Home > Blog > Employment Based Immigration

The Complete Guide to the L1 Business Plan: 7 Helpful Tips for a Solid Case

Last Updated On: September 29, 2023 | Published On: March 21, 2017

Immigration law is complex, to say the least. Obtaining a visa is often a long process that requires applicants to adhere to strict requirements. That’s why, if you’re going through the L1 visa process, it’s always a good idea to have an L1 business plan if you are looking to maximize your chances of success.
L1 Background
If you are a foreign professional or business owner who is in the market for a visa, then you have several options to choose from. In this post, we’ll cover the best strategy for an L1 visa for employee transfers. We’ll start with a brief background on this helpful visa.
The L1 is a nonimmigrant visa classification that is designed for multinational employers to transfer their employees from a branch or affiliate in a foreign country to one that is based in the U.S. These employees can be managers , executives, or employees with specialized knowledge.
If you and your employer qualify according to these guidelines, then the most difficult aspect will most likely be proving that your position falls under the USCIS regulations for either a manager, executive, or specialized employee (this last position being the most difficult to prove and therefore resulting in the most denials).
Your employer will also need to prove that the branch or affiliate, whether it is new or previously established, has the potential for growth that will allow the USCIS to project a positive impact on the U.S. economy and job market.
Is an L1 Business Plan Required?
The official USCIS regulations do not state that an L1 business plan is required to obtain a visa. However, as previously stated, the main difficulty lies with convincing the USCIS that your position is legitimate and that the business is set up with the potential to succeed.
Because of that, having an L1 business plan is invaluable and often necessary to gain approval . In fact, very few L1 visas are granted to those whose employers do not present viable business plans to the USCIS. That’s why we’ll be covering what you need to know in order to create a plan that will maximize your potential for approval.
However, an online guide should not be a substitute for qualified legal counsel. It is important to always retain an immigration attorney whenever working through the issues surrounding immigration law. This will help avoid unnecessary and costly mistakes.
Tips for Creating a Solid Business Plan
The idea behind the business plan is to get it right the first time. After reading your plan, the immigration officers at the USCIS should have no questions regarding the nature of your business, your competitiveness in the industry markets, or how your transferee fits into the plan.
So without further ado, here are seven helpful tips for developing an effective L1 business plan.
Tip #1: Organize Necessary Documents
Step one to any immigration filing process is to identify which documents are required and to organize them in an easy-to-access way. Here is a quick list of the required documentation for your business plan:
- Proof of a rented or bought physical premises for the U.S. branch. This can be through either the lease or the deed to the premises.
- Statements related to the foreign branch’s finances over the last three years.
- A chart showing the organizational hierarchy within the foreign branch and another chart showing the expected hierarchy in the U.S. branch over the next five years.
- If you are buying a company or franchise, you will need the buy-sell agreement for that deal.
- Documents that support your business whether it is a corporation or an LLC.
- The L1 visa beneficiary’s resume as well as the resumes of all managers in the company.
- Documents that give evidence to whether the foreign branch is either the parent company or an affiliate of the company.
Tip #2: Give a Summary of Your Business
Because the immigration officer will encounter your business summary first, it is important to make this part water-tight . Your summary should be brief but packed with information. It should be one page long and include the following items about both the U.S. company and the foreign parent or affiliate:
- When your company was founded and who founded it
- Who currently owns the company
- What kind of business your company conducts
- Where your company has its premises
- What your company’s goals are
- How you plan to grow your business
- What the target market is
- How many employees currently work at the company
- What the L1 visa holder will be doing in the U.S. branch or affiliate
- How many employees the company plans to hire in the first five years
- A statement of projected revenue through the first five years
Tip #3: Demonstrate the Structure of Ownership
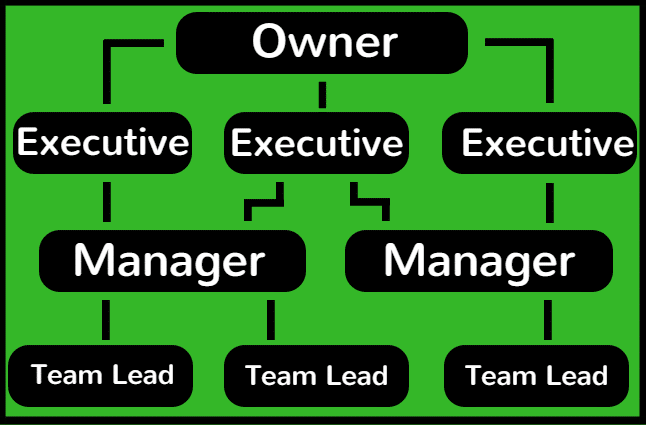
Tip #4: Explain Your Business’s Industry
This section should be written in a way that makes the immigration officer aware of the particulars and details associated with your particular industry. For example, if you have a web marketing business, then it would be important to highlight some of the specifics that go into this business such as content creation, analytics, and research.
Tip #5: Understand the Market
Or rather, have the immigration officer understand the market. It is not only important that you highlight the industry itself, but also your company’s place in it . You must prove that your company will be able to enter the U.S. market through a careful analysis of how it differs from the market in your foreign branch. So your business plan should present your market in a way that shows how the industry as a whole is growing and how you plan to grow with it.
Tip #6: Perform Competitor Analysis
One of the hallmarks of marketing is to analyze your competitors. Each successful business keeps close tabs on their competitors, and you should too. Doing this can help alert you to changes or updates in the industry and give you an idea of what is working and what isn’t. Having a detailed competitor analysis report can show the USCIS that you are a serious company that is willing to put the effort necessary to succeed.
Tip #7: Show How You Plan to Grow Your Business
This should be a detailed plan involving strategies for marketing, expansion, and personnel growth. However, while the temptation may be strong to bolster this with unrealistic growth expectations to impress the immigration officer, this strategy is often the cause of rejections and denials. Therefore, it is important to present a practical growth business plan.
Tip #8: Show Your Financial Projections
Here, you should endeavor to show a detailed report of your company’s previous financial growth and how that is projected to continue on to the U.S. branch or affiliate through the L1 holder. Again, like in the previous tip, it is important not to embellish these projections . Take a very realistic approach to this plan as anything else threatens to arouse the USCIS suspicions that you or your employees are trying to enter the U.S. fraudulently.
At the end of the day, the immigration officer needs to be relatively certain that your business and proposed growth will be a valuable asset to both the U.S. economy and job market. It can be easy to think of this L1 business plan as any other plan you would develop for an investor or merger. However, this immigration plan should be created with the intention of highlighting the positive impact your company is projected to make in the U.S.
How VisaNation Law Group Immigration Attorneys Can Help
If you are interested in petitioning for an L1 visa, then the only thing more important than having a solid L1 business plan is having an experienced immigration lawyer helping you. Many of the common mistakes that people make during the filing process that result in rejections can easily be avoided by retaining a qualified attorney.
VisaNation Law Group’s L1 lawyers have extensive experience working with multi-national companies and their employees alike to help them develop the business plans that are crucial to L1 visa approval. To speak with a VisaNation Law Group attorney, you can fill out our contact form and schedule a consultation today.
Tags: L-1 Visa
Share this article
- Citizenship
- Employment Based Immigration
- Family Based Immigration
- Immigration News
- Investment Based Immigration
- Marriage Green Card
- Other Immigration Matters
- PERM Labor Certification
- Perspectives
Immigration Tips
Home Blog Business Plan Step by Step L1 Visa Business Plan Guide
Step by Step L1 Visa Business Plan Guide
Home » Step by Step L1 Visa Business Plan Guide
Recent Posts
- Unlocking the Potential of Your Business June 6, 2024
- The Importance of a Well-Crafted Business Plan June 6, 2024
- Managing Change Effectively with a Business Plan Consultant June 6, 2024
- Implementing Strategic Partnerships with a Business Plan Writer June 6, 2024
- Boosting Revenue with a Business Plan Writer June 6, 2024
There’s no content to show here yet.
Ready To Get Started?
Our team of business consultants can provide you with one-on-one consulting and strategic advisory to launch or grow your business.
SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
- Unlocking the Potential of Your Business
- The Importance of a Well-Crafted Business Plan
- Managing Change Effectively with a Business Plan Consultant
- Implementing Strategic Partnerships with a Business Plan Writer
- Boosting Revenue with a Business Plan Writer
- Business Plan
- Business Plan Writer
- Client Press

