- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

How Apple Is Organized for Innovation
- Joel M. Podolny
- Morten T. Hansen

When Steve Jobs returned to Apple, in 1997, it had a conventional structure for a company of its size and scope. It was divided into business units, each with its own P&L responsibilities. Believing that conventional management had stifled innovation, Jobs laid off the general managers of all the business units (in a single day), put the entire company under one P&L, and combined the disparate functional departments of the business units into one functional organization. Although such a structure is common for small entrepreneurial firms, Apple—remarkably—retains it today, even though the company is nearly 40 times as large in terms of revenue and far more complex than it was in 1997. In this article the authors discuss the innovation benefits and leadership challenges of Apple’s distinctive and ever-evolving organizational model in the belief that it may be useful for other companies competing in rapidly changing environments.
It’s about experts leading experts.
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Major companies competing in many industries struggle to stay abreast of rapidly changing technologies.
One Major Cause
They are typically organized into business units, each with its own set of functions. Thus the key decision makers—the unit leaders—lack a deep understanding of all the domains that answer to them.
The Apple Model
The company is organized around functions, and expertise aligns with decision rights. Leaders are cross-functionally collaborative and deeply knowledgeable about details.
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to 137,000 employees and $260 billion in revenue in 2019. Much less well-known are the organizational design and the associated leadership model that have played a crucial role in the company’s innovation success.
- Joel M. Podolny is the dean and vice president of Apple University in Cupertino, California. The former dean of the Yale School of Management, Podolny was a professor at Harvard Business School and the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
- MH Morten T. Hansen is a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, and a faculty member at Apple University, Apple. He is the author of Great at Work and Collaboration and coauthor of Great by Choice . He was named one of the top management thinkers in the world by the Thinkers50 in 2019. MortentHansen
Partner Center
Table of Contents
Apple target audience , marketing strategy of apple, 5 key takeaways from apple marketing strategy, a case study on apple marketing strategy.

Breaking through with several inventions in the world of technology, Apple Inc. has been carving infinite milestones ever since its inception. Even though its innovations speak for themselves, this highly-valued giant corporation has invested heavily in its marketing team to soar high up as a tech maestro. Apple Inc. realized the role of brand marketing in the success of a venture from the start as a crucial way to connect with its target audience. This brand's marketing is so vigorously carried out and well-thought that it is often an inspiration and a place of research for marketing professionals. Here we bring you a well-curated case study on Apple's marketing strategy, the key takeaways to learn from this venture, and how to incorporate the same in your business and marketing strategies.
Become a Certified Marketing Expert in 8 Months
To understand its key strategies for marketing Apple products, let's first understand what Apple's target audience is like. Apple's target audience consists of middle-class and upper-class users who can pay higher for products that provide them with an incredible user experience. This means that these users have a higher disposable income and are willing to pay more for as high-priced products as Apple's.
Let's take a look at Apple's target audience with this comprehensive analysis sourced from Business Research Methodology's report on Apple Segmentation :
| Areas | Urban |
| Gender | All |
| Age | 20-45 |
| Life phase | Bachelors to Married both |
| Earnings | High |
| Jobs | Working professionals, managers & executive level workers |
Besides this primary classification, Apple also explicitly targets professionals working in specialized software like music, video, photography and all kinds of design careers. These working professionals prefer Adobe’s Final Cut, Photoshop and related editing software which work well with Macbooks and IPads than other operating systems.
Even better, business professionals prefer Apple products such as iPods and Macbooks for their day-to-day work. Products like iPads and Macbooks are lighter and portable, so they are often selected by students (upper-class), educational institutions and teaching.
Now coming to the marketing strategy of Apple, it is a combination of well-designed products with the right user experience, promotional campaigns, distribution, and pricing. Let’s take a look at all these features of Apple marketing strategy in detail:
Focus on Finer User Experience
Apple’s branding strategy is based on its stylish, more straightforward and lush products that focus on providing a user interface that is very simple to use and learn. They are lighter, easy to carry as well as durable. This minimal look and user experience makes it a perfect sell to its target audience, which comes from the middle to upper class.
Suave Yet Simple Advertising
Storytelling is such an essential part of every Apple ad as well as a marketing campaign. Often these ads focus on minimal design as well as high-quality images. They are either blended with music or a simple story. Apple consciously ensures that its advertising and marketing don’t use too much jargon or filler language in its ads. Instead, it shines a light on the product to let it speak for itself without showing what the price is like or using complicated words for its features.
Targeting the Right Markets
Apple is excellent at tapping into its target audiences like a genuine tech witch who knows their aspirations, preferences and pain points! Its market research is always on-point and crystal clear in its products, curation, and features.
Here are the major critical takeaways from Apple Marketing Strategy:
- Tapping into your target markets and audience is the key to curating and selling user experiences that value the preferences of its people.
- With simplicity and finesse in design, the right products with minimal designs and features can create a perfect impact for your brand.
- Incorporating emotion in your advertising and marketing can also help you connect with your audience better.
- Don’t exaggerate the copy and conceptualizing of your advertising and marketing campaigns and prefer the “less is more” approach. Create shorter yet emotional and empathetic ads to captivate your target audience.
- When you create an international brand value through quality and minimal, sophisticated design, you don’t need to compete in terms of price. Instead, your price will set you apart for your user experience and design features.
Become a millennial Digital Marketer in just 6 months. Enroll now for our PGP in Digital Marketing course in collaboration with Purdue University!
Thus, we hope we have helped you understand what Apple’s marketing strategy is about! Want to read more case studies about top brands and their marketing strategies? Join Simplilearn’s specialized PGP Digital Marketing certification in collaboration with Meta Blueprint and Harvard Publishing. This certification can help you level up your career in digital marketing through case studies, industry projects, masterclasses from industry experts, ad marketing tools from Facebook, Google, and related marketing tools.
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 1,699 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 999 |
Recommended Reads
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
Apple Interview Questions 2024
12 Powerful Instagram Marketing Strategies To Follow in 2021
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
Walmart Marketing Strategy
What is Digital Marketing and How Does It Work?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

Apple’s Product Development Process – Inside the World’s Greatest Design Organization
Apple’s Product Development Process may be one of the most successful design processes ever implemented. With a valuation that exceeds $2 trillion, there’s a lot that designers can learn from Apple and introduce into their own design environments.
Apple is a notoriously secretive business. In Steve Jobs’ time at the company it would have been near impossible to find out about the internal workings of the business. This isn’t surprising when a business’s market advantage is its design approach. It’s worth keeping it under wraps.
However, Adam Lashinsky, the author of Inside Apple: How America’s most Admired and Secretive Company Really Works has been given a look at the process. While there are still aspects of the way that Apple works that are shrouded in secrecy , you can get a good idea of the overall high level process through this book. And in this article, we’ve distilled the key takeaways from the book.
Apple’s Product Development Process
Design is at the forefront.

Author/Copyright holder: GiuliaPiccoliTrapletti . Copyright terms and licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
How do you give designers the freedom to design and ensure that the products they produce fulfil their visions? Well at Apple they put design at the forefront.
Jony Ive, the British designer who was the Chief Design Officer (CDO) at Apple, and his design team do not report to finance, manufacturing, etc. They are given free rein to set their own budgets and are given the ability to ignore manufacturing practicalities.
At the heart of the design department is the Industrial Design Studio where only a select few Apple employees have access.
It’s a simple concept that allows for the creation of incredible products.
Design Teams are Separated From the Larger Company
When a design team works on a new product they are then cut off from the rest of the Apple business. They may even implement physical controls to prevent the team from interacting with other Apple employees during the day.
The team is also removed from the traditional Apple hierarchy at this point. They create their own reporting structures and report directly to the executive team. This leaves them free to focus on design rather than day-to-day minutiae.
A Documented Development Process

Author/Copyright holder: Ed Uthman . Copyright terms and licence: CC BY-SA 2.5
The Apple New Product Process (ANPP) information is given to a product development team when they begin work. It details every stage of the design process and it goes into elaborate detail. The idea is to define what stages the product creation team will go through, who will be responsible for delivering the final product, who works on which stage and where they work and also when the product is expected to be completed.
Monday is Review Day
The Apple Executive Team holds a regular Monday meeting to examine every single product that the company has in design phase at that point in time. This isn’t as daunting as it may sound; one of the keys to Apple’s success is that they don’t work on hundreds of new products at once. Instead, resources are concentrated on a handful of projects that are expected to bear fruit rather than being diluted over many lesser projects.
If a product cannot be reviewed at one meeting – it’s automatically at the top of the agenda for the next meeting. In practice, this should mean that every single Apple product is inspected by the executive team at least once a fortnight. This keeps delays in decision making to a minimum and enables the company to be very lean with its approach to design.
The EPM and the GSM
The EPM is the engineering program manager and the GSM is the global supply manager. Together they are known within Apple as the “EPM Mafia”. It’s their job to take over when a product moves from design to production.
As you might expect, these people are usually going to be found in China, Apple does very little of its own manufacturing. Instead it relies on contract outsourcing companies like Foxconn (one of the largest employers in the world) to do this for them. This removes much of the headache of manufacturing for Apple whilst keeping production costs as low as possible. There is a significant market advantage to this approach and its one that many other electronics manufacturers are emulating now.
The EPM Mafia may sound scary (and they probably are to the suppliers) but their real job is simply to ensure that products are delivered to market in the right way, at the right time and at the right cost. They may disagree at points but their guiding principle is to act in the interests of the product at all times.
Iteration Is Key
Like any good design company , the design process at Apple is not over when manufacturing begins. In fact, Apple iterates the design throughout manufacturing. The product is built, it’s tested and reviewed, then the design team improves on it and it’s built all over again. These cycles take 4-6 weeks at a time and may be run many times over a product’s development lifecycle.

Author/Copyright holder: CyberDoc LLC . Copyright terms and licence: Fair Use.
When production is complete the EPM will take possession of some or all of the test devices and then take them back to Apple’s headquarters at Cupertino.
This is a very costly approach but it’s one of the reasons that Apple has a reputation for quality. The more you invest in design, the more likely you are to build incredible market changing products. It’s the process that the iPod, the iPhone and the iPad went through.
The Packaging Room
This is a very-high security area in Apple and it’s where prototypes are unboxed. As you might expect, the security is to prevent leaks to the outside world. If you ever do see a leaked prototype for an Apple product – it won’t have come from here. It’s more likely to have vanished from a production line in China.
A Launch Plan

Author/Copyright holder: Manutaus. Copyright terms and licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
The final step in Apple’s product development is product launch. When the product is considered to be as good as it can be – it enters an action plan known as “the Rules of the Road”. This explains all the responsibilities and actions that must be taken prior to a commercial launch of the product.
It must be a nerve-wracking experience to be privy to the “Rules of the Road” because if you lose it or leak it… you’re immediately fired. This is explained in the document itself.
The Take Away
Apple’s process is complex, expensive and demanding. If you compare it to most business theories – it shouldn’t work. However, to date it has out-performed even the wildest of expectations.
You may not be able to emulate all of their processes within the space of your own workplace but there’s no reason that you can’t develop written processes for design phases and launch phases of your projects, for example. And, of course, there is no reason at all for you in not iterating!
The more you know about successful design processes, the more you can take some of the best aspects of them and use them to enhance your own products.
Find out all the details of the design process in: Inside Apple: How America's Most Admired--and Secretive--Company Really Works by Adam Lashinsky ISBN 97814555512157, Published January 25, 2012
And take an insight into Apple’s greatest designer’s mind in : JonyIve: The Genius Behind Apple's Greatest Products by Leander Kahney ISBN 159184617X, Published November 14, 2013
Hero Image: Author/Copyright holder: Sreejithk2000. Copyright terms and licence: Public Domain.
Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide

Get Weekly Design Tips
Topics in this article, what you should read next, what is interaction design.

- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Graphic Design to UX Design
Shneiderman’s Eight Golden Rules Will Help You Design Better Interfaces

- 1.3k shares
The Principles of Service Design Thinking - Building Better Services

A Simple Introduction to Lean UX
- 3 years ago
Dieter Rams: 10 Timeless Commandments for Good Design

- 4 years ago
The 7 Factors that Influence User Experience
- 1.2k shares
Adaptive vs. Responsive Design
The Grid System: Building a Solid Design Layout
10 Free-to-Use Wireframing Tools [Updated for 2024]

