
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

16.2 Sociological Perspectives on Education
Learning objectives.
- List the major functions of education.
- Explain the problems that conflict theory sees in education.
- Describe how symbolic interactionism understands education.
The major sociological perspectives on education fall nicely into the functional, conflict, and symbolic interactionist approaches (Ballantine & Hammack, 2009). Table 16.1 “Theory Snapshot” summarizes what these approaches say.
Table 16.1 Theory Snapshot
The Functions of Education
Functional theory stresses the functions that education serves in fulfilling a society’s various needs. Perhaps the most important function of education is socialization . If children need to learn the norms, values, and skills they need to function in society, then education is a primary vehicle for such learning. Schools teach the three Rs, as we all know, but they also teach many of the society’s norms and values. In the United States, these norms and values include respect for authority, patriotism (remember the Pledge of Allegiance?), punctuality, individualism, and competition. Regarding these last two values, American students from an early age compete as individuals over grades and other rewards. The situation is quite the opposite in Japan, where, as we saw in Chapter 4 “Socialization” , children learn the traditional Japanese values of harmony and group belonging from their schooling (Schneider & Silverman, 2010). They learn to value their membership in their homeroom, or kumi , and are evaluated more on their kumi ’s performance than on their own individual performance. How well a Japanese child’s kumi does is more important than how well the child does as an individual.
A second function of education is social integration . For a society to work, functionalists say, people must subscribe to a common set of beliefs and values. As we saw, the development of such common views was a goal of the system of free, compulsory education that developed in the 19th century. Thousands of immigrant children in the United States today are learning English, U.S. history, and other subjects that help prepare them for the workforce and integrate them into American life. Such integration is a major goal of the English-only movement, whose advocates say that only English should be used to teach children whose native tongue is Spanish, Vietnamese, or whatever other language their parents speak at home. Critics of this movement say it slows down these children’s education and weakens their ethnic identity (Schildkraut, 2005).
A third function of education is social placement . Beginning in grade school, students are identified by teachers and other school officials either as bright and motivated or as less bright and even educationally challenged. Depending on how they are identified, children are taught at the level that is thought to suit them best. In this way they are prepared in the most appropriate way possible for their later station in life. Whether this process works as well as it should is an important issue, and we explore it further when we discuss school tracking shortly.