As one of the members of the Go Business Plans business plan team, the most important question that every visa applicant has to ask when creating a business plan is: What will my business bring to the U.S.?
An immigration business plan may seem like a regular business plan but it actually has a very different audience. An immigration business plan seeks to fulfil the main visa requirements set by United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). Immigration business plans are not written for investors who may or may not invest in your business or for a bank that may or may not loan money or open a credit line. An immigration business plan is for an immigration officer who will decide whether or not your application should be approved. Our team at Go Business Plans regularly completes more than 300 immigration business plans every year. We have a 100% approval rate and our L1 visa business plan writers and consultants can help you complete your business plan. There are four major requirements you must fulfill to apply for an L-1 Visa:
Requirement 1 The petitioning U.S. entity must have a qualifying relationship with your entity abroad.
Requirement 2 Sufficient physical space must be secured for a new office.
Requirement 3 A new office must be active and operating within one year after the L-1’s admission to the United States if requesting an extension of stay.
Requirement 4 After 1 year the new office must support a managerial or executive position if you are requesting an extension of stay in the L-1A classification.
Essentially, the USCIS wants to know the ways your business can be valuable for the country and the way it can be beneficial overall. This can be portrayed through a number of ways including but not limited to: the number of jobs created, the added value your services or products will bring to customers, the investment that is put at risk while setting up your business and through the sustainability of your business. In the following guide, we have laid out the key components that your L1 Visa Business Plan should include to give yourself the best chance to secure your visa and fulfill the aforementioned requirements.
SECTION 1: GATHER NECESSARY DOCUMENTS
Having all necessary supporting documentation is the most important step in the L1 visa business plan writing process. It will be much easier to write the plan once you have gathered all of the documents. To write a detailed L1 visa business plan, you will need the following documentation:
- Lease or deed agreement if you are renting business space, or buy-sell agreement if you are using company-owned business space
- Foreign company’s financial statements for each of the past three years
- Current organizational chart of the foreign company and expected organizational chart of the U.S. company in year 5
- Business buy-sell agreement if you are purchasing an existing business, or franchise agreement if you are purchasing a franchise
- Articles of incorporation or articles of organization depending on whether your firm is a corporation or a limited liability company
- Resume of the applicant and resume of employees already hired and occupying management positions
- List of capital invested by the applicant including expenses already incurred and the working capital remaining
- Finally, you need to determine if the foreign company is a parent company or an affiliated company
Again, having your documents readily on hand will make your writing process with GoBusinessPlans much smoother.
SECTION 2: TONE, STRUCTURE, GRAMMAR, AND PROOFREADING
What is said in the business plan and how its said is equally important when it comes to your immigration business plan. In order to complete your business plan at the optimal level, we follow the following guidelines:
- If the company is already in operation, use present tense; if not, use future tense
- Stay away from passive language and use active verbs instead
- Use concise sentences
- Do not use contractions
- Do not use familiar or slang words
- Always use the third person when speaking of the applicant
- Company should be addressed as “Company, LLC” or “Company, Inc.”
- Try to include photos of the company’s location, website, social media sites, flyers, etc.
Finally, you will want to have somebody else proofread your business plan. You will of course proofread your own business plan several times yourself, but having an outsider’s perspective is always helpful.
SECTION 3: BUSINESS OVERVIEW
The business overview is the first thing that the application reviewer will read. The business overview is also called the executive summary. The executive summary needs to be concise and well prepared, as it is a summary of the entire immigration business plan. Executive summaries are usually one to four pages long and list: the nature of the company, expansion strategy, target market, marketing strategy, and number of employees.
In order to prepare the best business overview, you should answer the following questions in your executive summary:
- When was the business created?
- Who are the business’ owners?
- What does the business do?
- Where is the business located?
- What is the business’ mission?
- What is the business’ expansion strategy?
- Who is the business’ target market?
- What is the business’ marketing strategy?
- What does the business’ foreign parent or affiliate company do?
- How many employees are there?
SECTION 4: FOREIGN BUSINESS OVERVIEW
The foreign business overview will include the foreign company’s business model, history, and market position. The purpose of this section is to give the USCIS an overview of the parent company’s activities, to prove it is financially stable, and to show how it is able to grow and sustain a business in the United States. The same questions that were presented in SECTION 3 should be answered for the foreign business overview. You should also add information or photos regarding the products or services offered by the foreign company, describe its position in the marketplace, quickly outline its competitors, and describe its expansion strategy for the next five years. Additionally, you should include information about the foreign business’ revenue growth over the last five years, its net worth, its employee count, and any awards or national certificate.
If you want to further improve your foreign company’s summary you can include information about the foreign company’s industry and market in its country. Although this is not necessary, it will show that the foreign company is in a growing industry and has a strong and sustainable potential for future growth.
Note: Do not forget to convert foreign currency to USD and to include the exchange rate, the source you obtained it from, and the date you obtained the rate you used.
In addition to the executive summary of the foreign business, you should also include a concise overview of the management team of the business. This can include an organizational chart of the foreign company and a description of its team. This section will provide the USCIS with a more precise description of the foreign company’s organizational structure.
SECTION 5: LOCATION
Location is everything when it comes to your business and this must be reflected in your immigration business plan. Choice of location is sometimes the ultimate marker of success for a business and may bring an enormous change in customer base for any given business. Therefore, showing that you have already signed or entered a lease gives credit to your business. This is also one of the most important factors that an immigration officer looks for in your plan.
You should use the information in your lease agreement, deed agreement, or buy-sell agreement to show the address where the business will operate, the premises, the square footage, and if it is an office with storage space. Remember that the square footage of an office cannot be less than 500 square feet. If you have a professional photo of the location or if you have renovated, you should include them here as well. You may also add the date the lease was signed, the length of the lease, with which company the leased was signed, the yearly base rate, and the yearly increase rate.
If you want to further improve your location section, you can include a map with your business on it, the business days and hours of operation, and an email address or phone number where customers will be able to reach you.
SECTION 6: OWNERSHIP
The structure of the company is vital for the business plan because it tells the immigration officer the number of people with decision-making power within the company. Use the information in the articles of incorporation or the articles of organization to complete this section. From an immigration point of view, it is necessary that the applicant proves majority ownership over the company.
This section should also show the company’s ownership structure (limited liability company, corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, etc.), the date of incorporation, and details about the owner. Any graphics that show investments of each shareholder is also a great way to show the immigration officers a clear and concise layout of ownership and structure of the company.
SECTION 7: BUSINESS OFFERINGS
This section should include a short description of your business, the products and/or services your business offers, as well as a description of your business’ suppliers. Below is more detailed information for each of these three sections.
Business description — Writing a short description of your business can be difficult, but it is necessary for you to summarize what you do in just a few sentences — similar to an elevator pitch. Do not provide too much information about the business offerings here, but instead focus on the overall goal, mission, and reason that the company exists in as few, concise, and descriptive sentences as possible.
Offerings description — The goal here is to describe the offerings your company will provide, as well as the ways in which the company will deliver its offerings. No matter the size of your product and service offerings list, you want to create simple and understandable categories. For each offering category, you must list and provide a description of your company’s products or services, include examples of specific products or services, and write why each specific product or service answers a need for the targeted market. Providing photos and price points are also great things to include.
Suppliers description — The importance of your business’ suppliers depends on what you are offering and what your activity is. If you know who your suppliers will be, you should mention them, as this improves your chances of getting approved. You should also emphasize why your business will be successful based on your relationship with the suppliers. If you have an exclusive distribution contract with your supplier, this is a great thing to indicate as well.
SECTION 8: INDUSTRY
The industry analysis gives the application reviewer a full understanding of the industry the company will be operating within. The industry analysis should include trends of the industry over the last five years how it has evolved, its current state, and the industry forecast for the next five years. The industry analysis section should also include data about the industry’s annual sales, yearly growth rates, sales forecasts for the next five years, and a summary about the industry’s future.
The goal in this section is to show that there is an environment where your company can grow within its industry. In general, you will want to edit out any negative data, statistics, or anecdotes about the industry that your company is operating within, and make sure to really highlight the positive aspect. Additionally, you should show how certain statistics and data speak to your company, and how your company will continue to enhance the industry in return.
SECTION 9: MARKET
The purpose of this section is to show that you have to know who your customers and clients are, and that you have a good idea of who you will target. These things will show that you understand your business and will give you a leg up when it comes to the immigration officer reading your application. In the beginning of this section, you should be sure to list which state, city, and neighborhood your company will be located, describe the median income or poverty level, and indicate if and how the city is ideal for the type of business you will establish. Below are further sub-sections you should include in your Market section:
Geography — Present the average annual revenue per business for firms operating in the same industry and area as your company. This will show that your company has the potential to generate revenue and that there will be a demand for the type of products or services that your company will offer.
