
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 8 Geography Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Case study questions class 8 geography chapter 2 land, soil, water, natural vegetation and wildlife resources.
CBSE Class 8 Case Study Questions Geography Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources. Important Case Study Questions for Class 8 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Geography Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Case study – 1.
In a small village in Tanzania, Africa, Mamba gets up very early in the morning to fetch water. She has to walk a long way and returns after a few hours. She then helps her mother in the house and joins her brothers in taking care of their goats. All her family owns is a piece of rocky land around their small hut. Mamba’s father can barely grow some maize and beans on it after toiling hard. This is not enough to feed their family for the whole year. Peter lives in the heart of the sheep rearing region in New Zealand where his family runs a wool processing factory. Everyday when he returns from school, Peter watches his uncle taking care of their sheep. Their sheep yard is situated on a wide grassy plain with hills in the far distance. It is managed in a scientific way using the latest technology. Peter’s family also grows vegetables through organic farming. Mamba and Peter stay in two different parts of the world and lead very different lives. This difference is because of the differences in the quality of land, soil, water, natural vegetation, animals and the usage of technology. The availability of such resources is the main reason places differ from each other.
QUESTION MARKS:1
1.Why does Mamba get up very early in the morning?
Ans: Mamba gets up very early in the morning to fetch water.
2.Where does Peterlive in?
Ans: Peter lives in the heart of the sheep rearing region in New Zealand.
QUESTION MARKS:2
1.Why Mamba and Peter lead very different kind of lives?
Ans: Mamba and Peter stay in two different parts of the world and lead very different lives. This difference is because of the differences in the quality of land, soil, water, natural vegetation, animals and the usage of technology.
2.Where Peter’s sheep yard is situated and how is it managed?
Ans:Peter’s sheep yard is situated on a wide grassy plain with hills in the far distance. It is managed in a scientific way using the latest technology.
Case Study – 2
Land is among the most important natural resources. It covers only about thirty per cent of the total area of the earth’s surface and all parts of this small percentage are not habitable. The uneven distribution of population in different parts of the world is mainly due to varied characteristics of land and climate. The rugged topography, steep slopes of the mountains, lowlying areas susceptible to water logging, desert areas, thick forested areas are normally sparsely populated or uninhabited. Plains and river valleys offer suitable land for agriculture. Hence, these are the densely populated areas of the world. Land is used for different purposes such as agriculture, forestry, mining, building houses, roads and setting up of industries. This is commonly termed as Land use. Can you list out the different ways in which Mamba’s and Peter’s family use their land? The use of land is determined by physical factors such as topography, soil, climate, minerals and availability of water. Human factors such as population and technology are also important determinants of land use pattern. Land can also be classified on the basis of ownership as – private land and community land. Private land is owned by individuals whereas, community land is owned by the community for common uses like collection of fodder, fruits, nuts or medicinal herbs. These community lands are also called common property resources.
QUESTIONS &ANSWERS: Marks: 1
1.What is the most important natural resource?
Ans: The most important natural resource is Land.
2. What is the main reason of uneven distribution of population in different parts of the world?
Ans: The uneven distribution of different population in different parts of the world is mainly due to varied characteristics of land and climate.
1. what is the meaning of ‘Land Use’?
Ans: Land is used for different purposes such as agriculture,forestry, mining, building houses, roads and setting up of industries. This is commonly Termed as Land use’.
2. What is the difference between private land and community land?
Ans:Private land is owned by individuals whereas, community land is owned by the community for common uses like collection of fodder, fruits, nuts or medical herbs.
Case Study – 3
The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil. It is closely linked to land. Landforms determine the type of soil. Soil is made up of organic matter, minerals and weathered rocks found on the earth. This happens through the process of weathering. The right mix of minerals and organic matter make the soil fertile. Landslides are simply defined as the mass movement of rock, debris or earth down a slope. They often take place in conjunction with earthquakes, floods and volcanoes. A prolonged spell of rainfall can cause heavy landslide that can block the flow of river for quite some time. The formation of river blocks can cause havoc to the settlements downstream on its bursting. In the hilly terrain landslides have been a major and widely spread natural disaster that often strike life and property and occupy a position of major concern.
QUESTIONS & ANSWERS: MARKS:1
1.What is closely linked to land?
Ans:Soil is closely linked to land.
2.What make the soil fertile?
Ans:The right mix of minerals and organic matter make the soil fertile.
1.What is called soil?
Ans: The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
2.What can cause heavy landslides?
Ans: A prolonged spell of rainfall can cause heavy landslide that can block the flow of river for quite some time.
Very good content
Very good this help us to do many things. This lead to many of technology problems. Thanks for this website.
Very useful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Wbchse english semester syllabus class 11 2024, tripura board class 6 bengali solutions chapter 7 বিয়েবাড়ির মজা, case study questions class 7 maths fractions, case study questions class 7 maths integers.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
- Last modified on: 7 months ago
- Reading Time: 14 Minutes

