

Technological Environment of Business: Definition, Factors, Examples, and Strategy
Table of Contents
What is a Technological Environment?
The technological environment of business encompasses external elements within technology that impact business operations. Changes in technology can reshape how a company operates, prompting significant shifts in the organization’s strategies.
It resides in the company’s external realm , is tied to technological developments, and holds the potential for both threats and opportunities. This facet is a vital component of the business environment , influencing operations and functions.
As a key aspect of PESTLE analysis , technological factors wield substantial influence on businesses globally, especially in today’s tech-dependent scenario. This realm signifies the state of technological advancement and its impact on a country’s economy, shaping progress in both scientific and economic realms.
How Technological Environment Affect Business?
The technological environment transforms businesses by shaping how they operate. Innovations impact everything from production to customer interactions. It can lead to higher productivity, cost reduction, and new product offerings.
However, it can also render existing products obsolete. Businesses must adapt to automation, digital marketing, and remote work. Staying current with tech trends is crucial for growth and competitiveness.
Related: Socio-Cultural Environment of Business
Factors of Technological Environment
Let’s look at the six key factors of the technological environment which affect the operations of organizations.
Innovations and Advancements
Technological innovations like new inventions and discoveries can revolutionize how a business operates. They bring opportunities for improved products, services, and processes. For example, the introduction of smartphones led to new ways of communication and changed how companies interact with customers.
Automation and Efficiency
Automation involves using machines and software to perform tasks previously done by humans. It boosts efficiency, reduces errors, and saves time. For instance, factories now use robots for assembly, leading to faster and more precise production.
Digital Transformation
Businesses are adopting digital tools and platforms to streamline operations and engage with customers. Digitalization enables online sales, data analysis, and personalized marketing. Companies that embrace this trend often have better customer experiences and reach a wider audience.
Data Management and Analytics
The ability to gather, analyze, and utilize data is crucial. It helps in making informed decisions, predicting trends, and understanding customer preferences. For instance, e-commerce platforms track user behavior to recommend products, enhancing sales.
E-commerce and Online Presence
The rise of e-commerce has transformed the way businesses sell products. Having an online presence through websites and social media is essential for reaching a global audience. This impacts sales, brand visibility, and customer engagement.
Cybersecurity and Privacy
As technology advances, so do cyber threats. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring customer privacy is paramount. Companies invest in cybersecurity measures to prevent breaches that could damage their reputation and result in financial losses.
Related : Economic Environment of Business
Examples of Affecting Technological Environment On Business
Here are four examples of how the technological environment affects businesses:
E-commerce Revolution
The rise of e-commerce has transformed the way companies sell and customers buy. Online shopping platforms allow businesses to reach a global audience and provide customers the convenience to shop from anywhere, impacting sales and expanding market reach.
Technology enables the automation of tasks, from manufacturing to customer service. Machines and software handle repetitive jobs, reducing errors and saving time. This efficiency leads to cost savings for businesses and improved quality for customers.
Data-driven Insights
Advanced tools let businesses collect and analyze data about customer behavior and market trends. This information helps in making informed decisions, creating personalized marketing strategies, and tailoring products and services to meet customer preferences.
Digital Marketing Dominance
Traditional advertising has shifted to digital platforms. Social media, search engines, and online ads reach target audiences more effectively. This change in marketing channels requires businesses to adapt their strategies, engaging customers through various online avenues.
Read Also: Political Environment of Business
Strategies To Minimize the Threats of Technological Environment
Along with various benefits, technological factors also provide threats to business organizations. Companies must overcome these threats in order to be competitive. Here are the five strategies you can employ in your business.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Stay updated about technological trends through regular learning. Embrace new tools and practices that align with your business goals. This flexibility ensures your company is prepared to adapt swiftly to changing tech landscapes.
Diversification and Redundancy
Don’t rely solely on one technology or platform. Have backup systems in place to ensure smooth operations if a technological failure occurs. This minimizes the risk of disruptions affecting your business.
Cybersecurity Measures
Invest in robust cybersecurity to protect your digital assets. Use strong passwords, encryption, and firewall systems to shield sensitive information from potential threats like data breaches or hacking.
Customer-Centric Approach
Understand your customers’ preferences and how they use technology. Tailor your products or services to meet their needs, making it more likely they’ll continue engaging with your business in the face of changing tech trends.
Collaboration and Networking
Connect with peers, experts, and industry associations. Collaborate to share insights and potential tech challenges. By working together, you can gain a collective understanding of how to navigate and address threats in the technological landscape.
Read Next: 10 Pros and 7 Cons of PESTLE Analysis

By profession, Sujan Chaudhary is a BBA (Bachelor in Business Administration) graduate, and by passion a blogger. He loves to share his business knowledge with the rest of the world. While not writing, he will be found reading and exploring the world.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Not logged in
Technological factors affecting business, page actions.
- View source
Technological factors affecting business (also called technological forces ) are all externally generated changes in technologies and processes which are used (or may be used) by the company or its competitors. Proper identification of this factor during strategic analysis ( PEST analysis , STEEP analysis , SWOT analysis , TOWS analysis ) could lead to better strategic decision about investments and development of the organization . Rapid technological development in modern economy requires quick and flexible reactions of managers to better adapt and to survive in turbulent competitive environment .
- 1 Technological factors connected to information revolution
- 2 Legislation of technological processes
- 3 Technological advances in production systems and logistics
- 4 Technological advances in business process management
- 5 References
Technological factors connected to information revolution
The information revolution refers to the rapid advancement of digital technologies and the widespread availability of information through the internet and other digital platforms. Some technological factors connected to the information revolution that can affect businesses include:
- The rapid development of advanced communication networks such as 5G, which enables faster data transfer and improves the connectivity of devices, has led to new opportunities for businesses to communicate and collaborate with customers, suppliers, and partners.
- The growing efficiency of computer systems , including the development of faster processors, larger database and memory capacity, and improved storage technology , has led to increased productivity and efficiency in various industries.
- The global reach of the internet has made it possible for businesses to easily access information about their competitors and the market , providing insights into new opportunities and trends.
- The emergence of web 2.0 and newer technologies, such as social media and collaboration tools, has made it easier for businesses to engage with customers and build relationships through dynamic communication and feedback.
- New IT security challenges : With the increasing amount of sensitive information being stored and transmitted electronically, businesses must constantly adapt to new IT security challenges. For example, encryption is used to protect data from unauthorized access, certificates are used to verify the identity of websites and users, SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are used to secure online transactions, and various other technologies are used to protect against malware, phishing, and other cyber threats.
- Internet infrastructure : The availability and speed of internet access is becoming increasingly important for businesses, as more and more transactions and communications are conducted online. The use of fiber optics and other advanced technologies is improving internet speed and reliability , and mobile capabilities are allowing businesses to reach customers and employees in more remote locations.
- Internet banking and shopping : The rise of e-commerce has made it possible for businesses to sell products and services online, and internet banking has made it easier for businesses to manage their finances. However, these developments have also brought new security risks, such as the risk of fraud and theft.
- Distribution of non-material goods over the internet : Many businesses are now distributing non-material goods such as music, movies, e-books, and software over the internet, rather than through traditional physical channels. This has led to new business models and has made it easier for businesses to reach global customers.
- Social media influence on marketing : Social media platforms have become an important tool for businesses to connect with customers and build brand awareness. Businesses use social media to share content and engage with customers, and social media influencers have become an important part of the marketing mix .
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization) activities : SEO refers to the process of optimizing a website to improve its visibility in search engine results. Businesses use SEO to increase their visibility on search engines and drive more traffic to their websites.
- Capabilities of CRM systems : CRM ( Customer Relationship Management ) systems are used by businesses to manage and analyze customer interactions and data. Modern CRM systems are able to track customer interactions across multiple channels, including social media, and provide businesses with insights into customer behavior and preferences.
- Information system security : The security of business information systems is a critical concern, as a security breach can lead to the loss of sensitive data and the disruption of business operations. Standards such as ISO 27001 provide guidelines for securing information systems and protecting against cyber threats.
Overall, the information revolution has had a significant impact on businesses, providing new opportunities and tools for growth and innovation , while also presenting challenges that need to be addressed.

Legislation of technological processes
Legislation of technological processes refers to laws and regulations that govern the development, use, and impact of technology . Some examples of legislation related to technology include:
- Privacy laws concerning customer privacy and data security : Privacy laws are designed to protect the personal information of individuals and businesses from being collected, stored, or used without their consent. These laws can include provisions related to data security, data breaches, and data retention, as well as regulations about how companies can use personal information for marketing and other purposes.
- Patents law and intellectual property legislation : Patents and intellectual property laws are designed to protect the rights of inventors, authors, and other creators of original works. These laws can include provisions related to patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, and they can have a significant impact on businesses, particularly those in the technology industry .
- Cybercrime protection, data protection, and cyber security laws: Cybercrime is a rapidly growing problem, as hackers and other cybercriminals use technology to steal sensitive information, disrupt business operations, and commit other crimes. Cybercrime protection laws, data protection laws, and cyber security laws are designed to protect against these types of crimes, and they can include provisions related to cybercrime reporting, data retention, and incident response.
- Government spending on technological research : Governments invest in technological research to promote innovation and economic growth. This can include funding for basic and applied research, as well as for the development of new technologies, such as renewable energy and autonomous systems.
