Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an expository essay

How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples
Published on July 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
“Expository” means “intended to explain or describe something.” An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a particular topic, process, or set of ideas. It doesn’t set out to prove a point, just to give a balanced view of its subject matter.
Expository essays are usually short assignments intended to test your composition skills or your understanding of a subject. They tend to involve less research and original arguments than argumentative essays .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should you write an expository essay, how to approach an expository essay, introducing your essay, writing the body paragraphs, concluding your essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about expository essays.
In school and university, you might have to write expository essays as in-class exercises, exam questions, or coursework assignments.
Sometimes it won’t be directly stated that the assignment is an expository essay, but there are certain keywords that imply expository writing is required. Consider the prompts below.
The word “explain” here is the clue: An essay responding to this prompt should provide an explanation of this historical process—not necessarily an original argument about it.
Sometimes you’ll be asked to define a particular term or concept. This means more than just copying down the dictionary definition; you’ll be expected to explore different ideas surrounding the term, as this prompt emphasizes.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An expository essay should take an objective approach: It isn’t about your personal opinions or experiences. Instead, your goal is to provide an informative and balanced explanation of your topic. Avoid using the first or second person (“I” or “you”).
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It’s worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline .
A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Like all essays, an expository essay begins with an introduction . This serves to hook the reader’s interest, briefly introduce your topic, and provide a thesis statement summarizing what you’re going to say about it.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
The body of your essay is where you cover your topic in depth. It often consists of three paragraphs, but may be more for a longer essay. This is where you present the details of the process, idea or topic you’re explaining.
It’s important to make sure each paragraph covers its own clearly defined topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Different topics (all related to the overall subject matter of the essay) should be presented in a logical order, with clear transitions between paragraphs.
Hover over different parts of the example paragraph below to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The conclusion of an expository essay serves to summarize the topic under discussion. It should not present any new information or evidence, but should instead focus on reinforcing the points made so far. Essentially, your conclusion is there to round off the essay in an engaging way.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a conclusion works.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Expository Essay | Structure, Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/expository-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, what is your plagiarism score.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Expository Writing: Definition and Examples

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is expository writing, what is an expository paragraph, expository writing examples, how prowritingaid can help you with expository composition.
One of the most common types of writing is expository writing. Whether you’re a student taking an English class or a professional trying to communicate to others in your field, you’ll need to use expository writing in your day-to-day work.
So, what exactly does this term mean?
The short answer is that expository writing refers to any writing designed primarily to explain or instruct.
Read on to learn the definition of expository writing as well as some examples of what this type of writing can look like.
Before we look at examples of expository writing, let’s start with a quick definition of what this term actually means.
Expository Writing Definition
The term expository writing refers to any writing that’s designed to explain something. We use the word expository to describe any passage of writing that’s supposed to present information and help you understand it in an objective way.
Some common examples of expository writing include academic essays, textbooks, instructional guides, and news reports. Good expository writing should be factual, objective, and clear.

To better understand what this term means, think about the difference between a scientific article, a short story, and an advertisement.
The scientific article is considered expository writing because its primary purpose is to explain a particular topic in more detail. It presents data, analyzes what that data means, and focuses on the facts.
On the other hand, the short story isn’t considered expository writing, because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s probably trying to entertain you or to take you on a journey. Short stories are narrative writing.
Similarly, an advertisement isn’t expository writing because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s trying to persuade you to buy what it’s selling. Advertisements are persuasive writing.
Here’s a quick rundown of what expository essays should and shouldn’t do.
An expository essay should:
Teach the reader about a particular topic
Focus on the facts
Follow a clearly organized structure
Present information and details from credible sources
An expository essay should not:
Try to change the reader’s mind about something
Present the author’s personal opinions
Include made-up narratives or stories
Follow experimental or nonlinear structures

An expository paragraph is exactly what it sounds like—a paragraph of expository writing.
A well-written expository paragraph should follow a specific format to make it as clear and easy to read as possible. Most expository paragraphs do the following things:
Start with a topic sentence, which explains what the paragraph will be about
Then, include 3 – 5 body sentences that provide supporting details for the topic sentence
Finally, wrap things up with a closing sentence that summarizes what the paragraph has said
Writing an expository paragraph is a great way to practice expository writing. That’s because the paragraph follows the same structure as a more complex expository essay, just on a smaller scale.
Most expository essays should follow this format:
Start with an introductory paragraph that includes the thesis statement, which tells the reader the core statement of the essay
Then, include 3 – 5 body paragraphs that provide factual evidence to support the thesis statement
Finally, wrap things up with a concluding paragraph that summarizes what the body paragraphs and thesis statement said
You can see the similarities between the two formats. If you can write a fantastic expository paragraph, you’ll be well-prepared to move on to writing a full expository essay.
Example of Expository Paragraph
Here’s an example of an expository paragraph that follows the structure described above.
The leading cause of death in the United States is heart disease, which can be fatal if it leads to heart attack or cardiac arrest. Heart attacks occur when a blockage in the coronary artery prevents oxygenated blood from reaching the heart. Cardiac arrests occur when the heart stops pumping entirely, which prevents the patient from breathing normally. Both of these problems can be deadly, even in seemingly healthy people who don’t have noticeable risk factors. As a result, heart disease is an important problem that many doctors and scientists are researching.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
There are many ways you can present information in an expository essay. Here are four of the most popular ways, along with examples of each one.
Problem and Solution Essay
A problem and solution essay presents the reader with a problem and then considers possible solutions to that problem.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a problem and solution essay:
Among the many proposed solutions to rising carbon emissions, one promising possibility is carbon trapping. Scientists are figuring out how to pull carbon emissions out of the atmosphere and trap it in less harmful forms, such as by injecting carbon dioxide underground so it will turn to stone.
Compare and Contrast Essay
This type of essay takes two subjects and compares and contrasts them. It focuses on highlighting the differences and similarities between those two things.
Here’s an example passage of this type of expository writing:
Though country music and R&B music have very different sounds, they also share many similarities. For one thing, both types of music embody a specific cultural identity. For another, both genres trace their roots back to the 1920s, when the Victor Talking Machine Company signed singers from the American South.
Classification Essay
In a classification essay, you describe the categories within a certain group of things.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a classification essay:
There are three ways in which artificial intelligence might become stronger than humans in the future: high speed, high collective intelligence, and high quality. A speed AI would be able to perform calculations and experience the world much faster than humans. A collective intelligence, like a hive mind, would be able to break down a complex task into several parts and pursue them simultaneously. Finally, a quality AI would simply be able to solve more complex problems than humans could.
Process Essay
In a process essay, you give the reader the steps for completing a specific process. This is similar to a how-to guide or an instruction manual.
Here’s an example passage you might find in this type of expository writing:
Caramelize the chopped onions in a frying pan. When the onions have caramelized, mix in the bell peppers, mushrooms, and tomatoes and stir for 4 – 6 minutes or until all the ingredients have softened. If you want to add meat, you can add ground beef and cook for another 4 – 6 minutes. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Good expository writing should be easy to read. After all, the purpose of exposition is to explain things to your readers, and you won’t be able to accomplish that if they have trouble understanding your writing.
That’s why ProWritingAid can help you write an expository essay. The grammar checker can help you ensure your sentences flow well, you’re not missing any necessary punctuation, and all your words are precise and clear.
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Expository Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an expository essay?
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
Please note : This genre is commonly assigned as a tool for classroom evaluation and is often found in various exam formats.
The structure of the expository essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the exposition of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. What is more, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
Often times, students are required to write expository essays with little or no preparation; therefore, such essays do not typically allow for a great deal of statistical or factual evidence.
- A bit of creativity!
Though creativity and artfulness are not always associated with essay writing, it is an art form nonetheless. Try not to get stuck on the formulaic nature of expository writing at the expense of writing something interesting. Remember, though you may not be crafting the next great novel, you are attempting to leave a lasting impression on the people evaluating your essay.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students will inevitably begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize and come to a conclusion concerning the information presented in the body of the essay.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of the Great Depression and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the exposition in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the Depression. Therefore, the expository essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph Essay
A common method for writing an expository essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of:
- an introductory paragraph
- three evidentiary body paragraphs
- a conclusion
Enter the characters you see below
Sorry, we just need to make sure you're not a robot. For best results, please make sure your browser is accepting cookies.
Type the characters you see in this image:

What Is Expository Writing?
How to Write an Expository Essay
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Expository writing is used to convey factual information (as opposed to creative writing, such as fiction). It is the language of learning and understanding the world around us. If you've ever read an encyclopedia entry, a how-to article on a website, or a chapter in a textbook, then you've encountered examples of expository writing.
Key Takeaways: Expository Writing
- Just the facts, M'am: Expository writing is informational, not creative writing.
- Anytime you write to describe or explain, you use expository writing.
- Use a logical flow when planning an expository essay, report, or article: introduction, body text, and conclusion.
- It's often easier to write the body of your article first, before composing the introduction or conclusion.
Expository writing is everywhere in everyday life, not just academic settings, as it's present anytime there's information to be conveyed. It can take form in an academic paper, an article for a newspaper, a report for a business, or even book-length nonfiction. It explains, informs, and describes.
Types of Expository Writing
In composition studies , expository writing (also called exposition ) is one of the four traditional modes of discourse . It may include elements of narration , description , and argumentation . Unlike creative or persuasive writing , which can appeal to emotions and use anecdotes, expository writing's primary purpose is to deliver information about an issue, subject, method, or idea using facts.
Exposition may take one of several forms:
- Descriptive/definition: In this style of writing, topics are defined by characteristics, traits, and examples. An encyclopedia entry is a kind of descriptive essay.
- Process/sequential: This essay outlines a series of steps needed in order to complete a task or produce something. A recipe at the end of an article in a food magazine is one example.
- Comparative/contrast: This kind of exposition is used to demonstrate how two or more subjects are the same and different. An article that explains the difference between owning and renting a home and the benefits and drawbacks of each is one such an example.
- Cause/effect: This kind of essay describes how one step leads to a result. An example is a personal blog chronicling a workout regimen and documenting the results over time.
- Problem/solution: This type of essay presents a problem and possible solutions, backed by data and facts, not just opinion.
- Classification: A classification essay breaks down a broad topic into categories or groupings.
Tips for Expository Writing
As you write, keep in mind some of these tips for creating an effective expository essay:
Start where you know the information best. You don't have to write your introduction first. In fact, it might be easier to wait until the end for that. If you don't like the look of a blank page, move over the slugs from your outline for the main body paragraphs and write the topic sentences for each. Then start putting in your information according to each paragraph's topic.
Be clear and concise. Readers have a limited attention span. Make your case succinctly in language that the average reader can understand.
Stick to the facts. Although an exposition can be persuasive, it should not be based on opinion only. Support your case with facts, data, and reputable sources that can be documented and verified.
Consider voice and tone. How you address the reader depends on the kind of essay you're writing. An essay written in the first person is fine for a personal travel essay but is inappropriate if you're a business reporter describing a patent lawsuit. Think about your audience before you begin writing.
Planning Your Essay
- Brainstorm: Jot down ideas on a blank piece of paper. Connect them with arrows and lines, or just make lists. Rigor doesn't matter at this stage. Bad ideas don't matter at this stage. Just write down ideas, and the engine in your head will lead you to a good one. When you've got that idea, then repeat the brainstorming exercise with ideas that you want to pursue on that topic and information you could put in. From this list, you'll start to see a path emerge for your research or narrative to follow.
- Compose your thesis: When your ideas coalesce into a sentence in which you can summarize the topic you're writing about, you're ready to compose your thesis sentence. Write down in one sentence the main idea that you'll explore in your paper.
- Examine your thesis: Is it clear? Does it contain opinion? If so, revise that out. For this type of essay, you stick to the facts and evidence. This isn't an editorial. Is the thesis' scope manageable? You don't want your topic too narrow or too broad to be covered in the amount of space you have for your paper. If it's not a manageable topic, refine it. Don't be dismayed if you have to come back and tweak it if your research finds that your initial idea was off-kilter. It's all just part of the process of focusing the material.
- Outline: It may seem inconsequential, but making even a quick outline can save you time by organizing your areas of pursuit and narrowing them down. When you see your topics in an organized list, you may be able to discard off-topic threads before you research them—or as you're researching them and you find they just don't work.
- Research: Find your data and sources to back up the areas you want to pursue to support your thesis statement. Look for sources written by experts, including organizations, and watch for bias. Possible sources include statistics, definitions, charts and graphs, and expert quotes and anecdotes. Compile descriptive details and comparisons to make your topic clear to your reader, when applicable.
What Is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay has three basic parts: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Each is crucial to writing a clear article or effective argument.
The introduction: The first paragraph is where you'll lay the foundation for your essay and give the reader an overview of your thesis. Use your opening sentence to get the reader's attention, and then follow up with a few sentences that give your reader some context for the information you're about to cover.
The body: At a minimum, include three to five paragraphs in the body of your expository essay. The body could be considerably longer, depending on your topic and audience. Each paragraph begins with a topic sentence where you state your case or objective. Each topic sentence supports your overall thesis statement. Then, each paragraph includes several sentences that expand on the information and/or support the topic sentence. Finally, a concluding sentence offers a transition to the following paragraph in the essay.
The conclusion: The final section of your expository essay should give the reader a concise overview of your thesis. The intent is not merely to summarize your argument but to use it as a means of proposing further action, offering a solution, or posing new questions to explore. Don't cover new material related to your thesis, though. This is where you wrap it all up.
Expository Examples
An expository article or report about a lake, for example, could discuss its ecosystem: the plants and animals that depend on it along with its climate. It could describe physical details about its size, depth, amount of rainfall each year, and the number of tourists it receives annually. Information on when it was formed, its best fishing spots, or its water quality could be included, depending on the audience for the piece.
An expository piece could be in third person or second person. Second-person examples could include, for example, how to test lake water for pollutants or how to kill invasive species. Expository writing is useful and informative.
In contrast, someone writing a creative nonfiction article about a lake might relate the place to a defining moment in his or her life, penning the piece in first person. It could be filled with emotion, opinion, sensory details, and even include dialogue and flashbacks. It's a much more evocative, personal type of writing than an expository piece, even though they're both nonfiction styles.
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Good Descriptive Paragraph
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- How to Structure an Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- Understanding What an Expository Essay Is
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- The Five Steps of Writing an Essay
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
Essay Papers Writing Online
Get the ultimate guide on writing an expository essay – step-by-step tips and examples.

Are you grappling with the challenge of composing a compelling expository essay? Look no further, as this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the essential tools and techniques to effectively convey your ideas and captivate your readers. By employing powerful writing strategies and supplementing your work with concrete examples and real-life anecdotes, you will unlock the true potential of your explanatory essay.
Begin your writing journey by harnessing the power of clarity and conciseness. Structuring your essay with a logical flow will allow your readers to effortlessly follow your thought process and grasp your central ideas. Employing strong transitions between paragraphs and employing cohesive language will ensure a seamless reading experience. Additionally, honing your analytical skills and supporting your claims with factual evidence will lend credibility to your work while fostering a deep understanding of the topic.
Furthermore, incorporating vivid examples and engaging anecdotes will breathe life into your expository essay, making your content relatable and memorable. By utilizing descriptive language and the art of storytelling, you will create a lasting impact in the minds of your readers. Whether it is a personal experience, a historical event, or a scientific study, weaving in these narratives will amplify the effectiveness and persuasiveness of your essay, leaving a lasting imprint on your audience.
Mastering the Art of Crafting a Compelling Expository Composition: Pointers and Illustrations

An in-depth exploration of the fundamentals behind composing an impactful expository essay can serve as an invaluable tool in your academic and professional endeavors. By harnessing the power of language, analysis, and evidence, you can construct a persuasive and enlightening piece of writing that will captivate your readers. Let us embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of crafting an exquisite expository essay.
1. Avoid monotony: Deliver your ideas in a fresh, stimulating manner to enthrall your audience. Strive to maintain a captivating narrative flow by skillfully employing synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and metaphors. This will invigorate your writing and make it truly memorable.
2. Be concise yet comprehensive: Accomplish the delicate balance of being succinct without sacrificing the clarity and depth of your exposition. Remember to select your words wisely, presenting each idea concisely while ensuring it is thorough and complete.
3. Provide evidence: Back up your statements with solid evidence and well-researched examples. Citing credible sources, such as reputable studies, expert opinions, and statistical data, will add credibility and weight to your arguments, making them more persuasive and powerful.
4. Organize your thoughts: Structure your essay in a logical and coherent manner, ensuring that each idea flows seamlessly into the next. Utilize transitional words and phrases to guide your readers through the different sections of your essay, enabling them to follow your line of reasoning effortlessly.
5. Cater to your audience: Tailor your language, tone, and examples to suit the preferences and background of your intended audience. Use relatable and engaging references to convey your message effectively and establish a connection with your readers.
6. Emphasize clarity: Clarity is key when it comes to expository writing. Avoid excessive jargon, convoluted sentences, and ambiguous expressions. Instead, strive for lucidity and precision, ensuring that your readers can easily grasp the main points of your essay.
7. Show don’t tell: Instead of merely stating information, aim to vividly illustrate your ideas through anecdotes, case studies, and real-life examples. This will make your essay more relatable and memorable, enabling your readers to form a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
8. Revise and refine: Do not underestimate the importance of the revision process. Review your essay meticulously, focusing on grammar, clarity, and coherence. Eliminate redundancies, enhance sentence structure, and refine your vocabulary to elevate the quality and impact of your writing.
By equipping yourself with these essential guidelines and examples, you are well-prepared to embark on your expository essay writing journey. Remember, mastering the art of crafting a compelling expository composition requires practice and perseverance. Let your ideas flow, embrace creativity, and allow your words to inspire, educate, and leave an indelible mark in the minds of your readers.
The Significance of an Expository Article
When it pertains to written compositions, the significance of an expository article cannot be underestimated. This type of writing piece serves a crucial purpose in communicating information, presenting facts, and explaining ideas in a clear and concise manner. By utilizing objective analysis, evidence-based reasoning, and logical arguments, an expository essay provides readers with a deeper understanding of a subject matter.
Unlike other forms of writing, an expository essay focuses on informing rather than persuading or entertaining. It acts as a reliable source of knowledge, offering readers an opportunity to broaden their horizons and gain new insights. Whether used in academic, professional, or personal settings, the expository essay serves as a valuable tool for conveying information accurately and objectively.
Furthermore, an expository essay aids in building critical thinking and analytical skills. Through the process of researching and organizing information, the writer develops the ability to evaluate sources, discern facts from opinions, and present arguments based on logical reasoning. This type of writing encourages readers to question assumptions, analyze evidence, and draw their own conclusions.
Moreover, mastering the art of composing an expository essay equips individuals with essential communication skills that are applicable in various aspects of life. By learning how to present complex ideas in a clear and coherent manner, one becomes an effective communicator across different fields and disciplines. Whether it be writing research papers, reports, or even delivering presentations, the skills acquired from writing an expository essay are invaluable in expressing ideas persuasively and engaging an audience.
In conclusion, the importance of an expository essay lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive and objective understanding of a subject matter. By offering factual information, logical arguments, and clear explanations, this type of writing contributes to the development of critical thinking skills and effective communication. Whether in academic, professional, or personal settings, the expository essay plays a vital role in disseminating knowledge and fostering intellectual growth.
Understanding the Purpose and Audience
In order to create a compelling and impactful expository essay, it is important to have a clear understanding of the purpose and audience of your writing.
The purpose of an expository essay is to explain or inform the reader about a specific topic or idea. Unlike other types of essays, the main goal is to provide a balanced analysis and present factual information in a clear and concise manner. The purpose may vary depending on the specific assignment or context, but it is important to always keep the purpose in mind when writing an expository essay.
Equally important is knowing your audience. Understanding who will be reading your essay will help you tailor your writing style, tone, and level of complexity to effectively communicate your ideas. Consider the background knowledge, interests, and beliefs of your audience to ensure that your essay is accessible and engaging.
- Start by identifying the demographic characteristics of your audience, such as age, education level, and background.
- Consider their prior knowledge on the topic. Are they familiar with the subject matter, or do you need to provide additional context?
- Think about their potential biases or preconceived notions. Are there any potential challenges or objections you need to address?
By understanding the purpose and audience of your expository essay, you can craft a well-written and relevant piece that effectively communicates your ideas and engages your readers.
Choosing the Right Topic and Gathering Information
One of the crucial steps in writing an outstanding expository essay is selecting a compelling topic and gathering relevant information. The topic should be interesting, relevant, and align with the purpose of your essay. It’s important to choose a topic that you are passionate about and have a good understanding of, as it will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and easier.
Start by brainstorming different ideas and concepts that you find intriguing. Consider your personal experiences, hobbies, or areas of expertise that you would like to explore further. You can also look for inspiration from current events, popular trends, or societal issues that grab your attention. Once you have a list of potential topics, narrow it down to the one that has enough depth and scope for exploration.
Once you have chosen a topic, it’s time to gather information to support your thesis statement and provide evidence for your claims. Start by conducting thorough research using various sources such as books, scholarly articles, reputable websites, and interviews with experts in the field. Take notes and keep track of the sources you use for referencing purposes.
| Tips for Gathering Information: |
|---|
| 1. Use reliable and credible sources to ensure the accuracy of the information. |
| 2. Take detailed notes and organize them based on different subtopics or arguments. |
| 3. Look for different perspectives and opinions on the topic to present a well-rounded view. |
| 4. Don’t rely solely on internet sources, but also explore books and academic journals. |
| 5. Use quotation marks or proper citation methods when including direct quotes or paraphrasing information from sources. |
| 6. Keep track of all the sources you use to avoid plagiarism and provide proper references in your essay. |
By choosing the right topic and gathering relevant information, you lay the foundation for a well-researched and compelling expository essay. Take the time to explore different ideas, conduct thorough research, and organize your findings effectively. Remember, a well-chosen topic and solid information will make your essay engaging and informative for your readers.
Structuring Your Expository Essay