Table of Contents
Here we are providing case study questions for class 8 social science Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources.
Case Study Question 1:
The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil. It is closely linked to the land. Landforms determine the type of soil. Soil is made up of organic matter, minerals and weathered rocks found on the earth. This happens through the process of weathering. The right mix of minerals and organic matter makes the soil fertile. The major factors of soil formation are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors. Other factors are the topography, role of organic material and time taken for the composition of soil formation. All these differ from place to place. Soil erosion and depletion are the major threats to the soil as a resource. Both human and natural factors can lead to the degradation of soils. Factors which lead to soil degradation are deforestation, overgrazing, overuse of chemical fertilisers or pesticides, rain wash, landslides and floods. Landslides are simply defined as the mass movement of rock, debris or earth down a slope. They often take place in conjunction with earthquakes, floods and volcanoes. A prolonged spell of rainfall can cause heavy landslides that can block the flow of rivers for quite some time. The formation of river blocks can cause havoc to the settlements downstream on its bursting. In the hilly terrain, landslides have been a major and widely spread natural disaster that often strike life and property and occupy a position of major concern.
Q. 1. Which is the most appropriate method to check the soil erosion on steep slopes? (a) Shelter belts (b) Mulching (c) Soil texture (d) Terrace cultivation
Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: Broad flat steps or terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops. They reduce surface runoff and soil erosion.
Q.2. refers to the destruction of soil by wind and water. (a) Soil erosion (b) Landslides (c) Land degradation (d) None of these
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Soil erosion and depletion are the major threats to soil as a resource. Both human and natural factors can lead to the degradation of soils. It refers to the destruction of soil by wind and water.
Q. 3. Which determines the type of soil? (a) Landforms (b) Soil erosion (c) Land degradation (d) None of these
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil. It is closely linked to land. Landforms determine the type of soil.
Q. 4. Soil is made up of: (a) Matter (b) Material (c) Matter, material and weathered rocks (d) None of these
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Soil is made up of organic matter, minerals and weathered rocks found on the earth. This happens through the process of weathering. The right mix of minerals and organic matter makes the soil fertile.
Q. 5. The method in which rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water. This prevents gullies and further soil loss. (a) Mulching (b) Rock dam (c) Terrace cultivation (d) Inter cropping
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Rock dam: Rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water. This prevents gullies and further soil loss.
Learning Outcomes
- Understand the importance of resources in our life.
- Appreciate the judicious use of resources for sustainable development.
- Develop awareness towards resource conservation.
- Take initiative towards the conservation process.
Important Keywords
- Parent Rock: The original rock from which a particular soil is formed is known as its parent rock.
- Water Cycle: The natural process of the constant motion of water by evaporation, condensation and rainfall is known as the water cycle.
- Rain Water Harvesting: This is the process of conservation of water under which rainwater is collected so that it can be used in times of water scarcity.
- Biosphere: It is the narrow zone of contact between the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
- Tundra: The type of vegetation found in extremely cold regions such as the Arctic.
- Scavenger: A bird or animal, which derives food from dead livestock.
- National Parks: A natural area dedicated to protect the ecological integrity of ecosystem(s) for the present and future generations.
- Vanamohatasava: The social programme of planting trees organised at community level.
- Biosphere Reserves: Series of protected areas linked by a global network, which demonstrate the relationship between conservation and development.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: This is similar to a national park, but it aims at the protection of a particular animal or general wildlife.
Related Posts
Social science class 8 chapter list, old chapter list.
Class 8 Social Science History: Our Pasts – III
Chapter 1 How, When and Where Chapter 2 From Trade to Territory Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside Chapter 4 Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age Chapter 5 When People Rebel Chapter 6 Colonialism and the City Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners Chapter 8 Civilising the “Native”, Educating the Nation Chapter 9 Women, Caste, and Reform Chapter 10 The Changing World of Visual Arts Chapter 11 The Making of the National Movement Chapter 12 India After Independence
Class 8 Social Science Geography
Class 8 Social Science Geography: Resources and Development
Chapter 1 Resources Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Chapter 4 Agriculture Chapter 5 Industries Chapter 6 Human Resource
Class 8 Social Science Civics NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics: Social and Political Life – II
Chapter 1 The Indian Constitution Chapter 2 Understanding Secularism Chapter 3 Why Do We Need a Parliament? Chapter 4 Understanding Laws Chapter 5 Judiciary Chapter 6 Understanding Our Criminal Justice System Chapter 7 Understanding Marginalisation Chapter 8 Confronting Marginalisation Chapter 9 Public Facilities Chapter 10 Law and Social Justice
What is Case Study Question in Class 8 Social Science?
Case study questions typically present a specific scenario or case related to a historical event, geographical issue, or social problem. Students are expected to read and understand the details of the case and then answer a set of questions based on their understanding and knowledge of the subject matter.
Case study questions can be an effective way to assess students’ understanding and ability to apply social science concepts to practical situations. They also encourage students to think critically, analyze information, and draw informed conclusions – skills that are valuable both inside and outside the classroom.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Extra Questions
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Extra Questions and Answers are provided here. These Extra Questions with solution are prepared by our team of expert teachers who are teaching in CBSE schools for years. Extra questions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Class 8 Geography Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer type question.
1. Which country has the highest percentage of land under forest?
Answer: Japan
2. Which country has the highest percentage of land under cropland?
Answer: India
3. Which country has the highest percentage of land under pasture?
Answer: Australia
4. What are the major threats to soil as a resource?
Answer: Soil erosion and depletion are the major threats to soil as a resource.
5. What method of soil conservation is used in coastal and dry regions?
Answer: Shelter belts are used to protect the soil in coastal and dry regions.
6. What percent of fresh water is fit for human use?
Answer: Only 1 per cent of freshwater is available and fit for human use.
7. What make the soil fertile?
Answer: The right mix of minerals and organic matter make the soil fertile.
8. What affect the rate of humus formation?
Answer: Flora, fauna and micro-organism affect the rate of humus formation.
9. Why is ocean water not fit for human consumption?
Answer: The ocean water is saline. Hence it is not fit for human consumption.
10. What is soil?
Answer: The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
Short Type Answer Questions
1. Which are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation?
Answer: Temperature and rainfall are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation.
2. Which method is most appropriate to check soil erosion on steep slopes?
Answer: Terrace farming is the most appropriate method to check soil erosion on steep slopes.
3. What do you mean by shelter belt?
Answer: Rows of trees planted in the coastal areas to check the wind movement is called shelter belt.
4. How are forest classified on the basis of latitude?
Answer: Forests are classified as tropical or temperate based on their location in different latitudes.
5. What are the major types of vegetation in the world?
Answer: The major vegetation types of the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, scrubs and tundra.
6. How are vultures important to the environment?
Answer: Vulture due to its ability to feed on dead livestock is a scavenger and considered a vital cleanser of the environment.
7. What percentage of Earth is covered by land?
Answer: Land covers only about thirty per cent of the total area of the earth’s surface and all parts of this small percentage are not habitable.
8. What is national park?
Answer: National park is a natural area designated to protect the ecological integrity of one or more ecosystems for present and future generations.
9. How is soil formed?
Answer: Soil is made up of organic matter, minerals and weathered rocks found on the earth. This happens through the process of weathering.
10. What is weathering?
Answer: Weathering is the breaking up and decay of exposed rocks, by temperature changes, frost action, plants, animals and man.
11. Why are plains and river valleys densely populated?
Answer: Plains and river valleys offer suitable land for agriculture. Hence, these are the densely populated areas of the world.
12. Why Ganga Brahmaputra plain of India is an over populated region?
Answer: Ganga Brahmaputra plain of India is an over populated region because it has even topography and highly fertile soil.
13. What are the different types of soil found in India?
Answer: Different types of soil found in India are alluvial, black, red, laterite, desertic and mountain soil.
14. Why is fresh water the most precious substance on earth?
Answer: Fresh water is the most precious substance on earth because only 1 per cent of freshwater is available and fit for human use.
15. What is rain water harvesting?
Answer: Rain water harvesting is the process of collecting rain water from roof tops and directing it to an appropriate location and storing if for future use.
16. Write any two reasons for land degradation today?
Answer: Reasons for land degradation are:
- Deforestation
- Overuse of chemical feritilisers or pesticides
17. What has led to a large scale destruction of forest cover and arable land?
Answer: Growing population and their ever growing demand has led to a large scale destruction of forest cover and arable land.
18. How to prevent surface runoff?
Answer: Forest and other vegetation cover slow the surface runoff and replenish underground water. Water harvesting is another method to save surface runoff.