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

- International Marketing
Apple’s Global Strategy: Simplicity, Innovation, and Adaptability
- January 19, 2024
- LinkedIn 24
Table of Contents
Delving into apple’s global strategy, apple’s core values and the simplicity mantra, apple’s global branding strategy, apple’s global marketing strategy, case studies, apple’s global tax strategy.
- The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strateg
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Apple stands as a beacon of innovation and design, captivating consumers worldwide with its sleek products and user-centric approach. With a global presence spanning over 150 countries and an estimated $383.29 billion in revenue in 2023, according to Statista , Apple’s success is a testament to its astute global strategy , a harmonious blend of differentiation, adaptability, and unwavering commitment to quality.
Apple’s global strategy is rooted in the concept of “differentiation,” a strategic approach that sets it apart from its competitors. By consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation, Apple has carved a niche for itself, offering products that are not only technologically advanced but also aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly . This differentiation has allowed Apple to capture a loyal customer base and establish a strong brand identity across the globe .
Apple’s global strategy has evolved over time, adapting to the changing dynamics of the international market. In its early days, the company focused heavily on innovation, relentlessly pursuing cutting-edge technologies and groundbreaking designs. However, as the company matured, it recognized the importance of customer experience and began placing a greater emphasis on this aspect . Today, Apple’s global strategy is a seamless blend of innovation and customer focus, ensuring that its products and services align with the needs and preferences of consumers worldwide.
At the heart of Apple’s global success lies a set of core values that permeate every aspect of the company’s operations , from product design to marketing campaigns. These values, deeply rooted in the company’s identity, guide Apple’s approach to innovation, customer experience, and global expansion.
- Accessibility: Apple strives to make its products and services accessible to everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. This commitment is evident in features like VoiceOver , which provides spoken feedback for visually impaired users, and AssistiveTouch , which allows users with limited mobility to control devices with gestures.
- Educational Support: Apple recognizes the transformative power of technology in education and actively supports initiatives that promote digital literacy and learning. The company’s initiatives include Apple Teacher certification programs, curriculum resources, and educational apps that enhance teaching and learning.
- Carbon Neutrality: Apple is committed to reducing its environmental impact and is working towards becoming carbon neutral by 2030 . The company has implemented numerous initiatives to minimize its carbon footprint, including transitioning to renewable energy sources, designing energy-efficient products, and recycling materials.
- Inclusive Work Environment: Apple is committed to creating a diverse and inclusive workplace where everyone is valued and respected. The company has implemented policies and programs that promote diversity hiring, provide equal opportunities for advancement, and foster a culture of inclusion.
- Privacy: Apple is a staunch advocate for user privacy and believes that individuals should have control over their personal data. The company has implemented robust privacy protections in its products and services, including encryption, data minimization, and transparency.
- Equity and Justice: Apple is committed to promoting equity and justice in its operations and throughout the world. The company supports initiatives that address social and economic inequalities, promotes human rights, and advocates for environmental sustainability.
- Supplier Responsibility: Apple is committed to ensuring that its suppliers adhere to high ethical standards and treat their workers with respect. The company has established stringent supplier codes of conduct and conducts regular audits to monitor compliance.
These core values, collectively, form the foundation of Apple’s global strategy. They guide the company’s product design, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions , ensuring that Apple delivers products and experiences that are not only technologically advanced but also aligned with its values of simplicity, accessibility, and inclusivity.
Simplicity is a cornerstone of Apple’s design philosophy, evident in the clean aesthetics, intuitive interfaces, and user-friendly features of its products. This emphasis on simplicity has resonated with consumers worldwide , making Apple products accessible to a broad audience and fostering a loyal customer base.
By upholding its core values and embracing simplicity, Apple has not only achieved global success but also established itself as a role model for other companies seeking to build a sustainable and ethical business model.
Apple’s global branding strategy is a delicate balance of standardization and adaptation, ensuring that the company maintains a consistent brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse cultures and markets. On the one hand, Apple strives to project a unified brand image, conveying its core values of innovation, simplicity, and elegance across all its products, marketing campaigns, and customer interactions. This standardization helps reinforce Apple’s reputation for quality and consistency, fostering brand loyalty and recognition worldwide.
On the other hand, Apple recognizes the need to adapt its branding to local markets and cultures. This adaptability is evident in the company’s product offerings, marketing messages, and customer support. For instance, Apple has developed localized versions of its products with features and specifications tailored to specific regions . Additionally, the company’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level.
Apple’s ability to balance standardization and adaptation has been a key factor in its global success. By maintaining a consistent brand identity, the company has built a strong foundation of brand recognition and loyalty . However, by adapting to local markets, Apple has been able to cater to the needs and preferences of consumers in different parts of the world, expanding its reach and deepening its customer base.
Examples of Apple’s Standardization
- Unifying Brand Elements: Apple employs a consistent design language across its products, including clean aesthetics, minimalist interfaces, and sleek silhouettes. This consistent visual language helps establish a cohesive brand identity.
- Global Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns often feature universal themes of innovation, creativity, and personal empowerment, appealing to a global audience.
- Seamless Customer Experience: Apple’s customer support is available in multiple languages, and the company’s online store can be accessed in over 40 countries, ensuring a consistent experience for customers worldwide.
Examples of Apple’s Adaptation
- Localization of Products: Apple offers localized versions of its products, such as the iPhone and iPad, with features and specifications tailored to specific regions. For instance, the iPhone SE 2020 is optimized for Indian consumers with support for two SIM cards and regional cellular bands.
- Culturally Sensitive Marketing: Apple’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level. For example, the company’s “ Shot on iPhone ” campaign features images captured by photographers from around the world, showcasing the diversity of visual storytelling.
- Localized Customer Support: Apple provides customer support in multiple languages and offers localized resources, such as online FAQs and tutorials, tailored to specific regions. The company also partners with local businesses to offer personalized support services.
Apple’s success in balancing standardization and adaptation is a testament to its understanding of the complexities of global branding. By striking this delicate balance, the company has been able to maintain a strong brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse markets , solidifying its position as one of the world’s most recognizable brands.
Apple’s global marketing strategy is a multifaceted approach that revolves around four key pillars: wide acceptance, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation . These pillars are intertwined, working together to propel Apple’s success in the global marketplace.
Wide Acceptance
Apple’s products have achieved widespread acceptance worldwide, attracting a loyal customer base across diverse demographics and regions . This widespread appeal is attributed to several factors, including:
- Innovative Designs: Apple consistently pushes the boundaries of design, creating products that are both aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. The company’s sleek, minimalist aesthetic has become synonymous with Apple’s brand identity.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Apple’s products are renowned for their intuitive interfaces, making them easy to navigate and use for people of all technical backgrounds.
- Effective Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns are known for their creativity and emotional appeal, resonating with consumers on a personal level. The company often uses storytelling and cultural references to connect with diverse audiences.
Brand Value
Apple has built a strong brand value over the years, characterized by perceptions of quality, innovation, and premium craftsmanship . This brand value has been instrumental in attracting consumers and fostering brand loyalty.
- Reputation for Quality: Apple is consistently rated among the most reliable and durable consumer electronics brands. This reputation for quality has earned the company a loyal following among consumers who value long-lasting products.
- Innovation: Apple is renowned for its pioneering spirit, consistently introducing innovative products that redefine the technological landscape. This focus on innovation has helped maintain Apple’s cutting-edge reputation and attract early adopters.
- Premium Branding: Apple’s products are positioned in the premium segment of the market , commanding higher prices than its competitors. This premium positioning contributes to the company’s brand value and reinforces its image as a luxury brand.
Competitive Advantage
Apple maintains a competitive advantage in the global market through a combination of factors, including:
- Strategic Product Differentiation: Apple differentiates its products from competitors through unique features, design elements, and user experiences. This differentiation strategy has helped the company carve out a distinct niche in the market.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Apple prioritizes customer satisfaction, creating a seamless and personalized experience for its users. This focus on customer experience has helped foster brand loyalty and attract new customers.
- Global Retail Presence: Apple has a strong global retail presence, with over 500 stores in 23 countries, as per Statista . This extensive retail network provides consumers with easy access to Apple products and services.
Low Imitation
Despite facing intense competition from numerous technology giants, Apple has been able to maintain a relatively low level of imitation . This is due to several factors, including:
- Continuous Innovation: Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation makes it difficult for competitors to replicate its products and services.
- Strengthened Intellectual Property Protection: Apple has a robust intellectual property portfolio, providing legal protection for its innovative designs and technologies.
- Brand Loyalty: Apple’s loyal customer base is less susceptible to imitation, as they are often willing to pay a premium for Apple products due to their brand loyalty and trust in the company.
Apple’s successful global marketing strategy is a testament to its ability to balance innovation, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation. By consistently delivering high-quality products, cultivating a strong brand reputation, and prioritizing customer experience, Apple has cemented its position as one of the world’s leading technology companies .
Apple’s remarkable global success is evident in its ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India. These two countries represent two of the world’s most populous and rapidly growing economies, offering significant opportunities for technology companies. Apple’s success in these markets is a testament to its ability to adapt its global strategy to local conditions and preferences .
China has become Apple’s second-largest market , with over 190 million active iPhones in use as of 2023 ( Statista , 2023). Apple’s success in China can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Pricing Strategy: Apple has adopted a tiered pricing strategy in China, offering a wider range of products at lower price points to cater to a broader range of consumers.
- Distribution Channels: Apple has established a strong network of authorized resellers and retail stores in China, making its products readily available to consumers across the country.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Chinese telecommunications companies, e-commerce platforms, and content providers to expand its reach and customer base.
- Localization: Apple has made sure to localize its products , marketing campaigns, and customer support for the Chinese market, ensuring that they resonate with local consumers.
Despite facing challenges such as piracy and counterfeiting, Apple has successfully established itself as a premium brand in China . The company’s commitment to innovation, design, and customer experience has resonated with Chinese consumers, who are increasingly embracing technology.
India is another key market for Apple, with a growing middle class and increasing smartphone penetration. Apple’s strategy in India has focused on tailoring its products and services to the specific needs and preferences of Indian consumers .
- Price Sensitivity: Apple has introduced more affordable iPhone models in India, such as the iPhone SE, to attract price-conscious consumers.
- Online Sales: Apple has heavily invested in its online presence in India, making it easier for consumers to purchase its products online.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Indian e-commerce platforms, mobile carriers, and banks to expand its distribution reach and payment options.
- Localization: Apple’s localization strategy for the Indian market has included the adaptation of its products, marketing campaigns, and customer support, including the development of Hindi-language versions of its software.
Apple’s success in India has been gradual but steady. The company has faced challenges such as competition from local smartphone brands and a lack of brand recognition in rural areas. However, Apple’s commitment to innovation and adaptation has helped it gain traction in this emerging market .
Apple’s global success has been accompanied by scrutiny over its tax practices, particularly its use of a subsidiary company in Ireland to minimize its global tax liability. This strategy, known as “ Double Irish with a Dutch Sandwich ,” has allowed Apple to shift profits offshore, effectively reducing its tax payments in the United States and other countries .
While Apple has defended its tax strategy, arguing that it complies with all applicable laws, it has faced criticism from governments, tax experts, and consumer advocacy groups . Critics argue that Apple’s tax practices amount to corporate tax avoidance, depriving governments of revenue that could be used for public services.
Advantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has several potential advantages for the company, including:
- Reduced Tax Burden: By shifting profits offshore, Apple can effectively reduce its tax payments, which can boost its profitability and financial returns to shareholders.
- Increased Competitiveness: Lowering tax costs can give Apple a competitive advantage over other companies, allowing it to invest more in research and development, marketing, and product development.
- Enhanced Shareholder Value: By reducing its tax burden and increasing profitability, Apple can improve its financial performance and boost shareholder value.
Disadvantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has also been criticized for several potential disadvantages, including:
- Public Image Concerns: Apple’s tax practices have tarnished its public image, raising concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior.
- Legal Challenges: Governments and tax authorities around the world have been investigating Apple’s tax strategy, and the company faces potential legal challenges that could lead to fines and penalties.
- Political Fallout: Apple’s tax practices have created political tensions, with some countries considering imposing stricter tax laws to prevent multinational corporations from shifting profits offshore.
A Balancing Act
Apple’s global tax strategy has been a source of controversy, highlighting the delicate balance between corporate profitability and societal responsibility . While the company may benefit financially from its tax practices, it also faces reputational risks and potential legal repercussions. Apple must carefully navigate this complex landscape to maintain its global success while addressing concerns about its ethical conduct.
The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strategy
Apple’s journey to becoming one of the world’s most recognizable and successful companies is a testament to its ability to balance simplicity, innovation, and adaptability. From its early days as a niche computer manufacturer to its current status as a global technology powerhouse, Apple has consistently demonstrated its knack for understanding and meeting the evolving needs of consumers worldwide .
Apple’s core values, particularly its emphasis on simplicity, have permeated every aspect of its business. The company’s products are renowned for their user-friendly interfaces and intuitive designs , making them accessible to a wide range of users, regardless of their technical expertise. This commitment to simplicity extends to Apple’s marketing campaigns, which often use storytelling and emotional appeals to resonate with consumers on a personal level.
Apple’s unwavering focus on innovation has been another driving force behind its global success. The company has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, introducing groundbreaking products that have transformed the way people interact with the digital world . From the revolutionary iPhone to the sleek AirPods, Apple has consistently redefined the standards for innovation in the technology industry.
Alongside innovation and simplicity, Apple has also demonstrated remarkable adaptability in its global expansion . The company has successfully tailored its products, marketing strategies, and customer support to suit the unique needs and preferences of different cultures. This adaptability has been crucial in Apple’s ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India, where local competitors pose significant challenges.
Apple’s approach to globalization is not without its critics. The company’s tax strategy, which has been the subject of intense scrutiny, has raised concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior. As Apple continues to expand its global footprint, it will need to address these concerns and demonstrate its commitment to operating responsibly and ethically in all the markets it serves.
Looking to the future, Apple faces a number of challenges and opportunities. The company will need to continue to innovate and adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape . It will also need to navigate the complexities of global markets, ensuring that its products and services remain relevant and appealing to consumers worldwide.
Apple’s journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and interconnected world .
As Apple embarks on the next chapter of its global journey, it remains to be seen how the company will navigate the evolving landscape of technology, consumerism, and globalization. However, one thing is certain: Apple’s commitment to innovation and its ability to understand the needs of consumers worldwide will continue to be key drivers of its success in the years to come.

Privacy Preferences
When you visit our website, it may store information through your browser from specific services, usually in the form of cookies. Here you can change your Privacy preferences. It is worth noting that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and the services we are able to offer.
Apple’s supply chain transformation
In 2022, Apple lost US$1.5 billion in Black Friday sales due to iPhone supply constraints. One in three retail stores across the US and Europe experienced stockouts of the new iPhone 14 Pro. China sales were down more than 30% year on year. Apple’s stock had dropped 29% in 2022. China’s zero-Covid policy resulted in massive lockdowns that made factory working conditions unbearable. In the second half of 2022, many Chinese workers quit their jobs at Apple’s Foxconn facilities. The Russia-Ukraine war that started in February 2022 and the ensuing Western sanctions spurred an unprecedented global energy crisis and double-digit inflation. Now that supply chain disruptions, component shortages and rising geopolitical tensions had become a reality, Apple had to decide on a transformation, knowing that the transition presented difficult trade-offs and would take years to complete: (1) Which elements to change in the company’s global value chain? How to approach change without hurting manufacturing continuity, product quality, revenue and profitability? (2) Should Apple further drive its vertical integration in the design of chips, semiconductors, screens and assembly? Or should it adopt the Android phone manufacturers’ model and develop a broader base of suppliers?
- Define Apple’s supply chain competitive advantages and dependencies
- Analyze the factors driving the need for transformation and their impact
- Assess the options available in Apple’s global value chain adaptation to a deglobalizing world
- Evaluate the strategy and tactics for Apple’s supply chain transformation
The Case Centre
Cranfield University
Wharley End Beds MK43 0JR, UK Tel +44 (0)1234 750903 Email [email protected]
Harvard Business School Publishing
60 Harvard Way, Boston MA 02163, USA Tel (800) 545-7685 Tel (617)-783-7600 Fax (617) 783-7666 Email [email protected]
Asia Pacific Case Center
NUCB Business School
1-3-1 Nishiki Naka Nagoya Aichi, Japan 460-0003 Tel +81 52 20 38 111 Email [email protected]
IMD retains all proprietary interests in its case studies and notes. Without prior written permission, IMD cases and notes may not be reproduced, used, translated, included in books or other publications, distributed in any form or by any means, stored in a database or in other retrieval systems. For additional copyright information related to case studies, please contact Case Services .
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications

Understanding your organizational capacity for agility and responding to events accordingly is the key to success in the new business environment, ...

In a post-pandemic era shaped by wars, climate change, and new technologies, Maha Hosain Aziz outlines the main risks and shock events that could d...
The case study examines recent aviation safety concerns at Boeing, focusing on manufacturing issues, leadership decisions and regulatory oversight....

Margherita Della Valle tells IMD President Jean-François Manzoni how she is delivering radical change to reenergize Vodafone and paving the way for...
The case is seen through the eyes of the newly appointed supply chain director at a cosmetics company based in Berlin. The general manager has task...
Few Business to Business (B2B) marketplaces have succeeded. Metalshub has successfully combined a software platform as a service, with a marketplac...
The case focuses on Contabilizei, a Brazilian startup providing online accounting services for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The case ...

IMD's Niccolò Pisani examines how a combination of clear-eyed analysis and a strong sense of purpose allowed the French biopharma to change course.
Companies that modularize and externalize their best capabilities are in a strong position to seize unexpected opportunities. Prediction is hard. T...