When it comes to composing an expository essay, the way you structure your piece is crucial. Organizing your thoughts and ideas in a clear and logical manner will not only make your writing more coherent and easy to follow, but it will also help you effectively convey your message to the readers.
One effective way to structure your expository essay is to use the traditional five-paragraph format. This format consists of an introduction paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall development of your essay.
The introduction paragraph is where you grab the attention of your readers and provide them with a brief overview of what your essay will be about. It should include a strong thesis statement that clearly states your main argument or point of view.
The body paragraphs are where you present your evidence, provide supporting details, and analyze your topic. Each body paragraph should focus on one main idea or aspect of your topic. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main point, and then provide examples, facts, or explanations to support your argument.
In the conclusion paragraph, you should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. Avoid introducing new information or arguments in this section. Instead, focus on leaving a lasting impression on your readers and reinforcing the main ideas discussed throughout your essay.
Remember to use appropriate transition words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas. Examples of transitional phrases include “firstly,” “in addition, “finally,” and “on the other hand,” among others.
By following a well-structured approach, you can effectively organize your expository essay and make it engaging and informative for your readers. Take the time to plan your essay, identify your main points, and arrange them in a logical order. With a clear structure, your expository essay will be a powerful piece of writing that effectively conveys your ideas.
Enhancing Clarity and Coherence
Creating a clear and coherent expository essay requires skillful use of language and organization. By carefully selecting words and arranging ideas logically, you can ensure that your essay is easy to understand and follow.
Word Choice: One of the most effective ways to enhance clarity is through thoughtful word choice. Consider using precise and specific language to convey your ideas. Instead of using general terms, opt for more descriptive words that accurately depict the information you are presenting.
Logical Organization: Coherence in your essay can be achieved through proper organization. Present your ideas in a logical progression, ensuring that each paragraph flows smoothly into the next. Use transitional words and phrases to connect your thoughts and guide the reader through your essay.
Consistent Structure: To enhance clarity and coherence, maintain a consistent structure throughout your essay. Use a clear introduction to outline your main points and a strong conclusion to summarize your findings. Each body paragraph should focus on a single topic and provide sufficient evidence and examples to support your claims.
Effective Transitions: Transitions are essential in ensuring a cohesive flow between ideas and paragraphs. Use transitional words and phrases such as “however,” “in addition,” and “furthermore” to link your ideas and create a smooth transition between different sections of your essay.
Eliminating Ambiguity: To enhance clarity, it is crucial to eliminate any ambiguity or confusion from your writing. Be precise in your language and avoid using vague terms or jargon. Make sure your ideas are clearly articulated and leave no room for misinterpretation.
Proofreading: Finally, closely edit and proofread your essay for clarity and coherence. Look for any unclear sentences or confusing phrases and revise them for greater clarity. Ensure that your ideas are presented in a logical and coherent manner, leaving no room for confusion.
By enhancing clarity and coherence in your expository essay, you can effectively communicate your ideas and engage your readers. Thoughtful word choice, logical organization, consistent structure, effective transitions, and careful proofreading all play important roles in creating a clear and coherent essay that will leave a lasting impact.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

The Admissions Strategist
Expository writing: how to write an incredible expository essay.
Expository essays are frequently assigned in English classes and are evaluated in various standardized exams.
But what exactly is an expository essay, and how do you write a good one?
In this article, we’ll tell you everything you need to know to pen a high-scoring expository paper.
What Is an Expository Essay?
The word expository means “intended to explain or describe something.”
An expository essay requires you to investigate an idea, gather supporting evidence, and present your point of view on a topic.
- You may be wondering how this differs from a persuasive essay.
- While both essay types require you to provide evidence to support a claim, persuasive essays are more argumentative.
A persuasive essay includes a counterargument, which addresses and rebuts an opposing viewpoint.
Expository essays, on the other hand, focus on clearly explaining and supporting your point of view.
Parts of an Expository Essay
A strong expository essay should consist of:
- An introductory paragraph with a clear thesis
- Evidence that supports the thesis (typically in three body paragraphs)
- A conclusion
Below, we’ll look at how to construct the expository essay piece by piece.
For clarity, we’ll focus on a somewhat formulaic process for expository writing.
Once you’ve mastered these basics, you can take risks and sprinkle more creativity throughout your essays.
Introduction
The introduction frames the topic of your essay.
It also provides readers with any necessary background information or context.
A simple format for your introduction is:
- Grabber/Hook – A compelling sentence or two that draws readers into your essay.
- Background Information (as needed) – Any basic information the reader needs to know about the topic to understand your essay.
- Thesis Statement – This is the most important sentence of your entire essay. See below for more information.
Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is the roadmap for your entire essay, so it must be clear and concise. It should state your point of view on the topic.
- The thesis may also briefly mention the supporting evidence you’ll expand on in the body of the essay.
For instance, a thesis statement might say:
Students should read more literature because it improves vocabulary, reading comprehension, and empathy.
The writer’s viewpoint is immediately clear: Students should read more literature.
The writer also indicates that her supporting evidence will mention several benefits of reading literature: improved vocabulary, better reading comprehension, and increased empathy.
- Most likely, each of these points will form one of the writer’s body paragraphs.
If your teacher (or a standardized test) assigns you a topic, here’s another way to think of a thesis statement: The thesis is your answer to the question being asked.
- Let’s say you receive a prompt that says, “Your community is thinking of starting a program encouraging people to limit car usage. Explain how limiting car usage would benefit your community.”
This prompt is essentially asking, “How would limiting car usage benefit your community ?”
- Thus, your thesis could answer the question by saying something like, “Limiting car usage would benefit the community because it would decrease traffic, improve public health, and reduce air pollution.”
This approach ensures that you’re on topic and directly addressing the prompt.
Supporting Evidence
Once you’ve clearly stated your point of view, it’s time to support it. To do this, you’ll need evidence . Sometimes, this will mean doing your own research.
On other occasions, especially exams, you’ll be provided with relevant resources.
These may include newspaper articles, primary sources, photos, or even audio recordings.
- Your job is to sort through these resources and find evidence that supports your thesis. It’s important to note that if you can’t find evidence supporting your thesis, you’ll need to change it.
Strong evidence may include research findings, quotes from experts, and statistics. Make sure that your evidence is from credible sources and clearly supports your thesis statement.
Organizing Evidence
After finding your supporting evidence, you’ll organize it into body paragraphs, typically three of them.
Each body paragraph should focus on one general idea.
In addition, each of these general ideas should be logically connected to your thesis statement.
- Your body paragraphs should start with a topic sentence that introduces the idea that the body paragraph will elaborate upon.
Remember our sample thesis about students reading more literature?
- The topic sentence of the first body paragraph could read, “To start with, reading literature is essential because it expands students’ vocabulary.”
After the topic sentence, the paragraph should introduce 2-3 pieces of evidence supporting this idea.
If a piece of evidence doesn’t clearly relate to the body paragraph’s topic sentence, it needs to be moved or deleted.
Analyzing Evidence
When you introduce a piece of evidence, follow it up with a sentence analyzing the evidence in your own words.
- Explain the connection between the evidence and your thesis statement.
- How does it support your point of view?
- How do you interpret this evidence?
Remember that essays don’t only reflect your writing skills; they also reflect your critical thinking skills.
Instead of merely quoting evidence, you must also explain your thought process.
As a result, an effective body paragraph can follow this formula:
- Topic sentence
- Evidence #1
- Analysis of Evidence #1
- Evidence #2
- Analysis of Evidence #2
- Evidence #3 (Optional)
- Analysis of Evidence #3 (Optional)
- Concluding/transitional sentence
The final sentence of the body paragraph should remind readers of the paragraph’s main point and connect it to the next paragraph.
Transitions are important because they help readers follow your train of thought without confusion.
They smoothly guide readers through your paper.
Transition words and phrases include:
- For example
- For instance
- To illustrate
- Specifically
- On the other hand
- Consequently
- As a result
- Additionally
- Furthermore
Get personalized advice!
Like stories, essays have a beginning, middle, and end.
- The introduction is your beginning, the body paragraphs form the middle, and the conclusion brings the paper to an end.
The conclusion synthesizes the information included in your essay.
As the name suggests, it also draws a conclusion from the information presented.
- Instead of simply restating the thesis, you should revisit the thesis in light of the supporting evidence you’ve provided. Do not introduce any new information in the conclusion.
Remember that the conclusion is your last chance to make an impression on the reader. It should be logical and convincing.
Try to end with a strong and/or memorable final sentence.
In total, an expository essay includes these pieces:
– Introduction
- Hook/grabber
- Background information
– Body paragraphs (usually three)
– conclusion.
- Synthesis of evidence
- Explanation of what this evidence shows (connected to thesis)
- Strong final sentence
If you include each of these pieces, you’ll have a clear, logical, and effective expository essay.
Once you become comfortable following this formula, you may wish to vary it or infuse it with your own style.
Just make sure that all the essential pieces are present in your essay.

