
- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions

Childhood and education
- From graduation to the “miracle year” of scientific theories
- General relativity and teaching career
- World renown and Nobel Prize
- Nazi backlash and coming to America
- Personal sorrow, World War II, and the atomic bomb
- Increasing professional isolation and death

What did Albert Einstein do?
What is albert einstein known for, what influence did albert einstein have on science, what was albert einstein’s family like, what did albert einstein mean when he wrote that god “does not play dice”.

Albert Einstein
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Wolfram Research - Eric Weisstein's World of Scientific Biography - Biography of Albert Einstein
- Nobel Prize - Biography of Albert Einstein
- PBS - A Science Odyssey: People and Discoveries: Albert Einstein
- DigitalCommons@CalPoly - Einstein’s 1935 Derivation of E=mc2
- Space.com - Albert Einstein: His life, theories and impact on science
- American Museum of Natural History - Albert Einstein
- Institute for Advanced Study - Albert Einstein: In Brief
- Famous Scientists - Albert Einstein
- The MY HERO Project - Albert Einstein
- Jewish Virtual Library - Biography of Albert Einstein
- Albert Einstein - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- Albert Einstein - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Albert Einstein was a famous physicist. His research spanned from quantum mechanics to theories about gravity and motion. After publishing some groundbreaking papers, Einstein toured the world and gave speeches about his discoveries. In 1921 he won the Nobel Prize for Physics for his discovery of the photoelectric effect .
Albert Einstein is best known for his equation E = mc 2 , which states that energy and mass (matter) are the same thing, just in different forms. He is also known for his discovery of the photoelectric effect , for which he won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921. Einstein developed a theory of special and general relativity, which helped to complicate and expand upon theories that had been put forth by Isaac Newton over 200 years prior.
Albert Einstein had a massive influence on contemporary physics. His theory of relativity shifted contemporary understanding of space completely. Along with his equation E = mc 2 , it also foreshadowed the creation of the atomic bomb . Einstein’s understanding of light as something which can function both as a wave and as a stream of particles became the basis for what is known today as quantum mechanics .
Albert Einstein was raised in a secular Jewish family and had one sister, Maja, who was two years younger than him. In 1903 Einstein married Milena Maric, a Serbian physics student whom he had met at school in Zürich. They had three children: a daughter, named Lieserl, and two sons, named Hans and Eduard. After a period of unrest, Einstein and Maric divorced in 1919. Einstein, during his marriage, had begun an affair with his cousin Elsa Löwenthal. They were married in 1919, the same year he divorced Maric.
How did Albert Einstein die?
After suffering an abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture several days before, Albert Einstein died on April 18, 1955, at age 76.
In December 1926 Albert Einstein wrote to Max Born that “[t]he theory produces a good deal but hardly brings us closer to the secret of the Old One. I am at all events convinced that He does not play dice.” Einstein was reacting to Born’s probabilistic interpretation of quantum mechanics and expressing a deterministic view of the world. Learn more.
Recent News
Trusted Britannica articles, summarized using artificial intelligence, to provide a quicker and simpler reading experience. This is a beta feature. Please verify important information in our full article.
This summary was created from our Britannica article using AI. Please verify important information in our full article.
Albert Einstein (born March 14, 1879, Ulm , Württemberg, Germany—died April 18, 1955, Princeton , New Jersey , U.S.) was a German-born physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity and won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect . Einstein is generally considered the most influential physicist of the 20th century.
(Read Einstein’s 1926 Britannica essay on space-time.)
Einstein’s parents were secular , middle-class Jews. His father, Hermann Einstein, was originally a featherbed salesman and later ran an electrochemical factory with moderate success. His mother, the former Pauline Koch, ran the family household. He had one sister, Maria (who went by the name Maja), born two years after Albert.
Einstein would write that two “wonders” deeply affected his early years. The first was his encounter with a compass at age five. He was mystified that invisible forces could deflect the needle. This would lead to a lifelong fascination with invisible forces. The second wonder came at age 12 when he discovered a book of geometry , which he devoured , calling it his “sacred little geometry book.”

Einstein became deeply religious at age 12, even composing several songs in praise of God and chanting religious songs on the way to school. This began to change, however, after he read science books that contradicted his religious beliefs. This challenge to established authority left a deep and lasting impression. At the Luitpold Gymnasium , Einstein often felt out of place and victimized by a Prussian-style educational system that seemed to stifle originality and creativity. One teacher even told him that he would never amount to anything.
Yet another important influence on Einstein was a young medical student, Max Talmud (later Max Talmey), who often had dinner at the Einstein home. Talmud became an informal tutor, introducing Einstein to higher mathematics and philosophy . A pivotal turning point occurred when Einstein was 16 years old. Talmud had earlier introduced him to a children’s science series by Aaron Bernstein, Naturwissenschaftliche Volksbucher (1867–68; Popular Books on Physical Science ), in which the author imagined riding alongside electricity that was traveling inside a telegraph wire. Einstein then asked himself the question that would dominate his thinking for the next 10 years: What would a light beam look like if you could run alongside it? If light were a wave , then the light beam should appear stationary, like a frozen wave. Even as a child, though, he knew that stationary light waves had never been seen, so there was a paradox . Einstein also wrote his first “scientific paper” at that time (“The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields”).
Einstein’s education was disrupted by his father’s repeated failures at business. In 1894, after his company failed to get an important contract to electrify the city of Munich , Hermann Einstein moved to Milan to work with a relative. Einstein was left at a boardinghouse in Munich and expected to finish his education. Alone, miserable, and repelled by the looming prospect of military duty when he turned 16, Einstein ran away six months later and landed on the doorstep of his surprised parents. His parents realized the enormous problems that he faced as a school dropout and draft dodger with no employable skills. His prospects did not look promising.
Fortunately, Einstein could apply directly to the Eidgenössische Polytechnische Schule (“Swiss Federal Polytechnic School”; in 1911, following expansion in 1909 to full university status, it was renamed the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or “Swiss Federal Institute of Technology”) in Zürich without the equivalent of a high school diploma if he passed its stiff entrance examinations. His marks showed that he excelled in mathematics and physics , but he failed at French , chemistry , and biology . Because of his exceptional math scores, he was allowed into the polytechnic on the condition that he first finish his formal schooling. He went to a special high school run by Jost Winteler in Aarau , Switzerland , and graduated in 1896. He also renounced his German citizenship at that time. (He was stateless until 1901, when he was granted Swiss citizenship.) He became lifelong friends with the Winteler family, with whom he had been boarding. (Winteler’s daughter, Marie, was Einstein’s first love; Einstein’s sister, Maja, would eventually marry Winteler’s son Paul; and his close friend Michele Besso would marry their eldest daughter, Anna.)
Einstein would recall that his years in Zürich were some of the happiest years of his life. He met many students who would become loyal friends, such as Marcel Grossmann, a mathematician, and Besso, with whom he enjoyed lengthy conversations about space and time. He also met his future wife, Mileva Maric, a fellow physics student from Serbia.
- The Big Think Interview
- Your Brain on Money
- Explore the Library
- Will true AI turn against us?
- Do we have free will?
- Why are there conspiracy theories?
- Is religion helping or hurting us?
- Are we alone in the universe?
- Should we trust science?
- Michio Kaku
- Neil deGrasse Tyson
- Michelle Thaller
- Steven Pinker
- Ray Kurzweil
- Cornel West
- Helen Fisher
- Smart Skills
- High Culture
- The Present
- Hard Science
- Special Issues
- Starts With A Bang
- Perception Box
- Strange Maps
- The Learning Curve
- Everyday Philosophy
- Free Newsletters
- Memberships
Albert Einstein’s Surprising Thoughts on the Meaning of Life

Albert Einstein was one of the world’s most brilliant thinkers, influencing scientific thought immeasurably. He was also not shy about sharing his wisdom about other topics , writing essays, articles, letters, giving interviews and speeches. His everyday-life opinions on social and intellectual issues that do not come from the world of physics give an insight into the spiritual and moral vision of the scientist , offering much to take to heart.
The collection of essays and ideas “The World As I See It” gathers Einstein’s thoughts from before 1935, when he was as the preface says “at the height of his scientific powers but not yet known as the sage of the atomic age”.
In the book, Einstein comes back to the question of the purpose of life, and what a meaningful life is, on several occasions. In one passage, he links it to a sense of religiosity.
“What is the meaning of human life, or, for that matter, of the life of any creature? To know an answer to this question means to be religious. You ask: Does it many any sense, then, to pose this question? I answer: The man who regards his own life and that of his fellow creatures as meaningless is not merely unhappy but hardly fit for life,” wrote Einstein.
Did Einstein himself hold religious beliefs ? Raised by secular Jewish parents, he had complex and evolving spiritual thoughts. He generally seemed to be open to the possibility of the scientific impulse and religious thoughts coexisting in people’s lives .
“Science without religion is lame, religion without science is blind,” said Einstein in his 1954 essay on science and religion.
Some (including the scientist himself) have called Einstein’s spiritual views pantheism , largely influenced by the philosophy of Baruch Spinoza . Pantheists see God as existing but abstract, equating all of reality with divinity. They also reject a specific personal God or a god that is somehow endowed with human attributes.
Himself a famous atheist, Richard Dawkins calls Einstein’s pantheism a “sexed-up atheism,” but other scholars point to the fact that Einstein did seem to believe in a supernatural intelligence that’s beyond the physical world. He referred to it in his writings as “a superior spirit,” “a superior mind” and a “spirit vastly superior to men”. Einstein was possibly a deist , although he was quite familiar with various religious teachings, including a strong knowledge of Jewish religious texts .
In another passage from 1934, Einstein talks about the value of a human being, reflecting a Buddhist-like approach:
“The true value of a human being is determined primarily by the measure and the sense in which he has attained liberation from the self”.
This theme of liberating the self to glimpse life’s true meaning is also echoed by Einstein later on, in a 1950 letter to console a grieving father Robert S. Marcus:
“A human being is a part of the whole, called by us “Universe,” a part limited in time and space. He experiences himself, his thoughts and feelings as something separate from the rest—a kind of optical delusion of his consciousness. The striving to free oneself from this delusion is the one issue of true religion. Not to nourish it but to try to overcome it is the way to reach the attainable measure of peace of mind.”
In case you are wondering whether Einstein saw value in material pursuits, here’s him talking about accumulating wealth in 1934, as part of the “The World As I See It”:
“I am absolutely convinced that no wealth in the world can help humanity forward, even in the hands of the most devoted worker in this cause. The example of great and pure characters is the only thing that can lead us to noble thoughts and deeds. Money only appeals to selfishness and irresistibly invites abuse. Can anyone imagine Moses, Jesus or Gandhi armed with the money-bags of Carnegie?”
In discussing the ultimate question of life’s real meaning , the famous physicist gives us plenty to think about when it comes to the human condition .
Can philosophy lead us to a good life ? Here, Columbia Professor Philip Kitcher explains how great minds—like Plato , Aristotle , Socrates , Confucius, Mencius, Immanuel Kant, Friedrich Nietzsche , Albert Camus , and Jean-Paul Sartre—can help us find meaning and wellbeing in human existence—even if there is no “ better place “.
Related reading: Sapiens: Can Humans Overcome Suffering and Find True Happiness?
Related reading: A Growing Number of Scholars Are Questioning the Historical Existence of Jesus Christ

Essay on Albert Einstein
500 words essay on albert einstein.
Albert Einstein was a physicist who is responsible for developing the famous general theory of relativity. Furthermore, he is one of the most influential and celebrated scientists of the 20th century. Let’s take a look at the life and achievements of this genius with the essay on Albert Einstein.

Essay On Albert Einstein
Early Life of Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was born in Germany into a Jewish family on 14th March 1879. Furthermore, Einstein had to deal with speech difficulties early on but was a brilliant student at his elementary school. His father, Hermann Einstein founded an electrical equipment manufacturing company with the help of his brother.
At the age of five, Albert’s father showed him a pocket compass . Moreover, this made him realize that the needle was moving due to something in empty space. According to Einstein, this experience left a deep and lasting impression on him.
In 1889, a ten-year-old Albert became introduced to popular science and philosophy texts. This happened due to a family friend named Max Talmud.
Albert Einstein spent time on books like Kant’s ‘Critique of Pure Reason’ and ‘Euclid’s Elements’. From the latter book, Albert developed an understanding of deductive reasoning. Furthermore, by the age of 12, he was able to learn Euclidian geometry from a school booklet.
Einstein’s father’s intention was to see his son pursue electrical engineering. However, a clash took place between Albert and the authorities. This was because Albert had resentment for rote learning as, according to him, it was against creative thought.
Achievements of Albert Einstein
In 1894, Einstein’s father’s business failed and his family went to Italy. At this time, Einstein was only fifteen. During this time, he wrote ‘The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields’, which was his first scientific work.
In 1901, there was the publishing of a paper by Einstein on the capillary forces of a straw in the prestigious ‘Annalen der Physik’. Furthermore, his graduation took place from ETH with a diploma in teaching.
In the year 1905, while working in the patent office, there took place the publishing of four papers by Einstein in the prestigious journal ‘Annalen der Physik’. Experts recognize all four papers as tremendous achievements of Albert Einstein. Therefore, people call the year 1905 as Einstein’s wonderful year’.
The four papers were special relativity, photoelectric effect, Brownian motion , and equivalence of matter and energy. He also made the discovery of the famous equation, E = mc².
The theory of relativity was completed by Einstein in 1915. The confirmation of his theory was by British astronomer, Sir Arthur Eddington, during the solar eclipse of 1919.
