- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Editing and Style

How to Write in Third Person
Last Updated: May 10, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Alicia Cook . Alicia Cook is a Professional Writer based in Newark, New Jersey. With over 12 years of experience, Alicia specializes in poetry and uses her platform to advocate for families affected by addiction and to fight for breaking the stigma against addiction and mental illness. She holds a BA in English and Journalism from Georgian Court University and an MBA from Saint Peter’s University. Alicia is a bestselling poet with Andrews McMeel Publishing and her work has been featured in numerous media outlets including the NY Post, CNN, USA Today, the HuffPost, the LA Times, American Songwriter Magazine, and Bustle. She was named by Teen Vogue as one of the 10 social media poets to know and her poetry mixtape, “Stuff I’ve Been Feeling Lately” was a finalist in the 2016 Goodreads Choice Awards. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,143,966 times.
Writing in third person can be a simple task, with a little practice. For academic purposes, third person writing means that the writer must avoid using subjective pronouns like “I” or “you.” For creative writing purposes, there are differences between third person omniscient, limited, objective, and episodically limited points of view. Choose which one fits your writing project.
Writing Third Person Point of View
The third-person point of view discusses the person or people being talked about in academic or creative writing. In this perspective, you’d shift focus from subject to subject. Use pronouns like he/him, she/her, they/them, or it/itself.
Writing in Third Person Academically

- Third person helps the writing stay focused on facts and evidence instead of personal opinion.

- Third person pronouns include: he, she, it; his, her, its; him, her, it; himself, herself, itself; they; them; their; themselves.
- Names of other people are also considered appropriate for third person use.
- Example: “ Smith believes differently. According to his research, earlier claims on the subject are incorrect.”

- First person pronouns include: I, me, my, mine, myself, we, us, our, ours, ourselves. [3] X Research source
- The problem with first person is that, academically speaking, it sounds too personalized and too subjective. In other words, it may be difficult to convince the reader that the views and ideas being expressed are unbiased and untainted by personal feelings. Many times, when using first person in academic writing, people use phrases like "I think," "I believe," or "in my opinion."
- Incorrect example: “Even though Smith thinks this way, I think his argument is incorrect.”
- Correct example: “Even though Smith thinks this way, others in the field disagree.”

- Second person pronouns include: you, your, yours, yourself. [4] X Research source
- One main problem with second person is that it can sound accusatory. It runs to risk of placing too much responsibility on the shoulders of the reader specifically and presently reading the work.
- Incorrect example: “If you still disagree nowadays, then you must be ignorant of the facts.”
- Correct example: “Someone who still disagrees nowadays must be ignorant of the facts.”

- Indefinite third person nouns common to academic writing include: the writer, the reader, individuals, students, a student, an instructor, people, a person, a woman, a man, a child, researchers, scientists, writers, experts.
- Example: “In spite of the challenges involved, researchers still persist in their claims.”
- Indefinite third person pronouns include: one, anyone, everyone, someone, no one, another, any, each, either, everybody, neither, nobody, other, anybody, somebody, everything, someone.
- Incorrect example: "You might be tempted to agree without all the facts."
- Correct example: “ One might be tempted to agree without all the facts.”
- This is usually done in an attempt to avoid the gender-specific “he” and “she” pronouns. The mistake here would be to use the “they” pronoun with singular conjugation. [5] X Research source
- Incorrect example: “The witness wanted to offer anonymous testimony. They was afraid of getting hurt if their name was spread.”
- Correct example: “The witness wanted to offer anonymous testimony. They were afraid of getting hurt if their name was spread.”
Writing in Third Person Omniscient

- For instance, a story may include four major characters: William, Bob, Erika, and Samantha. At various points throughout the story, the thoughts and actions of each character should be portrayed. These thoughts can occur within the same chapter or block of narration.
- Writers of omniscient narratives should be conscious of “head-hopping” — that is, shifting character perspectives within a scene. While this does not technically break the rules of Third Person Omniscience, it is widely considered a hallmark of narrative laziness.
- In a sense, the writer of a third person omniscient story is somewhat like the “god” of that story. The writer can observe the external actions of any character at any time, but unlike a limited human observer, the writer can also peek into the inner workings of that character at will, as well.
- Know when to hold back. Even though a writer can reveal any information they choose to reveal, it may be more beneficial to reveal some things gradually. For instance, if one character is supposed to have a mysterious aura, it would be wise to limit access to that character's inner feelings for a while before revealing his or her true motives.

- Do not use first person and second person points of view in the narrative or descriptive portions of the text.
- Correct example: Bob said to Erika, “I think this is creepy. What do you think?”
- Incorrect example: I thought this was creepy, and Bob and Erika thought so, too. What do you think?
Writing in Third Person Limited

- The thoughts and feelings of other characters remain an unknown for the writer throughout the duration of the text. There should be no switching back and forth between characters for this specific type of narrative viewpoint.
- Unlike first person, where the narrator and protagonist are the same, third person limited puts a critical sliver of distance between protagonist and narrator. The writer has the choice to describe one main character’s nasty habit — something they wouldn’t readily reveal if the narration were left entirely to them.

- In other words, do not use first person pronouns like “I,” “me,” “my,” “we,” or “our” outside of dialog. The main character's thoughts and feelings are transparent to the writer, but that character should not double as a narrator.
- Correct example: “Tiffany felt awful after the argument with her boyfriend.”
- Correct example: “Tiffany thought, “I feel awful after that argument with my boyfriend.”
- Incorrect example: “I felt awful after the argument with my boyfriend.”

- Note that the writer can offer insight or guesses regarding the thoughts of other characters, but those guesses must be presented through the perspective of the main character.
- Correct example: “Tiffany felt awful, but judging by the expression on Carl's face, she imagined that he felt just as bad if not worse.”
- Incorrect example: “Tiffany felt awful. What she didn't know was that Carl felt even worse.”

- Correct example: “Tiffany watched from the window as Carl walked up to her house and rang the doorbell.”
- Incorrect example: “As soon as Tiffany left the room, Carl let out a sigh of relief.”
Writing in Episodically Limited Third Person

- Limit the amount of pov characters you include. You don't want to have too many characters that confuse your reader or serve no purpose. Each pov character should have a specific purpose for having a unique point of view. Ask yourself what each pov character contributes to the story.
- For instance, in a romance story following two main characters, Kevin and Felicia, the writer may opt to explain the inner workings of both characters at different moments in the story.
- One character may receive more attention than any other, but all main characters being followed should receive attention at some point in the story.

- Multiple perspectives should not appear within the same narrative space. When one character's perspective ends, another character's can begin. The two perspectives should not be intermixed within the same space.
- Incorrect example: “Kevin felt completely enamored of Felicia from the moment he met her. Felicia, on the other hand, had difficulty trusting Kevin.”

- In a novel-length work, a good time to switch perspective is at the start of a new chapter or at a chapter break.
- The writer should also identify the character whose perspective is being followed at the start of the section, preferably in the first sentence. Otherwise, the reader may waste too much energy guessing.
- Correct example: “Felicia hated to admit it, but the roses Kevin left on her doorstep were a pleasant surprise.”
- Incorrect example: “The roses left on the doorstep seemed like a nice touch.”

- For instance, if Kevin had a talk with Felicia's best friend about Felicia's feelings for him, Felicia herself would have no way of knowing what was said unless she witnessed the conversation or heard about it from either Kevin or her friend.
Writing in Third Person Objective

- There does not need to be a single main character to focus on. The writer can switch between characters, following different characters throughout the course of the narrative, as often as needed.
- Stay away from first person terms like “I” and second person terms like “you” in the narrative, though. Only use first and second person within dialog.

- Imagine that you are an invisible bystander observing the actions and dialog of the characters in your story. You are not omniscient, so you do not have access to any character's inner thoughts and feelings. You only have access to each character's actions.
- Correct example: “After class, Graham hurriedly left the room and rushed back to his dorm room.”
- Incorrect example: “After class, Graham raced from the room and rushed back to his dorm room. The lecture had made him so angry that he felt as though he might snap at the next person he met.”

- Correct example: “When no one else was watching her, Isabelle began to cry.”
- Incorrect example: “Isabelle was too prideful to cry in front of other people, but she felt completely broken-hearted and began crying once she was alone.”

- Let the reader draw his or her own conclusions. Present the actions of the character without analyzing them or explaining how those actions should be viewed.
- Correct example: “Yolanda looked over her shoulder three times before sitting down.”
- Incorrect example: “It might seem like a strange action, but Yolanda looked over her shoulder three times before sitting down. This compulsive habit is an indication of her paranoid state of mind.”
Examples of Third Person POV

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://stlcc.edu/student-support/academic-success-and-tutoring/writing-center/writing-resources/point-of-view-in-academic-writing.aspx
- ↑ http://studysupportresources.port.ac.uk/Writing%20in%20the%20third%20peson.pdf
- ↑ http://www.grammar-monster.com/glossary/third_person.htm
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/use-the-singular-they/
- ↑ Alicia Cook. Professional Writer. Expert Interview. 11 December 2020.
- ↑ https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/point-of-view-first-second-third-person-difference
- ↑ https://ojs.library.dal.ca/YAHS/article/viewFile/7236/6278
About This Article

To write in third person, refer to people or characters by name or use third person pronouns like he, she, it; his, her, its; him, her, it; himself, herself, itself; they; them; their; and themselves. Avoid first and second person pronouns completely. For academic writing, focus on a general viewpoint rather than a specific person's to keep things in third person. In other types of writing, you can write in third person by shifting your focus from character to character or by focusing on a single character. To learn more from our Literary Studies Ph.D., like the differences between third person omniscient and third person limited writing, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jul 31, 2016
Did this article help you?
Jean Scicluna
Jan 31, 2021
Nov 4, 2016
Karen Evans
Aug 5, 2016
Oct 20, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- [email protected]
- (650) 338-8226
Cupertino, CA

- Our Philosophy
- Our Results
- News, Media, and Press
- Common Application
- College Application Essay Editing
- Extracurricular Planning
- Academic Guidance
- Summer Programs
- Interview Preparation
Middle School
- Pre-High School Consultation
- Boarding School Admissions
College Admissions
- Academic and Extracurricular Profile Evaluation
- Senior Editor College Application Program
- Summer Program Applications
- Private Consulting Program
- Transfer Admissions
- UC Transfer Admissions
- Ivy League Transfer Admissions
Graduate Admissions
- Graduate School Admissions
- MBA Admissions
Private Tutoring
- SAT/ACT Tutoring
- AP Exam Tutoring
- Olympiad Training
Research Programs
- Science Research Program
- Humanities Competitions
- Passion Project Program
- Ad Hoc Consulting
- Athletic Recruitment
- National Universities Rankings
- Liberal Arts Colleges Rankings
- Public Schools Rankings
Acceptance Rates
- University Acceptance Rates
- Transfer Acceptance Rates
- Supplemental Essays
- College Admissions Data
- Chances Calculator
- GPA Calculator
National Universities
- College Acceptance Rates
- College Overall Acceptance Rates
- College Regular Acceptance Rates
- College Early Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Overall Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Regular Acceptance Rates
- Ivy League Early Acceptance Rates
Public Schools
- Public Schools Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Overall Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Regular Acceptance Rates
- Public Schools Early Acceptance Rates
Liberal Arts
- Liberal Arts Colleges Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Overall Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Regular Acceptance Rates
- Liberal Arts Colleges Early Acceptance Rates

Third-Person Writing: A Guide for Effective Academic Writing

By Eric Eng

In this post, we will explore the concept of third-person writing and its importance for academic writing. We will discuss the benefits of using third-person language, provide examples of how it can be used in different types of academic writing, and offer practical tips for incorporating it into your writing. By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of third-person writing and how to use it effectively in your academic work.
Academic writing is a fundamental part of any high school student’s education, and mastering the art of writing in a clear and concise manner is essential to academic success. One key aspect of effective academic writing is the use of third-person language, which can help writers create a more objective and authoritative tone.
What is third-person writing?
What is third-person writing? Third-person writing is a style of writing that involves using pronouns such as “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” or “one” to refer to individuals or objects instead of using first- or second-person pronouns like “I,” “me,” “we,” “us,” “you,” or “your.” Third-person language is commonly used in academic writing to create a more objective and authoritative tone.
For instance, instead of saying “I believe,” third-person writing would say, “It can be argued.” This writing style can be particularly effective when presenting research or making a persuasive argument, as it allows the writer to distance themselves from their ideas and present them as more balanced and objective.
Writing in the third person differs from first- and second-person writing in several key ways. First-person writing involves using pronouns like “I,” “me,” “we,” or “us” to refer to oneself or a group of individuals. This writing style is often used in personal narratives, memoirs, or opinion pieces, where the writer’s personal experiences or opinions are central to the piece.
Conversely, second-person writing involves using pronouns like “you” or “your” to address the reader directly.

This writing style is often used in instructional or self-help texts, where the writer gives advice or instructions to the reader. In contrast, writing in the third person avoids direct references to the writer or reader and instead focuses on the topic or subject. This writing style can be particularly effective in academic writing , where objectivity and a neutral tone are often valued.
The benefits of using third-person writing in academic writing
Using the third-person point of view in academic writing offers several benefits, including creating a more objective and authoritative tone. By using third-person pronouns instead of first-person pronouns, writers can present information more neutral and unbiased. This can be particularly important in academic writing, where presenting a balanced and objective perspective is often valued.
Writing in the third person can also help writers distance themselves from their arguments and present a more balanced perspective. By using third-person pronouns, writers can avoid appearing overly confident or biased. Instead, they can present their arguments in a more measured and thoughtful way, allowing readers to make their judgments about the validity of the arguments presented.
Moreover, it can be especially useful in academic writing that involves research. When presenting research findings or making a persuasive argument, writers may be tempted to rely heavily on first-person language to convince readers of the validity of their claims. However, this can undermine the persuasiveness of the argument.
Using third-person writing instead can help writers present their research findings and arguments in a more objective and authoritative way, ultimately making their work more convincing to readers.
In summary, using a third-person point of view in academic writing can help writers create a more objective and authoritative tone, distance themselves from their arguments, and present a more balanced perspective. By using third-person pronouns and language effectively, writers can make their writing more persuasive and ultimately more successful in communicating their ideas to their readers.
What are the words to avoid in third-person writing?
What are the words to avoid in third-person writing? When writing in the third person, it’s important to avoid using first- and second-person language, as these types can make the writing appear less objective and authoritative. Here are some examples of words and phrases to avoid when writing in the third person:
- First-person pronouns: This includes words like “I,” “me,” “my,” “we,” and “us.” Avoid using these pronouns in the third-person point of view.
- Second-person pronouns include words like “you” and “your.” Avoid using these pronouns, as they can make the writing feel more direct and less objective.
- Imperative verbs: Imperative verbs are those that give commands or instructions, such as “do,” “make,” or “take.” These verbs should generally be avoided as they can make the writing feel less objective and more directive.
- Personal opinions: It’s important to avoid including personal opinions or biases. Instead, focus on presenting the facts and allowing readers to draw their conclusions.
By avoiding these words and phrases, writers can create more effective and authoritative third-person writing better suited for academic and professional contexts.
Examples of third-person writing in academic writing
The third-person point of view is commonly used in various academic writing contexts, including research papers, literature reviews, and essays . Here are some examples of how third-person writing can be used effectively in these contexts:

- Research papers: In research papers, it can be used to present research findings and conclusions in a more objective and authoritative manner. For example, instead of saying, “I found that,” a third-person point of view would say, “It was found that.” This helps to create a more neutral tone and emphasizes the importance of the research itself rather than the researcher’s personal experience.
- Literature reviews: In literature reviews , it can be used to summarize and analyze existing research in an objective and authoritative way. For example, instead of saying, “I think that this study is important,” third-person writing would say, “This study has been found to be important by previous researchers.” This helps to emphasize the research’s importance and present it more objectively and neutrally.
- Essays: In essays, it can be used to present arguments and evidence in a more balanced and persuasive manner. For example, instead of saying, “I believe that,” a third-person point of view would say, “It can be argued that.” This helps to present the argument in a more objective and authoritative way, which can be particularly important in persuasive essays.
The potential benefits of using third-person writing in each of these contexts include the following:
- Creating a more objective and authoritative tone.
- Emphasizing the importance of the research or argument rather than the writer’s personal experience or opinion.
- Presenting information in a more balanced and neutral way.
By writing in the third person effectively, writers can make their academic writing more effective and persuasive, ultimately helping to communicate their ideas more effectively to their readers.
Tips for using third-person writing in academic writing
To effectively incorporate third-person writing into academic writing, consider the following tips:
- Use active voice: Using active voice can help to make the third-person point of view more engaging and direct. For example, instead of saying, “It was found that,” say, “Researchers found that.” This can make the writing feel engaging rather than passive and dull.
- Vary sentence structure: To avoid overusing third-person pronouns, try to vary sentence structure. For example, instead of repeatedly using “he” or “she,” try using more descriptive phrases or words, such as “the researcher” or “the author.”
- Avoid personal opinions: In third-person writing, it’s important to avoid personal opinions or biases. Instead, focus on presenting the facts and allowing readers to draw their own conclusions.
- Use reliable sources: In academic writing, it’s important to use reliable and trustworthy sources to support your arguments. Make sure to cite your sources properly and avoid using biased or unreliable sources.
- Proofread carefully: Finally, proofread your writing carefully to ensure you’ve used third-person language consistently and effectively. Look for instances of first- or second-person language and replace them with third-person language, as necessary.
Common mistakes to avoid when using third-person writing in academic writing include overusing third-person pronouns, failing to vary sentence structure, and using vague or ambiguous language. Additionally, it’s important to avoid using personal opinions or biases, as this can undermine the objectivity and authority of your writing.

By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can effectively incorporate third-person pov into your academic writing and create more persuasive and authoritative pieces.
In conclusion, using third-person writing can be a powerful tool for high school students looking to improve their academic writing. Students can create a more objective, authoritative, and balanced tone in their writing by avoiding first- and second-person language and using third-person pronouns and another language.
The benefits of using third-person writing include presenting research findings and arguments in a more neutral and objective manner, emphasizing the importance of the research or argument rather than the writer’s personal experience or opinion, and presenting information in a more balanced and neutral way.
By incorporating these tips and avoiding common mistakes, students can make their academic writing more effective and persuasive.
Having all the necessary information is important before choosing any course of action. AdmissionSight is always here to assist you with any questions or concerns. We have more than ten years of expertise assisting students in successfully navigating the challenging admissions process.
Consult with AdmissionSight and find out what we can do to help you get into the school of your choice by ensuring that you are sufficiently aware and well-prepared for the application process.
Want to assess your chances of admission? Take our FREE chances calculator today!

Why College Admissions Isn’t Perfect

US News Rankings

The Personal Statement: The Holy Grail of College Admissions

The Modern Day 4.0 and 1600 SAT Score Student Is No Longer Impressive

The Competitive Nature of College Admissions for Asian Americans

The College Application

Our Comprehensive Approach

Ivy League Schools

How Early Should You Prepare for College?

Featured in US News & World Report Best Colleges Publication
Congratulations to AdmissionSight Students and their Acceptances!

College Rejection

College Rankings

College Consultants Could Make A Difference

College Admissions Scandal and Higher Education

How to Submit Supplemental Materials to Colleges

How to Apply for BS/DO Programs

How to Update Cornell After Submitting Your Application

How to Update Columbia After Submitting Your Application

How to Update Harvard After Submitting Your Application

What Should You Write in Your MIT FUN Form?

How to Secure an Internal Transfer and Dual Degree to Wharton

100 Research Topics for High School Students

SAT Test Dates and Deadlines for 2024-2025

How to Join the FBLA Competitive Events

How to Apply for the Coolidge Scholarship

Top 33 Colleges That Require Test Scores

How to Apply for RISE by Schmidt Futures and the Rhodes Trust

Top 50 Test-Optional Colleges

Balancing Cost and Comfort: Finding the Right Student Accommodation for You

How to Compete In the USA Math Olympiad (USAMO)

How to Get the Cameron Impact Scholarship
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Articles

How to Submit Supplemental Materials...

How to Apply for BS/DO...

How to Update Cornell After...

How to Update Columbia After...

How to Update Harvard After...

What Should You Write in...

How to Secure an Internal...

100 Research Topics for High...

SAT Test Dates and Deadlines...

How to Join the FBLA...

How to Apply for the...

Top 33 Colleges That Require...
Sign up now to receive insights on how to navigate the college admissions process..

Admissions Counseling
- Academic & Extracurricular Profile Evaluation
Copyright © AdmissionSight 2024
Privacy Policy - Terms and Conditions
Writing in Third Person – Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
The third-person narrative is often employed in narrative writing because it zooms in and out of character perspectives to describe actions, feelings, emotions, and thoughts. If you’re unsure how to use the 3rd person perspective in writing, here are some tips and examples.
What is Third Person Narrative?

The third person is one of three perspectives employed in speaking and writing. It’s used to describe the point of view of a third party and uses a variety of pronouns derived from he, her, and it. Books written in third person are often more popular, as well, for their ease of reading.
I often write in first-person narrative, but when I’m writing a complex story from the point of view of multiple characters, I use third person to make things more rounded and streamlined for the reader.
Using Third Person
Third person is a perspective used based on whoever the story or writing in question is about. The subject pronoun is outside of the narrator themself. Third-person texts do not include the perspective of the narrator/writer, nor does it address the reader directly. It also uses certain personal pronouns and possessive pronouns.
Example of a third person sentence:
Jeremy knew it was destined to be. He placed the dog in the backseat of his car and drove away. All he wanted at that time was to ensure the animal got the loving home he deserved.
Third Person Possessive Adjectives in Third Person
So, instead of using me, mine, ours, etc., you would use hers, his, theirs when writing in third person.
Does “You” Belong in 3rd Person Writing?
Third-person writing requires using third-person pronouns, including he, she, it, him, her, them, themselves, himself, herself, or a name. Using “you” means you’re switching to the second person.
How to Introduce Yourself in the Third Person
People typically use the first-person point of view when talking about themselves and their experiences. It would be odd to talk about oneself in the third person all the time, but you might use it occasionally for the sake of humorous effect or attract the attention of another person.
The third person introduces a third party to the person you’re speaking with. If you are a narrator, it’s best to introduce yourself in the first person and start narrating the events in the third person.
How to Start a Story in Third Person

In a story, narrators use the third person if they are not part of the story themselves. Third-person narratives show us a person’s actions, feelings, and thoughts.
Example of how to write in third person:
Nadia dreamt about being a gymnast her entire life. Ever since she can remember, she’s worked hard, sacrificed a lot, and hoped someone would notice all her efforts. She was never the smartest kid in school, but she believed in herself enough to never give up on that spot on the podium.
What Are the 3 Types of 3rd Person?
In writing, there are three ways to approach third-person writing.
Third-Person Omniscient
The story’s narrator is all-knowing and can see into the past, present, and future. This narrator can assume other people’s perspectives, jumping around in time and providing the reader with their thoughts and observations.
Third-Person Limited Omniscient
In this point of view, the author focuses on one persona and never switches to another. In a novel, the narrator may use this technique throughout the work or employ it in alternating chapters or sections.
The author can regulate the reader’s knowledge and experience by writing from a limited point of view. Used effectively, it can create a palpable sense of anticipation and excitement.
Third-Person Objective
The narrator of a story told from the third-person objective perspective is unbiased and does not share the viewpoint of the character’s emotional reactions. The story is told in an objective, third-person style.
How to Write In Third Person About Yourself
The easiest way to approach this problem is to create a character. You can also use your actual name to write from the third-person perspective.
Why Write in Third-Person?
Fiction writing uses third-person POV quite often. Here are some advantages of employing it as part of your narrative style.
Strong Character Growth Is Emphasized
More characters can be highlighted in a story told from the third-person perspective than in the first- or second-person. These varying perspectives give the reader a complete understanding of the story since they shed light on the plot in ways the other characters cannot.
It Employs Flexible Narrative Possibilities
The advantages of writing in the third person include greater freedom to move around, giving the reader a comprehensive view, and shifting perspectives among multiple characters. You can switch between being completely all-knowing and having only partial or first-person knowledge.
This latter technique allows the reader to experience the world through the eyes of a character, allowing for a more profound understanding of that person and their surroundings.
Makes the Author More Reliable
Third-person narration places the reader in a vantage point far above the action. With the author/narrator not part of the story, they can rise above it, having nothing to lose or gain from certain narrative developments. This makes the story more reliable and lends the story more authority and credibility.
First, Second, and Third Person Pronouns
If you’re confused about the types of pronouns used in each of the three main perspectives, here is a comprehensive list:
- First person pronouns: I, me, mine, myself, we, us, ourselves, ours.
- Second person pronouns: you, your, yours.
- Third person singular pronouns: he, him, his, she, her, it,
- Third person plural pronouns: its, itself, they, them, their, theirs, themselves.
Bottom Line on Third Person
Writing in 3rd person grants the author more credibility and offers a more objective perspective of the characters in the text. Often employed in fictional and academic writing, the third-person point of view makes the text seem more authentic and factually correct.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write in third-person