The Expository Essay Writing Process
Before you can effectively assemble an expository essay, you’ll need to gather information and plan your approach.
Typically, the writing process includes:
- Carefully reading the prompt (if applicable)
- Brainstorming
- Gathering evidence
- Revising/editing
Let’s take a closer look at each step in the process.
1. Reading the Prompt
If you’re provided with a prompt, understanding it is an essential first step.
Misinterpreting the prompt will result in a low score, even if your essay is well-written.
- Read the prompt at least 2-3 times, underline key words and phrases. If the prompt is complicated, you may want to rewrite it in your own words.
Does the prompt have multiple parts? If so, make sure you understand each part and that your essay clearly addresses all of them.
2. Brainstorming
Once you’ve read the prompt, begin brainstorming how you will approach it.
- If you’ve been provided with relevant resources, this may also include a first read-through or skimming of these texts.
What position will you take? How are you planning to support your viewpoint? Jot down any idea that pops into your head.
- It doesn’t matter if the idea is good—right now, you’re just trying to find inspiration. You’ll change, add, or remove information later.
If you haven’t been provided with a prompt, you’ll need to brainstorm a topic that interests you.
It should also be a topic on which you’re at least somewhat knowledgeable.
3. Gathering Evidence
At this point, you’ll find evidence that supports your point of view.
- It helps to write at least a rough draft of your thesis statement before beginning this step.
- This way, you’ll have a clear idea of what sort of evidence you need to find.
After writing your thesis statement, find credible evidence that supports it.
- This may require you to go to the library or browse scholarly databases on the Internet.
Alternatively, you may have been provided with resources.
In that case, read through the resources carefully, underlining or circling evidence that reinforces your thesis.
4. Planning
Planning ensures that your essay is organized, focused, and cohesive.
It also allows you to catch potential mistakes before they happen.
- For instance, you might realize that some of your evidence doesn’t fit, or that one of your body paragraphs is lacking support.
You can then address these areas of weakness before writing your essay.
- At the top of your planning sheet (or a document on your computer) write your thesis statement.
- Continually reference the thesis to ensure that you’re focused and on topic.
- Next, determine the focus of each body paragraph and the 2-3 pieces of evidence that will support it.
Sometimes, students think that planning is too time-consuming.
However, a plan will save you time in the long run.
With all your quotes and evidence organized in one place, writing your essay is much faster and easier.
Once you have a completed plan, begin writing your essay.
- Remember to analyze each piece of evidence and clearly connect your points with transitions.
Use a formal, academic tone and avoid slang or overly casual language.
Vary your sentence structure, including both short and long sentences. Pay attention to spelling, grammar, and punctuation.
6. Revising
Students often skip the revising and editing step of the writing process.
This is a mistake. Slowly read through your essay at least once before submitting it.
- Look for misspelled words, incorrect verb tenses, and punctuation or grammar mistakes. Does your writing flow well? Does everything make sense?
- Are all of your points clear? Have you used the same word or phrase repetitively? (If you have, try to substitute a synonym.) Did you use transitions connecting your ideas?
Ensure that you submit the best, most polished version of your essay possible. Mistakes and unclear sentences make a poor impression.
Advice From the Experts:
From Dr. Carrie Brown, professor of English and creative writing at Sweet Briar College and novelist :
When I’m working with students on expository writing — on writing in any rhetorical mode, really — I remind them that almost inevitably they have to stumble their way through some lousy sentences before they discover what they actually want to say. (This takes us back to that famous question: How do I know what I mean until I see what I say?) Some messy writing usually precedes orderly, elegant writing, and every writer needs patience during that messy process, because that process is important: out of that process emerges clear thinking, which is the true key to clear writing. Once writers have waded around in the muck for a while, then they can step back and examine those sentences or numbered phrases or bulleted points — whatever method felt most natural to the writer by which to set down emerging thoughts — to discover which are relevant, which are simply repetitions of earlier thoughts, which are superfluous or meaningless, and in what order they ought to proceed. A trick that seems to work for students with a strong tendency toward auditory learning can actually record themselves speaking aloud, trying to address the topic, and then play back that recording, meanwhile transposing ideas — and usually improving and clarifying them — as they go.
From Adam Cole, author and writing expert:
Know your audience – Whatever you are writing, you will get the best results if you are thinking about who is reading it, why they are reading it, and what you should do to make sure the interaction between you and the reader is optimal. While the audience for an expository piece may be obvious, writing directly to that audience is not so obvious. It affords you an opportunity to think clearly and write clearly without having to worry about your identity, ego or success. If you are in school, the audience for expository writing is your professor, and you should be fulfilling the boxes in their rubric to the letter. If they haven’t given you a rubric, ask for one. If they won’t, find one or create one based on conversations with them, their former students, or another professor.
From Tangela Walker-Craft – Simply Necessary, Inc. , Family and Parenting Blogger:
Write in complete sentences. Write in paragraph form. Each paragraph should contain 3 to 5 sentences for short essay questions, and 5 to 10 sentences for long essay questions. Vary sentence length and structure; try not to begin sentences with the same word or words. Use facts and information taken from reading passages to answer questions; refer back to the reading passage to stay focused. Underline important information in reading passages to make it easier to go back to them when answering questions. Proofread. Proofreading sentences backwards makes finding spelling mistakes and punctuation errors easier because it forces test-takers to focus on individual words instead of automatically “seeing” what he or she intended to write.
From Peter Donahue, a writing expert and teacher:
1. Write for clarity, not formality. As a teacher, I see a lot of expository writing where the writer is more concerned with following the conventions of academic jargon than she is with expressing ideas. A good example is the use of “utilize” instead of “use,” because it “sounds more formal,” or the avoidance of the pronoun “I” because it “sounds too informal.” So, rather than trying to appear formal, expository writing should aim to be clear. George Orwell’s 1946 essay, “Politics and the English Language,” says more on this topic, and is a worthwhile read. 2. Think synthetically, write analytically. Synthetic thinking starts with small details, or an open-ended question. As thoughts continue to develop, the main idea is clarified (or discovered) at the end the process. Contrariwise, Analytical thinking starts with a “given:” a major premise or generalization. It then proceeds to break down the main idea into its components and deal with each separately. Expository writing is usually presented most effectively in an analytic format — the main idea first, the support afterwards. On the other hand, literary writing, like a poem or discursive essay, is often presented synthetically. The key is knowing the difference between thought process and written format. We can think something synthetically, and then write it analytically. And in fact, this process can be the key to effective expository writing for many people. Don’t assume that because a thesis appears in the first paragraph, you have to think of it first. You could try drafting it synthetically, to clarify your thinking. Then rewrite it analytically to present it more effectively for your reader.
From Jessica Moody, curriculum expert :
Expository writing is first about structure, second about clarity, and third about content. Depending on the type of expository writing there is a specific structure expected. Even in college essays each sentence on the essay has a purpose and can be labeled as a thesis statement, topic sentence, evidence, or explanation of evidence. If the structure is not there, most of the time there is not much clarity and the content is lacking because it is confusing. This is the same for any type of expository writing. My suggestion for people becoming better at expository writing is to study the structure of the piece, the paragraph structures and the sentence structures. If you understand how to break down the structure then you can learn to replicate any style or form you want.
Final Touches: Expository Essay Writing
Writing an excellent expository essay isn’t as complicated as it seems. Simply follow the steps and include the essential pieces outlined here.
Your essay is sure to showcase both your thinking and writing skills —and earn you a high score!
Learn how we can help you with college and career guidance! Check out our YouTube channel!
Click Here to Schedule a Free Consult!

Calm your anxiety by learning every aspect of the college application process and how to excel at navigating it.

- Ethics & Honesty
- Privacy Policy
- Join Our Team
(732) 339-3835
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Expository Essays: Overview
What is exposition writing.
Exposition can be either oral or written. It is used to explain, interpret, inform, or describe. An expository writer must assume that the audience has no prior knowledge regarding the topic being discussed. So the topic must be written in a clear manner explaining how things work (you can however, leave out common knowledge –you probably are not writing for first graders). Exposition reaches beyond the obvious. Its underlying purpose in explaining, interpreting, informing, or describing is to reveal aspects of substance. Exposition does not simply provide a definition of the term “fake news”; it explores the inherent danger in using a terms that grossly oversimplifies the true nature of news. In an essay one would explore how the term “fake news” should but often does not refer to unreliable news sources, rumor mills, and blogs or social media sites that purposely spread unsourced stories to fulfill a political or personal agenda. One might also write that “fake news” is a term applied to news that is sourced but that someone simply choices to openly discredit.