- Government actions in areas of education and training of highly competent engineers and technology users : Governments also invest in education and training programs to ensure that the workforce has the necessary skills to support technological innovation. This can include funding for science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) education, as well as for training programs in specific areas, such as cybersecurity and data analytics.
- Regulations concerning licensing of technologies : Governments also regulate the licensing of technologies to ensure that they are used in a safe and responsible manner. This can include regulations related to the licensing of software, hardware, and other technologies, as well as regulations related to the use of technologies in specific industries, such as healthcare and transportation.
- Regulations concerning online money transfer , offshore accounts and protection against competitive technologies from abroad: Governments also regulate the use of online money transfer and offshore accounts to prevent money laundering , tax evasion , and other financial crimes. They also regulate the import and export of technology products to protect domestic businesses from unfair competition from abroad.
These laws and regulations can have a significant impact on businesses and technology companies, as they can shape the development and use of technology and affect their operations and bottom line. Companies must be aware of and comply with relevant laws and regulations to avoid penalties and legal liabilities.
Technological advances in production systems and logistics
- New machinery and services : New machinery and services can greatly improve the efficiency and productivity of a business, but it also requires significant investment and training for employees to use these new technologies.
- Equipment : Upgraded equipment can improve the quality and speed of production , but it also requires regular maintenance and may have higher costs associated with it.
- Research and development software : CAD/CAM, CIM, and simulation software are important tools for research and development, but they also require specialized skills and knowledge to use effectively.
- Environmentally friendly technologies : Environmentally friendly technologies can help reduce the environmental impact of a business, but it also requires changes in production processes and additional costs for implementation.
- Reduced need for manual labor : Automation and robotization can greatly increase productivity and efficiency, but it also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for retraining of employees.
- Better productivity, speed of work and accuracy: New technologies can improve productivity, speed, and accuracy, but it also requires businesses to adapt to new processes and tools.
- Shorter life cycles of technology increase cost of updating of machinery : The rapid pace of technological change can make it difficult for businesses to keep up with the latest advancements, and the cost of updating machinery can be significant.
- New generations of equipment could be incompatible with old : New generations of equipment can be incompatible with older versions, which can lead to higher costs of service and a lack of spare parts.
- Smart technologies : Smart technologies such as the Internet of Things can greatly improve the efficiency and productivity of a business, but it also requires businesses to adapt to new technologies and processes.
- Cooperation with scientific institutions allows faster implementation of innovative product and technological ideas : Collaboration with scientific institutions can accelerate the development and implementation of new products and technologies, but it also requires businesses to navigate the complex landscape of academic research and intellectual property laws.
- Lowering of health hazards for workers : New technologies can greatly improve the health and safety of workers, but it also requires businesses to invest in new equipment and processes, as well as training for employees.
Technological advances in business process management
- BPNM software : BPNM (Business Process and Network Management) software allows businesses to monitor and manage their processes and network, but it also requires businesses to have a clear understanding of their processes and networks in order to effectively use the software.
- Work-flow software : Work-flow software allows businesses to simulate and optimize complex business processes, but it also requires businesses to have a clear understanding of their processes in order to effectively use the software.
- MRP, ERP and other types of integrated IT systems : MRP (Material Resource Planning ) and ERP ( Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are integrated IT systems that allow businesses to manage their resources, but it also requires businesses to have a clear understanding of their processes in order to effectively use the software.
- Outsourcing of production to other countries : Outsourcing production to other countries can allow businesses to take advantage of technological capabilities, logistics networks, and lower labor costs, but it also requires businesses to navigate the complexities of international trade and cultural differences.
- Supply chain capabilities of producers and suppliers allowing easy integration of complex processes, faster delivery speeds: Advancements in supply chain management technologies have made it possible for businesses to easily integrate complex processes and achieve faster delivery speeds, but it also requires businesses to have a clear understanding of their supply chain and supplier capabilities.
- New transport routes and means : New transport routes and means can improve the quality and cost efficiency of transport, but it also requires businesses to adapt to new transport systems and logistics networks.
- Possibility to retain organizational knowledge in IT supported knowledge bases : IT-supported knowledge bases allow businesses to retain organizational knowledge, but it also requires businesses to have a clear understanding of their processes and knowledge management systems.
- Technological forces used in area of organizational development : Technological forces can be used to improve organizational development, but it also requires businesses to have a clear understanding of their processes and organizational development strategies.
Check also other:
- Social and cultural factors affecting business
- Economic factors affecting business
- Ecological factors affecting business
- Political factors affecting business
- Legal factors affecting business
- Ethical factors affecting business
| — |
| — — — — — — — — |
- Croteau, A. M., & Bergeron, F. (2001). An information technology trilogy: business strategy, technological deployment and organizational performance . The journal of strategic information systems, 10(2), 77-99.
- Edelman, L. B., & Suchman, M. C. (1997). The legal environments of organizations . Annual review of sociology, 479-515.
- Pearce, J. A., Robinson, R. B., & Subramanian, R. (2000). Strategic management : Formulation, implementation, and control . Columbus, OH: Irwin/McGraw-Hill.
- Ritter, T., & Gemünden, H. G. (2004). The impact of a company's business strategy on its technological competence, network competence and innovation success . Journal of business research, 57(5), 548-556.
- Coccia, M. (2014). Driving forces of technological change: the relation between population growth and technological innovation: analysis of the optimal interaction across countries. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 82, 52-65.
Author: Krzysztof Wozniak
- Strategic management methods
- Recent changes
- Random page
- Page information
Table of Contents
- Special pages
User page tools
- What links here
- Related changes
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- This page was last edited on 18 November 2023, at 03:49.
- Content is available under CC BY-SA Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International unless otherwise noted.
- Privacy policy
- About CEOpedia | Management online
- Disclaimers
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is PEST Analysis?
- How It Works
- Applications
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
- Financial Analysis
What Is PEST Analysis? Its Applications and Uses in Business
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Investopedia / Ellen Lindner
PEST analysis (political, economic, social, and technological) is a management method whereby an organization can assess major external factors that influence its operation in order to become more competitive in the market. As described by the acronym, those four areas are central to this model.
A popular variation on the PEST analysis format, especially in the U.K., is the PESTLE strategic planning approach, which includes the additional aspects of legal and environmental.
Key Takeaways
- PEST analysis stands for political, economic, social, and technological.
- This type of analysis is used to gauge external factors that could impact the profitability of a company.
- Generally, it is more effective with larger organizations that are more likely to experience the effects of macro events.
- PEST analysis is commonly used in conjunction with SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Understanding PEST Analysis
It is believed that PEST analysis was first introduced under the name ETPS by Harvard professor Francis J. Aguilar. In the 1967 publication "Scanning the Business Environment," Aguilar presented the economic, technical, political, and social factors as being major influences on the business environment. Subsequently, the letters were rearranged to create a convenient and quirky acronym used today.
The core of PEST analysis is the belief that a comprehensive assessment of the major areas of influence that affect the sector in which an organization is positioned, as well as the organization itself, can facilitate more effective strategic planning.
This planning can be undertaken to maximize the organization’s ability to capitalize on conditions as they exist and to be forewarned of and better prepared for imminent changes, allowing the organization to stay ahead of competitors.
Components of PEST Analysis
Political: The political aspect of PEST analysis focuses on the areas in which government policy and/or changes in legislation affect the economy, the specific industry, and the organization in question. Areas of policy that may particularly affect an organization include tax and employment laws. The general political climate of a nation or region, as well as international relations , can also greatly influence the organization.
Economic: The economic portion of the analysis targets the key factors of interest and exchange rates , economic growth, supply and demand , inflation , and recession.
Social: The social factors that may be included in a PEST analysis are demographics and age distribution, cultural attitudes, and workplace and lifestyle trends.
Technological: The technological component considers the specific role and development of technologies within the sector and organization, as well as the wider uses, trends, and changes in technology. Government spending on technological research may also be a point of interest in this area.
Applications of PEST Analysis
PEST analysis can assist an organization in recognizing and thereby capitalizing on opportunities offered by existing conditions in the business environment. It can also be used for identifying current or possible future challenges, allowing for effective planning of how to best manage these challenges.
PEST analysis can also be applied in assessing the in-house structure of an organization in order to identify strengths and weaknesses in its internal politics, economic outlook , social climate, and technology base. The results of this analysis can facilitate changes or improvements in areas identified as subpar.
PEST analysis can be used in conjunction with other forms of strategic business analysis, such as the SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) model, for an even more comprehensive result. Conducting a comparison between these completed analyses can provide a very solid basis for informed decision-making.
What Is PEST vs. PESTLE Analysis?
PEST analysis stands for "political, economic, social, and technological" whereas PESTLE stands for the same but adds "legal" and "environmental" factors to the analysis. These areas are considered when assessing the impact of external factors on a company's profitability.
How Do You Do a PEST Analysis?
To do a PEST analysis, you must consider the different factors under each category (political, economic, social, and technological), and how these factors affect your business. For the political component, you would assess laws, regulations, government policies, and tariffs, for example. For the economic component, some of the topics you would assess would include access to financing, cost of living, interest rates, inflation, and labor costs. For the social component, you would consider consumer trends and behaviors, education, division of wealth, population growth rates, and health. For the technological component, you would assess areas such as artificial intelligence growth, innovation, research and development, social networking, and cybersecurity.
