the culture which frames it.
- Choose an expansion model: You can expand into new markets via a range of expansion models , including exportation, licensing, franchising, partnerships and joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions, and greenfield investments. Knowing which will work best for you is crucial.
- Consider building overseas infrastructure: International expansion is best supported by the establishment of local infrastructure on the ground. This infrastructure can comprise a foreign office or subsidiary, a remote workforce of employees and/or freelancers , or a network of third-party local partners.
- Reconsider branding in an international context: A different audience will likely respond quite differently to your branding, compared to the home audience it was developed for. Consider how best to rework your branding in an international context.
- Tailor your offering to the new market: Similarly to your branding, your offering – whether products or services, B2C or B2B – should be reevaluated with the target international demographic in mind.
- Equip your teams to work internationally: Working effectively across time, cultural, and linguistic barriers is not easy. Adapt your management style to consider the potential benefits of asynchronous work and strategic human resource management .
- Budget: Draft a budget which considers all the various costs of international expansion , and which can be consistently guided by KPIs established during your ‘goal-setting’ phase.
- Risk assessment: Understand the risks specific to your particular international expansion plans, and determine how best to mitigate these whilst ensuring 100% compliance with all relevant labour and tax laws.
- Partner with an expert in global business expansions: Refocus your own role in international expansion to those elements most important to you and your business, whilst reducing stress, costs, and ensuring compliance, by utilising the expertise of Mauve Group .
How to choose which international business expansion methods will suit your business best
The expansion model you choose – exportation, licensing, franchising, etc. – will very much depend on the goals you set for your expansion. Each model has a different set of requirements, challenges, and potential benefits.
For example, consider that fast-food chain McDonald’s’ success rests on the franchising model: approximately 93% of all McDonald’s restaurants worldwide are “owned and operated by independent local business owners.” For Netflix, on the other hand, partnership deals with local mobile operators and TV providers were key to its successful expansion into around 190 countries across the globe.
Seek the advice of professionals when determining which model might work best for you.
When to establish a foreign subsidiary
Establishing a foreign subsidiary is arguably one of the most involved international business expansion methods. A foreign subsidiary is a separate legal entity based on the ground in the overseas country, and majority owned or controlled by your company whilst remaining responsible for its own taxes and assets.
Establishing a foreign subsidiary gives you a stable and potentially impactful foothold in the target country, but equally carries with it high costs, a great number of compliance hoops to jump through, and many additional managerial considerations.
Oftentimes, establishing foreign subsidiaries may not be cost-effective nor practicable to the smaller enterprise seeking to expand overseas. In such instances, the business owner may wish instead to leverage the existing international presence of an Employer of Record .
Go global with Mauve
It is our hope that having read our complete guide to global business expansion strategy, you feel better equipped to begin your own journey toward international expansion.
Many of the risks and costs associated with business expansion can be mitigated with the help of a trusted partner like Mauve, whose extensive experience in overseas expansion can aid start-ups, SMEs, and larger enterprises with compliant international hiring of employees and contractors , visa and immigration support , global payroll , and expansion strategising .
Mauve Newsletter
No spam. Just the latest information on solutions and services, new countries and interesting articles directly to your inbox.
Read about our Privacy Policy .
More from Mauve Innovation Hub
Blog posts, news articles, videos, podcasts and more...

Permanent establishment risk factors and how to avoid them: international compliance guide 2024
Learn how to avoid permanent establishment risk factors with Mauve. By identifying different types of PE and how to navigate them, you safeguard your business against financial and reputational damage.

Breaking news in global HR
Discover the latest major global HR updates, spanning immigration, payroll, and employee benefits.

Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Global Marketing Business Plan
Start your own global marketing business plan
West Pacific Marketing
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
West Pacific Marketing Consultants aims to provide marketing services to targeted business environments in Indonesia, Asia, and the west Pacific region. This plan seeks to generate a significant increase in company sales and profits from the delivery of retainer consulting, project consulting, market research and industrial analysis, feasibility studies, and strategic analysis and reporting services, compared to the preceding year.
The highlights of this plan are the targeted gross margin and sales-revenue. The targeted gross margin and sales-revenue for each of the first five years of this plan are presented in the following chart and the tables presented later in this plan. These figures represent the key prospects available for West Pacific Marketing Consultants. These targets are attainable through a proactive approach to the candidacy of clients, teaming-up with technology providers, and partnering with reputable local and regional engineering suppliers and construction firms to reduce competition, improve pricing, and reduce risks.
This business plan has been created on the basis of five years of market research. Data conclude the size and growth of the market and geographical segments, customer needs, perception, and buying behavior trends have been on the upswing, and are expected to continue in this trend for the next five years. West Pacific Marketing Consultants feels that it is able to fill the hole in the marketing niche, and will benefit from operations beginning in January, Year 1.
Note: All figures within this plan are in the U.S. dollar, and reflect the currency exchange rate of $1 = Rp 7,200.
1.1 Objectives
West Pacific Marketing Consultants’ objectives are to make an equal and fair profit in the business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) marketing services industry. This goal is to be reached by attaining the numbers presented in the Sales Forecast and Financial Plan topics.
1.2 Mission
West Pacific Marketing Consultants offers companies, government institutions, nongovernment organizations (NGO), and individuals reliable, high-quality, and cost-effective consulting services for various purposes. Our services include business development, market development, market intelligence, industrial sectors analysis, and channel development on a global scale, as well as sales assistance for global companies in the Indonesian market.
The situation in Indonesia is currently characterized by the facts that times are tough, investment appetites are low, industries are cutting costs, and budgets are being slashed. Fully aware of this situation, West Pacific Marketing Consultants, after completing a five year research study, has come to the conclusion that its potential clients would be interested in doing things in a smarter way, with good support of a reliable and efficient market intelligence. West Pacific Marketing Consultants believes that it can provide both solutions and value creations to its clients. Its senior executive consultants have been working with some reputable U.S.-based global companies for more than 14 years, and have extensive knowledge of Indonesian, Asian, and Pacific business environments.
1.3 Keys to Success
The are two keys to success that West Pacific Marketing Consultants is focused on. These are broadlky characterized as Internal and External Factors, and are explained in more detail in the following two sections.
1.3.1 External (Business Environment) Factors
The Asia-Pacific Region is now living in an interesting era: the process of change from the “old economy” to the “global new economy” brings a tremendous development growth of e-commerce, mobility of capital, and liberalization to the region. Since the new global economy brings new economics, new market structures, new industry structures, and new company structures, the profile of customers has also changed. Customers have evolved from “solution demander” to “value demander,” and from “clients” to “business partners.”
West Pacific Marketing Consultants is proactively focused on establishing relationships with multiple digital contents, companies, government institutions, regional (provincial) government offices, NGOs, and individual customers as its prospective business partners.
1.3.2 Internal Factors
The company feels that it controls its own success through some basic internal factors. These are:
- Key management team . The right management team is integral, and must have a strong foundation in marketing, management, finance, and services development. The company is confident in its team.

Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
The founders of West Pacific Marketing Consultants are former marketers of large multinational engineering, procurement, and construction contracting services and, at the same time, are experienced market researchers in global markets. They founded West Pacific Global Trading Portal (SiliconOctopus.com), the parent company of West Pacific Marketing Consultants, to formalize the integrated B2B, B2C, and consumer-to-consumer services they offer.
The parent company was founded by Jaka J. Legawa and his business partners from Chicago, Kansas City, and Singapore. This company was originally installed in a home office and moved into its new office space in January, last year. The subsidiary company, West Pacific Marketing Consultants, was founded in April, last year by these same investors.
2.1 Company Ownership
West Pacific Marketing Consultants was created as an Indonesian “Perseroan Terbatas” (PT) corporation based in Jakarta, namely “PT. Portal Bisnis Pasifik Barat,” owned by its principal investors and principal operators. It was created in April, last year
2.2 Company History
Between April and December of the previous year, West Pacific Marketing Consultants achieved excellent performance ratings. The sales revenue of $1.9 million, with a gross margin of $1.6 million, was 15% higher than the projected sales for that year.
From its recent growth until the time of this writing, West Pacific Marketing Consultants has costs and cash flow under control.

| Past Performance | |||
| 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | |
| Sales | $0 | $0 | $1,895,000 |
| Gross Margin | $0 | $0 | $1,516,000 |
| Gross Margin % | 0.00% | 0.00% | 80.00% |
| Operating Expenses | $0 | $0 | $84,400 |
| Collection Period (days) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Balance Sheet | |||
| 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | |
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $0 | $0 | $656,086 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $0 | $118,438 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $774,524 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $126,588 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $126,588 |
| Total Assets | $0 | $0 | $901,112 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $0 | $5,000 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $5,000 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $5,000 |
| Paid-in Capital | $0 | $0 | $37,800 |
| Retained Earnings | $0 | $0 | $12,762 |
| Earnings | $0 | $0 | $845,550 |
| Total Capital | $0 | $0 | $896,112 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $901,112 |
| Other Inputs | |||
| Payment Days | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| Sales on Credit | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Receivables Turnover | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |

2.3 Company Locations and Facilities
The office is located in one of the strategic locations in the heart of the Indonesian business area, at Komplek Pertanian, in Jakarta.
West Pacific Marketing Consultants is an e-business-based market-development consulting firm specializing in the marketing of a comprehensive set of integrated professional services that provide our customers with high-quality consulting services for business development, market development, market intelligence, industrial sectors analysis, and channel development on a global scale, as well as sales assistance for global companies in the Indonesian market.
3.1 Service Description
West Pacific Marketing Consultants offers expertise in the services it provides. With much experience in this field, the company is able to sell and package its services in various ways that allow clients to choose their preferred benefit(s). These include:
- Strategic Analysis and Reports
3.2 Competitive Comparison
Within its niche, West Pacific Marketing Consultants does not have any competitors, but rather has “prospective business partners.” This is because the cmpany provides its clients with solutions as well as value creations. Its services have been sought out by companies ranging from high-level management firms to international market research companies. Companies choosing to do business development, channel development, and in-house market research, will seek West Pacific Marketing Consultants to deliver the following value creations:
Consulting/Market Researchers/Traders/Suppliers:
- Improved communication
- Access to new markets
- Broader products offering
- Lower cost of doing business
- New ways of adding value
Technology Providers/Manufacturers:
- Lower cost of sales
- Access to niche markets
- Better cost of identification
New business models (outsourcing alliances)
Individual Clients:
- Shopping convenience
- Immediate delivery
- More frequent updates
- Access to more products and services
- Better pricing
3.3 Sales Literature
The business began with a general corporate brochure establishing the positioning. This brochure was developed, and was included as part of last year’s start-up expenses.
Literature and mailings for the market forums will be very important.
3.4 Fulfillment
The key fulfillment and delivery will be provided by the principals of the business. The core value is professional expertise provided by a combination of experience, smart and hard work, discipline, improvements, and education (in that order).
West Pacific Marketing Consultants will turn to qualified professionals for freelance back-up in market research, presentation, and report development; these areas are ones that the company can afford to sub-contract without risking the core values provided to the clients.
3.5 Technology
West Pacific Marketing Consultants maintains the latest Windows and Macintosh capabilities including:
- Desktop publishing facilities for delivery of regular retainer reports, project output reports, marketing materials, and market research reports.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
West Pacific Marketing Consultants has a unique offering of services that appeals to a large customer base. The company will concentrate on large corporations because they provide the maximum profit potential. The following sections outline key information regarding the target markets.
4.1 Market Segmentation
The groups of potential customers for West Pacific Marketing Consultants are, in order of importance:
- Individual Customers
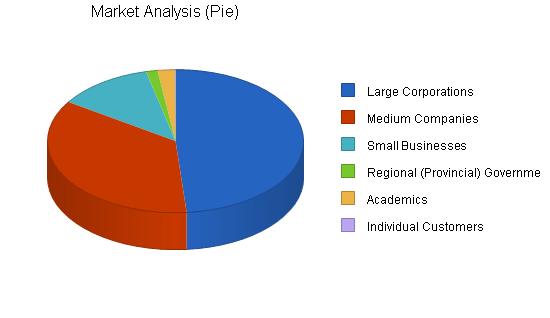
| Market Analysis | |||||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Large Corporations | 11% | 50,500,000 | 56,034,800 | 62,176,214 | 68,990,727 | 76,552,111 | 10.96% |
| Medium Companies | 35% | 37,000,000 | 49,950,000 | 67,432,500 | 91,033,875 | 122,895,731 | 35.00% |
| Small Businesses | 5% | 12,500,000 | 13,125,000 | 13,781,250 | 14,470,313 | 15,193,829 | 5.00% |
| Regional (Provincial) Governments | 2% | 1,500,000 | 1,530,000 | 1,560,600 | 1,591,812 | 1,623,648 | 2.00% |
| Academics | 1% | 2,250,000 | 2,272,500 | 2,295,225 | 2,318,177 | 2,341,359 | 1.00% |
| Individual Customers | 332% | 87,500 | 377,580 | 1,629,333 | 7,030,898 | 30,339,731 | 331.52% |
| Total | 24.43% | 103,837,500 | 123,289,880 | 148,875,122 | 185,435,802 | 248,946,409 | 24.43% |
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
As indicated by the previous chart and table, West Pacific Marketing Consultants must focus on large corporations, medium companies, small businesses, and individual customers in the global market; and in the Indonesian market, regional (provincial) government offices, NGOs, academics, and individual customers will be the core of profits.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
The following companies are major players in Indonesian market research consulting business:
- SOFRES FSA Jakarta (Taylor Nelson Sofres Group)
4.4 Competition and Buying Patterns
Recent analysis indicated that consultant costs (in US$/man-hour) in Indonesia have decreased by 12% since the economic turmoil of 1996. This analysis is based on the assumptions that the local senior consultants’ and senior engineers’ salaries have increased by 25% at the average exchange rate of US$1 = Rp 7,200. This is because the Indonesian skilled manpower market offers the lowest man-hour cost in the world, even with the estimated average increasing 20% per year.
To take advantage of this situation, West Pacific Marketing Consultants utilizes Indonesian resources for serving both global and regional markets.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
West Pacific Marketing Consultants will focus on six technographical market segments as follows:
- Individual customers . Influential people such as boards of directors, marketing managers, general managers, sales managers, and government officials.
5.1 Competitive Edge
West Pacific Marketing Consultants has close and effective relationships with its end-users, vendors (suppliers and sub-contractors), and even competitors. On several occasions, West Pacific Marketing Consultants has teamed-up with its end-user or supplier in a consortium partnership to perform projects.
West Pacific Marketing Consultants combines unparalleled quality with a cost-effective package to create a consulting service with many competitive advantages. The seasoned management is qualified for multiple services, such as: business development, market development, market intelligence, industrial sectors analysis, and channel development. We provide this range of services to anyone from a high-level marketing firm to a home-based business owner; clients can always count on quick, accurate services from the company.
5.2 Sales Strategy
West Pacific Marketing Consultants’ strategy focuses first on maintaining the identity of the high-end buyer who appreciates quality service, but is also very demanding regarding value creations. West Pacific Marketing Consultants has been able to find these customers using a combination of social and interactive email relationships.
Even when a business offers a standard service, it is not making a standard sales offer. The customer is able to choose a tailored offering mix of elements, such as optional services benefits, delivery conditions, training, financing alternatives, technical services options, sales assistance options, etc.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The sales forecast monthly summary is included in the appendix. The annual sales projections are included here in the following chart and table.
The sales forecast assumes that the yearly change in costs or prices will average 20%, which is a reasonable assumption based on the last few years.
West Pacific Marketing Consultants is expecting to increase sales modestly in 2001 and 2002, with sales growth accelerating in 2003-2005. It is the expectation that the company will double its starting sales within five years.

