- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades

Human Body Essay | Essay on Human Body in Life for Students and Children in English
February 12, 2024 by sastry
Human Body Essay: Human body is truly a marvel. It is perhaps the most evolved living thing. It is, in fact, like a highly sophisticated machine.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Short Essay on Human Body 200 Words for Kids and Students in English
Below we have given a short essay on Human Body is for Classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. This short essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 6 and below.
To prevent it from diseases and illnesses, a thorough knowledge of the human body is necessary. Medical science has unravelled many mysteries of the functions of our body. And, the more we find out, the more fascinating the human body appears to be. But there is still a lot that we don’t know or can’t explain.
The human skeleton is like a cage. It provides the necessary support to the body. It also helps in protecting our vital organs. There are 206 bones in an adult human body. These bones are made up of calcium and phosphorus. The box-like skull structure protects our brain.
The muscles constitute the flesh. There are over 600 muscles in our body. All our movements are the direct result of the contraction and expansion of these muscles.
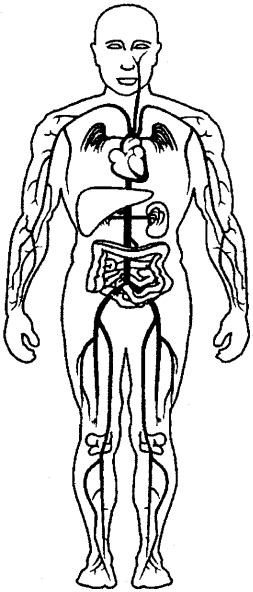
A cell is the basic unit of the body and there are millions of cells in each human body. These cells get nourishment through food, drink and oxygen. The cell suffer wear and tear during work. But through adequate rest and food the damage to the cell is repaired.
Then, there are the circulatory, respiratory, disgestive and nervous systems in our body. They are all highly complex systems but each is wonderful in its own way. Human heart and brain must be two of the most wonderful creations ever. They are extremely complicated but also very efficient parts of our body.
For us to live and remain healthy, it is important for all these parts and systems to work well together, in harmony with each other.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education

- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
Chemical composition of the body
Organization of the body.
- Basic form and development
- Effects of aging
- Change incident to environmental factors

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Biology LibreTexts - Introduction to the Human Body
- Healthline - The Human Body
- National Institutes of Health - National Cancer Institute - Introduction to the Human Body
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - Thoughts on the Human Body
- MSD Manual - Consumer Version - The Human Body
- LiveScience - The Human Body: Anatomy, Facts and Functions
- human body - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- human body - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

What is the chemical composition of the human body?
Chemically, the human body consists mainly of water and organic compounds—i.e., lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. The human body is about 60 percent water by weight.
What are the four main types of tissue in the human body?
The four main types of tissue in the human body are epithelial , muscle , nerve , and connective .
What are the nine major organ systems in the human body?
The nine major organ systems in the human body are the integumentary system, the musculoskeletal system, the respiratory system, the circulatory system, the digestive system, the excretory system, the nervous system, the endocrine system, and the reproductive system.
human body , the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues , organs , and systems.
Human anatomy and physiology are treated in many different articles. For detailed discussions of specific tissues, organs, and systems, see human blood ; cardiovascular system ; human digestive system ; human endocrine system ; renal system ; skin ; human muscle system ; nervous system ; human reproductive system ; human respiration ; human sensory reception ; and human skeletal system . For a description of how the body develops, from conception through old age , see aging ; growth ; prenatal development ; and human development .
For detailed coverage of the body’s biochemical constituents , see protein ; carbohydrate ; lipid ; nucleic acid ; vitamin ; and hormone . For information on the structure and function of the cells that constitute the body, see cell .
Many entries describe the body’s major structures. For example, see abdominal cavity ; adrenal gland ; aorta ; bone ; brain ; ear ; eye ; heart ; kidney ; large intestine ; lung ; nose ; ovary ; pancreas ; pituitary gland ; small intestine ; spinal cord ; spleen ; stomach ; testis ; thymus ; thyroid gland ; tooth ; uterus ; and vertebral column .

Humans are, of course, animals —more particularly, members of the order Primates in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata. Like all chordates , the human animal has a bilaterally symmetrical body that is characterized at some point during its development by a dorsal supporting rod (the notochord ), gill slits in the region of the pharynx , and a hollow dorsal nerve cord. Of these features, the first two are present only during the embryonic stage in the human; the notochord is replaced by the vertebral column, and the pharyngeal gill slits are lost completely. The dorsal nerve cord is the spinal cord in humans; it remains throughout life.

Characteristic of the vertebrate form, the human body has an internal skeleton that includes a backbone of vertebrae. Typical of mammalian structure, the human body shows such characteristics as hair , mammary glands , and highly developed sense organs.
Beyond these similarities, however, lie some profound differences. Among the mammals , only humans have a predominantly two-legged ( bipedal ) posture, a fact that has greatly modified the general mammalian body plan. (Even the kangaroo , which hops on two legs when moving rapidly, walks on four legs and uses its tail as a “third leg” when standing.) Moreover, the human brain, particularly the neocortex, is far and away the most highly developed in the animal kingdom. As intelligent as are many other mammals—such as chimpanzees and dolphins —none have achieved the intellectual status of the human species.
Chemically, the human body consists mainly of water and of organic compounds —i.e., lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Water is found in the extracellular fluids of the body (the blood plasma , the lymph , and the interstitial fluid) and within the cells themselves. It serves as a solvent without which the chemistry of life could not take place. The human body is about 60 percent water by weight.
Lipids —chiefly fats , phospholipids , and steroids —are major structural components of the human body. Fats provide an energy reserve for the body, and fat pads also serve as insulation and shock absorbers. Phospholipids and the steroid compound cholesterol are major components of the membrane that surrounds each cell.
Proteins also serve as a major structural component of the body. Like lipids, proteins are an important constituent of the cell membrane . In addition, such extracellular materials as hair and nails are composed of protein. So also is collagen , the fibrous, elastic material that makes up much of the body’s skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments. Proteins also perform numerous functional roles in the body. Particularly important are cellular proteins called enzymes , which catalyze the chemical reactions necessary for life.
Carbohydrates are present in the human body largely as fuels, either as simple sugars circulating through the bloodstream or as glycogen , a storage compound found in the liver and the muscles. Small amounts of carbohydrates also occur in cell membranes, but, in contrast to plants and many invertebrate animals, humans have little structural carbohydrate in their bodies.
Nucleic acids make up the genetic materials of the body. Deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) carries the body’s hereditary master code, the instructions according to which each cell operates. It is DNA, passed from parents to offspring, that dictates the inherited characteristics of each individual human. Ribonucleic acid ( RNA ), of which there are several types, helps carry out the instructions encoded in the DNA.
Along with water and organic compounds , the body’s constituents include various inorganic minerals. Chief among these are calcium , phosphorus , sodium , magnesium , and iron . Calcium and phosphorus, combined as calcium-phosphate crystals, form a large part of the body’s bones. Calcium is also present as ions in the blood and interstitial fluid , as is sodium. Ions of phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium, on the other hand , are abundant within the intercellular fluid. All of these ions play vital roles in the body’s metabolic processes. Iron is present mainly as part of hemoglobin , the oxygen-carrying pigment of the red blood cells . Other mineral constituents of the body, found in minute but necessary concentrations, include cobalt , copper , iodine , manganese , and zinc .

The cell is the basic living unit of the human body—indeed, of all organisms. The human body consists of trillions of cells, each capable of growth, metabolism , response to stimuli , and, with some exceptions, reproduction. Although there are some 200 different types of cells in the body, these can be grouped into four basic classes. These four basic cell types, together with their extracellular materials, form the fundamental tissues of the human body:
- epithelial tissues, which cover the body’s surface and line the internal organs, body cavities, and passageways
- muscle tissues, which are capable of contraction and form the body’s musculature
- nerve tissues, which conduct electrical impulses and make up the nervous system
- connective tissues , which are composed of widely spaced cells and large amounts of intercellular matrix and which bind together various body structures
Bone and blood are considered specialized connective tissues, in which the intercellular matrix is, respectively, hard and liquid.

The next level of organization in the body is that of the organ . An organ is a group of tissues that constitutes a distinct structural and functional unit. Thus, the heart is an organ composed of all four tissues, whose function is to pump blood throughout the body. Of course, the heart does not function in isolation; it is part of a system composed of blood and blood vessels as well. The highest level of body organization, then, is that of the organ system.
The body includes nine major organ systems, each composed of various organs and tissues that work together as a functional unit. The chief constituents and prime functions of each system are:
- The integumentary system , composed of the skin and associated structures, protects the body from invasion by harmful microorganisms and chemicals; it also prevents water loss from the body.
- The musculoskeletal system (also referred to separately as the muscle system and the skeletal system ), composed of the skeletal muscles and bones (with about 206 of the latter in adults), moves the body and protectively houses its internal organs.
- The respiratory system , composed of the breathing passages, lungs, and muscles of respiration , obtains from the air the oxygen necessary for cellular metabolism; it also returns to the air the carbon dioxide that forms as a waste product of such metabolism.
- The circulatory system , composed of the heart, blood, and blood vessels, circulates a transport fluid throughout the body, providing the cells with a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients and carrying away waste products such as carbon dioxide and toxic nitrogen compounds.
- The digestive system , composed of the mouth, esophagus , stomach, and intestines, breaks down food into usable substances (nutrients), which are then absorbed from the blood or lymph; this system also eliminates the unusable or excess portion of the food as fecal matter.
- The excretory system , composed of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder , and urethra , removes toxic nitrogen compounds and other wastes from the blood.
- The nervous system , composed of the sensory organs, brain, spinal cord, and nerves, transmits, integrates , and analyzes sensory information and carries impulses to effect the appropriate muscular or glandular responses.
- The endocrine system , composed of the hormone -secreting glands and tissues, provides a chemical communications network for coordinating various body processes.
- The reproductive system , composed of the male or female sex organs, enables reproduction and thereby ensures the continuation of the species.
Home — Essay Samples — Psychology — Body Image — The beauty of the human body
The Beauty of The Human Body
- Categories: Body Image
About this sample

Words: 1544 |
Published: Sep 12, 2018
Words: 1544 | Pages: 3 | 8 min read
Works Cited
- Brazier, Y. (2017). The media's influence on body image disturbance and eating disorders: We've reviled them, now can we rehabilitate them? Journal of Eating Disorders, 5(1), 1-7.
- Brown University. (n.d.). Body image and the media. Retrieved from https://www.brown.edu/campus-life/health/services/promotion/nutrition-eating-concerns/eating-concerns/body-image-and-media
- Conway, K. (2013). Media and body image. The Prevention Researcher, 20(3), 8-11.
- Fardouly, J., & Vartanian, L. R. (2016). Social media and body image concerns: Current research and future directions. Current Opinion in Psychology, 9, 1-5.
- GoodTherapy.org. (n.d.). Body image and the media. Retrieved from https://www.goodtherapy.org/learn-about-therapy/issues/body-image-media
- Jowett, S., Jarvie, I. C., & Fuller, J. (1969). The media and socialization. In S. Jowett & L. O'Donnell (Eds.), Propaganda and persuasion (pp. 109-126). Sage Publications.
- Kirsh, S. J. (2010). Media and youth: A developmental perspective. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 1(2), 162-171.
- Sparhawk, K. (2003). Cognitive influences on body image dissatisfaction: A review of theory and research. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 22(2), 138-156.
- Starker, S. (1989). Ideologies of the image of the body in film. Cultural Studies, 3(3), 381-398.
- University of Minnesota. (n.d.). Body image and the media. Retrieved from https://www.cehd.umn.edu/fsos/projects/bodyimage/effects/