There was the continuation of research works by Einstein and finally, in 1921, his efforts bore fruits. Most noteworthy, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Einstein for his services to Theoretical Physics.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein’s contribution to the field of physics is priceless. Furthermore, his ideas and theories are still authoritative for many physicists. Einstein’s lasting legacy in physics will continue to be an inspiration for young science enthusiasts.
FAQs For Essay on Albert Einstein
Question 1: What is the legacy of Albert Einstein?
Answer 1: Albert Einstein is one of the world’s greatest physicists and a Nobel Laureate. Furthermore, his greatest achievement is the theory of relativity which made a significant change in our understanding of the universe like. However, this wasn’t his only legacy as Einstein was also a refugee and a humanitarian.
Question 2: What is the equation E = MC 2 ?
Answer 2: Einstein’s E = MC 2 is the world’s most famous equation. Furthermore, this equation means that energy is equal to mass times the speed of light squared. Moreover, on the most basic level, this equation tells us that energy and mass happen to be interchangeable and that they are different forms of the same thing.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Albert Einstein
By: History.com Editors
Updated: May 16, 2019 | Original: October 27, 2009

The German-born physicist Albert Einstein developed the first of his groundbreaking theories while working as a clerk in the Swiss patent office in Bern. After making his name with four scientific articles published in 1905, he went on to win worldwide fame for his general theory of relativity and a Nobel Prize in 1921 for his explanation of the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. An outspoken pacifist who was publicly identified with the Zionist movement, Einstein emigrated from Germany to the United States when the Nazis took power before World War II. He lived and worked in Princeton, New Jersey, for the remainder of his life.
Einstein’s Early Life (1879-1904)
Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich. As a child, Einstein became fascinated by music (he played the violin), mathematics and science. He dropped out of school in 1894 and moved to Switzerland, where he resumed his schooling and later gained admission to the Swiss Federal Polytechnic Institute in Zurich. In 1896, he renounced his German citizenship, and remained officially stateless before becoming a Swiss citizen in 1901.
Did you know? Almost immediately after Albert Einstein learned of the atomic bomb's use in Japan, he became an advocate for nuclear disarmament. He formed the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists and backed Manhattan Project scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer in his opposition to the hydrogen bomb.
While at Zurich Polytechnic, Einstein fell in love with his fellow student Mileva Maric, but his parents opposed the match and he lacked the money to marry. The couple had an illegitimate daughter, Lieserl, born in early 1902, of whom little is known. After finding a position as a clerk at the Swiss patent office in Bern, Einstein married Maric in 1903; they would have two more children, Hans Albert (born 1904) and Eduard (born 1910).
Einstein’s Miracle Year (1905)
While working at the patent office, Einstein did some of the most creative work of his life, producing no fewer than four groundbreaking articles in 1905 alone. In the first paper, he applied the quantum theory (developed by German physicist Max Planck) to light in order to explain the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect, by which a material will emit electrically charged particles when hit by light. The second article contained Einstein’s experimental proof of the existence of atoms, which he got by analyzing the phenomenon of Brownian motion, in which tiny particles were suspended in water.
In the third and most famous article, titled “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” Einstein confronted the apparent contradiction between two principal theories of physics: Isaac Newton’s concepts of absolute space and time and James Clerk Maxwell’s idea that the speed of light was a constant. To do this, Einstein introduced his special theory of relativity, which held that the laws of physics are the same even for objects moving in different inertial frames (i.e. at constant speeds relative to each other), and that the speed of light is a constant in all inertial frames. A fourth paper concerned the fundamental relationship between mass and energy, concepts viewed previously as completely separate. Einstein’s famous equation E = mc2 (where “c” was the constant speed of light) expressed this relationship.
From Zurich to Berlin (1906-1932)
Einstein continued working at the patent office until 1909, when he finally found a full-time academic post at the University of Zurich. In 1913, he arrived at the University of Berlin, where he was made director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics. The move coincided with the beginning of Einstein’s romantic relationship with a cousin of his, Elsa Lowenthal, whom he would eventually marry after divorcing Mileva. In 1915, Einstein published the general theory of relativity, which he considered his masterwork. This theory found that gravity, as well as motion, can affect time and space. According to Einstein’s equivalence principle–which held that gravity’s pull in one direction is equivalent to an acceleration of speed in the opposite direction–if light is bent by acceleration, it must also be bent by gravity. In 1919, two expeditions sent to perform experiments during a solar eclipse found that light rays from distant stars were deflected or bent by the gravity of the sun in just the way Einstein had predicted.
The general theory of relativity was the first major theory of gravity since Newton’s, more than 250 years before, and the results made a tremendous splash worldwide, with the London Times proclaiming a “Revolution in Science” and a “New Theory of the Universe.” Einstein began touring the world, speaking in front of crowds of thousands in the United States, Britain, France and Japan. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize for his work on the photoelectric effect, as his work on relativity remained controversial at the time. Einstein soon began building on his theories to form a new science of cosmology, which held that the universe was dynamic instead of static, and was capable of expanding and contracting.
Einstein Moves to the United States (1933-39)
A longtime pacifist and a Jew, Einstein became the target of hostility in Weimar Germany, where many citizens were suffering plummeting economic fortunes in the aftermath of defeat in the Great War. In December 1932, a month before Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany, Einstein made the decision to emigrate to the United States, where he took a position at the newly founded Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey . He would never again enter the country of his birth.
By the time Einstein’s wife Elsa died in 1936, he had been involved for more than a decade with his efforts to find a unified field theory, which would incorporate all the laws of the universe, and those of physics, into a single framework. In the process, Einstein became increasingly isolated from many of his colleagues, who were focused mainly on the quantum theory and its implications, rather than on relativity.
Einstein’s Later Life (1939-1955)
In the late 1930s, Einstein’s theories, including his equation E=mc2, helped form the basis of the development of the atomic bomb. In 1939, at the urging of the Hungarian physicist Leo Szilard, Einstein wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt advising him to approve funding for the development of uranium before Germany could gain the upper hand. Einstein, who became a U.S. citizen in 1940 but retained his Swiss citizenship, was never asked to participate in the resulting Manhattan Project , as the U.S. government suspected his socialist and pacifist views. In 1952, Einstein declined an offer extended by David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s premier, to become president of Israel .
Throughout the last years of his life, Einstein continued his quest for a unified field theory. Though he published an article on the theory in Scientific American in 1950, it remained unfinished when he died, of an aortic aneurysm, five years later. In the decades following his death, Einstein’s reputation and stature in the world of physics only grew, as physicists began to unravel the mystery of the so-called “strong force” (the missing piece of his unified field theory) and space satellites further verified the principles of his cosmology.

HISTORY Vault: Secrets of Einstein's Brain
Originally stolen by the doctor trusted to perform his autopsy, scientists over the decades have examined the brain of Albert Einstein to try and determine what made this seemingly normal man tick.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Albert EinsteinOne of the most influential scientists of the 20 th century, Albert Einstein was a physicist who developed the theory of relativity.  We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Quick FactsEarly life, family, and education, einstein’s iq, patent clerk, inventions and discoveries, nobel prize in physics, wives and children, travel diaries, becoming a u.s. citizen, einstein and the atomic bomb, time travel and quantum theory, personal life, death and final words, einstein’s brain, einstein in books and movies: "oppenheimer" and more, who was albert einstein. Albert Einstein was a German mathematician and physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. In the following decade, he immigrated to the United States after being targeted by the German Nazi Party. His work also had a major impact on the development of atomic energy. In his later years, Einstein focused on unified field theory. He died in April 1955 at age 76. With his passion for inquiry, Einstein is generally considered the most influential physicist of the 20 th century. FULL NAME: Albert Einstein BORN: March 14, 1879 DIED: April 18, 1955 BIRTHPLACE: Ulm, Württemberg, Germany SPOUSES: Mileva Einstein-Maric (1903-1919) and Elsa Einstein (1919-1936) CHILDREN: Lieserl, Hans, and Eduard ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Pisces Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. He grew up in a secular Jewish family. His father, Hermann Einstein, was a salesman and engineer who, with his brother, founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a Munich-based company that mass-produced electrical equipment. Einstein’s mother, the former Pauline Koch, ran the family household. Einstein had one sister, Maja, born two years after him. Einstein attended elementary school at the Luitpold Gymnasium in Munich. However, he felt alienated there and struggled with the institution’s rigid pedagogical style. He also had what were considered speech challenges. However, he developed a passion for classical music and playing the violin, which would stay with him into his later years. Most significantly, Einstein’s youth was marked by deep inquisitiveness and inquiry. Toward the end of the 1880s, Max Talmud, a Polish medical student who sometimes dined with the Einstein family, became an informal tutor to young Einstein. Talmud had introduced his pupil to a children’s science text that inspired Einstein to dream about the nature of light. Thus, during his teens, Einstein penned what would be seen as his first major paper, “The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields.” Hermann relocated the family to Milan, Italy, in the mid-1890s after his business lost out on a major contract. Einstein was left at a relative’s boarding house in Munich to complete his schooling at the Luitpold. Faced with military duty when he turned of age, Einstein allegedly withdrew from classes, using a doctor’s note to excuse himself and claim nervous exhaustion. With their son rejoining them in Italy, his parents understood Einstein’s perspective but were concerned about his future prospects as a school dropout and draft dodger. Einstein was eventually able to gain admission into the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, specifically due to his superb mathematics and physics scores on the entrance exam. He was still required to complete his pre-university education first and thus attended a high school in Aarau, Switzerland, helmed by Jost Winteler. Einstein lived with the schoolmaster’s family and fell in love with Winteler’s daughter Marie. Einstein later renounced his German citizenship and became a Swiss citizen at the dawn of the new century. Einstein’s intelligence quotient was estimated to be around 160, but there are no indications he was ever actually tested. Psychologist David Wechsler didn’t release the first edition of the WAIS cognitive test, which evolved into the WAIS-IV test commonly used today, until 1955—shortly before Einstein’s death. The maximum score of the current version is 160, with an IQ of 135 or higher ranking in the 99 th percentile. Magazine columnist Marilyn vos Savant has the highest-ever recorded IQ at 228 and was featured in the Guinness Book of World Records in the late 1980s. However, Guinness discontinued the category because of debates about testing accuracy. According to Parade , individuals believed to have higher IQs than Einstein include Leonardo Da Vinci , Marie Curie , Nikola Tesla , and Nicolaus Copernicus . After graduating from university, Einstein faced major challenges in terms of finding academic positions, having alienated some professors over not attending class more regularly in lieu of studying independently. Einstein eventually found steady work in 1902 after receiving a referral for a clerk position in a Swiss patent office. While working at the patent office, Einstein had the time to further explore ideas that had taken hold during his university studies and thus cemented his theorems on what would be known as the principle of relativity. In 1905—seen by many as a “miracle year” for the theorist—Einstein had four papers published in the Annalen der Physik , one of the best-known physics journals of the era. Two focused on the photoelectric effect and Brownian motion. The two others, which outlined E=MC 2 and the special theory of relativity, were defining for Einstein’s career and the course of the study of physics. As a physicist, Einstein had many discoveries, but he is perhaps best known for his theory of relativity and the equation E=MC 2 , which foreshadowed the development of atomic power and the atomic bomb. Theory of RelativityEinstein first proposed a special theory of relativity in 1905 in his paper “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” which took physics in an electrifying new direction. The theory explains that space and time are actually connected, and Einstein called this joint structure space-time. By November 1915, Einstein completed the general theory of relativity, which accounted for gravity’s relationship to space-time. Einstein considered this theory the culmination of his life research. He was convinced of the merits of general relativity because it allowed for a more accurate prediction of planetary orbits around the sun, which fell short in Isaac Newton ’s theory. It also offered a more expansive, nuanced explanation of how gravitational forces worked. Einstein’s assertions were affirmed via observations and measurements by British astronomers Sir Frank Dyson and Sir Arthur Eddington during the 1919 solar eclipse, and thus a global science icon was born. Today, the theories of relativity underpin the accuracy of GPS technology, among other phenomena. Even so, Einstein did make one mistake when developing his general theory, which naturally predicted the universe is either expanding or contracting. Einstein didn’t believe this prediction initially, instead holding onto the belief that the universe was a fixed, static entity. To account for, this he factored in a “cosmological constant” to his equation. His later theories directly contracted this idea and asserted that the universe could be in a state of flux. Then, astronomer Edwin Hubble deduced that we indeed inhabit an expanding universe. Hubble and Einstein met at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles in 1931. Decades after Einstein’s death, in 2018, a team of scientists confirmed one aspect of Einstein’s general theory of relativity: that the light from a star passing close to a black hole would be stretched to longer wavelengths by the overwhelming gravitational field. Tracking star S2, their measurements indicated that the star’s orbital velocity increased to over 25 million kph as it neared the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy, its appearance shifting from blue to red as its wavelengths stretched to escape the pull of gravity. Einstein’s E=MC²Einstein’s 1905 paper on the matter-energy relationship proposed the equation E=MC²: the energy of a body (E) is equal to the mass (M) of that body times the speed of light squared (C²). This equation suggested that tiny particles of matter could be converted into huge amounts of energy, a discovery that heralded atomic power. Famed quantum theorist Max Planck backed up the assertions of Einstein, who thus became a star of the lecture circuit and academia, taking on various positions before becoming director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics (today is known as the Max Planck Institute for Physics) from 1917 to 1933. In 1921, Einstein won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect, since his ideas on relativity were still considered questionable. He wasn’t actually given the award until the following year due to a bureaucratic ruling, and during his acceptance speech, he still opted to speak about relativity.