How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project .
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement , devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes , demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:

Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Once you have outlined your goals, objectives, steps, and tasks, it’s time to drill down on selecting research methods . You’ll want to leverage specific research strategies and processes. When you know what methods will help you reach your goals, you and your teams will have direction to perform and execute your assigned tasks.
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews : this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies : this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting : participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups : use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies : ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys : get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing : tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing : ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project . Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty . But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
FLEET LIBRARY | Research Guides
Rhode island school of design, create a research plan: research plan.
- Research Plan
- Literature Review
- Ulrich's Global Serials Directory
- Related Guides
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan
1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question
2. Research methodology - describes your approach to the research question
3. Literature review, critical evaluation and synthesis - systematic approach to locating,
reviewing and evaluating the work (text, exhibitions, critiques, etc) relating to your topic
4. Communication - geared toward an intended audience, shows evidence of your inquiry
Research conceptualization refers to the ability to identify specific research questions, problems or opportunities that are worthy of inquiry. Research conceptualization also includes the skills and discipline that go beyond the initial moment of conception, and which enable the researcher to formulate and develop an idea into something researchable ( Newbury 373).
Research methodology refers to the knowledge and skills required to select and apply appropriate methods to carry through the research project ( Newbury 374) .
Method describes a single mode of proceeding; methodology describes the overall process.
Method - a way of doing anything especially according to a defined and regular plan; a mode of procedure in any activity
Methodology - the study of the direction and implications of empirical research, or the sustainability of techniques employed in it; a method or body of methods used in a particular field of study or activity *Browse a list of research methodology books or this guide on Art & Design Research
Literature Review, critical evaluation & synthesis
A literature review is a systematic approach to locating, reviewing, and evaluating the published work and work in progress of scholars, researchers, and practitioners on a given topic.
Critical evaluation and synthesis is the ability to handle (or process) existing sources. It includes knowledge of the sources of literature and contextual research field within which the person is working ( Newbury 373).
Literature reviews are done for many reasons and situations. Here's a short list:
| to learn about a field of study to understand current knowledge on a subject to formulate questions & identify a research problem to focus the purpose of one's research to contribute new knowledge to a field personal knowledge intellectual curiosity | to prepare for architectural program writing academic degrees grant applications proposal writing academic research planning funding |
Sources to consult while conducting a literature review:
Online catalogs of local, regional, national, and special libraries
meta-catalogs such as worldcat , Art Discovery Group , europeana , world digital library or RIBA
subject-specific online article databases (such as the Avery Index, JSTOR, Project Muse)
digital institutional repositories such as Digital Commons @RISD ; see Registry of Open Access Repositories
Open Access Resources recommended by RISD Research LIbrarians
works cited in scholarly books and articles
print bibliographies
the internet-locate major nonprofit, research institutes, museum, university, and government websites
search google scholar to locate grey literature & referenced citations
trade and scholarly publishers
fellow scholars and peers
Communication
Communication refers to the ability to
- structure a coherent line of inquiry
- communicate your findings to your intended audience
- make skilled use of visual material to express ideas for presentations, writing, and the creation of exhibitions ( Newbury 374)
Research plan framework: Newbury, Darren. "Research Training in the Creative Arts and Design." The Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts . Ed. Michael Biggs and Henrik Karlsson. New York: Routledge, 2010. 368-87. Print.
About the author
Except where otherwise noted, this guide is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution license
source document
Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Sep 20, 2023 5:05 PM
- URL: https://risd.libguides.com/researchplan
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write a Research Plan
- Research plan definition
- Purpose of a research plan
- Research plan structure
- Step-by-step writing guide
Tips for creating a research plan
- Research plan examples
Research plan: definition and significance
What is the purpose of a research plan.
- Bridging gaps in the existing knowledge related to their subject.
- Reinforcing established research about their subject.
- Introducing insights that contribute to subject understanding.
Research plan structure & template
Introduction.
- What is the existing knowledge about the subject?
- What gaps remain unanswered?
- How will your research enrich understanding, practice, and policy?
Literature review
Expected results.
- Express how your research can challenge established theories in your field.
- Highlight how your work lays the groundwork for future research endeavors.
- Emphasize how your work can potentially address real-world problems.
5 Steps to crafting an effective research plan
Step 1: define the project purpose, step 2: select the research method, step 3: manage the task and timeline, step 4: write a summary, step 5: plan the result presentation.
- Brainstorm Collaboratively: Initiate a collective brainstorming session with peers or experts. Outline the essential questions that warrant exploration and answers within your research.
- Prioritize and Feasibility: Evaluate the list of questions and prioritize those that are achievable and important. Focus on questions that can realistically be addressed.
- Define Key Terminology: Define technical terms pertinent to your research, fostering a shared understanding. Ensure that terms like “church” or “unreached people group” are well-defined to prevent ambiguity.
- Organize your approach: Once well-acquainted with your institution’s regulations, organize each aspect of your research by these guidelines. Allocate appropriate word counts for different sections and components of your research paper.
Research plan example

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to Write a Research Plan

Your answers to these questions form your research strategy. Most likely, you’ve addressed some of these issues in your proposal. But you are further along now, and you can flesh out your answers. With your instructor’s help, you should make some basic decisions about what information to collect and what methods to use in analyzing it. You will probably develop this research strategy gradually and, if you are like the rest of us, you will make some changes, large and small, along the way. Still, it is useful to devise a general plan early, even though you will modify it as you progress. Develop a tentative research plan early in the project. Write it down and share it with your instructor. The more concrete and detailed the plan, the better the feedback you’ll get.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
This research plan does not need to be elaborate or time-consuming. Like your working bibliography, it is provisional, a work in progress. Still, it is helpful to write it down since it will clarify a number of issues for you and your professor.
Writing a Research Plan
To write out your research plan, begin by restating your main thesis question and any secondary ones. They may have changed a bit since your original proposal. If these questions bear on a particular theory or analytic perspective, state that briefly. In the social sciences, for example, two or three prominent theories might offer different predictions about your subject. If so, then you might want to explore these differences in your thesis and explain why some theories work better (or worse) in this particular case. Likewise, in the humanities, you might consider how different theories offer different insights and contrasting perspectives on the particular novel or film you are studying. If you intend to explore these differences, state your goal clearly in the research plan so you can discuss it later with your professor. Next, turn to the heart of this exercise, your proposed research strategy. Try to explain your basic approach, the materials you will use, and your method of analysis. You may not know all of these elements yet, but do the best you can. Briefly say how and why you think they will help answer your main questions.
Be concrete. What data will you collect? Which poems will you read? Which paintings will you compare? Which historical cases will you examine? If you plan to use case studies, say whether you have already selected them or settled on the criteria for choosing them. Have you decided which documents and secondary sources are most important? Do you have easy access to the data, documents, or other materials you need? Are they reliable sources—the best information you can get on the subject? Give the answers if you have them, or say plainly that you don’t know so your instructor can help. You should also discuss whether your research requires any special skills and, of course, whether you have them. You can—and should—tailor your work to fit your skills.
If you expect to challenge other approaches—an important element of some theses—which ones will you take on, and why? This last point can be put another way: Your project will be informed by some theoretical traditions and research perspectives and not others. Your research will be stronger if you clarify your own perspective and show how it usefully informs your work. Later, you may also enter the jousts and explain why your approach is superior to the alternatives, in this particular study and perhaps more generally. Your research plan should state these issues clearly so you can discuss them candidly and think them through.
If you plan to conduct tests, experiments, or surveys, discuss them, too. They are common research tools in many fields, from psychology and education to public health. Now is the time to spell out the details—the ones you have nailed down tight and the ones that are still rattling around, unresolved. It’s important to bring up the right questions here, even if you don’t have all the answers yet. Raising these questions directly is the best way to get the answers. What kinds of tests or experiments do you plan, and how will you measure the results? How will you recruit your test subjects, and how many will be included in your sample? What test instruments or observational techniques will you use? How reliable and valid are they? Your instructor can be a great source of feedback here.
Your research plan should say:
- What materials you will use
- What methods you will use to investigate them
- Whether your work follow a particular approach or theory
There are also ethical issues to consider. They crop up in any research involving humans or animals. You need to think carefully about them, underscore potential problems, and discuss them with your professor. You also need to clear this research in advance with the appropriate authorities at your school, such as the committee that reviews proposals for research on human subjects.
Not all these issues and questions will bear on your particular project. But some do, and you should wrestle with them as you begin research. Even if your answers are tentative, you will still gain from writing them down and sharing them with your instructor. That’s how you will get the most comprehensive advice, the most pointed recommendations. If some of these issues puzzle you, or if you have already encountered some obstacles, share them, too, so you can either resolve the problems or find ways to work around them.
Remember, your research plan is simply a working product, designed to guide your ongoing inquiry. It’s not a final paper for a grade; it’s a step toward your final paper. Your goal in sketching it out now is to understand these issues better and get feedback from faculty early in the project. It may be a pain to write it out, but it’s a minor sting compared to major surgery later.
Checklist for Conducting Research
- Familiarize yourself with major questions and debates about your topic.
- Is appropriate to your topic;
- Addresses the main questions you propose in your thesis;
- Relies on materials to which you have access;
- Can be accomplished within the time available;
- Uses skills you have or can acquire.
- Divide your topic into smaller projects and do research on each in turn.
- Write informally as you do research; do not postpone this prewriting until all your research is complete.
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


Illustration by James Round
How to plan a research project
Whether for a paper or a thesis, define your question, review the work of others – and leave yourself open to discovery.
by Brooke Harrington + BIO
is professor of sociology at Dartmouth College in New Hampshire. Her research has won international awards both for scholarly quality and impact on public life. She has published dozens of articles and three books, most recently the bestseller Capital without Borders (2016), now translated into five languages.
Edited by Sam Haselby
Need to know
‘When curiosity turns to serious matters, it’s called research.’ – From Aphorisms (1880-1905) by Marie von Ebner-Eschenbach
Planning research projects is a time-honoured intellectual exercise: one that requires both creativity and sharp analytical skills. The purpose of this Guide is to make the process systematic and easy to understand. While there is a great deal of freedom and discovery involved – from the topics you choose, to the data and methods you apply – there are also some norms and constraints that obtain, no matter what your academic level or field of study. For those in high school through to doctoral students, and from art history to archaeology, research planning involves broadly similar steps, including: formulating a question, developing an argument or predictions based on previous research, then selecting the information needed to answer your question.
Some of this might sound self-evident but, as you’ll find, research requires a different way of approaching and using information than most of us are accustomed to in everyday life. That is why I include orienting yourself to knowledge-creation as an initial step in the process. This is a crucial and underappreciated phase in education, akin to making the transition from salaried employment to entrepreneurship: suddenly, you’re on your own, and that requires a new way of thinking about your work.
What follows is a distillation of what I’ve learned about this process over 27 years as a professional social scientist. It reflects the skills that my own professors imparted in the sociology doctoral programme at Harvard, as well as what I learned later on as a research supervisor for Ivy League PhD and MA students, and then as the author of award-winning scholarly books and articles. It can be adapted to the demands of both short projects (such as course term papers) and long ones, such as a thesis.
At its simplest, research planning involves the four distinct steps outlined below: orienting yourself to knowledge-creation; defining your research question; reviewing previous research on your question; and then choosing relevant data to formulate your own answers. Because the focus of this Guide is on planning a research project, as opposed to conducting a research project, this section won’t delve into the details of data-collection or analysis; those steps happen after you plan the project. In addition, the topic is vast: year-long doctoral courses are devoted to data and analysis. Instead, the fourth part of this section will outline some basic strategies you could use in planning a data-selection and analysis process appropriate to your research question.
Step 1: Orient yourself
Planning and conducting research requires you to make a transition, from thinking like a consumer of information to thinking like a producer of information. That sounds simple, but it’s actually a complex task. As a practical matter, this means putting aside the mindset of a student, which treats knowledge as something created by other people. As students, we are often passive receivers of knowledge: asked to do a specified set of readings, then graded on how well we reproduce what we’ve read.
Researchers, however, must take on an active role as knowledge producers . Doing research requires more of you than reading and absorbing what other people have written: you have to engage in a dialogue with it. That includes arguing with previous knowledge and perhaps trying to show that ideas we have accepted as given are actually wrong or incomplete. For example, rather than simply taking in the claims of an author you read, you’ll need to draw out the implications of those claims: if what the author is saying is true, what else does that suggest must be true? What predictions could you make based on the author’s claims?
In other words, rather than treating a reading as a source of truth – even if it comes from a revered source, such as Plato or Marie Curie – this orientation step asks you to treat the claims you read as provisional and subject to interrogation. That is one of the great pieces of wisdom that science and philosophy can teach us: that the biggest advances in human understanding have been made not by being correct about trivial things, but by being wrong in an interesting way . For example, Albert Einstein was wrong about quantum mechanics, but his arguments about it with his fellow physicist Niels Bohr have led to some of the biggest breakthroughs in science, even a century later.
Step 2: Define your research question
Students often give this step cursory attention, but experienced researchers know that formulating a good question is sometimes the most difficult part of the research planning process. That is because the precise language of the question frames the rest of the project. It’s therefore important to pose the question carefully, in a way that’s both possible to answer and likely to yield interesting results. Of course, you must choose a question that interests you, but that’s only the beginning of what’s likely to be an iterative process: most researchers come back to this step repeatedly, modifying their questions in light of previous research, resource limitations and other considerations.
Researchers face limits in terms of time and money. They, like everyone else, have to pose research questions that they can plausibly answer given the constraints they face. For example, it would be inadvisable to frame a project around the question ‘What are the roots of the Arab-Israeli conflict?’ if you have only a week to develop an answer and no background on that topic. That’s not to limit your imagination: you can come up with any question you’d like. But it typically does require some creativity to frame a question that you can answer well – that is, by investigating thoroughly and providing new insights – within the limits you face.
In addition to being interesting to you, and feasible within your resource constraints, the third and most important characteristic of a ‘good’ research topic is whether it allows you to create new knowledge. It might turn out that your question has already been asked and answered to your satisfaction: if so, you’ll find out in the next step of this process. On the other hand, you might come up with a research question that hasn’t been addressed previously. Before you get too excited about breaking uncharted ground, consider this: a lot of potentially researchable questions haven’t been studied for good reason ; they might have answers that are trivial or of very limited interest. This could include questions such as ‘Why does the area of a circle equal π r²?’ or ‘Did winter conditions affect Napoleon’s plans to invade Russia?’ Of course, you might be able to make the argument that a seemingly trivial question is actually vitally important, but you must be prepared to back that up with convincing evidence. The exercise in the ‘Learn More’ section below will help you think through some of these issues.
Finally, scholarly research questions must in some way lead to new and distinctive insights. For example, lots of people have studied gender roles in sports teams; what can you ask that hasn’t been asked before? Reinventing the wheel is the number-one no-no in this endeavour. That’s why the next step is so important: reviewing previous research on your topic. Depending on what you find in that step, you might need to revise your research question; iterating between your question and the existing literature is a normal process. But don’t worry: it doesn’t go on forever. In fact, the iterations taper off – and your research question stabilises – as you develop a firm grasp of the current state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 3: Review previous research
In academic research, from articles to books, it’s common to find a section called a ‘literature review’. The purpose of that section is to describe the state of the art in knowledge on the research question that a project has posed. It demonstrates that researchers have thoroughly and systematically reviewed the relevant findings of previous studies on their topic, and that they have something novel to contribute.
Your own research project should include something like this, even if it’s a high-school term paper. In the research planning process, you’ll want to list at least half a dozen bullet points stating the major findings on your topic by other people. In relation to those findings, you should be able to specify where your project could provide new and necessary insights. There are two basic rhetorical positions one can take in framing the novelty-plus-importance argument required of academic research:
- Position 1 requires you to build on or extend a set of existing ideas; that means saying something like: ‘Person A has argued that X is true about gender; this implies Y, which has not yet been tested. My project will test Y, and if I find evidence to support it, that will change the way we understand gender.’
- Position 2 is to argue that there is a gap in existing knowledge, either because previous research has reached conflicting conclusions or has failed to consider something important. For example, one could say that research on middle schoolers and gender has been limited by being conducted primarily in coeducational environments, and that findings might differ dramatically if research were conducted in more schools where the student body was all-male or all-female.
Your overall goal in this step of the process is to show that your research will be part of a larger conversation: that is, how your project flows from what’s already known, and how it advances, extends or challenges that existing body of knowledge. That will be the contribution of your project, and it constitutes the motivation for your research.
Two things are worth mentioning about your search for sources of relevant previous research. First, you needn’t look only at studies on your precise topic. For example, if you want to study gender-identity formation in schools, you shouldn’t restrict yourself to studies of schools; the empirical setting (schools) is secondary to the larger social process that interests you (how people form gender identity). That process occurs in many different settings, so cast a wide net. Second, be sure to use legitimate sources – meaning publications that have been through some sort of vetting process, whether that involves peer review (as with academic journal articles you might find via Google Scholar) or editorial review (as you’d find in well-known mass media publications, such as The Economist or The Washington Post ). What you’ll want to avoid is using unvetted sources such as personal blogs or Wikipedia. Why? Because anybody can write anything in those forums, and there is no way to know – unless you’re already an expert – if the claims you find there are accurate. Often, they’re not.
Step 4: Choose your data and methods
Whatever your research question is, eventually you’ll need to consider which data source and analytical strategy are most likely to provide the answers you’re seeking. One starting point is to consider whether your question would be best addressed by qualitative data (such as interviews, observations or historical records), quantitative data (such as surveys or census records) or some combination of both. Your ideas about data sources will, in turn, suggest options for analytical methods.
You might need to collect your own data, or you might find everything you need readily available in an existing dataset someone else has created. A great place to start is with a research librarian: university libraries always have them and, at public universities, those librarians can work with the public, including people who aren’t affiliated with the university. If you don’t happen to have a public university and its library close at hand, an ordinary public library can still be a good place to start: the librarians are often well versed in accessing data sources that might be relevant to your study, such as the census, or historical archives, or the Survey of Consumer Finances.
Because your task at this point is to plan research, rather than conduct it, the purpose of this step is not to commit you irrevocably to a course of action. Instead, your goal here is to think through a feasible approach to answering your research question. You’ll need to find out, for example, whether the data you want exist; if not, do you have a realistic chance of gathering the data yourself, or would it be better to modify your research question? In terms of analysis, would your strategy require you to apply statistical methods? If so, do you have those skills? If not, do you have time to learn them, or money to hire a research assistant to run the analysis for you?
Please be aware that qualitative methods in particular are not the casual undertaking they might appear to be. Many people make the mistake of thinking that only quantitative data and methods are scientific and systematic, while qualitative methods are just a fancy way of saying: ‘I talked to some people, read some old newspapers, and drew my own conclusions.’ Nothing could be further from the truth. In the final section of this guide, you’ll find some links to resources that will provide more insight on standards and procedures governing qualitative research, but suffice it to say: there are rules about what constitutes legitimate evidence and valid analytical procedure for qualitative data, just as there are for quantitative data.
Circle back and consider revising your initial plans
As you work through these four steps in planning your project, it’s perfectly normal to circle back and revise. Research planning is rarely a linear process. It’s also common for new and unexpected avenues to suggest themselves. As the sociologist Thorstein Veblen wrote in 1908 : ‘The outcome of any serious research can only be to make two questions grow where only one grew before.’ That’s as true of research planning as it is of a completed project. Try to enjoy the horizons that open up for you in this process, rather than becoming overwhelmed; the four steps, along with the two exercises that follow, will help you focus your plan and make it manageable.
Key points – How to plan a research project
- Planning a research project is essential no matter your academic level or field of study. There is no one ‘best’ way to design research, but there are certain guidelines that can be helpfully applied across disciplines.
- Orient yourself to knowledge-creation. Make the shift from being a consumer of information to being a producer of information.
- Define your research question. Your question frames the rest of your project, sets the scope, and determines the kinds of answers you can find.
- Review previous research on your question. Survey the existing body of relevant knowledge to ensure that your research will be part of a larger conversation.
- Choose your data and methods. For instance, will you be collecting qualitative data, via interviews, or numerical data, via surveys?
- Circle back and consider revising your initial plans. Expect your research question in particular to undergo multiple rounds of refinement as you learn more about your topic.
Good research questions tend to beget more questions. This can be frustrating for those who want to get down to business right away. Try to make room for the unexpected: this is usually how knowledge advances. Many of the most significant discoveries in human history have been made by people who were looking for something else entirely. There are ways to structure your research planning process without over-constraining yourself; the two exercises below are a start, and you can find further methods in the Links and Books section.
The following exercise provides a structured process for advancing your research project planning. After completing it, you’ll be able to do the following:
- describe clearly and concisely the question you’ve chosen to study
- summarise the state of the art in knowledge about the question, and where your project could contribute new insight
- identify the best strategy for gathering and analysing relevant data
In other words, the following provides a systematic means to establish the building blocks of your research project.
Exercise 1: Definition of research question and sources
This exercise prompts you to select and clarify your general interest area, develop a research question, and investigate sources of information. The annotated bibliography will also help you refine your research question so that you can begin the second assignment, a description of the phenomenon you wish to study.
Jot down a few bullet points in response to these two questions, with the understanding that you’ll probably go back and modify your answers as you begin reading other studies relevant to your topic:
- What will be the general topic of your paper?
- What will be the specific topic of your paper?
b) Research question(s)
Use the following guidelines to frame a research question – or questions – that will drive your analysis. As with Part 1 above, you’ll probably find it necessary to change or refine your research question(s) as you complete future assignments.
- Your question should be phrased so that it can’t be answered with a simple ‘yes’ or ‘no’.
- Your question should have more than one plausible answer.
- Your question should draw relationships between two or more concepts; framing the question in terms of How? or What? often works better than asking Why ?
c) Annotated bibliography
Most or all of your background information should come from two sources: scholarly books and journals, or reputable mass media sources. You might be able to access journal articles electronically through your library, using search engines such as JSTOR and Google Scholar. This can save you a great deal of time compared with going to the library in person to search periodicals. General news sources, such as those accessible through LexisNexis, are acceptable, but should be cited sparingly, since they don’t carry the same level of credibility as scholarly sources. As discussed above, unvetted sources such as blogs and Wikipedia should be avoided, because the quality of the information they provide is unreliable and often misleading.
To create an annotated bibliography, provide the following information for at least 10 sources relevant to your specific topic, using the format suggested below.
Name of author(s):
Publication date:
Title of book, chapter, or article:
If a chapter or article, title of journal or book where they appear:
Brief description of this work, including main findings and methods ( c 75 words):
Summary of how this work contributes to your project ( c 75 words):
Brief description of the implications of this work ( c 25 words):
Identify any gap or controversy in knowledge this work points up, and how your project could address those problems ( c 50 words):
Exercise 2: Towards an analysis
Develop a short statement ( c 250 words) about the kind of data that would be useful to address your research question, and how you’d analyse it. Some questions to consider in writing this statement include:
- What are the central concepts or variables in your project? Offer a brief definition of each.
- Do any data sources exist on those concepts or variables, or would you need to collect data?
- Of the analytical strategies you could apply to that data, which would be the most appropriate to answer your question? Which would be the most feasible for you? Consider at least two methods, noting their advantages or disadvantages for your project.
Links & books
One of the best texts ever written about planning and executing research comes from a source that might be unexpected: a 60-year-old work on urban planning by a self-trained scholar. The classic book The Death and Life of Great American Cities (1961) by Jane Jacobs (available complete and free of charge via this link ) is worth reading in its entirety just for the pleasure of it. But the final 20 pages – a concluding chapter titled ‘The Kind of Problem a City Is’ – are really about the process of thinking through and investigating a problem. Highly recommended as a window into the craft of research.
Jacobs’s text references an essay on advancing human knowledge by the mathematician Warren Weaver. At the time, Weaver was director of the Rockefeller Foundation, in charge of funding basic research in the natural and medical sciences. Although the essay is titled ‘A Quarter Century in the Natural Sciences’ (1960) and appears at first blush to be merely a summation of one man’s career, it turns out to be something much bigger and more interesting: a meditation on the history of human beings seeking answers to big questions about the world. Weaver goes back to the 17th century to trace the origins of systematic research thinking, with enthusiasm and vivid anecdotes that make the process come alive. The essay is worth reading in its entirety, and is available free of charge via this link .
For those seeking a more in-depth, professional-level discussion of the logic of research design, the political scientist Harvey Starr provides insight in a compact format in the article ‘Cumulation from Proper Specification: Theory, Logic, Research Design, and “Nice” Laws’ (2005). Starr reviews the ‘research triad’, consisting of the interlinked considerations of formulating a question, selecting relevant theories and applying appropriate methods. The full text of the article, published in the scholarly journal Conflict Management and Peace Science , is available, free of charge, via this link .
Finally, the book Getting What You Came For (1992) by Robert Peters is not only an outstanding guide for anyone contemplating graduate school – from the application process onward – but it also includes several excellent chapters on planning and executing research, applicable across a wide variety of subject areas. It was an invaluable resource for me 25 years ago, and it remains in print with good reason; I recommend it to all my students, particularly Chapter 16 (‘The Thesis Topic: Finding It’), Chapter 17 (‘The Thesis Proposal’) and Chapter 18 (‘The Thesis: Writing It’).

