Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Books — 1984

Essays on 1984
Hook examples for "1984" essays, the dystopian warning hook.
Open your essay by discussing George Orwell's "1984" as a prophetic warning against totalitarianism and government surveillance. Explore how the novel's themes are eerily relevant in today's world.
The Orwellian Language Hook
Delve into the concept of Newspeak in "1984" and its parallels to modern language manipulation. Discuss how the novel's portrayal of controlled language reflects real-world instances of propaganda and censorship.
Big Brother is Watching Hook
Begin with a focus on surveillance and privacy concerns. Analyze the omnipresent surveillance in the novel and draw connections to contemporary debates over surveillance technologies, data privacy, and civil liberties.
The Power of Doublethink Hook
Explore the psychological manipulation in "1984" through the concept of doublethink. Discuss how individuals in the novel are coerced into accepting contradictory beliefs, and examine instances of cognitive dissonance in society today.
The Character of Winston Smith Hook
Introduce your readers to the protagonist, Winston Smith, and his journey of rebellion against the Party. Analyze his character development and the universal theme of resistance against oppressive regimes.
Technology and Control Hook
Discuss the role of technology in "1984" and its implications for control. Explore how advancements in surveillance technology, social media, and artificial intelligence resonate with the novel's themes of control and manipulation.
The Ministry of Truth Hook
Examine the Ministry of Truth in the novel, responsible for rewriting history. Compare this to the manipulation of information and historical revisionism in contemporary politics and media.
Media Manipulation and Fake News Hook
Draw parallels between the Party's manipulation of information in "1984" and the spread of misinformation and fake news in today's media landscape. Discuss the consequences of a distorted reality.
Relevance of Thoughtcrime Hook
Explore the concept of thoughtcrime and its impact on individual freedom in the novel. Discuss how society today grapples with issues related to freedom of thought, expression, and censorship.
Surveillance and Totalitarian Control in George Orwell's "1984"
George orwell’s representation of authority as illustrated in his book, 1984, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Orwell's Use of Literary Devices to Portray The Theme of Totalitarianism in 1984
The culture of fear in 1984, a novel by george orwell, 1984 by george orwell: literary devices to portray government controlling its citizens, the use of language to control people in 1984, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Dictatorship of The People: Orwell's 1984 as an Allegory for The Early Soviet Union
Searching for truth in 1984, a world without love: the ramifications of an affectionless society in 1984, on double-think and newspeak: orwell's language, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Theme of Survival and Selfishness in The Handmaid's Tale in 1984
Government surveillance in 1984 by george orwell: bogus security, george orwell's 1984 as a historical allegory, exploitation of language in george orwell's 1984, how orwell's 1984 is relevant to today's audience, the relation of orwel’s 1984 to the uighur conflict in china, symbolism in 1984: the soviet union as representation of the fears people, parallels to today in 1984 by george orwell, the relationship between power and emotions in 1984, proletariat vs protagonist: winston smith's class conflict in 1984, a review of george orwell’s book, 1984, o'brien as a dehumanizing villain in 1984, family in 1984 and persepolis, the philosophy of determinism in 1984, orwell's use of rhetorical strategies in 1984, control the citizens in the orwell's novel 1984, dangers of totalitarianism as depicted in 1984, dystopian life in '1984' was a real-life in china, dystopian world in the novel '1984' awaits us in the future, the internal conflict of the protagonist of the dystopia '1984'.
8 June 1949, George Orwell
Novel; Dystopia, Political Fiction, Social Science Fiction Novel
Winston Smith, Julia, O'Brien, Aaronson, Jones, and Rutherford, Ampleforth, Charrington, Tom Parsons, Syme, Mrs. Parsons, Katharine Smith
Since Orwell has been a democratic socialist, he has modelled his book and motives after the Stalinist Russia
Power, Repressive Behaviors, Totalitarianism, Mass Surveillance, Human Behaviors
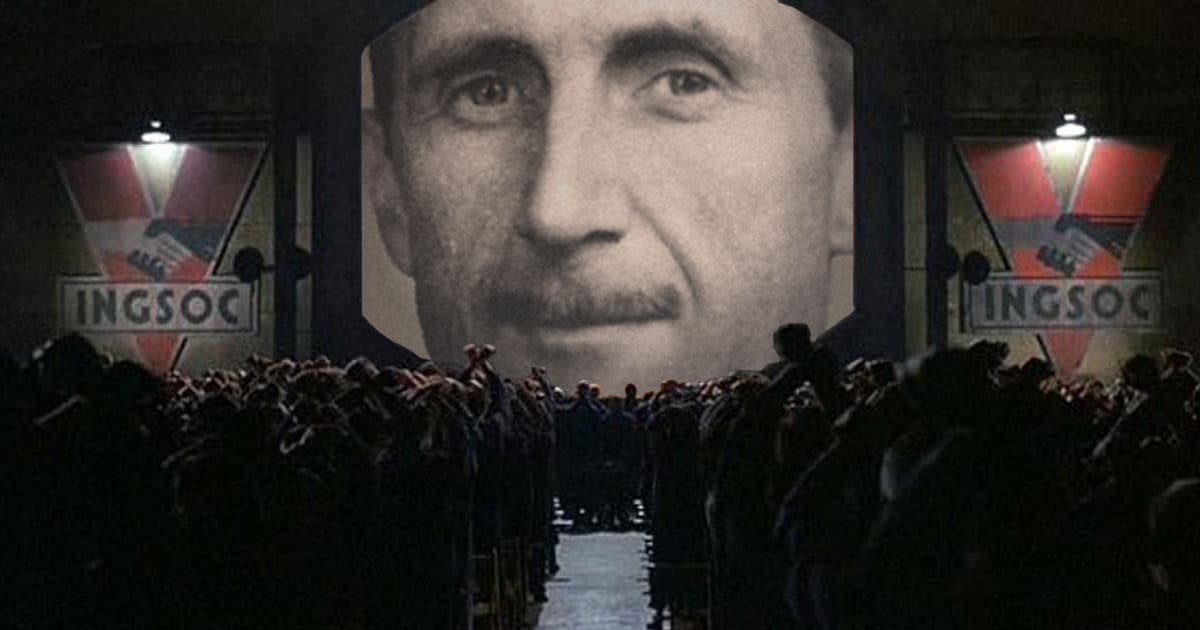
The novel has brought up the "Orwellian" term, which stands for "Big Brother" "Thoughtcrime" and many other terms that we know well. It has been the reflection of totalitarianism
1984 represents a dystopian writing that has followed the life of Winston Smith who belongs to the "Party",which stands for the total control, which is also known as the Big Brother. It controls every aspect of people's lives. Is it ever possible to go against the system or will it take even more control. It constantly follows the fear and oppression with the surveillance being the main part of 1984. There is Party’s official O’Brien who is following the resistance movement, which represents an alternative, which is the symbol of hope.
Before George Orwell wrote his famous book, he worked for the BBC as the propagandist during World War II. The novel has been named 1980, then 1982 before finally settling on its name. Orwell fought tuberculosis while writing the novel. He died seven months after 1984 was published. Orwell almost died during the boating trip while he was writing the novel. Orwell himself has been under government surveillance. It was because of his socialist opinions. The slogan that the book uses "2 + 2 = 5" originally came from Communist Russia and stood for the five-year plan that had to be achieved during only four years. Orwell also used various Japanese propaganda when writing his novel, precisely his "Thought Police" idea.
“Who controls the past controls the future. Who controls the present controls the past.” “But if thought corrupts language, language can also corrupt thought.” “Being in a minority, even in a minority of one, did not make you mad. There was truth and there was untruth, and if you clung to the truth even against the whole world, you were not mad.” “Confession is not betrayal. What you say or do doesn't matter; only feelings matter. If they could make me stop loving you-that would be the real betrayal.” “Power is in tearing human minds to pieces and putting them together again in new shapes of your own choosing.” "But you could not have pure love or pure lust nowadays. No emotion was pure, because everything was mixed up with fear and hatred."
The most important aspect of 1984 is Thought Police, which controls every thought. It has been featured in numerous books, plays, music pieces, poetry, and anything that has been created when one had to deal with Social Science and Politics. Another factor that represents culmination is thinking about overthrowing the system or trying to organize a resistance movement. It has numerous reflections of the post WW2 world. Although the novella is graphic and quite intense, it portrays dictatorship and is driven by fear through the lens of its characters.
This essay topic is often used when writing about “The Big Brother” or totalitarian regimes, which makes 1984 a flexible topic that can be taken as the foundation. Even if you have to write about the use of fear by the political regimes, knowing the facts about this novel will help you to provide an example.
1. Enteen, G. M. (1984). George Orwell And the Theory of Totalitarianism: A 1984 Retrospective. The Journal of General Education, 36(3), 206-215. (https://www.jstor.org/stable/27797000) 2. Hughes, I. (2021). 1984. Literary Cultures, 4(2). (https://journals.ntu.ac.uk/index.php/litc/article/view/340) 3. Patai, D. (1982). Gamesmanship and Androcentrism in Orwell's 1984. PMLA, 97(5), 856-870. (https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/pmla/article/abs/gamesmanship-and-androcentrism-in-orwells-1984/F1B026BE9D97EE0114E248AA733B189D) 4. Paden, R. (1984). Surveillance and Torture: Foucault and Orwell on the Methods of Discipline. Social Theory and Practice, 10(3), 261-271. (https://www.pdcnet.org/soctheorpract/content/soctheorpract_1984_0010_0003_0261_0272) 5. Tyner, J. A. (2004). Self and space, resistance and discipline: a Foucauldian reading of George Orwell's 1984. Social & Cultural Geography, 5(1), 129-149. (https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1464936032000137966) 6. Kellner, D. (1990). From 1984 to one-dimensional man: Critical reflections on Orwell and Marcuse. Current Perspectives in Social Theory, 10, 223-52. (https://pages.gseis.ucla.edu/faculty/kellner/essays/from1984toonedimensional.pdf) 7. Samuelson, P. (1984). Good legal writing: of Orwell and window panes. U. Pitt. L. Rev., 46, 149. (https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/upitt46&div=13&id=&page=) 8. Fadaee, E. (2011). Translation techniques of figures of speech: A case study of George Orwell's" 1984 and Animal Farm. Journal of English and Literature, 2(8), 174-181. (https://academicjournals.org/article/article1379427897_Fadaee.pdf) 9. Patai, D. (1984, January). Orwell's despair, Burdekin's hope: Gender and power in dystopia. In Women's Studies International Forum (Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 85-95). Pergamon. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0277539584900621) 10. Cole, M. B. (2022). The Desperate Radicalism of Orwell’s 1984: Power, Socialism, and Utopia in Dystopian Times. Political Research Quarterly, 10659129221083286. (https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/10659129221083286)
Relevant topics
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Thank You Ma Am
- In The Time of The Butterflies
- Bartleby The Scrivener
- Their Eyes Were Watching God
- Brave New World
- The Alchemist
- The Story of An Hour
- The Things They Carried
- Never Let Me Go
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Common Module State-Rank Essay Showcase: Nineteen Eighty-Four
The following essay was written by Project Academy English Tutor, Marko Beocanin

Marko Beocanin
99.95 ATAR & 3 x State Ranker
The following essay was written by Project Academy English Teacher, Marko Beocanin.
Marko’s Achievements:
- 8th in NSW for English Advanced (98/100)
- Rank 1 in English Advanced, Extension 1 and Extension 2
- School Captain of Normanhurst Boys High School
Marko kindly agreed to share his essay and thorough annotations to help demystify for HSC students what comprises an upper Band 6 response!
Common Module: Nineteen Eighty-Four Essay Question
Marko’s following essay was written in response to the question:
“The representation of human experiences makes us more aware of the intricate nature of humanity.” In your response, discuss this statement with detailed reference to George Orwell’s ‘Nineteen Eighty-Four’.
State-Ranking Common Module Essay Response
George Orwell’s 1949 Swiftian satire Nineteen Eighty-Four invites us to appreciate the intricate nature of humanity by representing how the abuse of power by totalitarian governments degrades our individual and collective experiences. (Link to rubric through individual/collective experiences, and a clear cause and effect argument: totalitarian governance -> degraded human experience. Also, comments on the genre of Swiftian satire. Value!) Orwell explores how oppressive authorities suppress the intricate societal pillars of culture, expression and freedom to maintain power. He then reveals how this suppression brutalises individual human behaviour and motivations because it undermines emotion and intricate thought. (Link to rubric through ‘human behaviour and motivations’, and extended cause and effect in which the first paragraph explores the collective ‘cause’ and the second paragraph explores the individual ‘effect’. This is an easy way to structure your arguments whilst continuously engaging with the rubric!) Ultimately, he argues that we must resist the political apathy that enables oppressive governments to maintain power and crush human intricacy. Therefore, his representation of human experiences not only challenges us to consider the intricate nature of humanity, but exhorts us to greater political vigilance so we can preserve it. (Concluding sentence that broadens the scope of the question and reaffirms the purpose of the text).
Orwell makes us aware of the intricate nature of humanity by representing how totalitarian authorities suppress intricate collective experiences of culture, expression and freedom in order to assert control. (This is the ‘collective’ paragraph – a cause and effect argument that relates the question to the loss of human intricacy in the collective as a result of totalitarian rule). His bleak vision was informed by Stalin’s USSR: a regime built upon the fabrication of history in Stalin’s ‘cult of personality’, and ruthlessly enforced by the NKVD. (Specific context – an actual specific regime is named and some details about its enforcement are given). The symbolic colourlessness and propaganda-poster motif he uses to describe London reflects the loss of human intricacy and culture under such leadership: “there seemed to be no colour in anything, except the posters that were plastered everywhere.” (First example sets up the world of the text, and the degraded collective experience). Orwell uses the telescreens, dramatically capitalised “BIG BROTHER IS WATCHING YOU” posters and allusions to Stalin in Big Brother’s “black-moustachio’d face” as metonyms for how governmental surveillance dominates both physical and cultural collective experiences. Winston’s metatextual construction of the fictitious “Comrade Ogilvy” serves as a symbol for the vast, worthless masses of information produced by totalitarian governments to undermine the intricacy of real human history: “Comrade Ogilvy, who had never existed…would exist just as authentically, and upon the same evidence, as Charlemagne or Julius Caesar.” Similarly, Orwell’s satirical representation of Newspeak ignites the idea that political slovenliness causes self-expression to degrade, which in turn destroys our capacity for intricate thought and resistance: “we shall make thoughtcrime literally impossible, because there will be no words in which to express it.” (The examples above prove that the government’s leadership style truly is totalitarian, and that it results in a loss of intricacy and ‘humanity’ in the collective. It’s good to cover a variety of examples that explore different facets of the collective – for example, the first example establishes the extreme surveillance, the second example establishes the loss of ‘truth’/history, and the third example establishes the loss of language). The political bitterness that marks Nineteen Eighty-Four as a Swiftian satire (This is a link to the ‘Swiftian’ term used in the thesis statement. It’s important to refer back to any descriptive terms you use in your thesis) ultimately culminates in O’Brien’s monologue, where Orwell juxtaposes the politicised verb “abolish” to symbols of human intricacy, “we shall abolish the orgasm…there will be no art, no literature, no science…when we are omnipotent”, to express how totalitarian rulers suppress collective experiences to gain metaphoric omnipotence. Thus, Orwell makes us aware of the intricate nature of humanity by representing a future in which totalitarian governments suppress it. (A linking sentence that ties it all back to the question and rephrases the point)
Orwell then argues that the effect of this suppression is a loss of human intricacy that brutalises society and devalues individual experiences. (Cause and effect argument that links collective suppression to a loss of human intricacy on an individual scale – continuous engagement with the question and the rubric!) Orwell’s exposure to the widespread hysteria of Hitler’s Nazi regime, caused by the Nuremberg Rallies and Joseph Goebbels’ virulent anti-semitic propaganda, informs his representation of Oceania’s dehumanised masses. (More specific context around the Nazis, and a specific link to how it informed his work) The burlesque Two Minute Hate reveals human inconsistency by representing how even introspective, intelligent characters can be stripped of their intricacy and compassion by the experience of collective hysteria: even Winston wishes to “flog [Julia] to death with a rubber truncheon…ravish her and cut her throat at the moment of climax”, and is only restored by compliance to the Christ-like totalitarian authority, “My-Saviour!”, Big Brother. (A link to the rubric with the ‘human inconsistency’ point) Orwell frequently juxtaposes dehumanising representations of the proles, “the proles are not human beings”, to political sloganism: “As the Party slogan put it: ‘Proles and animals are free’”, to argue that in such a collectively suppressed society, the upper class grow insensitive towards the intricate nature of those less privileged. (It’s important to link the proles into your argument – they’re often forgotten, but they’re a big part of the text!) He asserts that this loss of empathy degrades the authenticity and intricacy of human relationships, characterised by Winson’s paradoxically hyperbolic repulsion towards his wife: “[Katharine] had without exception the most stupid, vulgar, empty mind that he had every encountered”. (Continuous engagement with the question and rubric: make sure to recycle rubric terms – here, done with ‘paradoxically’ – and question terms – here, with ‘intricacy’) Winston’s “betrayal” of Julia symbolises how totalitarianism ultimately brutalises individuals by replacing their compassion for intricate ideals such as love with selfish pragmatism: “Do it to Julia…Tear her face off, strip her to the bones. Not me!” Therefore, Orwell makes us more aware of the intricate nature of humanity by demonstrating how it can be robbed by suppressive governments and collective hysteria. (A linking sentence that sums up the paragraph).
By making us aware of how totalitarian governments suppress meaningful human experiences both individually and collectively, Orwell challenges us to resist so we can preserve our intricate nature. (This third paragraph discusses Orwell’s purpose as a composer. This can in general be a helpful way to structure paragraphs: Collective, Individual, Purpose) Orwell’s service in the 1930s Spanish Civil War as part of the Republican militia fighting against fascist-supported rebels positions him to satirise the political apathy of his audience. (Integration of personal context is useful here to justify Orwell’s motivations. It’s also a lot fresher than just including another totalitarian regime Orwell was exposed to) Orwell alludes to this through the metaphor of Winston’s diarising as an anomalous individual experience of resistance, ““[Winston] was a lonely ghost uttering a truth that nobody would ever hear,” which highlights how his intricate nature persists even in a suppressive society. Often, Orwell meta-fictively addresses his own context, as “a time when thought is free…when truth exists”, to establish an imperative to preserve our intricate human nature while we still can. The Julia romance trope (It’s good to include terms such as ‘trope’ which reflect your understanding of narrative structure and the overall form of the work.) represents how Winston’s gradual rejection of his political apathy empowered him to experience an authentic, intricately human relationship that subverts his totalitarian society: “the gesture with which [Julia] had thrown her clothes aside…[belonged] to an ancient time. Winston woke up with the word ‘Shakespeare’ on his lips.” Orwell juxtaposes Julia’s sexuality to Shakespeare, an immediately-recognisable metonym for culture and history, to argue that human intricacy can only be restored by actively resisting the dehumanising influence of the government. Orwell also represents Winston’s desensitised and immediate devotion to the Brotherhood to reflect how the preservation of human intricacy is a cause worth rebelling for, even by paradoxically unjust means: “[Winston was] prepared to commit murder…acts of sabotage which may cause the deaths of hundreds of innocent people…throw sulphuric acid in a child’s face.” (More chronological examples that show Winston’s transformation throughout the text. It’s useful to explore and contrast those who resist with those who don’t resist, and how just the act of resistance in some way restores our humanity! That’s why this paragraph comes after the ‘brutalised individual experience’ paragraph) However, Orwell ultimately asserts that it is too late for Winston to meaningfully restore humanity’s intricate nature, and concludes the text with his symbolic death and acceptance of the regime, “[Winston] had won the victory over himself. He loved Big Brother.” (It’s important to remember that Orwell ends the text so miserably so that he can motivate his audiences not to do the same thing). The futility of this ending ignites the idea that we must not only be aware of our intricate nature, but must actively resist oppressive governments while we still can in order to preserve it. (A linking sentence that ties the paragraph together and justifies the futility of the ending)
Therefore, Orwell’s representation of human experiences in Nineteen Eighty-Four encourages us to reflect personally on our own intricate human nature, and challenges us to fight to preserve it. (Engages with the question (through the reflection point), and includes Orwell’s purpose as a composer). His depiction of a totalitarian government’s unchecked assertion of power on human culture and freedom, and the brutalising impact this has on individual and collective experiences, ultimately galvanises us to reject political apathy. (Your argument summaries can often be combined into a sentence or two in the conclusion now that the marker knows what you’re talking about. This reinforces the cause and effect structure as well.) Thus, the role of storytelling for Orwell is not only to make us more aware of our intricate nature, but to prove that we must actively resist oppressive governments while we still can in order to preserve it. (The clincher! It’s often useful to add “not only” in your final sentence to reinforce the massive scope of the text)
If reading this essay has helped you, you may also enjoy reading Marko’s ultimate guide to writing 20/20 HSC English essays .
P.S If you have any questions about aceing HSC English , you are welcome to learn from Marko and join one of Project Academy’s HSC English classes on a 3 week trial .