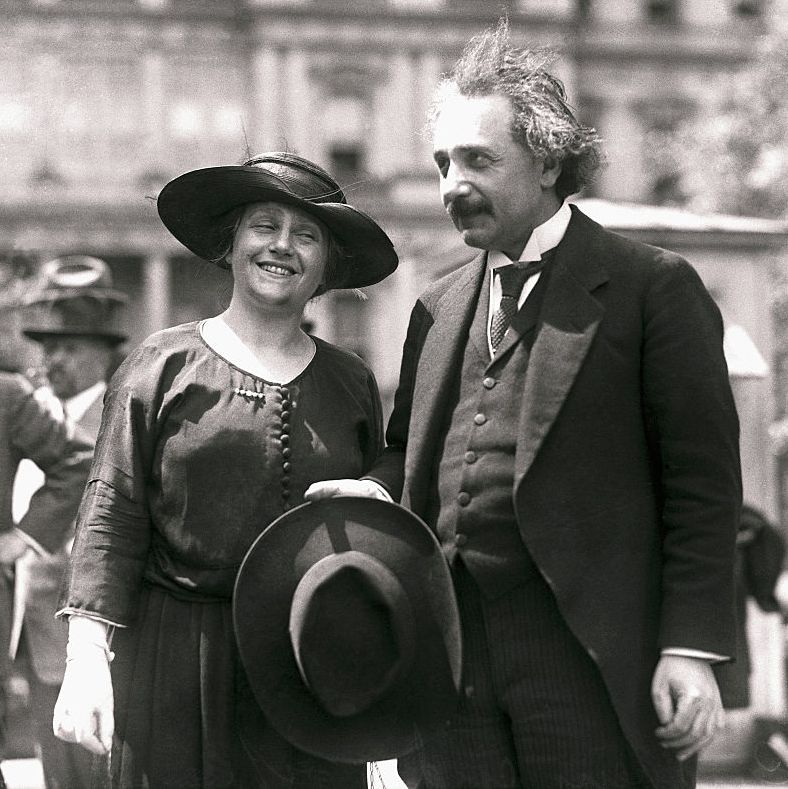  Einstein married Mileva Maric on January 6, 1903. While attending school in Zurich, Einstein met Maric, a Serbian physics student. Einstein continued to grow closer to Maric, but his parents were strongly against the relationship due to her ethnic background. Nonetheless, Einstein continued to see her, with the two developing a correspondence via letters in which he expressed many of his scientific ideas. Einstein’s father passed away in 1902, and the couple married shortly thereafter. Einstein and Mavic had three children. Their daughter, Lieserl, was born in 1902 before their wedding and might have been later raised by Maric’s relatives or given up for adoption. Her ultimate fate and whereabouts remain a mystery. The couple also had two sons: Hans Albert Einstein, who became a well-known hydraulic engineer, and Eduard “Tete” Einstein, who was diagnosed with schizophrenia as a young man. The Einsteins’ marriage would not be a happy one, with the two divorcing in 1919 and Maric having an emotional breakdown in connection to the split. Einstein, as part of a settlement, agreed to give Maric any funds he might receive from possibly winning the Nobel Prize in the future. During his marriage to Maric, Einstein had also begun an affair some time earlier with a cousin, Elsa Löwenthal . The couple wed in 1919, the same year of Einstein’s divorce. He would continue to see other women throughout his second marriage, which ended with Löwenthal’s death in 1936. In his 40s, Einstein traveled extensively and journaled about his experiences. Some of his unfiltered private thoughts are shared two volumes of The Travel Diaries of Albert Einstein . The first volume , published in 2018, focuses on his five-and-a-half month trip to the Far East, Palestine, and Spain. The scientist started a sea journey to Japan in Marseille, France, in autumn of 1922, accompanied by his second wife, Elsa. They journeyed through the Suez Canal, then to Sri Lanka, Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Japan. The couple returned to Germany via Palestine and Spain in March 1923. The second volume , released in 2023, covers three months that he spent lecturing and traveling in Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil in 1925. The Travel Diaries contain unflattering analyses of the people he came across, including the Chinese, Sri Lankans, and Argentinians, a surprise coming from a man known for vehemently denouncing racism in his later years. In an entry for November 1922, Einstein refers to residents of Hong Kong as “industrious, filthy, lethargic people.” In 1933, Einstein took on a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, where he would spend the rest of his life. At the time the Nazis, led by Adolf Hitler , were gaining prominence with violent propaganda and vitriol in an impoverished post-World War I Germany. The Nazi Party influenced other scientists to label Einstein’s work “Jewish physics.” Jewish citizens were barred from university work and other official jobs, and Einstein himself was targeted to be killed. Meanwhile, other European scientists also left regions threatened by Germany and immigrated to the United States, with concern over Nazi strategies to create an atomic weapon. Not long after moving and beginning his career at IAS, Einstein expressed an appreciation for American meritocracy and the opportunities people had for free thought, a stark contrast to his own experiences coming of age. In 1935, Einstein was granted permanent residency in his adopted country and became an American citizen five years later. In America, Einstein mostly devoted himself to working on a unified field theory, an all-embracing paradigm meant to unify the varied laws of physics. However, during World War II, he worked on Navy-based weapons systems and made big monetary donations to the military by auctioning off manuscripts worth millions.  In 1939, Einstein and fellow physicist Leo Szilard wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt to alert him of the possibility of a Nazi bomb and to galvanize the United States to create its own nuclear weapons. The United States would eventually initiate the Manhattan Project , though Einstein wouldn’t take a direct part in its implementation due to his pacifist and socialist affiliations. Einstein was also the recipient of much scrutiny and major distrust from FBI director J. Edgar Hoover . In July 1940, the U.S. Army Intelligence office denied Einstein a security clearance to participate in the project, meaning J. Robert Oppenheimer and the scientists working in Los Alamos were forbidden from consulting with him. Einstein had no knowledge of the U.S. plan to use atomic bombs in Japan in 1945. When he heard of the first bombing at Hiroshima, he reportedly said, “Ach! The world is not ready for it.” Einstein became a major player in efforts to curtail usage of the A-bomb. The following year, he and Szilard founded the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists, and in 1947, via an essay for The Atlantic Monthly , Einstein espoused working with the United Nations to maintain nuclear weapons as a deterrent to conflict. After World War II, Einstein continued to work on his unified field theory and key aspects of his general theory of relativity, including time travel, wormholes, black holes, and the origins of the universe. However, he felt isolated in his endeavors since the majority of his colleagues had begun focusing their attention on quantum theory. In the last decade of his life, Einstein, who had always seen himself as a loner, withdrew even further from any sort of spotlight, preferring to stay close to Princeton and immerse himself in processing ideas with colleagues. In the late 1940s, Einstein became a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), seeing the parallels between the treatment of Jews in Germany and Black people in the United States. He corresponded with scholar and activist W.E.B. Du Bois as well as performer Paul Robeson and campaigned for civil rights, calling racism a “disease” in a 1946 Lincoln University speech. Einstein was very particular about his sleep schedule, claiming he needed 10 hours of sleep per day to function well. His theory of relativity allegedly came to him in a dream about cows being electrocuted. He was also known to take regular naps. He is said to have held objects like a spoon or pencil in his hand while falling asleep. That way, he could wake up before hitting the second stage of sleep—a hypnagogic process believed to boost creativity and capture sleep-inspired ideas. Although sleep was important to Einstein, socks were not. He was famous for refusing to wear them. According to a letter he wrote to future wife Elsa, he stopped wearing them because he was annoyed by his big toe pushing through the material and creating a hole.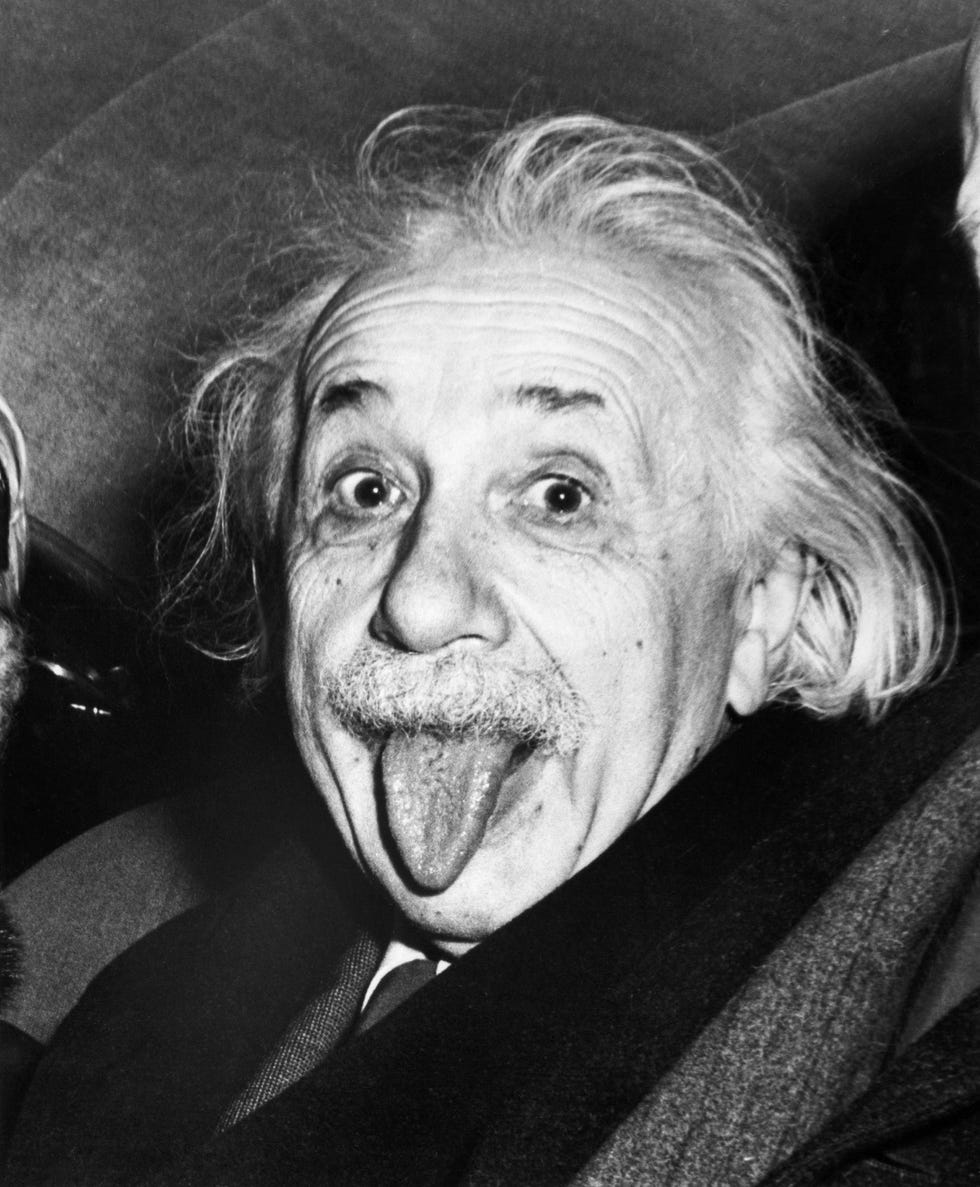  One of the most recognizable photos of the 20 th century shows Einstein sticking out his tongue while leaving his 72 nd birthday party on March 14, 1951. According to Discovery.com , Einstein was leaving his party at Princeton when a swarm of reporters and photographers approached and asked him to smile. Tired from doing so all night, he refused and rebelliously stuck his tongue out at the crowd for a moment before turning away. UPI photographer Arthur Sasse captured the shot. Einstein was amused by the picture and ordered several prints to give to his friends. He also signed a copy of the photo that sold for $125,000 at a 2017 auction. Einstein died on April 18, 1955, at age 76 at the University Medical Center at Princeton. The previous day, while working on a speech to honor Israel’s seventh anniversary, Einstein suffered an abdominal aortic aneurysm. He was taken to the hospital for treatment but refused surgery, believing that he had lived his life and was content to accept his fate. “I want to go when I want,” he stated at the time. “It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.” According to the BBC, Einstein muttered a few words in German at the moment of his death. However, the nurse on duty didn’t speak German so their translation was lost forever. In a 2014 interview , Life magazine photographer Ralph Morse said the hospital was swarmed by journalists, photographers, and onlookers once word of Einstein’s death spread. Morse decided to travel to Einstein’s office at the Institute for Advanced Studies, offering the superintendent alcohol to gain access. He was able to photograph the office just as Einstein left it. After an autopsy, Einstein’s corpse was moved to a Princeton funeral home later that afternoon and then taken to Trenton, New Jersey, for a cremation ceremony. Morse said he was the only photographer present for the cremation, but Life managing editor Ed Thompson decided not to publish an exclusive story at the request of Einstein’s son Hans. During Einstein’s autopsy, pathologist Thomas Stoltz Harvey had removed his brain, reportedly without his family’s consent, for preservation and future study by doctors of neuroscience. However, during his life, Einstein participated in brain studies, and at least one biography claimed he hoped researchers would study his brain after he died. Einstein’s brain is now located at the Princeton University Medical Center. In keeping with his wishes, the rest of his body was cremated and the ashes scattered in a secret location. In 1999, Canadian scientists who were studying Einstein’s brain found that his inferior parietal lobe, the area that processes spatial relationships, 3D-visualization, and mathematical thought, was 15 percent wider than in people who possess normal intelligence. According to The New York Times , the researchers believe it might help explain why Einstein was so intelligent. In 2011, the Mütter Museum in Philadelphia received thin slices of Einstein’s brain from Dr. Lucy Rorke-Adams, a neuropathologist at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and put them on display. Rorke-Adams said she received the brain slides from Harvey. Since Einstein’s death, a veritable mountain of books have been written on the iconic thinker’s life, including Einstein: His Life and Universe by Walter Isaacson and Einstein: A Biography by Jürgen Neffe, both from 2007. Einstein’s own words are presented in the collection The World As I See It . Einstein has also been portrayed on screen. Michael Emil played a character called “The Professor,” clearly based on Einstein, in the 1985 film Insignificance —in which alternate versions of Einstein, Marilyn Monroe , Joe DiMaggio , and Joseph McCarthy cross paths in a New York City hotel. Walter Matthau portrayed Einstein in the fictional 1994 comedy I.Q. , in which he plays matchmaker for his niece played by Meg Ryan . Einstein was also a character in the obscure comedy films I Killed Einstein, Gentlemen (1970) and Young Einstein (1988). A much more historically accurate depiction of Einstein came in 2017, when he was the subject of the first season of Genius , a 10-part scripted miniseries by National Geographic. Johnny Flynn played a younger version of the scientist, while Geoffrey Rush portrayed Einstein in his later years after he had fled Germany. Ron Howard was the director. Tom Conti plays Einstein in the 2023 biopic Oppenheimer , directed by Christopher Nolan and starring Cillian Murphy as scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer during his involvement with the Manhattan Project.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us ! The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us Tyler Piccotti first joined the Biography.com staff as an Associate News Editor in February 2023, and before that worked almost eight years as a newspaper reporter and copy editor. He is a graduate of Syracuse University. When he's not writing and researching his next story, you can find him at the nearest amusement park, catching the latest movie, or cheering on his favorite sports teams. Nobel Prize Winners Chien-Shiung Wu  The Solar Eclipse That Made Albert Einstein a Star  14 Hispanic Women Who Have Made History  Marie Curie  Martin Luther King Jr.  Henry Kissinger  Malala Yousafzai  Jimmy Carter  10 Famous Poets Whose Enduring Works We Still Read  22 Famous Scientists You Should Know  Wole Soyinka Biography: Albert Einstein
Legendary scientist Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) first gained worldwide prominence in 1919 after British astronomers verified predictions of Einstein's general theory of relativity through measurements taken during a total eclipse. Einstein's theories expanded upon universal laws formulated by physicist Isaac Newton in the late seventeenth century. Before E=MC2Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child. The compass convinced him that there had to be "something behind things, something deeply hidden." Even as a small boy Einstein was self-sufficient and thoughtful. According to one account, he was a slow talker, often pausing to consider what he would say next. His sister would recount the concentration and perseverance with which he would build houses of cards. Einstein's first job was that of patent clerk. In 1933, he joined the staff of the newly created Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. He accepted this position for life, and lived there until his death. Einstein is probably familiar to most people for his mathematical equation about the nature of energy, E = MC2. E = MC2, Light and HeatThe formula E=MC2 is probably the most famous calculation from Einstein's special theory of relativity . The formula basically states that energy (E) equals mass (m) times the speed of light (c) squared (2). In essence, it means mass is just one form of energy. Since the speed of light squared is an enormous number, a small amount of mass can be converted to a phenomenal amount of energy. Or if there's a lot of energy available, some energy can be converted to mass and a new particle can be created. Nuclear reactors, for instance, work because nuclear reactions convert small amounts of mass into large amounts of energy. Einstein wrote a paper based on the new understanding of the structure of light. He argued that light can act as though it consists of discrete, independent particles of energy similar to particles of a gas. A few years before, Max Planck's work had contained the first suggestion of discrete particles in energy. Einstein went far beyond this though and his revolutionary proposal seemed to contradict the universally accepted theory that light consists of smoothly oscillating electromagnetic waves. Einstein showed that light quanta, as he called the particles of energy, could help to explain phenomena being studied by experimental physicists. For example, he explained how light ejects electrons from metals. While there was a well-known kinetic energy theory that explained heat as an effect of the ceaseless motion of atoms, it was Einstein who proposed a way to put the theory to a new and crucial experimental test. If tiny but visible particles were suspended in a liquid, he argued, the irregular bombardment by the liquid's invisible atoms should cause the suspended particles to move in a random jittering pattern. This should be observable through a microscope. If the predicted motion is not seen, the whole kinetic theory would be in grave danger. But such a random dance of microscopic particles had long since been observed. With the motion demonstrated in detail, Einstein had reinforced the kinetic theory and created a powerful new tool for studying the movement of atoms.