Although there are three narratives you can use in any form of writing when it comes to your papers and anything academic you produce, it’s best to choose the third-person. It’s pretty simple with a bit of practice, but if you’re completely new to this writing style, here’s what you need to know about how to write in third-person.
What does writing in third-person mean?
Writing in third-person is one of the three styles you can use when describing a point of view. Even though you might not know it, chances are you’ve used first, second and third person in writing projects throughout your education.
It’s a narrative where you’re totally independent of the subject you’re analyzing and writing about. You don’t take sides. You don’t try to influence what readers feel. It’s a completely unbiased, objective way of writing that tells a story or dissects a topic right down the middle.
There’s a lot of information out there about how you can differentiate between the three in roundabout ways, making it unnecessarily complicated. Here’s a quick breakdown to understand the differences for when you write your following paper:
First-person
This is from the I/we perspective. It’s where we talk about us , ourselves, and our opinions. If we go down the first-person route, writing will include pronouns like I , me , myself, and mine .
Second-person
This point of view belongs to the person you’re addressing — so its a you perspective. In your writing, you’d use second-person pronouns such as you , your, and yourselves .
Third-person
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you’d find in stories. In this perspective, you’d use pronouns like he , she , him , her , his , hers , himself , herself , it , them , their, and themselves . Or, you’d use a name. But that tends to happen more in stories than research papers.
Notice the difference between the three?
When to write in third-person
The third-person point of view tells the reader a story and it’s often the go-to when you’re taking an authoritative stance in your papers, which is why it’s so common in academic writing.
So, always choose the third-person stance when writing academic copy, such as essays and research papers.
The reason for this is it’ll make your papers less personal and more objective, meaning the objectivity will make you come across as more credible and less biased. Ultimately, this will help your grades as the third-person view keeps you focused on evidence and facts instead of your opinion.
You can break third-person perspectives into three other types, including omniscient, limited, and objective. Although they’re more associated with creative writing than academic work and essays, your writing is likely to fall under the third-person objective point of view.
A third-person objective point of view is about being neutral and presenting your findings and research in an observational way, rather than influencing the reader with your opinions.
How to use the third-person point of view
Rule number one: Never refer to yourself in your essay in the third-person. That’s a no-no.
For instance, here’s how you shouldn’t write a sentence in your essay if you’re writing about virtual learning as an example.
“I feel like students perform better at home because they have more freedom and are more comfortable.”
It’s a simple sentence, but there’s a lot wrong with it when you’re talking about research papers and adopting a third-person narrative. Why? Because you’re using first-person pronouns and, as it sounds like an opinion, you can’t back up your claims with a stat or any credible research. There’s no substance to it whatsoever.
Also, it isn’t very assertive. The person marking your work won’t be impressed by “I feel like,” because it shows no authority and highlights that it came from your brain and not anywhere of note.
By including terms like “I think” or “I feel” like in the example above, you’re already off to a bad start.
But when you switch that example to the third-person point of view, you can cite your sources , which is precisely what you need to do in your essays and research papers to achieve higher grades.
Let’s switch that sentence up and expand it using the third-person point of view:
“A psychological study from Karrie Goodwin shows that students thrive in virtual classrooms as it offers flexibility. They can make their own hours and take regular breaks. Another study from high school teacher, Ashlee Trip, highlighted that children enjoy freedom, the ability to work at their own pace and decide what their day will look like.”
With a third-person narrative, you can present evidence to the reader and back up the claims you make. So, it not only shows what you know, but it also shows you took the time to research and strengthen your paper with credible resources and facts — not just opinions.
6 tips for writing in third-person
1. understand your voice won’t always shine in your essays.
Every single piece of writing tends to have a voice or point of view as if you’re speaking to the reader directly. However, that can’t always happen in academic writing as it’s objective compared to a novel, for example. Don’t try to ‘fluff’ up your piece to try and cram your personality in, as your academic work doesn’t need it.
2. Don’t focus on yourself or the reader — focus on the text
An academic piece of work always has a formal tone as it’s objective. When you write your next paper, focus on the writing itself rather than the writer or the reader.
3. Coach yourself out of using first-person pronouns
This is easier said than done if all you’ve ever done is first- or second-person writing. When you write your next paper, scan through it to see if you’ve written anything in first-person and replace it with the third-person narrative.
Here are a few regular offenders that pop up in academic papers — along with how you can switch the statements to third-person:
- I argue should be this essay argues
- I found that should be it was found that
- We researched should be the group researched
- I will also analyze should be topic X will also be analyzed
The same applies to second-person, as there are plenty of cases where it tends to slip through in academic writing. Again, it’s pretty straightforward to switch the more you practice. For instance:
- Your paper will be marked higher if you use a citation tool should be the use of a citation tool will improve one’s grades
4. Be as specific as possible
This is where things can get a little bit confusing. Writing in third-person is all about including pronouns like he, she, it, and they. However, using them towards the beginning of sentences can be pretty vague and might even confuse the reader — this is the last thing you want from your essay or paper.
Instead, try using nouns towards the beginning of sentences. For example, use the actual subject, such as the interviewer or the writer, rather than he, she, or they when you begin the sentence.
The same applies to terms like it. Start the sentence with the ‘it’ is that you’re describing. If it’s a citation tool, begin the sentence by referencing what you’re discussing, so you aren’t vague. Clarity is key.
5. Write in the present tense when using third-person
In any form of academic writing, you need to write your reports, essays, and research papers in the present tense, especially when introducing different subjects or findings.
So, rather than saying “This paper analyzed” (which does seem correct as technically that part was in the past and the writing is in the present), you should write “This report analyzes” — as if you’re analyzing right here and now.
However, the difference is when you highlight how you did the research, that should be in the past tense. This means you’d use third-person phrases like “The equipment that was used” or “The results were analyzed by”, for instance.
6. Avoid adding your own thoughts
If your report is on a subject that’s close to your heart, it can be super tempting to sprinkle in your own thoughts. It’s a challenge, but you need to coach yourself out of it.
In academic writing, you aren’t a commentator. You’re a reporter. You need to let readers draw their conclusions without over-analyzing them or making the reader lean one way or another.
The easiest way to get to grips with writing your academic papers in the third-person is to be consistent and practice often. Criticize your work and analyze it until it becomes the norm. Yes, it can be a little complex in the early days, but before you know it, you’d have mastered the technique, helping you take your papers and reports up a level.
Frequently Asked Questions about writing in third-person
In third-person, you’d use pronouns like he , she , him , her , his , hers , himself , herself , it , them , their, and themselves . Or, you’d use a name.
You is used in second person and is therefore not used in third person. The second person is used for the person that is being addressed.
The third-person point of view is aimed at the person or people being talked about, which is the type of writing you’d find in stories. When writing in third-person view, make sure to write in the present tense and avoid adding your own thoughts.
When writing in third person, you should actually always write in the present tense since you are mostly presenting results in this view.
The second person point of view belongs to the person you’re addressing — so its a you perspective. In your writing, you’d use second-person pronouns such as you , your, and yourselves .

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write in Third Person Point of View

Sarah Oakley

Whether you’re going to write a short story, a novella, or a novel, one of the most important decisions you’ll need to make is which point of view (POV) to use.
Third person is the most popular POV for fiction writers to use. It gives the reader a chance to experience the narrative from a perspective above, or on the shoulder of, the characters.
In this article, we’ll learn what the third person POV is, how it compares to other points of view, and how to write in third person point of view.
What Is Third Person Point of View?
Third person pov meaning, how to write in third person, third person pov examples, conclusion on how to write in third person pov.
Third person POV is when the narrator exists outside of the story. This narrator relates the actions of the characters by using their name or third person pronouns such as “she,” “he,” and “they.”
There are three types of third person POV that you can choose from. Each POV provides a different reader experience as they reveal different amounts of information about the narrative, characters, and setting.
To decide on a POV, think about the type of story you are telling and whether your readers need to be aware of certain details at each point in the plot.

1. Third Person Objective Point of View
The third person objective POV is a way to tell your story by giving the reader all the details within the scenes without including what is going on in the characters’ minds.
To write in the third person objective POV, you will need to create an unbiased narrator who doesn’t tell the reader the thoughts and feelings of the characters. Instead, your narrator will simply relay the actions and dialogue of the story in an objective, impartial telling of the events.
This is great for keeping distance between the reader and the characters. It’s like looking through the window of a stranger’s house and trying to figure out why everything is happening.
2. Third Person Omniscient Point of View
When writing in the third person omniscient POV, you give your reader an all-access pass to the thoughts and feelings of any character in each scene of your story. You can give as much detail about the scene as you can in the third person objective POV, but this time you can also include information from the characters’ perspectives.
The narrator you create to speak in the third person omniscient POV will need to relay the thoughts and feelings of all the relevant characters in the scene. You can do this by switching perspectives. This is sometimes called “head hopping.”
You can use head hopping to show conflict in the story. For example, one paragraph is from the main character’s perspective, as they give some important information to another character. Then, the next paragraph is from the perspective of the person who received the information, which shows their reaction to what the main character just said.
Third person omniscient is perfect for sharing all the little details about the world you have created and allows the reader to pick up clues that some characters might not have noticed. Some writers refer to the third person omniscient POV as an all-seeing being who likes to give their thoughts on the plot.
3. Third Person Limited Point of View
This narrator sits on the shoulder of your main character and tells the story from their perspective. It’s close to being first person, but the reader isn’t solely within the character’s mind and this narrator still uses third person pronouns and verbs.
Sometimes, the third person limited POV narrator sticks to a different character each chapter instead of one character throughout the entire story. We refer to this as a viewpoint character, as we are seeing the world from their perspective.
You are controlling the amount of information given to the reader by focusing on one character’s awareness, rather than all characters’.
First Person vs Third Person
First person POV gives readers full access to the thoughts and feelings of the main character, as they are the one telling the story. There isn’t a narrator getting between the reader and the character.
Another key part of writing in the first person POV is that the character uses first person pronouns to tell the story. They use “I,” “me,” “my,” and “myself” as they are talking about actions and experiences.
Remember : not all main characters notice everything going on around them. It can break the reader’s immersion if they are wondering how the main character knew they were about to die, but there were no clues it was about to happen. Not all characters are psychic!

If you’re aiming to stick to one character’s thoughts and feelings, but you also want to add in some extra details that are in the character’s peripheral vision, try the third person limited perspective.
This POV can be used to great effect in thrillers where you want to stay close to the main character, so the reader connects with them.
Meanwhile, you can also give clues about things that are about to happen that the character is unaware of. Let us watch in horror as the character falls down a hole we all saw coming, but could do nothing to stop them.
Second Person vs Third Person
Second person POV puts you, the reader, in the driving seat as the main character. The narrator breaks the fourth wall and speaks to you directly.
This perspective uses second person pronouns such as “you,” “your,” and “yourself” to bring the reader into the narrative. The narrator uses third person pronouns to refer to other characters.
Second person works well in stories where you want full immersion for the reader. Some people love the feeling of being dropped onto the rollercoaster of drama in a good story. This is why second person is used in video games and Choose Your Own Adventure stories.
However, it is one of the least used POV types by fiction writers. One reason for this is that it takes a lot of skill to write about the reader in a way that feels natural to them while also giving away the right amount of information for the story. You don’t want your reader to lose interest because they don’t agree with something the narrator has said.

Third person objective would be a better option if you don’t want to write as though your story is about the person reading it. The third person POV allows the reader to focus more on the narrative and everything else that’s going on around the characters.
So far, we’ve discussed what the third person POV is, but what does the “third person” part of that mean?
Third person is a grammatical style of writing that uses pronouns such as “she,” “he,” “they,” and “it.” It also uses proper nouns and names when referring to specific individuals and objects.
1. Decide If Third Person Provides the Right Reader Experience
Do you want to tell the story from within the mind of your main character? Do you want to make the reader the main character of the story? If the answer is no to both questions, it’s time to look at your options for writing in the third person.
2. Pick the Type of Third Person Narrator
Go over the details of your story and your characters. You will need to establish whether third person limited, third person objective, or third person omniscient is the best POV for your story.
3. Read Examples of Writing in Third Person
It’s important to take the time to analyze what works and what doesn’t work in third person narration. The best way to do this is by reading other works that use third person points of view.
Focus on the information they are sharing. Did it work? Would you have used a different type of narrator for that story?
4. Use a Consistent POV
Switching POVs is a habit that a lot of writers do if they’re writing in a POV they’re not used to. Don’t worry, it happens. However, being aware that this is something to avoid before you get 200 pages into your novel and realize you switched POVs back on page 90 can help you be more observant of your writing habits.
5. Use the Correct Pronouns—ProWritingAid Can Help!
The third person POV means using third person pronouns when your narrator is speaking. Remembering this is one of the best ways to catch yourself from slipping into different points of view.

You can stop yourself from using the wrong pronouns by using ProWritingAid’s pronoun report. It’ll highlight all the examples of pronouns in your text, so you can easily work through your story and change them back into the third person if you’ve made any mistakes.
6. Create a Trustworthy Third Person Narrator
Your third person narrator is the voice of your narrative. How do they tell the story? Do we believe them?
Readers need to feel like your narrator has the authority to tell these events in a way that satisfies them. If you want to share the thoughts and feelings of the characters, the narrator needs to sound like they are confident in the details they are sharing.
Third Person Objective Example
If you’re wondering how to show conflict when writing in the third person objective POV, we would recommend reading Hills Like White Elephants by Ernest Hemingway.
Let’s look at an excerpt from the story:
The woman brought two glasses of beer and two felt pads. She put the felt pads and the beer glasses on the table and looked at the man and the girl. The girl was looking off at the line of hills. They were white in the sun and the country was brown and dry. “They look like white elephants,” she said. “I’ve never seen one.” The man drank his beer. “No, you wouldn’t have.” “I might have,” the man said. “Just because you say I wouldn’t have doesn’t prove anything.” The girl looked at the bead curtain. “They’ve painted something on it,” she said. “What does it say?” “Anis del Toro. It’s a drink.”
As you can see from this extract, the third person objective narrator is relaying the information about the scene without being biased to either of the characters. They do not quote the characters’ thoughts or feelings; they simply give details about their actions and words.
As a reader, you can still imagine what the characters are thinking and feeling, as the conflict is laid out bare for you to witness.
Third Person Omniscient Example
Readers of the third person omniscient POV expect the narrator to be all-seeing and all-knowing, so it makes sense that the narrator in Good Omens by Neil Gaiman and Terry Pratchett is “God” or the “Almighty.”
Here’s an extract from the novel:
“Er. Okay,” he said. “I’ll, er, be off then. Shall I? Get it over with. Not that I want to get it over with,” he added hurriedly, aware of the things that could happen if Hastur turned in an unfavourable report. “But you know me. Keen. So I’ll be popping along,” Cowley babbled. “See you guys... see you. Er. Great. Fine. Ciao.” As the Bentley skipped off into the darkness Ligur said, “Wossat mean?” “It’s Italian,” said Hastur. “I think it means food .” “Funny thing to say, then.” Ligur stared at the retreating tail-lights. “You trust him?” he said. “No,” said Hastur. “Right,” said Ligur. It’d be a funny old world, he reflected, if demons went round trusting one another.
This example shows how the third person omniscient narrator pops into the heads of several characters in one passage. At the beginning, we’re in Cowley’s mind, which is shown by the phrase “aware of things that could happen if Hastur turned in an unfavourable report.” However, within a few lines, we pop into Ligur’s mind, which is apparent in the sentence, “It’d be a funny old world, he reflected, if demons went round trusting one another.”
Third Person Limited Example
If you’re looking for examples of third person limited narrators that tell the story from one character’s perspective, we would recommend reading Happily Ever After by Harriet Evans.
Let’s check out a section of the novel:
She knew his face so well, knew him so well, how he drummed his fingers on any spare surface, how he looked vague when trying to get out of things, how his mouth curled to the side when he was making a joke. But she’d never sat this close to him before, because he was her boss. It didn’t feel like that tonight. It was as if they were different people. It was nice. Rory was nice, but then, she’d always known that.
Romance writers like writing first person POV, but third person limited also works well in this genre, like in this extract. The narrator is giving us a direct connection to the mind of the main character (Elle). They do this by describing everything Elle’s noticed about the man she’s attracted to.
Elle realizes her boss has always been nice and we get the impression she’s always secretly wanted to date him. The narrator shows us this by giving us Elle’s perspective on what’s happening in the scene. It’s as close as the narrator can be without Elle telling the story herself.
As you can see, writing in the third person isn’t hard when you follow the step-by-step process. It’s a lot of fun to experiment with the different types of third person POV. Which one do you prefer?
Don’t forget, if you’re worried about slipping into different POVs within your writing, you can always use the ProWritingAid pronoun report to keep you in check!
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
##About Sarah is a romance writer with a passion for studying human connections and psychology. She lives with her fiancé and two cats in Gloucester, UK. When she’s not writing, Sarah enjoys visiting theme parks, singing along to rock songs, and planning her next vacation. ##Writing Experience Sarah is an aspiring screenwriter who hopes to see her name in the credits of a romance film one day. She has also written short stories and has had many ideas for novels in a variety of genres. ##Education Sarah has been studying the art of writing and film from the age of 16 and she holds a BA in Creative Writing.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
How to Write in the Third Person
You may have heard someone talking about third person POV in an English class or on a writers’ panel. What does it mean? POV stands for point of view, and any piece of prose writing has one. The point of view helps anchor the reader, and it makes the text easier to understand. Even in a story that doesn’t appear to come from a particular character’s voice, we can still assign the narration a point of view. When the point of view isn’t yours (second person) or mine (first person), then we call it third person narration. In this article, we’ll give you some tips to help you learn to write this way.
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
Avoid First Person
First person emphasizes the subjective point of view, and you can easily identify this writing style through the use of the pronouns “I” and “me”. Imagine an autobiography. The narrator explains his or her life by using phrases like this one: “I was born in a small town.” In a biography, written by another person, the text might read: “She was born in a small town.” That’s the difference between first person and third person. In first person, the narrator is the main character or, if not the main character, a character in the action. On the other hand, when a book is written in the third person, the story does not come from the point of view of a character. Instead, the writing describes things that happen to other people, characters besides the writer or the reader.
First person writing can be identified by the use of the following pronouns:

Avoid Second Person
Second person narration comes from the point of view of the reader. A second person point of view can often be found in the self-help or how-to genres, as well as in choice-based adventure books. “Choose Your Own Adventure® gamebooks began life in 1979 as the first publishing effort of a new division at Bantam Books focused on younger readers,” according to Chooseco LLC . Today, 265 million books have been published in this style. Let’s look at the summary of one of these books for a memorable example of second person narration:
“ You are a mountain climber, headed to the Himalayas to find proof that the mysterious yeti really exists. When your best friend Carlos goes missing from base camp, the fate of the expedition is in your hands.” — The Abominable Snowman
We added the bold font above to draw attention to some important pronouns. It’s easy to identify second person narration because it features second person pronouns:
What Is Third Person?
When a piece of writing does not assume the perspective of either the reader or the writer, it’s written in the third person point of view. Third person narratives have three distinct styles, known as third person objective, third person omniscient, and third person limited omniscient. You can recognize all three of these points of view through the use of third person pronouns, which include:
Third Person Objective
Imagine a history essay or a science article, written by a distant and neutral third party. The writer does not attempt to explain the perspective of any character; instead, he or she reports on the events with dispassion. If any opinions made their way into the text, they are properly attributed to the source.
Congressman Smith said, “X, Y, Z.” His constituent disagreed, arguing A.
The author of a third person objective article would never presume to speak for another person’s inner thoughts. Instead, the writer aims to present the facts and events in an orderly way, attributing the actions and dialogue to the proper characters.
This writing style is frequently used in academic writing and professional writing, but it can be used by fiction writers as well. As long as the author does not place thoughts inside the heads of characters, third person objective can work for any style of prose writing. If a writer wanted the reader to understand a character’s emotional state, he or she would have to make reference to body language, facial expression, and dialogue; otherwise, the character’s thoughts would remain opaque. The internal monologue of any character remains off limits from the objective point of view.
Third Person Omniscient
The third person omniscient point of view frequently appears in fiction writing. With this style, an all-knowing narrator has the ability to get inside any character’s head. That’s why an omniscient point of view can be thought of as “head-hopping.” The narrator has knowledge of everything. The characters have nowhere to hide—even their most intimate thoughts may be plumbed. Personal opinions and internal dialogue are all fair game, for any of the characters. In this style of writing, you can expect to see different points of view. As a reader, you can expect to know more about the different characters than the characters know about each other.
Third Person Limited Omniscient
Sometimes a writer engages a third person perspective, but they elevate one character above the rest. The writer may expound on that character’s thoughts, inner dialogue, and perspective. The focal character for the third person limited point of view is often called the viewpoint character. Typically, the viewpoint character is a main character in the story. The writer provides the reader with comprehensive access to this character’s thoughts, but all the other characters must be understood through actions, gestures, and dialogue. The reader must get by with limited information, since they rely on what the viewpoint character knows.
Still, the reader does not go “inside the head” of the viewpoint character completely. Rather than writing from the main character’s perspective in the first person point of view, the writer maintains a third person writing style. Without using first person pronouns, the author explores the thoughts of a single character. The narrator describes she and her, not I and me.
She worried that she would be late, but didn’t bother to tell her sister.
In the example above, the reader understands what the viewpoint character is thinking. On the other hand, the sister cannot read the viewpoint character’s thoughts. Likewise, the reader is not privy to the sister’s thoughts.
The omniscient limited and omniscient POV appear most commonly in creative writing. In general terms, third person objective or first person would be a more common choice for essays, articles, and nonfiction books.
Blending Perspectives
Now that you know the conventions for writing in first person, second person, third person objective, third person limited, and third person limited omniscient, you may want to revisit some of your favorite works of literature. Try to figure out their points of view, and think about why the author picked that perspective.
In your research, you may come across some books that defy categorization. Moby Dick by Herman Melville and Ulysses by James Joyce come to mind. Both books shift between third person and first person narration. Many fiction writers, especially modernist writers, flout convention by using a number of different narrative styles within the same work.
In creative writing, you should feel free to break the rules. Just be sure to understand the rules as you break them!
- https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-point-of-view.html
- https://www.britannica.com/art/novel/Narrative-method-and-point-of-view
- https://www.dictionary.com/e/1st-person-vs-2nd-person-vs-3rd-person-pov/
- https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/point-of-view-first-second-third-person-difference
- https://www.cyoa.com/

Kari Lisa Johnson
I’m an award-winning playwright with a penchant for wordplay. After earning a perfect score on the Writing SAT, I worked my way through Brown University by moonlighting as a Kaplan Test Prep tutor. I received a BA with honors in Literary Arts (Playwriting)—which gave me the opportunity to study under Pulitzer Prize-winner Paula Vogel. In my previous roles as new media producer with Rosetta Stone, director of marketing for global ventures with The Juilliard School, and vice president of digital strategy with Up & Coming Media, I helped develop the voice for international brands. From my home office in Maui, Hawaii, I currently work on freelance and ghostwriting projects.
Recent Posts

Bare Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

??? Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Domicile Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
Thin Blue Line Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
7 Essential Tips for Writing in the Third Person

Table of contents

Alana Chase
Whether you’re a student, business professional, or writer, knowing how to write well in the third person is an essential skill.
But you may not be sure of all the rules or how to make your third-person writing shine.
As an editor and writing coach of 11 years, I’ve taught students and writers at all levels how to master the third-person point of view (POV). All you need to get started is a good understanding of third-person pronouns and a bit of practice for consistency.
By the end of this article, you’ll know when and how to use third-person perspective. You'll also find helpful tips for taking your third-person writing to the next level.
Key takeaways
- In the third-person perspective, the narrator is separate from the story.
- Third-person perspective uses he/him/his, she/her/hers, and they/them/their pronouns.
- Consistency is key: Don’t switch between perspectives in a single document.
- Practicing third-person writing and editing your work is vital to improving your skills.
What is third-person point of view (POV)?
In writing, there are three ways to tell a story: first-person, second-person, or third-person POV.
First-person POV is from the narrator’s perspective:
“ I saw the bird steal my sandwich, and I ran after it.”
Second-person POV is from the reader’s perspective:
“ You saw the bird steal your sandwich, and you ran after it.”
Third-person POV, however, separates the narrator from the story and uses third-person pronouns (like he/him, she/her, and they/them) to describe events, actions, thoughts, and emotions. Characters are referred to by name or one of these pronouns:
“ Alex saw the bird steal his/her/their sandwich, and he/she/they ran after it.”
Third-person POV is used in all kinds of writing — from novels to research papers, journalistic articles, copywriting materials, and more. Check out some examples below.
Examples of third-person perspective
- In a novel: “Robb and Jon sat tall and still on their horses, with Bran between them on his pony, trying to seem older than seven, trying to pretend that he’d seen all this before.” (From A Game of Thrones by George R. R. Martin)
- In a news article : “This weekend, Iceland experienced nearly 2,000 earthquakes within 48 hours. And they’ve kept coming since then – in swarms.” (From “Thousands of earthquakes have scientists watching for a volcanic eruption in Iceland” on NPR’s website )
- In copywriting : “Balm Dotcom’s formula has antioxidants and natural emollients to nourish dry lips.” (Website copy describing Glossier’s Balm Dotcom lip product )
7 tips for writing in the third person
Just like the first and second person, you’ve probably already written in the third person before. But to do it well , you’ll need some key tips and tricks in your writing toolkit.
Let’s dive into the seven essentials for third-person writing.
Tip 1: Use third-person determiners and pronouns
In grammar, determiners introduce and modify nouns. They’re used to specify what a noun refers to (like “ my laptop”) or the quantity of it (like “ many sandwiches”).
Meanwhile, pronouns are substitutes for nouns, referring to people, places, or things. For example, “Caroline [noun] is a skilled musician, and she [pronoun] especially loves playing the piano.”
When you write in the third person, use only third-person determiners and pronouns. Let’s take a look at the different types of pronouns.

