Reference management. Clean and simple.

How to write an excellent thesis conclusion [with examples]

Restate the thesis
Review or reiterate key points of your work, explain why your work is relevant, a take-away for the reader, more resources on writing thesis conclusions, frequently asked questions about writing an excellent thesis conclusion, related articles.
At this point in your writing, you have most likely finished your introduction and the body of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper . While this is a reason to celebrate, you should not underestimate the importance of your conclusion. The conclusion is the last thing that your reader will see, so it should be memorable.
A good conclusion will review the key points of the thesis and explain to the reader why the information is relevant, applicable, or related to the world as a whole. Make sure to dedicate enough of your writing time to the conclusion and do not put it off until the very last minute.
This article provides an effective technique for writing a conclusion adapted from Erika Eby’s The College Student's Guide to Writing a Good Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips & Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out .
While the thesis introduction starts out with broad statements about the topic, and then narrows it down to the thesis statement , a thesis conclusion does the same in the opposite order.
- Restate the thesis.
- Review or reiterate key points of your work.
- Explain why your work is relevant.
- Include a core take-away message for the reader.
Tip: Don’t just copy and paste your thesis into your conclusion. Restate it in different words.
The best way to start a conclusion is simply by restating the thesis statement. That does not mean just copying and pasting it from the introduction, but putting it into different words.
You will need to change the structure and wording of it to avoid sounding repetitive. Also, be firm in your conclusion just as you were in the introduction. Try to avoid sounding apologetic by using phrases like "This paper has tried to show..."
The conclusion should address all the same parts as the thesis while making it clear that the reader has reached the end. You are telling the reader that your research is finished and what your findings are.
I have argued throughout this work that the point of critical mass for biopolitical immunity occurred during the Romantic period because of that era's unique combination of post-revolutionary politics and innovations in smallpox prevention. In particular, I demonstrated that the French Revolution and the discovery of vaccination in the 1790s triggered a reconsideration of the relationship between bodies and the state.
Tip: Try to reiterate points from your introduction in your thesis conclusion.
The next step is to review the main points of the thesis as a whole. Look back at the body of of your project and make a note of the key ideas. You can reword these ideas the same way you reworded your thesis statement and then incorporate that into the conclusion.
You can also repeat striking quotations or statistics, but do not use more than two. As the conclusion represents your own closing thoughts on the topic , it should mainly consist of your own words.
In addition, conclusions can contain recommendations to the reader or relevant questions that further the thesis. You should ask yourself:
- What you would ideally like to see your readers do in reaction to your paper?
- Do you want them to take a certain action or investigate further?
- Is there a bigger issue that your paper wants to draw attention to?
Also, try to reference your introduction in your conclusion. You have already taken a first step by restating your thesis. Now, check whether there are other key words, phrases or ideas that are mentioned in your introduction that fit into your conclusion. Connecting the introduction to the conclusion in this way will help readers feel satisfied.
I explored how Mary Wollstonecraft, in both her fiction and political writings, envisions an ideal medico-political state, and how other writers like William Wordsworth and Mary Shelley increasingly imagined the body politic literally, as an incorporated political collective made up of bodies whose immunity to political and medical ills was essential to a healthy state.
Tip: Make sure to explain why your thesis is relevant to your field of research.
Although you can encourage readers to question their opinions and reflect on your topic, do not leave loose ends. You should provide a sense of resolution and make sure your conclusion wraps up your argument. Make sure you explain why your thesis is relevant to your field of research and how your research intervenes within, or substantially revises, existing scholarly debates.
This project challenged conventional ideas about the relationship among Romanticism, medicine, and politics by reading the unfolding of Romantic literature and biopolitical immunity as mutual, co-productive processes. In doing so, this thesis revises the ways in which biopolitics has been theorized by insisting on the inherent connections between Romantic literature and the forms of biopower that characterize early modernity.
Tip: If you began your thesis with an anecdote or historical example, you may want to return to that in your conclusion.
End your conclusion with something memorable, such as:
- a call to action
- a recommendation
- a gesture towards future research
- a brief explanation of how the problem or idea you covered remains relevant
Ultimately, you want readers to feel more informed, or ready to act, as they read your conclusion.
Yet, the Romantic period is only the beginning of modern thought on immunity and biopolitics. Victorian writers, doctors, and politicians upheld the Romantic idea that a "healthy state" was a literal condition that could be achieved by combining politics and medicine, but augmented that idea through legislation and widespread public health measures. While many nineteenth-century efforts to improve citizens' health were successful, the fight against disease ultimately changed course in the twentieth century as global immunological threats such as SARS occupied public consciousness. Indeed, as subsequent public health events make apparent, biopolitical immunity persists as a viable concept for thinking about the relationship between medicine and politics in modernity.
Need more advice? Read our 5 additional tips on how to write a good thesis conclusion.
The conclusion is the last thing that your reader will see, so it should be memorable. To write a great thesis conclusion you should:
The basic content of a conclusion is to review the main points from the paper. This part represents your own closing thoughts on the topic. It should mainly consist of the outcome of the research in your own words.
The length of the conclusion will depend on the length of the whole thesis. Usually, a conclusion should be around 5-7% of the overall word count.
End your conclusion with something memorable, such as a question, warning, or call to action. Depending on the topic, you can also end with a recommendation.
In Open Access: Theses and Dissertations you can find thousands of completed works. Take a look at any of the theses or dissertations for real-life examples of conclusions that were already approved.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How To Write The Conclusion Chapter
A Simple Explainer With Examples + Free Template
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | September 2021
So, you’ve wrapped up your results and discussion chapters, and you’re finally on the home stretch – the conclusion chapter . In this post, we’ll discuss everything you need to know to craft a high-quality conclusion chapter for your dissertation or thesis project.
Overview: The Conclusion Chapter
- What the thesis/dissertation conclusion chapter is
- What to include in your conclusion
- How to structure and write up your conclusion
- A few tips to help you ace the chapter
- FREE conclusion template
What is the conclusion chapter?
The conclusion chapter is typically the final major chapter of a dissertation or thesis. As such, it serves as a concluding summary of your research findings and wraps up the document. While some publications such as journal articles and research reports combine the discussion and conclusion sections, these are typically separate chapters in a dissertation or thesis. As always, be sure to check what your university’s structural preference is before you start writing up these chapters.
So, what’s the difference between the discussion and the conclusion chapter?
Well, the two chapters are quite similar , as they both discuss the key findings of the study. However, the conclusion chapter is typically more general and high-level in nature. In your discussion chapter, you’ll typically discuss the intricate details of your study, but in your conclusion chapter, you’ll take a broader perspective, reporting on the main research outcomes and how these addressed your research aim (or aims) .
A core function of the conclusion chapter is to synthesise all major points covered in your study and to tell the reader what they should take away from your work. Basically, you need to tell them what you found , why it’s valuable , how it can be applied , and what further research can be done.
Whatever you do, don’t just copy and paste what you’ve written in your discussion chapter! The conclusion chapter should not be a simple rehash of the discussion chapter. While the two chapters are similar, they have distinctly different functions.

What should I include in the conclusion chapter?
To understand what needs to go into your conclusion chapter, it’s useful to understand what the chapter needs to achieve. In general, a good dissertation conclusion chapter should achieve the following:
- Summarise the key findings of the study
- Explicitly answer the research question(s) and address the research aims
- Inform the reader of the study’s main contributions
- Discuss any limitations or weaknesses of the study
- Present recommendations for future research
Therefore, your conclusion chapter needs to cover these core components. Importantly, you need to be careful not to include any new findings or data points. Your conclusion chapter should be based purely on data and analysis findings that you’ve already presented in the earlier chapters. If there’s a new point you want to introduce, you’ll need to go back to your results and discussion chapters to weave the foundation in there.
In many cases, readers will jump from the introduction chapter directly to the conclusions chapter to get a quick overview of the study’s purpose and key findings. Therefore, when you write up your conclusion chapter, it’s useful to assume that the reader hasn’t consumed the inner chapters of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, craft your conclusion chapter such that there’s a strong connection and smooth flow between the introduction and conclusion chapters, even though they’re on opposite ends of your document.
Need a helping hand?
How to write the conclusion chapter
Now that you have a clearer view of what the conclusion chapter is about, let’s break down the structure of this chapter so that you can get writing. Keep in mind that this is merely a typical structure – it’s not set in stone or universal. Some universities will prefer that you cover some of these points in the discussion chapter , or that you cover the points at different levels in different chapters.
Step 1: Craft a brief introduction section
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the conclusions chapter needs to start with a brief introduction. In this introductory section, you’ll want to tell the reader what they can expect to find in the chapter, and in what order . Here’s an example of what this might look like:
This chapter will conclude the study by summarising the key research findings in relation to the research aims and questions and discussing the value and contribution thereof. It will also review the limitations of the study and propose opportunities for future research.
Importantly, the objective here is just to give the reader a taste of what’s to come (a roadmap of sorts), not a summary of the chapter. So, keep it short and sweet – a paragraph or two should be ample.
Step 2: Discuss the overall findings in relation to the research aims
The next step in writing your conclusions chapter is to discuss the overall findings of your study , as they relate to the research aims and research questions . You would have likely covered similar ground in the discussion chapter, so it’s important to zoom out a little bit here and focus on the broader findings – specifically, how these help address the research aims .
In practical terms, it’s useful to start this section by reminding your reader of your research aims and research questions, so that the findings are well contextualised. In this section, phrases such as, “This study aimed to…” and “the results indicate that…” will likely come in handy. For example, you could say something like the following:
This study aimed to investigate the feeding habits of the naked mole-rat. The results indicate that naked mole rats feed on underground roots and tubers. Further findings show that these creatures eat only a part of the plant, leaving essential parts to ensure long-term food stability.
Be careful not to make overly bold claims here. Avoid claims such as “this study proves that” or “the findings disprove existing the existing theory”. It’s seldom the case that a single study can prove or disprove something. Typically, this is achieved by a broader body of research, not a single study – especially not a dissertation or thesis which will inherently have significant limitations . We’ll discuss those limitations a little later.