Albert Einstein: His life, theories and impact on scienceWhere would science be without Albert Einstein? 
Career highlightsEinstein's remarkable brain, einstein's scientific legacy.
Additional resourcesAlbert Einstein is often cited as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century. His work continues to help astronomers study everything from gravitational waves to Mercury 's orbit. The scientist's equation that helped explain special relativity – E = mc^2 – is famous even among those who don't understand its underlying physics. Einstein is also known for his theory of general relativity (an explanation of gravity ), and the photoelectric effect (which explains the behavior of electrons under certain circumstances); his work on the latter earned him a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921. Einstein also tried in vain to unify all the forces of the universe in a single theory, or a theory of everything, which he was still working on at the time of his death. Related: What is the Theory of Everything? Einstein's early yearsEinstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Germany, a town that today has a population of just more than 120,000. There is a small commemorative plaque where his house used to stand (it was destroyed during World War II). The family moved to Munich shortly after his birth, according to the Nobel Prize website , and later to Italy when his father faced problems with running his own business. Einstein's father, Hermann, ran an electrochemical factory and his mother Pauline took care of Albert and his younger sister, Maria. — What is wormhole theory? — Was Einstein wrong? Why some astrophysicists are questioning the theory of space-time — Albert Einstein: Before and after relativity Einstein would write in his memoirs that two "wonders" deeply affected his early years, according to Hans-Josef Küpper, an Albert Einstein scholar. Young Einstein encountered his first wonder — a compass — at age 5: He was mystified that invisible forces could deflect the needle. This would lead to a lifelong fascination with unseen forces. The second wonder came at age 12 when he discovered a book of geometry, which he worshipped, calling it his "holy geometry book." Contrary to popular belief, young Albert was a good student, according to an online archive . He excelled in physics and mathematics , but was a more "moderate" pupil in other subjects, Küpper wrote on his website. However, Einstein rebelled against the authoritarian attitude of some of his teachers and dropped out of school at 16. He later took an entrance exam for the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich, and while his performances in physics and math were excellent, his marks in other areas were subpar, and he did not pass the exam. The aspiring physicist took additional courses to close the gap in his knowledge and was admitted to the Swiss Polytechnic in 1896. In 1901 he received his diploma to teach physics and mathematics.  However, Einstein could not find a teaching position, and began work in a Bern patent office in 1901, according to his Nobel Prize biography . It was while there that, in between analyzing patent applications, he developed his work in special relativity and other areas of physics that later made him famous. Einstein married Mileva Maric, a longtime love of his from Zurich, in 1903. Their children, Hans Albert and Eduard, were born in 1904 and 1910. (The fate of a child born to them in 1902 before their marriage, Lieserl, is unknown.) Einstein divorced Maric in 1919 and soon after married Elsa Löwenthal. Löwenthal died in 1933. Einstein's career sent him to multiple countries. He earned his doctorate from the University of Zurich in 1905 and subsequently took on professor positions in Zurich (1909), Prague (1911) and Zurich again (1912). Next, he moved to Berlin to become director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute and a professor at the University of Berlin (1914). He also became a German citizen. A major validation of Einstein's work came in 1919, when Sir Arthur Eddington, secretary of the Royal Astronomical Society, led an expedition to Africa that measured the position of stars during a total solar eclipse . The group found that the position of stars was shifted due to the bending of light around the sun . (In 2008, a BBC/HBO production dramatized the story in " Einstein and Eddington .") Einstein remained in Germany until 1933 when dictator Adolf Hitler rose to power. The physicist then renounced his German citizenship and moved to the United States to become a professor of theoretical physics at Princeton. He became a U.S. citizen in 1940 and retired in 1945. Einstein remained active in the physics community throughout his later years. In 1939, he famously penned a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt warning that uranium could be used for an atomic bomb. Late in Einstein's life, he engaged in a series of private debates with physicist Niels Bohr about the validity of quantum theory . Bohr's theories held the day, and Einstein later incorporated quantum theory into his own calculations.  Einstein's deathEinstein died of an aortic aneurysm on April 18, 1955. A blood vessel burst near his heart, according to the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) . When asked if he wanted to have surgery, Einstein refused. "I want to go when I want to go," he said. "It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share; it is time to go. I will do it elegantly." Einstein's body — most of it, anyway — was cremated; his ashes were spread in an undisclosed location, according to the AMNH. However, a doctor at Princeton Hospital, Thomas Harvey, had controversially performed an autopsy, and removed Einstein's brain and eyeballs, according to the BBC . Harvey sliced hundreds of thin sections of brain tissue to place on microscope slides and snapped 14 photos of the brain from several angles. He took the brain tissue, slides and images with him when he moved to Wichita, Kansas, where he was a medical supervisor in a biological testing lab. Over the next 30 years, Harvey sent a few slides to other researchers who requested them, but kept the rest of the brain in two glass jars, sometimes in a cider box under a beer cooler. The story of Einstein's brain was largely forgotten until 1985, when Harvey and his colleagues published their study results in the journal Experimental Neurology . Harvey failed a competency exam in 1988, and his medical license was revoked, Blitz wrote. Harvey eventually donated the brain to Princeton Hospital, where the brain's journey had begun. Harvey died in 2007. Pieces of Einstein's brain are now at the Mütter Museum in Philadelphia, Live Science reported .  Harvey's 1985 study authors reported that Einstein's brain had a higher number of glial cells (those that support and insulate the nervous system) per neurons (nerve cells) than other brains they examined. They concluded that it might indicate the neurons had a higher metabolic need — in other words, Einstein's brain cells needed and used more energy, which could have been why he had such advanced thinking abilities and conceptual skills. However, other researchers have pointed out a few problems with that study, according to Eric H. Chudler , a neuroscientist at the University of Washington. First, for example, the other brains used in the study were all younger than Einstein's brain. Second, the "experimental group" had only one subject — Einstein. Additional studies are needed to see if these anatomical differences are found in other people. And third, only a small part of Einstein's brain was studied. Another study, published in 1996 in the journal Neuroscience Letters , found that Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 g). Also, the scientist's cerebral cortex was thinner than that of five control brains, but the density of neurons was higher. A study published in 2012 in the journal Brain revealed that Einstein's brain had extra folding in the gray matter , the site of conscious thinking. In particular, the frontal lobes, regions tied to abstract thought and planning, had unusually elaborate folding.  Einstein's legacy in physics is significant. Here are some of the key scientific principles that he pioneered: Theory of special relativity : Einstein showed that physical laws are identical for all observers, as long as they are not under acceleration. However, the speed of light in a vacuum is always the same, no matter at what speed the observer is traveling. This work led to his realization that space and time are linked to what we now call space-time . So, an event seen by one observer may also be seen at a different time by another observer. Theory of general relativity : This was a reformulation of the law of gravity. In the 1600s, Newton formulated three laws of motion, among them, outlining how gravity works between two bodies. The force between them depends on how massive each object is, and how far apart the objects are. Einstein determined that when thinking about space-time, a massive object causes a distortion in space-time (like putting a heavy ball on a trampoline). Gravity is exerted when other objects fall into the "well" created by the distortion in space-time, like a marble rolling towards a large ball. General relativity passed a major test in 2019 in an experiment involving a supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way . Photoelectric effect : Einstein's work in 1905 proposed that light should be thought of as a stream of particles (photons) instead of just a single wave, as was commonly thought at the time. His work helped decipher curious results scientists were previously unable to explain. Unified field theory : Einstein spent much of his later years trying to merge the fields of electromagnetism and gravity. He was unsuccessful but may have been ahead of his time. Other physicists are still working on this problem. Einstein's astronomical legacyThere are many applications of Einstein's work, but here are some of the most notable ones in astronomy : Gravitational waves : In 2016, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detected space-time ripples — otherwise known as gravitational waves— that occurred after black holes collided about 1.4 billion light-years from Earth . LIGO also made an initial detection of gravitational waves in 2015, a century after Einstein predicted these ripples existed. The waves are a facet of Einstein's theory of general relativity. Mercury's orbit : Mercury is a small planet orbiting close to a very massive object relative to its size — the sun. Its orbit could not be understood until general relativity showed that the curvature of space-time is affecting Mercury's motions and changing its orbit. There is a small chance that over billions of years, Mercury could be ejected from our solar system due to these changes (with an even smaller chance that it could collide with Earth). Gravitational lensing : This is a phenomenon by which a massive object (like a galaxy cluster or a black hole) bends light around it. Astronomers looking at that region through a telescope can then see objects directly behind the massive object, due to the light being bent. A famous example of this is Einstein's Cross, a quasar in the constellation Pegasus : A galaxy roughly 400 million light-years away bends the light of the quasar so that it appears four times around the galaxy. Black holes : In April 2019, the Event Horizon telescope showed the first-ever images of a black hole . The photos again confirmed several facets of general relativity, including not only that black holes exist, but also that they have a circular event horizon — a point at which nothing can escape, not even light. To find the answers to frequently asked questions about Albert Einstein , visit The Nobel Prize website. Additionally, you can learn about The Einstein Memorial at the National Academy of Sciences building in Washington, D.C. Bibliography"Einstein: The Life and Times". American Journal of Physics (1973). https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1119/1 "On the brain of a scientist: Albert Einstein". Experimental Neurology (1985). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3979509/ "The fascinating life and theory of Albert Einstein". Mih, W. C. Nova Publishers (2000). https://books.google.co.uk/books "Alterations in cortical thickness and neuronal density in the frontal cortex of Albert Einstein". Neuroscience Letters (1996). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8805120/ "The cerebral cortex of Albert Einstein: a description and preliminary analysis of unpublished photographs". Brain, Volume 136, Issue 4 (2012). https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/136/4/1304/356614?login=true Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected]. Get the Space.com NewsletterBreaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more! Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., is a staff writer in the spaceflight channel since 2022 covering diversity, education and gaming as well. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years before joining full-time. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House and Office of the Vice-President of the United States, an exclusive conversation with aspiring space tourist (and NSYNC bassist) Lance Bass, speaking several times with the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, " Why Am I Taller ?", is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams. Elizabeth holds a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Space Studies from the University of North Dakota, a Bachelor of Journalism from Canada's Carleton University and a Bachelor of History from Canada's Athabasca University. Elizabeth is also a post-secondary instructor in communications and science at several institutions since 2015; her experience includes developing and teaching an astronomy course at Canada's Algonquin College (with Indigenous content as well) to more than 1,000 students since 2020. Elizabeth first got interested in space after watching the movie Apollo 13 in 1996, and still wants to be an astronaut someday. Mastodon: https://qoto.org/@howellspace 'Stellar tanning salon' brings light of alien suns to Earth Tour the famous 'Pillars of Creation' with gorgeous new 3D views from Hubble and JWST (video) Scientists tap into 2 new quantum methods to catch dark matter suspects Most Popular
Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius Essay (Biography)