How Often Should a PEST Analysis Be Done?
A PEST analysis can be done as often as a business would like. It is good to perform a PEST analysis when there have been significant changes that may impact a business, such as a change in interest rates, new government policies, or the introduction of new technology. It should be done often so as not to become outdated.
By analyzing the political, economic, societal, and technological factors that impact its business, a company can plan, reorganize, and adjust to these external factors in order to become a more successful operation. A business's success is not only predicated on how well it internally manages its operations but also on how it functions in the larger world. PEST analysis helps it to succeed in that aspect.
Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. “ PESTLE Analysis .”
Rastogi, Nitank and Trivedi, M.K. “ PESTLE Technique—A Tool to Identify External Risks in Construction Projects .” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology , vol. 3, no 1, 2016, pp. 385-386.
PESTLE Analysis. “ What Is PESTLE Analysis? An Important Business Analysis Tool .”
PESTLE Analysis. “ What Is a SWOT Analysis? 2 Examples of What It’s Used For .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SWOTAnalysis_final-899758832a37461c819fc13d7c4b98b2.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Technology Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Technology Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your own Technology business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Technology businesses.
Technology Business Plan Example & Template
Below is a Technology business plan template and sample to help you create each section of your own business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Kearney Tech Inc., located in Houston, Texas is a tech startup that focuses on developing and commercializing new artificial intelligence (AI) technology applications designed for small-to-medium sized businesses. The company has created proprietary technology that helps businesses improve their profitability by using AI to increase customer engagement. We offer multiple products, including AI hardware, marketing AI software, and CRM AI software. Many of our most basic services are free, but the rest can be accessed by paying a subscription fee. By providing flexible and affordable subscription options for our clients, Kearney Tech Inc. aims to be the next big technology company in the AI space for small and medium-sized businesses.
Kearney Tech Inc. was founded and is led by Abigail Kearney. Abigail has been a senior software engineer for nearly 10 years and has extensive experience in artificial intelligence and machine learning. In addition to her experience, she has a bachelor’s degree in computer science and an MBA. Her education and experience are sure to lead Kearney Tech Inc. to success.
Product Offering
Kearney Tech Inc. will showcase a variety of different applications for its AI technology that companies can utilize to increase their customer engagement from day one. Businesses can choose the platform package that works for them, based on a freemium subscription pricing structure.
The following are the services that Kearney Tech Inc. will provide:
- AI Hardware
- Marketing AI Software
- Customer Relationship Management AI Software
- Customer Support AI Software
- Technology Training: Training sessions on how to use our AI solutions and integrate them into their businesses
Customer Focus
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve small to medium-sized businesses within a 30-mile radius of Houston, Texas. Many of the businesses in our target demographic are startups looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer base.
Management Team
Kearney Tech Inc. will also employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office. She will also hire several developers, salesmen, and other administrative staff to assist her.
Success Factors
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: Abigail Kearney has been extremely successful working in the technology industry and will be able to use her previous experience to provide the best service experience. Her unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than Kearney Tech Inc.’s competitors.
- Relationships: Abigail Kearney knows many of the local leaders, business managers, and other influencers within Houston, Texas. With her 10 years of experience and good relationships with business leaders in the area, she will be able to develop an initial client base.
- Proprietary technology : The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
- Client-oriented service: Kearney Tech Inc. will have full-time customer service and sales managers to keep in contact with clients and answer their everyday questions.
Financial Highlights
Kearney Tech Inc. is seeking a total funding of $400,000 of debt capital to open its office. The funding will be dedicated to office design, software development, marketing, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Office design/build: $50,000
- Software development: $150,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $25,000
- Working capital: $25,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Kearney Tech Inc.:
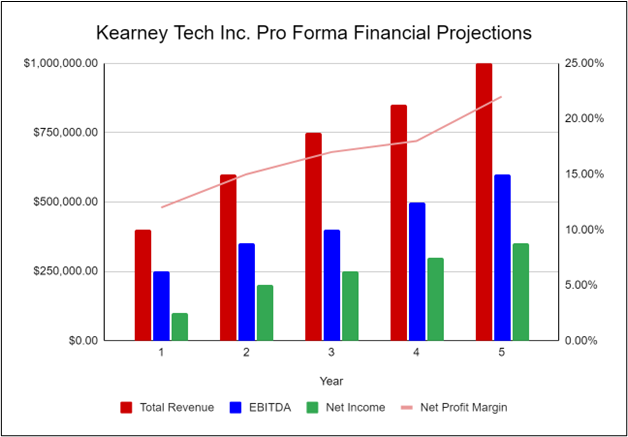
Company Overview
Who is kearney tech inc..
Abigail began researching what it would take to create her own technology company and did a thorough analysis of the costs, market, demographics, and competition. Abigail has compiled enough information to develop her business plan in order to approach investors.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s History
Once her market analysis was complete, Abigail Kearney began surveying the local vacant office space and located an ideal location to house the technology company. Abigail Kearney incorporated Kearney Tech Inc. as a Limited Liability Corporation in April 2023.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located available office space for rent
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Began recruiting key employees
Kearney Tech Inc. Services
Industry analysis.
As of 2021, the global technology industry was valued at approximately $5.2T. Of all countries worldwide, the United States currently has the largest technology market, with 32% of the market share at $1.7T. The technology industry in the U.S. accounts for a large part of the nation’s economy.
The Information Technology market can be segmented by categories such as software, devices, infrastructure IT and business services, emerging technology, and telecom services. In the United States, IT and business services hold the greatest market share (30%), followed by software (20%) and telecom services (20%).
Market drivers include the economy, employment rates, and the digital transformation of daily life for a growing number of people and businesses worldwide. Corporations and organizations are seeking IT service providers that can help improve their software, cybersecurity, data, and infrastructure. Technology companies that can provide products and services that cater to these issues can be competitive in the constantly evolving market.
Technology is an integral part of society. Developments in AI and machine learning are essential to keep society moving forward and make businesses more efficient. Therefore, businesses will always be in need of AI solutions to bring in more customers and streamline their services and products. According to Market Watch, the Technology industry is set to grow at a CAGR of 25.73% from now until 2027. Very few industries see this growth, which shows how much demand there is for technological solutions. Therefore, we expect Kearney Tech Inc. to see great success in our local market.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve the small and medium-sized businesses of Houston, Texas, and the surrounding areas.
Many small businesses in the community are startups or established enterprises looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer engagement.
Customer Segmentation
Kearney Tech Inc. will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Small businesses
- Medium-sized businesses
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Kearney Tech Inc. will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Tekuserv has been a reliable technology company in Houston, Texas for more than fifteen years. The company is known for its wide range of technology solutions that serve many small-to-medium-sized businesses. With its large number of experts focused on delivering customer satisfaction, the organization maintains its high standard of developing quality products and providing exceptional customer service. Tekuserv provides business software on a freemium subscription basis. It develops enterprise technology solutions with a focus on customer relationship management.
Prime AI Business Solutions
Prime AI Business Solutions is a technology development company in Houston, Texas. In business for several years, the company has developed highly-rated AI solutions used by many well-known businesses in a variety of industries. Prime AI Business Solutions now offers a range of AI hardware and software products geared toward helping businesses of all sizes increase their customer base. The company has also introduced a “pay-as-you-grow” pricing model that scales to provide users with more support as they scale up.
AICE Developments
AICE stands for Artificial Intelligence for Customer Engagement. AICE Developments is also a local technology company that manufactures and distributes a variety of technology products. AICE Developments was established in 2009 in Houston, Texas, providing integrated AI applications and platform services. Its products include applications and infrastructure offerings delivered through various IT deployment models, including on-premise deployments, cloud-based deployments, and hybrid deployments. The company serves automotive, financial services, healthcare, hospitality, retail, utilities, construction, etc. It provides AI solutions for enterprise marketing and customer engagement.
Competitive Advantage
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to offer the following advantages over the competition:
- Proprietary technology: The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Kearney Tech Inc. will offer a unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Big-firm expertise in a small-firm environment
- Thorough knowledge of the clients and their varying needs
- Proprietary technology developed by skilled software engineers
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Kearney Tech Inc. is as follows:
Kearney Tech Inc. understands that the best promotion comes from satisfied customers. The company will encourage its clients to refer other businesses by providing economic or financial incentives for every new client produced. This strategy will increase in effectiveness after the business has already been established.
Social Media
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the technology company. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
Kearney Tech Inc. will blanket businesses with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on Kearney Tech Inc., offer discounts, and/or provide other incentives for companies to use the AI platform.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s pricing will be on par with competitors so clients feel they receive great value when purchasing the technology.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Kearney Tech Inc.:
Operation Functions:
- Abigail Kearney will be the Owner and CEO of the company. She will oversee all the operations and executive functions of the company. In the beginning, she will also provide customer support and market/sell AI products to potential clients.
- Abigail will employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office.
- Abigail will also hire several developers to maintain and develop AI products and services.
- Abigail will also hire a solid sales team to sell our products to potential clients. As the company grows, she will also hire a team that is solely dedicated to customer service.
Milestones:
Kearney Tech Inc. will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
5/2023 – Finalize lease agreement
6/2023 – Design and build out Kearney Tech Inc.