Emotion regulation
How to take the high road
When someone provokes you, it’s easy to react without thinking. Learn to slow down and respond in ways you’ll be proud of
by Alissa Hebbeln & Russell Kolts

Goals and motivation
How to do mental time travel
Feeling overwhelmed by the present moment? Find a connection to the longer view and a wiser perspective on what matters
by Richard Fisher

How to cope with climate anxiety
It’s normal to feel troubled by the climate crisis. These practices can help keep your response manageable and constructive
by Lucia Tecuta
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Table of Contents

Research Proposal
Research proposal is a document that outlines a proposed research project . It is typically written by researchers, scholars, or students who intend to conduct research to address a specific research question or problem.
Types of Research Proposal
Research proposals can vary depending on the nature of the research project and the specific requirements of the funding agency, academic institution, or research program. Here are some common types of research proposals:
Academic Research Proposal
This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review , methodology , and expected outcomes.
Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is specifically designed to secure funding from external sources, such as government agencies, foundations, or private organizations. It typically includes additional sections, such as a detailed budget, project timeline, evaluation plan, and a description of the project’s alignment with the funding agency’s priorities and objectives.
Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Students pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree often need to submit a proposal outlining their intended research for their dissertation or thesis. These proposals are usually more extensive and comprehensive, including an in-depth literature review, theoretical framework, research questions or hypotheses, and a detailed methodology.
Research Project Proposal
This type of proposal is often prepared by researchers or research teams within an organization or institution. It outlines a specific research project that aims to address a particular problem, explore a specific area of interest, or provide insights for decision-making. Research project proposals may include sections on project management, collaboration, and dissemination of results.
Research Fellowship Proposal
Researchers or scholars applying for research fellowships may be required to submit a proposal outlining their proposed research project. These proposals often emphasize the novelty and significance of the research and its alignment with the goals and objectives of the fellowship program.
Collaborative Research Proposal
In cases where researchers from multiple institutions or disciplines collaborate on a research project, a collaborative research proposal is prepared. This proposal highlights the objectives, responsibilities, and contributions of each collaborator, as well as the overall research plan and coordination mechanisms.
Research Proposal Outline
A research proposal typically follows a standard outline that helps structure the document and ensure all essential components are included. While the specific headings and subheadings may vary slightly depending on the requirements of your institution or funding agency, the following outline provides a general structure for a research proposal:
- Title of the research proposal
- Name of the researcher(s) or principal investigator(s)
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of submission
- A concise summary of the research proposal, typically limited to 200-300 words.
- Briefly introduce the research problem or question, state the objectives, summarize the methodology, and highlight the expected outcomes or significance of the research.
- Provide an overview of the subject area and the specific research problem or question.
- Present relevant background information, theories, or concepts to establish the need for the research.
- Clearly state the research objectives or research questions that the study aims to address.
- Indicate the significance or potential contributions of the research.
- Summarize and analyze relevant studies, theories, or scholarly works.
- Identify research gaps or unresolved issues that your study intends to address.
- Highlight the novelty or uniqueness of your research.
- Describe the overall approach or research design that will be used (e.g., experimental, qualitative, quantitative).
- Justify the chosen approach based on the research objectives and question.
- Explain how data will be collected (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments).
- Describe the sampling strategy and sample size, if applicable.
- Address any ethical considerations related to data collection.
- Outline the data analysis techniques or statistical methods that will be applied.
- Explain how the data will be interpreted and analyzed to answer the research question(s).
- Provide a detailed schedule or timeline that outlines the various stages of the research project.
- Specify the estimated duration for each stage, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
- State the potential outcomes or results of the research.
- Discuss the potential significance or contributions of the study to the field.
- Address any potential limitations or challenges that may be encountered.
- Identify the resources required to conduct the research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- Specify any collaborations or partnerships necessary for the successful completion of the study.
- Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
———————————————————————————————–
Research Proposal Example Template
Here’s an example of a research proposal to give you an idea of how it can be structured:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being: A Mixed-Methods Study
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of social media on the well-being of adolescents. The study will employ a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews to gather comprehensive data. The research objectives include examining the relationship between social media use and mental health, exploring the role of peer influence in shaping online behaviors, and identifying strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents. The findings of this study will contribute to the understanding of the effects of social media on adolescent well-being and inform the development of targeted interventions.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background and Context:
Adolescents today are immersed in social media platforms, which have become integral to their daily lives. However, concerns have been raised about the potential negative impact of social media on their well-being, including increased rates of depression, anxiety, and body dissatisfaction. It is crucial to investigate this phenomenon further and understand the underlying mechanisms to develop effective strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents.
1.2 Research Objectives:
The main objectives of this study are:
- To examine the association between social media use and mental health outcomes among adolescents.
- To explore the influence of peer relationships and social comparison on online behaviors.
- To identify strategies and interventions to foster positive social media use and enhance adolescent well-being.
2. Literature Review
Extensive research has been conducted on the impact of social media on adolescents. Existing literature suggests that excessive social media use can contribute to negative outcomes, such as low self-esteem, cyberbullying, and addictive behaviors. However, some studies have also highlighted the positive aspects of social media, such as providing opportunities for self-expression and social support. This study will build upon this literature by incorporating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to gain a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between social media and adolescent well-being.
3. Methodology
3.1 Research Design:
This study will adopt a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. The quantitative phase will involve administering standardized questionnaires to a representative sample of adolescents to assess their social media use, mental health indicators, and perceived social support. The qualitative phase will include in-depth interviews with a subset of participants to explore their experiences, motivations, and perceptions related to social media use.
3.2 Data Collection Methods:
Quantitative data will be collected through an online survey distributed to schools in the target region. The survey will include validated scales to measure social media use, mental health outcomes, and perceived social support. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a purposive sample of participants. The interviews will be audio-recorded and transcribed for thematic analysis.
3.3 Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis to examine the relationships between variables. Qualitative data will be analyzed thematically to identify common themes and patterns within participants’ narratives. Integration of quantitative and qualitative findings will provide a comprehensive understanding of the research questions.
4. Timeline
The research project will be conducted over a period of 12 months, divided into specific phases, including literature review, study design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. A detailed timeline outlining the key milestones and activities is provided in Appendix A.
5. Expected Outcomes and Significance
This study aims to contribute to the existing literature on the impact of social media on adolescent well-being by employing a mixed-methods approach. The findings will inform the development of evidence-based interventions and guidelines to promote healthy social media use among adolescents. This research has the potential to benefit adolescents, parents, educators, and policymakers by providing insights into the complex relationship between social media and well-being and offering strategies for fostering positive online experiences.
6. Resources
The resources required for this research include access to a representative sample of adolescents, research assistants for data collection, statistical software for data analysis, and funding to cover survey administration and participant incentives. Ethical considerations will be taken into account, ensuring participant confidentiality and obtaining informed consent.
7. References
Research Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a research proposal can be a complex task, but with proper guidance and organization, you can create a compelling and well-structured proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the guidelines and requirements provided by your institution, funding agency, or program. Pay attention to formatting, page limits, specific sections or headings, and any other instructions.
- Identify your research topic: Choose a research topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the goals of your program or funding opportunity. Ensure that your topic is specific, focused, and relevant to the field of study.
- Conduct a literature review : Review existing literature and research relevant to your topic. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and findings related to your research question. This will help you establish the context, identify research gaps, and demonstrate the significance of your proposed study.
- Define your research objectives and research question(s): Clearly state the objectives you aim to achieve with your research. Formulate research questions that address the gaps identified in the literature review. Your research objectives and questions should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a research methodology: Determine the most appropriate research design and methodology for your study. Consider whether quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods approaches will best address your research question(s). Describe the data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations associated with your research.
- Create a research plan and timeline: Outline the various stages of your research project, including tasks, milestones, and deadlines. Develop a realistic timeline that considers factors such as data collection, analysis, and report writing. This plan will help you stay organized and manage your time effectively throughout the research process.
- A. Introduction: Provide background information on the research problem, highlight its significance, and introduce your research objectives and questions.
- B. Literature review: Summarize relevant literature, identify gaps, and justify the need for your proposed research.
- C . Methodology: Describe your research design, data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
- D . Expected outcomes and significance: Explain the potential outcomes, contributions, and implications of your research.
- E. Resources: Identify the resources required to conduct your research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- F . References: Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style.
- Revise and proofread: Review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for grammar and spelling errors. Seek feedback from mentors, colleagues, or advisors to refine and improve your proposal.
- Finalize and submit: Make any necessary revisions based on feedback and finalize your research proposal. Ensure that you have met all the requirements and formatting guidelines. Submit your proposal within the specified deadline.
Research Proposal Length
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. However, research proposals typically range from 1,500 to 3,000 words, excluding references and any additional supporting documents.
Purpose of Research Proposal
The purpose of a research proposal is to outline and communicate your research project to others, such as academic institutions, funding agencies, or potential collaborators. It serves several important purposes:
- Demonstrate the significance of the research: A research proposal explains the importance and relevance of your research project. It outlines the research problem or question, highlights the gaps in existing knowledge, and explains how your study will contribute to the field. By clearly articulating the significance of your research, you can convince others of its value and potential impact.
- Provide a clear research plan: A research proposal outlines the methodology, design, and approach you will use to conduct your study. It describes the research objectives, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and potential outcomes. By presenting a clear research plan, you demonstrate that your study is well-thought-out, feasible, and likely to produce meaningful results.
- Secure funding or support: For researchers seeking funding or support for their projects, a research proposal is essential. It allows you to make a persuasive case for why your research is deserving of financial resources or institutional backing. The proposal explains the budgetary requirements, resources needed, and potential benefits of the research, helping you secure the necessary funding or support.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to receive feedback and guidance from experts in your field. It allows you to engage in discussions and receive suggestions for refining your research plan, improving the methodology, or addressing any potential limitations. This feedback can enhance the quality of your study and increase its chances of success.
- Establish ethical considerations: A research proposal also addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will ensure participant confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. By demonstrating your awareness and commitment to ethical research practices, you build trust and credibility in your proposed study.
Importance of Research Proposal
The research proposal holds significant importance in the research process. Here are some key reasons why research proposals are important:
- Planning and organization: A research proposal requires careful planning and organization of your research project. It forces you to think through the research objectives, research questions, methodology, and potential outcomes before embarking on the actual study. This planning phase helps you establish a clear direction and framework for your research, ensuring that your efforts are focused and purposeful.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: A research proposal allows you to articulate the significance and relevance of your study. By providing a thorough literature review and clearly defining the research problem or question, you can showcase the gaps in existing knowledge that your research aims to address. This demonstrates to others, such as funding agencies or academic institutions, why your research is important and deserving of support.
- Obtaining funding and resources: Research proposals are often required to secure funding for your research project. Funding agencies and organizations need to evaluate the feasibility and potential impact of the proposed research before allocating resources. A well-crafted research proposal helps convince funders of the value of your research and increases the likelihood of securing financial support, grants, or scholarships.
- Receiving feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to seek feedback and guidance from experts in your field. By sharing your research plan and objectives with others, you can benefit from their insights and suggestions. This feedback can help refine your research design, strengthen your methodology, and ensure that your study is rigorous and well-informed.
- Ethical considerations: A research proposal addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will protect the rights and welfare of participants, maintain confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. This emphasis on ethical practices ensures that your research is conducted responsibly and with integrity.
- Enhancing collaboration and partnerships: A research proposal can facilitate collaborations and partnerships with other researchers, institutions, or organizations. When presenting your research plan, you may attract the interest of potential collaborators who share similar research interests or possess complementary expertise. Collaborative partnerships can enrich your study, expand your resources, and foster knowledge exchange.
- Establishing a research trajectory: A research proposal serves as a foundation for your research project. Once approved, it becomes a roadmap that guides your study’s implementation, data collection, analysis, and reporting. It helps maintain focus and ensures that your research stays on track and aligned with the initial objectives.
When to Write Research Proposal
The timing of when to write a research proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements and circumstances. However, here are a few common situations when it is appropriate to write a research proposal:
- Academic research: If you are a student pursuing a research degree, such as a Ph.D. or Master’s by research, you will typically be required to write a research proposal as part of the application process. This is usually done before starting the research program to outline your proposed study and seek approval from the academic institution.
- Funding applications: When applying for research grants, scholarships, or funding from organizations or institutions, you will often need to submit a research proposal. Funding agencies require a detailed description of your research project, including its objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. Writing a research proposal in this context is necessary to secure financial support for your study.
- Research collaborations: When collaborating with other researchers, institutions, or organizations on a research project, it is common to prepare a research proposal. This helps outline the research objectives, roles and responsibilities, and expected contributions from each party. Writing a research proposal in this case allows all collaborators to align their efforts and ensure a shared understanding of the project.
- Research project within an organization: If you are conducting research within an organization, such as a company or government agency, you may be required to write a research proposal to gain approval and support for your study. This proposal outlines the research objectives, methodology, resources needed, and expected outcomes, ensuring that the project aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Independent research projects: Even if you are not required to write a research proposal, it can still be beneficial to develop one for your independent research projects. Writing a research proposal helps you plan and structure your study, clarify your research objectives, and anticipate potential challenges or limitations. It also allows you to communicate your research plans effectively to supervisors, mentors, or collaborators.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