19. Suggest one way to control water pollution.
Answer: Water pollution can be controlled by treating sewage, agricultural chemicals and industrial effluents suitably before releasing them in water bodies.
20. What is intercropping?
Answer: Intercropping is a multiple cropping practice in which different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the soil from rain wash.
21. Why Earth is called water planet?
Answer: Water is a vital renewable natural resource. Three-fourth’s of the earth’s surface is covered with water. It is therefore appropriately called the ‘water planet’.
22. What is biosphere?
Answer: Natural vegetation and wildlife exist only in the narrow zone of contact between the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere that we call biosphere.
23. What do you mean by ecosystem?
Answer: In the biosphere living beings are inter-related and interdependent on each other for survival. This life supporting system is known as the ecosystem.
24. What is termed as Land use?
Answer: Land is used for different purposes such as agriculture, forestry, mining, building houses, roads and setting up of industries. This is commonly termed as Land use.
25. Why land is considered an important resource?
Answer: Land is considered an important resource because it is used for different purposes such as agriculture, forestry, mining, building houses, roads and setting up of industries.
26. Which areas are sparsely populated or uninhabited?
Answer: The rugged topography, steep slopes of the mountains, low-lying areas susceptible to water logging, desert areas, and thick forested areas are normally sparsely populated or uninhabited.
27. How much land on Earth is inhabited?
Answer: Ninety per cent of the world population occupies only thirty per cent of land area. The remaining seventy per cent of the land is either sparsely populated or uninhabited.
28. What are the major threats to the environment due to over exploitation of land resources?
Answer: Land degradation, landslides, soil erosion, desertification are the major threats to the environment because of the expansion of agriculture and constructional activities.
29. What are the reasons for water shortage?
Answer: Water shortage may be a consequence of variation in seasonal or annual precipitation or the scarcity is caused by overexploitation and contamination of water sources.
30. What is the major cause of water pollution?
Answer: Discharge of untreated or partially treated sewage, agricultural chemicals and industrial effluents in water bodies are major contaminants. They pollute water with nitrates, metals and pesticides.
Long Type Answer Questions
1. What is ‘water cycle’?
Answer: Water is in constant motion, cycling through the oceans, the air, the land and back again, through the processes of evaporation, precipitation and run-off. This is referred to as the ‘water cycle’.
2. What are the major factors affecting soil formation?
Answer: The major factors of soil formation are the nature of the parent rock and climatic factors. Other factors are the topography, role of organic material and time taken for the composition of soil formation.
3. What are the uses of water resources?
Answer: Humans use huge amounts of water not only for drinking and washing but also in the process of production. Water for agriculture, industries, generating electricity through reservoirs of dams are the other usages.
4. What do you mean by private land and community land?
Answer: Private land is owned by individuals whereas, community land is owned by the community for common uses like collection of fodder, fruits, nuts or medicinal herbs. These community lands are also called common property resources.
5. Which countries in the world are facing water shortage?
Answer: There is scarcity of water in many regions of the world. Most of Africa, West Asia, South Asia, parts of western USA, north-west Mexico, parts of South America and entire Australia are facing shortages in fresh water supply.
6. What human factors determine land use pattern? Or What factors determine land use pattern?
Answer: The use of land is determined by physical factors such as topography, soil, climate, minerals and availability of water. Human factors such as population and technology are also important determinants of land use pattern.
7. What are landslides and how do they occur?
Answer: Landslides are simply defined as the mass movement of rock, debris or earth down a slope. They often take place in conjunction with earthquakes, floods and volcanoes. A prolonged spell of rainfall can cause heavy landslide that can block the flow of river for quite some time.
8. Why water availability per person in India is declining?
Answer: Increasing population, rising demands for food and cash crops, increasing urbanisation and rising standards of living are the major factors leading to shortages in supply of fresh water either due to drying up of water sources or water pollution.
9. What are the reasons for the degradation of the soil?
Answer: Soil erosion and depletion are the major threats to soil as a resource. Both human and natural factors can lead to degradation of soils. Factors which lead to soil degradation are deforestation, overgrazing, overuse of chemical feritilisers or pesticides, rain wash, landslides and floods.
10. Differentiate between tropical evergreen forests and deciduous forests.
11. Name any two steps that government has taken to conserve plants and animals.
Answer: Two steps that government has taken to conserve plants and animals are:
- It has set up national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves to protect our natural vegetation and wildlife.
- It has banned the killing of lions, tigers, deers, great Indian bustards and peacocks.
12. Suggest three ways to conserve water.
Answer: Ways to conserve water:
- Rain water harvesting.
- The canals should be properly lined to minimise losses by water seepage.
- In dry regions with high rates of evaporation, drip or trickle irrigation is very useful.
13. In what forms is freshwater found on the earth?
Answer: Fresh water accounts for only about 2.7 per cent. Nearly 70 per cent of this occurs as ice sheets and glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland and mountain regions. Due to their location they are inaccessible. Only 1 per cent of freshwater is available and fit for human use. It is found as ground water, as surface water in rivers and lakes and as water vapour in the atmosphere.
14. What do you know about CITES?
Answer: CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) is an international agreement between governments. It aims to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival. Roughly 5,000 species of animals and 28,000 species of plants are protected. Bears, dolphins, cacti, corals, orchids and aloes are some examples.
15. Why there is uneven distribution of population in different parts of the world?
Answer: The uneven distribution of population in different parts of the world is mainly due to varied characteristics of land and climate. The rugged topography, steep slopes of the mountains, low-lying areas susceptible to water logging, desert areas, and thick forested areas are normally sparsely populated or uninhabited. Plains and river valleys offer suitable land for agriculture. Hence, these are the densely populated areas of the world.
16. How does rainfall affect vegetation?
Answer: In areas of heavy rainfall, huge trees may thrive. The forests are thus associated with areas having abundant water supply. As the amount of moisture decreases the size of trees and their density reduces. In the regions of moderate rainfall short stunted trees and grasses grow forming the grasslands of the world. In dry areas of low rainfall, thorny shrubs and scrubs grow. In such areas plants have deep roots and leaves have thorny and waxy surface to reduce loss of moisture by transpiration.
17. Why is wildlife important to us?
Answer: Wildlife is important to us because
- They provide us milk, meat, hides and wool.
- Insects like bees provide us honey, help in pollination of flowers and have an important role to play as decomposers in the ecosystem.
- The birds feed on insects and act as decomposers as well.
- Vulture due to its ability to feed on dead livestock is a scavenger and considered a vital cleanser of the environment.
18. What are the factors affecting soil formation?
Answer: Factors affecting soil formation are: Parent Rock – Determines colour, texture, chemical properties mineral, content, permeability of soil. Climate – Temperature and rainfall influence rate of weathering and humus. Relief – Altitude and slope, determine accumulation of soil. Flora, Fauna and Micro-organism – Affect the rate of humus formation. Time – Determines thickness of soil profile.
19. “Vegetation and wildlife are valuable resources.” Comment
Answer: Vegetation and wildlife are valuable resources.
- Plants provide us with timber, give shelter to animals, produce oxygen we breathe, protects soils so essential for growing crops, act as shelter belts, help in storage of underground water, give us fruits, nuts, latex, turpentine oil, gum, medicinal plants and paper.
- Wildlife includes animals, birds, insects as well as the aquatic life forms. They provide us milk, meat, hides and wool. Insects like bees provide us honey, help in pollination of flowers and have an important role to play as decomposers in the ecosystem. The birds feed on insects and act as decomposers as well. Vulture due to its ability to feed on dead livestock is a scavenger and considered a vital cleanser of the environment.
20. What are the threats to natural vegetation and wildlife?
Answer: Threats to natural vegetation and wildlife are:
- Changes of climate and human interferences can cause the loss of natural habitats for the plants and animals. Many species have become vulnerable or endangered and some are on the verge of extinction.
- Deforestation, soil erosion, constructional activities, forest fires, tsunami and landslides are some of the human made and natural factors which together accelerate the process of extinction of these great natural resources.
- One of the major concerns is the increasing incidents of poaching that result in a sharp decline in the number of particular species.
21. Suggest some methods of soil conservation.
Answer: Some methods of soil conservation are
Mulching: The bare ground between plants is covered with a layer of organic matter like straw. It helps to retain soil moisture.
Contour barriers: Stones, grass, soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches are made in front of the barriers to collect water.
Rock dam: Rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water. This prevents gullies and further soil loss.
Terrace farming: These are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops. They can reduce surface run-off and soil erosion.
Intercropping: Different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the soil from rain wash.
Contour ploughing: Ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope to form a natural barrier for water to flow down the slope.
Shelter belts: In the coastal and dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check the wind movement to protect soil cover.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Resources Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes
- Social Science: Geography
- Chapter 1 Resources