7/2023 – Hire and train initial staff
8/2023 – Kickoff of promotional campaign
9/2023 – Launch Kearney Tech Inc.
10/2023 – Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s revenues will come primarily from its technology solution subscription sales. The company will use a freemium subscription model, in which basic functions can be used by any company for free. Additional solutions and support will be available in a tiered package model based on the enterprises’ size and the number of users.
The office lease, equipment, supplies, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Kearney Tech Inc. Ongoing marketing expenditures are also notable cost drivers for Kearney Tech Inc.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average number of clients per month
- Annual rent: $20,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Technology Business Plan FAQs
What is a technology business plan.
A technology business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your technology business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. You can easily complete your Technology business plan using our Technology Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Technology Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of technology businesses, some examples include: Network technology, Software technology, and Customer relationship technology.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Technology Business Plan?
Technology businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Technology Business?
Starting a technology business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Technology Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed technology business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your technology business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your technology business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Technology Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your technology business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your technology business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Technology Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your technology business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your technology business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful Technology business: How to Start a Tech Company

More From Forbes
Five benefits and three challenges technology can bring to global companies.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Computers, the internet, robots and artificial intelligence (AI): these are some of the first things that come to mind when we talk about the technology businesses use. There’s no doubt that they can improve the operations of trade and commerce; they create notable advantages. However, even the most advanced technology products are far from perfect. They often have drawbacks or present challenges before they can deliver benefits. What do global businesses gain from adopting technology?
For a company like ours that supports telecommuting, reliable and faster communication systems are essential. Likewise, when talks about new technology began in our industry, employees' fear that they would be replaced by computers was palpable. Of course, once they understood the tech tools, their fear turned into acceptance. Without any delay, here’s a list of the most important benefits I believe global companies can derive from technology based on my experience using and implementing it. There may not be anything surprising on this list, but it’s worth emphasizing how important these advantages can be for businesses that operate on a worldwide scale.
1. Faster and more reliable communication: For businesses that operate internationally, reliable communication is a must. If telephone lines are not available, you should have readily usable alternatives such as VoIP or live chat. Thanks to the fact that companies have developed numerous methods of communication, global businesses can be sure that their operations will not be easily disrupted. Fast internet connections make it possible to transmit various forms of information across vast distances in seconds. Faster and more reliable communication is also an important factor that enables telecommuting, a work setup that I've found offers its own set of advantages — particularly the potential for lower human resources costs and access to high-quality talent in places that are far from the physical address of a business.
2. Enhanced efficiency and productivity: Technology ushers in efficiency and productivity in many ways. Multinational companies can employ accounting, billing, payroll, asset management and other business software to manage their operations more effectively. On the other hand, technology can help companies automate repetitive tasks that don’t require sophisticated decision-making. This can result in greater productivity and efficiency.
3. Cost reduction and profit boost: I've found that increased efficiency and productivity from technology can result in a decrease in operating costs (and a corresponding increase in profits). Using technology has also helped me avoid opportunity costs, as systems backed by modern tech may be less prone to breaking down or succumbing to avoidable issues.
Also, using advanced communication technologies makes it unnecessary to constantly travel for meetings and supervisory work, as you can carry out these tasks through live video chat and collaboration platforms. This does not mean you should totally eliminate personal meetings and workplace inspections, but rather that you can reduce the need to be physically present in one location to work with other employees. Cost reduction is also a benefit I've seen from the teleworking setup, which is powered by modern technology.
4. Greater transparency and interconnected operations: It’s not easy managing businesses with complex bureaucratic processes and countless types of transactions. However, with the help of advanced business software, you can seamlessly integrate all business processes, even those in locations where you need to use different languages or currencies. When it comes to sharing and processing business data, you can automatically gather, process, and present everything in a form everyone can use.
You can also make accounting, marketing, sales, and other activities of a global business more easily accessible with the right tools. It’s even possible to use multiple types of business software from different developers, as most software nowadays supports integration with third-party software or comes with application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow developers to find ways to integrate other software.
5. Improved security: New technologies such as blockchain can allow businesses to implement better ways to secure business transactions without compromising transparency and creating delaying layers of bureaucracy and security measures. Blockchain could be used to secure financial transactions and the files companies collaborate on , for example.
What are the major challenges of using technology for business?
As I mentioned, the advantages don’t come without hurdles. There are challenges businesses need to deal with, primarily the employees’ resistance to change, lack or inadequacy of training, and choosing the wrong technology.
1. Resistance to change: Some employees simply don’t want to move beyond what they have been accustomed to. They could have a case of technophobia or a fear of trying new things. Either way, it’s something businesses need to address. It may be necessary to conduct demonstrations or seminars to show how technology can greatly benefit business operations and more importantly, how it can make jobs easier. Others may have a fear that technology will take over jobs from humans. Employers can allay such fears by supporting professional development and showing employees that new job opportunities arise as some of the jobs are automated or taken over by artificial intelligence and robots.
2. Lack of or inadequate training: Don’t expect employees to immediately know what to do with the new technology you provide them. To make the most of a tech investment, it’s important to allocate some resources and time for the corresponding training. Some employees may dislike a new system at first but begin to like it after they get properly acquainted with its proper use and the palpable benefits.
3. Wrong choice of technology: This is a mistake on the management's part. If you pick an inappropriate software solution, platform, or piece of equipment, employees may develop an unfavorable perception of these technological augmentations or the adoption of tech-powered systems in general. It’s important to conduct thorough studies first before deciding on a technology to adopt. Aside from the fact that the wrong technology choice can essentially become a loss or unnecessary expenditure, spending money on the wrong tech choice can also drag down your employees' efficiency and productivity.
In my experience, going global inevitably means having to rely on technology. Businesses that refuse to do so may be bound for failure. It’s just important to be well acquainted with the benefits and the challenges that come along the way.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Better Knowledge. Your Insight Is Sharper
Technology Factor. What’s that? Examples and Impacts to Business
Updated: July 6, 2024 · Reviewed by: Ahmad Nasrudin
Technological factors refer to elements related to or using technology. It is the company’s external environment in addition to political , economic , sociodemographic , legal, and environmental factors.
The word ‘technology’ is usually associated with the techniques, tools, devices, and knowledge surrounding it. Technological developments and changes raise threats and opportunities for companies. And it usually happens quickly and dramatically, making the old obsolete and therefore abandoned and disrupting business.
Why is the technological environment important?
The technological environment influences business success in several ways. And in general, changes and developments create opportunities or threats to the business.
But, just like any other external factor. Companies cannot control technological factors. They can only respond to minimize threats and optimize opportunities. Thus, they must be able to adapt to new technological developments.
Flexibility and responsiveness in adapting to new technologies are essential. Early adopters often achieve a higher market share and earn higher returns. They scan trends and technological changes to map potential opportunities and threats, including their impact on the competitive landscape.
Threat and opportunity scanning is the first step before a company formulates a strategy. After understanding what threats and potential opportunities are coming, they try to utilize or build new resources to maximize internal strengths to optimize opportunities while minimizing threats to internal weaknesses. That way, the company can build a sustainable competitive advantage.
Several reasons explain why the technological factor is important. Let’s take three reasons.
First , technological changes have brought new business models and made old ones irrelevant. A good example is how e-commerce replaces the “brick-and-mortar” business model.
Second , new technologies contribute to changes in production processes. It is not only related to more advanced machines and equipment. But, it also stimulates companies to develop new, better techniques because technology often makes what was once impossible possible. Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) is an example.
Third , technological changes advance communication channels. Information technology contributes to reducing operating costs and time, operating efficiency, and becoming a critical managerial tool in business decision-making. For example, email allows companies to send messages to suppliers instantly without going through the mail. The Internet has made it possible for businesses to adopt the official business concept.
How technology factors impact the business
Technological changes not only affect products and how they are marketed. But, it also affects business in several ways.
For example, in a production process, technology can increase total output through increased productivity . Companies can produce more output per unit with the same inputs as before.
In addition, new technologies contribute to reducing operating costs. For example, adopting robotic technology reduces labor. In addition, it also reduces waste with higher precision and reduces human errors.
Increases in output and cost reductions ultimately contribute to increased supply, product variations, and reduced prices. Thus, consumers have more choices to match the money in their pockets.
The technology also allows companies to produce new products. For example, internet technology enables book publishers to launch e-books.
Although some have positive impacts, technological advances also pose risks and threats to business. It makes old products obsolete faster. For example, smartphones with high-resolution cameras reduce interest in conventional camera products, making them all-purpose.
Now, let’s break down how technological changes are affecting business.
Product selling techniques . For example, more stores are turning online. The change had a significant impact on their sales strategy.
Product manufacturing method. For example, automation through robotics and computer-assisted machines replaces human hands.
Market research. Advances in technology gave rise to what we call big data . Marketers find it easier and more accurate to analyze the market with database systems because they can access more data, enabling them to plan their marketing better.
Company management and operations . For example, the Internet and electronic devices have led to remote working, such as working from home, as a common practice today. So, employees do not need to come to the office to work. Instead, they can do it at home, as long as they are connected to the Internet.
Ways to communicate. Many new channels are emerging to facilitate companies in communicating with stakeholders. Websites, social media, and email are examples.
Need for new expertise. For example, companies increasingly need data analysts and programmers to collect, process, and interpret data and process digital information. They are increasingly required to develop data-driven decision-making.