Ultimate Guide To Getting A Co-Op Scholarship Offer
This is a summary of the best tips, tricks and techniques accumulated over...

Project Academy
TEAM OF ACADEMIC ADVISORS

Practical Guide on How to Collect Statistics for HSC & Prelim Economics
This is my state-ranking guide to collecting statistics for HSC Economics!

Zack Bolland
99.80 ATAR, Dux, 8th in NSW for Econ

Top 5 Tips for Acing HSC Biology
The Head of Biology, Alex's guide to acing HSC Biology

Alex Loustau
Head of Biology & 99.45 ATAR

How to study for HSC: Constructing Study Habits
Learn how to construct the best study habits in to ace the HSC, written by 99+ ATAR tutors and distinguished achievers.

Riddhish Chanda
Chemistry Team at Project Academy
Maximise Your Chances Of Coming First At School
Trial any Project Academy course for 3 weeks.
NSW's Top 1% Tutors
Unlimited Tutorials
NSW's Most Effective Courses
Access to Project's iPad
Access to Exclusive Resources
Access to Project's Study Space
- Create list
- Request a book

Thank You For Reading
Orwell's true and secret ending for 1984.
20 mins to read 7,500 words
The dystopian classic introduced the world to doublethink, thoughtcrime, and Newspeak. And while its ending may seem final, Orwell lays the clues for a much more subtle ending open for discussion. What is the ultimate fate of Big Brother, the Party, and totalitarianism after 1984?
And what does a 17th century nursery rhyme have to do with it all?
- Introduction
Questions of class
From police to tramp, a time of war, the world of 1984, orwell's true ending, oranges and lemons.
In 1903 British India, a baby boy named Eric Arthur Blair was born. His great-grandfather had been an affluent country gentleman and a slave-owner. His grandfather was an unexceptional Reverend. And his father worked as a minor bureaucrat in the Opium Department of the Indian Civil Service.
What would Eric Arthur Blair grow up to do? Well, the world would come to know him by his pen name: George Orwell.
Orwell grew up and was educated in an England stratified by class. In The Road to Wigan Pier (1937) , Orwell recounts one of his earliest memories and the first moment he became aware of this:
I was very young, not much more than six, when I first became aware of class-distinctions. Before that age my chief heroes had generally been working-class people, because they always seemed to do such interesting things, such as being fishermen and blacksmiths and bricklayers. I remember the farm hands on a farm in Cornwall who used to let me ride on the drill when they were sowing turnips and would sometimes catch the ewes and milk them to give me a drink; and the workmen building the new house next door, who let me play with the wet mortar and from whom I first learned the word ‘b—’; and the plumber up the road with whose children I used to go out bird-nesting. But it was not long before I was forbidden to play with the plumber's children; they were 'common' and I was told to keep away from them.
So, very early, the working class ceased to be a race of friendly and wonderful beings and became a race of enemies. We realized that they hated us, but we could never understand why, and naturally we set it down to pure, vicious malignity. To me in my early boyhood, to nearly all children of families like mine, 'common' people seemed almost sub-human.
What exactly was it about the working class that so offended Orwell's family and class?
It is summed up in four frightful words which people nowadays are chary of uttering, but which were bandied about quite freely in my childhood. The words were: The lower classes smell.
That was what we were taught--the lower classes smell. And here, obviously, you are at an impassable barrier. For no feeling of like or dislike is quite so fundamental as a physical feeling. Race-hatred, religious hatred, differences of education, of temperament, of intellect, even differences of moral code, can be got over; but physical repulsion cannot.
Very early in life you acquired the idea that there was something subtly repulsive about a working-class body; you would not get nearer to it than you could help. And even 'lower-class' people whom you knew to be quite clean--servants, for instance--were faintly unappetizing. The smell of their sweat, the very texture of their skins, were mysteriously different from yours.
And though his family were not wealthy, the Blairs still considered themselves as part of the gentry and certainly above the working class. Orwell explains:
I was born into what you might describe as the lower-upper-middle class. The upper-middle class, which had its heyday in the eighties and nineties, with Kipling as its poet laureate, was a sort of mound of wreckage left behind when the tide of Victorian prosperity receded. Or perhaps it would be better to change the metaphor and describe it not as a mound but as a layer--the layer of society lying between £2000 and £300 [approx $350,000 - $55,000 today] a year: my own family was not far from the bottom.
You notice that I define it in terms of money, because that is always the quickest way of making yourself understood. Nevertheless, the essential point about the English class-system is that it is not entirely explicable in terms of money. Hence the fact that the upper- middle class extends or extended to incomes as low as £300 a year--to incomes, that is, much lower than those of merely middle-class people with no social pretensions.
Probably there are countries where you can predict a man's opinions from his income, but it is never quite safe to do so in England; you have always got to take his traditions into consideration as well. A naval officer and his grocer very likely have the same income, but they are not equivalent person.
When he was 15, and just as Europe plunged into the Great War, Orwell won a scholarship to Eton, an elite boy's boarding school. (This was the only way his family could afford to send him.) It was here that he would discover first-hand the differences within the upper-middle class that could exist:
I had been made to understand that I was not on the same footing as most of the other boys. In effect there were three castes in the school. There was the minority with an aristocratic or millionaire background, there were the children of the ordinary suburban rich, who made up the bulk of the school, and there were a few underlings like myself, the sons of clergyman, Indian civil servants, struggling widows and the like. These poorer ones were discouraged from going in for ‘extras’ such as shooting and carpentry, and were humiliated over clothes and petty possessions. I never, for instance, succeeded in getting a cricket bat of my own, because ‘Your parents wouldn't be able to afford it’. This phrase pursued me throughout my schooldays.
Orwell did not have the money to attend university and he did not have the academics for another scholarship. The career choices open to him as an adult were few:
Probably the distinguishing mark of the upper-middle class was that its traditions were not to any extent commercial, but mainly military, official, and professional. It was this that explained the attraction of India (more recently Kenya, Nigeria, etc.) for the lower-upper-middle class. The people who went there as soldiers and officials did not go there to make money, for a soldier or an official does not want money; they went there because in India, with cheap horses, free shooting, and hordes of black servants, it was so easy to play at being a gentleman.
And so Orwell would leave England for the first time. He joined the Imperial Police and, sailing through the Suez Canal and Ceylon, arrived at his new station as a policeman in the hot, humid country of Burma.
Orwell's monthly salary as a policeman was Rs. 255 (approx. $30 today). But in Burma, it was not social class nor wealth that mattered, but race:
In an 'outpost of Empire' like Burma the class-question appeared at first sight to have been shelved. There was no obvious class-friction here, because the all-important thing was not whether you had been to one of the right schools but whether your skin was technically white.
And yet, a twenty-something year old Orwell became increasingly ill-at-ease. The more he socialized with the locals, the priests, the prostitutes, and with other fellow British drop-outs; the more he performed the brutal beatings and imprisonments that was demanded of his police enforcement role; the more negative his view of colonialism became:
I was in the Indian Police five years, and by the end of that time I hated the imperialism I was serving with a bitterness which I probably cannot make clear. In the free air of England that kind of thing is not fully intelligible. In order to hate imperialism you have got to be part of it.
I was in the police, which is to say that I was part of the actual machinery of despotism. Moreover, in the police you see the dirty work of Empire at close quarters, and there is an appreciable difference between doing dirty work and merely profiting by it. Most people approve of capital punishment, but most people wouldn't do the hangman's job. Even the other Europeans in Burma slightly looked down on the police because of the brutal work they had to do.
I should expect to find that even in England many policemen, judges, prison warders, and the like are haunted by a secret horror of what they do. But in Burma it was a double oppression that we were committing. Not only were we hanging people and putting them in jail and so forth; we were doing it in the capacity of unwanted foreign invaders. The Burmese themselves never really recognized our jurisdiction. The thief whom we put in prison did not think of himself as a criminal justly punished, he thought of himself as the victim of a foreign conqueror. The thing that was done to him was merely a wanton meaningless cruelty. His face, behind the stout teak bars of the lock-up and the iron bars of the jail, said so clearly. And unfortunately I had not trained myself to be indifferent to the expression of the human face.
(Orwell would later draw from his personal experience and publish his first fiction book Burmese Days (1934), a scathing critique of colonialism.)
And when Orwell saw the similarities between the colonizer and the colonized in Burma with the ruling class and the working class back home, his views on class began to shift too:
It was the first time that I had ever been really aware of the working class, and to begin with it was only because they supplied an analogy. They were the symbolic victims of injustice, playing the same part in England as the Burmese played in Burma. In Burma the issue had been quite simple. The whites were up and the blacks were down, and therefore as a matter of course one's sympathy was with the blacks. I now realized that there was no need to go as far as Burma to find tyranny and exploitation.
In a sort of personal crisis, Orwell quit the police force, returned to England, and decided to try to understand the working class that he had previously so deplored.
I knew nothing about working-class conditions. When I thought of poverty I thought of it in terms of brute starvation. Therefore my mind turned immediately towards the extreme cases, the social outcasts: tramps, beggars, criminals, prostitutes. These were 'the lowest of the low', and these were the people with whom I wanted to get in contact. What I profoundly wanted, at that time, was to find some way of getting out of the respectable world altogether.
Not quite 25 yet, Orwell began to explore the roughest parts of London and meet with its poorest people. Soon, he would go further: dressing as a tramp named "P.J. Burton" and living among them:
I could go among these people, see what their lives were like and feel myself temporarily part of their world. Once I had been among them and accepted by them, I should have touched bottom, and--this is what I felt: I was aware even then that it was irrational--part of my guilt would drop from me.
Orwell would continue to lead this double life for the next five years - sometimes by choice and sometimes by necessicity - sometimes for just a night and sometimes for months at a time. He became obsessed with exploring poverty and understanding the lower class - and not just in London but in Paris too, where he lived and tramped for another two years.
He would eventually publish his very first book, a memoir called Down and Out in Paris and London (1933) about his experience to favorable reviews. It was here, for the first time, that the world was introduced to "George Orwell" - after the patron Saint of England and the River Orwell.
(Eric Arthur Blair very seriously considered choosing "P.J. Burton" as his pen name instead.)
By now, he had stopped tramping, but he had not stopped writing nor had he stopped thinking about social and political conditions. Since returning from Burma, Orwell had called himself an anarchist. But as events developed in Europe, for the first time, Orwell would identify as a socialist and take direct political - and military - action.
By the 1930s, the Bourbon Restoration had failed and the Kingdom of Spain had had given way to an equally unstable Second Spanish Republic. Following an attempted military coup in 1936, Spain would plunge into total civil war for the next three years.
On one side: the Republican government co-operating with communist and anarchist forces; and on the other: the Nationalist rebels spearhearded by a military junta in alliance with Falangists, monarchists, conservatives, and traditionalists.
In his essay Why I Write (1946), Orwell outlines his political development:
First I spent five years in an unsuitable profession (the Indian Imperial Police, in Burma), and then I underwent poverty and the sense of failure. This increased my natural hatred of authority and made me for the first time fully aware of the existence of the working classes, and the job in Burma had given me some understanding of the nature of imperialism: but these experiences were not enough to give me an accurate political orientation. Then came Hitler, the Spanish Civil War, etc. By the end of 1935 I had still failed to reach a firm decision.
The Spanish war and other events in 1936-37 turned the scale and thereafter I knew where I stood. Every line of serious work that I have written since 1936 has been written, directly or indirectly, against totalitarianism and for democratic socialism, as I understand it. It seems to me nonsense, in a period like our own, to think that one can avoid writing of such subjects.
Orwell would spend Christmas 1936 travelling to Spain to support the Republican faction. Its unclear if Orwell initially intended to participate simply as a journalist or if he had always planned on being a combatant - but become a soldier he did:
I knew there was a war on, but I had no notion what kind of a war. If you had asked me why I had joined the militia I should have answered: ‘To fight against Fascism,’ and if you had asked me what I was fighting for, I should have answered: ‘Common decency.’
In May 1937, after a few months rotating between fighting on the streets and on the frontlines, Orwell was spotted by an enemy sniper and shot through the throat - just barely missing his main artery. He was rushed to the hospital and declared unfit for further service.
In Homage to Catalonia (1938), Orwell recounts his experience in the war, his opposition to fascism, and particularly his disillusionment with political factionalism and and misinformation.
The Republican alliance was breaking down and Orwell's milita was under political attack from its own side. As his comrades were arrested, imprisoned, and tortured, Orwell manages to flee the country. He is tried in absentia as a fascist and a Trotskyist agent.
Back home, Orwell finds his political views out of favor and struggles to find work - with his health also beginning to deteriorate.
When World War II arrives in England, Orwell is rejected for military service due to his ill health. Instead, he works in the propaganda wing of the BBC until 1943, when he resigns to focus on writing a new novel shaped by his experience of factionalism during the Spanish Civil War: Animal Farm (1945).
Animal Farm was almost lost when a V-1 bomb is dropped on Orwell's home. Orwell spends hours sifting through the rubble to find the manuscript - but by the time it is ready for publication, Orwell had larger concerns: The United States had just dropped two nuclear bombs on Japan to finish the Pacific War and usher in the Atomic Age.
Orwell envisioned a new type of future that he coined the "Cold War" in You and the Atomic Bomb (1945):
So we have before us the prospect of two or three monstrous super-states, each possessed of a weapon by which millions of people can be wiped out in a few seconds, dividing the world between them. It has been rather hastily assumed that this means bigger and bloodier wars, and perhaps an actual end to the machine civilisation. But suppose – and really this the likeliest development – that the surviving great nations make a tacit agreement never to use the atomic bomb against one another? Suppose they only use it, or the threat of it, against people who are unable to retaliate? In that case we are back where we were before, the only difference being that power is concentrated in still fewer hands and that the outlook for subject peoples and oppressed classes is still more hopeless.
We may be heading not for general breakdown but for an epoch as horribly stable as the slave empires of antiquity. Few people have yet considered its ideological implications – that is, the kind of world-view, the kind of beliefs, and the social structure that would probably prevail in a state which was at once unconquerable and in a permanent state of “cold war” with its neighbours.
When Animal Farm is published, Orwell experiences unprecendented commercial and critical success, catapulting him into a world-wide celebrity and intellectual. But Orwell did not want to rest on his laurels.
From Why I Write :
Animal Farm was the first book in which I tried, with full consciousness of what I was doing, to fuse political purpose and artistic purpose into one whole. I have not written a novel for seven years, but I hope to write another fairly soon. It is bound to be a failure, every book is a failure, but I do know with some clarity what kind of book I want to write.
That book would be Nineteen Eighty-Four .
It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.
And so Nineteen Eighty-Four begins with these iconic lines. We follow one Winston Smith, living in a a recognizable (particuarly to those who had lived through the Blitz) but unfamiliar London:
This, he thought with a sort of vague distaste --this was London, chief city of Airstrip One, itself the third most populous of the provinces of Oceania. He tried to squeeze out some childhood memory that should tell him whether London had always been quite like this. Were there always these vistas of rotting nineteenth-century houses, their sides shored up with baulks of timber, their windows patched with cardboard and their roofs with corrugated iron, their crazy garden walls sagging in all directions? And the bombed sites where the plaster dust swirled in the air and the willow-herb straggled over the heaps of rubble; and the places where the bombs had cleared a larger patch and there had sprung up sordid colonies of wooden dwellings like chicken-houses?
This world is dominated by the omnipresence of a surveillance state in the form of Big Brother, telescreens, and the Thought Police:
The black moustachio’d face gazed down from every commanding corner. There was one on the house-front immediately opposite. BIG BROTHER IS WATCHING YOU, the caption said, while the dark eyes looked deep into Winston’s own. Down at street level another poster, torn at one corner, flapped fitfully in the wind, alternately covering and uncovering thesingle word INGSOC. In the far distance a helicopter skimmed down between the roofs, hovered for an instant like a bluebottle, and darted away again with a curving flight. It was the police patrol, snooping into people’s windows. The patrols did not matter, however. Only the Thought Police mattered.
The telescreen received and transmitted simultaneously. Any sound that Winston made, above the level of a very low whisper, would be picked up by it, moreover, so long as he remained within the field of vision which the metal plaque commanded, he could be seen as well as heard. There was of course no way of knowing whether you were being watched at any given moment. How often, or on what system, the Thought Police plugged in on any individual wire was guesswork. It was even conceivable that they watched everybody all the time. But at any rate they could plug in your wire whenever they wanted to. Youhad to live --did live, from habit that became instinct --in the assumption that every sound you made was overheard, and, except in darkness, every movement scrutinized.
And its population is driven by daily and unending propaganda - particularly in the form of the Two Minutes Hate - against the enemy, Emmanuel Goldstein; his organization, the Brotherhood; and his ideology, as espoused in the book :
The next moment a hideous, grinding speech, as of some monstrous machine running without oil, burst from the big telescreen at the end of the room. It was a noise that set one’s teethon edge and bristled the hair at the back of one’s neck. The Hate had started. As usual, the face of Emmanuel Goldstein, the Enemy of the People, had flashed on to thescreen. There were hisses here and there among the audience. Goldstein was the renegade and backslider who once, long ago (how long ago, nobody quite remembered), had been one of the leading figures of the Party, almost on a level with Big Brother himself, and then had engaged in counter-revolutionary activities, had been condemned to death, and had mysteriously escaped and disappeared.
A day never passed when spies and saboteurs acting under his directions were not unmasked by the Thought Police. He was the commander of a vast shadowy army, an underground network of conspirators dedicated to the overthrow of the State. The Brotherhood, its name was supposed to be. There were also whispered stories of a terrible book, a compendium of all the heresies, of which Goldstein was the author and which circulated clandestinely here and there. It was a book without a title. People referred to it, if at all, simply as the book .
The oppressive but supposedly benevolent nature of the government captured in its paradoxical catchphrase:
WAR IS PEACE FREEDOM IS SLAVERY IGNORANCE IS STRENGTH
And just like its three slogans, the function and organization of the ruling Party is self-contradictory:
The four Ministries between which the entire apparatus of government was divided. The Ministry of Truth, which concerned itself with news, entertainment, education, and the fine arts. The Ministry of Peace, which concerned itself with war. The Ministry of Love, which maintained law and order. And the Ministry of Plenty, which was responsible for economic affairs. Their names, in Newspeak: Minitrue, Minipax, Miniluv, and Miniplenty.
Winston works in the Ministry of Truth - which is actually concerned with lies:
There were the huge printing-shops with their sub-editors, their typography experts, and their elaborately equipped studios for the faking of photographs. There was the tele-programmes section with its engineers, its producers, and its teams of actors specially chosen for their skill in imitating voices. There were the armies of reference clerks whose job was simply to draw up lists of books and periodicals whichwere due for recall. There were the vast repositories where the corrected documents were stored, and the hidden furnaces where the original copies were destroyed. And somewhere or other, quite anonymous, there were the directing brains who co-ordinated the whole effort and laid down the lines of policy which made it necessary that this fragment of the past should be preserved, that one falsified, and the other rubbed out of existence.
Winston's job is to rewrite historical records to match the state's official and ever-changing version of history - and particularly in regards to Oceania's perpetual war and alliance with the two other superstates in the world:
Oceania was at war with Eurasia and in alliance with Eastasia. In no public or private utterance was it ever admitted that the three powers had at any time been grouped along different lines. Actually, as Winston well knew, it was only four years since Oceania had been at war with Eastasia and in alliance with Eurasia. But that was merely a piece of furtive knowledge which he happened to possess because his memory was not satisfactorily under control. Officially the change of partners had never happened. Oceania was at war with Eurasia: therefore Oceania had always been at war with Eurasia. The enemy of the moment always represented absolute evil, and it followed that any past or future agreement with him was impossible.
Nothing is too large or too minute to be rewritten - from altering a Big Brother speech to correctly predict a military attack, to inventing a wholly fictional person to replace a disgraced former hero, to adjusting past chocolate ration projections to match current shortages.
And it is here that Winston begins to question the nature of reality and truth against the totalitarian machine:
The frightening thing was that it might all be true. If the Party could thrust its hand into the past and say of this or that event, it never happened --that, surely, was more terrifying than mere torture and death? He, Winston Smith, knew that Oceania had been in alliance with Eurasia as short a time as four years ago. But wheredid that knowledge exist? Only in his own consciousness, which in any case must soon be annihilated. And if all others accepted the lie which the Party imposed -- if all records told the same tale --then the lie passed into history and became truth. “Who controls the past,” ran the Party slogan, “controls the future: who controls the present controls the past.” And yet the past, though of its nature alterable, never had been altered. Whatever was true now was true from everlasting to everlasting. It was quite simple. All that was needed was an unending series of victories over your own memory. “Reality control”, they called it: in Newspeak, ‘doublethink’
Winston's defiance begins when he procures pen and paper and confronts his own memory:
The thing that he was about to do was to open a diary. This was not illegal (nothing was illegal, since there were no longer any laws), but if detected it was reasonably certain that it would be punished by death, or at least by twenty-five years in a forced-labour camp. He dipped the pen into the ink and then faltered for just asecond. A tremor had gone through his bowels. To mark the paper was the decisive act. In small clumsy letters he wrote: April 4th, 1984.
But even that is a futile exercise:
He sat back. A sense of complete helplessness had descended upon him. To begin with, he did not know with any certainty that this was 1984. It must be round about that date, since he was fairly sure that his age was thirty-nine, and he believed that he had been born in 1944 or 1945; but it was never possible nowadays to pin down any date within a year or two.
(Orwell himself was born in 1944.)
Events accelerate when one of Winston's colleagues named Julia hands him a love note and they begin a passionate secret affair - solidfying his resistance to the Party's narrative.
Winston is invited to the flat of his superior, O'Brien, who reveals himself to be a member of the Brotherhood and gives Winston a copy of Goldstein's book, The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism , which he reads to understand the means and ends of the Party - but not its motivation.
Inevitably, Winston is betrayed and revealed; he is tortured and made to denounce Julia; and the story ends with Winston effectively converted and a true believer:
But it was all right, everything was all right, the struggle was finished. He had won the victory over himself. He loved Big Brother.
Orwell's intentions for such a bleak finish have been discussed and argued over since its publication. Is the ending a prophecy? A warning? A parody? All of the above?
And if a totalitarian state such as the one in 1984 was to arise, can it be resisted or even defeated? If so, how?
Is it, as Winston believes early on, "If there is hope, it lies in the proles"? Is it, as outlined in The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism , the result of the Middle overthrowing the High? Could one of the foreign powers Eurasia or Eastasia emerge triumphant?
What exactly is the ultimate fate of Big Brother, the Party, and totalitarianism about 1984?
Although Winston's story ends there, Nineteen Eighty-Four the book continues; there is an appendix after the final chapter.
And this appendix does not necessarily appear at the end of the book only. Less than a thousand words into the story, there is the one and only footnote in the entire novel pointing towards it:
The Ministry of Truth --Minitrue, in Newspeak 1 --was startlingly different from any other object in sight. 1 Newspeak was the official language of Oceania. For an account of its structure and etymology see Appendix.
The appendix, titled The Principles of Newspeak, explains and outlines the rules and reasoning behind Newspeak - as well as offering tantalizing hints about the future of the world of 1984:
Newspeak was the official language of Oceania and had been devised to meet the ideological needs of Ingsoc, or English Socialism. In the year 1984 there was not as yet anyone who used Newspeak as his sole means of communication, either in speech or writing. The leading articles in the Times were written in it, but this was a tour de force which could only be carried out by a specialist. It was expected that Newspeak would have finally superseded Oldspeak (or Standard English, as we should call it) by about the year 2050. Meanwhile it gained ground steadily, all Party members tending to use Newspeak words and grammatical constructions more and more in their everyday speech. The version in use in 1984, and embodied in the Ninth and Tenth Editions of the Newspeak dictionary, was a provisional one, and contained many superfluous words and archaic formations which were due to be suppressed later. It is with the final, perfected version, as embodied in the Eleventh Edition of the dictionary, that we are concerned here.
Clearly, the Eleventh Edition of Newspeak is not so final or perfect - the appendix is written in our own Standard English. And from its first sentence, both the footnote and the appendix is written in the past tense:
Newspeak was the official language of Oceania.
So the appendix is written post- 1984 , in a world where Newspeak is of the past (and by extension, so too are Big Brother, the Party, and Ingsoc totalitarianism) and the author is able to discuss it freely and critically.
Therefore Newspeak fails and Big Brother falls after 1984, right? Maybe not. The appendix provides more questions than it does answers.
First: who is the author of this appendix? Clearly the author of the appendix is not the same as the narrator of the novel. Whereas the story in 1984 is told solely through Winston's limited perspective, the appendix consciously acknowledges its author and an audience ("we," "we now," "our own day").
Certain critics have placed it in the same category as Goldstein's The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism - a document from the world of 1984 that provides true and uncensored information about it.
And this certainly may be feasible - but why include the only footnote in the novel and point it towards a document from the future? Is it really Orwell or Nineteen Eighty-Four 's style to suddenly insert such a metafictive strain in the story?
Why would Orwell include the appendix in such a manner that draws so much attention to itself and seemingly introduces a new narrator out of nowhere?
(Orwell would later adamantly refuse to remove the appendix at the request of a U.S. publisher.)
In his essay, "The Two Narrators and Happy Ending of Nineteen Eighty-Four," Richard K. Sanderson draws a comparison between Goldstein's book and Nineteen Eighty-Four's appendix:
Along with Winston, we are led to believe that this book, unlike all the other documents, has escaped the clutches of the Party censors and could therefore give us an independent if not purely "objective" view of Oceanian society. Winston is excited to find that the book confirms many of his own thoughts and seems to be a solid explanation of how things "really" are. But later this confidence is shattered when O'Brien declares that he himself, in collaboration with others, authored this tract. This gameplaying sadist has lied before and could be lying now, but we have no way to be certain. Most readings of Nineteen Eighty-Four depend to some extent on information that is provided only in the "Goldstein" tract: the historical formation of the three superstates that rule the world, the si;:e and structure of the Party (six million people belong to the Inner Party), the class structure of Oceania (the proles are eighty-five percent of the population).
I would suggest that the real horror of the "Goldstein" book is not that it verifies the world of the novel but that it fails to verify any world. Does Big Brother exist? Does Goldstein exist? Does the Brotherhood exist? Did the Party write the "Goldstein" book? Winston cannot get straight answers to his questions and neither can the reader
The truthfulness of "The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism" is in doubt largely because of uncertainty about its authorship, and, as we have seen, a nearly identical ambiguity surrounds the Appendix.
During the Spanish Civil War, Orwell became disillusioned with the idea of objective journalistic truth as he saw both sides mis-represented and mis-representing.
(In fact, upon completing Nineteen Eighty-Four , Orwell would revisit Homage to Catalonia and place two chapters into a newly created appendix. His reason for doing so? To seperate the personal account from the historical and poltiical discussion.)
And just as O'Brien traps and manipulates Winston with Goldstein's book, Orwell does the same for the reader with the appendix:
There are strong resemblances between O'Brien's manipulation of Winston and Orwell's manipulation of the reader. Just as O'Brien plays upon Winston's desire for certain knowledge about Oceania's social and political structure, leading him on with the possibly spurious "Goldstein" tract, so the story's narrator draws the truth-seeking reader into an Appendix whose truth value cannot be determined.
The footnote's implied promise of verification is hollow, and the reader's attempts to determine the "objective truth" about Oceania —its social and political structure, its language, its fate —are frustrated. By trying to reconcile the novel and the Appendix, we experience for ourselves —"outside" the novel, as it were —what it might be like to inhabit a world in which the authenticity (never mind the accuracy or objectivity) of all documents is in doubt, in which documents are almost dreamlike, unfixed in time, infused with self-contradiction, at once recognizable and cryptic.
So... there's no answer then? Not quite.
Nineteen Eighty-Four 's true resolution does not lie in the appendix (and its accompanying footnote), but in a 14th century nursery rhyme.
Throughout Nineteen Eighty-Four , a nursery rhyme is repeated in parts by multiple characters. It is first introduced in Part I by Mr. Charrington, the shop-owner (and secret Thought Police agent), as he shows Winston an old picture of a church:
“I know that building,” said Winston finally. “It’s a ruin now. It’s in the middle of the street outside the Palace of Justice.” “That’s right. Outside the Law Courts. It was bombed in --oh, many years ago. It was a church at one time, St. Clement’s Danes, its name was.” He smiled apologetically, as though conscious of saying something slightly ridiculous, and added: “Oranges and lemons, say the bells of St. Clement’s!” “What’s that?” said Winston. “Oh -- ‘Oranges and lemons, say the bells of St. Clement’s.’ That was a rhyme we had when I was a little boy. How it goes on I don’t remember, but I do know it ended up, ‘Here comes a candle to light you to bed, Here comes a chopper to chop off your head.’
It lodges itself in Winston's brain as a gateway to an alternate London:
the half-remembered rhyme kept running through Winston’s head. Oranges and lemons say the bells of St. Clement’s, You owe me three farthings, say the bells of St. Martin’s! It was curious, but when you said it to yourself you had the illusion of actually hearing bells, the bells of a lost London that still existed somewhere orother, disguised and forgotten. From one ghostly steeple after another he seemed to hear them pealing forth. Yet so far as he could remember he had never in real life heard church bells ringing.
In Part II, the rhyme re-appears as Winston and Julia admire the picture after making love:
“It’s a church, or at least it used to be. St. Clement’s Danes its name was.” The fragment of rhyme that Mr. Charrington had taught him came back into his head, and he added half-nostalgically: ‘Oranges and lemons, say the bells of St. Clement’s!’” To his astonishment she capped the line: “You owe me three farthings, say the bells of St. Martin’s,“When will you pay me? say the bells of Old Bailey- “I can’t remember how it goes on after that. But anyway I remember it ends up, ‘Here comes a candle to light you to bed, here comes a chopper to chop off your head!’” It was like the two halves of a countersign. But there must be another line after “the bells of Old Bailey”. Perhaps it could be dug out of Mr. Charrington’s memory, if he were suitably prompted. “Who taught you that?“ he said. “My grandfather. He used to say it to me when I was a little girl. He was vaporized when I was eight - at any rate, he disappeared. I wonder what a lemon was,” she added inconsequently. “I’ve seen oranges. They’re a kind of round yellow fruit with a thick skin.”
One more stanza is revealed after O'Brien inducts Winston and Julia into the Brotherhood:
Almost at random Winston said: “Did you ever happen to hear an old rhyme that begins ‘Oranges and lemons, say the bells of St Clement’s’?” Again O’Brien nodded. With a sort of grave courtesy he completed the stanza: “‘Oranges and lemons, say the bells of St. Clement’s, You owe me three farthings, say the bells of St. Martin’s, When will you pay me? say the bells of Old Bailey, When I grow rich, say the bells of Shoreditch.’” “You knew the last line!” said Winston. “Yes, I knew the last line. And now, I am afraid, it is time for you to go.
And then finally, when Charrington reveals himself as an agent of the Thought Police, he quotes the last line:
“You may as well say good-bye,” said the voice. And then another quite different voice, a thin, cultivated voice which Winston had the impression of having heard before, struck in; “And by the way, while we are on the subject, Here comes a candle to light you to bed, here comes a chopper to chop off your head!”
But there are more stanzas to the rhyme that neither O'Brien nor Charrington recite, most commonly:
When will that be? Say the bells of Stepney. I do not know, Says the great bell at Bow.
Alternative versions of the nursery also include St. Margret's, St. Giles', St. Peter's, Whitechapel, and so on - all of them actual churches in the real world.
Nor is "here comes a chopper to chop off your head!" the end of the rhyme. There remains one more line that is never quoted:
Here comes a candle to light you to bed, And here comes a chopper to chop off your head! Chip chop chip chop the last man is dead
(In fact, Orwell's working title for Nineteen Eighty-Four was "The Last Man in Europe").
Textual references to Oranges and Lemons date back to the 17th century but the rhyme is almost certainly older - and some of the churches themselves date back to before the Norman Conquest.
So what does it mean?
In his essay The Prevention of Literature (1946) Orwell meditates on the resistance of poetry - and especially lyrics - compared to prose:
It is not certain whether the effects of totalitarianism upon verse need be so deadly as its effects on prose. Above all, good verse, unlike good prose, is not necessarily and individual product. Certain kinds of poems, such as ballads, or, on the other hand, very artificial verse forms, can be composed co-operatively by groups of people. Whether the ancient English and Scottish ballads were originally produced by individuals, or by the people at large, is disputed; but at any rate they are non-individual in the sense that they constantly change in passing from mouth to mouth. Even in print no two versions of a ballad are ever quite the same. Many primitive peoples compose verse communally. Someone begins to improvise, probably accompanying himself on a musical instrument, somebody else chips in with a line or a rhyme when the first singer breaks down, and so the process continues until there exists a whole song or ballad which has no identifiable author.
The reader is welcome to analyze the geographical and historical significance of Oranges and Lemons endlessly, as well as its poetical and literary meaning, and come to any number of conclusions - but all that is almost incidental.
Totalitarianism can be resisted so long as an individual exists outside the machine to resist it - whether through history or memory; language or poetry; action or hope.
And just as these things can destroy totalitarianism, so too can they create it. Big Brother is born through history (having swallowed memory), matures through language (having swallowed poetry), and rules through action (having swallowed hope).
The appendix demonstrates this for literature through an example converting the Declaration of Independence (1776) to Newspeak:
It would have been quite impossible to render this into Newspeak while keeping to the sense of the original. The nearest one could come to doing so would be to swallow the whole passage up in the single word crimethink. A full translation could only be an ideological translation, whereby Jefferson's words would be changed into a panegyric on absolute government.
Likewise, in O'Brien's interrogation of Winston, he reveals this necessary symbiotic relationship:
Always, at every moment, there will be the thrill of victory, the sensation of trampling on an enemy who is helpless. If you want a picture of the future, imagine a boot stamping on a human face— forever.
O'Brien's picture cannot exist without a human face for Big Brother's boot to stamp on; doublethink by definition requires the double.
Through this end, it is entirely possible to read Nineteen Eighty-Four as an endorsement of totalitarianism and a manual for fascism.
And therein lies Orwell's motivation for for writing Nineteen Eighty-Four and inventing doublethink ; for including an appendix after the novel and a footnote within it; for incorporating a real poem but concealing parts of it: it is to stimulate discussion (and action if need be!) and to serve as both proscription and prescription against totalitarianism.
And that is Orwell's true and secret ending for 1984 .
It took four years for Orwell to write Nineteen Eighty-Four , during which his health continued to decline. He finished the manuscript in December 1948 and left for a sanatorium the following month.
Orwell would not live to see Nineteen Eighty-Four published. Early on the morning of January 21, an artery burst in Orwell's lungs, killing him at the age of 46.
In Why I Write Orwell identifies the "four great motives for writing": sheer egoism, aesthetic enthusiasm, historical impulse, and political impulse.
I am a person in whom the first three motives would outweigh the fourth. In a peaceful age I might have written ornate or merely descriptive books, and might have remained almost unaware of my political loyalties. As it is I have been forced into becoming a sort of pamphleteer.
In peacetime, perhaps, George Orwell would have been a very different type of author. It's hard to imagine that an Orwell writing for egoism or historical impulse could have produced Nineteen Eighty-Four . And if he did, the ending could have been merely aesthetic: pessimistic and nihilistic or parodic and farcical.
But the Orwell who who grew up during WWI, fought in the Spanish Civil War, was bombed in WWII, and foresaw the Cold War; the George Orwell who contains Eric Arthur Blair, P.J. Burton, and Winston Smith; the George Orwell who wrote Nineteen Eighty-Four and then added an appendix to it - that George Orwell wrote for a clear purpose:
A desire to push the world in a certain direction, to alter other peoples’ idea of the kind of society that they should strive after.
Further Readings
- Appendix: The Principles of Newspeak
- Oranges and Lemons (1744)
- The Road to 1984 by Thomas Pynchon
- The Two Narrators and Happy Ending of Nineteen Eighty-Four by R.K. Sanderson
- The masterpiece that killed George Orwell by Robert McCrum
Books by George Orwell
- Down and Out in Paris and London (1933)
- Burmese Days (1934)
- Homage to Catalonia (1938)
- The Road to Wigan Pier (1937)
- Animal Farm (1945)
Essays by George Orwell
- You and the Atom Bomb (1945)
- Politics and the English Language (1946)
- The Prevention of Literature (1946)
- Why I Write (1946)
Or why not read the Russian dystopian classic that inspired Nineteen Eighty-Four : We by Yevgeny Zamyatin (1920)?
Join the newsletter. Publishes every other Tuesday.