| Sales Forecast | |||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Sales | |||||
| Retainer Consulting | $580,000 | $696,000 | $835,200 | $1,002,240 | $1,202,688 |
| Project Consulting | $480,000 | $576,000 | $691,200 | $829,440 | $995,328 |
| Market Research & Industrial Analyses | $360,000 | $432,000 | $518,400 | $622,080 | $746,496 |
| Feasibility Studies | $360,000 | $432,000 | $518,400 | $622,080 | $746,496 |
| Strategic Analysis and Reports | $300,000 | $360,000 | $432,000 | $518,400 | $622,080 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $2,080,000 | $2,496,000 | $2,995,200 | $3,594,240 | $4,313,088 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 |
| Retainer Consulting | $116,040 | $139,248 | $167,098 | $200,517 | $240,621 |
| Project Consulting | $93,720 | $112,464 | $134,957 | $161,948 | $194,334 |
| Market Research & Industrial Analyses | $72,000 | $86,400 | $103,680 | $124,416 | $149,299 |
| Feasibility Studies | $72,000 | $86,400 | $103,680 | $124,416 | $149,299 |
| Strategic Analysis and Reports | $58,560 | $70,272 | $84,236 | $101,192 | $121,430 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $412,320 | $494,784 | $593,651 | $712,489 | $854,983 |
5.3 Milestones
The accompanying chart and table show specific milestones, with responsibilities assigned, dates, and budgets. West Pacific Marketing Consultants is focusing on a few key milestones that are to be accomplished.
Print adverstising will target newspapers and magazines, while Internet advertising will appear on both websites and search engines.
Participation in Indonesian business and trade exhibitions will be important as well.