Step 3: Discuss how your study contributes to the field
Next, you’ll need to discuss how your research has contributed to the field – both in terms of theory and practice . This involves talking about what you achieved in your study, highlighting why this is important and valuable, and how it can be used or applied.
In this section you’ll want to:
- Mention any research outputs created as a result of your study (e.g., articles, publications, etc.)
- Inform the reader on just how your research solves your research problem , and why that matters
- Reflect on gaps in the existing research and discuss how your study contributes towards addressing these gaps
- Discuss your study in relation to relevant theories . For example, does it confirm these theories or constructively challenge them?
- Discuss how your research findings can be applied in the real world . For example, what specific actions can practitioners take, based on your findings?
Be careful to strike a careful balance between being firm but humble in your arguments here. It’s unlikely that your one study will fundamentally change paradigms or shake up the discipline, so making claims to this effect will be frowned upon . At the same time though, you need to present your arguments with confidence, firmly asserting the contribution your research has made, however small that contribution may be. Simply put, you need to keep it balanced .
Step 4: Reflect on the limitations of your study
Now that you’ve pumped your research up, the next step is to critically reflect on the limitations and potential shortcomings of your study. You may have already covered this in the discussion chapter, depending on your university’s structural preferences, so be careful not to repeat yourself unnecessarily.
There are many potential limitations that can apply to any given study. Some common ones include:
- Sampling issues that reduce the generalisability of the findings (e.g., non-probability sampling )
- Insufficient sample size (e.g., not getting enough survey responses ) or limited data access
- Low-resolution data collection or analysis techniques
- Researcher bias or lack of experience
- Lack of access to research equipment
- Time constraints that limit the methodology (e.g. cross-sectional vs longitudinal time horizon)
- Budget constraints that limit various aspects of the study
Discussing the limitations of your research may feel self-defeating (no one wants to highlight their weaknesses, right), but it’s a critical component of high-quality research. It’s important to appreciate that all studies have limitations (even well-funded studies by expert researchers) – therefore acknowledging these limitations adds credibility to your research by showing that you understand the limitations of your research design .
That being said, keep an eye on your wording and make sure that you don’t undermine your research . It’s important to strike a balance between recognising the limitations, but also highlighting the value of your research despite those limitations. Show the reader that you understand the limitations, that these were justified given your constraints, and that you know how they can be improved upon – this will get you marks.

Next, you’ll need to make recommendations for future studies. This will largely be built on the limitations you just discussed. For example, if one of your study’s weaknesses was related to a specific data collection or analysis method, you can make a recommendation that future researchers undertake similar research using a more sophisticated method.
Another potential source of future research recommendations is any data points or analysis findings that were interesting or surprising , but not directly related to your study’s research aims and research questions. So, if you observed anything that “stood out” in your analysis, but you didn’t explore it in your discussion (due to a lack of relevance to your research aims), you can earmark that for further exploration in this section.
Essentially, this section is an opportunity to outline how other researchers can build on your study to take the research further and help develop the body of knowledge. So, think carefully about the new questions that your study has raised, and clearly outline these for future researchers to pick up on.
Step 6: Wrap up with a closing summary
Tips for a top-notch conclusion chapter
Now that we’ve covered the what , why and how of the conclusion chapter, here are some quick tips and suggestions to help you craft a rock-solid conclusion.
- Don’t ramble . The conclusion chapter usually consumes 5-7% of the total word count (although this will vary between universities), so you need to be concise. Edit this chapter thoroughly with a focus on brevity and clarity.
- Be very careful about the claims you make in terms of your study’s contribution. Nothing will make the marker’s eyes roll back faster than exaggerated or unfounded claims. Be humble but firm in your claim-making.
- Use clear and simple language that can be easily understood by an intelligent layman. Remember that not every reader will be an expert in your field, so it’s important to make your writing accessible. Bear in mind that no one knows your research better than you do, so it’s important to spell things out clearly for readers.
Hopefully, this post has given you some direction and confidence to take on the conclusion chapter of your dissertation or thesis with confidence. If you’re still feeling a little shaky and need a helping hand, consider booking a free initial consultation with a friendly Grad Coach to discuss how we can help you with hands-on, private coaching.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

17 Comments
Really you team are doing great!
Your guide on writing the concluding chapter of a research is really informative especially to the beginners who really do not know where to start. Im now ready to start. Keep it up guys
Really your team are doing great!
Very helpful guidelines, timely saved. Thanks so much for the tips.
This post was very helpful and informative. Thank you team.
A very enjoyable, understandable and crisp presentation on how to write a conclusion chapter. I thoroughly enjoyed it. Thanks Jenna.
This was a very helpful article which really gave me practical pointers for my concluding chapter. Keep doing what you are doing! It meant a lot to me to be able to have this guide. Thank you so much.
Nice content dealing with the conclusion chapter, it’s a relief after the streneous task of completing discussion part.Thanks for valuable guidance
Thanks for your guidance
I get all my doubts clarified regarding the conclusion chapter. It’s really amazing. Many thanks.
Very helpful tips. Thanks so much for the guidance
Thank you very much for this piece. It offers a very helpful starting point in writing the conclusion chapter of my thesis.
It’s awesome! Most useful and timely too. Thanks a million times
Bundle of thanks for your guidance. It was greatly helpful.
Wonderful, clear, practical guidance. So grateful to read this as I conclude my research. Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
25 Thesis Statement Examples
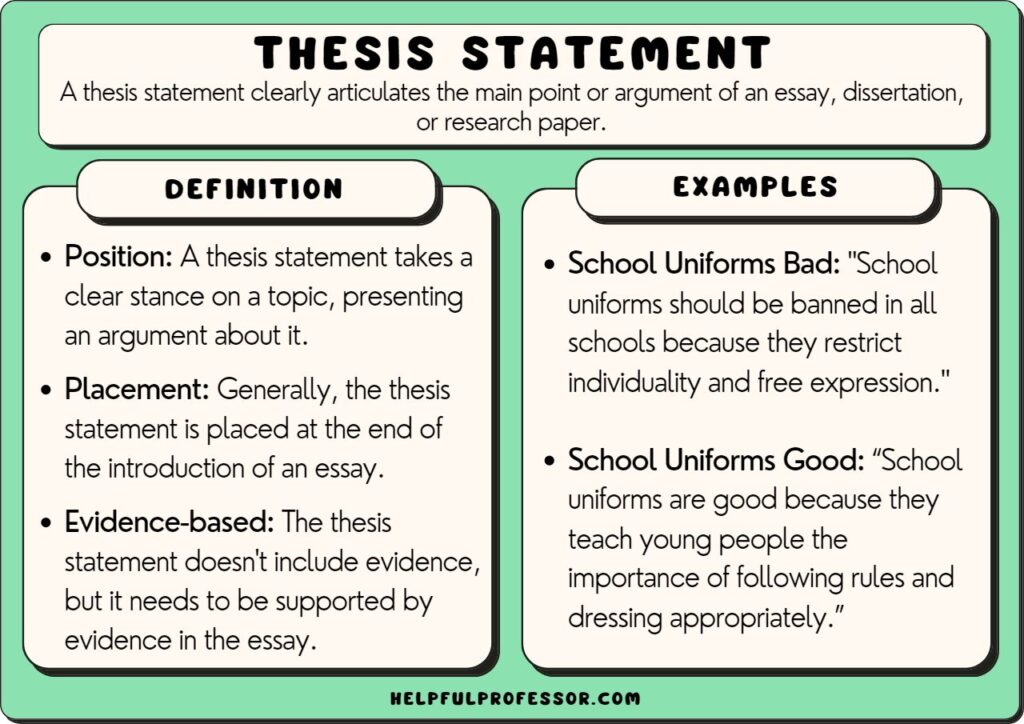
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
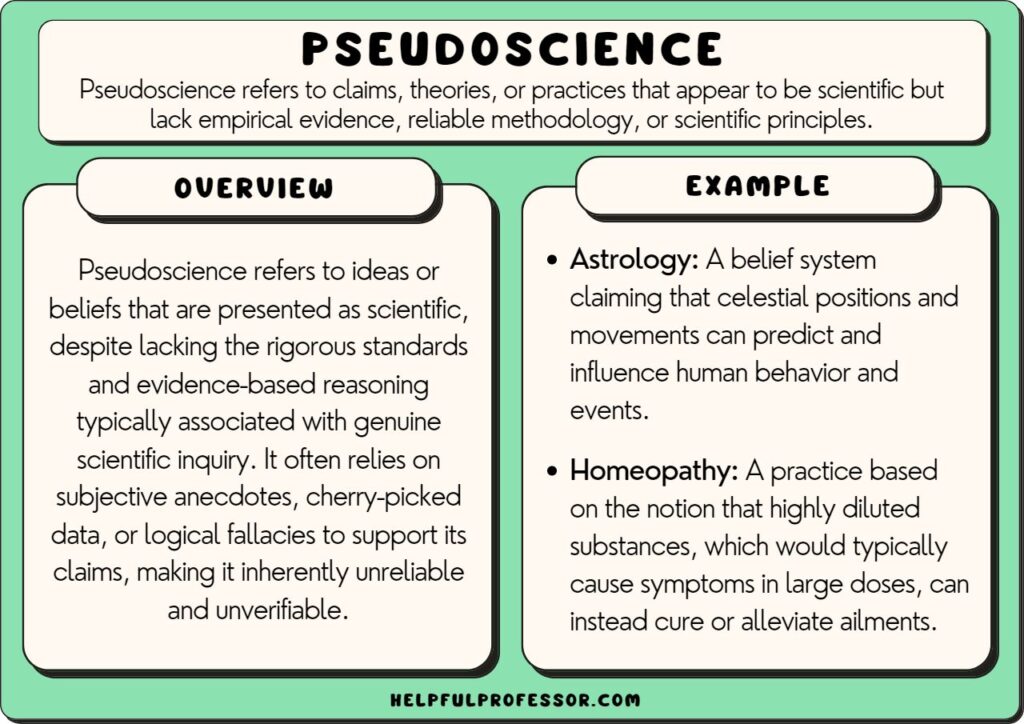
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
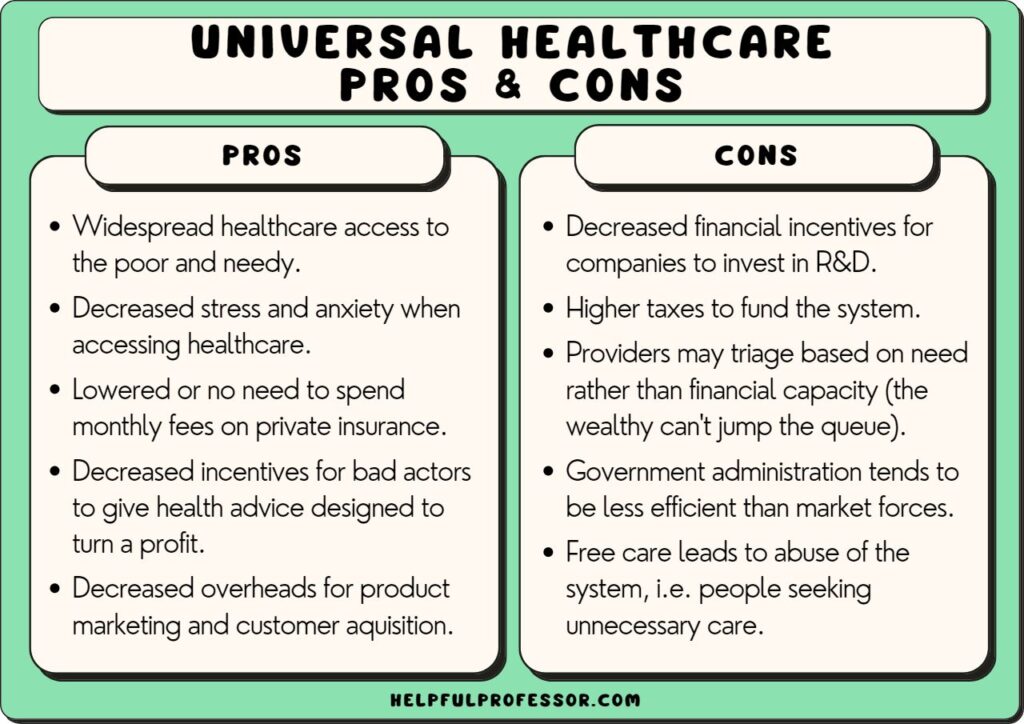
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned


19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
How To Write a Thesis Conclusion – Example & Tips

A thesis conclusion is the last and the most crucial section of your thesis or dissertation. It is the summary of the dissertation. Put it this way: the conclusion paragraph is your entire dissertation wrapped in a few paragraphs. But, concluding a thesis is never easy for many people. Therefore, what is the best way for concluding a thesis or dissertation?
In this post, we will take a closer look at the dissertation conclusion to help you understand how to write a winning conclusion for a research paper as well as a thesis. We will narrow it down further to outline the best structure of a conclusion.
What is the Importance of the Conclusion Paragraph?
Discussion vs conclusion, what is the best format for writing a conclusion, get a sigh of relief concluding thesis.
Before digging deeper into the mechanics of how to write a conclusion for a research paper or thesis, you need to ask yourself the question: “Why is it important?”
Your dissertation conclusion is the last part that you work on after completing the research and the write-up. No matter the area of study you are focusing on, the conclusion can help you to achieve the following goals:
- Answering the research questions that you posed in the first chapter of the dissertation.
- The conclusion paragraph is the part where you reflect on the dissertation.
- In the conclusion, you draw the recommendations for additional studies in areas where you found gaps.
- When writing a dissertation conclusion, you demonstrate what new knowledge you are contributing to the field.
Note that just like the rest of the dissertation, you should not shy from asking your supervisor for a great dissertation conclusion example, especially from past students. This is very important because your department might have a preferred format for writing dissertation conclusions. You can also get a perfect example of a conclusion in the thesis as you research your topic.
When designing a conclusion format, it is important to differentiate it from the results and discussion parts of the thesis. This will help you to strike the perfect flow and win the readers’ affection.
The dissertation results chapter outlines the findings you generated from the research. You should use tables and graphs to demonstrate the findings of the study. The results chapter comes before the discussion.
In the discussion section, you delve deeper into the results you have just presented. You are simply deciphering the findings in line with your research questions. It is the discussion that will set the stage for approving or disproving the thesis statement that you outlined in the first chapter.
NOTE: In some colleges, the results and discussions are put together into one chapter. Therefore, it is very important to follow your college’s recommendation.
While the results and discussions focus more on the results, the conclusion wraps up the entire dissertation. If your dissertation ends at the discussion part, the reader will be left hanging. But writing the conclusion makes the dissertation feel complete and authentic.
As you think about how to write a conclusion, there is one question you need to get right: “How long should a conclusion be?” If you are writing a conclusion for a standard research paper or short thesis, one to three paragraphs should suffice. To put it in percentage, the conclusion should be about 5% of the overall word count. Therefore, you should start by establishing “how long should a thesis be”.
In most cases, the conclusion for empirical scientific research is generally short while that of humanities dissertations is longer. Here is the best format for how to end a research paper or thesis.
- Start by answering the thesis question: Your conclusion should commence by restating the main thesis question that you anticipate answering. Finally, you have the opportunity to answer the question. Ensure the answer is clear and concise.
- Reflect on the research that you have just finished: After stating the study question, you need to remind the marker or readers why the study was important. Why did you set off on the journey, what was the anticipation, and did the results confirm the expectation? Give an overview of steps that were used during the research and construction of your argument.
At this point, you might be wondering – do I summarize every chapter? The answer is ‘no.’ Instead, you should write more reflectively and answer whether the methodology used was effective in answering the study questions. Make sure also to mention the limitations you experienced during the study.
- Outline recommendations: Although you might have noted the areas that need further research when discussing results, the conclusion is a perfect place to elaborate. Its recommendations interweave well with personal reflections. Try to make recommendations specific. Here are some examples of how to frame recommendations:
Further studies are needed to establish the implications of …. From the conclusion, sociology researchers should consider ….. To understand the effects of the findings, further research can help to ….
- What was your contribution? This part of the conclusion is used to answer the question: “So what?” It provides the right impression of how the thesis contributed to the researcher’s field of study. To achieve this, you can use the following strategies:
Revisit the study problem statement and explain how the thesis helped to solve it. Refer to the study’s literature review to demonstrate how the dissertation has helped to fill the existing gap. If your dissertation is in humanities, you can demonstrate how the findings challenged or confirmed the current viewpoints, assumptions, or theories.
Note that the conclusion should not appear as a stand-alone chapter in the dissertation. Rather, it should articulately interweave with the rest of the paper. To perfect your skills, make sure to also check top conclusion paragraph examples from other students.
From this post on how to write a conclusion paragraph, there is no doubt that you should find it an easy and enjoyable process. After working so hard to complete the dissertation, the conclusion paragraph is simply aimed at wrapping everything up. To get the best conclusions, you should also read top-rated conclusion paragraph examples to see how experts do it. But we must agree that even with this simplified demonstration, crafting the perfect conclusion paragraph is no easy task. It takes time and practice.
There are times when students, even after working on the biggest chunk of their dissertations, feel inadequate to write the conclusions. Often, the process can be complicated when you are required to follow specific models such as MLA or APA conclusions. Even if you have the best conclusion examples and working hard to hone your writing skills, a tight deadline or other engagements might make it hard to craft the best. If you feel inadequate about writing a Harvard or MLA format conclusion because of any reason, do not hesitate to seek writing help.
Writing help is offered by expert writers who understand the structure of Ph.D. conclusion chapters to guarantee you the best grades. No matter your area of study, the experts are cheap and will get you the best. In addition to helping you write the conclusion, they can also provide you with the best sample of a conclusion paragraph for practice. What a great way to sharpen your skills in dissertation writing?
Do not let writing a thesis conclusion stress you: Use this post to make it fun!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings your readers back to your thesis or main idea and reminds your readers where you began and how far you have traveled.
So, for example, in a paper about the relationship between ADHD and rejection sensitivity, Vanessa Roser begins by introducing readers to the fact that researchers have studied the relationship between the two conditions and then provides her explanation of that relationship. Here’s her thesis: “While socialization may indeed be an important factor in RS, I argue that individuals with ADHD may also possess a neurological predisposition to RS that is exacerbated by the differing executive and emotional regulation characteristic of ADHD.”
In her final paragraph, Roser reminds us of where she started by echoing her thesis: “This literature demonstrates that, as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Highlight the “so what”
At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what’s at stake—why they should care about the argument you’re making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put those stakes into a new or broader context.
In the conclusion to her paper about ADHD and RS, Roser echoes the stakes she established in her introduction—that research into connections between ADHD and RS has led to contradictory results, raising questions about the “behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
She writes, “as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Leave your readers with the “now what”
After the “what” and the “so what,” you should leave your reader with some final thoughts. If you have written a strong introduction, your readers will know why you have been arguing what you have been arguing—and why they should care. And if you’ve made a good case for your thesis, then your readers should be in a position to see things in a new way, understand new questions, or be ready for something that they weren’t ready for before they read your paper.
In her conclusion, Roser offers two “now what” statements. First, she explains that it is important to recognize that the flawed behavioral mediation hypothesis “seems to place a degree of fault on the individual. It implies that individuals with ADHD must have elicited such frequent or intense rejection by virtue of their inadequate social skills, erasing the possibility that they may simply possess a natural sensitivity to emotion.” She then highlights the broader implications for treatment of people with ADHD, noting that recognizing the actual connection between rejection sensitivity and ADHD “has profound implications for understanding how individuals with ADHD might best be treated in educational settings, by counselors, family, peers, or even society as a whole.”
To find your own “now what” for your essay’s conclusion, try asking yourself these questions:
- What can my readers now understand, see in a new light, or grapple with that they would not have understood in the same way before reading my paper? Are we a step closer to understanding a larger phenomenon or to understanding why what was at stake is so important?
- What questions can I now raise that would not have made sense at the beginning of my paper? Questions for further research? Other ways that this topic could be approached?
- Are there other applications for my research? Could my questions be asked about different data in a different context? Could I use my methods to answer a different question?
- What action should be taken in light of this argument? What action do I predict will be taken or could lead to a solution?
- What larger context might my argument be a part of?
What to avoid in your conclusion
- a complete restatement of all that you have said in your paper.
- a substantial counterargument that you do not have space to refute; you should introduce counterarguments before your conclusion.
- an apology for what you have not said. If you need to explain the scope of your paper, you should do this sooner—but don’t apologize for what you have not discussed in your paper.
- fake transitions like “in conclusion” that are followed by sentences that aren’t actually conclusions. (“In conclusion, I have now demonstrated that my thesis is correct.”)
- picture_as_pdf Conclusions
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on 10 October 2022.
The conclusion is the very last part of your thesis or dissertation . It should be concise and engaging, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your main findings, as well as the answer to your research question .
In it, you should:
- Clearly state the answer to your main research question
- Summarise and reflect on your research process
- Make recommendations for future work on your topic
- Show what new knowledge you have contributed to your field
- Wrap up your thesis or dissertation
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Discussion vs. conclusion, how long should your conclusion be, step 1: answer your research question, step 2: summarise and reflect on your research, step 3: make future recommendations, step 4: emphasise your contributions to your field, step 5: wrap up your thesis or dissertation, full conclusion example, conclusion checklist, frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
While your conclusion contains similar elements to your discussion section , they are not the same thing.
Your conclusion should be shorter and more general than your discussion. Instead of repeating literature from your literature review , discussing specific research results , or interpreting your data in detail, concentrate on making broad statements that sum up the most important insights of your research.
As a rule of thumb, your conclusion should not introduce new data, interpretations, or arguments.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Depending on whether you are writing a thesis or dissertation, your length will vary. Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5–7% of your overall word count.
An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research. A humanities topic or systematic review , on the other hand, might require more space to conclude its analysis, tying all the previous sections together in an overall argument.
Your conclusion should begin with the main question that your thesis or dissertation aimed to address. This is your final chance to show that you’ve done what you set out to do, so make sure to formulate a clear, concise answer.
- Don’t repeat a list of all the results that you already discussed
- Do synthesise them into a final takeaway that the reader will remember.
An empirical thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
A case study –based thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
In the second example, the research aim is not directly restated, but rather added implicitly to the statement. To avoid repeating yourself, it is helpful to reformulate your aims and questions into an overall statement of what you did and how you did it.
Your conclusion is an opportunity to remind your reader why you took the approach you did, what you expected to find, and how well the results matched your expectations.
To avoid repetition , consider writing more reflectively here, rather than just writing a summary of each preceding section. Consider mentioning the effectiveness of your methodology , or perhaps any new questions or unexpected insights that arose in the process.
You can also mention any limitations of your research, but only if you haven’t already included these in the discussion. Don’t dwell on them at length, though – focus on the positives of your work.
- While x limits the generalisability of the results, this approach provides new insight into y .
- This research clearly illustrates x , but it also raises the question of y .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms.
- Based on these conclusions, practitioners should consider …
- To better understand the implications of these results, future studies could address …
- Further research is needed to determine the causes of/effects of/relationship between …
When making recommendations for further research, be sure not to undermine your own work. Relatedly, while future studies might confirm, build on, or enrich your conclusions, they shouldn’t be required for your argument to feel complete. Your work should stand alone on its own merits.
Just as you should avoid too much self-criticism, you should also avoid exaggerating the applicability of your research. If you’re making recommendations for policy, business, or other practical implementations, it’s generally best to frame them as ‘shoulds’ rather than ‘musts’. All in all, the purpose of academic research is to inform, explain, and explore – not to demand.
Make sure your reader is left with a strong impression of what your research has contributed to the state of your field.
Some strategies to achieve this include:
- Returning to your problem statement to explain how your research helps solve the problem
- Referring back to the literature review and showing how you have addressed a gap in knowledge
- Discussing how your findings confirm or challenge an existing theory or assumption
Again, avoid simply repeating what you’ve already covered in the discussion in your conclusion. Instead, pick out the most important points and sum them up succinctly, situating your project in a broader context.
The end is near! Once you’ve finished writing your conclusion, it’s time to wrap up your thesis or dissertation with a few final steps:
- It’s a good idea to write your abstract next, while the research is still fresh in your mind.
- Next, make sure your reference list is complete and correctly formatted. To speed up the process, you can use our free APA citation generator .
- Once you’ve added any appendices , you can create a table of contents and title page .
- Finally, read through the whole document again to make sure your thesis is clearly written and free from language errors. You can proofread it yourself , ask a friend, or consider Scribbr’s proofreading and editing service .
Here is an example of how you can write your conclusion section. Notice how it includes everything mentioned above:
V. Conclusion
The current research aimed to identify acoustic speech characteristics which mark the beginning of an exacerbation in COPD patients.
The central questions for this research were as follows: 1. Which acoustic measures extracted from read speech differ between COPD speakers in stable condition and healthy speakers? 2. In what ways does the speech of COPD patients during an exacerbation differ from speech of COPD patients during stable periods?
All recordings were aligned using a script. Subsequently, they were manually annotated to indicate respiratory actions such as inhaling and exhaling. The recordings of 9 stable COPD patients reading aloud were then compared with the recordings of 5 healthy control subjects reading aloud. The results showed a significant effect of condition on the number of in- and exhalations per syllable, the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable, and the ratio of voiced and silence intervals. The number of in- and exhalations per syllable and the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable were higher for COPD patients than for healthy controls, which confirmed both hypotheses.
However, the higher ratio of voiced and silence intervals for COPD patients compared to healthy controls was not in line with the hypotheses. This unpredicted result might have been caused by the different reading materials or recording procedures for both groups, or by a difference in reading skills. Moreover, there was a trend regarding the effect of condition on the number of syllables per breath group. The number of syllables per breath group was higher for healthy controls than for COPD patients, which was in line with the hypothesis. There was no effect of condition on pitch, intensity, center of gravity, pitch variability, speaking rate, or articulation rate.
This research has shown that the speech of COPD patients in exacerbation differs from the speech of COPD patients in stable condition. This might have potential for the detection of exacerbations. However, sustained vowels rarely occur in spontaneous speech. Therefore, the last two outcome measures might have greater potential for the detection of beginning exacerbations, but further research on the different outcome measures and their potential for the detection of exacerbations is needed due to the limitations of the current study.
Checklist: Conclusion
I have clearly and concisely answered the main research question .
I have summarized my overall argument or key takeaways.
I have mentioned any important limitations of the research.
I have given relevant recommendations .
I have clearly explained what my research has contributed to my field.
I have not introduced any new data or arguments.
You've written a great conclusion! Use the other checklists to further improve your dissertation.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 31 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write an abstract | steps & examples.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

Everything You Need to Know About Citing a Poem

How Does a Hypothesis Differ From a Research Question?
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?