Write Your Research Plan
In this part, we give you detailed information about writing an effective Research Plan. We start with the importance and parameters of significance and innovation.
We then discuss how to focus the Research Plan, relying on the iterative process described in the Iterative Approach to Application Planning Checklist shown at Draft Specific Aims and give you advice for filling out the forms.
You'll also learn the importance of having a well-organized, visually appealing application that avoids common missteps and the importance of preparing your just-in-time information early.
While this document is geared toward the basic research project grant, the R01, much of it is useful for other grant types.
Table of Contents
Research plan overview and your approach, craft a title, explain your aims, research strategy instructions, advice for a successful research strategy, graphics and video, significance, innovation, and approach, tracking for your budget, preliminary studies or progress report, referencing publications, review and finalize your research plan, abstract and narrative.
Your application's Research Plan has two sections:
- Specific Aims —a one-page statement of your objectives for the project.
- Research Strategy —a description of the rationale for your research and your experiments in 12 pages for an R01.
In your Specific Aims, you note the significance and innovation of your research; then list your two to three concrete objectives, your aims.
Your Research Strategy is the nuts and bolts of your application, where you describe your research rationale and the experiments you will conduct to accomplish each aim. Though how you organize it is largely up to you, NIH expects you to follow these guidelines.
- Organize using bold headers or an outline or numbering system—or both—that you use consistently throughout.
- Start each section with the appropriate header: Significance, Innovation, or Approach.
- Organize the Approach section around your Specific Aims.
Format of Your Research Plan
To write the Research Plan, you don't need the application forms. Write the text in your word processor, turn it into a PDF file, and upload it into the application form when it's final.
Because NIH may return your application if it doesn't meet all requirements, be sure to follow the rules for font, page limits, and more. Read the instructions at NIH’s Format Attachments .
For an R01, the Research Strategy can be up to 12 pages, plus one page for Specific Aims. Don't pad other sections with information that belongs in the Research Plan. NIH is on the lookout and may return your application to you if you try to evade page limits.
Follow Examples
As you read this page, look at our Sample Applications and More to see some of the different strategies successful PIs use to create an outstanding Research Plan.
Keeping It All In Sync
Writing in a logical sequence will save you time.
Information you put in the Research Plan affects just about every other application part. You'll need to keep everything in sync as your plans evolve during the writing phase.
It's best to consider your writing as an iterative process. As you develop and finalize your experiments, you will go back and check other parts of the application to make sure everything is in sync: the "who, what, when, where, and how (much money)" as well as look again at the scope of your plans.
In that vein, writing in a logical sequence is a good approach that will save you time. We suggest proceeding in the following order:
- Create a provisional title.
- Write a draft of your Specific Aims.
- Start with your Significance and Innovation sections.
- Then draft the Approach section considering the personnel and skills you'll need for each step.
- Evaluate your Specific Aims and methods in light of your expected budget (for a new PI, it should be modest, probably under the $250,000 for NIH's modular budget).
- As you design experiments, reevaluate your hypothesis, aims, and title to make sure they still reflect your plans.
- Prepare your Abstract (a summary of your Specific Aims).
- Complete the other forms.
Even the smaller sections of your application need to be well-organized and readable so reviewers can readily grasp the information. If writing is not your forte, get help.
To view writing strategies for successful applications, see our Sample Applications and More . There are many ways to create a great application, so explore your options.
Within the character limit, include the important information to distinguish your project within the research area, your project's goals, and the research problem.
Giving your project a title at the outset can help you stay focused and avoid a meandering Research Plan. So you may want to launch your writing by creating a well-defined title.
NIH gives you a 200 character limit, but don’t feel obliged to use all of that allotment. Instead, we advise you to keep the title as succinct as possible while including the important information to distinguish your project within the research area. Make your title reflect your project's goals, the problem your project addresses, and possibly your approach to studying it. Make your title specific: saying you are studying lymphocyte trafficking is not informative enough.
For examples of strong titles, see our Sample Applications and More .
After you write a preliminary title, check that
- My title is specific, indicating at least the research area and the goals of my project.
- It is 200 characters or less.
- I use as simple language as possible.
- I state the research problem and, possibly, my approach to studying it.
- I use a different title for each of my applications. (Note: there are exceptions, for example, for a renewal—see Apply for Renewal for details.)
- My title has appropriate keywords.
Later you may want to change your initial title. That's fine—at this point, it's just an aid to keep your plans focused.
Since all your reviewers read your Specific Aims, you want to excite them about your project.
If testing your hypothesis is the destination for your research, your Research Plan is the map that takes you there.
You'll start by writing the smaller part, the Specific Aims. Think of the one-page Specific Aims as a capsule of your Research Plan. Since all your reviewers read your Specific Aims, you want to excite them about your project.
For more on crafting your Specific Aims, see Draft Specific Aims .
Write a Narrative
Use at least half the page to provide the rationale and significance of your planned research. A good way to start is with a sentence that states your project's goals.
For the rest of the narrative, you will describe the significance of your research, and give your rationale for choosing the project. In some cases, you may want to explain why you did not take an alternative route.
Then, briefly describe your aims, and show how they build on your preliminary studies and your previous research. State your hypothesis.
If it is likely your application will be reviewed by a study section with broad expertise, summarize the status of research in your field and explain how your project fits in.
In the narrative part of the Specific Aims of many outstanding applications, people also used their aims to
- State the technologies they plan to use.
- Note their expertise to do a specific task or that of collaborators.
- Describe past accomplishments related to the project.
- Describe preliminary studies and new and highly relevant findings in the field.
- Explain their area's biology.
- Show how the aims relate to one another.
- Describe expected outcomes for each aim.
- Explain how they plan to interpret data from the aim’s efforts.
- Describe how to address potential pitfalls with contingency plans.
Depending on your situation, decide which items are important for you. For example, a new investigator would likely want to highlight preliminary data and qualifications to do the work.
Many people use bold or italics to emphasize items they want to bring to the reviewers' attention, such as the hypothesis or rationale.
Detail Your Aims
After the narrative, enter your aims as bold bullets, or stand-alone or run-on headers.
- State your plans using strong verbs like identify, define, quantify, establish, determine.
- Describe each aim in one to three sentences.
- Consider adding bullets under each aim to refine your objectives.
How focused should your aims be? Look at the example below.
Spot the Sample
Read the Specific Aims of the Application from Drs. Li and Samulski , "Enhance AAV Liver Transduction with Capsid Immune Evasion."
- Aim 1. Study the effect of adeno-associated virus (AAV) empty particles on AAV capsid antigen cross-presentation in vivo .
- Aim 2. Investigate AAV capsid antigen presentation following administration of AAV mutants and/or proteasome inhibitors for enhanced liver transduction in vivo .
- Aim 3. Isolate AAV chimeric capsids with human hepatocyte tropism and the capacity for cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) evasion.
After finishing the draft Specific Aims, check that
- I keep to the one-page limit.
- Each of my two or three aims is a narrowly focused, concrete objective I can achieve during the grant.
- They give a clear picture of how my project can generate knowledge that may improve human health.
- They show my project's importance to science, how it addresses a critical research opportunity that can move my field forward.
- My text states how my work is innovative.
- I describe the biology to the extent needed for my reviewers.
- I give a rationale for choosing the topic and approach.
- I tie the project to my preliminary data and other new findings in the field.
- I explicitly state my hypothesis and why testing it is important.
- My aims can test my hypothesis and are logical.
- I can design and lead the execution of two or three sets of experiments that will strive to accomplish each aim.
- As much as possible, I use language that an educated person without expertise can understand.
- My text has bullets, bolding, or headers so reviewers can easily spot my aims (and other key items).
For each element listed above, analyze your text and revise it until your Specific Aims hit all the key points you'd like to make.
After the list of aims, some people add a closing paragraph, emphasizing the significance of the work, their collaborators, or whatever else they want to focus reviewers' attention on.
Your Research Strategy is the bigger part of your application's Research Plan (the other part is the Specific Aims—discussed above.)
The Research Strategy is the nuts and bolts of your application, describing the rationale for your research and the experiments you will do to accomplish each aim. It is structured as follows:
- Significance
- You can either include this information as a subsection of Approach or integrate it into any or all of the three main sections.
- If you do the latter, be sure to mark the information clearly, for example, with a bold subhead.
- Possible other sections, for example, human subjects, vertebrate animals, select agents, and others (these do not count toward the page limit).
Though how you organize your application is largely up to you, NIH does want you to follow these guidelines:
- Add bold headers or an outlining or numbering system—or both—that you use consistently throughout.
- Start each of the Research Strategy's sections with a header: Significance, Innovation, and Approach.
For an R01, the Research Strategy is limited to 12 pages for the three main sections and the preliminary studies only. Other items are not included in the page limit.
Find instructions for R01s in the SF 424 Application Guide—go to NIH's SF 424 (R&R) Application and Electronic Submission Information for the generic SF 424 Application Guide or find it in your notice of funding opportunity (NOFO).
For most applications, you need to address Rigor and Reproducibility by describing the experimental design and methods you propose and how they will achieve robust and unbiased results. The requirement applies to research grant, career development, fellowship, and training applications.
If you're responding to an institute-specific program announcement (PA) (not a parent program announcement) or a request for applications (RFA), check the NIH Guide notice, which has additional information you need. Should it differ from the NOFO, go with the NIH Guide .
Also note that your application must meet the initiative's objectives and special requirements. NIAID program staff will check your application, and if it is not responsive to the announcement, your application will be returned to you without a review.
When writing your Research Strategy, your goal is to present a well-organized, visually appealing, and readable description of your proposed project. That means your writing should be streamlined and organized so your reviewers can readily grasp the information. If writing is not your forte, get help.
There are many ways to create an outstanding Research Plan, so explore your options.
What Success Looks Like
Your application's Research Plan is the map that shows your reviewers how you plan to test your hypothesis.
It not only lays out your experiments and expected outcomes, but must also convince your reviewers of your likely success by allaying any doubts that may cross their minds that you will be able to conduct the research.
Notice in the sample applications how the writing keeps reviewers' eyes on the ball by bringing them back to the main points the PIs want to make. Write yourself an insurance policy against human fallibility: if it's a key point, repeat it, then repeat it again.