| Milestones | |||||
| Milestone | Start Date | End Date | Budget | Manager | Department |
| Business Plan | 11/20/2000 | 11/24/2000 | $3,500 | Jaka Legawa | CEO |
| Stationery | 11/1/2000 | 11/3/2000 | $3,000 | VP Internal Bus. Mngt. | Internal Bus. Mngt. |
| Brochures | 11/6/2000 | 12/1/2000 | $5,000 | VP Internal Bus. Mngt. | Internal Bus. Mngt. |
| Office Equipment | 12/4/2000 | 12/6/2000 | $3,000 | VP Internal Bus. Mngt. | Internal Bus. Mngt. |
| Advertising — Print | 1/2/2001 | 2/28/2001 | $3,000 | VP Sales & Marketing | Sales & Marketing |
| Advertising — Internet | 1/2/2001 | 2/28/2001 | $2,000 | VP Sales & Marketing | Sales & Marketing |
| Exports Exhibition/Jakarta | 4/9/2001 | 4/13/2001 | $2,500 | VP Sales & Marketing | Sales & Marketing |
| Trade Exhibition/Bali | 8/6/2001 | 8/17/2001 | $13,000 | VP Sales & Marketing | Sales & Marketing |
| Computer Tech Exhibition/Jakarta | 11/12/2001 | 11/17/2001 | $6,000 | VP Sales & Marketing | Sales & Marketing |
| Totals | $41,000 | ||||
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
The initial management team depends on the founders themselves, with little back-up. As it grows, West Pacific Marketing Consultants will establish a team that includes 17 employees who operate under a president and three vice-presidents.
The management philosophy is based on responsibility and mutual respect. People who work at West Pacific Marketing Consultants want to work at the company because it has an environment that encourages “C4A,” which is: Creativity, Concepts, Competencies, Connections, and Achievement. This C4A concept is our tool in performing the Shareholders Value Creation of West Pacific Marketing Consultants.
6.1 Personnel Plan
The team includes 17 employees, under a president and three vice-presidents.
The three main management divisions are Sales and Marketing, Operations, and Internal Business Management. The departments managed by the Sales and Marketing division are: marketing, sales, products and services, research and development, and public relations operations. The departments managed by the Internal Business Management division are: accounting, administration, and human resources development.
Note: The following table reflects the currency exchange rate of US$1 = Rp 7,2000
| Personnel Plan | |||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Vice President Sales & Marketing | $24,000 | $26,400 | $29,040 | $31,944 | $35,138 |
| Technical Sales B2B | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Technical Sales B2C | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Secretary – Sales & Marketing Office | $3,600 | $3,960 | $4,356 | $4,792 | $5,271 |
| Vice President Operations | $24,000 | $26,400 | $29,040 | $31,944 | $35,138 |
| Senior Consultant – Marketing | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Senior Consultant – Finance Management | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Senior Consultant – Strategic Management | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Secretary – Operations Office | $3,600 | $3,960 | $4,356 | $4,792 | $5,271 |
| VP Internal Business Management | $24,000 | $26,400 | $29,040 | $31,944 | $35,138 |
| Accountant | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Legal Officer | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| Administrative Officer | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| HRD Officer | $14,400 | $15,840 | $17,424 | $19,166 | $21,083 |
| President/CEO | $48,000 | $52,800 | $58,080 | $63,888 | $70,277 |
| Secretary to the CEO | $6,000 | $6,600 | $7,260 | $7,986 | $8,785 |
| Bookkeeper | $3,600 | $3,960 | $4,356 | $4,792 | $5,271 |
| Clerical | $1,200 | $1,320 | $1,452 | $1,597 | $1,757 |
| Clerical | $1,200 | $1,320 | $1,452 | $1,597 | $1,757 |
| Clerical | $1,200 | $1,320 | $1,452 | $1,597 | $1,757 |
| Clerical | $1,200 | $1,320 | $1,452 | $1,597 | $1,757 |
| Total People | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Payroll | $271,200 | $298,320 | $328,152 | $360,967 | $397,064 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The financial picture is quite encouraging. West Pacific Marketing Consultants does not foresee a debt situation.
The company does expect to be able to take some money out as dividends. The owners don’t take overly generous salaries, so some draw is appropriate.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The accompanying table lists West Pacific Marketing Consultants’ main assumptions for developing its financial projections. The most sensitive assumption is the collection days. West Pacific Marketing Consultants would like to improve collection days to take pressure off of its working capital.
| General Assumptions | |||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Current Interest Rate | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| Tax Rate | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
7.2 Business Ratios
The following table presents significant business ratios for West Pacific Marketing Consultants. The last column, Industry Profiles, contains ratios based on the management consulting services industry, as defined by the Standard Industry Classification (SIC) Index code 8742.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 9.76% | 20.00% | 20.00% | 20.00% | 20.00% | 8.60% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||||
| Accounts Receivable | 9.13% | 6.82% | 5.61% | 4.86% | 4.36% | 24.40% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 46.70% |
| Total Current Assets | 93.28% | 95.82% | 97.14% | 97.93% | 98.45% | 74.90% |
| Long-term Assets | 6.72% | 4.18% | 2.86% | 2.07% | 1.55% | 25.10% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 3.75% | 2.92% | 2.40% | 2.09% | 1.88% | 42.80% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 17.20% |
| Total Liabilities | 3.75% | 2.92% | 2.40% | 2.09% | 1.88% | 60.00% |
| Net Worth | 96.25% | 97.08% | 97.60% | 97.91% | 98.12% | 40.00% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 80.18% | 80.18% | 80.18% | 80.18% | 80.18% | 0.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 36.08% | 35.14% | 34.28% | 33.49% | 32.77% | 83.50% |
| Advertising Expenses | 1.27% | 1.27% | 1.27% | 1.27% | 1.27% | 1.20% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 58.80% | 60.05% | 61.20% | 62.25% | 63.21% | 2.60% |
| Main Ratios | ||||||
| Current | 24.86 | 32.86 | 40.41 | 46.87 | 52.42 | 1.59 |
| Quick | 24.86 | 32.86 | 40.41 | 46.87 | 52.42 | 1.26 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 3.75% | 2.92% | 2.40% | 2.09% | 1.88% | 60.00% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 67.44% | 51.02% | 42.51% | 37.35% | 33.93% | 4.40% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 64.91% | 49.54% | 41.49% | 36.57% | 33.29% | 10.90% |
| Additional Ratios | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 44.10% | 45.04% | 45.90% | 46.69% | 47.41% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 50.58% | 38.27% | 31.88% | 28.01% | 25.45% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 6.04 | 6.04 | 6.04 | 6.04 | 6.04 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 59 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 12.61 | 12.17 | 12.17 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 1.10 | 0.82 | 0.68 | 0.59 | 0.53 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||||
| Net Working Capital | $1,686,804 | $2,810,931 | $4,185,741 | $5,863,735 | $7,908,464 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.91 | 1.21 | 1.48 | 1.70 | 1.90 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 4% | 3% | 2% | 2% | 2% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 22.42 | 30.52 | 38.08 | 44.54 | 50.10 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 1.15 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.60 | 0.54 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
7.3 Break-even Analysis
The following chart and table summarize the break-even analysis, including monthly units and sales break-even points.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $46,214 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 20% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $37,053 |
7.4 Projected Profit and Loss
The detailed monthly pro-forma income statement for the first year is included in the appendix. The annual estimates are included here.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Sales | $2,080,000 | $2,496,000 | $2,995,200 | $3,594,240 | $4,313,088 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $412,320 | $494,784 | $593,651 | $712,489 | $854,983 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $412,320 | $494,784 | $593,651 | $712,489 | $854,983 |
| Gross Margin | $1,667,680 | $2,001,216 | $2,401,549 | $2,881,751 | $3,458,105 |
| Gross Margin % | 80.18% | 80.18% | 80.18% | 80.18% | 80.18% |
| Expenses | |||||
| Payroll | $271,200 | $298,320 | $328,152 | $360,967 | $397,064 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $85,000 | $102,000 | $122,320 | $146,784 | $176,141 |
| Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Utilities | $7,200 | $8,640 | $10,368 | $12,442 | $14,930 |
| Insurance | $2,160 | $2,592 | $3,110 | $3,732 | $4,479 |
| Office Rent | $38,400 | $46,080 | $55,296 | $66,355 | $79,626 |
| Payroll Taxes | $40,680 | $44,748 | $49,223 | $54,145 | $59,560 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $444,640 | $502,380 | $568,469 | $644,426 | $731,799 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $1,223,040 | $1,498,836 | $1,833,080 | $2,237,325 | $2,726,306 |
| EBITDA | $1,223,040 | $1,498,836 | $1,833,080 | $2,237,325 | $2,726,306 |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Taxes Incurred | $305,760 | $374,709 | $458,270 | $559,331 | $681,576 |
| Net Profit | $917,280 | $1,124,127 | $1,374,810 | $1,677,994 | $2,044,729 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 44.10% | 45.04% | 45.90% | 46.69% | 47.41% |
7.5 Projected Cash Flow
Cash flow projections are critical to West Pacific Marketing Consultants’ success. The monthly cash flow is shown in the illustration, with one bar representing the cash flow per month and the other representing the monthly balance. The annual cash flow figures are included below in the following chart and table. Detailed monthly numbers are included in the appendix.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Cash Received | |||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||
| Cash Sales | $1,040,000 | $1,248,000 | $1,497,600 | $1,797,120 | $2,156,544 |
| Cash from Receivables | $986,355 | $1,213,583 | $1,456,300 | $1,747,560 | $2,097,072 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $2,026,355 | $2,461,583 | $2,953,900 | $3,544,680 | $4,253,616 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $2,026,355 | $2,461,583 | $2,953,900 | $3,544,680 | $4,253,616 |
| Expenditures | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||
| Cash Spending | $271,200 | $298,320 | $328,152 | $360,967 | $397,064 |
| Bill Payments | $825,811 | $1,056,025 | $1,274,264 | $1,533,659 | $1,845,321 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $1,097,011 | $1,354,345 | $1,602,416 | $1,894,626 | $2,242,385 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $1,097,011 | $1,354,345 | $1,602,416 | $1,894,626 | $2,242,385 |
| Net Cash Flow | $929,344 | $1,107,238 | $1,351,484 | $1,650,054 | $2,011,231 |
| Cash Balance | $1,585,430 | $2,692,668 | $4,044,152 | $5,694,206 | $7,705,437 |