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Psychology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2378 words
3 pages / 1439 words
2 pages / 732 words
2 pages / 715 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Ballaro, B., & Wagner, A. (n.d.). Body Image in the Media. In Media and Society (pp. 72-83). Retrieved from [...]
Physical appearance and personality are two interconnected aspects of an individual's identity, each playing a significant role in shaping how we perceive ourselves and others. While physical appearance is the immediate visual [...]
Beauty standards portrayed in media images have a significant impact on body image in today's society. While some experts argue that these standards have positive effects, there is a significant amount of evidence suggesting [...]
Essay about self-image delves into the intricate relationship between how we perceive ourselves and how others perceive us. Our self-image plays a pivotal role in shaping our confidence, choices, and interactions with the world. [...]
In today's time many of the stimulants that Bodybuilders use for strength boosting, Clenbuterol reactions can and do happen. A portion of these are gentle and leave alone after some time. However, others may turn out to be [...]
The 1950s were a time of significant change in American society, particularly when it came to body image. This era marked the beginning of the modern obsession with thinness, as the hourglass figure of the 1940s gave way to a [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Essay on Human Body System
Students are often asked to write an essay on Human Body System in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Human Body System
Introduction to the human body system.
The human body is like a complex machine made up of different parts that work together. These parts are called systems. Each system has a special job that helps our body to run smoothly, like how different parts of a car work together to make it drive.
Our Breathing System
The respiratory system lets us breathe. When we inhale, our lungs fill with air. They take oxygen from the air and send it to our blood. When we exhale, we push out carbon dioxide, a waste gas.
Our Heart and Blood System
The circulatory system includes our heart and blood vessels. The heart pumps blood, which carries oxygen and food to every part of our body. It also takes away waste.
Our Eating and Energy System
The digestive system is where food goes when we eat. It breaks down the food into small parts our body can use for energy, growth, and repair.
Our Moving System
Our defense system.
The immune system fights germs that can make us sick. It’s like our body’s superhero, protecting us from illnesses and helping us heal when we get hurt.
250 Words Essay on Human Body System
The human body is like a complex machine with many parts working together. Imagine it like a team, where each player has a special job. The team is made up of different systems, and each system has organs that do specific tasks.
Different Systems in Our Body
First, we have the skeletal system. This is like the frame of a building. It gives our body shape and protects important parts like the brain and heart. The muscles are attached to bones and help us move.
Next is the digestive system. It’s like a food processor. We put food in our mouth, and it travels down to the stomach and intestines. Here, the body breaks it down to get energy and nutrients.
Breathing and Circulation
Our respiratory system helps us breathe. We take in air through the nose or mouth, and it goes to the lungs. Here, the body takes oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide, which is a waste gas.
Fighting Germs and Controlling the Body
The immune system keeps us healthy by fighting germs. It has special cells that attack viruses and bacteria that can make us sick.
Lastly, the nervous system is like the body’s computer. The brain sends messages through nerves to tell the body what to do, like when to move or feel things.
Each system in our body works together to keep us alive and well. It’s amazing how all these parts coordinate to help us eat, play, think, and do everything else we do every day.
500 Words Essay on Human Body System
The human body is an amazing and complex machine. It is made up of many parts that work together to keep us alive and healthy. These parts are grouped into systems, each with a special job to do. Let’s explore some of these systems and understand how they help us in our daily lives.
The Skeletal System
Our bones form the skeletal system. This system gives our body its shape and protects our internal organs. Imagine your bones as a strong framework, like the frame of a house. They also work with muscles to help us move around. Inside the bones is marrow, which makes blood cells.
The Muscular System
The circulatory system.
The circulatory system is like a delivery service. It uses blood vessels to send blood throughout the body. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to every part of our body and takes away waste like carbon dioxide. The heart is the pump that keeps this system going.
The Respiratory System
Breathing is the job of the respiratory system. Our lungs are like big sponges that take in air. When we breathe in, we get oxygen from the air, and when we breathe out, we remove carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is vital for our survival.
The Digestive System
The digestive system is like a food processor. It breaks down the food we eat into tiny pieces that our body can use for energy and building materials. Starting from the mouth, going down the food pipe, into the stomach, and then through the intestines, our food is turned into nutrients that the body absorbs.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is the boss of all the other systems. It includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It sends signals around the body to control everything we do, from moving our arms and legs to feeling pain or pleasure.
The Excretory System
The excretory system is our body’s cleanup crew. It gets rid of waste products that our body doesn’t need anymore. The kidneys filter our blood and make urine, which carries the waste out of our body.
The Immune System
The immune system is our body’s defense force. It fights off germs like bacteria and viruses that can make us sick. It has many parts, including white blood cells that search and destroy these unwanted invaders.
In conclusion, our body is made up of different systems, each with an important role. They work together like a team to keep us functioning and healthy. Just like a team, if one part isn’t working well, it can affect the whole body. That’s why it’s important to take good care of our body by eating right, exercising, and getting enough rest. Understanding these systems can help us appreciate how amazing our bodies truly are.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Biology Article
- Human Body Anatomy
About Human Body
If we were to “break apart” the human body at the microscopic level, then the cell would constitute its most basic unit.
The average adult has somewhere between 30 – 40 trillion cells, and an estimated 242 billion new cells are produced every day. When a select group of cells with similar functions come together, it forms a tissue.
Tissues cumulate into organs, group of organs form organ systems and eventually, a complete organism.
Cells -> Tissues -> Organs -> Organ System -> Organism
Human Anatomy
Circulatory system, digestive system, reproductive system, respiratory system, nervous system, key points about the human body.
The human body exhibits a variety of movements from walking and running to crawling, jumping and climbing. The framework that enables us to do all these activities is the skeleton. Humans have as much as 300 bones at birth. However, the bones start to fuse with age. At adulthood, the total number of bones is reduced to 206.
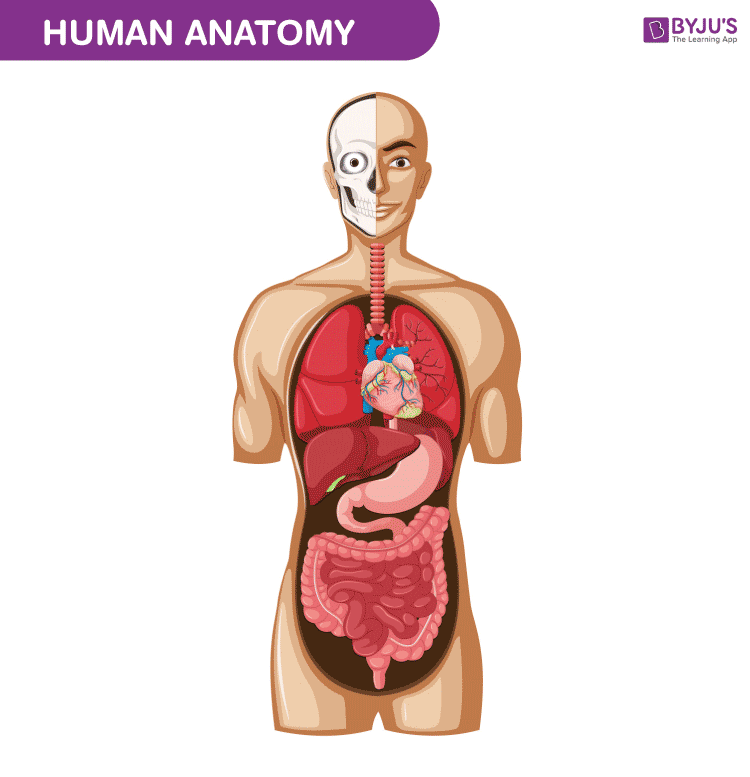
Human Anatomy is the scientific study of form and shapes of human beings
The skeleton also protects several vital organs such as the heart, lungs and the liver. Bones are attached to other bones through ligaments, a fibrous connective tissue.
Joints are the points at which two or more bones meet. They enable a range of movements like rotation, abduction, adduction, protraction, retraction and more. Based on flexibility and mobility, joints can be further classified into movable joints and immovable joints. Movable joints are flexible while immovable joints (also called fixed joints) are non-flexible since the bones are fused.
Muscles are specialised tissues which assist the bones in locomotion. Muscles are attached to the bones through tendons. Movement of limbs happens due to the contraction and relaxation of the corresponding muscles present in that region. Joints help in the flexibility of bones, but a bone cannot be bent or stretched until a muscle acts on it. In other words, the muscles attached to that bone pulls it to the direction of movement.
Furthermore, most movement involves muscles that work as a pair. For example, when we bend our arm, muscles in that region contract, become shorter and stiffer and pull the bones to the direction of movement. For relaxation (stretching), muscles in the opposite direction have to pull the bones towards it.
Also Read: What is Liver
List of Human Body Parts
- Human body parts comprise a head, neck and four limbs that are connected to a torso.
- Giving the body its shape is the skeleton, which is composed of cartilage and bone.
- Human body internal parts such as the lungs, heart, and brain, are enclosed within the skeletal system and are housed within the different internal body cavities.
- The spinal cord connects the brain with the rest of the body.
Human Body Structure
There are different cavities in the human body that house various organ systems.
- The cranial cavity is the space within the skull, it protects the brain and other parts of the central nervous system.
- The lungs are protected in the pleural cavity.
- The abdominal cavity houses the intestines, liver and spleen.
Humans have evolved separately from other animals, but since we share a distant common ancestor, we mostly have a body plan that is similar to other organisms, with just the muscles and bones in different proportions.
For example, we might assume giraffes have more vertebrae in its neck than humans. No, despite being incredibly tall, giraffes have the same number of vertebrae, i.e. they also have seven vertebrae in their neck.
One of the most prominent characteristic features is the ability to use our hands, especially for tasks that require dexterity, such as writing, opening a bottle of water, opening a doorknob, etc.
This is the result of humans having ancestors that began walking on their hind limbs rather than using all four limbs. Most of our anatomical insight was gained through the dissection of corpses (cadavers), and for a long time, it was the only way we could gain anatomical knowledge about the human body. It was a rather grotesque affair, but it made up the bulk of medical literature for centuries. These days, technological innovation has made it possible to explore human anatomy at a microscopic level.
Even to this day, scientists are newly discovering organs that were previously overlooked or have been mistakenly identified as other existing tissues. In 2018, scientists had discovered a new, body-wide organ called the Interstitium that exists right under the skin.
Human Physiology
It is referred to the physical, mechanical, and biochemical function of humans. This connects health, medicine, and science in a way that studies how the human body acquaints itself to physical activity, stress, and diseases.
The person who is trained to study human physiology is called a physiologist. Claude Bernard is referred to as the father of Physiology for his exemplary research.
Read More: Physiology
Human Body Parts and their Functions
The list of human body parts vary as the standard definition of an organ is still up for debate. However, there are an estimated 79 organs identified to date. We also possess organs that have “lost” their function throughout our evolution. Such organs are called vestigial organs.
Some of these organs work together and form systems that are specialised to perform a specific function or a set of functions. Collectively, these are known as organ systems.
And out of these 79 organs, five are crucial for survival, and any damage to these five organs might result in termination of life. These five crucial human body parts are the brain, heart, liver, lungs and kidneys. Read on to explore more about these body parts and their functions in detail:
The circulatory system is also referred to as the cardiovascular system. It comprises the heart and all the blood vessels: arteries, capillaries, and veins. There are essentially two components of circulation, namely:
- Systemic circulation
- Pulmonary circulation
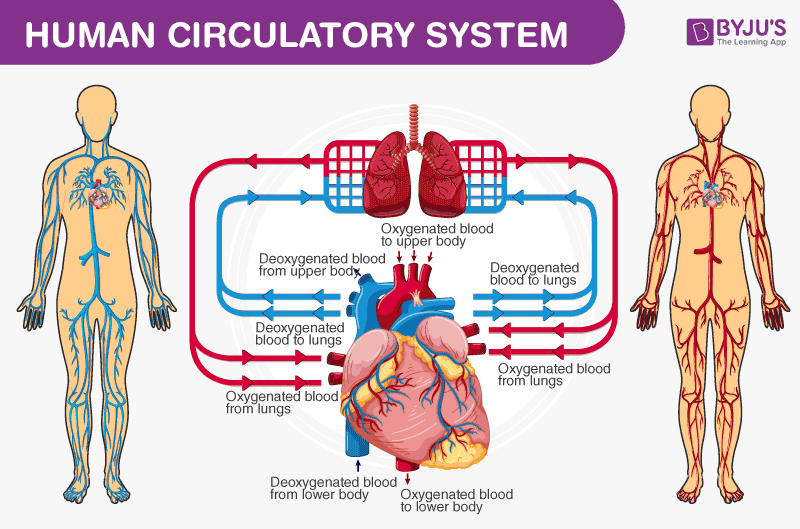
Diagram showing pulmonary ( blue ) and systemic circulation ( red )
Besides these two, there is a third type of circulation called Coronary circulation. Because blood is the body’s connective tissue, it helps to transport essential nutrients and minerals to the cells and waste byproducts away from it.
Hence, it is also known as the body’s “transport system.” Anatomically, the human heart is similar to other vertebrate hearts in the animal kingdom and hence, is a homologous organ.
Also Read: Double Circulation
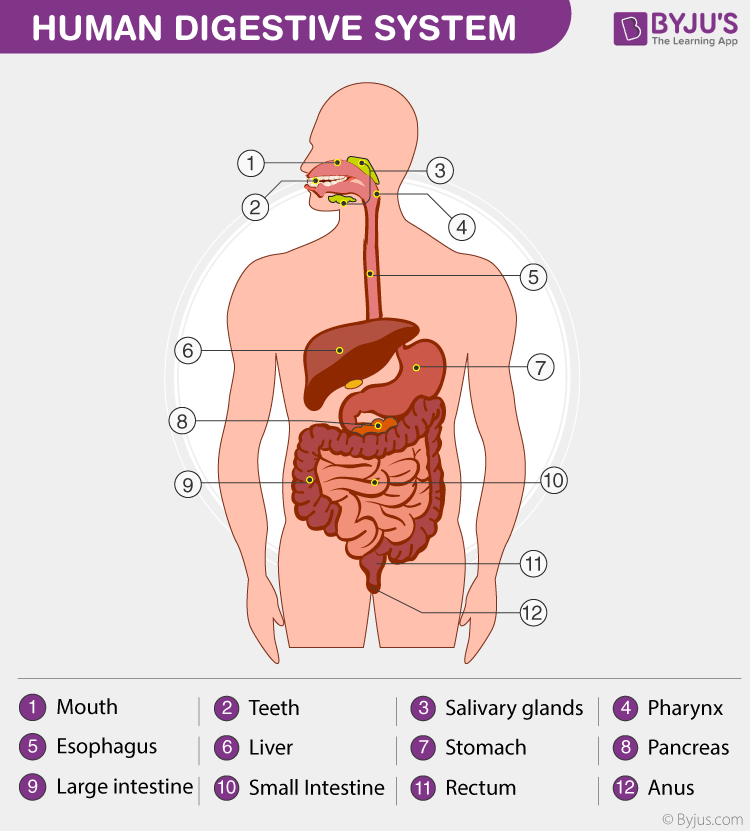
A diagram of the human digestive system detailing various components
The digestive system breaks down food and assimilates nutrients into the body, which the body then uses for growth and cell repair.
The major components of the digestive system are:
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Small and large intestines
The process of digestion starts with mastication (chewing food). Then, the saliva mixes with food and forms a bolus, a small rounded mass that can be easily swallowed. Once swallowed, the food travels down the oesophagus and into the stomach. The stomach secretes strong acids and powerful enzymes that break the food down into a paste.
It then moves into the small intestine where the food is broken down even more because of the bile secreted by the liver and powerful, digestive enzymes from the pancreas. This is the stage at which nutrients are absorbed from the food.
The leftover materials (stool) then move on to the large intestine where it transforms from liquid to solid, as water is removed. Finally, it gets pushed into the rectum, ready to be eliminated from the body.
Explore: The Structure and Function of the Alimentary Canal
The human reproductive system is also known as the genital system that comprises internal and external organs that help in reproduction. It varies for both males and females. Hormones, fluids, and pheromones are all connective accessories for the reproductive organs to function.
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system consists of the following:
- Ovaries : Produces ovum – female egg as well as the hormone estrogen.
- Uterine tubes : Oviducts or fallopian tubes are the other names given for uterus tubes.
Also known as the womb, the uterus is a pear-shaped organ where the fetus grows. The cervix is the route to the vagina and gateway for sperm to enter. Vagina acts as the route for a penis to enter during intercourse and the exit of the fetus during delivery.

