Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
User Experience
- User Experience Research

Try Qualtrics for free
User experience (ux) research: definition and methodology.
17 min read To build outstanding products and services for your customers, you need a thorough understanding of who they are, what they need and where their pain points and priorities lie. UX research helps you fully step into your customers’ shoes.
What do we mean by user experience?
User experience (UX) is a customer’s-eye view of your business as it relates to completing tasks and using interactive platforms and services.
It’s closely tied to the idea of customer experience (CX) , but rather than being a holistic view of your brand, it’s more focused on utility and usability testing – the hands-on side of things. You can think of UX as a sub-discipline of CX .
For example, CX research might consider how customers perceive a company’s customer service levels and how confident they feel in having their issues resolved. Meanwhile, UX research would focus on how successfully those customers navigate a self-service website, whether the language on that site is clear and how easy it is to use.
Free eBook: The essential website experience & UX playbook
What is user experience (UX) research?
User experience (UX) research is about diving deep into how customers interact with your brand on a practical, functional level, and observing how easily they can complete their tasks and meet their goals.
User research is the process of discovering the behaviors , motivations, and needs of your customers through observation, task analysis, and other types of user feedback . It can involve working directly with members of your target audience through UX testing sessions, remote session observation using digital tools, surveys to collect user feedback, and many more UX research methods and techniques.
Why is UX research important?
So what exactly is the value of user experience research? After all, you understand your business and its workings better than anyone. How can uninformed external users help you learn more?
The fresh perspective of your end-users is exactly why UX research is so valuable. Because they’re not already immersed in your language, processes, and systems, user testing participants are in the best position to help you see where things might be confusing to a newcomer who isn’t involved with your business.
Better yet, they can show you where confusion or frustration might lead a new or potential customer to miss out on product benefits, fail to convert, or even give up and look toward your competitors instead.
In areas like new product design and development , user research allows you to head off potential issues with products and services before they even hit the shelves. You can design the product correctly the first time, instead of having to fix it later when customers are unhappy.
Simply put, UX research is critical because it keeps you from wasting time, money, and effort designing the wrong product or solution. It’s valuable for all areas of your business and yields clear benefits for your product, your users, and your bottom line.
- Product benefits By asking your customers for direct feedback about a potential product, you can discover how and when customers prefer to use a product, what pain points your product will solve, and how to improve your product design .
- User benefits UX research is unbiased feedback, straight from the most valuable source: your customers. Because this type of research is not biased by investors, company leaders, or outside influences, it is the best resource for getting actionable product feedback.
- Business benefits Knowing what your users value helps you spend less time and money fixing flawed designs, speeds up the product development process , and increases customer satisfaction.
UX research helps brands and organizations to:
- Understand how users experience products, websites, mobile apps, and prototypes
- Evaluate and optimize prototypes and ideas based on UX research discoveries – and nail the design and experience early in a product’s life cycle
- Unearth new customer needs and business opportunities
- Find and fix hidden problems with products and services that arise in real-world use cases
- Make informed decisions through the product development process by testing various aspects of product designs
- Provide user experiences that outperform other businesses in your sector ( UX competitor research )
- Understand each user interaction across complete customer journeys
- Build a richer, more useful picture of your target audiences for better marketing and advertising
What’s the ROI of performing UX research?
The ROI of UX research is tricky to pin down because there often isn’t a direct, easy-to-spot correlation between time spent on it and resulting revenue. UX research can and does drive revenue, but it more directly influences metrics that show customer satisfaction, customer retention, and behavioral goals like user signups.
A simple way to draw a straight (if basic) line between UX research and its associated ROI is to calculate your conversion rate, where ‘conversion’ simply means completing the action you had in mind:
Number of people who took your desired action
————————————————————— x 100
Total visitors/users
That percentage can be calculated and revisited over time to see how UX changes resulting from your research are having an effect.
Generally, when we talk about ROI, we’re talking about the highest possible rates of return you can attribute to an investment. But – while PWC research suggests that ROI on UX research can rise to as high as 301% – it’s better not to get caught up in absolutes with operational data like revenue.
Instead, it’s worth thinking more about the benefits that come out of tracking human behavior associated with improving your UX in general.
For example, IBM research states that 3 out of 5 users think that a positive user experience is more influential than strong advertising, while Forrester Research estimates that as many as 50% of potential sales fall through because users can’t find the information they need.
Thorough UX research can also cut a project’s development time by up to 50% .
Ultimately, when trying to track the ROI of your time spent doing quantitative and qualitative research on UX, you want to look at behavior and sentiment. If your main goal is website use, you should notice a decline in bounce rate as a sign of positive ROI. If you sell services, run regular CSAT surveys to determine how satisfied customers are with everything.
You might also find that data in unusual places. For example, if you spot a decline in chatbot requests around how to do or perform certain actions, or for information, then you know your new UX implementations are working as desired.
Those kinds of behavioral data points will shine a light on how worthwhile your UX research has been more readily than changes in revenue.
User experience research methods
The type of UX research techniques you choose will depend on the type of research question you’re tackling, your deadline, the size of your UX research team, and your environment.
There are three research dimensions to consider as you decide which methods are best for your project:
Attitudinal and behavioral
“Attitudinal” refers to what people say, while “ behavioral ” refers to what people actually do – and these are often very different. Attitudinal research is often used in marketing because it measures people’s stated beliefs and needs. However, in product design and user experience research, what people do tends to be more relevant.
For example, A/B testing shows visitors different versions of a site at random to track the effect of site design on conversion and behavior.
Another behavioral method is eye tracking, which helps researchers understand how users interact and visually engage with the design of an interface by following their gaze.
Qualitative and quantitative methods
Quantitative UX research studies collect and analyze results, then generalize findings from a sample to a population. They typically require large numbers of representative cases to work with and are structured in their approach.
Quantitative research uses measurement tools like surveys or analytics to gather data about how subjects use a product and are generally more mathematical in nature. This type of inquiry aims to answer questions like ‘what,’ ‘where’ and ‘when’.
Qualitative research methods, on the other hand, gather information about users by observing them directly, as in focus groups or field studies.
Qualitative research aims to understand the human side of data by gaining a sense of the underlying reasons and motivations surrounding consumer behavior. It tends to use small numbers of diverse (rather than representative) cases, and the data collection approach is less structured. Qualitative methods are best suited to address the ‘how’ or ‘why’ of consumer behavior.
Qualitative UX research methods
Several UX research methodologies can help UX researchers answer those big ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions, and influence the design process of any product or service you’ve got cooking. Here are just a few …
1. Participatory design
In participatory design, people are asked to draw or design their own best-case version of the tool, product, or service in question. This gives UX researchers the ability to ask qualitative questions about why specific choices have been made. If multiple participants make similar choices, it’s easy to spot patterns that should be adopted.
You might ask participants how they would redesign your website. While their responses will naturally vary, you might spot that several of them have moved your site’s navigation to a more prominent spot, or have moved the checkout from the left of the screen to the right.
2. Card sorting
Card sorting involves giving participants a range of cards that represent business-specific topics and asking them how they would sort them into groups. UX researchers are then able to probe into why their audience might group certain things, and make changes to existing offerings as a result.
If you have a wide range of products and solutions, card sorting would be a useful way to gauge how your target audience would naturally bucket them on your website. A furniture seller, for example, might use this technique to find that people are naturally inclined to group items by room, rather than by furniture type.
3. Diary studies
If you’d like to know how the UX of your product or service varies over time or throughout the length of its use, a diary study can help. Here, participants are given a way to record their thoughts as they set about using the product or service in question, noting things that occur to them as they go. This is useful as it provides real-world insight over a longer period than a one-off focus group.
Giving people access to an early build of an app and asking them to keep usability testing notes can highlight pain points in the user interface. In a one-off focus group, having to tap three times to get to an oft-used screen might seem fine – whereas participants are more likely to find it annoying in the day-to-day. This kind of longer-term usability test can provide really valuable insights.
Both quantitative and qualitative UX research methodologies can be useful when planning the design and development of your brand presence, as well as for usability testing when it comes to product and service design.
Context-of-use
By collecting and analyzing information about users, the intended use of the application, the tasks they perform with the application, and the technical constraints presented by the application, context-of-use analysis allow UX researchers to better understand the overall experience.
Typically, context-of-use analysis data is collected through research surveys, focus groups, interviews, site visits, and observational studies.
Context-of use-analysis is one method for identifying the most important elements of an application or product in the context of using that application or product. This type of UX research is typically done early in the product lifecycle and continued as data identifies which components of the product and UX are most critical.
Types of user research tools
There are many types of user research methods for discovering data useful for product design and development. Below are some common examples of tools user experience researchers may use to gather information and draw insights into mental models, or users’ thought processes.
UX research surveys or questionnaires can discover data at scale through in-person or remote polling, with specific questions designed to collate useful information about user experience.
User groups or focus groups are a form of a structured interview that consults members of a target audience on their experience, views, and attitudes towards the product or solution. They usually involve neutral parties, such as a moderator and note-taker, and are led by a researcher who asks open-ended questions focused on specific aspects of an investigation.
User interviews are one-on-one structured interviews with a target audience member, led by a UX researcher to understand more about personal experiences with the product. These user interviews can be directed to compare and contrast answers between users, or non-directed, where users lead the conversation.
Ethnographic interviews take place within the target users’ typical environment to get a better context-of-use view. Field studies and site visits are similarly observational in nature, and take place in situ where the product or service is used, but may involve larger groups.
This is not a comprehensive list of research techniques but represents some of the main ways UX researchers might perform usability testing or trial UX design.
When to conduct user experience research
Before launching a new product or service, understanding user preferences that could impact your design or development is key to success. The earlier user experience research is performed, the more effective the end product or service will be, as it should encompass the insights learned about your target audience.
As a product and service’s use and value evolve over its lifecycle, the user experience will change over time. User research should be undertaken on an ongoing basis to determine how to adapt to users’ new needs and preferences.
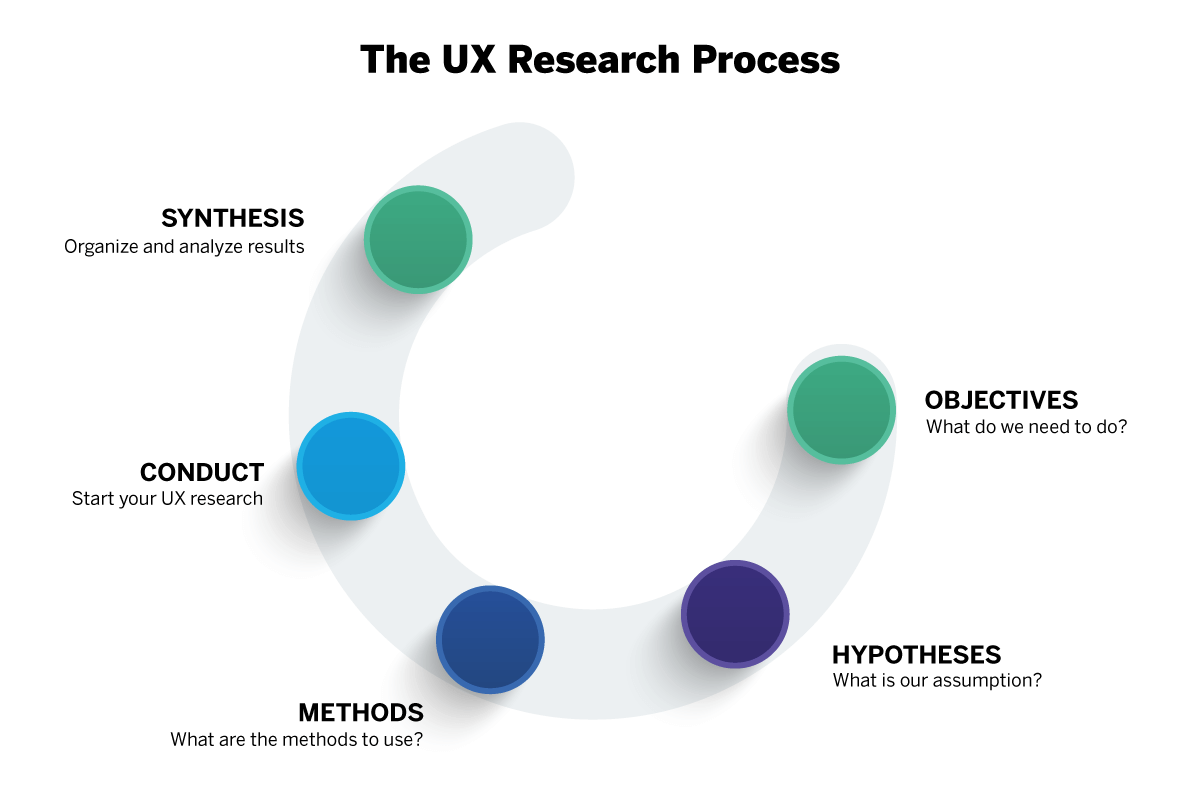
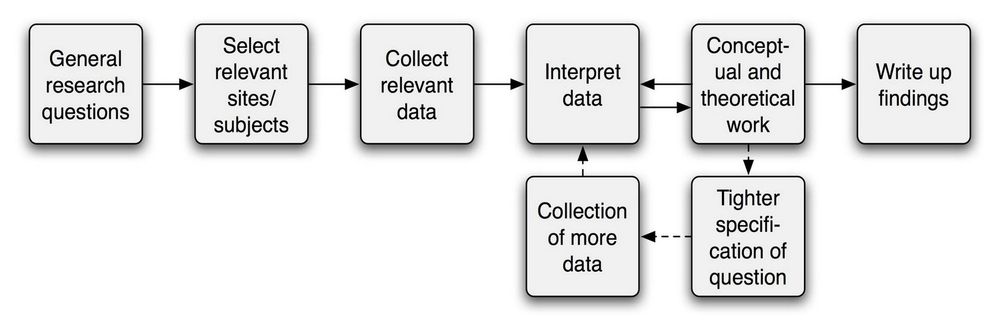
Five basic steps to conducting UX research
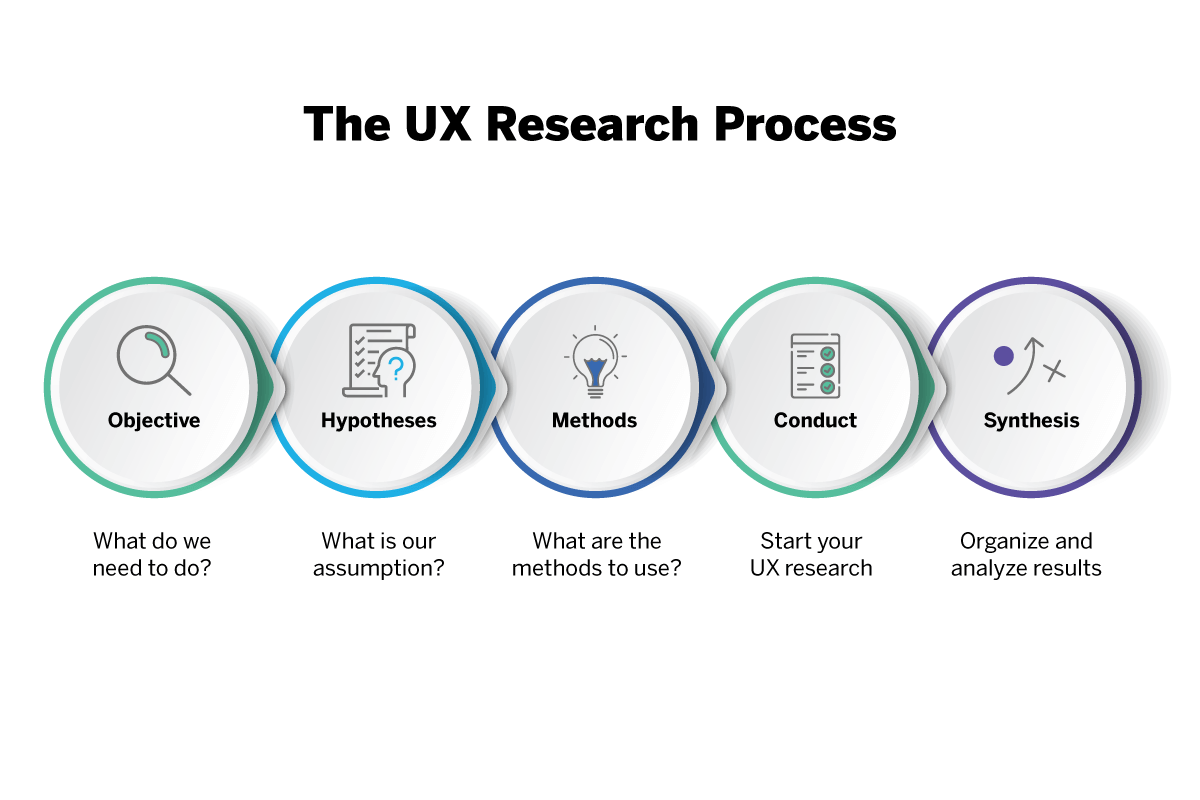
If you’re new to UX research, here’s a step-by-step list of what to consider before you begin your UX testing program:
- Objectives What do you need to find out about your users and their needs?
- Hypothesis What do you think you already know about your users?
- Methods Based on your deadline, project type, and the size of your research team, what UX research methods should you use?
- Process Using your selected UX research method(s), begin collecting data about your users, their preferences, and their needs.
- Synthesis Analyze the data you collected to fill in your knowledge gaps, address your hypothesis and create a plan to improve your product based on user feedback.
Qualtrics makes UX research simple and easy
User experience research and user testing are multifaceted and can involve a lot of both quantitative and qualitative data. To ease the process and make sure it is efficient and scalable, it’s best conducted using a highly responsive platform that allows you to collect data, analyze trends and draw conclusions all in one place.
Whether you need attitudinal or behavioral insights, Qualtrics is your go-to solution for collecting all kinds of UX data and making use of it in the context of your wider CX program .
Conduct in-person studies or send beautifully designed surveys easily and quickly, and view your results via custom dashboards and reports using the most sophisticated research platform on the planet.
Related resources
User experience 20 min read, user experience surveys 9 min read, ux research tools 8 min read, user analytics 11 min read, rage clicks 11 min read, user experience analytics 10 min read, website user experience 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
UX Research
What is ux research.
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
See why UX research is a critical part of the UX design process.
- Transcript loading…
UX Research is about Finding Insights to Guide Successful Designs
When you do UX research, you’ll be better able to give users the best solutions—because you can discover exactly what they need. You can apply UX research at any stage of the design process. UX researchers often begin with qualitative measures, to determine users’ motivations and needs . Later, they might use quantitative measures to test their results . To do UX research well, you must take a structured approach when you gather data from your users. It’s vital to use methods that 1) are right for the purpose of your research and 2) will give you the clearest information. Then, you can interpret your findings so you can build valuable insights into your design .
“I get very uncomfortable when someone makes a design decision without customer contact.” – Dan Ritzenthaler, Senior Product Designer at HubSpot
We can divide UX research into two subsets:
Qualitative research – Using methods such as interviews and ethnographic field studies, you work to get an in-depth understanding of why users do what they do (e.g., why they missed a call to action, why they feel how they do about a website). For example, you can do user interviews with a small number of users and ask open-ended questions to get personal insights into their exercise habits. Another aspect of qualitative research is usability testing , to monitor (e.g.) users’ stress responses. You should do qualitative research carefully. As it involves collecting non-numerical data (e.g., opinions, motivations), there’s a risk that your personal opinions will influence findings.
Quantitative research – Using more-structured methods (e.g., surveys, analytics), you gather measurable data about what users do and test assumptions you drew from qualitative research. For example, you can give users an online survey to answer questions about their exercise habits (e.g., “How many hours do you work out per week?”). With this data, you can discover patterns among a large user group. If you have a large enough sample of representative test users, you’ll have a more statistically reliable way of assessing the population of target users. Whatever the method, with careful research design you can gather objective data that’s unbiased by your presence, personality or assumptions. However, quantitative data alone can’t reveal deeper human insights.
We can additionally divide UX research into two approaches:
Attitudinal – you listen to what users say—e.g., in interviews.
Behavioral – you see what users do through observational studies.
When you use a mix of both quantitative and qualitative research as well as a mix of attitudinal and behavioral approaches, you can usually get the clearest view of a design problem.

© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
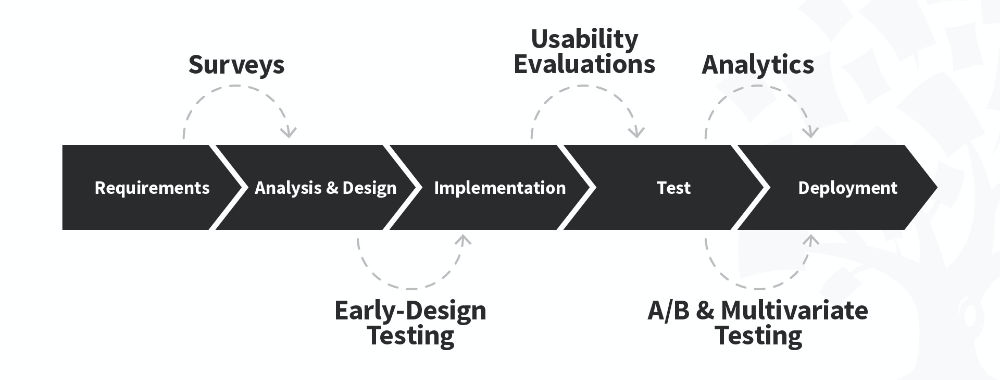
Use UX Research Methods throughout Development
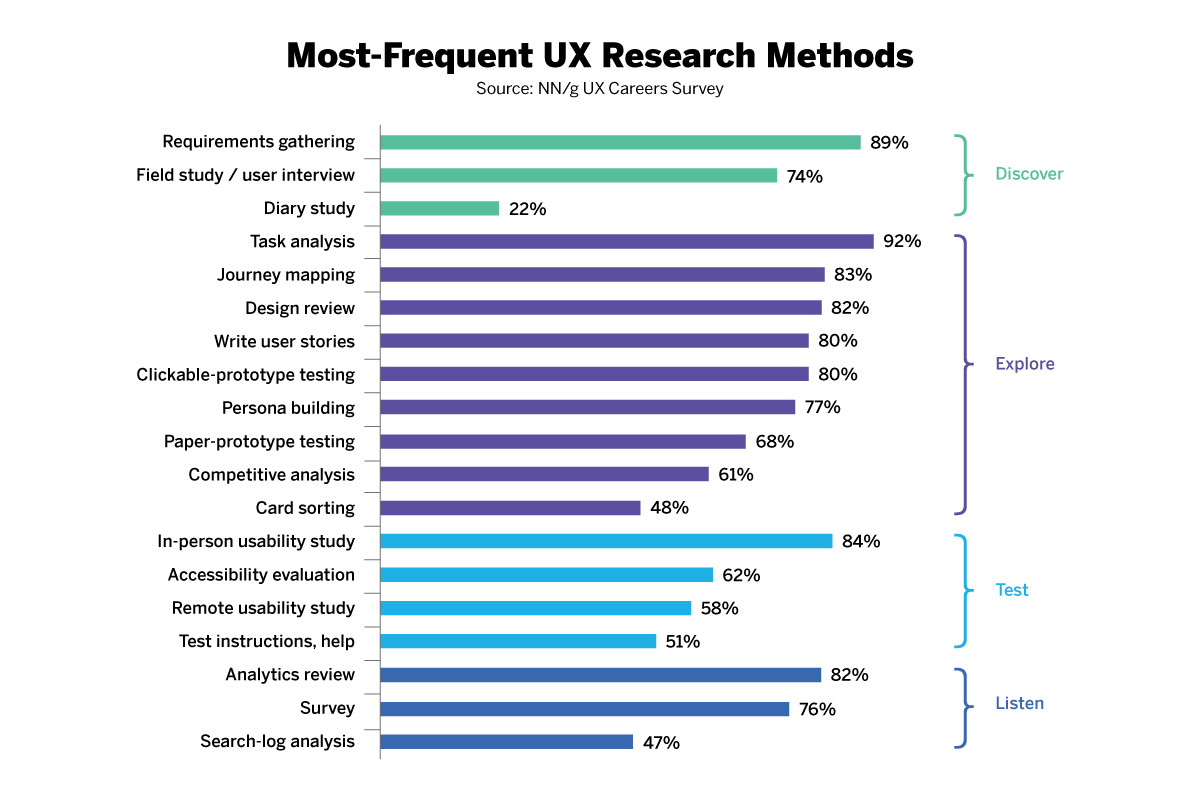
The Nielsen Norman Group—an industry-leading UX consulting organization—identifies appropriate UX research methods which you can use during a project’s four stages . Key methods are:
Discover – Determine what is relevant for users.
Contextual inquiries – Interview suitable users in their own environment to see how they perform the task/s in question.
Diary studies – Have users record their daily interactions with a design or log their performance of activities.
Explore – Examine how to address all users’ needs.
Card sorting – Write words and phrases on cards; then let participants organize them in the most meaningful way and label categories to ensure that your design is structured in a logical way.
Customer journey maps – Create user journeys to expose potential pitfalls and crucial moments.
Test – Evaluate your designs.
Usability testing – Ensure your design is easy to use.
Accessibility evaluations – Test your design to ensure it’s accessible to everyone.
Listen – Put issues in perspective, find any new problems and notice trends.
Surveys/Questionnaires – Use these to track how users’ feel about your product.
Analytics – Collect analytics/metrics to chart (e.g.) website traffic and build reports.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Whichever UX research method you choose, you need to consider the pros and cons of the different techniques . For instance, card sorting is cheap and easy, but you may find it time-consuming when it comes to analysis. Also, it might not give you in-depth contextual meaning. Another constraint is your available resources , which will dictate when, how much and which type of UX research you can do. So, decide carefully on the most relevant method/s for your research . Moreover, involve stakeholders from your organization early on . They can reveal valuable UX insights and help keep your research in line with business goals. Remember, a design team values UX research as a way to validate its assumptions about users in the field , slash the cost of the best deliverables and keep products in high demand —ahead of competitors’.
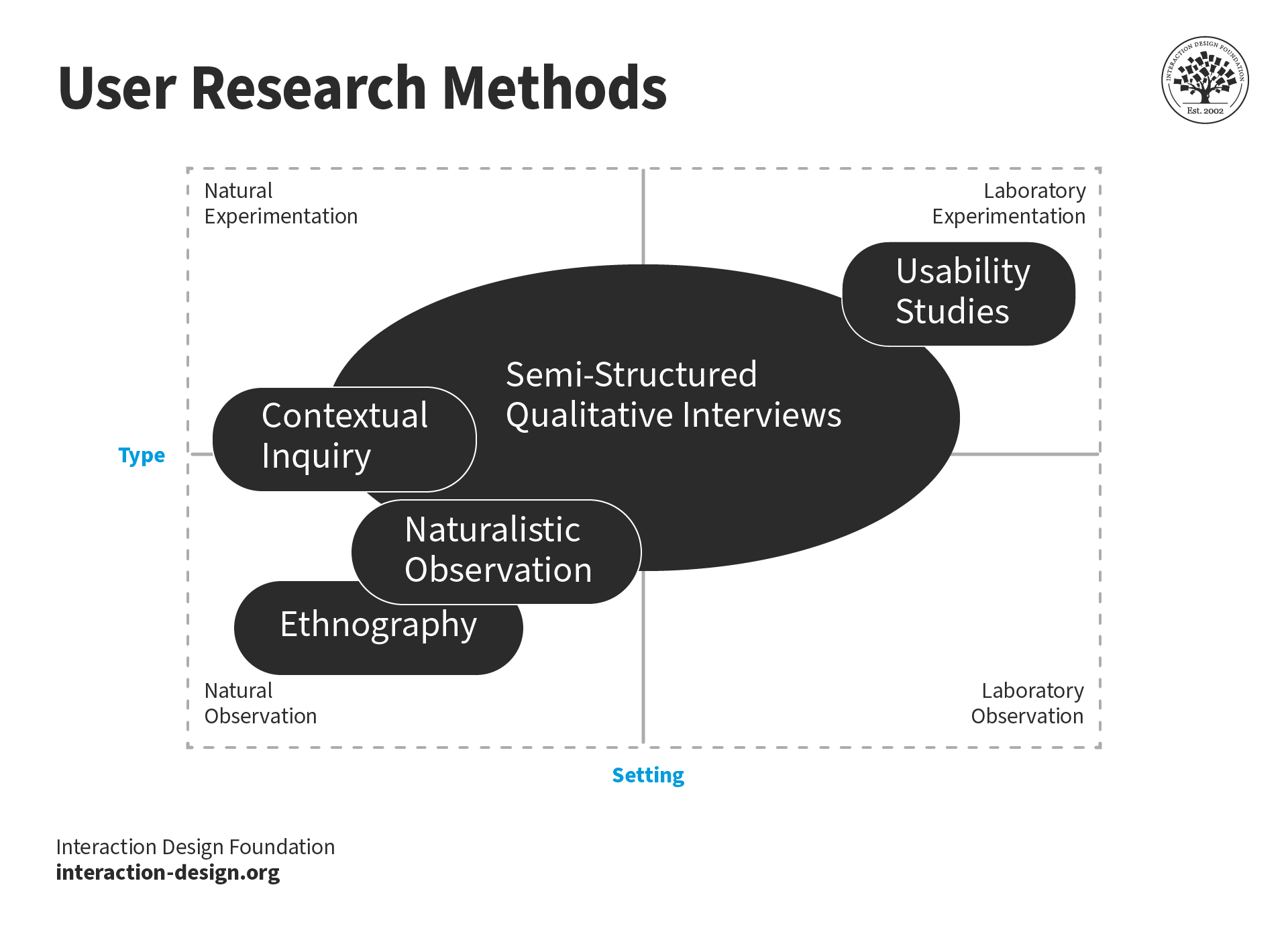
User research methods have different pros and cons,and vary from observations of users in context to controlled experiments in lab settings.
Learn More about UX Research
For a thorough grasp of UX research, take our course here: User Research – Methods and Best Practices
Read an extensive range of UX research considerations, discussed in Smashing Magazine: A Comprehensive Guide To UX Research
See the Nielsen Norman Group’s list of UX research tips: UX Research Cheat Sheet
Here’s a handy, example-rich catalog of UX research tools: 43 UX research tools for optimizing your product
Questions related to UX Research
UX research is a good career for those who enjoy working with a team and have strong communication skills. As a researcher, you play a crucial role in helping your team understand users and deliver valuable and delightful experiences. You will find a UX research career appealing if you enjoy scientific and creative pursuits.
Start exploring this career option; see the User Researcher Learning Path .
Studies suggest that companies are also willing to pay well for research roles. The average salary for a UX researcher ranges from $92,000 to $146,000 per year.
In smaller companies, user research may be one of the responsibilities of a generalist UX designer. How much can your salary vary based on your region? Find out in UI & UX Designer Salaries: How Much Can I Earn .
Research is one part of the overall UX design process. UX research helps inform the design strategy and decisions made at every step of the design process. In smaller teams, a generalist designer may end up conducting research.
A UX researcher aims to understand users and their needs. A UX designer seeks to create a product that meets those needs.
A UX researcher gathers information. A UX designer uses that information to create a user-friendly and visually appealing product.
Learn more about the relationship between UX research and UX design in the course:
User Experience: The Beginner’s Guide
If we consider a very broad definition of UX, then all user research is UX research.
However, in practice, there is a subtle difference between user research and UX research. While both involve understanding people, user research can involve users in any kind of research question, and some questions may not be that directly connected to user experience.
For example, you might do user research relating to a customer’s experience in relation to pricing, delivery or the experience across multiple channels.
Common UX research methods are usability testing, A/B testing, surveys, card sorting, user interviews, usage analytics and ethnographic research. Each method has its pros and cons and is useful in different scenarios. Hence, you must select the appropriate research method for the research question and target audience. Learn more about these methods in 7 Great, Tried and Tested UX Research Techniques .
Get started with user research. Download the User Research template bundle .

For a deep dive into usability testing—the most common research method, take the course Conducting Usability Testing .
Having a degree in a related field can give you an advantage. However, you don’t need a specific degree to become a UX researcher. A combination of relevant education, practical experience, and continuous learning can help you pursue a career in UX research. Many UX researchers come from diverse educational backgrounds, including psychology, statistics, human-computer interaction, information systems, design and anthropology.
Some employers may prefer candidates with at least a bachelor’s degree. However, it does not have to be in a UX-related field. There are relatively fewer degrees that focus solely on user research.
Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX
User Research – Methods and Best Practices
Every research project will vary. However, there are some common steps in conducting research, no matter which method or tool you decide to use:
Define the research question
Select the appropriate research method
Recruit participants
Conduct the research
Analyze the data
Present the findings
You can choose from various UX research tools . Your choice depends on your research question, how you're researching, the size of your organization, and your project. For instance:
Survey tools such as Typeform and Google Forms.
Card sorting tools such as Maze and UXtweak.
Heatmap tools such as HotJar and CrazyEgg
Usability testing (through first-click testing and tree-testing) tools such as Optimal Workshop and Loop 11
Diagramming applications such as Miro and Whimsical to analyze qualitative data through affinity diagramming.
Spreadsheet tools such as Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel for quantitative data analysis
Interface design and prototyping tools like Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch and Marvel to conduct usability testing.
Presentation tools such as Keynote, Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Many of these tools offer additional features you can leverage for multiple purposes. To understand how you can make the most of these tools, we recommend these courses:
There are relatively fewer degrees that focus solely on user research.
While there are no universal research case study formats, here’s one suggested outline:
An overview of the project: Include the problem statement, goals and objectives.
The research methods and methodology: For example, surveys, interviews, or usability testing).
Research findings
The design process: How the research findings led to design decisions.
Impact of design decisions on users and the business: Include metrics such as conversion and error rates to demonstrate the impact.
Optionally, include notes on what you learned and how you can improve the process in the future.
Learn how to showcase your portfolio to wow your future employer/client in the How to Create a UX Portfolio course.
While AI can help automate tasks and help UX researchers, it will not completely replace them. AI lacks the creativity and empathy that human designers bring to the table.
Human researchers are better at understanding the nuances of human behavior and emotions. They can also think outside the box and develop creative solutions that AI cannot. So, AI can help researchers be more efficient and effective through data analysis, smart suggestions and automation. But it cannot replace them.
Watch AI-Powered UX Design: How to Elevate Your UX Career to learn how you can work with AI.
Agile teams often struggle to incorporate user research in their workflows due to the time pressure of short sprints. However, that doesn’t mean agile teams can’t conduct research. Instead of seeing research as one big project, teams can break it into bite-sized chunks. Researchers regularly conduct research and share their findings in every sprint.
Researchers can involve engineers and other stakeholders in decision-making to give everyone the context they need to make better decisions. When engineers participate in the decision-making process, they can ensure that the design will be technically feasible. There will also be lower chances of errors when the team actually builds the feature. Here’s more on how to make research a team effort .
For more on bite-sized research, see this Master Class: Continuous Product Discovery: The What and Why
For more practical tips and methods to work in an agile environment, take our Agile Methods for UX Design course.
User research is very important in designing products people will want and use. It helps us avoid designing based on what we think instead of what users actually want.
UX research helps designers understand their users’ needs, behaviors, attitudes and how they interact with a product or service. Research helps identify usability problems, gather feedback on design concepts, and validate design decisions. This ultimately benefits businesses by improving the product, brand reputation and loyalty. A good user experience provides a competitive edge and reduces the risk of product failure.
Learn more about the importance of user research in the design process in these courses:
Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide
Answer a Short Quiz to Earn a Gift
What is the primary purpose of UX research in design processes?
- To ensure the product is visually appealing.
- To reduce the cost of marketing the product.
- To understand user needs and enhance design decisions.
Which type of UX research do designers use to collect non-numerical data such as opinions and motivations?
- Behavioral research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
Which UX research method involves users sorting terms into categories to help structure design logically?
- Card sorting
- Information architecture
- Usability testing
What is a potential drawback of using card sorting in UX research?
- It can be expensive and requires special software.
- It may not provide deep contextual insights.
- It only works for digital products.
How does UX research primarily benefit a design team in a business context?
- It focuses exclusively on the aesthetic aspects of product design.
- It reduces dependency on technology.
- It validates design assumptions and keeps products competitive.
Better luck next time!
Do you want to improve your UX / UI Design skills? Join us now
Congratulations! You did amazing
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
Check Your Inbox
We’ve emailed your gift to [email protected] .
Literature on UX Research
Here’s the entire UX literature on UX Research by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about UX Research
Take a deep dive into UX Research with our course User Research – Methods and Best Practices .
How do you plan to design a product or service that your users will love , if you don't know what they want in the first place? As a user experience designer, you shouldn't leave it to chance to design something outstanding; you should make the effort to understand your users and build on that knowledge from the outset. User research is the way to do this, and it can therefore be thought of as the largest part of user experience design .
In fact, user research is often the first step of a UX design process—after all, you cannot begin to design a product or service without first understanding what your users want! As you gain the skills required, and learn about the best practices in user research, you’ll get first-hand knowledge of your users and be able to design the optimal product—one that’s truly relevant for your users and, subsequently, outperforms your competitors’ .
This course will give you insights into the most essential qualitative research methods around and will teach you how to put them into practice in your design work. You’ll also have the opportunity to embark on three practical projects where you can apply what you’ve learned to carry out user research in the real world . You’ll learn details about how to plan user research projects and fit them into your own work processes in a way that maximizes the impact your research can have on your designs. On top of that, you’ll gain practice with different methods that will help you analyze the results of your research and communicate your findings to your clients and stakeholders—workshops, user journeys and personas, just to name a few!
By the end of the course, you’ll have not only a Course Certificate but also three case studies to add to your portfolio. And remember, a portfolio with engaging case studies is invaluable if you are looking to break into a career in UX design or user research!
We believe you should learn from the best, so we’ve gathered a team of experts to help teach this course alongside our own course instructors. That means you’ll meet a new instructor in each of the lessons on research methods who is an expert in their field—we hope you enjoy what they have in store for you!
All open-source articles on UX Research
7 great, tried and tested ux research techniques.

- 1.2k shares
- 3 years ago
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
Shadowing in User Research - Do You See What They See?
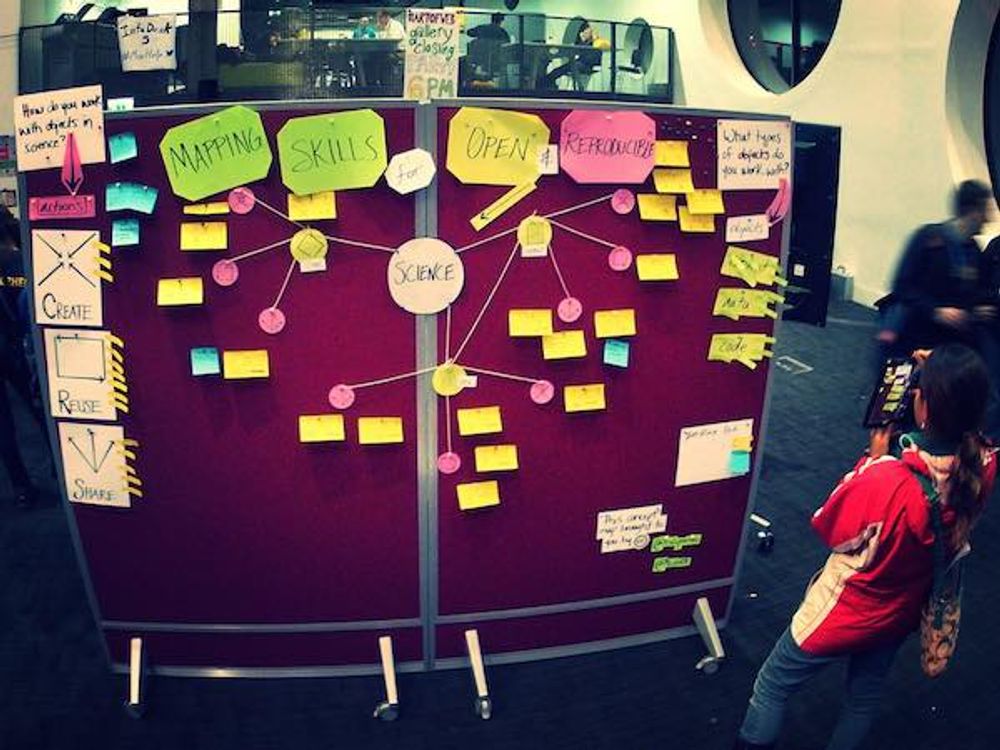

Contextual Interviews and How to Handle Them

15 Guiding Principles for UX Researchers

Ethnography

Porter’s 5 Forces Model - Design in Context, Understand the Market
- 7 years ago
Ideas for Conducting UX Research with Children

Laddering Questions Drilling Down Deep and Moving Sideways in UX Research

- 8 years ago
Action Research
4 common pitfalls in usability testing and how to avoid them to get more honest feedback.
- 2 years ago
Confirmation Bias – It’s Not What We Think We Know That Counts

User Research Methods for Mobile UX

The Top UX Design Books You Need to Read in 2024: Beginner to Expert

6 Tips for Better International UX Research

Collaborating with Your Team for Research

Common UX Research Interview Questions

Adding Quality to Your Design Research with an SSQS Checklist
The Best Free UX Design Courses in 2024

How to Fit Quantitative Research into the Project Lifecycle
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Integrations
What's new?
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Interview Studies
Prototype Testing
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
Live Website Testing
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Maze Guides | Resources Hub
What is UX Research: The Ultimate Guide for UX Researchers
0% complete
User experience research is a crucial component of the human-centered design process and an essential part of creating solutions that meet user expectations and deliver value to customers. This comprehensive guide to UX research dives into the fundamentals of research and its various methods and includes tips and best practices from leading industry experts.
Make informed design decisions with user research
Validate ideas, test prototypes, assess usability, and deliver real, actionable insights to your product team.
UX research: Your ultimate guide to nailing user experience and exceeding expectation
User experience research, or UX research , is the process of gathering insights about users' behaviors, needs, and pain points through observation techniques and feedback methodologies. It’s a form of user research that looks at how users interact with your product, helping bridge the gaps between what you think users need, what users say they need—and what they actually need.
The goal of UX research is to understand your users and gain context and perspectives to help make informed decisions and build user-centered products. It’s an essential part of designing, developing, and launching a product that will be an instant hit—but it should also be used throughout the product’s lifecycle post-launch to keep updated, and ensure new features are relevant to your audience.
As Sinéad Davis Cochrane , UX Manager at Workday, explains: “UX research represents insights gathered directly from users and customers, that helps you make product decisions at every stage of the development process.”
Is UX research the same as user research?
The terms ‘user research’ and ‘UX research’ are often used interchangeably, but they do differ. User research is the parent of UX research; it’s a broader research effort that aims to understand the demographics, behaviors, and sentiments of your users and personas.
UX research, on the other hand, is a type of user research that’s specific to your product or platform. Where user research focuses on the user as a whole, UX research considers how they interact with, respond to, and feel about your product or concept itself.
In both cases, the overarching goal is to get to know your users, understand what they need from your product, gain context to help make informed decisions, and build human-centered experiences.
Involve your users at every stage of your design process
Create research projects with Maze using customizable templates, and start making data-informed product decisions
Why is conducting UX research important?
In an ideal world, users would find your product easy to navigate, your net promoter score (NPS) would be off the charts, and you’d see adoption and activation rates skyrocket. In reality, however, this can be a challenging dream to achieve—but it is possible. The only way to build a product that users really resonate with is by involving them throughout the development process and building with them.
UX research is more than just a single ‘step’ in the development process: it should happen continuously, throughout the product lifecycle—so whether you’re building new products or iterating on existing ones, every decision is informed by user insights.
Here’s what you can achieve with continuous UX research:
Make informed decisions based on data
Our 2023 Continuous Research Report shows that 74% of people who do research (PWDR) believe research is crucial to guiding product decisions. Plus, 60% of respondents find that user recommendations inspire new product ideas.
Getting stakeholder buy-in to product decisions can be challenging, but when you suggest changes based on UX research, you have data to back up your suggestions. Your users inform your product, becoming the decision-makers as well as the customer.
UX research helps reduce and mitigate the risk of building the wrong thing—or building the right thing in the wrong way.

Sinéad Davis Cochrane , UX Manager at Workday
Reduce bias in the UX design process
There are hundreds of cognitive biases identified by psychologists, many of which unknowingly influence our decisions and the products we build. But a key principle of great UX design is to put aside existing beliefs, and learn from your users.
“You have to be humble, optimistic, and open-minded,” says Bertrand Berlureau , Senior Product Designer at iMSA. Using effective UX research, you can root out bias or assumptions, and follow real human behavior to inform product decisions.
According to Sinéad, you should consider these questions early in the design process:
- “What are your assumptions?”
- “What are some of the assumptions you’ve been making about your end-users and product without any evidence?”
- “What are the anecdotes or coincidental pieces of information that you hold, and how can you challenge them?”
Biases can subconsciously affect research and UX design, and it can be tricky to identify them. The first step to overcoming cognitive biases is by being aware of them. Head to chapter three of our cognitive biases guide to discover how.
Test and validate concepts
The power of UX research is that it can prove you right or wrong—but either way, you’ll end up knowing more and creating a product that provides a better user experience. For Bertrand, an idea without a test is just an idea. So, before the design process, his team starts with these user research methods:
- Face-to-face and remote user interviews
- Focus groups
- Co-creativity sessions through design sprints, quick prototyping, and hypothesis concepts
- User testing
UX research is the only way to unequivocally confirm your product is solving the right problem, in the right way. By speaking directly to real users, you can pinpoint what ideas to focus on, then validate your proposed solution, before investing too much time or money into the wrong concept.
Work on solutions that bring real value to customers
Another main benefit of UX research is that it allows product teams to mitigate risk and come up with products users want to use. “One of the main risks we need to control is whether users actually want to use a solution we've implemented,” explains Luke Vella , Group Product Manager at Maze. “UX research helps us reduce this risk, allowing us to build solutions that our customers see as valuable and make sure that they know how to unlock that value.”
Luke works on pricing and packaging, an area that requires constant user research. On one hand, he and his team want to understand which problems their users are facing and come up with plans to satisfy those different needs. On the other hand, they need to make sure they can monetize in a sustainable way to further invest in the product. You can only get this perfect balance by speaking to users to inform each step of the decision.
Market your product internally and externally
UX research also plays a crucial role in helping product marketers understand the customer and effectively communicate a product's value to the market—after all, a product can only help those who know about it.
For example, Naomi Francis , Senior Product Marketing Manager at Maze, uses different research methods to inform marketing strategy. Naomi conducts user interviews to build personas, using user research to collect insights on messaging drafts, product naming, and running surveys to gather user feedback on beta products and onboarding.
Understanding how and why customers need and use our product pushes marketing launches to the next level—you can get a steer on everything from messaging to language and approach.