7.6 Projected Balance Sheet
The following balance sheet shows healthy growth of net worth, and strong financial position. The monthly estimates are included in the appendix.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||
| 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| Assets | |||||
| Current Assets | |||||
| Cash | $1,585,430 | $2,692,668 | $4,044,152 | $5,694,206 | $7,705,437 |
| Accounts Receivable | $172,083 | $206,500 | $247,800 | $297,360 | $356,832 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $1,757,513 | $2,899,168 | $4,291,952 | $5,991,566 | $8,062,269 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||
| Long-term Assets | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 |
| Total Assets | $1,884,101 | $3,025,756 | $4,418,540 | $6,118,154 | $8,188,857 |
| Liabilities and Capital | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 |
| Current Liabilities | |||||
| Accounts Payable | $70,709 | $88,237 | $106,211 | $127,831 | $153,805 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $70,709 | $88,237 | $106,211 | $127,831 | $153,805 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $70,709 | $88,237 | $106,211 | $127,831 | $153,805 |
| Paid-in Capital | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 |
| Retained Earnings | $858,312 | $1,775,592 | $2,899,719 | $4,274,528 | $5,952,522 |
| Earnings | $917,280 | $1,124,127 | $1,374,810 | $1,677,994 | $2,044,729 |
| Total Capital | $1,813,392 | $2,937,519 | $4,312,328 | $5,990,322 | $8,035,052 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $1,884,101 | $3,025,756 | $4,418,540 | $6,118,154 | $8,188,857 |
| Net Worth | $1,813,392 | $2,937,519 | $4,312,328 | $5,990,322 | $8,035,052 |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Retainer Consulting | 0% | $46,000 | $46,000 | $46,000 | $46,000 | $46,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 |
| Project Consulting | 0% | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 |
| Market Research & Industrial Analyses | 0% | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 |
| Feasibility Studies | 0% | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 |
| Strategic Analysis and Reports | 0% | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 |
| Other | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
| Retainer Consulting | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | $9,670 | |
| Project Consulting | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | $7,810 | |
| Market Research & Industrial Analyses | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | |
| Feasibility Studies | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | |
| Strategic Analysis and Reports | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | $4,880 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Vice President Sales & Marketing | 0% | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| Technical Sales B2B | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Technical Sales B2C | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Secretary – Sales & Marketing Office | 0% | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 |
| Vice President Operations | 0% | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| Senior Consultant – Marketing | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Senior Consultant – Finance Management | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Senior Consultant – Strategic Management | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Secretary – Operations Office | 0% | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 |
| VP Internal Business Management | 0% | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| Accountant | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Legal Officer | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Administrative Officer | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| HRD Officer | 0% | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| President/CEO | 0% | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 |
| Secretary to the CEO | 0% | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $500 |
| Bookkeeper | 0% | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 |
| Clerical | 0% | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 |
| Clerical | 0% | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 |
| Clerical | 0% | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 |
| Clerical | 0% | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 |
| Total People | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total Payroll | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Sales | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | $34,360 | |
| Gross Margin | $136,640 | $136,640 | $136,640 | $136,640 | $136,640 | $140,640 | $140,640 | $140,640 | $140,640 | $140,640 | $140,640 | $140,640 | |
| Gross Margin % | 79.91% | 79.91% | 79.91% | 79.91% | 79.91% | 80.37% | 80.37% | 80.37% | 80.37% | 80.37% | 80.37% | 80.37% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $10,500 | $4,500 | $2,000 | $12,500 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $8,000 | $15,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $19,500 | $5,000 | |
| Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Utilities | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | |
| Insurance | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | |
| Office Rent | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | $3,200 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 | $3,390 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $40,470 | $34,470 | $31,970 | $42,470 | $31,970 | $31,970 | $37,970 | $44,970 | $31,970 | $31,970 | $49,470 | $34,970 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $96,170 | $102,170 | $104,670 | $94,170 | $104,670 | $108,670 | $102,670 | $95,670 | $108,670 | $108,670 | $91,170 | $105,670 | |
| EBITDA | $96,170 | $102,170 | $104,670 | $94,170 | $104,670 | $108,670 | $102,670 | $95,670 | $108,670 | $108,670 | $91,170 | $105,670 | |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxes Incurred | $24,043 | $25,543 | $26,168 | $23,543 | $26,168 | $27,168 | $25,668 | $23,918 | $27,168 | $27,168 | $22,793 | $26,418 | |
| Net Profit | $72,128 | $76,628 | $78,503 | $70,628 | $78,503 | $81,503 | $77,003 | $71,753 | $81,503 | $81,503 | $68,378 | $79,253 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | 42.18% | 44.81% | 45.91% | 41.30% | 45.91% | 46.57% | 44.00% | 41.00% | 46.57% | 46.57% | 39.07% | 45.29% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $85,500 | $85,500 | $85,500 | $85,500 | $85,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $59,219 | $62,069 | $85,500 | $85,500 | $85,500 | $85,500 | $85,567 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | $87,500 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $144,719 | $147,569 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $173,000 | $173,067 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $144,719 | $147,569 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $171,000 | $173,000 | $173,067 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | $175,000 | |
| Expenditures | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | $22,600 | |
| Bill Payments | $7,542 | $76,123 | $71,710 | $70,160 | $77,510 | $69,931 | $71,048 | $75,573 | $80,323 | $70,898 | $71,335 | $83,660 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $30,142 | $98,723 | $94,310 | $92,760 | $100,110 | $92,531 | $93,648 | $98,173 | $102,923 | $93,498 | $93,935 | $106,260 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $30,142 | $98,723 | $94,310 | $92,760 | $100,110 | $92,531 | $93,648 | $98,173 | $102,923 | $93,498 | $93,935 | $106,260 | |
| Net Cash Flow | $114,577 | $48,847 | $76,690 | $78,240 | $70,890 | $80,469 | $79,419 | $76,828 | $72,078 | $81,503 | $81,065 | $68,740 | |
| Cash Balance | $770,663 | $819,509 | $896,199 | $974,439 | $1,045,329 | $1,125,798 | $1,205,217 | $1,282,045 | $1,354,122 | $1,435,625 | $1,516,690 | $1,585,430 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $656,086 | $770,663 | $819,509 | $896,199 | $974,439 | $1,045,329 | $1,125,798 | $1,205,217 | $1,282,045 | $1,354,122 | $1,435,625 | $1,516,690 | $1,585,430 |
| Accounts Receivable | $118,438 | $144,719 | $168,150 | $168,150 | $168,150 | $168,150 | $170,150 | $172,083 | $172,083 | $172,083 | $172,083 | $172,083 | $172,083 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $774,524 | $915,382 | $987,659 | $1,064,349 | $1,142,589 | $1,213,479 | $1,295,948 | $1,377,301 | $1,454,128 | $1,526,206 | $1,607,708 | $1,688,773 | $1,757,513 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 | $126,588 |
| Total Assets | $901,112 | $1,041,969 | $1,114,247 | $1,190,937 | $1,269,177 | $1,340,067 | $1,422,536 | $1,503,888 | $1,580,716 | $1,652,793 | $1,734,296 | $1,815,361 | $1,884,101 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $5,000 | $73,730 | $69,380 | $67,568 | $75,180 | $67,568 | $68,534 | $72,884 | $77,959 | $68,534 | $68,534 | $81,222 | $70,709 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $5,000 | $73,730 | $69,380 | $67,568 | $75,180 | $67,568 | $68,534 | $72,884 | $77,959 | $68,534 | $68,534 | $81,222 | $70,709 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $5,000 | $73,730 | $69,380 | $67,568 | $75,180 | $67,568 | $68,534 | $72,884 | $77,959 | $68,534 | $68,534 | $81,222 | $70,709 |
| Paid-in Capital | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 | $37,800 |
| Retained Earnings | $12,762 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 | $858,312 |
| Earnings | $845,550 | $72,128 | $148,755 | $227,258 | $297,885 | $376,388 | $457,890 | $534,893 | $606,645 | $688,148 | $769,650 | $838,028 | $917,280 |
| Total Capital | $896,112 | $968,239 | $1,044,867 | $1,123,369 | $1,193,997 | $1,272,499 | $1,354,002 | $1,431,004 | $1,502,757 | $1,584,259 | $1,665,762 | $1,734,139 | $1,813,392 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $901,112 | $1,041,969 | $1,114,247 | $1,190,937 | $1,269,177 | $1,340,067 | $1,422,536 | $1,503,888 | $1,580,716 | $1,652,793 | $1,734,296 | $1,815,361 | $1,884,101 |
| Net Worth | $896,112 | $968,239 | $1,044,867 | $1,123,369 | $1,193,997 | $1,272,499 | $1,354,002 | $1,431,004 | $1,502,757 | $1,584,259 | $1,665,762 | $1,734,139 | $1,813,392 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
What Are the Components of a Global Business Plan?
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Elements of Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
How to Create a Business Plan & Where Should the Executive Summary Be Located?
How to write a business plan template for a cable channel, how to internationally outsource manufacturing.
- How to Write a Business Plan Outline
- How to Write a Business Description