Albert Einstein is arguably one of the most influential individuals in the modern world. He played a role in the development and physics, and also dabbled with the politics of his day-even though at a small scale level. During the period around the First World War, Einstein was among the individuals that were against the usage of violence in resolution of conflicts. This was one of the ethical standpoints that have made him receive credence, years after his death. Albert Einstein was born in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879 (Meltzer 2). Less than two months after his birth his family relocated to Munich where he started his education. As years passed by, Einstein and his family again relocated, this time to Switzerland, where the young Albert gained a diploma in physics and mathematics (Lakin 20). After his graduation, Einstein tried to find a job as a teacher but instead landed a position in Switzerland’s patent office (Frisch 12). In 1905, at just 26, Einstein received a doctoral degree. It was during this period that he published most his remarkable theories. By 1911 he had been declared Professor Extraordinary and Professor of Theoretical Physics in different cities across Switzerland (Frisch 23). Einstein was fundamentally a pacifist when it came to conflict resolution and this was well manifested in the First World War. During this time, 93 German professors supported a manifesto for the conduct of the nation in war, while Einstein and three other intellectuals gave their support to an anti-war counter manifesto (Calaprice and Lipscombe 121). Einstein played a critical role in the establishment of a non-partisan coalition that fronted the idea of just piece and international cooperation in the prevention of wars in the future. During his stay in Switzerland, Einstein spent his days as a theoretical physicist but also dedicated some time to uniting the warring factions. He even once declared his stand thus: “My pacifism is an instinctive feeling, a feeling that possesses me because the murder of men is disgusting. My attitude is not derived from any intellectual theory but is based on my deepest antipathy to every kind of cruelty and hatred ” (Calaprice and Lipscombe 55.) In 1914, he moved back to Germany where he stayed as a citizen for the next nineteen years, only to renounce his citizenship on political grounds. He moved the United States where he stayed for seven years before acquiring American Citizenship. In the meantime, he continued teaching Theoretical Physics at Princeton University. After the Second World War, Albert Einstein was a key official in the World Government Movement. He was even accorded the presidency of Israel but he turned down the offer instead choosing to spearhead the establishment of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. When it came to science, Einstein had a proper knowledge of the challenges in the field and also had a well developed way of dealing with them. His was a methodological approach with clear-cut steps towards the attainment of the goal. According to Einstein, any of his achievements was merely seen as a stepping stone to even more achievements. In his early professional years, Albert Einstein hypothesized that the right explanation of the special theory of relativity should also inform the theory of gravitation (McPherson 21). In 1916 he published his paper on the general theory of relativity (McPherson 26). It was around this period that he took time to find solutions to the challenges of the theory of radiation. In the 1920’s, Einstein started working on the unified field theories but still continued his work on the quantum theory (Calaprice and Lipscombe 92). By the time he was retiring, Einstein had made substantial achievements in relativistic cosmology and unification of basic concepts of Physics. Owing to his accomplishments, Einstein was awarded several honorary doctorate degrees in various scientific fields by many European and American universities (Lakin 33-35). A number of prestigious societies also accorded him awards, most notably the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London in 1925 (Lakin 43). Because of his involvement in research, Einstein spent a lot of time in solitude and his only form of recreation was listening to music. In 1903, he got married and had two children before filing for a divorce sixteen years later only to marry his cousin, Elsa Löwenthal, who passed away in 1936 (Meachen 13). Einstein died in New Jersey, 19 years after Elsa’s death Einstein’s theories survived the test of time primarily because of two reasons. One, because most of his work was based on the findings of scholars that became before him, and two because the field in which he was involved had no room for more advancement without scholars taking his findings into consideration. His ethical views regarding the war have long been overshadowed by the entry of other more popular individuals, most of them being politicians. As a pacifist, his political views did not initially find popularity with the rulers of his time because most of them believed in national supremacy. As a matter of fact, most individuals dismissed his and his associate’s viewpoints as the ranting of mad scientists. Various life lessons can be picked from how Einstein conducted himself. First is the commitment to one’s job. Most individuals always complain of how bad their current job is without even making an effort to attain their best in what they do. For instance, with the global boundaries becoming more and more irrelevant owing to increasing international migration, the United States is gradually becoming multicultural. Individuals from all over the world have over time appreciated the United States as the land of opportunity. Hence, most persons ranging from professionals to unskilled individuals are looking for ways to gain an entry into America where they earnings are thought to be better than in other regions around the world. The search for jobs and better livelihoods has resulted in an increased diversification of the American workforce which in turn calls for institutions to adopt and develop strategies for strengthening the relationship between individuals of varied socio-cultural backgrounds. What most individuals fail to notice, is that if they commit themselves to what they are good at, they can end up making notable achievements in their lives. Another ethical lesson that can be picked from Einstein’s life is his belief in peaceful resolution of national and international conflicts. This is something that Einstein directly linked to leadership whereby leadership is the definite role assigned to each and every president/country. The most common and wrong presumption by most presidents is that since their job title puts them in a position of leadership, the individuals who work under them will automatically be subject to their every word. In actual sense, however, the title presidency is not necessarily directly linked to leadership. Einstein believed in proper communication among communities as a way of reaching amicable solutions to disagreements. Community communication is the practice of sharing information amongst individual of a given society. Communication has always been hailed as one of the key unifiers of members of particular communities. The easier it is for individuals to share what is in their minds, the easier it is for them to relate with one another. Communication as a social aspect is multi faceted in the sense that it comprises various different aspects working both independently and in conjunction with other components to maintain a harmonious understanding between parties. In most societies around the world business is regarded as the mainstay. All activities within a given community generally tend to be under the influence of economic activities both directly and indirectly. In order for effectiveness to be achieved in leadership, the person in charge must constantly ensure that his/her influence to the people subordinate to him/her is always positive and intended to achieve the unique goals of the country. Furthermore, and in line with Einstein’s beliefs, it has been proven that the leadership style adopted can make people in governmental control either excellent or terrible leaders. In this regard, if the leaders of two nations are pacifiers, then there is a reduced likelihood of international wars. Another trait that made Einstein a great person was his belief in giving everyone a chance to be heard. Good listenership has been given immense appreciation amongst the most successful communities in the world. The doctrines of these societies propose that for anyone to have a meaningful conversation and particularly in business, he or she must be in a position to take time and listen to what the other person is saying. It is quite unlikely that communication can occur if both of the parties involved talk at the same time. Communication is a two way event that calls for one of the parties to stay quite and receive the message and then respond as the other party stays quiet. At national levels, if all the leaders sit down and agree to communicate sanely, then there is little likelihood of disagreements occurring on account of misunderstanding. Einstein’s persona and ethical beliefs redefined the meaning of the word school as a place where people spend time with an aim of becoming more knowledgeable. According to him, it is in schools that students are exposed to basic political values particularly of their country as well as going through extensive studies of how political systems operate. As a result, the students are able to come up with independent opinions regarding politics and the political elites. This is fundamentally the root of conservatism which has a number of assumptions. One of these sensible assumptions is the imperfection of the human nature. This is because human beings are inherently selfish and will generally be driven to act in ways that are only beneficial to them. Human imperfection also reveals in the corruptible nature of persons. Another sensible assumption of conservatism, and which was also reflected in Einstein’s persona, is the belief that people basically get their individual identity from their nation and family. This is practically true because the learning process demands that persons learn from the people closest to them as well as from their country of habitation. The traditionalism ideology based on the fact that institutions which have existed for long periods of time have most credibility also makes a lot of sense. This is a self-explanatory concept especially since it is well known that experience makes the best teacher. Einstein also put strong emphasis on respect of the rule of law by citizens. This is a very sensible conservative assumption as it is by individuals observing established regulations and trusting the various arms of government to implement such regulations that stability can be obtained now and in the future. Annotated BibliographyCalaprice, Alice and Trevor Lipscombe. Albert Einstein: A biography. Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005. Print. Selecting this book for research was practically easy owing to the usage of online library catalogues. The search word used was Einstein which was a straight forward choice and it listed this book as one of the favorite choices. The authors of this book recognize Einstein as one of the most recognizable scientists of all time. They however go on to point out that most people do not know much about Einstein’s life outside his profession. This book provides a clear evaluation of his life beginning with his birth going all the way to his marriage and children. The authors, in this book, confirm that aside from being a genius, Einstein was just an average person with weaknesses. This is clearly presented in the way Einstein comfortably went through school only to fail to get a job, ending up as a government clerk. His difficult marriages and family life as well as his use of his international acclaim to fight from world peace has also been given a critical review in the book. This book also carries a bibliography of publications that can be used to properly analyze Einstein’s life and this is one of the fundamental reasons as to why it was selected to inform the research. Frisch, Aaron. Albert Einstein. Minnesota: The Creative Company, 2005. Print. In this book, the author also looks at the entire life of Albert Einstein. As far as his younger life was concerned, Aaron tries to dispel the myth that Einstein had learning difficulties. The failures of his marriages and his inappopriate relation with his children have also been well described. Aaron also goes a step further to analyze the scientists life in peace activism while emphasizing the importance of the theoretical findings that Einstein made as far as the development of physics is concerned. The search word was Einstein and this book was listed among the most appropriate publications to guide any research into the life of the scientist Lakin, Patricia. Albert Einstein: Genius of the Twentieth Century. North Carolina: Baker & Taylor, 2009. Print This book was easy to find in the library especially by using the online catalogues. The search words were Albert Einstein, and this book was listed among the most appropriate volumes that fitted the description. In this publication, the author looks at younger life of the world renowned scientist and the challenges that he went through on his way to gaining international acclaim in science. The author analyzes both the public and private lives of Einstein giving particular emphasis to his overshadowed family life. This book covers almost every aspect of the scientist’s life and this is the primary reason as to why it has been selected for the bibliography of this essay. McPherson, Stephanie S. Albert Einstein. Minnesota:Lerner Publications, 2004. Print. In identifying this book, a library was visited and the online catalogue utilized to list the most recent and relevant publication as far as the topic of research was concerned. The search words used were Albert Einstein and this publication showed up among the ideal choices. This book analyzes the life and times of Albert Einstein with particular focus on his lifetime achievements. The authors provide a timeline listing the particular periods around which the great scientist made certain discoveries. The author also looks at the younger years of Einstein while dispelling the myth that he had learning difficulties. His short-lived marriages and his poor relation with his children has also been well highlighted. The strength of Albert Einstein’s scientific theories and his entry into world politics through advocating for peaceful resolution of conflicts have also been well addressed in the publication. Towards the end of the book is a bibliography listing all the books and journals that have been consulted by this particular author hence making it an ideal starting point for any research into Einstein’s life. Meachen, Dana R. Albert Einstein. Minneapolis: Compass Point Books, 2003. Print Dana Meachen Rau writes about Albert Einstein’s life. The book is in light of the scientist’s private and public eventful life. The author elicits that Einstein, after graduation, missed an opportunity to be a teacher, as he had wished, and had to settle for a job as a government clerk. In later pages, Rau looks at how Einstein continued studying and became a professor at various universities in Germany, Switzerland and in the United States of America, as well as how he came up with the quantum theory in physics and contributed greatly in the science field. One fact that have been presented in the book and which is very little known is that Einstein married and had three children with his first wife. He divorced after seventeen years and married his cousin. They never had children. He had a stint in politics which did not last long. Einstein thought governments should use peaceful means to solve conflicts rather than always going to war. This publication is very relevant in the investigation of Einstein’s life as it clearly analyzes his life as a person and as a celebrity physicist. Meltzer, Milton. Albert Einstein: A Biography. New York: Holiday House, 2007. Print In this publication, the author defines Albert Einstein as a man who always questioned and provided answers. He notes the fact that aside from being a well-known physicist, Einstein also doubled up as a peace activist. The author studies the entire life of Einstein, from the time of his birth, all the way to his death while giving appropriate details pertaining to his private life. This book contains numerous pictures of the scientist and this makes it an even more interesting piece of literature for the research. In looking for the book, a library was visited and the online catalogue utilized. The search word was Einstein and this publication showed up among the most recent and ideal publications.