The Big Three
So as you write, put the big picture squarely in your sights. When reviewers read your application, they'll look for the answers to three basic questions:
- Can your research move your field forward?
- Is the field important—will progress make a difference to human health?
- Can you and your team carry out the work?
Add Emphasis
Savvy PIs create opportunities to drive their main points home. They don't stop at the Significance section to emphasize their project's importance, and they look beyond their biosketches to highlight their team's expertise.
Don't take a chance your reviewer will gloss over that one critical sentence buried somewhere in your Research Strategy or elsewhere. Write yourself an insurance policy against human fallibility: if it's a key point, repeat it, then repeat it again.
Add more emphasis by putting the text in bold, or bold italics (in the modern age, we skip underlining—it's for typewriters).
Here are more strategies from our successful PIs:
- While describing a method in the Approach section, they state their or collaborators' experience with it.
- They point out that they have access to a necessary piece of equipment.
- When explaining their field and the status of current research, they weave in their own work and their preliminary data.
- They delve into the biology of the area to make sure reviewers will grasp the importance of their research and understand their field and how their work fits into it.
You can see many of these principles at work in the Approach section of the Application from Dr. William Faubion , "Inflammatory cascades disrupt Treg function through epigenetic mechanisms."
- Reviewers felt that the experiments described for Aim 1 will yield clear results.
- The plans to translate those findings to gene targets of relevance are well outlined and focused.
- He ties his proposed experiments to the larger picture, including past research and strong preliminary data for the current application.
Anticipate Reviewer Questions
Our applicants not only wrote with their reviewers in mind they seemed to anticipate their questions. You may think: how can I anticipate all the questions people may have? Of course you can't, but there are some basic items (in addition to the "big three" listed above) that will surely be on your reviewers' minds:
- Will the investigators be able to get the work done within the project period, or is the proposed work over ambitious?
- Did the PI describe potential pitfalls and possible alternatives?
- Will the experiments generate meaningful data?
- Could the resulting data prove the hypothesis?
- Are others already doing the work, or has it been already completed?
Address these questions; then spend time thinking about more potential issues specific to you and your research—and address those too.
For applications, a picture can truly be worth a thousand words. Graphics can illustrate complex information in a small space and add visual interest to your application.
Look at our sample applications to see how the investigators included schematics, tables, illustrations, graphs, and other types of graphics to enhance their applications.
Consider adding a timetable or flowchart to illustrate your experimental plan, including decision trees with alternative experimental pathways to help your reviewers understand your plans.
Plan Ahead for Video
If you plan to send one or more videos, you'll need to meet certain standards and include key information in your Research Strategy now.
To present some concepts or demonstrations, video may enhance your application beyond what graphics alone can achieve. However, you can't count on all reviewers being able to see or hear video, so you'll want to be strategic in how you incorporate it into your application.
Be reviewer-friendly. Help your cause by taking the following steps:
- Caption any narration in the video.
- Choose evocative still images from your video to accompany your summary.
- Write your summary of the video carefully so the text would make sense even without the video.
In addition to those considerations, create your videos to fit NIH’s technical requirements. Learn more in the SF 424 Form Instructions .
Next, as you write your Research Strategy, include key images from the video and a brief description.
Then, state in your cover letter that you plan to send video later. (Don't attach your files to the application.)
After you apply and get assignment information from the Commons, ask your assigned scientific review officer (SRO) how your business official should send the files. Your video files are due at least one month before the peer review meeting.
Know Your Audience's Perspective
The primary audience for your application is your peer review group. Learn how to write for the reviewers who are experts in your field and those who are experts in other fields by reading Know Your Audience .
Be Organized: A B C or 1 2 3?
In the top-notch applications we reviewed, organization ruled but followed few rules. While you want to be organized, how you go about it is up to you.
Nevertheless, here are some principles to follow:
- Start each of the Research Strategy's sections with a header: Significance, Innovation, and Approach—this you must do.
The Research Strategy's page limit—12 for R01s—is for the three main parts: Significance, Innovation, and Approach and your preliminary studies (or a progress report if you're renewing your grant). Other sections, for example, research animals or select agents, do not have a page limit.
Although you will emphasize your project's significance throughout the application, the Significance section should give the most details. Don't skimp—the farther removed your reviewers are from your field, the more information you'll need to provide on basic biology, importance of the area, research opportunities, and new findings.
When you describe your project's significance, put it in the context of 1) the state of your field, 2) your long-term research plans, and 3) your preliminary data.
In our Sample Applications , you can see that both investigators and reviewers made a case for the importance of the research to improving human health as well as to the scientific field.
Look at the Significance section of the Application from Dr. Mengxi Jiang , "Intersection of polyomavirus infection and host cellular responses," to see how these elements combine to make a strong case for significance.
- Dr. Jiang starts with a summary of the field of polyomavirus research, identifying critical knowledge gaps in the field.
- The application ties the lab's previous discoveries and new research plans to filling those gaps, establishing the significance with context.
- Note the use of formatting, whitespace, and sectioning to highlight key points and make it easier for reviewers to read the text.
After conveying the significance of the research in several parts of the application, check that
- In the Significance section, I describe the importance of my hypothesis to the field (especially if my reviewers are not in it) and human disease.
- I also point out the project's significance throughout the application.
- The application shows that I am aware of opportunities, gaps, roadblocks, and research underway in my field.
- I state how my research will advance my field, highlighting knowledge gaps and showing how my project fills one or more of them.
- Based on my scan of the review committee roster, I determine whether I cannot assume my reviewers will know my field and provide some information on basic biology, the importance of the area, knowledge gaps, and new findings.
If you are either a new PI or entering a new area: be cautious about seeming too innovative. Not only is innovation just one of five review criteria, but there might be a paradigm shift in your area of science. A reviewer may take a challenge to the status quo as a challenge to his or her world view.
When you look at our sample applications, you see that both the new and experienced investigators are not generally shifting paradigms. They are using new approaches or models, working in new areas, or testing innovative ideas.
After finishing the draft innovation section, check that
- I show how my proposed research is new and unique, e.g., explores new scientific avenues, has a novel hypothesis, will create new knowledge.
- Most likely, I explain how my project's research can refine, improve, or propose a new application of an existing concept or method.
- Make a very strong case for challenging the existing paradigm.
- Have data to support the innovative approach.
- Have strong evidence that I can do the work.
In your Approach, you spell out a few sets of experiments to address each aim. As we noted above, it's a good idea to restate the key points you've made about your project's significance, its place in your field, and your long-term goals.
You're probably wondering how much detail to include.
If you look at our sample applications as a guide, you can see very different approaches. Though people generally used less detail than you'd see in a scientific paper, they do include some experimental detail.
Expect your assigned reviewers to scrutinize your approach: they will want to know what you plan to do and how you plan to do it.
NIH data show that of the peer review criteria, approach has the highest correlation with the overall impact score.
Look at the Application from Dr. Mengxi Jiang , "Intersection of polyomavirus infection and host cellular responses," to see how a new investigator handled the Approach section.
For an example of an experienced investigator's well-received Approach section, see the Application from Dr. William Faubion , "Inflammatory cascades disrupt Treg function through epigenetic mechanisms."
Especially if you are a new investigator, you need enough detail to convince reviewers that you understand what you are undertaking and can handle the method.
- Cite a publication that shows you can handle the method where you can, but give more details if you and your team don't have a proven record using the method—and state explicitly why you think you will succeed.
- If space is short, you could also focus on experiments that highlight your expertise or are especially interesting. For experiments that are pedestrian or contracted out, just list the method.
Be sure to lay out a plan for alternative experiments and approaches in case you get negative or surprising results. Show reviewers you have a plan for spending the four or five years you will be funded no matter where the experiments lead.
See the Application from Drs. Li and Samulski , "Enhance AAV Liver Transduction with Capsid Immune Evasion," for a strong Approach section covering potential. As an example, see section C.1.3.'s alternative approaches.
Here are some pointers for organizing your Approach:
- Enter a bold header for each Specific Aim.
- Under each aim, describe the first set of experiments.
- If you get result X, you will follow pathway X; if you get result Y, you will follow pathway Y.
- Consider illustrating this with a flowchart.
Trim the fat—omit all information not needed to make your case. If you try to wow reviewers with your knowledge, they'll find flaws and penalize you heavily. Don't give them ammunition by including anything you don't need.
As you design your experiments, keep a running tab of the following essential data on a separate piece of paper:
- Who. A list of people who will help you for your Key Personnel section later.
- What. A list of equipment and supplies for the experiments you plan.
- Time. Notes on how long each step takes. Timing directly affects your budget as well as how many Specific Aims you can realistically achieve.
Jotting this information down will help you Create a Budget and complete other sections later.
After finishing a draft Approach section, check that
- I include enough background and preliminary data to give reviewers the context and significance of my plans.
- They can test the hypothesis (or hypotheses).
- I show alternative experiments and approaches in case I get negative or surprising results.
- My experiments can yield meaningful data to test my hypothesis (or hypotheses).
- As a new investigator, I include enough detail to convince reviewers I understand and can handle a method. I reviewed the sample applications to see how much detail to use.
- If I or my team has experience with a method, I cite it; otherwise I include enough details to convince reviewers we can handle it.
- I describe the results I anticipate and their implications.
- I omit all information not needed to state my case.
- I keep track of and explain who will do what, what they will do, when and where they will do it, how long it will take, and how much money it will cost.
- My timeline shows when I expect to complete my aims.
If you are applying for a new application, include preliminary studies; for a renewal or a revision (a competing supplement to an existing grant), prepare a progress report instead.
Describing Preliminary Studies
Your preliminary studies show that you can handle the methods and interpret results. Here's where you build reviewer confidence that you are headed in the right direction by pursuing research that builds on your accomplishments.
Reviewers use your preliminary studies together with the biosketches to assess the investigator review criterion, which reflects the competence of the research team.
Give alternative interpretations to your data to show reviewers you've thought through problems in-depth and are prepared to meet future challenges. If you don't do this, the reviewers will!
Though you may include other people's publications, focus on your preliminary data or unpublished data from your lab and the labs of your team members as much as you can.
As we noted above, you can put your preliminary data anywhere in the Research Strategy that you feel is appropriate, but just make sure your reviewers will be able to distinguish it. Alternatively, you can create a separate section with its own header.
Including a Progress Report
If you are applying for a renewal or a revision (a competing supplement to an existing grant), prepare a progress report instead of preliminary studies.
Create a header so your program officer can easily find it and include the following information:
- Project period beginning and end dates.
- Summary of the importance of your findings in relation to your Specific Aims.
- Account of published and unpublished results, highlighting your progress toward achieving your Specific Aims.
Note: if you submit a renewal application before the due date of your progress report, you do not need to submit a separate progress report for your grant. However, you will need to submit it, if your renewal is not funded.
After finishing the draft, check that
- I interpret my preliminary results critically.
- There is enough information to show I know what I'm talking about.
- If my project is complex, I give more preliminary studies.
- I show how my previous experience prepared me for the new project.
- It's clear which data are mine and which are not.
References show your breadth of knowledge of the field. If you leave out an important work, reviewers may assume you're not aware of it.
Throughout your application, you will reference all relevant publications for the concepts underlying your research and your methods.
Read more about your Bibliography and References Cited at Add a Bibliography and Appendix .
- Throughout my application I cite the literature thoroughly but not excessively, adding citations for all references important to my work.
- I cite all papers important to my field, including those from potential reviewers.
- I include fewer than 100 citations (if possible).
- My Bibliography and References Cited form lists all my references.
- I refer to unpublished work, including information I learned through personal contacts.
- If I do not describe a method, I add a reference to the literature.
Look over what you've written with a critical eye of a reviewer to identify potential questions or weak spots.
Enlist others to do that too—they can look at your application with a fresh eye. Include people who aren't familiar with your research to make sure you can get your point across to someone outside your field.
As you finalize the details of your Research Strategy, you will also need to return to your Specific Aims to see if you must revise. See Draft Specific Aims .
After you finish your Research Plan, you are ready to write your Abstract (called Project Summary/Abstract) and Project Narrative, which are attachments to the Other Project Information form.
These sections may be small, but they're important.
- All your peer reviewers read your Abstract and narrative.
- Staff and automated systems in NIH's Center for Scientific Review use them to decide where to assign your application, even if you requested an institute and study section.
- They show the importance and health relevance of your research to members of the public and Congress who are interested in what NIH is funding with taxpayer dollars.
Be sure to omit confidential or proprietary information in these sections! When your application is funded, NIH enters your title and Abstract in the public RePORTER database.
Think brief and simple: to the extent that you can, write these sections in lay language, and include appropriate keywords, e.g., immunotherapy, genetic risk factors.
As NIH referral officers use these parts to direct your application to an institute for possible funding, your description can influence the choice they make.
Write a succinct summary of your project that both a scientist and a lay person can understand (to the extent that you can).
- Use your Specific Aims as a template—shorten it and simplify the language.
- In the first sentence, state the significance of your research to your field and relevance to NIAID's mission: to better understand, treat, and prevent infectious, immunologic, and allergic diseases.
- Next state your hypothesis and the innovative potential of your research.
- Then list and briefly describe your Specific Aims and long-term objectives.
In your Project Narrative, you have only a few sentences to drive home your project's potential to improve public health.
Check out these effective Abstracts and Narratives from our R01 Sample Applications :
- Application from Dr. Mengxi Jiang , "Intersection of polyomavirus infection and host cellular responses"
- Application from Dr. William Faubion , "Inflammatory cascades disrupt Treg function through epigenetic mechanisms"
- My Project Summary/Abstract and Project Narrative (and title) are accessible to a broad audience.
- They describe the significance of my research to my field and state my hypothesis, my aims, and the innovative potential of my research.
- My narrative describes my project's potential to improve public health.
- I do not include any confidential or proprietary information.
- I do not use graphs or images.
- My Abstract has keywords that are appropriate and distinct enough to avoid confusion with other terms.
- My title is specific and informative.
Previous Step
Have questions.
A program officer in your area of science can give you application advice, NIAID's perspective on your research, and confirmation that your proposed research fits within NIAID’s mission.
Find contacts and instructions at When to Contact an NIAID Program Officer .
Section 4. Stages of Mentoring
4.5 Implementing an Individual Research Plan
Depending on the details of the research plan, mentor and mentee have various ways to implement it. A research project proposes questions to be explored. In many cases, the research plan includes the following four components:
Literature Reading
Information gathering, research analysis, conclusion and summary.
At the beginning of the research project, mentees need to do a general study of the topic(s) by reading the relevant literature. Often mentors help mentees to look for appropriate reading materials. This step helps the mentee to form a big picture of the field or topic by knowing what has been done and what can be done. The process can be short or long depending on how knowledgeable the mentee is with the field of study. If it takes too long for a mentee to read papers or articles, then it might be an indicator that this project is not yet part of the student researcher’s skills set or has to be better scaffolded into the research plan. This may happen when the student has not had experiences in reading articles in that discipline. After the literature review, the mentee, with the help of the mentor, may propose a researchable question.
Implementing a research plan often requires gathering information through mentor- recommended methods. These methods may include surveys, scientific experiments, sampling, observations, and literature queries. The quality of the gathered information greatly determines the quality of the research results.
Analyzing gathered information usually requires knowledge of mathematics and statistics. It includes organizing the information and choosing and applying appropriate methods to draw and present conclusions. The mentee may need help in this process, particularly those who belong to the STEM fields. This process of analyzing real problems will allow the mentee to expand their knowledge and gain deeper understanding of abstract concepts.
The mentee can learn how to summarize the results from the research and draw meaningful conclusions. As they draw these conclusions, the mentee should be aware that the conclusions may not be permanent. Drawn conclusions in STEM are usually interpreted in light of the constraints placed on the research paradigm, system studied, assumptions made, quality of the data, instrumentation, and methods used.
It is important for the mentors to be able to adjust the research plan as they get to know the mentees and their skills set. The successful implement of the research plan entails open communication of ideas and results between mentors and mentees. The commitment of time and effort from both parties, including the setting and the following of a fixed meeting schedule, is critical in determining whether the research project will be successfully implemented.
A Handbook on Mentoring Students in Undergraduate Research, 2nd Edition Copyright © by Undergraduate Research Committee, New York City College of Technology is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
The value of a good research plan
A research plan is a guiding framework that can make or break the efficiency and success of your research project. Oftentimes teams avoid them because they’ve earned a reputation as a dry or actionless document — however, this doesn’t have to be the case.
In this article, we’ll go over the most important aspects of a good research plan and show you how they can be visual and actionable with monday.com Work OS.
Don’t miss more quality content!
Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project.
A research plan is pivotal to a research project because it identifies and helps define your focus, method, and goals while also outlining the research project from start to finish.
This type of plan is often necessary to:
- Apply for grants or internal company funding.
- Discover possible research partners or business partners.
- Take your research from an idea into reality.
It will also control the entire journey of the research project through every stage by defining crucial research questions and the hypothesis (theory) that you’ll strive to prove or disprove.
What goes into a research plan?
The contents of a thorough research plan should include a hypothesis, methodology, and more. There is some variation between academic and commercial research, but these are common elements:
- Hypothesis: the problem you are trying to solve and the basis for a theoretical solution. For example, if I reduce my intake of calories, I’ll lose weight.
- Research questions: research questions help guide your investigation into particular issues. If you were looking into the potential impact of outsourcing production, you might ask something like: how would outsourcing impact our production costs?
- Research method: the method you’ll use to get the data for your research. For example, a case study, survey, interviews, a clinical trial, or user tests.
- Definitions: a glossary for the research plan, explaining the terminology that you use throughout the document.
- Conceptual frameworks: a conceptual framework helps illustrate what you think you’ll discover with your research. In a sense, it’s a visual representation of a more complex hypothesis.
For commercial plans, there will also likely be a budget and timeline estimate, as well as concrete hypothetical benefits for the company (such as how much money the project should save you).
OK, so you’ve got a handle on the building blocks of a research plan, but how should you actually write it?
How do you write a research plan on monday.com?
The first, and perhaps most crucial part of having a good research plan is having the right medium for creating and sharing it. Using a pre-defined template can also make it much easier to get started.
On monday.com, you can choose from several templates like the Project Proposal Template or better yet the Research Power Tools Template to manage all aspects of your project including important communication with internal and external stakeholders and teammates.
Use your template to:
- Create workdocs
- Upload assets
- Provide feedback
- Assign task owners
- Automate communication
The next step in writing a research plan is choosing the topic. To pick the right topic, focus on these factors:
- What are the priorities of the potential funder/employer, such as the company or institution?
- Are there any relevant recent studies with results you can build on and explore with further research?
- Can you creatively adapt your experience — whether post-grad or professional — to make you the natural candidate? They don’t just need to believe in the research project, but also in your ability to manage it successfully.
Do your research, no pun intended. Once you’ve got the topic, you need to work on fleshing out the core ideas with the building blocks we mentioned above.
- Get specific with your research questions and goals. Don’t go with, “how can we revolutionize our HR practices?” Instead use, “what is the economic and environmental impact of only accepting digital CVs?”
- Use clear language aimed at gatekeepers. If it’s a CTO (Chief Technology Officer) or a lab committee, you can use well-known technical terms. If they aren’t technical experts, adjust accordingly.
- Include preliminary data or highlight similar studies. For companies, showing that a similar approach helped a competitor is a better argument than an empty assertion.
The recommended length of the plan depends on who you’re sending it to and their expectations. If possible, look at successful examples or directly ask your potential employers about their preferences. Not only do you need the right idea, but you also need to present it in the right way for your research project to have a fighting chance.
What is a good research plan?
A good research plan is one that gets accepted and funded to start doing the research.
If you want to plan a pivotal study, it’s not enough to consider the problem in a vacuum. You also need to evaluate how you can best communicate the value of your project to the gatekeepers.
Consider the entirety of your current situation and what that means for your project.
For example, inputs like funding, staff, IP, and how the scale of the project lines up with your company’s research budget. Or how it aligns with the goals of a University program. If the primary goal of the research is to impact a company or government agency directly, you should consider these stages of research engagement.

( Image Source )
- Inputs: anything from funding and staff to company IP that you need to both run the project and implement any results. Does this line up with the budget?
- Activities: case studies, trials, surveys, the actual research.
- Outputs: the final reports, any publications, and raw data.
- Outcome: how will it directly impact the company, organization, or larger society?
- Impacts: what are the indirect benefits or downsides?
In an internal research proposal, you can outline these aspects in separate sections. That allows different execs or managers to focus on the details that matter most to them. You must also work to engage stakeholders and make sure that they understand the importance of your project.
Frequently asked questions
What are the 5 purposes of research.
The 2 primary purposes of research are to gather information or test an existing theory. When broken down further, you can see 5 more specific purposes:
- Exploratory research is an early-stage inquiry that explores a topic for further study down the line, like exploring the deep ocean with a submersible vehicle.
- Descriptive research aims to explore and describe a specific substance, person, or phenomenon.
- Explanatory research is about figuring out the causal relationship, why something happens.
- Predictive research is all about trying to predict what might happen in specific situations based on the properties of the research object.
- Meta-research looks for overarching insights from multiple sources and tests the validity of common hypotheses.
What is a research work plan?
A research work plan is another name for a research plan, which is a critical component of any research proposal. Universities, labs, and companies use them to evaluate research projects before they decide to accept them.
As a researcher, it’s essential when targeting a funding opportunity of any kind.
What are the methods of research?
There are many research methods ranging from a simple online survey to a high-budget clinical study. Here are some examples of popular data collection methods:
- Clinical trials
- Experiments
- Case studies
- Observations
Which one is right for your plan depends on your hypothesis, goals, industry regulations, and more.
Create a dynamic research plan
If you want to turn your research project into a reality, you need to go beyond the academic and into management mode.
With a template from monday.com, you can plan out a research project from start to finish. Including goals and objectives, budget estimates, milestones, and more.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.
Research Plan
Define how to conduct a research activity by writing the protocol before starting., applied for.
Stakeholders
also called
Research Protocol
related content
Hypothesis Generation
Interview Guide
Diary Study
The research plan is a document that clarifies how to approach the research, touching upon research goals, selected methodologies, types of participants and tools used, timeline and locations. This planning activity needs to be done upfront, before starting the actual research, and help maximizing the effort and modeling the activities in the best way possible, according to the specific research purpose. The plan becomes even more important when the research requires to travel in the field, or coordinate different teams in various locations.
Design the research and explain the approach to other team members or stakeholders.
remember to
Include debriefing sessions in the schedule in order to make the work effective and avoid team burnout.
Grow with us! Share your case studies
The collection is always evolving, following the development of our practice. If you have any interesting tools or example of application to share, please get in touch.
This website uses cookies to collect anonymized usage statistics so that we can improve the overall user experience. If you want to know more or change your preferences, read our Cookie Policy . By clicking Accept you are giving consent to the use of cookies.
No, thank you.