Male Reproductive System

Next to the testis is the vas deferens that are the accessory ducts for the male sexual system. When sperm is formed, it is mixed with fluids that are produced by seminal glands, prostate gland, and Cowper’s gland. The primary purpose of Cowper gland is to hike the semen volume and lubrication during coitus.
More to Explore: Reproductive System
The respiratory process involves the intake of oxygen, and the exhale of carbon dioxide from the body. This system is also known as the ventilatory system, gas exchange system or respiratory apparatus. Vertebrates like human beings possess lungs for respiration. The process of respiration starts with the cycle of inhalation and exhalation.
Inhalation results in the oxygen entering into the body and exhalation results in carbon dioxide exiting from the body. Anatomically, the respiratory system comprises the following organs:
- Bronchioles

A diagram of the human respiratory system highlighting the gas exchange process
By diffusion, molecules of carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged passively among the blood cells and external environment. This swap is done through alveoli (which are the air sacs) in the lungs.
More About: Respiratory System
The voluntary and involuntary actions are maintained and taken care of by the central nervous system. It helps to channel the signals to and from different parts of our body. Nervous System is broadly classified into two categories:
- Central Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System
Distribution of Nerves in humans (top) and the Neuron (bottom)
The central nervous system contains the brain and the spinal cord , while the peripheral nervous system includes nerves and ganglia that are present outside the brain and spinal cord. Through the axons, every part of the body gets connected.
Central Nervous System consists of:
- Forebrain: It comprises the cerebrum, hypothalamus, and thalamus. The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum. Thinking, perceiving, controlling motor function, receiving and processing information and understanding language are the main functions done by this section of the brain. Also, sexual development and emotion functions are attached to the fore-brain.
- Midbrain: It is situated between the hypothalamus and thalamus. The brain stem is associated with the midbrain. Auditory and visual responses are controlled by the mid-brain.
- Hindbrain: The medulla, pons, and cerebellum are together, tied in the hind-brain. Interconnections of different parts of the brain’s surface that helps to accommodate neurons and connect them to the spinal column are done by the Hind brain.
Peripheral Nervous System consists of:
- Somatic nervous system: The system’s primary purpose is to transmit the motor and sensory impulses from CNS and back. It is linked to all the sensory organs, limbs and skeletal system. Imagine a scenario where you are riding a bicycle, and suddenly, you spot an obstacle (say a dog) on the road. Your ability to immediately swerve out of the obstacle’s path and avoid the crash is the result of the somatic nervous system taking action.
- Autonomic Nervous System: This system works without the person’s effort. The system helps to relay impulse from the central nervous system to smooth muscles and involuntary organs such as your heart, lungs etc. Also, it prepares the body against any violent attacks or abnormal conditions such as high body temperature during a fever or high rate of breathing and blood pressure after a strenuous exercise.
Further Reading: Nervous System
Every human being, tissues, human body parts and the organ systems are made up of cells- the fundamental unit of life. Anatomy is the science of understanding the structure and the parts of living organisms. Physiology, on the other hand, deals with the internal mechanisms and the processes that work towards sustaining life.
These can include biochemical and physical interactions between various factors and components in our body. With the progress of evolution, organisms began to exhibit advanced characteristics and features that enabled them to be more efficient and thrive in their respective environment.
The human structure can be described as bipedal, with hair covering the body, presence of mammary glands and a set of extremely well-developed sense organs. With respect to human body anatomy, we have a specialized circulatory system that enables the efficient transport of materials and nutrients within the body.
The presence of a well-developed digestive system helps to extract essential nutrients and minerals required by the body. A well developed respiratory system ensures the efficient gas exchange and the nervous system enables coordination and interaction within the body and also the external environment, thereby ensuring survival.
Frequently Asked Questions on Human Anatomy And Physiology
What do you mean by human anatomy, what do you understand by human physiology, who is the father of human physiology, what is the importance of human physiology, who is the father of human anatomy, what are the different types of anatomy, how is human anatomy relevant, how are anatomy and physiology different from each other, what are the important organs of the human body, what are the different systems of our body.
For more information about human body, human body parts, or any other related topic, please visit BYJU’S Biology .

