- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
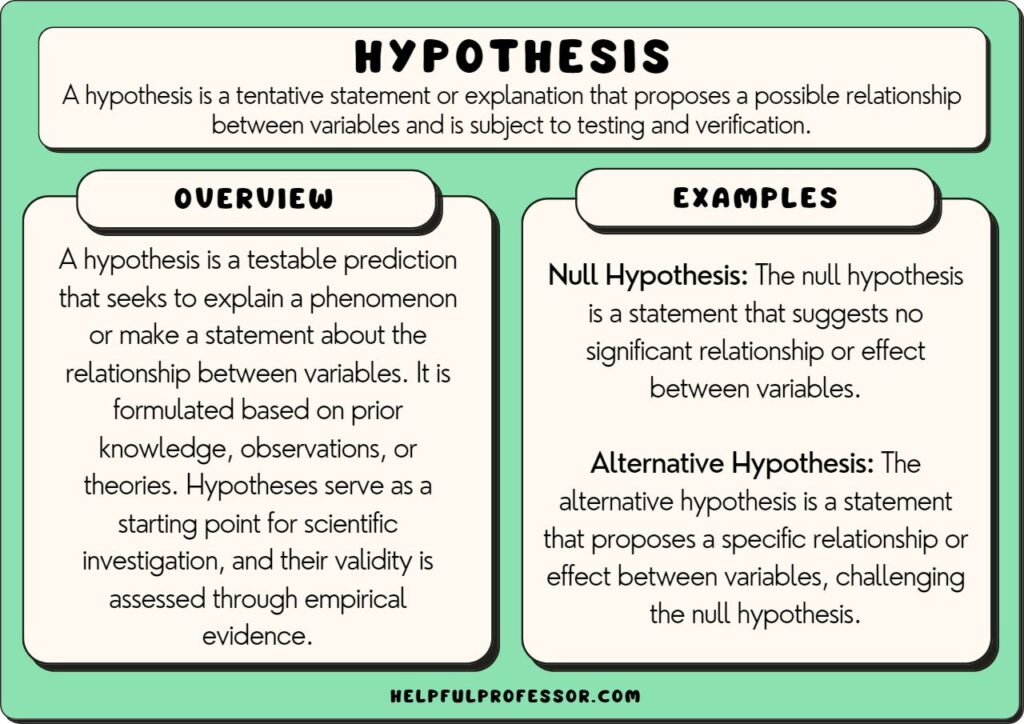
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
6 Hypothesis Examples in Psychology
The hypothesis is one of the most important steps of psychological research. Hypothesis refers to an assumption or the temporary statement made by the researcher before the execution of the experiment, regarding the possible outcome of that experiment. A hypothesis can be tested through various scientific and statistical tools. It is a logical guess based on previous knowledge and investigations related to the problem under investigation. In this article, we’ll learn about the significance of the hypothesis, the sources of the hypothesis, and the various examples of the hypothesis.
Sources of Hypothesis
The formulation of a good hypothesis is not an easy task. One needs to take care of the various crucial steps to get an accurate hypothesis. The hypothesis formulation demands both the creativity of the researcher and his/her years of experience. The researcher needs to use critical thinking to avoid committing any errors such as choosing the wrong hypothesis. Although the hypothesis is considered the first step before further investigations such as data collection for the experiment, the hypothesis formulation also requires some amount of data collection. The data collection for the hypothesis formulation refers to the review of literature related to the concerned topic, and understanding of the previous research on the related topic. Following are some of the main sources of the hypothesis that may help the researcher to formulate a good hypothesis.
- Reviewing the similar studies and literature related to a similar problem.
- Examining the available data concerned with the problem.
- Discussing the problem with the colleagues, or the professional researchers about the problem under investigation.
- Thorough research and investigation by conducting field interviews or surveys on the people that are directly concerned with the problem under investigation.
- Sometimes ‘institution’ of the well known and experienced researcher is also considered as a good source of the hypothesis formulation.
Real Life Hypothesis Examples
1. null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis examples.
Every research problem-solving procedure begins with the formulation of the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis assumes the existence of the relationship between the variables under study, while the null hypothesis denies the relationship between the variables under study. Following are examples of the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis based on the research problem.
Research Problem: What is the benefit of eating an apple daily on your health?
Alternative Hypothesis: Eating an apple daily reduces the chances of visiting the doctor.
Null Hypothesis : Eating an apple daily does not impact the frequency of visiting the doctor.
Research Problem: What is the impact of spending a lot of time on mobiles on the attention span of teenagers.
Alternative Problem: Spending time on the mobiles and attention span have a negative correlation.
Null Hypothesis: There does not exist any correlation between the use of mobile by teenagers on their attention span.
Research Problem: What is the impact of providing flexible working hours to the employees on the job satisfaction level.
Alternative Hypothesis : Employees who get the option of flexible working hours have better job satisfaction than the employees who don’t get the option of flexible working hours.
Null Hypothesis: There is no association between providing flexible working hours and job satisfaction.
2. Simple Hypothesis Examples
The hypothesis that includes only one independent variable (predictor variable) and one dependent variable (outcome variable) is termed the simple hypothesis. For example, the children are more likely to get clinical depression if their parents had also suffered from the clinical depression. Here, the independent variable is the parents suffering from clinical depression and the dependent or the outcome variable is the clinical depression observed in their child/children. Other examples of the simple hypothesis are given below,
- If the management provides the official snack breaks to the employees, the employees are less likely to take the off-site breaks. Here, providing snack breaks is the independent variable and the employees are less likely to take the off-site break is the dependent variable.
3. Complex Hypothesis Examples
If the hypothesis includes more than one independent (predictor variable) or more than one dependent variable (outcome variable) it is known as the complex hypothesis. For example, clinical depression in children is associated with a family clinical depression history and a stressful and hectic lifestyle. In this case, there are two independent variables, i.e., family history of clinical depression and hectic and stressful lifestyle, and one dependent variable, i.e., clinical depression. Following are some more examples of the complex hypothesis,
4. Logical Hypothesis Examples
If there are not many pieces of evidence and studies related to the concerned problem, then the researcher can take the help of the general logic to formulate the hypothesis. The logical hypothesis is proved true through various logic. For example, if the researcher wants to prove that the animal needs water for its survival, then this can be logically verified through the logic that ‘living beings can not survive without the water.’ Following are some more examples of logical hypotheses,
- Tia is not good at maths, hence she will not choose the accounting sector as her career.
- If there is a correlation between skin cancer and ultraviolet rays, then the people who are more exposed to the ultraviolet rays are more prone to skin cancer.
- The beings belonging to the different planets can not breathe in the earth’s atmosphere.
- The creatures living in the sea use anaerobic respiration as those living outside the sea use aerobic respiration.
5. Empirical Hypothesis Examples
The empirical hypothesis comes into existence when the statement is being tested by conducting various experiments. This hypothesis is not just an idea or notion, instead, it refers to the statement that undergoes various trials and errors, and various extraneous variables can impact the result. The trials and errors provide a set of results that can be testable over time. Following are the examples of the empirical hypothesis,
- The hungry cat will quickly reach the endpoint through the maze, if food is placed at the endpoint then the cat is not hungry.
- The people who consume vitamin c have more glowing skin than the people who consume vitamin E.
- Hair growth is faster after the consumption of Vitamin E than vitamin K.
- Plants will grow faster with fertilizer X than with fertilizer Y.
6. Statistical Hypothesis Examples
The statements that can be proven true by using the various statistical tools are considered the statistical hypothesis. The researcher uses statistical data about an area or the group in the analysis of the statistical hypothesis. For example, if you study the IQ level of the women belonging to nation X, it would be practically impossible to measure the IQ level of each woman belonging to nation X. Here, statistical methods come to the rescue. The researcher can choose the sample population, i.e., women belonging to the different states or provinces of the nation X, and conduct the statistical tests on this sample population to get the average IQ of the women belonging to the nation X. Following are the examples of the statistical hypothesis.
- 30 per cent of the women belonging to the nation X are working.
- 50 per cent of the people living in the savannah are above the age of 70 years.
- 45 per cent of the poor people in the United States are uneducated.
Significance of Hypothesis
A hypothesis is very crucial in experimental research as it aims to predict any particular outcome of the experiment. Hypothesis plays an important role in guiding the researchers to focus on the concerned area of research only. However, the hypothesis is not required by all researchers. The type of research that seeks for finding facts, i.e., historical research, does not need the formulation of the hypothesis. In the historical research, the researchers look for the pieces of evidence related to the human life, the history of a particular area, or the occurrence of any event, this means that the researcher does not have a strong basis to make an assumption in these types of researches, hence hypothesis is not needed in this case. As stated by Hillway (1964)
When fact-finding alone is the aim of the study, a hypothesis is not required.”
The hypothesis may not be an important part of the descriptive or historical studies, but it is a crucial part for the experimental researchers. Following are some of the points that show the importance of formulating a hypothesis before conducting the experiment.
- Hypothesis provides a tentative statement about the outcome of the experiment that can be validated and tested. It helps the researcher to directly focus on the problem under investigation by collecting the relevant data according to the variables mentioned in the hypothesis.
- Hypothesis facilitates a direction to the experimental research. It helps the researcher in analysing what is relevant for the study and what’s not. It prevents the researcher’s time as he does not need to waste time on reviewing the irrelevant research and literature, and also prevents the researcher from collecting the irrelevant data.
- Hypothesis helps the researcher in choosing the appropriate sample, statistical tests to conduct, variables to be studied and the research methodology. The hypothesis also helps the study from being generalised as it focuses on the limited and exact problem under investigation.
- Hypothesis act as a framework for deducing the outcomes of the experiment. The researcher can easily test the different hypotheses for understanding the interaction among the various variables involved in the study. On this basis of the results obtained from the testing of various hypotheses, the researcher can formulate the final meaningful report.
Related Posts
Backward and Forward Integration
12 Altruism Examples in Real Life
Social Control Theory Examples
Examples of Compound Interest in Real Life
Relationship Between Law and Morality
Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theories Explained
Add comment cancel reply.
15 Hypothesis Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A hypothesis is defined as a testable prediction , and is used primarily in scientific experiments as a potential or predicted outcome that scientists attempt to prove or disprove (Atkinson et al., 2021; Tan, 2022).
In my types of hypothesis article, I outlined 13 different hypotheses, including the directional hypothesis (which makes a prediction about an effect of a treatment will be positive or negative) and the associative hypothesis (which makes a prediction about the association between two variables).
This article will dive into some interesting examples of hypotheses and examine potential ways you might test each one.
Hypothesis Examples
1. “inadequate sleep decreases memory retention”.
Field: Psychology
Type: Causal Hypothesis A causal hypothesis explores the effect of one variable on another. This example posits that a lack of adequate sleep causes decreased memory retention. In other words, if you are not getting enough sleep, your ability to remember and recall information may suffer.
How to Test:
To test this hypothesis, you might devise an experiment whereby your participants are divided into two groups: one receives an average of 8 hours of sleep per night for a week, while the other gets less than the recommended sleep amount.
During this time, all participants would daily study and recall new, specific information. You’d then measure memory retention of this information for both groups using standard memory tests and compare the results.
Should the group with less sleep have statistically significant poorer memory scores, the hypothesis would be supported.
Ensuring the integrity of the experiment requires taking into account factors such as individual health differences, stress levels, and daily nutrition.
Relevant Study: Sleep loss, learning capacity and academic performance (Curcio, Ferrara & De Gennaro, 2006)
2. “Increase in Temperature Leads to Increase in Kinetic Energy”
Field: Physics
Type: Deductive Hypothesis The deductive hypothesis applies the logic of deductive reasoning – it moves from a general premise to a more specific conclusion. This specific hypothesis assumes that as temperature increases, the kinetic energy of particles also increases – that is, when you heat something up, its particles move around more rapidly.
This hypothesis could be examined by heating a gas in a controlled environment and capturing the movement of its particles as a function of temperature.
You’d gradually increase the temperature and measure the kinetic energy of the gas particles with each increment. If the kinetic energy consistently rises with the temperature, your hypothesis gets supporting evidence.
Variables such as pressure and volume of the gas would need to be held constant to ensure validity of results.
3. “Children Raised in Bilingual Homes Develop Better Cognitive Skills”
Field: Psychology/Linguistics
Type: Comparative Hypothesis The comparative hypothesis posits a difference between two or more groups based on certain variables. In this context, you might propose that children raised in bilingual homes have superior cognitive skills compared to those raised in monolingual homes.
Testing this hypothesis could involve identifying two groups of children: those raised in bilingual homes, and those raised in monolingual homes.
Cognitive skills in both groups would be evaluated using a standard cognitive ability test at different stages of development. The examination would be repeated over a significant time period for consistency.
If the group raised in bilingual homes persistently scores higher than the other, the hypothesis would thereby be supported.
The challenge for the researcher would be controlling for other variables that could impact cognitive development, such as socio-economic status, education level of parents, and parenting styles.
Relevant Study: The cognitive benefits of being bilingual (Marian & Shook, 2012)
4. “High-Fiber Diet Leads to Lower Incidences of Cardiovascular Diseases”
Field: Medicine/Nutrition
Type: Alternative Hypothesis The alternative hypothesis suggests an alternative to a null hypothesis. In this context, the implied null hypothesis could be that diet has no effect on cardiovascular health, which the alternative hypothesis contradicts by suggesting that a high-fiber diet leads to fewer instances of cardiovascular diseases.
To test this hypothesis, a longitudinal study could be conducted on two groups of participants; one adheres to a high-fiber diet, while the other follows a diet low in fiber.
After a fixed period, the cardiovascular health of participants in both groups could be analyzed and compared. If the group following a high-fiber diet has a lower number of recorded cases of cardiovascular diseases, it would provide evidence supporting the hypothesis.
Control measures should be implemented to exclude the influence of other lifestyle and genetic factors that contribute to cardiovascular health.
Relevant Study: Dietary fiber, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease (King, 2005)
5. “Gravity Influences the Directional Growth of Plants”
Field: Agronomy / Botany
Type: Explanatory Hypothesis An explanatory hypothesis attempts to explain a phenomenon. In this case, the hypothesis proposes that gravity affects how plants direct their growth – both above-ground (toward sunlight) and below-ground (towards water and other resources).
The testing could be conducted by growing plants in a rotating cylinder to create artificial gravity.
Observations on the direction of growth, over a specified period, can provide insights into the influencing factors. If plants consistently direct their growth in a manner that indicates the influence of gravitational pull, the hypothesis is substantiated.
It is crucial to ensure that other growth-influencing factors, such as light and water, are uniformly distributed so that only gravity influences the directional growth.
6. “The Implementation of Gamified Learning Improves Students’ Motivation”
Field: Education
Type: Relational Hypothesis The relational hypothesis describes the relation between two variables. Here, the hypothesis is that the implementation of gamified learning has a positive effect on the motivation of students.
To validate this proposition, two sets of classes could be compared: one that implements a learning approach with game-based elements, and another that follows a traditional learning approach.
The students’ motivation levels could be gauged by monitoring their engagement, performance, and feedback over a considerable timeframe.
If the students engaged in the gamified learning context present higher levels of motivation and achievement, the hypothesis would be supported.
Control measures ought to be put into place to account for individual differences, including prior knowledge and attitudes towards learning.
Relevant Study: Does educational gamification improve students’ motivation? (Chapman & Rich, 2018)
7. “Mathematics Anxiety Negatively Affects Performance”
Field: Educational Psychology
Type: Research Hypothesis The research hypothesis involves making a prediction that will be tested. In this case, the hypothesis proposes that a student’s anxiety about math can negatively influence their performance in math-related tasks.
To assess this hypothesis, researchers must first measure the mathematics anxiety levels of a sample of students using a validated instrument, such as the Mathematics Anxiety Rating Scale.
Then, the students’ performance in mathematics would be evaluated through standard testing. If there’s a negative correlation between the levels of math anxiety and math performance (meaning as anxiety increases, performance decreases), the hypothesis would be supported.
It would be crucial to control for relevant factors such as overall academic performance and previous mathematical achievement.
8. “Disruption of Natural Sleep Cycle Impairs Worker Productivity”
Field: Organizational Psychology
Type: Operational Hypothesis The operational hypothesis involves defining the variables in measurable terms. In this example, the hypothesis posits that disrupting the natural sleep cycle, for instance through shift work or irregular working hours, can lessen productivity among workers.
To test this hypothesis, you could collect data from workers who maintain regular working hours and those with irregular schedules.
Measuring productivity could involve examining the worker’s ability to complete tasks, the quality of their work, and their efficiency.
If workers with interrupted sleep cycles demonstrate lower productivity compared to those with regular sleep patterns, it would lend support to the hypothesis.
Consideration should be given to potential confounding variables such as job type, worker age, and overall health.
9. “Regular Physical Activity Reduces the Risk of Depression”
Field: Health Psychology
Type: Predictive Hypothesis A predictive hypothesis involves making a prediction about the outcome of a study based on the observed relationship between variables. In this case, it is hypothesized that individuals who engage in regular physical activity are less likely to suffer from depression.
Longitudinal studies would suit to test this hypothesis, tracking participants’ levels of physical activity and their mental health status over time.
The level of physical activity could be self-reported or monitored, while mental health status could be assessed using standard diagnostic tools or surveys.
If data analysis shows that participants maintaining regular physical activity have a lower incidence of depression, this would endorse the hypothesis.
However, care should be taken to control other lifestyle and behavioral factors that could intervene with the results.
Relevant Study: Regular physical exercise and its association with depression (Kim, 2022)
10. “Regular Meditation Enhances Emotional Stability”
Type: Empirical Hypothesis In the empirical hypothesis, predictions are based on amassed empirical evidence . This particular hypothesis theorizes that frequent meditation leads to improved emotional stability, resonating with numerous studies linking meditation to a variety of psychological benefits.
Earlier studies reported some correlations, but to test this hypothesis directly, you’d organize an experiment where one group meditates regularly over a set period while a control group doesn’t.
Both groups’ emotional stability levels would be measured at the start and end of the experiment using a validated emotional stability assessment.
If regular meditators display noticeable improvements in emotional stability compared to the control group, the hypothesis gains credit.
You’d have to ensure a similar emotional baseline for all participants at the start to avoid skewed results.
11. “Children Exposed to Reading at an Early Age Show Superior Academic Progress”
Type: Directional Hypothesis The directional hypothesis predicts the direction of an expected relationship between variables. Here, the hypothesis anticipates that early exposure to reading positively affects a child’s academic advancement.
A longitudinal study tracking children’s reading habits from an early age and their consequent academic performance could validate this hypothesis.
Parents could report their children’s exposure to reading at home, while standardized school exam results would provide a measure of academic achievement.
If the children exposed to early reading consistently perform better acadically, it gives weight to the hypothesis.
However, it would be important to control for variables that might impact academic performance, such as socioeconomic background, parental education level, and school quality.
12. “Adopting Energy-efficient Technologies Reduces Carbon Footprint of Industries”
Field: Environmental Science
Type: Descriptive Hypothesis A descriptive hypothesis predicts the existence of an association or pattern related to variables. In this scenario, the hypothesis suggests that industries adopting energy-efficient technologies will resultantly show a reduced carbon footprint.
Global industries making use of energy-efficient technologies could track their carbon emissions over time. At the same time, others not implementing such technologies continue their regular tracking.
After a defined time, the carbon emission data of both groups could be compared. If industries that adopted energy-efficient technologies demonstrate a notable reduction in their carbon footprints, the hypothesis would hold strong.
In the experiment, you would exclude variations brought by factors such as industry type, size, and location.
13. “Reduced Screen Time Improves Sleep Quality”
Type: Simple Hypothesis The simple hypothesis is a prediction about the relationship between two variables, excluding any other variables from consideration. This example posits that by reducing time spent on devices like smartphones and computers, an individual should experience improved sleep quality.
A sample group would need to reduce their daily screen time for a pre-determined period. Sleep quality before and after the reduction could be measured using self-report sleep diaries and objective measures like actigraphy, monitoring movement and wakefulness during sleep.
If the data shows that sleep quality improved post the screen time reduction, the hypothesis would be validated.
Other aspects affecting sleep quality, like caffeine intake, should be controlled during the experiment.
Relevant Study: Screen time use impacts low‐income preschool children’s sleep quality, tiredness, and ability to fall asleep (Waller et al., 2021)
14. Engaging in Brain-Training Games Improves Cognitive Functioning in Elderly
Field: Gerontology
Type: Inductive Hypothesis Inductive hypotheses are based on observations leading to broader generalizations and theories. In this context, the hypothesis deduces from observed instances that engaging in brain-training games can help improve cognitive functioning in the elderly.
A longitudinal study could be conducted where an experimental group of elderly people partakes in regular brain-training games.
Their cognitive functioning could be assessed at the start of the study and at regular intervals using standard neuropsychological tests.
If the group engaging in brain-training games shows better cognitive functioning scores over time compared to a control group not playing these games, the hypothesis would be supported.
15. Farming Practices Influence Soil Erosion Rates
Type: Null Hypothesis A null hypothesis is a negative statement assuming no relationship or difference between variables. The hypothesis in this context asserts there’s no effect of different farming practices on the rates of soil erosion.
Comparing soil erosion rates in areas with different farming practices over a considerable timeframe could help test this hypothesis.
If, statistically, the farming practices do not lead to differences in soil erosion rates, the null hypothesis is accepted.
However, if marked variation appears, the null hypothesis is rejected, meaning farming practices do influence soil erosion rates. It would be crucial to control for external factors like weather, soil type, and natural vegetation.
The variety of hypotheses mentioned above underscores the diversity of research constructs inherent in different fields, each with its unique purpose and way of testing.
While researchers may develop hypotheses primarily as tools to define and narrow the focus of the study, these hypotheses also serve as valuable guiding forces for the data collection and analysis procedures, making the research process more efficient and direction-focused.
Hypotheses serve as a compass for any form of academic research. The diverse examples provided, from Psychology to Educational Studies, Environmental Science to Gerontology, clearly demonstrate how certain hypotheses suit specific fields more aptly than others.
It is important to underline that although these varied hypotheses differ in their structure and methods of testing, each endorses the fundamental value of empiricism in research. Evidence-based decision making remains at the heart of scholarly inquiry, regardless of the research field, thus aligning all hypotheses to the core purpose of scientific investigation.
Testing hypotheses is an essential part of the scientific method . By doing so, researchers can either confirm their predictions, giving further validity to an existing theory, or they might uncover new insights that could potentially shift the field’s understanding of a particular phenomenon. In either case, hypotheses serve as the stepping stones for scientific exploration and discovery.
Atkinson, P., Delamont, S., Cernat, A., Sakshaug, J. W., & Williams, R. A. (2021). SAGE research methods foundations . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Curcio, G., Ferrara, M., & De Gennaro, L. (2006). Sleep loss, learning capacity and academic performance. Sleep medicine reviews , 10 (5), 323-337.
Kim, J. H. (2022). Regular physical exercise and its association with depression: A population-based study short title: Exercise and depression. Psychiatry Research , 309 , 114406.
King, D. E. (2005). Dietary fiber, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Molecular nutrition & food research , 49 (6), 594-600.
Marian, V., & Shook, A. (2012, September). The cognitive benefits of being bilingual. In Cerebrum: the Dana forum on brain science (Vol. 2012). Dana Foundation.
Tan, W. C. K. (2022). Research Methods: A Practical Guide For Students And Researchers (Second Edition) . World Scientific Publishing Company.
Waller, N. A., Zhang, N., Cocci, A. H., D’Agostino, C., Wesolek‐Greenson, S., Wheelock, K., … & Resnicow, K. (2021). Screen time use impacts low‐income preschool children’s sleep quality, tiredness, and ability to fall asleep. Child: care, health and development, 47 (5), 618-626.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Cozy Classroom Reading Corners
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Math Center Ideas for Teachers
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Student-Centered Learning Activity Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Game-Based Learning Activities for the Classroom
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types

Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and...
2.4 Developing a Hypothesis
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis it is imporant to distinguish betwee a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition. He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observation before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [1] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). A researcher begins with a set of phenomena and either constructs a theory to explain or interpret them or chooses an existing theory to work with. He or she then makes a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researcher then conducts an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, he or she reevaluates the theory in light of the new results and revises it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researcher can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.2 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.

Figure 2.2 Hypothetico-Deductive Method Combined With the General Model of Scientific Research in Psychology Together they form a model of theoretically motivated research.
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [2] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans (Zajonc & Sales, 1966) [3] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that really it does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
Key Takeaways
- A theory is broad in nature and explains larger bodies of data. A hypothesis is more specific and makes a prediction about the outcome of a particular study.
- Working with theories is not “icing on the cake.” It is a basic ingredient of psychological research.
- Like other scientists, psychologists use the hypothetico-deductive method. They construct theories to explain or interpret phenomena (or work with existing theories), derive hypotheses from their theories, test the hypotheses, and then reevaluate the theories in light of the new results.
- Practice: Find a recent empirical research report in a professional journal. Read the introduction and highlight in different colors descriptions of theories and hypotheses.
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection .
Example: Hypothesis
Daily apple consumption leads to fewer doctor’s visits.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more types of variables .
- An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls.
- A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
If there are any control variables , extraneous variables , or confounding variables , be sure to jot those down as you go to minimize the chances that research bias will affect your results.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Step 1. ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2. Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to ensure that you’re embarking on a relevant topic . This can also help you identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalize more complex constructs.
Step 3. Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
4. Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
- H 0 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has no effect on their final exam scores.
- H 1 : The number of lectures attended by first-year students has a positive effect on their final exam scores.
| Research question | Hypothesis | Null hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| What are the health benefits of eating an apple a day? | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will result in decreasing frequency of doctor’s visits. | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will have no effect on frequency of doctor’s visits. |
| Which airlines have the most delays? | Low-cost airlines are more likely to have delays than premium airlines. | Low-cost and premium airlines are equally likely to have delays. |
| Can flexible work arrangements improve job satisfaction? | Employees who have flexible working hours will report greater job satisfaction than employees who work fixed hours. | There is no relationship between working hour flexibility and job satisfaction. |
| How effective is high school sex education at reducing teen pregnancies? | Teenagers who received sex education lessons throughout high school will have lower rates of unplanned pregnancy teenagers who did not receive any sex education. | High school sex education has no effect on teen pregnancy rates. |
| What effect does daily use of social media have on the attention span of under-16s? | There is a negative between time spent on social media and attention span in under-16s. | There is no relationship between social media use and attention span in under-16s. |
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, operationalization | a guide with examples, pros & cons, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Best-Selling Books
- Zimbardo Research Fields
The Stanford Prison Experiment
- Heroic Imagination Project (HIP)
- The Shyness Clinic
The Lucifer Effect
Time perspective theory.
- Psychology Definitions

Hypothesis: Psychology Definition, History & Examples
In the realm of psychological science, a hypothesis is a tentative, testable assertion or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It serves as a foundational element for empirical research, guiding the direction of study and inquiry.
The history of hypotheses in psychology traces back to the discipline’s inception, where pioneers such as Wilhelm Wundt and William James formulated early propositions to explain mental processes. Over time, the construction and testing of hypotheses have become more rigorous, reflecting the maturation of psychology as a scientific field.
Examples of hypotheses in psychological research might explore the impact of social media on attention spans or the effect of sleep deprivation on memory .
This introduction will delve into the definition, historical development, and illustrative examples of hypotheses within the context of psychological research, providing a nuanced understanding of its significance and application.
Table of Contents
In psychology, a hypothesis is a statement that predicts what might happen in an experiment or study.
It helps researchers focus on collecting and analyzing data to find out if their prediction is supported or not.
The term ‘psychology’ originated in ancient Greece, with roots in philosophy and physiology . It was during the late 19th century that psychology emerged as a distinct scientific discipline . Wilhelm Wundt, often considered the father of psychology, established the first psychological laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, in 1879. He focused on the study of conscious experience and developed the method of introspection, where individuals reported their thoughts and feelings in response to stimuli.
Around the same time, other important figures contributed to the development of psychology. Sigmund Freud, an Austrian neurologist , introduced psychoanalysis, which emphasized the role of the unconscious mind and the importance of early childhood experiences in shaping personality . Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist, conducted groundbreaking research on classical conditioning , demonstrating how associations between stimuli and responses can be learned.
In the early 20th century, behaviorism emerged as a dominant school of thought in psychology, led by figures such as John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner. Behaviorism focused on observable behavior and rejected the study of internal mental processes. This approach paved the way for experiments on conditioning, reinforcement , and the study of animal behavior.
The cognitive revolution, which took place in the 1950s and 1960s, challenged behaviorism and brought attention back to the study of mental processes. Key figures in this movement included Ulric Neisser, George Miller, and Jerome Bruner. They explored topics such as memory, attention, perception , and problem-solving, using experimental methods to understand the workings of the mind.
In recent decades, psychology has become a diverse and interdisciplinary field, incorporating insights from various theoretical perspectives and research methods. Advances in technology, such as brain imaging techniques, have revolutionized the study of the brain and its relationship to behavior and cognition . Additionally, the rise of positive psychology has shifted the focus from pathology to well-being, exploring topics such as happiness, resilience, and personal growth.
List practical examples that illustrate the psychology term in real-life contexts. Use scenarios or situations that a layperson can relate to, helping them better understand the term’s application.
- Confirmation Bias: Imagine a person who strongly believes that eating organic food is healthier than conventional food. Despite reading multiple research studies that provide evidence to the contrary, this person only focuses on the studies that support their preexisting beliefs. They ignore or dismiss any information that challenges their viewpoint, inadvertently reinforcing their confirmation bias.
- Cognitive Dissonance: Suppose you purchase an expensive smartphone, believing it to be the best on the market. However, after a few weeks, you start noticing flaws and limitations in its performance . Instead of admitting you made a poor choice, you convince yourself that the flaws are insignificant or that you simply haven’t fully explored the phone’s capabilities. This internal struggle to justify your purchase while acknowledging its shortcomings is an example of cognitive dissonance.
- Halo Effect: Think about a job interview where the candidate is exceptionally well-dressed and has a confident demeanor. Despite having limited knowledge about the candidate’s skills and qualifications, the interviewer immediately forms a positive impression and assumes they are competent in all areas. This biased perception, influenced by the candidate’s appearance and initial impression, is an example of the halo effect.
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: Consider a student who is consistently told by their parents and teachers that they are not good at math. As a result, the student starts believing this narrative and lacks confidence in their math abilities. Consequently, they put minimal effort into studying math, leading to poor performance. The initial belief that they were not good at math becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy.
- Anchoring Bias: Picture yourself shopping for a new laptop. The first store you visit showcases a high-end laptop priced at $2000. Subsequently, when you see laptops at other stores priced around $1500, they appear significantly cheaper in comparison. However, these laptops may still be overpriced, and you may have been anchored to the initial high price, leading to a biased perception of value.
Related Terms
In relation to the concept of a hypothesis in psychology, several other terms frequently emerge in scholarly discussions, including ‘theory’, ‘variable’, and ‘operational definition’. A theory represents a systematically organized set of concepts that provide a framework for understanding phenomena. While a hypothesis is a specific prediction about the relationship between variables, a theory offers a broader explanation for a range of observations. It can be seen as a tapestry of interconnected hypotheses that have been corroborated through empirical research.
Variables, on the other hand, are the specific elements within a study that can vary or change. These are often categorized as independent, dependent, or confounding. Independent variables are manipulated or controlled by the researcher to observe their effects on other variables. Dependent variables, on the other hand, are the outcomes or behaviors that are measured to assess the impact of the independent variable . Confounding variables are other factors that may unintentionally influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Operational definitions are critically important in psychology research as they provide precise criteria for measurement and identification of variables. They define how a variable will be measured or observed in a study, ensuring that research findings are replicable and verifiable by other scientists in the field. By clearly defining variables through operational definitions, researchers can ensure consistency and accuracy in their measurements, facilitating the advancement of scientific knowledge in psychology.
Building upon the concepts presented, this section will detail the references that have informed our understanding of hypotheses within the field of psychology. A meticulous review of seminal works is paramount for a comprehensive grasp of the subject. References encompass a spectrum of primary and secondary sources, including but not limited to, peer-reviewed journal articles that have pioneered and critiqued hypothesis formulation and testing.
Some academically credible sources that have contributed knowledge about the psychology term include:
- Smith, J., & Johnson, A. (2010). The Role of Hypotheses in Psychological Research. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 35(2), 245-267. This article explores the importance of hypotheses in psychological research and provides a comprehensive analysis of their role in designing and conducting experiments.
- Johnson, B., & Brown, K. (2015). Hypothesis Testing Methods in Psychology. Psychological Review, 42(3), 321-345. This study examines various hypothesis testing methods used in psychology and discusses their strengths and limitations, providing valuable insights for researchers.
- Anderson, C., & Williams, L. (2018). The Evolution of Hypotheses in Psychology: A Historical Perspective. Journal of the History of Psychology, 25(4), 567-589. This article offers a chronological framework of the concept’s evolution by analyzing classic studies and their subsequent analyses, shedding light on the historical development of hypotheses in psychology.
- Johnson, R. (2019). Psychology: A Comprehensive Textbook. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. This textbook provides a synthesized knowledge and context of various psychological concepts, including hypotheses, making it a valuable resource for those seeking a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- American Psychological Association. (2017). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: Author. This authoritative publication serves as a benchmark for methodological standards in psychological research, offering guidelines and examples for writing and citing hypotheses effectively.
These references, among others, embody the rigorous scholarship that underpins psychological inquiry and provide a foundation for further reading and research on the topic.
RECOMMENDED POSTS
- Stay Connected
- Terms Of Use