Changing consumer needs and wants. For example, buying a data package for communication services is a new need for consumers because they must stay online daily.
Changing consumer behavior. For example, the Internet makes consumers more price-conscious because they can easily and inexpensively compare products without physically seeing them.
Bring up new competitors. Technology gives rise to competitors with new business models. E-Commerce is a good example.
Examples of how technological change is transforming business
Research and development (R&D) has driven innovation in various business areas, including those related to products, business processes, or production techniques. The results are 3D printers, smartphones, electric cars, and self-driving cars.
Big data allows companies to access more accurate data, which enables them to plan and make better decisions.
Technology allows companies to capture data from various sources, including internal networks, websites, and social media. Advances in analytical techniques, software, and computer processing capabilities have allowed them to extract deeper information from this data.
E-Commerce allows consumers to shop anywhere and anytime via their smartphone. It saves them cost and time.
For example, they no longer need to visit a retail store. In addition, they find it easier to compare prices between products, reducing switching costs and strengthening their bargaining power.
Robotics allows companies to design, construct, and operate production facilities with minimal human assistance. That enables them to produce on a mass scale. In addition, precision increases due to less human error.
3D printers allow us to quickly create models and product prototypes. We can also use them to make jewelry, tools, and toys.
Social media changes the way consumers interact with others. Moreover, it facilitates them to disseminate information more quickly, cheaply, and massively. For example, companies use it to stay connected with their consumers.
In addition, social media gave rise to viral marketing . Companies design engaging messages and encourage consumers to share them. The impact can be significant due to its wide exposure, making products popular quickly with low promotional costs.
- Economic Environment: Examples, Indicators, Impacts
- Political Factors: Examples and Influence On Business
- Technology Diffusion. How it Works, Determinants, vs. Technology Infusion and Transfer
- Socio-cultural Factors: Examples and How They Impact Business
- Macroeconomic Factors: Meaning, Examples and Impacts on Business
- Micro Environment: Factors and Their Influence On Business
About Ahmad Nasrudin
Introverted writer with a passion for storytelling. Leveraged analytical skills from financial background (equity research, credit risk) at a leading rating agency to enhance writing with a unique statistical and macroeconomic perspective. Learn more about me

- Innovative Prompts
- Strategies Packs
- Skills Packs
- SOPs Toolkits
- Business Ideas
- Super Guides
- Innovation Report
- Canvas Examples
- Presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Discounted Bundles
- Search for:
No products in the cart.
Return to shop
PESTLE Analysis: Environmental Factors Affecting Business

The PESTLE analysis is a strategic tool used to gain information and insight into the external factors that may affect a business. It is an extension of the PEST analysis, which stands for political, economic, social, and technological factors. This acronym further expands by adding legal and environmental considerations. As part of this process, businesses like to gain insight into various environmental factors to identify potential opportunities and risks that could shape their strategies.
The environmental analysis looks at the physical environment as well as climate change policies or directives from governmental entities, energy availability or related pricing trends (e.g., scarcity of oil could create rising gas prices), animal-related laws impacting specific product categories, etc.
All these variables can have an immense impact on both operations and other vital aspects like customer willingness to buy a product or employee efficiency. As such, it is paramount that business owners consider the implications associated with environmental forces when making important strategic decisions — failure to do so could prove disastrous for both short-term profitability goals and sustainability initiatives if not managed properly.
Environmental Factors in Business
Climate change.
- Availability of non-renewable goods
Weather can have a significant impact on businesses due to the potential damages it might cause. Natural disasters such as flooding, hurricanes, and tornadoes can all disrupt business operations, or even damage valuable assets. Businesses that operate outdoors, like construction companies or landscaping services, are particularly vulnerable to weather-related disruptions.
Even for businesses with indoor operations like supermarkets and retail stores, extreme weather conditions such as heat waves or blizzards can affect customer behavior by decreasing the number of people coming into the premises, thus reducing sales revenue. In addition, severe weather affects transportation networks, which can be detrimental to businesses reliant on the movement of goods and materials within a certain timeframe.
Climate change refers to any significant long-term shift in global weather patterns or temperatures caused by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels. This issue affects businesses in a variety of ways and has both short-term consequences and implications for future planning.
In the short term, climate change can lead to extreme weather events like droughts, floods, hurricanes, and heat waves. These events can cause physical damage to infrastructure and supply chains, as well as lead to the loss of life. They also often require an emergency response from businesses, including those tasked with setting up shelters or delivering relief supplies. Companies must also factor increased energy costs due to extreme weather into their budgets if temperatures become abnormally high or cold for extended periods in certain regions.
The long-term effects of climate change also concern for business owners. Rising sea levels due to ice cap melting could lead to devastating flooding in coastal cities where many industries are based; likewise, rising temperatures could cause reductions in agricultural production yields, leading to food shortages and economic disruption.
Businesses must plan for these scenarios by ensuring adequate insurance coverage against climate-related risks and taking steps to reduce their carbon footprints through more sustainable practices like sourcing green energy or investing in renewable technologies like solar power instead of relying on nonrenewable resources like oil or gas, which contribute significantly more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere (CO2).
Governments have set regulations on industry’s carbon emissions to manage global warming, meaning businesses require compliance solutions that satisfy both local laws and cost-effectiveness to not restrain growth. Companies should evaluate current legislation impacting them and keep pace with updates from international governing entities such as the UNFCCC , which provide guidance for tackling climate-related matters within specific sectors or industries (e.g., shipping).
By doing this, a business may gain an advantage over competitors who fail to act according to accepted standards laid out by global organizations when it comes to keeping environmental impact low without sacrificing operational efficiency at the same time, thereby giving themselves a better position within the market, which will ultimately benefit bottom line profits over the long run.
Pollution can have direct and indirect impacts on business operations, such as negative impacts on operations and costs or positive impacts from investments in pollution prevention or compliance with local regulations.
When it comes to pollution, businesses must consider the physical environment (such as air and water) and the information environment (data about environmental performance). Different types of pollution can affect businesses. Air pollutants can cause health problems for workers and customers if not properly managed; some may damage buildings and equipment.
Water pollutants may contaminate groundwater supplies used for drinking, production processes, or other uses. Noise pollution can result in employee fatigue, decreased productivity, and hearing loss; certain types of noise may also impact customer perceptions of a business’s facilities. Pollution related to hazardous waste is another factor that companies should take into account when managing their operations: Chemicals produced during manufacturing activities may have negative effects on human health or wildlife if not properly disposed of according to local laws.
Businesses must be familiar with the legal requirements related to pollution control and management in their jurisdiction, such as emissions permits, effluent standards, and technology requirements for industry-specific processes like chemical processing plants that create wastewater discharges that need treatment prior to release into public water sources, and zoning restrictions limiting certain types of manufacturing activities.
Companies should also invest resources in renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines, solar panels, and geothermal plants to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and protect natural habitats, ecosystems, agricultural lands, etc. Pollution prevention initiatives that include modified raw material usage, better process designs, energy efficiency measures, and waste minimization initiatives can provide additional benefits for the company in terms of market access and brand recognition.
How some of these factors can affect businesses
Availability of certain renewable goods.
Renewable goods, such as solar or wind energy, have the potential to greatly reduce costs for businesses that actively use them, as they can be accessed without paying any kind of fee and may even offer tax credits if properly used. If renewable goods are available in plentiful quantities, then this could lead to lower prices, which will obviously be beneficial to businesses.
On the other hand, a shortage of renewable goods could cause prices to rise dramatically. This would affect businesses negatively, as they may not be willing or able to pay higher rates for using renewables.
In addition to potentially changing market prices related to the cost of goods available on the market, the availability of renewable goods also affects regulations related to their use and production.
For example, increasing access to and use of renewable energies might result in stricter regulations regarding emissions from non-renewable sources, something that could make it more difficult for specific industries (such as transportation) or businesses (such as factory owners) to operate with such fuels or goods.
Similarly, certain incentives from governments targeting increased usage or production of renewable goods may help push companies towards greener initiatives or investments in clean technology projects, something that would result in long-term benefits but short-term changes due to the financial outlays required by these measures.
Existence of certain biological species
The existence of certain biological species can have a significant impact on businesses, especially those in the food production industry. For example, if climate change were to make cows and goats extinct, it would be devastating for businesses in the dairy industry. Without access to these animals’ milk, companies would need to look elsewhere for their supplies or find alternative methods of producing products normally reliant on cow or goat milk.
In addition, many businesses rely on particular species’ materials as raw ingredients. If such species were to become endangered due to environmental concerns, then companies relying on them could face severe disruption as they search for substitutes or explore new supply chains. This is especially true when it comes to leather goods manufacturers, which use animal hides coming from specific areas to have a consistent quality product.
On a larger scale, the presence (or absence) of specific wildlife populations can lead to ecological changes that impact the economy at large. If certain migratory birds stop visiting an area due to habitat destruction, this could mean fewer eco-tourists come to visit, resulting in a lower influx of money into local communities near bird reserves and other related attractions.
Changing patterns in biodiversity can also affect businesses indirectly through government regulations and policy initiatives; e.g., if sea turtle populations are dwindling due to some pollution incident, such as an oil spill, then governments might implement legislation that restricts activities offshore to protect the turtles and their habitats, thus resulting in businesses having compliance issues with local laws or even facing fines or shutdowns should they fail to abide by any implemented regulations.