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
| BIOLOGY Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Excellent 😊 app 👍👍 all students should learn from this app.
It’s very beneficial such a clear-cut app👍
Byju’s is a very good app, it is very simple learning app
It is very interesting app
Byjus helps me learn better. I like science classes
Byjus us the best platform for learing childrens can explore many different types of curriculam and its very benefical too childrens concept and doubts are cleared very easily and appropriately.
The best teachers over here thank you soo much for helping as my phone is not working i am not able to give thumps up ..
Great App. Very lucid language to understand. Also, videos help assuming before a teacher. Very useful. I will definitely recommend students/ parents to Byjus.
It’s so intresting
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
The Essence of Water in the Human Body
This essay discusses the fundamental role of water in the human body. It highlights how approximately 60% of our body weight is composed of water, which is essential for various physiological processes. From maintaining cell structure and facilitating biochemical reactions to regulating body temperature and aiding digestion, water’s functions are indispensable. The essay explains how water supports cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and mood regulation. It also emphasizes the importance of adequate hydration for overall well-being. The narrative underscores the significance of water in our daily lives and its impact on maintaining a healthy body.
How it works
The human body, an intricate marvel of biology, owes much of its complexity to a single, ubiquitous substance: water. Comprising approximately 60% of our body weight, water is an essential component that facilitates a myriad of physiological processes. This seemingly simple molecule, with its two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom, is fundamental to life as we know it.
From the moment we are born, water becomes a vital part of our existence. Newborns, in fact, have an even higher water content, roughly 75%, which gradually decreases as we age.
By adulthood, the average percentage of water stabilizes around 60%, though this can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and body composition. Men typically have a higher percentage of water compared to women, primarily due to a greater muscle mass, which holds more water than fat tissue.
Water plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of cells. It acts as a solvent, allowing various biochemical reactions to occur within our cells. Enzymes, which catalyze these reactions, often require an aqueous environment to function properly. Water also serves as a medium for transporting nutrients, hormones, and waste products in and out of cells. This constant movement ensures that our cells are nourished and can efficiently remove toxins.
In addition to its cellular functions, water is integral to the regulation of our body temperature. Through the process of sweating, our bodies can dissipate excess heat, maintaining a stable internal temperature. This is particularly important during physical exertion or in hot environments, where the risk of overheating is significant. Water’s high heat capacity allows it to absorb and release heat with minimal temperature changes, making it an ideal coolant for our bodies.
Moreover, water is essential for the proper functioning of our cardiovascular system. Blood, which is about 90% water, serves as the main transportation system for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. The heart pumps this fluid continuously, ensuring that every cell receives the necessary components for survival. Without adequate water intake, blood volume decreases, leading to a drop in blood pressure and potentially causing serious health issues.
Digestion is another process heavily reliant on water. Saliva, which begins the digestive process in the mouth, is primarily water. It not only helps in breaking down food but also aids in its smooth passage through the esophagus and into the stomach. In the stomach, water is crucial for the secretion of digestive juices that further break down food particles. The intestines then absorb the nutrients, with water facilitating this absorption and ensuring that waste is efficiently excreted.
Hydration levels also have a direct impact on cognitive function and mood. The brain, composed of about 73% water, relies on a delicate balance of hydration to maintain its function. Even slight dehydration can impair concentration, short-term memory, and the ability to think clearly. Additionally, water aids in the production of neurotransmitters and hormones that regulate our mood, highlighting its role in mental well-being.
While we lose water continuously through breathing, sweating, and excretion, maintaining adequate hydration is crucial. The recommended daily intake varies, but a general guideline is about eight 8-ounce glasses, or roughly 2 liters, for the average adult. This can vary based on individual needs, physical activity levels, and environmental conditions.
In conclusion, water is far more than just a refreshing beverage; it is a cornerstone of human physiology. From cellular processes to temperature regulation, cardiovascular health to digestion, and even cognitive function, water’s role is indispensable. Understanding the importance of maintaining proper hydration can lead to better health outcomes and overall well-being. So next time you take a sip of water, remember the profound impact it has on every aspect of your body’s functioning.
Cite this page
The Essence of Water in the Human Body. (2024, Jul 16). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-water-in-the-human-body/
"The Essence of Water in the Human Body." PapersOwl.com , 16 Jul 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-water-in-the-human-body/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Essence of Water in the Human Body . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-water-in-the-human-body/ [Accessed: 17 Jul. 2024]
"The Essence of Water in the Human Body." PapersOwl.com, Jul 16, 2024. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-water-in-the-human-body/
"The Essence of Water in the Human Body," PapersOwl.com , 16-Jul-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-water-in-the-human-body/. [Accessed: 17-Jul-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Essence of Water in the Human Body . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-water-in-the-human-body/ [Accessed: 17-Jul-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Health and Fitness Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on health and fitness.
We have always heard the word ‘health’ and ‘fitness’. We use it ourselves when we say phrases like ‘health is wealth’ and ‘fitness is the key’. What does the word health really mean? It implies the idea of ‘being well’. We call a person healthy and fit when he/she function well physically as well as mentally.

Factors Affecting our Health and Fitness
Good health and fitness is not something which one can achieve entirely on our own. It depends on their physical environment and the quality of food intake. We live in villages, towns, and cities.
In such places, even our physical environment affects our health. Therefore, our social responsibility of pollution-free environment directly affects our health. Our day-to-day habits also determine our fitness level. The quality of food, air, water all helps in building our fitness level.
Role of Nutritious Diet on our Health and Fitness
The first thing about where fitness starts is food. We should take nutritious food. Food rich in protein, vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates is very essential. Protein is necessary for body growth. Carbohydrates provide the required energy in performing various tasks. Vitamin and minerals help in building bones and boosting our immune system.
However, taking food in uneven quantity is not good for the body. Taking essential nutrients in adequate amount is called a balanced diet. Taking a balanced diet keep body and mind strong and healthy. Good food helps in better sleep, proper brain functioning and healthy body weight.
Include vegetables, fruits, and pulses in daily diet. One must have a three-course meal. Having roughage helps in cleaning inner body organs. Healthy food habit prevents various diseases. Reducing the amount of fat in the diet prevents cholesterol and heart diseases.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Impact of Exercise on our Health
Routine exercise helps improve our muscle power. Exercise helps in good oxygen supply and blood flow throughout the body. Heart and lungs work efficiently. Our bones get strong and joints have the pain free movement.
We should daily spend at least twenty minutes in our exercise. Daily morning walk improves our fitness level. We should avoid strenuous Gym activities. Exercise burns our fat and controls the cholesterol level in the body. Various outdoor games like cricket, football, volleyball, etc keeps our body fit. Regular exercise maintains our body shape.

Meditation, Yoga, and Health
Meditation and yoga are part of our life from ancient time. They not only make us physically fit but mentally strong as well. Meditation improves our concentration level. Our mind gets relaxed and thinking becomes positive.
A healthy mind is key for a healthy body. Yoga makes us stressfree and improves the endurance power of the mind. Yoga controls our blood pressure. With yoga, a strong bond with nature is established. Meditation is considered the best way to fight depression.
A person stays happier when he/she is fit and healthy. A fit and healthy person is less prone to chronic diseases. The healthy mind reacts better in a pressure situation. The self-confidence of a person is increased. Risk of heart failure is reduced drastically. With the increased immunity power body could fight cancerous cells. The intensity of the fracture is decreased with regular exercise.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Success stories
- Spine and back
- Pelvis and perineum
- Head and neck
- Neuroanatomy
- Cross sections
- Radiological anatomy
- Types of tissues
- Body systems
Register now and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide!