Naomi Francis , Senior Product Marketing Manager at Maze
Types of UX research
All UX research methods fit into broader UX research techniques that drive different goals, and provide different types of insight. You can skip to chapter seven for a rundown of the top 9 UX research methods , or keep reading for a deep dive on the main types of UX research:
- Moderated and unmoderated
- Remote and in-person
- Generate and evaluate
- Qualitative and quantitative
- Behavioral and attitudinal
Where moderated/unmoderated and remote/in-person refer to the way research is conducted , the other types of UX research reflect the type of data they gather.
The most powerful insights come from a mixture of testing types—e.g. attitudinal and behavioral, generative and evaluative, and quantitative and qualitative. You don’t need to run all types of research at all times, but you’ll benefit from gathering multiple types of data throughout different stages of product development.
Moderated research
Moderated research is any research conducted with a facilitator or researcher present. A moderator may observe research sessions and take notes, ask questions, or provide instruction to participants where needed.
Like all research, it’s crucial a moderator doesn’t overly guide participants or influence results. Due to certain types of cognitive biases , people may behave differently while being observed, so researchers often opt for unmoderated methods to avoid results being impacted.
UX research methods for moderated research
- User interviews to speak directly with your target user face-to-face
- Focus groups to gather feedback on a variety of topics
- Moderated usability testing to hear the thought process behind the actions
Unmoderated research
As the name suggests, unmoderated research refers to the lack of a moderator. Often used in tandem with remote research , users complete tasks independently, guided by pre-written instructions.
Unmoderated research is helpful to ensure users are acting entirely of their own volition, and it has a lower cost and quicker turnaround than moderated research—however it does require efficient planning and preparation, to ensure users can navigate the tasks unaided.
UX research methods for unmoderated research
- Unmoderated usability testing to see how easily users navigate your product
- Live website testing to witness users interacting with your product in real time
- Surveys to have users answer specific questions and rate design elements
Remote research
An incredibly flexible approach, remote research is often favored due to its time-to-results and cost savings. Remote research can be moderated or unmoderated, and is conducted using UX research tools which record user behavior, feedback, and screen recordings.
Another key benefit is its reach and accessibility—by moving research to a virtual platform, you can access users from anywhere in the world, and ensure research is inclusive of those with different abilities or requirements, who may otherwise be unable to take part in traditional in-person research.
UX research methods for remote research
- Usability testing to evaluate how accessible your product is
- Card sorting to understand how users categorize and group topics
- Concept testing to assess what ideas users are drawn to
- Wireframe or prototype testing to invite users to test a rough version of the design
In-person research
Research conducted in-person is typically more expensive, as it may require travel, accommodation, or equipment. Many traditionally in-person research methods can easily be performed remotely, so in-person research is often reserved for if there’s additional needs for accessibility, or if your product requires physical testing, safety considerations or supervision while being tested.
UX research methods for in-person research
- Guerrilla research to speak to random users and gather feedback
- User interviews to connect with users and read body language
- Field studies to gauge how your product fits into a real world environment
Generative research
Generative research provides a deep understanding of your target audience’s motivations, challenges, and behaviors. Broadly speaking, it pinpoints a problem statement, identifies the problem to be solved, and collects enough data to move forward.
It should happen before you even begin designing, as it helps you identify what to build, the types of problems your user is facing, and how you can solve them with your product or service.
UX research methods for generative research
- Field studies to get familiar with users in their authentic environment
- User interviews to ask open-ended questions about pain points
- Diary research to keep a log of users’ behaviors, activities, and beliefs over time
- Open card sorting to have users define and name their own categories
Evaluative research
Evaluative research focuses on evaluating a product or concept in order to collect data that will improve the solution. Evaluative research usually happens early on and is used in a continuous, iterative way throughout the design process and following launch. You can use this type of UX research to assess an idea, check navigation, or see if your prototype meets your user’s needs.
UX research methods for evaluative research
- Usability testing to see if your platform is easy and intuitive to use
- A/B testing two versions of a design to see which one works best
- Tree testing to assess if your website’s information architecture (IA) makes sense
- Five-second tests to collect first impressions
Behavioral research
This type of research refers to observation—it’s human nature that sometimes what we say, or what we think we’ll do doesn’t match up to what we actually do in a situation. Behavioral research is about observing how users interact with your product or how they behave in certain situations, without any intervention.
UX research methods for behavioral research
- Observation in labs or real environments to witness behavior in real time
- Tree testing to view which paths users take on a website
- Diary research to see how users interact with your product in real life
Attitudinal research
Attitudinal research is the companion to behavioral research—it’s about what people say, and how they feel. In attitudinal research, you ask users to share their own experiences and opinions; this may be about your product, a concept, or specific design element. With a mix of attitudinal and behavioral research, you can get a broader picture of what your user truly needs.
UX research methods for attitudinal research
- Focus groups to understand users’ perspectives on your product
- User interviews to ask people questions about your product directly
- Surveys to gather insights on user preferences and opinions
Quantitative research
Quantitative and qualitative research methods are two types of research that can be used in unison or separately. Quantitative research comes from data and statistics, and results in numerical data.
It allows you to identify patterns, make predictions, and generalize findings about a target audience or topic. “[At iMSA] We analyze a lot of metrics and specific data like traffic analytics, chatbot feedback, user surveys, user testing, etc. to make decisions,” explains Bertrand. “The convergence of all the data, our user’s needs, governs the choices we make.”
Types of quantitative results you can find through UX research include:
- Time spent on tasks
- Net promoter score (NPS)
- System usability score (SUS)
- Number of clicks taken to complete a task
- Preference percentage on A/B tests
UX research methods for quantitative research
- A/B testing to see which option your users likes best
- Tree testing to get data on which paths users follow on your website
- Usability testing to get a score on system usability
- Heatmaps to spot where users spend most of their session time
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is about understanding the why behind the data. It comes from comments, opinions, and observations—this type of research answers why and how users think or act in a certain way. Qualitative data helps you understand the underlying motivations, thoughts, and attitudes of target users. For this reason, attitudinal research is often qualitative (though not always).
UX research methods for qualitative research
- Interviews to discover your users’ motivations and frustrations
- Open question surveys to learn users’ pain points in their own words
- Focus groups to observe users’ interacting with your product
- Think aloud usability tests to hear commentary behind each user decision
💡 Product tip:
Maze allows you to record your participants' screen, audio, and video with Clips, so you can collect qualitative and quantitative insights simultaneously.
When should you conduct UX research?
The truth is, you should always be researching. When NASA wants to send a new shuttle into space, they don't build a rocket and launch it right away. They develop a design, test it in simulations and lab environments, and iterate between each stage. Only once they’ve run all the foreseeable scenarios do they put a person on the ship. Why should your product be any different?
With an overwhelming 83% of product professionals surveyed in our 2023 Continuous Research Report believing research should happen at all stages, it’s surprising that just 36% run tests after launch. While time and budget can make continuous research a challenge, testing at different stages gives you access to unique insights about your users and how they interact with your product.

That being said, if you can only afford to research a few times throughout the development process , here are some key moments to focus on:
Before developing the product
This is when you need to conduct the most extensive and detailed part of your research. During this phase, you’ll want to conduct generative research to get to know exactly:
- Who your user is
- The types of problems they’re facing (and what kind of product they want to solve them)
- What their expectations on a product or service like yours are
- What they like or dislike about your competitors
- Where they currently go to solve the mentioned problems
- What needs to happen for them to change companies (if they’re using a different product)
You can use a variety of UX research methods like focus groups and surveys to gather insights during this stage.
Remember: This step applies even if your product is already live, if you’re thinking of introducing a new feature. Validate your idea and investigate potential alternatives before you spend time and money developing and designing new functionality.
When you want to validate your decisions
This is the point where you’ll run through a few cycles of researching, building, and iterating, before launching your product. The Maze Product team does this through continuous product discovery, via a dual-track habit:
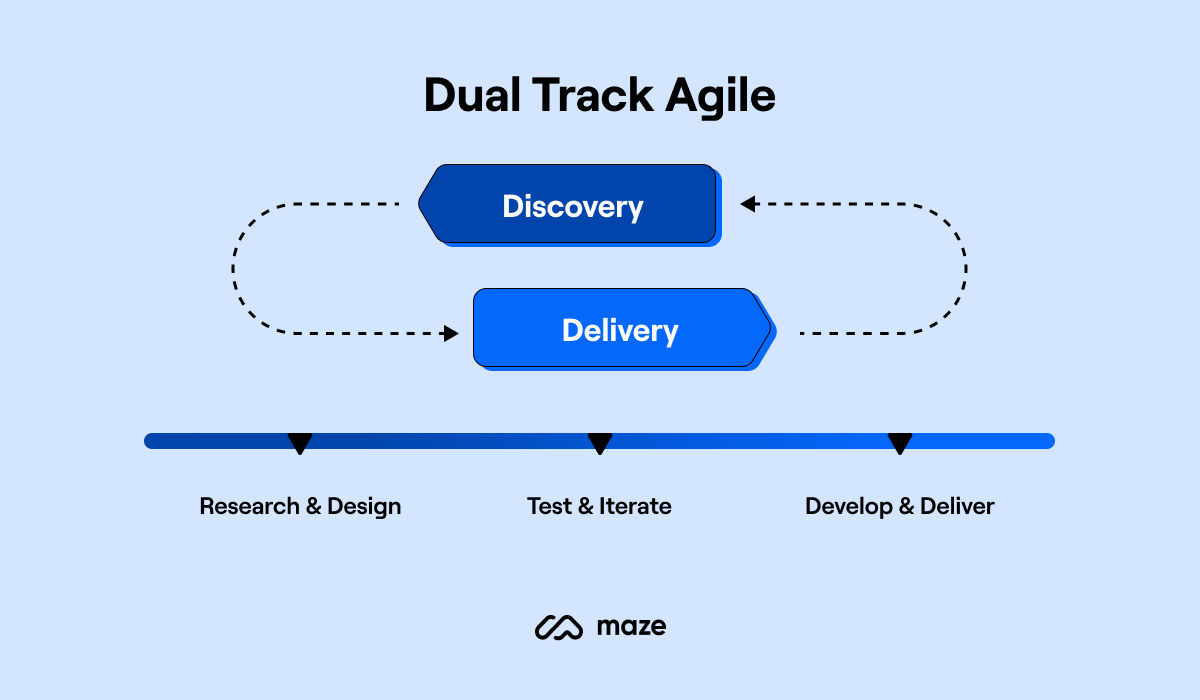
Conduct research regularly while developing and building your product to see if you’re headed in the right direction. Let the research findings feed your deliverables.
Gather qualitative insights on user sentiment through surveys or focus groups. Test your wireframe or sketches to get quantitative answers in the form of clicks, heatmaps, or SUS. Use card sorting to generate ideas, tree testing to assess IA, or prototype testing to assess the usability of a beta version. The options are endless, so there’s no reason to miss maximizing your research at this stage and gather insights to power product decisions.
To evaluate product accessibility
Your product will be used by a multitude of diverse, unique users. Your research participants should be representative of your real audience, which means including all usage scenarios and user personas. Usability testing is one form of UX research that can be used here to ensure your product works for all its users, regardless of ability or need.
There are many ways to ensure your design is inclusive and accessible , including:
- Testing alt-texts, screen-reading capabilities, and color combinations
- Avoiding screen flashes or sudden pop-ups that may be triggering for certain conditions
- Being intentional in what language and imagery is used
Once your product is live
Research doesn’t end once you push your platform to production. Conduct Live Website Testing to evaluate how well your product is meeting your users' expectations and needs. This type of research invites you to answer the question: did we nail it?
Testing your live website also allows you to see how your users interact with your design in a real environment, so you can identify and solve mistakes fast. Pay close attention to loading times, error messages, and other quantitative data that may indicate bugs. You can also conduct regular sentiment checks by embedding feedback surveys into your product itself, to assess user satisfaction and NPS in a few clicks.
TL;DR: Why, how, and when to conduct UX research
The more you understand your customers, the better you can create products that meet expectations, tailor your strategy to their specific needs, and increase your chances for success. Plus, UX research allows you to create unbiased products that put your customers at the center of your business.
To conduct UX research, you’ll need to mix the stage of your product lifecycle with the right research type and methods. Meaning, while you need to conduct UX research continuously, you should look for different types of insights depending on the development stage you’re at and what your current objective is.
For example, if you want to test your live product, you should conduct a mix of quantitative and qualitative evaluative research. That means you might want to perform:
- Usability tests
- Feedback surveys
- Five-second tests
- Prototype testing
Now we’ve covered the what and why of UX research, let’s get into the how. Continue to the next chapter to learn how to create a UX research strategy that blows your competitors away.
Frequently asked questions
What are some examples of UX research?
Some examples of UX research include:
- A/B testing
- Prototype or wireframe testing
- Card sorting
- User interviews
- Tree testing
- 5-second testing
- Usability testing
What are the basics of UX research?
The basics of UX research are simple: you just need a clear goal in mind and a mix of quantitative and qualitative tests. Then, it's a case of:
- Determining the right testing methods
- Testing on an audience that’s an accurate representation of your real users
- Doing continuous product discovery
- Performing unbiased research to build an unbiased design
- Iterating and building user-centric products
UX research gets easier when you use a product discovery platform like Maze. This tool allows you to run multiple types of product research such as usability, prototype, card sorting, and wireframe tests—and get answers within hours.
Is UX research hard?
UX research isn’t hard, especially when you use an intuitive tool for product discovery—like Maze. Maze allows you to build tests using its multiple available templates. It also lets you bring your own users or recruit from its panel and creates an automated, ready-to-share metrics report. Maze gives you answers to tests within hours so you can improve your UX based on real user feedback fast.
Building a UX research strategy
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
A guide to using user-experience research methods.

August 21, 2022 2022-08-21
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter

For further detail, see When to Use Which User-Experience Research Methods .
Free Downloads
Related courses, user research methods: from strategy to requirements to design.
Pick the best UX research method for each stage in the design process
Discovery: Building the Right Thing
Conduct successful discovery phases to ensure you build the best solution
Usability Testing
Learn how to plan, conduct, and analyze your own studies, whether in person or remote
Related Topics
- Research Methods Research Methods
- User Testing
Learn More:

Competitive Reviews vs. Competitive Research
Therese Fessenden · 4 min

15 User Research Methods to Know Beyond Usability Testing
Samhita Tankala · 3 min

Always Pilot Test User Research Studies
Kim Salazar · 3 min
Related Articles:
Obtaining Consent for User Research
Therese Fessenden · 8 min
Open-Ended vs. Closed Questions in User Research
Maria Rosala · 5 min
When to Use Which User-Experience Research Methods
Christian Rohrer · 9 min
UX Research Methods: Glossary
Raluca Budiu · 12 min
Secondary Research in UX
Mayya Azarova · 5 min
Recruiting and Screening Candidates for User Research Projects
Therese Fessenden · 10 min
Skip to main content
COVID-19 update: Google is prioritizing everyone's health and safety, this may impact UX Research. Learn More
- English (United Kingdom)
- Español (Latinoamérica)
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Jump to Content
Help shape the future of Google
Your feedback is important to us.
We’d love to know your thoughts, so we can keep making Google products that fit your needs. You’ll get to influence things millions of people use every day, from email and productivity apps to tools for developers and educators.
Even if you don’t currently use Google products, you can still sign up for a chance to participate in our research. If one of our studies is a good fit for you, we’ll get in touch with details and next steps. Most participants will get a thank-you gift.
Every study opportunity is:
Open - Whether you are a newbie or an experienced Google product user, anyone can sign up to participate.
Secure - You can trust us to never share your data with third parties.
Flexible - Participation can be remote or in person. It’s up to you.
Beneficial - After you participate you may receive a small gift, like a Visa or a retailer-specific gift card.
Valuable - Your feedback will help us build better products for everyone.
Tell us a little bit about yourself by filling out a form . It’ll help us determine if any of the upcoming UX research studies would be a good match.
Join a research session
If a study is a good fit for you, you’ll get a follow-up questionnaire and details about what the study involves, including next steps and location.
Accept our thanks
After completing the study, most participants will get a giftcard to thank them for their time.
Your feedback will make it possible for us to continue our mission of building a more helpful Google for everyone – no matter who they are, where they live, or what they want to accomplish.
For more information, take a look at our FAQ .
What is UX Research? Methods, Process, Tools, Examples
Appinio Research · 15.02.2024 · 40min read