Resources Class 8 Notes Geography Chapter 1 - PDF Download
The class 8 geography chapter 1 notes are mostly concerned with topographical considerations and the external variables present in an environment. The textbook, Resource and Development, goes into great detail about class 8 geography and its constituent elements. Class 8 geography covers a wide range of topics, all of which are covered in six chapters. These six chapters include subjects such as resources, mineral and power resources, industries, human resource development, and so on. To build a solid foundation in this topic, look over the class 8 geography notes to understand what questions will most likely arise in the exams.
By reviewing resources class 8 notes, a student can be more assured about themselves and confidently appear in exams. While text-books may contain exhaustive paragraphs out of which only one or two points may be necessary to learn, the class 8 Geography chapter 1 resources notes will have the most important parts of the topics present within the textbook. The notes themselves are a coalition of the various chapters and their key concepts. The class 8 Geography notes contain a compilation of the chapters: (i) Resources; (ii) Land, soil, water, natural vegetation and Wildlife Resources; (iii) Mineral and Power resources; (iv) Agriculture; (v) Industries; and (vi) Human resources.
Download CBSE Class 8 Geography Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 8 Geography revision notes for All chapters:

Access Class 8 Social Science (Geography) Chapter 1 - Resources Notes
What are resources.
Anything that can be used to fulfil a need and has some value is a resource. Substances like water, electricity, vegetables, cars and textbooks all have a specific utility and hence they are considered as resources. Some resources are economically valuable while some are not. Beautiful scenery does not have an economical value like gold, but it is equally important to satisfy human utility. Some resources may gain value with time while some may lose their value.
Time and Technology
Time and technology play a significant role in changing substances into valuable resources. These two factors are related to the needs of the people. As people themselves are the most significant resource, their ideas, knowledge, inventions and discoveries with time lead to the formation of more resources. With the advancement of technology, every discovery or invention leads to many other subsequent ones. Here are a few examples:
The discovery of fire gave the idea of cooking.
Agricultural development came out as a result of domestication of animals.
The invention of the wheel caused the invention of various modes of transport.
The technology to produce hydroelectricity has resulted in the successful harnessing of energy present in fast-flowing water.
Types of Resources
Resources are classified into natural, man- made and human resources.
Natural Resources are extracted from nature and are mainly utilized without making any change in their form. For example, air, water, minerals, etc.
Man Made Resources are the ones which are made by humans. They are derived from natural resources but are not used in their original form. For example, roads, machines, etc.
Human Resources are the quality and quantity of humans who can use their skills to create more resources for mankind. Every human is a resource if they can create man made resources.
The natural resources can be either Renewable or Non-Renewable . Renewable resources can be renewed easily and quickly and they can be used for millions of years. For example, sunlight, wind, etc. but the non-renewable resources take millions of years to form and get renewed so they can be used only for a few centuries. For example, coal, petroleum, etc.
The training and improvement of skills of a human by education is called Human Resource Development . It enhances the mental and physical capability of humans so that they can be of use to humanity.
Conservation of Resources
The use of resources for need, without greed is called conservation of resources. It enables the resources to be renewed for future generations. Also, when the resources are used in a manner that they remain useful for the future generations too, it is called Sustainable Development . We can do this by recycling and reusing things. We can also follow a reduction of use for the unimportant things in our life.
Principles of Sustainable Development
Respect and care for all forms of life
Improve the quality of human life
Conserve the earth’s vitality and diversity
Minimise the depletion of natural resources
Change personal attitude and practices towards the environment
Enable communities to care for their own environment
Important Questions and Answers
1. Explain how resources have value.
Ans: Resources have a value if they are of any use to the people, directly or indirectly. The resources can either have a commercial value or they do not have a commercial value. Here are some examples:
Platinum is a resource that has economic value as we make many valuable products from it like jewellery.
A beautiful landscape that you observe may not have economic value but is still said to be a resource as it is functional in providing pleasure to the human mind.
2. What is wind energy and why is it becoming important?
Ans: Wind energy is the use of power of wind to generate electricity which we can use for other purposes. A turbine is rotated using wind energy and this generates electricity we can use.
As wind turbines are an environmentally clean and sustainable renewable form of electricity, wind power is gaining popularity. Wind energy is also emerging as an economically competitive source of energy as compared to most conventional power sources.
3. Why is a human resource important?
Ans: Human resources are important because humans are sometimes skilled and can be trained to make the best use of nature in order to use the existing resources and also generate more resources using the knowledge and technology that they gain over time.
4. Mention and define the major types of natural resources.
Ans: Broadly, there are two types of resources:
Renewable Resources whose availability is not affected by human consumption. These resources get renewed quickly even with constant human usage.
Non-Renewable Resources which have a limited supply and are highly affected by human consumption. These resources decline with human consumption. They take thousands of years to get formed. For example, coal and petroleum.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - Resources
benefits of studying from the class 8 geography notes .
The notes highlight significant topics which are found in the 6 chapters.
They are highly recommended for those who wish to revise and practice their knowledge on the subject before they give their board exams.
Insightful and it provides students with an opportunity to gain a holistic view of how all the chapters are interrelated.
Revision notes also help in exam preparation.
The notes are cumulative of all the chapters and are a short-cut way of understanding all the various nuances of the subject itself.
(Image to be added soon)
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources
This chapter is primarily concerned with resources such as transportation systems, power (electricity), food, and water. The chapter categorises these resources based on the usefulness that a product provides. One of the most important aspects of a resource is its usability and how the entire population of a country may profit from it. In other words, it must be valuable. Each thing or substance that has the potential to be valuable to humans is immediately turned into a resource on the spot. Furthermore, some resources are known to be efficient to use and to have inherent economic value. A student can learn about different types of resources in geography class 8. The notes contain very specific information on the topic, but it is best to consult the text-book before revising with class 8 geography chapter 1 notes.
Anything that can be converted into something of value is a resource. A resource is usually used to satisfy a need or a want of an economy. Resources are also involved in the ‘allocation of resources’ process that is involved in economics. That is the capacity for intersectionality that this chapter has. Moreover, resources are one of the most essential components of any business. Workforces, labour market, etc. are all examples of what all come under the umbrella term ‘resources’.
Types of Resources
Universally, there are considered three main types of resources under which all the other types are situated. The three kinds are natural; man-made; human.
Natural Resources
These types of resources are naturally found in nature itself as the name suggests. Some natural resources are the air we breathe, water for drinking or bathing, oil resources, minerals in the soil, the soil itself for plantation purposes, etc. Anything that can be found in nature which can be put to use by the human race is supposed to be a natural resource. Thus, renewable energies like the sun and wind energy also come under this definition.
Man-Made Resources
Some natural resources which can be moulded into resources by humans are considered a man-made resource. All man-made/human-made resources are essentially materials or substances found in nature that had to be refined and processed for humans to gain some sort of benefit out of it.
Human Resource
As mentioned earlier, labour markets and such constitute a resource. This resource is known as the human resource, and the NCERT class 8 geography chapter 1 notes elucidates further about its importance. Human resources are defined as a resource that refers to the number of people and the mental/physical capacity of people who are willing to work. The business sector especially treats human resource as one of the most valuable resources one can find.
Conserving Resources
The stock of natural resources is limited. It is better to conserve the natural resources by using them carefully so that they get the time to be renewed. Careful use of these resources balances the need for using them and the conservation for the future. Due to the excessive use of water, its scarcity can be seen in many places, and coal and petroleum are also going to be exhausted in the near future. It is our duty to preserve natural resources and to use them in a proper manner. Three most efficient ways to conserve natural resources are reducing the consumption of natural resources, reusing in them if possible, and recycling of discarded items.
Conclusion
The Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 - Resources, available as a free PDF download, provide a comprehensive and structured overview of the concept of resources and their significance in our lives. These notes serve as a valuable resource for students to understand the various types of resources, their distribution, and the sustainable use of resources.
The notes begin by introducing the concept of resources and explain the difference between natural resources and human-made resources. They cover the three main categories of resources: natural resources, human resources, and capital resources. Students gain insights into the importance of conserving and managing resources for sustainable development.
Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 delves into the classification of resources based on their origin, renewable and non-renewable nature, and exhaustibility. Students learn about the distribution of resources across different regions and the factors influencing their availability.