Human body systems
Author: Jana Vasković, MD • Reviewer: Nicola McLaren, MSc Last reviewed: November 03, 2023 Reading time: 24 minutes
/images/vimeo_thumbnails/258834949/cY8bHB92Lt23QbFNaX7LVA_overlay.jpg)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11115/pasted_image_0.png)
The human body is a biological machine made of body systems; groups of organs that work together to produce and sustain life. Sometimes we get lost while studying about cells and molecules and can’t see the forest for the trees. It can be helpful to step back and look at the bigger anatomical picture.
This topic page will provide you with a quick introduction to the systems of the human body, so that every organ you learn later on will add a superstructure to the basic concept you adopt here.
| System of organs | A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions in the body. |
| Musculoskeletal system | Mechanical support, posture and locomotion |
| Cardiovascular system | Transportation of oxygen, nutrients and hormones throughout the body and elimination of cellular metabolic waste |
| Respiratory system | Exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide between the body and air, acid-base balance regulation, phonation. |
| Nervous system | Initiation and regulation of vital body functions, sensation and body movements. |
| Digestive system | Mechanical and chemical degradation of food with purpose of absorbing into the body and using as energy. |
| Urinary system | Filtration of blood and eliminating unnecessary compounds and waste by producing and excreting urine. |
| Endocrine system | Production of hormones in order to regulate a wide variety of bodily functions (e.g. menstrual cycle, sugar levels, etc) |
| Lymphatic system | Draining of excess tissue fluid, immune defense of the body. |
| Reproductive system | Production of reproductive cells and contribution towards the reproduction process. |
| Integumentary system | Physical protection of the body surface, sensory reception, vitamin synthesis. |
Skeletal system
Muscular system, cardiovascular system.
- Respiratory system
Central nervous system
Peripheral nervous system, somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
- Digestive system
Urinary system
Endocrine system.
- Lymphatic system
Reproductive system
- Integumentary system
Related articles
The skeletal system is composed of bones and cartilages . There are two parts of the skeleton; axial and appendicular. The axial skeleton consists of the bones of the head and trunk . The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones within the limbs, as well as supporting pectoral and pelvic girdles .
There are 206 bones in an adult human body. The place at which two bones are fitted together is called the joint or articulation. Joints are supported by cartilages and reinforced with ligaments . Functions of the skeletal system are mechanical support, movement , protection, blood cell production, calcium storage and endocrine regulation.
Elements of the skeletal system are adjusted to the function of the body part they support. Thus, the anatomy of bones, joints and ligaments is studied topographically, as the bones of the; head and neck , thorax , abdomen , upper and lower limbs .
Get started with skeletal system anatomy by checking out the study unit and custom quiz below.
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/bones-skeletal-system/bX3KgmwVAC3JsO181kB6w_Skeletal_system.png)
The muscular system consists of all the body muscles. There are three muscle types ; smooth , cardiac and skeletal muscles. Smooth muscle is found within walls of blood vessels and hollow organs such as the stomach or intestines. Cardiac muscle cells form the heart muscle, also called the false . Skeletal muscles attach to the bones of the body.Among these three, only skeletal muscles can be controlled consciously and enable us to produce body movement, while the function of other two muscle types is regulated by the autonomic nervous system and is absolutely unconscious.
Histologically, skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers are arranged in a repetitive fashion giving a striped appearance, hence are called striated muscle .
Smooth muscle does not contain repetitive sarcomeres , thus is non-striated muscle.
Learn all about the muscular system in the study unit below, or consolidate what you already learned with our fully customizable quiz.
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/anatomy-muscular-system/jLSroxCALl5kA7VwfWgHOg_Muscular_Thumbnail.png)
The cardiovascular system is comprised of the heart and the circulatory system of blood vessels. The heart is composed of four chambers; two atria and two ventricles . Blood enters the heart through the upper chambers of the left and right atria and exits via the left and right ventricles. Heart valves prevent the backflow of blood.
The heart acts as a two-way pump. The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circulation of the lungs , where the blood is reoxygenated again. While the left side of the heart simultaneously pumps oxygenated blood into the systemic circulation, distributing it to the peripheral tissues . The regular pumping, or heartbeat , is controlled by the conduction system of the heart .
The circulatory system, also called the vascular system, consists of arteries, veins and capillaries . They all comprise a continuous network of vessels which act to carry blood around the body. Blood leaves the heart via arteries , these progressively reduce in size to continue as smaller arterial vessels called arterioles . Arterioles end in a web of even smaller vessels called capillaries . The exchange of gases and nutrients occurs through the capillary walls.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/984/jRIADP50Dac6ZpgzLiAddQ_cardiovascular-system-up_english.jpg)
Small veins, called venules , leave from capillaries and gradually increase their lumen on the way to the heart to end as veins . There is a certain histological difference between arteries and veins , but their main functional difference reflects the direction in which they conduct blood: the arteries convey blood from the heart to the periphery, whereas the veins convey blood from the periphery to the heart.
There are three separate circuits to the circulatory system.
- The pulmonary circulation which carries blood between the heart and the lungs;
- The coronary circulation which supplies blood to the muscle of the heart;
- And the systemic circulation which carries blood to the rest of the body.
Major arteries within the systemic circulatory system are the aorta and its branches, while the main representatives of the veins are the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava .
Learn everything about the heart, arteries and veins faster with our cardiovascular system diagrams, quizzes and free worksheets .
Major functions of the cardiovascular system include transportation of oxygen, nutrients and hormones throughout the body within the blood, and as well as eliminating carbon dioxide and other metabolic waste.
Learn more about the major arteries, veins and nerves of the body with Kenhub resources!
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/arteries-and-veins-of-cardiovascular-system/P3ZW8DsgrrPtPdEfmgy0A_Cardiovascular_system.png)
The respiratory system consists of a series of organs; the nasal cavity , pharynx , larynx , trachea , bronchi , bronchioles and lungs ( alveoli ). The nasal cavity and pharynx are together called the upper respiratory system , while the remainder of the organs comprise the lower respiratory system .
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/133/1H5s6zxsxdNrfKQE2BJuw_anatomy-of-respiratory-system_english.jpg)
Respiratory system organs, with the exception of the alveoli, function to conduct air into the lungs aided by the muscles of respiration (mainly the diaphragm and intercostal muscles ).
Once air is in the lungs it enters alveoli (the site of gas exchange) and interacts with blood transported by the pulmonary circulation. Here carbon dioxide is removed from, and oxygen returned to, the blood. Thus the major respiratory system function is to bring oxygen into the body and expel carbon dioxide.
Fortify your knowledge about the respiratory system with this content we have prepared for you.
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/anatomy-of-respiratory-system/YD2p5K2CMSsj9sCa1MbA_respiratory_system_anterior_view.png)
- Nervous system
Nervous system controls how we interact with and respond to our environment, by controlling the function of the organs in our other body systems. The nervous system organs are the brain , spinal cord and sensory organs. These are connected by neurons , which act to transmit neural signals around the body.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/124/akwidctLYvuNiZhnZFtcQ_anatomy-of-nervous-system_english.jpg)
Morphologically and topographically, the nervous system is divided into the central (CNS) and peripheral (PNS) nervous systems. Whilst functionally, the nervous system is considered as two parts; the somatic (SNS) or voluntary nervous system, and the autonomic (ANS) or involuntary nervous system.
The central nervous system definition is that it receives information from the body’s environment and generates instructions, thereby controlling all the activities of the human body. This two-way information flow into, and out of, the CNS is conveyed by the peripheral nervous system.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/endbrain/t33KJubDawexQCugCkDng_Cerebrum.png)
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is placed within the neurocranium , and is formed from the cerebrum , cerebellum and brainstem ( pons and medulla oblongata ). The central parts of the CNS are occupied by spaces called ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) . The spinal cord is placed within the vertebral column . The spinal canal extends through the central part of the spinal cord. It is also filled with CSF and it communicates with the ventricles of the brain.
The CNS is made of neurons and their processes ( axons ). Gray matter is made of neuron cell bodies, it is found in the cerebral cortex and the central portion of the spinal cord. White matter is made of axons, which combine and build neural pathways . The gray matter is where the instructions generate, while the white matter is the path through which the instructions travel toward the organs.
The peripheral nervous system definition is that it conducts information from the CNS to the target tissues, and from the target tissues to the CNS. It consists of nerves and their ganglia . Nerves that carry information from peripheral sense organs (for example eye , tongue , nasal mucosa, ear , skin ) to the CNS are called the ascending, afferent or sensory nerve fibers. Fibers that carry information from the CNS to the periphery (muscles and glands) are the descending, efferent , motor or secretory nerve fibers.
A ganglion is a cluster of neural tissue outside of the CNS, made of neuronal cell bodies. Ganglia can be both sensory and autonomic. Sensory ganglia are associated with spinal nerves and some cranial nerves ( V , VII , IX , X ).
Peripheral nerves emerge from the CNS. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves which arise from the brain, and 31 pairs of spinal nerves which extend from the spinal cord. Cranial nerves are named I to XII, determined by their skull exit location (anterior to posterior). Spinal nerves are divided into 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal nerve , depending on vertebral level from which they arise. In certain areas of the body peripheral nerves interconnect, creating neural networks called plexuses . Notable plexuses are the:
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/plexus-cervicalis-3/OE1ehQxnSl0vAYWKwoSMjg_cervical_plexus.png)
- Cervical plexus (C1-C4) – innervates the back of the head , some neck muscles , pericardium and diaphragm via great auricular, transverse cervical nerve , lesser occipital, supraclavicular, and phrenic nerves .
- Brachial plexus (C5-T1) – innervates the upper limb with nerves such as median , ulnar , radial , musculocutaneous and axillary nerve .
- Lumbar plexus (L1-L4) – innervates the muscles and the skin of the abdomen and pelvis , as well as thigh muscles via iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral , lateral femoral cutaneous, obturator, femoral nerves .
- Sacral plexus (S1-S4, with branches from L4, L5) – innervates the muscles and skin of parts of the pelvis, posterior thigh , lower leg and foot via the following nerves; gluteal, sciatic , posterior femoral cutaneous, pudendal, nerve to piriformis, nerve to obturator internus , and nerve to quadratus femoris .
The somatic nervous system (SNS) and autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divisions of the peripheral nervous system, with information conveyed through the cranial and spinal nerves.
The somatic nervous system definition is that it allows voluntary control over our movements and responses. It conveys sensory and motor information between the skin, sensory organs, skeletal muscles and the CNS; establishing communication of the human body with its environment and response to outside stimuli. Major somatic peripheral nerves include the median nerve, sciatic nerve and femoral nerve.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/truncus-sympathicus-2/zOGSdPag8gpKnJgyn9cz4g_Truncus_sympathicus_01.png)
The autonomic nervous system definition is that it controls all the internal organs unconsciously, through the associated smooth muscle and glands . Functionally, the ANS is divided into sympathetic (SANS) and parasympathetic (PANS) autonomic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system definition is informally known as producing the „flight or fight“ state as it is the part of the ANS which is mostly active during stress.PANS dominates during rest, and is more active in „rest and digest“ or „feed and breed“ activities. The centers of SANS and PANS are within the brainstem and spinal cord, and they communicate with SANS and PANS ganglia located throughout the body. Note that there isn’t any pure SANS or pure PANS nerve, instead their fibers are added to the specific somatic nerves, making them mixed.
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/anatomy-of-nervous-system/P4VlaE7lWkpjgYEkkXUmQ_nervous_system.png)
The digestive system function is to degrade food into smaller and smaller compounds, until they can be absorbed into the body and used as energy. It consists of a series of gastrointestinal tract organs and accessory digestive organs.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/340/SP4RNcapdAGqtn7LCoQlPw_anatomy-of-digestive-system_english.jpg)
The digestive system organs spread from the mouth to the anal canal. So it’s actually a tube consisting of the mouth , pharynx , esophagus , stomach , small intestine , large intestine , and anal canal . Accessory digestive organs assist with the mechanical and chemical food breakdown, these are the tongue, salivary glands , pancreas , liver and gallbladder .
Master the digestive system anatomy starting with this study unit and custom quiz:
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/anatomy-of-digestive-system/DxaA1MAHsRt2P0gFda42rQ_digestive7.png)
Urinary system is a body drainage system comprised of the group of organs that produce and excrete urine. It consists of the kidneys, ureters , urinary bladder and urethra .
Kidneys are paired bean-shaped organs placed retroperitoneally. The kidneys have a rich blood supply provided by the renal artery . Nephrons within the kidneys filter the blood that passes through their web of capillaries ( glomerulus ). The blood filtrate then passes through a series of tubules and collecting ducts, eventually forming the final ultrafiltrate, urine . Urine passes into the ureters , tubes of smooth muscle that convey urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder . The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that collects and stores urine before disposal by urination (micturition). Functions of the urinary system include; elimination of body waste, regulation of blood volume and blood pressure, regulation of electrolyte levels and blood pH.
Get started with the urinary system with these resources:
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/kidney-structure/R2JcC5cwozGlXaHivvZeqQ_Kidney_surface.png)
The endocrine system is a collection of specialised organs (endocrine glands) scattered throughout the body that act to produce hormones. The main organs of the endocrine system can be seen in the diagram below.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/409/TrwbUVmYfTBDZQiCLXJzaw_organs-endocrine-system_english.jpg)
With regards to the endocrine system function; hormones produced by the endocrine system act to regulate a wide variety of bodily functions, such as triiodothyronine which regulates metabolism, or estrogen and progesterone which regulate the menstrual cycle. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to regulate the function of distant target organs.
We have you covered with everything you need to know about the endocrine system here.
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/organs-endocrine-system/dotyNOINCGPJY6rPYVeA_T950_endocrine_female_body_anterior.png)
The lymphatic system is a network of lymphatic vessels that drains excess tissue fluid (lymph) from the intercellular fluid compartment, filters it through lymph nodes, exposes it to lymphocytes (white blood cells) of the immune system and returns the fluid to the circulatory system. The lymphatic system consists of lymph, lymphatic plexuses, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes and lymphoid organs. The lymphatic system function is to; convey and eliminate toxins and waste from the body; recirculate proteins; and defend the body from microorganisms.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/624/pi72itJricGjthbgDF2O4w_lymphatic-system_english.jpg)
Lymph is a watery tissue fluid with a similar consistency to blood plasma. It starts as interstitial fluid which occupies the spaces between cells. Excess fluid is picked up by lymphatic capillaries and transported through lymphatic plexuses into lymphatic vessels , filtering through lymph nodes along its journey. Superficial lymphatic vessels are found in the subcutaneous tissue alongside veins. They drain into deep lymphatic vessels that follow the arteries. Lymphatic vessels empty into larger lymphatic trunks, which unite to form one of the two main collecting ducts; the thoracic duct and the right lymphatic duct .
The thoracic duct begins at the cisterna chyli , collecting lymph from the left side of head, neck and thorax, left upper limb, abdomen and both lower limbs and draining it into the left venous angle (junction of the left internal jugular and left subclavian veins). The right lymphatic duct drains the rest of the body and empties into the right venous angle. From the venous angles, cleaned lymph is returned to the circulatory system, rejoining with the fluid of the blood. Note that the central nervous system was previously thought to have no lymphatic vessels. However, recent research has shown its lymph is drained by lymph vessel-like structures found in the meninges.
Lymphatic system organs are divided into primary and secondary organs. Primary lymphatic organs produce lymphocytes and release them into lymphatic vessels. The two primary lymphoid organs are the thymus and red bone marrow . Secondary lymphatic organs include lymph nodes, tonsils , appendix and spleen . Lymph nodes are masses of lymphocyte containing lymphoid tissues, attached to lymphoid vessels. Lymph nodes function to filter cellular debris, foreign pathogens, excess tissue fluid, and leaked plasma proteins. There are aggregations of lymph nodes at key points around the body (cervical, axillary , tracheal, inguinal, femoral, and deep nodes related to the aorta).
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/lymphatic-system/oD4KesPCHp3uwv1sGdmWg_Lymphatic6.png)
The reproductive system, or genital system, is a system of internal and external sex organs which work together to contribute towards the reproduction process. Unlike other systems of organs, the genital system has significant differences among sexes.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/vulva/DIPGYniQT3jutmiUEfaQ_vulva_magni.png)
The external female sex organs , also known as the genitals, are the organs of the vulva (the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening). The internal sex organs are the ovaries , fallopian tubes , uterus and vagina . The vulva provides an entry to, and protection, for the vagina and uterus, as well as the proper warmth and moisture that aids in its sexual and reproductive functions. In addition, it is important for the sexual arousal and orgasm in females.
The vagina is the canal leading from the outside of the body to the cervix (neck) of the uterus. Ovaries secrete hormones and produce egg cells, which are transported to the uterus fallopian tubes . The uterus provides protection, nutrition, and waste removal for the developing embryo and fetus. In addition, contractions in the muscular wall of the uterus contribute to pushing out the fetus at the time of birth.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/testis/Xvboe0XUR1OoKAX2GnfdQ_Testes.png)
The external male sex organs are the testes and penis , while the internal are the epididymis, ductus deferens and accessory glands. Functionally, they can be grouped into three categories.The first category is for sperm production (the testes ), and storage ( epididymis ). The second category organs produce ejaculatory fluid; the ductus deferens and the accessory glands ( seminal vesicles and prostate ). The final category is those used for copulation and deposition of the sperm, these include the penis , urethra and ductus deferens.
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/anatomy-testis-and-epididymis/C1wk67nXQrAgWTBGA36g_Testis_Thumbnail_3.jpg)
The integumentary system is the set of organs that forms the external covering of the body. It includes the skin, skin appendages , sweat glands and sensory receptors.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/93/LSK8Ip22hSV9UleOyLOg_anatomy-of-integumentary-system_english.jpg)
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It has three layers; epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is a thick keratinized epithelium made of multiple cell layers. Underneath the epidermis is the dermis , a layer of connective tissue that contains blood vessels and nerves that supply the skin. The underlying fascia, also called the hypodermis , consists of fat , connective tissue and skin appendages (hair, nails, sebaceous and sweat glands).The integumentary system functions are various. It forms a continuous layer that protects the body from various damaging events, such as external injuries, loss of water and heat, and the carcinogenic effects of UV rays. It also excretes waste, contains sensory receptors to detect pain, sensation, pressure, and temperature, and provides for vitamin D synthesis.
Go through these resources to reinforce your knowledge of the skin:
:format(jpeg)/images/study_unit/anatomy-of-integumentary-system/VvlGGjgS9TupZgGvTC3A_Integumentary_system.png)
References:
- Haines, D. E., Mihailoff, G. A. (2018). Fundamental neuroscience for basic and clinical applications. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
- Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2014). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Netter, F. (2019). Atlas of Human Anatomy (7th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders.
- Standring, S. (2016). Gray's Anatomy (41st ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone.
- Tamura, R., Yoshida, K., & Toda, M. (2019). Current understanding of lymphatic vessels in the central nervous system. Neurosurgical Review, 43(4), 1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143...
Article, review and layout:
- Jana Vaskovic
- Nicola McLaren
Illustrations:
- Digestive system (anterior view) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Skeletal system (an overview) - Irina Münstermann
- Cardiovascular system (a diagram) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Respiratory system (a diagram) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Nervous system (an overview) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Cranial nerves (a diagram) - Paul Kim
- Digestive system (a diagram) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Organs of the endocrine system (a diagram) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Lymphatic system (a diagram) - Begoña Rodriguez
- Integumentary system (a diagram) - Paul Kim
Articles within this topic:
- Anatomy of breathing
- Autonomic nervous system
- Central nervous system and brain lymphatics
- Circulatory (cardiovascular) system
- Clinical case: Schwannoma of the nasal cavity
- Development of the central nervous system
- Development of the digestive system
- Digestive system quizzes and free learning tools
- Embryology: 3rd week of development
- Endocrine system: Quiz questions, diagrams and study tools
- How many bones can you find in the human body?
- Hyperthyroidism
- Learn the bones of the body with skeletal system quizzes
- Lymph nodes of the head, neck and arm
- Main bones, joints and muscles of the body
- Musculoskeletal system
- Nervous system anatomy practice: Quizzes and more!
- Organs of the endocrine system
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Respiratory system and lung development
- Respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams
- Subcutaneous tissue
- Think you know the integumentary system? Quiz yourself!
- What is a nerve?
Human body systems: want to learn more about it?
Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster.
What do you prefer to learn with?
“I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half.” – Read more.