Leading Chinese companies are preparing to take advantage of exposure and opportunities as top sponsors and suppliers to the UEFA EURO 2024 Men’s S...
The Brand Hopper
All Brand Stories At One Place
A Case Study on Apple’s “Shot on iPhone” Brand Campaign
A Case Study on Apple’s “Shot on iPhone” Brand Campaign 5 min read
Apple, the tech giant known for its innovative products and sleek designs, has been successful in creating a strong brand identity that resonates with consumers worldwide. One of their most notable brand campaigns is the “Shot on iPhone” series, which showcases the quality of the camera on their smartphones. In this case study, we will explore how Apple effectively used this campaign to build brand awareness, increase customer engagement, and drive sales.
Background:
The “Shot on iPhone” campaign was launched in 2015 as part of Apple’s strategy to promote the iPhone 6s, which featured a new 12-megapixel camera . The campaign aimed to highlight the phone’s impressive photography capabilities by encouraging users to share their photos taken with the device on social media platforms like Instagram and Twitter.
Target audience:
The target audience for the campaign was millennials who are passionate about photography and frequently use social media to share their experiences and creations. This demographic is also likely to be interested in upgrading to the latest technology, making them an ideal target for promoting the new iPhone model.
Marketing Objectives:
- Build brand awareness and reinforce the reputation of the iPhone as a high-quality camera phone
- Showcase the improved camera features of the iPhone 6s
- Encourage user-generated content and increase customer engagement on social media
- Drive sales of the new iPhone model
Campaign Strategy:
To achieve these objectives, Apple implemented several strategies across various channels:
Social Media Contest: Apple created a dedicated microsite where users could submit their best photos taken with an iPhone. Participants were asked to tag their posts with #shotoniphone and #contest, and a selection of the best images would win prizes such as featuring in a future ad or receiving a free iPhone.
Influencer Marketing: Apple partnered with popular photographers and influencers on Instagram to create stunning visual content shot entirely on iPhones. These influencers shared their photos and videos on their accounts, giving their followers a glimpse into the quality of the iPhone’s camera.
Print Advertising: Apple placed print ads in major newspapers and magazines, showcasing beautiful images captured on the iPhone 6s. The ads featured minimal copy and let the images speak for themselves, emphasizing the quality of the camera.
TV Commercial: A television commercial was produced, featuring a montage of breathtaking shots taken by everyday iPhone users, set to a powerful narration about capturing life’s moments. The ad ended with the tagline “Shot on iPhone 6s.”
In-Store Displays: Apple retail stores displayed large prints of the winning photos from the social media contest, creating an immersive experience for customers and further demonstrating the camera’s capabilities.
The “Shot on iPhone” campaign was highly successful, achieving remarkable results for Apple:
User Engagement: The campaign generated significant buzz on social media, with over 70 million interactions (likes, comments, shares) on Instagram alone. Users enthusiastically participated in the contest, submitting over 100,000 photos and videos.
Sales Growth: The campaign contributed to increased sales of the iPhone 6s, particularly among the target audience. According to Apple’s Q4 2015 earnings report, iPhone sales reached a record high, with the iPhone 6s being the most popular model.
Brand Perception: The campaign strengthened Apple’s position as a leader in the smartphone industry, solidifying the brand’s association with premium design, innovation, and user experience.
Long-term Impact: The success of the “Shot on iPhone” campaign paved the way for subsequent iterations, including “Shot on iPhone X,” “Shot on iPhone XR,” and “Shot on iPhone 12 Pro.” Each new installment builds upon the previous one, showcasing the continuous improvement in camera technology and encouraging user participation.
Conclusion:
Apple’s “Shot on iPhone” campaign effectively achieved its marketing objectives by leveraging user-generated content, collaborating with influencers, and utilizing multiple advertising channels. By highlighting the exceptional camera quality of the iPhone 6s, the campaign not only drove sales but also reinforced the brand’s commitment to delivering cutting-edge technology and exceptional user experiences. The campaign’s focus on showcasing real-life moments captured by everyday people helped to create a sense of authenticity and relatability, making the brand more accessible and appealing to a wider audience.
Additionally, the campaign’s emphasis on creativity and storytelling helped to differentiate Apple from its competitors and reinforce its position as a leader in the tech industry. By encouraging users to share their own stories and experiences, the campaign fostered a sense of community and loyalty around the brand, leading to increased customer retention and advocacy.
Overall, the “Shot on iPhone” campaign was a resounding success for Apple, driving business results while also building brand awareness and affinity. The campaign’s impact can be seen in the following key metrics:
- Sales : The campaign contributed to increased sales of the iPhone 6s, with Apple reporting a record number of sales during the quarter the campaign was launched.
- Brand Awareness : The campaign helped to reinforce Apple’s position as a leader in the tech industry, with the brand becoming synonymous with high-quality cameras and innovative technology.
- Customer Engagement : The campaign’s social media component resulted in millions of interactions and user-generated content, fostering a sense of community and customer loyalty around the brand.
- Marketing Effectiveness : The campaign won several awards, including a Cannes Lion Grand Prix for Outdoor, a D&AD Pencil for Digital Advertising, and a CLIO Award for Integrated Campaign.
In conclusion, the “Shot on iPhone” campaign was a groundbreaking initiative that successfully combined user-generated content, influencer partnerships, and traditional advertising to showcase the iPhone 6s’ camera capabilities and reinforce Apple’s brand values. The campaign’s impact on business results, brand awareness, customer engagement, and marketing effectiveness makes it a standout example of effective marketing in the tech industry.
Also Read: Case Study : Apple’s “Creativity Goes On” Brand Campaign
To read more content like this, subscribe to our newsletter
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts
The Rise and Fall of the Apple iCar: A $10 Billion Failure
A case study on the “got milk” campaign, a case study of doritos locos tacos campaign: taco bell & doritos co-branding.
Terms and Conditions

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Apple’s Company Culture: An Organizational Analysis

Apple’s organizational culture is a key factor in the continuing success of its business. The consumer electronics company’s organizational or corporate culture establishes and maintains the business philosophy, core values, beliefs, and related behaviors among employees. This business analysis case shows that Apple has a work culture that motivates human resources to support strategic objectives for competitiveness. For example, the company’s cultural traits are aligned with the drive for innovation, which is a major factor that determines business competitiveness in the information technology, online services, and consumer electronics industries. With this company culture, business operations facilitate the fulfillment of Apple’s mission and vision . Through the leadership of Tim Cook, the company continues to enhance its cultural characteristics to maximize human resource support for business relevance in various markets around the world. Apple shapes its business culture and uses it as a tool for strategic management and multinational business success.
Apple’s company culture strengthens competitive advantages over other firms in various industries. The company’s products compete with the consumer electronics and online services of Google (Alphabet) , Samsung , Microsoft , Amazon , and Sony . Also, Apple TV Plus competes with the video streaming services of Disney , Facebook (Meta) , and Netflix . These competitors impose a strong external force that influences strategic management among firms in the industry, as illustrated in the Five Forces analysis of Apple Inc . As a result, cultural traits must reinforce the iPhone maker’s business competitive advantages through its workforce. It can be argued that Apple partially achieves this strategic objective through the effects of its organizational culture on workers’ behavior and job performance.
Apple’s Culture Type and Traits
Apple has an organizational culture for creative innovation . The company’s cultural features focus on maintaining a high level of innovation that involves workers’ creativity and a mindset that challenges conventions and standards, such as in consumer electronics design. Apple’s IT business depends on cultural support and coherence, which are determinants of competitiveness and industry leadership, especially in addressing aggressive and rapid technological innovation and product development. The following are the main characteristics of Apple’s culture:
- Top-notch excellence
- Moderate combativeness
Top-notch Excellence . Apple’s organizational culture comes with a human resource policy of hiring only the best of the best in the labor market. Steve Jobs was known to fire employees who did not meet his expectations. This tradition continues under Tim Cook. Such a tradition maintains and reinforces a company culture that promotes, appreciates, and expects top-notch excellence among the technology company’s employees. This cultural trait is also institutionalized in Apple’s organization. For example, the company has programs that recognize and reward excellence among workers in software design. Excellence is emphasized as a critical success factor in the business, especially in product design and development, which is a major growth strategy described in Apple’s competitive strategy and growth strategies .
Creativity . This cultural trait pertains to creating new ideas that help improve the technology business and its products. Apple’s management favors creativity among employees’ knowledge, skills, and abilities. This characteristic of the work culture enables the company to ensure sufficient creativity, especially among employees involved in consumer electronics product design and development processes. Creativity is observable in the design and features of iPhones, Macs, iPads, and other products included in Apple’s marketing mix (4Ps) . Along with creativity, originality is also culturally emphasized as a way of maximizing the company’s intellectual properties, such as patents for new mobile devices. In this regard, the organizational culture helps maintain Apple’s capacity to satisfy and exceed customers’ expectations and preferences.
Innovation . Apple’s company culture supports rapid innovation. The technology business is frequently appraised as one of the most innovative companies in the world. Based on this cultural trait, Apple trains and motivates its employees to innovate in terms of individual work performance and idea contributions for product development, design, and other processes. The work culture facilitates rapid innovation, which is at the heart of Apple’s operations management . Rapid innovation ensures that the company continues to introduce new products that are profitable and attractive to target customers in the global consumer electronics and Internet services market.
Secrecy . Apple has a secretive organizational culture. This cultural characteristic defines the MacBook maker’s human resource development and management practices. Secrecy is part of the company’s strategy to prevent theft of proprietary information or intellectual property, such as designs for the next generations of the iPhone. It is also a strategic management approach that enables Apple Inc. to maximize its leading edge against competitors. Through the company culture, employees are motivated and expected to keep business information within the technology business organization. This cultural trait is reinforced through Apple’s organizational structure (business structure) and related policies, rules, and employment contracts that prohibit the disclosure of information, such as technological breakthroughs in the company’s consumer electronics. In this context, Apple’s work culture helps protect the business from corporate espionage and the negative effects of employee poaching.
Moderate Combativeness . Apple’s company culture has moderate combativeness. This feature is linked to Steve Jobs and his combative approach to leadership. He was known to randomly challenge employees to ensure that they have what it takes to work at Apple. Today, under Tim Cook’s leadership, the company has been changing its corporate culture to a more sociable and a less combative one. Nonetheless, combativeness remains a major influence in the technology business. Apple’s business culture exhibits a moderate degree of combativeness that presents challenges that motivate employees to enhance their output.
Apple’s Organizational Culture: Advantages, Disadvantages, Recommendations
Advantages and Benefits . The combination of top-notch excellence, creativity, and innovation in Apple’s organizational culture supports the company’s industry leadership. The business is widely regarded as a leader in terms of innovation and product design, especially in consumer electronics. These cultural characteristics empower Apple and its human resources to stand out and stay ahead of competitors. This company culture enables success and competitive advantages, as well as the further strengthening of the company’s brand, which is one of the key business strengths shown in the SWOT analysis of Apple Inc . Creativity and excellence are especially important in the company’s rapid innovation processes for continuous competitiveness and business development despite aggressive competition with Samsung and other firms.
Drawbacks and Weaknesses . Apple’s corporate culture brings challenges because of the emphasis on secrecy and the moderate degree of combativeness. An atmosphere of secrecy can limit rapport among workers, while moderate combativeness has the potential to limit or reduce employees’ morale. These cultural issues can reduce business effectiveness and increase employee turnover. Apple Inc. can address this situation by modifying its organizational culture to reduce combativeness, but not necessarily remove it. This recommendation focuses on reducing the disadvantages of combativeness, without eliminating the benefits of combative approaches in the technology company’s operations. Also, Apple can integrate new cultural traits to keep the business relevant, given trends and changes in the information technology, cloud services, digital content distribution, and consumer electronics industries’ environment.
- Choi, Y., Ingram, P., & Han, S. W. (2023). Cultural breadth and embeddedness: The individual adoption of organizational culture as a determinant of creativity. Administrative Science Quarterly, 68 (2), 429-464.
- Apple Inc. – Inclusion & Diversity .
- Apple Inc. – Life at Apple .
- Apple Inc. – Work at Apple .
- Dyer, C. (2023). The Power of Company Culture: How any business can build a culture that improves productivity, performance and profits . Kogan Page Publishers.
- Zhang, W., Zeng, X., Liang, H., Xue, Y., & Cao, X. (2023). Understanding how organizational culture affects innovation performance: A management context perspective. Sustainability, 15 (8), 6644.
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- May 2018 (Revised December 2019)
- HBS Case Collection
Apple Inc. in 2018
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 30
About The Author
David B. Yoffie
Related work.
- June 2018 (Revised January 2020)
- Faculty Research
Apple Inc. in 2020
- Apple Inc. in 2018 By: David B. Yoffie
- Apple Inc. in 2018 By: David B. Yoffie and Eric Baldwin
- Apple Inc. in 2020 By: David B. Yoffie and Daniel Fisher

Apple Case Study – How Steve Jobs built Apple around simplicity

This article is written by Graham Robertson, the founder of Beloved Brands
Brand Toolkit
Our Apple case study starts with 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗱𝗮𝘆 𝗦𝘁𝗲𝘃𝗲 𝗝𝗼𝗯𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗻𝗲𝗱 𝘁𝗼 𝗔𝗽𝗽𝗹𝗲. This is the starting point that 𝘁𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗱 𝗔𝗽𝗽𝗹𝗲 𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗼 𝗼𝗻𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝘁𝗼𝗱𝗮𝘆’𝘀 𝗺𝗼𝘀𝘁 𝗮𝗱𝗺𝗶𝗿𝗲𝗱 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗱 s . Steve Jobs recognized that consumers were frustrated by how all the other technology brands designed their products in a lab without any thought for the consumer. Steve Jobs made the most significant contribution to the Apple brand strategy by starting with the consumer experience and then working back to the technology. The Apple brand positioning builds everything around the idea that “Apple makes technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future.”
Moreover, we witnessed the most incredible decade that any company has ever seen, with Apple launching iTunes, iPod, iMac, the MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, iPhone, and the iPad.
If you are a marketer looking to improve your knowledge by looking at what Apple has done so well, our Apple case study will teach plenty of lessons for using a brand idea to inspire and steer everyone who works on the brand. At every step of the Apple brand strategy, we will provide a link to click on and learn how the process can work on your brand.
If you are a fan of Apple, click on this link to view their best store locations: Apple Store locations . Or come see some of their best advertising: Apple Advertising .

Apple Case Study - Table of Contents
Building the apple brand.
Our Apple case study will show how to develop Apple’s brand positioning statement and plan . Then, I will show how Steve Jobs pushed to stretch their “simplicity” brand idea across their company. Everyone who works behind the scenes knows their role in delivering simplicity.
Simplicity drives all Apple advertising.
In the 1980s, Apple started with “technology for the rest of us” when they took on IBM. And they continued that attack with “I’m a Mac” ads that took on Microsoft. Simplicity drives Apple’s innovation. Steve Jobs pushed for great advertising.
The beauty of Apple is how they take complex technology and simplify it so consumers can do more with Apple products.
The Apple brand strategy even drives their retail stores. Their Genius bar helps answer technology questions. They allow consumers to play with their products. Apple salespeople are trained to avoid “geek speak.”
The return of Steve Jobs
After Steve Jobs returned in 1997, he shifted the focus to rebuilding around the brand idea of “Apple makes technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future.” Jobs came in with a consumer-first approach in a market dominated by an obsession with gadgets, bits, and bytes. At the heart of our Apple case study is the use of the brand idea of simplicity and its impact on the brand strategy.

Undoubtedly, simplicity is one of the values Steve Jobs held very close to his heart. For example, he built simplicity into everything Apple did and everything it stood for. Even over the last decade, Apple is still following the Steve Jobs playbook.
Apple Brand Positioning - how they use 'simplicity'
The apple brand positioning builds everything behind the “simplicity” brand idea..
We use our consumer benefit ladder to find differentiation. Importantly, turn your brand’s features into consumer benefits. Stop thinking about what your brand does. And, start thinking about what your consumer gets. That’s when the Apple brand positioning statement comes alive.
Functional consumer benefits.
To help brand leaders kickstart their brand positioning work, I have created 12 functional zones that expand to over 50 potential functional benefits. For instance, as you look through the list, gravitate to the functional benefits you think will fit your consumers’ needs and differentiate your brand by looking for words where your brand does it better than competitors. While you might start with our words, try to layer in your own creative language with the specific category or consumer language.