Tip 2: Use names for clarity
In third-person writing, using names is crucial for clarity, especially when multiple people/characters share similar pronouns. Strategically incorporate names into your writing to help readers keep track of who’s who.
For example:
“She submitted the script draft to her, and she made suggestions for changes.”
“Mira submitted the script draft to Lynn, and Lynn made suggestions for changes.”
Tip: Use a character or person’s name when introducing them in your writing. Then, alternate between using pronouns and their name to prevent confusion.
Tip 3: Keep the narration neutral
When you write in the third person, your narrator is an uninvolved observer. They have no opinions on the people, places, things, or events they describe. Their words and tone should be neutral (but not boring).
To achieve this in your writing:
- Think of your narrator as a reporter. Their job is to detail what’s happening, when and why it’s occurring, who’s involved, and any background information that can give context. They don’t offer a personal interpretation of events. Instead, they provide facts and supporting details.
- Save the judgment for characters. Rather than having your narrator share their critique of events or individuals, have a character offer their opinion — either through dialogue, actions, or reactions. For instance, instead of writing, “Dr. Shaw was a courageous woman,” let a character convey admiration by telling Dr. Shaw, “I’ve always admired your fearlessness.”
- Be objective with your descriptions. Avoid subjective adjectives and focus on observable features. For example, instead of describing a landscape as “breathtaking,” write that it’s “marked with snow-capped mountains and patches of tall pine trees.”
Tip 4: Use descriptive language
Showing — and not just telling — is essential when writing in the third person. Instead of stating emotions and experiences outright, immerse your reader in your character’s reality. Create vivid descriptions of their thoughts, feelings, and surroundings. Use language that engages the senses: sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste.
For example:
“Aisha was nervous.”
“Aisha’s hands trembled, and her tongue felt dry against the roof of her mouth. The spotlight above the stage shone white-hot, causing beads of sweat to form along Aisha’s hairline.”
Tip 5: Be consistent
Once you establish a third-person POV, stick to it . Avoid switching from the third person to the first or second person. Otherwise, you’ll confuse the reader and disrupt the flow of your writing.
“Hannah felt a surge of excitement when her telephone rang, anticipating good news about her mortgage application. I felt my heart rate quicken as I answered.” (Switches from the third person to the first person)
“Hannah felt a surge of excitement when her telephone rang, anticipating good news about her mortgage application. She felt her heart rate quicken as she answered.” (Remains in the third person)
Tip 6: Practice
Writing in the third person might feel strange at first, especially if you’re used to using the first or second person. However, it’ll come more naturally to you with practice.
Here are two writing exercises you can try right now:
Writing Exercise #1
Take an excerpt from an article or book written in the first or second person and rewrite it in the third person. Below is an example using The Catcher in the Rye , whose main character is named Holden.
Before: “The other reason I wasn’t down at the game was because I was on my way to say good-by to old Spencer, my history teacher.”
After: “The other reason Holden wasn’t down at the game was because he was on his way to say good-by to old Spencer, his history teacher.”
Writing Exercise #2
Turn on a movie or television show, mute the sound, and closely observe two characters. Give them each a name. Using third-person pronouns and their names, describe the characters’ actions and what you believe they’re thinking and feeling.
Above all, write in the third person as often as possible , following the tips in this guide. Remember, your writing skills are like muscles: The more you exercise them, the stronger they become.
Tip 7: Carefully revise
After you’ve written something in the third person, carefully review and revise your work.
Check that your writing :
- Uses third-person determiners and pronouns accurately and consistently
- Incorporates names where pronouns may cause confusion
- Maintains a neutral tone, where your narrator doesn’t offer personal opinions or interpretations
- Doesn’t shift to the first or second person
Make changes where necessary, then read through your work a final time.
AI tip: Wordtune can help you self-edit and help improve your writing overall.
Paste your work into Wordtune’s Editor, or write in it directly, and use the features to shorten or expand your sentences, make your tone more casual or formal, and more. Wordtune will also automatically flag spelling and grammar errors and suggest ways to improve concision, clarity, and flow.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Bonus tip (advanced): Learn the different types of third-person POV
Did you know there are three types of third-person POV? Getting familiar with them can help you make your writing even more impactful.
- Third-person objective , where the narrator is “a fly on the wall”: They provide an objective account of events without exploring people/characters’ emotions or thoughts.
- Third-person omniscient , where the narrator has unlimited knowledge of all events and characters’ thoughts and feelings.
- Third-person limited , also called “close third,” where the narrator has access to just one character’s emotions, thoughts, and experiences.
With this knowledge, you can choose the right perspective for your writing depending on its purpose, tone, and goals.
For instance, use third-person omniscient to show readers what’s happening with everyone in your novel. Or, you could go for third-person objective in an academic paper where you must present facts without sharing your interpretation of them.
Writing well in the third person takes thought and effort. You must use third-person determiners and pronouns, weave in descriptive language, and keep your narration neutral. You also need to be consistent with your POV, ensuring you don’t accidentally switch to the first or second person. Finally, review and revise your work to make sure it’s clear and error-free.
Using this guide — and Wordtune’s tools to polish your writing — you’ll get the hang of the third-person perspective in no time.
To continue sharpening your writing skills, read our articles on mastering tone of voice and writing concisely (with help from AI). Then, check out our proofreading guide to keep your work flawless .
What is a third-person word example?
Third-person words are pronouns like “he,” “her,” “they,” “it,” “hers,” and “theirs.”
Should I write in the first or third person?
It depends on the closeness you want to create with your audience. The first person allows for a personal connection between the narrator and the reader, while the third person creates distance between the narrator and the audience.
What are the disadvantages of writing in the third person?
Third-person writing can lead to a lack of intimacy with the reader. This can be a disadvantage for some writers but an advantage for others, like those in academic and professional settings.
Share This Article:

The Dos and Don’ts of Using AI to Study
.webp)
How to Use Modal Verbs for Clear Communication

A Friendly Guide to Apostrophes vs Quotation Marks
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, third-person point of view.
Many academic disciplines ask their writers to use third person point of view (POV). If so, then writing in the third person is important because your writing will appear professional and credible.
You may occasionally use first person POV to create a more personal tone, or second person POV to command a reader to do something. This depends on the assignment requirements, or on what your instructor recommends. If you are receiving this comment, then you should consider revising your use of other points-of-view to write your project in third person POV.
Third Person Personal Pronouns
| person | he, she, it, they | him, her, it, them | his, her, hers, its, their, theirs |
Note: While the above pronouns represent the third person, instead of using it , that , these , those or this , specific words or phrases will better help readers follow the writer’s logic.

How do you change first or second person to third person?
Here is a table that shows several common instances of first or second person in essays and some examples of how to revise to the third person.
When is third-person point of view used?
Third person is used when a degree of objectivity is intended, and it is often used in academic documents, such as research and argument papers. This perspective directs the reader’s attention to the subject being presented and discussed. Third person personal pronouns include he, she, it, they, him, her, them, his, her, hers, its, their, and theirs .
Examples of sentences written from the third person point of view:
- She went to the library to consult with the reference librarian about her paper’s topic.
- When he got to his car, he was glad to see that his friend was waiting for him .
- The students entered the classroom nervously on the first day of class; they had not had the opportunity to become acquainted with their professor or with each other.
- Jenny and her friend used backpacks to simplify the task of carrying books, notebooks, writing tools and a laptop around campus.
- Human sex trafficking is a social problem that requires decisive action; its victims should be given the opportunity to escape the cycle of exploitation to which they have become slaves.

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
Style Changes in the seventh edition of the APA Manual:
Bias-free language, first, second and third person definitions, use third person for formal writing, be comfortable with exceptions, watch your grammar, writing in third person in apa style.
As the "Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association" attests, style and tone are important elements of APA papers and publications since they affect how a reader understands information. Point of view is one of the elements that can determine how information is received by a reader.
- Use “they” for a person whose gender is unknown or irrelevant.
- Use non-human relative pronouns like “that,” and “which” for inanimate objects and animals -- rather than use “who.”
- Use "they" for a person who uses “they” as their personal pronoun. Plural verbs even when "they" is referring to a single person or entity:
They are a great artist is preferred rather than They is a great artist.
Use “person-first” language whenever possible.
A man with leprosy rather than A leper
Avoid using adjectives as nouns to describe groups of people: use the people who are ill rather than the sick.
Three different points of view exist: first person, second person and third person. First person reflects the writer's voice with pronouns such as:
Second person speaks directly to a reader, using pronouns such as "you" and "your."
Third person uses a more general voice that reflects neither the writer nor reader specifically, using words like "students" and "participants" and pronouns such as "he," "they" and "it."
Good writing typically begins in one point of view and retains that perspective throughout in order to avoid confusion for the reader.
Most formal writing, including APA papers, uses the third person point of view. Third person makes ideas sound less subjective since it removes direct reference to the writer. It also creates a more generalized statement.
For example
"Researchers first need to determine participants" (written in the third person) conveys a more formal, objective tone than "You first need to determine participants" (second person) and "I first needed to determine participants" (first person).
Instructors, institutions and publishers generally require writing in the third person to maintain a more formal tone.
The APA manual explains that third person may not always be appropriate in APA papers. When describing activities you performed in your research or when third person language may confuse the reader, use first person instead.
For instance, after a reference to an outside source, if you then write, "The author developed the program," your reader cannot be certain if "the author" refers to the referenced source or yourself. Using the first person in such cases clarifies your intention.
Pronoun use is a significant grammatical issue involving the third person point of view. Pronouns must agree in number with the nouns they refer to. For instance, for the plural noun "participants" and the pronoun "they" agree in number while "he" does not.
In the third person point of view, writers should use gender-neutral pronouns when appropriate, such as "they." Some writers consider the use of "he or she" awkward, but the use of "they" can lead to agreement issues. When using "they," make certain the antecedent noun is also plural.
- Purdue University OWL: APA Style Basics
- University of Arizona Writing Center: First vs. Third Person
- Purdue University OWL - APA 7th Edition style Changes
Kristie Sweet has been writing professionally since 1982, most recently publishing for various websites on topics like health and wellness, and education. She holds a Master of Arts in English from the University of Northern Colorado.
How to Do the Write Thing
Get Paid to Write through the Power of Storytelling and Make Money Online to Work from Home
Everything You Need to Know for Writing in Third Person | 11 Tips

Everything You Need to Know for Writing in Third Person
What is writing in third person point of view?
“In third-person point of view, the author is narrating a story about the characters, referring to them by name, or using the third-person pronouns “he,“” she,” and “they.” The other points of view in writing are first person and second person.” Source.
What does writing in third person mean?
“When you are writing in the third person, the story is about other people. Not yourself or the reader. Use the character’s name or pronouns such as ‘he’ or ‘she’.”
What are the 3 types of third person point of view?
1. third-person omniscient point of view: .
“The omniscient narrator knows everything about the story and its characters. This narrator can enter any character’s mind, move freely through time, and give the reader their own opinions and observations as well as those of the characters. For example, Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice is told from a third-person omniscient point of view, giving the reader full access to the main character, Elizabeth, as well as the characters around her.” Source.
2. Third-person limited point of view:
“The third-person limited point of view (often called a “close third”) is when an author sticks closely to a single character but remains in third-person. The narrator can do this for the entire novel or switch between different characters for different chapters or sections. This point of view allows the author to limit a reader’s perspective and control what information the reader knows. It is used to build interest and heighten suspense.” Source.
3. Third-person objective point of view:
“Third-person objective point of view has a neutral narrator that is not privy to any character’s thoughts or feelings. The narrator presents the story with an observational tone. Ernest Hemingway employs this third-person narrative voice in his short story “Hills Like White Elephants.” An unknown narrator relays the dialogue between a couple as they wait for a train in Spain. This point of view puts the reader in the position of a voyeur, eavesdropping on a scene or story.” Source.
Writing in third person examples:
Famous quotes written in third person: .
- “Those who find ugly meanings in beautiful things are corrupt without being charming. This is a fault. Those who find beautiful meanings in beautiful things are the cultivated. For these there is hope. They are the elect to whom beautiful things mean only Beauty. There is no such thing as a moral or an immoral book. Books are well written, or badly written. That is all.” ― Oscar Wilde, The Picture of Dorian Gray
- “No tears in the writer, no tears in the reader. No surprise in the writer, no surprise in the reader.”― Robert Frost
- “Read, read, read. Read everything — trash, classics, good and bad, and see how they do it. Just like a carpenter who works as an apprentice and studies the master…” ― William Faulkner
- “Fantasy is hardly an escape from reality. It’s a way of understanding it.” ― Lloyd Alexander
- “A dreamer is one who can only find his way by moonlight, and his punishment is that he sees the dawn before the rest of the world.” – Oscar Wilde
- “A pessimist sees the difficulty in every opportunity; an optimist sees the opportunity in every difficulty.” – Winston Churchill
- “A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new.” – Albert Einstein
- “Life is a succession of lessons which must be lived to be understood.” – Helen Keller
- “Music expresses that which cannot be said and on which it is impossible to be silent.” – Victor Hugo
- “Failure is simply the opportunity to begin again, this time more intelligently.” – Henry Ford
- “Family is not an important thing. It’s everything.” – Michael J. Fox
- “It is not a lack of love, but a lack of friendship that makes unhappy marriages.” – Friedrich Nietzsche
- “A bird doesn’t sing because it has an answer, it sings because it has a song.” – Lou Holtz
Third person writing in everyday advertising:
- Plop Plop Fizz Fizz. Oh, what a relief it is – Alka-Seltzer
- The King of Beers – Budweiser
- It’s the real thing – Coca-Cola
- A diamond is forever – De Beers
- The happiest place on earth – Disneyland
- It keeps going and going and going – Energizer
- When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight – FedEx
- The Possibilities are Infinite – Fujitsu
- The best a man can get – Gillette
- It wouldn’t be home without Hellmann’s – Hellman’s
- It’s finger lickin’ good – KFC
- Nobody can do it like McDonald’s can – McDonald’s
- Good to the last drop – Maxwell House
- Maybe she’s born with it. Maybe it’s Maybelline – Maybelline
- The greatest tragedy is indifference – Red Cross
- Takes a licking and keeps on ticking – Timex
Third person point of view examples are all around us. We just have to keep an eye-out for them.
Third person writing in Known Literature:
- “”What are you doing?” Yossarian asked guardedly when he entered the tent, although he saw at once.”There’s a leak here,” Orr said. “I’m trying to fix it.” – Joseph Heller, Catch 22
- “Please stop it,” said Yossarian. “You’re making me nervous.” – Joseph Heller, Catch 22
- “When I was a kid,” Orr replied, “I used to walk around all day with crab apples in my cheeks. One in each cheek.” – Joseph Heller, Catch 22
- “Yossarian put aside his musette bag from which he had begun removing his toilet articles and braced himself suspiciously. A minute passed. “Why?” he found himself forced to ask finally.” – Joseph Heller, Catch 22
- “Orr tittered triumphantly. “Because they’re better than horse chestnuts,” he answered.” – Joseph Heller, Catch 22
- “When Jane and Elizabeth were alone, the former, who had been cautious in her praise of Mr. Bingley before, expressed to her sister how very much she admired him.” – Jane Austin, Pride and Prejudice
- “He is just what a young man ought to be,” said she, “sensible, good humoured, lively; and I never saw such happy manners! — so much ease, with such perfect good breeding!” – Jane Austin, Pride and Prejudice
- “He is also handsome,” replied Elizabeth, “which a young man ought likewise to be, if he possibly can. His character is thereby complete.” – Jane Austin, Pride and Prejudice
- “It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.” – George Orwell, 1984
- “Their commander was a middle-aged corporal-red-eyed, scrawny, tough as dried beef, sick of war. He had been wounded four times-and patched up, and sent back to war.” – Kurt Vonnegut, Slaughterhouse-Five
- “It was a dark and stormy night; the rain fell in torrents, except at occasional intervals, when it was checked by a violent gust of wind which swept up the streets.” – Edward George Bulwer-Lytton, Paul Clifford
- “He drank an Anis at the bar and looked at the people. They were all waiting reasonably for the train. He went out through the bead curtain. She was sitting at the table and smiled at him.” – Ernest Hemingway, “Hills Like White Elephants”
- “She walks in beauty, like the night Of cloudless climes and starry skies; And all that’s best of dark and bright Meet in her aspect and her eyes” – Lord Byron, “She Walks in Beauty”
Third person writing academic example:
“Third-person point of view identifies people by proper noun (a given name such as
Ella Clark) or noun (such as teachers, students, doctors, or players) and uses the
pronouns he, she, and they. Third person also includes the use of one, everyone, and
anyone. Most formal, academic writing uses the third person. Note the use of various
third-person nouns and pronouns in the following:
“ The bosses at the factory have decided that employees need a day of in-house
training. Times have been scheduled for everyone. Several senior employees will
be required to make five-minute presentations. One is not eager to speak in front of
others since she’s very shy. Another one, however, is anxious to relate her
expertise. The variation in routine should provide an interesting day for all people
concerned. ””
“Use third person for all academic writing:
For formal writing, such as research and argumentative papers, use the third person. Third person makes your writing more objective and less personal. For academic and professional writing, this sense of objectivity allows the writer to seem less biased and, therefore, more credible.[1]
Third person helps the writing stay focused on facts and evidence instead of personal opinion.”
How to write in third person about yourself.
Even though third person speaks about others and doesn’t use the pronouns I or we, how do I write about myself in third person?
Just use a story or event that you experienced and give the character you are following (yourself) a different name and write about that character as if you were talking about someone else. “Jimmy went to the park. He rode his bike there. On the way, he crashed. He had to go to the ER.” Even if those events really happened to you, you were still able to write about your true to life experiences in the third person.
Tips and Tricks for Writing in Third Person:
1. create a narrator’s voice.
When writing in third person, speak with authority. Show your reader that the narrator’s voice is trustworthy. Give them the inner thoughts of at least one character. The main narrator voice you use will give them the idea that you are in-the-know and can carry them well through the events to come.
2. Make sure to use the right pronouns
“Third person pronouns include: he, she, it; his, her, its; him, her, it; himself, herself, itself; they; them; their; themselves.”
3. If you choose third person objective point of view the narrator doesn’t know what anyone is thinking
If you choose this point of view remember that you are just an observer. You will have to make a point to work harder on conveying the emotions each character is experiencing. The reader won’t get to hear the inner feelings and thoughts of any of the characters. That makes it really important to emphasize the right character facial expressions and describe them adequately but not overdo it.
4. Be aware of singular and plural pronoun use.
“Incorrect example: “The witness wanted to offer anonymous testimony. They’ were afraid of getting hurt if their name was spread.”
“Correct example: “The witness wanted to offer anonymous testimony. He or she was afraid of getting hurt if his or her name was spread.”
5. If you write in third person limited you only know what the protagonist knows
If you write in third person limited, remember that you are limited by the same knowledge that the main character you are following knows. Be strategic with this and give the reader the same feelings the protagonist has at their limited knowledge of the events befalling them.
6. Avoid slipping into other points of view
It is easy while you are writing to accidentally and mindlessly slip into first and second person point of view.
When you go back to edit, keep this in mind and watch out for any accidental “I” or “you” statements.
7. Understand that there are 3 types
Be sure to glance up at the top of this post and see that there are 3 different types of third person point of views. Choose wisely as you begin your story which one you would like to limit yourself to or not limit to.
My personal favorite to date is definitely third person omniscient. I like being able to say whatever whenever and even break down the third wall at times just for fun.
8. Watch your pronouns and be consistent
Whichever style you choose to start out, stick with it. Be consistent or it may take away from the story if you jump in and out of multiple points of view. (I would say multiple points of view is possible, but only for the right kind of story.)
9. You can use second and first person in dialogue
Don’t forget to use your character’s dialogue to its full advantages. “I’m tired,” “I’m hungry,” “can we slow down?” “Is it hot or is it just me?” “You’re a liar!” “You melt my heart and soul.”
Just because you can’t say “you” or “I” doesn’t mean your character can’t. Just because your character doesn’t know how someone is feeling, doesn’t mean that character can’t say it out loud at the appropriate times to give your reader an inside look at another character’s personality.
10. Have a strategy for when you switch viewpoints
In the movie “Wonder,” they do an awesome job of switching viewpoints strategically and at pivotal moments.
This does a lot for the audience. We are surprised to get to go into the life of another character and get to know them intimately just like we did the main character.
11. Follow the character with the most weight
If you have a dynamic cast of characters, how do you choose which one to follow?
Margaret Atwood would say, “When choosing which character will serve as your main point of view for any chapter or scene, hone in on the person who has the most to lose or learn.”
This might change depending on what part of the plot you are headed into, but if it just follows one or two characters the entire time choose the one that has the most to lose.
Interested in starting a blog of your own? Check out Bluehost.
After checking out Bluehost, see how we made a profit FAST with our blog and how you can too: Our #1 Easy way that we made a profit with our blog on year 1, not year 5.
Need a Cheaper Plan? Try DreamHost.
Already own a blog? Monetize with Ezoic. Make 5X more on ads with Ezoic! See for yourself. – These ads use machine learning. Set it and leave it.
Try Grammarly, The Free tool that should be in every writer’s toolbelt.
Try it for free now.
Hope this helps!
Happy Writing!
Another Post you Might like:
Mythical Creatures | 7 Tips on How to Write Mythical Creatures
Other Popular Posts you might enjoy:
5 Tricks How to Hide Your Villain Right Before Their Eyes
10 Tips How to Write Villains that Play Mind Games with Their Victims
4 Tips How to Write your Character Hitting Rock Bottom
10 Toxic Bad Habits That’ll Crush Your Fictional Character’s Relationships
How to Write From Your Villain’s Mind.
How To Write 4 Scenes That Reveal Who Your Character Is Seamlessly
Psychopath: How to Write The Perfect Psychopath
8 Tips How to Write the Perfect Sociopath
Fictional Characters: 28+ Bad Habits to Introduce to Your Fictional Characters
List of 10 Weapons for Fictional Characters
List of 10 Bad Habits Fictional Characters Need Help Breaking
Why Start a Blog
How to Start a Blog in 11 Simple Easy Steps in 2020
For Blogging AND More
How to Write a Book: 32 Tips | Your MASSIVE Guide How to Write a Book
What is Theme?
The Hero’s Journey
Define Self-Esteem for Writing Characters: 10 Ideas
Covert Narcissist and Why You Should Write One
Inspiring Quotes Posts:
Inspiring Quotes | 101+ Inspirational Quotes to Motivate You Today
190+ Inspirational Quotes for Women
303+ Funny Inspirational Quotes
115+ Inspirational Quotes in Short
99+ Good Night with Quotes
103+ Quotes About What is Love
Enjoying Everything You Need to Know for Writing in Third Person? Take a moment and consider sharing this social-friendly image to say thanks and feel free to comment with your thoughts below! 🙂

Make sure your posts are readable. Use this readability score check
Want to check out a writer’s community to test your writing and get feedback?
Want to know more about us?
Check out these FREE trial resources from Amazon for when you work from home (or are stuck at home 🙂 ) As an Amazon associate, if you do sign up or buy anything using Amazon links from our site we make a commission at no extra cost to you.
Free Prime Membership Trial:
Try Amazon Prime 30-Day Free Trial
Try Prime Discounted (Free Trial)
Make your Free Amazon Wedding Registry:
Create an Amazon Wedding Registry
Get Free Video Channels Trial with Prime:
Join Prime Video Channels Free Trial
Try a Free Amazon Family Trial:
Join Amazon Family (30-day Free Trial)
Get Unlimited Music for Free (30-day free trial):
Join Amazon Prime Music – The Only Music Streaming Service with Free 2-day Shipping – 30-day Free Trial
Free movies and TV shows trial:
Join Amazon Prime – Watch Thousands of Movies & TV Shows Anytime – Start Free Trial Now
Free Prime for students trial:
Prime Student 6-month Trial
Free Baby Registry:
Shop Amazon – Create an Amazon Baby Registry
Free trial of Twitch Prime:
Try Twitch Prime
And for when you REALLY work at home:
Create Amazon Business Account
It is the Amazon you love, for work. Make workplace procurement easier with convenient delivery options, simplified purchasing workflows, multiple payment options, and a competitive marketplace with business-only pricing and quantity discounts. Anyone who makes purchases for work (eg. procurement specialists, office administration, IT departments, etc.) can create a FREE account for their business. Customer must be from a verified business in order to successfully create their Amazon Business account.