FAQs on Resources Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
1. What is the importance of conserving resources?
Conserving resources is necessary for humans to sustain themselves without destroying the world in the process. As you would know, many topographical changes in the world occur due to the pace at which the human race is consuming resources. Every natural resource, except for renewable resources, is susceptible to being scarce and can be exhausted very quickly if non-renewable resources are not sustainably used. Global warming is an example of the negative effects of consuming oil - a non-renewable resource - at a rapid pace without caring about how fast it's being consumed or the air-pollution created by it.
2. Why should one refer to notes on Class 8 Geography Chapter 1?
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 notes provide a more explicit and technical definition of resources in Geography class 8. The efficiency of using class 8 geography chapter 1 notes are purely supposed to be used on a revision-basis. It will make it easier to study for the chapter because it contains anchor points that are necessary to refer to when reading a chapter from the text-book. As you would know, a text-book has too much information, some of which is redundant. The notes make it easier to skim through the subject-matter.
3. Are these Resources Class 8, Chapter 1 notes aligned with the CBSE curriculum for Class 8 Geography?
Yes, these notes are specifically designed to align with the CBSE curriculum for Class 8 Geography. They cover the topics and concepts prescribed by the CBSE board for this chapter.
4. Can I download Resources Class 8 CBSE Geography Chapter 1 notes as a free PDF?
Yes, these notes are available as a free PDF download. You can access them from various educational websites or platforms that offer CBSE study materials.
5. Can I use Resources Class 8 CBSE Geography Chapter 1 notes for self-study?
Absolutely! These notes are designed to be self-explanatory and can be used for self-study. They provide clear explanations, examples, and illustrations to aid your learning process.
STUDY MATERIALS FOR CLASS 8
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science . Here we have given. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
1. Answer the following questions.
Question 1(1). Which are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation? Answer: Temperature and rainfall
Question 1(2). Write any two reasons for land degradation today. Answer: Reasons for land degradation (Any two):
- Soil erosion
- Soil depletion
- Deforestation
- Overgrazing
- Overuse of chemical fertilisers and pesticides
Question 1(3). Why is land considered an important resource? Answer: Land is considered as an important resource because all the activities of human beings are carried out on land.
Question 1(4). Name any two steps that the government has taken to conserve plants and animals. Answer: Steps were taken by the government to conserve plants and animals (Any two):
- Setting up of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, biosphere reserves.
- Conservation of creeks, lakes, and wetlands.
- Ban on killing, hunting, and poaching.
- Social forestry and Vanamohatasava.
Question 1(5). Suggest three ways to conserve water. Answer: Ways to conserve water (Any three):
- Forest and other vegetation covers.
- Water harvesting.
- Canals to be properly lined.
- Use of sprinklers in irrigation.
- Drip or trickle methods of irrigation in dry areas.
Question 2. Tick the correct answer 1. Which one of the following is NOT a factor of soil formation? (a) time (b) soil texture (c) organic matter
2. Which one of the following methods is most appropriate to check soil erosion on steep slopes? (a) shelterbelts (b) mulching (c) terrace cultivation
3. Which one of the following is NOT in favour of the conservation of nature? (a) switch off the bulb when not in use. (b) close the tap immediately after using it. (c) dispose of polypacks after shopping.

Question 4. State whether the given statement is True or False. If true, write the reasons. (1) Ganga-Brahmaputra plain of India is an overpopulated region. True Reasons: Fertile land—agriculture main occupation, easily available job opportunities, developed agriculture-based industries, developed means of transport and communication.
(2) Water availability per person in India is declining. True Reasons: Due to overuse, pollution, and increasing population.
(3) Rows of trees planted in the coastal areas to check the wind movement is called t intercropping. False.
(4) Human interference and changes of climate can maintain the ecosystem. False.
Question 5. Activity Discuss some more reasons which are responsible for changes in land-use patterns. Has your place undergone any change in the land use pattern in recent years? Answer: Reasons responsible for change of land use pattern.
- People and their demands are ever-growing.
- The availability of land is limited.
- The quality of land also differs from place to place.
- People started encroaching common lands to build up commercial areas, housing complexes in the urban areas and to expand agricultural land in rural areas.
- Today vast changes in the land use pattern also reflect the cultural changes in our society.
- Expansion of agriculture and constructional activities have caused these problems.
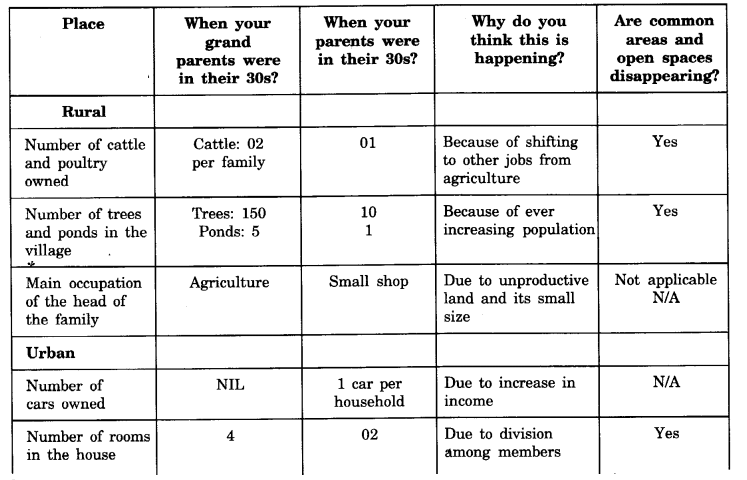
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Exercise Questions
Question 1. Multiple Choice Questions Choose the correct option. (i) Which of these resources covers about three-fourths of the total surface of earth? (a) land (b) soil (c) air (d) water
(ii) What are low-lying areas very susceptible to? (a) earthquakes (b) landslides (c) flooding (d) tsunamis
(iii) Which of these physical features are best suited for living? (a) plains and river valleys (b) mountains (c) deserts (d) lakes and rivers
(iv) Which of these is example of community land? (a) the Sunderban forests (b) a bungalow (c) the Parliament House (d) none of these
(v) What is the majority of land in India used for? (a) cultivation (b) pasture (c) forests (d) none of these
(vi) Which of these countries is mainly covered with forest land? (a) India (b) Brazil (c) USA (d) both b and c
( vii) Due to what feature is ocean water unfit for human consumption? (a) poisonous (b) salinity (c) water temperature (d) none of these Answer: (i)(d), (ii)(c), (iii)(a), (iv)(a), (v)(a), (vi)(d), (vii)(b).
Question 2. Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- The percentage of fresh water on …………..
- The process responsible for soil formation is called ……………
- Private land is owned‘by a fan ………………
- The grainy layer on land is called …………….
- Soil becomes fertile due to the right mix of …………… and ……….
- The colour, texture, etc of soil is determined by ……………….
- Climate factors influencing rate of weathering include and …………….
- ………….. is the growing of different crops in alternate rows.
- 70% of fresh water exists as ……………..
- weathering,
- minerals, organic matter
- parent rock
- rainfall, temperature
- intercropping
- ice sheets.
Question 3. State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- The land has similar features all over the surface of the earth.
- Plains and valleys are densely populated because of soil fertility.
- Population and technology are important factors that determine land use pattern.
- The growing population is not a cause of soil erosion.
- Topography and organic material affect the soil composition of soil.
- Time affects the rate of humus formation during the process of soil formation.
- The earth is called the water planet because of the large amount of water available over it.
- Africa and West Asia are areas facing serious water scarcity.
- Forest and other vegetation promote surface run-off.
- The convention, CITES, lists species which should not be traded.

Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are the possible reasons behind the uneven distribution of population around the world? Answer. The reasons behind uneven population distribution are mainly the varied conditions of land and climate.
Question 2. Give three common forms of land use. Answer. Three common land use forms are: (i) As cropland, (ii) Pasture, (iii) Forests.
Question 3. What human factors determine land use pattern? Answer. Human factors affecting land use pattern are population and technology.
Question 4. Define soil. Answer. The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
Question 5. What is required to make soil fertile? Answer. The right mix of minerals and organic matter is needed to make soil fertile.
Question 6. What is parent rock? Answer. The rock from which soil is derived is called parent rock.
Question 7. What are the factors threatening soil as a resource? Answer. Two factors that threaten soil as a resource are soil erosion and its depletion.
Question 8. What method of soil conservation may be used in coastal and dry reqions? Answer. Shelter belts are used to protect the soil in coastal and dry regions.
Question 9. Why is the earth called the “water planet”? Answer. The earth’s surface has about three- fourths water, so it is called “water planet”.
Question 10. In what forms is fresh water found on the earth? Answer. Fresh water is found in the forms of groundwater, water in rivers and lakes, and water vapour.
Question 11 . What is the name given to the process involved in rain formation? Answer. The process involved in the formation of rain is called “water cycle”.
Question 12. Name some regions of water scarcity in the world. Answer. Africa, West Asia, South Asia, parts of western USA, northwest Mexico, parts of South America, and Australia face water scarcity.
Question 13. Name a method to save surface run-off. Answer. Water harvesting is a method to save surface run-off.
Question 14. How is a bird like vulture important for the ecosystem? Answer. A vulture feeds on dead livestock and so it cleanses the environment.
Question 15. What is the distinguishing feature between evergreen and deciduous forests? Answer. Evergreen forests never shed their leaves whereas deciduous forests shed their leaves once a year.
Question 16. What is the Vanamahotsava? Answer. The social programme of planting trees, organized at the community level is called vanamahotsava.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How is land being degraded? Suggest methods to conserve land resource. Answer. The ever-growing population has increased demand for living space, due to which forests are being destroyed, thus causing land degradation. The rate of degradation of land resources can be checked by promoting afforestation, land reclamation, regulated use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers, and checking to overgraze.
Question 2. What is weathering? Answer. Weathering refers to the breaking up and decay of exposed rocks. This breaking up and decay are caused by temperature fluctuations between too high and too low, frost action, plants, animals, and even human activity. Weathering is the major process involved in the formation of soil. It takes millions of years to form soil by this process.
Question 3. How is water an important resource? Answer. Water is an indispensable resource of life. Firstly water serves the most basic purpose of drinking, without which life is impossible. It is helpful in cleaning our bodies, clothes, and utensils. Farmers depend on water for irrigation. Water is also used in cooking food. Water is a source of electricity as well. Plants require water for their growth. Water is required for various industrial purposes in factories.
Question 4. Write a short note on wildlife. Answer. The animal kingdom, which consists of animals, birds, aquatic creatures and insects, is called wildlife. These creatures provide us various important products such as milk, meat, hides, and wool. Bees give us honey and help in pollination. They play the role of decomposers in the environment. Birds like the vulture are scavengers and they help in cleansing the environment. All forms of wildlife are an integral part of our ecosystem.
Question 5. What are the major types of vegetation in the world? Describe vegetation in different rainfall conditions. Answer. The major types of vegetation in the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, scrubs and tundra.” In areas of heavy rain, huge trees can be found. Forests are abundant in areas of heavy rainfall. With moisture and rainfall the density of forests declines. In moderate rainfall areas, grasslands are found. In diy areas, we find thorny shrubs and scrubs. Plants here have deep roots and leaves have thorny surface to reduce loss of moisture. The tundra vegetation consists of mosses and lichens.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe methods of soil conservation. Answer. Some common methods of soil conservation are mentioned below: Mulching. Mulching is the process of covering the bare ground between plants with a layer of organic matter like straw. It contributes in retaining soil moisture.
Terrace Farming. Terrace farming is the method of farming in which broad flat steps or terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops 4 They reduce run-off and soil erosion. Intercropping. In intercropping, different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the soil from being washed away by rain. Contour Ploughing. Ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope to form a natural barrier for water to flow down a slope is called contour ploughing.
Shelter Belts. Rows of trees that are planted in certain areas to check wind movement are called shelter belts. Contour Barriers. Stones, grass, and soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches are made in front of the barriers to collect water. Rock Dams. This prevents gullies and further soil loss since rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water. Q.2. What is the threat to vegetation and wildlife? What is the need to conserve them? How can we do this? [V. Imp.] Ans. Forests and wildlife are an important resource. Climate change and human interferences in the animal kingdom can cause loss of natural habitat for plants and animals. Certain species have become endangered and many have become extinct now.
Poaching incidents contribute to their extinction. Plants and animals are an important part of the ecosystem. Plants provide food, oxygen and shelter to humans and animals. Animals provide us important products such as milk, meat, honey, etc. There exists a balance in the environment if we do not disturb the natural number of species living on the earth. A single extinction can affect the ecosystem badly. So animals and plants obviously need to be conserved. The government has introduced national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves for this purpose. Poaching should be severely dealt with. Indiscriminate killings need to be discouraged. Social awareness must be created about the importance of trees, social forestry. Students should be involved in vanamahotsavas at regional and community levels.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 ‘Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources’ (Free PDF)

- Updated on
- Apr 12, 2024

We are providing NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 ‘Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources’. A PDF of these solutions is also available for download. These will help you in preparing for your school exams. You can refer to these and ace your exams! Let us get started!
Download the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 PDF Here!
Explore Solutions of all the Chapters of Class 8 Geography :
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 ‘Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources’
Here are NCERT Solutions of Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 ‘Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources’ to the questions in the exercise section of the lesson.
1. Answer the following questions.
(i) Which are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation?
Answer : Two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation include rainfall and temperature. In these, the rainfall influences the rate of humus formation and weathering.
(ii) Write any two reasons for land degradation today.
Answer : the rate of degradation of land is of concern today. The two reasons for land degradation are deforestation and overgrazing by cattle.
(iii) Why is land considered an important resource?
Answer : Land is one of the most important natural resources because it covers almost 30% area of the total Earth’s surface and can be used in many ways such as agriculture, forestry, etc.
(iv) Name any two steps that the government has taken to conserve plants and animals.
Answer : Two major steps taken by the government to protect and conserve plants, animals and natural vegetation are:
- National parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves are made to protect our natural vegetation and wildlife.
- Awareness programmes like social forestry and Vanamohatasava are being encouraged at the regional and community level.
(v) Suggest three ways to conserve water.
Answer : Three main ways to conserve water are:
a. Aforestation that is Increasing forest cover and other vegetation to slow the surface runoff.
b. Using rainwater harvesting to replenish groundwater.
c. Using less water-intensive methods in agriculture.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which one of the following is NOT a factor of soil formation?
(b) Soil texture
(c) Organic matter
Answe r: b. Soil Texture
(ii) Which one of the following methods is most appropriate to check soil erosion on steep slopes?
(a) Shelterbelts
(b) Mulching
(c) Terrace cultivation
Answer : c) Terrace cultivation
(iii) Which one of the following is NOT in favour of the conservation of nature?
(a) switch off the bulb when not in use
(b) close the tap immediately after using
(c) dispose poly packs after shopping
Answer : c) Dispose poly packs after shopping
3. Match the following .
Answer :
4: State whether the given statement is true or false. If true, give the reasons.
(i). Ganga–Brahmaputra plain of India is an overpopulated region .
Answer : True.
(ii) Water availability per person in India is declining.
Answer : True
(iii) Rows of trees planted in the coastal areas to check the wind movement are called intercropping.
Answer : False
(iv). Human interference and changes of climate can maintain the ecosystem.
Related Reads :
Explore Notes of All subjects of CBSE Class 8:
Ans: The name of SST Geography Class 8 Chapter 2 is “Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources”.
Ans: Land is one of the most important natural resources and covers almost 30% area of the total Earth’s surface.
Ans: Wildlife includes animals, birds, insects as well as aquatic life forms. Animals big or small, all are integral to maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
Follow Leverage Edu for complete study material on CBSE Notes of Class 8 Geography .
Deepansh Gautam
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us