Emotional consumer benefits.
Below is a list of 40 potential emotional benefits that help build an emotional brand positioning statement that differentiates your brand. Importantly, you want to own one emotional space in the consumer’s heart as much as you own the rational space in the consumer’s mind.
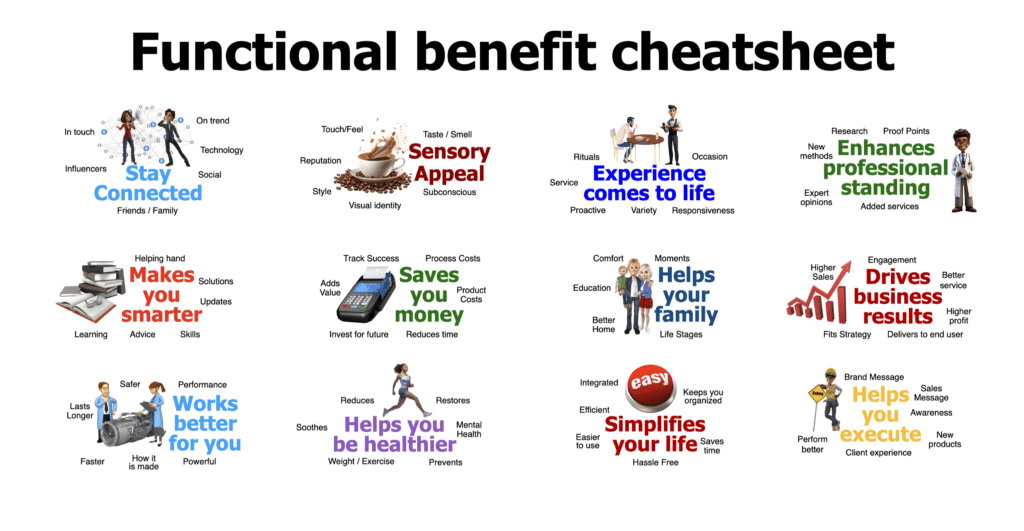
To illustrate, click on our Consumer Benefit Cheatsheet to build the Apple brand positioning .
Choosing the right benefit clusters for Apple
Using our brand positioning process, the Apple brand positioning narrows in on the brand’s potential benefit clusters of the functional and emotional benefits.
What Apple does: best features
- Intuitive and easy to use: Apple allows everyone to do more and get more from their devices.
- Stylish designs: Fashion-forward designed so that people want to show them off.
- Integrated technology: All devices, software, and services work harmoniously, enhancing user experience.
- Fresh innovation: Apple customers always have access to cutting-edge features and advancements.
What Apple consumers get: functional benefits
- Simplifies your life: Hassle free, easier to use, integrated.
- Sensory Appeal: Touch/feel, subconscious, and style.
- Experience: Responsiveness, rituals, and service.
How Apple consumers feel: emotional benefits
- Feel free: Alive, excited, exhilarating.
- Get noticed: Cool, trendy, popular, and playful.
- Optimism: Successful, inspired, and motivated.
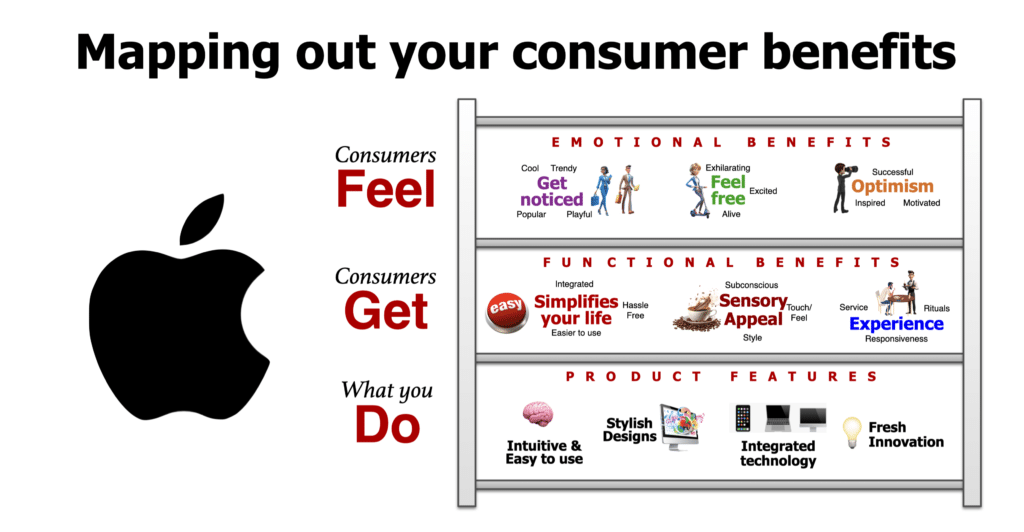
To illustrate, click on our Consumer Benefit ladder we use to build the Apple brand positioning .
Apple Brand positioning statement
Once everything is settled, the overall Apple brand positioning statement focuses on simplifying technology to help you feel smarter so you can do more with every device.
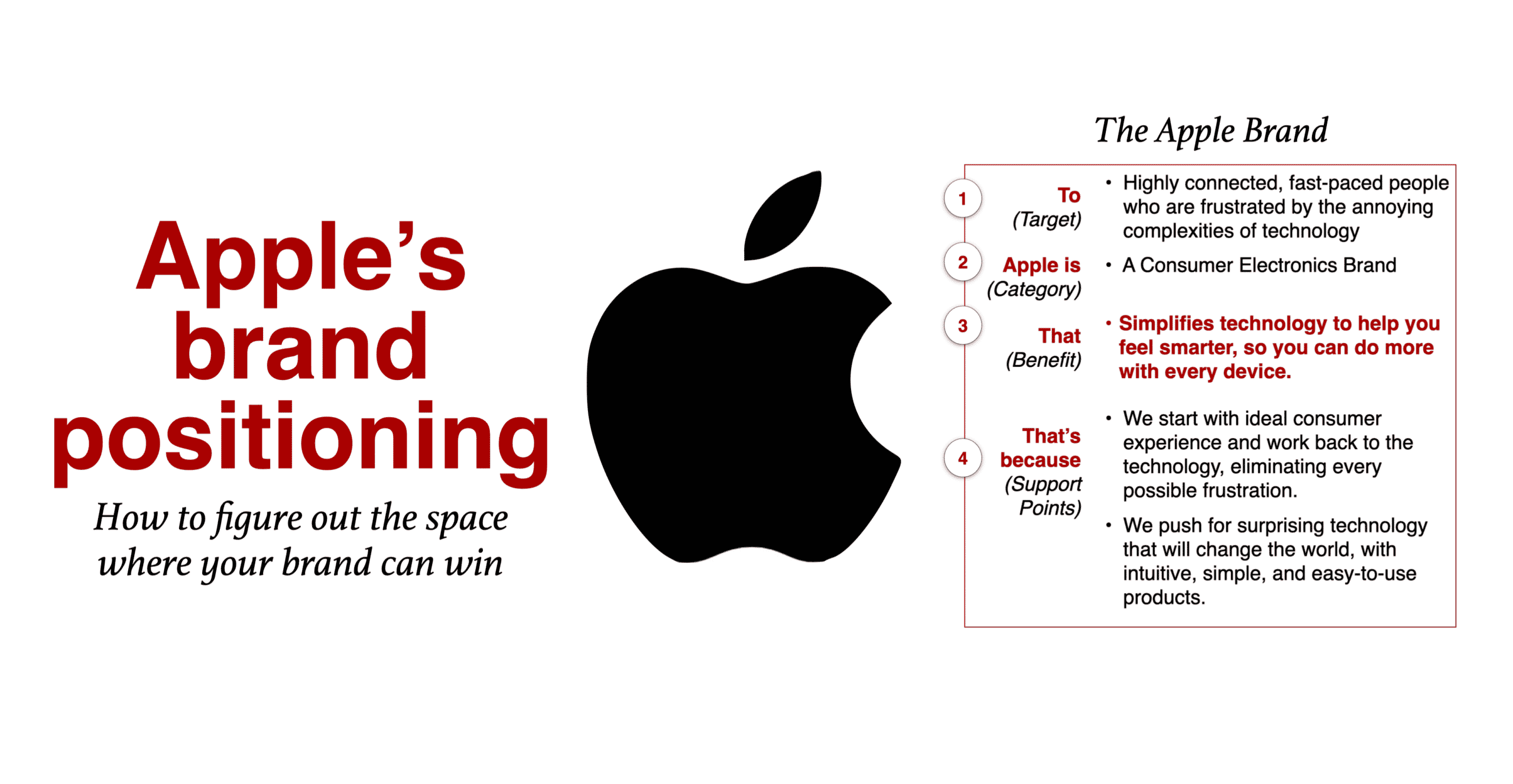
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Positioning Statement . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.