Ever wondered how successful products and services are meticulously crafted to cater to your needs and preferences? User Experience (UX) research is the key that unlocks the secrets behind creating user-centered designs. In this guide, we will delve deep into UX research, uncovering its methods, strategies, and practical applications. Whether you're a designer, developer, product manager, or simply curious about the science of user satisfaction, this guide will empower you with the knowledge and tools to understand, implement, and benefit from UX research principles.
What is UX Research?
User Experience (UX) Research is a systematic process of understanding and evaluating how users interact with a product, service, or system. It encompasses a wide range of research methods and techniques to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, needs, and pain points. The ultimate goal of UX research is to inform and improve the design and functionality of products and services to enhance user satisfaction and usability.
Importance of UX Research
Effective UX research plays a pivotal role in shaping user-centered design and development processes. Its significance can be understood through several key points:
- User-Centered Design : UX research places users at the forefront of design decisions, ensuring that products and services are tailored to meet their needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Usability : Research findings lead to improvements that enhance the overall usability of products, reducing user frustration and increasing engagement.
- Cost Reduction : Identifying and addressing usability issues early in the design process can save time and resources by avoiding costly redesigns or post-launch fixes.
- Competitive Advantage : Organizations prioritizing UX research gain a competitive edge by delivering superior user experiences that attract and retain customers.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction : User satisfaction is closely linked to loyalty and positive word-of-mouth, making UX research an investment in long-term customer relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making : Research data provides valuable insights that inform strategic decisions, reducing the guesswork and subjectivity in design choices.
UX Research Goals and Objectives
The primary goals and objectives of UX research revolve around understanding user needs, improving usability, and driving user-centered design. Here are the key objectives that guide UX research efforts:
- User Understanding : Gain a deep understanding of the target audience, including their demographics, behaviors, motivations, and pain points.
- Usability Evaluation : Identify usability issues and challenges users encounter during interactions with a product or service.
- Task Efficiency : Determine how efficiently users can accomplish tasks within a system, with a focus on minimizing friction and errors.
- User Satisfaction : Measure user satisfaction and gather feedback to uncover areas where improvements can enhance overall user experience.
- Feature Prioritization : Assess which features or functionalities are most valuable to users, guiding feature prioritization in development.
- Validation and Iteration : Validate design decisions through testing and iteration, ensuring that changes align with user expectations and preferences.
- Benchmarking : Establish benchmarks to track improvements over time and compare performance to industry standards.
- Evidence-Based Design : Base design decisions on empirical data and user insights, fostering a user-centered and data-driven design culture.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity : Ensure that products and services are accessible to a diverse range of users, including those with disabilities.
- Risk Mitigation : Identify and mitigate potential risks and challenges early in the design process, reducing the likelihood of post-launch issues.
- Continuous Improvement : Embrace a culture of constant improvement, where UX research is an ongoing process that informs product enhancements and updates.
By aligning research efforts with these objectives, organizations can create products and services that resonate with users, leading to increased user satisfaction and business success.
How to Plan UX Research?
Planning is the foundation of any successful UX research project. It sets the direction, defines your objectives, and ensures that your efforts are focused on achieving meaningful outcomes.
Setting Clear Objectives
Setting clear objectives is the first and most crucial step in planning UX research. Your objectives guide the entire research process, helping you stay on track and measure success effectively. When defining objectives, consider the following:
- Specificity : Objectives should be clear and specific. Vague goals can lead to ambiguous research outcomes.
- Relevance : Ensure that your objectives align with the overall goals of your product or project. How will the research contribute to the success of the endeavor?
- Measurability : Define objectives that are measurable. You should be able to determine whether you've achieved them or not.
- Timeframe : Consider the timeline for your research. Are your objectives achievable within the given time frame?
A well-defined objective might look something like this: "To identify pain points in our mobile app's onboarding process by conducting usability testing with 15 participants, with the aim of reducing drop-off rates by 20% within the next quarter."
Identifying Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is fundamental to effective UX research. Your product or service is designed for specific users, and knowing them intimately is essential. When identifying your target audience, keep the following in mind:
- Demographics : Who are your users? What are their age, gender, location, and other relevant demographics?
- Psychographics : Dig deeper into their lifestyles, values, interests, and behaviors. What motivates them, and what are their pain points?
- User Personas : Create user personas to visualize your target audience. Personas help in humanizing and empathizing with your users.
- User Journeys : Map out the typical user journeys to understand the various touchpoints and interactions users have with your product.
Defining Research Questions
Research questions act as the compass that guides your journey through the UX research landscape. They should be well-crafted and directly tied to your objectives. When defining research questions, consider the following:
- Open-Endedness : Craft questions that allow for open-ended responses . Closed-ended questions with yes/no answers can limit the depth of insights.
- Unbiased Language : Ensure that your questions are phrased in a neutral and impartial manner. Biased questions can lead to skewed results.
- Relevance : Are your research questions directly related to your objectives? Avoid asking questions that do not contribute to your research goals.
- User-Centered : Frame questions from the user's perspective. What would users want to know or share about their experience?
For instance, if your objective is to improve the checkout process of an e-commerce website, a research question could be: "What challenges do users encounter during the checkout process, and how can we simplify it to enhance their experience?"
Budgeting and Resource Allocation
Effective UX research requires proper allocation of resources, both in terms of budget and personnel. Before embarking on your research journey:
- Financial Resources : Determine the budget available for your research project. This budget should cover participant incentives, research tools, and any other associated costs.
- Time Allocation : Allocate time appropriately for each phase of the research process, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and reporting.
- Human Resources : Identify the team members or researchers responsible for conducting the research. Ensure they have the necessary skills and expertise.
- Tools and Software : Assess whether you have access to the required research tools, such as usability testing software, survey platforms, or analytics tools.
Proper budgeting and resource allocation prevent unexpected obstacles and ensure a seamless research process. Remember that investing in UX research is an investment in the overall success of your product or service.
Types of UX Research
When it comes to User Experience (UX) research, understanding the different types of research methodologies is crucial. Each type has its own strengths and applications, allowing you to gather specific insights into user behavior, preferences, and interactions. These are the three primary types of UX research.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on collecting numerical data to quantify user behaviors, preferences, or attitudes. It involves systematic data collection and statistical analysis. Here's a deeper look into quantitative research:
- Data Collection : Quantitative research relies on structured data collection methods, such as surveys, questionnaires, or data analytics tools. These methods yield data in numerical form.
- Objective Measurement : It aims to provide objective and measurable data. This is particularly useful for answering questions like "How many users performed a specific action?" or "What percentage of users prefer feature A over feature B?"
- Large Sample Sizes : Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance. This allows for generalizable findings.
- Statistical Analysis : Statistical analysis plays a central role in quantitative research. It helps identify trends, correlations, and patterns within the data.
- A/B Testing : A common application of quantitative research is A/B testing, where two versions of a design or feature are compared to determine which performs better based on quantifiable metrics.
Quantitative research provides valuable insights when you need to make data-driven decisions and understand the broader user trends and preferences within your target audience.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research dives deep into the subjective aspects of the user experience. It seeks to understand the "why" behind user behaviors and motivations. Here's a closer look at qualitative research:
- Data Collection : Qualitative research relies on methods such as user interviews, usability testing, focus groups , and ethnographic studies. These methods capture rich, non-numerical data.
- Subjective Insights : Qualitative research aims to uncover subjective insights. It helps answer questions like "Why do users find a particular feature frustrating?" or "What emotions do users experience during a specific interaction?"
- Small Sample Sizes : Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes but offers in-depth insights into individual experiences.
- Contextual Understanding : Researchers often engage with users in their natural environment or within the context of product use. This provides a holistic understanding of user behaviors.
- Thematic Analysis : Qualitative data is analyzed through techniques like thematic coding, where common themes and patterns in user feedback are identified.
Qualitative research is particularly valuable when you want to gain a deeper understanding of user needs, pain points, and the emotional aspects of their interactions with your product or service.
Mixed-Methods Research
Mixed-methods research combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research approaches. It offers a comprehensive view of the user experience by leveraging the strengths of both methodologies. Here's what you need to know about mixed-methods research:
- Data Variety : Mixed-methods research involves collecting both numerical and non-numerical data. This includes quantitative data from surveys and qualitative data from interviews or observations.
- Holistic Insights : By combining quantitative and qualitative data, researchers can gain a more complete and nuanced understanding of user behavior and preferences.
- Sequential or Concurrent : Mixed-methods research can be conducted sequentially (first quantitative, then qualitative) or concurrently (simultaneously collecting both types of data).
- Data Integration : Researchers must carefully integrate and analyze the data from both sources to draw comprehensive conclusions.
- Complementary Insights : The aim is to complement the strengths of one method with the weaknesses of the other, providing a more well-rounded perspective.
Mixed-methods research is valuable when you want to explore complex user experiences, understand the reasons behind quantitative trends, or validate findings from one method with the other. It offers a holistic approach to UX research that can lead to more informed design decisions.
How to Conduct UX Research?
Now that you've laid the groundwork and explored the types of UX research, it's time to delve into the practical aspects of conducting UX research.
Recruitment: Finding the Right Participants
Recruiting participants is a crucial step in UX research. The quality of your research outcomes depends on selecting the right participants who represent your target audience. Here's how to do it effectively:
- Define Participant Criteria : Begin by defining specific criteria for your participants. These criteria should align with your research objectives. For instance, if you're testing a healthcare app, you might require participants who have experience with healthcare services.
- Recruitment Channels : Determine where and how you will find participants. Common recruitment channels include online platforms, user testing services, or in-house databases.
- Incentives : Consider offering incentives to motivate participants. This could be monetary compensation, gift cards, or access to your product or service.
- Screening : Screen potential participants to ensure they meet your criteria. Conducting a screening interview or questionnaire can help filter out inappropriate candidates.
Sampling: Choosing the Right Sample Size
Sampling involves selecting a subset of your target audience for research. The size and representativeness of your sample are critical for obtaining reliable results:
- Sample Size : Determine the appropriate sample size based on your research goals and statistical requirements. Larger samples enhance the reliability of your findings.
- Random Sampling : Whenever possible, aim for random sampling to reduce bias. Randomly selecting participants from your target population increases the likelihood of obtaining a representative sample.
- Stratified Sampling : In cases where certain user segments are essential, consider stratified sampling. This ensures that each segment is adequately represented in your sample.
Recruitment and sampling are foundational elements of UX research, ensuring that the data collected accurately reflects the perspectives of your intended user base.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Methods
Selecting the most suitable data collection methods is vital for gathering relevant and meaningful information. Depending on your research objectives, you can utilize various methods:
- Usability Testing : Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with your product or prototype. It provides direct insights into how users navigate and use your design.
- Surveys and Questionnaires : Surveys are useful for gathering structured, quantitative data. They allow you to collect responses from a large number of participants quickly.
- Interviews : Interviews offer a deeper understanding of user experiences by engaging participants in open-ended conversations. They are particularly effective for uncovering motivations and pain points.
- Observations : Observational studies involve watching users in their natural context, providing insights into real-world behavior.
- Eye-Tracking : Eye-tracking technology can reveal where users focus their attention within your design, helping to optimize layouts and content placement.
- Heatmaps : Heatmaps display aggregated user interactions, highlighting areas of interest and interaction intensity within your design.
- Card Sorting : Card sorting exercises help organize information and navigation structures based on how users group and label items.
Choosing the proper data collection methods depends on your research goals, the type of insights you seek, and the available resources. When it comes to data collection, Appinio offers a streamlined solution that simplifies the process and ensures actionable results.
With Appinio , you can effortlessly design surveys, target specific demographics, and gather insights from a diverse pool of respondents. Whether you're conducting usability testing, administering surveys, or conducting interviews, Appinio provides the tools you need to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
Ready to elevate your UX research? Book a demo with Appinio today and experience the power of real-time consumer insights firsthand!
Book a Demo
Making Sense of Collected Data
Once data is collected, the next step is to analyze it effectively. Proper data analysis is critical for drawing meaningful insights and conclusions:
- Quantitative Analysis : For quantitative data collected through surveys or analytics, use statistical analysis techniques to identify patterns, correlations, and statistically significant findings.
- Qualitative Analysis : Qualitative data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses, requires thematic coding and content analysis to uncover themes, trends, and user sentiments.
- Mixed-Methods Integration : In mixed-methods research, integrate both quantitative and qualitative data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the user experience.
- Usability Metrics : When conducting usability testing, use established usability metrics such as task completion rates, time on task, and error rates to evaluate user performance.
- Data Visualization : Visualize your data using charts, graphs, and diagrams to make complex information more accessible and understandable.
Data analysis transforms raw data into actionable insights that inform design improvements and decision-making.
Improving User Experience Through Testing
Usability testing is a fundamental UX research method that involves observing users as they interact with your product or prototype. It helps identify usability issues and gather direct feedback for improvement:
- Test Planning : Begin by creating test scenarios and tasks that align with your research objectives. Determine what you want participants to accomplish during the test.
- Recruitment : Recruit participants who match your target audience and meet your criteria. Ensure they represent the diversity of your user base.
- Moderated vs. Unmoderated Testing : Choose between moderated (where a facilitator guides participants) and unmoderated (participants complete tasks independently) usability testing, depending on your needs and resources.
- Task Observation : Observe participants as they navigate your design, paying attention to their interactions, struggles, and feedback.
- Think-Aloud Protocol : Encourage participants to vocalize their thoughts and feelings during the test. This provides insights into their cognitive processes.
- Post-Test Interviews : Conduct post-test interviews to gather deeper insights. Ask participants about their overall experience, pain points, and suggestions for improvement.
- Iterative Testing : Usability testing is often an iterative process. After making design changes based on feedback, conduct additional tests to validate improvements.
Usability testing helps uncover issues that may not be apparent through other research methods, leading to improved user satisfaction and product usability.
Collecting Quantitative Insights
Surveys and questionnaires are valuable tools for collecting structured, quantitative data from a large number of participants. They can provide insights into user preferences, satisfaction, and demographics:
- Survey Design : Carefully design your survey or questionnaire , ensuring questions are clear, concise, and relevant to your research objectives.
- Sampling : Distribute your survey to a representative sample of your target audience to obtain meaningful results.
- Response Scale : Choose an appropriate response scale, such as Likert scales or multiple-choice questions, depending on the type of data you want to collect.
- Pre-Testing : Before launching your survey, conduct pre-testing to identify and address any potential issues with question wording or survey flow.
- Data Analysis : Once survey responses are collected, perform statistical analysis to uncover patterns and correlations within the data.
Surveys and questionnaires are efficient tools for gathering quantitative data, making them ideal for measuring user satisfaction, preferences, and trends.
Interviews and Observations
Interviews and observations provide qualitative insights that can help you understand the "why" behind user behaviors and motivations:
- Interview Types : Choose between structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interviews, depending on your research goals. Structured interviews use predefined questions, while unstructured interviews allow for open-ended conversations.
- Participant Selection : Select participants who represent your target audience and can provide diverse perspectives.
- Interview Moderation : During interviews, create a comfortable environment for participants to share their thoughts openly. Encourage them to expand on their responses.
- Observations : When conducting observational research, carefully observe users in their natural context or during product use. Take notes on their actions, gestures, and expressions.
- Contextual Inquiry : Contextual inquiries involve observing users while they perform specific tasks related to your product or service. This approach provides insights into real-world behavior.
- Data Interpretation : Analyze interview transcripts and observational notes using thematic coding or content analysis to identify recurring themes and patterns.
Interviews and observations allow you to gain a deep understanding of user experiences, uncover pain points, and inform design decisions from a user-centered perspective.
With these data collection methods at your disposal, you can tailor your approach to gather the most relevant insights for your specific UX research objectives. Whether you choose to observe user interactions, administer surveys, conduct interviews, or run usability tests , each method offers unique advantages for understanding and improving the user experience.
How to Interpret UX Research Data?
As you gather data through various UX research methods, the next critical step is to analyze and interpret this data effectively. This process involves transforming raw information into actionable insights that can drive design improvements and strategic decisions.
Visualizing Insights for Clarity
Data visualization is a powerful technique for making complex data more accessible and understandable. It involves representing data graphically through charts, graphs, and diagrams. Here's why data visualization matters and how to use it effectively:
- Simplify Complex Data : Data visualization simplifies large datasets and helps users quickly grasp trends and patterns.
- Enhance Communication : Visual representations of data are often more effective in conveying information than raw numbers or text.
- Choose the Right Visualization : Select the appropriate type of visualization based on the data and the story you want to tell. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and heatmaps.
- Labels and Legends : Ensure that your visualizations have clear labels, legends, and scales. This makes it easier for viewers to understand and interpret the data.
- Interactivity : In digital formats, consider adding interactivity to allow users to explore data further by hovering, clicking, or filtering.
- Data Storytelling : Use data visualizations to tell a compelling story. Explain the context, highlight key findings, and guide viewers through the insights.
Data visualization aids in identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies within your data, helping you make informed decisions based on a visual representation of your research findings.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Identifying patterns and trends within your data is essential for understanding user behavior and preferences. Here's how to effectively uncover these insights:
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) : Begin with an exploratory analysis of your data. Visualizations, such as histograms, box plots, and scatterplots, can reveal patterns and outliers.
- Segmentation : Segment your data by relevant variables (e.g., demographics , psychographic , user behaviors) to identify patterns within specific groups.
- Statistical Analysis : Use statistical methods to analyze your data quantitatively. Techniques like regression analysis, correlation, and hypothesis testing can uncover relationships and trends.
- Time Series Analysis : If your data includes time-based information, such as user interactions over time, use time series analysis to identify temporal trends and seasonality.
- Qualitative Data : For qualitative data from interviews or open-ended survey responses, use thematic coding to identify recurring themes and insights.
- Comparative Analysis : Compare data before and after design changes or between different user groups to assess the impact of interventions.
Identifying patterns and trends in your data allows you to deeply understand user behaviors, preferences, and pain points, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Turning Data into Actionable Knowledge
Drawing insights and conclusions from your data is the ultimate goal of UX research. It's the stage where you transform data into actionable knowledge that informs design improvements and strategic decisions:
- Hypothesis Validation : Determine whether your research findings align with your initial hypotheses and objectives.
- Prioritization : Prioritize the most significant insights and findings. Focus on those that have the most substantial impact on the user experience.
- User-Centered Recommendations : Frame your insights in a user-centered manner. Consider how the findings can benefit users and enhance their interactions with your product or service.
- Iterative Design : Use insights to inform iterative design improvements. Test and validate changes based on research findings to ensure they address identified issues.
- Communicate Effectively : Communicate your insights and conclusions clearly to stakeholders, designers, and developers. Use data-driven evidence to support your recommendations.
- Continuous Learning : UX research is an ongoing process. Continue to learn and adapt based on user feedback and new research findings.
Ultimately, the ability to draw meaningful insights and conclusions from your UX research data is what drives the improvement of user experiences and the success of your products and services. It's the bridge between data collection and impactful action.
Examples of UX Research
To gain a deeper understanding of how UX research is applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore some concrete examples that illustrate its importance and impact.
E-Commerce Website Optimization
Scenario : An e-commerce company notices a high cart abandonment rate on their website, with users frequently leaving before completing their purchases.
UX Research Approach : The company conducts usability testing with a group of participants. They observe users as they navigate the website, add products to their carts, and attempt to complete the checkout process.
Findings : Through usability testing, the research team identifies several issues contributing to cart abandonment. Users struggle with unclear product descriptions, a complex checkout process, and a lack of payment options. Additionally, users express concerns about data security during the payment phase.
Impact : Armed with these insights, the company makes a series of improvements. They streamline the checkout process, improve product descriptions, add multiple payment options, and prominently display security certifications. As a result, cart abandonment rates decrease significantly, leading to a notable increase in completed purchases and revenue.
Mobile App Redesign
Scenario : A mobile app development company receives user feedback indicating that their app is challenging to navigate and lacks key features.
UX Research Approach : The company initiates a comprehensive research effort that includes user interviews, surveys, and competitor analysis . They aim to understand user expectations, pain points, and the strengths of competing apps.
Findings : User interviews reveal that users desire a more intuitive navigation structure and specific features that rival apps offer. Surveys confirm these preferences and competitor analysis uncovers successful design patterns.
Impact : The company embarks on a redesign project based on user feedback and industry best practices. They restructure the app's interface, add requested features, and enhance the overall user experience. As a result, user satisfaction increases, app ratings improve, and user engagement metrics rise.
Healthcare Information Portal Enhancement
Scenario : A healthcare organization operates an online portal where patients access medical records and communicate with healthcare providers. Users report difficulties in finding information and engaging with the portal.
UX Research Approach : The organization employs a mixed-methods research approach, combining quantitative data analysis with qualitative research. They analyze user interactions and survey responses while also conducting in-depth interviews with patients.
Findings : Quantitative data analysis reveals that users frequently abandon tasks without completion, such as accessing test results. Surveys and interviews uncover confusion related to navigation, terminology, and information layout.
Impact : Armed with a comprehensive understanding of user challenges, the organization revamps the portal's navigation, rewrites content in plain language, and introduces user-friendly features such as task wizards. User engagement with the portal increases, and patients report improved satisfaction with the online experience, leading to enhanced patient-provider interactions.
Social Media Platform Feature Expansion
Scenario : A popular social media platform aims to expand its feature set to stay competitive and retain users. However, the platform's leadership wants to ensure that any new features align with user preferences.
UX Research Approach : The social media platform initiates a series of surveys and user feedback sessions. They present users with potential feature concepts and gather their opinions, expectations, and concerns.
Findings : Through surveys and user feedback sessions, the platform discovers that users desire enhanced privacy controls, a more user-friendly post creation process, and better content filtering options. Additionally, users express concerns about the potential impact of new features on their data privacy.
Impact : Armed with user insights, the platform introduces new features while addressing user concerns. They implement robust privacy settings, simplify post creation, and provide users with customizable content filters. User engagement increases as users appreciate the platform's responsiveness to their needs, and user satisfaction remains high.
These examples highlight how UX research methods, such as usability testing, interviews, surveys, and data analysis, can identify specific issues, inform design improvements, and ultimately enhance the user experience. By investing in UX research, organizations can address user pain points, improve product offerings, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to Report UX Research Findings?
After conducting UX research and drawing valuable insights, the next crucial step is effectively communicating your findings to stakeholders and team members.
Creating Research Reports
Research reports are comprehensive documents that encapsulate your entire UX research process and findings. They serve as a valuable reference for team members and stakeholders. Here's how to create effective research reports:
- Structured Format : Organize your report in a structured format that includes sections such as an executive summary, methodology, key findings, and recommendations.
- Visual Aids : Use visuals such as charts, graphs, and screenshots to illustrate your findings. Visual aids make complex data more accessible.
- Clear Language : Write in clear, concise language that is easily understandable by both technical and non-technical readers.
- Methodology Details : Provide a detailed account of your research methodology, including participant recruitment, data collection methods, and analysis techniques.
- Key Insights : Summarize the most critical findings and insights that emerged from your research. Highlight what these findings mean for the user experience.
- Actionable Recommendations : Include actionable recommendations for improving the product or service based on your research insights.
Creating a well-structured research report ensures that your findings are documented comprehensively and can be referred to as a reference for future decision-making.
Presenting to Stakeholders
Presenting your research findings to stakeholders is essential in the UX research process. It's an opportunity to convey the significance of your insights and garner support for implementing changes.
- Know Your Audience : Understand the background and interests of your audience. Tailor your presentation to their level of expertise and concerns.
- Storytelling : Craft a compelling narrative around your research. Use storytelling techniques to engage your audience and convey the user experience effectively.
- Visuals : Incorporate visuals, such as charts, graphs, and user personas, to illustrate key points and findings.
- Interactive Demonstrations : If possible, demonstrate user interactions or showcase usability improvements through interactive prototypes.
- Key Takeaways : Summarize the main takeaways and actionable recommendations. Highlight how implementing these changes can benefit the organization and users.
- Address Questions : Be prepared to answer questions and provide additional context during the presentation.
Effective presentations not only convey the value of your research but also foster collaboration and support for user-centered improvements.
Making Recommendations
One of the most critical aspects of UX research is translating findings into actionable recommendations that drive improvements in the user experience. Here's how to make recommendations effectively:
- Prioritize Recommendations : Identify and prioritize recommendations based on their potential impact and feasibility. Consider short-term and long-term goals.
- User-Centered Focus : Frame recommendations in a user-centered manner. Explain how implementing each recommendation will directly benefit users.
- Specificity : Make recommendations specific and actionable. Avoid vague suggestions. For example, instead of saying "improve navigation," specify "simplify the main menu structure."
- Data-Backed Evidence : Support recommendations with data-backed evidence from your research. Reference specific findings or user feedback that led to each recommendation.
- Collaboration : Collaborate with designers, developers, and other stakeholders to implement recommendations effectively. Provide guidance and support during the implementation phase.
- Iterative Approach : Recognize that UX research is an ongoing process. Encourage an iterative approach where recommendations are tested, refined, and re-evaluated over time.
Effective recommendations bridge the gap between research findings and meaningful changes that enhance the user experience. They guide product development efforts toward user-centered design and improved satisfaction.
Iterative UX Research
Iterative UX research is a fundamental practice that involves continuous feedback and improvement throughout the product development lifecycle. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing research, testing, and refinement to create user-centered designs.
Here's how it works:
- Feedback Loops : Establish feedback loops where user feedback and insights are collected continuously, not just at specific project phases.
- Regular Testing : Conduct regular usability testing, user interviews, or surveys to gather insights and validate design decisions.
- A/B Testing : Implement A/B testing to compare different design variations and make data-driven decisions on feature implementations.
- Prototyping : Create prototypes and gather user feedback early in the design process. Use this feedback to refine and iterate on designs.
- Monitoring Metrics : Continuously monitor key performance metrics, such as user engagement and conversion rates, to identify areas for improvement.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration : Promote collaboration between UX researchers, designers, developers, and product managers to ensure that research findings inform design and development decisions.
Iterative UX research ensures that user feedback is integrated into the design and development process, leading to products and services that continually evolve to meet user needs and preferences.
Ethical Considerations in UX Research
Ethical considerations in UX research are paramount to protect the rights and well-being of participants and ensure the integrity of the research process. Here are some ethical principles to adhere to:
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from participants, clearly explaining the research purpose, procedures, and any potential risks involved.
- Privacy and Data Security : Safeguard participant privacy by anonymizing and securely storing sensitive data. Follow data protection regulations, such as GDPR.
- Transparency : Be transparent about the research objectives, methodologies, and the use of collected data. Avoid misleading or deceptive practices.
- Avoiding Harm : Ensure that research activities do not harm participants physically or emotionally. Minimize any potential discomfort or stress.
- Respect and Dignity : Treat participants with respect and dignity. Avoid any form of discrimination, bias, or exploitation.
- Bias Awareness : Be aware of potential biases in research design and analysis . Strive for inclusivity and fairness in participant selection and interpretation of findings.
- Debriefing : Provide participants with a debriefing session after their involvement in research, explaining the purpose of the study and addressing any questions or concerns.
Ethical UX research practices uphold the principles of integrity, transparency, and respect, fostering trust between researchers and participants and ensuring the ethical integrity of the research process.
Conclusion for UX Research
UX research is the compass that guides the creation of products and services with you, the user, at the center. By understanding your needs, preferences, and challenges, organizations can craft experiences that truly resonate with you. From setting clear objectives and conducting research to analyzing data and making improvements, the journey of UX research is a continuous cycle of enhancement, ensuring that the digital world becomes more user-friendly with each iteration. Remember, UX research is a powerful tool that empowers teams to create products that delight users and drive success. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just beginning your journey into UX, the principles and practices outlined in this guide can help you make a positive impact in the ever-evolving landscape of user experience.
How to Conduct UX Research in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the ultimate solution for lightning-fast UX research! As a real-time market research platform, Appinio specializes in providing companies with instantaneous consumer insights, revolutionizing the way businesses make data-driven decisions.
With our intuitive platform, conducting your own market research becomes a breeze, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: swift, informed choices for your business. Say goodbye to lengthy research processes and hello to quick, reliable results with Appinio.
Here's why you should choose Appinio:
- Instant Insights : From questions to actionable insights in a matter of minutes, empowering you to make decisions on the fly.
- User-Friendly Interface : No need for a research degree; our platform is designed for simplicity and ease of use, making it accessible to everyone.
- Global Reach : Reach your target audience anywhere in the world, with the ability to define precise demographics and survey respondents across over 90 countries.
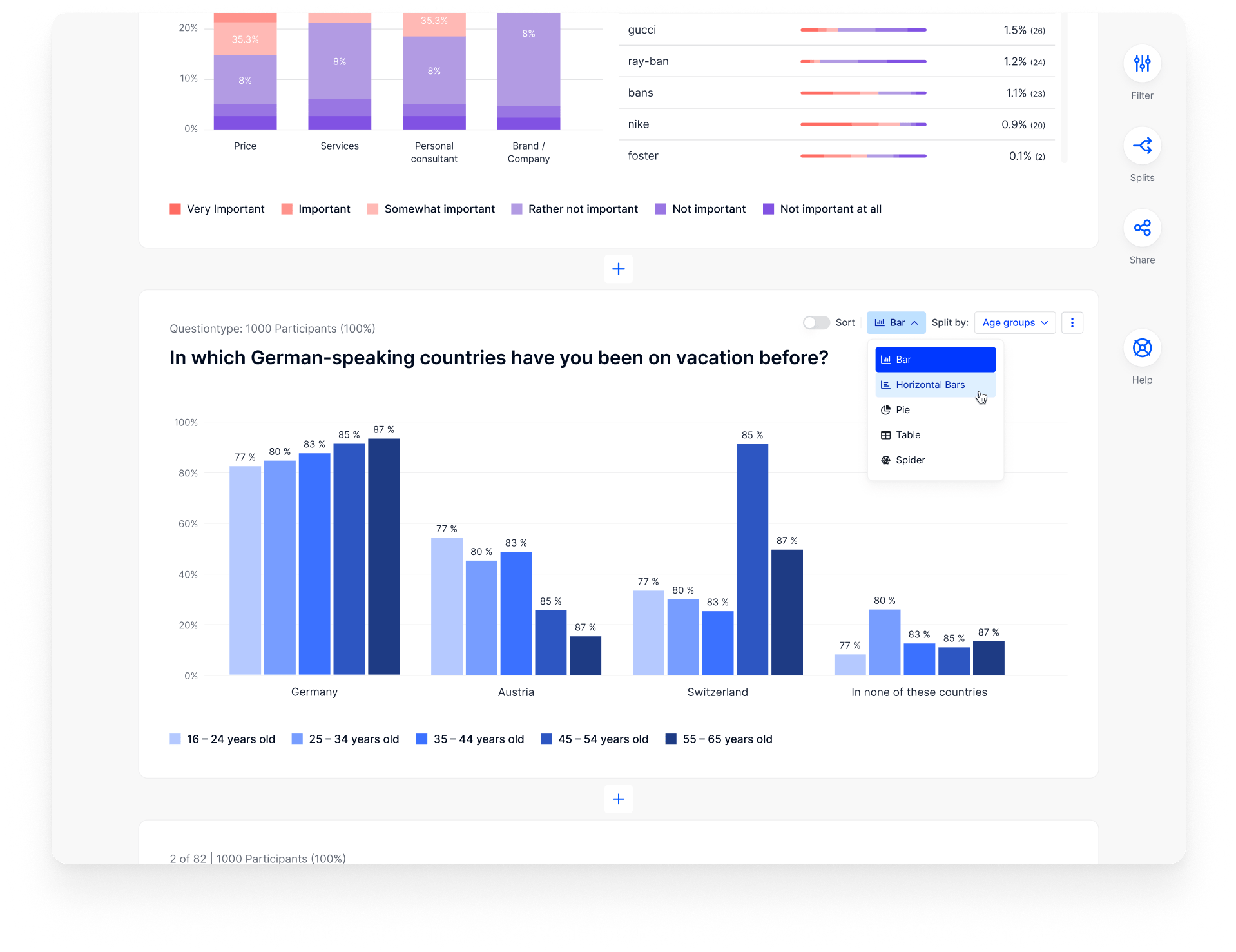
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

26.06.2024 | 35min read
Brand Development: Definition, Process, Strategies, Examples

18.06.2024 | 7min read
Future Flavors: How Burger King nailed Concept Testing with Appinio's Predictive Insights

18.06.2024 | 32min read
What is a Pulse Survey? Definition, Types, Questions
How to Conduct User Experience Research Like a Professional
Whether you’re looking to develop a broad UX design skillset, or you’re exploring UX research as a design specialization , here’s your complete introduction to conducting user research like a pro.
Hello, I’m Raven, a mentor for aspiring UX designers enrolled in the CareerFoundry UX Design Course . I also work as a UX Research Assistant at IBM and studied behavioral science at the University of Texas. I have 10 years of experience studying and analyzing human behavior—user research is definitely my thing.
During the past few years, I’ve worked with major companies, academic institutions, and non-profit organizations to develop and improve impactful products and applications. I’ve moderated focus groups, designed and administered surveys, carried out usability testing, and conducted user interviews. I also know a thing or two about creating a good persona!
In this guide, we’re going to cover the basics of UX research. We’ll start with exactly what it is, and then move on to discuss the various steps and associated terminology of UX research , as well as its role and value within the broader design process . We’ll then review the most common UX research methods, diving into how they’re conducted and a few best practices.
If you’re particularly interested in one of these topics, simply select it from the list below to jump straight to it. I’ve also added videos throughout the guide for those of you who prefer to learn with both eyes and ears—and I recommend you save this set of free UX research tutorials for later, too. Sound good? Let’s get started!
Introduction To User Experience (UX) Research
- What is UX research?
- What’s the difference between good and bad UX research?
- What are the five steps of UX research?
- What’s the role of research in the UX design process?
- Whats the value of UX research?
Introduction To User Experience Research Methods
- User Groups
- Usability Testing
- User Interviews
- Online Surveys
- User Personas
- What Next? User Research Analysis
1. What is UX research?
You read my bio in the introduction. Using only this information, could you explain why I recently switched from one time management app to another? Probably not. In order to answer this question, you need more context. UX research provides that context. So, what is UX research and what is its purpose ?
“User research is how you will know your product or service will work in the real world, with real people. It’s where you will uncover or validate the user needs which should form the basis of what you are designing.”
— Chris Mears, UXr
According to Design Modo , UX research is; “The process of understanding user behaviors, needs, and attitudes using different observation and feedback collection methods.” One of the other benefits of user experience research is that it helps us understand how people live their lives so that we can respond to their needs with informed design solutions. Good UX research involves using the right method at the right time during the development of a product.
Maria Arvidsson, Head of Product and UX at Usabilla , describes UX research as:
“The means through which you try to understand your users’ needs, behaviors and motivations and validate your assumptions and solutions.”