Social and cultural innovation is a fourth function of education. Our scientists cannot make important scientific discoveries and our artists and thinkers cannot come up with great works of art, poetry, and prose unless they have first been educated in the many subjects they need to know for their chosen path.
Figure 16.1 The Functions of Education
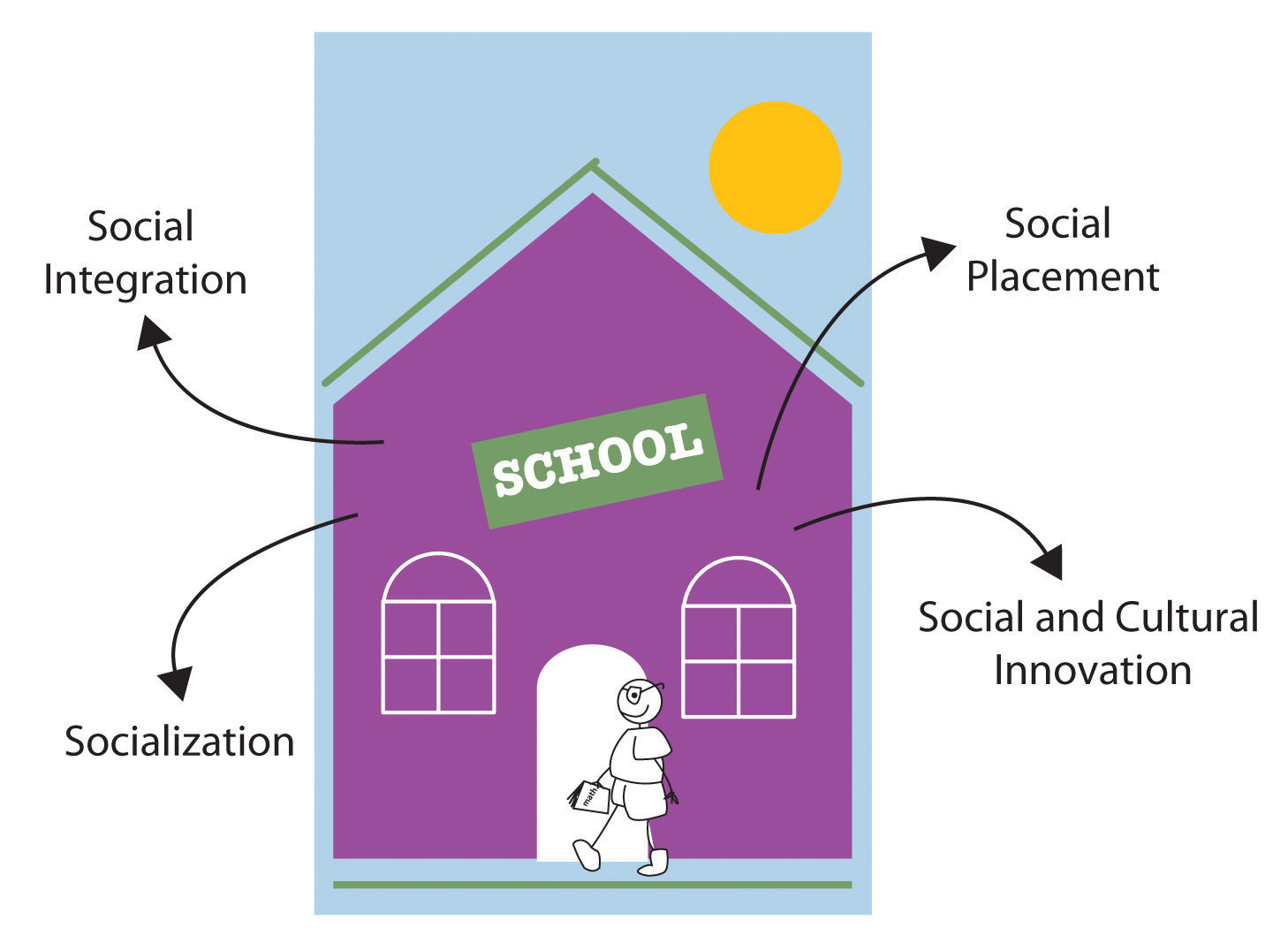
Schools ideally perform many important functions in modern society. These include socialization, social integration, social placement, and social and cultural innovation.
Education also involves several latent functions, functions that are by-products of going to school and receiving an education rather than a direct effect of the education itself. One of these is child care . Once a child starts kindergarten and then first grade, for several hours a day the child is taken care of for free. The establishment of peer relationships is another latent function of schooling. Most of us met many of our friends while we were in school at whatever grade level, and some of those friendships endure the rest of our lives. A final latent function of education is that it keeps millions of high school students out of the full-time labor force . This fact keeps the unemployment rate lower than it would be if they were in the labor force.
Education and Inequality
Conflict theory does not dispute most of the functions just described. However, it does give some of them a different slant and talks about various ways in which education perpetuates social inequality (Hill, Macrine, & Gabbard, 2010; Liston, 1990). One example involves the function of social placement. As most schools track their students starting in grade school, the students thought by their teachers to be bright are placed in the faster tracks (especially in reading and arithmetic), while the slower students are placed in the slower tracks; in high school, three common tracks are the college track, vocational track, and general track.
Such tracking does have its advantages; it helps ensure that bright students learn as much as their abilities allow them, and it helps ensure that slower students are not taught over their heads. But, conflict theorists say, tracking also helps perpetuate social inequality by locking students into faster and lower tracks. Worse yet, several studies show that students’ social class and race and ethnicity affect the track into which they are placed, even though their intellectual abilities and potential should be the only things that matter: white, middle-class students are more likely to be tracked “up,” while poorer students and students of color are more likely to be tracked “down.” Once they are tracked, students learn more if they are tracked up and less if they are tracked down. The latter tend to lose self-esteem and begin to think they have little academic ability and thus do worse in school because they were tracked down. In this way, tracking is thought to be good for those tracked up and bad for those tracked down. Conflict theorists thus say that tracking perpetuates social inequality based on social class and race and ethnicity (Ansalone, 2006; Oakes, 2005).