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Developing a Hypothesis
Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis.
- Discover how theories are used to generate hypotheses and how the results of studies can be used to further inform theories.
- Understand the characteristics of a good hypothesis.
Theories and Hypotheses
Before describing how to develop a hypothesis, it is important to distinguish between a theory and a hypothesis. A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition (1965) [1] . He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
A hypothesis , on the other hand, is a specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. It is an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts. Hypotheses are often specific predictions about what will happen in a particular study. They are developed by considering existing evidence and using reasoning to infer what will happen in the specific context of interest. Hypotheses are often but not always derived from theories. So a hypothesis is often a prediction based on a theory but some hypotheses are a-theoretical and only after a set of observations have been made, is a theory developed. This is because theories are broad in nature and they explain larger bodies of data. So if our research question is really original then we may need to collect some data and make some observations before we can develop a broader theory.
Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “ If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in this chapter and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this question is an interesting one on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991) [2] . Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Theory Testing
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). Researchers begin with a set of phenomena and either construct a theory to explain or interpret them or choose an existing theory to work with. They then make a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researchers then conduct an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, they reevaluate the theory in light of the new results and revise it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researchers can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. As Figure 2.3 shows, this approach meshes nicely with the model of scientific research in psychology presented earlier in the textbook—creating a more detailed model of “theoretically motivated” or “theory-driven” research.
As an example, let us consider Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This theory predicts social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969) [3] . The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory. (Zajonc also showed that drive theory existed in humans [Zajonc & Sales, 1966] [4] in many other studies afterward).
Incorporating Theory into Your Research
When you write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
To use theories in your research will not only give you guidance in coming up with experiment ideas and possible projects, but it lends legitimacy to your work. Psychologists have been interested in a variety of human behaviors and have developed many theories along the way. Using established theories will help you break new ground as a researcher, not limit you from developing your own ideas.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
There are three general characteristics of a good hypothesis. First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable . We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you’ll recall Popper’s falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical. As described above, hypotheses are more than just a random guess. Hypotheses should be informed by previous theories or observations and logical reasoning. Typically, we begin with a broad and general theory and use deductive reasoning to generate a more specific hypothesis to test based on that theory. Occasionally, however, when there is no theory to inform our hypothesis, we use inductive reasoning which involves using specific observations or research findings to form a more general hypothesis. Finally, the hypothesis should be positive. That is, the hypothesis should make a positive statement about the existence of a relationship or effect, rather than a statement that a relationship or effect does not exist. As scientists, we don’t set out to show that relationships do not exist or that effects do not occur so our hypotheses should not be worded in a way to suggest that an effect or relationship does not exist. The nature of science is to assume that something does not exist and then seek to find evidence to prove this wrong, to show that it really does exist. That may seem backward to you but that is the nature of the scientific method. The underlying reason for this is beyond the scope of this chapter but it has to do with statistical theory.
- Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274 ↵
- Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., & Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61 , 195–202. ↵
- Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., & Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13 , 83–92. ↵
- Zajonc, R.B. & Sales, S.M. (1966). Social facilitation of dominant and subordinate responses. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 2 , 160-168. ↵
A coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena.
A specific prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate.
A cyclical process of theory development, starting with an observed phenomenon, then developing or using a theory to make a specific prediction of what should happen if that theory is correct, testing that prediction, refining the theory in light of the findings, and using that refined theory to develop new hypotheses, and so on.
The ability to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and the possibility to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false.
Developing a Hypothesis Copyright © by Rajiv S. Jhangiani; I-Chant A. Chiang; Carrie Cuttler; and Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3 Chapter 3: From Theory to Hypothesis
From theory to hypothesis, 3.1 phenomena and theories.
A phenomenon (plural, phenomena) is a general result that has been observed reliably in systematic empirical research. In essence, it is an established answer to a research question. Some phenomena we have encountered in this book are that expressive writing improves health, women do not talk more than men, and cell phone usage impairs driving ability. Some others are that dissociative identity disorder (formerly called multiple personality disorder) increased greatly in prevalence during the late 20th century, people perform better on easy tasks when they are being watched by others (and worse on difficult tasks), and people recall items presented at the beginning and end of a list better than items presented in the middle.
Some Famous Psychological Phenomena
Phenomena are often given names by their discoverers or other researchers, and these names can catch on and become widely known. The following list is a small sample of famous phenomena in psychology.
· Blindsight. People with damage to their visual cortex are often able to respond to visual stimuli that they do not consciously see.
· Bystander effect. The more people who are present at an emergency situation, the less likely it is that any one of them will help.
· Fundamental attribution error. People tend to explain others’ behavior in terms of their personal characteristics as opposed to the situation they are in.
· McGurk effect. When audio of a basic speech sound is combined with video of a person making mouth movements for a different speech sound, people often perceive a sound that is intermediate between the two.
· Own-race effect. People recognize faces of people of their own race more accurately than faces of people of other races.
· Placebo effect. Placebos (fake psychological or medical treatments) often lead to improvements in people’s symptoms and functioning.
· Mere exposure effect. The more often people have been exposed to a stimulus, the more they like it—even when the stimulus is presented subliminally.
· Serial position effect. Stimuli presented near the beginning and end of a list are remembered better than stimuli presented in the middle.
· Spontaneous recovery. A conditioned response that has been extinguished often returns with no further training after the passage of time.
Although an empirical result might be referred to as a phenomenon after being observed only once, this term is more likely to be used for results that have been replicated. Replication means conducting a study again—either exactly as it was originally conducted or with modifications—to be sure that it produces the same results. Individual researchers usually replicate their own studies before publishing them. Many empirical research reports include an initial study and then one or more follow-up studies that replicate the initial study with minor modifications. Particularly interesting results come to the attention of other researchers who conduct their own replications. The positive effect of expressive writing on health and the negative effect of cell phone usage on driving ability are examples of phenomena that have been replicated many times by many different researchers.
Sometimes a replication of a study produces results that differ from the results of the initial study. This could mean that the results of the initial study or the results of the replication were a fluke—they occurred by chance and do not reflect something that is generally true. In either case, additional replications would be likely to resolve this. A failure to produce the same results could also mean that the replication differed in some important way from the initial study. For example, early studies showed that people performed a variety of tasks better and faster when they were watched by others than when they were alone. Some later replications, however, showed that people performed worse when they were watched by others. Eventually researcher Robert Zajonc identified a key difference between the two types of studies. People seemed to perform better when being watched on highly practiced tasks but worse when being watched on relatively unpracticed tasks (Zajonc, 1965). These two phenomena have now come to be called social facilitation and social inhibition.
What Is a Theory?
A theory is a coherent explanation or interpretation of one or more phenomena. Although theories can take a variety of forms, one thing they have in common is that they go beyond the phenomena they explain by including variables, structures, processes, functions, or organizing principles that have not been observed directly. Consider, for example, Zajonc’s theory of social facilitation and social inhibition. He proposed that being watched by others while performing a task creates a general state of physiological arousal, which increases the likelihood of the dominant (most likely) response. So for highly practiced tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make correct responses, but for relatively unpracticed tasks, being watched increases the tendency to make incorrect responses. Notice that this theory—which has come to be called drive theory—provides an explanation of both social facilitation and social inhibition that goes beyond the phenomena themselves by including concepts such as “arousal” and “dominant response,” along with processes such as the effect of arousal on the dominant response.
Outside of science, referring to an idea as a theory often implies that it is untested—perhaps no more than a wild guess. In science, however, the term theory has no such implication. A theory is simply an explanation or interpretation of a set of phenomena. It can be untested, but it can also be extensively tested, well supported, and accepted as an accurate description of the world by the scientific community. The theory of evolution by natural selection, for example, is a theory because it is an explanation of the diversity of life on earth—not because it is untested or unsupported by scientific research. On the contrary, the evidence for this theory is overwhelmingly positive and nearly all scientists accept its basic assumptions as accurate. Similarly, the “germ theory” of disease is a theory because it is an explanation of the origin of various diseases, not because there is any doubt that many diseases are caused by microorganisms that infect the body.
In addition to theory, researchers in psychology use several related terms to refer to their explanations and interpretations of phenomena. A perspective is a broad approach—more general than a theory—to explaining and interpreting phenomena. For example, researchers who take a biological perspective tend to explain phenomena in terms of genetics or nervous and endocrine system structures and processes, while researchers who take a behavioral perspective tend to explain phenomena in terms of reinforcement, punishment, and other external events. A model is a precise explanation or interpretation of a specific phenomenon—often expressed in terms of equations, computer programs, or biological structures and processes. A hypothesis can be an explanation that relies on just a few key concepts—although this term more commonly refers to a prediction about a new phenomenon based on a theory. Adding to the confusion is the fact that researchers often use these terms interchangeably. It would not be considered wrong to refer to the drive theory as the drive model or even the drive hypothesis. And the biopsychosocial model of health psychology—the general idea that health is determined by an interaction of biological, psychological, and social factors—is really more like a perspective as defined here. Keep in mind, however, that the most important distinction remains that between observations and interpretations.
What Are Theories For?
Of course, scientific theories are meant to provide accurate explanations or interpretations of phenomena. But there must be more to it than this. Consider that a theory can be accurate without being very useful. To say that expressive writing helps people “deal with their emotions” might be accurate as far as it goes, but it seems too vague to be of much use. Consider also that a theory can be useful without being entirely accurate.
3.2 Additional Purposes of Theories
Here we look at three additional purposes of theories: the organization of known phenomena, the prediction of outcomes in new situations, and the generation of new research.
Organization
One important purpose of scientific theories is to organize phenomena in ways that help people think about them clearly and efficiently. The drive theory of social facilitation and social inhibition, for example, helps to organize and make sense of a large number of seemingly contradictory results. The multistore model of human memory efficiently summarizes many important phenomena: the limited capacity and short retention time of information that is attended to but not rehearsed, the importance of rehearsing information for long-term retention, the serial-position effect, and so on.
Thus theories are good or useful to the extent that they organize more phenomena with greater clarity and efficiency. Scientists generally follow the principle of parsimony, which holds that a theory should include only as many concepts as are necessary to explain or interpret the phenomena of interest. Simpler, more parsimonious theories organize phenomena more efficiently than more complex, less parsimonious theories.
A second purpose of theories is to allow researchers and others to make predictions about what will happen in new situations. For example, a gymnastics coach might wonder whether a student’s performance is likely to be better or worse during a competition than when practicing alone. Even if this particular question has never been studied empirically, Zajonc’s drive theory suggests an answer. If the student generally performs with no mistakes, she is likely to perform better during competition. If she generally performs with many mistakes, she is likely to perform worse.
In clinical psychology, treatment decisions are often guided by theories. Consider, for example, dissociative identity disorder (formerly called multiple personality disorder). The prevailing scientific theory of dissociative identity disorder is that people develop multiple personalities (also called alters) because they are familiar with this idea from popular portrayals (e.g., the movie Sybil) and because they are unintentionally encouraged to do so by their clinicians (e.g., by asking to “meet” an alter). This theory implies that rather than encouraging patients to act out multiple personalities, treatment should involve discouraging them from doing this (Lilienfeld & Lynn, 2003).
Generation of New Research
A third purpose of theories is to generate new research by raising new questions. Consider, for example, the theory that people engage in self-injurious behavior such as cutting because it reduces negative emotions such as sadness, anxiety, and anger. This theory immediately suggests several new and interesting questions. Is there, in fact, a statistical relationship between cutting and the amount of negative emotions experienced? Is it causal? If so, what is it about cutting that has this effect? Is it the pain, the sight of the injury, or something else? Does cutting affect all negative emotions equally?
Notice that a theory does not have to be accurate to serve this purpose. Even an inaccurate theory can generate new and interesting research questions. Of course, if the theory is inaccurate, the answers to the new questions will tend to be inconsistent with the theory. This will lead researchers to reevaluate the theory and either revise it or abandon it for a new one. And this is how scientific theories become more detailed and accurate over time.
Multiple Theories
At any point in time, researchers are usually considering multiple theories for any set of phenomena. One reason is that because human behavior is extremely complex, it is always possible to look at it from different perspectives. For example, a biological theory of sexual orientation might focus on the role of sex hormones during critical periods of brain development, while a sociocultural theory might focus on cultural factors that influence how underlying biological tendencies are expressed. A second reason is that—even from the same perspective—there are usually different ways to “go beyond” the phenomena of interest. For example, in addition to the drive theory of social facilitation and social inhibition, there is another theory that explains them in terms of a construct called “evaluation apprehension”—anxiety about being evaluated by the audience. Both theories go beyond the phenomena to be interpreted, but they do so by proposing somewhat different underlying processes.
Different theories of the same set of phenomena can be complementary—with each one supplying one piece of a larger puzzle. A biological theory of sexual orientation and a sociocultural theory of sexual orientation might accurately describe different aspects of the same complex phenomenon. Similarly, social facilitation could be the result of both general physiological arousal and evaluation apprehension. But different theories of the same phenomena can also be competing in the sense that if one is accurate, the other is probably not. For example, an alternative theory of dissociative identity disorder—the posttraumatic theory—holds that alters are created unconsciously by the patient as a means of coping with sexual abuse or some other traumatic experience. Because the sociocognitive theory and the posttraumatic theories attribute dissociative identity disorder to fundamentally different processes, it seems unlikely that both can be accurate.
The fact that there are multiple theories for any set of phenomena does not mean that any theory is as good as any other or that it is impossible to know whether a theory provides an accurate explanation or interpretation. On the contrary, scientists are continually comparing theories in terms of their ability to organize phenomena, predict outcomes in new situations, and generate research. Those that fare poorly are assumed to be less accurate and are abandoned, while those that fare well are assumed to be more accurate and are retained and compared with newer—and hopefully better—theories. Although scientists generally do not believe that their theories ever provide perfectly accurate descriptions of the world, they do assume that this process produces theories that come closer and closer to that ideal.
Key Takeaways
· Scientists distinguish between phenomena, which are their systematic observations, and theories, which are their explanations or interpretations of phenomena.
· In addition to providing accurate explanations or interpretations, scientific theories have three basic purposes. They organize phenomena, allow people to predict what will happen in new situations, and help generate new research.
· Researchers generally consider multiple theories for any set of phenomena. Different theories of the same set of phenomena can be complementary or competing.
3.3 Using Theories in Psychological Research
We have now seen what theories are, what they are for, and the variety of forms that they take in psychological research. In this section we look more closely at how researchers actually use them. We begin with a general description of how researchers test and revise their theories, and we end with some practical advice for beginning researchers who want to incorporate theory into their research.
Theory Testing and Revision
The primary way that scientific researchers use theories is sometimes called the hypothetico-deductive method (although this term is much more likely to be used by philosophers of science than by scientists themselves). A researcher begins with a set of phenomena and either constructs a theory to explain or interpret them or chooses an existing theory to work with. He or she then makes a prediction about some new phenomenon that should be observed if the theory is correct. Again, this prediction is called a hypothesis. The researcher then conducts an empirical study to test the hypothesis. Finally, he or she reevaluates the theory in light of the new results and revises it if necessary. This process is usually conceptualized as a cycle because the researcher can then derive a new hypothesis from the revised theory, conduct a new empirical study to test the hypothesis, and so on. Together they form a model of theoretically motivated research.
As an example, let us return to Zajonc’s research on social facilitation and inhibition. He started with a somewhat contradictory pattern of results from the research literature. He then constructed his drive theory, according to which being watched by others while performing a task causes physiological arousal, which increases an organism’s tendency to make the dominant response. This leads to social facilitation for well-learned tasks and social inhibition for poorly learned tasks. He now had a theory that organized previous results in a meaningful way—but he still needed to test it. He hypothesized that if his theory was correct, he should observe that the presence of others improves performance in a simple laboratory task but inhibits performance in a difficult version of the very same laboratory task. To test this hypothesis, one of the studies he conducted used cockroaches as subjects (Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman, 1969). The cockroaches ran either down a straight runway (an easy task for a cockroach) or through a cross-shaped maze (a difficult task for a cockroach) to escape into a dark chamber when a light was shined on them. They did this either while alone or in the presence of other cockroaches in clear plastic “audience boxes.” Zajonc found that cockroaches in the straight runway reached their goal more quickly in the presence of other cockroaches, but cockroaches in the cross-shaped maze reached their goal more slowly when they were in the presence of other cockroaches. Thus he confirmed his hypothesis and provided support for his drive theory.
Constructing or Choosing a Theory
Along with generating research questions, constructing theories is one of the more creative parts of scientific research. But as with all creative activities, success requires preparation and hard work more than anything else. To construct a good theory, a researcher must know in detail about the phenomena of interest and about any existing theories based on a thorough review of the literature. The new theory must provide a coherent explanation or interpretation of the phenomena of interest and have some advantage over existing theories. It could be more formal and therefore more precise, broader in scope, more parsimonious, or it could take a new perspective or theoretical approach. If there is no existing theory, then almost any theory can be a step in the right direction.
As we have seen, formality, scope, and theoretical approach are determined in part by the nature of the phenomena to be interpreted. But the researcher’s interests and abilities play a role too. For example, constructing a theory that specifies the neural structures and processes underlying a set of phenomena requires specialized knowledge and experience in neuroscience (which most professional researchers would acquire in college and then graduate school). But again, many theories in psychology are relatively informal, narrow in scope, and expressed in terms that even a beginning researcher can understand and even use to construct his or her own new theory.
It is probably more common, however, for a researcher to start with a theory that was originally constructed by someone else—giving due credit to the originator of the theory. This is another example of how researchers work collectively to advance scientific knowledge. Once they have identified an existing theory, they might derive a hypothesis from the theory and test it or modify the theory to account for some new phenomenon and then test the modified theory.
Deriving Hypotheses
Again, a hypothesis is a prediction about a new phenomenon that should be observed if a particular theory is accurate. Theories and hypotheses always have this if-then relationship. “If drive theory is correct, then cockroaches should run through a straight runway faster, and a branching runway more slowly, when other cockroaches are present.” Although hypotheses are usually expressed as statements, they can always be rephrased as questions. “Do cockroaches run through a straight runway faster when other cockroaches are present?” Thus deriving hypotheses from theories is an excellent way of generating interesting research questions.
But how do researchers derive hypotheses from theories? One way is to generate a research question using the techniques discussed in Chapter 2 and then ask whether any theory implies an answer to that question. For example, you might wonder whether expressive writing about positive experiences improves health as much as expressive writing about traumatic experiences. Although this is an interesting question on its own, you might then ask whether the habituation theory—the idea that expressive writing causes people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings—implies an answer. In this case, it seems clear that if the habituation theory is correct, then expressive writing about positive experiences should not be effective because it would not cause people to habituate to negative thoughts and feelings. A second way to derive hypotheses from theories is to focus on some component of the theory that has not yet been directly observed. For example, a researcher could focus on the process of habituation—perhaps hypothesizing that people should show fewer signs of emotional distress with each new writing session.
Among the very best hypotheses are those that distinguish between competing theories. For example, Norbert Schwarz and his colleagues considered two theories of how people make judgments about themselves, such as how assertive they are (Schwarz et al., 1991). Both theories held that such judgments are based on relevant examples that people bring to mind. However, one theory was that people base their judgments on the number of examples they bring to mind and the other was that people base their judgments on how easily they bring those examples to mind. To test these theories, the researchers asked people to recall either six times when they were assertive (which is easy for most people) or 12 times (which is difficult for most people). Then they asked them to judge their own assertiveness. Note that the number-of-examples theory implies that people who recalled 12 examples should judge themselves to be more assertive because they recalled more examples, but the ease-of-examples theory implies that participants who recalled six examples should judge themselves as more assertive because recalling the examples was easier. Thus the two theories made opposite predictions so that only one of the predictions could be confirmed. The surprising result was that participants who recalled fewer examples judged themselves to be more assertive—providing particularly convincing evidence in favor of the ease-of-retrieval theory over the number-of-examples theory.
Evaluating and Revising Theories
If a hypothesis is confirmed in a systematic empirical study, then the theory has been strengthened. Not only did the theory make an accurate prediction, but there is now a new phenomenon that the theory accounts for. If a hypothesis is disconfirmed in a systematic empirical study, then the theory has been weakened. It made an inaccurate prediction, and there is now a new phenomenon that it does not account for.
Although this seems straightforward, there are some complications. First, confirming a hypothesis can strengthen a theory but it can never prove a theory. In fact, scientists tend to avoid the word “prove” when talking and writing about theories. One reason for this is that there may be other plausible theories that imply the same hypothesis, which means that confirming the hypothesis strengthens all those theories equally. A second reason is that it is always possible that another test of the hypothesis or a test of a new hypothesis derived from the theory will be disconfirmed. This is a version of the famous philosophical “problem of induction.” One cannot definitively prove a general principle (e.g., “All swans are white.”) just by observing confirming cases (e.g., white swans)—no matter how many. It is always possible that a disconfirming case (e.g., a black swan) will eventually come along. For these reasons, scientists tend to think of theories—even highly successful ones—as subject to revision based on new and unexpected observations.
A second complication has to do with what it means when a hypothesis is disconfirmed. According to the strictest version of the hypothetico-deductive method, disconfirming a hypothesis disproves the theory it was derived from. In formal logic, the premises “if A then B” and “not B” necessarily lead to the conclusion “not A.” If A is the theory and B is the hypothesis (“if A then B”), then disconfirming the hypothesis (“not B”) must mean that the theory is incorrect (“not A”). In practice, however, scientists do not give up on their theories so easily. One reason is that one disconfirmed hypothesis could be a fluke or it could be the result of a faulty research design. Perhaps the researcher did not successfully manipulate the independent variable or measure the dependent variable. A disconfirmed hypothesis could also mean that some unstated but relatively minor assumption of the theory was not met. For example, if Zajonc had failed to find social facilitation in cockroaches, he could have concluded that drive theory is still correct but it applies only to animals with sufficiently complex nervous systems.
This does not mean that researchers are free to ignore disconfirmations of their theories. If they cannot improve their research designs or modify their theories to account for repeated disconfirmations, then they eventually abandon their theories and replace them with ones that are more successful.
Incorporating Theory Into Your Research
It should be clear from this chapter that theories are not just “icing on the cake” of scientific research; they are a basic ingredient. If you can understand and use them, you will be much more successful at reading and understanding the research literature, generating interesting research questions, and writing and conversing about research. Of course, your ability to understand and use theories will improve with practice. But there are several things that you can do to incorporate theory into your research right from the start.
The first thing is to distinguish the phenomena you are interested in from any theories of those phenomena. Beware especially of the tendency to “fuse” a phenomenon to a commonsense theory of it. For example, it might be tempting to describe the negative effect of cell phone usage on driving ability by saying, “Cell phone usage distracts people from driving.” Or it might be tempting to describe the positive effect of expressive writing on health by saying, “Dealing with your emotions through writing makes you healthier.” In both of these examples, however, a vague commonsense explanation (distraction, “dealing with” emotions) has been fused to the phenomenon itself. The problem is that this gives the impression that the phenomenon has already been adequately explained and closes off further inquiry into precisely why or how it happens.
As another example, researcher Jerry Burger and his colleagues were interested in the phenomenon that people are more willing to comply with a simple request from someone with whom they are familiar (Burger, Soroka, Gonzago, Murphy, & Somervell, 1999). A beginning researcher who is asked to explain why this is the case might be at a complete loss or say something like, “Well, because they are familiar with them.” But digging just a bit deeper, Burger and his colleagues realized that there are several possible explanations. Among them are that complying with people we know creates positive feelings, that we anticipate needing something from them in the future, and that we like them more and follow an automatic rule that says to help people we like.
The next thing to do is turn to the research literature to identify existing theories of the phenomena you are interested in. Remember that there will usually be more than one plausible theory. Existing theories may be complementary or competing, but it is essential to know what they are. If there are no existing theories, you should come up with two or three of your own—even if they are informal and limited in scope. Then get in the habit of describing the phenomena you are interested in, followed by the two or three best theories of it. Do this whether you are speaking or writing about your research. When asked what their research was about, for example, Burger and his colleagues could have said something like the following:
It’s about the fact that we’re more likely to comply with requests from people we know [the phenomenon]. This is interesting because it could be because it makes us feel good [Theory 1], because we think we might get something in return [Theory 2], or because we like them more and have an automatic tendency to comply with people we like [Theory 3].
At this point, you may be able to derive a hypothesis from one of the theories. At the very least, for each research question you generate, you should ask what each plausible theory implies about the answer to that question. If one of them implies a particular answer, then you may have an interesting hypothesis to test. Burger and colleagues, for example, asked what would happen if a request came from a stranger whom participants had sat next to only briefly, did not interact with, and had no expectation of interacting with in the future. They reasoned that if familiarity created liking, and liking increased people’s tendency to comply (Theory 3), then this situation should still result in increased rates of compliance (which it did). If the question is interesting but no theory implies an answer to it, this might suggest that a new theory needs to be constructed or that existing theories need to be modified in some way. These would make excellent points of discussion in the introduction or discussion of an American Psychological Association (APA) style research report or research presentation.
When you do write your research report or plan your presentation, be aware that there are two basic ways that researchers usually include theory. The first is to raise a research question, answer that question by conducting a new study, and then offer one or more theories (usually more) to explain or interpret the results. This format works well for applied research questions and for research questions that existing theories do not address. The second way is to describe one or more existing theories, derive a hypothesis from one of those theories, test the hypothesis in a new study, and finally reevaluate the theory. This format works well when there is an existing theory that addresses the research question—especially if the resulting hypothesis is surprising or conflicts with a hypothesis derived from a different theory.
· Working with theories is not “icing on the cake.” It is a basic ingredient of psychological research.
· Like other scientists, psychologists use the hypothetico-deductive method. They construct theories to explain or interpret phenomena (or work with existing theories), derive hypotheses from their theories, test the hypotheses, and then reevaluate the theories in light of the new results.
· There are several things that even beginning researchers can do to incorporate theory into their research. These include clearly distinguishing phenomena from theories, knowing about existing theories, constructing one’s own simple theories, using theories to make predictions about the answers to research questions, and incorporating theories into one’s writing and speaking.
3.4 Understanding Null Hypothesis Testing
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing
As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables for a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher’s goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the sample was selected from. Thus researchers must use sample statistics to draw conclusions about the corresponding values in the population. These corresponding values in the population are called parameters. Imagine, for example, that a researcher measures the number of depressive symptoms exhibited by each of 50 clinically depressed adults and computes the mean number of symptoms. The researcher probably wants to use this sample statistic (the mean number of symptoms for the sample) to draw conclusions about the corresponding population parameter (the mean number of symptoms for clinically depressed adults).
Unfortunately, sample statistics are not perfect estimates of their corresponding population parameters. This is because there is a certain amount of random variability in any statistic from sample to sample. This random variability in a statistic from sample to sample is called sampling error.
One implication of this is that when there is a statistical relationship in a sample, it is not always clear that there is a statistical relationship in the population. A small difference between two group means in a sample might indicate that there is a small difference between the two group means in the population. But it could also be that there is no difference between the means in the population and that the difference in the sample is just a matter of sampling error. Similarly, a Pearson’s r value of −.29 in a sample might mean that there is a negative relationship in the population. But it could also be that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample is just a matter of sampling error.
In fact, any statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in two ways:
- There is a relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects this.
- There is no relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The purpose of null hypothesis testing is simply to help researchers decide between these two interpretations.
The Logic of Null Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis (often symbolized H0 and read as “H-naught”). This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error. Informally, the null hypothesis is that the sample relationship “occurred by chance.” The other interpretation is called the alternative hypothesis (often symbolized as H1). This is the idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
Again, every statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in either of these two ways: It might have occurred by chance, or it might reflect a relationship in the population. So researchers need a way to decide between them. Although there are many specific null hypothesis testing techniques, they are all based on the same general logic. The steps are as follows:
- Assume for the moment that the null hypothesis is true. There is no relationship between the variables in the population.
- Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true.
- If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, then reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be extremely unlikely, then retain the null hypothesis.
Following this logic, we can begin to understand why Mehl and his colleagues concluded that there is no difference in talkativeness between women and men in the population. In essence, they asked the following question: “If there were no difference in the population, how likely is it that we would find a small difference of d = 0.06 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly likely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they retained the null hypothesis—concluding that there is no evidence of a sex difference in the population. We can also see why Kanner and his colleagues concluded that there is a correlation between hassles and symptoms in the population. They asked, “If the null hypothesis were true, how likely is it that we would find a strong correlation of +.60 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly unlikely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they rejected the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis—concluding that there is a positive correlation between these variables in the population.
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample result would be likely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the retention of the null hypothesis. But how low must the p value be before the sample result is considered unlikely enough to reject the null hypothesis? In null hypothesis testing, this criterion is called α (alpha) and is almost always set to .05. If there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true, then the null hypothesis is rejected. When this happens, the result is said to be statistically significant. If there is greater than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result when the null hypothesis is true, then the null hypothesis is retained. This does not necessarily mean that the researcher accepts the null hypothesis as true—only that there is not currently enough evidence to conclude that it is true. Researchers often use the expression “fail to reject the null hypothesis” rather than “retain the null hypothesis,” but they never use the expression “accept the null hypothesis.”
The Misunderstood p Value
The p value is one of the most misunderstood quantities in psychological research (Cohen, 1994). Even professional researchers misinterpret it, and it is not unusual for such misinterpretations to appear in statistics textbooks!
The most common misinterpretation is that the p value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true—that the sample result occurred by chance. For example, a misguided researcher might say that because the p value is .02, there is only a 2% chance that the result is due to chance and a 98% chance that it reflects a real relationship in the population. But this is incorrect. The p value is really the probability of a result at least as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would occur only 2% of the time.
You can avoid this misunderstanding by remembering that the p value is not the probability that any particular hypothesis is true or false. Instead, it is the probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true.
Role of Sample Size and Relationship Strength
Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, “If the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as this one?” In other words, “What is the p value?” It can be helpful to see that the answer to this question depends on just two considerations: the strength of the relationship and the size of the sample. Specifically, the stronger the sample relationship and the larger the sample, the less likely the result would be if the null hypothesis were true. That is, the lower the p value. This should make sense. Imagine a study in which a sample of 500 women is compared with a sample of 500 men in terms of some psychological characteristic, and Cohen’s d is a strong 0.50. If there were really no sex difference in the population, then a result this strong based on such a large sample should seem highly unlikely. Now imagine a similar study in which a sample of three women is compared with a sample of three men, and Cohen’s d is a weak 0.10. If there were no sex difference in the population, then a relationship this weak based on such a small sample should seem likely. And this is precisely why the null hypothesis would be rejected in the first example and retained in the second.
Of course, sometimes the result can be weak and the sample large, or the result can be strong and the sample small. In these cases, the two considerations trade off against each other so that a weak result can be statistically significant if the sample is large enough and a strong relationship can be statistically significant even if the sample is small. Weak relationships based on medium or small samples are never statistically significant and that strong relationships based on medium or larger samples are always statistically significant. If you keep this in mind, you will often know whether a result is statistically significant based on the descriptive statistics alone. It is extremely useful to be able to develop this kind of intuitive judgment. One reason is that it allows you to develop expectations about how your formal null hypothesis tests are going to come out, which in turn allows you to detect problems in your analyses. For example, if your sample relationship is strong and your sample is medium, then you would expect to reject the null hypothesis. If for some reason your formal null hypothesis test indicates otherwise, then you need to double-check your computations and interpretations. A second reason is that the ability to make this kind of intuitive judgment is an indication that you understand the basic logic of this approach in addition to being able to do the computations.
Statistical Significance Versus Practical Significance
A statistically significant result is not necessarily a strong one. Even a very weak result can be statistically significant if it is based on a large enough sample. This is closely related to Janet Shibley Hyde’s argument about sex differences (Hyde, 2007). The differences between women and men in mathematical problem solving and leadership ability are statistically significant. But the word significant can cause people to interpret these differences as strong and important—perhaps even important enough to influence the college courses they take or even who they vote for. As we have seen, however, these statistically significant differences are actually quite weak—perhaps even “trivial.”
This is why it is important to distinguish between the statistical significance of a result and the practical significance of that result. Practical significance refers to the importance or usefulness of the result in some real-world context. Many sex differences are statistically significant—and may even be interesting for purely scientific reasons—but they are not practically significant. In clinical practice, this same concept is often referred to as “clinical significance.” For example, a study on a new treatment for social phobia might show that it produces a statistically significant positive effect. Yet this effect still might not be strong enough to justify the time, effort, and other costs of putting it into practice—especially if easier and cheaper treatments that work almost as well already exist. Although statistically significant, this result would be said to lack practical or clinical significance.
· Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding whether a statistical relationship in a sample reflects a real relationship in the population or is just due to chance.
· The logic of null hypothesis testing involves assuming that the null hypothesis is true, finding how likely the sample result would be if this assumption were correct, and then making a decision. If the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true, then it is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be unlikely, then the null hypothesis is retained.
· The probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true (the p value) is based on two considerations: relationship strength and sample size. Reasonable judgments about whether a sample relationship is statistically significant can often be made by quickly considering these two factors.
· Statistical significance is not the same as relationship strength or importance. Even weak relationships can be statistically significant if the sample size is large enough. It is important to consider relationship strength and the practical significance of a result in addition to its statistical significance.
References from Chapter 3
Burger, J. M., Soroka, S., Gonzago, K., Murphy, E., Somervell, E. (1999). The effect of fleeting attraction on compliance to requests. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 27, 1578–1586.
Cohen, J. (1994). The world is round: p .05. American Psychologist, 49, 997–1003.
Hyde, J. S. (2007). New directions in the study of gender similarities and differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16, 259–263.
Izawa, C. (Ed.) (1999). On human memory: Evolution, progress, and reflections on the 30th anniversary of the Atkinson-Shiffrin model. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Lilienfeld, S. O., Lynn, S. J. (2003). Dissociative identity disorder: Multiplepersonalities, multiple controversies. In S. O. Lilienfeld, S. J. Lynn, J. M. Lohr (Eds.), Science and pseudoscience in clinical psychology (pp. 109–142). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Neisser, U., Boodoo, G., Bouchard, T. J., Boykin, A. W., Brody, N., Ceci,…Urbina, S. (1996). Intelligence: Knowns and unknowns. American Psychologist, 51, 77–101.
Schwarz, N., Bless, H., Strack, F., Klumpp, G., Rittenauer-Schatka, H., Simons, A. (1991). Ease of retrieval as information: Another look at the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61, 195–202.
Zajonc, R. B. (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149, 269–274.
Zajonc, R. B., Heingartner, A., Herman, E. M. (1969). Social enhancement and impairment of performance in the cockroach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 13, 83–92.
Research Methods in Psychology & Neuroscience Copyright © by Dalhousie University Introduction to Psychology and Neuroscience Team. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