Competition — Outlining competitors in the area gives an idea of how hard it will be for your business to obtain market share. However, having competitors does not always mean bad luck for your company. If the area you operate within has a demand for your offerings, competitors can actually be good for your business, and this should be detailed in your business plan. You can also display a map where competitors can be found.
Target Market — In this sub-section you will want to answer the following questions:
- Who are your customers?
- What is your target market’s predominant gender?
- What age are the individuals within your target group(s)?
- Where do the individuals within your target group(s) live?
- What are the jobs of individuals within your target group(s)?
- How much do the individuals within your target group(s) earn?
- What factors may cause your target group(s) to not want to or to not be able to purchase your products or services?
While these are all important questions to answer, feel free to answer as many questions as you can think of to further define this target market. The more you know about your target market the more you will convince the application reviewer that you know your business and you know how to operate within the industry.
SECTION 10: COMPETITION
One of the key features of great business plans is highlighting competitors to the company and showing how the company will out perform the competitors. Furthermore, the competition analysis section shows how the company does or will do compared to its competitors, and should include a table comparing the business to its competitors. The table should summarize each competitor’s business overview, the products and services offered, the average price, the targeted audience, the segmentation of the products and services offered, and the company’s ability to specialize and improve its efficiency.
There should also be a small section at the end of the competition section that highlights your business’ advantages over its competitors. The purpose of this section is to show that the company will thrive in its location and will be able to surpass its competitors. You can also list the competitors that the parent company faced in the country of origin, as some may differ from the United States.
SECTION 11: MARKETING
Your marketing strategy is vital in helping you reach and attract your target market. Currently, online marketing is the main focus of many marketing strategies and efforts for companies all over the globe. However, there are several forms of marketing strategies that must be considered and put into place. Below is a list and short description of these strategies:
Search Engine Optimization — Search engine optimization (SEO) campaigns help a website to appear on the first page of results when typing certain words into a search engine such as Google or Yahoo. Appearing on the first page of results is vital because very few internet browsers click to the second page of results. Therefore, it is important to dedicate a certain amount of your financials to SEO every month.
Social Media — Having a website is no longer enough to market your business. There are target markets on every social media network and they are waiting to be engaged. Social media has many advantages, such as directly conversing with your target market, finding new ways to grow your business, and increasing the company’s online exposure. You can also list the social media sites that the parent company used in the country of origin, as some may differ from the United States.
Print, TV, And Radio Advertising — Print, TV, and radio advertising offer the the company a way to explain their product or services in traditional formats. Brochures, commercials, flyers, and letters can all be effective marketing techniques. Include information about the traditional media you will be using, their targeted audience, and why using them would be beneficial to the company. You can also list the traditional formats that the parent company used in the country of origin, as some may differ from the United States.
Trade Shows — Trade shows are an efficient way to showcase the company’s products to an interested audience and potential customers. More importantly, attending trade shows is an advertising opportunity where you can also have media exposure. You can also list the different types of trade shows that the parent company used in the country of origin.
While the above are certainly not all of the marketing strategies available, they are the main ones that many business implement.
Finally, you should include a marketing timeline in this section. The marketing timeline should summarize all of your marketing strategies and give an idea of your marketing strategy as a whole. The timeline will include when each campaign will begin and state the marketing goals that you are hoping to reach. You can also briefly list the marketing timeline for the parent company and how it benefitted the business in the country of origin.
SECTION 12: MANAGEMENT
This is the most important section of your L1 visa business plan because it displays your ability to efficiently and effectively manage your business and manage a team of qualified employees. Make sure you explain the information in this section as clearly as possible because the number one reason that L-1 applications receive denials is the USCIS’s dissatisfaction with the sufficiency, clarity, feasibility, or level of detail in the personnel sections. In addition, it is recommended for the foreign company to have been established for at least three years and to be able to show the financial status of the foreign company over the past three years. This will allow the USCIS to decide whether or not the foreign company can support the U.S. company.
Before you start this section, you must again start gathering documents including:
- Resume of applicant
- Resumes of all employees already hired that operate at managerial positions
- Employees’ positions, salaries, and job descriptions
Once you have gathered all of the resumes and information you can begin outlining each employee. This section should include outlines that consist of:
- A description for all the employees already hired
- A description for all the employees the company plans to hire
- Year of hiring
- Tasks, roles, and responsibilities
- How they will contribute to the growth and success of your company
- How qualified the person should be
Note: Keep in mind that you can increase your chances of getting approved if you state that you expect to hire at least five employees by the end of year 5.
It is not only important to present what your employees will be doing, but it is also important to provide the detailed personnel numbers, including the number of employees per each position and employee salaries. This will allow the application reviewer to see how realistic your personnel plan is, and will provide a concrete number showing how high your taxable salary mass will be, which is of high interest to the USCIS.
Hiring Strategy
This portion of the management section explains how many employees the company will hire from year 1 to year 5. This can include an explanation for the increase in personnel using information from the sales forecast and also to justify the payroll for employees that receive tips or the equivalent. If your company plans to hire contractors or part-time workers, include a description of their job responsibilities and add them to the personnel tables. You can begin by indicating the payroll expenses in years 1 and 5.
Applicant’s Role
Remember that you are also an employee of the company, so you must include your detailed job description as well. Usually, you should emphasize your importance and how the company cannot operate without you. You should be at the top of the management pyramid, and have a minimum of three managers below you in the pyramid by the end of the first year of operations. Additionally, you will need to outline your involvement in the business. This will need to be broken down into year 1 and year 5 increments as detailed below:
Applicant’s Time Allocation in Year 1
This section is a specification for the L-1 visa application, and is extremely important for the business plan. This part requires a lot of detail that may be better organized into a table. This table should include:
- The specific tasks that will be completed by the applicant (classified by department and employees involved)
- The amount of time the applicant will allocate to each task (as a percentage of the applicant’s total available working time)
- The other positions in the company that will be involved with and affected by each task that the applicant is completing
Applicant’s Time Allocation in Year 5
This part highlights the importance of the applicant in the U.S. company by emphasizing each task that will be performed by the applicant in the company’s fifth year of operations. However, the goal of this section is different from the goal of the previous section. Here is where you show that in the company’s fifth year of operations, the applicant’s only role will be to supervise and oversee tasks — not to perform hands-on activities.
SECTION 13: FINANCIALS
The financials section is the backbone of your L1 visa business plan. This will show your company’s expected growth using revenue, costs of production, and net profit for the coming five years. A typical L-1 financial projection plan is composed of six sections: investment summary, sales forecast, feasibility analysis, profit and loss statement, break-even analysis, and the balance sheet. Below is a breakdown of what each section should include:
Investment Summary — For L-1 visa applications, the investment summary section is optional, but it could strengthen your L-1 application. The categories that typically qualify as investment are working capital, professional fees, starting inventory, equipment, rent, and marketing expenses. This part should be completed with a lawyer’s approval, as all expenses need to be proved to the application reviewer.
Sales Forecast — This is educated guessing, so do not expect to get this section perfect. However, you do want to make this section reasonable. A sales forecast should show the following items:
- The number of products or services you will sell during each of the next five years
- The price per unit of your products or services for each of the next five years
- The total revenue of your company
- The cost per unit for each of your products or services
- The total cost of goods sold for the next five years
Feasibility Analysis — The feasibility analysis explains how the company will reach its sales growth from year 1 to year 5. The feasibility study’s goal is to prove that the company’s total revenue estimate in each of the coming five years will be achieved by its substantial investment into marketing and sales efforts, as well as by the influence of external factors such as exponential industry growth.
Note: In 2016, there was an increase in the number of requests for evidence issued by the USCIS because of nonexistent, poorly prepared, or vague feasibility analyses submitted by L-1 visa applicants. Therefore, this section should be created with extreme care.
Profit and Loss Statement — The profit and loss statement summarizes company’s sales and expenses. This portion also calculates net profit. You can decide over how long of a period you would like to depreciate your long-term assets, but it is usually recommended that you depreciate them over 5 or 10 years.
Break-Even Analysis — The break-even analysis determines whether and when your business will start covering all of its expenses and begin to make a profit. The key to this portion is to have a clear understanding of your company’s operating business expenses, sales, and cost of sales in each period. Identify your costs in each period to help determine the revenue needed to pay ongoing business expenses.
Balance Sheet — It is highly recommended to include a balance sheet in the financials section. The balance sheet summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. The balance sheet is an overview of the company’s financials, and proof of the company’s health. The balance sheet is composed of sections for assets, liabilities, and equity.
If you need help with your business plan, please don’t hesitate to contact us by clicking this link . We have successfully completed more than 1200+ L1 visa business plan projects and look forward to working on your business plan project.
You can learn more about our L1 visa business plan service by clicking here: https://www.gobusinessplans.com/l1-business-plan/
- Author Details
- Service Area
- Our Clients
- Frequently Asks Questions
Services Overview