- CREd Library , Planning, Managing, and Publishing Research
Developing a Five-Year Research Plan
Cathy binger and lizbeth finestack, doi: 10.1044/cred-pvd-path006.
The following is a transcript of the presentation videos, edited for clarity.
What Is a Research Plan, and Why Do You Need One?
Presented by Cathy Binger

First we’re going to talk about what a research plan is, why it’s important to write one, and why five years—why not one year, why not ten years. So we’ll do some of those basic things, then Liza is going to get down and dirty into the nitty-gritty of “now what” how do I go about writing that research plan.

First of all, what is a research plan? I’m sure some of you have taken a stab at these already. In case you haven’t, this is a real personalized map that relates your projects to goals. It’s exactly what it sounds like, it’s a plan of how you’re going to go about doing your research. It doesn’t necessarily just include research.
It’s something that you need to put a little time and effort into in the beginning. And then, if you don’t revisit it, it’s really a useless document. It’s something that you need to come back to repeatedly, at least annually, and you need to make it visible. So it’s not a document that sits around and once a year you pull it out and look at it.
It can and should be designed, especially initially, with the help of a mentor or colleague. And it does serve multiple purposes, with different lengths and different amounts of detail.
I forgot to say, too, getting started, the slides for this talk were started using as a jumping off point Ray Kent’s talk from last year. So some of the slides we’ve borrowed from him, so many thanks to him for that.

But why do we want to do a research plan? Well, to me the big thing is the vision. Dr. Barlow talked this morning about your line of research and really knowing where you want to go, and this is where that shows up with all the nuts and bolts in place.
What do you want to accomplish? What do you want to contribute? Most of you are at the stage in your career where maybe you have started out with that you want to change the world scenario and realized that whatever you wanted your first research project to be, really, is your entire career. You need to get that down to the point where it is manageable projects that you can do—this is where you map out what those projects are and set reasonable timelines for that.
You want to really demonstrate your independent thinking and your own creativity, whatever that is that you then establish as a PhD student, postdoc, and beyond—this is where you come back to, okay, here’s how I’m going to go about achieving all of that.
This next point, learning to realistically gauge how long it takes to achieve each goal, this for most of us is a phenomenally challenging thing to do. Most of us really overestimate what we can do in a certain amount of time, and we learn the hard way that you can’t, and that’s another reason why you keep coming back to these plans repeatedly and learning over time what’s really manageable, what’s really doable, so we can still reach our goals and be very strategic about how we do that.
When you’re not strategic, you just don’t meet the goals. Your time gets sucked into so many different things. We need to be really practical and strategic.
Everything we do is going to take longer than we think.
I think this last one is something that maybe we don’t talk about enough. Really being honest with ourselves about the role of research in our lives. Not all of you are at very high-level research universities. Some of you have chosen to go elsewhere, where research maybe isn’t going to be playing the same role as it is for other people. The research plan for someone at an R One research intensive university is going to look quite different from someone who is at a primary teaching university. We need to be open and practical about that.

Getting sidetracked. I love this picture, I just found this picture the other day. This feels like my life. You can get pulled in so many different directions once you are a professor. You will get asked to do a thousand different things. There are lots of great opportunities that are out there. Especially initially, it’s tempting to say yes to all of them. But if you’re going to be productive, you have to be very strategic. I’m going to be a little bit sexist against my own sex here for a minute, but my observation has been that women tend to fall into this a little bit more than men do in wanting to say yes and be people pleasers for everything that comes down the pike.
It is a professional skill to learn how to say no. And to do that in such a way that you are not burning bridges as you go down the path. That is a critical skill if you are going to be a successful researcher. I can’t tell you how many countless people I’ve seen who are very bright, very dedicated, have the skills that it takes in terms of doing the work—but then they are not successful because they’ve gotten sidetracked and they try to be too much of a good citizen, give too much service to the department, too much “sure I’ll take on that extra class” or whatever else comes down the line.
I just spoke with a professor recently who had something like five hours a week of office hours scheduled every single week for one class. Margaret is shaking her head like “are you kidding?” That’s crazy stuff. But he wanted to really support his students. His students loved him, but he was not going to get tenure. That’s the story.
So we have to be very thoughtful and strategic, and what can help you with this, and ASHA very firmly recognizes which is why we’re here—is that your mentors in your life should be there to help you learn these skills and learn what to say yes to, and learn what to say no to. I’ve learned to say things like, “Let me check with my mentor before I agree to that.” And it gives you a way out of that. The line that I use a lot is, “Let me check with my department head” or, I just said this to somebody last week, “I just promised my department head two weeks ago that I would only do X number of external workshops this year, so I’m going to have to turn this one down.” Those are really important skills to develop.
And having that research plan in place that you can go back to and say, know what, it’s not on my plan I can’t do it. If I do it—I have to go back to my research plan and figure out what I’m going to kick off in order to review this extra paper, in order to take on this extra task. The plan also helps me to know exactly what to say no to. And to be very direct and have a very strong visual.
I actually have my research plan up on a giant whiteboard in my office, so I can always go back to that and see where I am, and I can say, “Okay, what am I going to kick off of here? Nothing. Okay, I have to say no to whatever comes up.” Just be strategic. This is where I see most beginning professors really end up taking that wrong fork in the road—taking that right instead of that left, and ending up not being the successful researcher that they wanted to be.

What evidence supports research planning? This was something Ray Kent had found. That a recent analysis had found that postdoc scholars who developed a written plan with their postdoc advisers were much more productive than those who didn’t. And your performance during a postdoc—and I know many of you have either finished your postdoc or decided not to—so more simply, just during those first six years, the decisions you make really do establish the foundation for the rest of your professional life. It’s very important to get started and get off on the right foot.

I love this quote, I just found it the other day: “Productivity is never an accident. It is always the result of a commitment to excellence, intelligent planning, and focused effort.”

What we see with productivity is that postdoc scholars who developed written productivity expectations with their advisers were more productive than those who didn’t. You see 23% more papers submitted, 30% more first-author papers, and more grant proposals as well.

So why five years? I’m going to start with number 5. It’s long enough to build a program of research, but short enough to deal with changing circumstances. That’s really the long and the short of the matter. As well as these other things as well that I won’t take the time to go through point by point.
What Should a Five-Year Plan Include?
Presented by Lizbeth Finestack

So, thinking about a five-year research plan, I like to think about it like your major “To Do List.” It’s what you’re going to accomplish in five years. Start thinking: What is going to be on my to do list?

You can also think about it like: Okay, I have research. I’ve got to do research. Maybe think about this as one big bucket, or maybe one humongous silo. I have some farm themes going on. Cathy was just on a farm, so I thought I’d tie that in.
So here’s your big silo. You can call that your research silo.

But more realistically, you need to think about it like separate buckets, separate silos, where research is just one of those. Just like Cathy indicated, there’s going to be lots of other things coming up that you’re going to have to manage. They are going to have to be on your to do list, you need to figure out how to fit everything in.
What all those other buckets or silos are, are really going to depend on your job. And maybe the size of the silos, and the size of the buckets are going to vary depending on where you are, what the expectations are at your institution.
That’s important to keep in mind, and Cathy said this too, it’s not going to be the same for everyone. The five-year plan has to be your plan, your to do list.

Here are some buckets or some silos that I have on my list and the way that I break it up, this is just one example, take it or leave it.
The first three are all very closely related, right? Thinking about grants, thinking about research, thinking about publications. I’m going to define grants as actual writing, getting the grant, getting the money.
Research is what you’re going to do once you get that money. Steps you need to take before you are getting the money. Any sorts of projects, the lab work, that’s why I have the lab picture there. Of course, publications are part of the product—what’s coming out of the research—but it also cycles in because you need publications to support that you are a researcher to apply for funding and show you have this line of research that you’ve established and you’ll be able to continue. So, those first three are really closely related. And that’s where I’ll go next. And then have teaching and service you see here at the bottom.

So thinking about research, in that broad sense. As you’re writing your five-year plan you’re going to want to think of, “What’s my long-term goal?” There’s lots of ways to think of long-term goals. You could think, before I die, this is what I want to accomplish. For me I kind of have that. My long-term goal is that I’m going to find the most effective and efficient interventions for kids with language impairment. Huge broad goal. But within that I can start narrowing it down.
Where am I within that? Within the next five years or maybe the next ten years, what is it I want to accomplish towards that goal. Then start thinking about: In order to accomplish that goal, what are the steps I need to take? Starting to break it down a little bit. Then it’s also going to be really important to think: where are you going to start? Where are you now? What do you need to have happen? And is it reasonable to accomplish this goal within five years? Is it going to take longer? Maybe you could do it in a couple years? Start thinking about the timeline that’s going to work for you.
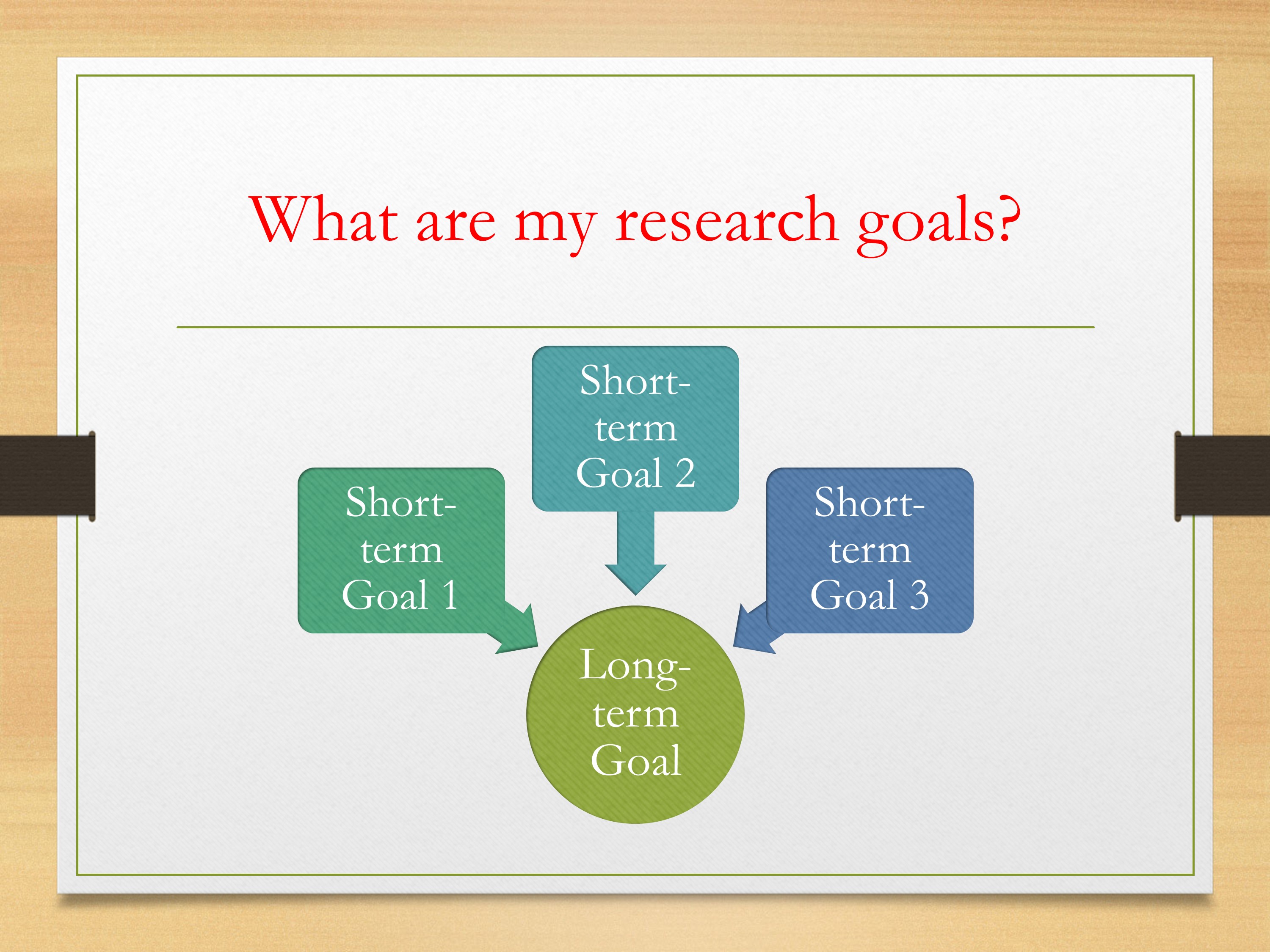
Then thinking about your goals—and everyone’s program is going to be different, like I said, there’s going to be a lot of individual needs, preferences. So it might be the case that you have this one long-term goal that you’re aiming for. Long-term goal in the sense of, maybe, what you want to study in your R01, perhaps something like that. But in order to get to that point, you’re going to have several short-term goals that need to be accomplished.
Or maybe it’s the case that you have two long-term goals. And with each of those you’re going to have multiple short-term goals that you’re working on. Maybe the scope of each of these long-term goals is a little bit less than in that first scenario.
Start thinking about my research, what I want to do, and how it might fit into these different circumstances.

Also thinking about your goals, this is a slide from Ray Kent from last year, was thinking about the different types of projects you might want to pursue, and thinking about ones that are definitely well on your way. They are safe bets. You have some funding. They are going to lead directly into your longer-term plan.
Those are going to be your front burner—things you can easily focus on. That said, don’t put everything there.
You can also have things on the back burner. Things that really excite you, might have huge benefits, big pay. But you don’t want to spend all of your time there because they could be pretty risky.
Start thinking about where you’re putting your time. Are you putting it all on this high-risk thing that if it doesn’t pan out you’re going to be in big trouble? Or balancing that somewhat with your front burner. Making that steady progress that will lead directly to help fund an R01 or whatever the mechanism that you’re looking for.

Then, thinking about your goals—if you have multiple long-term goals, or thinking about your short-term goals, you could think about your process. Is it something where you need to do study 1 then study 2, then study 3—each of those building on each other, that’s leading to that long-term goal. In many cases, that is the case, where you have to get information from the first study which is going to lead directly to the second study and so forth.

Or is it the case that you can be working on these three short-term goals simultaneously? Spreading your resources at the same time. Maybe it will take longer for any one study, but across a longer period of time you’ll get the information that you need to reach that long-term goal.
Lots and lots of different ways to go about it. The important thing is to think about what your needs are and what makes the most sense for you.
Here’s my own little personal example. Starting over here, I have my dissertation study. My dissertation study was this early efficacy study looking at one treatment approach using novel forms that really can’t generalize to anything too useful, but it was important.
Then I did a follow up study, where I was taking that same paradigm, looking to see where kids with typical development perform on the task. So I have these two studies, and they served as my preliminary studies for an R03. So I just finished an R03 where I was looking at different treatment approaching for kids with primary language impairment. At the same time, while conducting my R03, I’m also looking at some different approaches that might help with language development. Also conducting surveys to see what current practices are.
I have these three projects going on simultaneously, that are going to lead to a bigger pilot study that are going to feed directly into my R01. All of this will serve as preliminary data to go into an R01.
Start thinking about your projects, what you have. Maybe starting with your dissertation project or work that you’re doing as a postdoc as seeing how that can feed into your long-term goal. And really utilizing it, building on it, to your benefit.