Argumentative Thesis Statement
Ai generator.

In the realm of persuasive writing, the argumentative thesis statement stands as a pivotal element, guiding the entire context of an essay or research paper. It serves as the beacon that directs your work, letting readers know not only what to expect but also the position you’re advocating. This article dives into the depths of argumentative thesis statement examples, unraveling their significance, and offering a step-by-step guide on how to create one effectively.
3+ Argumentative Thesis Statement Examples
1. argumentative essay thesis statement.

Size: 637 KB
2. Argumentative Thesis Statement Example

Size: 418 KB
3. Printable Argumentative Thesis Statement

Size: 19 KB
4. New Argumentative Thesis Statement

Size: 356 KB
What is an Argumentative Thesis Statement?
Before we delve into the intricacies of crafting a compelling argumentative thesis statement, let’s clarify what this vital element entails. An argumentative thesis statement serves as the core assertion of your essay, presenting your stance on a particular theme or topic. It goes beyond a mere description of the subject; it takes a firm position that you will defend with logical reasoning, evidence, and persuasion.
How to Craft an Argumentative Thesis Statement
Creating an argumentative thesis statement requires a methodical approach. By following these steps, you’ll be better equipped to develop a thesis that not only captures the essence of your argument but also engages readers from the outset.
Step 1: Identify Your Topic and Stance
The first step involves identifying the simple subject you’re addressing and your position on it before starting with the introduction . Your stance could be an assertion, a judgment, or an evaluation, shaping the tone and direction of your entire argument.
Step 2: Analyze Your Audience
Understanding your audience is crucial. Consider their perspectives, beliefs, and potential objections. Tailoring your argumentative thesis statement to resonate with your readers enhances the persuasiveness of your message.
Step 3: Develop a Concise Thesis
A strong thesis is concise and focused. It should encapsulate your main argument while giving a glimpse of the supporting points you’ll discuss. Avoid vague language and ensure your thesis statement is clear and direct.
Step 4: Incorporate Cause and Effect
A compelling argumentative thesis statement often involves demonstrating the cause-and-effect relationship between your stance and the topic. Highlight how certain actions, beliefs, or decisions lead to specific outcomes.
Can my argumentative thesis statement evolve as I research and write?
Absolutely. Your thesis can and should evolve based on your research findings and the development of your argument. Flexibility allows you to refine and strengthen your position.
How can I avoid falling into clichés when crafting my thesis statement?
To avoid clichés , strive for originality. Instead of using well-worn phrases, express your position in a unique way that showcases your perspective and analytical depth.
Should I include counterarguments in my thesis statement?
While it’s not necessary to include counterarguments in your thesis statement, acknowledging opposing viewpoints can add credibility to your argument. However, save the detailed counterarguments for the body of your essay.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

How can a thesis statement be competently transmitted to its intended readership?
What thesis statement state.
Let’s know the understanding of a thesis statement and why should one commence it during their journey toward a degree.
It is thereby important to study and mention the thesis statement in your assignment or the dissertation format. However, the Thesis statement is a strong focal point sanctioned by the students which usually falls under the introductory part of the written work. Its critical role is to lead the main point or argument of your drafted piece of manuscript. Acknowledging the importance of a thesis statement helps to draw the reader’s attention and their understanding by demonstrating the integrity of the academic.
Whereby, one needs to look and make sure that the passed thesis statement is related to the topic, must be concise and clear, and should draft a roadmap to what it is about to address. However, your thesis must be an objective statement and not a question. Your literature review must draw the attention of the readers and should hold uniqueness and transparency, followed by the rules that are adhered to by academics.
There are certain pieces of advice mentioned to which one can craft their thesis writing easily:
Your thesis help must highlight its motive.
Make sure the dissertation help is beneficial and works on today’s date.
The thesis statement must be very clear and to the point, and is highly recommended to refuse unnecessary arguments.
It is also essential that the thesis help UK go through a mixture of editing and proofreading so that it holds a refined manner.
Guide of tips and tricks on How to write a thesis statement:
1. Selecting the topic: The thesis writing service must always work on a topic that pulls out attention and interest, this is to do because if the chosen topic inspires you it will help you to stay motivated and work on it with full focus.
2. Critical Analysis of Data: Once the selection is done, make sure that it carries good references and analyse and figure out the missing details and gaps in the existing thesis.
3. Relevancy of data: When drafting make sure your thesis holds relevant information and facts and figures, and if not, then the thesis help seems to be of no use.
4. Search for your arguments: This is the most crucial part of your written work. The arguments must be strong and positive so that it helps the thesis statement to be competitive, also it is recommended to avoid statements that are lengthy as people do lack interest in reading such forms.
5. Deal with the scope and pathways: Custom thesis writing services need to mark the position of the thesis so that it is easy for the readers to differentiate it and align it to the right path.
6. Revise and Polish: To revise and refine your thesis is very essential and significant as it helps to identify the errors or spot the missing outsources, we know that the thesis is a lengthy process, and missing out on some sort of information is not a big task.
7. Feedback: Gaining feedback from your superiors or academic advisors is one necessary part as it helps to meet the inclinations and requirements of your thesis writing services .
What is an example of a thesis statement?
The thesis statement passed by you should state exactly about your written work. The statement should highlight your topic and its body totally, wherein the example of a thesis statement according to hunger might be like; world hunger has many consequences.
What are the 3 parts of thesis statement?
When working on a thesis statement three parts should be majorly paid attention to. Which is the introduction title, claim, and sub-topics. These three areas must be highly maintained during the performance of the thesis.
What is the correct format for a thesis statement?
The correct format for a thesis statement is based on a few tips like clarity, scope, purpose, etc. But mainly the actual format has three following. The title, the argument section, and the last the supporting points to those arguments.
What are the 5 steps in writing a thesis statement?
In the draft of a thesis statement the following 5 pointers should be the main ones:
1. Know about the assignment
2. The topic selection
3. In-depth study
4. Framing of the research
5. Edit and Polish
How to start a thesis?
To start working on a thesis, one needs to find the scope of the area, followed by mentioning a title and studying it with proper research and analysis, whereby sticking to the writing part and lastly the wrap-up area.
Finding an end to your discussion is very difficult, but as your thesis is a lengthy process several pointers should be followed while designing your written work. The above-highlighted tips help one to deal with a good and supportive thesis statement while dealing with the guidelines too. If your thesis has a true and good impact then it helps you to further discover and encourages you to work on it, but make sure to revise and refine your thesis as it helps you to discover areas that are missed out.
So, it is highly recommended to draw a good thesis statement as it helps you to stand out among the available and holds a worthwhile writing capability which helps others too.
Note: This article is for information purposes only and does not contain any recommendation.
This article may contain affiliate links that Microsoft and/or the publisher may receive a commission from if you buy a product or service through those links.

Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: a Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products
This essay about Whole Foods Market’s mission statement highlights the company’s commitment to promoting health, sustainability, and ethical business practices. It discusses how Whole Foods emphasizes the importance of offering high-quality, natural, and organic products while prioritizing initiatives to minimize its ecological footprint. Additionally, the essay explores the company’s dedication to fostering community engagement and social responsibility through partnerships and outreach programs. Whole Foods Market serves as a model for businesses seeking to align profit with purpose, inspiring consumers to prioritize health, environmental sustainability, and social impact in their purchasing decisions.
How it works
Whole Foods Market, the renowned grocery chain synonymous with natural and organic foods, operates with a clear mission that extends beyond mere profitability. Founded in 1980 in Austin, Texas, by John Mackey and Renee Lawson Hardy, Whole Foods has grown into a global brand with over 500 stores in North America and the United Kingdom. At the heart of its operations lies a steadfast commitment to its mission statement, which encapsulates its values, goals, and vision for the future.
Central to Whole Foods Market’s mission is the promotion of healthy living through the provision of high-quality, natural, and organic products.
Embracing a holistic approach to wellness, the company emphasizes the importance of wholesome, minimally processed foods that nourish the body and support overall well-being. This dedication to offering products free from artificial additives, preservatives, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) resonates with health-conscious consumers seeking transparency and authenticity in their food choices.
Moreover, Whole Foods Market champions sustainability and environmental stewardship as core pillars of its mission. Recognizing the interconnectedness of human health and the health of the planet, the company strives to minimize its ecological footprint across all facets of its operations. From sourcing locally grown produce to reducing packaging waste and promoting energy efficiency, Whole Foods prioritizes initiatives that foster sustainability and mitigate environmental impact. By partnering with like-minded suppliers and implementing innovative practices, the company aims to lead by example in the pursuit of a more sustainable future.
In addition to its commitment to product quality and sustainability, Whole Foods Market prioritizes ethical business practices and community engagement. Upholding the principles of fair trade and responsible sourcing, the company cultivates relationships with farmers, artisans, and producers who share its values of integrity and social responsibility. Through initiatives such as the Whole Planet Foundation and community outreach programs, Whole Foods demonstrates its dedication to making a positive impact beyond the walls of its stores. By supporting local economies, empowering disadvantaged communities, and fostering a culture of inclusivity, the company endeavors to create meaningful change and strengthen the social fabric.
As Whole Foods Market continues to evolve in response to changing consumer preferences and market dynamics, its mission remains a guiding force that informs its decisions and actions. By staying true to its founding principles while embracing innovation and adaptation, the company endeavors to inspire others to embrace a healthier, more sustainable lifestyle. In an increasingly complex and interconnected world, Whole Foods Market stands as a beacon of integrity, offering not just products, but a vision of a better future for people and the planet.
In conclusion, Whole Foods Market’s mission statement encapsulates its commitment to promoting health, sustainability, and ethical business practices. With a focus on quality, transparency, and community engagement, the company strives to be a catalyst for positive change in the food industry and beyond. As consumers increasingly prioritize health, environmental sustainability, and social responsibility, Whole Foods Market serves as a model for businesses seeking to align profit with purpose.
Cite this page
Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/whole-foods-market-mission-statement-a-commitment-to-sustainable-practices-and-quality-products/
"Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/whole-foods-market-mission-statement-a-commitment-to-sustainable-practices-and-quality-products/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/whole-foods-market-mission-statement-a-commitment-to-sustainable-practices-and-quality-products/ [Accessed: 2 Jun. 2024]
"Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 2, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/whole-foods-market-mission-statement-a-commitment-to-sustainable-practices-and-quality-products/
"Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/whole-foods-market-mission-statement-a-commitment-to-sustainable-practices-and-quality-products/. [Accessed: 2-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Whole Foods Market Mission Statement: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Quality Products . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/whole-foods-market-mission-statement-a-commitment-to-sustainable-practices-and-quality-products/ [Accessed: 2-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