2. What’s the difference between good and bad UX research?
The biggest sign of an amateur UX designer is excluding end users from the design process. At the very start of my career I held the attitude that I could test any app, website, or product on myself, replacing the act of speaking with users. Never a good idea. It took time for me to learn a more professional approach, which is to start the design process by listening to the end user. Overall, UX research helps us avoid our biases since we are required to design solutions for people who are not like us.
“Insights that are received directly from user experience research are like muscle memory; the more you do research, the more insights you build up. But just like muscle memory, YOU have to be a part of the hard work in order to enjoy the lasting benefits of it that are specific to you. While it may be tempting to outsource research to a specialized team (and sometimes you can’t avoid it), you should try your utmost best to engage in at least a little bit of the research so that the insights grow under your skin instead of being handed to you from someone else who has sweated it.”
—UX designer Ali Rushdan Tariq from ARTariq
A quick plug before we continue: If you’re looking to become a professional in this subdomain of UX, be sure to take a look at our guide to becoming a UX researcher
3. What are the five steps of UX research?
Created by Erin Sanders , the Research Learning Spiral provides five main steps for conducting UX research. The first two steps are about forming questions and hypotheses, and the last three steps are about gathering knowledge through selected UX research methods.
- Objectives: What are the knowledge gaps we need to fill?
- Hypotheses: What do we think we understand about our users?
- Methods: Based on time and manpower, what methods should we select?
- Conduct: Gather data through the selected methods.
- Synthesize: Fill in the knowledge gaps, prove or disprove our hypotheses, and discover opportunities for our design efforts.
4. What’s the role of research in the UX design process?
UX research is the starting point for a project . Research helps us learn about the users and their behavior, goals, motivations, and needs. It also shows us how they currently navigate a system, where they have problems and, most importantly, how they feel when interacting with our product.
UX research comes first in the UX design process because without it, our work can only be based on our own experiences and assumptions, which is not objective. As Neil Turner, founder of UX for the Masses told us, a good foundation is key to successful design:
“Good user research is key to designing a great user experience. Designing without good user research is like building a house without solid foundations—your design will soon start to crumble and eventually fall apart.”
5. What’s the value of UX research?
In the current digital product landscape, the real value of UX research is its ability to reduce uncertainty in terms of what users want and need , which yields benefits for the product, the business, and, of course, the users themselves.
1. Product Benefits
UX research provides data about the end user of the product, how and when the user will use the product, and the main problems the product will solve. UX research is also helpful when UX designers and the rest of the team (and stakeholders) have to decide between multiple design solutions.
2. Business Benefits
UX research brings a lot of a value to businesses. By knowing the end users and incorporating design requirements upfront, businesses can speed up the product development process, eliminate redesign costs, and increase user satisfaction.
3. User Benefits
One of the greatest values of user experience research is that it’s unbiased user feedback. Simply put, UX research speaks the user’s thoughts—without any influence from outside authority. It also serves as a bridge between users and the company.
“User experience research provides powerful insights that allow companies to humanize their customers and insert their needs, intentions, and behaviors into the design and development process. In turn, these insights enable companies to create experiences that meet—and sometimes exceed—customer needs and expectations. User experience research should be conducted well before the first sketch is drawn and integrated throughout the concept, iterative design, and launch phases of a product.”
—Janelle Estes, Director of Research Strategy at UserTesting
UX research is based on observation, understanding, and analysis. With the help of various UX research techniques, you will:
- O bserve your users , keeping an eye out for non-verbal clues as to how they are feeling;
- Develop an understanding of the user’s mental model : what does the user anticipate when using a certain product? Based on their previous experience, how do they expect this particular product to work?
- A nalyze the insights you’ve gathered and try to identify patterns and trends. Eventually, these insights will inform the decisions you make about the product and how it is designed.
With that in mind, let’s consider some of the most valuable user research techniques.
1. User Groups
User groups—also called “focus group discussions” or “focus groups”—are structured interviews that quickly and inexpensively reveal the desires, experiences, and attitudes of a target audience. User groups are a helpful user experience research method when a company needs a lot of insight in a short amount of time. If you are unsure when to use a user experience research method, user groups can be a good one to start with.
Why Do We Conduct User Groups?
User groups can help your company better understand:
1) How users perceive a product
2) What users believe are a product’s most important features
3) What problems users experience with the product
4) Where users feel the product fails to meet expectations
User groups can also be used to generate ideas of what users want to see in the future.
What people say and what people do are often very different, therefore user groups do not provide an accurate measurement of behavior . And because user groups are conducted with more than one user at a time, participants may influence each other’s opinions and preferences (aka “groupthink”), thus introducing bias and producing inaccurate data.
Best Practices For User Groups
Getting the most out of your user group is straightforward if you consider the following best practices when conducting this particular user research technique.
- Ask good questions: Make sure your questions are clear, open-ended, and focused on the topics you’re investigating.
- Choose a few topics: On average, plan to discuss 3-5 topics during a 90-minute focus group.
- Include the right amount of people: A good focus group should include 3-6 users—large enough to include a variety of perspectives, but small enough so everyone has a chance to speak.
“Conducting user research allows you to dive deep beneath the surface of what your users say they want, to instead uncover what they actually need. It’s the key to ensuring that your products and features will actually solve the problems that your clients face on a day to day basis. User research is imperative if you want to create a successful, habit forming product.”
— Jennifer Aldrich, UX and Content Strategist at InVisionApp
How To Conduct User Experience Research With User Groups
Conducting user groups can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Create a schedule that provides enough time for recruiting, testing, analyzing, and integrating results.
- Assemble your team, and establish roles: choose a moderator, note-taker, and discussion leader.
- Define the scope of your research: what questions will you ask? And how in-depth do you want to explore the answers? This will determine the number of people and the number of groups that need to be tested.
- Create a discussion guide that includes 3-5 topics for discussion.
- Recruit potential or existing users who are likely to provide good feedback.
- Conduct user group testing, and record data.
- Analyze and report findings.
“It’s really hard to design products by user groups. A lot of times, people don’t know what they want until you show it to them.”
—Steve Jobs
2. Usability Testing
According to the usability.gov website, usability testing refers to “evaluating a product or service by testing it with representative users.” During a test, participants will be asked to complete specific tasks while one or more observers watch, listen, and record notes. The main goal of this user experience testing method is to identify usability problems, collect qualitative data, and determine participants’ overall satisfaction with the product.
Why Do We Perform Usability Testing?
Usability testing helps identify problems before they are coded. When development issues are identified early on, it is typically less expensive to fix them. Usability testing also reveals how satisfied users are with the product , as well as what changes are required to improve user satisfaction and performance .
Unfortunately, usability testing is not 100% representative of the real life scenario in which a user will engage with your product. Also, because the data is qualitative, this kind of UX testing method doesn’t provide the large samples of feedback a questionnaire might. The good news it that the qualitative feedback you receive can be far more accurate and insightful.
Best Practices For Usability Testing
- Test with five users: Testing five users is typically enough to identify a design’s most important usability problems.
- Invite your team to the testing sessions: Anyone who is involved with how fast and how well problems are addressed should be invited to the usability testing sessions. These stakeholders may include the executive team, and lead developers or designers.
- Keep the findings brief and to-the-point: When you report the findings of a usability test, limit the comments to the ones that are really important. One good rule of thumb is to include the top three positive comments and the top three problems. The overall report should be no more than approximately 50 comments and 30 pages.
How to Conduct UX Research with Usability Testing
Usability testing can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Identify what needs to be tested and why (e.g. a new product, feature, etc.)
- Identify the target audience (or your desired customers).
- Create a list of tasks for the participants to work through.
- Recruit the right participants for the test.
- Involve the right stakeholders.
- Apply what you learn.
“One of usability’s most hard-earned lessons is that ‘you are not the user.’ If you work on a development project, you’re atypical by definition. Design to optimize the user experience for outsiders, not insiders.”
– Jakob Nielsen
3. User Interviews
A well-known user experience methodology is an interview. An interview is a user experience research method used to discover the attitudes, beliefs, and experiences of users (and potential users) of a product. Interviews are typically conducted by one interviewer speaking to one user at a time for 30 minutes to an hour. Interviews can take place face-to-face, over the phone, or via video streaming.
Why Do We Conduct Interviews?
Of all the user experience design methods, interviews are typically conducted at the beginning of the product development cycle when reviewing product goals. Because of the one-to-one nature of the interview, individual concerns and misunderstandings can be directly addressed and cleared up.
Face-to-face interviews also allow you to capture verbal and nonverbal cues, such as emotions and body language, which may identify enthusiasm for the product or discomfort with the questions.
When thinking about what research methodology to use, bear in mind that interviews are also a good supplement to online surveys: conducting an interview beforehand helps you refine questions for the survey, while conducting an interview afterwards allows you to gain explanations for survey answers.
There are a few drawbacks, however. First, because interviews require a team of people to conduct them, personnel costs are usually difficult to keep low. Sample size is also limited to the size of the interviewing staff.
Best Practices For User Interviews
- Hire a skilled interviewer: A skilled interviewer asks questions in a neutral manner, listens well, makes users feel comfortable, and knows when and how to probe for more details.
- Create a discussion guide: Write up a discussion guide (or an interview protocol) for all interviewers to follow. This guide should include questions and follow-up questions.
- Get informed consent: Before conducting the interview, make sure to get permission or consent to record the session. It’s also good to have one or two note takers on hand.
How To Conduct User Experience Research With User Interviews
Conducting an interview can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Prepare a discussion guide, or a list of questions to ask participants.
- Select a recording method (e.g. written notes, tape recorder, video).
- Conduct at least one trial run of the interview.
- Recruit the right participants for the interview.
- Conduct the interview.
- Analyze and report the results.
“Curiosity is a natural outcome of caring, and it is the single greatest contributor to effective user research … Caring and curiosity engender personal investment, and investment motivates a researcher to develop a deep understanding of users.”
– Demetrius Madrigal
4. Online Surveys
A survey is a research tool that typically includes a set of questions used to find out the preferences, attitudes, and opinions of your users on a given topic. Today, surveys are generally conducted online and in various lengths and formats. Data collected from surveys is received automatically, and the survey tool selected generally provides some level of analysis, the data from which can then be used for user experience studies further down the line to inform your product.
“It is so important to avoid using leading questions when it comes to surveys. It’s a common mistake that many people make. For example phrasing a question like “What do you dislike about Uber?” assumes the user has a negative preference for the service off the bat. A more neutral phrase would be “Tell us about your experience getting around town.” – this elicits more natural user feedback and behavior instead of forcing them down a funnel.”
– Top tip from UXBeginner
Why Do We Conduct Online Surveys?
Unlike traditional surveys, online surveys enable companies to quickly collect data from a broad (and sometimes remote) audience for free—or a low price. Surveys also help you discover who your users are , what your users want to accomplish, and what information your users are looking for.
Unfortunately, what users say versus what they do are two different things and can often yield inaccurate results. Furthermore, poorly worded questions can negatively influence how users respond. Length can also be an issue—many people hate taking long surveys. This is why it’s important to create short surveys so users are more likely to complete them and participate in future research efforts.
Best Practices For Online Surveys
- Keep it short: Keep your surveys brief, especially if participants will be compensated little or not at all. Only focus on what is truly important.
- Keep it simple: Make sure questions can be easily understood: ambiguous or complex wording can make questions more difficult to understand, which can bring the data into question.
- Keep it engaging: Include a mix of both multiple choice questions and open-ended questions (or questions in which users complete the answer).
How To Conduct User Experience Research With Online Surveys
Conducting an online survey can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Identify goals and objectives of the survey.
- Create survey questions.
Note: Consider collecting information about how satisfied users are with your product, what users like/dislike, and if they have suggestions for improvement.
- Select an online survey tool (e.g. SurveyMonkey, Qualtrics).
- Recruit participants.
- Conduct the survey.
“We have to arm ourselves with data, research … and a clear understanding of our users so our decisions are not made out of fear but out of real, actionable information. Although our clients may not have articulated reasons for why they want what they want, it is our responsibility to have an ironclad rationale to support our design decisions.”
– Debra Levin Gelman
5. User Personas
A user persona is a fictional representation of your ideal customer. A persona is generally based on user research and includes the needs, goals, and observed behavior patterns of your target audience. You can find out how to create a user persona in this detailed guide .
Why Do We Create User Personas?
Whether you’re developing a smartphone app or a mobile-responsive website, any user experience research job will require you to understand who will be using the product. Knowing your audience will help influence the features and design elements you choose, thus making your product more useful. A persona clarifies who is in your target audience by answering the following questions:
- Who is my ideal customer?
- What are the current behavior patterns of my users?
- What are the needs and goals of my users?
Understanding the needs of your users is vital to developing a successful product. Well-defined personas will enable you to efficiently identify and communicate user needs. Personas will also help you describe the individuals who use your product, which is essential to your overall value proposition.
Unfortunately, creating personas can be expensive — it all depends on how deep into user research your organization is willing to go. There is also no real “scientific logic” behind persona building, which makes some people a little more hesitant to accept them.
Best Practices For User Personas
- Create a well-defined user persona: A great persona contains four key pieces of information: header, demographic profile, end goal(s), scenario.
- Keep personas brief: As a rule of thumb, avoid adding extra details that cannot be used to influence the design. If it does not affect the final design or help make any decisions easier: omit it.
- Make personas specific and realistic: Avoid exaggerated caricatures, and include enough detail to help you find real-life representation.
How To Conduct User Experience Research By Creating Personas
Creating user personas can be broken down into these main steps:
- Discuss and identify who your target users are with stakeholders (e.g. UX team, marketing team, product manager).
- Survey and/or interview real users to get their demographic information, pain points, and preferences.
- Condense the research, and look for themes to define your groups.
- Organize your groups into personas.
- Test your personas.
“Be someone else. It takes great empathy to create a good experience. To create relevant experiences, you have to forget everything you know and design for others. Align with the expected patience, level of interest, and depth of knowledge of your users. Talk in the user’s language.”
– Niko Nyman
Which User Experience Research Method Should You Use?
Now that you know more about the various user experience research methods, which one do you choose? Well, it all depends on your overall research goals.
You’ll also need to consider what stage you’re at in the design process. If you’re just starting out, you’ll want to focus on understanding your users and the underlying problem . What are you trying to solve? Who are you trying to solve it for? At this early stage in the design process, you’ll typically use a mixture of both qualitative and quantitative methods such as field studies, diary studies, surveys, and data mining.
Once you’ve established a direction for your design, you’ll start to think about actually building your product. Your UX research will now focus on evaluating your designs and making sure that they adequately address your users’ needs . So, you’ll choose research methods that can help you to optimize your designs and improve usability—such as card sorting and usability testing.
Eventually, you’ll have finalized your design and developed a working product—but this doesn’t mean your research is done! This is the ideal time to investigate how well the product performs in the real world. At this point, you’ll focus mainly on quantitative research methods , such as usability benchmarking, surveys, and A/B testing.
To help you with the task of choosing your research methods, let’s explore some important distinctions between the various techniques.
Behavioral vs. Attitudinal Research
As mentioned before, there is a big difference between “what people do” versus “what people say.” Attitudinal research is used to understand or measure attitudes and beliefs, whereas behavioral research is used to measure behaviors. For example, usability testing is a behavioral user research method that focuses on action and performance. By contrast, user research methods like user groups, interviews, and persona creation focus on how people think about a product.
UX designers often conduct task analysis to see not how users say they complete tasks in a user flow, but how they actually do.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
When conducting UX research and choosing a suitable method, it’s important to understand the difference between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research gathers data that is measurable. It gives you clear-cut figures to work with, such as how many users purchased an item via your e-commerce app, or what percentage of visitors added an item to their wishlist. “Quant methods”, as they’re sometimes called in the industry, help you to put a number on the usability of your product. They also allow you to compare different designs and determine if one version performs significantly better than another.
Qualitative research explores the reasons or motivations behind these actions. Why did the user bounce from your website? What made them “wishlist” an item instead of purchasing it? While quantitative data is fixed, qualitative data is more descriptive and open-ended. You can learn all about qualitative research in the video guide below, in which CareerFoundry graduate and professional UX designer Maureen Herben takes you through the most common qualitative user research processes and tools.
A further distinction to make is between how qualitative and quantitative studies go about collecting data. Studies that are qualitative in nature are based on direct observation. For example, you’ll gather data about the user’s behaviours or attitudes by observing them directly in action. Quantitative studies gather this data indirectly—through an online survey, for example.
Qualitative research methods (e.g. usability testing, user groups, interviews) are better for answering questions about why or how to fix a problem, whereas quantitative methods (e.g. online surveys) are great for answering questions about how many and how much.
Ideally, you’ll use a mixture of both qualitative and quantitative methods throughout your user research, and work hard to ensure that the UX research you conduct is inclusive !
6. What Next? Conducting User Research Analysis
Once you’ve conducted extensive user research, you’ll move on to the analysis phase. This is where you’ll turn the raw data you’ve gathered into valuable insights. The purpose of UX research analysis is to interpret what the data means; what does it tell you about the product you’re designing, and the people you’re designing it for? How can you use the data you’ve gathered to inform the design process?
Watch this video to learn how to conduct user research analysis in five simple steps:
Final thoughts
“User experience research is the work that uncovers and articulates the needs of individuals and/or groups in order to inform the design of products and services in a structured manner.”
—Nick Remis, Adaptive Path
Overall, the purpose of user experience research is simple: to discover patterns and reveal unknown insights and preferences from the people who use your product. It basically provides the context for our design. Research also helps us fight the tendency to design for ourselves (or our stakeholders)—and returns the focus on designing for the user.
If you’d like to learn more about UX research, check out these articles:
- What Does a UX Researcher Actually Do? The Ultimate Career Guide
- The Ultimate Guide to UX Research Bootcamps
- Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid in Your UX Research Portfolio
- Interview Toolkit: Top 5 UX Research Questions to Prepare For
And to get inspired, check out these 15 quotes from influential designers in the industry.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
User Experience Research: Definition, Types, Steps, + Uses

Have you ever noticed how your favorite applications and websites appear to read your mind? How do they smoothly anticipate your wants and make you feel like a tech-savvy superhero? It isn’t magic; it is the result of User Experience Research!
UX research is a dynamic and ongoing process that is essential in developing effective and user-friendly products or services. It fills the gap between user expectations and design decisions, resulting in higher product satisfaction and better business-related results.
Continue reading to learn more about user experience research, how to do it, and how researchers may use it.
What is User Experience research?
User Experience research or UX research is defined as users’ systematic study to discover behaviors, needs, motivations, and trends through observations, analysis, and other user feedback.
UX researchers use different methods to understand problems and draw opportunities to stand out amongst their competition. Organizations conduct UX research to precisely understand how real customers react to the products or services in the real world.
Types of UX research methods
We can divide UX research into two dimensions depending on the product type, its environment, the research size, and your timelines. Let’s look at both measurements.
Quantitative vs. qualitative research
Quantitative research is the study of a population through the use of surveys and questionnaires. Quantitative research helps to generalize findings and understand what a specific population likes and dislikes. This data collection technique is generally mathematical in nature.
Qualitative research helps researchers gather information by observing users in field studies or focus groups. Qualitative research brings sense to the motivations and reasons for consumer behavior. The users are generally in small numbers belonging to diverse backgrounds and help answer the ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions about consumer behavior.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
Attitudinal vs. behavioral research
“Attitudinal research” applies to what users say, while “behavioral” applies to what they really do. What users and customers usually say and what they do are sometimes pretty different. Researchers often conduct attitudinal research to measure customers’ needs and beliefs.
However, researchers lean towards behavioral research for insights as data on what users tend to do is more relevant. Website A/B testing is an excellent example of behavioral research because it gives researchers critical insights into how users perceive and act on different versions of the same site.
Steps to conduct user experience research
Conducting user experience research is a structured procedure that helps discover significant insights for improving the user experience. Here are the five steps to conducting user experience research:
Step 1: Define objectives
Always define the goals of your research before you act. Understand what you want to discover about your customers and their requirements.
By defining the objectives of your study, you can set the foundation for targeted and purposeful studies. Your goals should include a thorough understanding of your clients and their individual needs. This first stage acts as a compass to ensure that your research efforts are focused on measurable outcomes.
Step 2: Set a hypothesis
Set a hypothesis on what you feel you know about the users. This hypothesis serves as a preliminary assumption, a starting point that you will test and modify during the study process. A well-crafted hypothesis helps guide your research efforts and serves as the foundation for structured inquiry.
Step 3: Choose a suitable method(s)
Choosing the best research techniques is similar to choosing the right tools for a job. The method you’ll adopt is heavily influenced by factors such as project kind, available resources, research team size, and deadlines.
Whether you use surveys, interviews, usability testing, or a combination of methodologies, the goal is to customize your options to the specific context of your research, assuring effective data collecting and insight development.
Step 4: Apply the research method(s)
Conduct research using the research method(s) you chose and start collecting user data about their preferences, likes, dislikes, and needs. Conducting user experience research involves actively engaging with your target users and collecting valuable data.
This step entails creating surveys, setting up usability testing, conducting user interviews, or deploying any other chosen methodologies. UX researchers use a number of user research methods to conduct UX research. By directly interacting with users, you gain firsthand insights into user behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
Step 5: Synthesize feedback
Compiling and synthesizing the feedback is critical as data from your research activity comes in. This involves thoroughly examining user data and discovering trends, patterns, and variations. Collect and analyze the user-feedback data to fill in your knowledge gaps. Use this knowledge to improve and enhance your offering.
You can develop and improve your offers based on actual consumer demands by using synthesized feedback as a source of insights to direct your decision-making.
Uses of User Experience Research
UX research is a comprehensive toolkit for researchers. It allows them to navigate different stages of design and development while uncovering a variety of user insights. Researchers use UX research for the following:
Discovery means understanding what the users find relevant. Researchers either interview the user in their environment or ask them to maintain a record of their daily interaction with a design. Researchers look for insights into user habits, needs, and preferences during this phase.
UX researchers may conduct interviews with users in their natural surroundings or ask them to keep a record of their everyday experiences with a specific design to do this. Researchers can better empathize with users’ experiences and discover insights that help drive the design process by immersing themselves in their reality.
Exploration involves investigating many options and solutions to meet the different requirements of customers. During this phase, researchers look at possibilities to address the needs of all users. Card sorting is one of the interactive UX research methods to understand precisely what people like and dislike.
This interaction method helps researchers better understand users’ mental models and how they expect information to be organized. By investigating these preferences, UX designers may create interfaces and structures that fit customers’ needs, resulting in more intuitive and user-friendly designs.
Usability Testing
Usability Testing is an important stage in the UX research process because it allows designs and prototypes to be thoroughly tested. Testing helps you evaluate the design process thoroughly. UX researchers evaluate the product’s usability, functionality, and overall experience.
Usability testing involves observing real users interact with a prototype, product, or service. A UX researcher can modify the design and make informed decisions to produce a more seamless user experience by identifying pain points, problems, and places of misunderstanding. Companies test products to ensure they’re easy to use and accessible to everyone.
Listening to user feedback and viewpoints is essential for getting insights and putting design issues into context. Listening assists UX researchers in putting issues in perspective. It helps them find unseen problems to fix quickly.
Surveys and Questionnaires are useful tools that help researchers track user feelings. UX researchers can frequently seek user feedback via surveys, questionnaires, and feedback sessions. This method enables researchers to measure user sentiments, identify potential problems that may not be obvious at first, and fix them as soon as possible.
Benefits of UX research
The benefits of conducting UX research are numerous, contributing to both product quality and business success. Here’s a closer look at the main benefits of incorporating UX research into your design and development processes:
Better products
Involving your potential customers directly helps you gain a lot of knowledge on what the customers prefer, what their pain points are, and what will help the overall improvement of the product.
Happy users
UX research helps you collect unbiased feedback directly from your customers – your most reliable feedback source. It is the best actionable feedback source because it is not influenced by company leaders, investors, or other outsiders.
Business growth
Understanding what your customers seek helps organizations spend less money and time correcting flawed designs. It helps to speed up the product development process and boosts customer satisfaction.
User Experience research is an ongoing process. It connects user expectations and design decisions to create seamless product experiences. It discovers user behaviors and preferences using approaches such as quantitative and qualitative research, as well as attitudinal and behavioral insights.
QuestionPro research enables you to effectively develop, distribute, and analyze surveys, acquire useful insights, and make data-driven decisions across a wide range of research areas. It speeds up the research process, increases user interaction, and ultimately helps you better understand your target audience and improve your products or services.
Looking to deliver an exceptional customer experience? Discover more about how to delight your customer at every touchpoint and turn them into brand advocates.
MORE LIKE THIS

Techathon by QuestionPro: An Amazing Showcase of Tech Brilliance
Jul 3, 2024

Stakeholder Interviews: A Guide to Effective Engagement
Jul 2, 2024

Zero Correlation: Definition, Examples + How to Determine It
Jul 1, 2024

When You Have Something Important to Say, You want to Shout it From the Rooftops
Jun 28, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
The Complete Guide To UX Research (User Research)