Social inequality is also perpetuated through the widespread use of standardized tests. Critics say these tests continue to be culturally biased, as they include questions whose answers are most likely to be known by white, middle-class students, whose backgrounds have afforded them various experiences that help them answer the questions. They also say that scores on standardized tests reflect students’ socioeconomic status and experiences in addition to their academic abilities. To the extent this critique is true, standardized tests perpetuate social inequality (Grodsky, Warren, & Felts, 2008).
As we will see, schools in the United States also differ mightily in their resources, learning conditions, and other aspects, all of which affect how much students can learn in them. Simply put, schools are unequal, and their very inequality helps perpetuate inequality in the larger society. Children going to the worst schools in urban areas face many more obstacles to their learning than those going to well-funded schools in suburban areas. Their lack of learning helps ensure they remain trapped in poverty and its related problems.
Conflict theorists also say that schooling teaches a hidden curriculum , by which they mean a set of values and beliefs that support the status quo, including the existing social hierarchy (Booher-Jennings, 2008) (see Chapter 4 “Socialization” ). Although no one plots this behind closed doors, our schoolchildren learn patriotic values and respect for authority from the books they read and from various classroom activities.
Symbolic Interactionism and School Behavior
Symbolic interactionist studies of education examine social interaction in the classroom, on the playground, and in other school venues. These studies help us understand what happens in the schools themselves, but they also help us understand how what occurs in school is relevant for the larger society. Some studies, for example, show how children’s playground activities reinforce gender-role socialization. Girls tend to play more cooperative games, while boys play more competitive sports (Thorne, 1993) (see Chapter 11 “Gender and Gender Inequality” ).
Another body of research shows that teachers’ views about students can affect how much the students learn. When teachers think students are smart, they tend to spend more time with them, to call on them, and to praise them when they give the right answer. Not surprisingly these students learn more because of their teachers’ behavior. But when teachers think students are less bright, they tend to spend less time with them and act in a way that leads the students to learn less. One of the first studies to find this example of a self-fulfilling prophecy was conducted by Robert Rosenthal and Lenore Jacobson (1968). They tested a group of students at the beginning of the school year and told their teachers which students were bright and which were not. They tested the students again at the end of the school year; not surprisingly the bright students had learned more during the year than the less bright ones. But it turned out that the researchers had randomly decided which students would be designated bright and less bright. Because the “bright” students learned more during the school year without actually being brighter at the beginning, their teachers’ behavior must have been the reason. In fact, their teachers did spend more time with them and praised them more often than was true for the “less bright” students. To the extent this type of self-fulfilling prophecy occurs, it helps us understand why tracking is bad for the students tracked down.

Research guided by the symbolic interactionist perspective suggests that teachers’ expectations may influence how much their students learn. When teachers expect little of their students, their students tend to learn less.
ijiwaru jimbo – Pre-school colour pack – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Other research focuses on how teachers treat girls and boys. Several studies from the 1970s through the 1990s found that teachers call on boys more often and praise them more often (American Association of University Women Educational Foundation, 1998; Jones & Dindia, 2004). Teachers did not do this consciously, but their behavior nonetheless sent an implicit message to girls that math and science are not for girls and that they are not suited to do well in these subjects. This body of research stimulated efforts to educate teachers about the ways in which they may unwittingly send these messages and about strategies they could use to promote greater interest and achievement by girls in math and science (Battey, Kafai, Nixon, & Kao, 2007).
Key Takeaways
- According to the functional perspective, education helps socialize children and prepare them for their eventual entrance into the larger society as adults.
- The conflict perspective emphasizes that education reinforces inequality in the larger society.