మంచి ముగింపును ఎలా వ్రాయాలి (ఉదాహరణలతో)
- స్మోడిన్ సంపాదకీయ బృందం
- ప్రచురణ: 31 మే, 2024
ముగింపును అనంతర ఆలోచనగా వదిలివేసేటప్పుడు విద్యార్థులు తరచుగా వ్యాస పరిచయాలను రూపొందించడానికి చాలా సమయాన్ని వెచ్చిస్తారు. ఉపోద్ఘాతం అనేది ఒక వ్యాసం యొక్క అత్యంత ముఖ్యమైన అంశాలలో ఒకటి అయితే, ఒక మంచి ముగింపు దాని ప్రభావంపై కూడా అంతే ప్రభావం చూపుతుంది. మంచి ముగింపును ఎలా వ్రాయాలో తెలుసుకోవడం చాలా ముఖ్యం, ఎందుకంటే ఇది మీ ప్రధాన అంశాలను పొందుపరుస్తుంది మరియు పాఠకులపై శాశ్వత ముద్ర వేస్తుంది.
చక్కగా రూపొందించబడిన ముగింపు మీ వాదనలకు చివరి పిచ్గా ఉపయోగపడుతుంది. మీ రీడర్ వారు ఇప్పుడే చదివిన దాని గురించి మరియు మీ థీసిస్ యొక్క కోర్కి ఎలా వర్తిస్తుంది అనేదానిపై స్పష్టమైన అవగాహనతో దూరంగా నడవాలి. సరైన విధానంతో, మీ ముగింపు మంచి వ్యాసాన్ని గొప్పగా మార్చగలదు, అది గుర్తుండిపోయేలా మరియు ప్రభావవంతంగా ఉంటుంది.
ఈ కథనం బలవంతపు ముగింపులను వ్రాయడానికి నాలుగు సాధారణ దశల ద్వారా మీకు మార్గనిర్దేశం చేస్తుంది. ప్రతి దశ మీ థీసిస్ను బలోపేతం చేయడంలో మరియు మీ ఉపాధ్యాయుడు లేదా ప్రొఫెసర్తో ప్రతిధ్వనించే విధంగా మీ తుది ఆలోచనలను వ్యక్తీకరించడంలో మీకు సహాయపడేలా రూపొందించబడింది. కొంచెం అభ్యాసంతో, మీరు ల్యాండింగ్ను ఎలా అంటుకోవాలో నేర్చుకోవచ్చు మరియు ప్రతి వ్యాసానికి అర్హమైన ముగింపును అందించవచ్చు.
ముగింపు పేరా యొక్క ఉద్దేశ్యం ఏమిటి?
ప్రభావవంతమైన వ్యాస రచన కోసం ముగింపు పేరా యొక్క ఉద్దేశ్యాన్ని అర్థం చేసుకోవడం చాలా అవసరం. ముగింపు పేరా మీ వ్యాసం యొక్క సారాంశం కంటే ఎక్కువగా ఉండాలి. ఇది ఏకీకృతం చేయాలి అన్ని మీ వాదనలు మరియు వాటిని తిరిగి మీ థీసిస్తో ముడిపెట్టండి.
గుర్తుంచుకోండి, అన్ని మంచి రచనలు భావోద్వేగాన్ని ప్రేరేపిస్తాయి. ప్రేరేపించడం, రెచ్చగొట్టడం లేదా నిమగ్నం చేయాలా అనేది మీ ఇష్టం, కానీ ముగింపు ఎల్లప్పుడూ శాశ్వతమైన ముద్ర వేయాలి.
అనుమానం ఉంటే, స్మోడిన్ యొక్క AI చాట్ మీ ముగింపు యొక్క భావోద్వేగ ప్రభావాన్ని అంచనా వేయడానికి సాధనం ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
శక్తివంతమైన ముగింపును వ్రాయడంలో నైపుణ్యం సాధించడం ద్వారా, మీ వ్యాసాలు ప్రత్యేకంగా ఉండేలా చూసుకోవడానికి మీరు సాధనాలతో మిమ్మల్ని మీరు సిద్ధం చేసుకుంటారు. ఇది మీరు తరగతి కోసం వ్రాసే మొదటి లేదా చివరి వ్యాసం అయినా, మీ పాఠకుడిపై ఖచ్చితమైన గుర్తును ఉంచడానికి ఇది మీ అవకాశం.
మంచి ముగింపును ఎలా వ్రాయాలి

ఈ విధానం మీ ముగింపు విలువను జోడిస్తుంది మరియు మీ వాదనల పొందికను బలపరుస్తుంది. మీరు దృఢమైన ముగింపును రూపొందించడంలో సహాయపడటానికి ఇక్కడ మూడు సులభమైన మరియు ప్రభావవంతమైన అభ్యాసాలు ఉన్నాయి.
మీ థీసిస్ని పునఃప్రారంభించడం
ముగింపులో మీ థీసిస్ను పునఃప్రారంభించడం అనేది వ్యాస రచనలో ఒక సాధారణ అభ్యాసం మరియు మంచి కారణం కోసం. మీరు అందించిన సాక్ష్యాధారాల ఆధారంగా మీ అవగాహన ఎలా లోతుగా పెరిగింది లేదా మార్చబడింది అనేది నొక్కి చెప్పడంలో సహాయపడుతుంది.
కేవలం అర్థం చేసుకోండి a పునః మీ అసలు థీసిస్ పూర్తి అని అర్థం కాదు పదం పదం పునరావృతం. మీరు మీ ఒరిజినల్ థీసిస్ను తిరిగి వ్రాయాలి, తద్వారా మీరు వ్యాసం అంతటా తాకిన అంతర్దృష్టులను ఇది విశదపరుస్తుంది. స్మోడిన్ యొక్క AI రీరైటర్ మీ రీస్టేట్మెంట్ తాజాగా మరియు ప్రభావవంతంగా ఉందని నిర్ధారించుకోవడానికి దాన్ని మెరుగుపరచడంలో సహాయపడుతుంది.
మీ థీసిస్ను ప్రభావవంతంగా పునఃప్రారంభించేందుకు ఇక్కడ కొన్ని చిట్కాలు ఉన్నాయి
- సంక్లిష్టతను చూపించు : మీ వ్యాసం ఒరిజినల్ స్టేట్మెంట్కు లేయర్లు లేదా సూక్ష్మ నైపుణ్యాలను జోడించినట్లయితే, దానిని స్పష్టంగా వ్యక్తీకరించండి.
- కీ అన్వేషణలను ఏకీకృతం చేయండి : వారు మీ థీసిస్కు ఎలా మద్దతు ఇచ్చారో లేదా శుద్ధి చేశారో పటిష్టం చేయడానికి మీ వ్యాసంలోని ప్రధాన ఫలితాలను పొందుపరచండి.
- తాజాగా ఉంచండి : మళ్ళీ, మీరు ఒకే విషయాలను రెండుసార్లు పునరావృతం చేయకుండా ఉండాలనుకుంటున్నారు. సూక్ష్మ దృక్పథాన్ని ప్రతిబింబించే విభిన్న పదాలను ఉపయోగించండి.
చివరగా, పునఃప్రారంభించబడిన థీసిస్ మీ మిగిలిన వ్యాసంతో సజావుగా కనెక్ట్ అవుతుందని ఎల్లప్పుడూ నిర్ధారించుకోండి. పాఠకుడికి బలమైన మూసివేత భావనను అందించడానికి ఎల్లప్పుడూ మీ రచన యొక్క పొందికను ప్రదర్శించడానికి ప్రయత్నించండి.
వంటి AI సాధనాలను ఉపయోగించడం స్మోడిన్ యొక్క అవుట్లైనర్ మరియు ఎస్సే రైటర్ మీ రచన సజావుగా సాగుతుందని మరియు అనుసరించడం సులభం అని నిర్ధారించుకోవచ్చు.
ప్రభావవంతమైన సంశ్లేషణను అందించడం
సమర్థవంతమైన సంశ్లేషణను అందించడం మీ అసలు థీసిస్ను మెరుగుపరుస్తుంది. అన్ని మంచి వాదనలు వ్యాసం అంతటా అభివృద్ధి చెందుతాయి మరియు మారాలి. ఈ ఫలితాలను సంగ్రహించడం కంటే, మీరు లోతైన లేదా మరింత సూక్ష్మమైన అవగాహనను ప్రదర్శించడానికి క్లిష్టమైన అంతర్దృష్టులు మరియు సాక్ష్యాలను ఏకీకృతం చేయాలి.
చర్చించబడిన ప్రధాన అంశాల మధ్య కనెక్షన్లను గీయండి మరియు అవి మీ థీసిస్కు సమిష్టిగా ఎలా మద్దతిస్తాయో చూపండి. అలాగే, మీ విషయం యొక్క విస్తృత సందర్భం కోసం ఈ అంతర్దృష్టుల యొక్క చిక్కులను ప్రతిబింబించండి. మరియు మరోసారి, పాఠకుల ఆసక్తిని కొనసాగించడానికి ఎల్లప్పుడూ తాజా మరియు ఆకర్షణీయమైన భాషను ఉపయోగించండి.
మీకు కావలసిన చివరి విషయం ఏమిటంటే, మీ పాఠకుడు మీ వ్యాసాన్ని వ్యక్తిగత పాయింట్ల సమాహారంగా చూడటం. ఒక మంచి వ్యాసం ఏకీకృత మొత్తంగా చదవాలి, అన్ని ముక్కలు సహజంగా కలిసి ఉంటాయి. మీరు మీ ముగింపులో అన్ని ముక్కలను కలిపి ఉంచినప్పుడు మీ వాదన యొక్క ప్రాముఖ్యతను మీరు ధృవీకరిస్తారు.
కొత్త అంతర్దృష్టులను అందిస్తోంది