UX Research is a term that has been trending in the past few years. There's no surprise why it's so popular - User Experience Research is all about understanding your customer and their needs, which can help you greatly improve your conversion rate and user experience on your website. In this article, we're going to provide a complete guide to UX research as well as how to start implementing it in your organisation.Throughout this article we will give you a complete high-level overview of the entire UX Research meaning, supported by more in-depth articles for each topic.
Introduction to UX Research
Wether you're a grizzled UX Researcher who's been in the field for decades or a UX Novice who's just getting started, UX Research is an integral aspect of the UX Design process. Before diving into this article on UX research methods and tools, let's first take some time to break down what UX research actually entails.
Each of these UX Research Methods has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it's important to understand your goals for the UX Research activities you want to complete.
What is UX Research?
UX research begins with UX designers and UX researchers studying the real world needs of users. User Experience Research is a process --it's not just one thing-- that involves collecting data, conducting interviews, usability testing prototypes or website designs with human participants in order to deeply understand what people are looking for when they interact with a product or service.
By using different sorts of user-research techniques you can better understand not only people desires from their product of service, but a deeper human need which can serve as an incredibly powerful opportunity.
There's an incredible amount of different sorts of research methods. Most of them can be divided in two camps: Qualitative and Quantitative Research.
Qualitative research - Understanding needs can be accomplished through observation, in depth interviews and ethnographic studies. Quantitative Research focusses more on the numbers, analysing data and collecting measurable statistics.
Within these two groups there's an incredible amount of research activities such as Card Sorting, Competitive Analysis, User Interviews, Usability Tests, Personas & Customer Journeys and many more. We've created our The Curated List of Research Techniques to always give you an up-to-date overview.
Why is UX Research so important?
When I started my career as a digital designer over 15 years ago, I felt like I was always hired to design the client's idea. Simply translate what they had in their head into a UI without even thinking about changing the user experience. Needless to say: This is a recipe for disaster. An no, this isn't a "Client's don't know anything" story. Nobody knows! At least in the beginning. The client had "the perfect idea" for a new digital feature. The launch date was already set and the development process had to start as soon as possible.
When the feature launched, we expected support might get a few questions or even receive a few thank-you emails. We surely must've affected the user experience somehow!
But that didn't happen. Nothing happened. The feature wasn't used.
Because nobody needed it.
This is exactly what happens when you skip user experience research because you think you're solving a problem that "everybody" has, but nobody really does.
Conducting User Experience research can help you to have a better understanding of your stakeholders and what they need. This is incredibly valuable information from which you can create personas and customer journeys. It doesn't matter if you're creating a new product or service or are improving an existing once.
Five Steps for conducting User Research
Created by Eric Sanders , the Research Learning Spiral provides five main steps for your user research.
- Objectives: What are the knowledge gaps we need to fill?
- Hypotheses: What do we think we understand about our users?
- Methods: Based on time and manpower, what methods should we select?
- Conduct: Gather data through the selected methods.
- Synthesize: Fill in the knowledge gaps, prove or disprove our hypotheses, and discover opportunities for our design efforts.
1: Objectives: Define the Problem Statement
A problem statement is a concise description of an issue to be addressed or a condition to be improved upon. It identifies the gap between the current (problem) state and desired (goal) state of a process or product.
Problem statements are the first steps in your research because they help you to understand what's wrong or needs improving. For example, if your product is a mobile app and the problem statement says that customers are having difficulty paying for items within the application, then UX research will lead you (hopefully) down that path. Most likely it will involve some form of usability testing.
Check out this article if you'd like to learn more about Problem Statements.
2: Hypotheses: What we think we know about our user groups
After getting your Problem Statement right, there's one more thing to do before doing any research. Make sure you have created a clear research goal for yourself. How do you identify Research Objectives? By asking questions:
- Who are we doing this for? The starting point for your personas!
- What are we doing? What's happening right now? What do our user want? What does the company need?
- Think about When. If you're creating a project plan, you'll need a timeline. It also helps to keep in mind when people are using your products or service.
- Where is the logical next step. Where do people use your product? Why there? What limitations are there to that location? Where can you perform research? Where do your users live?
- Why are we doing this? Why should or shouldn't we be doing this? Why teaches you all about motivations from people and for the project.
- Last but not least: How? Besides thinking about the research activities itself, think about how people will test a product or feature. How will the user insights (outcome of the research) work be used in the User Centered Design - and development process?
3: Methods: Choose the right research method
UX research is about exploration, and you want to make sure that your method fits the needs of what you're trying to explore. There are many different methods. In a later chapter we'll go over the most common UX research methods .
For now, all you need to keep in mind that that there are a lot of different ways of doing research.
You definitely don't need to do every type of activity but it would be useful to have a decent understanding of the options you have available, so you pick the right tools for the job.
4. Conduct: Putting in the work
Apply your chosen user research methods to your Hypotheses and Objectives! The various techniques used by the senior product designer in the BTNG Design Process can definitely be overwhelming. The product development process is not a straight line from A to B. UX Researchers often discover new qualitative insights in the user experience due to uncovering new (or incorrect) user needs. So please do understand that UX Design is a lot more than simply creating a design.
5. Synthesise: Evaluating Research Outcome
So you started with your Problem Statement (Objectives), you drafted your hypotheses, chose the top research methods, conducted your research as stated in the research process and now "YOU ARE HERE".
The last step is to Synthesise what you've learned. Start by filling in the knowledge gaps. What unknowns are you now able to answer?
Which of your hypotheses are proven (or disproven)?
And lastly, which new exciting new opportunities did you discover!
Evaluating the outcome of the User Experience Research is an essential part of the work.
Make sure to keep them brief and to-the-point. A good rule of thumb is to include the top three positive comments and the top three problems.
UX Research Methods
Choosing the right ux research method.
Making sure you use the right types of user experience research in any project is essential. Since time and money is always limited, we need to make sure we always get the most bang-for-our-buck. This means we need to pick the UX research method that will give us the most insights as possible for a project.
Three things to keep in mind when making a choice among research methodologies:
- Stages of the product life cycle - Is it a new or existing product?
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative - In depth talk directly with people or data?
- Attitudinal vs. Behavioural - What people say vs what people do

Image from Nielsen Norman Group
Most frequently used methods of UX Research
- Card Sorting: Way before UX Research even was a "thing", psychological research originally used Card Sorting. With Card Sorting, you try to find out how people group things and what sort of hierarchies they use. The BTNG Research Team is specialised in remote research. So our modern Card Sorting user experience research have a few modern surprises.
- Usability Testing: Before launching a new feature or product it is important to do user testing. Give them tasks to complete and see how well the prototype works and learn more about user behaviours.
- Remote Usability Testing: During the COVID-19 lockdown, finding the appropriate ux research methods haven't always been that easy. Luckily, we've adopted plenty of modern solutions that help us with collecting customer feedback even with a remote usability test.
- Research-Based User Personas: A profile of a fictional character representing a specific stakeholder relevant to your product or service. Combine goals and objections with attitude and personality. The BTNG Research Team creates these personas for the target users after conducing both quantitative and qualitative user research.
- Field Studies: Yes, we actually like to go outside. What if your product isn't a B2B desktop application which is being used behind a computer during office hours? At BTNG we have different types of Field Studies which all help you gain valuable insights into human behaviour and the user experience.
- The Expert Interview: Combine your talent with that of one of BTNG's senior researcher. Conducting ux research without talking to the experts on your team would be a waste of time. In every organisation there are people who know a lot about their product or service and have unique insights. We always like to include them in the UX Research!
- Eye Movement Tracking: If you have an existing digital experience up and running - Eye Movement Tracking can help you to identify user experience challenges in your funnel. The outcome shows a heatmap of where the user looks (and doesn't).
Check out this article for a in-depth guide on UX Research Methods.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative UX research methods
Since this is a topic that we can on about for hours, we decided to split this section up in a few parts. First let's start with the difference.
Qualitative UX Research is based on an in-depth understanding of the human behaviour and needs. Qualitative user research includes interviews, observations (in natural settings), usability tests or contextual inquiry. More than often you'll obtain unexpected, valuable insights through this from of user experience research methods.
Quantitative UX Research relies on statistical analysis to make sense out of data (quantitative data) gathered from UX measurements: A/B Tests - Surveys etc. Quantitative UX Research is as you might have guessed, a lot more data-orientated.
If you'd like to learn more about these two types of research, check out these articles:
Get the most out of your User Research with Qualitative Research
Quantitative Research: The Science of Mining Data for Insights
Balancing qualitative and quantitative UX research
Both types of research have amazing benefits but also challenges. Depending on the research goal, it would be wise to have a good understanding which types of research you would like to be part of the ux design and would make the most impact.
The BTNG Research Team loves to start with Qualitative Research to first get a better understanding of the WHY and gain new insights. To validate these new learning they use Quantitative Research in your user experience research.
A handful of helpful UX Research Tools
The landscape of UX research tools has been growing rapidly. The BTNG Research team use a variety of UX research tools to help with well, almost everything. From running usability tests, creating prototypes and even for recruiting participants.
In the not-too-distant future, we'll create a Curated UX Research Tool article. For now, a handful of helpful UX Research Tools should do the trick.
- For surveys : Typeform
- For UX Research Recruitment: Dscout
- For analytics and heatmaps: VWO
- For documenting research: Notion & Airtable
- For Customer Journey Management : TheyDo
- For transcriptions: Descript
- For remote user testing: Maze
- For Calls : Zoom
Surveys: Typeform
What does it do? Survey Forms can be boring. Typeform is one of those ux research tools that helps you to create beautiful surveys with customisable templates and an online editor. For example, you can add videos to your survey or even let people draw their answers instead of typing them in a text box. Who is this for? Startup teams that want to quickly create engaging and modern looking surveys but don't know how to code it themselves.
Highlights: Amazing UX, looks and feel very modern, create forms with ease that match your branding, great reports and automation.
Why is it our top pick? Stop wasting time on ux research tools with too many buttons. Always keep the goal of your ux research methods in mind. Keep things lean, fast and simple with a product with amazing UX.
https://www.typeform.com/
UX Research Recruitment: Dscout
What does it do? Dscout is a remote research platform that helps you recruit participants for your ux research (the right ones). With a pool of +100.000 real users, our user researchers can hop on video calls and collect data for your qualitative user research. So test out those mobile apps user experience and collect all the data! Isn't remote research amazing?
Highlights: User Research Participant Recruitment, Live Sessions,Prototype feedback, competitive analysis, in-the-wild product discovery, field work supplementations, shopalongs.
Why is it our top pick? Finding the right people is more important than finding people fast. BTNG helps corporate clients in all types of industries which require a unique set of users, each time. Dscout helps us to quickly find the right people and make sure our user research is delivered on time and our research process stays in tact.
https://dscout.com/
Analytics and heatmaps: VWO
What does it do? When we were helping the Financial Times, our BTNG Research Team collaborated with FT Marketing Team who were already running experiments with VWO. 50% of the traffic would see one version of a certain page while 50% saw a different version. Which performed best? Perhaps you'd take a look at time-on-page. But more importantly: Which converts better!
Hotjar provides Product Experience Insights that show how users behave and what they feel strongly about, so product teams can deliver real value to them.
Highlights: VWO is an amazing suite that does it all:Automated Feedback, Heatmaps, EyeTracking, User Session Recordings (Participant Tracking) and one thing that Hotjar doesn't do: A/B Testing.
Why is it our top pick? Even tho it's an expensive product, it does give you value for money. Especially the reports with very black and white outcomes are great for presenting the results you've made.
https://vwo.com/
Documenting research: Notion
What does it do? Notion is our command center, where we store and constantly update our studio's aggregate wisdom. It is a super-flexible tool that helps to organise project documentation, prepare for interviews with either clients or their product users, accumulate feedback, or simply take notes.
Highlights: A very clean, structured way to write and share information with your team in a beautiful designed app with an amazing user experience.
Why is it our top pick? There's no better, more structured way to share information.
https://www.notion.so/
Customer Journey Management: TheyDo
What does it do? TheyDo is a modern Journey Management Platform. It centralises your journeys in an easy to manage system, where everyone has access to a single source of truth of the customer experience. It’s like a CMS for journeys.
Highlights: Customer Journey Map designer, Personas and 2x2 Persona Matrix, Opportunity & Solution Management & Prioritisation.
Why is it our top pick? TheyDo fits perfectly with BTNG's way of helping companies become more customer-centric. It helps to visualise the current experience of stakeholders. With those insight which we capture from interviews or usability testing, we discover new opportunities. A perfect starting point for creating solutions!
https://www.theydo.io/
Transcriptions: Descript
What does it do? Descript is an all-in-one solution for audio & video recording, editing and transcription. The editing is as easy as a doc. Imagine you’ve interviewed 20 different people about a new flavor of soda or a feature for your app. You just drop all those files into a Descript Project, and they show up in different “Compositions” (documents) in the sidebar. In a couple of minutes they’ll be transcribed, with speaker labels added automatically.
Highlights: Overdub, Filler Word Removal, Collaboration, Subtitles, Remote Recording and Studio Sound.
Why is it our top pick? Descript is an absolute monster when it comes to recording, editing and transcribing videos. It truly makes digesting the work after recording fast and even fun!
https://www.descript.com/
Remote user testing: Maze
What does it do? Maze is a-mazing remote user testing platform for unmoderated usability tests. With Maze, you can create and run in-depth usability tests and share them with your testers via a link to get actionable insights. Maze also generates a usability study report instantly so that you can share it with anyone.
It’s handy that the tool integrates directly with Figma, InVision, Marvel, and Sketch, thus, you can import a working prototype directly from the design tool you use. The BTNG Design Team with their Figma skills has an amazing chemistry with the Research Team due to that Figma/Maze integration.
Highlights: Besides unmoderated usability testing, Maze can help with different UX Research Methods, like card sorting, tree testing, 5-second testing, A/B testing, and more.
Why is it our top pick? Usability testing has been a time consuming way of qualitative research. Trying to find out how users interact (Task analysis) during an Interviews combined with keeping an eye on the prototype can be... a challenge. The way that Maze allows us to run (besides our hands on usability test) now also run unmoderated usability testing is a powerful weapon in our arsenal.
https://maze.co/
Calls: Zoom
What does it do? As the other video conferencing tools you can run video calls. But what makes Zoom a great tool? We feel that the integration with conferencing equipment is huge for our bigger clients. Now that there's also a Miro integration we can make our user interviews even more fun and interactive!
Highlights: Call Recording, Collaboration tools, Screen Sharing, Free trial, connects to conferencing equipment, host up to 500 people!
Why is it our top pick? Giving the research participants of your user interviews a pleasant experience is so important. Especially when you're looking for qualitative feedback on your ux design, you want to make sure they feel comfortable. And yes, you'll have to start using a paid version - but the user interface of Zoom alone is worth it. Even the Mobile App is really solid.
https://zoom.us/
In Conclusion
No matter what research methodology you rely on if it is qualitative research methods or perhaps quantitative data - keep in mind that user research is an essential part of the Design Process. Not only your UX designer will thank you, but also your users.
In every UX project we've spoken to multiple users - no matter if it was a task analysis, attitudinal research or focus groups... They all had one thing in common:
People thanked us for taking the time to listen to them.
So please, stop thinking about the potential UX research methods you might use in your design process and consider what it REALLY is about:
Solving the right problems for the right people.
And there's only one way to get there: Trying things out, listening, learning and improving.
Looking for help? Reach out!
See the Nielsen Norman Group’s list of user research tips: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/ux-research-cheat-sheet/
Find an extensive range of user research considerations, discussed in Smashing Magazine: https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2018/01/comprehensive-guide-ux-research/
Here’s a convenient and example-rich catalogue of user research tools: https://blog.airtable.com/43-ux-research-tools-for-optimizing-your-product/
Related Posts

How to generate UX Insights

The importance of User Research

How to recruit participants
What is ux research.

UX Research Tools

- ALL BLOG POSTS /
20 Essential UX research methods and how they help you build better products
The product development process has many aspects to take care of with decisions that can lead to success or disappointment. Finding the right path might seem tricky, but UX research methods become invaluable insights, which we’ll talk about today.

When every business is battling for attention, the importance of understanding your customers cannot be overstated. User experience (UX) research stands at the forefront, providing valuable data about user behaviors, preferences, and pain points, which is essential for tailoring products that truly resonate with and captivate your audience. In this article, we’ll figure out what exactly UX research is and, as a bonus, provide the 20 essential techniques shaping the world of user-centric product design in 2023.
What is UX research?
UX research is all about understanding the people who will use your product. It’s a way to discover what they need, what they like, and how they behave. There are different methods to do this, like asking questions, analyzing how customers interact with a product, or studying data about their behavior. By doing UX research, you can avoid guessing what users want and instead give them something they will really like and find helpful.
UX research? It’s like chatting with your users to get what they want — no guesswork needed!
Why UX research is important for your product creation
You can’t create a product “just because you want to.” Well, in fact, you can, but will it be useful? Understanding why UX research is crucial in developing a product is the first step toward building something truly remarkable. There are a number of advantages you should consider, so let’s discuss them in detail.
- User satisfaction. First off, UX research puts you in your users’ shoes. It’s the best way to uncover what they need, what frustrates them, and what makes them happy. When you understand these pain points and desires, you can create solutions that potential customers will love.
- Reduced development cost. Investing in UX analysis might seem like an extra expense, but it actually saves you money down the line. While making changes after a product launch is expensive and time-consuming, UX research helps you get it right the first time.
- Product usability. Usability is essential to any successful product, and this is where UX research shines. With proper analysis and focus on usability, you can enhance user satisfaction, making the website or app more appealing and encouraging for repeat usage.
- Increase conversion rates. It’s pretty straightforward — when you understand what users need and how they interact with the product, you can make improvements that hit the mark. These tweaks can make their experience smoother, encouraging more people to leap from being interested to making a purchase.
- Competitive advantage. Every business aims to gain a competitive edge, and UX research is exactly what you need for it. By understanding users and what they need, you can make your product stand out from the crowd. This isn’t just about being different — it’s about being better in a way that matters to your users.
- Informed decision-making. UX research can significantly help when it comes to making decisions in the process of product creation. It gives real, user-based insights, so you’re not just guessing what might work but making informed choices based on what users want and need.
- Brand loyalty. When users feel that a product is made with their needs in mind, they’re more likely to stick around. This loyalty stems from a sense of being understood and valued, a crucial outcome of effective UX research. In short, good UX leads to satisfied users, who, in turn, become loyal supporters of your brand.
With all of these benefits, it’s clear that starting with UX research, you’re starting on the path to success. It bridges the gap between user needs and business goals, leading to effective, efficient, and emotionally engaging solutions.

Types of user research
There are various types of UX research, each with its goals and objectives. From unique insights to different aspects of gathering information, every method helps to craft products that truly resonate with your audience. Overall, there are six main types of user research, which we’re going to discuss below.
Attitudinal vs. behavioral
When we talk about user research, we primarily look at two types: attitudinal and behavioral. The attitudinal type focuses on what users say. It’s all about understanding their attitudes, preferences, and opinions by using tools like surveys, interviews, and questionnaires. Think of it as having a direct conversation with your users to learn how they feel about your product or what they wish for.
In contrast, behavioral research is based on what users actually do. It involves being an observer, watching how people interact with your product. In that case, you can use such methods as usability testing, session recordings, and heatmaps to get the necessary data. This approach is crucial for understanding the true user experience and pinpointing areas for improvement.
Together, these two research methods give a comprehensive view of the customers, blending what they tell with what their actions show.
Qualitative vs. quantitative
Alright, let’s talk about more types of user research: qualitative and quantitative. They both play crucial roles in crafting a complete picture of customer engagement and preferences.
Qualitative research gathers stories about users’ experiences, thoughts, and feelings regarding your product. hrough interviews, focus groups, and direct observations, you gain insights into the “why” and “how” people behave while interacting with a website or app.
Now, let’s switch to quantitative research. This one deals with the hard data and is full of numbers. To get exact answers about what is happening on the website, use tools like surveys with fixed responses, website analytics, and statistical analysis. How many people clicked here? What percentage completed their purchase? Quantitative research gives you these facts and, most importantly, stats.
Qualitative research is about the quality of data — the stories and experiences, while quantitative focuses on the numbers.
Generative vs. evaluative
Among the various user research methods, it’s worth discussing generative and evaluative approaches. Both of them are super important to get a well-rounded understanding of your users and, as a result, create a successful product based on these insights.
Generative research is the go-to at the beginning stages of product development or when brainstorming for innovative solutions. It is all about coming up with new ideas and understanding broader user needs and behaviors through interviews, field studies, and diary studies. This type of research outlines what users need and want, helping to figure out what products or features to develop.
Following generative research, as your product ideas take shape, shift to evaluative research. This phase is crucial for assessing what you’ve created. It’s focused on refinement and improvement, using tools like usability testing, A/B testing, and specific surveys. The goal is to test your products against real user expectations and experiences, ensuring that the crafted product resonates with them and effectively meets their needs.

Top 20 UX design research methods and when to use them
Understanding users is the basis of impactful design, and the right research methods are key to gaining this insight. Scroll further as we explore 20 essential UX research techniques, each with its specific application context.