The Definitive Guide to Analysing ‘1984’ for English: Summary, Context, Themes & Characters

Newspeak? Doublethink? What do all of these words mean? If you need help analysing 1984 by George Orwell, you’ve come to the right place — we’ve got all you need to know with a summary, list of key characters, themes and a 3-step essay analysis guide!
We’ve even got an analysis table and a sample paragraph that’s all free for you to download on 1984.
So, let’s throw back into 1984 (the fictional one of course)!
1984 by George Orwell Summary & Key Messages Key Characters in 1984 Context Themes Explored in 1984 Essay Analysis of 1984
1984 by George Orwell Summary & Key Messages
The politics of oceania.
1984 belongs in the dystopian, science fiction genre as it explores the dangers of corrupted power under a totalitarian regime. Totalitarianism is a government system that dictates how its citizens think, behave and act by constantly keeping an eye on them and carrying out punishments for those who don’t obey. Sounds strict, hey?
Sadly, this is the life of our protagonist, Winston Smith. Winston lives in a nation that resembles London in Oceania, which has been in a war with Eurasia and Eastasia since forever but no one really knows what the war is about. This is because the Party controls its people through rewriting history in the Ministry of Truth, where Winston edits historical records as part of his job.
The Party also invented a new language called “Newspeak” , which eliminates any words associated with rebellion to ensure full subservience of their nation.