- Business Plan Writers

- Investor Presentation

- Business Plan Consultants

- Bank Business Plan
Immigration

- E2 Visa Business Plan

- EB-5 Visa Business Plan

- L1 Visa Business Plan
Fully Customized Business Plans – No Templates
Schedule free consultation.
Our business plain team is here to help
Shedule Consulation
Our business plan team is here to help
View sample
Check example of our work

- Business Plan Consulting
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Visa Business Plans
How to Write a Winning Business Plan for L1 Visa Program
Are you applying for the L1 visa? If YES, here is a sample template on how to write a business plan for L1 visa program that is immigration compliant.
What is a L1 Visa?
The L1 visa is a temporary visa for individuals who do not want to immigrate permanently but want to become business owners, managers, or specialized knowledge employee. The L1 visa being an employment-based non-immigrant visa, it is also a “dual intent” visa. This simply means that an L1 visa holder and their dependents may apply for permanent residency without jeopardizing their L visa status.
There are many requirements for anyone looking to secure this visa. For instance, the business owner or employee must have worked for the subsidiary, head or branch office or affiliate office for at least one continuous year. The year that they were employed must be within the past three years.
Also, the U.S. company must be the parent, branch or affiliate company of the overseas company that the business owner or employee will be coming from. Note that when it comes to the L-1A Visa, it’s a particularly efficient way for small companies or even start-ups to expand their market to the united states.
Why Apply for an L1 Visa?
By leveraging this visa, a business owner (or part-owner), manager, or highly-qualified member of staff (with specialized knowledge) can come over and set up the new subsidiary exactly to the company’s specifications, making sure that standards are maintained and followed from the get-go.
Another marvellous thing about an L1 Visa is that you are also allowed to bring over your spouse and any children that you have, but your spouse will be granted an L-2 visa, allowing them to work for any company in the United States. Additionally, any of your dependent children who are under the age of 21 would also be granted an L-2 visa, allowing them to work or study while they are living temporarily in the U.S.
But just like many other types of visas offered by the U.S. Immigration Service, the L1 Visa is subject to strenuous scrutiny, particularly for smaller businesses or new start-ups. Although big multinational corporations or household names may only need a letter from the company director or minimal information to secure this kind of visa, this is not really the case for younger or less known businesses.
You should also understand that during the processing stages of this visa, providing a professional, well-written business plan detailing your expansion to the United States will greatly improve your chances of approval. With this business plan, you can show the U.S. Immigration Services (USCIS) that you mean business. Not only can this kind of plan be helpful for your immigration application, but it can also be helpful to your company as a whole.
How to Write a Winning Business Plan for L1 Visa Program That is Immigration Compliant
The L1 visa was established to allow companies to transfer employees from one of its affiliated foreign offices to one of its offices in the United States under certain conditions. It is divided in 2 types: The L1a visa allows the transfer of an acknowledged executive or manager to the company’s US office, while the L1b visa makes it possible for an employee with a special knowledge relating to the organization’s interests to be transferred.
There also is the L2 visa that is intended for the family of an L1 visa beneficiary. Agreeably, the L1 visa requirements may seem very hard at first, but they can be met with a well-developed L1 Visa Business Plan. Below is a guide on how to achieve this aim.