Psychology Hypothesis
Ai generator.

Delving into the realm of human behavior and cognition, Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples illuminate the intricate workings of the mind. These thesis statement examples span various psychological phenomena, offering insights into crafting hypotheses that drive impactful research. From personality traits to cognitive processes, explore the guide to formulate precise and insightful psychology hypothesis statements that shed light on the complexities of human psychology.
What is the Psychology Hypothesis?
In psychology, a good hypothesis is a tentative statement or educated guess that proposes a potential relationship between variables. It serves as a foundation for research, guiding the investigation into specific psychological phenomena or behaviors. A well-constructed psychology hypothesis outlines the expected outcome of the study and provides a framework for data collection and analysis.
Example of a Psychology Hypothesis Statement :
Research Question: Does exposure to nature improve individuals’ mood and well-being?
Hypothesis Statement: “Individuals who spend more time in natural environments will report higher levels of positive mood and overall well-being compared to those who spend less time outdoors.”
In this example, the psychology hypothesis predicts a positive relationship between exposure to nature and improved mood and well-being. The statement sets the direction for the study and provides a clear basis for data collection and analysis.
100 Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples

Size: 202 KB
Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples encompass a diverse range of human behaviors and mental processes. Dive into the complexities of the human mind with Simple hypothesis that explore relationships, patterns, and influences on behavior. From memory recall to social interactions, these examples offer insights into crafting precise and impactful psychology hypotheses that drive meaningful research.
- Effect of Color on Mood : Exposure to blue hues elevates mood in individuals.
- Social Media and Self-Esteem : Higher social media usage correlates with lower self-esteem levels.
- Sleep Quality and Cognitive Performance : Improved sleep quality enhances cognitive performance.
- Personality Traits and Leadership : Extroverted individuals are more likely to assume leadership roles.
- Parent-Child Attachment and Behavior : Strong parent-child attachment fosters positive behavior in children.
- Cognitive Load and Decision Making : Increased cognitive load leads to poorer decision-making abilities.
- Mindfulness Meditation and Stress Reduction : Regular mindfulness practice reduces stress levels.
- Empathy and Altruistic Behavior : Higher empathy levels predict increased altruistic actions.
- Positive Reinforcement and Learning : Positive reinforcement enhances learning outcomes in children.
- Attachment Style and Romantic Relationships : Securely attached individuals experience more satisfying romantic relationships.
- Body Image and Media Exposure : Greater exposure to idealized body images leads to negative body image perceptions.
- Anxiety Levels and Academic Performance : Higher anxiety levels negatively impact academic achievement.
- Parenting Style and Aggression : Authoritarian parenting style correlates with higher aggression in children.
- Cognitive Aging and Memory Recall : Older adults experience reduced memory recall compared to younger individuals.
- Peer Pressure and Risky Behavior : Peer pressure increases engagement in risky behaviors among adolescents.
- Emotional Intelligence and Relationship Satisfaction : High emotional intelligence leads to greater relationship satisfaction.
- Attachment Style and Coping Mechanisms : Insecure attachment is linked to maladaptive coping strategies.
- Perceived Control and Stress Resilience : Higher perceived control buffers against the negative effects of stress.
- Social Comparison and Self-Esteem : Frequent social comparison diminishes self-esteem levels.
- Gender Stereotypes and Career Aspirations : Gender stereotypes influence career aspirations of young adults.
- Technology Usage and Social Isolation : Increased technology usage contributes to feelings of social isolation.
- Empathy and Conflict Resolution : Higher empathy levels facilitate effective conflict resolution.
- Parental Influence and Academic Motivation : Parental involvement positively impacts student academic motivation.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Video Games : Children with ADHD show increased hyperactivity after playing video games.
- Positive Psychology Interventions and Well-being : Engaging in positive psychology interventions enhances overall well-being.
- Social Support and Mental Health : Adequate social support leads to better mental health outcomes.
- Parent-Child Communication and Risky Behavior : Open parent-child communication reduces engagement in risky behaviors.
- Social Media and Body Dissatisfaction : Extensive social media use is linked to increased body dissatisfaction.
- Personality Traits and Coping Strategies : Different personality traits influence varied coping mechanisms.
- Peer Influence and Substance Abuse : Peer influence contributes to higher rates of substance abuse among adolescents.
- Attentional Bias and Anxiety : Individuals with attentional bias are more prone to experiencing anxiety.
- Attachment Style and Romantic Jealousy : Insecure attachment predicts higher levels of romantic jealousy.
- Emotion Regulation and Well-being : Effective emotion regulation leads to greater overall well-being.
- Parenting Styles and Academic Resilience : Supportive parenting styles enhance academic resilience in children.
- Cultural Identity and Self-Esteem : Strong cultural identity is linked to higher self-esteem among minority individuals.
- Working Memory and Problem-Solving : Better working memory capacity improves problem-solving abilities.
- Fear Conditioning and Phobias : Fear conditioning contributes to the development of specific phobias.
- Empathy and Prosocial Behavior : Higher empathy levels result in increased prosocial behaviors.
- Social Anxiety and Online Communication : Individuals with social anxiety prefer online communication over face-to-face interactions.
- Cognitive Biases and Decision-Making Errors : Cognitive biases lead to errors in judgment and decision-making.
- Attachment Style and Romantic Attachment Patterns : Attachment style influences the development of romantic attachment patterns.
- Self-Efficacy and Goal Achievement : Higher self-efficacy predicts greater success in achieving personal goals.
- Stress Levels and Immune System Functioning : Elevated stress levels impair immune system functioning.
- Social Media Use and Loneliness : Excessive social media use is associated with increased feelings of loneliness.
- Emotion Recognition and Social Interaction : Improved emotion recognition skills enhance positive social interactions.
- Perceived Control and Psychological Resilience : Strong perceived control fosters psychological resilience in adverse situations.
- Narcissism and Online Self-Presentation : Narcissistic individuals engage in heightened self-promotion on social media.
- Fear of Failure and Performance Anxiety : Fear of failure contributes to performance anxiety in high-pressure situations.
- Gratitude Practice and Well-being : Regular gratitude practice leads to improved overall well-being.
- Cultural Norms and Communication Styles : Cultural norms shape distinct communication styles among different groups.
- Gender Identity and Mental Health : The alignment between gender identity and assigned sex at birth affects mental health outcomes.
- Social Influence and Conformity : Social influence leads to increased conformity in group settings.
- Parenting Styles and Attachment Security : Parenting styles influence the development of secure or insecure attachment in children.
- Perceived Discrimination and Psychological Distress : Perceived discrimination is associated with higher levels of psychological distress.
- Emotional Regulation Strategies and Impulse Control : Effective emotional regulation strategies enhance impulse control.
- Cognitive Dissonance and Attitude Change : Cognitive dissonance prompts individuals to change attitudes to reduce discomfort.
- Prejudice and Stereotype Formation : Exposure to prejudiced attitudes contributes to the formation of stereotypes.
- Motivation and Goal Setting : High intrinsic motivation leads to more effective goal setting and achievement.
- Coping Mechanisms and Trauma Recovery : Adaptive coping mechanisms facilitate better trauma recovery outcomes.
- Personality Traits and Perceived Stress : Certain personality traits influence how individuals perceive and respond to stress.
- Cognitive Biases and Decision-Making Strategies : Cognitive biases impact the strategies individuals use in decision-making.
- Emotional Intelligence and Interpersonal Relationships : High emotional intelligence fosters healthier and more fulfilling interpersonal relationships.
- Sensory Perception and Memory Formation : The accuracy of sensory perception influences the formation of memories.
- Parental Influences and Peer Relationships : Parental attitudes shape the quality of adolescents’ peer relationships.
- Social Comparison and Body Image : Frequent social comparison contributes to negative body image perceptions.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Academic Achievement : Children with ADHD face challenges in achieving academic success.
- Cultural Identity and Mental Health Stigma : Strong cultural identity buffers against the negative effects of mental health stigma.
- Self-Esteem and Risk-Taking Behavior : Individuals with high self-esteem are more likely to engage in risk-taking behaviors.
- Resilience and Adversity Coping : High resilience levels enhance individuals’ ability to cope with adversity.
- Motivation and Learning Styles : Different types of motivation influence preferred learning styles.
- Body Language and Nonverbal Communication : Body language cues play a significant role in nonverbal communication effectiveness.
- Social Identity and Intergroup Bias : Strong identification with a social group contributes to intergroup bias.
- Mindfulness Practice and Anxiety Reduction : Regular mindfulness practice leads to decreased levels of anxiety.
- Attachment Style and Romantic Satisfaction : Attachment style influences satisfaction levels in romantic relationships.
- Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation : Intrinsic motivation yields more sustainable outcomes than extrinsic motivation.
- Attention Allocation and Multitasking Performance : Efficient attention allocation enhances multitasking performance.
- Neuroplasticity and Skill Acquisition : Neuroplasticity supports the acquisition and refinement of new skills.
- Prejudice Reduction Interventions and Attitude Change : Prejudice reduction interventions lead to positive attitude changes.
- Parental Support and Adolescent Resilience : Strong parental support enhances resilience in adolescents facing challenges.
- Social Media Use and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) : Extensive social media use contributes to higher levels of FOMO.
- Mood and Decision-Making Biases : Different mood states influence cognitive biases in decision-making.
- Parental Attachment and Peer Influence : Strong parental attachment moderates the impact of peer influence on adolescents.
- Personality Traits and Job Satisfaction : Certain personality traits predict higher job satisfaction levels.
- Social Support and Post-Traumatic Growth : Adequate social support fosters post-traumatic growth after adversity.
- Cognitive Load and Creativity : High cognitive load impedes creative thinking and problem-solving.
- Self-Efficacy and Goal Persistence : Higher self-efficacy leads to increased persistence in achieving goals.
- Stress and Physical Health : Chronic stress negatively affects physical health outcomes.
- Perceived Control and Psychological Well-being : Strong perceived control is linked to greater psychological well-being.
- Parenting Styles and Emotional Regulation in Children : Authoritative parenting styles promote effective emotional regulation.
- Cultural Exposure and Empathy Levels : Exposure to diverse cultures enhances empathetic understanding.
- Emotional Intelligence and Conflict Resolution : High emotional intelligence leads to more effective conflict resolution strategies.
- Personality Traits and Leadership Styles : Different personality traits align with distinct leadership approaches.
- Attachment Style and Romantic Relationship Quality : Secure attachment predicts higher quality romantic relationships.
- Social Comparison and Self-Perception : Frequent social comparison impacts individuals’ self-perception and self-esteem.
- Mindfulness Meditation and Stress Resilience : Regular mindfulness practice enhances resilience in the face of stress.
- Cognitive Biases and Prejudice Formation : Cognitive biases contribute to the formation and reinforcement of prejudices.
- Parenting Styles and Social Skills Development : Authoritative parenting styles foster positive social skills in children.
- Emotion Regulation Strategies and Mental Health : Effective emotion regulation strategies contribute to better mental health outcomes.
- Self-Esteem and Academic Achievement : Higher self-esteem correlates with improved academic performance.
- Cultural Identity and Intergroup Bias : Strong cultural identity buffers against the effects of intergroup bias.
Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples for Social Experiments & Studies : Dive into social dynamics with hypotheses that explore human behavior in various contexts. These examples delve into the intricate interplay of psychological factors in social experiments and studies, shedding light on how individuals interact, perceive, and respond within social environments. You may also be interested in our two tailed hypothesis .
- Influence of Group Size on Conformity : Larger group sizes lead to higher levels of conformity in social experiments.
- Effects of Positive Reinforcement on Prosocial Behavior : Positive reinforcement increases the likelihood of engaging in prosocial actions.
- Role of Normative Social Influence in Decision Making : Normative social influence influences decision-making processes in group settings.
- Impact of Obedience to Authority on Ethical Decision Making : Obedience to authority influences ethical decision-making tendencies.
- Attribution Bias in Social Interactions : Attribution bias leads individuals to attribute their successes to internal factors and failures to external factors.
- Social Comparison and Body Dissatisfaction : Frequent social comparison contributes to negative body image perceptions.
- Perceived Control and Social Stress Resilience : Strong perceived control mitigates the negative effects of social stress.
- Impression Management in Online Social Networks : Individuals engage in impression management to create a favorable online image.
- Social Identity and Group Behavior : Strong social identity fosters a sense of belonging and influences group behavior.
- Altruistic Behavior and Empathy Levels : Higher empathy levels correlate with increased engagement in altruistic actions.
Social Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples : Explore the intricacies of human behavior within social contexts through these social psychology hypotheses. These examples delve into the dynamics of social interactions, group dynamics, and the psychological factors that influence how individuals perceive and respond to the social world.
- Social Norms and Conformity : Individuals conform to social norms to gain social acceptance and avoid rejection.
- Bystander Effect and Helping Behavior : The bystander effect decreases the likelihood of individuals offering help in emergency situations.
- In-Group Bias and Intergroup Relations : In-group bias leads to favoritism toward members of one’s own social group.
- Social Influence and Decision Making : Social influence impacts decision-making processes in group settings.
- Deindividuation and Uninhibited Behavior : Deindividuation leads to reduced self-awareness and increased uninhibited behavior.
- Perceived Social Support and Coping Mechanisms : Adequate social support enhances effective coping strategies in challenging situations.
- Group Polarization and Risky Decision Making : Group discussions intensify individuals’ pre-existing inclinations, leading to riskier decisions.
- Self-Esteem and Social Comparison : Individuals with lower self-esteem are more prone to engaging in negative social comparison.
- Cultural Norms and Nonverbal Communication : Cultural norms influence nonverbal communication cues and interpretations.
Alternative Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples : Explore alternative hypothesis perspectives on psychological phenomena with these hypotheses. These examples challenge conventional wisdom and encourage critical thinking, providing a fresh outlook on various aspects of human behavior, cognition, and emotions.
- Nonverbal Communication and Introversion : Nonverbal cues may play a more significant role in communication for introverted individuals.
- Perceived Control and External Locus of Control : High perceived control may lead to an external locus of control in certain situations.
- Cognitive Dissonance and Reinforcement Theory : Cognitive dissonance can be explained through the lens of reinforcement theory.
- Bystander Effect and Social Responsibility : The bystander effect may stem from individuals’ heightened sense of social responsibility.
- Emotion Regulation and Emotional Suppression : Emotion regulation strategies like emotional suppression might lead to long-term emotional well-being.
- Perceived Social Support and Emotional Independence : Adequate social support may contribute to emotional independence rather than dependence.
- Cultural Identity and Interpersonal Conflict : Strong cultural identity might lead to increased interpersonal conflict due to differing values.