Wherever Winston goes, he is bombarded with posters of their omnipresent leader, Big Brother. There are also hidden cameras and microphones that are implanted everywhere by the thought police to monitor every move of its citizens.
It’s a scary place because if you do or say anything wrong, the thought police will capture you and force you into lifelong labour . In this world, people cannot have close friends, cannot date whoever they want and cannot have intimate relationships.
Instead, the people pent up these emotions and channel them into aggressive patriotism for their government which are expressed in two minute hate rallies.
The Start of Winston’s Rebellion
Winston has had enough of the Party and its strict control. He purchases an illegal diary to commit crimethink, where he expresses his own thoughts and feelings about the Party through writing. He also writes about his interest in O’Brien, a member of the Inner Party who he believes could be part of the underground rebellion group called the Brotherhood.
Access 1984 Downloadable Sample Paragraph and Examples of Analysis
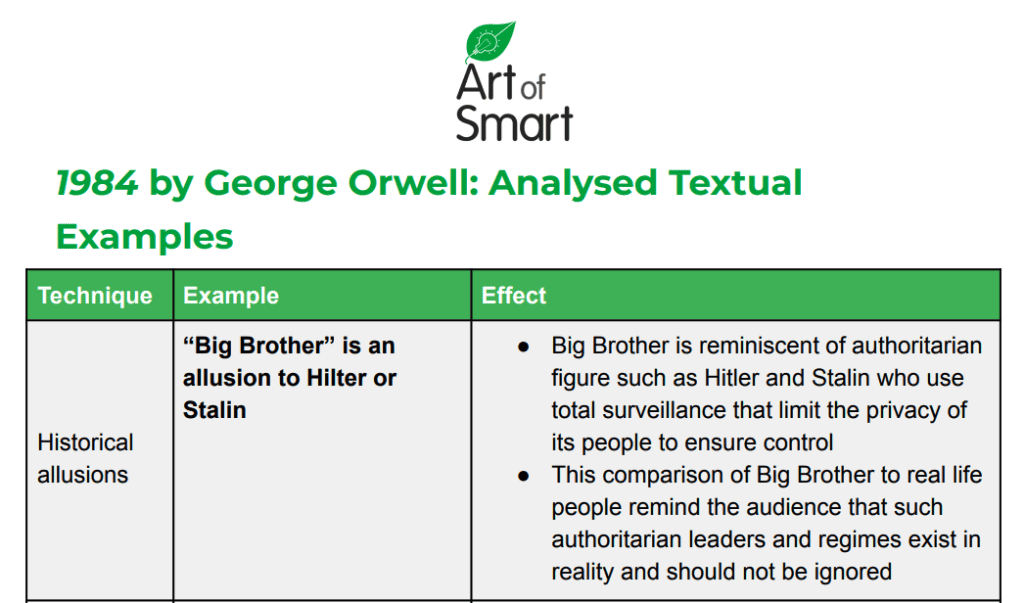
Winston’s and Julia’s Relationship
At work, Winston realises that his historical records were not aligning with his memories . He notices Julia, a young beautiful girl staring at him, and he is afraid that she will turn him into the “thought police”.
However, Julia passes him a note that says “I love you” and they start an affair.
O’Brien’s Betrayal
As their relationship grows more seriously, so does Winston’s hatred for the Party. He and Julia decided to reveal their rebellion to O’Brien, who also appeared to be on their side .
O’Brien welcomes them into the Brotherhood and passed Winston a copy of Emmanuel Goldstein’s book. As Winston starts reading the book, the thought police charge in, arrest Winston and Julia and bring them to the Ministry of Love. Turns out, O’Brien is a snake.
The Party Tortures Winston
At the Ministry of Love, Winston is tortured mercilessly and this makes him confess everything he knows about Julia and the rebellion .
It is then revealed that the government carries out these acts to exercise total power and control over the people of Oceania, to the extent where people not only do things out of fear, but genuinely believe in what they are doing even if it doesn’t make sense.
Winston’s Loss of Individuality
In Room 101, Winston experiences a true Fear Factor episode. The thought police threaten Winston with his ultimate fear, rats that would eat his face off. This caused Winston to scream “Do it to Julia, not me!”, which represents his betrayal to the only person that held value to him.
After this, the thought police let both Winston and Julia go, but the two ex-lovers can no longer look at each other face to face as they are both broken inside. Winston becomes a changed man who does not want to think about rebelling and instead becomes highly supportive of the Party and Big Brother.
Key Characters in 1984
Winston Smith The main protagonist who works under the Ministry of Truth in London, Oceania. His appearance is frail, pensive and intelligent. He hates the Party and its totalitarian system with a desire to revolutionise his current political situation. He can be emotional and idealistic with his goals.
Julia A beautiful young girl who is Winston’s love interest. Julia is sex-positive with an optimistic attitude about the future of the Party. She represents parts of humanity that Winston lacks, such as passive survival, intimacy, intuition and pragmatism.
O’Brien A mysterious leader of the Inner Party who Winston trusts as Winston believes that O’Brien is a member of the legendary rebellion group, the Brotherhood. It is revealed later in the novel that O’Brien is a leader of The Party who has been keeping a close eye on Winston. His betrayal launches us into the inner mechanisms of The Party and its totalitarian rule. O’Brien’s character parallels that of famous dictators in modern history such as Stalin and Hitler, as he is determined to indoctrinate Winston in the name of “purity.”
Big Brother Have you watched the show Big Brother? His character in the show is almost the same as in 1984, except a lot more controlling. In 1984, Big Brother is the most dominating figure in Oceania as he is perceived to be the ruler, although Orwell does not specify whether he really exists or not. Big Brother’s face is plastered among posters, coins and telescreens with the slogan “BIG BROTHER IS WATCHING YOU” so it’s impossible to avoid him anywhere.
Emmanuel Goldstein As the leader of the legendary group of rebels called the Brotherhood, Emmanuel Goldstein is the opposing figure of Big Brother. Although he never appears in the novel, he has had a profound impact on Winston’s hope for the future. He is the most dangerous man in Oceania, according to the Party.
Context in 1984
To understand 1984’s context, we must first understand the author’s personal background to craft a well thought-out essay analysis. This is because the author’s personal and historical experiences do shape the novel and its themes. So, let’s start with Orwell’s schooling days.
If you ever felt suppressed at school, Orwell can definitely relate with you on that. As a “lower-upper-middle class”, Orwell didn’t fit in with his peers and was upset with the restricted routine that schools impose on their students.

He then went on to become a British Imperial Policeman in Burma where he hated his job as he had to execute strict laws under a political system he didn’t like. After this, he moved to England and became a full-time writer.
Orwell experienced poverty for awhile, and even lived as a coal miner in northern England which caused him to shift from capitalist ideals to democratic socialism. Here are the simplified definitions of the political concepts that influenced Orwell’s beliefs and 1984’s themes:
- Capitalism: An economic system where property is owned and controlled by private actors, rather than by state. As such individuals can control how much they set their prices, instead of leaving it to the government to dictate.
- Democratic Socialism: Unlike capitalism, democratic socialism is an economic system whereby property and products are owned and controlled by the entire society, alongside governments. So, the main difference here is that governments have a say in trade whereas in capitalism, governments do not interfere with private owner’s business.
Orwell was also concerned with the rise of Thatcherism.
In the year 1936, Orwell fought as a socialist in the Spanish Civil War during World War II, where he became familiar with totalitarian systems that are under leaders such as Hitler and Stalin. Although Orwell was passionate about socialism at first, he soon became disillusioned and disappointed with its ideals as Stalin used communism as the foundation of his authoritarian system.
Stalin of the Soviet Union was also an important influence in shaping 1984’s totalitarian regime of Oceania, as Stalin used secret police to force confessions out of enemies through torture alike how the Ministry of Love did with Winston . Like the Party, the Soviet Union also tampered with physical records of people as they imprison and/or eliminate millions of lives.

With the rise of the nuclear age and television in 1949, Orwell envisioned a future where everyone would always be monitored through screens in a post-atomic dictatorship . This became a fear that was highly possible when speculated thirty five years into the future.
But as we all know, this did not become true. In the early 1990s, the Cold War ended with the triumph of democracy, as signified by the fall of the Berlin Wall and the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Even so, Orwell’s 1984 still serves as a precautionary tale against the corruption and abuse of totalitarian regimes, along with a profound insight into the use of language and history to manipulate one’s individuality.
Want more information on George Orwell? Take a look at this biography found via the Orwell Foundation page!
Themes Explored in 1984
To help you get started on your thesis or topic sentence , here are three key themes from 1984 that you can write about in your essay analysis !
The Consequences of Totalitarianism
After experiencing the violence and corruption of totalitarian regimes in Spain and Russia, Orwell wrote 1984 as a warning about the dangers of an authoritarian regime where the government holds the most power. As such, the Party in 1984 administered extreme methods of physical and psychological manipulation to enforce total submission of its people.
Physical control by the Party includes total surveillance of its people to the extent where even a twitch in the face can be enough to warrant an arrest. Morning exercises, called Physical Jerks, are also carried out before long hours at work to tire people out so they don’t have the energy to think beyond the Party’s propaganda.
The Party also uses physical torture to “re-educate” and punish those who rebel against them. It is this physical pain that causes Winston to lose his own individuality and moral beliefs, allowing the Party to infiltrate his mind and dictate his sense of reality.
Meanwhile, the Party also uses psychological tactics to saturate the individual’s mind with propaganda and disable its ability for independent thinking. On top of watching everyone everywhere, the telescreens are also used to indoctrinate (ie. brainwash) people into supporting the Party despite its flaws.

The telescreens also perpetuate slogans such as “BIG BROTHER IS WATCHING YOU” , to remind people that their government is always watching their back so they better behave according to the Party’s standards.
The Party also deems close friendships and conversations with others illegal. So, if you’re itching to spill the tea, your only method of venting your emotions out is through pep rallies, where the Party encourages you to show extreme expressions of hatred to its political enemies. Ultimately, this allows the Party to dictate how and where you should express your emotions, keeping you from expressing your individual feelings, thoughts and opinions.
Here are some quotes that illustrate the perils of totalitarianism:
| Quote | Link to the Consequences of Totalitarianism |
|---|---|
| “Big Brother is Watching You” | This slogan represents how the Party constantly monitors its people and instills psychological fear to enforce total control over its citizens. |
| “We convert him, we capture his inner mind, we reshape him” | This line from O’Brien reveals the Party’s motive of gaining total control over people’s minds by forcing them to forfeit their independent thought and truly believing in whatever the Party wants them to believe in. |
| “You want it to happen to the other person. You don’t give a damn what they suffer. All you care about is yourself.” | This line from Julia as she speaks to Winston about what happened in 101 reveals that the both of them have betrayed one another as a result of the torture they’ve experienced under the Party, which represents their loss of morality and individual values under cruel physical control of authoritarian regimes. |
The Power of Language to Liberate and Control
In 1984, language has the dual capacity to both restrain and facilitate individual expression. This is another key message that Orwell imparts, as he highlights how language can either promote or limit ideas which influence our beliefs, behaviour and identity.
The Party uses Newspeak as a way of controlling the language that its people speak, which in turn dictates the people’s thoughts, actions and personalities (or lack thereof).
By eliminating words that are associated with rebellious thoughts, the Party essentially removes the people’s ability to think of resistance because there are no words to conceive it. With continual edits with Newspeak, the Party inches a step closer to their ultimate goal of total coercion from their people.
Yet, in Winston’s case, he uses language as a vehicle of self-expression as he purchases a diary for himself and writes his everyday thoughts, opinions and feelings into it . By writing in his own words, he is able to build himself an identity with his own passions, goals and perspective.

Sadly, in a world where the government overrules individual expression, Winston’s use of language dwindles, though it is encouraging to see how language can still work to preserve independent thought.
Here are three quotes that can help you get started on this theme:
| Quote | Link to the Consequences of Totalitarianism |
|---|---|
| “WAR IS PEACE FREEDOM IS SLAVERY IGNORANCE IS STRENGTH” | This official slogan of the Party is an example of “doublethink” that is used to instil propaganda and fear, forcing its people to believe anything they say even when it is contradictory and illogical. (eg. Ministry of Truth is where history is rewritten, Ministry of Love is where people are tortured, Ministry of Peace is head of war). |
| “Don’t you see that the whole aim of Newspeak is to narrow the range of thought? In the end we shall make thoughtcrime literally impossible, because there will be no words in which to express it.." | This represents the Party’s use of language to restrain any thought of rebellion against its political campaign and enforce subservience. |
| “Freedom is the freedom to say that two plus two make four. If that is granted, all else follows” | This line from Winston reinforces the power of language to reclaim his perspective of the world moves beyond the indoctrinations from the Party. |
The Importance of Preserving Our Identity and Individualism
What happens if we lose everything that defines us as us?
1984 truly delves into this scary concept as the Party removes everyone’s personal details so they are not able to establish their own identity. For example, even Winston does not know his own age, who his real parents are nor can he trust his own childhood memories as there are no photographs or evidences to help him differentiate between reality and imagination.
Aside from Winston, the rest of Oceania are also denied documents that could give them a sense of individuality and help them differentiate themselves from others . This causes their memories to grow fuzzy, thus making the people of Oceania vulnerable and dependent on the stories that the Party tells them.
In turn, by controlling the present, the Party can re-engineer the past. Simultaneously, by controlling the past, the Party can rationalise its shortcomings and project a perfect government that is far from the truth.
With no recollection of the past, the people of Oceania can no longer stay in touch with their real identities and instead, become identical as they wear the same uniform, drink the same brand of alcohol and more. Yet, Winston builds his own sense of identity through recording his thoughts, experiences and emotions in his diary. This act along with his relationship with Julia symbolises Winston’s declaration of his own independence and identity as a rebel who disagrees with the Party’s system.
Despite this, Winston’s own sense of individuality and identity dissolves after his torturous experience at the Ministry of Love, which transforms him into another member of the Outer Party who blends into the crowd. By asserting a dark vision of humanity’s individualism, Orwell urges audiences in the present to truly value their freedom to express and preserve their identity.
Here are some quotes that are related to this idea which you may find helpful:
| Quote | Link to the Consequences of Totalitarianism |
|---|---|
| “Who controls the past, controls the future: who controls the present controls the past” | This slogan from the Party reveals that by rewriting history, the Party can justify their actions and systems in the present. Alternatively, by controlling the present, they can choose to manipulate history however they like. |
| “What appealed to [Winston] about [the coral paperweight] was not so much its beauty as the air it seemed to possess of belonging to an age quite different to the present one” | This quote from Winston represents his act of rebellion which helps him to assert his own independence in determining what he likes or does not like that are outside of the Party’s influence. |
| “And when memory failed and written records were falsified… the claim of the Party to have improved the conditions of human life had go to be accepted, because there did not exist, and never again could exist.” | This quote represents Winston’s realisation that the Party purposefully erodes people’s memories of the past to disable their sense of identity and gain full control of their sense of self. |
Of course, 1984 also includes other themes that you may be thinking about writing analysis for, such as:
- Rebellion and Patriotism
- Active versus Passive Survival
- The Corrupt Use of Technology
Check out our recommended related text for 1984 .
Essay Analysis: How to Analyse 1984 in 3 Steps
Analysing your text is always the first step to writing an amazing essay! Lots of students make the mistake of jumping right into writing without really understanding what the text is about.
This leads to arguments that only skim the surface of the complex ideas, techniques and elements of the text. So, let’s build a comprehensive thesis through an in-depth analysis of the 1984.
Here are three easy steps that you can use to analyse 1984 and really impress your English teachers!
Step 1: Select your example(s)
1984 is a world of its own with its totalitarian systems, use of foreign words and more. So, we totally understand if you’re feeling lost and don’t know where to begin.
Our piece of advice is to look for examples that come with a technique. Techniques offer you a chance to delve into the text’s underlying meaning, which would help you deepen your analysis and enrich your essay writing.
Find our extensive list of quotes from 1984 by George Orwell!
Here are two quotes that relate to consequences of totalitarian power, which we have picked to help you visualise which examples can provide a deeper meaning:
“Big Brother is Watching You.” “WAR IS PEACE FREEDOM IS SLAVERY IGNORANCE IS STRENGTH”
Step 2: Identify your technique(s)
Getting a good grade in English is more than listing out every technique that you can find in the text. Instead, it’s about finding techniques that allow you to dive deeper into the themes you’re focussing on, while also supporting your argument.
Try to look for techniques that allow you to explain its effects and link to your argument such as symbols, metaphors, connotations, similes and historical allegories . In Orwell’s case, he uses a lot of language techniques such as neologism, where he makes up his own words such as “Doublethink” or “Newspeak”.
For the two quotes above, its three techniques include historical allusion, rhetoric and oxymoron.
If possible, you can look out for a quote that encompasses a few techniques to really pack a punch in your analysis.
Step 3: Write the analysis
Once you’re done collecting your examples and techniques, the next part is writing. You must remember to explain what the effect of the technique is and how it supports your argument. Otherwise, it’s not going to be a cohesive essay if you’re just listing out techniques.
An example of listing out techniques looks like this:
“The rhetoric “Big Brother is Watching You” is also a historical allusion while “War is Peace, Freedom is Slavery and Ignorance is Strength” is oxymoronic.”
Instead, you must elaborate on how each of these techniques link to your argument.
“Big Brother is Watching You” is a rhetoric imposed by the Party to instil psychological fear and submission of the people of Oceania, whereby Orwell uses to warn the dangers of totalitarianism. “Big Brother” is also a historical allusion to Hitler to remind the audience that 1984 is not entirely fictional but a possible future of our reality, urging us to take action against totalitarian regimes with the autonomy we have now.
Meanwhile, the slogan ““WAR IS PEACE, FREEDOM IS SLAVERY, IGNORANCE IS STRENGTH” represents the oxymoronic mentalities that have been indoctrinated into the people of Oceania, highlighting how totalitarian regimes would force its people to think whatever they want their people to think, no matter how illogical it is.
Together, your analysis should look something like:
The Party perpetuates the rhetoric, “Big Brother is Watching You” to instil psychological fear and coercion of the the people of Oceania, which forewarns a lack of individual freedom and private reflection within authoritarian regimes. As “Big Brother” is a historical allusion to Hitler, Orwell reminds the audience that 1984 and its extremist politics is a reality, urging us to defend our independence before it’s forbidden. Furthermore, the slogan “War is Peace, Freedom is Slavery, Ignorance is Strength” embodies the oxymoronic mentalities that the Party indoctrinates into its people, revealing the extreme extent of psychological control an authoritarian regime strives to ensure their power is never questioned, no matter how irrational it is.
Need some help with your essay analysis of other texts aside from 1984?
Check out other texts we’ve created guides for below:
- Romeo and Juliet
- Run Lola Run
- The Meursault Investigation
- In Cold Blood
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- The Book Thief
- The Tempest
- Blade Runner
- Things Fall Apart
- Mrs Dalloway
Are you looking for some extra help with your essay analysis of 1984?
We have an incredible team of tutors and mentors.
We can help you master your essay analysis of 1984 by taking you through the summary, context, key characters and themes. We’ll also help you ace your upcoming English assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years , and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Kate Lynn Law graduated in 2017 with an all rounders HSC award and an ATAR of 97.65. Passionate about mentoring, she enjoys working with high school students to improve their academic, work and life skills in preparation for the HSC and what comes next. An avid blogger, Kate had administered a creative writing page for over 2000 people since 2013, writing to an international audience since her early teenage years.
- Topics: ✏️ English , ✍️ Learn
Related Articles
Everything you need to know about analysing ‘jasper jones’ for english – summary, context, themes & characters, a comprehensive guide to analysing ‘the book thief’: summary, context, themes & characters, the definitive guide to analysing ‘in cold blood’: summary, context & themes, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for English Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in
Home ➔ Free Essay Examples ➔ 1984 Essay
Writing an Essay on George Orwell’s 1984
George Orwell’s dystopian novel 1984 masterfully depicts a society dominated by a totalitarian government. Through extensive imagery, Orwell reveals the nature of an anti-utopian regime from the viewpoint of Winston Smith, an outer party member tasked with rewriting history, indicative of the past controls in the novel. His perspectives reflect the present controls in the novel and unveil the dystopian totalitarian society of Oceania, a nation in constant antagonism with others.

1984 by George Orwell is recognized as a must-read literary masterpiece, engaging readers across all age groups with its rich characters and stimulating essay topics. The novel’s detailed historicism and depiction of the dominant political party’s actions, echoing their party slogan, have inspired numerous thought-provoking essays.