That’s all fine and dandy. You can draw these great pictures. But you still have to break it down some more. It’s not like, “Oh, I’m just going to do this project.” There are other steps involved, and lots of the time these steps are going to be just as time consuming.
Starting to think about: well, if you have the funding. Saying, “I want to do this study, but I have no money to do it.” What are the steps in order to get the money to do it? Do you have a pilot study? What do you need?
Start thinking about the resources? Do you need to develop stimuli, protocols, procedures? Start working on that. All of these can be very time consuming, and if you don’t jump on that immediately, it’s going to delay when you can start that project.
Thinking about IRB. Relationships for recruitment, if you’re working with special populations especially? Do you have necessary personnel, grad students, people to help you with the project? Do you need to train them? What’s the timeline of the study?
Start thinking about all these pieces, and how they are going to fit in that timeline.
This is one way that might help you start thinking about the resources that you need. This is online—Ray Kent had it in his talk, and when I was doing my searches I came across it too and I have the website at the end. Just different ways to think about the resources you might need.
Let’s talk about mapping it out. You have your long-term goal. You have your short-term goals. You’re breaking it down thinking about all those little steps that you need to accomplish. We gotta put it on a calendar. When is it going to happen?
This is an example—you might have your five years. Each month plugging in what are you going to accomplish by that time. Maybe it’s when are grant applications due? It’s going to be important to put those on there to go what do I need to do to make that deadline. Maybe it’s putting when you’re going to get publications out. Things like that.
Honestly, looking at this drives me a little bit crazy, it seems a bit overwhelming. But it’s important to get to these details.
This is an example from, I did Lessons for Success a few years ago and they had their format for doing your plan. I wrote out all my projects, started thinking about all the different aspects. So if something like this works for you, by all means you could use that type of procedure.
Here’s a grid that Ray Kent showed last year. We’re breaking it down by semester. Thinking about each of your semesters, what manuscripts you’re going to be working on, what data collection, your grant applications. Starting to get into some of those other buckets: course preparation, conference submissions.
We also need to include teaching and service.
You probably can’t see this very well. This is similar to that last slide Ray Kent had used last year.
I have my five year plan: what studies I want to accomplish, start thinking about breaking it down.
Then at the beginning of each semester, I fill in a grid like this. Where at the top, I have each of my buckets. I have my grant bucket, my writing bucket which is going to include publications. I also include doing article reviews in my writing bucket, because that’s my writing time. My teaching bucket, my research bucket. Then at the end, my service bucket.
At the beginning of the semester, I think about the big things I want to accomplish. I list those at the top. Then at the beginning of each month, I say, okay what are the things I’m going to accomplish this month, write those in. Then at the beginning of each week, I start looking at whether I’m dedicating any time to the things I said I was going to do that month. I start listing those out saying, this is the amount of time I’m going to spend on that. Of course, I have to take data on what I actually do, so I plug in how much time I’m spending on each of the tasks. Then I graph it, because that’s rewarding to see how much time you’re spending on things, and I get a little side-tracked sometimes.
Think about a system that will help you keep on track, to make sure you’re meeting the goals that you want to meet in terms of your research. But also getting the other things done that you need to get done in terms of teaching and service.
Discussion and Questions
Compiled from comments made during the Pathways 2014 and 2015 conferences. (Video unavailable.)
Building Flexibility into Your Five-Year Plan Comments by Ray Kent, University of Wisconsin-Madison
The five-year plan is not a contract. It’s a map or a compass. A general set of directions to help you plan ahead. It’s not even a contract with yourself, because it will inevitably be revised in some ways.
Sometimes cool things land in your lap. Very often it turns out that through serendipity or whatever else, you find opportunities that are very enticing. Some of those can be path to an entirely new line of research. Some of them can be a huge distraction and a waste of time. It’s a really cool part of science that new things come along. If we put on blinders and say, “I’m committed to my research plan,” and we don’t look to the left or the right, we’re really robbing ourselves of much of the richness of the scientific life. Science is full of surprises, and sometimes those surprises are going to appear as research projects. The problem is you don’t want to redirect all your time and resources to those until you’re really sure they are going to pay off. I personally believe, some of those high risk but really appealing projects are things you can nurse along. You can devote some time and build some collaborations – far enough to determine how realistic and viable they are. That’s important because those things can be the core of your next research program.
It’s very easy to get overcommitted. We all know people who always say “yes”—and we know those people, and they are often disappointing because they can’t get things done. It’s important to have new directions, but limit them. Don’t say, “I’m going to have 12 new directions this year.” Maybe one or two. Weigh them carefully. Talk about them with other people to get a judgment about how difficult it might be to implement them. It enriches science: not only our knowledge, but the way we acquire new knowledge. A psychologist, George Miller—this is the guy with the magic number 7 +- 2—when we interviewed him years ago at Boystown, he said, “My conviction is that everybody should be able to learn a new area of study within three months.” That’s what he thought for a scientist was a goal.
The idea is that you can learn new things. And that’s very important because when you think of it in terms of a 30-year career, how likely is it that the project that you’re undertaking at age 28 is the same project you’ll be working on at age 68? Not very likely. You’re going to be reinventing yourself as a scientist. And reinventing yourself is one of the most important things you can do, because otherwise you’re going to be dead wood. Some projects aren’t worth carrying beyond five or ten years. They have an expiration date.
Building Risk into Your Five-Year Plan Comments by Ray Kent, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Your doctoral study should generally be low-risk research. As you move into a postdoctoral fellowship, think about having two studies—one low-risk, one high-risk with a potential for high impact. At this time you can begin to play the risk factor a little bit differently.
When you are tenure-track you can have a mix of significance with low-risk and high-risk studies. And when you are tenured, then you can go for high risk, clinical trials, and collaborations. Because you have established your independence, so you do not need to worry about losing your visibility. You can be recognized as a legitimate member of the team.
As you plan your career, you should take risk into account. Just as you manage your money taking risk into account, we should manage our careers taking risk into account. I have met people who did not really think about that, and they embarked on some very risky procedures and wasted a lot of time and resources with very little to show for it. For example, don’t put everything into an untested technology basket. You want to be using state of the art technology, but you want to be sure it is going to give you what you need.
Other Formats and Uses of Your Research Plan Audience Comments
- If you do your job right with your job talk, there’s a lot of cross-pollination between your job talk and your research plan. Ideally your job talk tells your colleagues that this is the long-term plan that you have. And they shouldn’t be surprised when you submit a more detailed research plan. They should say, “okay this is very consistent with the job talk.” In my view, the job talk should be a crystal summary of the major aspects of that research program. Of course, much of the talk will be about a specific project or two—but it should always be embedded within the larger program. That helps the audience keep sight of the fact that you are looking at the program. You can say that this is one project that I’ve done, and I plan to do more of these, and this is how they are conceptually related. That’s a good example of why the research plan has multiple purposes – it can be a research statement, it can be the core of your job talk, it can be the nature of your elevator message, and it can be a version of your research plan for a K award application or R01 application or anything else of that nature.
- I think what’s useful is to actually draft your NIH biosketch. The new biosketch has a section called “contributions to science.” It’s really helpful to think about all your projects. It’s hard to start with a blank sheet of paper. But to have it in the format of a biosketch can be really helpful.
Avoiding Overcommitment Audience Comments
- One of the things that is amazing about planning is that if you put an estimate on the level of effort for each part of your plan, you’ll quickly find that you are living three or four lives. Some 300% of your time is spent. It’s helpful for those of us who might share my lack of ability to see constraints or limitations to reel it back and say, “I have a lot on my plate.” Which allows you to say no—which is not something we all do very well when it comes to those nice colleagues and those people you want to impress nationally and connect with. But it allows you to look at what’s planned and go, “I don’t know where I’d find the time to do that.” Which will hopefully help you stay on track.
- I keep a to do list, but I also keep a “to not do” list. One of the things I will keep on my plan is the maximum number of papers I will review in a year. If I hit that number in March, that’s it. I say no to every other paper that comes down the pike. That’s something to work out with your mentor as far as what’s realistic and what’s okay for you. Every time I get a request, I think, “That’s my reading and writing time, so what am I willing to give up. If it means I won’t be able to write on my own paper this week, am I willing to do this?”
Staying on Schedule with Reading, Writing, and Reviewing Audience Comments
- You have to do what works for you. Some people do wait for big blocks of time for writing—which are hard to come by. But the most important thing is to block off your time. Put it on your schedule, or it is the first thing that will get pushed aside.
- Another thing I’ve done with some of my colleagues is writing retreats. So maybe once a year, twice a year, we’ll get together. Usually we’ll go to a hotel or somewhere, and we’re just writing. It’s a great way to get a jumpstart on a project. Like, I need to sit down and start this manuscript, and you can keep going once you’ve got that momentum.
- My input would be that you really have to write all the time, every day. It’s a skill. I’ve found that if I take time off, my writing deteriorates. It’s something you need to keep up with.
- I would look at it like a savings account that you put money into on a daily, weekly, monthly basis. The flip side of writing is reading. I would read constantly, widely, and not just in the discipline. That will give you not only a breadth in terms of your understanding of your field and the world around you, but it will also give you an incentive to make your own contributions. I think we don’t talk enough about the comprehensive side to this, and being receptive to the reading. I have a book, or something, by my bedside every night. And I read that until I fall asleep every night. And it’s done me in good stead over the years.
- Reviewing articles can help advance your career, but it is something you need to weigh carefully as a draw on your time. You get a lot from it. You get to see what’s out there. You get to see what’s coming down the pipe before publication. To me that’s a huge benefit. You get to learn from other people’s writing, and that’s part of your reading you get to do. But it is time consuming. And it depends on the kinds of papers you get. Sometimes you’re lucky and sometimes you’re not.
- If someone else is reviewing your grants and your articles, at some point you owe it back. You should at least be in break-even mode. Now, pre-tenure or postdoc your mentor should be doing that or senior faculty in the department. But there are so many articles to review. I review so many articles, but I am also at the tail end of my career. The bottom line is, if you don’t put on your schedule that if you don’t put time on your schedule for reading, reviewing articles forces you to look at and think about the literature, so you can be accomplishing what you owe back to the field—and at the same time, staying one step ahead knowledge wise. It forces you to do what you should be doing all along, which is keeping up with the literature.
Further Reading: Web Resources
Golash-Boza, T. (2014). In Response to Popular Demand, More on the 5-Year Plan. The Professor Is In . Available at http://theprofessorisin.com/2014/05/09/in-response-to-popular-demand-more-on-the-5-year-plan
Kelsky, K. (2010). The Five-Year Plan for Tenure-Track Professors. Get a life, PhD . Available at http://getalifephd.blogspot.com/2010/07/five-year-plan-for-tenure-track.html
National Association of Geoscience Teachers (NAGT). (2012). Planning Worksheets . Planning your Research Program (Available from the Science Education Resource Center at Carelton College Website at http://serc.carleton.edu/).
Pfirman, S., Bell, R., Culligan, P., Balsam, P. & Laird, J. (2008) . Maximizing Productivity and Recognition , Part 3: Developing a Research Plan. Science Careers. Available at http://sciencecareers.sciencemag.org/career_magazine/previous_issues/articles/2008_10_10/caredit.a0800148
Cathy Binger University of New Mexico
Lizbeth Finestack University of Minnesota
Based on a presentation and slides originally developed by Ray Kent, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Presented at Pathways (2015). Hosted by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Research Mentoring Network.
Pathways is sponsored by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through a U24 grant awarded to ASHA.
Copyrighted Material. Reproduced by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association in the Clinical Research Education Library with permission from the author or presenter.

Clinical Research Education
More from the cred library, innovative treatments for persons with dementia, implementation science resources for crisp, when the ears interact with the brain, follow asha journals on twitter.

© 1997-2024 American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Privacy Notice Terms of Use