1. Surveys
In UX research, surveys are handy for getting user feedback and can be qualitative or quantitative, depending on the type of questions asked. Qualitative surveys include open-ended questions to gain insights into what users think and feel, while quantitative use closed-ended questions (like multiple choice or ratings) to get data that’s easy to measure. There are two ways to conduct surveys, namely:
- Email surveys. Sent directly to users’ inboxes, these surveys help reach a broad audience by asking specific things about your product or service. To recruit participants for email surveys, utilize your existing customer database or sign-up forms on your website.
- On-site surveys. They pop up while users browse the website or app, letting you grab feedback about their experience right then and there. For on-site surveys, you can target customers who are actively engaging with your site.
Surveys are versatile. You can use them at various stages of the product development process — from the initial conceptualization phase to after the launch. They help collect data from many users, spot trends in user behavior, and gather thoughts on specific features.
2. Interviews
A key qualitative method in UX research is interviews, where a researcher meets one-on-one with users to discuss a particular topic. This method includes two main types: in-depth interviews (IDIs) and intercept interviews.
- In-depth interviews (IDIs). They’re usually conducted in a relaxed and cozy environment where participants can talk through everything in detail. If you want to find people for IDIs who match your user profile, surf online, through social media, or use your customer list.
- Intercept interviews. They happen right where the action is — on a website, wherever users interact with your product or service. You’ll approach visitors while they’re using the website or just after they’ve used it. It’s free-flowing, so you rely on their willingness to chat there and then.
This UX method fits perfectly at different stages of your project development, from concept to release. In the early phases, it acts as a tool for gathering the target audience and shaping the user base. Towards the end, this approach becomes a great possibility for getting the lowdown on how people find your product’s usability and appeal.
3. Personas
Think of personas as characters in a story, but in this case, they are based on real users. This qualitative method helps you make design decisions in the early stages of product development based on what people need and expect. It means ensuring your website or product is a hit with your audience, not just an imaginary user.
But how do you start creating these personas? First, you need actual user data, which you can gather from online platforms, social media, or customer lists. This process isn’t about guessing who your users are but understanding them through in-depth interviews or observational studies. The great decision is to prepare a set of questions or scenarios to gain insights into people’s lifestyles, preferences, and challenges to paint a comprehensive picture of your user base. This way, every design decision you make is grounded in reality, not assumptions.
4. Usability testing
You’ve got your product or service, and now it’s time to see it in action with people through usability testing. During this process, real users tackle tasks by interacting with your product while a researcher observes their experience, gathering insights on how they use it and where improvements might be needed.
Whether you are wondering when to conduct usability testing, here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
- Before the design stage. Such an early insight can influence the direction of your design, ensuring it meets the user requirements from the start.
- After wireframe or prototype creation. It helps identify usability issues early on, saving time and resources by preventing costly redesigns later.
- Ahead of the product launch. This step is crucial to eliminate last-minute issues and boost user confidence in your product’s reliability.
- Regularly after roll-out. Ongoing testing helps identify areas for improvement and ensures the product remains relevant and user-friendly.
This method can be both qualitative and quantitative. On the qualitative side, you’re watching and listening to participants, getting their thoughts and feelings on the experience. Quantitatively, you measure how long it takes to complete tasks or count errors. Finding the participants for usability testing can be done through online ads, social media, customer databases, or recruitment agencies.
5. Field studies
Another aspect of UX research is field studies, where the action happens in places users typically hang out, like their homes or offices. Social media, customer lists, or special outreach programs are your go-to tools for finding people, but remember, you’re asking to step into their space, and it’s crucial they’re comfortable with that.
This qualitative approach offers a reliable overview of your products during the discovery stage or a ready-made prototype to see whether it fits into customers’ daily lives. Researchers are there to watch and learn — how people interact with the product, what’s happening around them, and all that jazz.
Field studies are about making sure your designs don’t just work in theory but really click in the everyday lives of your users.
6. Focus groups
A classic tool in UX research is focus groups that bring together a small number of people (typically around 6 to 10 participants) to discuss and share their thoughts about your product or service. It’s kind of a hangout, but instead of casual chit-chat, you’re talking about what they think and feel using your creation.
You need a diverse mix of participants representing different facets of your target audience. To find them, try advertising, searching customer databases, or reaching out to communities relevant to your product.
This qualitative method is thoughtful research of people’s opinions, attitudes, and experiences while formulating your website or service concept. The cool thing is, when customers start talking and bouncing ideas off each other, you get to uncover insights that might not pop up in a one-on-one chat.
7. Eye-tracking
Eye-tracking is one of the more fascinating and technological UX research methods used to analyze how users view a website or app. Special equipment follows the movement of a visitor’s eyes, showing what catches their attention, for how long, and in what order. Since eye-tracking is a bit more high-tech, you can search for participants through online platforms, social media, or customer databases.
It is a quantitative process that gives you hard data — numbers and patterns demonstrating where people’s attention goes on the screen. This info is super valuable in the mid to late stages of product development to understand what draws users in and what might be getting overlooked.
8. Remote moderated testing
For remote moderated testing, you can reach out to people through social media, email, or online ads, as this method permits people to join from anywhere. Whether at home, in a cafe, or any comfortable place, this handy UX research technique allows everyone to chill in their favorite spot using video calls and screen-sharing software for testing.
Remote moderated testing can provide qualitative insights by observing and talking to users as they navigate your product in different stages of development. At the same time, you can collect quantitative data like task completion times or error rates. This combo gives you a well-rounded view of the user experience to make iterative improvements based on what real users do and say.
9. Concept testing
Take a glimpse into how potential users might react to a new idea or design before you start the development phase with the concept testing. It involves presenting a concept — like a product idea, feature, or design element — to users and getting their feedback.
Concept testing can swing both ways — qualitative and quantitative. You can gather feedback by engaging users through social media or online communities to share their thoughts and feelings about the website idea. Hard data comes into play when you ask specific questions that can be measured, like rating scales or choice preferences.
10. Diary studies
In the method of diary studies, you make participants keep a record — like a diary — of their experiences with your finished product over a period of time. They jot down their thoughts, feelings, and actions, providing a window into daily interactions with what you’ve created.
Diary studies are mainly qualitative and focused on customers’ personal and detailed experiences. You can reach out to users who are already engaged with your product or use a database, social media platforms, or community forums. By analyzing their information, you get rich, narrative insights into how people navigate and feel about your product in their everyday lives.
11. Customer feedback
You can have a direct line to your users’ thoughts and experiences through customer feedback. That looks like a casual chat with your audience to find out what they love, what frustrates them, and what could be better about your product or service. This communication can be built through a prominent button on your website, a form in your app, or even follow-up emails after a purchase or service use.
Qualitative customer feedback comes from open-ended questions where users share their thoughts in their own words about any stage of your product’s lifecycle. On the other hand, quantitative data is derived from closed-ended questions, such as ratings or multiple-choice queries, offering measurable insights.
12. Desirability studies
With desirability studies, you focus on the visual appeal and emotional impact of your product’s design. In these tests, you show participants different style options for your product and ask them to match these ideas with specific feelings or attributes from a list. It’s a bit like a game, where your design elements correspond to feelings like “exciting,” “modern,” or “user-friendly.”
Desirability studies are primarily quantitative and rely on structured feedback, where participants, who you can find through social media, online ads, or user groups, choose from a ready-made list of attributes. This approach provides measurable data about how users perceive the visual aspects of your product, revealing critical insights into their preferences, design effectiveness, and potential areas for visual enhancement.
13. Card sorting
When it comes to designing the layout and structuring content, card sorting — a user-friendly and insightful method in UX research — kicks in. The main idea is to give participants a set of cards, each labeled with a piece of content or a feature, and ask them to sort it into categories that make sense.
Qualitatively, this method helps you understand how users think and why they group things a certain way. Quantitatively, when you analyze the patterns in how different people sort the cards, you get measurable data on common groupings and preferences.
Your participants don’t need to be current users of your product but should have interests relevant to your offerings. To find them, surf through online forums and social media or rely on your customer database.
14. Tree testing
If you want to evaluate the information architecture of your product during the mid-design phase, try tree testing.
Recruit participants through social media, online ads, or existing customer databases and ask them to find a way through a simplified, text-only map of your website or app — a “tree.” Their mission is to complete specific tasks like finding a particular piece of information or performing an action.
This quantitative research focuses on measurable outcomes like the success rate of finding information, the time taken to complete tasks, and the paths users take. This data provides clear insights into the effectiveness of your site’s or app’s navigational structure.
15. Analytics
UX research analytics involves exploring user behavior through clues like clicks, form fillings, and other interactions when your product is out in the real world. It’s all about gathering little breadcrumbs of data from actual users to form an overall picture.
This method is quantitative, measuring actions relying on numbers. By analyzing this data, you get objective insights into how users interact with your product, like which features are popular, where they might get stuck, and how they navigate through your site or app.
With UX analytics, every click tells a story, painting a clear picture of user journeys and experiences in the world of numbers.
16. Clickstream analytics
There is a specific type of UX research — clickstream analytics. This method tracks the digital footprints of your users as they hop from page to page on your live site or app. It’s all about mapping their journey, seeing their paths, the stops they make, and for how long. By applying this research technique, you can gain valuable insight into how users navigate, what they like, and where they might run into trouble.
You don’t need to send out invites for a study or round up a group of participants because the data comes directly from the click and scroll of actual users. It’s a continuous stream of information that lets you tweak, adjust, and perfect a visitor’s experience over time.
Clickstream analytics is inherently quantitative. It deals with concrete data like the sequence of pages visited, the time spent on each page, and the transitions between different parts of the site or app. This data helps quantify user behavior, revealing trends and common navigation paths.
17. A/B testing
Split testing, or A/B testing, is a method in UX research where you compare two versions of a webpage or app to see which one performs better. Essentially, you create two different versions — A and B — and show them to users. You analyze which is more effective based on specific metrics like clicks, conversions, or customer engagement.
A/B testing is a quantitative research method all about numbers and measurable results. You’re looking at data from current users to see which version leads to better performance regarding their actions and reactions. This approach provides concrete evidence about which design or content choices are more effective in achieving your goals.
18. Five second testing
Quick and powerful — that’s exactly what five second testing is. The main idea is to show users a webpage, ad, or app screen — for just five seconds. After that brief glimpse, ask questions about what they remember or how they felt to identify the immediate impact and clarity of your designs. This method is flexible and fast, ensuring minimal disruption to your users, whom you can engage through online platforms, social media, or in-person meetings.
The five-second technique can provide both qualitative and quantitative data from the early to mid phases of design. Qualitatively, you can gather insights about participants’ initial feelings and thoughts. Quantitatively, you can measure aspects like recall accuracy, which provides data on the most memorable or attention-grabbing design elements.
19. Prototyping
Another essential step in the UX design process is prototyping, where the design team creates a mini-version of a site or product. This mock-up can be as simple as a hand-drawn paper layout or as sophisticated as interactive HTML pages. The idea is to explore and visualize design concepts before fully implementing them, allowing for adjustments based on feedback.
You can gather qualitative information from the target audience to understand user reactions, thoughts, and feelings about the design. Quantitatively, you can test specific functions, like the ease of navigation or the effectiveness of user interfaces, by measuring task completion time and rates.
20. Competitor analysis and benchmarking
The last critical method is to assess your product compared to others in the market. This involves analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of competitor products and benchmarking them against industry standards. The goal is to understand where your creation stands in the competitive landscape and identify opportunities for improvement or differentiation.
This method is valuable at every stage of your product’s life and can be both qualitative and quantitative. It allows you to analyze things like design style, how user-friendly its features are, and the overall website or app vibe compared to competitors. You can also acquire critical numbers, such as performance metrics, user engagement levels, and conversion rates, that’ll help you identify where your product stands in the market and how it can be improved.
What UX research technique is thought to be the best?
The best UX research technique depends on the specifics of your project, your goals, and the stage of development you’re in. For example, if you’re just starting out with a new app idea and want to understand your potential users’ needs and behaviors, generative research methods like interviews or surveys might be your go-to. These techniques help gather insights that can shape your initial design concepts.
On the other hand, if your app is already developed and you’re looking to refine the user interface, usability testing or A/B testing could be more beneficial. These evaluative methods allow you to observe how users interact with your app and make data-driven improvements.
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer — the key is to match the research method with your specific needs at each stage of your project.
How to choose UX research methods
When it comes to picking user experience research methods, a great factor to consider is your company’s budget. The amount of money you’re able to allocate for analysis can guide which strategies are feasible and most effective for your needs. But it’s not the only one, as there are other aspects to consider, which we’ll cover in the following paragraphs.

Define your objectives and problems
When starting with UX research, define your objectives and the problems you aim to solve. This step sets the direction of the study and helps you choose the most effective methods to achieve your goals. Knowing exactly what you want to understand or improve in your user experience guides your entire research process.
When defining your objectives and problems in UX research, we recommend you answer these key questions to set clear goals:
- What are the user’s needs?
- What challenges do the users face?
- How can you address user requirements?
Understand the stage of the design process
Choosing the right UX research methods depends on where you are in the design process. Each stage of your project has unique needs and goals, which require different research approaches and can be divided into three main stages, namely:
- Start of the project. This is the exploratory phase, where you gather initial insights to shape your concept. Methods like user interviews, surveys, and market analysis are ideal to understand user needs and market gaps.
- Formative phase. Here, you are in the process of shaping and testing your design. Techniques like prototyping, usability testing, and card sorting help refine your product, ensuring it meets user expectations and usability standards.
- Summative part. At this final point, your product is complete, and you’re assessing its overall performance. Methods like A/B testing, analytics, and satisfaction surveys are used to evaluate the user experience, measure effectiveness, and identify areas for future improvement.
Each phase has distinct goals, and understanding where you are in the process helps you choose research methods that provide the most valuable insights for that particular stage.
Determine the type of information you need
In UX research, determining the necessary information type will guide you in selecting the most appropriate research methods.
If your goal is to explore more the thoughts, behaviors, and motivations of your users, qualitative methods like interviews and observational studies are your best bet. They give a rich, narrative understanding of customers’ experiences. On the other hand, when looking for concrete, data-driven insights, quantitative methods such as surveys and analytics are more suitable. They provide objective, numerical data that can reveal trends and patterns in user behavior.
Sometimes, a mix of both qualitative and quantitative data is necessary to get a full picture. Such an approach allows you to understand not just what users are doing but also why they’re doing it, combining in-depth insights with measurable facts.
By pinpointing the information you need, you can select UX research methods that provide the most relevant and valuable insights for your project.
Before you start
Eye-tracking, A/B testing, surveys — each method offers unique insights that can shape and refine your website or app development process. By carefully selecting and applying these research techniques, you are equipped to deeply understand user needs, behaviors, and preferences.
Ultimately, the success of a product in the market hinges on how well it meets the requirements and expectations of its customers. Integrating the 20 essential UX research methods outlined above into your development cycle increases the chances of achieving this alignment.
Whether you’re at the concept stage or refining an existing product, these practices provide the necessary data to make informed decisions, ensuring your product is user-centric, innovative, and competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape.

Frequently Asked Questions
- Tools to use when creating your PoC
You may also like

Black and orange web designs for inspiration

How to design a SaaS product: best practices & tips

How to design a logo: the essential guide
Ready to discuss your project with us, thank you we will contact you asap.

Hmm...something went wrong. Please try again 🙏
Our clients say.

Join Halo Lab’s newsletter!
Get weekly updates on the newest stories, posts and case studies right in your mailbox.
What is User Experience Research, and Why Does it Matter?

Whatever your organization does, there’s always opportunity for improvement, and sometimes the best way to find them is by checking in on the end users themselves. It’s a tricky thing to accomplish, to be sure, since there are a lot of intangible factors that play into how an employee might be feeling about their experience at any given moment. However, user experience research can be a great ally to achieve it.
Essentially, user research allows for the study of target users, and finding out their needs and pain points so that managers can obtain a customer’s-eye view of the organization. This helps outline the things about it that are working (or otherwise) from the point of view of an employee. Plus, i t helps managers identify key points of improvement as well as processes that have become irrelevant, outdated, or obsolete.
There are various ways of performing user experience research; face-to-face interviews, online and offline surveys , observation, task analysis, and other types of user feedback.
Why is user experience research important?
In the world of UX , constant user feedback is important to figure out how designs can be improved. Observing how users of a software platform struggle to complete a certain task, for example, goes a long way to showing designers whether an icon needs to be larger, a color needs to be lighter, or a hyperlink is too hidden away for easy finding.
Similarly, user research can be used in a broader way to find the users’ pain points in their everyday lives at work to improve the employee experience – whether they’re overwhelmed, whether they’ve been able to complete certain tasks, whether they think they’ve been properly assisted by the help desk, whether they are in need of a different service platform altogether. You want your employees to be as content as they can possibly be, and finding out how to make it happen starts by figuring out where they currently are.
In order to do this, you must choose methods that suit your research’s purpose and will yield the clearest information (figuring out what those methods are can also be tricky – we’ll get to that in a moment). Afterwards, in order to turn that data into insights, you’ll need to interpret these findings. And that can be especially hard, since people sometimes have a hard time understanding why they feel the way they do.
It doesn’t help you much to know that an employee finds a particular task overwhelming or frustrating if you don’t understand why that is. Taking that a step further, you might not be privy to certain elements that influence their emotions at the time of gathering the data, leaving out a lot of useful context that could color how you interpret the data.
There are many factors at play when we talk about converting human emotions to data and turning it into useful insights.
What are the main benefits of user experience research?
The benefits of user experience research are many. Just for starts:
- User benefits - By getting the information straight from your end-users through direct feedback, you are able to identify areas of improvement that will boost the employee experience considerably.
- Product benefits - If your UX research is focused on a particular product, this helps you identify areas of improvement in the product design and overall functionality.
- Business benefits - Simply said, having unhappy customers is bad for business. You want to make sure that morale is in good shape and your users are getting value from the solutions you are providing.
Through user experience research, you’ll be able to:
- Better understand how users experience your products and platforms.
- Discover new customer needs as well as opportunities for your business.
- Optimize internal processes based on the users’ direct feedback.
- Apply the insights learned to provide user experiences that outperform your competitors.
- Get a better understanding of your target audiences .
What are some common methods of user experience research?
There are two main subsets of user experience research : qualitative and quantitative research. Let's take a closer look at each one.
Qualitative research
This is the case of interviews and field studies, through which you can have a better understanding of what drives your users’ behavior.
This might involve interviewing a small number of users and asking open-ended questions about their experience and habits, which can help you get sharp insights into what needs to be improved or changed within your organization. Furthermore, this can include different types of usability testing (such as examining users’ stress levels when they’re attempting to complete a task on a platform).
Qualitative research is extremely valuable but you also need to remember that it involves collecting non-numerical data (which is to say, opinions), and findings may be influenced by your own opinions.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research refers to more structured methods such as surveys and digital experience monitoring . It attempts to gather measurable data about what users do, as well as test assumptions you developed from qualitative research. Also, it can help you find patterns within a large user group. Of course, with quantitative data you’re not getting a full sense of deeper human insights.
User experience research can also be split into attitudinal (listening to your users’ words – interviews and the like) and behavioral (watching their actions through observational studies). Usually a combination of both methods will provide the best data.
|
|
But what about surveys?
Surveys are a very popular tool for managers. And they have their uses: surveys help us measure intangible human reactions, and gather opinions and perceptions of the experiences we deliver every day. These measurements, through analysis, give us the opportunity to know our people better and adapt our services to their needs and expectations.
But this is just one way to focus on improving experiences . Sometimes, simply choosing not to send a survey saves you time, money, and morale.
Surveys typically gather data on several fronts in the experience management field, such as customer satisfaction, customer effort, net promoter scores, and more. The problem with using them this way is that there are various elements that will influence these scores on your service transactions, some of which fall outside of the scope of service.
For instance, is the employee happy in their position at the company? Did they miss a goal or bonus based on the service availability? Was there some loud construction nearby? What kind of technical difficulties were they experiencing?
Context will heavily influence this score, and something as subjective as a scale of 1-10 or 1-5 is difficult to quantify and analyze.
As much as organizations rely on surveys, there are ways to get better, more useful data without negatively impacting your users’ experience, and by avoiding sending surveys at all .
Read other articles like this : Experience Management
Read other articles like this:
Evaluate invgate as your itsm solution, 30-day free trial - no credit card needed.
ACM Interactions
- About Interactions
- Current Issue
- Submissions

- May - June 2024
How Far Can We Go with Synthetic User Experience Research?
User experience research (UXR) plays an important role in uncovering user personas, their contexts of use, and their detailed needs. UXR employs a range of research methodologies, such as surveys, interviews, diary studies, and observations, all of which can be time-consuming and costly. With the advent of advanced generative AI (GenAI) tools capable of producing humanlike responses from multimodal inputs such as ChatGPT-4 and Gemini, UX researchers are exploring whether large language models (LLMs)—trained on trillions of pieces of text data from a variety of domains accumulated over decades—can effectively simulate user interactions, preferences, needs, and scenarios for product development. UX researchers also realized, however, that while the vast amounts of text data are typically from the Internet and cover various topics, they are not necessarily user research data. The reliability of AI-facilitated research is now a topic often debated among researchers.
Despite the current hype surrounding GenAI and synthetic UXR, I still flew 10 hours recently to a coastal area to conduct an "old-fashioned" field user study, using pen and paper—based observation grids, as well as conducting in-person interviews with real human participants, to test a new product.
Since the start of my Ph.D. in 2012, I have had only a few chances to conduct field research. To study crowd management strategies and crowd behavior, I spent days at festivals, theme parks, concert halls, and train stations, observing the construction of sites and architecture, as well as the placement of facilities such as fences and one-way gates. A few years ago, I spent a week conducting observational studies on an outside broadcasting truck at the MotoGP races at Silverstone, aiming to understand live sports broadcasting workflows and design new solutions for it. Recently, I conducted an outdoor field study to evaluate a physical product for water activities. I spent hours on the water, observing how users interacted with the product and talking with them about the culture of water activities in that region. One of the reasons for the limited opportunities for field studies is the cost involved. It is costly in terms of human labor and resources to prepare research materials and immerse oneself in the real environment for extended periods of time. In addition, conducting field studies often requires the physical presence of study subjects.
In addition to cost, many other challenges can arise during a field study. Weather, in particular, is unpredictable when the study is conducted outdoors. Despite careful planning, unexpected rain can disrupt observations. Sometimes, we are required to conduct observations under unpleasant weather conditions, such as observing how 50,000 people were evacuated from a music festival when a thunderstorm was forecast. Getting quickly adapted to the user environment can also be challenging, as evidenced by my experience with the MotoGP study. As I had to remain silent during observation and refrain from asking the broadcasting team any questions to avoid distractions, I struggled to understand each person's responsibility within the team and capture their jargon-heavy conversations and workflows during the extremely fast-paced live broadcasting sessions. Recruitment is often challenging as well. Recruiting participants through our convenient but relatively narrow network may lead to a nonrepresentative sample and bias in study results. Alternatively, using professional recruitment agencies can be costly, with fees often reaching hundreds of euros per participant.
The reliability of AI-facilitated research is now a topic often debated among researchers.
Despite these challenges, I enjoy conducting field studies. The authentic connections with participants, observations, and shared laughter lead us to study the product or user behavior and also contribute to a deeper contextual understanding and reflection on the collected data. Moreover, conducting challenging field research can foster closer bonds within the research team, turning each project into not only a research endeavor but also a valuable team-building opportunity.
Let's get back to the question I asked in the title: How far can we go with synthetic UXR? It sounds really fancy when we hear advertisements from some synthetic user research platforms that "we don't need users, recruitment, scheduling, synthesizing, and high costs," or comments like "soon we will have AI-generated researchers conduct research on AI-generated users." As a researcher, I often ask: How much do we want AI to be involved in our research process—as an obedient tool, as an assistive companion, or even as a collaborator? Do we really want the joy of connecting with real human users, stepping into their shoes, and designing solutions based on an in-depth understanding of their needs and contexts of use to be replaced by AI?
I asked these questions to a number of researchers and professors in the field of human-computer interaction and UXR, including Cher Lowies, Sara Bouzit, Ye Dong, Hamada Rizk, Hiroshi Ishii, and Kai Kunze.
Lowies expressed skepticism about the effectiveness of synthetic user research. She notes that, based on her experience with AI user research platforms such as Synthetic Users ( https://www.syntheticusers.com ), a significant 70 percent of the AI-generated data does not delve deep enough into nuanced user experiences compared with research studies conducted by human researchers, leading to generalized themes and averaged results that might not accurately represent the complexity and diversity of real user interactions. Similarly, Dong emphasized the "human touch (人味)" [ 1 ] in data sources. She pointed out that synthetic user data often provides only summary answers, leaving out context-rich, unexpected responses linked to the personal and emotional experiences of unique users. Dong criticizes synthetic user research for being overly reliant on average, past, or sample data and cautions against using it to predict the future. As Ishii commented, "There is no such thing as an average user."
Taking a different point of view, Rizk and Bouzit both believe in the added value of using AI-generated synthetic user data to increase the volume of minority data and reduce bias in training data. For instance, in the medical domain, a shortage of annotated data poses a significant limitation in medical image processing, particularly for diagnosing rare diseases and ensuring data diversity that includes various ethnic groups. To address this data shortage and potential bias, synthetic user datasets are often generated to provide an effective amount of diverse training data for medical applications (e.g., [ 2 ]). In other words, AI-generated synthetic data could reveal overlooked nuances in user studies by simulating user groups that are often not represented (e.g., users with color vision deficiencies in HCI studies). This approach helps mitigate bias when real human data resources are lacking [ 3 ].
Kunze, on the other hand, spoke to the limitations of using synthetic UXR in innovative technology fields where established user data is scarce. Synthetic UXR based on established user data may provide predictions within the range of existing data, but may fall short of capturing the full complexity and unpredictability of real human behavior and making predictions beyond the known data range. As I commented in my previous column, artificial intelligence interpolates, while we humans extrapolate [ 4 ]. While my colleagues and I are convinced that the empathy of human researchers is a unique skill that cannot be easily replaced by AI [ 5 ], Kunze makes a critical distinction between empathy and sympathy in user research. He argues that while it's vital to understand users, being too empathetic with them may hinder our ability to make objective evaluations and decisions. Thus, he questions whether sympathy is a better quality for researchers to cultivate in order to maintain a rational distance and better inspect user needs. This then raises the question of how effectively AI-facilitated research can simulate the empathy and sympathy of human researchers. Instead of creating synthetic users, AI tools could potentially play a crucial role in helping researchers and developers maintain a balanced approach to empathy in their work.
A survey posted on User Interviews showed that 77.1 percent of the researchers in their research sample audience are using AI in at least some of their work, with thematic coding being the most popular analysis use case for AI [ 6 ]. When I asked my peer researchers about what GenAI can and cannot do, all of them mentioned that AI can help them overcome the fear of a blank canvas by providing a starting point to develop from. This includes generating a list of questions for the interview guide as inspirations or offering a template for building an observation grid. They expressed concerns, however, about accidentally leaking sensitive data while using AI tools such as ChatGPT for thematic analysis, as well as concerns about the accuracy of the analysis.
AI tools could potentially play a crucial role in helping researchers and developers maintain a balanced approach to empathy in their work.
Reflecting on the typical methods in the four main stages of UXR [ 7 ] and considering the comments from HCI and UXR experts, I have summarized in Figure 1 how GenAI, or synthetic UXR, can assist in accelerating our research process and enhance the quality of research. The figure also highlights areas where human researchers are essential for validation and making final decisions.
| ]. |
During the Discover stage, GenAI can provide templates, offer cultural insights, and analyze existing research to identify gaps in knowledge, but it cannot fully replace the need for in-depth fieldwork or grasp subtle cultural dynamics without human interpretation. In the Explore phase, it is useful for transcribing and coding audio data, assisting with user pattern identification, and suggesting additional variables during data collection. GenAI falls short, however, in capturing the complete emotional journey of users or providing the context-rich qualitative insights that stem from direct user interaction. In the Test phase, GenAI can standardize usability and accessibility assessments, automate video captioning of user actions, and cross-reference findings to suggest best practices. Its limitations here include an inability to provide nuanced critiques like human testers, detect subtle emotional reactions, or account for unstated emotional cues. In the Listen phase, GenAI excels at offering survey templates, simulating survey answers for pilot testing, identifying patterns in usability issues, and automating feedback categorization. Yet it cannot replicate the human experience or strategic decision making derived from deep, human-led analysis of feedback. To conclude, while GenAI may be a helpful tool for augmenting UXR processes, it does not replace the nuanced understanding, empathy, and contextual awareness that human researchers contribute.
Another important aspect we shouldn't allow GenAI to deprive us of is the joy and meaning we find in doing our work. In my recent research study about UX professionals' perceptions of GenAI, enjoyment and meaning were two recurring keywords in our conversations [ 5 ]. The meaning of our work is not just about work per se but also the pleasure derived from it. A recent study found that the user experience of early users of ChatGPT was affected not just by pragmatic attributes but also by hedonic attributes such as entertainment and creative interactions that impressed or surprised the users [ 8 ]. Enjoyment in work can be viewed through the lens of motivation theory, including both extrinsic and intrinsic motivations [ 9 ]. Extrinsic motivations revolve around whether the technology efficiently serves as a means to accomplish tasks, treating technology such as GenAI as a tool. Intrinsic motivations center on whether we find our work inherently rewarding and the engagement with technology enjoyable, considering technology such as GenAI as a toy. Our work is driven not just by the end results; we also seek fulfillment and enjoyment throughout the process. The joy of connecting with real users is irreplaceable, and the joy of engaging in thematic analysis with the team, as well as smiling at participants' funny quotes, is irreplaceable.
So, how far can we go with synthetic UXR? GenAI is inevitably going to affect how we conduct user research. There's a potential future scenario for human-AI collaboration where we'll need to start considering AI as both a stakeholder and a user in our UXR. In this scenario, AI is not just a basic obedient tool but rather a collaborator that can cross-reference findings, suggest overlooked factors, and identify best practices using existing databases that are difficult for human researchers to comprehend quickly [ 3 ]. However, I still believe that no matter how advanced AI becomes in facilitating research, and regardless of how well it can simulate real users or how extensively it's been programmed for empathy or sympathy, we must ensure that real data from real users is not overshadowed by AI-generated insights and it continues to play the major role in depicting human experiences. Relying solely on synthetic user research data to guide strategic product development and predict the future is risky.
1. 人味 (pronounced "rénwèi" in Mandarin) is a Chinese concept that translates literally to "human flavor" or "human taste." In this context, it is better understood as referring to the human touch, or the qualities that convey human warmth, personality, and authenticity.
2. Bauer, D.F. et al. Generation of annotated multimodal ground truth datasets for abdominal medical image registration. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery 16 (2021), 1277–1285.
3. Schmidt, A., Elagroudy, P., Draxler, F., Kreuter, F., and Welsch, R. Simulating the human in HCD with ChatGPT: Redesigning interaction design with AI. Interactions 31 , 1 (2024), 24–31.
4. Li, J. Experimentation everywhere and every day: Running A/B testing in corporate environments. Interactions 31 , 1 (2024), 20–22.
5. Li, J., Cao, H,, Lin, L., Hou, Y., Zhu, R., and El Ali, A. User experience design professionals' perceptions of generative artificial intelligence. Proc. of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. ACM, New York, 2024; https://doi.org/10.1145/3613904.3642114
6. Burnam, L. We surveyed 1093 researchers about how they use AI—here's what we learned. User Interviews. Sep. 15, 2023; https://www.userinterviews.com/ai-in-ux-research-report
7. Farrell, S. UX research cheat sheet. Nielsen Norman Group. Feb. 12, 2017; https://www.nngroup.com/articles/ux-research-cheat-sheet/
8. Skjuve, M., Følstad, A., and Brandtzaeg, P.B. The user experience of ChatGPT: Findings from a questionnaire study of early users. Proc. of the 5th International Conference on Conversational User Interfaces. ACM, New York, 2023, 1–10.
9. Isen, A.M. and Reeve, J. The influence of positive affect on intrinsic and extrinsic motivation: Facilitating enjoyment of play, responsible work behavior, and self-control. Motivation and Emotion 29 (2005), 295–323.
Jie Li is an HCI researcher with a background in industrial design engineering. Her research focuses on developing evaluation metrics for immersive experiences. She is head of research and insights at EPAM Netherlands as well as a creative cake designer and the owner of Cake Researcher, a boutique cafe. [email protected]
Copyright held by author
The Digital Library is published by the Association for Computing Machinery. Copyright © 2024 ACM, Inc.
Post Comment
Comments submitted to this site are moderated and will appear if they are relevant to the topic.
No Comments Found
View This Article
- FULL-TEXT (HTML)
- FULL-TEXT (PDF)
- IN DIGITAL EDITION
Reader Tools