While some may believe that all possible essay topics on 1984 have been explored, this is only partially true. Every essay uniquely explores an author’s thought process, offering new perspectives even on familiar themes. For instance, the concept of doublethink, central to Orwell’s political fiction narrative, continues to be a subject of lively debate. Moreover, the novel raises complex issues worth exploring, such as the effects of government surveillance and the erosion of civil liberties in a dystopian society.
How to Choose an Effective Topic

Consider the social problems highlighted in this dystopian literature to select a relevant essay topic. Possible research subjects include:
- Gender balance in the novel: Examine the roles of men and women, particularly focusing on Winston Smith and Julia’s relationship.
- Symbolism in the novel: Identify images and ideas that relate to real-world events and explore the author’s intentions behind these metaphors.
- Brainwashing: Analyze how altering history impacts the novel’s characters and how doublethink affects their behavior.
- Room 101 metaphor: Contemplate the symbolic significance of Room 101, where individuals confront their worst fears and psychological effects.
- Power display: Investigate how power is portrayed in the book and the Party’s methods to demonstrate its supremacy.
- Technology use: Discuss how technology is employed to limit freedom and its effects on characters’ mental and physical health.
- Historicism: Examine the correlation between events in the book and real-world history, comparing Orwell’s portrayal to historical periods like World War II or the Soviet Union.
These research ideas can become fascinating and purposeful essay topics . Consider each and choose a subject that offers fresh perspectives, ensuring to express your own opinions and attitudes.
How to Come Up With an Innovative Idea
Engaging your reader, sparking curiosity, and presenting fresh insights are the hallmarks of a compelling essay . But how does one achieve these? The answer lies in innovation. Innovation in essay writing is not just about uniqueness; it’s about offering a new understanding of a familiar subject. An innovative idea can challenge established viewpoints, connect disparate concepts, or revitalize well-trodden debates. Writing about a widely studied text like 1984 by George Orwell requires an innovative approach to stand out and encourage deeper discussion.
Understanding the Novel
To create innovative essay ideas, it is essential to understand “1984” thoroughly. Dive into the novel’s world, absorbing the plot’s nuances, character dynamics, themes, and Orwell’s distinct style. Reflect on the characters’ actions and the story’s development. Understand Orwell’s historical context and motivations, whether as a warning, critique, or dystopian vision. This deep comprehension will fuel unique essay topics.
Brainstorming Techniques
Enhance your brainstorming with techniques like mind mapping, starting with core concepts like ‘totalitarianism’ or ‘doublethink’ and expanding into related areas. Use free writing to unleash subconscious thoughts and insights. The questioning method can lead to innovative ideas by asking probing questions about the novel’s characters, themes, or Orwell’s intentions.
Connecting to Contemporary Themes
Consider how “1984” reflects our contemporary society. Draw parallels between Orwell’s dystopian world and current political and social issues. Analyze the novel’s portrayal of surveillance and propaganda in relation to modern discussions about privacy and misinformation. By linking these themes, you bring your essay a modern, innovative perspective.
Diving Deeper into Characters and Themes
Go beyond surface-level understanding. Explore the psychological depths of characters like Winston Smith, Julia, and Big Brother. Analyze how their motivations interact with Orwell’s overarching themes. Investigate themes like totalitarianism, privacy, and the nature of power. Such exploration will reveal fresh perspectives and groundbreaking essay topics.
Here is a comprehensive, comma-separated list of themes found in George Orwell’s “1984”:
Totalitarianism, censorship, manipulation of information, propaganda, surveillance, resistance to power, psychological manipulation, physical control, the alteration of reality, loss of individuality, loyalty, nationalism, sexuality and love, class struggle, language as mind control, memory and the past, fear, betrayal, fatalism, repression, truth, power, control, privacy, rebellion.
Examining Literary Devices
Study Orwell’s literary craft, focusing on how his use of metaphor, simile, irony, and foreshadowing enhances the narrative and themes. Understanding these devices is key to unlocking deeper meanings and forming the basis of insightful essays.
Here is an exhaustive, comma-separated list of literary devices found in George Orwell’s “1984”:
Allegory, allusion, analogy, antithesis, aphorism, apostrophe, assonance, cacophony, characterization, conflict, connotation, denotation, dialogue, dramatic irony, dystopia, euphemism, foreshadowing, hyperbole, imagery, irony, juxtaposition, metaphor, metonymy, mood, motif, paradox, parallelism, personification, plot, point of view, prose, repetition, satire , setting, simile, symbolism, syntax, theme, tone, understatement, foreshadowing, flashback, alliteration.
Encouraging Multiple Perspectives
View 1984, a classic in social science fiction, from different angles. Consider the story from the perspectives of various characters under the party’s control or through different theoretical lenses like feminist, Marxist, or postcolonial theories. These diverse viewpoints can illuminate the text and inspire unique essay topics.
Consult Secondary Sources
Expand your research with secondary sources like scholarly articles and literary critiques, seeing ‘1984’ as a prime example in its genre. They can provide new interpretations and context, enriching your essay with a well-rounded perspective. Critically evaluate these sources and integrate them to support your unique viewpoint.
Evaluating Ideas
Once you’ve generated various ideas, it’s time to evaluate them. Not all ideas are created equal. Ask yourself: Which of my ideas are truly innovative? Which ones offer fresh insights and perspectives on “1984”? Which will engage my audience most effectively? Consider the scope, depth, and relevance of each idea. Can you find enough evidence in the text to support your argument ? Will your idea contribute to the existing discourse around the novel, or does it risk rehashing well-trodden arguments? This critical evaluation will ensure that you choose the most innovative and effective idea for your essay.
Comparative Analysis with Other Dystopian Novels
Innovate by comparing “1984” with other dystopian works like “Brave New World” or “Fahrenheit 451”. This comparison can highlight common themes and narrative techniques in dystopian literature, providing a fresh angle for your essay.
1984 Topic Examples

When choosing an essay topic for “1984”, it’s important to select a subject that resonates with you. Here are some topic ideas to consider:
- Mechanisms of Control : Explore how the Inner Party employs various methods to instill paranoia in Oceania’s citizens and analyze their effectiveness in maintaining the regime’s rule.
- Historical Parallels : Examine elements within “1984” that mirror real-world instances of totalitarian rule, such as the parallels between the Party’s tactics and those used in historical dictatorships.
- Winston’s Rebellion and Failure : Discuss the complex dynamics that lead to Winston’s inability to overthrow the oppressive government, focusing on the interplay between his character traits, the political environment, and societal structures.
- Effective Methods of Totalitarian Rule : Identify and argue the most effective strategy used by Big Brother to maintain control over society, comparing it with other methods depicted in the novel.
- The Role of Propaganda : Analyze the use of propaganda in the novel and its effectiveness in controlling the populace within a totalitarian society.
- The Power of Language : Delve into Orwell’s introduction of ‘Newspeak’ and discuss how language manipulation consolidates a totalitarian state.
- Technology and Control : Scrutinize how Orwell portrays technology as a tool for surveillance and societal manipulation in the novel.
- Dehumanization in Totalitarian Regimes : Discuss the dehumanizing effects of living under a totalitarian regime as portrayed in “1984”, focusing on how the regime’s control over individuality and personal life affects the characters.
- Doublethink as a Tool of Control : Examine how the concept of doublethink is used to maintain the totalitarian government, analyzing its role in perpetuating the state.
- The Role of the Proles : Analyze the depiction of ‘the proles’ in “1984” and discuss their potential as a disruptive force against the oppressive regime.
The Perils of Doublethink in 1984 (Essay Sample)
George Orwell’s “1984” provides a chilling exploration of a dystopian society under a totalitarian regime, where citizens are compelled to accept contradictory beliefs simultaneously – a concept Orwell termed as “doublethink.” This novel vividly portrays the sinister consequences of doublethink on personal freedom and objective reality. In this essay, we delve into Orwell’s critique of doublethink, elucidating its damaging impacts on individual freedom of thought and the recognition of objective reality.
In the world Orwell conjures, doublethink becomes a psychological instrument of the totalitarian government, meticulously designed to manipulate citizens into submissively endorsing the regime’s ideology. An instance of this can be seen in the paradoxical statement, “two and two equal five,” a governmental doctrine the citizens are forced to embrace despite its glaring falsity. This powerful manifestation of doublethink unveils the ability of the Party to distort the truth and disseminate its propaganda without any resistance. The collective acceptance of these blatant lies not only obstructs free thinking but also paves the way for a society in which objective reality is perpetually challenged.
The insidious nature of doublethink lies in its capacity to coerce citizens into abandoning their personal convictions and accepting the Party’s dictates, thereby suppressing their freedom of thought and action. Such mental manipulation leads to a society of individuals unable to discern truth from falsehood, submissively adhering to any propaganda the government propagates. Scholars argue that through doublethink, people are psychologically conditioned to accept lies as truth, demonstrating the horrifying extent of control the Party exerts over the masses (Orwell, 1990).
More alarmingly, doublethink blurs the boundary between reality and fiction, contributing to a society where the concept of objective truth becomes obsolete. In Orwell’s words, doublethink “negates the existence of objective reality while simultaneously accounting for the reality it denies” (Orwell, 1990). This suggests that proponents of doublethink willingly forsake objective truth, accepting any belief propagated by the Party irrespective of its veracity. An illustration of this is when citizens believe that consuming fruits is harmful, despite their inherent knowledge of their nutritional benefits. This form of cognitive distortion serves the interests of autocratic leaders, providing them with unwavering control over the populace.
Overall, Orwell’s “1984” paints a disturbing picture of a society crippled by doublethink, an instrument of manipulation stemming from totalitarian ideology. The consequences of this dangerous practice are the suppression of individual freedom of thought and the denial of objective reality, all serving to solidify the unyielding control of a corrupt government. Therefore, Orwell’s novel stands as a stark warning against the acceptance of doublethink, reinforcing the vital importance of independent thought and the recognition of objective reality in a democratic society.
- Anderson, M. (2016). Charter school reform: doublethink and the assault on the vulnerable. Journal of Thought , 50 (3-4), 33-48.
- Kaye, S., & Chin, C. (2017). Donald Trump’s use of post-truth double-think politics is a threat to liberal democratic norms. USA pp–American Politics and Policy Blog .
- Moran, S. (2018). Control in WWII Novels: 1984 and Brave New World (Doctoral dissertation, Worcester Polytechnic Institute).
- Orwell, G. (1990). Nineteen Eighty-Four. 1949. The Complete Novels , 7.
Writing the Thesis Statement and Conclusion
Crafting the thesis statement.
An impactful thesis statement is the linchpin of a compelling essay. It presents your central argument clearly and concisely and guides the structure of your essay . When writing a thesis statement for an essay on “1984”, ensure it communicates your unique perspective and directly addresses the essay question or topic.
Your thesis statement should make an argument rather than stating a fact. For example, rather than saying, “George Orwell’s ‘1984’ presents a dystopian society,” you might argue, “Through the portrayal of a dystopian society in ‘1984’, George Orwell critiques the misuse of political power and the erosion of individual freedoms.”
Ensure your thesis is specific enough to be covered effectively in your essay and broad enough to allow you to discuss multiple aspects of the text. Your thesis statement should also indicate the key points you will use to support your argument.
For example: “In ‘1984’, George Orwell uses the motif of Big Brother, the concept of doublethink, and the character arc of Winston Smith to critique the totalitarian government’s manipulative control over individuals’ thoughts and actions.”
Finally, position your thesis statement at the end of your introduction . This placement effectively sets the stage for the rest of your essay and guides your readers on the journey of your argument.
Constructing the Conclusion
The conclusion is your final chance to make an impact on your readers, so make it count. It ties up your argument and gives your essay a sense of completion.
Begin your conclusion by rephrasing your thesis statement in a new way. Do not simply repeat your thesis verbatim—instead, revisit it in light of the arguments and evidence you’ve presented. This reinforces your central argument and demonstrates how your essay has supported it.
Next, summarize the key points you’ve made in your body paragraphs . This should not simply be a list but a synthesis of your main arguments demonstrating how they support your thesis.
Finally, consider the broader implications of your argument. What does your analysis of “1984” contribute to the understanding of the novel or the broader discussions around it? How does your essay connect to the world today? By ending your essay with a thought-provoking conclusion, you leave your readers with a lasting impression and demonstrate the relevance and impact of your arguments. For instance, you might conclude with a statement: “Orwell’s ‘1984’ serves as a chilling reminder of the power of propaganda and manipulation, urging contemporary societies to be vigilant against any infringement on individual liberties.”
Remember, your conclusion should not introduce any new arguments or information. Its goal is to wrap up your essay in a satisfying and coherent way, leaving your readers with a clear understanding of your argument and its significance.
Conclusion example
“ George Orwell’s dystopian novel “1984” profoundly illustrates the grim outcomes of totalitarian rule, creating a cautionary tale of manipulated consciousness and obliterated freedoms. [Introduction of main theme] The exploration of language manipulation, the concept of doublethink, and the pervasive presence of Big Brother exemplify Orwell’s portrayal of the dangerous potential of absolute power to manipulate reality and alter citizens’ perceptions of truth and morality. [Key themes & concepts] The novel’s relevance in today’s digital age is undeniable, with increasing surveillance technology and the proliferation of ‘fake news’ raising urgent questions about privacy, truth, and the power of political manipulation. [Contemporary relevance] More than a mere work of fiction, ‘1984’ serves as a chilling prophecy and stark reminder of the importance of critical thinking, freedom of expression, and individual autonomy. As we delve deeper into an era marked by digital surveillance and data manipulation, Orwell’s ‘1984’ remains a necessary critique and potent warning, underscoring the need for constant vigilance and resistance against any threats to our freedoms. [Conclusion & broader implications] ”
Was this article helpful?
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Literature
Essay Samples on 1984
Comparison of "v for vendetta" and "1984".
Two iconic dystopian works, "V for Vendetta" by Alan Moore and David Lloyd, and "1984" by George Orwell, explore themes of totalitarian control, resistance, and the human quest for freedom. While set in different fictional worlds, both narratives offer thought-provoking reflections on power, authority, and...
- V For Vendetta