1. Obtain necessary documents
Being equipped with all necessary supporting documentation is the most vital step in the L-1 Visa business plan writing process. It will be much easier to write the plan once you have gathered all of the documents. To write a detailed L-1 business plan , you will need the following documentation:
- Lease or deed agreement if you are planning on renting business space, or buy-sell agreement if you are using company-owned business space
- Foreign company’s financial statements for each of the past three years
- Current organizational chart of the foreign company and expected organizational chart of the U.S. company in year 5
- Business buy-sell agreement if you are purchasing an existing business, or franchise agreement if you are purchasing a franchise
- Articles of incorporation or articles of organization depending on whether your firm is a corporation or a Limited Liability Company
- Resume of the applicant and resume of employees already hired and occupying management positions
- List of capital invested by the applicant including expenses already incurred and the working capital remaining
2. Tone, Structure, Grammar, and Proofreading
You have to understand that what is said in the business plan and how it’s said is very vital when it comes to the success of your immigration business plan. So to complete your business plan at the optimal level, follow the following guidelines:
- When company is already in operation, use present tense; if not, use future tense
- Stay away from passive language and use active verbs instead
- Use concise sentences
- Do not use contractions
- Do not use familiar or slang words
- Always use the third person when speaking of the applicant
- Company should be addressed as “Company, LLC” or “Company, Inc.”
- Try to include photos of the company’s location, website, social media sites, flyers, etc.
- Let someone else proofread it.
3. Executive Summary
Have it in mind that executive summary is the first thing that the application reviewer will go through. The executive summary needs to be concise and well prepared as it is a summary of the entire immigration business plan.
Executive summaries are usually one to four pages long they list: the nature of the company, expansion strategy, target market , marketing strategy, and number of employees. To prepare the best executive summary, you should answer the following questions in your executive summary:
- When was the business created?
- Who are the business’ owners?
- What does the business do?
- Where is the business located?
- What is the business’ mission?
- What is the business’ expansion strategy?
- Who is the business’ target market?
- What is the business’ marketing strategy?
- What does the business’ foreign parent or affiliate company do?
- How many employees are there?
4. Foreign Executive Summary
Note that your foreign executive summary is expected to include the foreign company’s , history, and market position. The objective of this section is to give the USCIS an overview of the parent company’s activities, to prove it is financially stable, and to show how it is able to grow and sustain a business in the United States.
The same questions that were presented in the main executive summary should be answered for the foreign executive summary.
You should also add information or photos regarding the products or services offered by the foreign company, describe its position in the marketplace, quickly outline its competitors, and describe its expansion strategy for the next five years.
Additionally, you should include information about the foreign business’ revenue growth over the last five years, its net worth, its employee count, and any awards or national certificate.
Also, if you want to further improve your foreign company’s summary you can include information about the foreign company’s industry and market in its country. Although this is not necessary, it will show that the foreign company is in a growing industry and has a strong and sustainable potential for future growth.
5. Choice of Location
Location is everything when it comes to your business and this must be reflected in your immigration business plan. Your choice of location is sometimes the ultimate marker of success for a business and may bring a massive change in customer base. That is why showing that you have already signed or entered a lease gives credit to your business. This is also one of the most important factors that an immigration officer looks for in your plan.
Do not forget to use the information in your lease agreement, deed agreement, or buy-sell agreement to show the address where the business will operate, the premises, the square footage, and if it is an office with storage space. Also, note that the square footage of an office cannot be less than 500 square feet.
If you have a professional photo of the location or if you have renovated, you should include them here as well. You may also add the date the lease was signed, the length of the lease, with which company the leased was signed, the yearly base rate, and the yearly increase rate.
6. Business Ownership
This particular information is very crucial in a business plan because it tells the immigration officer the number of people with decision-making power within the company. Leverage the information in the articles of incorporation or the articles of organization to complete this section. From an immigration point of view, it is necessary that the applicant proves majority ownership over the company.
Also note that this section should also show the company’s ownership structure (Limited Liability Company, corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship , etc.), the date of incorporation, and details about the owner. Any graphics that show investments of each shareholder is also a great way to show the immigration officers a clear and concise layout of ownership and structure of the company.
7. Products and Services
This very important sector is expected to include a short description of your business, the products and/or services your business offers, as well as a description of your business’ suppliers. Below is more detailed information for each of these three sections.
- Business description : Have it in mind that writing a short description of your business can be hard, but it is necessary for you to summarize what you do in just a few sentences — similar to an elevator pitch. Do not provide too much information about the business offerings here, but instead focus on the overall goal, mission, and reason that the company exists in as few, concise, and descriptive sentences as possible.
- Offerings description : Here the sole aim is to explain the offerings your company will provide, as well as the ways in which the company will deliver its offerings. No matter the size of your product and service offerings list, you want to create simple and understandable categories.
For each offering category, you must list and provide a description of your company’s products or services, include examples of specific products or services, and write why each specific product or service answers a need for the targeted market.
- Suppliers’ description : How important your business’ suppliers are depends on what you are offering and what your activity is.
If you know who your suppliers will be, you should mention them, as this improves your chances of getting approved. Do not forget to emphasize on why your business will be successful based on your relationship with the suppliers. If you have an exclusive distribution contract with your supplier, this is a great thing to indicate as well.
8. Industry Analysis
This sector of the business plan gives the application reviewer a full grasp of the industry the company that will be operating within. Make sure your industry analysis include trends of the industry over the last five years how it has evolved, its current state, and the industry forecast for the next five years.
The industry analysis section should also include data about the industry’s annual sales, yearly growth rates, sales forecasts for the next five years, and a summary about the industry’s future.
Don’t forget that the aim of this section is to show that there is an environment where your company can grow within its industry. Generally, you will want to edit out any negative data, statistics, or anecdotes about the industry that your company is operating within, and make sure to really highlight the positive aspect.
9. Business market