IvyPanda. (2020, April 24). Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/ "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." IvyPanda , 24 Apr. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/. IvyPanda . (2020) 'Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius'. 24 April. IvyPanda . 2020. "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." April 24, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/. 1. IvyPanda . "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." April 24, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/. Bibliography IvyPanda . "Albert Einstein: The Life of a Genius." April 24, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/albert-einsteins-biography/.
This I BelieveAn ideal of service to our fellow man. Albert Einstein Listen to Robert Krulwich Read Einstein's Essay Albert Einstein published his general theory of relativity in 1916, profoundly affecting the study of physics and cosmology for years. He won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 for his work on the photo-electric effect. Einstein taught for many years at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton. Yousef Karsh hide caption  NPR's Robert Krulwich. hide caption NPR's Robert Krulwich reads Albert Einstein's This I Believe essay, which first aired circa 1954. The most beautiful thing we can experience is the Mysterious — the knowledge of the existence of something unfathomable to us, the manifestation of the most profound reason coupled with the most brilliant beauty. I cannot imagine a God who rewards and punishes the objects of his creation, or who has a will of the kind we experience in ourselves. I am satisfied with the mystery of life's eternity and with the awareness of — and glimpse into — the marvelous construction of the existing world together with the steadfast determination to comprehend a portion, be it ever so tiny, of the reason that manifests itself in nature. This is the basis of cosmic religiosity, and it appears to me that the most important function of art and science is to awaken this feeling among the receptive and keep it alive. I sense that it is not the State that has intrinsic value in the machinery of humankind, but rather the creative, feeling individual, the personality alone that creates the noble and sublime. Man's ethical behavior should be effectively grounded on compassion, nurture and social bonds. What is moral is not the divine, but rather a purely human matter, albeit the most important of all human matters. In the course of history, the ideals pertaining to human beings' behavior towards each other and pertaining to the preferred organization of their communities have been espoused and taught by enlightened individuals. These ideals and convictions — results of historical experience, empathy and the need for beauty and harmony — have usually been willingly recognized by human beings, at least in theory. The highest principles for our aspirations and judgments are given to us westerners in the Jewish-Christian religious tradition. It is a very high goal: free and responsible development of the individual, so that he may place his powers freely and gladly in the service of all mankind. The pursuit of recognition for their own sake, an almost fanatical love of justice and the quest for personal independence form the traditional themes of the Jewish people, of which I am a member. But if one holds these high principles clearly before one's eyes and compares them with the life and spirit of our times, then it is glaringly apparent that mankind finds itself at present in grave danger. I see the nature of the current crises in the juxtaposition of the individual to society. The individual feels more than ever dependent on society, but he feels this dependence not in the positive sense — cradled, connected as part of an organic whole. He sees it as a threat to his natural rights and even his economic existence. His position in society, then, is such that that which drives his ego is encouraged and developed, and that which would drive him toward other men (a weak impulse to begin with) is left to atrophy. It is my belief that there is only one way to eliminate these evils, namely, the establishment of a planned economy coupled with an education geared towards social goals. Alongside the development of individual abilities, the education of the individual aspires to revive an ideal that is geared towards the service of our fellow man, and that needs to take the place of the glorification of power and outer success. Translation by David Domine. Essay courtesy of the Albert Einstein Archives at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. More 'This I Believe' EssaysMiles goodwin: the connection between strangers, brian greene: science nourishes the mind and the soul, roald hoffmann: the tense middle, related npr stories, einstein: relatively speaking, a complicated life, author interviews, the life behind einstein's world-changing ideas, 1905: science's miracle year, test of einstein's theory of gravity hits a snag, krulwich on science, krulwich wonders..., ides of march after-party: roman drinking songs, zero gravity zzzs: joys of sleeping in outer space, the 'highest' spot on earth. Talk to our experts 1800-120-456-456
 Read Albert Einstein Essay on VedantuAlbert Einstein was a Theoretical Physicist of German origin. He is the one who developed a pillar of modern Physics, the Theory of Relativity. Be it his mass-energy equivalence formula or his law of photoelectric effect, the theories he postulated changed the history of science forever. His works are still studied in standard institutions of learning throughout the world. About Albert EinsteinAlbert Einstein was born on 14th March 1879 in Ulm in the Kingdom of Wurttemberg in the German empire. His father's name was Herman Einstein and his mother's name was Pauline Koch. His father worked as a salesman and as an engineer. In 1880, his father along with his family moved to Munich. His father and his uncle founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie. It is a company that manufactures electrical equipment based on direct current. After birth, Albert Einstein's head was much larger than his body and he was born as a deformed abnormal child. Usually, children start speaking at the age of 2, but Albert Einstein started speaking after 4 years of age. When Einstein was 5 years old, his father gifted him with a magnetic compass on his birthday. The needle of the compass used to be in the North Direction, and seeing this, he became very fascinated and developed an interest to explore science well. His ChildhoodAlbert Einstein was born on 14th March 1879, in Ulm, where his family ran a small shop. He had two siblings, an elder sister named Maja and a younger brother named Hans Albert. The Einsteins were non-observant Jews and moved to Munich when Albert was one year old. His parents wanted him to become a businessman, but he showed scientific inclinations from his childhood days. From 1890, the family resided in Milan where Einstein underwent Technical High School education. Since his father had relocated to Italy for work purposes, Albert Einstein decided not to move with his family to Berlin after matriculating from the Zurich Polytechnic in 1896. He had problems with authority and left his academic institutions without a degree on several occasions. He started working as a patent clerk at the Swiss Patent Office in 1902, where he spent most of his time on theoretical physics. In 1905, he published four papers that revolutionized Physics. They were on (I) Brownian motion, (ii) photoelectric effect, (iii) special relativity and (iv) equivalence of mass and energy, which is famously known as the E=mc 2 equation. He worked on unified field Theory for more than ten years but was unable to complete it. At the age of 5, he joined the Catholic Elementary School in Munich. After that, he enrolled in Luitpold Gymnasium, where he received his primary and secondary school education. When Albert Einstein was 15 years old, his father wanted him to do electrical engineering but Einstein used to fight with the authority of his school, about their way of teaching. He believed that due to so many strict rules and regulations in the school, the creative mind of children was lost and they only knew the strict rote learning. Einstein was thrown out of school too many times due to this behavior of his. He used to fight with his teachers, he also raised questions about their way of teaching. At the age of 12, Einstein started learning Calculus on his own, and when he became 14 years old, he mastered Integral and Differential Calculus. Einstein got married in 1903 to Marci. In 1904 his son named Hans Albert Einstein was born, and in 1910 his second son Eduard was born. Contribution Towards ScienceAlbert received a patent officer job at the Federal Office for Intellectual Property in Bern, Switzerland, at the age of 23, after completing college. While working there, he completed his Ph.D., after which he became a professor at the University of Zurich. During this period he gave the theory of mass-energy (E = mc 2 ). The atomic bombs dropped in Japan were built on this principle. However, throughout his life, Albert Einstein was against the atomic bomb dropped on Japan. He then gave a new theory of relativity, falsifying the old rules of relativity given by Isaac Newton, which proved that time and light are not constant. If traveling at the speed of light, i.e. 300000 km, it will be slow, and millions of years have passed on Earth. That is, he proved that time travel can be done. However, till date scientists have not been able to build a spaceship that can travel at the speed of light. In 1977, NASA conducted an experiment to prove this theory in which they set the clock in a satellite and were left to orbit the Earth. After a few years, when the satellite's clock was checked, it was much slower than the Earth's clock. In this theory of quantum physics, Indian scientist Satyendra Nath Bose wrote a letter from India to Albert Einstein in which he said that Newton's relativity theory is wrong. Albert Einstein then agreed to the letter of Satyendra Nath Bose, and he published that paper and later gave a new theory of relativity. Albert Einstein made many other inventions with this theory. He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1981 for his photoelectric effect. In 1933, Hitler killed millions of people in Germany, and at the same time, Albert Einstein was changing the whole world with science. He went to America from Europe forever, taking the citizenship there because Hitler placed a reward of \[$\]5000 on Albert Einstein's head and burned all his research books. Moving to the United StatesDuring World War-I, he was invited to join the Bureau of Standards in Washington before accepting its offer officially. He moved to the United States of America with his family in April 1933 after Hitler's rise to power. He advised breaking up Bell Labs and nationalizing the electricity supply industry, worked on defense projects during World War II, and became a citizen of the United States in 1940. In 1951, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect." Albert Einstein died on 18th April 1955 at Princeton Hospital, New Jersey. He was 76 years old. Death and AwardsOn 17th April 1955, Einstein underwent internal bleeding in the Lower Abdominal, and he was taken to a hospital where the doctor asked him to undergo a surgery. Albert Einstein refused to undergo the surgery, and said that he would go when he wanted, and that it is tasteless to prolong life artificially. He told me that he would like to die like that. Later research was done on Albert Einstein's brain and it was found that the parts of Einstein's brain that were for mathematical calculus had developed 15% more as compared to the brains of normal people. The whole world celebrates Albert Einstein's birthday on 14th March as World Genius Day. He had published more than 300 research papers on science in his life and had contributed to the advancement of science. This is the reason that Times magazine has awarded Albert Einstein the title of Person of the Century. Einstein received numerous awards and honors, and in 1922, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". ConclusionAlbert Einstein was one of the best scientists, mathematicians, and physicists of the 20th century. In the early twentieth century, Albert Einstein formulated theories that changed the thinking of physicists and non-specialists alike. He will always be remembered for his law of photoelectric effect and mass-energy equivalence formula. His body of work is studied in universities across the world to this day. He is a famous and known name in the world of Physics, he also achieved a lot, and was awarded the Nobel Prize for his commendable research and accomplishments.   FAQs on Albert Einstein Essay1. Why did Albert Einstein Have No Social Life? Albert Einstein was a very intelligent person. He had no time for a social life because he was always busy with his research and work. Albert Einstein had more than 40 publications to his credit. His life and work were on research and inventions. His life revolved around his work and family. The work-life of Albert Einstein is an inspiration to all the people who are working day and night to achieve something great in their lives. One of the best scientists, mathematicians and physicists of the 20th century was none other than Albert Einstein. His achievement includes the most discussed formula in his name- the mass-energy equivalence equation. He was known for the impact he made on the world of physics and also for the awards and honors he received in his lifetime. 2. What Was the Theory of Relativity by Albert Einstein? The theory of relativity is the scientific theory developed by Albert Einstein between 1905 and 1915. It is a theory of gravity and space-time. The theory revolutionized physics by proposing that the laws of physics are the same for all inertial frames of reference. That is, the laws of physics are the same whether an observer is stationary or in motion. The theory also proposed that the speed of light is a constant for all observers, regardless of their relative motion. This was a radical departure from classical mechanics and Newton's view of the universe. His theory is the basis for many features of our modern life and is used in daily applications. You can learn more about the theory of relativity in any good physics textbook. 3. What Did Albert Einstein Do for Science? Albert Einstein was a German theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. He is best known in popular culture for his mass-energy equivalence formula E = mc 2 (which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation"). He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". This makes Einstein the only physicist to win twice. He is also known for his other great works, such as the world's smallest unit of time and explaining the Brownian motion of particles. His life's work has had a great impact on the modern world and the way we see things. 4. What Awards Did Albert Einstein Receive in His Lifetime? Albert Einstein was one of the most genius scientists of all time. He is known for his great works in Physics. He also received a lot of awards in his lifetime. Albert Einstein won the Nobel Prize in 1921 for physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". He is the only physicist to have been awarded a Nobel Prize twice. In 1921, he received the Nobel Prize in physics. In his acceptance lecture, titled "The Field Theory of Matter", he provided what is now viewed as a foundation for relativistic quantum field theory. Einstein was voted number 3 in BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. 5. Why Was Einstein Thought of as a Genius? Albert Einstein was a brilliant and intelligent man. He changed the world because of his scientific ideas and theories. He is known for the mass-energy equivalence formula (E=mc 2 ); he came up with it in 1905; before coming to this theory, he did not have any notable publications. However, by the end of this year, he had already submitted two articles to Annalen der Physik. One of these was on the photoelectric effect, while the other was on "A new determination of molecular dimensions". Albert Einstein is considered a genius because he looked at things in an entirely different way than anyone else did before him. He also had wonderful ideas about space and time that changed the way we think about those things. 6. What Were the Names of Albert Einstein’s Father and Mother? Albert Einstein was born on 14th March 1879 in Ulm in the Kingdom of Wurttemberg in the German empire. His father’s name was Herman Einstein and His Mother’s name was Pauline Koch. 7. How Albert Einstein Was Different from Normal Kids? After birth, Albert Einstein's head was much larger than his body and he was born as a deformed abnormal child. Usually, children start speaking at the age of 2, but in the case of Albert Einstein, he started speaking after 4 years of age. At the age of 12, Einstein learning Calculus and when he became 14 years old he had mastered Integral and Differential Calculus which is obviously not normal for any other kid.