PHILO-notes
Free Online Learning Materials
Research Plan: Definition and How to Prepare It
The research plan , which is also called “ research proposal ” before acceptance by competent authority, is a scholarly paper. As is well-known, it must conform to accepted conventions of academic and scientific procedure. It is expected to show evidence of intelligent grasp of the problem being proposed for solution, and fields related to it. It must also present appropriate and valid method and procedure for the solution of the problem.
Allowing for certain variations due to preferences of scholars, disciplines, and institutions, a research plan generally contains the following:
1) The title of the personal study,
2) Statement of the problem,
3) Review of related literature, and
4) Scope and limitation of the study,
5) Importance or significance of the study,
6) Definition of terms, and theoretical framework,
7) Methods and procedure,
8) Bibliography.
The title of the research plan should be brief but descriptive and comprehensive. The title should also be an adequate index to the key contents of the following: 1) the statement of the problem, 2) the method(s) used, and 3) the expected or hypothetical conclusion(s).
Although it is the first to appear on the research plan, it can remain tentative until the problem and methodology have been clearly formulated. (See also W. C. Campbell & S. V. Ballou, Form and Style: Theses, Reports, Term Papers, 4 th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Miffin, 1974, p. 15).
The Statement of the Problem
The statement of the problem is the part of the research plan, which contains two parts, namely: 1) a careful exposition of an area involving significant problems, and how such problems affect knowledge in the given discipline, and 2) a clear and concise statement of the problem. The first is an essay that demonstrates the researcher’s intelligent and broad grasp of the key problem currently confronting her discipline. The second is a clear statement of the question(s) to be answered or hypothesis to be tested.
The statement of the problem in experimental research is usually in the form of a hypothesis or a series of related hypotheses which call for proof or disproof. Other types of research require that the problem be stated categorically in the form of a question or series of related questions. In case a question needs further specification by means of sub-questions, care is to be taken that the sub-questions are all comprehended by the primary question. Multiple questions and questions which add new problems not expressed or implied in the primary question must be avoided. (See Campbell & Ballou, p. 18).
It must be remembered that the statement of the problem is not the same with the statement of the purpose of the study. The first is the question to be answered, while the second is the reason for answering the question.
A good statement of the problem must be consistent with the title and the methods and procedure to be used in the research.
Review of Related Literature
It is assumed that before the researcher starts making the research plan, she has read many important works related to the proposed study. The aims of the review of related literature are:
1) to show that the researcher is familiar with key ideas in his field of study;
2) to show that the knowledge in the field is incomplete, unreliable, or both; and
3) to show that the findings of the proposed study will: a) add to, b) supplement,
and/or c) correct present knowledge.
The tone and tenor of the review of related literature are both expository and evaluative or critical.
The materials subject to review under this heading are both published and unpublished materials containing anything that have some pertinence to the proposed subject of study. These include books, periodicals, documents, theses, dissertations, and all papers that are conventionally regarded among scholars as disciplinary literature. This explains why it is redundant to say “literature and studies” because the term “literature” includes all studies, which are on record and reported.
Scope and Limitation of the Study
The scope of the study refers to the
1) specific source(s) of information, and
2) time involved in the study.
Since the scope of the study directly affect the validity of the conclusion derived from it, it may be assumed that a study that has no specifically defined scope and limitation of sources and time cannot lead to a definite and valid generalization and/or conclusion.
The limitation of the study refers to shortcoming or source of weakness of the study. The honest researcher must admit the weakness or limitation of any aspect of her investigation or her tools of investigation, and source of information. This fundamental rule is required by intellectual honesty. For example, using translation as reference due to one’s lack of proficiency in the original language of the source is a limitation of the investigator. Limitations that are so great as to cause doubt concerning the validity or conclusion of the study invalidate a research plan.
Significance of the Study
The significance of the study is generally of two kinds, namely, 1) the significance of the expected findings of the study to the specific discipline to which the study belongs, and 2) the benefit that human world may derive from the findings. Evidence of significance on the first level is generally sufficient. Significance of the second level if not discreetly put tends to be pretentious and violates the modesty generally expected of scholars. It is, therefore, generally best to convince the reader that the answer(s) one is trying to discover are important mainly to one’s line of study, and leave the “earth-shaking” value of the study understated or implied.
Research on the graduate school level is expected to show evidence of 1) mastery of scientific and rational methods of arriving at conclusions, and 2) actual contribution of new knowledge to the pool of human knowledge. Unless the study meets this requirement, the study is not significant, and this could imply that the student fails even in the first.
Definition of Terms and Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework of the study is stated here. This is the place to present 1) the assumption of the study, that is, proposition regarded are true and therefore not requiring proof in the proposed research, and 2) the definition of key terms.
It is usual that scholars or researchers work within the framework of a discipline, which have generally accepted principles or law which need simply to be assumed as true, and within whose framework the researcher performs his reflected thinking. This means placing the proposed study in the context of a specific school of thought in the researcher’s field of study. It may also require statement of ideas already proved satisfactory by other or previous researchers.
When the theoretical framework in the form of assumptions has been completed, key terms, especially those that are used in a particular or unusual sense, are defined. Operational definitions are preferred. Sources of definitions are properly indicated. Definitions not indicated as having been borrowed from sources are assumed to belong to the author of the research plan.
Operational definitions reduce abstract terms (for example, education) to concrete or quantifiable or measurable terms. The term “development”, for example, is defined operationally as “getting people to know, desire, and be capable of doing better things”. Operational definitions are always in a framework of a study.
Methods and Procedure
Methods refer to the set of procedures or steps to be undertaken for discovering knowledge with reference to the time setting of the truth to be known, that is, the past, present, and the future.
Truth of the past is historical. That of the present is described or pictured. And that of the future can be experimented, that is, create a situation whereby an unknown truth can be observed under controlled conditions. Therefore, there are three methods in general use in the scholarly world.
One method may be used, or where necessary, a combination of all three. But the use of these in combination must be done with great care so that it is always clear when each of the methods is being used, especially in the writing of the research report.
In certain disciplines, such as Literature and Philosophy, textual studies are usual. Studies of text are historical because the ordinary aim of this type of study is to arrive at the original intent of the author insofar as this is possible. This involved an attempt to situate words in their historical or biological context, with reference to their import at the time and place the document was written.
In the research plan, it is sufficient to indicate which method is proposed to be used.
Procedures are sub-items under methods. They are steps in logical or chronological sequence which are seen as an organized system of steps toward the discovery of truth, which involve 1) analyzing, 2) classifying, 3) comparing, 4) narrating, and 5) making conclusions regarding what causes produced what effects. One should not confuse method with the steps in a method.
After the procedures have been presented, a proposed outline of the expected report (for example, thesis, dissertation, and term paper) is presented. This outline shows clearly the proposed titles and subsections under each title. Parts or chapters are presented in their expected final sequence which indicate how the successive parts lead to the findings and conclusion.
Bibliography
This is a systematic listing of all available references in libraries, archives, collections, and in other sources. Exhaustiveness is ideal. Although last in the research plan, it is the first to be done in the order of procedure and time. This is because before anyone can formulate a title or problem for the research plan, one has to know whether there are available sources, or whether there already exist and completed studies covering the same area and problem. The way to discover the sources is to look for them wherever they may be an make a listing of these sources.
Final Note : Sometimes, a research plan or proposal may be presented for evaluation in order to secure funding. When this is the case, two things must be added to the foregoing parts: 1) a timetable indicating the schedule of research activities and the time each step in the research is expected to be completed, and 2) a statement of expenses properly itemized to indicate which amount is for which activity, and for which logistics (that is, tools, equipment, instruments, postage, and the like) and related expenses, such as salaries and publication expenses. It is important to note that the budget is not only itemized but also justified.
Human Subjects Office
Medical terms in lay language.
Please use these descriptions in place of medical jargon in consent documents, recruitment materials and other study documents. Note: These terms are not the only acceptable plain language alternatives for these vocabulary words.
This glossary of terms is derived from a list copyrighted by the University of Kentucky, Office of Research Integrity (1990).
For clinical research-specific definitions, see also the Clinical Research Glossary developed by the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials (MRCT) Center of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard and the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) .
Alternative Lay Language for Medical Terms for use in Informed Consent Documents
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
ABDOMEN/ABDOMINAL body cavity below diaphragm that contains stomach, intestines, liver and other organs ABSORB take up fluids, take in ACIDOSIS condition when blood contains more acid than normal ACUITY clearness, keenness, esp. of vision and airways ACUTE new, recent, sudden, urgent ADENOPATHY swollen lymph nodes (glands) ADJUVANT helpful, assisting, aiding, supportive ADJUVANT TREATMENT added treatment (usually to a standard treatment) ANTIBIOTIC drug that kills bacteria and other germs ANTIMICROBIAL drug that kills bacteria and other germs ANTIRETROVIRAL drug that works against the growth of certain viruses ADVERSE EFFECT side effect, bad reaction, unwanted response ALLERGIC REACTION rash, hives, swelling, trouble breathing AMBULATE/AMBULATION/AMBULATORY walk, able to walk ANAPHYLAXIS serious, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction ANEMIA decreased red blood cells; low red cell blood count ANESTHETIC a drug or agent used to decrease the feeling of pain, or eliminate the feeling of pain by putting you to sleep ANGINA pain resulting from not enough blood flowing to the heart ANGINA PECTORIS pain resulting from not enough blood flowing to the heart ANOREXIA disorder in which person will not eat; lack of appetite ANTECUBITAL related to the inner side of the forearm ANTIBODY protein made in the body in response to foreign substance ANTICONVULSANT drug used to prevent seizures ANTILIPEMIC a drug that lowers fat levels in the blood ANTITUSSIVE a drug used to relieve coughing ARRHYTHMIA abnormal heartbeat; any change from the normal heartbeat ASPIRATION fluid entering the lungs, such as after vomiting ASSAY lab test ASSESS to learn about, measure, evaluate, look at ASTHMA lung disease associated with tightening of air passages, making breathing difficult ASYMPTOMATIC without symptoms AXILLA armpit
BENIGN not malignant, without serious consequences BID twice a day BINDING/BOUND carried by, to make stick together, transported BIOAVAILABILITY the extent to which a drug or other substance becomes available to the body BLOOD PROFILE series of blood tests BOLUS a large amount given all at once BONE MASS the amount of calcium and other minerals in a given amount of bone BRADYARRHYTHMIAS slow, irregular heartbeats BRADYCARDIA slow heartbeat BRONCHOSPASM breathing distress caused by narrowing of the airways
CARCINOGENIC cancer-causing CARCINOMA type of cancer CARDIAC related to the heart CARDIOVERSION return to normal heartbeat by electric shock CATHETER a tube for withdrawing or giving fluids CATHETER a tube placed near the spinal cord and used for anesthesia (indwelling epidural) during surgery CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) brain and spinal cord CEREBRAL TRAUMA damage to the brain CESSATION stopping CHD coronary heart disease CHEMOTHERAPY treatment of disease, usually cancer, by chemical agents CHRONIC continuing for a long time, ongoing CLINICAL pertaining to medical care CLINICAL TRIAL an experiment involving human subjects COMA unconscious state COMPLETE RESPONSE total disappearance of disease CONGENITAL present before birth CONJUNCTIVITIS redness and irritation of the thin membrane that covers the eye CONSOLIDATION PHASE treatment phase intended to make a remission permanent (follows induction phase) CONTROLLED TRIAL research study in which the experimental treatment or procedure is compared to a standard (control) treatment or procedure COOPERATIVE GROUP association of multiple institutions to perform clinical trials CORONARY related to the blood vessels that supply the heart, or to the heart itself CT SCAN (CAT) computerized series of x-rays (computerized tomography) CULTURE test for infection, or for organisms that could cause infection CUMULATIVE added together from the beginning CUTANEOUS relating to the skin CVA stroke (cerebrovascular accident)
DERMATOLOGIC pertaining to the skin DIASTOLIC lower number in a blood pressure reading DISTAL toward the end, away from the center of the body DIURETIC "water pill" or drug that causes increase in urination DOPPLER device using sound waves to diagnose or test DOUBLE BLIND study in which neither investigators nor subjects know what drug or treatment the subject is receiving DYSFUNCTION state of improper function DYSPLASIA abnormal cells
ECHOCARDIOGRAM sound wave test of the heart EDEMA excess fluid collecting in tissue EEG electric brain wave tracing (electroencephalogram) EFFICACY effectiveness ELECTROCARDIOGRAM electrical tracing of the heartbeat (ECG or EKG) ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE an imbalance of minerals in the blood EMESIS vomiting EMPIRIC based on experience ENDOSCOPIC EXAMINATION viewing an internal part of the body with a lighted tube ENTERAL by way of the intestines EPIDURAL outside the spinal cord ERADICATE get rid of (such as disease) Page 2 of 7 EVALUATED, ASSESSED examined for a medical condition EXPEDITED REVIEW rapid review of a protocol by the IRB Chair without full committee approval, permitted with certain low-risk research studies EXTERNAL outside the body EXTRAVASATE to leak outside of a planned area, such as out of a blood vessel
FDA U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the branch of federal government that approves new drugs FIBROUS having many fibers, such as scar tissue FIBRILLATION irregular beat of the heart or other muscle
GENERAL ANESTHESIA pain prevention by giving drugs to cause loss of consciousness, as during surgery GESTATIONAL pertaining to pregnancy
HEMATOCRIT amount of red blood cells in the blood HEMATOMA a bruise, a black and blue mark HEMODYNAMIC MEASURING blood flow HEMOLYSIS breakdown in red blood cells HEPARIN LOCK needle placed in the arm with blood thinner to keep the blood from clotting HEPATOMA cancer or tumor of the liver HERITABLE DISEASE can be transmitted to one’s offspring, resulting in damage to future children HISTOPATHOLOGIC pertaining to the disease status of body tissues or cells HOLTER MONITOR a portable machine for recording heart beats HYPERCALCEMIA high blood calcium level HYPERKALEMIA high blood potassium level HYPERNATREMIA high blood sodium level HYPERTENSION high blood pressure HYPOCALCEMIA low blood calcium level HYPOKALEMIA low blood potassium level HYPONATREMIA low blood sodium level HYPOTENSION low blood pressure HYPOXEMIA a decrease of oxygen in the blood HYPOXIA a decrease of oxygen reaching body tissues HYSTERECTOMY surgical removal of the uterus, ovaries (female sex glands), or both uterus and ovaries
IATROGENIC caused by a physician or by treatment IDE investigational device exemption, the license to test an unapproved new medical device IDIOPATHIC of unknown cause IMMUNITY defense against, protection from IMMUNOGLOBIN a protein that makes antibodies IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE drug which works against the body's immune (protective) response, often used in transplantation and diseases caused by immune system malfunction IMMUNOTHERAPY giving of drugs to help the body's immune (protective) system; usually used to destroy cancer cells IMPAIRED FUNCTION abnormal function IMPLANTED placed in the body IND investigational new drug, the license to test an unapproved new drug INDUCTION PHASE beginning phase or stage of a treatment INDURATION hardening INDWELLING remaining in a given location, such as a catheter INFARCT death of tissue due to lack of blood supply INFECTIOUS DISEASE transmitted from one person to the next INFLAMMATION swelling that is generally painful, red, and warm INFUSION slow injection of a substance into the body, usually into the blood by means of a catheter INGESTION eating; taking by mouth INTERFERON drug which acts against viruses; antiviral agent INTERMITTENT occurring (regularly or irregularly) between two time points; repeatedly stopping, then starting again INTERNAL within the body INTERIOR inside of the body INTRAMUSCULAR into the muscle; within the muscle INTRAPERITONEAL into the abdominal cavity INTRATHECAL into the spinal fluid INTRAVENOUS (IV) through the vein INTRAVESICAL in the bladder INTUBATE the placement of a tube into the airway INVASIVE PROCEDURE puncturing, opening, or cutting the skin INVESTIGATIONAL NEW DRUG (IND) a new drug that has not been approved by the FDA INVESTIGATIONAL METHOD a treatment method which has not been proven to be beneficial or has not been accepted as standard care ISCHEMIA decreased oxygen in a tissue (usually because of decreased blood flow)
LAPAROTOMY surgical procedure in which an incision is made in the abdominal wall to enable a doctor to look at the organs inside LESION wound or injury; a diseased patch of skin LETHARGY sleepiness, tiredness LEUKOPENIA low white blood cell count LIPID fat LIPID CONTENT fat content in the blood LIPID PROFILE (PANEL) fat and cholesterol levels in the blood LOCAL ANESTHESIA creation of insensitivity to pain in a small, local area of the body, usually by injection of numbing drugs LOCALIZED restricted to one area, limited to one area LUMEN the cavity of an organ or tube (e.g., blood vessel) LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY an x-ray of the lymph nodes or tissues after injecting dye into lymph vessels (e.g., in feet) LYMPHOCYTE a type of white blood cell important in immunity (protection) against infection LYMPHOMA a cancer of the lymph nodes (or tissues)
MALAISE a vague feeling of bodily discomfort, feeling badly MALFUNCTION condition in which something is not functioning properly MALIGNANCY cancer or other progressively enlarging and spreading tumor, usually fatal if not successfully treated MEDULLABLASTOMA a type of brain tumor MEGALOBLASTOSIS change in red blood cells METABOLIZE process of breaking down substances in the cells to obtain energy METASTASIS spread of cancer cells from one part of the body to another METRONIDAZOLE drug used to treat infections caused by parasites (invading organisms that take up living in the body) or other causes of anaerobic infection (not requiring oxygen to survive) MI myocardial infarction, heart attack MINIMAL slight MINIMIZE reduce as much as possible Page 4 of 7 MONITOR check on; keep track of; watch carefully MOBILITY ease of movement MORBIDITY undesired result or complication MORTALITY death MOTILITY the ability to move MRI magnetic resonance imaging, diagnostic pictures of the inside of the body, created using magnetic rather than x-ray energy MUCOSA, MUCOUS MEMBRANE moist lining of digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts MYALGIA muscle aches MYOCARDIAL pertaining to the heart muscle MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION heart attack
NASOGASTRIC TUBE placed in the nose, reaching to the stomach NCI the National Cancer Institute NECROSIS death of tissue NEOPLASIA/NEOPLASM tumor, may be benign or malignant NEUROBLASTOMA a cancer of nerve tissue NEUROLOGICAL pertaining to the nervous system NEUTROPENIA decrease in the main part of the white blood cells NIH the National Institutes of Health NONINVASIVE not breaking, cutting, or entering the skin NOSOCOMIAL acquired in the hospital
OCCLUSION closing; blockage; obstruction ONCOLOGY the study of tumors or cancer OPHTHALMIC pertaining to the eye OPTIMAL best, most favorable or desirable ORAL ADMINISTRATION by mouth ORTHOPEDIC pertaining to the bones OSTEOPETROSIS rare bone disorder characterized by dense bone OSTEOPOROSIS softening of the bones OVARIES female sex glands
PARENTERAL given by injection PATENCY condition of being open PATHOGENESIS development of a disease or unhealthy condition PERCUTANEOUS through the skin PERIPHERAL not central PER OS (PO) by mouth PHARMACOKINETICS the study of the way the body absorbs, distributes, and gets rid of a drug PHASE I first phase of study of a new drug in humans to determine action, safety, and proper dosing PHASE II second phase of study of a new drug in humans, intended to gather information about safety and effectiveness of the drug for certain uses PHASE III large-scale studies to confirm and expand information on safety and effectiveness of new drug for certain uses, and to study common side effects PHASE IV studies done after the drug is approved by the FDA, especially to compare it to standard care or to try it for new uses PHLEBITIS irritation or inflammation of the vein PLACEBO an inactive substance; a pill/liquid that contains no medicine PLACEBO EFFECT improvement seen with giving subjects a placebo, though it contains no active drug/treatment PLATELETS small particles in the blood that help with clotting POTENTIAL possible POTENTIATE increase or multiply the effect of a drug or toxin (poison) by giving another drug or toxin at the same time (sometimes an unintentional result) POTENTIATOR an agent that helps another agent work better PRENATAL before birth PROPHYLAXIS a drug given to prevent disease or infection PER OS (PO) by mouth PRN as needed PROGNOSIS outlook, probable outcomes PRONE lying on the stomach PROSPECTIVE STUDY following patients forward in time PROSTHESIS artificial part, most often limbs, such as arms or legs PROTOCOL plan of study PROXIMAL closer to the center of the body, away from the end PULMONARY pertaining to the lungs
QD every day; daily QID four times a day
RADIATION THERAPY x-ray or cobalt treatment RANDOM by chance (like the flip of a coin) RANDOMIZATION chance selection RBC red blood cell RECOMBINANT formation of new combinations of genes RECONSTITUTION putting back together the original parts or elements RECUR happen again REFRACTORY not responding to treatment REGENERATION re-growth of a structure or of lost tissue REGIMEN pattern of giving treatment RELAPSE the return of a disease REMISSION disappearance of evidence of cancer or other disease RENAL pertaining to the kidneys REPLICABLE possible to duplicate RESECT remove or cut out surgically RETROSPECTIVE STUDY looking back over past experience
SARCOMA a type of cancer SEDATIVE a drug to calm or make less anxious SEMINOMA a type of testicular cancer (found in the male sex glands) SEQUENTIALLY in a row, in order SOMNOLENCE sleepiness SPIROMETER an instrument to measure the amount of air taken into and exhaled from the lungs STAGING an evaluation of the extent of the disease STANDARD OF CARE a treatment plan that the majority of the medical community would accept as appropriate STENOSIS narrowing of a duct, tube, or one of the blood vessels in the heart STOMATITIS mouth sores, inflammation of the mouth STRATIFY arrange in groups for analysis of results (e.g., stratify by age, sex, etc.) STUPOR stunned state in which it is difficult to get a response or the attention of the subject SUBCLAVIAN under the collarbone SUBCUTANEOUS under the skin SUPINE lying on the back SUPPORTIVE CARE general medical care aimed at symptoms, not intended to improve or cure underlying disease SYMPTOMATIC having symptoms SYNDROME a condition characterized by a set of symptoms SYSTOLIC top number in blood pressure; pressure during active contraction of the heart
TERATOGENIC capable of causing malformations in a fetus (developing baby still inside the mother’s body) TESTES/TESTICLES male sex glands THROMBOSIS clotting THROMBUS blood clot TID three times a day TITRATION a method for deciding on the strength of a drug or solution; gradually increasing the dose T-LYMPHOCYTES type of white blood cells TOPICAL on the surface TOPICAL ANESTHETIC applied to a certain area of the skin and reducing pain only in the area to which applied TOXICITY side effects or undesirable effects of a drug or treatment TRANSDERMAL through the skin TRANSIENTLY temporarily TRAUMA injury; wound TREADMILL walking machine used to test heart function
UPTAKE absorbing and taking in of a substance by living tissue
VALVULOPLASTY plastic repair of a valve, especially a heart valve VARICES enlarged veins VASOSPASM narrowing of the blood vessels VECTOR a carrier that can transmit disease-causing microorganisms (germs and viruses) VENIPUNCTURE needle stick, blood draw, entering the skin with a needle VERTICAL TRANSMISSION spread of disease
WBC white blood cell
- News & Updates
NEW REPORT: The People's Guide to Project 2025
The People’s Guide to Project 2025

Project 2025 is among the most profound threats to the American people.
We read Project 2025’s entire 900+ page “Mandate for Leadership” so that you don’t have to.
What we discovered was a systemic, ruthless plan to undermine the quality of life of millions of Americans, remove critical protections and dismantle programs for communities across the nation, and prioritize special interests and ideological extremism over people.
From attacking overtime pay, student loans, and reproductive rights, to allowing more discrimination, pollution, and price gouging, those behind Project 2025 are preparing to go to incredible lengths to create a country only for some, not for all of us.
If these plans are enacted, which Project 2025’s authors claim can happen without congressional approval, 4.3 million people could lose overtime protections, 40 million people could have their food assistance reduced, 220,000 American jobs could be lost, and much, much, more. The stakes are higher than ever for democracy and for people.
These threats aren’t hypothetical. These are their real plans.
The Heritage Foundation and the 100+ organizations that make up the Project 2025 Advisory Board have mapped out exactly how they will achieve their extreme ends. They aim to try and carry out many of the most troubling proposals through an anti-democratic president and political loyalists installed in the executive branch, without waiting for congressional action. And, while many of these plans are unlawful, winning in court is not guaranteed given that the same far-right movement that is behind Project 2025 has shaped our current court system.
To combat the threats posed by Project 2025, we have to first understand them.
What follows are some of the most dangerous proposals that make up Project 2025, specifically those that they plan to implement through federal agencies and a far-right executive branch.
The majority of Americans share the same values and priorities, but Project 2025 wants to push an extreme, out-of-touch agenda on all of us . By reading this guide and sharing it, we can begin to address these threats and go on offense towards building a bold, inclusive democracy for all people.
Download PDF
What is Project 2025?
The Project 2025 Presidential Transition Project is a well-funded (eight-figure) effort of the Heritage Foundation and more than 100 organizations to enable a future anti-democratic presidential administration to take swift, far-right action that would cut wages for working people, dismantle social safety net programs, reverse decades of progress for civil rights, redefine the way our society operates, and undermine our economy.
A central pillar of Project 2025 is the “Mandate for Leadership,” a 900+ page policy playbook authored by former Trump administration officials and other extremists that provides a radical vision for our nation and a roadmap to implement it.
Project 2025 Snapshot
Proposals from Project 2025, discussed in detail throughout this guide, that they claim could be implemented through executive branch action alone — so without new legislation — include:
- Cut overtime protections for 4.3 million workers
- Stop efforts to lower prescription drug prices
- Limit access to food assistance, which an average of more than 40 million people in 21.6 million households rely on monthly
- Eliminate the Head Start early education program, which serves over 1 million children annually
- Cut American Rescue Plan (ARP) programs that have created or saved 220,000 jobs
- Restrict access to medication abortion
- Push more of the 33 million people enrolled in Medicare towards Medicare Advantage and other worse, private options
- Expose the 368,000 children in foster care to risk of increased discrimination
- Deny students in 25 states and Washington, D.C. access to student loans because their state provides in-state tuition to undocumented immigrants
- Roll back civil rights protections across multiple fronts, including cutting diversity, equity, and inclusion-related (DEI) programs and LGBTQ+ rights in health care, education, and workplaces
Explore Project 2025's Plans:
Cut wages, create unsafe workplaces, and destabilize our economy.
Project 2025 would enable corporations to cut overtime pay, relax worker safety rules, allow workplace discrimination, and more.
Make It Harder for Americans to Make Ends Meet
A strong democracy is one where people have the resources they need to thrive, not worry about how they will make ends meet. Project 2025 proposals would only make daily life harder for people – with fewer people able to access food assistance and affordable early education, less support for veterans with disabilities, and cuts to support for farmers.
Restrict Reproductive Rights and Access to Health Care
Despite the majority of Americans supporting comprehensive health care and reproductive freedom, Project 2025 would prefer a far different reality. Their attacks would undermine Medicare, keep prescription drug prices high, and restrict access to reproductive care.
Enable Discrimination Across Society
Threatened by decades of progress in advancing civil rights and equality for all, the authors of Project 2025 want to create a country that allows for more discrimination where we live, study, work, and play — and roll back hard-fought victories by our movements for progress.
Set Polluters Loose and Undo Climate Action
We’ve waited decades for meaningful and robust federal action to combat climate change and protect people from the harms of pollution. Project 2025 couldn’t care less about these threats — and now they want to destroy our hard-fought gains.
Make Education Unaffordable and Unwelcoming
Our public schools are foundational to our democracy. When special interests undermine public schools, they undermine the ability of students from all backgrounds to learn, feel safe in their community, and develop skills and knowledge that enable students to thrive. If Project 2025 has their way, our public schools could be stripped of funding, protections for students, and high-quality curricula.
Undermine Government’s Ability to Deliver for People
Civil servants are federal employees who work and live in all 50 states — the more than 2 million people who keep our air clean, water safe, consumers protected, and mail delivered. Attacks on the nation’s civil service are attacks on the government’s ability to work for the people.
The threats from Project 2025 do not end here.
This People’s Guide only begins to catalog the people and communities who would be harmed if a future presidential administration began to implement Project 2025’s proposals. Businesses and industry across the country could be harmed not just from the lack of data collection discussed above, but also from proposals to politicize the Federal Reserve or to restrict free trade. Our country’s national security itself, too, is threatened by proposals to concentrate military decisionmaking, further undermine our intelligence agencies, or promote isolationist policies.
We continue to analyze these policies and their harms to people, and expect to release updated versions of the People’s Guide with reports on the threats that would make it harder to run a business, put our security at risk, and more. Click here to sign up to receive the updated reports directly in your inbox.
We cannot let Project 2025 write the next chapter of our nation’s story.
To learn more about how we can confront the threats presented in this guide head-on and begin to build a bold, vibrant democracy for all people, visit democracyforward.org/join-2025 .
Our three pillars to advance a bold, vibrant democracy for all people:
Defending democracy and policies that propel progress through public education, regulatory and legal support.
Disrupting unlawful, regressive, and anti-democratic activity through litigation, investigations, and public education.
Building coalitions, supporting communities, and creating a more democratic and just future through the law.
Join us in this generational fight for people and democracy.
New york times: “the resistance to a new trump administration has already started”.
As first reported in The New York Times : Democracy Forward is “ensuring that people and communities that would be affected by a range of policies that we see with respect to Project 2025 know their legal rights and remedies and are able to access legal representation, should that be necessary.”
How to Write a Business Plan: Your Step-by-Step Guide