You will have to use this sector to show that you know who your customers and clients are, and that you have a good idea of who you will target. These things will show that you understand your business and will give you a leg up when it comes to the immigration officer reading your application.
In the beginning of this section, you should list which state, city, and neighbourhood your company will be located, describe the median income or poverty level, and indicate if and how the city is ideal for the type of business you will establish.
Be sure to present the average annual revenue per business for firms operating in the same industry and area as your company. This will show that your company has the potential to generate revenue and that there will be a demand for the type of products or services that your company will offer.
10. Direct and Indirect Competitors
You need to understand that one of the major features of workable business plans is thorough analysis of competitors to the company and showing how the company will outperform the competitors. It should include a table comparing the business to its competitors.
The table should summarize each competitor’s executive summary, the products and services offered the average price, the targeted audience, the segmentation of the products and services offered, and the company’s ability to specialize and improve its efficiency. Don’t forget to add a small section at the end of the competition section that highlights your business’ advantages over its competitors.
Note that the key aim of this section is to show that the company will succeed in its location and will be able to surpass its competitors. You can also list the competitors that the parent company faced in the country of origin, as some may differ from the United States.
11. Promotion and
Marketing strategy is very crucial in helping you reach and attract your target market. Presently, online marketing is the key focus of many marketing strategies. But, there are several forms of marketing strategies that must be considered. Below is a list and short description of these strategies:
- Search Engine Optimization : Search engine optimization (SEO) campaigns help a website to appear on the first page of results when typing certain words into a search engine such as Google or Yahoo.
- Social Media : hashing a website is no longer enough to market your business. There are target markets on every social media network and they are waiting to be engaged. Social media has many advantages, such as directly conversing with your target market, finding new ways to grow your business, and increasing the company’s online exposure.
- Print, TV, And Radio Advertising — Print, TV, and radio advertising provides the company a way to explain their product or services in traditional formats. Brochures, commercials, flyers, and letters can all be effective marketing techniques. Include information about the traditional media you will be using, their targeted audience, and why using them would be beneficial to the company.
- Trade Shows : Trade shows are an efficient way to showcase the company’s products to an interested audience. More importantly, attending trade shows is an advertising opportunity where you can also have media exposure. You can also list the different types of trade shows that the parent company used in the country of origin.
12. Business Management and Hiring Strategy
This is the most important section of your L-1 immigration business plan because it shows your ability to efficiently and effectively manage your business. Take your time and ensure you explain the information in this section as clearly as possible because the number one reason that L-1 applications receive denials is the USCIS’s dissatisfaction with the sufficiency, clarity, feasibility, or level of detail in the personnel sections.
In addition, it is recommended for the foreign company to have been established for at least three years and to be able to show the financial status of the foreign company over the past three years. This will allow the USCIS to decide whether or not the foreign company can support the U.S. Company.
Before you start this section, you must gather documents including: Resume of applicant, Resumes of all employees already hired that operate at managerial positions, Employees’ positions, salaries, and job descriptions Employees. Once you have gathered all of the resumes and information you can begin outlining each employee. This section should include:
- A description for all the employees already hired
- A description for all the employees the company plans to hire
- Year of hiring
- Tasks, roles, and responsibilities
- How they will contribute to the growth and success of your company
- How qualified the person should be
It is not only important to present what your employees will be doing, but also important to provide the detailed personnel numbers, including the number of employees per each position and employee salaries. This will allow the application reviewer to see how realistic your personnel plan is, and will provide a concrete number showing how high your taxable salary mass will be, which is of high interest to the USCIS.
Also don’t forget that the hiring strategy section explains how many employees the company will hire from year 1 to year 5. If your company plans to hire contractors or part-time workers, include a description of their job responsibilities and add them to the personnel tables. You can begin by indicating the payroll expenses in years 1 and 5.
13. Financials
This section of your business plan is the backbone of your L1 visa business plan. This will explain your company’s expected growth using revenue, cost of production, and net profit for the coming five years. Note that a good L1 financial projection plan is made up of six sections: investment summary, sales forecast, feasibility analysis, profit and loss statement, break-even analysis, and the balance sheet. Below is a breakdown of what each section should include:
- Investment Summary : For L-1 visa applications, the investment summary section is optional, but it could strengthen your L-1 application. The categories that typically qualify as investment are working capital, professional fees, starting inventory, equipment, rent, and marketing expenses. This part should be completed with a lawyer’s approval, as all expenses need to be proved to the application reviewer.
- Sales Forecast : This is educated guessing, so do not expect to get this section perfect. However, you do want to make this section reasonable.
- Feasibility Analysis: The feasibility analysis describes how the company will reach its sales growth from year 1 to year 5. The goal is to prove that the company’s total revenue estimate in each of the coming five years will be achieved by its substantial investment into marketing and sales, as well as by the influence of external factors such as exponential industry growth.
- Profit and Loss Statement : The profit and loss statement summarizes company’s sales and expenses. This portion also calculates net profit. You can decide over how long of a period you would like to depreciate your long-term assets, but it is usually recommended that you depreciate them over 5 or 10 years.
- Break-Even Analysis : The break-even analysis determines whether and when your business will start covering all of its expenses and begin to make a profit. The key to this portion is to have a clear understanding of your company’s operating business expenses, sales, and cost of sales in each period. Identify your costs in each period to help determine the revenue needed to pay ongoing business expenses .
- Balance Sheet : It is highly recommended to include a balance sheet in the financial section. The balance sheet summarizes a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. The balance sheet is an overview of the company’s financials, and proof of the company’s health. The balance sheet is composed of sections for assets, liabilities, and equity.
Always have it in mind that the USCIS alone wants to know the ways your business can be valuable for the country and the way it can be beneficial overall. This can be shown through a number of ways made up but not limited to: the number of jobs established, the added value your services or products will bring to customers and the investment that is put at risk while setting up your business.
More on Visa Business Plans
Buffalo: (716) 970-4007 | Toronto: (866) 697-1832