Surveillance in George Orwell's "1984": The Perils of Totalitarian Control
George Orwell's novel "1984" serves as a chilling depiction of a dystopian society where surveillance is used as a tool of control and manipulation. The novel explores the devastating consequences of a government that employs surveillance to monitor and regulate every aspect of its citizens'...
- Surveillance
The Dynamics of Power in George Orwell's "1984"
George Orwell's novel "1984" presents a harrowing exploration of power and its various manifestations within a dystopian society. The novel delves into the complex dynamics of power, including the ways it is exercised, maintained, and resisted. Through the lens of the Party's authoritarian regime, this...
Government Surveillance in George Orwell's "1984": The Illusion of Security
George Orwell's novel "1984" serves as a haunting portrayal of a dystopian society dominated by government surveillance and control. The government's use of surveillance technologies to monitor and manipulate citizens is presented as a mechanism for maintaining power and suppressing dissent. In this essay, we...
- Government Surveillance
The Viability of a Society Based on Hate in George Orwell's "1984"
George Orwell's dystopian novel "1984" presents a chilling depiction of a society dominated by hatred, oppression, and totalitarian control. The novel explores the consequences of a society built on hate and examines whether such a system can sustain itself in the long term. Through the...
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Propaganda and Manipulation in George Orwell's "1984"
George Orwell's dystopian novel "1984" offers a haunting portrayal of a society dominated by propaganda, where truth is distorted, and reality is manipulated by those in power. The novel explores the insidious nature of propaganda and its role in controlling thought, erasing history, and perpetuating...
The Human Experience in George Orwell's "1984"
George Orwell's dystopian novel "1984" paints a bleak and haunting portrayal of a totalitarian society where individuality is suppressed, truth is manipulated, and human experience is tightly controlled. Through the lens of the protagonist, Winston Smith, the novel delves into the complexities of the human...
"Brave New World" and "1984": Comparison of the Depiction of Power and Control
Introduction Christian Nestell Bovee once said, 'No one is happy without a delusion of some kind. Delusions are as necessary to our happiness as realities.' Bovee's quote applies to the dystopian genre, as evident in Aldous Huxley's novel Brave New World and George Orwell's film...
- Brave New World
"Animal Farm" and "1984": Comparison of George Orwell’s Notable Novels
Introduction In this essay, I will perform a comparison of George Orwell's two renowned books, '1984' and 'Animal Farm.' Furthermore, I will argue that '1984' holds greater relevance in our modern society, which, in my opinion, is heading towards a future that closely aligns with...
- Animal Farm
- George Orwell
1984' Book Review: Anomalies and Paradoxes of Human Behaviour
Through the representation of individual and collective human experiences, composers are able to challenge our assumptions on the complexity of human behaviour. Through the '1984' book review essay we cam analyse the anomalies and paradoxes of human behaviour that are revealed in Orwell's novel. These paradoxes...
Theme, Setting and Symbolism in 1984: an Overview of Orwell's Novel
For this 'Theme, Setting and Symbolism in 1984' essay the task for an author is to discuss how effectively Orwell uses one of the following literary devices in 1984: symbolism, theme, setting or point of view. In the hard hitting and some could say most...
1984 Compared to Today: George Orwell's Use of Themes in the Novel
As in many other novels, the use of multiple themes is evident throughout George Orwell’s 1984. Theme can be used in a variety of ways by the author to add to the complexity of a novel, and promote critical thinking by the audience. Orwell’s 1984...
1984 Compared to Today: Comparison of Technology in the Book and Today
¨It was the Police Patrol, snooping into peopleś windows… only the Thought Police mattered.¨ (P.6) In the novel 1984 by George Orwell, people do not have privacy with the Thought Police always watching them. People do not feel safe knowing they are always being watched....
The Characterization And Orwell's Mood In 1984
Bob Dylan, a singer-songwriter, once stated that “No one is free, even the birds are chained to the sky”, but little did he know the prominence of his speech as it pertains to the novel 1984 by George Orwell. The novel depicts a totalitarian dystopia,...
- Mood in Literature
Allegory Elements In George Orwell's 1984
Dystopian novels allow people to envision and fear what is possible to happen in the future, but it also shows that there will always be people hanging on to hope, and people who wish for change. This is what the book 1984, written by George...
- Allegory in Literature
The Grim Imagery Used In 1984
George Orwell’s prose fiction novel Nineteen Eighty-Four (1949) and Yevgeny Zamyatin’s dystopian novel We (1924) provide projections of the adverse effects of oppressive governments and how their insidious nature restrains one’s individuality and humanity. Both authors by exemplifying the fundamental human qualities of communion, morality,...
- Imagery in Literature
Presentation Of Authoritarian Control In George Orwell's 1984 And Brave New World
In the two novels ’Brave New World’ by Aldous Huxley and ‘1984’ by George Orwell, authoritarian control is a recurring theme throughout both plots. The two authors, who were influenced by their experiences of war on a large scale during the twentieth century were saddened...
Literary Devices Used In George Orwell's 1984
Most of the authors in the literary devices intend to pass certain and specific messages to their audience. Majority of them evaluate the happenings in the society. As such, the messages aim at changing the society towards the ability by the people to maintain the...
The Use Of Literary Devices And Other Techniques In Orwell's "1984"
The horrendousness of the truth is often masked by the distortion of the reality that is present in truth. The purpose behind George Orwell’s 1984 was to expose this truth of the world in a manner that would not take away from what was plainly...
The Comparison Of Dystopian Worlds In 1984 And Brave New World
Huxley's Brave New World and Orwell's 1984 are both Dystopian novels written ahead of their time that, in their own way, frighteningly predicted the western world of today. 21st Century western society has turned out to be a combination of both Huxley and Orwell’s visions...
Theme Of Double-thinking In Orwellian Writing: Analysis Of Thematic Similarities In A Hanging And 1984
“We walked out of the gallows yard, past the condemned cells with their waiting prisoners, into the big central yard of the prison… it seemed quite a homely, jolly scene, after the hanging. An enormous relief had come upon us now that the job was...
The Empowerment of Language in Understanding and Changing the World
Human nature relies on the ability to formulate thought - to generate the id, ego, and super ego’s into one’s needs, however, to communicate these needs depends on an underlying principle. Without language as an underlying mechanism, the human needs would not be able to...
- Frankenstein
Panopticism and Loss of Individuality in the Novel 1984 and movie Equilibrium
Through the readings of Michel Foucault’s Discipline And Punish, we discover that there are many new strategies that leaders began employing which allowed for more psychological control over the public. Some of these new themes can be observed in various films and texts such as...
- Michel Foucault
- Panopticism
Justification of Violence for Reforms in 1984 and V for Vendetta
Both in '1984' and in 'V for Vendetta', vivid symbolism allows the reader to catch the meaningful message hidden behind the words. They include a message addressing society today to think about the dangers of totalitarian societies. 1984 is a novel written by George Orwell...
V for Vendetta and 1984: The Revolt Againsts the Authority
The movie V for Vendetta, based on the same title novel, can be seen as George Orwell's sequel to the 1984 script. This depicts a world in V for Vendetta, close to ours, though in the future, where it is governed by an autocratic dictator....
Depiction of Dystopian Worlds in The Handmaid's Tale and 1984
Dystopian literature questions the power of language, both Atwood’s ‘The Handmaid’s Tale’ and Orwell’s ‘Nineteen Eighty - four’ showcases a variety of qualities necessary to advocate one’s freedom. Whilst both novelists share the common theme of language limiting both freedom and knowledge the two texts...
- The Handmaid's Tale
Parallels in Authority System in 1984 and North Korea
North Korea, officially recognized as the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, or DPRK is a country situated in East Asia that is home to approximately 25 million people. It constitutes the northern part of the Korean Peninsula and was established in 1948 in the aftermath...
- North Korea
The Representation of Oppresion in "1984" and "Never Let Me Go"
Both texts present a protagonist who is oppressed by a group which are higher than themselves as these groups have full control over the characters and their respective societies, the characters arc are displayed to the reader through a first person narrator within “Never Let...
- Never Let Me Go
George Orwell's Achievements and Impact as an Author
George had an eventful early life, traveling to different places such as Paris and London, then later Spain. For example, Orwell moved to Paris and then later London with no money and worked as a factory worker to understand life as a commoner (Bloom 7)....
George Orwell and His Unique Perception of Language
George Orwell has earned the right to be called one of the finer writers in the English language through such novels as 1984, Animal Farm, and Down and Out in Paris and London. Orwell heavily criticized totalitarian governments in his writing and carried that same...
- English Language
Examining the Impact of George Orwell on American Society
George Orwell was born in 1903 in Motihari, India, under the name Eric Arthur Blair. In his web article about Orwell, George Woodcock explains Orwell grew up in an atmosphere of “impoverished snobbery” (2018). At an early age his parents sent him to a preparatory...
1984: Frightening Resemblance to America's Reality
George Orwell's dystopian vision of an authoritarianism society, in his novel 1984, was not as far-fetched as those during his time once believed. There are numerous parallels between 1984 and present day governments around the world, including the United States government. The connections are sometimes...
1984: Parallels Between Reality and Dystopian Fiction
“The best books... are those that tell you what you know already.” In the weeks following the ‘inauguration’ of Donald J. Trump, the sales of George Orwell’s most distinguished novel skyrocketed. 1984 flew off the virtual shelves as it hit Amazon’s best-selling book in January...
George Orwell’s “1984” Reflecting the Realities of Life in 21st Century
”Are living in 1984?” - this question can be asked by the readers of the 1984 book by George Orwell. To be more accurate, we should ask, if we live in totalitarian system. Unfortunately, the answer might be really concerned for many people. Despite of...
- Literature Review
Portrait Of Totalitarian Government In Book "1984"
Being a man born into the first half of the twentieth century, George Orwell was forced to endure both World Wars, as well as the start of the Cold War. His experience with national relations and the lessons that war brings allowed him to pen...
Best topics on 1984
1. Comparison of “V for Vendetta” and “1984”
2. Surveillance in George Orwell’s “1984”: The Perils of Totalitarian Control
3. The Dynamics of Power in George Orwell’s “1984”
4. Government Surveillance in George Orwell’s “1984”: The Illusion of Security
5. The Viability of a Society Based on Hate in George Orwell’s “1984”
6. Propaganda and Manipulation in George Orwell’s “1984”
7. The Human Experience in George Orwell’s “1984”
8. “Brave New World” and “1984”: Comparison of the Depiction of Power and Control
9. “Animal Farm” and “1984”: Comparison of George Orwell’s Notable Novels
10. 1984′ Book Review: Anomalies and Paradoxes of Human Behaviour
11. Theme, Setting and Symbolism in 1984: an Overview of Orwell’s Novel
12. 1984 Compared to Today: George Orwell’s Use of Themes in the Novel
13. 1984 Compared to Today: Comparison of Technology in the Book and Today
14. The Characterization And Orwell’s Mood In 1984
15. Allegory Elements In George Orwell’s 1984
- Hidden Intellectualism
- A Raisin in The Sun
- Sonny's Blues
- William Shakespeare
- Who Was Chris Mccandless
- Amigo Brothers
- A Sound of Thunder
- Anna Quindlen
- A Very Old Man With Enormous Wings
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Akron’s Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James
This essay is about the significant influence of Akron Ohio on the life and legacy of basketball legend LeBron James. Born in Akron LeBron’s early years were shaped by the city’s community spirit and challenges. The support from local mentors and his time at St. Vincent-St. Mary High School were pivotal in his development. Beyond his basketball career LeBron’s deep connection to Akron is evident through his philanthropic efforts particularly the LeBron James Family Foundation and the I PROMISE School. These initiatives aim to provide educational opportunities and support to underprivileged children in his hometown. LeBron’s story is a testament to the impact of his roots showcasing his dedication to giving back and inspiring others.
How it works
LeBron James often hailed as one of the greatest basketball players of all time was born on December 30 1984 in Akron Ohio. Akron a city in the northeastern part of the state is known for its rich history in the rubber and tire industry. However for sports enthusiasts Akron is more than just a historical industrial hub; it is the birthplace of a basketball legend whose impact on the game transcends generations.
Akron’s role in shaping LeBron James cannot be overstated.
Growing up in this mid-sized city LeBron was exposed to both the challenges and opportunities that defined his early life and career. Akron with its diverse socio-economic landscape presented a unique backdrop for his formative years. The city’s community spirit coupled with its struggles provided LeBron with a grounded perspective and an indomitable will to succeed.
From a young age LeBron showed prodigious talent on the basketball court. His early years were marked by the support of his mother Gloria James who worked tirelessly to provide for him. The community of Akron played a crucial role in LeBron’s development with local mentors and coaches recognizing his potential and nurturing his skills. St. Vincent-St. Mary High School where LeBron attended became the launchpad for his meteoric rise. The school located in the heart of Akron witnessed some of the earliest glimpses of his greatness with LeBron leading their basketball team to national prominence.
LeBron’s connection to Akron goes beyond basketball. The city’s influence is evident in his philanthropic efforts. In 2011 he established the LeBron James Family Foundation which has been instrumental in providing educational opportunities and resources to underprivileged children in Akron. One of the foundation’s most notable initiatives is the “I PROMISE” program which aims to support and mentor at-risk students ensuring they graduate and pursue higher education. This initiative led to the opening of the I PROMISE School in 2018 a public school in Akron dedicated to helping the city’s most vulnerable students.
The I PROMISE School is a testament to LeBron’s commitment to his roots. It symbolizes his belief in giving back to the community that shaped him. The school provides a holistic approach to education offering not only academic support but also addressing the social and emotional needs of its students. LeBron’s hands-on involvement in the school’s development highlights his dedication to making a lasting impact on Akron.
LeBron’s legacy in Akron is not confined to education and philanthropy. His presence has revitalized the city’s sense of pride and unity. Each time he returned to Ohio during his NBA career particularly during his tenure with the Cleveland Cavaliers Akron felt the ripple effects of his success. His championships with the Cavaliers in 2016 brought immense pride to the state with Akron celebrating alongside Cleveland.
Beyond his material accomplishments LeBron’s life narrative inspires many people in Akron and beyond. His transformation from a difficult childhood in Akron to a world-famous athlete epitomizes the idea that greatness can come from any situation. LeBron’s accomplishments serve as an example of the value of perseverance hard effort and loyalty to one’s roots.
In conclusion Akron Ohio is an integral component of LeBron James’ personality and heritage and is more than just the place of his birth. His achievements in both his personal and professional life clearly reflect the city’s effect on him. LeBron’s dedication to Akron is demonstrated by his charitable endeavors and involvement in the community which highlights the close bond he has with his hometown. Akron is a constant and serves as a reminder of LeBron’s beginnings even as he continues to inspire and affect people worldwide.
Cite this page
Akron's Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James. (2024, Jul 06). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/akrons-influence-on-the-legacy-of-lebron-james/
"Akron's Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James." PapersOwl.com , 6 Jul 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/akrons-influence-on-the-legacy-of-lebron-james/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Akron's Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/akrons-influence-on-the-legacy-of-lebron-james/ [Accessed: 7 Jul. 2024]
"Akron's Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James." PapersOwl.com, Jul 06, 2024. Accessed July 7, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/akrons-influence-on-the-legacy-of-lebron-james/
"Akron's Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James," PapersOwl.com , 06-Jul-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/akrons-influence-on-the-legacy-of-lebron-james/. [Accessed: 7-Jul-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Akron's Influence on the Legacy of LeBron James . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/akrons-influence-on-the-legacy-of-lebron-james/ [Accessed: 7-Jul-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Essays by Karen Anderson: Awake at Night

My mother told me that when she was a little girl, there were times she couldn’t sleep at night. “I would lie in bed and imagine that somewhere in the world a single gas station was open,” she said. “Then I didn’t feel so lonely and could go back to sleep.”
Her story comforted me, too, when I was awake in the quiet darkness. I could picture that same gas station—the pump out front and a light on inside, with one guy at a desk reading a magazine. Somehow, the world wasn’t so scary and I wasn’t so alone.
Of course, even when my mother was a child, there must have been a hospital open at night or a police station. And after all, it was daytime on the other side of the planet. But those things don’t necessarily occur to a small child. They didn’t occur to me.
Just recently, I remembered my mother’s imaginary gas station when I couldn’t sleep—and thought that today , there are countless businesses open twenty-four hours. And I wondered, why am I not comforted?
Because everything feels too wide-awake now, too round-the-clock, nonstop. Hectic, demanding, exhausting. I can’t find the OFF button—for the world, or for my mind. So, I picture that single gas station, with a light on inside.

by George Orwell
- 1984 Summary
The novel's protagonist, Winston Smith , is a citizen of Oceania, one of the world's three superstates (along with Eurasia and Eastasia). It is the year 1984, and Winston lives in Airstrip One, which used to be known as Great Britain. Winston is a member of the Party, which rules Oceania under the principles of Ingsoc (English Socialism). Oceania is an oligarchy, under hierarchical rule. The Party consists of Inner Party members, who are the ruling elite, and regular Party members, who are citizens of Oceania. Outside of the Party are the proles, non-Party members and simple people who live in poverty and are free from Party regulations. The Party's leader is Big Brother , and there are massive images of his kind visage, complete with dark hair and a substantial mustache, displayed throughout London, some accompanied by the words "Big Brother is Watching You." The Party's three slogans are: "War is Peace," "Freedom is Slavery," and "Ignorance is Strength."
Winston lost his parents and little sister during the Revolutionary period that destroyed capitalism and instituted Ingsoc in Oceania. He was placed in a Party orphanage and integrated into the Party system. Now he works in the Records Department of the Ministry of Truth, which handles all Party publications and propaganda, altering previously published Party publications to ensure that the Party's version of the Past is never questioned. Such alterations often remove a person from history, or make previously flawed predictions accurate. The other three ministries are the Ministry of Love, which handles all Party prisoners, the Ministry of Peace, which handles war, and the Ministry of Plenty, which manages the production of Party goods, including Victory cigarettes, Victory gin, and Victory coffee, all of which are of extremely poor quality.
Winston has never quite accepted the principles of Ingsoc and the Party. He believes in an unalterable past, and finds Party politics reprehensible. Winston wishes for privacy, intimacy, freedom and love, but cannot express any of this in the open for fear of death. Such thoughts constitute "throughtcrimes," which are highly punishable offenses resulting in arrest, imprisonment, torture, and often death.
When the book opens, Winston is at home during his lunch break. He has returned to his apartment in the Victory Mansions, a dilapidated Party housing building, to write in a diary, a relic of the past he obtained from an old junk shop. Winston's apartment is meager, and like every other Party member's home, contains a telescreen. The telescreen transmits Party information and propaganda, and also allows the Thought Police to watch and listen to Party members at all times. In Oceania, there is no such thing as privacy. Winston is fortunate to have a small nook in his apartment out of the view of the telescreen, and it is in this nook that he begins to write in his diary, despite his overwhelming fear of being caught. Undoubtedly, Winston will eventually be caught, imprisoned, and tortured by the Thought Police. For now, however, he chooses to forge ahead with his rebellion.
Winston writes of various memories, all related to the Party and his life. Many include violent imagery, which is quite common in the age of Oceania, and reveal anti-Party feelings. Winston clearly does not subscribe to Party doctrine. Winston is briefly interrupted at one point by a knock on his door. At first he panics, thinking he has already been caught, but it is only his neighbor, Mrs. Parsons , who needs help unclogging her sink. Winston obliges, and interacts briefly with Mrs. Parsons' two hellish children who are members of the Spies and Youth League, and clearly powerfully indoctrinated in the ways of the Party. Winston predicts that eventually these children will turn their loyal, simple, innocent parents into the Thought Police. Such tragedies, it seems, are quite common.
Winston returns to his diary, and in one of his reveries reflecting on the past and his memories and dreams, finds himself writing "DOWN WITH BIG BROTHER" in large letters over and over on the page. Eventually, time runs out and Winston must return to work, which he enjoys. Once Winston found a newspaper clipping among his daily assignments that proved the innocence of three men: Jones, Aaronson, and Rutherford. In examining the clipping, he knew it meant the Party was wrong, and that he had real evidence of an accurate version of the past. Rather than risk discovery, however, he destroyed the clipping, placing it in a memory hole that sucked it into the building's internal furnaces.
At the Ministry of Truth Winston is surrounded by loyal Party members, and is always on guard to prevent his true feelings from being perceived by others. At work, Winston sits through the daily Two Minutes Hate, which rails against Oceania's enemy, Eurasia, and the supposed leader of the opposition movement, Emmanuel Goldstein. The propaganda is powerful, and the people around him begin shouting at the screen. Of course, Winston must join in to avoid suspicion.
Finding himself increasingly curious about the past, Winston wanders the streets, among the proles. He believes that if there is hope for a successful rebellion, it lies in the proles. Winston meets an old man in a prole pub and questions him about life before the Revolution. To his frustration, the man focuses on his own personal memories rather than on the generalities and conceptual differences Winston is interested in. Winston returns to the junk shop where he bought his diary and purchases a glass paperweight with a piece of coral inside. The proprietor, a kind old man named Mr. Charrington , shows him a room above the shop and Winston thinks about what it might be like to rent it out and live among old things, free from the constant presence of the telescreen.
At work and on his walk, Winston sees a dark-haired girl who is seemingly a violently loyal Party member and apparently has taken notice of him. He fears she is a member of the Thought Police. One day, at the Ministry of Truth, the girl slips him a note after falling down in the hallway, requiring Winston's assistance. The note says "I love you." Winston is astounded, but extremely excited by the possibility of a love affair. The affair must be secret, as the Party is entirely against any sort of sexual pleasure. In fact, sexual repression is a tenet of Ingsoc. The Party must approve every marriage, and it is unacceptable for a man and a woman to express any physical attraction for one another. All energy must be devoted to the Party. Winston was once in such a marriage. His wife Katharine was a frigid, mindless woman who was extremely loyal to the Party, but thought sex was a vile activity. However, she regularly scheduled times for her and Winston to make love, calling it her "duty to the Party." She had been taught from childhood that she must bear children.
With a great deal of effort to remain undetected, the girl finally tells Winston where and how they can meet. On a Sunday afternoon, he travels into the country, as per Julia 's instructions, to meet her in a secluded clearing in a wooded area. Finally, they can speak. Winston learns that her name is Julia, they discuss their beliefs regarding the Party, and they begin their love affair. At one point, Winston notices that the secluded spot she has led them to exactly matches a place he constantly sees in his dreams that he has termed the Golden Country.
Winston and Julia, who has a knack for finding abandoned locales and for obtaining black market goods such as real coffee, bread and sugar, continue to meet in secret. They are limited to interacting only in public places and having only the most minimal conversations, but the two discover a mutual hatred of the Party and eventually fall in love. Winston believes that it is possible to overthrow the Party, while Julia is satisfied simply living a double life. On the surface, she is loyal to the extreme, a member of the Junior Anti-Sex League, a volunteer in many Party activities, and a vocal participant in loyalty-testing events such as the Two Minutes Hate. On the inside, she thinks of it all as a game. She hates the Party and all it stands for, but knows she can do nothing to change it.
Eventually Winston rents the room above Mr. Charrington's flat. Winston and Julia meet often in the room, which is simply furnished, with an old twelve-hour clock (the Party uses twenty-four hour time), and a picture of an old London church, St. Clement's Dane. Mr. Charrington taught him the first lines of an old poem about the church, "Oranges and lemons say the bells of St. Clement's," and Julia knows a few more lines that her grandfather taught her when she was very small. Outside their window, a middle-aged prole woman is constantly hanging her wash and singing simple prole songs, many of which have been created by machines in the Ministry of Truth specifically for the proles.
Another Party member suddenly takes on an important role in Winston's life. Winston has always noticed O'Brien at the Ministry of Truth. He seems to be an intelligent man, and Winston believes in his heart that O'Brien feels the same way he does about the Party. Once, during the Two Minutes Hate, the two men locked eyes and Winston felt sure of O'Brien's thoughts. In a dream, Winston once heard someone tell him, "We will meet in the place where there is no darkness," and he believes the voice to have been O'Brien's. For Winston, O'Brien represents the possibility of an underground movement. Perhaps the Brotherhood, led my Emmanuel Goldstein, is real.
O'Brien approaches Winston at work under the pretense of discussing the Tenth Edition of the Newspeak Dictionary (Newspeak is the official language of Oceania, and its goal is to reduce and simplify vocabulary). O'Brien gives Winston his home address, supposedly so he can come pick up an advance copy of the new book. Winston takes the slip of paper with amazement. He knows that O'Brien has approached him because he is part of the underground movement. His true path towards rebellion has begun.
After some time, Winston and Julia visit O'Brien, an Inner Party member who has a lush apartment, a servant, and the freedom to turn off his telescreen. Winston renounces the Party and discusses his belief in the Brotherhood. O'Brien welcomes Winston and Julia into the Brotherhood and tells them that they must be willing to do anything to work towards its cause. They agree, but say that they will not do anything that would prevent them from seeing each other ever again. O'Brien tells Winston that he will give him a copy of Goldstein's book, and outlines a complicated version of events that will lead toward the exchange. Winston leaves after a final toast with O'Brien, in which Winston finishes O'Brien's statement, saying that they "will meet in the place with no darkness."
During Hate Week, the Party's enemy becomes Eastasia rather than Eurasia, and Winston must spend a great deal of time at work, sometimes even staying overnight, to "correct" all Party publications previously referring to war with Eurasia. The Party is at war with Eastasia, and has always been at war with Eastasia. In the midst of Hate Week, a man brings Winston a brief case, suggests that he dropped it, and leaves. The book is inside. When he has finally completed the Hate Week corrections, Winston escapes to Mr. Charrington's apartment and begins to read. Julia arrives, and he reads aloud to her about the history of Oceania, capitalism versus totalitarianism, and the main goals of the Party. Most of this information Winston already knows, but he finds it helpful to read it in the detailed, clear words of Emmanuel Goldstein.
Winston and Julia eventually fall asleep. The wake hours later, and go to stand at the window. Winston repeats his oft-stated phrase, "We are the dead." Suddenly, a voice coming from the wall echoes him, "You are the dead." There is a telescreen hidden behind the picture of St. Clement's Dane. They are caught. The Thought Police storm the room. Mr. Charrington walks in, and it becomes clear that he is a member of the Thought Police. He has been disguised as a kind old man, but is far younger than Winston imagined, with different hair and eyes. Winston and Julia are arrested, separated, and brought to the Ministry of Love.
While in a holding cell, Winston sees men from the Ministry of Truth come and go. Each has been arrested for thoughtcrime. Parsons arrives, and it turns out that his daughter turned him in, claiming to have heard him say "Down with Big Brother" in his sleep. Winston's prediction, it appears, was sadly accurate. In his holding cell, Winston sees a great deal of violence, and notices guards constantly referring to "Room 101," a phrase that seems to instill great fear in some of the prisoners.
Eventually, O'Brien arrives. It becomes clear that he was never part of the underground movement, but actually works in the Ministry of Love. Winston's entire interaction with O'Brien was a ruse. Winston is removed from the holding cell, and his torture begins. At first the torture is extremely violent, and he is forced to admit to a litany of crimes he did not commit, including murder and espionage. Eventually, the torture becomes less violent and O'Brien takes over. He begins to break Winston's spirit, telling him that his memory is flawed and that he is insane. Winston's discussions with O'Brien dwell on the nature of the past and reality, and reveal much about the Party's approach to those concepts. The Party, O'Brien explains with a lunatic intensity, seeks absolute power, for power's own sake. This is why it will always be successful, is always right, and will ultimately control the entire world. Winston cannot argue; every time he does, he is faced with obstinate logical fallacies, a completely different system of reasoning that runs counter to all reason. Winston believes in a past that never existed, and is hounded by false memories. To be cured, Winston must overcome his own insanity and win the war against his own mind.
Little by little, O'Brien shows Winston, with the use of electric shock machines, beatings and starvation, the way of the Party. He forces Winston to accept that if the Party says so, two plus two equals five. Winston had once written in his diary that freedom meant being able to say that two plus two is four. His final attempt to argue with O'Brien ends in O'Brien showing Winston himself in the mirror. Winston is beyond horrified to see that he has turned into a sickly, disgusting sack of bones, beaten into a new face. Broken to the core, Winston finally submits to his re-education. He is no longer beaten, is fed at regular intervals, is allowed to sleep (though the lights, of course, never go out), and begins to regain his health. Although seemingly making progress in accepting the reality of the Party, Winston is still holding onto the last remaining kernel of himself and his humanity: his love for Julia. This comes out when, in the midst of a dream, Winston cries aloud, "Julia! Julia! Julia, my love! Julia!"
O'Brien's last efforts with Winston are focused on forcing him to betray Julia. He takes Winston to Room 101, containing the worst thing in the world, which is different for everyone. For Winston, "the worst thing in the world" is a rat. Winston is tied to a chair, and O'Brien begins to attach a mask/cage contraption containing huge, hungry, carnivorous rats to his face. Winston feels a desperate, deep, panicked fear. He cannot take it, and finally screams for O'Brien to put someone else in his place - anyone, even Julia. O'Brien has succeeded.
Winston, a damaged, changed, empty shell of a man, is released into the world. In his new life, he sees Julia once, by chance, but they are no longer in love. Each betrayed the other, and prison changed them powerfully. There is no hope for their relationship. Winston obtains a somewhat trivial, meaningless job that pays surprisingly well. He spends his time at the Chestnut Tree Cafe drinking Victory Gin and playing chess. His life is buried in gin. In the final pages of the novel, we find Winston in his regular seat at the cafe, drinking gin, playing chess, and waiting for a report from the front in Central Africa, where Eurasia (Oceania was always at war with Eurasia) has invaded. He is excited about the report, because with this invasion, Eurasia might actually be able to break Oceania's line of defense and put the entire nation at risk for takeover. A Eurasian success in Central Africa might mean the end of the Party. Before the report comes, Winston suddenly recalls a very happy day in his childhood spent playing board games with his mother and little sister. He pushes it out of his mind, realizing it is a false memory and resolving to allow fewer of those to creep up on him. Eventually, the report reveals that Oceania has succeeded in repelling the Eurasian advance. There is jubilation on the telescreen and in the streets. Staring into the eyes of a poster of Big Brother, Winston realizes that he knew this news would come. With tears dripping down his face, Winston realizes he has finally completed the rehabilitation he started in the Ministry of Love. He loves Big Brother.