- Parenting Styles and Personality Development : Parenting styles might have a limited impact on the formation of certain personality traits.
- Social Media Use and Positive Self-Presentation : Extensive social media use may lead to a more authentic self-presentation.
- Attentional Bias and Cognitive Flexibility : Attentional bias might enhance cognitive flexibility in specific cognitive tasks.
Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples in Research : Explore the realms of psychological research hypothesis that guide scientific inquiry. These examples span various subfields of psychology, offering insights into human behavior, cognition, and emotions through the lens of empirical investigation.
- Effects of Meditation on Mindfulness : Regular meditation practice enhances individuals’ mindfulness levels.
- Impact of Parenting Styles on Self-Esteem : Parenting styles significantly influence children’s self-esteem development.
- Emotion Regulation Strategies and Anxiety Levels : Effective emotion regulation strategies lead to decreased anxiety levels.
- Cultural Identity and Academic Achievement : Strong cultural identity positively impacts academic achievement in multicultural settings.
- Influence of Peer Pressure on Risky Behavior : Peer pressure increases engagement in risky behaviors among adolescents.
- Effects of Social Support on Depression : Adequate social support leads to decreased depression symptoms in individuals.
- Mindfulness Meditation and Attention Span : Regular mindfulness practice improves individuals’ attention span and focus.
- Attachment Style and Romantic Satisfaction : Attachment style predicts satisfaction levels in romantic relationships.
- Effects of Positive Feedback on Motivation : Positive feedback enhances intrinsic motivation for challenging tasks.
- Impact of Sleep Quality on Memory Consolidation : Better sleep quality leads to improved memory consolidation during sleep.
Experimental Research in Psychology Hypothesis Examples : Embark on experimental journeys with hypotheses that guide controlled investigations into psychological phenomena. These examples facilitate the design and execution of experiments, allowing researchers to manipulate variables, observe outcomes, and draw evidence-based conclusions.
- Effects of Color on Mood : Exposure to warm colors enhances positive mood, while cool colors evoke calmness.
- Impact of Visual Distractions on Concentration : Visual distractions negatively affect individuals’ ability to concentrate on tasks.
- Influence of Music Tempo on Heart Rate : Upbeat music tempo leads to increased heart rate and arousal.
- Effects of Humor on Stress Reduction : Humor interventions reduce stress levels and increase feelings of relaxation.
- Impact of Exercise on Cognitive Function : Regular aerobic exercise improves cognitive function and memory retention.
- Influence of Social Norms on Helping Behavior : Observing prosocial behavior in others increases individuals’ likelihood of offering help.
- Effects of Sleep Duration on Reaction Time : Longer sleep duration leads to faster reaction times in cognitive tasks.
- Impact of Positive Affirmations on Self-Esteem : Repeating positive affirmations boosts self-esteem and self-confidence.
- Influence of Noise Levels on Task Performance : High noise levels impair individuals’ performance on cognitive tasks.
- Effects of Temperature on Aggressive Behavior : Elevated temperatures lead to an increase in aggressive behavior.
Psychology Hypothesis Tentative Statement Examples : Embark on the journey of exploration and inquiry with these tentative hypotheses. These examples reflect the initial assumptions and predictions that researchers formulate before conducting in-depth investigations, paving the way for further study and empirical examination.
- Possible Effects of Mindfulness on Stress Reduction : Mindfulness practices might contribute to reduced stress levels in individuals.
- Potential Impact of Social Media Use on Loneliness : Extensive social media use could be linked to increased feelings of loneliness.
- Tentative Connection Between Personality Traits and Leadership Styles : Certain personality traits may align with specific leadership approaches.
- Potential Relationship Between Parenting Styles and Academic Motivation : Different parenting styles might influence students’ motivation for academics.
- Hypothesized Impact of Cognitive Training on Memory Enhancement : Cognitive training interventions may lead to improved memory function.
- Preliminary Association Between Emotional Intelligence and Conflict Resolution : Higher emotional intelligence might be related to more effective conflict resolution.
- Possible Effects of Music Exposure on Emotional Regulation : Listening to music might impact individuals’ ability to regulate emotions.
- Tentative Link Between Self-Esteem and Resilience : Higher self-esteem may contribute to increased resilience in the face of challenges.
- Potential Connection Between Cultural Exposure and Empathy Levels : Exposure to diverse cultures might influence individuals’ empathetic understanding.
- Tentative Association Between Sleep Quality and Cognitive Performance : Better sleep quality could be linked to improved cognitive function.
Psychology Hypothesis Development Statement Examples : Formulate hypotheses that lay the groundwork for deeper exploration and understanding. These examples illustrate the process of hypothesis development, where researchers craft well-structured statements that guide empirical investigations and contribute to the advancement of psychological knowledge.
- Development of a Hypothesis on Emotional Intelligence and Workplace Performance : Emotional intelligence positively influences workplace performance through enhanced interpersonal interactions and adaptive coping mechanisms.
- Constructing a Hypothesis on Social Media Use and Well-being : Extensive social media use negatively impacts psychological well-being by fostering social comparison, reducing real-life social interactions, and increasing feelings of inadequacy.
- Formulating a Hypothesis on Attachment Styles and Relationship Satisfaction : Secure attachment styles correlate positively with higher relationship satisfaction due to increased trust, effective communication, and emotional support.
- Creating a Hypothesis on Parenting Styles and Child Aggression : Authoritative parenting styles lead to reduced child aggression through the cultivation of emotional regulation skills, consistent discipline, and nurturance.
- Developing a Hypothesis on Cognitive Biases and Decision Making : Cognitive biases influence decision-making processes by shaping information processing, leading to deviations from rational decision-making models.
- Constructing a Hypothesis on Cultural Identity and Psychological Well-being : Strong cultural identity positively impacts psychological well-being by fostering a sense of belonging, social support, and cultural pride.
- Formulating a Hypothesis on Attachment Style and Coping Mechanisms : Attachment style influences coping mechanisms in response to stress, with secure attachments leading to adaptive strategies and insecure attachments resulting in maladaptive ones.
- Creating a Hypothesis on Self-Efficacy and Academic Performance : High self-efficacy predicts better academic performance due to increased motivation, perseverance, and effective learning strategies.
- Developing a Hypothesis on Gender Stereotypes and Career Aspirations : Gender stereotypes negatively impact women’s career aspirations by reinforcing traditional gender roles and limiting their perceived competence in certain fields.
- Constructing a Hypothesis on Cultural Exposure and Empathy Levels : Exposure to diverse cultures enhances empathy levels by fostering cross-cultural understanding, reducing ethnocentrism, and promoting perspective-taking.
These psychology hypothesis development statement examples showcase the critical process of crafting hypotheses that guide research investigations and contribute to the depth and breadth of psychological knowledge. In addition, you should review our biology hypothesis .
How Do You Write a Psychology Hypothesis Statement? – Step by Step Guide
Crafting a psychology hypothesis statement is a crucial step in formulating research questions and hypothesis designing empirical investigations. A well-structured hypothesis guides your research, helping you explore, analyze, and understand psychological phenomena. Follow this step-by-step guide to create effective psychology hypothesis statements:
- Identify Your Research Question : Start by identifying the specific psychological phenomenon or relationship you want to explore. Your hypothesis should address a clear research question.
- Choose the Appropriate Type of Hypothesis : Decide whether your hypothesis will be directional (predicting a specific relationship) or non-directional (predicting a relationship without specifying its direction).
- State Your Variables : Clearly identify the independent variable (the factor you’re manipulating or examining) and the dependent variable (the outcome you’re measuring).
- Write a Null Hypothesis (If Applicable) : If your research involves comparing groups or conditions, formulate a null hypothesis that states there’s no significant difference or relationship.
- Formulate the Hypothesis : Craft a clear and concise statement that predicts the expected relationship between your variables. Use specific language and avoid vague terms.
- Use Clear Language : Write your hypothesis in a simple, straightforward manner that is easily understandable by both researchers and readers.
- Ensure Testability : Your hypothesis should be testable through empirical research. It should allow you to collect data, analyze results, and draw conclusions.
- Consider the Population : Specify the population you’re studying (e.g., adults, adolescents, specific groups) to make your hypothesis more precise.
- Be Falsifiable : A good hypothesis can be proven false through empirical evidence. Avoid making statements that cannot be tested or verified.
- Revise and Refine : Review your hypothesis for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Make revisions as needed to ensure it accurately reflects your research question.
Tips for Writing a Psychology Hypothesis
Writing an effective psychology hypothesis statement requires careful consideration and attention to detail. Follow these tips to craft compelling hypotheses:
- Be Specific : Clearly define your variables and the expected relationship between them. Avoid vague or ambiguous language.
- Avoid Bias : Ensure your hypothesis is objective and unbiased. Avoid making assumptions or including personal opinions.
- Use Measurable Terms : Use terms that can be quantified and measured in your research. This makes data collection and analysis more manageable.
- Consult Existing Literature : Review relevant literature to ensure your hypothesis aligns with existing research and theories in the field.
- Consider Alternative Explanations : Acknowledge other potential explanations for your findings and consider how they might influence your hypothesis.
- Stay Consistent : Keep your hypothesis consistent with the overall research question and objectives of your study.
- Keep It Concise : Write your hypothesis in a concise manner, avoiding unnecessary complexity or jargon.
- Test Your Hypothesis : Consider how you would test your hypothesis using empirical methods. Ensure it’s feasible and practical to gather data to support or refute it.
- Seek Feedback : Share your hypothesis with peers, mentors, or advisors to receive constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Refine as Needed : As you gather data and analyze results, be open to revising your hypothesis based on the evidence you uncover.
Crafting a psychology hypothesis statement is a dynamic process that involves careful thought, research, and refinement. A well-constructed hypothesis sets the stage for rigorous and meaningful scientific inquiry in the field of psychology.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
IResearchNet
In scientific research, a hypothesis is a statement about a predicted relationship between variables. A good research hypothesis can be formulated as an “if-then” statement:
- If a child is exposed to the music of Mozart, then that child’s intelligence will increase.
- If students learn a math lesson by interacting with a computer, then they will solve math problems more accurately than students who learn the same lesson by listening to a lecture.
Notice that a hypothesis is not a question. It is a statement, a prediction that requires the researcher to go out on a limb and say what he or she thinks will happen in a given situation. When stating a hypothesis, the researcher must run the risk of being wrong—a scientific hypothesis must be falsifiable.
Hypotheses come from many sources. Researchers are not all wildly creative people, but they do tend to be careful observers of the world around them. One’s own everyday observations can lead to the formulation of a hypothesis, as when a babysitter observes that “children who eat ice cream before bedtime have a harder time falling asleep.” That simple observation can lead to a formal hypothesis about the relationship between sugar consumption and sleep onset. A famous hypothesis in social psychology was generated from a news story, when a woman in New York City was murdered in full view of dozens of onlookers. Instead of simply shaking their heads in sadness, psychologists John Darley and Bibb Latané developed a hypothesis about the relationship between helping behavior and the number of bystanders present, and that hypothesis was subsequently supported by research. This type of reasoning from a specific case to a more general principle is called inductive logic.
Reading existing research and theory can also lead to the generation of hypotheses. Through the process of deductiv e logic, a general theory leads to the prediction of a specific effect or conclusion. For example, someone who is familiar with Piaget’s theories of human development might predict that “if a child is younger than the age of 12, then that child will be unable to solve an abstract reasoning problem.” Such a hypothesis could then be put to the test in systematic research.
Hypotheses can be either directional or nondirectional. A directional hypothesis states a specific prediction about the precise type of effect that a variable is expected to have on another variable—for example, “If the number of bystanders increases, then the probability of any given bystander rendering help decreases.” A nondirectional hypothesis states that a relationship will exist between two variables, but it is not specific about the nature of that relationship: “If the number of bystanders increases, then the probability of any given bystander rendering help will change.” This type of hypothesis can be confirmed if the probability of help increases or if it decreases. Nondirectional hypotheses are useful in the early stages of research in a given area, when the researcher may not have enough information to make a more specific prediction. A nondirectional hypothesis is still falsifiable, however, if the data suggest that there is no systematic relationship between the variables after all.
Whether directional or nondirectional, a good research hypothesis must ultimately be objectively testable. Before actually turning a hypothesis into a study, the researcher must develop operational definitions of the variables stated in the hypothesis. If the hypothesis postulates that “If a child is exposed to the music of Mozart, then that child’s intelligence will increase,” then the researcher must define what specifically is meant by “child” (a person under the age of ?), by “intelligence” (a score on a particular standardized test, perhaps), and what it means to be “exposed” to the music of Mozart (Which compositions by Mozart? For how long? Played how loudly?). Thus, the development of the hypothesis is only the beginning of the process of psychological research.
References:
- Beins, C. (2004). Research methods: A tool for life. Boston: Pearson.
- Dunn, D. S. (1999). The practical researcher. Boston: McGraw-Hill.
- Smith, A., & Davis, S. F. (2004). The psychologist as detective (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Stockburger, W. (n.d.). Hypothesis testing . Retrieved from http://www.psychstat.smsu.edu/introbook/SBK18.htm
- Trochim, W. (2002). Research methods knowledge base . Retrieved from http://www.socialresearchmethods.net/kb/index.htm
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Psychology news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Psychology Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
A hypothesis is a testable prediction about the variables in a study. The hypothesis should always contain the independent variable (IV) and the dependent variable (DV). A hypothesis can be directional (one-tailed) or non-directional (two-tailed).
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Example Answers for Research Methods: A Level Psychology, Paper 2, June 2019 (AQA)
Exam Support
Research Methods: MCQ Revision Test 1 for AQA A Level Psychology
Topic Videos
Example Answers for Research Methods: A Level Psychology, Paper 2, June 2018 (AQA)
Example answer for question 14 paper 2: as psychology, june 2017 (aqa), a level psychology topic quiz - research methods.
Quizzes & Activities
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
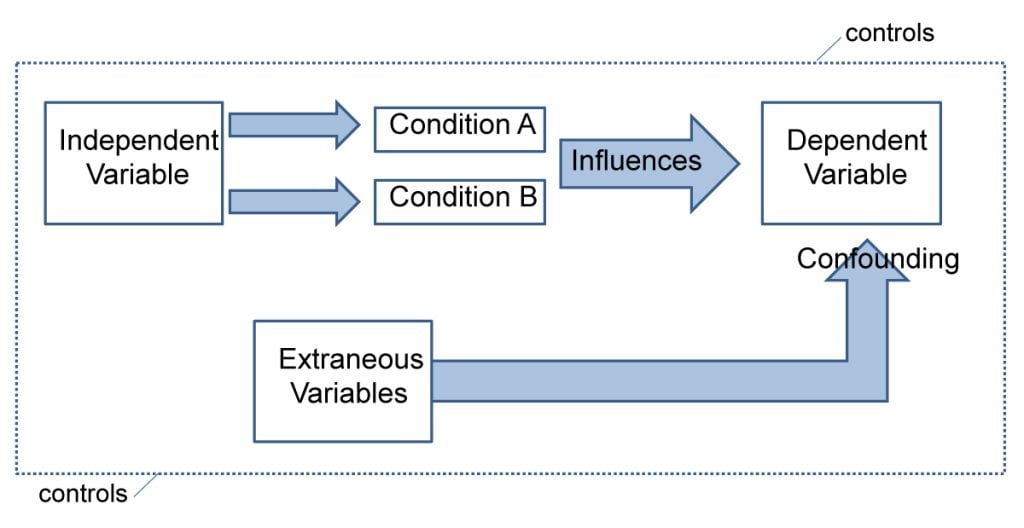
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
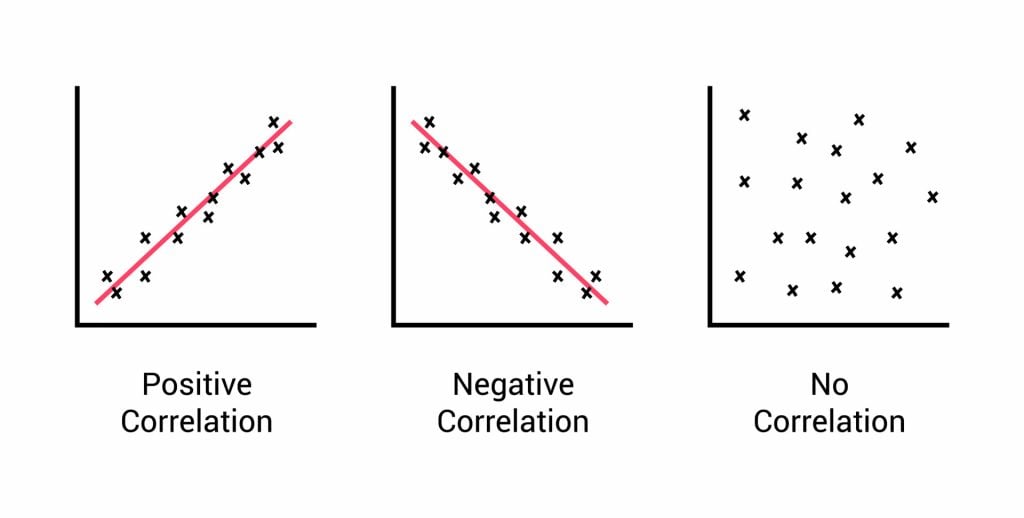
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
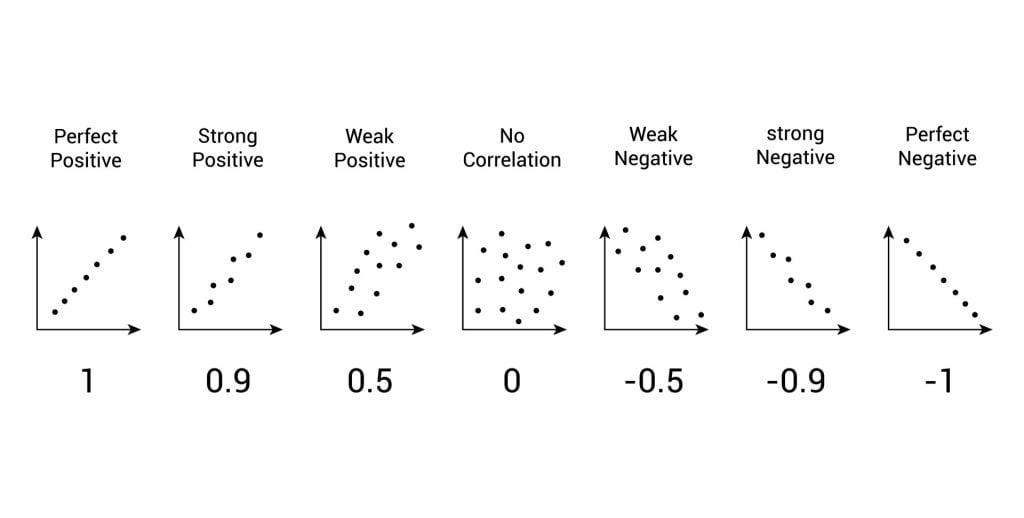
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
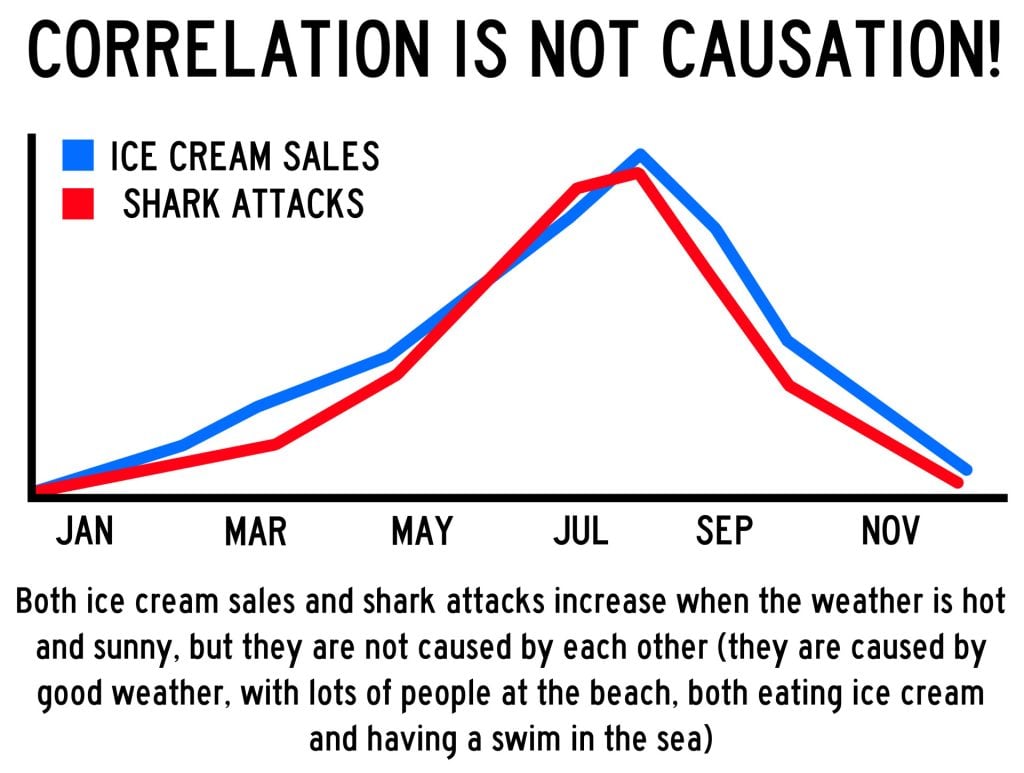
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- Why students love us
- Why professors love us
- Rebels Blog (Free)
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
Exploring Research Question and Hypothesis Examples: A Comprehensive Guide