Buffalo: (716) 970-4007 | Toronto: (866) 697-1832
L-1 & E-2 Visas: The Need of a Immigration Business Plan

When navigating the complexities of L-1 and E-2 visa applications, a tailored immigration business plan is not just beneficial—it’s essential. Such a plan goes beyond the scope of traditional business plans by focusing on specific visa requirements and demonstrating your venture’s potential contribution to the U.S. economy. Below, we go into each critical component of a successful immigration business plan, offering insights and guidance to bolster your application.
1. Comprehensive Business Overview
Objective: This section aims to introduce your business to immigration officials comprehensively and concisely. It should lay out the foundation of your business, explaining what it does, its target market, and its unique value proposition.
Details to Include:
- Nature of the Business: Explain whether it’s a service, manufacturing, or product-oriented venture and the industry it operates within.
- Business Goals and Objectives: Outline what your business aims to achieve in the short and long term.
- Unique Selling Proposition: Highlight what sets your business apart from competitors in the same market.
2. Detailed Proof of Investment
Objective: To demonstrate your financial commitment and the viability of your business through a detailed financial plan.
- Capital Investment: Provide specifics on the amount of capital invested in the business and the sources of this capital.
- Operational Costs: Break down the operational expenses, including rent, payroll, utilities, and marketing.
- Financial Projections: A five-year financial forecast showing projected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
3. Compliance with Business Requirements
Objective: Showcase your business’s adherence to all relevant U.S. laws, regulations, and standards.
- Licenses and Permits: List all the necessary operational licenses and permits you have acquired or are acquiring.
- Regulatory Compliance: Explain how your business complies with relevant local, state, and federal regulations, including environmental, health, and safety standards.
4. Job Creation and Employment Outlook
Objective: Illustrate your business’s potential to contribute positively to the U.S. labor market.
- Organizational Structure: Present an organizational chart detailing current and future positions.
- Hiring Timeline: Offer a timeline for new hires, including the types of positions and the expected impact on business growth.
- Job Descriptions: Provide detailed descriptions for each role, emphasizing the qualifications and responsibilities.
5. Establishment of Physical Premises
Objective: Demonstrate the suitability of your U.S. business premises for operational needs.
- Location Details: Describe the location of your business, including advantages related to logistics, market access, or clientele.
- Lease or Purchase Agreements: Present evidence of ownership or lease agreements for the property.
- Facility Readiness: Discuss any modifications or preparations to ensure the facility meets your business needs.
6. In-depth Market Analysis and Strategy
Objective: To affirm your business’s viability and competitive edge within the U.S. market.
- Market Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to evaluate market conditions, competition, and potential challenges.
- Marketing Strategy: Outline your approach to capturing your target market, including digital marketing, advertising, and sales strategies.
- Long-term Sustainability: Discuss how your business plans to adapt and grow over time, ensuring long-term success.
7. Demonstrating Ability to Develop and Direct
Objective: Prove your capability to lead and grow your business effectively.
- Background and Experience: Detail your educational background, relevant work experience, and any entrepreneurial ventures, highlighting how these contribute to your ability to manage the business.
- Leadership Qualities: Share examples of leadership experience, problem-solving skills, and any recognitions or awards.
- Vision for the Business: Convey your strategic vision for growth and how you plan to achieve it.
A detailed and well-structured immigration business plan is pivotal to your L-1 or E-2 visa application. It demonstrates your commitment and capability to operate a successful business in the U.S. and how your venture will positively impact the economy. By thoroughly addressing each of these components, your business plan will stand as a robust testament to the viability and value of your business proposition, significantly enhancing the likelihood of visa approval. We recommend working with a professional business plan writer with specific expertise in immigration business plans.
Subscribe to Our Resources Blog
Schedule a Consultation with an Immigration Lawyer
- 9 FAM E Visas: Treaty Traders and Investors
- 9 FAM L1 Visas for Intracompany Transferees
- USCIS: E Visas for Treaty Traders and Investors
- USCIS: L Visas for Intracompany Transferees
- Matter of Ho – Business Plan Requirements
We Can Help!
You may have questions regarding U.S. immigration laws and visas. We invite you to contact our team at Richards and Jurusik for detailed guidance and assistance. We aim to provide the most accurate and up-to-date information to make your immigration process smoother and less stressful. The immigration lawyers at Richards and Jurusik have decades of experience helping people to work and live in the United States. Read some of our hundreds of 5-star client reviews ! Contact us today to assess your legal situation.
Similar Posts
L-1A Visa to EB-1C Green Card: A Successful Business Expansion Story
Explore the journey from an L-1A visa to a coveted EB-1C Green Card through strategic business expansion. This success story highlights the advantages, step-by-step process, and a surprisingly swift timeline, shedding light on the potential for business owners, executives, and managers to achieve US permanent residency.

Intra-Company Transfer Visas: The Matter of Chartier Case
The Matter of Chartier, decided on August 3, 1977, provides an understanding of the nuances of intra-company transfer visas (L-1 visas) under U.S. immigration law. This case particularly pertains to the transfer of international employees between the global office and a U.S. office. We discuss how this case is applied in L1 Visa cases below.

Employment Authorization for E and L Visa Spouses
In recent developments, USCIS has offered new guidance on the documentation required for employment authorization for nonimmigrant spouses under the E Visa and L Visa categories. Effective January 30, 2022, USCIS and CBP introduced I-94 codes that signify work authorization. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know:

Navigating the Complexity: A Successful L1B Visa Approval for a Technical Sales Professional
Discover the nuances of securing L1B visa approval for a Technical Sales Professional in this insightful case study. Uncover the hurdles faced and the strategies that led to a successful outcome, providing valuable insights into navigating the complexities of USCIS L1B visa approval.

Choosing a Port of Entry for TN and L-1 Visa Applications
Applying for a TN or L-1 Visa? The choice of your port of entry plays a key role in the application process. Designated ports offer enhanced expertise in processing TN and L-1 Visa applications, providing consistent treatment and increasing your likelihood of success.