We hope you enjoyed: Everything You Need to Know for Writing in Third Person!

Can You Become a Successful Self Publisher Today Without a Website? I’ve seen this question before and thought it could Read more

5 Tips How to Make Editing More Enjoyable Editing can be a very dull process. At times, it can seem Read more

Can I Make My Story Setting in a Place I Have Not Been? You might be feeling trepidation about where Read more

How to Write for Yourself | Is it Odd to Just Write for Yourself? Some people are out there writing Read more
Published by Jeremy
View all posts by Jeremy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Enjoy this blog? Please spread the word :)
- More Networks

Point of View in Academic Writing
Point of view is the perspective from which an essay is written. The following chart lists both the personal pronouns and their possessive forms used with these points of view:
| Singular | Plural | |
| I, me (my, mine) | we, us (our, ours) | |
| you (your, yours) | you (your, yours) | |
| they, them (their, theirs) she, her (her, hers) he, him (his) it (its) one (one’s) | they, them (their, theirs) |
When choosing appropriate point of view for academic or formal writing, consider the type and purpose of the assignment.
| When using any of the three points of view, maintaining consistency is vital. Switching between points of view can be confusing for the reader. Choose a suitable perspective and then stay with it. Unclear: The accident happened right in front of so could see who was at fault. |
First Person
First-person point of view is used to write stories/narratives or examples about personal experiences from your own life. Note the following paragraph:
Several people have made a lasting impression on me . I remember one person in particular who was significant to me . Dr. Smith, my high school English teacher, helped my family and me through a difficult time during my junior year. We appreciated her care, kindness, and financial help after the loss of our home in a devastating fire.
Note : Academic writing often requires us to avoid first-person point of view in favor of third-person point of view, which can be more objective and convincing. Often, students will say, “ I think the author is very convincing.” Taking out I makes a stronger statement or claim: “The author is very convincing.”
Second Person
Second-person point of view, which directly addresses the reader, works well for giving advice or explaining how to do something. A process analysis paper would be a good choice for using the second-person point of view, as shown in this paragraph:
In order to prepare microwave popcorn, you will need a microwave and a box of microwave popcorn which you’ve purchased at a grocery store. First of all, you need to remove the popcorn package from the box and take off the plastic wrap. Next, open your microwave and place the package in the center with the proper side up. Then set your microwave for the suggested number of minutes as stated on the box. Finally, when the popcorn is popped, you’re ready for a great treat.
Note : Academic writing generally avoids second-person point of view in favor of third-person point of view. Second person can be too casual for formal writing, and it can also alienate the reader if the reader does not identify with the idea.
Replacing You
In academic writing, sometimes "you" needs to be replaced with nouns or proper nouns to create more formality or to clarify the idea. Here are some examples:
| Quality of education decreases when allow overcrowded classrooms. (Are you, the reader, allowing the conditions?) | Quality of education decreases when allow overcrowded classrooms. (Identifies who is doing what.) |
| On Saturday afternoons, usually have to stand in long lines to buy groceries. | Saturday afternoon usually have to stand in long lines to buy groceries. (Identifies who is doing what.) |
| In many states, have prisons with few rehabilitation programs. (Do you, the reader, have prisons?) | In many states, have few rehabilitation programs. (Identifies the actual subject of the sentence.) |
Third Person
Third-person point of view identifies people by proper noun (a given name such as Shema Ahemed) or noun (such as teachers, students, players, or doctors ) and uses the pronouns they, she, and he . Third person also includes the use of one, everyone, and anyone. Most formal, academic writing uses the third person. Note the use of various third-person nouns and pronouns in the following:
The bosses at the company have decided that employees need a day of in-house training. Times have been scheduled for everyone . Several senior employees will be required to make five-minute presentations. One is not eager to speak in front of others since he’s very shy. Another one , however, is anxious to relate their expertise. The variation in routine should provide an interesting day for all people concerned.
Third Person Pronouns: Gender-Fair Use of Language and Singular “They”
In the past, if you wanted to refer to one unnamed person, you used the masculine pronoun: If a person is strong, he will stand up for himself . Today, you should avoid the automatic use of the masculine pronoun because it is considered sexist language.
Also avoid perpetuating gender stereotypes by assigning a particular gendered pronoun: A doctor should listen to his patients. A nurse should listen to her patients . These examples make assumptions that doctors are men and nurses are women, which is a sexist stereotype.
Instead, use the pronouns they or them to refer to a person whose gender is undisclosed or irrelevant to the context of the usage: If a person is strong, they will stand up for themselves when they believe in something.
Types of Point of View: The Ultimate Guide to First Person and Third Person POV
by Joe Bunting | 75 comments
In my experience as an editor, point of view problems are among the top mistakes I see new writers make, and they instantly erode credibility and reader trust. Point of view isn't easy though, since there are so many to choose from: first person point of view, third person limited, third person omniscient, and second person.
What do those even mean? And how do you choose the right one for your story?
All stories are written from a point of view. However, when point of view goes wrong—and believe me, it goes wrong often—you threaten whatever trust you have with your reader. You also fracture their suspension of disbelief.
However, point of view is simple to master if you use common sense.
This post will define point of view, go over each of the major POVs, explain a few of the POV rules, and then point out the major pitfalls writers make when dealing with that point of view.
Table of Contents
Point of View Definition The 4 Types of Point of View The #1 POV Mistake First Person Point of View Second Person Point of View Third Person Limited Point of View Third Person Omniscient Point of View FAQ: Can you change POV in a Series? Practice Exercise
Point of View Definition
The point of view, or POV, in a story is the narrator's position in the description of events, and comes from the Latin word, punctum visus , which literally means point sight. The point of view is where a writer points the sight of the reader.
Note that point of view also has a second definition.
In a discussion, an argument, or nonfiction writing, a point of view is an opinion about a subject. This is not the type of point of view we're going to focus on in this article (although it is helpful for nonfiction writers, and for more information, I recommend checking out Wikipedia's neutral point of view policy ).
I especially like the German word for POV, which is Gesichtspunkt , translated “face point,” or where your face is pointed. Isn't that a good visual for what's involved in point of view? It's the limited perspective of what you show your reader.
Note too that point of view is sometimes called narrative mode or narrative perspective.
Why Point of View Is So Important
Why does point of view matter so much?
For a fiction writer, point of view filters everything in your story. Everything in your story must come from a point of view.
Which means if you get it wrong, your entire story is damaged.
For example, I've personally read and judged thousands of stories for literary contests, and I've found point of view mistakes in about twenty percent of them. Many of these stories would have placed much higher if only the writers hadn't made the mistakes we're going to talk about soon.
The worst part is these mistakes are easily avoidable if you're aware of them. But before we get into the common point of view mistakes, let's go over each of the four types of narrative perspective.
The Four Types of Point of View
Here are the four primary types of narration in fiction:
- First person point of view. First person perspective is when “I” am telling the story. The character is in the story, relating his or her experiences directly.
- Second person point of view. The story is told to “you.” This POV is not common in fiction, but it's still good to know (it is common in nonfiction).
- Third person point of view, limited. The story is about “he” or “she.” This is the most common point of view in commercial fiction. The narrator is outside of the story and relating the experiences of a character.
- Third person point of view, omniscient. The story is still about “he” or “she,” but the narrator has full access to the thoughts and experiences of all characters in the story. This is a much broader perspective.
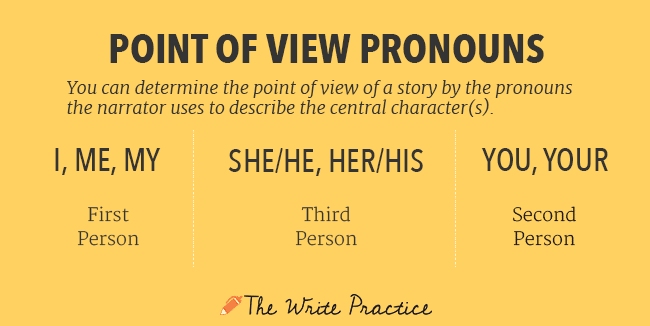
I know you've seen and probably even used most of these point of views.
While these are the only types of POV, there are additional narrative techniques you can use to tell an interesting story. To learn how to use devices like epistolary and framing stories, check out our full narrative devices guide here .
Let's discuss each of the four types, using examples to see how they affect your story. We'll also go over the rules for each type, but first let me explain the big mistake you don't want to make with point of view.
The #1 POV Mistake
Do not begin your story with a first person narrator and then switch to a third person narrator. Do not start with third person limited and then abruptly give your narrator full omniscience. This is the most common type of error I see writers make with POV.
The guideline I learned in my first creative writing class in college is a good one:
Establish the point of view within the first two paragraphs of your story.
And above all, don't change your point of view . If you do, it creates a jarring experience for the reader and you'll threaten your reader's trust. You could even fracture the architecture of your story.
That being said, as long as you're consistent, you can sometimes get away with using multiple POV types. This isn't easy and isn't recommended, but for example, one of my favorite stories, a 7,000 page web serial called Worm , uses two point of views—first person with interludes of third-person limited—very effectively. (By the way, if you're looking for a novel to read over the next two to six months, I highly recommend it—here's the link to read for free online .) The first time the author switched point of views, he nearly lost my trust. However, he kept this dual-POV consistent over 7,000 pages and made it work.
Whatever point of view choices you make, be consistent. Your readers will thank you!
Now, let's go into detail on each of the four narrative perspective types, their best practices, and mistakes to avoid.
First Person Point of View
In first person point of view, the narrator is in the story and telling the events he or she is personally experiencing.
The simplest way to understand first person is that the narrative will use first-person pronouns like I, me, and my.
Here's a first person point of view example from Herman Melville's Moby Dick :
Call me Ishmael. Some years ago—never mind how long precisely—having little or no money in my purse, and nothing particular to interest me on shore, I thought I would sail about a little and see the watery part of the world
First person narrative perspective is one of the most common POVs in fiction. If you haven't read a book in first person point of view, you haven't been reading.
What makes this point of view interesting, and challenging, is that all of the events in the story are filtered through the narrator and explained in his or her own unique narrative voice.
This means first person narrative is both biased and incomplete, but it can also deliver a level of intimacy other POVs can't.
Other first person point of view examples can be found in these popular novels :
- The Sun Also Rises by Ernest Hemingway
- Twilight by Stephenie Meyer
- Ready Player One by Ernest Cline
- The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
- The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brönte
First Person Narrative is Unique to Writing
There's no such thing as first person in film or theater—although voiceovers and mockumentary interviews like the ones in The Office and Modern Family provide a level of first person narrative in third person perspective film and television.
In fact, the very first novels were written in first person, modeled after popular journals and autobiographies which were first-person stories of nonfiction..
First Person Point of View is Limited
First person narrators are narrated from a single character's perspective at a time. They cannot be everywhere at once and thus cannot get all sides of the story.
They are telling their story, not necessarily the story.
First Person Point of View is Biased
In first person novels, the reader almost always sympathizes with a first person narrator, even if the narrator is an anti-hero with major flaws.
Of course, this is why we love first person narrative, because it's imbued with the character's personality, their unique perspective on the world.
The most extreme use of this bias is called an unreliable narrator. Unreliable narration is a technique used by novelists to surprise the reader by capitalize on the limitations of first person narration to make the narrator's version of events extremely prejudicial to their side and/or highly separated from reality.
You'll notice this form of narration being used when you, as the reader or audience, discover that you can't trust the narrator.
For example, Gillian Flynn's Gone Girl pits two unreliable narrators against one another. Each relates their conflicting version of events, one through typical narration and the other through journal entries. Another example is Fight Club , in which *SPOILER* the narrator has a split personality and imagines another character who drives the plot.
Other Interesting Uses of First Person Narrative:
- The classic novel Heart of Darkness is actually a first person narrative within a first person narrative. The narrator recounts verbatim the story Charles Marlow tells about his trip up the Congo river while they sit at port in England.
- William Faulkner's Absalom, Absalom is told from the first person point of view of Quentin Compson; however, most of the story is a third person account of Thomas Sutpen, his grandfather, as told to Quentin by Rosa Coldfield. Yes, it's just as complicated as it sounds!
- Salman Rushdie's award-winning Midnight's Children is told in first person, but spends most of the first several hundred pages giving a precise third person account of the narrator's ancestors. It's still first person, just a first person narrator telling a story about someone else.
Two Big Mistakes Writers Make with First Person Point of View
When writing in first person, there are two major mistakes writers make :
1. The narrator isn't likable. Your protagonist doesn't have to be a cliché hero. She doesn't even need to be good. However, she must be interesting .
The audience will not stick around for 300 pages listening to a character they don't enjoy. This is one reason why anti-heroes make great first person narrators.
They may not be morally perfect, but they're almost always interesting. (Remember Holden Caulfield in The Catcher in the Rye ?)
2. The narrator tells but doesn't show. The danger with first person is that you could spend too much time in your character's head, explaining what he's thinking and how he feels about the situation.
You're allowed to mention the character's mood, but don't forget that your reader's trust and attention relies on what your character does , not what he thinks about doing.
Second Person Point of View
While not used often in fiction—it is used regularly in nonfiction, song lyrics, and even video games—second person POV is still helpful to understand.
In this point of view, the narrator relates the experiences using second person pronouns like you and your. Thus, you become the protagonist, you carry the plot, and your fate determines the story.
We've written elsewhere about why you should try writing in second person , but in short we like second person because it:
- Pulls the reader into the action of the story
- Makes the story personal
- Surprises the reader
- Stretches your skills as a writer
Here's an example from the breakout bestseller Bright Lights, Big City by Jay Mclnerney (probably the most popular example that uses second person point of view):
You have friends who actually care about you and speak the language of the inner self. You have avoided them of late. Your soul is as disheveled as your apartment, and until you can clean it up a little you don't want to invite anyone inside.
Second person narration isn't used frequently, however there are some notable examples of it.
Some other novels that use second person point of view are:
- Remember the Choose Your Own Adventure series? If you've ever read one of these novels where you get to decide the fate of the character (I always killed my character, unfortunately), you've read second person narrative.
- The Fifth Season by N.K. Jemison
- The opening of The Night Circus by Erin Morgenstern
There are also many experimental novels and short stories that use second person, and writers such as William Faulkner, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Albert Camus played with the style.
Breaking the fourth wall:
In the plays of William Shakespeare, a character will sometimes turn toward the audience and speak directly to them. In A Midsummer Night's Dream , Puck says:
If we shadows have offended, think but this, and all is mended, that you have but slumbered here while these visions did appear.
This narrative device of speaking directly to the audience or the reader is called breaking the fourth wall (the other three walls being the setting of the story).
To think of it another way, it's a way the writer can briefly use second person in a first or third person narrative.
It's a lot of fun! You should try it.
Third Person Point of View
In third person narration, the narrator is outside of the story and relating the experiences of a character.
The central character is not the narrator. In fact, the narrator is not present in the story at all.
The simplest way to understand third person narration is that it uses third-person pronouns, like he/she, his/hers, they/theirs.
There are two types of this point of view:
Third Person Omniscient
The all-knowing narrator has full access to all the thoughts and experiences of all the characters in the story.
Examples of Third Person Omniscient:
While much less common today, third person omniscient narration was once the predominant type, used by most classic authors. Here are some of the novels using omniscient perspective today.
- War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy
- Middlemarch by George Eliot
- Where the Crawdad's Sing by Delia Owens
- The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
- Still Life by Louise Penny (and all the Inspector Gamache series, which is amazing, by the way)
- Gossip Girl by Cecily von Ziegesar
- Strange the Dreamer by Laini Taylor
- Little Women by Louisa May Alcott
- Crazy Rich Asians by Kevin Kwan (one of my favorites!)
- A Wizard of Earthsea by Ursula Le Guin
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
- More third person omniscient examples can be found here
Third Person Limited
The narrator has only some, if any, access to the thoughts and experiences of the characters in the story, often just to one character .
Examples of Third Person Limited
Here's an example of a third person limited narrator from Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone by J.K. Rowling:
A breeze ruffled the neat hedges of Privet Drive, which lay silent and tidy under the inky sky, the very last place you would expect astonishing things to happen. Harry Potter rolled over inside his blankets without waking up. One small hand closed on the letter beside him and he slept on, not knowing he was special, not knowing he was famous…. He couldn't know that at this very moment, people meeting in secret all over the country were holding up their glasses and saying in hushed voices: “To Harry Potter—the boy who lived!”
Some other examples of third person limited narration include:
- Game of Thrones s eries by George R.R. Martin (this has an ensemble cast, but Martin stays in one character's point of view at a time, making it a clear example of limited POV with multiple viewpoint characters, which we'll talk about in just a moment)
- For Whom the Bell Tolls by Ernest Hemingway
- The Way of Kings by Brandon Sanderson
- The Da Vinci Code by Dan Brown
- The Girl with the Dragon Tattoo by Stieg Larsson
- Ulysses by James Joyce
- Love in the Time of Cholera by Gabriel Garcia Marquez
- 1984 by George Orwell
- Orphan Train by Christina Baker Kline
- Fates and Furies by Lauren Groff
Should You Use Multiple Viewpoint Characters vs. a Single Perspective?
One feature of third person limited and first person narrative is that you have the option of having multiple viewpoint characters.
A viewpoint character is simply the character whose thoughts the reader has access to. This character become the focus of the perspective during the section of story or the story as a whole.
While it increases the difficulty, you can have multiple viewpoint characters for each narrative. For example, Game of Thrones has more than a dozen viewpoint characters throughout the series. Fifth Season has three viewpoint characters. Most romance novels have at least two viewpoint characters.
The rule is to only focus on one viewpoint character at a time (or else it changes to third person omniscient).
Usually authors with multiple viewpoint characters will change viewpoints every chapter. Some will change after section breaks. However, make sure there is some kind of break before changing so as to prepare the reader for the shift.
Should You Use Third Person Omniscient or Third Person Limited
The distinction between third persons limited and omniscient is messy and somewhat artificial.
Full omniscience in novels is rare—it's almost always limited in some way—if only because the human mind isn't comfortable handling all the thoughts and emotions of multiple people at once.
The most important consideration in third person point of view is this:
How omniscient are you going to be? How deep are you going to go into your character's mind? Will you read their thoughts frequently and deeply at any chance? Or will you rarely, if ever, delve into their emotions?
To see this question in action, imagine a couple having an argument.
Tina wants Fred to go to the store to pickup the cilantro she forgot she needed for the meal she's cooking. Fred is frustrated that she didn't ask him to pick up the cilantro on the way home from the office, before he had changed into his “homey” clothes (AKA boxer shorts).
If the narrator is fully omniscient, do you parse both Fred and Tina's emotions during each back and forth?
“Do you want to eat ? If you do, then you need to get cilantro instead of acting like a lazy pig,” Tina said, thinking, I can't believe I married this jerk. At least back then he had a six pack, not this hairy potbelly . “Figure it out, Tina. I'm sick of rushing to the store every time you forget something,” said Fred. He felt the anger pulsing through his large belly.
Going back and forth between multiple characters' emotions like this can give a reader whiplash, especially if this pattern continued over several pages and with more than two characters. This is an example of an omniscient narrator who perhaps is a little too comfortable explaining the characters' inner workings.
“ Show, don't tell ,” we're told. Sharing all the emotions of all your characters can become distraction. It can even destroy any tension you've built.
Drama requires mystery. If the reader knows each character's emotions all the time, there will be no space for drama.
How do You Handle Third Person Omniscient Well?
The way many editors and many famous authors handle this is to show the thoughts and emotions of only one character per scene (or per chapter).
George R.R. Martin, for example, uses “ point of view characters ,” characters whom he always has full access to understanding. He will write a full chapter from their perspective before switching to the next point of view character.
For the rest of the cast, he stays out of their heads.
This is an effective guideline, if not a strict rule, and it's one I would suggest to any first-time author experimenting with third person narrative. Overall, though, the principle to show, don't tell should be your guide.
The Biggest Third Person Omniscient Point of View Mistake
The biggest mistake I see writers make constantly in third person is head hopping .
When you switch point of view characters too quickly, or dive into the heads of too many characters at once, you could be in danger of what editors call “head hopping.”
When the narrator switches from one character’s thoughts to another’s too quickly, it can jar the reader and break the intimacy with the scene’s main character.
We've written about how you can get away with head hopping elsewhere , but it's a good idea to try to avoid going into more than one character's thoughts per scene or per chapter.
Can You Change POV Between Books In a Series?
What if you're writing a novel series? Can you change point of view or even POV characters between books?
The answer is yes, you can, but whether you should or not is the big question.
In general, it's best to keep your POV consistent within the same series. However, there are many examples of series that have altered perspectives or POV characters between series, either because the character in the previous books has died, for other plot reasons, or simply because of author choice.
For more on this, watch this coaching video where we get into how and why to change POV characters between books in a series:

Which Point of View Will You Use?
Here's a helpful point of view infographic to help you decide which POV to use in your writing:
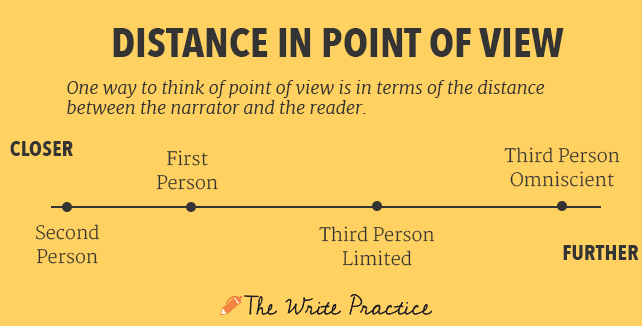
Note that these distances should be thought of as ranges, not precise calculations. A third person narrator could conceivably draw closer to the reader than a first person narrator.
Most importantly, there is no best point of view. All of these points of view are effective in various types of stories.
If you're just getting started, I would encourage you to use either first person or third person limited point of view because they're easy to understand.
However, that shouldn't stop you from experimenting. After all, you'll only get comfortable with other points of view by trying them!
Whatever you choose, be consistent. Avoid the mistakes I mentioned under each point of view.
And above all, have fun!
How about you? Which of the four points of view have you used in your writing? Why did you use it, and what did you like about it? Share in the comments .
Using a point of view you've never used before, write a brief story about a teenager who has just discovered he or she has superpowers.
Make sure to avoid the POV mistakes listed in the article above.
Write for fifteen minutes . When your time is up, post your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop (if you’re not a member yet, you can join here ). And if you post, please be sure to give feedback to your fellow writers.
We can gain just as much value giving feedback as we can writing our own books!
Happy writing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