1984 Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for 1984 is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
Describe O’Briens apartment and lifestyle. How do they differ from Winston’s?
From the text:
It was only on very rare occasions that one saw inside the dwelling-places of the Inner Party, or even penetrated into the quarter of the town where they lived. The whole atmosphere of the huge block of flats, the richness and...
What was the result of Washington exam
Sorry, I'm not sure what you are asking here.
how is one put into the inner or outer party in the book 1984
The Outer Party is a huge government bureaucracy. They hold positions of trust but are largely responsible for keeping the totalitarian structure of Big Brother functional. The Outer Party numbers around 18 to 19 percent of the population and the...
Study Guide for 1984
1984 study guide contains a biography of George Orwell, literature essays, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- Character List
Essays for 1984
1984 essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of 1984 by George Orwell.
- The Reflection of George Orwell
- Totalitarian Collectivism in 1984, or, Big Brother Loves You
- Sex as Rebellion
- Class Ties: The Dealings of Human Nature Depicted through Social Classes in 1984
- 1984: The Ultimate Parody of the Utopian World
Lesson Plan for 1984
- About the Author
- Study Objectives
- Common Core Standards
- Introduction to 1984
- Relationship to Other Books
- Bringing in Technology
- Notes to the Teacher
- Related Links
- 1984 Bibliography
Wikipedia Entries for 1984
- Introduction
- Writing and publication
- Career Advice
Anatomy of an AI Essay
How might you distinguish one from a human-composed counterpart? After analyzing dozens, Elizabeth Steere lists some key predictable features.
By Elizabeth Steere
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

baona /iStock/Getty images Plus
Since OpenAI launched ChatGPT in 2022, educators have been grappling with the problem of how to recognize and address AI-generated writing. The host of AI-detection tools that have emerged over the past year vary greatly in their capabilities and reliability. For example, mere months after OpenAI launched its own AI detector, the company shut it down due to its low accuracy rate.
Understandably, students have expressed concerns over the possibility of their work receiving false positives as AI-generated content. Some institutions have disabled Turnitin’s AI-detection feature due to concerns over potential false allegations of AI plagiarism that may disproportionately affect English-language learners . At the same time, tools that rephrase AI writing—such as text spinners, text inflators or text “humanizers”—can effectively disguise AI-generated text from detection. There are even tools that mimic human typing to conceal AI use in a document’s metadata.
While the capabilities of large language models such as ChatGPT are impressive, they are also limited, as they strongly adhere to specific formulas and phrasing . Turnitin’s website explains that its AI-detection tool relies on the fact that “GPT-3 and ChatGPT tend to generate the next word in a sequence of words in a consistent and highly probable fashion.” I am not a computer programmer or statistician, but I have noticed certain attributes in text that point to the probable involvement of AI, and in February, I collected and quantified some of those characteristics in hopes to better recognize AI essays and to share those characteristics with students and other faculty members.
I asked ChatGPT 3.5 and the generative AI tool included in the free version of Grammarly each to generate more than 50 analytical essays on early American literature, using texts and prompts from classes I have taught over the past decade. I took note of the characteristics of AI essays that differentiated them from what I have come to expect from their human-composed counterparts. Here are some of the key features I noticed.
AI essays tend to get straight to the point. Human-written work often gradually leads up to its topic, offering personal anecdotes, definitions or rhetorical questions before getting to the topic at hand.
AI-generated essays are often list-like. They may feature numbered body paragraphs or multiple headings and subheadings.
The paragraphs of AI-generated essays also often begin with formulaic transitional phrases. As an example, here are the first words of each paragraph in one essay that ChatGPT produced:
- “In contrast”
- “Furthermore”
- “On the other hand”
- “In conclusion.”
Notably, AI-generated essays were far more likely than human-written essays to begin paragraphs with “Furthermore,” “Moreover” and “Overall.”
AI-generated work is often banal. It does not break new ground or demonstrate originality; its assertions sound familiar.
AI-generated text tends to remain in the third person. That’s the case even when asked a reader response–style question. For example, when I asked ChatGPT what it personally found intriguing, meaningful or resonant about one of Edgar Allan Poe’s poems, it produced six paragraphs, but the pronoun “I” was included only once. The rest of the text described the poem’s atmosphere, themes and use of language in dispassionate prose. Grammarly prefaced its answer with “I’m sorry, but I cannot have preferences as I am an AI-powered assistant and do not have emotions or personal opinions,” followed by similarly clinical observations about the text.
AI-produced text tends to discuss “readers” being “challenged” to “confront” ideologies or being “invited” to “reflect” on key topics. In contrast, I have found that human-written text tends to focus on hypothetically what “the reader” might “see,” “feel” or “learn.”
AI-generated essays are often confidently wrong. Human writing is more prone to hedging, using phrases like “I think,” “I feel,” “this might mean …” or “this could be a symbol of …” and so on.
AI-generated essays are often repetitive. An essay that ChatGPT produced on the setting of Rebecca Harding Davis’s short story “Life in the Iron Mills” contained the following assertions among its five brief paragraphs: “The setting serves as a powerful symbol,” “the industrial town itself serves as a central aspect of the setting,” “the roar of furnaces serve as a constant reminder of the relentless pace of industrial production,” “the setting serves as a catalyst for the characters’ struggles and aspirations,” “the setting serves as a microcosm of the larger societal issues of the time,” and “the setting … serves as a powerful symbol of the dehumanizing effects of industrialization.”
Editors’ Picks
- DEI Ban Prompts Utah Colleges to Close Cultural Centers, Too
- Supreme Court Decision Weakens Education Department
- The Only Certainty Is Uncertainty
AI writing is often hyperbolic or overreaching. The quotes above describe a “powerful symbol,” for example. AI essays frequently describe even the most mundane topics as “groundbreaking,” “vital,” “esteemed,” “invaluable,” “indelible,” “essential,” “poignant” or “profound.”
AI-produced texts frequently use metaphors, sometimes awkwardly. ChatGPT produced several essays that compared writing to “weaving” a “rich” or “intricate tapestry” or “painting” a “vivid picture.”
AI-generated essays tend to overexplain. They often use appositives to define people or terms, as in “Margaret Fuller, a pioneering feminist and transcendentalist thinker, explored themes such as individualism, self-reliance and the search for meaning in her writings …”
AI-generated academic writing often employs certain verbs. They include “delve,” “shed light,” “highlight,” “illuminate,” “underscore,” “showcase,” “embody,” “transcend,” “navigate,” “foster,” “grapple,” “strive,” “intertwine,” “espouse” and “endeavor.”
AI-generated essays tend to end with a sweeping broad-scale statement. They talk about “the human condition,” “American society,” “the search for meaning” or “the resilience of the human spirit.” Texts are often described as a “testament to” variations on these concepts.
AI-generated writing often invents sources. ChatGPT can compose a “research paper” using MLA-style in-text parenthetical citations and Works Cited entries that look correct and convincing, but the supposed sources are often nonexistent. In my experiment, ChatGPT referenced a purported article titled “Poe, ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ and the Gothic’s Creation of the Unconscious,” which it claimed was published in PMLA , vol. 96, no. 5, 1981, pp. 900–908. The author cited was an actual Poe scholar, but this particular article does not appear on his CV, and while volume 96, number 5 of PMLA did appear in 1981, the pages cited in that issue of PMLA actually span two articles: one on Frankenstein and one on lyric poetry.
AI-generated essays include hallucinations. Ted Chiang’s article on this phenomenon offers a useful explanation for why large language models such as ChatGPT generate fabricated facts and incorrect assertions. My AI-generated essays included references to nonexistent events, characters and quotes. For example, ChatGPT attributed the dubious quote “Half invoked, half spontaneous, full of ill-concealed enthusiasms, her wild heart lay out there” to a lesser-known short story by Herman Melville, yet nothing resembling that quote appears in the actual text. More hallucinations were evident when AI was generating text about less canonical or more recently published literary texts.
This is not an exhaustive list, and I know that AI-generated text in other formats or relating to other fields probably features different patterns and tendencies . I also used only very basic prompts and did not delineate many specific parameters for the output beyond the topic and the format of an essay.
It is also important to remember that the attributes I’ve described are not exclusive to AI-generated texts. In fact, I noticed that the phrase “It is important to … [note/understand/consider]” was a frequent sentence starter in AI-generated work, but, as evidenced in the previous sentence, humans use these constructions, too. After all, large language models train on human-generated text.
And none of these characteristics alone definitively point to a text having been created by AI. Unless a text begins with the phrase “As an AI language model,” it can be difficult to say whether it was entirely or partially generated by AI. Thus, if the nature of a student submission suggests AI involvement, my first course of action is always to reach out to the student themselves for more information. I try to bear in mind that this is a new technology for both students and instructors, and we are all still working to adapt accordingly.
Students may have received mixed messages on what degree or type of AI use is considered acceptable. Since AI is also now integrated into tools their institutions or instructors have encouraged them to use—such as Grammarly , Microsoft Word or Google Docs —the boundaries of how they should use technology to augment human writing may be especially unclear. Students may turn to AI because they lack confidence in their own writing abilities. Ultimately, however, I hope that by discussing the limits and the predictability of AI-generated prose, we can encourage them to embrace and celebrate their unique writerly voices.
Elizabeth Steere is a lecturer in English at the University of North Georgia.

A Nonprofit Says Colleges Spend Big on DEI. Is It ‘Wildly’ Overstating the Case?
American Transparency publishes spending investigations under the moniker OpenTheBooks but doesn’t say where it gets
Share This Article
More from teaching.

Our students have been drifting away, Helen Kapstein writes, but we want them to drift back to the mindset of being c

We See You, Student Parents
Alex Rockey recommends eight principles for transforming academic access for them through mobile-friendly courses.

Beyond the Research
Michel Estefan offers a roadmap for helping graduate student instructors cultivate their distinct teaching style.
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE

Revealed: Harvard Business School’s New MBA Essays For Applicants
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on Reddit

Harvard Business School’s Baker Library.
With just 10 weeks before its first application deadline on Sept. 4th, Harvard Business School today (June 25) revealed a newly revised application for MBA candidates, including a new set of three short essays along with a refresh on how it will evaluate applicants for future classes.
The new prompts?
Business-Minded Essay : Please reflect on how your experiences have influenced your career choices and aspirations and the impact you will have on the businesses, organizations, and communities you plan to serve. (up to 300 words)
Leadership-Focused Essay : What experiences have shaped who you are, how you invest in others, and what kind of leader you want to become? (up to 250 words)
Growth-Oriented Essay : Curiosity can be seen in many ways. Please share an example of how you have demonstrated curiosity and how that has influenced your growth. (up to 250 words)
NEW HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL ESSAYS PUT THROUGH BY NEW MBA ADMISSIONS CHIEF
Eagerly awaited by thousands of prospective students and admission consultants, you can bet that the admissions pages of the HBS website were continually refreshed all morning for a glimpse at the new essay. The Harvard Business School essay prompt for the Class of 2027 was posted at 10:30 a.m. with the opening of the 2024-2025 application online.
This year’s change was put through by Rupal Gadhia , who joined the school as managing director of admissions and financial aid last October. A 2004 Harvard MBA, Gadhia came to the school with no previous admissions experience, having been the global head of marketing for SharkNinja robots.
In explaining the change in a blog post , Gadhia noted that “we have refreshed the criteria on which we evaluate candidates. We are looking for applicants who are business-minded, leadership-focused, and growth-oriented…This is your opportunity to discuss meaningful or formative experiences that are important to you that you haven’t had a chance to fully explore elsewhere in your application…Be authentic, be yourself.”
WHAT HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL IS REALLY LOOKING FOR IN THE NEW ESSAYS
The school added some context to its new criteria for admission, more clearly defining what it means by business-minded, leadership-focused, and growth-oriented.
Business-Minded
We are looking for individuals who are passionate about using business as a force for good – who strive to improve and transform companies, industries, and the world. We are seeking those who are eager to solve today’s biggest problems and shape the future through creative and integrated thinking. Being business-minded is about the interest to help organizations succeed, whether in the private, public, or non-profit sector. This business inclination can be found in individuals with a variety of professional and educational experiences, not just those who come from traditional business backgrounds.
In Your Application: We will look for evidence of your interpersonal skills, quantitative abilities, and the ways in which you plan to create impact through business in the future.
Leadership-Focused
We are looking for individuals who aspire to lead others toward making a difference in the world, and those who recognize that to build and sustain successful organizations, they must develop and nurture diverse teams. Leadership takes many forms in many contexts – you do not have to have a formal leadership role to make a difference. We deliberately create a class that includes different kinds of leaders, from the front-line manager to the startup founder to the behind-the-scenes thought leader.
In Your Application: Your leadership impact may be most evident in extracurriculars, community initiatives, or your professional work.
Growth-Oriented
We are looking for individuals who desire to broaden their perspectives through creative problem solving, active listening, and lively discussion. At HBS you will be surrounded by future leaders from around the world who will make you think more expansively about what impact you might have. Our case and field-based learning methods depend on the active participation of curious students who are excited to listen and learn from faculty and classmates, as well as contribute their own ideas and perspectives.
In Your Application: We will look for the ways in which you have grown, developed, and how you engage with the world around you.
TIGHTER TIMEFRAME FOR ROUND ONE APPLICANTS
The new essay prompts come nearly two months after candidates to the school’s MBA program would more typically know what was expected of them. Some admission consultants say the delay over the prompt’s release, along with nearly a month’s slow down in releasing application deadlines, is “wildly insensitive” to applicants who will have less time than normal to prepare for the round one deadline of Sept. 4th.
That’s especially true because the most successful applicants to HBS have highly demanding jobs that consume the vast majority of their time. Many candidates go through multiple drafts of their essays to get them as close to perfection as humanly possible. MBA admission consultants are expecting a lot of up-to-the-deadline work this year to help prep candidates for Harvard and other top business schools.
The new application still preserves the post-interview reflection for applicants who are invited to a 30-minute admissions interview. Within 24 hours of the interview, candidates are required to submit a written reflection through the school’s online application system.
REACTION TO THE NEW CHANGE IS MIXED
Early reaction to the change suggests the likelihood of mixed reviews. “This is an uninspired and odd set of questions,” says Sandy Kreisberg, founder of HBSGuru.com and an MBA admissions consultant who closely reads the tea leaves of Harvard’s admissions process. “I don’t know how it’s different from what else do you want us to know about you, frankly,” he adds in a reference to last year’s single essay prompt.
“HBS has certainly moved from the abstract to the concrete,” believes Jeremy Shinewald, founder and CEO of mbaMission, a leading MBA admissions consulting firm. “Some applicants previously felt like they didn’t know where to start and some weren’t sure if they had answered the question, even when they were done. Now, the questions are quite straightforward and all have a cause and effect relationship — one where the applicant discusses the past to reveal the present or future. Smart applicants will understand how to share their experiences and, more importantly, how to relay their values. Some will mistakenly try to whack HBS over the head with stories of their epic feats, but the key isn’t to brag or embellish – the key is to simply create a clear relationship, via narrative, between past experience and true motivations.”
Shinewald found it astonishing that Harvard could not have made the change earlier. “It is, of course, surprising that HBS left applicants on edge until the last minute, all to create very traditional essays,” he adds. “As applicants learn in MBA classrooms, change can be hard and take time. The bottom line here is that these essays are somewhat of an applicant’s dream – they allow the savvy applicant to play to their strengths and draw on their best anecdotes and experiences to create a complete story. Some applicants will lament the absence of a ‘Why HBS?’ prompt, but my guess is that the admissions committee recognized that they would get an almost homogenous collection of essays touting the case method and other well known features. HBS gets some kudos for keeping the focus on the applicant.”
Adds Petia Whitmore of My MBA Path: “I think they reflect one of the traits of this new generation of candidates which is that they don’t handle ambiguity well. So it seems like Harvard had to spell out what they’re looking for way more prescriptively than in the past.”
Some, however, find the new essays a return to the past. “To me, the prompts feel quite regressive, and a return to the more formulaic approach that pervaded MBA applications two decades ago,” believes Justin Marshall, a New York-based MBA admissions consultant. “Because the previous prompt was so open ended, it forced applicants to be introspective and self-aware. You couldn’t just ramble for 900 words; you had to identify themes in your life to show how your personal experiences shaped your values, your leadership style, and your goals. Comparatively, these new prompts are much more paint-by-numbers. Applicants will likely cover the same ground in terms of topic, but there’s very little room for nuance and self-expression. I think it will be harder for applicants with less conventional backgrounds and experiences to differentiate themselves. I’m sure HBS grew tired of reading so many painfully earnest ‘life story’ essays, but I suspect they’ll soon find themselves yearning for essays that have a heartbeat and personality. 250 words just doesn’t allow for that unless you’re a very crafty writer.”
Whatever the case, getting into Harvard’s MBA program is still a daunting exercise. Last year, 1,076 of the 8,264 candidates who applied for admission to Harvard Business School gained admission, an acceptance rate of 13.2%, making HBS the second most selective prestige MBA program in the country after Stanford Graduate School of Business which had an admit rate of 8.4%. Harvard saw a 15.4% drop in MBA applications from the 9,773 it received a year-earlier.
Joint degree applicants for the Harvard Medical School, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, Harvard Law School, and Harvard Kennedy School must provide an additional essay: How do you expect the joint degree experience to benefit you on both a professional and a personal level? (up to 400 words)
BIGGEST CHANGE IN HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL ESSAY IN NEARLY A DECADE
Joint degree applicants for the Harvard Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences must provide an additional essay: The MS/MBA Engineering Sciences program is focused on entrepreneurship, design, and innovation. Describe your past experiences in these areas and your reasons for pursuing a program with this focus. (recommended length: 500 words). Applicants will also be able to respond to an optional essay.
In any case, it’s the biggest change in Harvard Business School’s application in nearly a decade. The last time HBS made a major switch, moving to the essay prompt it just eliminated, was in 2016. That change to just one essay with no word limit and a post-interview reflection was made by then admissions chief Dee Leopold.
When Leopold applied to Harvard as an MBA candidate in 1978, she had to write eight essays. Over her years as managing director of admissions, she first cut the essays down to four and then one, making it optional, and finally the one last prompt with a post-interview reflection, saying that applying to HBS should not be a writing contest .