Old school brand positioning vs new school
When brand positioning began in the 1970s and 80s, the goal was to stay single-minded and focused and even get down to one word. For example, Volvo was about SAFETY. I still believe in that thinking for marketing communications. If all Volvo does is “safety,” no one would pay $50,000 to $70,000 USD for their cars. The additional benefits earn extra money for the comfortable leather seats, stylish design, and high-quality radio.
However, as brands have matured, the brand positioning should drive product innovation, the purchase moment, and the ideal consumer experience. One word might not be enough. Now, we can see brands can own a cluster of benefits.
Below, we can see the cluster of benefits, both functional and emotional, to create a word cloud for Apple. These words can show up as support communications to the ‘simplicity’ idea. Moreover, these words should appear in product design, in-store layout, people management, and consumer experience. These words should drive every part of the Apple brand strategy.
In a similar vein, the pharmaceutical industry has also adapted its marketing strategies to meet the changing demands and expectations of consumers. Take, for example, Motilium, a medication used to treat nausea and vomiting. As brand positioning evolves, the marketing for Motilium not only highlights its effectiveness but also emphasizes convenience and accessibility by promoting the option to buy Motilium online ( reference ). This adaptation ensures that the messaging is not just about the functional benefit of symptom relief but also about making the purchase process as easy as possible for the consumer, aligning with modern expectations of convenience and immediate availability.
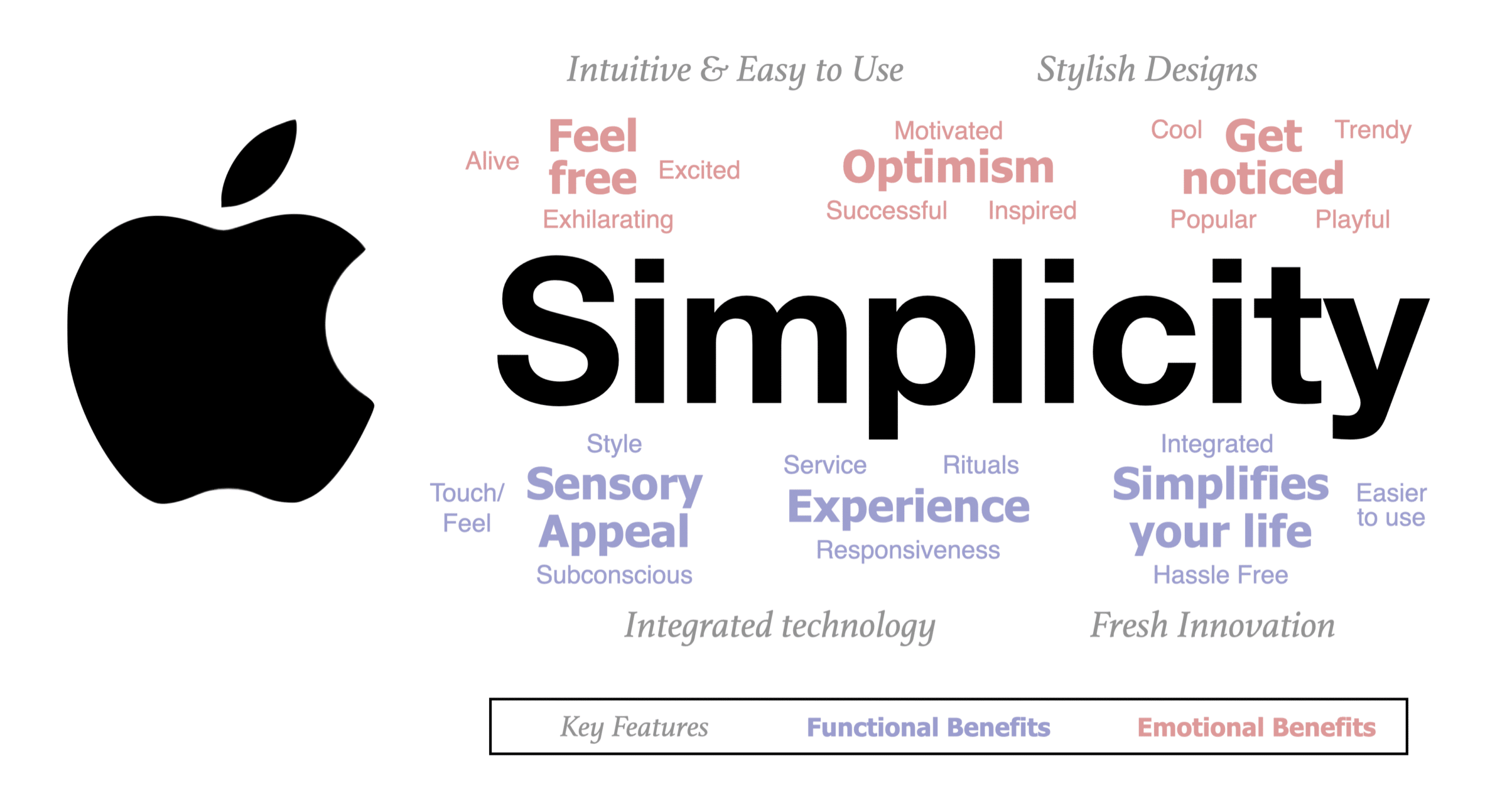
To illustrate, click on our Cluster of Consumer Benefits that we use to build the Apple brand positioning .
Beloved Brands Marketing Training
To view, use the arrow to see our Beloved Brands Marketing Training program video.
It's time to elevate your marketing team's performance with our Beloved Brands Marketing Training program.
Our marketing training makes your marketers smarter with brand analytics, strategic thinking, brand positioning, brand plans, and marketing execution.
Building Apple's brand idea
Everyone seems to call the short-form description of a brand by different names; brand DNA, big idea, brand essence or shout from the mountain. I keep it simple by calling it the brand idea. To win in the marketplace, your brand idea must be interesting, simple, unique, inspiring, motivating, and ownable.
I created a brand idea blueprint with five ideas that surround it.
On the internal brand soul side, describe the products and services and the cultural inspiration, which is the internal rallying cry to everyone who works on the brand. On the external brand reputation side, define the ideal consumer reputation and the reputation among necessary influencers or partners. The brand role acts as a bridge between the internal and external sides.
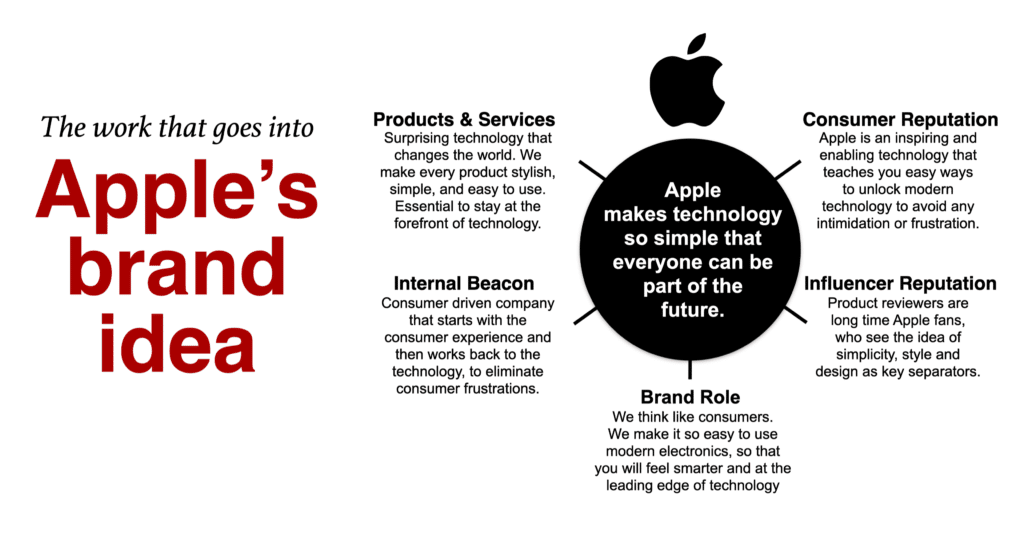
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Idea we use to build upon the Apple brand positioning .
The Apple case study uses the brand idea for Apple is “making technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future.” Most importantly, Steve Jobs insisted they take a consumer-first mentality as they transformed leading technology advancements into “consumer-accessible” technology, helping fuel the perception among the mass audience that Apple is an innovative leader.
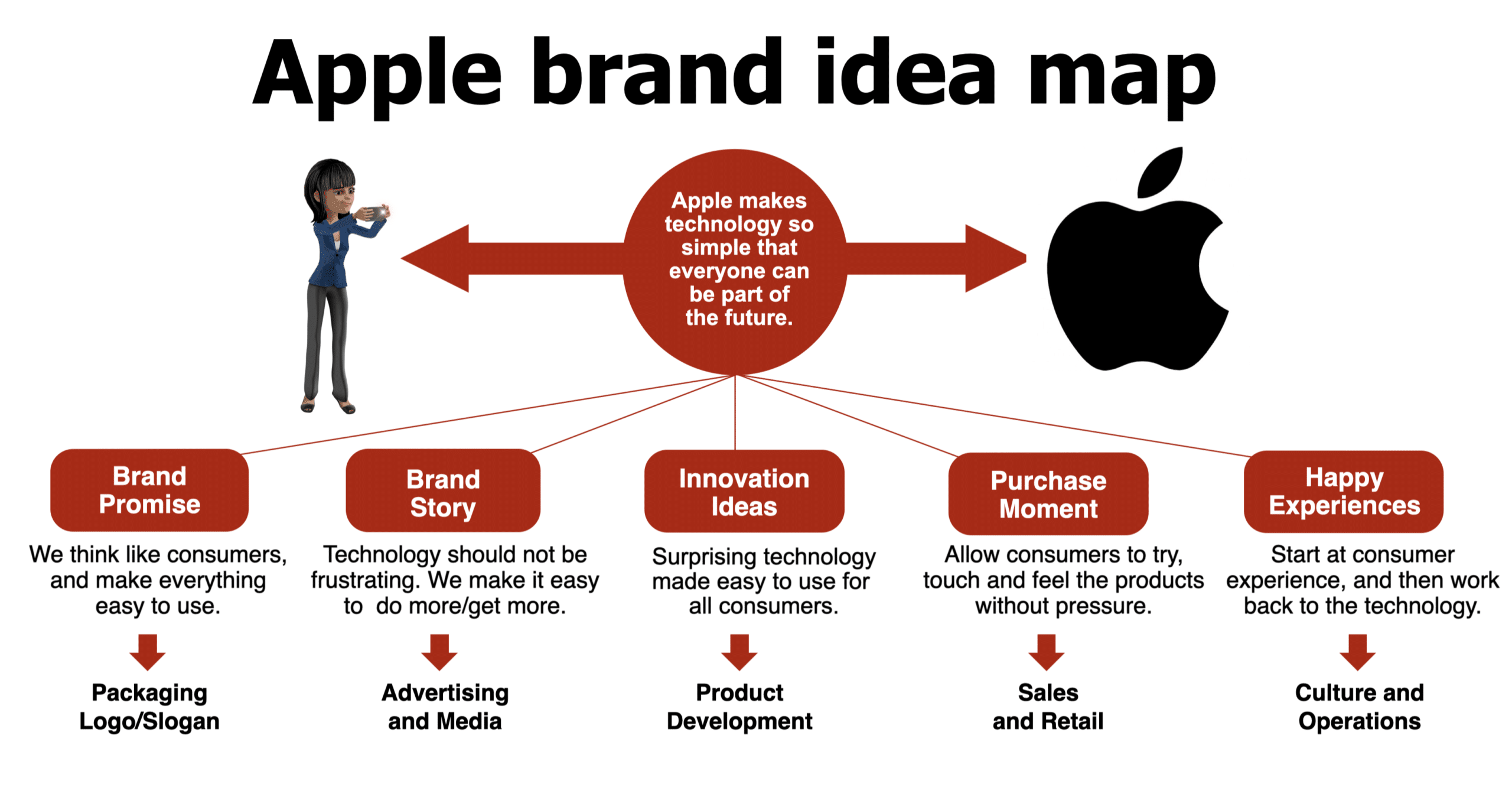
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Idea Map we use to build upon the Apple brand positioning .
Apple Case Study - video
Our apple case study is part of our beloved brands mini mba. take a look..
Below is an example video (30 minutes) from our Beloved Brands Mini MBA. We use the Apple case study to demonstrate the Apple brand positioning tools.
To view the Beloved Brands Mini MBA video , use the ▶️ button to play.
Apple's Brand Key Model
A Brand Key model is a tool from consumer marketing that allows marketers to lay out their brand’s unique selling proposition (USP) elements on one page. This article will go through the Brand Key model with nine elements that build the USP. And, with each element, we will show you the work you need to do.
Below is the Brand Key example for the Apple brand. It brings to life Apple’s unique selling proposition of simplicity. To read more on brand key models, click this link: Using a Brand Key Model to Define your Brand’s USP.
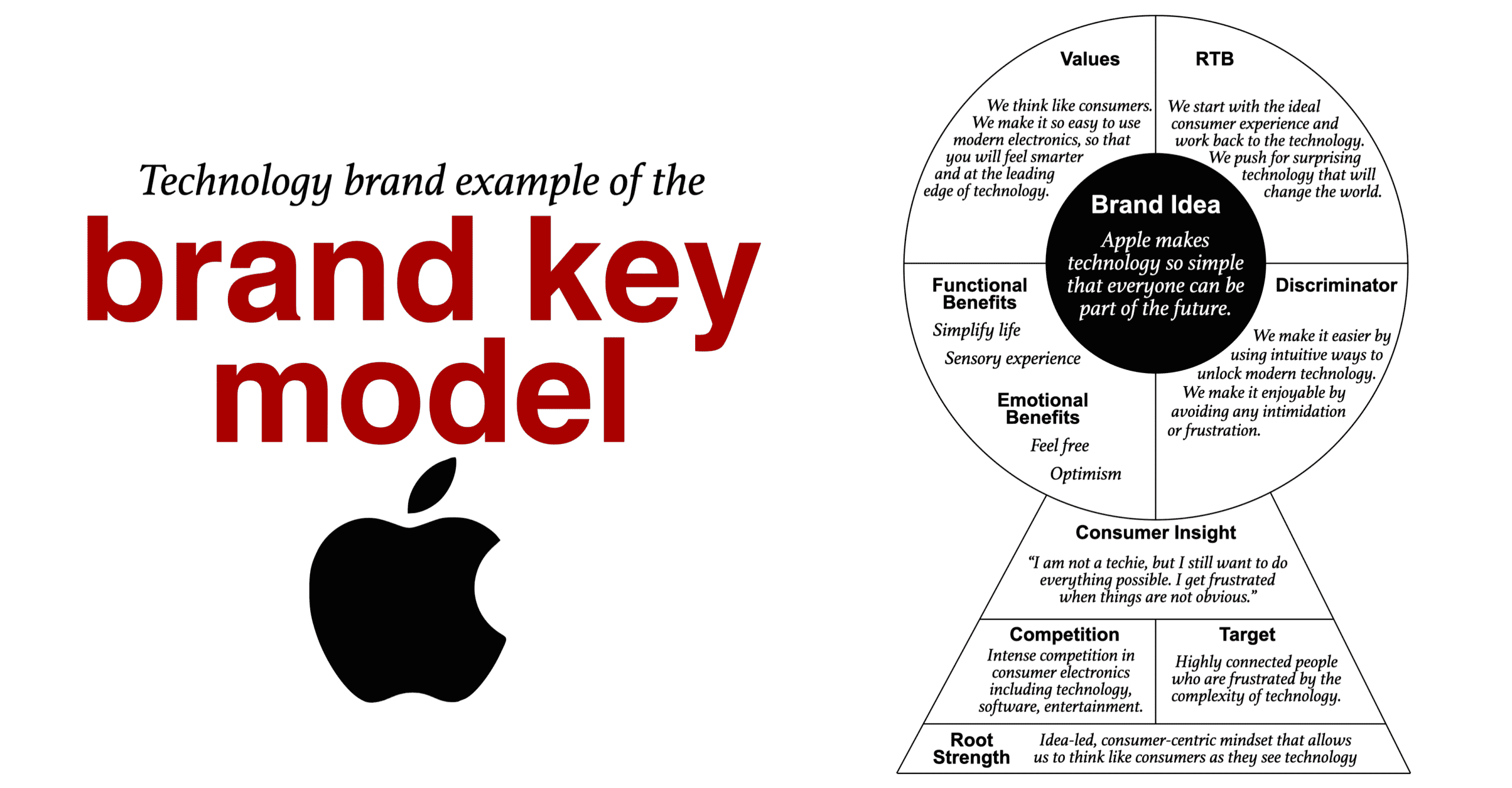
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Key we use to express the Apple brand positioning .
Our best posts
Click on any story below to read the more.
Use Apple's brand idea as a lens to see the problems not delivering
Apple has done a great job taking that simple brand idea and stretching it across its brand story through advertising and its innovation plan (as they have entered many new technology categories).
They have also used their brand idea to guide how they manage the purchase moment (to make sure their retail outlets are easy for consumers) and how they create happy experiences. And, when they don’t nail the ideal consumer experience, they go out of their way to help. They also have the genius bar and on-site lessons, which help increase consumers’ knowledge.
The other beauty of having a crystal clear brand idea is that everything that goes against that brand idea almost acts like an obvious virus. Below are four examples of where Apple is missing out on “simplicity,” which puts the brand idea at risk. Above all, these should trigger action plans to build into your brand plan. In pointing out these flaws within our Apple case study, I am yet to see Apple take action.
I wonder what Steve Jobs would think of these flaws.
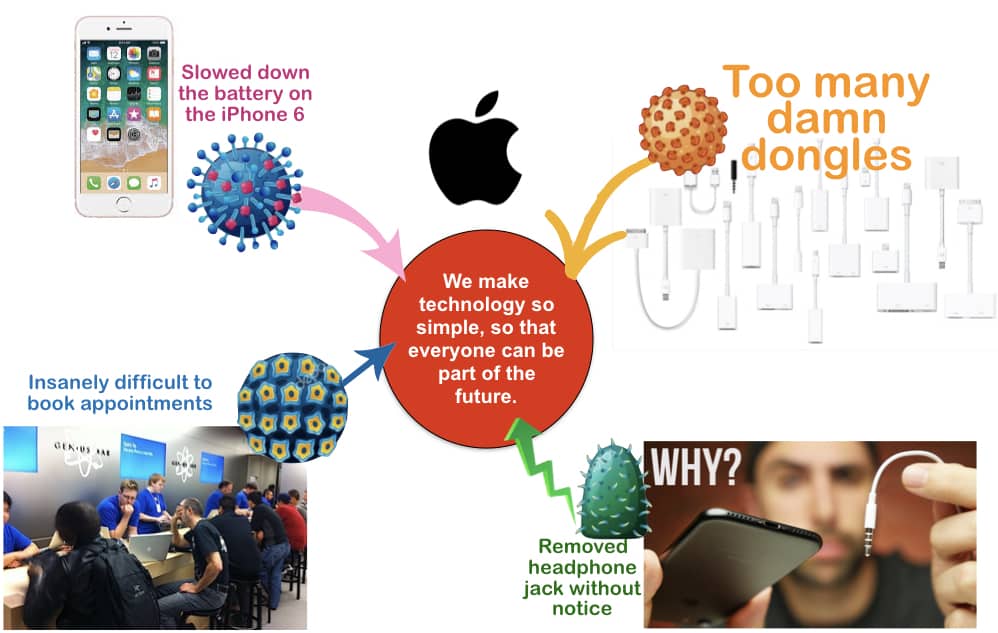
To illustrate, click on the Apple Case Study diagram to show where they go aga inst the Apple brand positioning.
Apple brand strategy
How the five elements of smart strategic thinking sets up apple's famous turnaround plan:, 1. set a vision of what you want..
To start our Apple case study, their vision is to make it easy for everyone to be part of technology in the future. The main issue was creating brand fans and then mobilizing them to spread the word to the masses.
2. Invest resources in a strategic program.
Next, Apple invested and aligned everything behind the Apple brand positioning and brand idea: “Apple makes technology so simple; everyone can be part of the future.” They use this brand idea at every touchpoint, including the brand positioning, communication, innovation, purchase moment, and experience.
3. Focus on an identified opportunity.
For decades, Apple consistently focused on empathizing with—and taking advantage of—the consumer’s frustration with technology. In the 1980s, they attacked IBM’s personal computers as too complicated. In 2005, they used “I’m a Mac, and I’m a PC” advertising to attack Microsoft. Each time, it used its “consumer-first” mentality to transform leading-edge technology into accessible consumer technology.
4. Leverage a breakthrough market impact.
Above all, the Apple brand strategy takes a fast-follower stance that takes current technology and makes it simple to use. Every platform, including desktops, laptops, phones, watches, tablets, and music streaming, delivers the brand idea of simplicity. They deploy high-profile launch hype to use vocal advocates to spread the word to their friends.
5. Performance result that pays back.
Most importantly, Apple created a consumer bond with its brand fans to enter new categories. On top of that, it is now the most beloved consumer-driven brand, with premium prices, stronger market share, sales, and profits. The Apple brand strategy used brand love to help drive a remarkable 40x revenue growth over ten years, skyrocketing from $5.7 billion in 2005 to $240 billion in 2015. This rapid growth helps cover the high costs of advertising and R&D, giving them very healthy operating margins, up over 35%. All this strategic effort has increased their market capitalization by over $1 trillion.
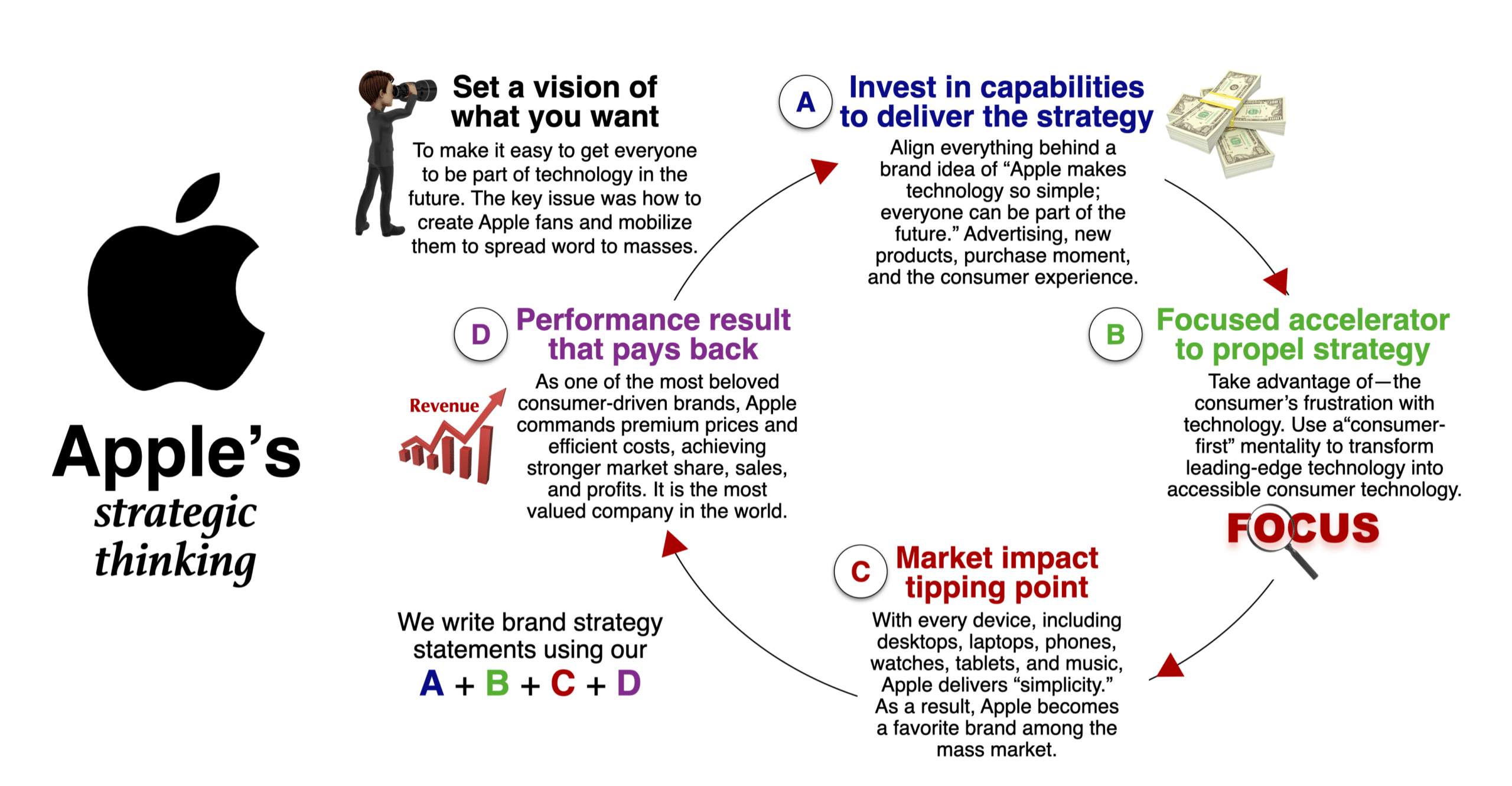
To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Strategy diagram . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Apple brand plan
We are going to build out a Brand Strategy Roadmap that can steer the brand for the next three to five years. And, we’ll show a one-page Annual Brand Plan. We’ll show the rough brand plan work you can do.