Environment-related laws
Environment-related laws are regulations that are put in place to ensure that businesses operate in an environmentally responsible manner. These laws help protect the environment, both for current and future generations, by ensuring that businesses adhere to environmental standards. By requiring businesses to meet specific environmental standards and comply with relevant regulations, these laws promote sustainability and help safeguard against potential ecological risks that may arise from business operations.
The scope of environment-related laws can vary depending on the jurisdiction where a business is located, but some key laws tend to be common across multiple regions. Some of these include regulations related to air quality, water pollution, hazardous waste disposal, land restoration after development activities have been completed, and energy efficiency requirements for certain types of machinery or equipment used in production processes.
- Air Quality Laws: Air quality legislation seeks to reduce or limit emissions into the atmosphere from sources such as factories, vehicles, and other sources of pollution. Such legislation typically sets maximum limits on the total allowable emissions, along with requirements for monitoring and reporting emissions data regularly. By helping to prevent excessive levels of pollution in the atmosphere due to industrial activity or transportation-related activities (e.g., burning fossil fuels), air quality legislation helps preserve clean air for everyone’s benefit now and into the future;
- Water Pollution Laws: Water pollution laws are designed to ensure that any water discharged from a facility does not exceed permissible levels set out by regulators when it comes to pollutants such as metals, chemicals, or other contaminants being introduced into nearby bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, or groundwater.
Typically, this includes setting the maximum levels of pollutants allowed in any effluent discharge, which must be monitored regularly by companies discharging wastewater into local systems throughout their operations. Water pollution laws also aim to limit incidental runoff from agricultural activities, where fertilizers or other soil enhancers may reach nearby waterways without prior filtering or treatment processes being applied first.
Examples of environmental factors affecting business
Environmental factors affecting coca-cola.
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on the success of companies, particularly those that operate on a global scale, like Coca-Cola. For them to remain competitive and operational, they need to have an active role in managing their environmental performance.
This includes understanding the different types of environmental issues that may affect their operations, as well as implementing strategies to mitigate potential impacts. Here are some of the environmental factors affecting Coca-Cola’s presence in the international market :
- Climate Change: As one of the world’s largest producers and consumers of energy, Coca-Cola is particularly vulnerable to climate change effects such as rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and water scarcity. To combat this issue, they have implemented initiatives such as water conservation efforts in their production methods, renewable energy sources , reducing travel emissions, and engaging with external stakeholders to collaborate on new solutions;
- Resource Sustainability: The availability and cost of resources used in producing goods have become increasingly important factors for many companies globally. For example, Coca-Cola uses large amounts of fresh water in its beverage production process, which must be replenished regularly from local sources or purchased elsewhere, impacting both resource sustainability (in terms of extraction limits) and operating costs (through increased transportation costs). To minimize these impacts, they focus on reducing non-renewable ingredients by substituting them with more sustainable options.
Environmental Factors Affecting the UAE
The UAE’s climate — due to its hot, arid region — can greatly impact how businesses operate there. The summer months alone can generate temperatures as high as 50 °C (122 °F), and most of the region receives very little rainfall, with an average annual precipitation rate of 140 mm/year . Consequently, the productivity of workers might be reduced due to extreme heat conditions that can make physical labor outside challenging or even dangerous, thus requiring extra safety precautions from employers.
Given its proximity to coastal areas, trade between the Emirates by sea appears more promising than in landlocked Middle Eastern nations due to their weaker infrastructure networks (e.g., roads).
This further reinforces the economic stability of nearby seaside cities such as Dubai or Abu Dhabi through import/export activities, resulting in an increase in investment opportunities; however, this necessitates strict maritime safety regulations to ensure human safety and prevent environmental catastrophes from ships transporting hazardous materials spilling them into nearby oceanic waters or emitting pollutants that could cause irreversible damage to marine life habitats if left unregulated by organizations like UNEP .
Environmental factors are an increasingly important concern in business. The PESTLE analysis framework can help organizations identify and respond to the most pressing environmental issues impacting their businesses.
By understanding the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental forces at play in the environment of a business, companies can anticipate potential disruptions and plan for long-term success. Companies must also be aware of how their operations may affect the environment by engaging in risk assessments to determine any potential liabilities related to sustainability issues. By taking proactive steps toward addressing these challenges now, companies can ensure they remain competitive while also doing their part to protect the planet.
Daniel Pereira
Related posts.

PESTLE Analysis: Legal Factors Affecting Business
When businesses analyze their external environment, PESTLE analysis is a standard tool that can be [...]
Key Activities
If the immediately preceding component of the Business Model Canvas is the Key Resources, which [...]
What is Lean Canvas?
The Lean Canvas is a business modeling tool created to help deconstruct a startup idea [...]
Revolutionize Your Business Model with ChatGPT: Discover Our New Course
If you’ve been following our blog on business model examples and types, you already understand [...]

PESTLE Analysis: Social Factors Affecting Business
In today’s ever-changing society, businesses must always be aware of the external influences that affect [...]

How to do a SWOT Analysis in 7 Steps (with Examples & Template)
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that an organization can use to thoroughly [...]
Customer Relationship
The Customer Relationship block of a Business Model is intrinsically dependent on the first block [...]
What is the difference between Business Model and Business Plan?
It’s very common to make confusion on what’s the difference between Business Model and Business [...]
RECEIVE OUR UPDATES
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?
Article Categories
Book categories, collections.
- Business, Careers, & Money Articles
- Business Articles
- General Business Articles
10 Forces that Impact Businesses
Company culture for dummies.

Sign up for the Dummies Beta Program to try Dummies' newest way to learn.
Competitive intelligence (CI) enables an organization to continually evolve in response to ever-changing conditions. These conditions, or forces, can be classified into ten distinct categories. The first two forces described in this article — market and technological forces — drive the velocity of change . In other words, changes in these areas require your organization to adapt very quickly to take advantage of opportunities and avoid threats. The remaining eight forces affect the complexity of change — the number of issues that may affect an organization.
To beat the competition, you need to constantly monitor the environment in which you operate for potential opportunities and threats. Ten-forces analysis provides a solid methodology for accomplishing that goal.
Market forces
Market forces are those that affect the supply, demand, and price of products, and they come in many forms. The competitive intelligence (CI) team commonly monitors and analyzes
Unmet customer needs, because they can be opportunities for your company to step in
New competitors, especially nontraditional competitors from other industries
Mergers and acquisitions that may strengthen a competitor or cause you to lose a supplier or distributor
Changes in the supply chain and distributors
Technological forces
Technological forces impact everything from how a product is produced to how a customer uses it and may affect every function in an organization, including what products are developed, how marketing reaches consumers, and how sales are tracked and managed. Technological changes even provide new and more effective ways to handle shipping and logistics. The CI team can play an important role in your company by tracking technological forces and providing insight into how they affect each area of the company.
Economic forces
All sorts of economic events may impact a business, from an economic downturn to sequestration to the government deciding to invest in solar energy. The CI team must continually monitor for such events so your organization isn’t blindsided by something that negatively affects its bottom line and doesn’t completely miss out on a golden opportunity.
Ideological forces
To compete in the global marketplace, you need to account for differences in ideologies. In some countries, for example, bribery is not only an accepted but an expected business practice. Certain practices that are acceptable in capitalist economies are shunned in communist or socialist states. In addition, religious beliefs may affect purchase decisions in a particular country or region. Competitive intelligence can play a key role in ensuring that an organization enters an area without committing a major faux pas.
Political and governmental forces
In the United States, the government plays a major role in determining how businesses operate, especially in relation to international trade, taxation, and regulations. If your business has government contracts, these forces may have an even bigger impact. The CI team needs to keep an eye on any government and political issues that may affect your organization.
Media forces
The media, including social media, can make or break a company. A bad-news story can go viral in a matter of minutes, and if your organization fails to deliver an acceptable response, the repercussions can last for months or even years. If the bad news is about a competitor, that could be good news for you, so be prepared to jump on such opportunities. The CI team can help monitor the media so your organization isn’t caught off guard in either situation.
Psychological/sociological forces
Psychological and sociological forces often drive what consumers buy and where and how they buy it. More and more consumers, for example, are purchasing products online and reading reviews before making a purchase. As consumer behavior evolves, your organization needs to adapt to serve developing needs and preferences.
Purchase decisions are increasingly affected by social media and attitudes of others as opposed to traditional advertising.
Moral/ethical forces
The safest approach to dealing with moral and ethical forces that impact business is to operate beyond reproach so that consumers hold your organization in the highest regard. Hire quality people to work for you, associate only with reputable organizations, hold everyone in your organization to the highest standards, and always treat everyone (customers, suppliers, distributors, and even competitors) with respect.
Competitive intelligence can help your organization gain insight into what’s expected and identify behaviors that can get organizations into trouble. It can also help leaders recognize problems in the organization that need to be corrected.
Weather and other environmental forces
Environmental issues relate to weather, natural disasters, climate change, pollution, and anything else that could impact business. A hurricane or tornado can completely wipe out businesses. Major environmental events can disrupt supply chains and increase the costs of raw materials. Part of the CI team’s job is to monitor for events that could impact your organization and help develop contingency plans in response to such events.