Global business plans resemble local and regional business plans in format. Global business plans differ from other business plans by serving as a company's communications vehicle for its global operations. Components of a global business plan, which differ from other focus on global customers, global pricing and currency issues, and international market legal factors, to name a few distinctions listed by Allegro Invest. The University of Houston Small Business Development Center offers workshops and seminars on all aspects of small business development, including creating business plans (See References).
Executive Summary Component

An executive summary describes the owner's goals and targets. An executive summary includes components, including but not limited to, a business overview, which describes the company, the projected market and the intended product or service. Include financial results, such as capital growth and profits, advises Allegro Invest. Provide any investment requirements for business operations. In an example offered by the website, BPlansWest, Pacific Marketing opens its Executive Summary, "West Pacific Marketing Consultants aims to provide marketing services to targeted business environments in Indonesia, Asia, and the west Pacific region."
Market Description
A market description for a global business reflects an in-depth international market study and offers analysis of the study findings. Key factors in a market description for an international company include "market size, share positioning of products, and competition, explains Allegro Invest. Allegro Invest advises entrepreneurs and executives to energetically research their targeted international market (See References).
Operations And Management Component
An Operations and Management Plan discusses operation factors. Operations components include, but are not limited to supply, production, marketing and distribution. This section will distinguish itself from a non-global business plan. You will discuss your research into the complexities of the global markets you are targeting, including how you plan to supply your product or service in targeted countries. If you plan to produce your product overseas, explain that dynamic here. Explain how you plan to market to the countries you will initially introduce your company. Include your management plan with strategies for global growth and successful attainment of international goals. For example, if you plan to start in one country and grow over time into other regions, discuss that plan.
Organizational Structure
The section of your global business plan on organizational structure describes your management model. Detail your organization's hierarchy of personnel, Allegro Invests advises. Potential investors want to know that their investments go to qualified executives and management. The people at the helm of your company must be savvy in your kind of business at an international level. Provide each person's credentials.
- University of Houston Small Business Development Center: Workshops and Seminars
- BPlans: Global Marketing Business Plan
Alyson Paige has a master's degree in canon law and began writing professionally in 1998. Her articles specialize in culture, business and home and garden, among many other topics.
Related Articles
How to implement a global business plan, essential elements of an international marketing plan, define a business plan, define global business plan, how to create a business plan as an entrepreneur, differences between a multidomestic & a transnational company, quick step process business plan, how to write a comprehensive business plan, how to prepare business plans, most popular.
- 1 How to Implement a Global Business Plan
- 2 Essential Elements of an International Marketing Plan
- 3 Define a Business Plan
- 4 Define Global Business Plan

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.

Global Business Strategy Plan Template

What is a Global Business Strategy Plan?
A global business strategy plan outlines the strategies, objectives and tactics that an organization or company plans to implement to achieve its global business goals. It is designed to provide a roadmap for the company's direction and serves to align the company's employees and stakeholders with the vision of the business. It also outlines the steps required to achieve the desired outcome and the resources necessary to carry out the plan.
What's included in this Global Business Strategy Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Global Business Strategy Plan template for?
This global business strategy plan template is for companies or organizations of all sizes and industries looking for an effective way to create and execute a plan for their global business strategies. The template provides a comprehensive framework for defining, measuring and monitoring progress towards your goals and objectives.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is the area of your business that you are looking to improve or grow. This could be anything from improving operational efficiency, to increasing customer service, to developing new digital engagement strategies. It is important to clearly define your focus areas before you start setting objectives and KPIs, so that you can ensure that your plan is aligned with your overall business goals.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the steps that need to be taken in order to achieve the goals of your focus area. They should be specific and measurable, and should be set in such a way that they can be tracked and monitored. Examples of some objectives for the focus area of Improve Operational Efficiency could be: Reduce Shipping Wait Time, and Increase On-Time Deliveries.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
KPIs, or key performance indicators, are the metrics that you use to measure the success of your objectives. These should be set to ensure that progress towards the objective can be tracked and monitored. An example of a KPI for the focus area of Improve Operational Efficiency could be: Decrease avg shipping wait time from 2.2 days to 1.5 days.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects are the actions or activities that you will take in order to achieve the KPIs that you have set. These should be specific and measurable, and should be set in such a way that they can be tracked and monitored. An example of a project related to Improve Operational Efficiency could be: Streamline Shipping Process.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade is an easy-to-use strategy execution platform that allows you to quickly and easily create, track, and monitor your strategy plan. With Cascade, you can easily define objectives and KPIs, assign tasks and projects, track progress, and monitor results so that you can see faster results from your strategy.
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