As most academic terms, exposition can acquire various definitions depending on the context in which a writer is using the word. The HarperCollins Collins English Dictionary defines exposition in seven different disciplinary contexts.
- Within the Communication Arts / Journalism & Publishing discipline exposition is defined as: a systematic, usually written statement about, commentary on, or explanation of a specific subject
- The act of expounding of setting forth information or a viewpoint
- (Business / Commerce) of a large public exhibition, especially of industrial products or arts and crafts
- The act of exposing or the state of being exposed
- (Performing Arts / Theatre) the part of a play, novel, etc., in which the theme and main characters are introduced.
- (Music / Classical Music) Music the first statement of the subjects or themes of a movement in sonata form or a fugue
- (Christianity / Roman Catholic Church) RC Church the exhibiting of the consecrated Eucharistic Host or a relic for public veneration (Harper Collins Dictionary)
TYPES OF EXPOSITION
- Description – The author explains a particular topic by showing characteristics, features, and examples.
- Comparison – The author shows how two or more topics are alike.
- Contrast – The author shows how two or more topics are different.
- Cause and Effect – The author demonstrates the cause while showing the effects of the cause.
- Problem and Solution – The author explains a problem, then explores possible solutions.
- Analytical – The author evaluates a topic or argument revealing its strengths and weaknesses.
- Classification – The author sorts things into useful categories, makes sure all the categories follow a single organizing principle, and gives examples that fit into each category.
- Sequence – The author lists items or events in numerical or chronological order.
FIND A TOPIC, READ, DISCUSS, AND RESEARCH
First you must find a specific aspect of a topic that would interest you. This means you will and must read about the topic. You will have to research the topic extensively so that you can explain it—what exposition is all about. Research your topic extensively if necessary. You will probably have to spend quite a bit of time, but remember that the researching can be exciting. The general initial researching may even provide some valuable information that you want to explain. Researching is like exercising: at first it hurts, but with time you become stronger and it’s easier to flex your researching muscles. After you have decided upon a topic, you can create a thesis.
When you read, read critically and actively as was discussed in the previous chapter. Question the author’s points, consider conflicting viewpoints and support evidence. Analysis and exposition is built upon disagreement. Don’t avoid it; explore it with an open mind.
Like reading and writing, writing and talking work in unison. Teachers often observe classes that actively read and then discuss what they have read are often much stronger writers. Moreover, some students find that discussion is an important step in articulating their ideas and galvanizing their viewpoints on a topic.
An expositional paper is most easily written when you have a “tight” thesis. This means that the focus of your topic is extremely specific. When your thesis is concise, you can write at length because you know exactly what you should be writing about. But when you have a sloppy, vague thesis, you can become lost and your writing reflects this. This goes back to choosing a topic focus that deals with something specific, and not overly general. A thesis makes a claim regarding your focus and is supported by details and facts. It is written in one or two complete sentences. An example of a thesis would be: “Gardening can be a rewarding hobby because of the creativity involved, the variety of plants, and the many uses of plants.”
Create a Sketchy Outline
After you write your thesis, create a sketchy outline so that you have a game plan for your paper. Your outline should have information that you want to include for each part of your thesis. For our thesis example, we could find lots of information that could support the different parts of gardening. Notice the word could –just because we have the information doesn’t mean we must use it in the paper. This is a rough outline after all.
Start Writing
Too often we don’t begin writing because we are stuck—don’t be, just start writing. You can begin anywhere. Start writing where you feel the most comfortable. When you have your outline, as sketchy as it may be, it reminds you of ideas that you want to include in your paper. Remember though that readers are interested in what YOU have to say—they don’t want to read regurgitated quotes and opinions of others, so make sure that your point is being heard.
STRUCTURE OF AN ANALYTICAL/EXPOSITORY ESSAY
The structure of an expository piece consists of first an introduction that contains the most crucial element—the thesis—the main point you wish to convey. After the introduction is the body, in which you clarify the different aspects of the thesis in great detail. The final piece, the conclusion, restates and rephrases (using different words) the thesis and ties up any “loose ends”.
Thesis Statements
A thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any successful expository essay. A thesis statement controls the subject matter of the essay and states something significant to the reader. It is the one statement that summarizes the main point of the essay and states why the essay is important and worth reading. An essay that lacks a strong thesis will have broad scope and lack focus.
The following are qualities of a well-crafted thesis statement:
- A thesis statement should identify a specific purpose for the essay.
- A thesis statement should assert something about the essay, and it should be something with which others can reasonably disagree.
- A thesis statement should be clear and easily identifiable by a reader.
- A thesis statement generally comes toward the end of the introduction and is usually the final sentence.
- A well-focused thesis statement, key to organizing an essay, contains two elements: a clear subject and a clear perspective on the topic.
- o Vague – Ecological disasters are a major concern today.
- o Precise – Pollution of underground water supplies threatens cities on the American West Coast.
A thesis should have the following characteristics:
- *It should be simple or complex, BUT never compound.
- *It should be stated positively.
- *It should be restricted, precise, and unified.
- *It should not contain figurative language.
INTRODUCTION
The very first part of your introduction should have an attention-grabbing device (a hook) to engage your readers. Hooks can be statistics, facts, questions, or unusual details. Don’t make general statements such as “it is clear that…” because you are trying to explain something that perhaps your reader doesn’t know, so it would not be clear to them. Instead be informative. The introduction will also contain your thesis. Good topic referring to Rhetoric. One can check it at the essays writing companies and already written essays accomplished by writing service writers.
Be creative in your introduction: use an anecdote, a provocative statement, a surprising or insightful quote, or even a shocking statistic. Bring the audience up to speed on the broader aspects of the subject on which you are basing your essay.
Consider starting with a criticism. For example, in Malcolm Gladwell’s book Outliers , people view his research as a key to unlocking human potential, but that’s an overstatement. One might consider challenging the more common and popular interpretations of the book as being a “self-help” book.
Consider starting with praise. The book Outliers is the first widely read and very honest discussion of the commonly held belief that success in America is only a matter of hard work. The reader is confronted with the reality that even in America, privilege provides opportunities poverty cannot. Such an introduction establishes a viewpoint while introducing an important element of the book.
Now that you have your specific thesis, along with your sketchy outline, you must support your thesis claim by using concrete evidence and examples. You should exfoliate your thesis. Remember that expositional writing assumes that your readers have no prior knowledge regarding your topic, so you must explain things very clearly. Parallelism can be very important in your paper. It can give the readers a feeling of structure and importance. Pick a method of organization and stick with it.
In our example, we would explain in detail how much creativity is involved in gardening. We could write about the style of impressive European or Oriental gardens. Next, we would show how there are a variety of plants. We could write about plants found in different climates. Finally, we would explain the many uses of plants. We could write about floral bouquets and vegetables.
Because exposition’s purpose is to inform, you will want to establish common ground with your readers. You should write objectively, which will fulfill the purpose of explaining things.
Topic Sentence:
It may help to use a topic sentence to focus each paragraph and to keep the writer and the reader on point. This is a statement of the point you’ll make usually in the introductory paragraph.
Support should always come from the articles you found in your research, your author research, and through passages from the text. BE SPECIFIC when you refer to any text. Paraphrase with detail, and use direct quotes when necessary. This is very, very important.
Developing Paragraphs:
To develop paragraphs, consider one of the following forms of support for your point of view:
- Use examples and illustrations (exemplification)
- Cite data (facts, statistics, evidence, details, and others)
- Examine testimony or authoritative statements and published passages (what other people say such as quotes and paraphrases)
- Use an anecdote or story (narrative)
- Define terms in the paragraph. These terms should be important to the topic under discussion.
- Compare and contrast (describe and explain the characteristics of two objects or ideas to draw attention to similarities and differences)
- Evaluate causes and reasons for the occurrences of an issue or condition in the world. What do you or others believe causes anything from car accidents or racism or juvenile diabetes.
- Examine effects and consequences of a particular action or state of being
- Analyze the topic, supporting texts or common beliefs about some aspect of your topic. For examples, tackle a stereotype or a common belief about the topic.
In each paragraph, explain what you believe the support means. Many of you were already doing this in your paragraphs.
A conclusion wraps up your paper by recalling your main points, but do not use the identical words that you used in your introduction. Conclusions and introductions are like frames, they should tie your whole paper together. You should explain your main points briefly and freshly. Don’t be sloppy–this is the last impression you are making.
Some combination of the following is always helpful:
- Refer back to your thesis.
- Tell us what you ultimately think about the topic under discussion.
- Tell us what readers can and should take from this discussion in terms of how we view the world, our families, specific populations, etc. Consider addressing these questions: What would you like us to learn from your discussion on the book? What points should we remember? What particular insights on the subject were most important?
- How can you make your reader remember this essay?
Sources Used to Create this Chapter
The majority of the content for this section has been adapted from the following OER Material:
- Let’s Get Writing by Elizabeth Browning et. al., which was published under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
- English Composition by Ann Inoshita et. al., which was published under a CC-BY 4.0 license.
- Expression and Inquiry by Sally Pierce and Melissa Lucken, which was published under a CC-BY 4.0 license.
Starting the Journey: An Intro to College Writing Copyright © by Leonard Owens III; Tim Bishop; and Scott Ortolano is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Write an Expository Essay
Last Updated: December 13, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 565,839 times.
Expository essays are often assigned in academic settings. In an expository essay, you need to consider an idea, investigate the idea, then explain the idea. Some expository essays may include an argument, while others are purely informative. [1] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source While it may seem overwhelming, writing an expository essay is easy if you take it one step at a time.
Sample Essay Conclusion

Planning Your Essay

- If you are writing an expository essay for an assignment, read the assignment guidelines. Ask your instructor if anything seems unclear.

- If you are writing your essay for a class assignment, consider what your instructor will expect you to include in your essay.

- Try listing. List all your ideas for your expository essay. Then look over the list you have made and group similar ideas together. Expand those lists by adding more ideas or by using another prewriting activity. [6] X Research source
- Try freewriting. Write nonstop for about 10 minutes. Write whatever comes to mind and don’t edit yourself. After you finish writing, review what you have written. Highlight or underline the most useful information for your expository essay. Repeat the freewriting exercise using the passages you underlined as a starting point. You can repeat this exercise many times to continue to refine and develop your ideas. [7] X Research source
- Try clustering. Write a brief explanation of the subject of your expository essay on the center of a piece of paper and circle it. Then draw three or more lines extending from the circle. Write a corresponding idea at the end of each of these lines. Continue developing your cluster until you have explored as many connections as you can. [8] X Research source
- Try questioning. On a piece of paper, write out “Who? What? When? Where? Why? How?” Space the questions about two or three lines apart on the paper so that you can write your answers on these lines. Respond to each question in as much detail as you can. [9] X Research source

- Trustworthy internet sources usually include academic institutions like universities or research labs, government websites, and non-profit organizations.

- Identify the author and his or her credentials. Think about what qualifies this person to write about their subject. If the source has no author or the author does not have adequate credentials, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Check for citations to see if this author has researched the topic well enough. If the author has provided few or no sources, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Look for bias. Think about whether or not this author has presented an objective, well-reasoned account of the topic. If the author seems to value a particular argument or slant that is not supported or only thinly supported by fact, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Consider the publication date to see if this source presents the most up to date information on the subject.
- Cross-check some of the information in the source. If you are still concerned about a source, cross-check some of its information against a trustworthy source.

- Show when you have quoted a source word for word by putting it into quotation marks. Include information about the source such as the author’s name, article title or book title, and page number.
- Write down the publishing information of each source. You will need this information for your "References," "Bibliography," or "Works Cited" pages. Format this page according to your instructor's guidelines.