Top Schools
Products & Resources
Colleges & Courses
Predictors & E-Books
Predictors & Articles
Top Courses & Careers
Quick Links
Diploma Colleges
Upcoming Events
Other Exams
Top Countries
Student Visas
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
Online Courses
Top Streams
Specializations
Top Providers
Essay on Albert EinsteinScience reached a high peak with the great scientist Albert Einstein. He is known as one of the greatest thinkers and scientists of the twentieth century. He is the one who advanced the pillar of Modern Physics. Albert Einstein is best known for introducing the theory of relativity in Physics, which helped us to understand time, universe, gravity, and space. Here are a few sample essays on Albert Einstein. 100 Words Essay on Albert Einstein200 words essay on albert einstein, 500 words essay on albert einstein.  Published in 1905, Einstein's first article established him as one of the world’s premier scientists. Einstein admired the environment much more compared to other children and wished to spend more time with nature as the sounds and sights fascinated him. While employed in the patent office, Einstein did not miss the opportunity to solve the beam light problem, which he had been fascinated with since he was 16. Albert Einstein spent his entire life working for harmony and abominated war. Albert was in support of the American Civil Right Movement, and he was totally against violence. For his law of photoelectric effect, Einstein received a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921. Born on March 14, 1879, Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist. Albert studied in a Catholic Elementary School in Munich. He was then transferred to the Luitpold Gymnasium (today known as Albert Einstein Gymnasium) at 8, where he received primary and secondary education. Albert Einstein was not much of a fan of education, yet he enjoyed learning and reading independently. Einstein had these two ‘wonders’ in his early years, which affected him greatly. At age five, an encounter with a compass mystified him that the invisible forces could divert the needle. Secondly, at age 12, he found a book of geometry, which he devoured, and gave it the name “sacred little geometry book”. Contribution To PhysicsHe significantly contributed to Physics in 1905 when he developed the Theory of Special Relativity. From a young age, Einstein excelled in Physics and Maths and even discovered his original Pythagorean theorem at age 12. His father wanted him to go with Electrical Engineering, but Einstein did not agree with him and resented the school’s regiment and the teaching method. Einstein was much ahead of his peers in Maths and Physics and excelled in them. His passion for algebra and geometry convinced everyone that nature could be understood as a mathematical structure. He was also awarded a Federal Teaching Diploma. Einstein was one of the founding members of the German Democratic Party in 1918. He was critical of capitalism and was a socialist. Impressed by Mahatma Gandhi, Einstein described him as a role model for future generations and exchanged written letters with him. Einstein was totally in support of non-violence. He was also a Nobel Prize winner. Childhood Issues | Einstein was unable to speak in his childhood because his skull was larger than the rest of his body. Slowly and gradually, his head began to improve and take shape. Still, everyone believed him to be sick until that time. Religious Beliefs | Albert Einstein did not believe in any personal God for all the fates, destiny and actions. He also clarified that he was not an atheist and instead called himself a deeply religious non-believer. He observed and admitted that without ethical culture, there is no stand for salvation for humanity. Stint With Music | Einstein’s mother played the piano quite well and wanted her son to learn the same, so he could develop a love for music. At age 5, Einstein began to play the piano, though he did not enjoy it much. He discovered the violin sonatas of Mozart at age 13, and at that time, he started to enjoy music. Einstein played Chamber music for his friends and family. Contribution To Physics | He received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the Photoelectric Effect. He also launched the new science of Cosmology. A Nobel Prize was awarded in 1993 to the discoverers of gravitational waves predicted by Einstein. Death | Einstein died in the University Medical Centre of Princeton and Plainsboro, after his death, during an autopsy, the pathologist removed Einstein’s brain without the permission of his family and preserved it to know the real cause of Einstein’s intelligence. Einstein’s legacy was passed on to other scientists. An Incident From Einstein’s LifeIn 1919, at the University of Berlin, while working as a theoretical physics professor, Einstein theorised that an impending solar eclipse would provide a rare opportunity to observe gravity’s effect on light. The reports proved his observation to be correct. This observation of Einstein sent a shock wave through the scientific community and the world. Einstein spent the next few years travelling, speaking engagements, and receiving awards. He also founded the Hebrew University in Jerusalem in 1921 and won the Nobel Prize in the same year. What Do We Learn From Einstein?Albert Einstein had the ability to think outside of the square and apply great imagination and creativity to science. This ability of his influenced many people to think outside their comfort zone, explore chances and the world around them. Einstein gave way to many younger generations to think and rethink what they want to do and focus on it, to give their hundred percent in achieving their desired goals. Einstein also taught us not to blindly believe in whatever is being told but to question everything and look for reasons. Albert Einstein taught us to live in the moment and to keep going in the right direction, and success will automatically follow. One should make mistakes but also learn from them, as one who does not commit mistakes practically does not do anything. Applications for Admissions are open. Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses  JEE Main Important Physics formulasAs per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters  JEE Main Important Chemistry formulasAs per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters  TOEFL ® Registrations 2024Accepted by more than 11,000 universities in over 150 countries worldwide  PTE Exam 2024 RegistrationsRegister now for PTE & Save 5% on English Proficiency Tests with ApplyShop Gift Cards  JEE Main high scoring chapters and topicsAs per latest 2024 syllabus. Study 40% syllabus and score upto 100% marks in JEE Download Careers360 App'sRegular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile Certifications We Appeared inAlbert Einstein: The Mind Behind the Theory of Relativity Life StoriesAlbert Einstein's groundbreaking discoveries in theoretical physics revolutionized our understanding of the universe and earned him a place among the greatest scientific minds in history. His relentless pursuit of knowledge, unorthodox thinking, and unwavering curiosity continue to inspire generations of scientists and thinkers worldwide. Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.
Top Podcasts In Education
Popular Searches Albert Einstein (1879-1955)How strange is the lot of us mortals! Each of us is here for a brief sojourn; for what purpose he knows not, though he sometimes thinks he senses it. But without deeper reflection one knows from daily life that one exists for other people – first of all for those upon whose smiles and well-being our own happiness is wholly dependent, and then for the many, unknown to us, to whose destinies we are bound by the ties of sympathy. Albert Einstein, The World as I See It (1935)  Albert Einstein was a German theoretical physicist and history’s most famous scientist. He was also a passionate humanist, who actively supported the Ethical Culture movement in the US, was a founder member of the First Humanist Society of New York, and an Honorary Associate of the Rationalist Press Association in the UK. Einstein wrote eloquently about his philosophy, which had human possibility and fellowship at its heart. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921, in 1955 he co-authored with fellow humanists Bertrand Russell and Joseph Rotblat a manifesto calling for peace and disarmament, prompting the creation of the Pugwash Conferences on Science and World Affairs, which would go on to win a Nobel Peace Prize four decades later. This central belief in the need for humanity in science – in the application of reason and compassion to curb the dangerous excesses of human ambition – is a key part of Einstein’s legacy, though his humanist convictions have been all too frequently left out of narratives of his genius.  Albert Einstein was born in Ulm, Germany, and raised in Munich, in a secular Jewish home. Fascinated from an early age by science and the forces of nature, he had an unusual and disrupted education, but was a devoted autodidact. For seven years from 1902 he worked in a patent office, during which time he earned his doctorate and – in 1905, his so-called ‘miracle year’ – published the papers which would profoundly alter our understanding of space and time. As the editor of the Literary Guide (now the New Humanist ) would write on his death in 1955, Einstein’s was a ‘combination of imaginative boldness and humility before facts’, which cemented his reputation as a pioneering scientific thinker, and a model of the humanist approach. Though his scientific achievements are widely, and rightly, known, Einstein’s contributions to the literature of humanism, and to efforts towards peace and international cooperation, are often less well-documented. As well as famed works such as his Special Theory of Relativity (1905), General Theory of Relativity (1916), and The Evolution of Physics (1938), Einstein wrote The World as I See It (1935) and Essays in Humanism (1950), giving voice to his philosophical ideals. In this latter collection, he outlined his belief that: …the most important factor in giving shape to our human existence is the setting up and establishment of a goal; the goal being a community of free and happy human beings who by constant inward endeavor strive to liberate themselves from the inheritance of anti-social and destructive instincts. In this effort the intellect can be the most powerful aid. The fruits of intellectual effort, together with the striving itself, in cooperation with the creative activity of the artist, lend content and meaning to life. ‘The Goal of Human Existence’ in Essays in Humanism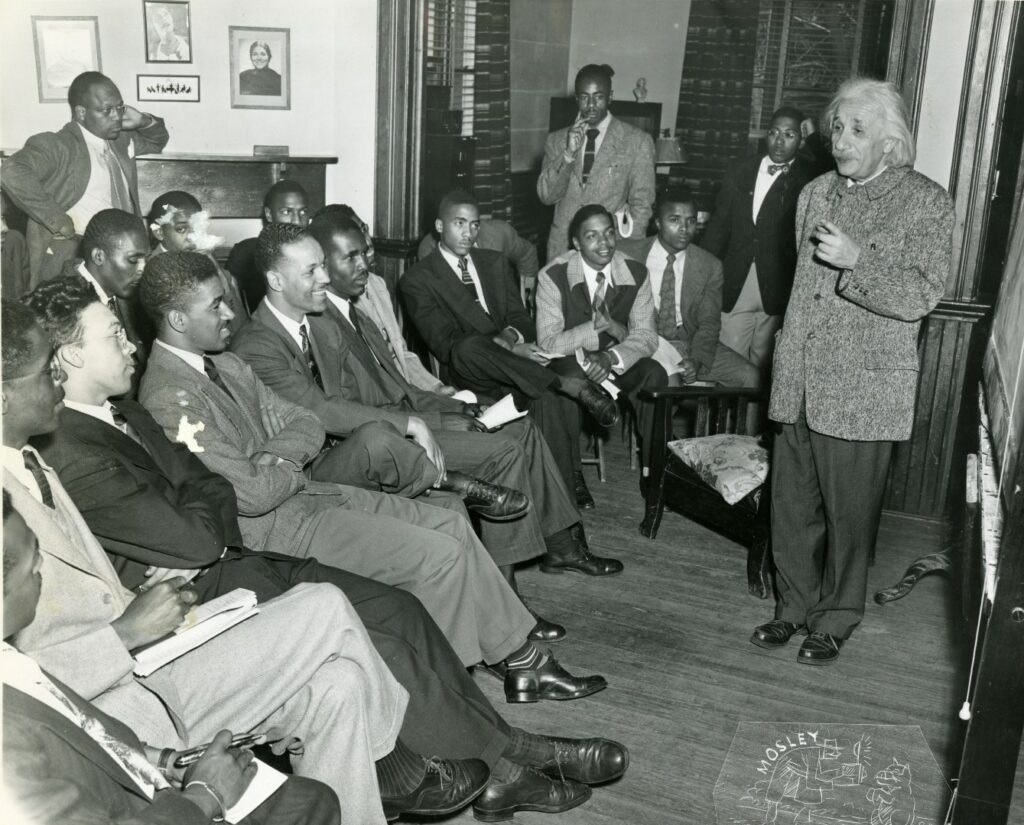  This sense of collective striving for greater freedom, happiness, and meaning, through knowledge and through art, underpinned Einstein’s outspoken support for world government, and for the Ethical movement. A longtime anti-militarist, Einstein had renounced his German citizenship in 1896, preferring to be ‘stateless’ rather than undertake military service. Later, he used his public profile to support calls for world disarmament, and to decry racism, drawing on his own experience of anti-semitism. During the 1930s and 1940s, now living in America, Einstein joined civil rights organisations including the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) and the American Crusade Against Lynching (ACAL), acting as co-chair for the latter, and lobbying for federal anti-lynching legislation alongside its founder Paul Robeson. In a commencement address for the historically black Lincoln University, Pennsylvania, he stated (using the term then generally accepted): There is separation of colored people from white people in the United States. That separation is not a disease of colored people. It is a disease of white people. I do not intend to be quiet about it.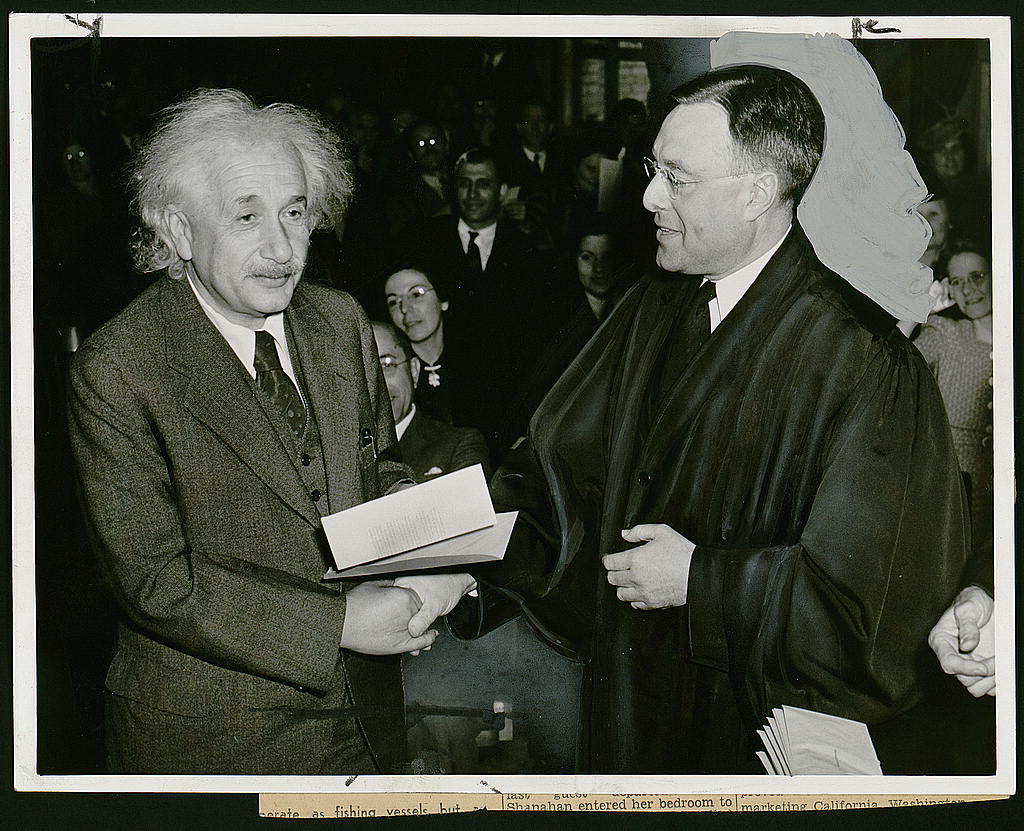  Einstein spent his final decades in the United States, employed at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. In the final year of his life, he issued a joint manifesto with humanist and philosopher Bertrand Russell calling for nuclear disarmament, and containing the immortal plea to world leaders: ‘Remember your humanity, and forget the rest’. This echoed Einstein’s belief, expressed in congratulating the New York Society for Ethical Culture on 75 years in existence, that ‘Without ‘ethical culture’ there is no salvation for humanity’. Without bringing human sympathy to bear on science, Einstein believed, the pursuit of the ‘eternally unattainable’ was empty. Albert Einstein died on 18 April 1955, having refused surgery to prolong his life. He met death calmly, telling his secretary and companion Helen Dukas, ‘I have to pass on sometime’. A famous photo of his desk at the time of his death shows the Rationalist Association’s latest periodical, today’s New Humanist magazine, sitting at the top of his to-read pile. I do not believe in a personal God and I have never denied this… If something is in me which can be called religious then it is the unbounded admiration for the structure of the world so far as our science can reveal it. Albert Einstein (1954) Albert Einstein was an innovative and imaginative scientist, whose pursuit of knowledge and fascination with the world gave rise to world-altering theories, and eloquent expressions of humanism. Einstein believed in the human responsibility for the world and for each other; in developing a moral system set apart from the supernatural; and in maintaining a sense of profound wonder, and active inquisitiveness, towards the universe at large. In setting reason, empathy, and principle at the heart of his philosophy, Einstein left a significant humanist legacy, and a remarkable reminder of the human side of science. How Albert Einstein Used His Fame to Denounce American Racism The Day Albert Einstein Died: A Photographer’s Story Related Topics University College LondonUniversity College London was founded in 1826 as the University of London; the city’s first university, and a consciously secular […]  Helena Swanwick (1864-1939)Life would be far more truly envisaged if we dropped the silly phrases “men’s and women’s questions”; for indeed there […]  Lilian Sauter 1864-1924Lift the heart to high endeavour! Fire the thought and nerve the will! Though the bonds be hard to sever, […]  Ford Madox Brown (1821-1893)A cheerful and reverent Agnostic, whose whole life was one of unselfishness and devotion to lofty aims, who was tolerant […] L.A.’s underground celebrates the life of punk iconoclast John Albert