75 Comments
My book is a memoir so first person is what I chose.
That was my choice for memoir, but am exploring other avenues for better character development.
I hate to be such a nag but isn’t the plural “points of view” and not “point of views”? As in brothers in law and not brother in laws
Joe, excellent post on POV. Probably the best I’ve read. Thanks!
I go for third person deep. In the PoV character’s head, using her unique voice, no author intrusion, no filter words. Am I doing it right? Far from it, but I’ve attended deep writing classes, an it’s easier to pinpoint slips.
Greetings from Greece!
Thanks for sharing this tit bit. I will be looking out for a deep writing class!
When deciding your POV, I strongly believe genre and tense should be considered as well.
Here is my first time ever uploading a “practice.” I chose to try second person, please be kind!
I couldn’t believe it when you called me, waking me from an intense fantasy dream, to tell me that you had been somehow magically transformed overnight into some type of superhero. You cannot blame me if my reaction appeared to be less than awe and more of disbelief and worry for your current state of mind. You will not want me to ask this, but have you started doing drugs? Remember, Freshman Health class, one of the signs to look for was if your friend suddenly changes or acts crazy. Well dude, you are acting more than just a little bit crazy.
Can you really fly? I have been waiting for 15 minutes for you to appear at my bedroom window, and so far nothing. I can envision you, at this very moment, running down the alley and between the houses. You will get to my back gate, jump over, and scurry behind the bushes; all bent over and believing that I can’t see you. When you are sure of your timing and that I have no idea at your mastery, you will jump out and try to convince me that you flew to your location. Please try to remember that I have known you since Kindergarten. Very little about you surprises me anymore, yet you are entertaining.
Although, you did sound different on the phone this morning, you voice had a quality I had never heard before. I would call it confidence. You weren’t trying to convince me that you had a special new talent. You were telling me, informing me.
You need new boots, I know this because I noticed the hole in the bottom of the left one as you slowly descended from the top of my window. Your smile was radiant, your arms crossed confidently across your puffed out chest. You are transformed.
Barbara! Thank you so much for your creativity. Keep sharing it with the world! The parts about the boots… wow!
Keep making lemonade from lemons, Barb. Be in touch.
You don’t look peaceful, but you look at peace. Morphine will do that to you. Your flaky, red eyes flutter in your sleep—do you dream, there? “The eyes are the windows to the soul,” so they say; with the curtains drawn, does your gaze turn inward? Do you dream of me amidst the pain, or are you cradled in the gentle embrace of the abyss?
This was your fault, you know; waving that gun in my face, pushing me around; what did you expect?
Certainly not this; no one could have expected this. Dazzling cords of fire springing from the fingertips of your would-be, should-be victim—perhaps it would’ve been wiser to hand over the money—but then, who next? Woudl you have let me go in the first place?
It wasn’t for anything venial, was it? Not for clothes or jewelry—not from what I can tell; you don’t seem the type. But it’s hard to tell. There’s not much left of your clothes, you know.
There’s not much left of you.
They’ll pour maggots over your chest and into your eyes, and flake off the blackness with gentle sponges, and alcohol over everything. That will hurt.
Your hair was so pretty. The doctor says most of it will grow back.
The cops are taking your side, you know. Figures. At least guns don’t burn. I wouldn’t be sticking around if they hadn’t cuffed me to the bed, and set it beside yours—someone in blue has a sick sense of irony.
There are birds fluttering by the windowpane, and whispers of white amidst pastels of blue. Your burns will heal. Mine have only just begun.
Yeah, having superpowers would actually be terrifying. Especially fire. Fire is bad.
I’ve used second-person before, but very rarely, so I went with it, since I’ve used all the points of view you mentioned.
Changing point of view is not only acceptable, it’s quite common. You just italicize it. I don’t know how to do that in a comment, but the general form would be something akin to: He felt around for the plot device. *Damn; I can’t find this thing. Woe is me, I am woe, woe unto me, woe betides me, etc.* He found it. *Huzzah!*
Further, your example for third-person POV includes a sputter of second-person: “the very last place *you* would expect astonishing things to happen.” This is the rhetorical “you,” not an actual pronoun—that is, “you” isn’t referring to anyone—but it still counts.
I think the argument shouldn’t be “never switch POV,” but, rather, “use the turn signal;” that is to say, give the reader an indication that the POV is changing, and why. Italics for brief periods, chapters for changing the individual narrator (you can have lots in one book), etc. Much like turning in traffic, problems generally arise not from the turn, but from the surprise. “Head hopping” is easy to avoid with, for instance, section separators—a vertical space, or a line of three little stars if the space breaks across a page, so that the reader knows a shift is happening. After familiarizing the reader with the mechanism, you can abuse it as much as you want.
Hemingway’s way works too, although I was never a big fan of Hemingway.
P.S. Give away an antique typewriter; brilliant—plenty of nostalgia; tangled ribbons, torn sheets, jammed keys; I can see why you want to inflict it on somebody else!
Wow, that was amazing descriptions. I loved your opening and closing lines as well. You did a great job of setting the dark mood of the story. Very well done.
Great post! It is quite thorough and engaging, and you offered plenty of terrific examples and practical tips.
I tend to write my stories more in the third person POV, I tend to focus on one main character but sometimes try to give some insight on another character’s perspective. The only reason I shy away from first person is because it can be emotionally exhausting to write. The funny thing is my most dramatic story was written in first person (though I did switch between two people) but I felt it would come off stonger in first person rather than third.
I’m not sure I qualify for this practice, because I’ve written in pretty much every POV: My novel is 3rd person deep, my short stories are first person, my articles are second, and my songs cover all of the above plus the others. 🙂 In my book I have several POVs, but I make sure to change the scene completely before changing the person. (Like Jerry Jenkins’/Tim Lahaye’s Left Behind.) I’m not breaking any rules like that, am I? This is a great and informative article that I’ll definitely reference in the future. Thanks for sharing your knowledge!
“Whatsoever ye do, do unto the Glory of God” Reagan
Nice post! Very helpful of keeping them strait. I tend to lean toward first person or third person limited, so I decided to try out second person for the prompt. I also used a dialogue prompt, which is the first line of the story. Here goes nothing!
“The last time I said yes to you, a lot of people died.” You say it low, under your breath, perhaps because you don’t really want him to hear you or perhaps because you don’t want to hear yourself, don’t want to remember that it happened.
“You know,” He reaches out to you, and you pull away, not wanting to touch his hands, hands that could have prevented the deaths of so many, but that have always been so gentle with you. He turns his face to the ground and, you realize, he is just as pained by the memory as you. “You know that I couldn’t have done it.”
“No.” The word comes out all wrong, because of your still upper lip, “You couldn’t have. I knew that then and I know that now.” You lock eyes with him, “Don’t you understand that’s what I’m saying? Don’t you understand that the answer is no?”
“But I can’t…” He grimaces, as though someone has twisted a knife in his gut, “I can’t just let you kill yourself.”
And now it’s your turn to grimace, to feel the pain twisting your stomach into knots. You don’t really know why you do it though. Are you afraid to die? No. That’s not it. You’re afraid for him. For the pain your death will cause him.
“You have to be strong.” You say, “For me.” This time it’s you that reaches out, to lay a hand gently on his shoulder, “You know if I don’t do this, a lot of people will die. Because I know, if I go berserk again, you won’t be able to pull the trigger. And it wouldn’t be fair to ask you to do that anyway. So the answer is no, I won’t let you be my safety net anymore.” His only response is a nod. You slide the hand gently off of his shoulder. That will be your only goodbye. It will be easier that way.
The cup that holds the poison looks normal. Just a regular coffee cup, containing your favorite blend of Colombian roast, and, of course, the substance that will kill you, quickly and painlessly, which is more then you deserve. You are not afraid. You are ready. You pick the cup up off the table and bring it close to your lips but then hesitate, because you see that shining in his eyes, the shining that means he’ll start crying. There is that twisting feeling in your stomach again. Seeing him in pain has always hurt the worst. But you can’t risk it anymore. You can’t let yourself live at the cost of more deaths.
Before you can hesitate, you take a gulp, the coffee burning your throat as it goes down. The room wobbles and you fall, but he catches you, like you knew he would, so that your head doesn’t crack open on the concrete floor.
You are paralyzed, but still conscious, and you know you only have a few seconds before the world grows dark.
He sinks to his knees, cradling you in his arms, like a child. He is no longer holding back his tears. Perhaps because he already thinks you dead.
“I wish,” He says, through sobs and tears and unbecoming bubbles of snot, “I wish you would have said yes.”
He puts his forehead to yours and you feel warm drops of moisture fall on your cheeks. In that moment you, too, wish you had said yes. That things could have been different. That you could have been alive and happy.
But you do not doubt your decision, not in the last seconds that you have breath. Because the last time you said yes to him, a lot of people died and this time, the death tole would be a single, solitary, one.
That was amazing and beautiful and very very emotional. You’ve used second person very effectively! I love it. Did this just come from the top of your head or is there a longer story behind it?
Thanks! It was a sort of top of my head thing. I used this writing prompt and also a dialogue prompt. Also, I’ve been thinking of werwolfs a lot lately for some odd reason (which is what the main character is). The rest of it kinda flowed from there. I’m glad you liked it!
Wonderful story
Not knowing much about POV, I believe I’ve been hedge hopping between them, but appear to prefer Third Person Omniscient, but will have to first discover what that last big word means? Then a re-write may well be called for!
The post is excellent, extending a warm hug of inspiration to the budding writers. I prefer ‘third person omniscient’ POV, with no room for any boredom in my narration.
Peter had his normal “I’m paying attention” look plastered on his face, but his mind was chasing super villains, decimating evil minions with mighty punches that laid ten low at one swipe.
One ear caught, “Good morning, we have a guest speaker this morning, the Rev. Charles Birch, from the 2nd Baptist Church. Rev. Birch will present the creationist side to what we have been studying in the physical sciences. Rev. Birch.”
“Blah … blah … blah,” Peter heard in his public ear but his private ear heard Dr. Daemon spewing his maleficent threats, “Capt. Magnificent, you have no hope of defeating my eco-destroying minions!” On and on it went, Birch preaching “let there be light … the dominion of man over all things … everything in it’s proper order … on the first day God created the second day … and on the third day blah blah blah,” and of course during all of this Dr. Daemon and Capt. Magnificent continued their mighty struggle on the farside of the moon, until Peters public ear heard, “of course the universe can only be 10,000 years old …”
What? What was that his public ear just heard? The Universe is a maximum of 10,000 years old? Peter was now attentive to what the pompous windbag in front of the class was saying.
A single hand raised itself amongst the sea of blank faces.
“Yes, young man?”
“Uh, Rev. Birch, how can the universe be 10,000 years old?”
“Easy uh huh,” Ms. Murphy whispered into the Reverends ear, “yes, Peter, we know the age of the universe from the generations that are recorded in the Bible.”
“But … I was at a dig in Colorado last summer and the rock strata around the fossils …”
“Humph, all conjecture. I believe God made the fossil and the rocks surrounding it ten thousand years ago.”
“All fossils are like that then?”
“Well of course. Given He made the fossils He made the surrounding rock. We only think that it took millions of years.”
Peter’s hand shot up again.
Rev. Birch tried to avoid him, but Peter was a persistent little son of… “Yes?”
“So God’s just a practical joker, creating false evidence to fool the sciences?”
The class was coming out it’s “guest speaker” lethargy, as Peter again had his hand up and spoke before acknowledged, “Does the Bible say what the speed of light is?”
“Well, now I think that has no bearing …”
Susan piped up, adding onto Peter’s question “How can Andromeda be millions of light-years away if the universe is only 10,000 years old?”
“Uh well … Andromeda?”
“No wonder He didn’t have time to save my baby sister if He wasted all that time making fossils look millions of years old,” came a loud, whispered, comment from the back of the room.
Ms. Murphy quickly ushered Rev. Birch from the classroom, and shook his hand in the hall, “Thank you so much for coming. We do appreciate all view points.”
“Who are those kids?” the Reverend asked.
“Oh, the Anderson District Scholars Program. Basically our high school geniuses in sciences and math. It’s required we allow all view points to be presented.”
Interesting. Uh, Gary, how could you have written the story in 15 minutes? Or did you dig up a fossil story you wrote millions of years ago…?
Does it matter?
It took a day and a half to percolate through my gray matter. I then took approximately 15 to 20 minutes to rough it out and get it into Draftin. Then another while, hours, lots of minutes, to get it to where I wanted to post it. Once posted, I’ve gone back and edited it, probably dozens of times, making changes as it has continued to peroclate.
I loved the flashing between reality and a story he is telling himself in his head. That’s me about 90% of the time. lol
I would also just like to add, that all creationists aren’t young earth creationists. There are a lot of different theories. Take the gap theory and theistic evolution for example. Then you have people who take it as a literal six days and others who don’t because of the bible verse that says “a day is like a thousand years and a thousand years is like a day”. Then, there are two different meanings to the word “day” if you look at the translation of the bible from Hebrew to English. So there is argument over which version of the word “day” is being used sense one can be taken literally and the other figuratively. There are literally of books written on these subjects, with Christians arguing amongst themselves over which is right. I have actually meet very few people who think the way the reverend in this story does, especially sense when you go to seminary they teach you how to not look like an idiot in these situations.
I think It’s important to remember when you’re writing Christians (or any group that often gets stereotyped) that they are not stereotypes. I’ve written atheists and it’s really easy just to make them injured people who are angry at God and dissatisfied with life, but that’s just not the reality. A lot of atheists know their stuff and have good reason for their beliefs. The same applies to Christians. If you still want to debunk the Christian in the end, I’m totally cool with it. I would just say, have the Christian have a better argument then “God put the fossils their like that”. Make it harder for your main character to debunk him, create more conflict, and make us cheer him on all the more when he wins.
Just thought that was worth mentioning. All in all, the piece is very well written.
Assumption: Pastors and or reverends have been to seminary. Not true. In the Southern Baptist Convention, at least when I was in the SBC, pastors were not assigned by the convention, nor was any kind of, pre or post graduate, pastoral education required. Pastors were called by the local church, without guidance from the convention, and could easily not even have finished high school. There are many churches that have no affiliation with any established denomination, and therefore call whomever they want as their pastor.
Oh, yes, you handled POV nicely. I’m just the kind of person that will comment on every part of the story. And I’m sorry if the comment was too much, or you didn’t find it helpful. I just tend to say what I think. But for the exercise you did a good job on the POV.
Oh the comment wasn’t too much. After 68 years my hide is pretty tough and criticism I tend to take in a constructive manner and/or with a grain of salt.
But you assumed something in your comment that, in my experience is simply not true. In my experience, the pastors that had graduated college, let alone ever attended seminary were zero. My denomination, at the time, was lucky to have pastors that finished high school.
68 years, wow that’s a lot of time and experience! You have the respect of a young Padawan.
You’re right. I was looking at it from a United Methodist view point (sense that’s the denomination I belong to). Our denomination is pretty strict with schooling and is very organized when it comes to chain of command. I discounted the fact that not all denominations and churches are like mine. My current pastor actually has a PhD and really knows what he’s talking about, so were lucky in that. I’ve also grown up in a home where ignorance isn’t tolerated. We learn about our religion (and everything else we can learn about) and are not victims of blind acceptance.
I’m sorry you had experiences with uneducated pastors. I hope they weren’t all as bad as the one in the story. If they were, then that stinks. And I do realize that there are, sadly, some pastors like the one from your story who don’t have very good arguments when it comes to the science of their faith. But I also hope that people know that all Christians aren’t, to put it frankly, stupid.
Again, assumptions. Christianity was never equated to stupidity, and above all else no attempt to equate uneducated to stupid was ever made. In all those 68 years I have seen incredibly educated people, read that doctorates, that were, above all else, stupid. I have also encountered uneducated people that could best be described as genius.
Birch was, at best, unprepared. His fault, Murphy’s fault, irrelevant, not what I was striving for. It was simply the vehicle used to convey POV switching from character to character. Birch could have been Islamic and quoting the Torah.
I wrote for 20 minutes before I realized it, so here’s what I got.
“Okay, calm down, calm down. You must get a hold of yourself” I murmured frantically to myself, I had to calm down before I blew another hole through the wall, or worse. I sat still on the hard floor, and I still couldn’t believe what had happened, it didn’t make sense at all, but there was evidence of it right before my eyes: a brick wall that now had a wide circle in its middle, still glowing hot from what I had done. Yet it was nothing compared to the silver glow that came from my hands, it felt strange, alien yet oddly comfortable, like I was wearing a glove while sparks coursed throug my arms.
I kept staring at my hands for a long time, trying to find some explanation for what had happened, it couldn’t have been me who did that, I wasn’t that special, I didn’t have some special blood, nor had I gone through any experiment, I didn’t even fit in any origin story of any Super. I was sure of that, I had even taken the tests at the Dome.
“This can’t be happening!” I screamed, letting loose all the emotions I had tried to hold back. “ARGGGHhhh!”
Then, it happened again, the room was bathed again in a silver hue as another silver beam left my hands and destroyed the wall a bit more, leaving behind only one third of what had been an sturdy wall once. That flash had confirmed my fears, this was the reality I had been the one to destroy the wall. I was angry, scared and happy at the same time, these emotions clashing one against the other as I witnessed the destruction I had wrecked in less than 10 minutes.
A grave sound pierced the old room I was in, it sounded like a lament, a sorrowful lament from a strange lonely monster. It only lasted a few seconds, and then, a piece of the roof fell about 5 meters from me. It was followed by another one, and another one bigger than the first two. Soon the whole roof was falling in, and fear once again took a hold of me. I was going to die, I knew I was going to die, buried beneath the rubis of the room.
“I, I don’t want to die” I screamed with all the force of my lungs while I tried to protect my head with my hands, I knew it wasn’t going to be enough, it wasn’t going to be enough if I wanted to live. I want to live. That thought was the last one I had before a surge of power coursed through my body, engulfing my vision in a white blanket before I passed out.
When I woke up, I felt groggy, moving my body was hard, and the air was packed with dust. But I didn’t hurt anywhere, not did I feel like I was buried under something. I slowly made my way to my knees, looking at myself for any sign of injuries, but there was none, in fact except for the dust my clothes were exactly the same as they had been before the fall in.
“This is impossible” I said out loud to no on, but how did this happen? I thought I was done for sure. It was only then that I looked around me and I was shocked for the fifth time that day.
There wasn’t any rubis near me, no for a meter around me. Was that possible? How?
Well done. There are a couple of times where the protagonist is thinking, not speaking. It would help to clarify that like using italics, or at least quoting.
Thanks for the advice- I usually use italics when it comes to thoughts, but I wasn’t sure if they were going to copy that way from writer. So I’ll try to use them next time.
I wrote one short story in the first person POV twenty five years ago. I never tried it again. Since I decided to face my fears, here I go again.
I had just opened my eyes and before I could see clearly, I was standing next to the bed jumping up and down. All of a sudden, i was standing next to the dresser drawer. did I run? I had so much energy. It seemed as if I had four cups of coffee and six energy pills. I looked across the room at the hamper. The hamper was empty and the clothes that were stuffed there were clean and folded. Last night the hamper was full of dirty clothes.. I head a soft voice that sounded like mine. “Esther, you now have super human power. The clothes were washed and folded last night. If you go to the kitchen, there is no longer a pile of dirty dishes. They have all be washed and put away. That’s all I have to say.” “What are you talking about? Who are you?” Suddenly, I was jumping up and down next to my dresser drawer.. I paused and looked into my mirror. I still looked the same. A long braid with a hair pin fastened to the left close to may ear. I did feel energized. At once I felt like I needed or wanted to run. I walked down the stairs toward the front door. The moment that i stepped out. I had dashed down the block, turned to the right and dashed down that block and Paused, standing in right in from of me was me. she looked exactly like me. She had a long braid that was pinned to the side like i did. She was wearing a light tan tee-shirt and black short shorts, blue gym shoes. Just like I am wearing. We both stood there, sweating, jumping up and down as though there were springs.under our shoes. ” Who are you?” ” I just you told you when we were in the house.” Then, she said “I’ll just tell you this much. Let’s race back to the house and up the stairs and stand next to the bed. Whoever get there first wins. “Win what,” “You’ll find out.” she dashed past me to the right. I spun back around so fast that I became dizzy. I dashed down the block and turned left. Before I knew it, I was in the kitchen. Mama was there. I was downstairs sitting at the table with her. “I am impressed. you have fixed breakfast and washed the dishes and I see you have been running.” Thanks mama, I said. Then in my mind and my ear I heard my own voice. There are two Esther. The one who procrastinate and don”t get things done and the one that get things done immediately without being told.. Then mama looked at me and smiled. She never smiles in the morning. but today, she did. She said, well today you cooked the breakfast and washed the dishes without waiting until you got home from school. I like this part of you, Esther. Then, I knew what had happened, KEN Well, there it is. Now, this means that I have used the first person again. I feel okay because, even if it’s terrible. I tried.
My go to POV is 3rd Person, limited.
Oops!! Just realized I completely blew the prompt.
Oh well … back to he drawing board (or computer).
This app helps me understand a lot about the 3d person
The first time it happened took me by surprise. It would anyone wouldn’t it? I was standing in line at the grocery store with my mom. I was tapping my foot to the beat of my own boredom, impatiently waiting for the guy ahead of us to move his cart; which if you ask me he didn’t even need. I added in some finger snaps. 1…2…and…3. The third snap brought with it an echo. When I looked around, I wasn’t in the grocery store anymore. I was in a cave.
I had waited for my eyes to adjust to the dark. The only light that was coming through was a small crack far ahead of me to my left side. I looked down at my feet for a path. Right in front of me the rock I was standing on dropped off into an abyss of black. Behind me stood the edge of the cave. I remember hyperventilating. I was so scared I couldn’t move. I started snapping my fingers again and said out loud, “think, think, think,” matching my snaps to the words in my head. On the third snap, I was back in the grocery store. Police were there talking with my mother. I had been gone a long time.
After that day I tried experimenting with my new formed ability. I started thinking of specific places that I wanted to visit; I wanted to see if I could control it. After a few failed attempts ending up in grungy basements, restaurant cooler storages, and an actor’s cottage, I got a hold of the pattern.
The success of my teleportation was contingent on my ability to breathe evenly. I needed to remain completely calm. When I realized that my ability was never going away, my excitement is what kept me from perfection. Failure after failure brought an increased frustration with myself.
It’s good. You haven’t overdone anything. You’ve shown what happened through your character really well. I particularly like the line “dropped off into an abyss of black.”
This was my attempt at using 2nd person. I rarely use it. Any advice would be appreciated. Thank you 🙂
“Now what can you tell me about God? Anybody? Yes, yes, um Alice?” “Alicia, Miss. God is often described with the three Os. He is omnipotent, all powerful, omnipresent, everywhere and omniscient, all knowing.” You suppress a groan. “Which textbook did she swallow to spew that out?” you whisper to your friend. She giggles quietly. “Shhhh,” she replies. You sigh and put your head on the table. You’ve been stuck in this stuffy classroom for half an hour and you really won’t last for another half. You can practically eat religion in this school.
“Hey you, you, sleepy child,” the teacher says. For a moment you’re confused but then your friend nudges you and you realise the woman is talking to you. ‘Can’t she learn our names?’ you think. “Yes, Miss?” you dare to risk saying. “What can you tell me about God?” she asks. ‘Oh for God’s sake,’ you think before realising the irony. “Um,” you reply. You could almost swear that time was slowing down. Everyone’s eyes turn towards you almost in slow motion before they stop as if frozen. You wish the ground would hurry up and swallow you. It takes you a moment to realise that no one is blinking. “Hello?” you say, hoping you don’t sound like an idiot. Nobody responds. ‘Okay, this is really creepy.’ You poke your friend but she doesn’t move. A bead of sweat trickles down your forehead that has nothing to do with the heat. What is going on? A cold feeling washes over you and you sit back in your seat feeling dizzy. You try to control your breathing but it is rapid and coming in gasps. You glance at the clock only to see that the second hand has stopped moving. Hands clammy, you glare at it willing it to move. Millimetre by millimetre it does. You sigh with relief when everybody’s movement resumes only to find yourself under the scrutiny of 30 pairs of eyes.
“Well?” asks the teacher. Suddenly desperate, you look at the clock and wonder if you can make time go faster.
Who’s point of view;
So there’s this guy, this one guy I never liked, he’s constantly stealing my ideas, getting credit for the success, or if the idea fails, that’s when he throws me under the bus. Oh it’s so aggravating when he takes the words right outta my mouth, when I try to participate in the discussion, he cuts me off, I swear he thinks he knows everything he’s talking about. Oh, yeah and he’s always making an ass out of me, no matter what it is, especially at every work party. This guy thinks he’s so slick, two steps ahead of everyone, but he’s not quick, I know every move he’s gonna make before he makes them. It’s also extremely embarrassing he always seems to wear what I have on, then to hear people say how good he looks, I swear his heads swelling from the compliments. Have you seen him? That car he’s driving, that watch he’s wearing, his house, and kids, and his wife, most people only dream of marrying. He has everything I ever wanted, yet he takes it all for granted, he won’t let anyone else enjoy the spot light, like it’s impossible for him to share it. He never talks to me, which makes it that much more awkward, because I always see him in the bathroom, and every time I wash my hands, there he is, just starring, blocking my reflection. When I try to move, he moves too, it’s so obvious he’s doing it on purpose, but I don’t like drama, quite frankly his demeanor makes me a little nervous. So I just ignore it, I’m starting to wonder if I should report him, but what if the boss thinks I’m jealous? I much rather prefer waiting until the day he quits, or who knows maybe he’ll get fired, I just hope he’s not still here up until the day that I retire.
Until the age of five almost six, I thought everyone could figure out how to walk through walls. The morning my mom was walking me to my first day of school she broke the news to me. Once we reached the first intersection, and we were standing at the corner waiting for the light to change, she first asked me, “Maddy, remember that I mentioned to you every person in the world is unique?” I nodded while I kept my eye on the street light. “and what did I say was so unique about you?” “That I have three freckles on my nose.” “Maddy! Not that but the one thing nobody can tell by looking at you.” I looked up at her and said, “That I am a smart kid and I figured out that walls don’t divide or separate?”