Learning anatomy isn't impossible. We're here to help.
Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours.
Want access to this video?
- Curated learning paths created by our anatomy experts
- 1000s of high quality anatomy illustrations and articles
- Free 60 minute trial of Kenhub Premium!
...it takes less than 60 seconds!
Want access to this quiz?
Want access to this gallery.
What are the systems of the body? Fast facts about the human body and how it works
Learn all about the human body's many systems and some of its individual organs, both vital and vestigial.

The human body is a complex network of systems that work together to keep life-sustaining processes running smoothly. These systems break down food for fuel, clear away waste, repair damaged tissues and DNA, fight infectious germs and monitor the outside world so we can move through it safely.
Many scientists spend their days working to understand how each bodily system performs its jobs, how the systems interact, and what can happen when one or more of them falter. Such malfunctions can stem from aging or disease, for instance, and through medical care, doctors aim to get derailed systems back on track.
Here's a quick rundown of the systems of the human body, its vital organs and its "vestigial" organs, as well as a few fascinating facts about how the body works.
What are the different systems of the human body?
Our bodies consist of a number of biological systems that carry out specific functions necessary for everyday living. Some organs and tissues play roles in multiple systems at once.
Related: Strange, two-faced brain cells confirmed to exist, and they may play a role in schizophrenia
Circulatory : The job of the circulatory system is to move blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones around the body. It consists of the heart, blood, blood vessels, arteries and veins. According to the Cleveland Clinic , the adult human body's network of blood vessels is more than 60,000 miles (around 100,000 kilometers) long.
Digestive: The digestive system consists of a series of connected organs that together allow the body to break down and absorb nutrients from food and remove waste. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine , large intestine, rectum and anus. The large intestine is home to microorganisms that are collectively called the gut microbiome and influence our health in various ways . The liver and pancreas also have roles in the digestive system because they produce digestive juices filled with enzymes to break down the components of food, such as carbohydrates , fats and proteins , according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases .
Endocrine: The endocrine system consists of a network of glands that secrete hormones — long-range chemical messengers that regulate how cells and tissue function — into the blood. These hormones, in turn, travel to different tissues and regulate many bodily functions, such as metabolism , growth and sexual function, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine . For example, the pancreas releases the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar . Conditions like diabetes and insulin resistance arise from the body having too little insulin or not responding to it adequately.
Related: Meet the 'exclusome': A mini-organ just discovered in cells that defends the genome from attack
Immune: The immune system is the body's defense against bacteria , viruses and other pathogens that may be harmful. Components of the system include the lymph nodes , which contain infection-fighting cells called lymphocytes. These lymphocytes are one of many types of leukocyte , or white blood cell. The immune system also includes the spleen , the bone marrow and a gland called the thymus . The immune system can learn to recognize antigens — proteins on the surface of bacteria, fungi and viruses — and alert the body to their presence. Some immune cells make proteins called antibodies that attach to these antigens and mark invaders for destruction.
Lymphatic: The lymphatic system includes the lymph nodes, lymph ducts and lymph vessels and is considered part of the immune system. Its main job is to make and move lymph , a clear fluid that contains white blood cells. The lymphatic system also removes excess lymph fluid from the body's tissues and returns it to the blood.
Nervous: The nervous system controls both voluntary actions, such as conscious movements, and involuntary actions,like breathing, and it sends signals to and detects signals from different parts of the body. Conscious actions are controlled by the somatic nervous system, while involuntary actions are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system dictates whether we're in " rest and digest " or " fight or flight " mode. The nervous system can further be split up into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, or the nerves connecting the CNS to every other part of the body.
Muscular: The body's muscular system consists of hundreds of muscles that aid movement, blood flow and other bodily functions, according to the Library of Congress . There are three types of muscle: skeletal, which is connected to bone and helps with voluntary movement; smooth, which is found inside organs and helps to move substances through them; and cardiac, which is found in the heart. The body's largest muscle by mass is the gluteus maximus, but the two latissimus dorsi are the largest in terms of surface area.
Related: Why is it harder for some people to build muscle than others?
Reproductive: The reproductive system allows humans to produce offspring. The male reproductive system includes the penis and the testes , which produce sperm. The female reproductive system includes the vagina, uterus and ovaries, which produce eggs. During fertilization, a sperm cell will fuse with an egg cell that, in a successful pregnancy, will then implant in the uterus. The fertilized egg will then mature into what's called a blastocyst, then an embryo and, finally, a fetus. A placenta forms to support this process.