అలాగే, మీ పరిశోధనల ఆధారంగా భవిష్యత్ పరిశోధన దిశలను ప్రతిపాదించడానికి ఈ దశను మీ అవకాశంగా భావించండి. ఒక విద్యార్థి లేదా పరిశోధకుడు తర్వాత ఏమి చదువుకోవచ్చు? సమాధానం లేని ప్రశ్నలు ఏవి మిగిలి ఉన్నాయి? ఈ ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానమివ్వడంలో మీకు సమస్య ఉంటే, ఉపయోగించడాన్ని పరిగణించండి స్మోడిన్ పరిశోధన సాధనాలు అంశం గురించి మీ జ్ఞానాన్ని విస్తరించడానికి.
మీరు మీ స్వంత థీసిస్ గురించి ఓపెన్-ఎండ్ లేదా సమాధానం లేని ప్రశ్నలను వదిలివేయవచ్చని చెప్పడం కాదు. దీనికి విరుద్ధంగా, మీ ముగింపు మీ వాదన యొక్క ప్రామాణికతను దృఢంగా నిర్ధారించాలి. ఏదైనా లోతైన మరియు తెలివైన విశ్లేషణ సహజంగా మరింత అన్వేషణకు దారి తీస్తుంది. విచారణ యొక్క ఈ సంభావ్య ప్రాంతాలపై దృష్టిని ఆకర్షించండి.
(ఐచ్ఛికం) రీడర్తో వ్యక్తిగత సంబంధాన్ని ఏర్పరుచుకోండి
ముగింపులో రీడర్తో కనెక్షన్ని ఏర్పరచుకోవడం ద్వారా మీ వ్యాసం యొక్క ప్రభావాన్ని వ్యక్తిగతీకరించవచ్చు మరియు బలోపేతం చేయవచ్చు. ఈ సాంకేతికత సరిగ్గా అమలు చేయబడితే శక్తివంతమైనది, మీ రచనను మరింత సాపేక్షంగా, మానవీయంగా మరియు చిరస్మరణీయంగా చేస్తుంది.
స్లిమ్ విద్యావేత్తలు అధికారిక వ్యాసాలలో "I"ని ఉపయోగించడాన్ని నిరుత్సాహపరుస్తారు. మీ గురువు లేదా ప్రొఫెసర్ వైఖరిని స్పష్టం చేయడం ఎల్లప్పుడూ ఉత్తమం ముందు మీ చివరి డ్రాఫ్ట్ను సమర్పించడం.
ఇది అనుమతించబడితే, మీ వ్యాసం యొక్క ప్రధాన ఇతివృత్తాలతో ముడిపడి ఉన్న సంక్షిప్త వ్యక్తిగత ప్రతిబింబం లేదా వృత్తాంతాన్ని భాగస్వామ్యం చేయండి. మీ వాదనలను మానవీకరించడానికి మరియు రీడర్తో కనెక్షన్ని సృష్టించడానికి వ్యక్తిగత స్పర్శ చాలా దూరం ఉంటుంది.
మీరు ఏది ఎంచుకున్నా, మీ ముగింపు ఎల్లప్పుడూ మీ వ్యాసం యొక్క విశ్లేషణాత్మక ఫలితాలను పూర్తి చేయాలని గుర్తుంచుకోండి. మీ థీసిస్ నుండి లేదా మీరు సమర్పించిన ఫలితాల నుండి తీసివేయబడే ఏదీ ఎప్పుడూ చెప్పకండి.
మంచి ముగింపులకు ఉదాహరణలు
చక్కగా రూపొందించబడిన ముగింపు ఎలా ఉంటుందో మరియు ఎలా ఉంటుందో వివరించడానికి కొన్ని ఉదాహరణలను అన్వేషిద్దాం. సైన్స్ మరియు సాహిత్య రంగాల నుండి క్రింది రెండు ఊహాత్మక థీసిస్ వ్యాసాలు ఉన్నాయి.
- థీసిస్ అంశం: పగడపు దిబ్బలపై వాతావరణ మార్పు ప్రభావం
- పరిచయం: “పగడపు దిబ్బలు సముద్ర జీవవైవిధ్యానికి సంరక్షకులుగా పనిచేస్తాయి. ఈ నీటి అడుగున పర్యావరణ వ్యవస్థలు మొత్తం గ్రహం మీద అత్యంత శక్తివంతమైన మరియు అవసరమైన వాటిలో ఒకటి. అయినప్పటికీ, పెరుగుతున్న వాతావరణ మార్పుల ప్రభావం వారి ఆరోగ్యానికి మరియు మనుగడకు తీవ్ర ముప్పును కలిగిస్తుంది. ఈ వ్యాసం పగడపు క్షీణతకు దోహదపడే నిర్దిష్ట పర్యావరణ మార్పులను విడదీయడం లక్ష్యంగా పెట్టుకుంది, అయితే ఉపశమన చర్యలను ప్రతిపాదిస్తుంది.
- ముగింపు: "పగడపు దిబ్బలపై వాతావరణ మార్పుల ప్రభావంపై ఈ పరిశోధన పగడపు బ్లీచింగ్ సంఘటనల యొక్క అవాంతర త్వరణం మరియు రీఫ్ జీవవైవిధ్యం యొక్క గణనీయమైన క్షీణతను వెల్లడించింది. ఈ అధ్యయనంలో సమర్పించబడిన ఫలితాలు పెరిగిన సముద్ర ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు మరియు పగడపు దిబ్బల మరణాల మధ్య స్పష్టమైన సంబంధాన్ని ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. భవిష్యత్ పరిశోధనలు పరిరక్షణ వ్యూహాలను ప్రభావితం చేసే పగడపు జాతుల యొక్క స్థితిస్థాపకత విధానాలపై దృష్టి పెట్టాలి. పగడపు దిబ్బల విధి ప్రపంచ ఉద్గారాలను అరికట్టడానికి మరియు భవిష్యత్ తరాలకు ఈ కీలక పర్యావరణ వ్యవస్థలను సంరక్షించడానికి మానవత్వం యొక్క తక్షణ మరియు కేంద్రీకృత చర్యపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది.
ముగింపు కేవలం థీసిస్ను ఎలా పునరుద్ఘాటించలేదని గమనించండి. బదులుగా, ఇది వాతావరణ మార్పు మరియు పగడపు ఆరోగ్యం మధ్య ఖచ్చితమైన సంబంధాన్ని హైలైట్ చేస్తుంది. ఇది సమస్య యొక్క ఆవశ్యకతను పునరుద్ఘాటిస్తుంది మరియు కొనసాగుతున్న జోక్యానికి చర్య యొక్క పిలుపుని కూడా విస్తరిస్తుంది. చివరి వాక్యం సూటిగా, పాయింట్కి సంబంధించినది మరియు పాఠకులపై శాశ్వత ముద్ర వేస్తుంది.
మీరు మీ ముగింపు వాక్యంతో పోరాడుతున్నట్లయితే (లేదా ఏదైనా వాక్యం, దాని కోసం) స్మోడిన్ యొక్క రీరైటర్ సెకన్లలో వందలాది విభిన్న వాక్యాలను సృష్టించగలదు. ఆపై, అత్యంత ప్రతిధ్వనించే వాక్యాలను మరియు పదబంధాలను ఎంచుకోండి మరియు బలవంతపు ముగింపును రూపొందించడానికి వాటిని ఉపయోగించండి.
- థీసిస్ అంశం: 20వ శతాబ్దపు అమెరికన్ సాహిత్యంలో అమెరికన్ డ్రీం యొక్క పరిణామం
- పరిచయం: "అమెరికన్ డ్రీం ఒకప్పుడు శ్రేయస్సు మరియు విజయం ద్వారా నిర్వచించబడింది. అయినప్పటికీ, 20వ శతాబ్దం అంతటా, ప్రముఖ సాహిత్యంలో అమెరికన్ డ్రీం యొక్క ప్రాతినిధ్యం గణనీయమైన మార్పులకు గురైంది. ఈ ప్రాతినిధ్యాలు అమెరికన్ ప్రజలలో నిద్రాణమైన సుదూర భావాన్ని సూచిస్తున్నాయా? లేదా ఈ రచనలు కేవలం భ్రమలకు లోనైన రచయితలు కాలంలోని అభివృద్ధి చెందుతున్న సవాళ్లకు ప్రతిస్పందించిన ఫలితమా?
- ముగింపు: "F. స్కాట్ ఫిట్జ్గెరాల్డ్, జాన్ స్టెయిన్బెక్ మరియు టోని మోరిసన్ రచనలు అమెరికన్ డ్రీమ్ యొక్క హద్దులేని ఆశావాదం నుండి అమెరికన్ ఎథోస్ యొక్క మరింత క్లిష్టమైన పరిశీలన వరకు పరిణామాన్ని వివరిస్తాయి. ఆధునికవాద మరియు పోస్ట్-మాడర్నిస్ట్ సాహిత్యం అంతటా, అమెరికన్ డ్రీం తరచుగా ప్రధాన అమెరికన్ విలువలతో విభేదిస్తుంది. ఈ నవలలు విస్తృత సామాజిక మార్పులను ప్రతిబింబిస్తాయి, ఇవి జాతీయ చైతన్యాన్ని ఆకృతి చేయడం కొనసాగించాయి. సమకాలీన సాహిత్యంపై మరింత పరిశోధన ఈ భావన యొక్క సంక్లిష్టతలపై ఎక్కువ అవగాహనను అందిస్తుంది."
పరిచయం మరియు ముగింపు మాత్రమే చదవడం ద్వారా ఈ వ్యాసం ఏమి కవర్ చేస్తుందో మీకు ఖచ్చితంగా తెలుస్తుంది. ఇది ముగ్గురు ప్రత్యేక రచయితల రచనలను పరిశీలించడం ద్వారా అమెరికన్ డ్రీం యొక్క పరిణామాన్ని సంగ్రహిస్తుంది. ఈ రచనలు విస్తృత సామాజిక మార్పులను ఎలా ప్రతిబింబిస్తాయో ప్రదర్శించడానికి ఇది విశ్లేషిస్తుంది. భవిష్యత్ విచారణలకు వేదికను సెట్ చేయడానికి ముగింపు ఒక క్యాప్స్టోన్ మరియు వంతెనగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
స్మోడిన్తో మెరుగైన ముగింపులను వ్రాయండి
దాని వెనుక ఉన్న మానవ మూలకాన్ని ఎల్లప్పుడూ గుర్తుంచుకోండి గ్రేడింగ్ ప్రక్రియ మీ వ్యాసాన్ని రూపొందించేటప్పుడు. మీ ఉపాధ్యాయులు లేదా ప్రొఫెసర్లు మనుషులు మరియు ఇలాంటి అంశాలపై వ్యాసాలను సమీక్షించడానికి లెక్కలేనన్ని గంటలు గడిపారు. గ్రేడింగ్ ప్రక్రియ సుదీర్ఘంగా మరియు సమగ్రంగా ఉంటుంది. మీ ముగింపు వారి పనిని సులభతరం చేయడం లక్ష్యంగా ఉండాలి, కష్టతరం కాదు.
చక్కగా రూపొందించబడిన ముగింపు మీ వాదనకు చివరి భాగం. ఇది అంశంపై కొత్త వెలుగును నింపేటప్పుడు పైన చర్చించిన క్లిష్టమైన అంతర్దృష్టులను పునశ్చరణ చేయాలి. వినూత్న అంశాలు మరియు అంతర్దృష్టి పరిశీలనలను చేర్చడం ద్వారా, మీ ముగింపు మీ వ్యాసం గుంపు నుండి నిలబడటానికి సహాయపడుతుంది.
ఇప్పుడు మరియు భవిష్యత్తులో మెరుగైన గ్రేడ్ను పొందే అవకాశాలను పెంచుకోవడానికి మీ వ్యాసం అధిక గమనికతో ముగుస్తుందని నిర్ధారించుకోండి. స్మోడిన్ యొక్క AI సాధనాల సమగ్ర సూట్ మీ వ్యాస రచన యొక్క ప్రతి అంశాన్ని మెరుగుపరచడంలో మీకు సహాయపడుతుంది. ప్రారంభ పరిశోధన నుండి నిర్మాణాత్మకంగా, ఈ సాధనాలు ప్రక్రియను క్రమబద్ధీకరించగలవు మరియు మీ వ్యాసాల నాణ్యతను మెరుగుపరుస్తాయి.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This article provides an effective technique for writing a conclusion adapted from Erika Eby's The College Student's Guide to Writing a Good Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips & Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out.. While the thesis introduction starts out with broad statements about the topic, and then narrows it down to the thesis statement, a thesis conclusion does the same in the opposite order.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Step 1: Answer your research question. Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles.