Once upon a time, the collected works of music journalists, film critics and other cultural correspondents appeared with regularity on the literary landscape. We relied on their observations to make sense not only of the art we admired and the artists who created it but of the times we lived in and the places we felt at home. Now? Not so much. The way culture is celebrated, disseminated and reported on has changed, probably forever. So when a book like “ Running With the Devil: Essays, Articles & Remembrances ” by John Albert appears on the horizon, it feels as anachronistic as a sailing vessel flying the skull and bones. But John Albert was no ordinary writer. When he died suddenly from a heart attack last year at the age of 58, he left behind a body of work scattered across the pages of books, anthologies, literary journals and alternative weeklies. His friend and editor, Joe Donnelly, hit on the idea to assemble these pieces in a collection. “Almost as soon as John died,” Donnelly said, “I started thinking about the responsibility to preserve his writing legacy.” Donnelly approached their mutual friend Iris Berry, co-founder of Punk Hostage Press , about the project. She didn’t need to be convinced. “There always seemed to be a kind of magic surrounding John Albert,” Berry said. “A mystery and a charisma that I can’t explain. He definitely left us too soon.”  It’s only fitting, then, that “Running With the Devil” will receive a grand, old-school book launch at Wacko Soap Plant from 4 to 7 p.m. on Sunday, June 30. Berry and Donnelly will be joined by a crew of underground all-stars that includes Jesse Albert, Jennifer Finch, Brett Gurewitz, Ben Harper, Keith Morris, Arty Nelson, Jerry Stahl, John Waldman and Justin Warfield. Albert emerged from the exurbs of Los Angeles and embraced the city in all its guises. He was an early member of Christian Death and Bad Religion, two bands whose names suggest a spiritual affinity, or at least a consensus, but couldn’t be more stylistically dissimilar. He wrote about discovering Black Flag and embracing punk rock with pulp panache: “I have cut my hair short and can’t stop smashing windows.” “In the Black Flag piece,” Berry said, “I love how he writes about the transition into punk rock in great detail. It affected everyone around him, especially his parents and friends. Throughout history, parents have always been horrified by their kids’ choices, but the punk movement was one of the toughest and John articulated it so well.” Albert was so much more than a former musician and occasional music writer. As a recovering addict, he found salvation in sport: first and most famously through baseball, which he wrote about in “The Wrecking Crew: The Really Bad News Griffith Park Pirates.” Writing about a team of recovering addicts, washed-up rockers and miscellaneous oddballs, he captured something magical about L.A. “He made sense of Los Angeles in a sort of Didion-esque and Eve Babitz way,” Donnelly said. “His best subjects were his friends and the people in his circle, and he had a unique window into Los Angeles during that time and place.” As Albert’s interests and experiences expanded, so did his writing: He wrote about surfing, living with Hepatitis C, the Red Hot Chili Peppers. As Keith Morris, founding vocalist for Black Flag and the Circle Jerks, puts it: “John was a stud prince rawker and had a great knowledge of all sorts of happening stuff.” Albert had a knack for writing about things that had been overlooked or pushed to the margins, and by training his lens on them helped make them culturally significant again. In a city that runs on hype, Albert was more interested in those who’d opted out, been left behind or were kicked to the curb by the dream factory.  “He was a throwback,” Donnelly said, “a punk-rock George Plimpton. He was in the mix of life and wrote from the perspective of lived experience, and not just helicoptering into an anthropological survey of something. He actually knew of what he spoke.” Although he wasn’t a sentimental writer, Albert wrote with great humor. His sarcasm could be devastating, but he saved it for those in his inner circle, the people he loved most. “John was such a talented writer,” said Berry. “He remembered so much. The feelings, the details of the feelings, and the places. He slides from comedy to tragedy and back to comedy with such grace. He was a true storyteller.” One of the many tragedies of Albert’s untimely passing is that we have been deprived a book about fatherhood in 21st century L.A. Albert loved his son, Ravi, and all the proceeds from the collection will go to him. “Getting to publish his book, ‘Running With the Devil,’ is bittersweet for me,” Berry said. “I’m honored to get to publish him, grateful to Joe Donnelly for bringing it to me and for editing it. I just wish it was under different circumstances. But knowing that it’s for his son, Ravi, is everything. As my mom would say, ‘It’s definitely a mitzvah.’” Join Iris Berry, Joe Donnelly and friends at Wacko Soap Plant, 4633 Hollywood Blvd., on Sunday, June 30, from 3 to 7 p.m. Jim Ruland is the author of the novel “Make It Stop” and “Corporate Rock Sucks: The Rise & Fall of SST Records.” More to Read Thirty years ago, Time magazine asked if L.A. was ‘going to hell.’ Are we there yet?Dec. 22, 2023  How to experience L.A. like a poetDec. 19, 2023  She created the Drag Queen Story Hour. Now she’s launching L.A.’s newest publisherDec. 18, 2023 Sign up for our Book Club newsletter Get the latest news, events and more from the Los Angeles Times Book Club, and help us get L.A. reading and talking. You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times. More From the Los Angeles Times The week’s bestselling books, July 1July 3, 2024  The 1999 novel that predicted our (traumatic, relentlessly bleak) futureJuly 1, 2024 The week’s bestselling books, June 30June 26, 2024  Former UFC, WWE star Ronda Rousey finds ‘path that I was meant for’ as graphic novelistJune 25, 2024  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
COMMENTS
Albert Einstein (born March 14, 1879, Ulm, Württemberg, Germany—died April 18, 1955, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.) was a German-born physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity and won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Albert Einstein was one of the world's most brilliant thinkers, influencing scientific thought immeasurably. He was also not shy about sharing his wisdom about other topics, writing essays ...
500 Words Essay On Albert Einstein. Albert Einstein was a physicist who is responsible for developing the famous general theory of relativity. Furthermore, he is one of the most influential and celebrated scientists of the 20th century. Let's take a look at the life and achievements of this genius with the essay on Albert Einstein.
Einstein's Early Life (1879-1904) Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich.
The text of Albert Einstein's copyrighted essay, "The World As I See It," was shortened for our Web exhibit. The essay was originally published in "Forum and Century," vol. 84, pp. 193-194, the thirteenth in the Forum series, Living Philosophies . It is also included in Living Philosophies (pp. 3-7) New York: Simon Schuster, 1931.
Early Life, Family, and Education. Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. ... via an essay for The Atlantic Monthly, Einstein espoused working with the United ...
Throughout his life, Einstein published hundreds of books and articles. He published more than 300 scientific papers and 150 non-scientific ones. On 5 December 2014, universities and archives announced the release of Einstein's papers, comprising more than 30,000 unique documents.
Einstein's gifts inevitably resulted in his dwelling much in intellectual solitude and, for relaxation, music played an important part in his life. He married Mileva Maric in 1903 and they had a daughter and two sons; their marriage was dissolved in 1919 and in the same year he married his cousin, Elsa Löwenthal, who died in 1936.
Albert Einstein's work in 1905 shook the world of physics. In his explanation of the photoelectric effect he introduced the photon theory of light. In his paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies," he introduced the concepts of special relativity . Einstein spent the rest of his life and career dealing with the consequences of these ...
A timelines of the life and career of Albert Einstein, including his theories of special and general relativity. ... in an essay about his impressions of the country he wrote "The American is ...
A visiting medical student named "Max Talmud introduced him to Euclid's book entitled Elements ." 7 Later on Einstein referred to this masterpiece as "the holy little geometry book." 8. Although he had a brilliant mind, he had trouble finishing his studies. He finally graduated in 1900 and earned a degree in physics.
Legendary scientist Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) first gained worldwide prominence in 1919 after British astronomers verified predictions of Einstein's general theory of relativity through measurements taken during a total eclipse. Einstein's theories expanded upon universal laws formulated by physicist Isaac Newton in the late seventeenth century.
Albert Einstein was one of the most influential scientists of all time. Born in Germany in 1879, Einstein was known for his remarkable curiosity and love for exploration from a very young age. This passion for discovery ultimately led him to science and mathematics, which he pursued throughout his academic career.
Einstein's death. Einstein died of an aortic aneurysm on April 18, 1955. A blood vessel burst near his heart, according to the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH). When asked if he wanted to ...
March 14, 1879—April 18, 1955. LD WHEELER*ALBERT EINSTEIN was born in Ulm, Germany on March -*. - 14, 1879. After education in Germany, Italy, and Swit-zerland, and professorships in Bern, Zurich, and Prague, he was appointed Director of Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Phy-sics in Ber. in in 1914. He became a professor in the School of ...
Albert Einstein was born in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879 (Meltzer 2). Less than two months after his birth his family relocated to Munich where he started his education. As years passed by, Einstein and his family again relocated, this time to Switzerland, where the young Albert gained a diploma in physics and mathematics (Lakin 20).
NPR's Robert Krulwich reads Albert Einstein's This I Believe essay, which first aired circa 1954.. The most beautiful thing we can experience is the Mysterious — the knowledge of the existence ...
Conclusion. Albert Einstein was one of the best scientists, mathematicians, and physicists of the 20th century. In the early twentieth century, Albert Einstein formulated theories that changed the thinking of physicists and non-specialists alike. He will always be remembered for his law of photoelectric effect and mass-energy equivalence formula.
Jamie Sayen has written that Einstein "came to play a critical role in the public life of his epoch as the preeminent moral figure of the Western world." Even with his stature as a spokesman for ...
500 Words Essay on Albert Einstein. Einstein was one of the founding members of the German Democratic Party in 1918. He was critical of capitalism and was a socialist. Impressed by Mahatma Gandhi, Einstein described him as a role model for future generations and exchanged written letters with him. Einstein was totally in support of non-violence.
Albert Einstein's groundbreaking discoveries in theoretical physics revolutionized our understanding of the universe and earned him a place among the greatest scientific minds in history. His relentless pursuit of knowledge, unorthodox thinking, and unwavering curiosity continue to inspire generations of scientists and thinkers worldwide.
Albert Einstein died on 18 April 1955, having refused surgery to prolong his life. He met death calmly, telling his secretary and companion Helen Dukas, 'I have to pass on sometime'. A famous photo of his desk at the time of his death shows the Rationalist Association's latest periodical, today's New Humanist magazine, sitting at the ...
Albert Einstein Life. Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in the small town of Ulm, in Southern Germany, near Europes longest river, the Danube. His parents, Hermann and Pauline, were Jewish. ... In one year, 1905, Einstein published four ...
In conclusion Albert Einstein was one of the best scientist, mathematical and physicist person of the 20th century. Albert even doe he wasn't the best on his class he changed the point of view of physics. He was not only a simple physics teacher in college he won a nobel price for all of his remarkable accomplishments and research. I truly ...
"Running With the Devil," Albert's book of essays and stories on LA punk culture, will receive a grand, old-school book launch at Wacko Soap Plant on June 30.