L1 Visa for Non-Profit Religious Organizations: Requirements
Establishing a qualifying relationship between entities hinges on ownership and control. In the L1 visa context, “ownership” signifies the legal right to possess assets with complete control, while “control” denotes the authority to oversee entity establishment and operations. The Matter of Church Scientology International has paved the way for religious organizations to align with these standards.
- Wed. Jun 26th, 2024
The Infusion Hub
Guide to Writing an Effective L1 Visa Business Plan
By Martin Gereta
Writing an effective L1 visa business plan is crucial for companies aiming to transfer employees from foreign offices to the United States. Not only does the business plan outline the business operations and strategies, but it also serves as a key piece of evidence demonstrating the viability and necessity of the proposed transfer. Therefore, crafting a comprehensive and persuasive business plan is essential. In this guide, we will delve into the step-by-step process of writing an effective L1 visa business plan .
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
First and foremost, the executive summary is the initial section of your business plan and should provide a succinct overview of your company and its plans. Consequently, it must be concise yet informative, grabbing the reader’s attention from the start. Specifically, include the company’s background, mission, vision, and the primary objectives for the U.S. operations. Additionally, introduce key personnel, particularly the L1 visa applicant, highlighting their role and contributions to the company.
Business Description
Subsequently, the business description offers an in-depth look at your company. It should cover several aspects to ensure a comprehensive understanding:
- Nature of Business : Clearly describe the products or services your company offers. This sets the foundation for understanding the business model and market potential.
- Industry Analysis : Provide an overview of the industry, including current trends, opportunities, and challenges. This contextualizes your business within the broader market environment.
- Business Model : Explain how your company operates and generates revenue. This demonstrates the business’s sustainability and potential for growth.
Market Analysis
Furthermore, a thorough market analysis is essential to prove the viability of your business in the U.S. market. Therefore, this section should be detailed and well-researched:
- Target Market : Identify your primary customer base, including demographic and psychographic details. Understanding your target audience is crucial for tailoring your marketing strategies.
- Market Needs : Analyze the specific needs and preferences of your target market. This helps in positioning your products or services effectively.
- Competitive Landscape : Identify key competitors and analyze their strengths and weaknesses. This provides insights into market positioning and potential strategies to differentiate your business.
Organizational Structure
As a result, a clear organizational structure is vital to demonstrate the roles and responsibilities within the company. This section should include:
- Company Hierarchy : Present an organizational chart that outlines the reporting lines and hierarchy within the U.S. operations. This visually represents the company’s structure.
- Roles and Responsibilities : Provide detailed descriptions of the roles of key personnel, particularly the L1 visa applicant, emphasizing their managerial or executive capacity. This is crucial for proving the necessity of their transfer.
- Staffing Plan : Outline the current and projected staffing needs, including job descriptions and recruitment plans. This demonstrates the company’s growth potential and operational readiness.
Operational Plan
Next, the operational plan outlines how the business will function on a day-to-day basis. Key elements include:
- Location : Describe the business location(s) in the U.S. and explain why these locations were chosen. The strategic importance of the location can enhance the business’s success.
- Facilities and Equipment : Detail the facilities and equipment required for operations. This shows the practical aspects of setting up and running the business.
- Production Processes : Explain the production or service delivery processes. This provides a clear understanding of how the business operates.
- Suppliers and Vendors : Include information about key suppliers and vendors. This establishes the business’s supply chain reliability.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Subsequently, a strong marketing and sales strategy is essential to demonstrate how you will attract and retain customers. This section should cover:
- Marketing Plan : Detail your marketing strategies, including digital marketing, advertising, public relations, and promotions. Effective marketing plans are crucial for reaching and engaging your target audience.
- Sales Strategy : Outline the sales processes and tactics, including sales channels and methods for customer acquisition and retention. A well-thought-out sales strategy drives revenue growth.
- Brand Positioning : Explain how you will position your brand in the market to differentiate from competitors. Strong brand positioning can significantly impact market perception and customer loyalty.
Financial Projections
Moreover, financial projections are critical to demonstrate the financial viability and potential growth of your U.S. operations. Include:
- Revenue Projections : Provide detailed revenue forecasts for the next three to five years. This shows expected income and financial health.
- Expense Projections : Break down projected expenses, including operational costs, salaries, and marketing expenses. Understanding expenses is crucial for maintaining profitability.
- Profit and Loss Statements : Include projected profit and loss statements to show expected profitability. This reassures stakeholders of the business’s financial stability.
- Cash Flow Analysis : Present cash flow projections to ensure the business will have sufficient liquidity. Cash flow is essential for sustaining daily operations and long-term growth.
Compliance with L1 Visa Requirements
Additionally, to strengthen your L1 visa application, your business plan must demonstrate compliance with L1 visa requirements. Therefore, ensure to include:
- Qualifying Relationship : Provide evidence of the qualifying relationship between the foreign and U.S. offices, such as parent, subsidiary, affiliate, or branch. This establishes the legitimacy of the business structure.
- Duration of Employment : Prove that the L1 visa applicant has been employed with the foreign entity for at least one continuous year within the last three years. This is a key eligibility criterion.
- Managerial or Executive Role : Provide a detailed description of the applicant’s managerial or executive role in the U.S. operations. Emphasize their responsibilities and impact on the business.
Supporting Documents
Furthermore, including supporting documents can significantly strengthen your business plan. These documents provide additional evidence and context:
- Resumes of Key Personnel : Include detailed resumes of key personnel to highlight their qualifications and experience. This underscores the team’s expertise and capability.
- Contracts and Agreements : Provide copies of significant contracts, agreements, or letters of intent. These documents demonstrate business commitments and relationships.
- Permits and Licenses : Include copies of any required permits or licenses for operating in the U.S. This ensures regulatory compliance and operational readiness.
In conclusion, crafting an effective L1 visa business plan requires meticulous planning, thorough research, and a clear presentation of your business strategy and objectives. By addressing all the key elements outlined above, you can create a comprehensive and persuasive business plan that demonstrates the viability and potential success of your U.S. operations, thereby strengthening your L1 visa application. Remember, a well-prepared business plan not only supports your visa application but also serves as a roadmap for your business’s growth and success in the U.S. market. Therefore, invest the necessary time and resources to ensure your business plan is detailed, accurate, and compelling.
Related Post
Bamboo queen sheets: the ultimate guide to luxurious comfort, janet truncale: a trailblazer in leadership – top ceo news, a complete step-by-step guide to printing custom stickers, discover nadra blue area by chakor ventures: modern living redefined, choosing the best online judiciary coaching for your state exam, level up your food handling skills: online courses for uk professionals.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The L1 is a nonimmigrant visa classification that is designed for multinational employers to transfer their employees from a branch or affiliate in a foreign country to one that is based in the U.S. These employees can be managers, executives, or employees with specialized knowledge.
Our team has compiled this easy step-by-step guide to complete a L1 visa business plan from. We also offer L1 business plan writing services.
Are you applying for the L1 visa? If YES, here is a sample template on how to write a business plan for L1 visa program that is immigration compliant
Learn the key elements of an immigration business plan for an L-1 or E-2 visa application. Includes insights on investment, compliance, and market strategy.
Whether you need an L-1 Visa for a startup or an existing business, it is important to be prepared with a detailed business plan that provides evidence that the U.S. entity will support the managerial or executive positions you are planning to transfer.
By addressing all the key elements outlined above, you can create a comprehensive and persuasive business plan that demonstrates the viability and potential success of your U.S. operations, thereby strengthening your L1 visa application.