So, you’ve got an idea and you want to start a business —great! Before you do anything else, like seek funding or build out a team, you'll need to know how to write a business plan. This plan will serve as the foundation of your company while also giving investors and future employees a clear idea of your purpose.
Below, Lauren Cobello, Founder and CEO of Leverage with Media PR , gives her best advice on how to make a business plan for your company.
Build your dream business with the help of a high-paying job—browse open jobs on The Muse »
What is a business plan, and when do you need one?
According to Cobello, a business plan is a document that contains the mission of the business and a brief overview of it, as well as the objectives, strategies, and financial plans of the founder. A business plan comes into play very early on in the process of starting a company—more or less before you do anything else.
“You should start a company with a business plan in mind—especially if you plan to get funding for the company,” Cobello says. “You’re going to need it.”
Whether that funding comes from a loan, an investor, or crowdsourcing, a business plan is imperative to secure the capital, says the U.S. Small Business Administration . Anyone who’s considering giving you money is going to want to review your business plan before doing so. That means before you head into any meeting, make sure you have physical copies of your business plan to share.
Different types of business plans
The four main types of business plans are:
Startup Business Plans
Internal business plans, strategic business plans, one-page business plans.
Let's break down each one:
If you're wondering how to write a business plan for a startup, Cobello has advice for you. Startup business plans are the most common type, she says, and they are a critical tool for new business ventures that want funding. A startup is defined as a company that’s in its first stages of operations, founded by an entrepreneur who has a product or service idea.
Most startups begin with very little money, so they need a strong business plan to convince family, friends, banks, and/or venture capitalists to invest in the new company.
Internal business plans “are for internal use only,” says Cobello. This kind of document is not public-facing, only company-facing, and it contains an outline of the company’s business strategy, financial goals and budgets, and performance data.
Internal business plans aren’t used to secure funding, but rather to set goals and get everyone working there tracking towards them.
As the name implies, strategic business plans are geared more towards strategy and they include an assessment of the current business landscape, notes Jérôme Côté, a Business Advisor at BDC Advisory Services .
Unlike a traditional business plan, Cobello adds, strategic plans include a SWOT analysis (which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) and an in-depth action plan for the next six to 12 months. Strategic plans are action-based and take into account the state of the company and the industry in which it exists.
Although a typical business plan falls between 15 to 30 pages, some companies opt for the much shorter One-Page Business Plan. A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you’ll make money).
A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage.
How to create a business plan in 7 steps
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here’s what Cobello recommends:
1. Conduct your research
Before writing your business plan, you’ll want to do a thorough investigation of what’s out there. Who will be the competitors for your product or service? Who is included in the target market? What industry trends are you capitalizing on, or rebuking? You want to figure out where you sit in the market and what your company’s value propositions are. What makes you different—and better?
2. Define your purpose for the business plan
The purpose of your business plan will determine which kind of plan you choose to create. Are you trying to drum up funding, or get the company employees focused on specific goals? (For the former, you’d want a startup business plan, while an internal plan would satisfy the latter.) Also, consider your audience. An investment firm that sees hundreds of potential business plans a day may prefer to see a one-pager upfront and, if they’re interested, a longer plan later.
3. Write your company description
Every business plan needs a company description—aka a summary of the company’s purpose, what they do/offer, and what makes it unique. Company descriptions should be clear and concise, avoiding the use of jargon, Cobello says. Ideally, descriptions should be a few paragraphs at most.
4. Explain and show how the company will make money
A business plan should be centered around the company’s goals, and it should clearly explain how the company will generate revenue. To do this, Cobello recommends using actual numbers and details, as opposed to just projections.
For instance, if the company is already making money, show how much and at what cost (e.g. what was the net profit). If it hasn’t generated revenue yet, outline the plan for how it will—including what the product/service will cost to produce and how much it will cost the consumer.
5. Outline your marketing strategy
How will you promote the business? Through what channels will you be promoting it? How are you going to reach and appeal to your target market? The more specific and thorough you can be with your plans here, the better, Cobello says.
6. Explain how you’ll spend your funding
What will you do with the money you raise? What are the first steps you plan to take? As a founder, you want to instill confidence in your investors and show them that the instant you receive their money, you’ll be taking smart actions that grow the company.
7. Include supporting documents
Creating a business plan is in some ways akin to building a legal case, but for your business. “You want to tell a story, and to be as thorough as possible, while keeping your plan succinct, clear, interesting, and visually appealing,” Cobello says. “Supporting documents could include financial projects, a competitive analysis of the market you’re entering into, and even any licenses, patents, or permits you’ve secured.”
A business plan is an individualized document—it’s ultimately up to you what information to include and what story you tell. But above all, Cobello says, your business plan should have a clear focus and goal in mind, because everything else will build off this cornerstone.
“Many people don’t realize how important business plans are for the health of their company,” she says. “Set aside time to make this a priority for your business, and make sure to keep it updated as you grow.”
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Research Objectives | Definition & Examples
Research Objectives | Definition & Examples
Published on July 12, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on November 20, 2023.
Research objectives describe what your research is trying to achieve and explain why you are pursuing it. They summarize the approach and purpose of your project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement . They should:
- Establish the scope and depth of your project
- Contribute to your research design
- Indicate how your project will contribute to existing knowledge
Table of contents
What is a research objective, why are research objectives important, how to write research aims and objectives, smart research objectives, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research objectives.
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process , including how you collect data , build your argument , and develop your conclusions .
Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried out and the actual content of your paper.
Research aims
A distinction is often made between research objectives and research aims.
A research aim typically refers to a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives.
Your research objectives are more specific than your research aim and indicate the particular focus and approach of your project. Though you will only have one research aim, you will likely have several research objectives.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Research objectives are important because they:
- Establish the scope and depth of your project: This helps you avoid unnecessary research. It also means that your research methods and conclusions can easily be evaluated .
- Contribute to your research design: When you know what your objectives are, you have a clearer idea of what methods are most appropriate for your research.
- Indicate how your project will contribute to extant research: They allow you to display your knowledge of up-to-date research, employ or build on current research methods, and attempt to contribute to recent debates.
Once you’ve established a research problem you want to address, you need to decide how you will address it. This is where your research aim and objectives come in.
Step 1: Decide on a general aim
Your research aim should reflect your research problem and should be relatively broad.
Step 2: Decide on specific objectives
Break down your aim into a limited number of steps that will help you resolve your research problem. What specific aspects of the problem do you want to examine or understand?
Step 3: Formulate your aims and objectives
Once you’ve established your research aim and objectives, you need to explain them clearly and concisely to the reader.
You’ll lay out your aims and objectives at the end of your problem statement, which appears in your introduction. Frame them as clear declarative statements, and use appropriate verbs to accurately characterize the work that you will carry out.
The acronym “SMART” is commonly used in relation to research objectives. It states that your objectives should be:
- Specific: Make sure your objectives aren’t overly vague. Your research needs to be clearly defined in order to get useful results.
- Measurable: Know how you’ll measure whether your objectives have been achieved.
- Achievable: Your objectives may be challenging, but they should be feasible. Make sure that relevant groundwork has been done on your topic or that relevant primary or secondary sources exist. Also ensure that you have access to relevant research facilities (labs, library resources , research databases , etc.).
- Relevant: Make sure that they directly address the research problem you want to work on and that they contribute to the current state of research in your field.
- Time-based: Set clear deadlines for objectives to ensure that the project stays on track.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, November 20). Research Objectives | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-objectives/
Is this article helpful?

SME definition
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) represent 99% of all businesses in the EU. The definition of an SME is important for access to finance and EU support programmes targeted specifically at these enterprises.
What is an SME?
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are defined in the EU recommendation 2003/361 .
The main factors determining whether an enterprise is an SME are
- staff headcount
- either turnover or balance sheet total
|
|
|
| or |
| |
| Medium-sized | < 250 | ≤ € 50 m | ≤ € 43 m | ||
| Small | < 50 | ≤ € 10 m | ≤ € 10 m | ||
| Micro | < 10 | ≤ € 2 m | ≤ € 2 m | ||
These ceilings apply to the figures for individual firms only. A firm that is part of a larger group may need to include staff headcount/turnover/balance sheet data from that group too.
Further details include
- The revised user guide to the SME definition (2020) (2 MB, available in all EU languages)
- Declaring your enterprise to be an SME (the form is available in all languages as an annex in the revised user guide)
- The SME self-assessment tool which you can use to determine whether your organisation qualifies as a small and medium-sized enterprise
What help can SMEs get?
There are 2 broad types of potential benefit for an enterprise if it meets the criteria
- eligibility for support under many EU business-support programmes targeted specifically at SMEs: research funding, competitiveness and innovation funding and similar national support programmes that could otherwise be banned as unfair government support ('state aid' – see block exemption regulation )
- fewer requirements or reduced fees for EU administrative compliance
Monitoring of the implementation of the SME definition
The Commission monitors the implementation of the SME definition and reviews it in irregular intervals. Pursuant to the latest evaluation, the Commission concluded that there is no need for a revision.
On 25 October 2021, we informed stakeholders by holding a webinar with presentations on the SME evaluation's results and next steps.
Supporting documents
- Study to map, measure and portray the EU mid-cap landscape (2022)
- Staff working document on the evaluation of the SME definition (2021)
- Executive summary on the evaluation of the SME definition (2021)
- Q&A on the evaluation of the SME definition (2021)
- Final report on evaluation of the SME definition (2018) (10 MB)
- Final report on evaluation of the SME definition (2012) (1.8 MB)
- Executive summary on evaluation of the SME definition (2012) (345 kB)
- Implementing the SME definition (2009) (50 kB)
- Implementing the SME definition (2006) (40 kB)
Share this page
The Daily Show Fan Page

Explore the latest interviews, correspondent coverage, best-of moments and more from The Daily Show.
The Daily Show
S29 E68 • July 8, 2024
Host Jon Stewart returns to his place behind the desk for an unvarnished look at the 2024 election, with expert analysis from the Daily Show news team.
Extended Interviews

The Daily Show Tickets
Attend a Live Taping
Find out how you can see The Daily Show live and in-person as a member of the studio audience.
Best of Jon Stewart

The Weekly Show with Jon Stewart
New Episodes Thursdays
Jon Stewart and special guests tackle complex issues.
Powerful Politicos

The Daily Show Shop
Great Things Are in Store
Become the proud owner of exclusive gear, including clothing, drinkware and must-have accessories.
About The Daily Show

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's an example outline of a research plan you might put together: Project title. Project members involved in the research plan. Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan's intent) Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective) Objective 2. Objective 3.
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan. 1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question.
Research plan: definition and significance. A research plan is a comprehensive documented outline of your entire project, encompassing the research process and the anticipated outcomes. This strategic document aids in defining objectives, summarizing the necessary steps to achieve them, and detailing the requirements for obtaining conclusive ...
A research plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the entirety of your research project. It details the research process, from defining the problem statement and research objectives to selecting the research method and outlining the expected outcomes. This plan serves as a blueprint for your research activities, ensuring a focused and ...
What is a research proposal? Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it's worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).. The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that ...
Writing a Research Plan. To write out your research plan, begin by restating your main thesis question and any secondary ones. They may have changed a bit since your original proposal. If these questions bear on a particular theory or analytic perspective, state that briefly. In the social sciences, for example, two or three prominent theories ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
The research plan, however, serves another, very important function: It contributes to your development as a scientist. Your research plan is a map for your career as a research science professional. As will become apparent later in this document, one of the functions of a research plan is to demonstrate your intellectual vision and aspirations.
In other words, the following provides a systematic means to establish the building blocks of your research project. Exercise 1: Definition of research question and sources. This exercise prompts you to select and clarify your general interest area, develop a research question, and investigate sources of information.
This article takes you through the first steps of the research process, helping you narrow down your ideas and build up a strong foundation for your research project. Table of contents. Step 1: Choose your topic. Step 2: Identify a problem. Step 3: Formulate research questions. Step 4: Create a research design. Step 5: Write a research proposal.
How to create a research plan. Here are seven steps you can follow to create a research proposal: 1. Define a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a statement that aims to explain the cause of a phenomenon or problem. To write a hypothesis, it's necessary for you to identify this phenomenon or problem and describe why you want to explain it.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Academic Research Proposal. This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, and expected outcomes.
Review and Finalize Your Research Plan; Abstract and Narrative; Research Plan Overview and Your Approach. Your application's Research Plan has two sections: Specific Aims—a one-page statement of your objectives for the project. Research Strategy—a description of the rationale for your research and your experiments in 12 pages for an R01.
A research plan is the main part of a grant application and describes a principal investigator's proposed research. This page describes the essential elements of a research plan. The research plan gives a principal investigator the opportunity to discuss proposed research, stating its importance and how it will be conducted.
A research project proposes questions to be explored. In many cases, the research plan includes the following four components: Literature Reading; Information Gathering; Research Analysis; Conclusion and Summary; Literature Reading. At the beginning of the research project, mentees need to do a general study of the topic(s) by reading the ...
A research plan is pivotal to a research project because it identifies and helps define your focus, method, and goals while also outlining the research project from start to finish. This type of plan is often necessary to: Apply for grants or internal company funding. Discover possible research partners or business partners.
The research plan is a document that clarifies how to approach the research, touching upon research goals, selected methodologies, types of participants and tools used, timeline and locations. This planning activity needs to be done upfront, before starting the actual research, and help maximizing the effort and modeling the activities in the ...
Presented by Cathy Binger. First we're going to talk about what a research plan is, why it's important to write one, and why five years—why not one year, why not ten years. So we'll do some of those basic things, then Liza is going to get down and dirty into the nitty-gritty of "now what" how do I go about writing that research plan.
The research plan, which is also called " research proposal " before acceptance by competent authority, is a scholarly paper. As is well-known, it must conform to accepted conventions of academic and scientific procedure. It is expected to show evidence of intelligent grasp of the problem being proposed for solution, and fields related to it.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a ...
definition. Research Plan shall have the meaning set forth in Section 2.1. Research Plan means the statement in Appendix A of the respective research and development commitments of the Parties. The Research Plan should describe the provisions for sponsoring the IND, clinical and safety monitoring, and data management.
For clinical research-specific definitions, see also the Clinical Research Glossary developed by the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials (MRCT) Center of Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard and the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC). Alternative Lay Language for Medical Terms for use in Informed Consent Documents
Research. Project 2025 is among the most profound threats to the American people. We read Project 2025's entire 900+ page "Mandate for Leadership" so that you don't have to. What we discovered was a systemic, ruthless plan to undermine the quality of life of millions of Americans, remove critical protections and dismantle programs for ...
A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you'll make money). A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage.
A 529 plan is a tax-advantaged savings plan designed to encourage saving for future education costs. 529 plans, legally known as "qualified tuition plans," are sponsored by states, state agencies, or educational institutions and are authorized by Section 529 of the Internal Revenue Code.
Example: Research aim. To examine contributory factors to muscle retention in a group of elderly people. Example: Research objectives. To assess the relationship between sedentary habits and muscle atrophy among the participants. To determine the impact of dietary factors, particularly protein consumption, on the muscular health of the ...
The definition of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is important for access to finance and EU support programmes targeted specifically at these enterprises. ... research funding, competitiveness and innovation funding and similar national support programmes that could otherwise be banned as unfair government support ('state aid' - see ...
The source for The Daily Show fans, with episodes hosted by Jon Stewart, Ronny Chieng, Jordan Klepper, Dulcé Sloan and more, plus interviews, highlights and The Weekly Show podcast.