- view in Digital Library
- Digital Edition Format
- view in PDF Format
Browse This Issue
- What are you reading?
- Making/breaking
- Community square
- Cover story
- Conversations in Sketch
- Create Web Account
- Join SIGCHI
- Subscribe to Interactions
- About interactions
- About SIGCHI
- For Authors
- For Advertisers
Interactions is a bi-monthly publication of the ACM | (c) 2024 ACM
https://interactions.acm.org/archive/view/may-june-2024/how-far-can-we-go-with-synthetic-user-experience-research
Skip to Content
- Faculty/Staff
- Global Community
- Current Students
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- University of Denver
- https://korbel.du.edu
9 of DU’s Coolest Undergrad Research Projects
Emma atkinson, supported by the undergraduate research center, dozens of students got the chance to present their work at this spring’s showcase..

From science to the arts, students from departments across the University of Denver gathered this spring to present their research projects at the annual Undergraduate Research Showcase.
The Undergraduate Research Center awarded many of these students grants to conduct their research, which culminated in a diverse display of creative and engaging projects. The research represents the a dvancing intellectual growth dimension of the 4D Experience.
“DU’s undergraduate research activities are truly premier, providing students with rigorous opportunities to work with thought leaders from across campus—flexing their muscles as thought explorers, translating and learning critical skills, and building the confidence to tackle the problems of tomorrow,” says Corinne Lengsfeld, senior vice provost for research and graduate education.
Here are descriptions of nine of this year’s coolest research projects, along with what students told us about their experience.
Saint Brigit and Her Habits: Exploring Queerness in Early Medieval Ireland
Jacqueline Stephenson

“By examining how scholars have used a lens of queerness and mediation to analyze key hagiographies—first of saints, more broadly, and then of female saints—and using these approaches to examine the inherently queer actions, positions and roles found in Saint Brigit’s First Life, we can gain a clearer view of societal views towards queerness during the early medieval period and in early medieval Ireland, in particular.
In doing so, this thesis will help chip away at the monolithic view of the period as well as the queer erasure within—demonstrating that queerness has always been a fundamental part of human society.”
What was the best part about doing this research?
The best part about doing this research was actually contributing to the scholarship and demonstrating that queerness has always been here, even in the places we might least expect. Additionally, seeing concepts we often don't associate with religion and this period were fascinating.
An example is one of her miracles being essentially an abortion, where a young unmarried woman didn't want to be pregnant and came to Saint Brigit, who made the fetus disappear. This is literally a celebrated miracle and not condemned—something shocking considering present-day religious attitudes toward abortion.
Questioning the Effectiveness of the Olympic Truce
Vincent Pandey
“A modern model for peace is the Olympic Truce, a United Nations General Assembly resolution that calls for the pausing and prevention of new conflicts from one week before the Olympic Games through one week after the Paralympic Games. Some argue that the symbolic nature of the truce allows it to create moments of peace in conflicts, while others argue that it is nothing more than a gesture of goodwill that has not actually been used for peace.
My research question is: Has the Olympic Truce ever been successfully implemented to prevent the onset of new conflict or in creating a ceasefire during an ongoing conflict? I use conflict data and case studies to determine the prevalence of conflict during Olympic Truce periods and four case studies to analyze attempts to use the Olympic Truce and some of the challenges faced.”
Hawai'i Uncovered
Lauren Tapper

“Through photography, Hawai'i Uncovered aims to explore the conflicting aspects of identity in Hawai'i, reveal the true characteristics of the state and separate its perception by tourists from the reality that locals know all too well. Photos were taken at popular tourist and lesser known ‘locals-only’ destinations on multiple of the Hawaiian Islands. The photos focused mostly on the way that people interact and exist within these places and amongst each other through a candid and observational lens.
The idea of community and belonging are both the saving grace and downfall of these islands, allowing many to be proud and excited about who they are while also leaving some cast out and forgotten. Both the romanticized and ignored aspects of these islands are what make the state unlike anywhere else in the world and are essential in defining Hawai'i in an honest fashion.”
How did the idea for this research come about?
I got the idea for this research as someone who was born and raised in Hawaii and came to the mainland to notice that there was a huge discrepancy between what people think they know about Hawaii versus what is true, or at least what I know to be true.
Flower Study
Haven Hinds

“This project is a study of extinct flowers, their histories, environments, biology, colors and assigned personalities—manifested in 3D models and a digital book. The goal was to select six flowers with interesting histories and/or cultural connections. Since the flowers can, for the most part, not be seen or kept, they were created in Blender as accurately as possible. To give people a means of connection with the flowers, each was assigned a personality based on different factors. These factors could be the colors they possess, where geographically they thrived, parts of their history or biological factors.
To allow these personalities to further flourish, color spaces were created in Affinity Designer to be applied not only as the background of the models but also as the background of half of the book’s pages. Each person who interacts with the book is encouraged to pick out flowers they connect to and create their own garden of these now-gone flowers.”
The best part about doing this research was finding out some of the love stories connected to these flowers. I am a hopeless romantic, so I enjoyed even the tragic ending to the ancient stories connected to the flowers. Their stories allowed me the opportunity to give the flowers personality traits, allowing others to further connect.
A Midsummer Night’s Dream Specialty Props
“ʽA Midsummer Night’s Dream’ is one of Shakespeare’s most renowned plays, steeped in a world of dreams and magic, and will be the second show in the Department of Theatre’s winter quarter season. This show has the goal of bringing in college audiences that have not had the full experience of witnessing live theatre and who may have previous, negative notions about Shakespearean plays. The goal was to transform our audience for the two hours they witnessed this play into people that can enter a world of magic, try something new, appreciate it, challenge their own thinking and revitalize an art that took a heavy blow in recent years.
In order to achieve this fantastical reality onstage, I worked closely with the costume designer (Janice Lacek) and director (Sabin Epstein) to research, design, prototype and fabricate specialty props and costumes to create the multiple distinct worlds present in ‘A Midsummer Night’s Dream.’ By the end of the project, I designed, prototyped and fabricated five large-scale specialty props sporting at least 50 separate pieces, each using advanced painting and texturing methods, LEDs lights and wiring techniques, foam molding, paper mâché, and wig making techniques.”
Immersive Stargazing: Leveraging VR for Astronomy Education
“This project leverages virtual reality (VR) technology to create an immersive stargazing experience that makes the wonders of the cosmos accessible to all. By integrating VR with educational strategies, we aim to revolutionize the teaching and experience of astronomy. Our primary objective is to enhance astronomy education by developing a VR platform that transcends conventional teaching methods, making celestial phenomena accessible and engaging for users from diverse educational and geographical backgrounds.
This initiative will democratize access to astronomy, promote STEM education and introduce users to advanced technological learning tools. The approach involves constructing detailed celestial models and integrating them into a user-friendly VR interface.”
Flamethrower Vol. 1-3: Innovation in Multidisciplinary Electronic and Acoustic Music
Trevor Briggs

“Flamethrower Vol. 1-3 is a series of three EPs (short albums) that combine jazz, classical and commercial electronic music to produce an artistic work in which the perception, function and musical context of electronic instruments is challenged. I approached these compositions treating electronic components as instruments, writing out scores as I would for brass and wind instruments. I also utilized cutting-edge electronic hardware to generate degenerated, fragmented and evolving sounds.
This type of in-depth sound design allowed me to write, perform and record novel parts for unique instruments. The remainder of the sounds on these recordings incorporate sampling of field recordings to generate new instruments or soundscapes and unconventional recordings of woodwinds (saxophone, clarinet, flute, bass clarinet and alto flute) from Professor Remy Le Boeuf, my faculty partner.”
The best parts of this project were tiny moments where I was really able to see how the final product was coming together. These times came through all parts of the writing and production process. I recorded Professor Remy Le Boeuf on woodwinds a few times for the album, and those sessions were full of those moments. There's a lot of momentary joy in making music with other people. As a recording engineer and producer, I have been feeling very lucky and grateful that I'm the one that gets to capture and shape these moments for others to listen to.
Technology and Homelessness: How Accessibility and Blockchain Technology Could Impact the Unhoused

“This paper discusses how the unhoused population suffers at the hand of technological inequality despite being relatively offline. It presents theories on how this would change if we reapproached how technology is used to assist the unhoused. It suggests implementing blockchain as a resource as well as modifying the websites built for the unhoused.
Employees at shelters are interviewed for this paper about their experiences with using digital resources to rehouse and restabilize the vulnerable. They are asked how the sites can be improved for more optimized use. The sites are also tested against current user experience (UX) standards for accessibility.”
My idea for this research came from two different sources. The first was the approximately 100 hours of volunteer work that I did with a local organization that works with the unhoused. I worked with caseworkers and other employees to get a better understanding of how the organization was run and what major needs were held by the unhoused population. It opened my eyes to a lot of problems that I hadn’t thought about before, especially how difficult it is to escape homelessness and why it is so difficult.
The second source came later, when I was already working on my thesis paper. I was studying abroad in Greece and took a really interesting UX design class. That class made me start thinking about what UX looked like throughout my life, so when I was looking at government sites to understand where the unhoused would need to be using personal identification, I started noticing all these UX problems that would be easy to fix, which was baffling and frustrating to me, so I decided to add a second part to my paper.
Data Quality Matters: Suicide Intention Detection on Social Media Posts Using RoBERTa-CNN
“Suicide remains a global health concern for the field of health, which urgently needs innovative approaches for early detection and intervention. This paper focuses on identifying suicidal intentions in SuicideWatch Reddit posts and presents a novel approach to detect suicide using the cutting-edge RoBERTa-CNN model, a variant of RoBERTa (Robustly Optimized BERT Approach). RoBERTa is a language model that captures textual information and forms semantic relationships within texts.
By adding the Convolution Neural Network (CNN) head, RoBERTa enhances its ability to capture important patterns from heavy datasets. To evaluate RoBERTa-CNN, we experimented on the Suicide and Depression Detection dataset and obtained solid results. For example, RoBERTa-CNN achieves 98% mean accuracy with the standard deviation (STD) of 0.0009. It also reaches over 97.5% mean area under the curve (AUC) value with an STD of 0.0013. Then, RoBERTa-CNN outperforms competitive methods, demonstrating the robustness and ability to capture nuanced linguistic patterns for suicidal intentions. Hence, RoBERTa-CNN can detect suicide intention on text data very well.”

Start Your Application
Undergraduate applicants.
The Common App is a universal application that can be sent to many schools, including the University of Denver.
First-Year Students Transfer Students
Graduate Applicants
Go to the graduate admission application to submit your information. For information on admission requirements, visit the graduate academic programs page and locate your program of interest.
Graduate Application
Explore Programs
Graduate Academic Programs
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Using AI at Work Makes Us Lonelier and Less Healthy
- David De Cremer
- Joel Koopman

Employees who use AI as a core part of their jobs report feeling more isolated, drinking more, and sleeping less than employees who don’t.
The promise of AI is alluring — optimized productivity, lightning-fast data analysis, and freedom from mundane tasks — and both companies and workers alike are fascinated (and more than a little dumbfounded) by how these tools allow them to do more and better work faster than ever before. Yet in fervor to keep pace with competitors and reap the efficiency gains associated with deploying AI, many organizations have lost sight of their most important asset: the humans whose jobs are being fragmented into tasks that are increasingly becoming automated. Across four studies, employees who use it as a core part of their jobs reported feeling lonelier, drinking more, and suffering from insomnia more than employees who don’t.
Imagine this: Jia, a marketing analyst, arrives at work, logs into her computer, and is greeted by an AI assistant that has already sorted through her emails, prioritized her tasks for the day, and generated first drafts of reports that used to take hours to write. Jia (like everyone who has spent time working with these tools) marvels at how much time she can save by using AI. Inspired by the efficiency-enhancing effects of AI, Jia feels that she can be so much more productive than before. As a result, she gets focused on completing as many tasks as possible in conjunction with her AI assistant.
- David De Cremer is a professor of management and technology at Northeastern University and the Dunton Family Dean of its D’Amore-McKim School of Business. His website is daviddecremer.com .
- JK Joel Koopman is the TJ Barlow Professor of Business Administration at the Mays Business School of Texas A&M University. His research interests include prosocial behavior, organizational justice, motivational processes, and research methodology. He has won multiple awards from Academy of Management’s HR Division (Early Career Achievement Award and David P. Lepak Service Award) along with the 2022 SIOP Distinguished Early Career Contributions award, and currently serves on the Leadership Committee for the HR Division of the Academy of Management .
Partner Center
- Computer Vision
- Federated Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- New Releases
- Advisory Board Members
- 🐝 Partnership and Promotion

In conclusion, a team from IEEE has proposed two themes, Search4LLM and LLM4Search. The Search4LLM idea highlights the potential of search engine datasets to improve the intelligence of LLMs, helping these models better handle complex queries. The other theme, LLM4Search demonstrates how LLMs can positively impact search engines by improving content understanding, search accuracy, and user satisfaction. However, complete integration of LLMs with search engines comes with challenges, such as technical difficulties, ethical concerns, and biases in model training. Despite these challenges, this work shows a promising future where combining LLMs and search engines could create a new era of intelligent, efficient, and user-friendly search services.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter .
Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Gr oup .
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 46k+ ML SubReddit

Sajjad Ansari
Sajjad Ansari is a final year undergraduate from IIT Kharagpur. As a Tech enthusiast, he delves into the practical applications of AI with a focus on understanding the impact of AI technologies and their real-world implications. He aims to articulate complex AI concepts in a clear and accessible manner.
- How AI Scales with Data Size? This Paper from Stanford Introduces a New Class of Individualized Data Scaling Laws for Machine Learning
- A Simple Open-loop Model-Free Baseline for Reinforcement Learning Locomotion Tasks without Using Complex Models or Computational Resources
- ScaleBiO: A Novel Machine Learning Based Bilevel Optimization Method Capable of Scaling to 34B LLMs on Data Reweighting Tasks
- Comprehensive Analysis of The Performance of Vision State Space Models (VSSMs), Vision Transformers, and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Top artificial intelligence ai search engines to know in 2024, policy learning with large world models: advancing multi-task reinforcement learning efficiency and performance, internlm2.5-7b-chat: open sourcing large language models with unmatched reasoning, long-context handling, and enhanced tool use, a survey of advanced retrieval algorithms in ad and content recommendation systems: mechanisms and challenges, worldbench: a dynamic and flexible llm benchmark composed of per-country data from the world bank, accelerating llm inference: introducing sampleattention for efficient long context processing, internlm2.5-7b-chat: open sourcing large language models with unmatched reasoning, long-context handling, and enhanced tool..., a survey of advanced retrieval algorithms in ad and content recommendation systems: mechanisms and..., worldbench: a dynamic and flexible llm benchmark composed of per-country data from the world....
- AI Magazine
- Privacy & TC
- Cookie Policy
🐝 🐝 Join the Fastest Growing AI Research Newsletter...
Thank You 🙌
Privacy Overview

COMMENTS
UX research helps brands and organizations to: Understand how users experience products, websites, mobile apps, and prototypes. Evaluate and optimize prototypes and ideas based on UX research discoveries - and nail the design and experience early in a product's life cycle. Unearth new customer needs and business opportunities.
A UX research method is a way of generating insights about your users, their behavior, motivations, and needs. These methods help: Learn about user behavior and attitudes. Identify key pain points and challenges in the user interface. Develop user personas to identify user needs and drive solutions.
UX Research Cheat Sheet. Susan Farrell. February 12, 2017. Summary: User research can be done at any point in the design cycle. This list of methods and activities can help you decide which to use when. User-experience research methods are great at producing data and insights, while ongoing activities help get the right things done.
The field of user experience has a wide range of research methods available, ranging from tried-and-true methods such as lab-based usability testing to those that have been more recently developed, such as unmoderated UX assessments. While it's not realistic to use the full set of methods on a given project, nearly all projects would benefit from multiple research methods and from combining ...
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
User experience research, or UX research, is the process of gathering insights about users' behaviors, needs, and pain points through observation techniques and feedback methodologies. It's a form of user research that looks at how users interact with your product, helping bridge the gaps between what you think users need, what users say they ...
A Guide to Using User-Experience Research Methods. Kelley Gordon and Christian Rohrer. August 21, 2022. Share. Summary: Modern day UX research methods answer a wide range of questions. To help you know when to use which user research method, each of 20 methods is mapped across 3 dimensions and over time within a typical product-development process.
You'll get to influence things millions of people use every day, from email and productivity apps to tools for developers and educators. Even if you don't currently use Google products, you can still sign up for a chance to participate in our research. If one of our studies is a good fit for you, we'll get in touch with details and next ...
User research, or UX research, is an absolutely vital part of the user experience design process. Typically done at the start of a project, it encompasses different types of research methodologies to gather valuable data and feedback. When conducting user research, you'll engage with and observe your target users, getting to know their needs ...
User Experience (UX) Research is a systematic process of understanding and evaluating how users interact with a product, service, or system. It encompasses a wide range of research methods and techniques to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, needs, and pain points. The ultimate goal of UX research is to inform and improve the ...
A Guide To UsingUser-Experience Research MethodsSummary: Modern day UX. esearch methods answer a wide range of questions. To help you know when to use which user-research method, each of methods is mapped across dimensions and over. which-ux-research-methods/A Landscape of MethodsThe field of user experien.
How to Conduct UX Research with Usability Testing. Usability testing can be broken down into a few major steps: Identify what needs to be tested and why (e.g. a new product, feature, etc.) Identify the target audience (or your desired customers). Create a list of tasks for the participants to work through.
Abstract. User experience (UX) researchers in technical communication (TC) and beyond still need a clear picture of the methods used to measure and evaluate UX. This article charts current UX methods through a systematic literature review of recent publications (2016-2018) and a survey of 52 UX practitioners in academia and industry.
User Experience research or UX research is defined as users' systematic study to discover behaviors, needs, motivations, and trends through observations, analysis, and other user feedback. UX researchers use different methods to understand problems and draw opportunities to stand out amongst their competition.
Product Discovery UX Research. User Experience Research Methods shape and reshape every digital touchpoint, from web applications to complex marketing sites. Companies are no longer content with merely producing functional products; they want them to be tailor-made for their users, addressing their needs and aspirations.
March 17, 2023. User experience research is the practice of identifying the behavior patterns, thoughts, and needs of customers by gathering user feedback from observation, task analysis, and other methods. In plain terms: UX research uncovers how a target audience interacts with your product to gain insights on the impact that it has on them.
Here it is, the UX research process in 7 (ish) steps: . Step 1. Identify your research goals. This is the first and most important step in any user research study. Without clear goals and objectives, you're just fumbling in the dark. And that's no way to conduct user research.
Qualitative UX Research is based on an in-depth understanding of the human behaviour and needs. Qualitative user research includes interviews, observations (in natural settings), usability tests or contextual inquiry. More than often you'll obtain unexpected, valuable insights through this from of user experience research methods.
User experience (UX) research stands at the forefront, providing valuable data about user behaviors, preferences, and pain points, which is essential for tailoring products that truly resonate with and captivate your audience. ... It gives real, user-based insights, so you're not just guessing what might work but making informed choices based ...
Attitudinal research looks at a user's feelings and attitudes toward an experience. UX research methods. One aspect of your role as a UX designer will be deciding which research method is appropriate for answering which questions. The UX research tool chest contains a variety of options to help you glean information from your users.
Feb 11, 2022. --. UX research is the methodical analysis of target users and their terms. It adds practical contexts and observations to design processes. We adopt multiple UX research methods and ...
Through user experience research, you'll be able to: Better understand how users experience your products and platforms. Discover new customer needs as well as opportunities for your business. Optimize internal processes based on the users' direct feedback. Apply the insights learned to provide user experiences that outperform your competitors.
User experience research (UXR) plays an important role in uncovering user personas, their contexts of use, and their detailed needs. UXR employs a range of research methodologies, such as surveys, interviews, diary studies, and observations, all of which can be time-consuming and costly. With the advent of advanced generative AI (GenAI) tools ...
When presenting UX research findings, it's crucial to prioritize the data based on its impact on user experience and business goals. Start by identifying the key insights that directly influence ...
Embarking on a Ph.D. in User Experience (UX) can be a transformative journey for your academic and research career. UX, the process of creating products that provide meaningful and relevant ...
From science to the arts, students from departments across the University of Denver gathered this spring to present their research projects at the annual Undergraduate Research Showcase.The Undergraduate Research Center awarded many of these students grants to conduct their research, which culminated in a diverse display of creative and engaging projects. The research represents the advancing ...
Summary. Gartner research shows 78% of organizational leaders report experiencing "collaboration drag" — too many meetings, too much peer feedback, unclear decision-making authority, and too ...
Joel Koopman is the TJ Barlow Professor of Business Administration at the Mays Business School of Texas A&M University. His research interests include prosocial behavior, organizational justice ...
The rise of the Internet has flooded with information, making search engines more important than ever for navigating this vast online world. However, as user queries become more complex and expectations for precise, relevant, and up-to-date answers increase, traditional search technologies face various challenges to meet the requirement. Significant progress has been made in natural language ...
The issuer hints feature greatly improves user experience by helping users to easily identify the right certificate for authentication. Vimala Ranganathan, Principal Product Manager on Microsoft Entra, will now walk you through these new features that will help you in your journey toward phishing-resistant multifactor authentication (MFA).