Best West Virginia Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Best Vermont Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Rhode Island Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Wisconsin Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best South Dakota Registered Agent Services Of 2024

B2B Marketing In 2024: The Ultimate Guide
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Project Planning
Main navigation.
Stanford is committed to facilitating faculty, staff, and student activities abroad. In furtherance of those activities, our Global Business Services (GBS) provides consultative support on a range of foreign operations. One of the key factors to ensuring the successful execution of any international activity is thoughtful planning. Although there are similarities between operating in the U.S. and operating in a foreign country, there are also many administrative, legal, tax, and safety implications to consider during project planning.
This section provides resources and guidance on how to budget for your global activity, as well as how to access and spend funds outside of the U.S. For long-term programs, it is especially recommended that financial planning begin at least 3-6 months prior to the planned activity while paying special attention to the many administrative, legal, tax, and safety implications of utilizing resources across borders.
This section provides guidance, information and resources related to Project Planning as follows:
- Due Diligence
- Budgeting Basics for International Projects
- Business Frameworks
What's Next?
International project planning is a complicated process. GBS is here to guide you through the due diligence considerations and help you explore the appropriate business frameworks and solutions. In consultation with other Stanford central offices, GBS serves as an advisor on international project matters and can be consulted in the project planning phase. Providing us with as much advance notice as possible will assist with efforts to conduct and provide relevant information to help in successful project planning from a business perspective.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
- Account Details
- Newsletters
- Group Subscription
Vietnam gas project receives $830m in Japanese loans
Natural gas to serve as transition energy source in Hanoi's decarbonization plan
HANOI -- The Japan Bank for International Cooperation and private lenders will extend roughly $832 million in syndicated loans to a gas development project in Vietnam, the state-backed lender announced on Monday.
JBIC is contributing about $415 million to the co-financing deal, with private financial groups providing the rest. The money will go toward developing the Block B gas field off the coast of southern Vietnam.
Will Vietnam face another power crisis this year?
Vietnam gas field secures $560m investment from japan's mitsui, taiwan's top power cable maker ventures into offshore wind, companies welcome common standards as vietnam prepares co2 rules, greenflation causes indonesia and vietnam to backtrack on renewables, indonesia's pertamina to invest $6.2bn in clean energy business, world's biggest fusion project faces massive delays, cost overruns, u.s. firm's vietnam coal deal 'undermines' climate goal: report, vietnam turns to rooftop solar as blackouts hit country, latest on energy, hsbc lends $23m for malaysian firm's vietnam solar project, germany to probe use of chinese wind turbines in north sea project, sponsored content, about sponsored content this content was commissioned by nikkei's global business bureau..
Nikkei Asian Review, now known as Nikkei Asia, will be the voice of the Asian Century.
Celebrate our next chapter Free access for everyone - Sep. 30

- The Star ePaper
- Subscriptions
- Manage Profile
- Change Password
- Manage Logins
- Manage Subscription
- Transaction History
- Manage Billing Info
- Manage For You
- Manage Bookmarks
- Package & Pricing
PETRONAS adds three new LNG vessels ahead of LNG Canada start-up
- Corporate News
Monday, 08 Jul 2024
Related News

Corporate lenders are locking down protection
Tencent’s hit game stays on top despite rival’s latest release, trading ideas: maybank, southern cable, fgv, ghl, eurospan, volcano, pestech, computer forms, tex cycle, hb global, techstore.
KUALA LUMPUR: Malaysian state energy firm Petroliam Nasional Berhad (Petronas) on Monday said it would add three energy-efficient liquefied natural gas (LNG) vessels to its North American operations.
The addition of the vessels, which brings the total number in Petronas' fleet in North America to six, comes ahead of the start-up of LNG Canada's gas-export facility due later this year, the company said in a statement.
Petronas has a 25% stake in the LNG Canada plant in Kitimat, British Columbia, on the west coast of Canada.
"With the arrival of these new vessels, Petronas reinforces its commitment to deliver this much needed fuel of choice to its customers in a cost-efficient and reliable manner," it said.
The vessels were built at the Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) shipyard in Ulsan, South Korea. Each has a cargo capacity of 174,000 cubic meters and are the largest ships in Petronas' fleet, the firm said. - Reuters
Tags / Keywords: Petronas , LNG , liquefied natural gas
Found a mistake in this article?
Report it to us.
Thank you for your report!

Uni-Charm’s MamyPoko teams up with MBPJ in dengue prevention efforts
Next in business news.

Trending in Business
Air pollutant index, highest api readings, select state and location to view the latest api reading.
- Select Location
Source: Department of Environment, Malaysia
Others Also Read
Best viewed on Chrome browsers.

We would love to keep you posted on the latest promotion. Kindly fill the form below
Thank you for downloading.
We hope you enjoy this feature!

MBA 541 - Global Business Plan Project Resource Guide
- Phase One: Choosing a Company and Global Business Opportunity
- Phase Two: Planning the Global Enterprise
- Phase Three: Organizing Global Business Activities
Phase Four: Implementing the Global Marketing Plan
This final research phase is designed to help you locate information to build a marketing strategy for your enterprise or product expansion. You'll likely find that most of this information is covered in items that you've already gathered. Be prepared to make marketing decisions by inferring, estimating, and making judgments based on related and relevant information.
Each section in this guide contains a research component or goal that will help you build your Global Business Plan for MBA 541. Resources to accomplish these goals are recommended. The guided "Pro-tips" will help you navigate some of the highlighted databases and websites.
As always, if you have any questions about the content in this guide, please ask a librarian. For more information about this project, please refer to your online course shell. Please direct any questions about assignment expectations or requirements directly to your instructor.
Section One
Product and target market planning for foreign markets.
Identify specific attributes and customer benefits for a proposed international product or service
Recommended Resources:
- Find Target Market Data
Pro-tip:
Of the resources outlined in the above how-to guide, Statista is probably the best for quantitative consumer information in international markets. You likely have already pulled a country report from this database.
Section Two
Designing a global distribution strategy.
Analyze distribution channels and intermediaries for global business operations
- Find Industry Reports
- International Trade Administration Country Commercial Guides US perspective
- Canada Trade Commissioner Service Country and Sector Information Canadian perspective
Pro-tip one:
The International Trade Administration has a section on selling US Products in their Country Commercial Guides. This section will help you both identify sales and distribution channels, as well as navigate any media or marketing regulations, which will be important in the next section.
Pro-tip two:
Refer to your previously found industry reports for additional distribution information. If you haven’t already, try to locate some global industry reports. Mergent Online is a great place to find global industry information by region. IBISWorld is great resource if you are looking to expand to Mexico or Canada. It also carries general global reports. These databases and others are linked in the Find Industry Reports guide (linked above).
Section Three
Planning a global promotion strategy.
Suggest advertising messages, media, and other promotional activities for an international enterprise
- CIA World Factbook US perspective
Many countries regulate advertising and marketing. It is important to identify these laws and regulations prior to suggesting any promotional activities. Additionally, research the communication systems available in your country. Internet broadband access, telephone access, etc. are all important factors to consider as you explore a promotional strategy.
- << Previous: Phase Three: Organizing Global Business Activities
- Last Updated: May 14, 2024 4:20 PM
CityU Home - CityU Catalog