Skeletal: Our bodies are supported by the skeletal system , which contains between 206 and 213 bones in an adult human body, due to slight variations in people's anatomy, according to the medical resource StatPearls . These bones are connected by tissues called tendons, ligaments and cartilage. As infants, humans have about 300 bones , but some fuse together as the child grows. The skeleton not only helps us move but is also involved in the production of blood cells and the storage of calcium. The teeth are also part of the skeletal system, but they aren't considered bones . The smallest bones in the body are found in the ear, and the largest is the femur, or thigh bone, which is also one of the heaviest body parts .
Respiratory: The respiratory system allows us to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide through breathing. It includes the lungs ; trachea, or windpipe; and the diaphragm, a muscle that pulls air into and pushes air out of the lungs.
Urinary: The urinary system helps eliminate a waste product called urea, which is produced when certain foods are broken down. The system includes the two kidneys; two ureters, or tubes leaving the kidneys; the bladder; two sphincter muscles; and the urethra. The kidneys filter blood in the body to make urine that then travels down the ureters to the bladder and exits the body through the urethra.
Integumentary: The skin, hair and nails make up the integumentary system. Skin is the body's largest organ . It protects our innards from the outside world, serving as our first defense against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens, for instance. Our skin also helps regulate body temperature and eliminate waste through perspiration, or sweat.
Related: Scientists discover new way humans feel touch
What are the body's vital organs?
Click the purple circles to learn about the body's vital organs, including the brain, lungs, heart, liver and kidneys. They're considered vital because you need a functioning brain, heart, liver, at least one kidney and at least one lung to survive. That said, there are medical devices and treatments that can make up for a loss of function in these organs, at least temporarily — for example, ECMO machines can do the work of the heart and lungs, and dialysis can filter the blood of people with kidney failure.
- The average adult male body contains about 36 trillion cells , the average adult female body contains 28 trillion cells and a 10-year-old has about 17 trillion.
- It's often said that there are 78 organs in the human body , but the number actually differs depending on whom you ask.
- There's a popular idea that the body replaces itself every seven years . But that's not really true, because tissues renew themselves at different rates.
- Oxygen is the most common element in the human body , followed by carbon.
- The average adult body contains about 1.2 to 1.5 gallons (4.5 to 5.5 liters) of blood .
- Humans' average body temperature has fallen slightly over time, so it's no longer 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius).
- The most detailed map of the human brain to date contains more than 3,300 types of brain cells .
What are vestigial organs?
There are arguably some parts of the human body that don't serve any useful purpose, such as the male nipple. That said, the usefulness of some organs is still up for debate , as scientists have often judged the worth of body parts before discovering their purposes.
Broadly speaking, vestigial body parts are defined as those that have lost their original physiological significance to humans over the course of evolutionary history. The idea is that, while we inherited them from an ancient ancestor, we could really do without them in the modern day.
— Scientists just discovered a new way cells control their genes — it's called 'backtracking'
— New part of the body found hiding in the lungs
— Scientists stumble upon a new part of a cell in one of the most studied animals on Earth
Wisdom teeth are held up as one example of a vestigial body part, as the modern human jaw is often too small to accommodate a third set of molars. Some people also carry remnants of a vomeronasal organ that is largely thought to be nonfunctional in humans; animals use equivalent organs to detect each other's pheromones.
Some scientists consider the human tailbone, or coccyx, vestigial because it's no longer a full-blown tail. But it's far from useless, as it still anchors many muscles, ligaments and tendons. And the appendix has gotten a bad rap for supposedly being both vestigial and useless, but more recently, scientists have uncovered possible functions for the long-maligned body part.
Ever wonder why some people build muscle more easily than others or why freckles come out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human body works to [email protected] with the subject line "Health Desk Q," and you may see your question answered on the website!
Editor's note: This page was last updated on April 5, 2024.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Rachael is a Live Science contributor, and was a former channel editor and senior writer for Live Science between 2010 and 2022. She has a master's degree in journalism from New York University's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. She also holds a B.S. in molecular biology and an M.S. in biology from the University of California, San Diego. Her work has appeared in Scienceline, The Washington Post and Scientific American.
Scientists are growing teensy hearts to learn which drugs raise risk of congenital defects
Scientists discover new type of cell in the liver
Save 20% on the LEGO Star Wars Millennium Falcon at Amazon
Most Popular
- 2 No, NASA hasn't warned of an impending asteroid strike in 2038. Here's what really happened.
- 3 James Webb Space Telescope spies strange shapes above Jupiter's Great Red Spot
- 4 What defines a species? Inside the fierce debate that's rocking biology to its core
- 5 Newly discovered asteroid larger than the Great Pyramid of Giza will zoom between Earth and the moon on Saturday
- 2 What causes you to get a 'stitch in your side'?
- 3 Tasselled wobbegong: The master of disguise that can eat a shark almost as big as itself
- 4 Self-healing 'living skin' can make robots more humanlike — and it looks just as creepy as you'd expect
- 5 This robot could leap higher than the Statue of Liberty — if we ever build it properly
- Website Inauguration Function.
- Vocational Placement Cell Inauguration
- Media Coverage.
- Certificate & Recommendations
- Privacy Policy
- Science Project Metric
- Social Studies 8 Class
- Computer Fundamentals
- Introduction to C++
- Programming Methodology
- Programming in C++
- Data structures
- Boolean Algebra
- Object Oriented Concepts
- Database Management Systems
- Open Source Software
- Operating System
- PHP Tutorials
- Earth Science
- Physical Science
- Sets & Functions
- Coordinate Geometry
- Mathematical Reasoning
- Statics and Probability
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- English (Sr. Secondary)
Hindi (Sr. Secondary)
- Punjab (Sr. Secondary)
- Accountancy and Auditing
- Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Technology
- Automobile Technology
- Electrical Technology
- Electronics Technology
- Hotel Management and Catering Technology
- IT Application
- Marketing and Salesmanship
- Office Secretaryship
- Stenography
- Hindi Essays
- English Essays
Letter Writing
- Shorthand Dictation
Essay, Paragraph or Speech on “Human Body: A Wonderful Machine” Complete Essay, Speech for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
Human Body: A Wonderful Machine
Human body is a wonderful machine. It performs several functions without rest from the birth. Our body continues to work, without stopping for a second. The main organs of the human body are lungs, heart, kidney, liver and brain. These organs work together which are controlled by the brain. Each system carries out a major function, digestive system, excretory system, circulatory system, endocrine system, nervous system, muscular system, etc. All are controlled by the brain. The brain gives us intelligence to use our physical and mental abilities. The body has more than 50,000 living cells of two hundred different types. These cells include neurons (nerve cells) and glands (specialized cells). The hormones and enzymes are produced and secreted by these glands. Various types of cells perform different functions. Cells doing similar job are grouped to form tissues. The tissues group together in a special manner to form organs.
The human body is covered by the skin. Skin is a flexible covering which protects the body. It keeps water and harmful germs out. It is war resistant. The body’s strong internal framework (skeleton) is made of 206 bones. These are connected at the joint, such as in legs. These joints help us to move. The backbone supports the head and limbs and protects the spinal cord. Between the skeleton and skin there are about 500 muscles. Nerves spread from the brain to all part of the body. They carry signals in the form of tiny electrical impulses, the sense organs, namely eyes, nose, ears, tongue and skin, pass the messages to brain through nerves. They take the instructions from brain to muscles. The brain automatically controls breathing, heart beat, digestion, etc. The body keeps on growing. The peak of physical growth is reached at about 18 to 25 years of age. When we grow old the skin becomes wrinkled and less elastic. The joints become inflexible, muscles loose, bones become weak. At the climax of life, the body gives up and death occurs.
Human body is the most valuable gift of God to human being. A healthy body contains a healthy brain. A healthy brain contains a healthy soul. As such, it is very important to take care of our body. For this regular exercise, control over eating habits, cleanliness of body and discipline are essential in daily life.
About evirtualguru_ajaygour

commentscomments
It’s good,
As a 12th grade Syrian student, I must express my admiration for the written composition that has been presented to me, as it pertains to the intricate and complex subject matter of the human body. The author has skillfully crafted a paragraph that has captured my attention and piqued my interest in this fascinating topic. The level of detail and precision in the language used is commendable, and I find myself thoroughly engrossed in the content. It is with great pleasure that I declare my appreciation for this written work, and I eagerly anticipate further exploration of this subject matter. This is truly one of the best paragraphs written in our textbook.
Oh, honestly it’s a rich text to read, learn and know more about our body.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

Popular Tags
Visitors question & answer.
- rrrr on Hindi Essay on “Pratahkal ki Sair” , ”प्रातःकाल की सैर ” Complete Hindi Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
- Mihir on CBSE ASL “Listening Test Worksheet” (ASL) 2017 for Class 11, Listening Test Audio Script 1
- Anska on Hindi Essay on “Parishram Saphalta ki Kunji Hai” , ”परिश्रम सफलता की कुंजी है ” Complete Hindi Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
- TEJAS on Hindi Essay on “Manoranjan Ke Adhunik Sadhan” , ” मनोरंजन के आधुनिक साधन” Complete Hindi Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
- Hania Shakeel on Hindi Essay on “Yadi mein Adhyapak Hota”, “यदि मैं अध्यापक होता” Complete Essay, Paragraph, Speech for Class 7, 8, 9, 10, 12 Students.
Download Our Educational Android Apps