Legal/regulatory forces
National, state, and local laws and regulations may impact everything from where you can set up shop to how much you have to pay your employees and the measures you must take to ensure their safety. Some regulations can be very costly, and failing to honor the regulations may be even more costly. Competitive intelligence can help your organization monitor for changes rules and regulations so its leaders are prepared to make the necessary adjustments.
About This Article
This article can be found in the category:.
- General Business ,
- Design Thinking: Making Ideas Clear and Tangible
- Design Thinking: Creativity Techniques
- Design Thinking: The Customer Journey
- Design Thinking: Using an Empathy Map
- Design Thinking: Characterizing a Customer Using the Persona Method
- View All Articles From Category
Technological Factors Affect Business Environment
Technological factors are variables that are being used for evaluating available alternatives with respect to technological capabilities. Organizations consider it an important tool for improving operations and functions. Technological factors are one of various external environment factors that affect businesses greatly and are also an integral component of the PESTLE analysis . In the present scenario, utmost dependence on equipment, technological factors can have more effect on business operation and success globally than ever before.
Table of Contents
How Technological Factors Affect Business Environment
Technology trends affect businesses on many levels. When an employee is efficient, he turns out to be productive. Additionally, when a business is more in touch with its present and potential customers, the more chance it has to build a strong customer loyalty base. Advancement of technology can make this possible. Strategic leaders are constantly looking for development and updates within the technological environment. In this way, they not only improve their operations but, they will also be well aware of business transformational phase. They will derive groundbreaking strategies to grow exponentially.
Technology Transforms Operations
The technological environment of business has changed the way in which businesses function. Advancements in information technology have almost taken over every department of the organization. Now, information is stored in data servers and cloud technology as against the old way of storing data in registers and files.
Furthermore, development of technology has also introduced digital marketing strategies through which companies are able to sell their products and services. Even the research and development R&D divisions in companies have changed its way of functioning and more advanced techniques in the development of products and services have been introduced only through technological advancements.
For example, Siemens and Boeing are hugely investing in the adaption of 3D printing technique for product designing. They believe that this will accelerate the designing process, reduces production cost as well as improves the effectiveness of designing.
Technology helps in Developing Marketing Strategies
Technology has brought in a transformation through which companies collect, record, retrieve and utilize data and which also helps them in coming up with groundbreaking business strategies. Through available data, companies are able to monitor and evaluate customer trends and their demands for a particular product. Thanks to the development of information technology, businesses can understand consumer behavior and conduct a macro environment analysis and develop marketing strategies accordingly.
Technology is not only useful for collecting and using data but, it is also being used by organizations to analyze data and make meaningful conclusions as well as informed decisions. Having more focus on the customers, business strategies will certainly prove out to be effective for the success of an organization.
Negative Impact of Technology on Business
Technological environment imposes positive effects on a business. Internet makes the communication process smoother and easier. Despite all the pros, technology has on the business environment, it also imposes some negative impacts as well.
Business Relationships. Internet technology like Skype and other chat rooms have made it possible for businesses hold meetings without having all the parties be physically present at the same place. This type of meeting is less personal as compared to a face-to-face meeting. In this way, the personal aspect of business relationships tends to reduce. Lack of physical proximity has reduced brainstorming and another form of communication which involves personal touch.
Brick and Mortar. Advancement in e-commerce technology holds a negative impact on brick-and-mortar stores . Small-scale businesses are finding it very difficult to compete with both online and larger businesses in the industry that are operating both in person and on the internet. This advancement in the technological environment of business eventually forces small organizations to go out of operation.
Examples of Technological Factors
Regardless of what your company is selling or offering it will be benefited immensely by using different types of technological factors.
- Internet : almost every business today has a website which helps them in making and maintaining a global presence. Utilizing the social media platform businesses can easily communicate with their targeted audience. In addition to this, through internet technology, you can also easily communicate with your employees, clients and co-workers in other countries.
- Automated Process : Automating various production lines allow companies to replace human unskilled tasks with completely machinery ones. This benefits the company by reducing the cost for manufacturers, suppliers, retail stores as well as other parties involved. This factor, however, imposes a negative impact on the employment level of an economy.
How Technological Factors affecting Tesco
Tesco is a British multifaction and merchandise retail company . Technological advancement brings Tesco new opportunities.
- Firstly , started FRID retail technology and added FRID tags to its product range. RFID technology automated administrative task like stock counting.
- Secondly, customers can pay as they want. Tesco launched PayQwiq a mobile payment platform application in more than 524 stores. Consumers can download the PayQwiq app and linked Clubcard or NFC technology. It allowed customers to pay for their shopping and get loyalty points.
- Thirdly, "scan as you shop" are checkout points that provided convenience for customers and minimized labour cost.
About The Author
Ahsan Ali Shaw
What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Entrepreneurs
- Permissions
- Privacy Policy

PESTEL Analysis of the Coffee Industry

What PESTEL analysis can tell us is that the overall business environment has both pluses and minuses for the coffee industry.
In this article, we'll use PESTEL analysis to evaluate the macro environment of the coffee industry. That means looking at the Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors affecting this industry to see how it might progress over the coming years. Coffee is a hot beverage that we as humans have been drinking for more than 500 years. Known and loved the world over, this drink represents an industry worth over $100 billion. With coffee being a mainstay of many individuals' day-to-day life, it's hard to imagine a future where the coffee industry doesn't thrive.
PESTLE analysis is a strategic planning tool used by business and project managers. It examines the Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors that affect a company or an entire industry.
Coffee Industry PESTLE Analysis
Political factors affecting the coffee industry.
Here is a Political factor affecting the coffee industry:
- Trade relationships : The business of coffee and running a coffee shop is highly dependent on international trade. The world's biggest coffee producers are located in Asia, South America, and Africa, and yet, the drink is especially popular in Europe and North America. Trade relationships between countries that produce and consume coffee play a big role in determining the final price tag of the beverage, which ultimately impacts sales. Currently, there are a number of international trade agreements ensuring the success of the coffee industry. Uncertain trade circumstances (such as those involving the US and China or the UK and Europe) are unlikely to affect the coffee industry.
Economic factors affecting the Coffee industry
Here is an Economic factor affecting the coffee industry:
- Growing incomes: As the world's many economies continue to grow, there's one common benefit: consumers have growing incomes . This means consumers have more money to spend every year. While this can hugely impact consumer goods industries (such as the consumer electronics industry), it also impacts food and drink industries. As consumers get richer, they are more likely to consume tea , coffee, and other such luxury beverages. Also, with growing incomes, consumers are more likely to splurge on higher quality produce, such as higher quality coffee grounds.
Social factors affecting the Coffee industry
Here are two Sociocultural factors affecting the coffee industry:
- Health consciousness: The 21st century has seen a lot of change in society's view of health. Making healthy choices is trendier than ever, and this is causing consumers to spend more time exercising, eat better food, and avoid certain habits. While numerous studies have confirmed that coffee is not "unhealthy", it does contain large amounts of caffeine. As part of the health consciousness trend, many consumers are choosing to give up caffeinated beverages for improved mood, sleep, and more. This may result in a reduced demand for coffee (and equally, a greater demand for decaffeinated coffee products).
- Fair trade: Another prominent sociocultural trend is fair trade . Fair trade is an international movement that seeks to better compensate the farmers behind produce, instead of the many middlemen that have historically reaped huge profits. Importantly, the coffee industry is one of the main targets for the fair trade movement. As consumers show greater demand for fair trade coffee products, farmers will earn more and middlemen will earn less. However, fair trade should not affect the overall size of the industry, unless fair trade coffee prices (which are higher than regular coffee prices) drive away consumers.
Technological Factors Affecting the Coffee industry
Here are two Technological factors affecting the coffee industry:
- Genetic engineering : One of the most important technological trends across all food and drink industries is that of genetic engineering. Genetic engineering involves modifying produce at the genetic level to improve yield, taste, shelf-life, and more. Genetically engineered coffee (which carries the "GMO" label) is quickly growing in popularity within the industry. On the whole, genetic engineering should help to grow the coffee industry, as it allows producers to generate larger profits. However, some consumers prefer not to consume genetically engineered products due to a number of purported side effects.
- Coffee machines: Another big change in the coffee industry is the advent of new, coffee-specific appliances. Coffee grinders, drip machines, and espresso makers are now available at every electronics store. These appliances make it easier than ever to consume coffee, thereby encouraging consumers to take up brewing at home. This shouldn't affect the overall size of the coffee industry, but may result in more consumers making and drinking coffee at home, with fewer consumers drinking coffee outside of the house in coffee shops.
Environmental factors affecting the Coffee industry
Here is an Environmental factor affecting the coffee industry:
- Sustainable farming: The world is facing numerous environmental issues. While some of these issues are unrelated to the food and drink industries — like automotive CO2 emissions — some of them are. In particular, unsustainable farming processes can result in deforestation . There are other concerns related to farming, such as the use of pesticides and fertilizers or water consumption. In any case, the world is pushing for more sustainable farming practices. Ultimately, this is likely to result in an increased cost for the consumer, which may harm the coffee industry.