The Daily Show Fan Page

Explore the latest interviews, correspondent coverage, best-of moments and more from The Daily Show.
The Daily Show
S29 E68 • July 8, 2024
Host Jon Stewarts talks with journalist and author A.J. Jacobs about his latest book “The Year of Living Constitutionally”.
Extended Interviews

The Daily Show Tickets
Attend a Live Taping
Find out how you can see The Daily Show live and in-person as a member of the studio audience.
Best of Jon Stewart

The Weekly Show with Jon Stewart
New Episodes Thursdays
Jon Stewart and special guests tackle complex issues.
Powerful Politicos

The Daily Show Shop
Great Things Are in Store
Become the proud owner of exclusive gear, including clothing, drinkware and must-have accessories.
About The Daily Show
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A strategic plan covers many of the same points as a business plan. However, a strategic plan sets out the detailed action plan to be followed to achieve the objectives of the international business plan. It must outline specific activities, their due dates and who is responsible for each activity. It is a project plan with a critical path.
The guide may be used for planning global expansion of an existing product or service or may be used to research a new foreign business opportunity. Each phase and section in this guide contains a research component or goal that will help you build your Global Business Plan for MBA 541. Delivery
0_Hisrich. 4. Developing the Global Business Plan. Profile: TOMS Shoes. Digital Vision/Digital Vision/Thinkstockphotos. 49. E ntrepreneurial inspiration can occur anywhere, as happened to Blake Mycoskie, founder of TOMS, a very successful shoe company with an extraordinary busi-ness model. For him, inspiration struck while on vacation in ...
Global business expansion - also known as international expansion, foreign expansion, or overseas expansion - is a business growth strategy used to enter new markets in other countries. It can include the movement of business operations, resources, workforces, products, and services. Successful expansion requires the tailoring of a global ...
Explore a real-world global marketing business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. Don't bother with copy and paste. ... project consulting, market research and industrial analysis, feasibility studies, and strategic analysis and reporting services, compared to the preceding ...
An Operations and Management Plan discusses operation factors. Operations components include, but are not limited to supply, production, marketing and distribution. This section will distinguish ...
MBA 541 - Global Business Plan Project Resource Guide. This project template is designed to provide the foundation for an international business plan. Overview; ... Each section in this guide contains a research component or goal that will help you build your Global Business Plan for MBA 541. Resources to accomplish these goals are recommended.
As noted above, the research you conduct throughout this course on this country will provide the basis of your Global Business Plan Project. Step Four. Teams will submit their high-level comparison and final country choice to their instructor for approval. In addition to the comparison, teams should submit a one to two paragraph justification ...
The template provides a comprehensive framework for businesses to establish effective international business relationships, utilize digital platforms, and recruit qualified international talent. It is a powerful tool that can help businesses develop and grow their international presence. 1. Define clear examples of your focus areas.
The first stage in developing an international business plan is to undertake a preliminary country analysis. Presented below are four separate sections to be completed for collection and analysis of market data and preparation of the plan: (1) Analysis: Cultural Environment; (2) Analysis: Economic; (3) Analysis: Market and Competitors; and (4 ...
The global business plan serves as a strategic guide that the organization relies on to make decisions regarding key business functions as it enters an international market. ... Global Project ...
• The purpose of an international business plan is to prepare your business for entering or expanding in the international market place. • No Business Plan Survives First Contact With A Customer - Steve Blank The 5.2 billion dollar mistake.
A global business strategy plan outlines the strategies, objectives and tactics that an organization or company plans to implement to achieve its global business goals. It is designed to provide a roadmap for the company's direction and serves to align the company's employees and stakeholders with the vision of the business. ... An example of a ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
an organization. A global business plan is a written document prepared by the entre-preneur that describes all the relevant external and internal elements in going global. By describing all the relevant external and internal elements involved in starting and managing a global organization, the business plan integrates the functional plans (such
Global Business Plan Project. Overview. Every organization conducts research to plan and implement a business idea. This project is designed to provide the foundation for an international business plan. These activities offer flexibility for many settings related to global business enterprises. The framework may be used for planning global ...
Download product. Price. 30,00 €. 30% Discount for the purchase of 2 or more products. The INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN is a practical guide and template for international market development used by companies, executives, consultants and students that require a practical tool for planning international activities.
International project planning is a complicated process. GBS is here to guide you through the due diligence considerations and help you explore the appropriate business frameworks and solutions. In consultation with other Stanford central offices, GBS serves as an advisor on international project matters and can be consulted in the project ...
ully better) opportunity comes along. A typical opportunity analysis plan has four sections: (1) a description of the idea and its competition, (2) an assessment of the domestic and international market for the idea, (3) an assessment of the entrepreneur and the team, and (4) a discussion of the steps needed to make the idea th.
Identify political factors affecting the business activities in a foreign country. Analyze trade barriers that may affect international business activities. Select an organization type that would be most appropriate for an international business setting. Outline a business plan for a global entrepreneurial enterprise.
Collaborative project management software—There are technology platforms that allow project team members to create and maintain the project management plan, to monitor the execution of the deliverables, to share the project logs, and to obtain approval from key stakeholders on documentation, business cases, and closing reports. In global ...
Global Business Plan Project The final result of your global plan must be in the format of a written report saved in pdf format with supplementary tables, graphs, charts, and visuals. You will choose a foreign country and product or service. The product or service must not be present or developed in a chosen foreign country. Then do additional research following the steps and detailed ...
HANOI -- The Japan Bank for International Cooperation and private lenders will extend roughly $832 million in syndicated loans to a gas development project in Vietnam, the state-backed lender ...
KUALA LUMPUR: Malaysian state energy firm Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS) on Monday said it would add three energy-efficient liquefied natural gas (LNG) vessels to its North American operations.
A right-wing leader said the U.S. is in the midst of 'a second American Revolution' that would see Trump win the presidency and implement troubling policy proposals known as Project 2025 ...
MBA 541 - Global Business Plan Project Resource Guide. This project template is designed to provide the foundation for an international business plan. Overview; ... Each section in this guide contains a research component or goal that will help you build your Global Business Plan for MBA 541. Resources to accomplish these goals are recommended.
The source for The Daily Show fans, with episodes hosted by Jon Stewart, Ronny Chieng, Jordan Klepper, Dulcé Sloan and more, plus interviews, highlights and The Weekly Show podcast.
A fire at Anglo American Plc's biggest metallurgical coal project in Australia halted production, with the miner saying it may take months for it to be extinguished. Anglo, which is seeking to ...