Latest Desk
- Raudra Ras Ki Paribhasha, Bhed, Kitne Prakar ke hote hai aur Udahran | रौद्र रस की परिभाषा, भेद, कितने प्रकार के होते है और उदाहरण
- Veer Ras Ki Paribhasha, Bhed, Kitne Prakar ke hote hai aur Udahran | वीर रस की परिभाषा, भेद, कितने प्रकार के होते है और उदाहरण
- Karun Ras Ki Paribhasha, Bhed, Kitne Prakar ke hote hai aur Udahran | करुण रस की परिभाषा, भेद, कितने प्रकार के होते है और उदाहरण
- Hasya Ras Ki Paribhasha, Bhed, Kitne Prakar ke hote hai aur Udahran हास्य रस की परिभाषा, भेद, कितने प्रकार के होते है और उदाहरण।
- Example Letter regarding election victory.
- Example Letter regarding the award of a Ph.D.
- Example Letter regarding the birth of a child.
- Example Letter regarding going abroad.
- Letter regarding the publishing of a Novel.
Vocational Edu.
- English Shorthand Dictation “East and Dwellings” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines.
- English Shorthand Dictation “Haryana General Sales Tax Act” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines meaning.
- English Shorthand Dictation “Deal with Export of Goods” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines meaning.
- English Shorthand Dictation “Interpreting a State Law” 80 and 100 wpm Legal Matters Dictation 500 Words with Outlines meaning.
Human Digestion Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Factors affecting the amount of time necessary to digest food and helpful foods, digestion in organs, breakdown of fats, carbohydrates and proteins, reference list.
Digestive system is one of the most important systems of any organism. It enables the organism get nutrients which are important for functioning. The most important organs of the human digestive system are mouth, salivary glands, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, small intestine, large intestine and anus (Grosvenor & Smolin, 2012). Food travels through the digestive system and each organ contributes to rendering food into molecules or nutrients.
It is necessary to note that this travel can take from 24 hours to 72 hours. A number of factors affect the amount of time necessary for digestion. Firstly, the type of food plays an important role in this process (Gropper & Smith, 2012). Such products as vegetables, fruit and grains are rich in fibre.
Thus, fibre moves quickly through the digestive tract. On the contrary, eating a lot of meat will slow down the process as this food needs more time to be digested. Notably, physical training positively affects digestion process as it helps food move through the digestive tract. Drugs containing enzymes can also reduce the amount of time necessary for digestion. Caffeine slows down digestive processes.
Digestion starts in the mouth. Food is grinded with the help of teeth. Notably, salivary glands secrete certain enzymes which start processing food in the mouth (Gropper & Smith, 2012). Saliva also moisturises food which helps it travel to the stomach. Food moves to the stomach through the pharynx and oesophagus with the help of contractions. In the stomach, food is grinded and mixed with the help of enzymes and acid secreted by this organ.
After this, food travels to the small intestine where it is processed with the help of enzymes secreted by pancreas and bile secreted by the liver. Bile is secreted by the liver but it is first stored in gallbladder which sends it to the small intestine. The small intestine is the organ which absorbs most nutrients. When all nutrients are absorbed, the food moves to the large intestine where liquid may be absorbed. Then the food leaves the body.
There are three types of nutrients. These are fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Each type of nutrient breaks down to be used in the body. Notably, the process of breakdown is different for all three types of nutrients (Gropper & Smith, 2012). With the help of enzymes, proteins are broken down into amino acids.
These acids are used to build other types of proteins necessary for transporting molecules and catalysing numerous chemical reactions which take place in the body. Fats are transformed into fatty acids travel to blood which transports them to cells which need these acids.
Acids which are not necessary are stored in fat cells. Fats are necessary for energy. Carbohydrates are also important for energy. These nutrients are broken down into glucose which is stored in liver for a short period of time until the needs of the body are met. Then glucose which is not needed is transformed into fats which are used for energy.
On balance, it is necessary to note that digestive system consists of several organs which perform certain roles. Remarkably, people need different types of nutrients which can be acquired from different foods, e.g. vegetables, fruit, meat, fish, grains, cereals, nuts, etc. Hence, people need a balanced diet consisting of proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
Gropper, S., & Smith, J. (2012). Advanced nutrition and human metabolism . Belmont, CA: Cengage Learning.
Grosvenor, M.B., & Smolin, L.A. (2012). Visualizing nutrition: Everyday choices . Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
- Definitions of Obesity and Criteria for Diagnosing It
- Eating Disorders: Assessment & Misconceptions
- The Digestive System and Its Functions
- Digestion of a Cheeseburger
- Radio Over Fibre or Fibre Wireless Systems
- Obesity Could Be Catching
- White Wines vs. Red Wines
- Increased Nutrition Regulations on Fast Food Restaurants
- Emerging Health Issues: Child Obesity in America
- Problems and Solutions of Child Obesity
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, November 28). Human Digestion. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-digestion/
"Human Digestion." IvyPanda , 28 Nov. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/human-digestion/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Human Digestion'. 28 November.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Human Digestion." November 28, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-digestion/.
1. IvyPanda . "Human Digestion." November 28, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-digestion/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Human Digestion." November 28, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-digestion/.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
How to Write the Body of an Essay | Drafting & Redrafting
Published on November 5, 2014 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023 by Shona McCombes.
The body is the longest part of an essay . This is where you lead the reader through your ideas, elaborating arguments and evidence for your thesis . The body is always divided into paragraphs .
You can work through the body in three main stages:
- Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order.
- Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper.
- Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together.
This article gives you some practical tips for how to approach each stage.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Start with an outline, write the first draft, write the second draft, other interesting articles.
Before you start, make a rough outline that sketches out the main points you want to make and the order you’ll make them in. This can help you remember how each part of the essay should relate to the other parts.
However, remember that the outline isn’t set in stone – don’t be afraid to change the organization if necessary. Work on an essay’s structure begins before you start writing, but it continues as you write, and goes on even after you’ve finished writing the first draft.
While you’re writing a certain section, if you come up with an idea for something elsewhere in the essay, take a few moments to add to your outline or make notes on your organizational plans.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Your goals in the first draft are to turn your rough ideas into workable arguments, add detail to those arguments, and get a sense of what the final product will actually look like.
Write strong body paragraphs
Start wherever you want
Many writers do not begin writing at the introduction , or even the early body paragraphs. Start writing your essay where it seems most natural for you to do so.
Some writers might prefer to start with the easiest section to write, while others prefer to get the most difficult section out of the way first. Think about what material you need to clarify for yourself, and consider beginning there.
Tackle one idea at a time
Each paragraph should aim to focus on one central idea, giving evidence, explanation, and arguments that relate to that idea.
At the start of each paragraph, write a topic sentence that expresses the main point. Then elaborate and expand on the topic sentence in the rest of the paragraph.
When you’ve said everything you have to say about the idea, move onto a new paragraph.
Keep your argument flexible
You may realize as you write that some of your ideas don’t work as well as you thought they would. Don’t give up on them too easily, but be prepared to change or abandon sections if you realize they don’t make sense.
You’ll probably also come up with new ideas that you’d not yet thought of when writing the outline. Note these ideas down and incorporate them into the essay if there’s a logical place for them.
If you’re stuck on one section, move on to another part of the essay and come back to it later.
Don’t delete content
If you begin to dislike a certain section or even the whole essay, don’t scrap it in fit of rage!
If something really isn’t working, you can paste it into a separate document, but keep what you have, even if you don’t plan on using it. You may find that it contains or inspires new ideas that you can use later.
Note your sources
Students often make work for themselves by forgetting to keep track of sources when writing drafts.
You can save yourself a lot of time later and ensure you avoid plagiarism by noting down the name, year, and page number every time you quote or paraphrase from a source.
You can also use a citation generator to save a list of your sources and copy-and-paste citations when you need them.
Avoid perfectionism
When you’re writing a first draft, it’s important not to get slowed down by small details. Get your ideas down on paper now and perfect them later. If you’re unsatisfied with a word, sentence, or argument, flag it in the draft and revisit it later.
When you finish the first draft, you will know which sections and paragraphs work and which might need to be changed. It doesn’t make sense to spend time polishing something you might later cut out or revise.
Working on the second draft means assessing what you’ve got and rewriting it when necessary. You’ll likely end up cutting some parts of the essay and adding new ones.
Check your ideas against your thesis
Everything you write should be driven by your thesis . Looking at each piece of information or argumentation, ask yourself:
- Does the reader need to know this in order to understand or accept my thesis?
- Does this give evidence for my thesis?
- Does this explain the reasoning behind my thesis?
- Does this show something about the consequences or importance of my thesis?
If you can’t answer yes to any of these questions, reconsider whether it’s relevant enough to include.
If your essay has gone in a different direction than you originally planned, you might have to rework your thesis statement to more accurately reflect the argument you’ve made.
Watch out for weak points
Be critical of your arguments, and identify any potential weak points:
- Unjustified assumptions: Can you be confident that your reader shares or will accept your assumptions, or do they need to be spelled out?
- Lack of evidence: Do you make claims without backing them up?
- Logical inconsistencies: Do any of your points contradict each other?
- Uncertainty: Are there points where you’re unsure about your own claims or where you don’t sound confident in what you’re saying?
Fixing these issues might require some more research to clarify your position and give convincing evidence for it.
Check the organization
When you’re happy with all the main parts of your essay, take another look at the overall shape of it. You want to make sure that everything proceeds in a logical order without unnecessary repetition.
Try listing only the topic sentence of each paragraph and reading them in order. Are any of the topic sentences too similar? Each paragraph should discuss something different; if two paragraphs are about the same topic, they must approach it in different ways, and these differences should be made clear in the topic sentences.
Does the order of information make sense? Looking at only topic sentences lets you see at a glance the route your paper takes from start to finish, allowing you to spot organizational errors more easily.
Draw clear connections between your ideas
Finally, you should assess how your ideas fit together both within and between paragraphs. The connections might be clear to you, but you need to make sure they’ll also be clear to your reader.
Within each paragraph, does each sentence follow logically from the one before it? If not, you might need to add new sentences to make the connections clear. Try using transition words to clarify what you want to say.
Between one paragraph and the next, is it clear how your points relate to one another? If you are moving onto an entirely new topic, consider starting the paragraph with a transition sentence that moves from the previous topic and shows how it relates to the new one.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write the Body of an Essay | Drafting & Redrafting. Scribbr. Retrieved July 17, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/body/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

COMMENTS
Human body is made up of many different parts. Let us introduce our kids to different body parts and their functions, through the BYJU'S human body essay in English.
High-quality essay on the topic of "Human Body" for students in schools and colleges.
Human Body Essay: Human body is truly a marvel. It is perhaps the most evolved living thing. It is, in fact, like a highly sophisticated machine. You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more. Short Essay on Human Body 200 Words for Kids and Students in English Below we have given a […]
The human body, the physical substance of the human organism, is composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Human anatomy and physiology are treated in many different articles. For detailed discussions of specific tissues, organs, and systems, see human blood; cardiovascular system; digestive system, human; endocrine system, human ...
The human body is the physical substance of the human organism. Characteristic of the vertebrate form, the human body has an internal skeleton with a backbone, and, as with the mammalian form, it has hair and mammary glands. Learn more about the composition, form, and physical adaptations of the human body.
The human body is very complex. It is like a job. You have to do a million things in one day to make it through the day. The body uses nine systems to do all of those jobs. They all have separate functions, but some work together. Each system is also made up of organs. There are many ways to care and protect the systems from the many different problems they can have. There are also many ...
The Institute of Human Anatomy's YouTube video, " The Anatomy of Pain ," visually explores the structures involved in pain's transmission and processing. The video was selected because it provides an excellent illustration of the physical basis for pain. The new knowledge acquired is that there are two facets to every person's ...
The Beauty of The Human Body. The body image has passed through history, where it has been concerned with the beauty of the human body. Every change in the society around it, the emergence of the media, the change of culture, and its impact on other cultures affect people's thinking of their body, but these changes in their lives are not ...
High-quality essay on the topic of "My Body" for students in schools and colleges.
High-quality essay on the topic of "Human Body System" for students in schools and colleges.
Every human being, tissues, human body parts and the organ systems are made up of cells- the fundamental unit of life. Anatomy is the science of understanding the structure and the parts of living organisms.
This essay discusses the fundamental role of water in the human body. It highlights how approximately 60% of our body weight is composed of water, which is essential for various physiological processes.
Get introduced to the major organ systems of the human body! You'll learn some general anatomy (a roadmap of your body), learn how the arm bone actually connects to the shoulder bone, and how the different organs work together to keep you alive.
Introduction Human biology is a field in biology that deals with nutrition, anthropology, and medicine. The body of a human being contains a digestive system that deals with the digestion and absorption of food nutrients into the body. The stomach, small intestines, and large intestines are part of the digestive system.
View our collection of human body essays. Find inspiration for topics, titles, outlines, & craft impactful human body papers. Read our human body papers today!
Essay On Human Body. 924 Words4 Pages. The human body is an amazing thing made up of many different parts. These parts are cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. For starters, one type of cell makes up one type of tissue. Next, two or more types of tissues make an organ.
Looking for a good essay, research or speech topic on Anatomy? Check our list of 103 interesting Anatomy title ideas to write about!
500+ Words Essay on Health and Fitness We have always heard the word 'health' and 'fitness'. We use it ourselves when we say phrases like 'health is wealth' and 'fitness is the key'. What does the word health really mean? It implies the idea of 'being well'. We call a person healthy and fit when he/she function well physically as well as mentally.
This page discusses the anatomy of the human body systems. Click now to learn everything about the all human systems of organs now at Kenhub!
Learn all about the human body's many systems and some of its individual organs, both vital and vestigial.
The human body has been regarded as a machine which has to do certain kinds of work or perform certain functions. These functions are: (i) Motion and locomotion (ii) Nutrition, which includes the digestion of food, respiration or breathing, the circulation of the blood etc.
Essay, Paragraph or Speech on "Human Body: A Wonderful Machine" Complete Essay, Speech for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes.
The most important organs of the human digestive system are mouth, salivary glands, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, small intestine, large intestine and anus (Grosvenor & Smolin, 2012). Food travels through the digestive system and each organ contributes to rendering food into molecules or nutrients.
The body is the largest part of an essay. You should start with an outline of its structure, but you can change the organization as you write.
Most of your marks in your UPSC Essays depend on the quality of the body of your essay. How to use the techniques of L.E.D and 4 blocks of Body Building to enrich this most important segment? Let's learn.