This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of formulating research questions and hypotheses across various academic disciplines. By delving into examples and methodological approaches, the article aims to provide scholars and researchers with the tools necessary to develop robust and effective research frameworks. Understanding and crafting well-formed research questions and hypotheses are pivotal in conducting meaningful research that can significantly contribute to knowledge within a field.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the fundamental differences and connections between research questions and hypotheses.
- Learn how to craft effective and precise research questions that guide the research process.
- Explore various types of hypotheses and methods for testing and refining them.
- Examine practical examples of research questions and hypotheses across multiple disciplines.
- Gain insights into the impact of well-constructed research questions and hypotheses on research outcomes, academic publishing, and grant applications.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Research Questions and Hypotheses
Defining research questions.
Research questions are the backbone of any scholarly inquiry, guiding you through the exploration of your chosen topic. They help you focus your study and determine the direction of your research. A well-crafted research question should be clear, focused, and answerable within the constraints of your study.
Characteristics of a Strong Hypothesis
A strong hypothesis provides a specific, testable prediction about the expected outcomes of your research. It is not merely a guess but is grounded in existing literature and theory. To develop a robust hypothesis, consider the variables involved and ensure that it is feasible to test them within your study's design.
Interrelation Between Research Questions and Hypotheses
Understanding the interrelation between research questions and hypotheses is crucial for structuring your research effectively. Your hypothesis should directly address the gap in the literature highlighted by your research question, providing a clear pathway for investigation. This alignment ensures that your study can contribute valuable insights to your field.
Crafting Effective Research Questions
Identifying the purpose.
To craft an effective research question , you must first identify the purpose of your study. This involves understanding what you aim to discover or elucidate through your research. Ask yourself what the core of your inquiry is and what outcomes you hope to achieve. This clarity will guide your entire research process, ensuring that your question is not only relevant but also deeply rooted in your specific academic or practical goals.
Scope and Limitations
It's crucial to define the scope and limitations of your research early on. This helps in setting realistic boundaries and expectations for your study. Consider factors such as time, resources, and the breadth of the subject area. Narrowing down your focus to a manageable scope can prevent the common pitfall of an overly broad or vague question, which can dilute the impact of your findings.
Formulating Questions that Drive Inquiry
The final step in crafting your research question is formulating it in a way that drives inquiry. This means your question should be clear, concise, and structured to prompt detailed investigation and critical analysis. It should challenge existing knowledge and push the boundaries of what is already known. Utilizing strategies like the Thesis Dialogue Blueprint or the Research Proposal Compass can be instrumental in refining your question to ensure it is both innovative and feasible.
Developing Hypotheses in Research
From research questions to hypotheses.
When you transition from research questions to hypotheses, you are essentially moving from what you want to know to what you predict will happen. This shift involves formulating a specific, testable prediction that directly stems from your initial question. Ensure your hypothesis is directly linked to and derived from your research question to maintain a coherent research strategy.
Types of Hypotheses
There are several types of hypotheses you might encounter, including simple, complex, directional, nondirectional, associative, causal, null, and alternative. Each type serves a different purpose and is chosen based on the specifics of the research question and the nature of the study. For instance, a null hypothesis might be used to test the effectiveness of a new teaching method compared to the standard.
Testing and Refining Hypotheses
Testing your hypothesis is a critical step in the research process. This phase involves collecting data, conducting experiments, or utilizing other research methods to determine the validity of your hypothesis. After testing, you may find that your hypothesis needs refining or even reformation based on the outcomes. This iterative process is essential for narrowing down the most accurate explanation or prediction for your research question.
Examples of Research Questions in Various Disciplines
Humanities and social sciences.
In the realm of Humanities and Social Sciences, research questions often explore cultural, social, historical, or philosophical aspects. How does gender representation in 20th-century American literature reflect broader social changes? This question not only seeks to uncover specific literary trends but also ties them to societal shifts, offering a rich field for analysis.
Natural Sciences
Research questions in the Natural Sciences are typically aimed at understanding natural phenomena or solving specific scientific problems. A common question might be, What are the effects of plastic pollutants on marine biodiversity? This inquiry highlights the environmental concerns and seeks empirical data to understand the impact.
Applied Sciences
In Applied Sciences, the focus is often on improving technology or engineering solutions. A pertinent question could be, How can renewable energy sources be integrated into existing power grids? This question addresses the practical challenges and potential innovations in energy systems, crucial for advancing sustainable technologies.
Analyzing Hypothesis Examples Across Fields
Case studies in psychology.
In psychology, hypotheses often explore the causal relationships between cognitive functions and behaviors. Consider how a hypothesis might predict the impact of stress on memory recall . By examining various case studies, you can see how hypotheses are specifically tailored to address intricate psychological phenomena.
Experimental Research in Biology
Biology experiments frequently test hypotheses about physiological processes or genetic information. For instance, a hypothesis might propose that a specific gene influences plant growth rates. Through rigorous testing, these hypotheses contribute significantly to our understanding of biological systems.
Field Studies in Environmental Science
Field studies in environmental science provide a rich ground for testing hypotheses related to ecosystem dynamics and conservation strategies. A common hypothesis might explore the effects of human activity on biodiversity. These studies often involve complex data collection and analysis, highlighting the interrelation between empirical evidence and theoretical predictions.
Methodological Approaches to Formulating Hypotheses
Quantitative vs. qualitative research.
When you embark on hypothesis formulation, understanding the distinction between quantitative and qualitative research methodologies is crucial. Quantitative research focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, ideal for hypotheses that require measurable evidence. In contrast, qualitative research delves into thematic and descriptive data, providing depth and context to hypotheses that explore behaviors, perceptions, and experiences.
The Role of Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks serve as the backbone for developing robust hypotheses. They provide a structured way to align your hypothesis with existing knowledge. By integrating theories and models relevant to your study, you ensure that your hypothesis has a solid foundation and aligns with established academic thought.
Utilizing Existing Literature to Form Hypotheses
A thorough review of existing literature is indispensable for crafting a well-informed hypothesis. This process not only highlights gaps in current research but also allows you to build on the work of others. By synthesizing findings from previous studies, you can formulate hypotheses that are both innovative and grounded in academic precedent.
Evaluating the Impact of Well-Formed Research Questions and Hypotheses
On research outcomes.
Understanding the impact of well-formed research questions and hypotheses on research outcomes is crucial. Well-crafted questions and hypotheses serve as a framework that guides the entire research process , ensuring that the study remains focused and relevant. They help in defining the scope of the study and in identifying the variables that need to be measured, thus directly influencing the validity and reliability of the research findings.
In Academic Publishing
The role of well-defined research questions and hypotheses extends beyond the research process into the realm of academic publishing. A clear hypothesis provides a strong foundation for the research paper, enhancing its chances of acceptance in prestigious journals. The clarity and direction afforded by a solid hypothesis make the research more appealing to a scholarly audience, potentially increasing citation rates and academic recognition.
In Grant Applications
When applying for research grants, the clarity of your research questions and hypotheses can significantly impact the decision-making process of funding bodies. A well-articulated hypothesis demonstrates a clear vision and a structured approach to addressing a specific issue, which can be crucial in securing funding. Grant reviewers often look for proposals that promise substantial contributions to the field, and a strong hypothesis can be a key factor in showcasing the potential impact of your research.
In our latest article, 'Evaluating the Impact of Well-Formed Research Questions and Hypotheses,' we delve into the crucial role that precise questions and hypotheses play in academic research. Understanding this can significantly enhance your thesis writing process. For a deeper exploration and practical tools to apply these concepts, visit our website and discover how our Thesis Action Plan can transform your academic journey. Don't miss out on our special offers tailored just for you!
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored various examples of research questions and hypotheses, shedding light on their significance and application in academic research. Understanding the distinction between a research question and a hypothesis, as well as knowing how to effectively formulate them, is crucial for conducting methodical and impactful studies. By examining different scenarios and examples, this guide aims to equip researchers with the knowledge to craft well-defined research questions and hypotheses that can drive meaningful investigations and contribute to the broader field of knowledge. As we continue to delve into the intricacies of research design, it is our hope that this guide serves as a valuable resource for both novice and experienced researchers in their scholarly endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a research question.
A research question is a clearly defined query that guides a scientific or academic study. It sets the scope and focus of the research by asking about a specific phenomenon or issue.
How does a hypothesis differ from a research question?
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what will happen in a study based on prior knowledge or theory, while a research question is an open query that guides the direction of the investigation.
What are the characteristics of a strong hypothesis?
A strong hypothesis is clear, testable, based on existing knowledge, and it states an expected relationship between variables.
How can research questions and hypotheses interrelate?
Research questions define the scope of inquiry, while hypotheses provide a specific prediction about the expected outcomes that can be tested through research methods.
What should be considered when formulating a research question?
When formulating a research question, consider clarity, focus, relevance, and the feasibility of answering the question through available research methods.
Why is it important to have a well-formed hypothesis?
A well-formed hypothesis directs the research process, allows for clear testing of assumptions, and helps in drawing meaningful conclusions that can contribute to the body of knowledge.