Legal factors affecting the Coffee industry
Here is a Legal factor affecting the coffee industry:
- Food standards: As a product designed for consumption, coffee falls under food and drink regulations in nearly all of the world's jurisdictions. This means it's subject to a wide range of laws on how it should be stored, transported, and brewed. Further to this, coffee contains large amounts of caffeine, so it's subject to caffeine standards in some parts of the world. These standards are only becoming tighter with time, but safe coffee handling is so easy to get right that it shouldn't be a problem for the industry.
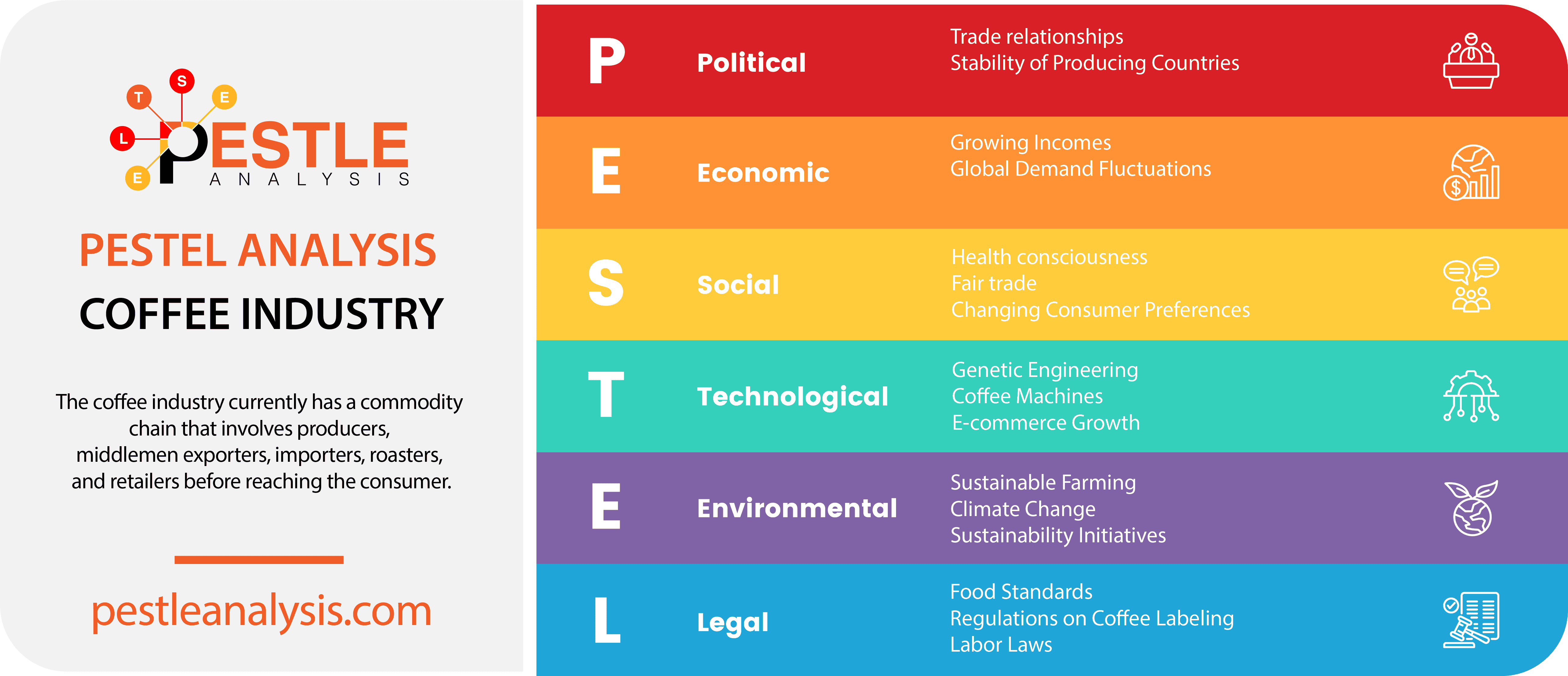
Recommendations: Taking action based on the PESTEL Analysis of the Coffee Industry
By this point, the coffee industry is well-established. From farm to cup, there are hundreds of cogs working together to power this multi-billion dollar industry. What PESTEL analysis can tell us is that the overall business environment has both pluses and minuses for the coffee industry.
On the plus side, the world currently has plenty of trade agreements, consumers' incomes are growing, and coffee appliances are more available than ever. The issue of genetically engineered coffee has both positives and negatives, allowing the industry to reap greater profits, but also scaring off some consumers. The fair trade movement and sustainable farming also have mixed consequences, ensuring benefits for the planet (and farmers) but higher costs for consumers. The main coffee-related downside in the current business environment is, without a doubt, growing caffeine consciousness.
For further reading, check out the following analysis of the coffee industry's leaders (or the industry's analysis here ):
- PESTLE Analysis of Starbucks
- PESTLE Analysis of Dunkin'
- PESTLE Analysis of Nestle
- SWOT Analysis of Costa Coffee
And that's not all. Check out many more PESTLE analysis examples and find everything you need to know about PESTLE analysis here !
UK Sugar Tax in PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE Analysis of Google (Alphabet) [2024 Updated]
Ralph lauren pestle analysis 2024.




IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In PESTLE analysis, technological factors are variables that relate to the existence, availability, and development of technology. These could include software development pace, digital marketing innovations, sustainable tech practices, and new information management systems. In general, technological factors are technological advancements ...
Technological factors refer to innovations that affect not only how products are created, but also how services provided by an organization function in terms of efficiency and effectiveness.
The technological environment of business encompasses external elements within technology that impact business operations. Changes in technology can reshape how a company operates, prompting significant shifts in the organization's strategies. It resides in the company's external realm, is tied to technological developments, and holds the ...
The PESTEL framework, or PESTEL analysis, is a business planning template that identifies and assesses how Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Economic, and Legal factors are affecting an organization or industry. Depending on the analysis results, businesses can improve their strategic management and planning while responding to forces ...
Discover what are technological factors and how they may impact business performance, including examples of typical technological factors in a PESTLE analysis.
Are you thinking about ways to grow your business' reach, efficiency, or staff? Consider these technological factors as part of your PESTEL Analysis.
Technological factors affecting business (also called technological forces) are all externally generated changes in technologies and processes which are used (or may be used) by the company or its competitors. Proper identification of this factor during strategic analysis ( PEST analysis, STEEP analysis, SWOT analysis, TOWS analysis) could lead to better strategic decision about investments ...
PEST Analysis (Political, Economic, Social, and Technological) is a method whereby an organization can assess major external factors that influence its operation in order to become more ...
PlanBuildr's Technology business plan template will help you to quickly and easily complete your Technology business plan.
What are Technological Factors in a Business? Technological factors in a business encompass the myriad of tools, innovations, and digital advancements a company employs to streamline operations, enhance product offerings, and improve customer engagement. These elements are integral to a company's ability to adapt, compete, and thrive in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Technology can bring many benefits to global companies, such as improved communication, collaboration, innovation, productivity and efficiency. However, technology also poses some challenges, such ...
Technological factors refer to elements related to or using technology. It is the company's external environment in addition to political , economic , sociodemographic, legal, and environmental factors.
By understanding the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental forces at play in the environment of a business, companies can anticipate potential disruptions and plan for long-term success.
From the reliability of your business network to the cloud software you choose for your team, each technology decision is important to business growth. A technology infrastructure is multi-layered, meaning you have several different considerations when planning how you set it up and deploy it.
These conditions, or forces, can be classified into ten distinct categories. The first two forces described in this article — market and technological forces — drive the velocity of change. In other words, changes in these areas require your organization to adapt very quickly to take advantage of opportunities and avoid threats.
Due to utmost dependence on equipment, technological factors have more effect on business environment and success globally than ever before.
What is PESTLE Analysis? PESTLE analysis is a strategic planning tool used by business and project managers. It examines the Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors that affect a company or an entire industry.
Technological forces represent major opportunities and threats that must be considered in formulating. strategies. Technological advancements dramatically can affect organizations' products, services, markets, suppliers, distributors, competitors, customers, manufacturing processes, marketing practices, and.
Technological Forces. The influences that developments in technology have on consumers, business and society in general. Some positive technological forces include increased leisure time, improved communication and better management information systems, while some negatives might include increased unemployment and information abuse.
Indeed, technology's transformative power emerges as the driving force behind resilience and innovation across all scenarios. Whether mitigating risks or capitalising on emerging opportunities, advanced digital solutions hold the key to success in the years to come.
The document discusses how technology, ecology, and legal forces impact the "Pintados" clothing line business plan. Some key points: 1) Technology can help increase production efficiency, reduce costs, and better promote and advertise products. The business aims to use technology to enhance marketing strategies. 2) Ecological factors like resource availability and environmental regulations ...
In particular, PESTEL reflects the names of the six forces of the macro-environment: (1) political, (2) economic, (3) social, (4) technological, (5) environmental, and (6) legal. Firms carefully examine each of these six segments to identify major opportunities and threats and adjust their firms' strategies accordingly.
It won't be cheap but money isn't the reason why students in the U.S. seek the services of premium writers. The main reason is that the writing quality premium writers produce is figuratively out of this world. An admission essay, for example, from a premium writer will definitely get you into any college despite the toughness of the ...
Canadian grain industry promoter faces questions from its members over plan to build $100M facility in Winnipeg ... $100-million Global Agriculture Technology Exchange, a research and technical ...