Chapbook 25
Last night I was scared, I had another bad dream I just wanted my mommy there but she was in another room asleep. It was a nightmare, the one I often have, about a monster, who’s over 6ft. He chases me down, grabs me by my hair, thrown me into walls, I don’t know why he’s so angry, he’s even kicked me down the stairs.
I woke up sweating, my eyes filled with tears, and what scared me the most was bruises had appeared. They covered me from head to toe, I couldn’t hide them underneath my clothes. Today I was supposed start my first day of school, but mommy said I couldn’t go.
Back to sleep, I don’t even remember getting ready for bed, I just blacked out, when I woke up a pain filled my head. My dream had some how become real, there was the monster, standing over my body, breathing, and grunting, where is my mommy. Why doesn’t she come and help, why isn’t she protecting me, can’t she hear me if I yell.
Can anyone hear me, why can’t anyone figure it out, I wish my daddy was here, but mommy won’t let him around. When will this nightmare finally end, what will it take for him to leave, one of us dead, or broken and bleeding?
Years have gone by, I’m learning to deal, he’s still in our lives, drinking his meal. He is always mad always drunk, never caring, incapable of feeling love. Beating satisfies a need inside him, one that reminds him he’s alive, he’s in control, that everyone’s beneath him, we do as were told.
My other siblings have dealt with it their own way, my oldest sibling has different personality traits. One minute he’s him, by the next someone else, he swears one day he’ll be free of this hell, and when he does he never wants to see any of us again, he disowns our family, he can’t be my friend. The pain is so much more than anyone should take, it won’t be long from now till one of us breaks.
It finally happened, as I began to prepare my food, cutting up vegetables, trying not to listen to them argue, but low and behold i couldnt ignore the thump, at that very moment I snapped into somebody else.
Someone stronger than who I thought I’d become, with a knife in one hand, and a plan in the other, I made my way to the second floor, and found the that thud was my mother. As the plaster in the wall shaped like her head, I looked for the monster, and seen him covered in red.
Like a bull I charged toward him, digging the knife in his gut, 1,2,3 times ain’t enough. Like the monster he’s always been, courage from his bottle, the pierces in his side didn’t stop him, he was numb from the booze, and like a mad man, he retaliated, nothing could keep him from trying to kill me.
I just woke up from a terrible dream, just to find myself in a worse reality. Laying at the bottom if the stair case, in a puddle of my own blood, flashing lights reassured me help had finally come, but I couldn’t move, my body paralyzed, what had I done? I see my mother screaming she is covered in blood, Then I seen the monster sitting up with tape across his abdomen arms crossed in cuffs, finally he will get what he deserves, but what does this mean or us?
The only girl out of eight kids, the second eldest of the bunch, I thought we stuck together this long, and through such hell, we’d most likely stay together, but only time could tell. If only the words for what’s felt could every truly be spoken, perhaps only then could anyone listening would know just what was dealt, but sometimes you can’t mutter out the words that would allow others to understand what kind of welt gets lashed across a tiny body when beaten with a belt.
Even after hundreds of beatings, thousands of black and blue marks, fractured bones like ribs and wrists, almost on a daily basis. I bet your thinking how the hell does this go on for so long, when a parent allows another adult to enter their home, use them for everything they own, get drunk and stands by as that person takes their angers and frustration out on the innocent lives they should be protecting. When a mother or father chooses a stranger over their own little ducklings. That is how monsters get away with it so long, because an active parent allows it to go on.
The truth is of all the afflictions none bare as much pain as the very thought that a mother could prefer a stranger, a monster, putting her babies in danger, actually acts like she doesn’t see what she did wrong. She won’t acknowledge her errors, and the ultimate worst, the day she would choose another guy over us, again, this guy just another monster, and yet he is her life, treats her like crap, calls her an asset, not as his wife. Let her keep him, and the life she’s made, I have my own daughter now, I will never allow her to grow up this way, I will be nothing like my momster, this is the ultimate promise I make, and would die before I’d ever let it break.
Great piece about a super villain, and how this kind of thing does not happen in a vacuum. Your POV was consistent, first person, but there are places where you need to highlight that these are the thoughts of the protagonist. Italics would work, or even quotes.
I only just came across this site today an I was immediately intrigued. I’ve always been self conscious about my writing but I like the idea of being about to just practice like this and get genuine feedback. Anyway I wrote mine in third person limited, I trying to practice how to use better descriptions without overdoing it and getting to fluffy. Here goes..
I remember the day Melissandra first told me she had superpowers. I would have laughed right then and there if I hadn’t learned to recognize the tension burrowed between her brows. Her pale youthful skin now sagged to that of a woman three times her age. The bags beneath her eyebrows had become so swollen and dark you would have thought she hadn’t slept in weeks. The dark shadows behind her eyes gave way to little life. She hunched over me, her body twitching like little jolts of electricity pulsed through her. In health classes we had often seen videos of the effects of hard drugs on addicts, the way they scratched and clawed, itching to escape their bodies. Could she had gotten herself into hard drugs? No, I definitely would have noticed. This was something worse, as a tenth grader living in the suburbs true terror had never struck me very hard, but the fear that gripped her eyes sent a chill through my spine.
“Mel, is everything okay?” I ask as we push our way through the crowded cafeteria.
Mel leans in close looking over her shoulder with unease checking to see that no one else is listening. She whispers, almost inaudibly.
“I think I have superpowers Suz.”
Laughter roars through my belly, which is quickly stifled by the lifeless expression on her face. I’ve never seen her so afraid.
“I’m sorry, did you say superpowers Mel?” I ask in disbelief.
Her eyes fix on me with a cold hard expression, there’s no laughter in her eyes, no punch line at the end of this story.
She lowers her voice as she begins to explain.
“Last night I went for a climb on Bears Peak. I must of got 150 feet when I lost my footing on the rocks. I was so sure I had all my ropes secured, but as I started to fall nothing caught. In that moment I thought I was going to die. Than, just before my body hit the ground I stopped. My body just suspended, hovering in mid air. It wasn’t long, only a moment, a few seconds at best, but enough time for my body to correct itself and find its footing on the ground.”
I stare at her in bewilderment, she’s not saying what I think she is, is she.
“Suzan!” she exclaims as her eyes show a flicker of light. “Last night I flew.”
I just discovered this site tonight, I like it already. I wrote mine in third person limited.
I remember the day Melissandra first told me she had superpowers. I would have laughed right then and there if I hadn’t learned to recognize the tension burrowed between her brows. Her pale youthful skin now sagged to that of a woman three times her age. The bags beneath her eyes had become so swollen and dark you would have thought she hadn’t slept in weeks. The dark shadows behind her eyes gave way to little life. She hunched over me, her body twitching like little jolts of electricity pulsed through her. In health classes we had often seen videos of the effects of hard drugs on addicts, the way they scratched and clawed, itching to escape their bodies. Could she had gotten herself into hard drugs? No, I definitely would have noticed. This was something worse, as a tenth grader living in the suburbs true terror had never struck me very hard, but the fear that gripped her eyes sent a chill through my spine.
Great article, Joe! I really appreciate the detail you went into. You made the different points of view so clear. The breadth of your knowledge of literature is awesome, and your two graphics were helpful and concise.
Katherine Rebekah, great story! You did the second-person POV seamlessly.
All the best, Deena
Well thanks, Deena. 🙂
My genre is romantic suspense, or romantic thrillers, if you will. I always write third person point of view, omniscient, and steer clear of first person for exactly the reasons you’ve stated above. I find first person too limited and stifling. When I read a novel written in first person I find myself distracted, wondering what the other main character(s) are thinking or feeling. Particuarly in a romance – I don’t want to spend my entire reading experience wondering: Is he feeling the same way way or she on her own here?
Granted, the authors that I habitually read do not typically write in first person, but when they do, I will admit, they’re pretty good at showing me the thoughts and feelings of the other party without actually going into their POV. But, I would say it is a tough thing to accomplish, and only the best writers do.
Any feedback would be nice, thanks!
There are no more villains to fight you. No more evil-doers who wish to challenge your right—the right the people gave you to defend their lives. The monument that watched over the city like an old father is the tribute they built for you. The responsibility that you now stand in. Watching over them. An extraterrestrial guardian.
You look up to see grey clouds swirling, forming some odd shape. You take flight, and burst through the glass pane, as people below begin to chant your name. The clouds merge with one another, swirling in and out of each other. With your vision you can see the faces of the ones you swore to protect, even at the cost of your life. Some are smiles, the faces of those that believe in you—the ones if they could would join you without a second thought. Others had grief-stricken eyes; doubt lined their faces. How could you protect them forever? Surely someone greater than you, stronger than you would destroy everything that you deemed worth saving. Maybe there was someone that could take your place, someone that made all this easier. Hopefully.
No. Your chest bursts out and the veins in your arms feel ready to explode. Your fists clench tighter with each breath. Your eyes narrow. Never will you doubt yourself ever again. A crash of lightning hit a nearby building, signifying your resolve. You charge into the vortex still swallowing the sky. The mass of clouds block your path and out the whirlwind a humanoid shape takes form. You. You face off against yourself. “Of course. A hero’s greatest challenge is his or herself,” you say.
How I hate head-hopping! This is a common mistake my students make – and an easy one that can slip into our drafts. Hence, the importance of revision and beta readers.
Thank you for this thorough discussion of such an important element of story!
The worst limitation I find writing in first person is exactly what Joe pointed out, that you cannot be everywhere at once. I find myself getting frustrated at having to switch POV’s between characters in order to be able to tell the story better and show how different characters are feeling because of certain situations; or in my story’s case: one very sinister character.
But since I’m using my past experiences as a means to write the way I do, I kind of need to stay in first person. It’s both a blessing and a curse.
How interesting that a man who has written a 7000-page story is the author of a bestselling book about writing a short story. 😉
“Tina, what the heck. Put me down.”
“Sorry Charlie, I just ate a spinach salad.”
“Clever, but not humorous. Popeye wouldn’t be so frivolous. What if mom and dad had seen you showing off, or worse, if one of the Dancings is spying on us.”
“You’re no fun, you’re boring and paranoid. Brother or not, I may look for another partner”
“Be my guest. I’ll find someone who takes our mission seriously. Who won’t jeopardize our friends and family out of boredom, and the childish need for attention. Grow up a little. You’re sixteen years old.”
“And, you’re eighteen going on eighty. It’s true what they say about friends and family.”
“Whose they?
“Idiot. They’re the consensus.”
“What does the consensus have to say on the subject?”
“Family is the luck of the draw. Friends are deliberate choices.”
“I’d mention a few of your choices but that won’t get this conversation on track. I, we, need to find out what the Dancings are up to. You need to get close enough to read their daughter’s mind. I’ve got a plan. It could work if you can augment your powers with a dash of maturity.”
My sister Tina and I were abducted a month ago while hiking in the Grand Canyon. If I had the words to describe the aliens or their vessel, I’d share them, but I don’t. They were spirits as much as anything and I may have been sedated somehow. They separated us. Apparently Tina was more qualified for mental and physical superpowers than I was. She can read minds and has the strength of The Hulk. My power is cooler though. My eyes shoot lasers when I squint and concentrate. If it was just a matter of squinting, the neighborhood would be ablaze. My vision is less than perfect. I’ve been squinting for years. Maybe that’s why I got this power? Whatever. If the Dancings are building a dirty bomb in their basement, I may need to set fire to them and their house. Soon maybe. First, I need to know that my suspicions are warranted.
Tina needed to befriend the Dancing’s daughter Tanya, an introvert who spoke to no one at school. If she couldn’t befriend her, Tina at least needed to sit by her at lunch, hopefully to learn something from her thoughts. My sister gets bored easily, so sitting near a person who won’t acknowledge her was going to be a challenge. That’s why I was so irritated with Tina and her circus tricks just now. I’m convinced our neighbors are terrorists. But I can’t just burn their house down. What if somebody died and I was wrong? It was time for my sister to step up and put her powers to good use.
Appreciate the write up Joe. Laura
I am having a lot of difficulty with point of view. For instance, Let’s say you have a Memoir or “Diary” type fiction. You want to it to be from the point of view of the person writing the diary; however, you need your reader to know facts about the characters the speaker interacts with that he couldn’t possible know. (perhaps he just met them, etc.) How can you give the reader information about a person that the speaker deosn’t know yet?
hey, I am in the same boat as you, and I uncovered something called First Person Omniscient, which is– if you are still not away after a year of writing the comment I am replying back to– the character is in first person, still uses “I” and “we” and such, but also knows information about other characters that he/she does not yet know, precisely as what you described in your comment. However, this type of first person is rare, as very few novels and authors decide to use this method. But whatever floats your boat! Hope I helped, even though I am clearly late!
Try second person
One question I have in regards to POV and which to choose, is suppose you’re writing a story about something that’s already happened. The story is being told by the main character in the story, years later after the story is “over” (kind of like in a journal of what happened, how it ended- to a certain point- leaving out what has happened to the main character due to his choices made). But, one of the unique situations is that the main character is not just one person, but a person literally divided into 3 separate selves. He himself is the Present self, the other two are what has already happened (past- alternate choice of reality) and the last one is “what could be if” situation” (future). The main (present) is part of the three, but only knows the whole story after it’s happened and how the other two responded to events as they occurred. How would the story be told in what point of view? Both first and third? I know it probably sounds confusing; so if you’re willing to give me advice and need some clarification I can do that. Thanks.
Amanda stared at herself in the mirror. She lifted her hands and gazed at all of the blood on them. “Why am I not dead?” she asked herself puzzled. “It was a head on collision…with a truck!” she exclaimed to herself in amazement. She turned on her heel and marched to her kitchen and grabbed a large knife. She waved the knife around in the air before placing it on her wrist. “If I can’t make it look like an accident, I guess my parents would have to deal with the fact I wanted to die.” Amanda spat. She winced as the blade dug deep into her delicate flesh and watched her blood flow. But the seconds later it stopped. Blinking, she brought her arm closer to her face and stared at her smooth skin -without a single scratch on it. In disbelief she dropped the knife and ran back into the bathroom and wiped her arm of its blood and confirmed there wasn’t a wound. Desperate, Amanda ran down into the basement and grabbed her father’s rifle. “Heal from this if you can.” Amanda put the point under her chin and pulled the trigger. Everything went black and she felt herself crash to the floor. Moments later, Amanda woke up with a huge headache. “What happened?” she groaned but then gasped when she remembered what she had tried to do. “What is happening to me?!” she cried. “I don’t want to be in this world anymore, let me die!” she screamed. Amanda got up from the floor and shuffled up stairs to take a warm shower. “Maybe drowning would work…”
You forgot deep pov; close third. >:(
Deep POV is still third person limited.
Great write-up! Worth sharing and bookmarking.
As for me, I prefer to write (and read) in either first person or third person limited.
Good article except that the plural of point of view is points of view and NOT point of views! C’mon!
Though I’ve only started writing in earnest this year, POV is a topic that has been pointed out to me again and again concerning my WIP. TODAY, as I go through the comments I received overnight POV is the stumbling block I inadvertently put in my story. I’m consciously employing the third person omniscient POV, but it’s not coming through to my readers. I’ve read this article before and anew and I still don’t get it… I’m doomed.
talented writer, Noddy, mentioned this article . is good read . reread since wanted to make the third person omniscient viewpoint cleaner without head hopping . soon peruse Italo Calvino book written in second person pov to see how a master wrote .
Write two pieces of 750 words. One will be from the point of view of a traveller travelling to a foreign country. The other will be from the point of view of a native of that country who receives that traveller which person do I write form the first person, second person or the third person please help
You know, i had a dream once… I wanted to redo my entire life, I’m getting a divorce from my wife, Scarlett. We have two children, Alex and Maggie, and they’e both seniors in the high school I used to attend. I was driving to Ned’s house one rainy night and saw a man on a bridge. I got out and ran after him. When I got there he jumped, i looked over the edge and then I fell off. I woke up in Ned’s house and looked in the mirror. I was my young self again… I was 17 again.
What about this post is actual, and what part’s a dream? It’s hard to distinguish what dialogue this follows, and what efforts are trying to be accomplished.
Everything about this was my dream… I woke up after i fell and thought, I need some pancakes.
Hi- I’m writing a novel in 3rd omniscient. I struggle with the point of view on a micro level, never dipping into 1st or second person. Here is an example of what I mean is this… ‘While Eunice and Barbara were in the nursery spending a few minutes with the baby boy, Margaret walked away from a group and then grabbed a quick nibble of cheese from the buffet. She continued on to the bar where she picked up a full glass of vodka with a twist of lemon. On her way out the door to the patio, she looked back over her shoulder directly to where Jules stood, as if she had known his position to the inch.’ Does ‘she looked back over her shoulder’ now put the reader in Margaret’s POV???
I could use some advice.
I have a novel focusing on the relationship of two people. This is entirely written in 3rd person limited with occasional internal dialogue.
Initially, this story was focused on one character (A); however, I realised the protagonist was the other character (B). I re-wrote the novel to be inside B’s head, and generally this works *much* better.
Here’s the problem. Although the entire novel is written in 3rd person limited for B, there are several action points within the novel that follows A, not B because there is not much going on with B during this time.
There’s no head hopping or reading of A’s mind in these few scenes, but nothing is happening to B at this point, so narrative-wise, it seems okay to follow A through action (not thought).
So, question 1) because there’s no head hopping, is following A occasionally too distracting for this story? And if so, 2) I’m open to suggestions on how to handle this, because it’s what happens to A in these scenes that changes things.
Very good article. Great examples.
Nice article
Understanding the difference between first person and third person point of view (POV) is crucial for any writer looking to master narrative technique. This “Ultimate Guide” promises to provide comprehensive insights into both POVs, which can significantly enhance storytelling skills. By delving into the nuances of each POV, writers can learn how to effectively convey characters’ perspectives, emotions, and experiences, ultimately enriching the reader’s engagement with the narrative. Whether you’re a beginner or seasoned writer, mastering these narrative techniques is essential for crafting compelling and immersive stories. Looking forward to exploring this guide and honing my storytelling skills further!
Point of view (POV) is crucial in storytelling, shaping how readers experience a narrative. First Person POV immerses readers in the narrator’s thoughts and feelings, creating intimacy and immediacy, making it ideal for character-driven stories, though it limits perspective to the narrator’s knowledge. On the other hand, Third Person POV offers more flexibility, with third person limited closely following one character and third person omniscient providing an all-knowing view of multiple characters. This flexibility allows for more complex narratives but can distance readers from the characters. Choosing the right POV depends on the story’s needs and can significantly enhance the reader’s experience.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- Are You Writing From the Right Point of View? - […] Want to know more about POV? See our definitive point of view guide here. […]
- Links To Blog Posts on Writing – September 2015 | Anna Butler - […] Point of View in Writing – Joe Bunting at The Write Practice, with an article that manages to cover…
- Why You Can’t Finish Writing Your Book - […] the Genre? 2. What are the conventions and obligatory scenes for that Genre? 3. What’s the point of view? 4.What are…
- Who’s on First? Exploring Point of View | Dawne Webber - […] I Write in First Person Point of View? @ Editor’s Quill Point of View in Writing @ The Write Practice What…
- Write From The Perspective of a Shoe - […] Seriously, if you want to know everything there is to know about Point Of View, or POV, read Joe’s…
- Last Weeks Writing Links 12/21-12/26 | B. Shaun Smith - […] Point of View in Writing […]
- How to Choose the RIGHT Tense for Your Novel - […] Lights, Big City is notable both for being written in present tense and second-person. While it’s not necessarily something you should use…
- A Matter of Perspective (#0039) | Dominika Lein - […] involving a narrator’s position, then feel free to read these decent articles on the issue; The Write Practice’s Point of…
- Blog – Writer's Thumbprint - […] All of this comes down to POV. The person who did make the movie is telling it from his/her…
- 10 Tips: How to Edit and Improve Your Writing – livewritelovelearn - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- The Power of Perspective: Understanding Point of View in Creative Writing – The Waterhole - […] to The Write Practice, “Point of View” refers to two things in […]
- Why You Should Consider Writing With an Omniscient Narrator | Creative Writing - […] But before you “stick it to the man” and start drafting your magnum opus in third person omniscient, let’s…
- Point of view guide – LOVE INDIE ROMANCE - […] Point of view guide […]
- POV Rules! - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Resources from WW | Elijah - […] Blog Posts: I didn’t read this entire article, but the first third of it seemed very good: https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ These…
- POV | Elijah - […] The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person […]
- Fixing POV Violations - Sun's Golden Ray Publishing - […] Violations (point of view violation). Basically, you have established a point of view for the book (First, Third Close,…
- Bibliography | 網站標題 - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Beyond NaNoWriMo: What Do You Do Next? - Story Grid - […] detailed descriptions of the four major types of point of view, read Joe Bunting’s article at The Write Practice.…
- Summer Solstice, New York City by Sharon – Nicholas Hacker's Moorpark College Spring '18 Website - […] [I’m looking at this point-of-view guide from thewritepractice.com to figure out what POV the spea… […]
- Writing Chapter 2: Developing your Opening Hook | Now Novel - […] change of POV: Describe what another character is going through, in an arc linked to the scenario in your…
- How to Publish a Short Story: Write Your First and Second Drafts - […] hopping: Stay in one point of view. There’s not enough time or space in a short to skip […]
- Guest Post - Como Criar Uma Proposta Irresistível - MBFA - […] Tom e perspectiva também usualmente são especificamente analisados. Muitas publicações preferem que você fale em primeira, segunda ou terceira pessoa.…
- Lesson 2: Point Of View – What's right Is Write - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- How to Write a Book from Multiple Perspectives - […] So if you’re ready for the challenge, here’s how to write a book from multiple perspectives. […]
- How do you develop your plot? – thefictionwritersfriendblog - […] a really good article on Point of View on the Write Practice site. It goes into in more detail…
- Getting to Step 8: Setting the Scenes (Gesichtpunkt) – Short Ramblings - […] your adventure’ books. The other POVs are best suited for my kind of project. (*[2] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- P.O.V | The Psychiatrist's Couch - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- How to Keep Your Point Of View Consistent – by Hannah Green | The Writers College Times - […] Bestselling author Joe Bunting put it best when he said: […]
- How to Leverage Point of View to Power Your Story - […] the purposes of this article, toss out second person and choose between first and third. Each has its strengths…
- How to Leverage Point of View to Power Your Story | rogerpseudonym - […] the purposes of this article, toss out second person and choose between first and third. Each has its strengths…
- Point of View Magic: How to Cast a Spell on Your Readers - […] crucial to understand that EVERY WORD of a story is told through a character’s point of view. If your…
- Henrik Widell – Lektör - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Which POV Is Best for Your Story? – Renea Guenther - […] Between Three Different Points of View Writing 101: Choosing the Best Point of View for Your Story The Ultimate…
- Bethany's Best: Writing Point of View & More - Bethany Henry - […] The Ultimate Point of View Guide – The Write Practice […]
- Wie man einen unwiderstehlichen Vorschlag für einen Gastbeitrag macht - […] Perspektive sind dabei auch sehr wichtig. Viele Blogs und Webseiten bevorzugen Artikel, die in der ersten, zweiten oder dritten…
- The Independent – Evila Penonymous - […] Literature reference: [1] […]
- What Is Self-Editing – Writing without Drama - […] https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/ […]
- Character Development: Create Characters that Readers Love - […] multiple is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- What Is an Epilogue? And Is It Okay to Use One in YOUR Book? - […] epilogues that tend to be shorter than other chapters. They are also usually different in tone, point of view,…
- What Is an Epilogue? And Is It Okay to Use One in YOUR Book? – Lederto.com Blog - […] epilogues that tend to be shorter than other chapters. They are also usually different in tone, point of view,…
- 5 Ways to Ruin Your Creative Writing – Books, Literature & Writing - […] Learn more: The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person […]
- What’s the most intriguing writing tip you’ve uncovered from this post? - […] ones is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- Character Development – Christina's blog - […] ones is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- Drop a link below if you’ve found anything cool for authors! - […] ones is a Point of View character. These characters carry the narrative, and in a story told in third…
- How to Craft Irresistible Guest Blogging Proposal - […] Tone and perspective are also specifically targeted often. Many publications prefer you speak in the first, second, or third…
- How to Write a Good First Chapter: A Checklist - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- How to Write a Good First Chapter: A Checklist – Lederto.com Blog - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- Hit the love button if you like this info! - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- How will you implement the tips from this post? - […] is your story’s point of view? Are you going to choose third person limited, third person omniscient, first person,…
- Preferred POV and Tense – My Ity Opinion | ItyReadsBooks - […] *Found on The Write Practice […]
- Point of View, or Who’s Telling the Story? – Amanda Down the Rabbit Hole - […] Joe Bunting, “The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person,” https://thewritepractice.com/point-of-view-guide/…
- Mastering Point of View: An In-depth Guide To Better Writing - […] The Ultimate Point of View Guide: Third Person Omniscient vs. Third Person Limited vs. First Person […]
- Welcome to YeahWrite’s Weekly Writing Challenge #484 - YeahWrite - […] sure what that means? Click here. Scroll past the introduction to the First Person banner heading, or read the entire…
- Welcome to YeahWrite’s Weekly Writing Challenge #485 - YeahWrite - […] sure what that means? Click here. Scroll past the introduction to the First Person banner heading, or read the entire…
- Rules and Fiction Writing - LaBine Editorial - […] to dig deeper into POV issues and rules in a later post, but if you’d like to learn more…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