45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Resources Class 8 Geography
Answer the following questions. Why are human resources important?
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
- Mineral and Power Resources
- Agriculture
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail
- Education Diary
- Advertising
- Privacy Policy
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students

NCERT 8th Class (CBSE) Social Science: Natural Resources – Land, Soil and Water
admin March 8, 2018 8th Class , Social Science 10,568 Views
Question: What are the possible reasons behind the uneven distribution of population around the world?
Answer: The reasons behind uneven population distribution are mainly the varied conditions of land and climate.
Question: Give three common forms of land use.
Answer: Three common land use forms are:
- As cropland
Question: What human factors determine land use pattern?
Answer: Human factors affecting land use pattern are population and technology.
Question: Define soil.
Answer: The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
Question: What is required to make soil fertile?
Answer: The right mix of minerals and organic matter is needed to make soil fertile.
Question: What is parent rock?
Answer: The rock from which soil is derived is called parent rock.
Question: What are the factors threatening soil as a resource?
Answer: Two factors that threaten soil as a resource are soil erosion and its depletion.
Question: What method of soil conservation may be used in coastal and dry reqions?
Answer: Shelter belts are used to protect the soil in coastal and dry regions.
Question: Why is the earth called the “water planet”?
Answer: The earth’s surface has about three- fourths water, so it is called “water planet”.
Question: In what forms is fresh water found on the earth?
Answer: Fresh water is found in the forms of groundwater, water in rivers and lakes and as water vapour.
Question: What is the name given to the process involved in rain formation?
Answer: The process involved in the formation of rain is called “water cycle”.
Question: Name some regions of water scarcity in the world.
Answer: Africa, West Asia, South Asia, parts of western USA, northwest Mexico, parts of South America and Australia face water scarcity.
Question: Name a method to save surface run-off.
Answer: Water harvesting is a method to save surface run-off.
Question: How is water an important resource?
Answer: Water is an indispensable resource of life. Firstly water serves the most basic purpose of drinking, without which life is impossible. It is helpful in cleaning our bodies, clothes and utensils. Farmers depend on water for irrigation. Water is also used in cooking food. Water is a source of electricity as well. Plants require water for their growth. Water is required for various industrial purposes in factories.
- Stumbleupon
Tags CBSE Class 8 Geography Solutions CBSE Class 8 NCERT Solutions CBSE Class 8 Social Science Solutions Free Class 8 Geography Solutions Free Class 8 Social Science Solutions Free NCERT Online Solutions NCERT Books Online Solutions NCERT CBSE Class 8 Geography Solutions NCERT CBSE Class 8 Social Science Solutions NCERT CBSE Solutions NCERT Class 8 Geography Chapter NCERT Class 8 Geography Solutions NCERT Class 8 Social Science Chapter NCERT Class 8 Social Science Solutions NCERT Solution for Class 8 Geography Chapter NCERT Solution for Class 8 Social Science Chapter NCERT Solutions NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Solutions NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Solutions
Related Articles

10th CBSE Board Social Science Examination Year 2023-24
April 14, 2024
10th CBSE Board Social Science Pre-board Test Year 2023-24
January 25, 2024

CBSE Class 9 Social Science Syllabus 2024
December 1, 2023
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Syllabus 2024
November 29, 2023
10 CBSE Social Science First Term Exam 2023-24: N.K. Bagrodia
October 26, 2023

CBSE Class 12 History 2020-21 Sample Paper
December 25, 2020

The Mughal Empire: 7th CBSE Social Science Chapter 04
The Mughal Empire: NCERT 7th CBSE Social Studies Chapter 04 Question: Match the following: Answer: mansab – …

Resources Extra Questions Chapter 1 Class 8 Geography
Chapter 1 Resources Class 8 Geography Extra Questions provided here is very useful in increasing concentration among students and increasing marks. Extra Questions for Class 8 will help you in understanding the concepts of the chapter properly.

Chapter 1 Resources Very Short Answer Questions (VSAQs):
Chapter 1 resources short answer questions (saqs):, chapter 1 resources long answer questions (laqs):, contact form.

- Free Case Studies
- Business Essays
Write My Case Study
Buy Case Study
Case Study Help
- Case Study For Sale
- Case Study Service
- Hire Writer
Case Study on Land Resources
Land resources case study:.
Land resources are the territories, like forests, plains, wetlands, hills, valleys, which exist without the influence of human beings, or are used for certain purposes like agriculture. Every country possesses vast lands, which are used in different ways.
Some territories are protected for the wildlife and people are forbidden to log wood and hunt there. Then, plains are generally used for the agricultural purposes. People grow vegetables, fruits, crops if the soil is enough good for this purpose. It is obvious that people should use land resources wisely. Unfortunately, the situation is often dramatic nowadays, because people do not use the soil professionally.Since the dawn of the human civilization people have created a special system and rules of growing crops.
We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically For You For Only $13.90/page!
For example, every year the kind of crops grown on the definite field should be changed (one year corn, the second year wheat, the third beet, etc); otherwise the soil will be exhausted and very soon the territory will become a wasteland. Then, vast lands are used for house building and the development of cities and villages. Sometimes, lands with rich soil or endangered species of animals and plants are devastated in order to build a block of flats, hypermarket, a highway, etc. The problem is that the government often fails to weigh the importance of the land soberly and allows cutting down forests, which are the homes of various species of animals, and devastating the river basins, which are also the important centers of flora and fauna.Numerous national and international organizations try to influence the human society to use land resources wisely. Most of people do not realize that careless growing of crops or spontaneous building of a district of a big city will affect the nature seriously.
Only the real professionals and scientists are able to predict and weigh the entire impact of the human activity on the environment and land resources in particular. So, if the government starts following the advice of the scientists, land resources of the country will stay in safety and will even bring profit to people. A good land resources case study should be interesting and thought provoking. One should research the cause and effect of the problem related to land resources and persuade the reader to take care of the environment.If a student wants to complete the case study well and provide the teacher with the reasonable solutions and rich methodology, he should take advantage of the free example case study on land resources in the web.
Due to a well-analyzed free sample case study on land resources in India one will learn to investigate the topic of the example of the definite place or the case site and format the paper according to the general requirements.
Related posts:
- This Land is My Land: A history of nativist attitudes in America
- Case Study on Land Pollution
- North Land Winery Case Study
- IMAX resources case study
- Case Study on Water Resources
- Midland Energy Resources, Inc. Case Study
- Water to Land
Quick Links
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Testimonials
Our Services
Case Study Writing Service
Case Studies For Sale
Our Company
Welcome to the world of case studies that can bring you high grades! Here, at ACaseStudy.com, we deliver professionally written papers, and the best grades for you from your professors are guaranteed!
[email protected] 804-506-0782 350 5th Ave, New York, NY 10118, USA
Acasestudy.com © 2007-2019 All rights reserved.