- Make sure your thesis is arguable. Do not state facts or matters of taste. For example, "George Washington was the first president of the United States," is not a good thesis because it states a fact. Likewise, "Die Hard is a great movie," is not a good thesis because it expresses a matter of taste. [16] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Make sure your thesis provides enough detail. In other words, avoid just saying that something is "good" or "effective." Instead, say what makes something "good" or "effective. [17] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
Introducing Your Essay

- An engaging hook can take many forms. You could start with an anecdote, an informative and attention-grabbing quote, a bold opinion statement, or anything that will make your readers want to continue with your essay.

- If you are writing about a book, provide the name of the work, the author, and a brief summary of the plot.
- If you are writing about a specific day in history, summarize the day's events. Then, explain how it fits into a broader historical scope.
- If you are writing about a person, name the person and provide a brief biography.
- Keep in mind that your context should lead up to your thesis statement. Explain everything your reader needs to know to understand what your topic is about. Then narrow it down until you reach the topic itself.

Expressing Your Main Points

- A five-paragraph essay should include three body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence that supports your thesis.
- Even if your essay is longer than five paragraphs, the same principles still apply. Each paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence.

- "Dogs played an active role in Marine Corps missions in the Pacific."
- "The Doberman Pinscher was the official dog of the US Marine Corps during WWII, but all breeds were eligible to train as war dogs."
- "War dogs were even eligible to receive military awards for their service."

- Most of your evidence should be in the form of cited quotes, paraphrases, and summaries from your research.
- Your evidence could also come from interviews, anecdotes, or personal experience.
- Try to provide at least two to three pieces of evidence to support each of your claims.
- For example, if a paragraph starts with, "War dogs were even eligible to receive military awards for their service," the supporting evidence might be a list of dogs who got awards and the awards they were given.

- You could write, "Even though Dobermans were the most common breed used in WWII, they were not the only breed, and were not the only dogs recognized for their help."
Concluding Your Essay

- Note that the second sentence repeats the information provided in your original thesis. It just says it in a new way while also hinting at the information you included in the body of the essay.

- Explain how the topic affects the reader
- Explain how your narrow topic applies to a broader theme or observation
- Call the reader to action or further exploration on the topic
- Present new questions that your essay introduced
Expert Q&A

- If you are unsure about anything as you work on your essay, talk to your instructor or meet with a writing tutor for help. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/expository_essays.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/expository-essay/
- ↑ Tristen Bonacci. Licensed English Teacher. Expert Interview. 21 December 2021.
- ↑ http://writing.ku.edu/prewriting-strategies
- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-on-writing-an-excellent-expository-essay.html
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/reading-and-researching/notes-from-research
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/using_research/quoting_paraphrasing_and_summarizing/index.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/conclusions.html
About this article

Before you write an expository essay, take some time to jot down ideas for your essay. Try the clustering method by writing a brief explanation of your subject in a bubble in the center of your page. Then, draw 3 or more lines extending from the circle and jot down idea bubbles that connect to your main theme. Once you have a plan for your expository essay, write out an outline to organize what you’re going to say. Make sure to begin your outline with an engaging introduction sentence. After the introduction sentence, provide some background information and include your thesis statement, which is your main argument. If you’re writing a 5 paragraph essay, you should include 3 body paragraphs after your introduction then a conclusion paragraph that summarizes your main points. However you organize your essay, make sure to include credible sources for important information, like statistics, so your teacher knows that it’s accurate. To learn how to use transitions in your essay, read more from our Writing co-author. Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Freida Ghabiliha
Nov 24, 2017
Did this article help you?

Qutaiba Raid
Jan 31, 2018
Maryanne Waqa
Aug 23, 2018
Apr 9, 2018
Nov 25, 2017

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Expository Essay
Expository Essay About A Book
Learn the Basics of Crafting an Expository Essay about a Book
-10257.jpg&w=640&q=75)
People also read
Complete Guide to Expository Essays: Writing Help and Topics
Interesting Expository Essay Topics For Your Next Paper
How to Write an Expository Essay Outline Like a Pro
Types of Expository Writing - Definition and Examples
Free Expository Essay Examples For Students
Ultimate Guide to Writing an Expository Essay About a Person
Learn to Write an Expository Essay About Yourself
Learn to Write Expository Essay About Mental Health - Examples & Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay about Bullying: A Guide
Expository Essay About Dogs: Steps, Examples & Topics
A Guide to Writing an Expository Essay about Education
Expository Essay About Friendship: A Writing Guide
Discover How to Write Expository Essays About Music – A Step-by-Step Guide
Looking for ways to write an effective expository essay on a book?
An expository essay about a book can be a challenging task, but it doesn’t have to be intimidating.
With the right approach and understanding of the basics, you can turn your assignment into an engaging exploration of your chosen text.
In this blog post, we’ll break down the steps for creating an effective expository essay about a book.
So let's begin!
- 1. What is an Expository Essay About a Book?
- 2. Expository Essay About a Book Examples
- 3. How To Write An Expository Essay About a Book?
What is an Expository Essay About a Book?
So what is an expository essay? An expository essay is a type of writing that examines and explains a topic in detail.
Writing an expository essay about a book can be a fun and educational way to explore the meaning of literature. It allows you to analyze the author’s writing style, themes, or various other aspects of a book.
In such an essay, you are expected to choose a particular aspect of a book and write an essay discussing that aspect in detail.
For example , you can write an expository essay about the depiction of authoritarianism in George Orwell's 1984. Similarly, you can choose to discuss any aspect of a book you’ve read.
Now that you know what an expository essay is, let's look at some examples.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Expository Essay About a Book Examples
To understand expository essays better, let’s take a look at some examples:
Expository Essay About a Book Example
Expository Essay About a Novel
Book Expository Essay Example
Reading these sample essays will help you understand what an expository essay about a book should look like.
Looking for more sample expository essays? Read our expository essay examples blog.
Now that you've read some essays, it's time for you to write one yourself. Let’s move on to the steps for writing your essay about a book.
How To Write An Expository Essay About a Book?
Expository writing requires a few simple steps to ensure your paper is well-structured and engaging.
Here are the steps you should follow to write an effective essay about a book:
Step 1. Read and Analyze the Book Thoroughly
Whether you have been assigned a book by your instructor or have chosen one yourself, you should read it thoroughly.
Before you begin writing your essay, it’s important to do your research. That means reading carefully through the book, taking notes on key aspects of the text, and making observations.
When analyzing a book, you may look for the following aspects:
- Prominent themes
- Important characters or events in the story
- Why the author chose to write the book
- How the text relates to its historical context
In short: read, take notes, and make observations.
Here’s a very useful video about how to discuss a book in your writing:
Step 2. Choose a Topic
Once you’ve read and analyzed the book in detail, pick out an interesting aspect you can write about.
Your chosen topic will serve as your essay’s focus and help guide your writing. It could be anything from a character’s development to an in-depth look at the themes or symbols in the book.
In addition to writing about a book, there are many other expository essay topics for you to explore.
Step 3. Outline Your Essay
Before diving into your essay, it’s important to create an expository essay outline that will serve as your roadmap. An expository essay commonly consists of five paragraphs, often referred to as the "five-paragraph essay" structure.
Your outline should contain:
Start by writing down your main points and supporting ideas and then organizing them into logical sections. It helps your essay flow logically.
Step 4. Write the First Draft of Your Essay
At this point, you can begin writing your essay.
Use the outline you created to structure your points and support them with evidence from the book. Make sure to remain objective in your analysis, citing facts and examples from the text.
Step 5. Edit & Revise
Once you’ve written your first draft, review it and make any changes or corrections necessary.
Make sure to double-check for grammar and spelling mistakes as well as the accuracy of facts. You may also want to get a second opinion from a friend or teacher before submitting your essay.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
To wrap it up,
Writing an expository essay assignment about a book can be a great way to explore literature.
By following the steps outlined in this blog, you’ll be well on your way to crafting an effective and engaging essay.
Still, facing difficulties writing your essay? Don't worry! MyPerfectWords is here to help.
MyPerfectWords.com is a reliable destination for your essay writing needs, catering to students across academic levels. Our expository essay writing service is conveniently accessible with just a few clicks.
Request ' do my essay ' and experience academic excellence with our expert help!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
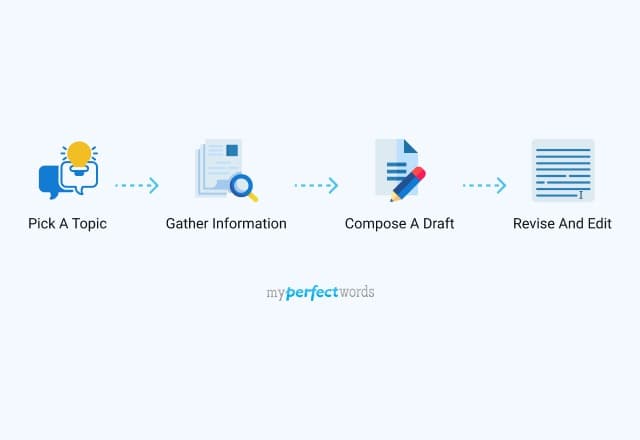