Now, Take Your Idea and Write a Book!
Enter your email to get a free 3-step worksheet and start writing your book in just a few minutes.
You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
Get the POV Cheatsheet for Writers
Enter your email for a free cheatsheet for the top two point of views!
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.

The Hyperbolit School
Your trusty englit guide.

First person vs third person: when to use which?
A question I often get about writing is whether it is ever ‘okay to write in first person’.
My answer to this is almost always – ‘it depends’:
It depends on the type of writing we’re talking about; whether you’re writing a personal essay, an argumentative essay, an expository essay, a literary commentary, a speech, a letter, a corporate communications document, or fiction (for this, using first or third person is entirely a personal decision).
It depends on the tone that you wish to convey; it depends on the audience that you intend to address; it depends, also, on the frequency with which you use it in a given piece of writing.
But first, let’s get our definitions in order –
First-person narrative: The use of the pronoun ‘I’ (singular) or ‘we’ (collective) to communicate or narrate from a subjective point of view. Second-person narrative: The use of the pronoun ‘you’ (singular or collective) to communicate or narrate in a way that directly addresses the reader Third-person narrative: The use of pronouns ‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’ (singular), ‘they’ (collective) to communicate or narrate from an external point of view
One interesting point to note is that first person is not always necessary for writing to come across as authentic or individual. An essay narrated in third person primarily focused on describing external elements such as the environment and material objects could very well convey deep, personal emotions; it is your craft, not the pronoun, that determines the depth of expression. An excellent example is Virginia Woolf’s description of London in Mrs Dalloway :
“In people’s eyes, in the swing, tramp, and trudge; in the bellow and the uproar; the carriages, motorcars, omnibuses, vans, sandwich men shuffling and swinging; brass bands; barrel organs; in the triumph and jingle and the strange high singing of some aeroplane overhead was what she loved; life; London; this moment of June.”

As a general rule of thumb, using first person as the predominant voice of your writing is going to make you sound less formal than if you were to use third person, which tends to come across more objective in tone.
Between “I think studying English is a waste of time” and “Studying English is a waste of time”, which one sounds more authoritative to you?
The former tells us that one person thinks studying English is a waste of time, but the latter makes the statement as if it were a general, accepted truth. Note that I say “as if”, because the statement itself is not, in fact, a general truth, but is only conveyed to sound that way through my deliberate omission of the first-person pronoun ‘I’.
So for types of writing that require a high degree of subjective opinion (e.g. anecdotal accounts, op-eds, public speeches, or indeed, blog posts), using first person would make sense.
On the other hand, for essays that are more concerned with relaying facts (or projecting the impression of doing so!) or opinions external to oneself – which don’t have to be ‘factual’ (e.g. argumentative essay, expository essay, news report, scientific article), then perhaps it would be better to opt for the third-person voice.

The use of first vs third person in literary analysis
In this post, let’s look at the use of first-person voice in a specific type of writing: the literary analysis essay. If you’re an English literature student, this should be no stranger to you. For others, think of this as the kind of writing one would find in literary criticism.
Unlike the argumentative essay or the personal essay, the literary analysis essay defies categorical lines when it comes to narrative voice. This is because, despite the clear subjectivity in a kind of writing that is, in essence, a personal response to a literary work, this ‘personal response’ nonetheless seeks to persuade and establish authority in the vessel of a ‘literary analysis’, specifically by formulating an argument based on ‘objective’ observations (i.e. ‘objective’ because you’re partly describing what’s written in a poem / a novel).
What does this mean, then?
Well, it tells us that while literary analysis is largely subjective in content, it often tries to be objective in tone. Commenting on literature isn’t quite the same as a casual book club conversation; it’s an exercise in rhetorical and aesthetic persuasion, for which you make a case about a specific interpretation of a text and convince your readers to see the logic behind it.
Of course, that’s not to say they necessarily have to agree with you (in fact it’s often better that they don’t), but unless you’re already an eminent literary scholar like Stephen Greenblatt or Christopher Ricks , then it’s probably best that you write your literary analysis more like a well thought-out argument, rather than a personal reflection.
In other words, use third-person where possible in your English essays, and feature the ‘I’ pronoun sparingly – if at all. There’s also a debate about whether using the first-person collective ‘we’ is acceptable (e.g. “We can infer from Macbeth’s speech that Shakespeare was wary of power’s effects on man.”) Some people think it’s presumptuous – and therefore dangerously collectivising; I actually think it’s marginally better than using ‘I’, but still less preferable to the trusty third-person voice (e.g. “Macbeth’s speech suggests that Shakespeare was wary of power’s effects on man.”)
I mentioned the English literary critic and professor Christopher Ricks, who has been called “the greatest living critic today” by even his most esteemed contemporaries. There’s no better way to learn than to learn from the best, so let’s examine how Ricks writes in a manner that doesn’t compromise the singularity of his views, but still manages to convey objective restraint in thought.
Christopher Ricks on Tennyson’s ‘Maud’ (from Tennyson )
Best known for his gothic, sentimental poetry, Alfred Lord Tennyson remains one of the most widely read Victorian poets today. His narrative poem, Maud: A Monodrama , tells of the tragic love between the eponymous character and the poem’s speaker. Our focus today is on the analysis, not the poem itself, so I’ll link to the poem here – if you’re interested in Victorian poetry or want to find a poem to practise your close reading skills on, I’d recommend that you give this a read.
Ricks, in his seminal study on Tennyson, demonstrates real elegance in his commentary on ‘Maud’, an excerpt of which I’ll reproduce below for your reference (and for some, enjoyment):
[Maud] is a poem about losing someone whom you have never really had. She is at first beautiful, but as a gem, as an epitome of womankind, as a phantasmal pulse, a dreamlike vision: Cold and clear-cut face, why come you so cruelly meek, Breaking a slumber in which all spleenful folly was drown’d, Pale with the golden beam of an eyelash dead on the cheek, Passionless, pale, cold face, star-sweet on a gloom profound; Womanlike, taking revenge too deep for a transient wrong Done but in thought to your beauty, and ever as pale as before Growing and fading and growing upon me without a sound, Luminous, gemlike, ghostlike, deathlike, half the night long Growing and fading and growing, till I could bear it no more, Among the things which [the speaker] cannot bear about Maud is the dread of her as a unique person; part of him wants her to be a snobbish puppet, part of him tries to divide her as he himself feels divided – and adore, Not her, who is neither courtly nor kind, Not her, not her, but a voice. His love never becomes perfect, so it never altogether casts out fear; but it replaces fear and masochism by awe: “And dream of her beauty with tender dread…” – tender, both as sympathetically moved and as touchingly bruisable. Tender dread is never in Maud to be succeeded by the sober certainty of waking bliss; but it is a human advance. For Maud is an unprecedented evocation of a deep fear of love. “And most of all would I flee from the cruel madness of love”: Maud is not a poem which uses the word ‘madness’ lightly; the essential madness is the fear of love, and the hero is thinking not of traditional cheerful pangs, but of the worst psychic cowardice and dismay. What he centrally fears is not that he cannot be loved but that he cannot love. Till a morbid hate and horror have grown Of a world in which I have hardly mixt, And a morbid eating lichen fixt On a heart half-turn’d to stone. ‘Hardly’ has a sardonic hardness. “Oh heart of stone, are you flesh, and caught/By that you swore to withstand?” Stone, but without the elegant fiction of statuary, which creates a flickering pun in “Wept over her” in these lines: She came to the village church, And sat by a pillar alone; An angel watching an urn Wept over her, carved in stone; So that it is not merely a social snub but an emasculating humiliation which is enforced by the threatening insouciance of Maud’s brother: But while I past he was humming an air, Stopt, and then with a riding whip Leisurely tapping a glossy boot, And curving a contumelious lip, Gorgonised me from head to foot With a stony British stare. The hideousness of the later debacle is that it forces the hero back into thinking he cannot love: “Courage, poor heart of stone!” he groans, “Courage, poor stupid heart of stone”. […]

While Ricks the person is never too close for comfort to the poem’s distraught speaker, Ricks the critic shows a level of microscopic sensitivity to the poet’s diction and a degree of fraternal empathy in his judicious, but not altogether detached, observation of the speaker’s conflicted emotions.
Notice as well that he’s able to convey his emotional response to Tennyson’s work without once having to summon the ‘I’ pronoun, or be jarringly explicit about his presence on the poem’s sidelines.
As an insightful observer of a poetic work, Ricks engages analytically through appreciation and personally through respect, most evidently shown by the constant ‘touchstones’ of quoted lines he uses to guide his commentary. He makes it clear that the critic’s opinion does not override the poet’s narrative.
This, surely, is no mere ‘analysis’, but intellectual pleasure in hermeneutic action.
From reading Ricks’ writing, then, it should become clear that using third-person is a good idea when writing English essays, as it enables you to write in a more sophisticated, considered manner, all the while expressing your unique views towards a text.
A final, but important note
As a final – and important – note, there’s another point to my meta-criticism of Ricks’ reading on Tennyson: reading literary criticism – good literary criticism – is absolutely necessary if you want to get better at writing literary analysis, or at English Literature in general.
While reading primary works (i.e. fiction and poetry) should always be the foundation of literary learning, it is equally important that we grant secondary work (i.e. literary criticism) the attention it deserves, because the act of interpreting literature is an art in itself.
Mind you, I’m not telling you to consciously mimic the way these critics write; my point is just that the more we read what they say and appreciate the way in which they say it, the more our writing style will take on the intellectual rigour and stylistic sophistication so evident in the prose of people like Ricks.
Do you use the first-person ‘I’ a lot in your writing? Or are you more partial to third-person? Comment below with your views!
share this with a friend!
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
2 thoughts on “ First person vs third person: when to use which? ”
[…] via First person vs third person: when to use which? — Hyperbolit […]
Thanks for sharing! I appreciate it.
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

How to Use Third Person in a Paragraph Essay

How to Identify Figurative Language
Writing in the third person is more formally known as using the third-person objective point of view. The third person point of view in an essay is characterized by the use of personal pronouns such as he, she, they or one rather than I, we or you. Formal essays as well as some types of informal essays are typically written in the third person. The third person can apply to single-paragraph essays as well as more common, longer essay formats.
Use the words he, she, it and they for your personal pronouns in the nominative case, meaning when they're the subject of a sentence or clause. Eliminate any references to I, we, or you. "A man's clothing affects how he looks," for example, is written in the third person. "Your clothing affects how you look" is written in the second person. "My clothing affects how I look" is first person.
Use the words him, her, it and them for your personal pronouns in the objective case. Eliminate any references to me, us or you in this case. "Clothes are important to them," for example, is written in the third person. "Clothes are important to you" is in the second person, while "Clothes are important to me" is written in the first person.
Use the words his, her, hers, it, their and theirs for your personal pronouns in the possessive case. Eliminate any references to my, mine, our, ours, your or yours in this case. "The clothes are theirs," for example, is written in the third person. "The clothes are yours" is written in the second person. "The clothes are mine" is first person.
Use indefinite pronouns such as anybody, anyone, both, each, everybody, somebody, someone and several. "Anybody can state an opinion," for example, is written in the third person. "I can state an opinion" is written in the first person.
Review your essay to ensure it remains in the third person throughout. "Unless someone trains harder, your fitness level will hit a plateau," for example, mixes third person with second person. Instead, write: "Unless someone trains harder, his fitness level will hit a plateau."
Related Articles

Purpose of a Pronoun

Difference Between Nominative & Objective Pronouns

How to Use Adverbs in Writing

The Difference Between Participles & Verbs

What Is the Relationship Between a Noun or Pronoun and the Rest of ...

How to Write a Retreat Letter

Properties of a Pronoun

How to Punctuate Song Titles
Steven Wilkens has been a professional editor and writer since 1994. His work has appeared in national newspapers and magazines, including "The Honolulu Advertiser" and "USA Today." Wilkens received a Bachelor of Arts in English from Saint Joseph's University.

paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Third Person
What is third person.
- I am speaking to you about her .
- The policeman is speaking to the teacher about Anne .
Table of Contents
"Third Person" Explained
Third person in grammar, examples of third person pronouns in different cases, first, second, and third person pronouns, why the third person is important, video lesson.

- Third Person Narrative . A third-person narrative is a story told using the pronouns "he," "she," "it," or "they" or using nouns. In other words, the story is not told from a personal perspective. A third-person narrative contrasts with a first-person narrative, which is a story told from a personal perspective using the pronoun "I" (and sometimes "we").
- To Write in the Third Person . "To write in the third person" means to use nouns or the pronouns "he," "she," "it," or "they." It is common in business writing.
- Third Party Insurance . Third-party insurance protects against the claims of others. Look at the following sentence: I (the first party) am ensured by you, the insurer (the second party), to protect me against them (the third party).
- First person : "I" and "we"
- Second person : "you"
- Third person: "He/She/It" and "They"

| Person | | Possessive Case | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third Person Singular | he / she / it Example: is not happy. | him / her / it Example: We saw . | his / her / its Example: We were support. | his / hers / its These were . |
| Third Person Plural | they Example: are leaving. | them Example: We like . | their Example: We were allies. | theirs These are . |
- Masculine gender : He, him, his
- Feminine gender : She, her, hers
- Neuter gender : It, its
| Person | | Possessive Case | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Person Singular | I | me | my | mine |
| Second Person Singular | you | you | your | yours |
| Third Person Singular | he/she/it | him/her/it | his/her/its | his/hers/its |
| First Person Plural | we | us | our | ours |
| Second Person Plural | you | you | your | yours |
| Third Person Plural | they | them | their | theirs |
(Reason 1) Understanding the person categories is useful for learning a foreign language.
| Person | English | German | French | Spanish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Person Singular | I play | ich spiele | je joue | yo juego |
| Second Person Singular | you play | du spielst | tu joues | tu juegas |
| Third Person Singular | he/she/it plays | er/sie/es spielt | il/elle joue | el/ella/usted juega |
| First Person Plural | we play | wir spielen | nous jouons | nosotros jugamos |
| Second Person Plural | you play | ihr spielt | vous jouez | vosotros jagais |
| Third Person Plural | they play | Sie spielen | ils/ells jouent | ellos/ellas/ustedes juegan |
(Reason 2) Using the third person presents a formal air.
- Avro Corps will handle your complaint within 48 hours.
- We will handle your complaint within 48 hours.
(Reason 3) Using the third person for storytelling can make you seem all-knowing.
- In business, write in the first person for a personal touch.
- When writing fiction, write in the first person to engage your audience quickly.
- Don't say or write "between you and I"...ever.
(Reason 4) The third-person possessive determiner "its" not "it's."
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
Point of View: It's Personal
What to Know The point of view of a story determines who is telling it and the narrator's relationship to the characters in the story. In first person point of view the narrator is a character in the story telling it from their perspective. In third person point of view the narrator is not part of the story and the characters never acknowledge the narrator's presence. Less common than first and third is second person point of view. In second person point of view the reader is part of the story. The narrator describes the reader's actions, thoughts, and background using "you."

It's all about how you look at it.
When you tell a story, an important thing to choose is the point of view that the story should take. Point of view determines who tells the story, as well as the relationship that the narrator has to the characters in the story. A story can have a much different feel depending on who is doing the telling.
The main points of view are first person and third person, with second person appearing less frequently but still common enough that it gets studied in writing classes. These are also the terms used to distinguish the personal pronouns. The pronouns I and we are first-person pronouns; they refer to the self. The pronoun you , used for both singular and plural antecedents, is the second-person pronoun, the person who is being addressed. The third person pronouns— he , she , it , they —refer to someone or something being referred to apart from the speaker or the person being addressed. Narratives are often identified as first, second, or third person based on the kinds of pronouns they utilize.
First Person Point of View
In first-person narration, the narrator is a person in the story, telling the story from their own point of view. The narration usually utilizes the pronoun I (or we , if the narrator is speaking as part of a group). The character who tells the story might be in the middle of the action or more of a character who observes the action from the outer limits, but in either case you are getting that character’s recounting of what happens.
It also means that impressions and descriptions are colored by that character’s opinions, mood, past experiences, or even their warped perceptions of what they see and hear.
There was no possibility of taking a walk that day. We had been wandering, indeed, in the leafless shrubbery an hour in the morning; but since dinner (Mrs. Reed, when there was no company, dined early) the cold winter wind had brought with it clouds so sombre, and a rain so penetrating, that further outdoor exercise was now out of the question. I was glad of it: I never liked long walks, especially on chilly afternoons: dreadful to me was the coming home in the raw twilight, with nipped fingers and toes, and a heart saddened by the chidings of Bessie, the nurse, and humbled by the consciousness of my physical inferiority to Eliza, John, and Georgiana Reed. — Charlotte Brontë, Jane Eyre , 1847
In Jane Eyre , the narration is provided by the story’s title character, a governess. The information shared comes from her memories and impressions—of the weather, her knowledge of Mrs. Reed’s dining habits, and her dread at receiving a lecture from Nurse Bessie. We are likewise shielded from information that Jane doesn’t know.
Many classic works of fiction feature characters made memorable by their first-person voices: The Catcher in the Rye (Holden Caulfield), The Handmaid's Tale (Offred), or To Kill a Mockingbird (Scout Finch). In some stories, such as in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby , the first person narrator (Nick Carraway) is an observer of the character around whom the story is centered (Jay Gatsby).
Second Person
Second-person narration is a little-used technique of narrative in which the action is driven by a character ascribed to the reader, one known as you . The reader is immersed into the narrative as a character involved in the story. The narrator describes what "you" do and lets you into your own thoughts and background. The most well-known piece of fiction that employs second-person narration might be Jay McInerney’s novel Bright Lights, Big City .
At the subway station you wait fifteen minutes on the platform for a train. Finally a local, enervated by graffiti, shuffles into the station. You get a seat and hoist a copy of the New York Post. The Post is the most shameful of your several addictions. — Jay McInerney, Bright Lights, Big City , 1984
You will also find second-person narration used in the "Choose Your Own Adventure" style of books popular with younger readers, in which readers determine where the story goes by which page they turn to next. Allowing the reader to "be" the central character in the story provides an immersive reading experience, enhancing what is at stake for the character and reader.
Third Person Point of View
In third-person narration, the narrator exists outside the events of the story, and relates the actions of the characters by referring to their names or by the third-person pronouns he, she, or they.
Third-person narration can be further classified into several types: omniscient, limited, and objective.
Third Person Omniscient
Omniscient means "all-knowing," and likewise an omniscient narrator knows every character’s thoughts, feelings, and motivations even if that character doesn’t reveal any of those things to the other characters.
Little Women by Louisa May Alcott serves as a good example of third-person omniscient narration:
"Christmas won't be Christmas without any presents," grumbled Jo, lying on the rug. "It's so dreadful to be poor!" sighed Meg, looking down at her old dress. "I don't think it's fair for some girls to have plenty of pretty things, and other girls nothing at all," added little Amy, with an injured sniff. "We've got Father and Mother, and each other," said Beth contentedly from her corner. The four young faces on which the firelight shone brightened at the cheerful words, but darkened again as Jo said sadly, "We haven't got Father, and shall not have him for a long time." She didn't say "perhaps never," but each silently added it, thinking of Father far away, where the fighting was. — Louisa May Alcott, Little Women , 1868
The story is not told from the point of view of Meg, Jo, Beth, or Amy, but from someone who is observing the four sisters as they talk to one another. Each character is therefore referred to by their names or the third-person pronoun she . The narrator does not exist as a character in the story, and the girls do not acknowledge the narrator’s presence.
However, the narrator is omniscient, which means that they know what the characters are thinking. This is demonstrated in the last line of the excerpt, when the girls silently ponder the thought of their father never returning from the war.
Third Person Limited
In third-person limited narration, the narrator still exists outside the events of the story, but does not know the motivations or thoughts of all the characters. Rather, one character is the driver of the story, and the reader is given a closer peek into that character’s psyche than the others.
J. K. Rowling utilizes third-person limited narration in the Harry Potter novels. Even though the narrator is not Harry, and Harry is referred to as 'he,' the reader is allowed into Harry's thoughts—what he is wondering without saying out loud. We are also, like Harry, left uncertain about what other characters are thinking:
Three days later, the Dursleys were showing no sign of relenting, and Harry couldn't see any way out of his situation. He lay on his bed watching the sun sinking behind the bars on the window and wondered miserably what was going to happen to him. What was the good of magicking himself out of his room if Hogwarts would expel him for doing it? Yet life at Privet Drive had reached an all-time low. Now that the Dursleys knew they weren't going to wake up as fruit bats, he had lost his only weapon. Dobby might have saved Harry from horrible happenings at Hogwarts, but the way things were going, he'd probably starve to death anyway. — J. K. Rowling, Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets , 1999
Third-Person Objective
In third-person objective narration, the narrator reports the events that take place without knowing the motivations or thoughts of any of the characters. We know little about what drives them until we hear them speak or observe their actions. The resulting tone is often matter-of-fact, not colored by any opinions or commentary, nor of knowledge of what takes place outside the scene.
The people of the village began to gather in the square, between the post office and the bank, around ten o'clock; in some towns there were so many people that the lottery took two days and had to be started on June 25th. But in this village, where there were only about three hundred people, the whole lottery took less than two hours, so it could begin at ten o'clock in the morning and still be through in time to allow the villagers to get home for noon dinner. — Shirley Jackson, "The Lottery," 1948
Word of the Day
Hue and cry.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, 33 transition words and phrases, is 'irregardless' a real word, 8 more grammar terms you used to know: special verb edition, 31 useful rhetorical devices, grammar & usage, more words you always have to look up, 'fewer' and 'less', 7 pairs of commonly confused words, plural and possessive names: a guide, more commonly misspelled words, pilfer: how to play and win, great big list of beautiful and useless words, vol. 4, 9 other words for beautiful, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, birds say the darndest things.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Nouns and pronouns
- Third-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation
Third-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation
Published on December 1, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on February 24, 2023.
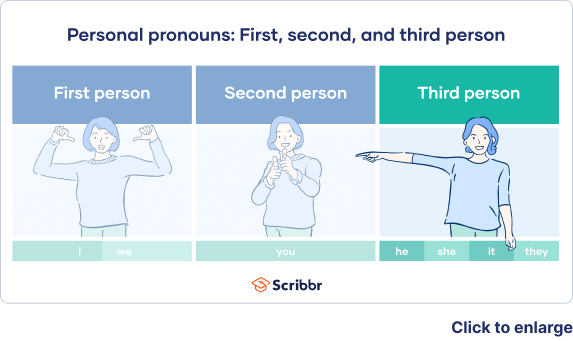
Third-person pronouns are words such as “she,” “it,” and “they” that are used to refer to other people and things that are not being directly addressed, without naming them specifically with a noun . Like first- and second-person pronouns , they are a type of personal pronoun .
There are quite a lot of third-person pronouns, since they differ based on the gender (or lack thereof) and number of who or what is being referred to. They also change based on whether they are used based on case: subject , object , possessive , or reflexive / intensive . The table below shows all the third-person pronouns.
| Subject | Object | Possessive | Reflexive | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| he | him | his | himself | |
| she | her | hers | herself | |
| it | its | itself | ||
| they | them | theirs | themself | |
| they | them | theirs | themselves | |
Table of contents
Masculine singular pronouns (“he”), feminine singular pronouns (“she”), neuter singular pronouns (“it”), third-person plural pronouns (“they”), the singular “they”, frequently asked questions.
The masculine singular pronouns are he , him , his , and himself . The masculine singular possessive determiner (used to modify a noun instead of replacing it) is also his .
These words are used to refer to individual men and boys—and sometimes to male animals.
| Subject | Ahmad is good at math, but doesn’t particularly enjoy it. |
|---|---|
| Object | After Jim started a fight with another attendee, event security kicked out. |
| Possessive | This isn’t my jacket, but Dolf was sitting here earlier. I think it’s . |
| Reflexive | Eric introduced already. We had a nice chat! |
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
The feminine singular pronouns are she , her , hers , and herself . The feminine singular possessive determiner is also her .
These words are used to refer to individual women and girls—and sometimes to female animals.
| Subject | Laura says can’t make it to the party. |
|---|---|
| Object | It’s not Ida’s fault. Leave alone! |
| Possessive | gift do you like better, mine or ? |
| Reflexive | Mei ought to realize she can just be around us, but she always tries to act tough. |
The neuter singular pronouns (also called inanimate singular pronouns) are it (used in both the subject and object position), its , and itself . The neuter singular possessive determiner is also its .
These words refer to something other than a person: a concept, object, place, or animal (although gendered pronouns are sometimes used instead for animals). It’s considered very rude to refer to a person as “it”; to refer to someone without specifying gender, use the singular “they” instead.
| Subject | wasn’t a great concert, but I’ve seen worse. |
|---|---|
| Object | Don’t say ! I know what you’re thinking. |
| Possessive | The flashing light on the side of the device indicates remaining battery life. |
| Reflexive | The average cat spends a lot of time washing . |
The third-person plural pronouns are they , them , theirs , and themselves . The third-person plural possessive determiner is their .
These words are used to refer to more than one of anything: people, things, concepts, places, animals, and so on. No distinction is made between people and things or between male and female in this case; the plural pronouns are always the same.
| Subject | are important, but can develop and change over time. |
|---|---|
| Object | I can’t decide whether to go to Paris or Berlin; I’d love to visit both. |
| Possessive | My flight home is on Sunday morning, and is in the afternoon. |
| Reflexive | Teaching can be stressful when the kids won’t behave . |
The third-person plural pronouns and possessive determiner— they , them , theirs , themselves , and their —are now commonly used as gender-neutral singular pronouns (also called epicene pronouns) to refer to people. This usage is often called the singular “they.”
The singular “they” has existed for a long time, but it was typically viewed as an error in the past. However, most style guides now endorse it, recognizing the need for a way to refer to individuals in a gender-neutral way.
These words are used (instead of “he or she”) when referring to a generic individual whose gender is unspecified or to an individual who identifies as neither male nor female.
| Subject | When someone signs up to participate in the trial, are given a preliminary questionnaire. |
|---|---|
| Object | It’s important to show the customer that you are listening to . |
| Possessive | Max is really smart. are always the best ideas. |
| Reflexive | Sacha will have the place all to . |
In grammar, person is how we distinguish between the speaker or writer (first person), the person being addressed (second person), and any other people, objects, ideas, etc. referred to (third person).
Person is expressed through the different personal pronouns , such as “I” ( first-person pronoun ), “you” ( second-person pronoun ), and “they” (third-person pronoun). It also affects how verbs are conjugated, due to subject-verb agreement (e.g., “I am” vs. “you are”).
In fiction, a first-person narrative is one written directly from the perspective of the protagonist . A third-person narrative describes the protagonist from the perspective of a separate narrator. A second-person narrative (very rare) addresses the reader as if they were the protagonist.
The term preferred pronouns is used to mean the (third-person) personal pronouns a person identifies with and would like to be referred to by. People usually state the subject and object pronoun (e.g., “she/her”) but may also include the possessive (e.g., “she/her/hers”).
Most people go by the masculine “he/him,” the feminine “she/her,” the gender-neutral singular “they/them,” or some combination of these. There are also neopronouns used to express nonbinary gender identity, such as “xe/xem.” These are less common than the singular “they.”
The practice of stating one’s preferred pronouns (e.g., in a professional context or on a social media profile) is meant to promote inclusion for transgender and gender-nonconforming people. The first- and second-person pronouns (“I” and “you”) are not included, since they’re the same for everyone.
In most contexts, you should use first-person pronouns (e.g., “I,” “me”) to refer to yourself. In some academic writing, the use of the first person is discouraged, and writers are advised to instead refer to themselves in the third person (e.g., as “the researcher”).
This convention is mainly restricted to the sciences, where it’s used to maintain an objective, impersonal tone. But many style guides (such as APA Style ) now advise you to simply use the first person, arguing that this style of writing is misleading and unnatural.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Caulfield, J. (2023, February 24). Third-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/nouns-and-pronouns/third-person-pronouns/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, first-person pronouns | list, examples & explanation, second-person pronouns | list, examples & explanation, what is a pronoun | definition, types & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Astrophysics
- Earth Science
- Environmental Science
- Organic Chemistry
- Precalculus
- Trigonometry
- English Grammar
- U.S. History
- World History
... and beyond
- Socratic Meta
- Featured Answers

How do you write an essay in third person?