How to Write a Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide with Tips for Success
How to start an introduction in a thesis: key strategies and examples, overcoming the fear of failure in your dissertation journey, what are the symptoms of phd burnout recognizing and overcoming it, how do i start writing my thesis expert advice and tips.

A Sample Master Thesis Outline for Reference

Demystifying Research: Understanding the Difference Between a Problem and a Hypothesis

Avoiding Procrastination Pitfalls: Bachelor Thesis Progress and Weekend Celebrations

How Do You Write a Hypothesis for a Research Paper? Step-by-Step Guide

How to Write a Thesis Fast: Tips and Strategies for Success

Thesis Action Plan

- Rebels Blog
- Blog Articles
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
Find Study Materials for
- Explanations
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
- Flashcards Create and find the best flashcards.
- Notes Create notes faster than ever before.
- Study Sets Everything you need for your studies in one place.
- Study Plans Stop procrastinating with our smart planner features.
- Aims and Hypotheses
There is no research without a proper aim and hypotheses – aims and hypotheses in research are the supporting frameworks on a path to new scientific discoveries. To better understand their importance, let us first analyse the difference between aims and hypotheses in psychology , examine their purpose, and give some examples.
Create learning materials about Aims and Hypotheses with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
Millions of flashcards designed to help you ace your studies
- Cell Biology
What is the definition of aims?
What is the definition of a hypothesis?
What is the purpose of research aims?
How are hypotheses different from aims?
What are the different types of hypotheses?
What type of hypothesis is the following statement: ‘There will be a difference between Mini-Mental Status Examination scores in students who were and were not sleep-deprived?
What type of hypothesis is the following statement: ‘There will be no difference in time recorded sleeping between students who received good and poor grades in their school report’?
What type of hypothesis is this statement ‘Students who were not sleep-deprived will have higher scores in the Mini-Mental Status Examination test than sleep-deprived students?
What happens when the research paper does not cover all the elements of aims and hypotheses?
What are the components the hypotheses have to include?
What do operationalising variables mean?
Convert documents into flashcards for free with AI!

- Approaches in Psychology
- Basic Psychology
- Biological Bases of Behavior
- Biopsychology
- Careers in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognition and Development
- Cognitive Psychology
- Data Handling and Analysis
- Developmental Psychology
- Eating Behaviour
- Emotion and Motivation
- Famous Psychologists
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- Individual Differences Psychology
- Issues and Debates in Psychology
- Personality in Psychology
- Psychological Treatment
- Relationships
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Causation in Psychology
- Coding Frame Psychology
- Correlational Studies
- Cross Cultural Research
- Cross Sectional Research
- Ethical Issues and Ways of Dealing with Them
- Experimental Designs
- Features of Science
- Field Experiment
- Independent Group Design
- Lab Experiment
- Longitudinal Research
- Matched Pairs Design
- Meta Analysis
- Natural Experiment
- Observational Design
- Online Research
- Paradigms and Falsifiability
- Peer Review and Economic Applications of Research
- Pilot Studies and the Aims of Piloting
- Quality Criteria
- Questionnaire Construction
- Repeated Measures Design
- Research Methods
- Sampling Frames
- Sampling Psychology
- Scientific Processes
- Scientific Report
- Scientific Research
- Self-Report Design
- Self-Report Techniques
- Semantic Differential Rating Scale
- Snowball Sampling
- Schizophrenia
- Scientific Foundations of Psychology
- Scientific Investigation
- Sensation and Perception
- Social Context of Behaviour
- Social Psychology
First, we will define the aims and hypotheses and learn the difference between aims and hypotheses in psychology .
Then, we will look at different types of hypotheses.
Next, we will look at the function of aims and hypotheses in research and psychology.
Later, we will look at specific aims and hypotheses in research examples.
Finally, we will discuss the need and how explicit research aims objectives and hypotheses are implemented.
Difference Between Aims and Hypotheses: Psychology
When you write a research report, you should state the aim first and then the hypothesis.
The aim is a summary of the goal or purpose of the research.
The aim is a broad starting point that gets narrowed down into the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis is a predictive, testable statement about what the researcher expects to find in the study.
Types of Hypotheses
Before we get into the types of hypotheses, let's quickly recap the hypotheses' components.
The independent variable (IV) is the factor that the researcher manipulates/ changes (this can be naturally occurring in some instances) and is theorised to be the cause of a phenomenon.
And the dependent variable (DV) is the factor that the researcher measures because they believe that the changes in the IV will affect the DV.
There are two types of hypotheses: null and alternative hypotheses.
A null hypothesis states that the independent variable does not influence the dependent variable. The null hypothesis states that changes/ manipulating the IV will not affect the DV.
Research scenario: Investigation of how test results affect sleep.
An example of a null hypothesis is there is no difference in recorded sleep time (dependent variable) between students who received good and poor grades (independent variable).
An alternative hypothesis states that the independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable. Often, it is the same (or very similar) to your research hypothesis.
Research scenario: Investigating how sleep deprivation affects performance on cognitive tests.
An alternative hypothesis may be that the less sleep students get (independent variable), the worse their performance will be on cognitive tests (dependent variable). Not sleep-deprived students will perform better on the Mini-Mental Status Examination test than sleep-deprived students.

The alternative hypothesis can be further sub-categorised into a one- or two-tailed hypothesis. A one-tailed hypothesis (also known as a directional hypothesis) suggests that the results can go one way, e.g. it may increase or decrease. And a two-tailed (also known as a non-directional hypothesis) is exactly the opposite; there are two ways the results could expectedly go.
An example of a two-tailed hypothesis is if you flip a coin, you could predict that it will land on either heads or tails.
Aims and Hypothesis in Research
In research, aims and hypotheses play major roles. They are the part of the research that sets you up for the rest of the study. Without strong research aims and hypotheses, your research will lack direction.
First, let's go over the function of research aims.
Research aims provide an overview of the research objective; this allows all researchers to be on the same page about the purpose of the research. Aims also describe why the research is needed and how it complements existing research in the field.
Duplicating research can sometimes be useful, but most times, researchers want to conduct their own new research.
Outside of the researchers, readers can then identify the research topic and whether it interests them.
The research aimed to examine the effects of sleep deprivation on test performance.
But what information do hypotheses provide?
Hypotheses identify the variables studied in an experiment. They describe expected results in terms of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. When readers see the hypothesis, they should know exactly what the researcher expected in the study's outcome (remember, sometimes the researcher can be wrong).
The hypothesis was that the less sleep a student gets (independent variable), the worse grades a student will achieve (dependent variable).
Typically, researchers use hypotheses for statistical tests such as hypothesis testing, which allows them to determine if the original predictions are correct. Hypotheses are helpful because the reader can quickly identify the variables , the expected results based on previous research, and how the experiment should measure these variables .
Hypotheses usually influence the research design and analysis used in conducting the research.
Psychological research must meet a standard for the psychological research community to accept it.
Components of Hypotheses
When writing research hypotheses, there are several essential things to consider, including:
The hypotheses must be clear and concise;
it must be easy to understand and not contain irrelevant details.
The researcher must predict what they expect to find based on reading previous research findings.
The researcher must explain how they arrived at their predictions, citing evidence from prior research.
The researcher must identify all variables they will study.
One study examined how sleep deprivation affects performance on cognitive tests. The hypothesis was to identify sleeping time as the independent variable and cognitive test scores as the dependent variable.
Additionally, the research must operationalise the hypotheses and describe how the variables will be measured.
When assessing cognitive abilities, the researcher should indicate how they will assess the cognitive skills. They could do so with a cognitive test, such as the Mini-Mental Status Examination scores.
Example Hypothesis
A hypothesis denotes a relationship between two variables, the independent and dependent variables. An example hypothesis is the more you sleep, the less tired you will feel.
Aims and Hypotheses: Psychology
Now that we understand the difference between aims and hypotheses, let's take a closer look at their function.
In psychology, aims and hypotheses function very similarly to other research fields. They set up the purpose of a study so that the researchers and readers understand its goals.
The aims establish the reasoning behind the study and why that specific topic is being researched. And the hypotheses share the researchers' expectations. It outlines what the researchers expect when the IV is manipulated.
Studies with well-defined aims and hypotheses allow the research to be more accessible. This means that a professional psychologist, a psychology student, or even someone who is simply curious about the topic can all read the research and understand its purpose.
Aims and Hypotheses in Research Example
As we have learned, aims and hypotheses are crucial in setting up successful research. They exist within every study and help outline the goals and outcomes the researchers expect. To further understand the aims and hypotheses in psychological research, let's look at a famous study – Asch's line experiment .
Solomon Asch conducted a study in 1951 about conformity . This study has become renowned for exposing the strong effects of conformity in a group setting. Asch put one participant in a room with seven strangers, people he said were other participants but were, in fact, confederates.
Confederates are hired actors who are told what to do in the experiment by the researcher.
The participants were tasked with trying to match one line to three other lines. Initially, the confederates would answer correctly, but as the trials continued, they all answered incorrectly. Would the participant still give the correct answer, or would they be swayed by conformity and be wrong?
Asch found that 74% of participants conformed at least once, even though they were obviously giving the wrong answer.

In this experiment, the aim was to look at the effects of conformity. More specifically, Asch aimed to see how impactful groups' pressures are on an individual's conformity. Asch hypothesised that participants would conform to the group when the confederates answered incorrectly due to social pressure.
Since we know the study's outcome, we know that Asch stayed true to his aims and provided supporting evidence for his hypothesis.
Explicit Research Aims, Objectives, and Hypotheses
An explicit research necessity across all disciplines is the operalisation of variables. When talking about operationalising a variable or hypothesis, it means that the term is defined so clearly and succinctly that there is no confusion or any grey area concerning what it means.
When operationally defining variables, researchers need to not only define what the variable is but also how they will measure it. Operationally defined hypotheses not only include detailed descriptions of variables and the outcome but also the relationship between the variables.
Remember, when studies and their results are replicated, they increase in reliability. Researchers operationally defining variables and hypotheses help future researchers replicate their study without confusion. If you do not operationally define key terms of your research and no one can replicate it, is there even a purpose to doing the research at all?
While operationally defining variables and hypotheses might seem like a simple task, it is extremely important for a successful outcome.
Aims and Hypotheses - Key takeaways
- For the scientific psychological community to accept the aim, the objective must explain why the research is needed and how it will expand our current knowledge.
- The two types of hypotheses are null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.
- For the scientific community of psychologists to accept a hypothesis, it must identify all variables, which researchers must operationalise.
Flashcards in Aims and Hypotheses 28
The hypothesis is a predictive, testable statement of what the researcher expects to find in the study.
The purpose of research aims are:
- provide a summary of what the research goal is
- describe why the research is needed and how it adds to existing research in the field
- so that the readers can identify what the research topic is and of interest to them
Hypotheses differ from aims because they are statements of the goals and purposes of the research. In contrast, hypotheses are predictive statements concerning expected results.
The types of hypotheses are:
- Null hypothesis.
- Alternative hypothesis.
- Directional alternative hypothesis (one-tailed) or non-directional (two-tailed).

Learn with 28 Aims and Hypotheses flashcards in the free StudySmarter app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Aims and Hypotheses
How to write aims and hypotheses?
When writing aims, researchers should summarise the research goal and purpose in a straightforward statement. Moreover, researchers must ensure that it is a predictive and testable statement when writing a hypothesis. This process should summarise the expected results of the study.
What comes first, hypothesis or aims?
Researchers should write the aims first and then the hypothesis when writing research.
What are the three types of hypotheses?
The three types of hypotheses are:
What is an aim in psychology?
An aim in psychology is a summary statement of the research's goal or purpose.
How are hypotheses different from aims and objectives?
Hypotheses differ from aims and objectives because aims are a general statement of the research's goals and purposes. In contrast, hypotheses explain precisely the predicted findings in terms of the independent and dependent variables.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free StudySmarter app

About StudySmarter
StudySmarter is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

StudySmarter Editorial Team
Team Psychology Teachers
- 9 minutes reading time
- Checked by StudySmarter Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Get unlimited access with a free StudySmarter account.
- Instant access to millions of learning materials.
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams, AI tools and more.
- Everything you need to ace your exams.
The Three Most Common Types of Hypotheses
In this post, I discuss three of the most common hypotheses in psychology research, and what statistics are often used to test them.
- Post author By sean
- Post date September 28, 2013
- 37 Comments on The Three Most Common Types of Hypotheses
Simple main effects (i.e., X leads to Y) are usually not going to get you published. Main effects can be exciting in the early stages of research to show the existence of a new effect, but as a field matures the types of questions that scientists are trying to answer tend to become more nuanced and specific. In this post, I’ll briefly describe the three most common kinds of hypotheses that expand upon simple main effects – at least, the most common ones I’ve seen in my research career in psychology – as well as providing some resources to help you learn about how to test these hypotheses using statistics.
Incremental Validity
“Can X predict Y over and above other important predictors?”

This is probably the simplest of the three hypotheses I propose. Basically, you attempt to rule out potential confounding variables by controlling for them in your analysis. We do this because (in many cases) our predictor variables are correlated with each other. This is undesirable from a statistical perspective, but is common with real data. The idea is that we want to see if X can predict unique variance in Y over and above the other variables you include.
In terms of analysis, you are probably going to use some variation of multiple regression or partial correlations. For example, in my own work I’ve shown in the past that friendship intimacy as coded from autobiographical narratives can predict concern for the next generation over and above numerous other variables, such as optimism, depression, and relationship status ( Mackinnon et al., 2011 ).
“Under what conditions does X lead to Y?”
Of the three techniques I describe, moderation is probably the most tricky to understand. Essentially, it proposes that the size of a relationship between two variables changes depending upon the value of a third variable, known as a “moderator.” For example, in the diagram below you might find a simple main effect that is moderated by sex. That is, the relationship is stronger for women than for men:
With moderation, it is important to note that the moderating variable can be a category (e.g., sex) or it can be a continuous variable (e.g., scores on a personality questionnaire). When a moderator is continuous, usually you’re making statements like: “As the value of the moderator increases, the relationship between X and Y also increases.”
“Does X predict M, which in turn predicts Y?”
We might know that X leads to Y, but a mediation hypothesis proposes a mediating, or intervening variable. That is, X leads to M, which in turn leads to Y. In the diagram below I use a different way of visually representing things consistent with how people typically report things when using path analysis.

I use mediation a lot in my own research. For example, I’ve published data suggesting the relationship between perfectionism and depression is mediated by relationship conflict ( Mackinnon et al., 2012 ). That is, perfectionism leads to increased conflict, which in turn leads to heightened depression. Another way of saying this is that perfectionism has an indirect effect on depression through conflict.
Helpful links to get you started testing these hypotheses
Depending on the nature of your data, there are multiple ways to address each of these hypotheses using statistics. They can also be combined together (e.g., mediated moderation). Nonetheless, a core understanding of these three hypotheses and how to analyze them using statistics is essential for any researcher in the social or health sciences. Below are a few links that might help you get started:
Are you a little rusty with multiple regression? The basics of this technique are required for most common tests of these hypotheses. You might check out this guide as a helpful resource:
https://statistics.laerd.com/spss-tutorials/multiple-regression-using-spss-statistics.php
David Kenny’s Mediation Website provides an excellent overview of mediation and moderation for the beginner.
http://davidakenny.net/cm/mediate.htm
http://davidakenny.net/cm/moderation.htm
Preacher and Haye’s INDIRECT Macro is a great, easy way to implement mediation in SPSS software, and their MODPROBE macro is a useful tool for testing moderation.
http://afhayes.com/spss-sas-and-mplus-macros-and-code.html
If you want to graph the results of your moderation analyses, the excel calculators provided on Jeremy Dawson’s webpage are fantastic, easy-to-use tools:
http://www.jeremydawson.co.uk/slopes.htm
- Tags mediation , moderation , regression , tutorial
37 replies on “The Three Most Common Types of Hypotheses”
I want to see clearly the three types of hypothesis
Thanks for your information. I really like this
Thank you so much, writing up my masters project now and wasn’t sure whether one of my variables was mediating or moderating….Much clearer now.
Thank you for simplified presentation. It is clearer to me now than ever before.
Thank you. Concise and clear
hello there
I would like to ask about mediation relationship: If I have three variables( X-M-Y)how many hypotheses should I write down? Should I have 2 or 3? In other words, should I have hypotheses for the mediating relationship? What about questions and objectives? Should be 3? Thank you.
Hi Osama. It’s really a stylistic thing. You could write it out as 3 separate hypotheses (X -> Y; X -> M; M -> Y) or you could just write out one mediation hypotheses “X will have an indirect effect on Y through M.” Usually, I’d write just the 1 because it conserves space, but either would be appropriate.
Hi Sean, according to the three steps model (Dudley, Benuzillo and Carrico, 2004; Pardo and Román, 2013)., we can test hypothesis of mediator variable in three steps: (X -> Y; X -> M; X and M -> Y). Then, we must use the Sobel test to make sure that the effect is significant after using the mediator variable.
Yes, but this is older advice. Best practice now is to calculate an indirect effect and use bootstrapping, rather than the causal steps approach and the more out-dated Sobel test. I’d recommend reading Hayes (2018) book for more info:
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach (2nd ed). Guilford Publications.
Hi! It’s been really helpful but I still don’t know how to formulate the hypothesis with my mediating variable.
I have one dependent variable DV which is formed by DV1 and DV2, then I have MV (mediating variable), and then 2 independent variables IV1, and IV2.
How many hypothesis should I write? I hope you can help me 🙂
Thank you so much!!
If I’m understanding you correctly, I guess 2 mediation hypotheses:
IV1 –> Med –> DV1&2 IV2 –> Med –> DV1&2
Thank you so much for your quick answer! ^^
Could you help me formulate my research question? English is not my mother language and I have trouble choosing the right words. My x = psychopathy y = aggression m = deficis in emotion recognition
thank you in advance
I have mediator and moderator how should I make my hypothesis
Can you have a negative partial effect? IV – M – DV. That is my M will have negative effect on the DV – e.g Social media usage (M) will partial negative mediate the relationship between father status (IV) and social connectedness (DV)?
Thanks in advance
Hi Ashley. Yes, this is possible, but often it means you have a condition known as “inconsistent mediation” which isn’t usually desirable. See this entry on David Kenny’s page:
Or look up “inconsistent mediation” in this reference:
MacKinnon, D. P., Fairchild, A. J., & Fritz, M. S. (2007). Mediation analysis. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 593-614.
This is very interesting presentation. i love it.
This is very interesting and educative. I love it.
Hello, you mentioned that for the moderator, it changes the relationship between iv and dv depending on its strength. How would one describe a situation where if the iv is high iv and dv relationship is opposite from when iv is low. And then a 3rd variable maybe the moderator increases dv when iv is low and decreases dv when iv is high.
This isn’t problematic for moderation. Moderation just proposes that the magnitude of the relationship changes as levels of the moderator changes. If the sign flips, probably the original relationship was small. Sometimes people call this a “cross-over” effect, but really, it’s nothing special and can happen in any moderation analysis.
i want to use an independent variable as moderator after this i will have 3 independent variable and 1 dependent variable…. my confusion is do i need to have some past evidence of the X variable moderate the relationship of Y independent variable and Z dependent variable.
Dear Sean It is really helpful as my research model will use mediation. Because I still face difficulty in developing hyphothesis, can you give examples ? Thank you
Hi! is it possible to have all three pathways negative? My regression analysis showed significant negative relationships between x to y, x to m and m to y.
Hi, I have 1 independent variable, 1 dependent variable and 4 mediating variable May I know how many hypothesis should I develop?
Hello I have 4 IV , 1 mediating Variable and 1 DV
My model says that 4 IVs when mediated by 1MV leads to 1 Dv
Pls tell me how to set the hypothesis for mediation
Hi I have 4 IVs ,2 Mediating Variables , 1DV and 3 Outcomes (criterion variables).
Pls can u tell me how many hypotheses to set.
Thankyou in advance
I am in fact happy to read this webpage posts which carries tons of useful information, thanks for providing such data.
I see you don’t monetize savvystatistics.com, don’t waste your traffic, you can earn additional bucks every month with new monetization method. This is the best adsense alternative for any type of website (they approve all websites), for more info simply search in gooogle: murgrabia’s tools
what if the hypothesis and moderator significant in regrestion and insgificant in moderation?
Thank you so much!! Your slide on the mediator variable let me understand!
Very informative material. The author has used very clear language and I would recommend this for any student of research/
Hi Sean, thanks for the nice material. I have a question: for the second type of hypothesis, you state “That is, the relationship is stronger for men than for women”. Based on the illustration, wouldn’t the opposite be true?
Yes, your right! I updated the post to fix the typo, thank you!
I have 3 independent variable one mediator and 2 dependant variable how many hypothesis I have 2 write?
Sounds like 6 mediation hypotheses total:
X1 -> M -> Y1 X2 -> M -> Y1 X3 -> M -> Y1 X1 -> M -> Y2 X2 -> M -> Y2 X3 -> M -> Y2
Clear explanation! Thanks!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Find Study Materials for
- Explanations
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Textbook Solutions
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
- Flashcards Create and find the best flashcards.
- Notes Create notes faster than ever before.
- Study Sets Everything you need for your studies in one place.
- Study Plans Stop procrastinating with our smart planner features.
- Aims and Hypotheses
There is no research without a proper aim and hypotheses – aims and hypotheses in research are the supporting frameworks on a path to new scientific discoveries. To better understand their importance, let us first analyse the difference between aims and hypotheses in psychology , examine their purpose, and give some examples.