Hi! I'm Anna
Would you like to get a custom case study? How about receiving a customized one?
Haven't Found The Case Study You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 Geography
- Chapter 1 Resources
NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Geography Social Science Chapter 1 Resources
Ncert solutions class 8 geography resources and development chapter 1 – resources.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources are provided here for students to study and score good marks in the exams. Anything that can be used to satisfy a need, from the water we drink to the electricity we use in our house and the rickshaw we use to get home from school, are all considered resources. All these objects are used by people, so they have utility. Utility or usability is what makes an object or substance a resource. We have compiled the NCERT Solutions to the exercises, which will be useful for school exams, as they are sourced from the NCERT textbooks .
These solutions are easy and accurate and will align students’ preparation with the questions asked in the examinations. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources contain solutions to the exercises given in the Geography book – Resources and Development. Students can refer to these NCERT Solutions and can achieve their desired goals.
- Chapter 2 Land Soil Water Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Industries
- Chapter 6 Human Resources
Students can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography PDF below.
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources
1. Answer the following questions.
(i) Why are resources distributed unequally over the earth?
Answer: Earth has different topography, climate and altitude at different places. The difference in these factors has resulted in unequal distribution of resources on the earth. Also, all these factors are different from place to place on the planet. Moreover, the level of development and technological levels determine the distribution.
(ii) What is resource conservation?
Answer: Saving resources for future generations is called conservation. It is the protection and ethical use of valuable resources such as minerals, water, trees, wildlife and others. Resource conservation focuses on maintaining the natural world in order to protect the sources of resources.
(iii) Why are human resources important?
Answer: Humans as a resource are important because they have the ability to extract value from all other resources. They can make the best use of nature to create more resources, as they have the knowledge, skill and technology to do so. Education and health help in making humans a valuable resource.
(iv) What is sustainable development?
Answer: Balancing the need to use resources and also conserving them for the future is called sustainable development. The future of our planet and its people is linked with our ability to maintain and preserve the life support system that nature provides. Sustainable development is when all renewable resources are used sustainably, the diversity of life on the earth is conserved, and the damage to the natural environmental system is minimised and saved for future generations.
2. Tick the correct Answer
(i) Which one of the following does NOT make the substance a resource?
Answer: 3 Quantity
(ii) Which one of the following is a human-made resource?
- Medicines to treat cancer
- Spring water
- Tropical forest
Answer: 1 Medicine to treat cancer
(iii) Complete the following statement:
Biotic resources are …………..
- Derived from living things
- Made by human beings
- Derived from non-living things
Answer: 1 Derived from living things
Chapter 1 – Resources Summary
Chapter 1 of Resources and Development deals with various types of resources available for existence on the earth.
Students will learn about human-made and natural resources and the current status of these resources.
The students will also get to know about the following topics:
- Types of resources
- The need for the conservation of resources
- Human-made resources
Resources and Development is an important book for the Class 8 Social Science subject. Apart from this chapter, the full set of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science is provided in the links. Students can refer to and easily download the solutions available in PDF format for free.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1
Explain sustainable development as learnt in chapter 1 of ncert solutions for class 8 geography., what will students learn from chapter 1 of ncert solutions for class 8 geography, list the merits of using the ncert solutions for class 8 geography chapter 1., leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
its a very helpful Whenever i will any problem it helps me to clear my doubt Thank you byjUs
Thank you for byjus
When ever I ask doubt they will give reply in seconds. Byjus helped me a lot in my studies and exams. Thank you byjus for your support
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Geography Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Case Study - 1
and Wildlife Resources Chapter-2.indd 7 8/17/2022 11:36:42 AM 8 ResouRces and development logging, desert areas, thick ... conserve land resources. soiL The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface ... A Case Study A massive landslide hit Pangi village near Reckong Peo in Kinnaur district of ...
To learn more thoroughly about topics such as Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources, students can study Chapter 1 of CBSE Class 8 Geography. Students can also revise with the help of CBSE Notes Class 8 Geography Chapter 2-Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Short Answer Type Questions. Question 1. How is land being degraded? Suggest methods to conserve land resource. Answer. The ever-growing population has increased demand for living space, due to which forests are being destroyed, thus causing land degradation.
Here we are providing case study questions for class 8 social science Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources. Case Study Question 1: The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
To learn more about topics such as land, soil, water, natural vegetation, and wildlife resources, students can study Chapter 2 of Geography. The Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 notes will provide deep insights on various natural resources including land, soil, natural vegetation, and wildlife resources.
Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Geography SST NCERT Class 8 Extra Questions Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Geography SST NCERT Class 8 Extra Questions Question 1 What are natural resources? Solution : Natural resources can be broadly categorized into 5 divisions, namely, land, soil, water, natural vegetation and wildlife […]
Introduction. • Natural Resources are anything that people can use which comes from nature such as land, water, air etc. Land. • One of the most important natural resources. • Covers about thirty percent of the total area of the earth's surface, however all parts are not habitable. • The reason behind uneven distribution of population ...
CBSE Notes CBSE Notes Class 8 Social NCERT Solutions Social. Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Class 8 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 2 SST Pdf free download is part of Class 8 Social Science Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Notes.
Answer: Different types of soil found in India are alluvial, black, red, laterite, desertic and mountain soil. 14. Why is fresh water the most precious substance on earth? Answer: Fresh water is the most precious substance on earth because only 1 per cent of freshwater is available and fit for human use. 15.
The Class 8 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 - Resources, available as a free PDF download, provide a comprehensive and structured overview of the concept of resources and their significance in our lives. These notes serve as a valuable resource for students to understand the various types of resources, their distribution, and the sustainable use ...
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources are given here for students to excel in their board exams. About 90% of the world population occupies only 30% of the land area.
Natural Resources. The resources that exist naturally without any effort or modifications from human beings are called natural resources. For example - Air, Solar Energy, Water, Coal, and Petroleum are natural resources. Natural Resources are further classified into two categories - Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Short Answer Type Questions. Question 1. How is land being degraded? Suggest methods to conserve land resource. Answer. The ever-growing population has increased demand for living space, due to which forests are being destroyed, thus causing land degradation.
The two reasons for land degradation are deforestation and overgrazing by cattle. (iii) Why is land considered an important resource? Answer: Land is one of the most important natural resources because it covers almost 30% area of the total Earth's surface and can be used in many ways such as agriculture, forestry, etc.
Answer. The distribution of resources depends upon a number of physical factors like terrain, climate and altitude. Since these factors differ so much over the Earth, the distribution of resources is unequal. Exercises Page Number 5. 1 (ii) Answer the following questions. What is resource conservation?
Answer: Water is an indispensable resource of life. Firstly water serves the most basic purpose of drinking, without which life is impossible. It is helpful in cleaning our bodies, clothes and utensils. Farmers depend on water for irrigation. Water is also used in cooking food.
On the basis of origin, a resource can be abiotic or biotic. • A biotic resource is the one that has life. • A abiotic resource is non-living. Natural resources may also be classified as renewable and non-renewable. • A renewable resource can be used without any risk of its ending up. They exist in unlimited quantity.
We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically. For You For Only $13.90/page! order now. For example, every year the kind of crops grown on the definite field should be changed (one year corn, the second year wheat, the third beet, etc); otherwise the soil will be exhausted and very soon the territory will become a wasteland.
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Geography Resources and Development Chapter 1 - Resources. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources are provided here for students to study and score good marks in the exams. Anything that can be used to satisfy a need, from the water we drink to the electricity we use in our house and the rickshaw we use to get home from school, are all ...
Write a case study on land as a resource. The word "land resources" refers to the physical, biotic, environmental, infrastructural, socioeconomic, and near-surface freshwater resources that are crucial for management of a natural land unit. Water, oil, copper, natural gas, coal, and forests are a few examples of common land or natural resources.