To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Strategy Roadmap . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
The rough brand plan for Apple
With the Apple case study, our strategic thinking model sets up the core elements of the Apple brand strategy:
Apple wants everyone in the world to be part of the future.
Continue aggressive sales growth, geographic expansion into China, and launch a major new consumer-friendly technology each year.
Key issues:
- How do we convey Mac’s superior user experience versus the traditional PC?
- How do we enter the music industry and increase the availability of online music to support our iPod?
Strategies:
- Apple will launch a full communications assault to challenge the PC/Microsoft Windows dominant position by finding flaws in the PC to contrast with Mac computers’ simplicity to steal significant market share by enticing frustrated PC consumers to buy a Mac.
- Apple will launch a full assault against the entire music industry with a disruptive innovator stance to show how iTunes provides higher quality digital music on your iPod much cheaper, faster, and smarter than CDs to gain an entry point into the music industry.
- TV advertising to highlight new features and challenge competitors.
- Launch innovation each year, including phones, tablets, online music, watches, and personal computers.
- Launch specific products for China. Increase retail space around the world. Build out the e-commerce program.

To illustrate, click on the Apple Brand Plan example that brings the Apple brand positioning to life.
Apple advertising
Advertising has delivered “simplicity” since the 1970s.
Apple’s advertising has been relatively consistent for over 40 years and incredibly connected with consumers. As Steve Jobs was launching Apple, the early print ads of the 1970s talked about how we designed the computer, so you don’t have to worry about the details.

Steve Jobs pushed for the “1984” TV ad for the Mackintosh launch that spoke about freedom from machines. Although the message was a little ahead of its time, it fit with simplicity. Above all, the brilliance of the side-by-side “I’m a Mac, and I’m a PC” TV ads epitomized the brand idea by making the PC seem overly complicated and frustrating while setting up the Mac as the simple alternative. These ads really express the Apple brand positioning statement.
Take a look at some of "I'm a Mac" TV ads. Enjoy!
To illustrate, click the ▶️ button to see the Apple brand advertising that brings the Apple brand positioning to life .
Apple innovation
Building product innovation around simplicity.
Apple has taken many failed technology ideas like online music, tablets, or mp3 players and turned them into consumer-friendly platforms such as iTunes, iPads, and iPods. With each new product, Apple uses launch hype to generate excitement to spark the enthusiasm of the early adopters who spread the word. Also, Apple has successfully taken its cherished brand fans into new categories.
The combination of Johnny Ives and Steve Jobs created many great Apple products.
Learn how to make innovation decisions.

Video on Apple's product innovation philosophy
To view the Apple brand innovation philosophy use the ▶️ button to play.
Apple retail
Purchasing apple products is very simple, including its own retail store experience.
Retail stores are a significant part of the Apple Case Study.
Steve Jobs saw a vision for retail to help Apple use simplicity to manage the purchase moment through its retail stores, ensuring the experience is simple and straightforward. All staff carry a credit card machine and complete the transaction very quickly. No lines or cash registers.
Simplicity shines through the store layout, with the genius bar for one-on-one tech questions and support and the training area to teach classes. The brand also displays every Apple product to allow consumers to take them for a test drive. It’s all about delivering the consumer experience that Steve Jobs loved so much.
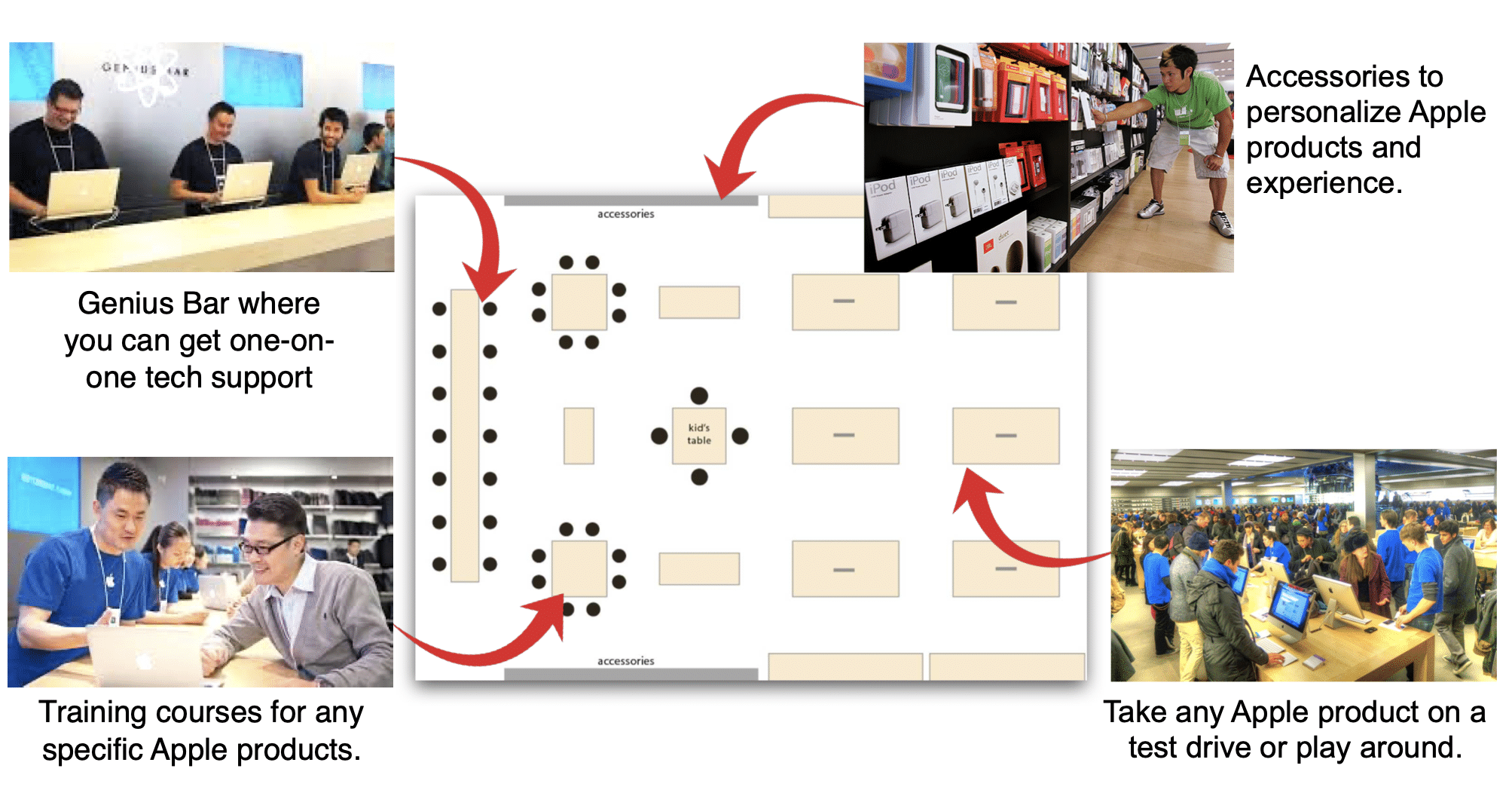
To illustrate, click on the Apple Store Layout. You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Even when Apple products are in other stores, the brand has used its power with that retailer to create a distinct store-within-a-store concept, replicating a similar look and experience from Apple’s retail locations.
Fifth Avenue Apple store in NYC

Tower Theater Apple store in LA

To illustrate, click on the Apple Store examples. You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Apple in Singapore
Milan Apple store