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1: Expository Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4531
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Understand the function and use of expository essays
- Identify eight types of expository essays
- Apply expository essay structure
What Is an Expository Essay?
An essay that explains a writer’s ideas by defining, explaining, informing, or elaborating on points to allow the reader to clearly understand the concept.
Many of your future academic workplace writing assignments will be expository–explaining your ideas or the significance of a concept or action. An expository essay allows the writer the opportunity to explain his or her ideas about a topic and to provide clarity for the reader by using:
- Explanations
- Definitions
It may also include the writer outlining steps of a procedure in a way that is straightforward for the reader to follow. It is purely informative and often contains elements of summary.
Imagine you need to verbally explain a concept to your classmates, maybe a behavioural theory. What are the key elements on which you would focus? How would you organize the information? You could explain who came up with the theory, the specific area of study to which it is related, its purpose, and the significant details to explain the theory. Telling these four elements to your classmates would give them a complete, yet summarized, picture of the theory, so they could apply the theory in future discussions.
Although you did this verbally, you were still fulfilling the elements of an expository essay by providing definition, details, explanations, and maybe even facts if you have a really good memory. This is the same process that you would use when you write an expository essay. You may actually be doing this all the time; for example, when you are giving someone directions to a place or explaining how to cook something. In the following sections of the chapter, you will practise doing this more in different expository written forms.
The Structure of an Expository Essay
Sections versus paragraphs.
Before looking at the general structure of an expository essay, you first need to know that in your post-secondary education, you should not consider your essay as writing being constructed with five paragraphs as you might have been used to in high school. You should instead think of your essay in terms of sections (there may be five), and each section may have multiple paragraphs.
To understand further why you need to think beyond the five-paragraph essay, imagine you have been asked to submit a six-page paper (approximately 1,500 words). You already know that each paragraph should be roughly 75 to 200 words long. If you divide the required word count by five paragraphs (1,500 by 5), you end with 300 words per paragraph, way above the number you should have in a paragraph. If your paragraphs are too long, they likely have too many ideas and your reader may become confused. Your paragraphs should be two-third of a page at most, and never longer than a page.
Instead, if you think of your essays being divided into sections (with possibly more than one paragraph per section), your writing will likely be more organized and allow your reader to follow your presentation of ideas without creating too much distance between your paragraph’s supporting points and its topic sentence.
As you will see in Section 4.5, some essay forms may require even more than five paragraphs or sections because of how many points are necessary to address. For the rest of this chapter, the term paragraph will also imply section.
Sections of an Expository Essay
An expository essay, regardless of its purpose, should have at least five sections, which are:
- Introduction
- First body section/paragraph
- Second body section/paragraph
- Third body section/paragraph
- Conclusion.
The introduction should state the topic of your paper: your thesis statement as well as brief signposts of what information the rest of the paper will include. That is, you only want to mention the content of the body paragraphs; you do not want to go in to a lot of detail and repeat what will be in the rest of the essay.
The first body section or paragraph should focus on one of your main points and provide evidence to support that point. There should be two to three supporting points: reasons, facts, statistics, quotations, examples, or a mix of these. Both the second and third body sections should follow the same pattern. Providing three body sections with one point each that supports the thesis should provide the reader with enough detail to be convinced of your argument or fully understand the concept you are explaining. However, remember that some sections will require more explanation, and you may need to separate this information into multiple paragraphs.
You can order your sections in the most logical way to explain your ideas. For example, if you are describing a process, you may use chronological order to show the definite time order in which the steps need to happen. You will learn about the different ways to organize your body paragraphs in the next chapter.
The concluding paragraph , or conclusion, can be a little tricky to compose because you need to make sure you give a concise summary of the body paragraphs, but you must be careful not to simply repeat what you have already written. Look back at the main idea of each section/paragraph, and try to summarize the point using words different from those you have already used. Do not include any new points in your concluding paragraph.
Consider Your Audience: How Much Do They Know?
Later in this chapter, you will work on determining and adapting to your audience when writing, but with an expository essay, since you are defining or informing your audience on a certain topic, you need to evaluate how much your audience knows about that topic (aside from having general common knowledge). You want to make sure you are giving thorough, comprehensive, and clear explanations on the topic. Never assume the reader knows everything about your topic (even if it is covered in the reader’s field of study). For example, even though some of your instructors may teach criminology, they may have specialized in different areas from the one about which you are writing; they most likely have a strong understanding of the concepts but may not recall all the small details on the topic. If your instructor specialized in crime mapping and data analysis for example, he or she may not have a strong recollection of specific criminological theories related to other areas of study. Providing enough background information without being too detailed is a fine balance, but you always want to ensure you have no gaps in the information, so your reader will not have to guess your intention. Again, we will practise this more in Section 4.9.
What Comes Next?
In the next eight sections (4.2 through 4.9), we will look at different expository modes, or rhetorical modes, you will often be assigned. These are:
- Illustration
- Description
- Classification
- Process analysis
- Compare and contrast
- Cause and effect
Rhetorical modes refers simply to the ways to communicate effectively through language. As you read about these modes, keep in mind that the rhetorical mode a writer chooses depends on his or her purpose for writing. Sometimes writers incorporate a variety of modes in any one essay. In this chapter, we also emphasize the rhetorical modes as a set of tools that will allow you greater flexibility and effectiveness in communicating with your audience and expressing your ideas.
In a few weeks, you will need to submit your first essay–an expository sample–and you will be given the choice of topic: one from each of the modes. Think about which types of expository essays are easier and which are more challenging for you. As mentioned, as you progress through your studies, you will be exposed to each of these types. You may want to explore a mode you find more challenging than the others in order to ensure you have a full grasp on developing each type. However, it is up to you. As you work through the sections, think about possible topics you may like to cover in your expository essay and start brainstorming as you work through the self-practice exercises.
After we explore each of the individual modes in the eight sections that follow, we will look at outlining and drafting; it is at this point you will want to fine tune and narrow the topic you will write about, so you can focus on that when doing the exercises.

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
10 Banned Books Written by LGBTQ+ Authors You Don’t Want to Miss
By melissa kravitz hoeffner | jun 19, 2024.

The freedom to read is essential to our democracy, but that hasn’t stopped folks from trying to ban books ; yes, in 2024—and long before that. The American Library Association (ALA) has tracked an increase in censorship attempts at public libraries and schools in recent years, with some groups demanding that certain titles be removed from circulation and curriculums across the nation.
Chances are, if a book contains any LGBTQ+ content, it’s been banned somewhere . According to ALA data, “titles representing the voices and lived experiences of LGBTQIA+ and BIPOC individuals made up 47 [percent] of those targeted in censorship attempts.” And, no surprise, research shows that these bans can be harmful to the communities most affected by them.
Luckily, plenty of efforts are underway to help readers of all ages engage with literature and material that opens their minds and makes them feel seen. Several libraries offer complimentary digital library cards to readers ages 13 to 21, regardless of residency, as part of the Books Unbanned Project . The Queer Liberation Library also provides online access to countless e-books.
With efforts to bury these books sadly underway, here are a few titles by LGBTQ+ authors that are banned in some places but worth adding to your reading list.
All Boys Aren't Blue: A Memoir-Manifesto by George M. Johnson
Gender queer by maia kobabe, go tell it on the mountain by james baldwin, last night at the telegraph club by malinda lo , the lesbiana's guide to catholic school by sonora reyes, fun home: a family tragicomic by alison bechdel, hijab butch blues by lamya h , beyond magenta: transgender teens speak out by susan kuklin, the perks of being a wallflower by stephen chbosky, sacrificio by ernesto mestre-reed.

One of the most banned books of 2023 , this 2020 essay collection by activist George M. Johnson recounts the beauty and the challenges of their upbringing, with a focus on what it’s like to come of age as a queer Black child in America.

Another oft-challenged title, this 2020 award-winning graphic memoir is an autobiography of author Kobabe’s adolescence and coming out. The nonbinary illustrator shares their lived experience with nuance and humor through teen crushes and difficult family dialogue.

James Baldwin is one of America’s prominent literary icons from the 20th century, but that doesn’t halt institutions from banning the Black, gay author’s works. His first novel , published in 1953, tells the story of a stepson of a Pentecostal Minister on one specific Saturday in Harlem in 1935.

Lo won the National Book Award for this novel in 2021, but that isn’t stopping the bigots from banning this YA page-turner for all ages. The story takes place in 1950s America, focusing on two young women who fall in love after passing each other under the neon sign of a lesbian bar, the Telegraph Club.

Pretty much anything melding sexuality and religion is going to be controversial, but that didn’t stop author Sonora Reyes, who has been outspoken on the effects of book banning for their readers. The novel follows Yami, one of the few Mexican students at a wealthy Catholic school, and how she navigates her identity, queerness, and just being a teen.

As an iconic component of the lesbian canon, this autobiographical graphic memoir by Dykes to Watch Out For cartoonist Alison Bechdel (of Bechdel test fame) is a quick and fascinating read. The comic strips detail her upbringing with a dysfunctional family at, where else, a funeral home. In 2013, the story was adapted into a musical , running on Broadway for several successful years.

This powerful memoir by Lamya H about growing up as a devout Muslim abroad and discovering her sexuality after moving to the United States was written anonymously for safety purposes. Despite winning multiple awards for the controversial book, the author has yet to be identified publicly, including at any book events or talks. It’s all the more reason to hear Lamya’s voice in the pages of the contentious book.

What could possibly be more dangerous than teens hearing from their peers? This now 10-year-old work of nonfiction , in which the author and photographer profile trans and nonbinary youth sharing their lived experiences, is often on the banned books list .

This 1999 classic about a teenage misfit used to appear on many curricula, but now, despite its relatively tame queer content and overall positive messaging, it’s one of the most banned books in America. It’s not hard to find a used copy: The bestseller about protagonist Charlie’s coming of age has sold millions of copies over the years and was adapted into a film in 2012.

Set in Cuba circa 1998, this literary novel follows an Afro-Cuban orphan as he joins a counterrevolutionary activist group, grapples with the AIDS crisis, and tries to survive on the margins of society.
Discover More Fascinating Facts About Pioneering LGBTQ+ Figures:
Now open: The Judith Yates Essay Prize in Economics
Eligible students completing the Bachelor of Economics and Bachelor of Advanced Studies can win $10,000 courtesy of The Judith Yates Essay Prize in Economics . The annual prize celebrates one winner who presents a solution to a real-world challenge facing Australia’s economy and population.
To enter, eligible students must write an essay in response to a single question addressing the issue of unmet social needs. In 2024, the question is:
"Within the next 20 years, it is predicted that 25% of the Australian population will be over the age of 65. This significant shift in demographics will impact older individuals, their families and communities, as well as the organizations that provide support for them. Identify and describe the possible challenges that the Australian economy may encounter due to this demographic change. Discuss appropriate government policies to address these challenges."
To be eligible to enter, students must be studying the Advanced Economics program in the Bachelor of Economics and Bachelor of Advanced Studies at the University of Sydney. They must also be enrolled in their second or third year of the pre-Honours pathway or enrolled in Honours (fourth year).
Applications for the prize are now open and will close on 12 October 2024 at 11:59 pm.
Why should you enter?
We spoke to the 2022 prize winner, Khloe Lizardo, about what winning the prize meant to her.
“Trying to balance work while studying as a full-time student was something I personally found a bit challenging,” says Khloe. “However, prizes that offer financial awards can be an incredibly helpful alternative, allowing you to study and spend quality time with family and friends.”
Outside of the financial incentive, Khloe found the process of writing her essays rewarding – helping her grow in confidence, improve her problem-solving skills, and tackle complex problems.
Read on to learn more about Khloe’s experience writing her award-winning essay, where she found inspiration, and how the prize has impacted her future.