In an argumentative paper, you will have presented a thesis statement in your introduction, expressing the overall claim your paper argues for. In the conclusion, you should restate the thesis and show how it has been developed through the body of the paper. ... Research paper conclusion examples. Full examples of research paper conclusions are ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Some universities will prefer that you cover some of these points in the discussion chapter, or that you cover the points at different levels in different chapters. Step 1: Craft a brief introduction section. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the conclusions chapter needs to start with a brief introduction.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Summarizes the Main Points. The conclusion summarizes the main points of the thesis and presents them in a concise manner, making it easier for the reader to understand the overall message of the thesis. Reiterates the Thesis Statement. The conclusion reiterates the thesis statement and reminds the reader of the central argument of the thesis.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go.
Here is the best format for how to end a research paper or thesis. Start by answering the thesis question: Your conclusion should commence by restating the main thesis question that you anticipate answering. Finally, you have the opportunity to answer the question. Ensure the answer is clear and concise.
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
Depending on the complexity of your research and document length, the length will differ. The thesis or dissertation conclusion should be 5-7% of your paper's overall word count. For example, if your thesis is 30,000 words, the conclusion can be 1,500-2100 words. The conclusion for empirical or scientific theses or dissertations is often brief.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Also read: How to Write a Thesis Statement. 2. Tying together the main points. Tying together all the main points of your essay does not mean simply summarizing them in an arbitrary manner. The key is to link each of your main essay points in a coherent structure. One point should follow the other in a logical format.
What your thesis statement includes is determined by three things: 1. The subject and topic of the essay. 2. The purpose of the essay. 3. The length of the essay. Let's examine each of those in more detail to see how they can help us refine our thesis statement.
Step 3: Make future recommendations. You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms. Example: Recommendation sentence.
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
The conclusion paragraph should be more than just a summary of your essay. It should consolidate all your arguments and tie them back to your thesis. Remember, all good writing inspires emotion. Whether to inspire, provoke, or engage is up to you, but the conclusion should always leave a lasting impression.
In conclusion, the argumentative thesis statement is the heart and soul of your persuasive composition.It shapes the theme, sets the tone, and guides the exploration of your chosen subject. Through careful consideration of your topic, audience, and the cause-and-effect relationships at play, you can draft a compelling and impactful thesis statement that forms the backbone of your argument.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Here are a few tips to effectively restate your thesis. Show Complexity: If your essay added layers or nuances to the original statement, be sure to articulate that clearly. Integrate Key Findings: Incorporate the main findings of your essay to reinforce how they supported or refined your thesis.
Guide of tips and tricks on How to write a thesis statement: 1. Selecting the topic: The thesis writing service must always work on a topic that pulls out attention and interest, this is to do ...
Examples of Good Conclusions. Let's explore some examples to illustrate what a well-crafted conclusion looks and sounds like. The following are two hypothetical thesis essays from the fields of science and literature. teadus. Thesis Topic: Kliimamuutuste mõju korallriffidele; Sissejuhatus: "Coral reefs act as the guardians of the ocean's ...
Creating a personal philosophy statement is a profound exercise in self-reflection and articulation of one's core beliefs and values. It is not merely a document but a vivid representation of an individual's guiding principles and ethical framework. This statement serves as a compass, providing direction and clarity in both personal and ...
This essay about State Farm's mission statement explains how the company's core values shape its operations and customer interactions. The mission, "To help people manage the risks of everyday life, recover from the unexpected, and realize their dreams," highlights State Farm's commitment to risk management, efficient recovery support, and enabling customers to pursue their goals.
In conclusion, Whole Foods Market's mission statement encapsulates its commitment to promoting health, sustainability, and ethical business practices. With a focus on quality, transparency, and community engagement, the company strives to be a catalyst for positive change in the food industry and beyond.
The conclusion paragraph should be more than just a summary of your essay. It should consolidate అన్ని your arguments and tie them back to your thesis. Remember, all good writing inspires emotion. Whether to inspire, provoke, or engage is up to you, but the conclusion should always leave a lasting impression.