Apple consumer experience
Obsessing about the consumer experience.
As Steve Jobs famously said, “You have to start with the customer experience and work backward to the technology.” Apple even believes opening your Apple products should be like unwrapping a gift.
Steve Jobs wanted the consumer to be able to use any Apple product right away rather than spending hours loading software or setting up their machine. Regarding product integration, Apple products work together, and they work the same way, which makes it very simple for consumers when they move from one Apple product to another.
Next time you are in a brainstorming session, try to think like Steve Jobs.
To illustrate, click on the Apple Consumer Experience . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
The power of the Apple brand - how loyalty drives profit
How apple's brand love leads to increased power.
As we continue our Apple case study, let’s look at the power and profit Apple generates through brand love.
As they achieved an extremely tight bond with loyal followers, they used the tight consumer bond to generate brand power that they quietly wield in the market. Apple’s retail network generates twice the sales per square foot of any retailer worldwide, yet it is a very soft-sell environment.
I was recently on a double-decker bus tour of New York City, and when the bus went past the 5th Avenue Apple flagship store, half the bus stood up to take a photo. And they have such power over the supplier network with an array of engineers following extremely tight procedures.
Also, they have power over the media, generating over $2 billion worth of free media each year. Moreover, Apple fans often want to work at Apple, giving up lucrative jobs to be part of the brand.
Smartphone loyalty scores
Below, we can see the loyalty scores of the various smartphones. Apple leads the way with over 90% loyalty, moving from one model to the next. Samsung’s loyalty is below 70%. And LG has fallen to 32%. At LG’s level, you constantly need to source new consumers. That’s an extremely expensive way to manage your brand.
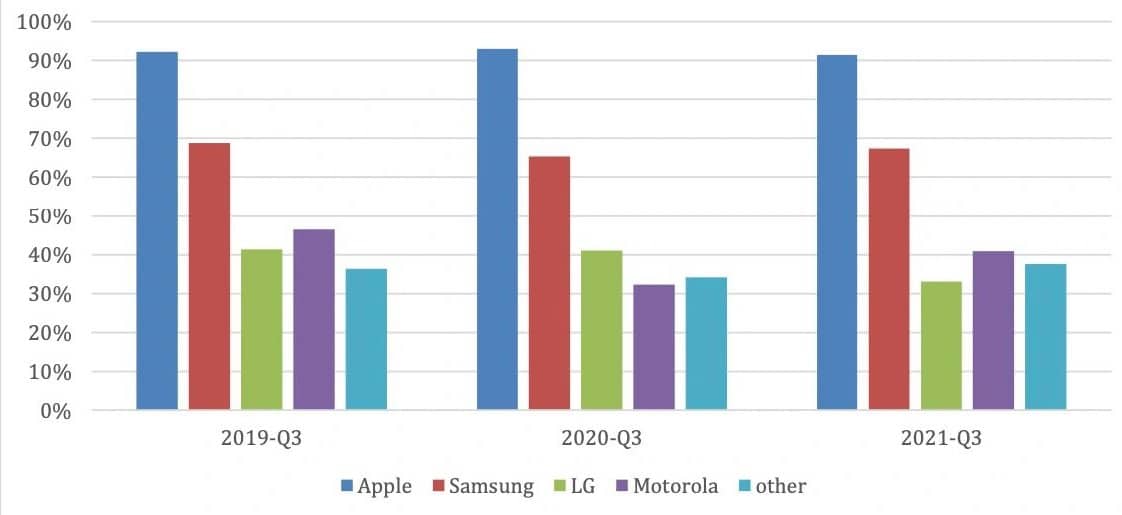
To illustrate, click on the Apple Case Study diagram . You can zoom in, download it, or share it.
Whoever says loyalty does not exist has not talked with Apple consumers. Apple significantly outperforms its competitors and uses that loyalty to drive future sales.
Apple's prices continue to increase
As Apple’s loyalty holds strong, they can increase their prices with each model. Loyal consumers are less price sensitive. This translates the Apple brand strategy into added profits. Steve Jobs used hype marketing to create a very tight bond with consumers.
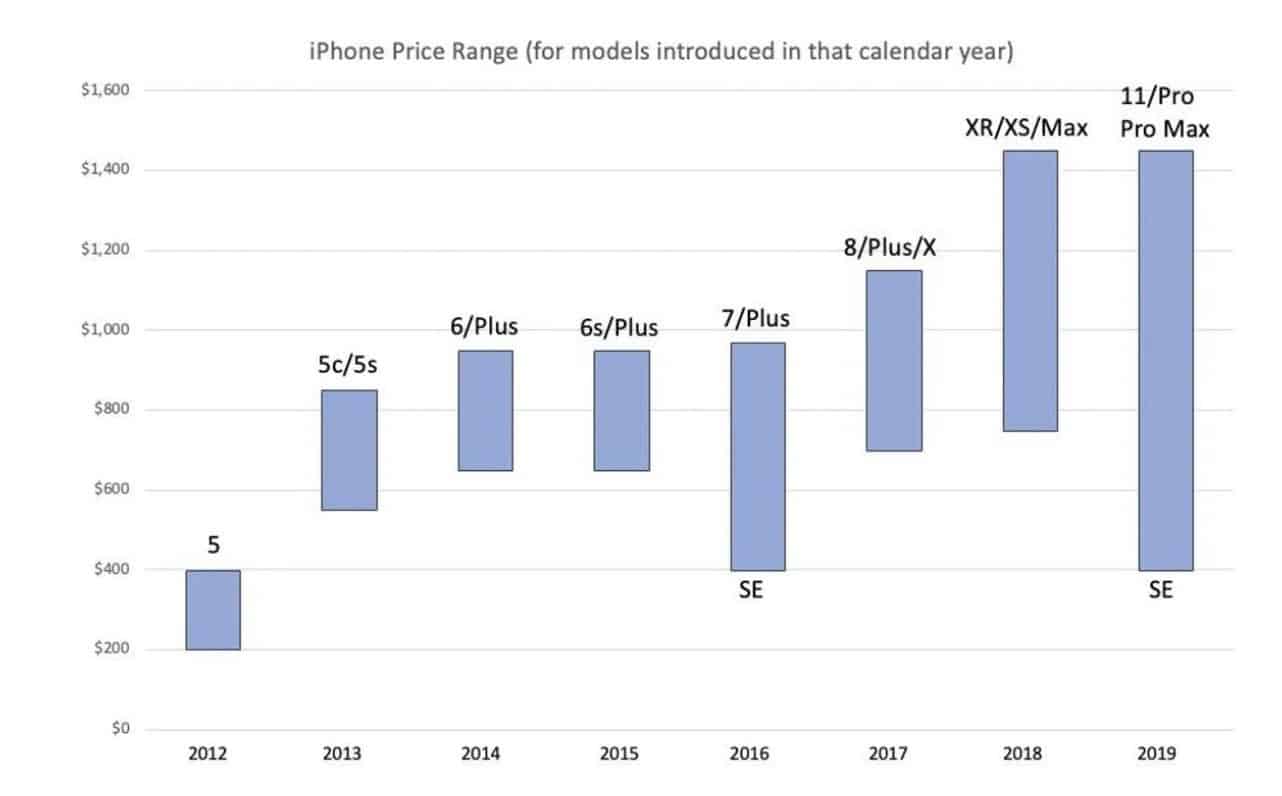
We can see how Apple uses power over its consumers to increase prices each year. Their iPhones deliver 40% profit margins, 4x higher than their competitor’s profits.
How Apple's brand power leads to increased profit
The Apple brand strategy extrapolates the power they generate into profit , with their incredible financial performance over the last 15 years. And they generate significant price premiums, relatively lower cost of goods, and moderate marketing spend ratios. Most importantly, this keeps their margins healthy for a technology firm.
Furthermore, Apple has entered many new categories over the past 15 years. Each time, their army of loyal fans has followed, moving into laptops, phones, tablets, and the music business. In each segment, they continue to gain market share to drive volumes.
Finally, the higher margins and volumes make for a beautiful profit statement.
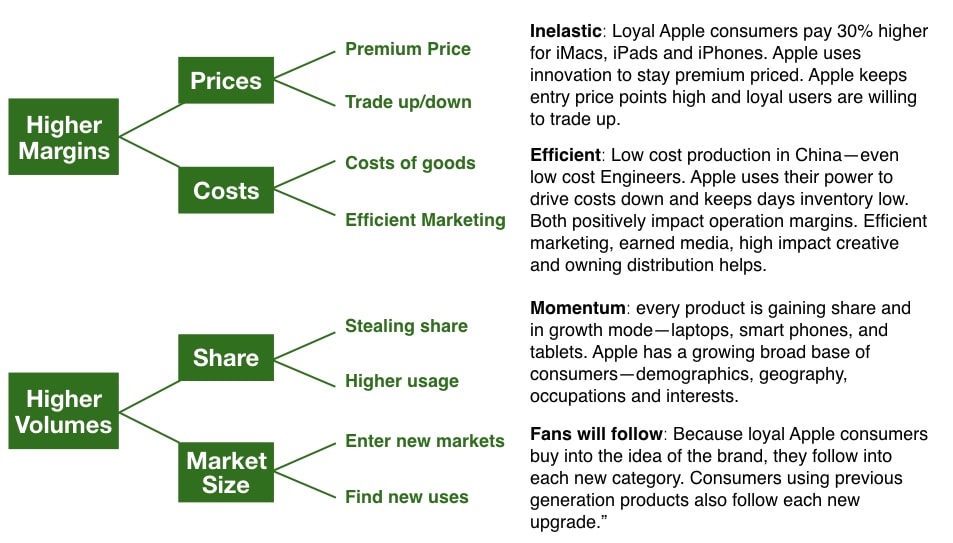
We can use our eight ways that a brand can drive profit to see the impact of the magic of the Apple brand on profits. Apple uses price, cost control, entry into new categories, and driving market share in each category.
Even though Apple gives the perception of an extremely friendly brand that is on the side of the consumer, they are now a huge mass market corporate brand, with a market capitalization of $500-600 billion, which is 2-3 times the value of companies like Coke, Procter & Gamble, Pfizer, and IBM.
So, if you invested a mere $10,000 in 2005, you would have $240,000 a decade later. The Apple case study is indeed a glorious look at the vision of Steve Jobs.
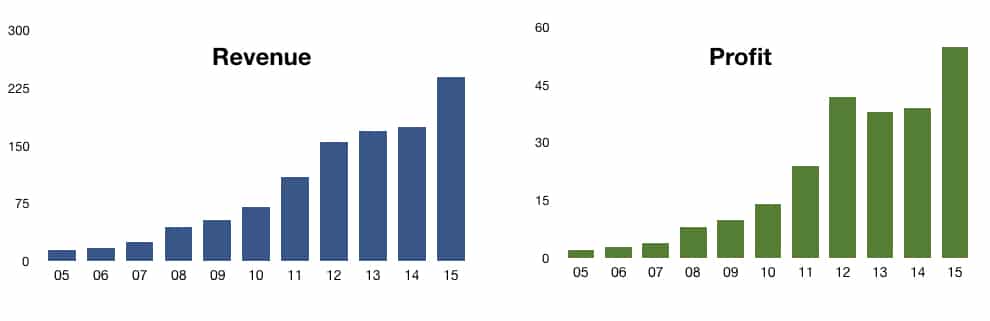
To conclude our case study, we can see how Apple uses its brand strategy to drive loyalty, revenue, and profitability each year. Their P&L is a thing of beauty.
Apple turns their brand love into higher power and profits

Graham Robertson
Email questions
Call 416 885 3911, follow us on linkedin, beloved brands book.

Beloved Brands Marketing Training Video
Elevate your team’s performance with our marketing training. The smarter they are, the greater your brand growth will be.

Click to read more

Find the template that fits your brand. Each of our templates is available for consumer, B2B, healthcare, or retailer brands.

Contact Information
Email: [email protected]
Phone: 416–885–3911
Search our site for any marketing topic
M a r k e t i n g B o o k
beloved brands
The playbook for how to create a brand your consumers will love.

With our Beloved Brands playbook , you will learn to think strategically, define your brand positioning, write a marketing plan, make execution decisions, and analyze your brand. Our readers tell us they reach for Beloved Brands as a reference tool to help them with the day-to-day management of their brand. We are proud that 89% of online reviewers have rated Beloved Brands a 5-star. As a result, Beloved Brands has been a #1 bestseller in brand management. We also have the B2B Brands playbook and our Healthcare Brands playbook .
Marketing Training
The smarter your team, the better the results you will see!
As a marketing team leader, you know that your team’s success is essential for your company’s growth. Our Beloved Brands marketing training gives your team the skills they need to make strategic decisions, produce exceptional work, and drive business growth. They will learn to define brand positioning, write effective plans, improve brief writing, make informed execution decisions, and analyze their brand’s performance.

We have designed our marketing training program to build the fundamental skills to help your team reach their full potential. We will work with your team to help them learn to take on Strategic Thinking, Brand Positioning, Marketing Planning, Marketing Execution, and Brand Analytics.

Popular Posts
Brand Positioning
Marketing Plans
Brand Strategy Roadmap
Creative Briefs
Marketing Career
Brand Key Model
Brand Toolkit for B2B
Brand Toolkit for Healthcare
Marketing Plan Template
Brand Plan template
Positioning template
Brand Consulting
Beloved Brands
Healthcare Brands
416 885 3911
[email protected]
We noticed you're visiting from Italy. We've updated our prices to Euro for your shopping convenience. Use United States (US) dollar instead. Dismiss
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple
Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple
Apple Inc is a multinational American company that design and sells computer software, consumer gadgets and personal computers. It was co-founded by Steve Jobs , Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne. Apple Inc is well-known for being innovative as they kept on producing new innovations from the first Apple computer Macintosh to the more recent iPhone and iPad series.
Today Apple Inc. is very well known in the world because of their advanced technology in products such as iPods, iPhone, Macbooks, Apple TV and other professional software. All the high tech products provide consumers with a better living standard in many different ways. Moreover, Apple Inc’s dominant position in the global market has changed the trend of consumer usage of electronic appliances such as in virtual communication. People will never need to carry multiple devices where each one only offers a handful of functions. Furthermore, Apple also created a substantial value in highly competitive market and industry which help them to achieve competitive advantages in an industry with stiff competition. In addition, it resolves the other external factors that present difficulty challenges to Apple Inc. Therefore, now Apple Inc is known as a strong company and the market leader in industry. Now, let us discuss about the current expansion strategy that used by Apple that make the company has greater success in marketplace.

The first strategy that use by Apple Inc for their current expansion strategy is creating innovative idea that slightly different from the competitors that already exists in market and industry. In order to make the company more innovative, Steve Jobs focused innovation on competitive pressure and value proposition by stressing his management style on customer center innovation and customer experience. As CEO in Apple, Steve Jobs carefully evaluated competitive pressure and opportunity in market place by continuously pursuit customer experience innovation. He also focused their business and IT strategy on customer center experience. It means that Apple will be more focused on looking outwards, market and business drivers rather than at the products or services that already exist. Steve Jobs focused on this strategy because the customers can help the company to understand what customers need and scarcity of the people so that he can use the feedbacks as inspiration to deeply investigate and then to create more innovative, creative and highly advanced technological product or services that can fulfill the needs of the customers. Therefore, Apple products design is always attractive and elegant compared to those existing competitors. Apple products like iPods and iPhones are good examples that show the innovation of Apple Company by creating digital lifestyle .
The second strategy applied by Apple is differentiation . Apple is using Macintosh as operating software whereas other personal computer’s producers are using Windows. The differentiation in operating software gives Apple a competitive advantage in the personal computer industry. Macbook users are satisfied with Macintosh performance because it is very energy saving where the processor will automatically “close” those programs which are not in use when it is in standby mode. On the other hand, Windows does not have such technology. Thus, Windows’ users might have to charge the laptop more often due to the battery consumption is higher than Macintosh.
In terms of design, Apple came out with an ultra-thin Macbook Air which is extremely thin compared to those existing laptops. To those consumers who prefer lighter and thinner laptops will definitely be attracted to the Macbook Air. Apple does not produce laptops in various colors like Dell or Hewlett Packard to increase the choices for consumers. However, to those consumers who are concerned about technology and high performance, Apple is still the preferable choice.
In terms of applications and software, Appstore provides a platform for customers to download software and applications according to categories. It is easy to search for any application or software by using Appstore. iTunes allow consumers to categorize and download songs easily . By using iTunes, consumers can choose their preferable album cover for their songs. They can also “synchronize” and update the songs in their iPhone with a laptop. Besides that, iTunes also allow consumers to transfer photos from iPhones to PCs.
As for pricing, Apple is using skimming pricing strategy where they set high selling price for their products. However, there are still a lot of loyal customers who prefer to spend more money on Apple products. This is due to the self esteem where consumers feel good by carrying Apple products because it somehow shows their status as being up-to-date and their taste is better than others. Some customers think that Apple products are not cheap but also not high-priced products because the value of Apple products bring to them is never disappointing.
Other than that, Apple is using specialization strategy where they customized customer’s laptop according to their requirements. Customers are required to add in features into the laptop which can serve them better. Beside this, Apple also emphasizes customizability on the part of entertainment that offer computer-build for high performance such as gaming. Gaming plays important roles to help Apple to customize in features and specification to make the products more attractiveness and creativity.
In a nutshell, the key to Apple’s success is down to creating a unique product with the ability for it to be customized to suit each individual’s needs.
Related posts:
- Case Study on Apple’s Business Strategies
- Case Study: Sony’s Business Strategy and It’s Failure
- Case Study: Business Strategy of Sony Corporation
- Case Study: Business Strategy Analysis of Wal-Mart
- Case Study of Papa John’s: Quality as a Core Business Strategy
- Case Study: Delta Airlines Successful Business Turnaround Strategy
- Case Study: Marketing Strategy Analysis of Apple iPad
- Case Study of Apple: Competitive Advantage Through Innovation
- Case Study of Apple Inc: An Apple for Your Enterprise
- Case Study: Kellogg’s Business Strategy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Apple Settles E.U. Case by Opening Its Payment Service to Rivals
Customers in Europe may see an influx of new apps and services for making tap-and-go purchases.