2022 winner, Khloe Lizardo pictured with Associate Professor Marian Vidal-Fernandez at the 2023 ceremony.
Meet our 2022 winner: Khloe Lizardo
Khloe won the Judith Yates Essay Prize in Economics when COVID-19 was one of the biggest socio-economic problems facing Australia. In response, Khloe wrote an essay about fiscal consolidation within the context of rising interest rates and record-high levels of public debt.
“As a productivity-boosting measure, I proposed the development of a school-level intervention aimed at upskilling the non-cognitive skills of students,” she explains. “Lastly, I suggested supporting our agricultural sector, as it is thought to be one of the most productive in the world.”
Khloe found one of the great benefits of entering the prize was discovering new-found confidence in being able to tackle the big issues affecting our world.
“Although I was constantly second-guessing myself throughout the whole writing process, I was still determined to give it my best shot,” she remembers. “Ultimately, winning the Judith Yates Essay Prize was particularly symbolic for me as it gave me the opportunity to challenge my self-limiting beliefs and inspired me to pursue even more ambitious academic challenges.”
The Judith Yates Essay Prize
Related articles, bridging the past and present: the new vere gordon childe centre, sydney anthropologist awarded three prestigious book prizes, arts and social sciences students shine at the honours showcase.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
A Year on Ozempic Taught Me We’re Thinking About Obesity All Wrong

By Johann Hari
Mr. Hari is a British journalist and the author of “Magic Pill: The Extraordinary Benefits — and Disturbing Risks — of the New Weight Loss Drugs.”
Ever since I was a teenager, I have dreamed of shedding a lot of weight. So when I shrank from 203 pounds to 161 in a year, I was baffled by my feelings. I was taking Ozempic, and I was haunted by the sense that I was cheating and doing something immoral.
I’m not the only one. In the United States (where I now split my time), over 70 percent of people are overweight or obese, and according to one poll, 47 percent of respondents said they were willing to pay to take the new weight-loss drugs. It’s not hard to see why. They cause users to lose an average of 10 to 20 percent of their body weight, and clinical trials suggest that the next generation of drugs (probably available soon) leads to a 24 percent loss, on average. Yet as more and more people take drugs like Ozempic, Wegovy and Mounjaro, we get more confused as a culture, bombarding anyone in the public eye who takes them with brutal shaming.
This is happening because we are trapped in a set of old stories about what obesity is and the morally acceptable ways to overcome it. But the fact that so many of us are turning to the new weight-loss drugs can be an opportunity to find a way out of that trap of shame and stigma — and to a more truthful story.
In my lifetime, obesity has exploded, from being rare to almost being the norm. I was born in 1979, and by the time I was 21, obesity rates in the United States had more than doubled . They have skyrocketed since. The obvious question is, why? And how do these new weight-loss drugs work? The answer to both lies in one word: satiety. It’s a concept that we don’t use much in everyday life but that we’ve all experienced at some point. It describes the sensation of having had enough and not wanting any more.
The primary reason we have gained weight at a pace unprecedented in human history is that our diets have radically changed in ways that have deeply undermined our ability to feel sated. My father grew up in a village in the Swiss mountains, where he ate fresh, whole foods that had been cooked from scratch and prepared on the day they were eaten. But in the 30 years between his childhood and mine, in the suburbs of London, the nature of food transformed across the Western world. He was horrified to see that almost everything I ate was reheated and heavily processed. The evidence is clear that the kind of food my father grew up eating quickly makes you feel full. But the kind of food I grew up eating, much of which is made in factories, often with artificial chemicals, left me feeling empty and as if I had a hole in my stomach. In a recent study of what American children eat, ultraprocessed food was found to make up 67 percent of their daily diet. This kind of food makes you want to eat more and more. Satiety comes late, if at all.
One scientific experiment — which I have nicknamed Cheesecake Park — seemed to me to crystallize this effect. Paul Kenny, a neuroscientist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, grew up in Ireland. After he moved in 2000 to the United States, when he was in his 20s, he gained 30 pounds in two years. He began to wonder if the American diet has some kind of strange effect on our brains and our cravings, so he designed an experiment to test it. He and his colleague Paul Johnson raised a group of rats in a cage and gave them an abundant supply of healthy, balanced rat chow made out of the kind of food rats had been eating for a very long time. The rats would eat it when they were hungry, and then they seemed to feel sated and stopped. They did not become fat.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
the body of the essay; and the fi fth paragraph is a conclusion (see diagram on page 4). This book will focus exclusively on the fi ve-paragraph essay. Although essays may vary in length, the fi ve-paragraph essay structure can be adapted for longer or shorter essays. 1. Introductory paragraph
We use the word expository to describe any passage of writing that's supposed to present information and help you understand it in an objective way. Some common examples of expository writing include academic essays, textbooks, instructional guides, and news reports. Good expository writing should be factual, objective, and clear.
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
An expository essay is a type of essay that involves explaining an idea or theme within a given subject or topic. We guide you through writing one with examples. ... Even simple book reports can get into the expository essay zone. If you've ever written a traditional five-paragraph essay, you've probably written an expository essay ...
The body of your essay can be anywhere from 2-3 paragraphs to several paragraphs long. As you compose your outline, write down the different headings for your paragraphs so you can see exactly how each one transitions into the next. 4. Write your first draft. Start with an introduction, where you include your thesis statement.
How to Write an Expository Essay in 5 Steps. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 3 min read. Learning how to write a good expository essay is an academic writing skill that lays the foundation for the type of expository writing that's necessary for numerous professions.
The expository essay guide details how to develop your ideas, structure the essay, and assists with transitions. It includes helpful hints and tips on avoiding writing pitfalls. Read more. 6 people found this helpful. Helpful. Report. Manasa. 5.0 out of 5 stars PERFECT!!
ENG 101: Introductory Expository Writing: Books. This guide has been created for Dr. Tracy Collins' course, ENG 101: Introductory Expository Writing, by Aparna Zambare. ... Call Number: PE1404 .S337 2017 - Park Library Book Collection 4th Floor. ISBN: 9780190297404. Publication Date: 2017. Understanding Style: Practical Ways to Improve Your ...
Writing Mastery: Expository Essay: Expository Essay Paperback - July 22, 2019 by Miriam Shumba Denenga (Author) 2.2 2.2 out of 5 stars 2 ratings
Key Takeaways: Expository Writing. Just the facts, M'am: Expository writing is informational, not creative writing. Anytime you write to describe or explain, you use expository writing. Use a logical flow when planning an expository essay, report, or article: introduction, body text, and conclusion. It's often easier to write the body of your ...
The purpose of an expository essay is to explain or inform the reader about a specific topic or idea. Unlike other types of essays, the main goal is to provide a balanced analysis and present factual information in a clear and concise manner. ... Don't rely solely on internet sources, but also explore books and academic journals. 5. Use ...
An expository essay [ik-SPOZ-ih-tohr-ee ess-ay] is an essay in which the writer researches a topic and uses evidence to inform their readers or clarify the topic. ... From Solnit's 2014 book of essays, Men Explain Things to Me, "The Longest War" explores issues of male violence against women. Solnit uses both statistical and anecdotal ...
An expository essay asks for a critical explanation of a specific idea, theory, or topic. Our expert tips can help you write a well-structured and informative piece.
However, a plan will save you time in the long run. With all your quotes and evidence organized in one place, writing your essay is much faster and easier. 5. Writing. Once you have a completed plan, begin writing your essay. Remember to analyze each piece of evidence and clearly connect your points with transitions.
WHAT IS EXPOSITION WRITING. Exposition can be either oral or written. It is used to explain, interpret, inform, or describe. An expository writer must assume that the audience has no prior knowledge regarding the topic being discussed. So the topic must be written in a clear manner explaining how things work (you can however, leave out common ...
3. Generate ideas for your expository essay. Before you begin writing your essay, you should take some time to flesh out your ideas and get some things down on paper. Invention activities like listing, freewriting, clustering, and questioning can help you to develop ideas for your expository essay. [5]
An expository essay about a book can be a challenging task, but it doesn't have to be intimidating. With the right approach and understanding of the basics, you can turn your assignment into an engaging exploration of your chosen text. In this blog post, we'll break down the steps for creating an effective expository essay about a book. ...
An essay that explains a writer's ideas by defining, explaining, informing, or elaborating on points to allow the reader to clearly understand the concept. Many of your future academic workplace writing assignments will be expository-explaining your ideas or the significance of a concept or action. An expository essay allows the writer the ...
An expository essay may describe a city. ... Expository text can be solely expository, such as in self-help books. Expository text can also be combined with a narrative. Learning Outcomes.
Get past the thesis statement with two examples of expository essays. Learn more about the format, requirements, and types of expository writing for middle and high school. Dictionary ... a relationship in a book, or a significant moment in history. Though the essay can be from the writer's perspective, ...
Lo won the National Book Award for this novel in 2021, but that isn't stopping the bigots from banning this YA page-turner for all ages. The story takes place in 1950s America, focusing on two ...
In her third essay collection, the poet and critic Elisa Gabbert celebrates literature and life through a voracious engagement with the world. By Lily Meyer Lily Meyer is a writer, critic and ...
In the time it takes to boil water for pasta, you can finish several of Licht's delightful hybrid recipe-essays. The 78-page zine-like book encourages home cooks to view the task of preparing a ...
Outside of the financial incentive, Khloe found the process of writing her essays rewarding - helping her grow in confidence, improve her problem-solving skills, and tackle complex problems. Read on to learn more about Khloe's experience writing her award-winning essay, where she found inspiration, and how the prize has impacted her future.
Guest Essay. A Year on Ozempic Taught Me We're Thinking About Obesity All Wrong. May 7, 2024 ... The Extraordinary Benefits — and Disturbing Risks — of the New Weight Loss Drugs," among ...
In his new book, "American Covenant," Yuval Levin argues that we have forgotten the Founders' way of thinking about these issues, and that this forgetfulness is one of the sources of ...
Format: Print book Giveaway ends in: a. Availability: 100 copies available, 2342 people requesting ... Ann's New York Times essay, "Rallying to Keep the Game Alive," was adapted for Amazon Prime's Modern Love TV Series and stars Tina Fey and J ...more. More about Ann Leary... 2,342 people entered this giveaway ...