OUR BUSINESS CASUAL PODCAST: The New HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL MBA Application: Fortuna Admissions’ Caroline Diarte-Edwards and ApplicantLab’s Maria Wich-Vila join P&Q’s John A. Byrne to offer applicant advice on how to answer the new HBS essay prompts
DON’T MISS: 2024-2024 MBA APPLICATION DEADLINES or HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL WILL NOW UPDATE ITS MBA ESSAY
Questions about this article? Email us or leave a comment below.
- Stay Informed. Sign Up! Login Logout Search for:

Advice Column: Insider Tips For Your MBA Applications

What Harvard Business School Really Wants: How To Ace The HBS Essay

How To Ace The INSEAD Video Questions

Why Are MBA Application Goals Important?
- How To Use Poets&Quants MBA Admissions Consultant Directory
- How To Select An MBA Admissions Consultant
- MBA Admission Consulting Claims: How Credible?
- Suddenly Cozy: MBA Consultants and B-Schools
- The Cost: $6,850 Result: B-School
Our Partner Sites: Poets&Quants for Execs | Poets&Quants for Undergrads | Tipping the Scales | We See Genius
More From Forbes
How not to write your college essay.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
If you are looking for the “secret formula” for writing a “winning” college essay, you have come to the wrong place. The reality is there is no silver bullet or strategy to write your way to an acceptance. There is not one topic or approach that will guarantee a favorable outcome.
At the end of the day, every admission office just wants to know more about you, what you value, and what excites you. They want to hear about your experiences through your own words and in your own voice. As you set out to write your essay, you will no doubt get input (both sought-after and unsolicited) on what to write. But how about what NOT Notcoin to write? There are avoidable blunders that applicants frequently make in drafting their essays. I asked college admission leaders, who have read thousands of submissions, to share their thoughts.
Don’t Go In There
There is wide consensus on this first one, so before you call on your Jedi mind tricks or predictive analytics, listen to the voices of a diverse range of admission deans. Peter Hagan, executive director of admissions at Syracuse University, sums it up best, saying, “I would recommend that students try not to get inside of our heads. He adds, “Too often the focus is on what they think we want.”
Andy Strickler, dean of admission and financial aid at Connecticut College agrees, warning, “Do NOT get caught in the trap of trying to figure out what is going to impress the admission committee. You have NO idea who is going to read your essay and what is going to connect with them. So, don't try to guess that.” Victoria Romero, vice president for enrollment, at Scripps College adds, “Do not write about something you don’t care about.” She says, “I think students try to figure out what an admission officer wants to read, and the reality is the reader begins every next essay with no expectations about the content THEY want to read.” Chrystal Russell, dean of admission at Hampden-Sydney College, agrees, saying, “If you're not interested in writing it, we will not be interested when reading it.” Jay Jacobs, vice provost for enrollment management at the University of Vermont elaborates, advising. “Don’t try to make yourself sound any different than you are.” He says, “The number one goal for admission officers is to better understand the applicant, what they like to do, what they want to do, where they spend the majority of their time, and what makes them tick. If a student stays genuine to that, it will shine through and make an engaging and successful essay.”
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
Don’t Be Artificial
The headlines about college admission are dominated by stories about artificial intelligence and the college essay. Let’s set some ground rules–to allow ChatGPT or some other tool to do your work is not only unethical, it is also unintelligent. The only worse mistake you could make is to let another human write your essay for you. Instead of preoccupying yourself with whether or not colleges are using AI detection software (most are not), spend your time focused on how best to express yourself authentically. Rick Clark is the executive director of strategic student success at Georgia Institute of Technology, one of the first institutions to clearly outline their AI policy for applicants. He says, “Much of a college application is devoted to lines, boxes, and numbers. Essays and supplements are the one place to establish connection, personality, and distinction. AI, in its current state, is terrible at all three.” He adds, “My hope is that students will use ChatGPT or other tools for brainstorming and to get started, but then move quickly into crafting an essay that will provide insight and value.”
Don’t Overdo It
Michael Stefanowicz, vice president for enrollment management at Landmark College says, “You can only cover so much detail about yourself in an admission essay, and a lot of students feel pressure to tell their life story or choose their most defining experience to date as an essay topic. Admission professionals know that you’re sharing just one part of your lived experience in the essay.” He adds, “Some of the favorite essays I’ve read have been episodic, reflecting on the way you’ve found meaning in a seemingly ordinary experience, advice you’ve lived out, a mistake you’ve learned from, or a special tradition in your life.” Gary Ross, vice president for admission and financial aid at Colgate University adds, “More than a few applicants each year craft essays that talk about the frustration and struggles they have experienced in identifying a topic for their college application essay. Presenting your college application essay as a smorgasbord of topics that ultimately landed on the cutting room floor does not give us much insight into an applicant.”
Don’t Believe In Magic
Jason Nevinger, senior director of admission at the University of Rochester warns, “Be skeptical of anyone or any company telling you, ‘This is the essay that got me into _____.’ There is no magic topic, approach, sentence structure, or prose that got any student into any institution ever.” Social media is littered with advertisements promising strategic essay help. Don’t waste your time, energy, or money trying to emulate a certain style, topic, or tone. Liz Cheron is chief executive officer for the Coalition for College and former assistant vice president of enrollment & dean of admissions at Northeastern University. She agrees with Nevinger, saying “Don't put pressure on yourself to find the perfect, slam dunk topic. The vast majority of college essays do exactly what they're supposed to do–they are well-written and tell the admission officer more about the student in that student's voice–and that can take many different forms.”
Don’t Over Recycle
Beatrice Atkinson-Myers, associate director of global recruitment at the University of California at Santa Cruz tells students, “Do not use the same response for each university; research and craft your essay to match the program at the university you are interested in studying. Don't waste time telling me things I can read elsewhere in your application. Use your essay to give the admissions officer insights into your motivations, interests, and thinking. Don't make your essay the kitchen sink, focus on one or two examples which demonstrate your depth and creativity.” Her UC colleague, Jim Rawlins, associate vice chancellor of enrollment management at the University of California at San Diego agrees, saying “Answer the question. Not doing so is the surest way we can tell you are simply giving us a snippet of something you actually wrote for a different purpose.”
Don’t Overedit
Emily Roper-Doten, vice president for undergraduate admissions and financial assistance at Clark University warns against “Too many editors!” She says, “Pick a couple of trusted folks to be your sounding board when considering topics and as readers once you have drafts. You don’t want too many voices in your essay to drown you out!” Scripps’ Romero agrees, suggesting, “Ask a good friend, someone you trust and knows you well, to read your essays.” She adds, “The goal is for the admission committee to get to know a little about you and who better to help you create that framework, than a good friend. This may not work for all students because of content but helps them understand it’s important to be themselves.” Whitney Soule, vice provost and dean of admissions at The University of Pennsylvania adds, “Avoid well-meaning editorial interference that might seem to polish your writing but actually takes your own personal ‘shine’ right out of the message.” She says, “As readers, we connect to applicants through their genuine tone and style. Considering editorial advice for flow and message is OK but hold on to the 'you' for what you want to say and how you want to say it.”
Don’t Get Showy
Palmer Muntz, senior regional admissions counselor at the University of Alaska Fairbanks cautions applicants, “Don’t be fancier than you are. You don’t need to put on airs.” He adds, “Yes, proofread your work for grammar and spelling, but be natural. Craft something you’d want to read yourself, which probably means keeping your paragraphs short, using familiar words, and writing in an active voice.” Connecticut College’s Strickler agrees, warning, “Don't try to be someone you are not. If you are not funny, don't try to write a funny essay. If you are not an intellectual, trying to write an intellectual essay is a bad idea.”
Anthony Jones, the vice president of enrollment management at Loyola University New Orleans offers a unique metaphor for thinking about the essay. He says, “In the new world of the hyper-fast college admission process, it's become easy to overlook the essential meaning of the college application. It's meant to reveal Y...O...U, the real you, not some phony digital avatar. Think of the essay as the essence of that voice but in analog. Like the completeness and authenticity captured in a vinyl record, the few lines you're given to explain your view should be a slow walk through unrestrained expression chock full of unapologetic nuances, crevices of emotion, and exactness about how you feel in the moment. Then, and only then, can you give the admissions officer an experience that makes them want to tune in and listen for more.”
Don’t Be A Downer
James Nondorf, vice president and dean of admissions and financial aid at The University of Chicago says, “Don’t be negative about other people, be appreciative of those who have supported you, and be excited about who you are and what you will bring to our campus!” He adds, “While admissions offices want smart students for our classrooms, we also want kind-hearted, caring, and joyous students who will add to our campus communities too.”
Don’t Pattern Match
Alan Ramirez is the dean of admission and financial aid at Sewanee, The University of the South. He explains, “A big concern I have is when students find themselves comparing their writing to other students or past applicants and transform their writing to be more like those individuals as a way to better their chances of offering a more-compelling essay.” He emphasizes that the result is that the “essay is no longer authentic nor the best representation of themselves and the whole point of the essay is lost. Their distinctive voice and viewpoint contribute to the range of voices in the incoming class, enhancing the diversity of perspectives we aim to achieve.” Ramirez simple tells students, “Be yourself, that’s what we want to see, plus there's no one else who can do it better than you!”
Don’t Feel Tied To A Topic
Jessica Ricker is the vice president for enrollment and dean of admissions and financial aid at Skidmore College. She says, “Sometimes students feel they must tell a story of grief or hardship, and then end up reliving that during the essay-writing process in ways that are emotionally detrimental. I encourage students to choose a topic they can reflect upon positively but recommend that if they choose a more challenging experience to write about, they avoid belaboring the details and instead focus on the outcome of that journey.” She adds, "They simply need to name it, frame its impact, and then help us as the reader understand how it has shaped their lens on life and their approach moving forward.”
Landmark College’s Stefanowicz adds, “A lot of students worry about how personal to get in sharing a part of their identity like your race or heritage (recalling last year’s Supreme Court case about race-conscious admissions), a learning difference or other disability, your religious values, LGBTQ identity…the list goes on.” He emphasizes, “This is always your choice, and your essay doesn’t have to be about a defining identity. But I encourage you to be fully yourself as you present yourself to colleges—because the college admission process is about finding a school where your whole self is welcome and you find a setting to flourish!”
Don’t Be Redundant
Hillen Grason Jr., dean of admission at Franklin & Marshall College, advises, “Don't repeat academic or co-curricular information that is easily identifiable within other parts of your application unless the topic is a core tenant of you as an individual.” He adds, “Use your essay, and other parts of your application, wisely. Your essay is the best way to convey who your authentic self is to the schools you apply. If you navigated a situation that led to a dip in your grades or co-curricular involvement, leverage the ‘additional information’ section of the application.
Thomas Marr is a regional manager of admissions for the Americas at The University of St Andrews in Scotland and points out that “Not all international schools use the main college essay as part of their assessment when reviewing student applications.” He says, “At the University of St Andrews, we focus on the supplemental essay and students should avoid the mistake of making the supplemental a repeat of their other essay. The supplemental (called the Personal Statement if using the UCAS application process) is to show the extent of their passion and enthusiasm for the subject/s to which they are applying and we expect about 75% of the content to cover this. They can use the remaining space to mention their interests outside of the classroom. Some students confuse passion for the school with passion for their subject; do not fall into that trap.”
A Few Final Don’ts
Don’t delay. Every college applicant I have ever worked with has wished they had started earlier. You can best avoid the pitfalls above if you give yourself the time and space to write a thoughtful essay and welcome feedback openly but cautiously. Don’t put too much pressure on yourself to be perfect . Do your best, share your voice, and stay true to who you are.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Samsung Unpacked 2024
- Best early Prime Day deals
- Smart highway coming to Michigan
- iPad Air M2 hits record-low price
- Prime Day 'Fire' sale
YouTube film essay pioneers 'Every Frame a Painting' are back
And the duo behind it will release a short film on july 20..
Between 2014 and 2016, a YouTube channel called Every Frame a Painting posted 28 video essays critiquing movies and dissecting different aspects of filmmaking before it went silent. Taylor Ramos and Tony Zhou, the people behind the channel, talked about how Robin Williams was a master at blocking and using movement to portray his characters, as well as how Steven Spielberg does one long takes all the time that tend to go unnoticed by the public, among many other topics. Now, the duo is back, promising another series of video essays followed by the debut of a short film at Fantasia International Film Festival on July 20.
Ramos and Zhou wrote and directed their upcoming film called The Second starring Paul Sun-Hyung Lee and Ethan Hwan. They didn't share a lot of details about the movie, but the film festival's website says it's about "an alternate version of today’s world where dueling is still acceptable" in which Philip "must perform the role of 'Second' on the day of his only son's duel."
Every Frame a Painting has over 2 million subscribers on YouTube and was one of the creators that helped legitimize video essays on the website. Ramos and Zhou also created the Netflix series Voir , produced by David Fincher, which featured video essays about film, as well. Seeing as they promised new posts on YouTube before their film premieres, we'll likely see them upload a fresh batch of videos in the coming days.
- Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Looking for 1984 essay tips? Use our free samples as guidelines. If you need rush essays, simply place an order and your papers will be delivered before the deadline. Hook Examples for "1984" Essays. The Dystopian Warning Hook. Open your essay by discussing George Orwell's "1984" as a prophetic warning against totalitarianism and government ...
99.95 ATAR & 3 x State Ranker. The following essay was written by Project Academy English Teacher, Marko Beocanin. Marko's Achievements: 8th in NSW for English Advanced (98/100) Rank 1 in English Advanced, Extension 1 and Extension 2. School Captain of Normanhurst Boys High School. 99.95 ATAR. Marko kindly agreed to share his essay and ...
While the ending to 1984 may seem final, Orwell lays the clues for a much more subtle ending open for discussion. ... In his essay Why I Write (1946), Orwell outlines his political development: ... Essays by George Orwell. You and the Atom Bomb (1945) Politics and the English Language (1946) The Prevention of Literature (1946) Why I Write (1946)
We can help you master your essay analysis of 1984 by taking you through the summary, context, key characters and themes. We'll also help you ace your upcoming English assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online! We've supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years, and on average our students ...
As Orwell was writing 1984 in 1948, television was just emerging from the developmental hiatus forced upon the broadcasting industry by World War II. Many people were worried, in the late 1940s ...
1984. The fear of a dystopian future that is explored in both Fritz Lang's film Metropolis and George Orwell's novel Nineteen Eighty Four is reflective of the values of the societies at the time and the context of the authors. As authors are considered... 1984 essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by ...
Critical Evaluation. Nineteen Eighty-Four is one of the keenest pieces of satire to be written in the twentieth century. It was George Orwell's last novel, written between 1946 and 1949 and ...
Essays for 1984. 1984 essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of 1984 by George Orwell. The Reflection of George Orwell; Totalitarian Collectivism in 1984, or, Big Brother Loves You; Sex as Rebellion; Class Ties: The Dealings of Human Nature Depicted through Social ...
Critical Overview. When 1984 was published, critics were impressed by the sheer power of George Orwell's grim and horrifying vision of the future. They praised Orwell's gripping prose, which ...
By ending your essay with a thought-provoking conclusion, you leave your readers with a lasting impression and demonstrate the relevance and impact of your arguments. For instance, you might conclude with a statement: "Orwell's '1984' serves as a chilling reminder of the power of propaganda and manipulation, urging contemporary ...
10. 1984′ Book Review: Anomalies and Paradoxes of Human Behaviour. 11. Theme, Setting and Symbolism in 1984: an Overview of Orwell's Novel. 12. 1984 Compared to Today: George Orwell's Use of Themes in the Novel. 13. 1984 Compared to Today: Comparison of Technology in the Book and Today. 14. The Characterization And Orwell's Mood In 1984 ...
Essays for 1984. 1984 essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of 1984 by George Orwell. The Reflection of George Orwell; Totalitarian Collectivism in 1984, or, Big Brother Loves You; Sex as Rebellion; Class Ties: The Dealings of Human Nature Depicted through Social ...
Winston knows that life is not meant to be lived as it is in Oceania, and he tries to construct his ideal society out of fragments of dreams, nursery rhymes, and his love for Julia. Their affair ...
A Succesful Conclusion to 1984. Decent Essays. 943 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. A novel's ending plays a very important role on the way it is perceived; for example, a novel could have a great plot and character development but having a dissatisfying ending will just make the reader want to toss it directly into the trash can. In his novel ...
Essay Example: LeBron James often hailed as one of the greatest basketball players of all time was born on December 30 1984 in Akron Ohio. Akron a city in the northeastern part of the state is known for its rich history in the rubber and tire industry. ... In conclusion Akron Ohio is an integral component of LeBron James' personality and ...
Humor and Honesty: The student's humor makes the essay enjoyable to read, while her honesty about her challenges adds depth. Self-Awareness: She demonstrates a strong sense of self-awareness ...
My mother told me that when she was a little girl, there were times she couldn't sleep at night. "I would lie in bed and imagine that somewhere in the world a single gas station was open," she said. "Then I didn't feel so lonely and could go back to sleep." Her story comforted me, too ...
Start writing essays early to allow time for research and editing. Grab the reader's attention immediately with a compelling story. Answer questions directly with sound grammar and style. With so ...
Essays for 1984. 1984 essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of 1984 by George Orwell. The Reflection of George Orwell; Totalitarian Collectivism in 1984, or, Big Brother Loves You; Sex as Rebellion; Class Ties: The Dealings of Human Nature Depicted through Social ...
AI-generated essays are often repetitive. An essay that ChatGPT produced on the setting of Rebecca Harding Davis's short story "Life in the Iron Mills" contained the following assertions among its five brief paragraphs: "The setting serves as a powerful symbol," "the industrial town itself serves as a central aspect of the setting ...
Essays and criticism on George Orwell's 1984 - Suggested Essay Topics. Select an area of the website to search ... "1984 - Suggested Essay Topics." MAXnotes to 1984, edited by Dr. M. Fogiel, ...
Part-photography collection (with more than 50 of her own black-and-white images), part-essay collection (featuring 17 contributors), Hanusik's own Louisiana story documents the state's coastal ...
The last time HBS made a major switch, moving to the essay prompt it just eliminated, was in 2016. That change to just one essay with no word limit and a post-interview reflection was made by then admissions chief Dee Leopold. When Leopold applied to Harvard as an MBA candidate in 1978, she had to write eight essays.
5. Cutting down the choice of words diminishes the range of thought. 6. The "A" vocabulary consists of words needed for everyday life, words already in existence. 7. The "A" vocabulary ...
At the end of the day, every admission office just wants to know more about you, what you value, and what excites you. They want to hear about your experiences through your own words and in your ...
Between 2014 and 2016, a YouTube channel called Every Frame a Painting posted 28 video essays critiquing movies and dissecting different aspects of filmmaking before it went silent. Taylor Ramos ...
Complete summary of George Orwell's 1984. eNotes plot summaries cover all the significant action of 1984. ... Start an essay Ask a ... Essays and Criticism