Create learning materials about Aims and Hypotheses with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
Millions of flashcards designed to help you ace your studies
- Cell Biology
What is the definition of aims?
What is the definition of a hypothesis?
What is the purpose of research aims?
How are hypotheses different from aims?
What are the different types of hypotheses?
What type of hypothesis is the following statement: ‘There will be a difference between Mini-Mental Status Examination scores in students who were and were not sleep-deprived?
What type of hypothesis is the following statement: ‘There will be no difference in time recorded sleeping between students who received good and poor grades in their school report’?
What type of hypothesis is this statement ‘Students who were not sleep-deprived will have higher scores in the Mini-Mental Status Examination test than sleep-deprived students?
What happens when the research paper does not cover all the elements of aims and hypotheses?
What are the components the hypotheses have to include?
What do operationalising variables mean?
Convert documents into flashcards for free with AI!

- Approaches in Psychology
- Basic Psychology
- Biological Bases of Behavior
- Biopsychology
- Careers in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognition and Development
- Cognitive Psychology
- Data Handling and Analysis
- Developmental Psychology
- Eating Behaviour
- Emotion and Motivation
- Famous Psychologists
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- Individual Differences Psychology
- Issues and Debates in Psychology
- Personality in Psychology
- Psychological Treatment
- Relationships
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Causation in Psychology
- Coding Frame Psychology
- Correlational Studies
- Cross Cultural Research
- Cross Sectional Research
- Ethical Issues and Ways of Dealing with Them
- Experimental Designs
- Features of Science
- Field Experiment
- Independent Group Design
- Lab Experiment
- Longitudinal Research
- Matched Pairs Design
- Meta Analysis
- Natural Experiment
- Observational Design
- Online Research
- Paradigms and Falsifiability
- Peer Review and Economic Applications of Research
- Pilot Studies and the Aims of Piloting
- Quality Criteria
- Questionnaire Construction
- Repeated Measures Design
- Research Methods
- Sampling Frames
- Sampling Psychology
- Scientific Processes
- Scientific Report
- Scientific Research
- Self-Report Design
- Self-Report Techniques
- Semantic Differential Rating Scale
- Snowball Sampling
- Schizophrenia
- Scientific Foundations of Psychology
- Scientific Investigation
- Sensation and Perception
- Social Context of Behaviour
- Social Psychology
First, we will define the aims and hypotheses and learn the difference between aims and hypotheses in psychology .
Then, we will look at different types of hypotheses.
Next, we will look at the function of aims and hypotheses in research and psychology.
Later, we will look at specific aims and hypotheses in research examples.
Finally, we will discuss the need and how explicit research aims objectives and hypotheses are implemented.
Difference Between Aims and Hypotheses: Psychology
When you write a research report, you should state the aim first and then the hypothesis.
The aim is a summary of the goal or purpose of the research.
The aim is a broad starting point that gets narrowed down into the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis is a predictive, testable statement about what the researcher expects to find in the study.
Types of Hypotheses
Before we get into the types of hypotheses, let's quickly recap the hypotheses' components.
The independent variable (IV) is the factor that the researcher manipulates/ changes (this can be naturally occurring in some instances) and is theorised to be the cause of a phenomenon.
And the dependent variable (DV) is the factor that the researcher measures because they believe that the changes in the IV will affect the DV.
There are two types of hypotheses: null and alternative hypotheses.
A null hypothesis states that the independent variable does not influence the dependent variable. The null hypothesis states that changes/ manipulating the IV will not affect the DV.
Research scenario: Investigation of how test results affect sleep.
An example of a null hypothesis is there is no difference in recorded sleep time (dependent variable) between students who received good and poor grades (independent variable).
An alternative hypothesis states that the independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable. Often, it is the same (or very similar) to your research hypothesis.
Research scenario: Investigating how sleep deprivation affects performance on cognitive tests.
An alternative hypothesis may be that the less sleep students get (independent variable), the worse their performance will be on cognitive tests (dependent variable). Not sleep-deprived students will perform better on the Mini-Mental Status Examination test than sleep-deprived students.

The alternative hypothesis can be further sub-categorised into a one- or two-tailed hypothesis. A one-tailed hypothesis (also known as a directional hypothesis) suggests that the results can go one way, e.g. it may increase or decrease. And a two-tailed (also known as a non-directional hypothesis) is exactly the opposite; there are two ways the results could expectedly go.
An example of a two-tailed hypothesis is if you flip a coin, you could predict that it will land on either heads or tails.
Aims and Hypothesis in Research
In research, aims and hypotheses play major roles. They are the part of the research that sets you up for the rest of the study. Without strong research aims and hypotheses, your research will lack direction.
First, let's go over the function of research aims.
Research aims provide an overview of the research objective; this allows all researchers to be on the same page about the purpose of the research. Aims also describe why the research is needed and how it complements existing research in the field.
Duplicating research can sometimes be useful, but most times, researchers want to conduct their own new research.
Outside of the researchers, readers can then identify the research topic and whether it interests them.
The research aimed to examine the effects of sleep deprivation on test performance.
But what information do hypotheses provide?
Hypotheses identify the variables studied in an experiment. They describe expected results in terms of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. When readers see the hypothesis, they should know exactly what the researcher expected in the study's outcome (remember, sometimes the researcher can be wrong).
The hypothesis was that the less sleep a student gets (independent variable), the worse grades a student will achieve (dependent variable).
Typically, researchers use hypotheses for statistical tests such as hypothesis testing, which allows them to determine if the original predictions are correct. Hypotheses are helpful because the reader can quickly identify the variables , the expected results based on previous research, and how the experiment should measure these variables .
Hypotheses usually influence the research design and analysis used in conducting the research.
Psychological research must meet a standard for the psychological research community to accept it.
Components of Hypotheses
When writing research hypotheses, there are several essential things to consider, including:
The hypotheses must be clear and concise;
it must be easy to understand and not contain irrelevant details.
The researcher must predict what they expect to find based on reading previous research findings.
The researcher must explain how they arrived at their predictions, citing evidence from prior research.
The researcher must identify all variables they will study.
One study examined how sleep deprivation affects performance on cognitive tests. The hypothesis was to identify sleeping time as the independent variable and cognitive test scores as the dependent variable.
Additionally, the research must operationalise the hypotheses and describe how the variables will be measured.
When assessing cognitive abilities, the researcher should indicate how they will assess the cognitive skills. They could do so with a cognitive test, such as the Mini-Mental Status Examination scores.
Example Hypothesis
A hypothesis denotes a relationship between two variables, the independent and dependent variables. An example hypothesis is the more you sleep, the less tired you will feel.
Aims and Hypotheses: Psychology
Now that we understand the difference between aims and hypotheses, let's take a closer look at their function.
In psychology, aims and hypotheses function very similarly to other research fields. They set up the purpose of a study so that the researchers and readers understand its goals.
The aims establish the reasoning behind the study and why that specific topic is being researched. And the hypotheses share the researchers' expectations. It outlines what the researchers expect when the IV is manipulated.
Studies with well-defined aims and hypotheses allow the research to be more accessible. This means that a professional psychologist, a psychology student, or even someone who is simply curious about the topic can all read the research and understand its purpose.
Aims and Hypotheses in Research Example
As we have learned, aims and hypotheses are crucial in setting up successful research. They exist within every study and help outline the goals and outcomes the researchers expect. To further understand the aims and hypotheses in psychological research, let's look at a famous study – Asch's line experiment .
Solomon Asch conducted a study in 1951 about conformity . This study has become renowned for exposing the strong effects of conformity in a group setting. Asch put one participant in a room with seven strangers, people he said were other participants but were, in fact, confederates.
Confederates are hired actors who are told what to do in the experiment by the researcher.
The participants were tasked with trying to match one line to three other lines. Initially, the confederates would answer correctly, but as the trials continued, they all answered incorrectly. Would the participant still give the correct answer, or would they be swayed by conformity and be wrong?
Asch found that 74% of participants conformed at least once, even though they were obviously giving the wrong answer.

In this experiment, the aim was to look at the effects of conformity. More specifically, Asch aimed to see how impactful groups' pressures are on an individual's conformity. Asch hypothesised that participants would conform to the group when the confederates answered incorrectly due to social pressure.
Since we know the study's outcome, we know that Asch stayed true to his aims and provided supporting evidence for his hypothesis.
Explicit Research Aims, Objectives, and Hypotheses
An explicit research necessity across all disciplines is the operalisation of variables. When talking about operationalising a variable or hypothesis, it means that the term is defined so clearly and succinctly that there is no confusion or any grey area concerning what it means.
When operationally defining variables, researchers need to not only define what the variable is but also how they will measure it. Operationally defined hypotheses not only include detailed descriptions of variables and the outcome but also the relationship between the variables.
Remember, when studies and their results are replicated, they increase in reliability. Researchers operationally defining variables and hypotheses help future researchers replicate their study without confusion. If you do not operationally define key terms of your research and no one can replicate it, is there even a purpose to doing the research at all?
While operationally defining variables and hypotheses might seem like a simple task, it is extremely important for a successful outcome.
Aims and Hypotheses - Key takeaways
- For the scientific psychological community to accept the aim, the objective must explain why the research is needed and how it will expand our current knowledge.
- The two types of hypotheses are null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.
- For the scientific community of psychologists to accept a hypothesis, it must identify all variables, which researchers must operationalise.
Flashcards in Aims and Hypotheses 28
The hypothesis is a predictive, testable statement of what the researcher expects to find in the study.
The purpose of research aims are:
- provide a summary of what the research goal is
- describe why the research is needed and how it adds to existing research in the field
- so that the readers can identify what the research topic is and of interest to them
Hypotheses differ from aims because they are statements of the goals and purposes of the research. In contrast, hypotheses are predictive statements concerning expected results.
The types of hypotheses are:
- Null hypothesis.
- Alternative hypothesis.
- Directional alternative hypothesis (one-tailed) or non-directional (two-tailed).

Learn with 28 Aims and Hypotheses flashcards in the free Vaia app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Aims and Hypotheses
How to write aims and hypotheses?
When writing aims, researchers should summarise the research goal and purpose in a straightforward statement. Moreover, researchers must ensure that it is a predictive and testable statement when writing a hypothesis. This process should summarise the expected results of the study.
What comes first, hypothesis or aims?
Researchers should write the aims first and then the hypothesis when writing research.
What are the three types of hypotheses?
The three types of hypotheses are:
What is an aim in psychology?
An aim in psychology is a summary statement of the research's goal or purpose.
How are hypotheses different from aims and objectives?
Hypotheses differ from aims and objectives because aims are a general statement of the research's goals and purposes. In contrast, hypotheses explain precisely the predicted findings in terms of the independent and dependent variables.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards

Join the Vaia App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free Vaia app

Vaia is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

Vaia Editorial Team
Team Psychology Teachers
- 9 minutes reading time
- Checked by Vaia Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of Vaia.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our Vaia App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Privacy Overview
Get unlimited access with a free vaia account..
- Instant access to millions of learning materials.
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams, AI tools and more.
- Everything you need to ace your exams.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples. A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
What is a hypothesis and how can you write a great one for your research? A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables that can be tested empirically. Find out how to formulate a clear, specific, and testable hypothesis with examples and tips from Verywell Mind, a trusted source of psychology and mental health information.
Alternative Hypothesis: Eating an apple daily reduces the chances of visiting the doctor. Null Hypothesis: Eating an apple daily does not impact the frequency of visiting the doctor. Example 2. Research Problem: What is the impact of spending a lot of time on mobiles on the attention span of teenagers.
Field: Psychology. Type: Simple Hypothesis The simple hypothesis is a prediction about the relationship between two variables, excluding any other variables from consideration. This example posits that by reducing time spent on devices like smartphones and computers, an individual should experience improved sleep quality. How to Test:
Psychology: In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior. ... For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can ...
First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical.
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
In the realm of psychological science, a hypothesis is a tentative, testable assertion or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It serves as a foundational element for empirical research, guiding the direction of study and inquiry. The history of hypotheses in psychology traces back to the discipline's inception ...
First, a good hypothesis must be testable and falsifiable. We must be able to test the hypothesis using the methods of science and if you'll recall Popper's falsifiability criterion, it must be possible to gather evidence that will disconfirm the hypothesis if it is indeed false. Second, a good hypothesis must be logical.
Some Famous Psychological Phenomena. Phenomena are often given names by their discoverers or other researchers, and these names can catch on and become widely known. The following list is a small sample of famous phenomena in psychology. ... So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would ...
In this case, we state a different type of hypothesis, one for a correlation. The hypothesis for the GCSE/A level example above is as follows… • There will be a correlation between participant's GCSE scores and their A level results A more psychological example is the correlation between how long a person is in an
The theory attempting to explain an observation will help to inform hypotheses - predictions of an investigation's outcome that make specific reference to the independent variables (IVs) manipulated and dependent variables (DVs) measured by the researchers. There are two types of hypothesis: H1 - The Research Hypothesis.
PDF. Size: 202 KB. Download. Psychology Hypothesis Statement Examples encompass a diverse range of human behaviors and mental processes. Dive into the complexities of the human mind with Simple hypothesis that explore relationships, patterns, and influences on behavior. From memory recall to social interactions, these examples offer insights ...
Hypothesis. In scientific research, a hypothesis is a statement about a predicted relationship between variables. A good research hypothesis can be formulated as an "if-then" statement: If a child is exposed to the music of Mozart, then that child's intelligence will increase. If students learn a math lesson by interacting with a computer ...
The goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample. In order to undertake hypothesis testing, you must express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. ... Psychological methods, 5(2), 241. Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test. Psychological ...
A Level Psychology Topic Quiz - Research Methods. A hypothesis is a testable prediction about the variables in a study. The hypothesis should always contain the independent variable (IV) and the dependent variable (DV). A hypothesis can be directional (one-tailed) or non-directional (two-tailed).
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc. Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
Analyzing Hypothesis Examples Across Fields Case Studies in Psychology. In psychology, hypotheses often explore the causal relationships between cognitive functions and behaviors. Consider how a hypothesis might predict the impact of stress on memory recall. By examining various case studies, you can see how hypotheses are specifically tailored ...
The way to write a good hypothesis is to follow a 3 step proess. 1) Identify your variables and operationalise them. 2) Identify whether you are looking for a difference or a relationship. 3) Identify whether you are going to write a directional or non-directional hypothesis. As long as your hypothesis includes these three things then it will ...
An example hypothesis is the more you sleep, the less tired you will feel. Aims and Hypotheses: Psychology. Now that we understand the difference between aims and hypotheses, let's take a closer look at their function. ... In psychology, aims and hypotheses function very similarly to other research fields. They set up the purpose of a study so ...
For example, in the diagram below you might find a simple main effect that is moderated by sex. That is, the relationship is stronger for women than for men: With moderation, it is important to note that the moderating variable can be a category (e.g., sex) or it can be a continuous variable (e.g., scores on a personality questionnaire).
EXEMPLAR ESSAYHow to write a 8-mark answer. Assess how hypotheses are used in the Cognitive Approach. (8 marks) A 8-mark "apply" question awards 4 marks for describing the use of hypotheses (AO1) and 4 marks for applying the Cognitive Approach to this (AO2). You need a conclusion to get a mark in the top band (7-8 marks).
For the scientific psychological community to accept the aim, the objective must explain why the research is needed and how it will expand our current knowledge. The hypothesis is a predictive, testable statement about what the researcher expects to find in the study. The two types of hypotheses are null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.