By Adam Satariano
Reporting from London
Apple will for the first time allow banks, payment services and other app developers to use the underlying technology behind Apple Pay to make rival tap-and-go payment services, settling a long-running European Union antitrust investigation, regulators said on Thursday.
The agreement applies only in the European Union, where consumers could see an influx of new apps and services to make payments on the go. Apple has until now refused to grant rivals access to the payment technology on iPhones, known as near field communication, essentially forcing people to use Apple Pay.
“Apple has committed to allow rivals to access the ‘tap and go’ technology of iPhones,” Margrethe Vestager, the European Commission’s executive vice president, who oversees competition policy, said in a statement . “It opens up competition in this crucial sector, by preventing Apple from excluding other mobile wallets from the iPhone’s ecosystem.”
The settlement stems from an investigation started in 2020 to determine if Apple was abusing its dominant position in the smartphone market to box out rival payment service providers. The announcement on Thursday does not apply to Apple Watch, which also has tap-and-go payment technology, an E.U. spokeswoman said.
Apple did not respond to a request for comment.
Apple’s policy shift shows how tech regulation in the European Union has resulted in notable product changes for products and services used every day by consumers. Earlier this year, Apple agreed to give iPhone and iPad users access to rival app stores for the first time to comply with new competition rules. Google has also changed how it displays certain search results in the European Union, while Meta introduced a new ad-free subscription service for Facebook and Instagram users in the region.
The changes are part of a broad shift in the global technology industry as a result of government policies. Products and services that were once available globally as the same offerings no matter where a person lived are now being altered or removed from certain markets as a result of regulations. For example, Apple said it would not release its latest artificial intelligence service in the European Union because of regulatory uncertainty, and TikTok is legally barred from India.
In Europe, the regulatory scrutiny is only expected to intensify. Apple was recently charged in another case with violating E.U. competition laws for its policies related to the App Store . The company is also appealing a 1.8 billion euro fine for thwarting competition in the music streaming market. Google, Meta, Microsoft and TikTok are also under E.U. investigation.
Adam Satariano is a technology correspondent for The Times, based in London. More about Adam Satariano
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Apple beats lawsuit over forcing developers to use its closed ecosystem

Apple wins case against App Store restrictions

As of January 2024 , Apple has stopped requiring all iOS browsers to use its WebKit technology in the EU. In that same month, three California residents sued Apple over its App Store practices, including requiring the use of WebKit.
According to Reuters , their filing challenged what they described as Apple's "closed ecosystem of apps and services."
The full text of the filing is chiefly an account of how expensive it would be to develop an alternative to either Apple or Google's app platforms. It then seeks to claim that Apple requiring iOS browser developers to use WebKit stifles competition, and also adds costs for consumers.
In that case, the logic appears to be that if a developer didn't have to use WebKit on iOS, they could develop once for both iPhone and Android. So there would be no further development cost for the iPhone, therefore consumers would pay less.
Alongside this, the suit claimed that Apple acted to block the use of Progressive Web Apps (PWA) to prevent them replacing native App Store apps. "Apple used contractual restraints on its iOS ecosystem," says the filing, "to exclude the
introduction of cross-platform PWAs on iPhones."
In February 2024, Apple did say that PWAs would no longer be allowed in the EU. It then reversed that decision in March 2024.
For this specific case, US District Judge Richard Seeborg in San Francisco does not have the required legal standing to pursue the case. That ruling was based in part on Apple's argument against the suit's claim of it artificially increasing prices.
"Apple's prices are not artificially inflated," Apple told the court in June, "they are competitive in light of the fierce competition Apple faces from its competitors."
Judge Seeborg said that Apple's argument for a dismissal of the case, "cast doubt on whether plaintiffs are the correct class of harmed individuals to bring this case."
The plaintiffs have been given 30 days to submit an amended lawsuit. Neither their lawyers nor Apple have commented.
This does appear to be a small case, but winning it also sets a precedent that Apple will doubtlessly refer to in other cases. The defeat of this particular filing may specifically help Apple because it was partly accusing the company of a duopoly with Google.
Apple's having won with its argument that it faces "fierce competition," could now well be used in its legal case with the Department of Justice. Central to the DOJ's case is the argument that Apple has become a monopoly.
The paragraph: "For this specific case, US District Judge Richard Seeborg in San Francisco does not have the required legal standing to pursue the case. That ruling was based in part on Apple's argument against the suit's claim of it artificially increasing prices." needs some work. I seriously doubt that a California judge does not have the required legal standing for the case. I presume it meant to say the litigants do not have the required legal standing. Sorry to get nit-pikky William, I do enjoy reading your articles!
The developer’s demands are borderline insanity. What’s next, requiring all framework and library developers to conform to using the same extensibility mechanisms? Programming languages? Runtime engines? Binaries? Providing cross platform compatibility for an app used to be a feather in the cap for the developers of the app. There’s never been a mandated method that requires all app binaries to run on every platform and operating system. Do they think Microsoft would accept the same type of demands being directed at Apple? Hell no.
At least they can fix the suit and try again. Apple's bad behavior needs to be smacked down.
Sponsored Content
Surfshark VPN review: Powerful protection and performance with few drawbacks
Top stories.

Apple has big camera upgrades lined up through iPhone 19 Pro

An exclusive, real-world look at the haptic buttons Apple developed for the iPhone 15 Pro

Samsung's Galaxy Ring is out, but it won't be a problem for the Apple Ring

Best monitor for MacBook Pro in 2024: best buys from Apple, Dell, LG & Samsung

MacBook Air M3 review three months later: The best Mac for nearly everyone
Featured deals.

Best early Apple Prime Day 2024 deals
Latest exclusives.
How Apple's software engineering teams manage and test new operating system features ahead of launch

Inside Apple hardware prototype and development stages
Apple's on-device email categorization is a feature years in the making
Latest comparisons.

Apple Watch Series 9 vs Samsung Galaxy Watch 7— Specs, price, and features, compared

AirPods Max vs. Sonos Ace: premium personal audio, compared

More Metal: Apple's iPad Pro Magic Keyboards, compared
Latest news.

Delta 1.6 classic game emulator now available for iPad
The Delta emulator app that allows players to use their own ROM files for various retro gaming systems on an iPhone is now also available for the iPad.

Is Apple finally serious about gaming after its latest push?
Apple has an absolutely dominant position in mobile gaming because of the ubiquity of the iPhone but a minuscule desktop market share. Apple has big plans for 2024, and we got a look at some of what's coming.

'Find My' feature helps diver recover lost Apple Watch nearly two years later
A YouTuber who lost his Apple Watch while swimming and diving in the summer of 2022 has had it returned to him, thanks to the Find My feature.

Lowest price ever: Apple's M3 16-inch MacBook Pro plunges to $1,899 ahead of Prime Day
Record-breaking deals are making an appearance ahead of the official start of Prime Day, as Amazon and Best Buy engage in an all-out M3 MacBook Pro price war.

Jake Gyllenhaal's 'Presumed Innocent' gets renewed for a second season
Apple has renewed its legal drama "Presumed Innocent" starring Jake Gyllenhaal for a second season on Apple TV+.

Amazon matches Best Buy's $799 M2 MacBook Air deal as Prime Day nears
The price wars continue with Amazon matching Best Buy in an early Prime Day MacBook Air showdown. Grab the lowest price on record for the M2 13-inch model.

Tim Cook, Eddy Cue, and Sam Altman hobnob at annual Sun Valley media retreat
Apple's Tim Cook and Eddy Cue have returned to the annual Allen & Company Sun Valley retreat, known for being where billionaires make significant deals.

India's antitrust regulator has decided that Apple abuses its market dominance
After three years of investigations, Indian regulators have concluded that Apple has been using antitrust behaviours by forcing App Store developers to use its in-app payment system.

Smart rings, Apple Watch rumors, and more betas on the AppleInsider Podcast
Apple Watch redesign rumors are on-again off-again, the iOS 16 beta keeps improving, and while the Apple Ring isn't even out yet, Samsung is still not looking very original this week, all on the AppleInsider Podcast.

Nearly every AT&T customer just had six months of call logs stolen
AT&T has just disclosed another old data breach, with this one exposing nearly every customer's phone call and text message records for a date range spanning six months in 2022.
Latest Videos

Retro gold rush: which emulators are on the App Store, and what's coming

iPhone 16 fast charging could get a 40W boost

Apple Watch Series 10 & Ultra 3 will be faster, but not an anniversary redesign
Latest reviews.

Logitech MX Keys S review: Great typing feel and feature packed

JSAUX FlipGo Portable Dual Monitor review: Double your screens, double your productivity

{{ title }}
{{ summary }}
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Exclusive: India antitrust probe finds Apple abused position in apps market
- Medium Text

- India latest in growing antitrust scrutiny of Apple globally
- India investigation says Apple policies hurt developers
- Apple has argued it is too small a player in India
- Company can argue against India findings in coming weeks
APPLE VS GOOGLE IN INDIA
Sign up here.
Reporting by Aditya Kalra; Editing by Hugh Lawson
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Aditya Kalra is the Company News Editor for Reuters in India, overseeing business coverage and reporting stories on some of the world's biggest companies. He joined Reuters in 2008 and has in recent years written stories on challenges and strategies of a wide array of companies -- from Amazon, Google and Walmart to Xiaomi, Starbucks and Reliance. He also extensively works on deeply-reported and investigative business stories.

Technology Chevron

OpenAI whistleblowers ask SEC to investigate alleged restrictive non-disclosure agreements
OpenAI whistleblowers have filed a complaint with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, calling for an investigation over the artificial intelligence company's allegedly restrictive non-disclosure agreements, according to a letter seen by Reuters.

Handling Tax Debt in Divorce with Morgan Anderson Broke Up, Not Broke(n)
Jamie M. Lima and Morgan Anderson discuss the critical role of addressing tax issues during divorce. They cover tax debt responsibility, the innocent spouse rule, strategies to minimize tax burdens, and filing status considerations. Morgan shares a case study and offers final advice on managing tax issues.
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
- Copyright 2024 Broke Up, Not Broke(n)

COMMENTS
Apple is well-known for its innovations in hardware, software, and services. Thanks to them, it grew from some 8,000 employees and $7 billion in revenue in 1997, the year Steve Jobs returned, to ...
Abstract. After a decade as CEO, Tim Cook is facing one of his biggest strategic transitions of his tenure. While Apple had performed spectacularly well under Cook, Apple's core business was maturing. Sales of iPhones, iPads, and Macs were flat or down. However, Apple's new hardware—Apple Watch and Airpods—as well as services were growing ...
A Case Study on Apple Marketing Strategy. Breaking through with several inventions in the world of technology, Apple Inc. has been carving infinite milestones ever since its inception. Even though its innovations speak for themselves, this highly-valued giant corporation has invested heavily in its marketing team to soar high up as a tech maestro.
Abstract. The essential components of carrying out an organizational analysis (a case study on Apple Inc) include evaluating external factors that can affect the organization's performance as well ...
Apple iPhone: A Market Case Study. Daylin Van De Vliert. Abstract. Founde d in 1976, Apple inc. quickly became one ofhe biggest companies in the world. Throughout the years, Apple has been a part ...
Yet, against all odds, Apple orchestrated a remarkable turnaround in 1997. The linchpin of this resurgence was the ingenious "Think Different" campaign. This case study delves into the genesis ...
Abstract. Under CEO Tim Cook, Apple became the first trillion dollar market cap company, the first two trillion dollar company, and the first three trillion dollar company. Since the COVID pandemic, Apple gained over 20% of the world smartphone market and 50% of the U.S. market, making Apple the largest seller of smartphones in 2023.
Describes Apple's approach to innovation, management, and design thinking. For several years, Apple has been ranked as the most innovative company in the world, but how it has achieved such success remains mysterious because of the company's obsession with secrecy. This note considers the ingredients of Apple's success and its quest to develop ...
This case explores Apple's history and Cook's strategic options for driving new hardware and services into Apple's mainstream in the next decade. Learning Objectives. This case can be used for several purposes, including industry analysis, introduction of complementary assets, sustaining competitive advantage and expanding corporate scope. ...
1,359 shares. Apple's Product Development Process may be one of the most successful design processes ever implemented. With a valuation that exceeds $2 trillion, there's a lot that designers can learn from Apple and introduce into their own design environments. Apple is a notoriously secretive business. In Steve Jobs' time at the company ...
Dean, Apple University Morten T. Hansen Faculty, Apple University AUTHORS FOR ARTICLE REPRINTS CALL 800-988-0886 OR 617-783-7500, OR VISIT HBR.ORG Harvard Business Review November-December 2020 3 This article is made available to you with compliments of Apple Inc for your personal use. Further posting, copying or distribution is not permitted.
Apple's journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and ...
Apple's brand nudges consumers to focus on the emotional connection rather than a rational analysis of product needs, creating a distinctive position in the market. In essence, Apple's success story becomes a compelling case study illustrating the symbiotic relationship between brand strategy, consumer psychology and technological innovation.
Research & Knowledge. Home Research & Knowledge Operations Apple's supply chain transformation. In 2022, Apple lost US$1.5 billion in Black Friday sales due to iPhone supply constraints. One in three retail stores across the US and Europe experienced stockouts of the new iPhone 14 Pro. China sales were down more than 30% year on year.
Headquartered in Cupertino, California, Apple Inc. has experienced many successes throughout. their business history. Apple's journey to success has not been without ethical challenges along. the way. Apple's success can be seen from their stock price, up from $3.30 per share in 1997 to. $320 per share in 2020.
Specifically, the case study considers how the Apple business model allows it to 'own the consumer' through its multi-channel platform that relies on the integration of content (software, media, and apps) and hardware (laptop, phones, and tablets) to drive growth. Apple's business model enables it to exercise unparalleled control over it ...
In this case study, we will explore how Apple effectively used this campaign to build brand awareness, increase customer engagement, and drive sales. Background: The "Shot on iPhone" campaign was launched in 2015 as part of Apple's strategy to promote the iPhone 6s, which featured a new 12-megapixel camera. The campaign aimed to highlight ...
Instructional case study of Apple Inc . View full-text. Article. Full-text available. Influence of Change in Management in Technological Enterprises. December 2016 · Procedia Economics and Finance.
Apple's Culture Type and Traits. Apple has an organizational culture for creative innovation. The company's cultural features focus on maintaining a high level of innovation that involves workers' creativity and a mindset that challenges conventions and standards, such as in consumer electronics design. Apple's IT business depends on ...
Apple's core business—the iPhone—continued to deliver spectacular results. In addition, Cook was aggressively introducing new products, ranging from Apple Watch to HomePod. Cook also had the world's biggest balance sheet to invest in new technologies and markets. ... Harvard Business School Case 718-439, May 2018. (Revised December 2019 ...
The Apple case study uses the brand idea for Apple is "making technology so simple that everyone can be part of the future." Most importantly, Steve Jobs insisted they take a consumer-first mentality as they transformed leading technology advancements into "consumer-accessible" technology, helping fuel the perception among the mass ...
Case Study on Apple's Business Strategies. Apple was founded by Steve Jobsand Stephen Wozniak in 1976; Apple Computers revolutionized the personal computer industry. Apple Computers Inc is considered to be one of the innovators in the computer industry. It brought about different changes to the industry; these changes are still visible in the ...
Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple. Apple Inc is a multinational American company that design and sells computer software, consumer gadgets and personal computers. It was co-founded by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne. Apple Inc is well-known for being innovative as they kept on producing new innovations from the first Apple ...
It needs a great engine and a lot of fuel, which in this case, is data. Apple has tons of fuel - but it doesn't have a great engine. That's where OpenAI comes into play.
Apple was recently charged in another case with violating E.U. competition laws for its policies related to the App Store. The company is also appealing a 1.8 billion euro fine for thwarting ...
Apple's having won with its argument that it faces "fierce competition," could now well be used in its legal case with the Department of Justice. Central to the DOJ's case is the argument that ...
Apple Inc. is seeking to get a Chinese court to alter its written ruling in a lawsuit the iPhone maker won, an unusual move that underscores the sensitivity of the US company's position in the ...
The Indian case was first filed by a little-known, non-profit group called "Together We Fight Society" which argued Apple's in-app fee of up to 30% hurts competition by raising costs for app ...
Apple is now facing a February 2026 trial in a $7 billion class action in California federal court that accuses the company of monopolizing the app market for its iPhones, causing tens of millions ...
Jamie M. Lima and Morgan Anderson discuss the critical role of addressing tax issues during divorce. They cover tax debt responsibility, the innocent spouse rule, strategies to minimize tax burdens, and filing status considerations. Morgan shares a case study and offers final advice on managing tax…