By putting it in third person, you are able to list sources, and you are encouraged to do so. That's why you're asked to write essays in third person.
This is the way your sentence should be:
School lunches are very bad because according to The New York Times , the 2012 Healthy Hunger-Free Kids Act causes children to not like how the food tastes, and so they do not eat it.
By writing in third-person, you are able to present evidence to your reader. So when you write in third person, show what you know, with evidence backing up your points.
It won't be as redundant as saying "I think/believe" or "I feel" when we know/hope you wrote the paper and you hopefully have sources to back up your claims.
Related questions
- Question #0c999
- What is a noun phrase in linguistics?
- Why is "internet" a proper noun?
- Which proper nouns should be capitalized?
- What are some examples of plural nouns?
- Can you change a common noun to a proper noun?
- What's the definition of a proper noun?
- What are some examples of collective nouns?
- What are some examples of common nouns?
- What are some examples of compound nouns?
Impact of this question


1st, 2nd, 3rd Person
Ai generator.

Understanding the concept of person in grammar is essential for effective communication. In English , the concept of person refers to the perspective from which a speaker is speaking or being spoken to, as well as the perspective of any individuals or objects being discussed. There are three main categories of person: 1st person, 2nd person, and 3rd person. Each person perspective offers a unique viewpoint and plays a crucial role in shaping the structure and clarity of language.
What Are First, Second, and Third Person?
- First, second, and third person are grammatical categories that determine the perspective from which a speaker communicates. In first person, the speaker refers to themselves, using pronouns like “I,” “me,” and “we,” thereby expressing their own thoughts, experiences, or actions.
- Second person involves addressing the listener directly, using pronouns such as “you,” creating a sense of direct engagement or instruction.
- Third person refers to individuals or objects outside of the speaker and listener, using pronouns like “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” or “them,” allowing for observations or descriptions of others without direct involvement. These distinctions are fundamental in constructing clear and precise communication across various forms of discourse.
1st, 2nd, 3rd Person Examples
1st Person:
- I love going for walks in the park.
- We are excited about our upcoming vacation.
- I need to buy groceries after work.
- We watched a movie last night.
- I can’t wait to see my friends this weekend.
- We are planning a surprise party for her birthday.
- I enjoy cooking new recipes.
- We visited the museum downtown.
- I am working on a project for school.
- We decided to adopt a pet from the shelter.
2nd Person:
- You should try the new restaurant in town.
- Do you want to join us for dinner?
- You need to take care of yourself.
- Have you finished your homework yet?
- You seem tired; maybe you should rest.
- Did you enjoy the concert last night?
- You can ask for help if you need it.
- Do you know where the nearest pharmacy is?
- You should wear a jacket; it’s cold outside.
- Are you ready for the meeting?
3rd Person:
- He walks his dog every morning.
- She is studying for her exams.
- They went to the beach last weekend.
- The cat chased the mouse around the house.
- It is snowing heavily outside.
- He works as a teacher at the local school.
- She enjoys playing the piano in her free time.
- They are renovating their house.
- The dog barks loudly whenever someone knocks on the door.
- It seems like it’s going to rain later.
1st, 2nd, 3rd person examples for students
- I need to study for my exams.
- We are excited about our class field trip.
- I enjoy participating in extracurricular activities.
- We should start working on our group project.
- I want to improve my grades this semester.
- We are looking forward to graduation day.
- You should review your notes before the test.
- Do you want to join the debate club?
- You need to submit your assignment by Friday.
- Have you chosen your elective courses yet?
- You should ask your teacher for clarification.
- Do you enjoy participating in sports?
- He studies diligently every night.
- She participates actively in class discussions.
- They excel in sports and academics.
- The student council organizes various events throughout the year.
- It seems like he’s struggling with the coursework.
- She volunteers at the local library after school.
- They often collaborate on group projects.
- The teacher assigns homework every day.
Sentence Examples of First, Second and Third Person Pronouns
- I am going to the store.
- We are planning a trip to the beach.
- I need to finish my homework before dinner.
- You should take a break and relax.
- Do you want to go for a walk with me?
- You need to turn in your assignment by tomorrow.
- He is reading a book in the library.
- She went to the park to play with her friends.
- They are planning a surprise party for their parents.
- The cat is sleeping on the couch.
Using First, Second and Third Person Pronouns in Table – Verb Conjugation
| I walk | I am walking | |
| We walk | We are walking | |
| You walk | You are walking | |
| You all walk | You all are walking | |
| He walks | He is walking | |
| She walks | She is walking | |
| It walks | It is walking | |
| They walk | They are walking |
1st, 2nd 3rd person singular and plural
First person.
First person refers to the speaker or writer themselves.
- Pronouns: I, me, my, mine
- My book is on the table.
- Pronouns: we, us, our, ours
- We are going to the park.
- Our project is due tomorrow.
Second Person
Second person addresses the reader or listener directly.
- Pronouns: you, your, yours
- You need to complete your homework.
- Is this book yours?
- Pronouns: you, your, yours (Same as singular)
- You all are invited to the party.
- Are these pens yours?
Third Person
Third person refers to someone or something being talked about.
- Pronouns: he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its
- He is a great teacher.
- She loves her new dress.
- The dog wagged its tail.
- Pronouns: they, them, their, theirs
- They are going to the movies.
- Their house is the big one on the corner.
- First Person: The speaker includes themselves.
- Second Person: The speaker addresses the audience directly.
- Third Person: The speaker talks about others.
1st 2nd 3rd person chart
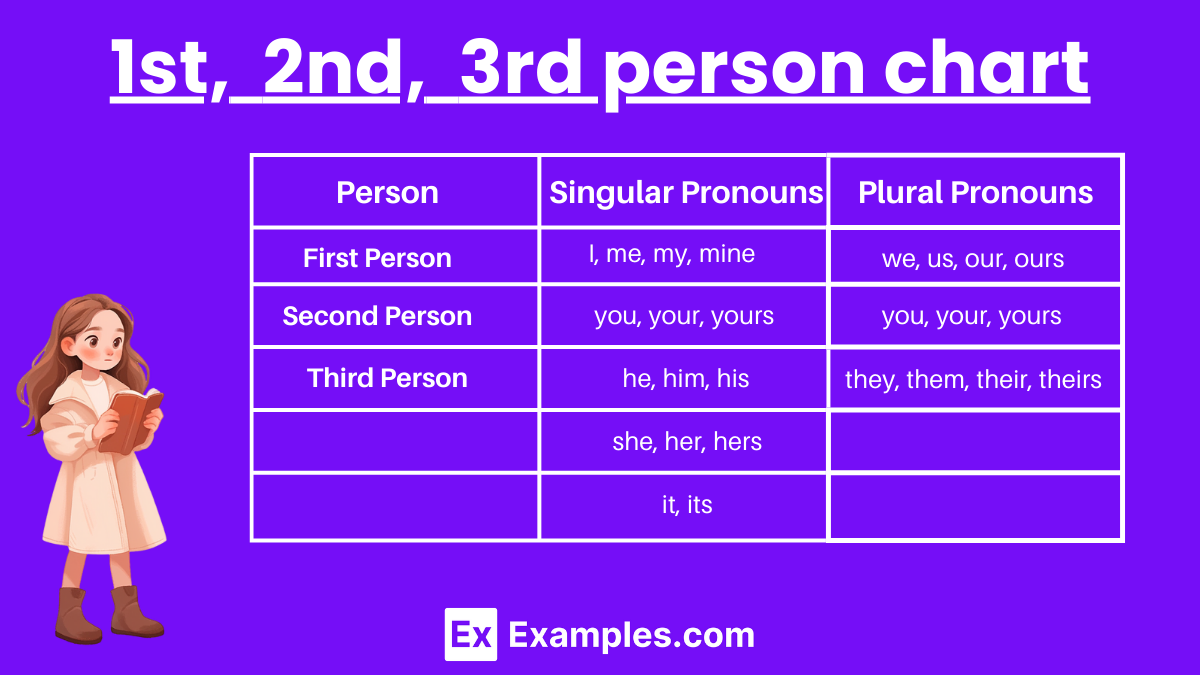
| Person | Singular Pronouns | Plural Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
| I, me, my, mine | we, us, our, ours | |
| you, your, yours | you, your, yours | |
| he, him, his | they, them, their, theirs | |
| she, her, hers | ||
| it, its |
Detailed Breakdown
First person singular.
- Subject Pronoun: I
- Object Pronoun: me
- Possessive Adjective: my
- Possessive Pronoun: mine
First Person Plural
- Subject Pronoun: we
- Object Pronoun: us
- Possessive Adjective: our
- Possessive Pronoun: ours
Second Person Singular and Plural (Same for Both)
- Subject Pronoun: you
- Object Pronoun: you
- Possessive Adjective: your
- Possessive Pronoun: yours
Third Person Singular
- Subject Pronoun (Male): he
- Object Pronoun (Male): him
- Possessive Adjective (Male): his
- Possessive Pronoun (Male): his
- Subject Pronoun (Female): she
- Object Pronoun (Female): her
- Possessive Adjective (Female): her
- Possessive Pronoun (Female): hers
- Subject Pronoun (Neutral): it
- Object Pronoun (Neutral): it
- Possessive Adjective (Neutral): its
- Possessive Pronoun (Neutral): its
Third Person Plural
- Subject Pronoun: they
- Object Pronoun: them
- Possessive Adjective: their
- Possessive Pronoun: theirs
Differentiation between 1st, 2nd, 3rd Person
| 1st Person | Narrator is a character in the story, uses “I,” “me,” “my.” | “I went to the store.” |
| 2nd Person | Narrator addresses the reader directly, uses “you.” | “You went to the store.” |
| 3rd Person | Narrator is not a character, uses “he,” “she,” “they.” | “He went to the store.” |
1st 2nd 3rd person speech
First person speech.
First person speech is used when the speaker is talking about themselves or their group.
- I am giving a presentation.
- My thoughts on this matter are clear.
- This idea is mine.
- We are organizing a meeting.
- Our team worked hard on this project.
- The success is ours.
Second Person Speech
Second person speech addresses the listener directly.
Singular and Plural
- You need to complete your assignment.
- Your feedback is appreciated.
Third Person Speech
Third person speech is used when talking about someone or something else.
- He will present his report tomorrow.
- She shared her insights on the topic.
- The cat licked its paw.
- They are planning their trip.
- The committee made their decision.
What is 1st 2nd 3rd person point of view examples
First person point of view.
First person point of view involves the narrator being a part of the story, sharing their own experiences and thoughts.
- Narrative: I walked to the store, feeling the crisp autumn air on my face. This journey was mine alone, and I relished every moment.
- Journal Entry: Today, I met an old friend. We reminisced about our school days, and I realized how much I missed those times.
- Narrative: We huddled together in the cabin, the storm raging outside. Our fears were shared, but so was our determination to survive.
- Diary Entry: Our team won the championship today! We celebrated our victory, knowing it was ours to cherish forever.
Second Person Point of View
Second person point of view directly addresses the reader, making them a part of the story.
- Narrative: You open the door and step into the dark room. Your heart races as you feel the presence of something unseen.
- Instructional: To bake the perfect cake, you need to follow these steps carefully. First, gather all your ingredients.
Third Person Point of View
Third person point of view involves the narrator being outside the story, describing the characters and events.
- Narrative: He glanced at his watch, realizing he was late. She hurried through the crowded streets, her thoughts racing with worry.
- Descriptive: The cat stretched lazily on its perch, basking in the sunlight.
- Narrative: They gathered around the campfire, sharing stories of their adventures. Their laughter echoed in the night air.
- Historical Account: The settlers faced many hardships, but their resilience and determination carried them through.
Check Your Understanding of First, Second and Third Person Pronouns
Practice exercise.
Identify the pronouns in the following sentences and determine if they are first, second, or third person pronouns:
- Answer: First person plural (we)
- Answer: Second person singular/plural (you, your)
- Answer: Third person singular (he, his)
- Answer: Second person singular/plural (you), First person singular (me)
- Answer: Third person plural (they, their)
- Answer: First person singular (I, my, I)
When should I use the first person point of view?
Use the first person when you are sharing personal experiences, opinions, or writing autobiographies.
What is the second person point of view?
The second person point of view uses the pronoun you. It directly addresses the reader or listener.
What is the third person point of view?
The third person point of view uses pronouns like he, she, it, and they. It’s used when the speaker or writer is referring to someone else.
When should I use the third person point of view?
Use the third person in formal writing, academic papers, fiction, and biographies.
Can first person be used in academic writing?
While typically avoided in academic writing, first person can be used when describing personal experiences or reflections relevant to the topic.
Why is third person preferred in formal writing?
Third person maintains objectivity and formality, which is often required in academic and professional writing.
How do first person and third person differ in storytelling?
First person provides an intimate, subjective perspective, while third person offers a broader, more objective view.
What are the risks of using second person in fiction?
Second person can be jarring or off-putting if not done well, as it directly involves the reader in the story, which not all readers enjoy.
Are there genres that favor specific points of view?
Yes, for example, memoirs and autobiographies favor first person, self-help books often use second person, and novels typically use third person.
How does point of view affect reader engagement?
First person can create a deep connection with the narrator, second person can draw readers in by addressing them directly, and third person can provide a comprehensive understanding of the story.
What is an omniscient third person point of view?
An omniscient third person narrator knows all the thoughts, actions, and feelings of every character in the story.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Advertisement
Supported by
An Essayist Who Revels in Glorious Chaos
In her third essay collection, the poet and critic Elisa Gabbert celebrates literature and life through a voracious engagement with the world.
- Share full article

By Lily Meyer
Lily Meyer is a writer, critic and translator. Her debut novel, “Short War,” came out in April.
ANY PERSON IS THE ONLY SELF: Essays , by Elisa Gabbert
“Any Person Is the Only Self,” the poet and critic Elisa Gabbert’s third collection of nonfiction, opens with an essay that should be, but isn’t quite, a mission statement. She starts by describing the Denver Public Library’s shelf for recent returns, a miscellaneous display of disconnected works she habitually browsed in the years she lived in Colorado. In part, Gabbert (who is also the Book Review’s poetry columnist) was drawn to the shelf for its “negative hype,” its opposition to the churn of literary publicity. But mainly, she enjoyed playing the odds. “Randomness is interesting,” she writes; “randomness looks beautiful to me.” At the essay’s end, she declares, “I need randomness to be happy.”
So does her prose. When “Any Person Is the Only Self” embraces the random, it’s terrific. When Gabbert neatens or narrows her essays, though, they can feel more dutiful.
“Any Person Is the Only Self” — a seemingly random title, and one to ignore; it’s fussier and vaguer than any of Gabbert’s actual prose — is primarily a collection about reading, akin to Anne Fadiman’s “Ex Libris” or Alejandro Zambra’s “Not to Read.” But it is also a loose meditation on the coronavirus pandemic and its impact on Gabbert’s life. During lockdown, she found herself yearning for the “subconscious energy” she gets “from strangers and from crowds, a complicating energy that produces ideas,” and relying on literature as a replacement. She developed a habit of listening to many hours of author interviews, seeking the social life she couldn’t have in person.
Unsurprisingly, this led to some soul-searching on the subject of writing, which appears in the gloriously scattershot “Somethingness (or, Why Write?).” In this essay, Gabbert is at her best. She strings together more than 30 writers’ reasons for writing, variously testing, mocking, admiring and relating to them. In doing this, she gives readers a kaleidoscopic view of ambition and inspiration, always looking toward the random or inexplicable elements of both. In her own case, she adds, she’s become obsessed with leaving behind a body of work, which, she’s decided, is “seven books, even short, minor books. … When I finish, if I finish, seven books I can retire from writing, or die.”
“Any Person Is the Only Self” is Gabbert’s seventh book, and although nothing about it is morbid, death shadows the text throughout. Of course, reflecting on Covid invites thoughts of mortality, but she also writes about her father-in-law’s passing, Sylvia Plath’s suicide and the recent trend of denouncing books by dead writers, as if it were “poor form to die.” (Gabbert, rightly, judges this both tacky and strange.)
But in literature, Gabbert finds not only life after death — she talks about the “metalife” of writing — but also a reason to live and engage with the world. “Any Person Is the Only Self” seems decidedly unlike the work of somebody who plans to retire from writing. Rather, it feels like an expression of gratitude for both the act of reading in itself and for reading as a route to conversation, a means of socializing, a way to connect.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

COMMENTS
Use third person for all academic writing. For formal writing, such as research and argumentative papers, use the third person. Third person makes writing more objective and less personal. For academic and professional writing, this sense of objectivity allows the writer to seem less biased and, therefore, more credible.
Third-person writing is a style of writing that involves using pronouns such as "he," "she," "it," "they," or "one" to refer to individuals or objects instead of using first- or second-person pronouns like "I," "me," "we," "us," "you," or "your.". Third-person language is commonly used in academic ...
In a story, narrators use the third person if they are not part of the story themselves. Third-person narratives show us a person's actions, feelings, and thoughts. Example of how to write in third person: Nadia dreamt about being a gymnast her entire life. Ever since she can remember, she's worked hard, sacrificed a lot, and hoped someone ...
6 tips for writing in third-person. 1. Understand your voice won't always shine in your essays. Every single piece of writing tends to have a voice or point of view as if you're speaking to the reader directly. However, that can't always happen in academic writing as it's objective compared to a novel, for example.
1. Third Person Objective Point of View. The third person objective POV is a way to tell your story by giving the reader all the details within the scenes without including what is going on in the characters' minds. To write in the third person objective POV, you will need to create an unbiased narrator who doesn't tell the reader the ...
Third Person Omniscient. The third person omniscient point of view frequently appears in fiction writing. With this style, an all-knowing narrator has the ability to get inside any character's head. That's why an omniscient point of view can be thought of as "head-hopping.". The narrator has knowledge of everything.
Tip 1: Use third-person determiners and pronouns. In grammar, determiners introduce and modify nouns. They're used to specify what a noun refers to (like " my laptop") or the quantity of it (like " many sandwiches"). Meanwhile, pronouns are substitutes for nouns, referring to people, places, or things. For example, "Caroline [noun ...
In literature, third-person point of view follows multiple characters and narrative arcs, zooming in and out of a story the way a camera does in a movie. A third-person narrator can be all-knowing (aware of every character's thoughts and feelings) or limited (focused on a single character, or aware only what certain characters say and do).
8 Tips for Writing in Third-Person Point of View. As the author of a novel, you get to decide who tells your story. Writing in the third-person point of view is like hearing an announcer call a sporting event—a narrator gives a play-by-play of the plot from an outside perspective. As the author of a novel, you get to decide who tells your story.
Third-Person Point of View. Many academic disciplines ask their writers to use third person point of view (POV). If so, then writing in the third person is important because your writing will appear professional and credible. You may occasionally use first person POV to create a more personal tone, or second person POV to command a reader to do ...
Third-person writing uses the pronouns they, him, her, and it, as well as proper nouns. This is the type of writing you would see in a novel with an outside narrator. Example: Teachers and students agree that third-person writing makes essays sound better. Here's one last video example, this one using third-person perspective, from the man ...
Writing in third person can give your reader the unique perspective of an outsider looking. Explore these notable examples of writing in third person.
First, Second and Third Person Definitions. Three different points of view exist: first person, second person and third person. First person reflects the writer's voice with pronouns such as: I. me. we. us. Second person speaks directly to a reader, using pronouns such as "you" and "your." Third person uses a more general voice that reflects ...
When writing in third person, speak with authority. Show your reader that the narrator's voice is trustworthy. Give them the inner thoughts of at least one character. The main narrator voice you use will give them the idea that you are in-the-know and can carry them well through the events to come. 2.
Third Person. Third-person point of view identifies people by proper noun (a given name such as Shema Ahemed) or noun (such as teachers, students, players, or doctors) and uses the pronouns they, she, and he.Third person also includes the use of one, everyone, and anyone. Most formal, academic writing uses the third person. Note the use of various third-person nouns and pronouns in the following:
Personal writing, such as for a reflective essay, or a "personal response" discussion posting, can be written in the first person (using "I" and "me"), and may use personal opinions and anecdotes as evidence for the point you are trying to make. ... Third person correction (appropriate for all other academic writing): Shakespeare's play Hamlet ...
First person perspective is when "I" am telling the story. The character is in the story, relating his or her experiences directly. Second person point of view. The story is told to "you.". This POV is not common in fiction, but it's still good to know (it is common in nonfiction). Third person point of view, limited.
First-person narrative: The use of the pronoun 'I' (singular) or 'we' (collective) to communicate or narrate from a subjective point of view. Second-person narrative: The use of the pronoun 'you' (singular or collective) to communicate or narrate in a way that directly addresses the reader. Third-person narrative: The use of ...
The third person point of view in an essay is characterized by the use of personal pronouns such as he, she, they or one rather than I, we or you. Formal essays as well as some types of informal essays are typically written in the third person. The third person can apply to single-paragraph essays as well as more common, longer essay formats.
I am speaking to you about her. ("I" is the speaker, so "I" is in the first person. "You" is the person being spoken to, so "you" is in the second person. "Her" is in the third person.) Whenever you use a noun (as opposed to pronoun like above), then the noun is in the third person. For example: The policeman is speaking to the teacher about Anne.
Third Person Point of View. In third-person narration, the narrator exists outside the events of the story, and relates the actions of the characters by referring to their names or by the third-person pronouns he, she, or they. Third-person narration can be further classified into several types: omniscient, limited, and objective.
Revised on February 24, 2023. Third-person pronouns are words such as "she," "it," and "they" that are used to refer to other people and things that are not being directly addressed, without naming them specifically with a noun. Like first- and second-person pronouns, they are a type of personal pronoun.
Answer link. Third person point of view is when you are writing with third person pronouns (he, she, one, etc.) When you write an essay in third person, you do not refer to yourself in the essay, but instead use sources while writing. For example, this is not the way you write a sentence in your essay with third person: I feel as if school ...
Understanding the concept of person in grammar is essential for effective communication. In English, the concept of person refers to the perspective from which a speaker is speaking or being spoken to, as well as the perspective of any individuals or objects being discussed.There are three main categories of person: 1st person, 2nd person, and 3rd person.
"Any Person Is the Only Self," the poet and critic Elisa Gabbert's third collection of nonfiction, opens with an essay that should be, but isn't quite, a mission statement.