- The symbolic interactionist perspective focuses on social interaction in the classroom, on school playgrounds, and at other school-related venues. Social interaction contributes to gender-role socialization, and teachers’ expectations may affect their students’ performance.
For Your Review
- Review how the functionalist, conflict, and symbolic interactionist perspectives understand and explain education. Which of these three approaches do you most prefer? Why?
American Association of University Women Educational Foundation. (1998). Gender gaps: Where schools still fail our children . Washington, DC: American Association of University Women Educational Foundation.
Ansalone, G. (2006). Tracking: A return to Jim Crow. Race, Gender & Class, 13 , 1–2.
Ballantine, J. H., & Hammack, F. M. (2009). The sociology of education: A systematic analysis (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Battey, D., Kafai, Y., Nixon, A. S., & Kao, L. L. (2007). Professional development for teachers on gender equity in the sciences: Initiating the conversation. Teachers College Record, 109 (1), 221–243.
Booher-Jennings, J. (2008). Learning to label: Socialisation, gender, and the hidden curriculum of high-stakes testing. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 29 , 149–160.
Grodsky, E., Warren, J. R., & Felts, E. (2008). Testing and social stratification in American education. Annual Review of Sociology, 34 (1), 385–404.
Hill, D., Macrine, S., & Gabbard, D. (Eds.). (2010). Capitalist education: Globalisation and the politics of inequality . New York, NY: Routledge; Liston, D. P. (1990). Capitalist schools: Explanation and ethics in radical studies of schooling . New York, NY: Routledge.
Jones, S. M., & Dindia, K. (2004). A meta-analystic perspective on sex equity in the classroom. Review of Educational Research, 74 , 443–471.
Oakes, J. (2005). Keeping track: How schools structure inequality (2nd ed.). New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Rosenthal, R., & Jacobson, L. (1968). Pygmalion in the classroom . New York, NY: Holt.
Schildkraut, D. J. (2005). Press “one” for English: Language policy, public opinion, and American identity . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Schneider, L., & Silverman, A. (2010). Global sociology: Introducing five contemporary societies (5th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Thorne, B. (1993). Gender play: Girls and boys in school . New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Sociology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Philosophy of Education
All human societies, past and present, have had a vested interest in education; and some wits have claimed that teaching (at its best an educational activity) is the second oldest profession. While not all societies channel sufficient resources into support for educational activities and institutions, all at the very least acknowledge their centrality—and for good reasons. For one thing, it is obvious that children are born illiterate and innumerate, and ignorant of the norms and cultural achievements of the community or society into which they have been thrust; but with the help of professional teachers and the dedicated amateurs in their families and immediate environs (and with the aid, too, of educational resources made available through the media and nowadays the internet), within a few years they can read, write, calculate, and act (at least often) in culturally-appropriate ways. Some learn these skills with more facility than others, and so education also serves as a social-sorting mechanism and undoubtedly has enormous impact on the economic fate of the individual. Put more abstractly, at its best education equips individuals with the skills and substantive knowledge that allows them to define and to pursue their own goals, and also allows them to participate in the life of their community as full-fledged, autonomous citizens.
But this is to cast matters in very individualistic terms, and it is fruitful also to take a societal perspective, where the picture changes somewhat. It emerges that in pluralistic societies such as the Western democracies there are some groups that do not wholeheartedly support the development of autonomous individuals, for such folk can weaken a group from within by thinking for themselves and challenging communal norms and beliefs; from the point of view of groups whose survival is thus threatened, formal, state-provided education is not necessarily a good thing. But in other ways even these groups depend for their continuing survival on educational processes, as do the larger societies and nation-states of which they are part; for as John Dewey put it in the opening chapter of his classic work Democracy and Education (1916), in its broadest sense education is the means of the “social continuity of life” (Dewey, 1916, 3). Dewey pointed out that the “primary ineluctable facts of the birth and death of each one of the constituent members in a social group” make education a necessity, for despite this biological inevitability “the life of the group goes on” (Dewey, 3). The great social importance of education is underscored, too, by the fact that when a society is shaken by a crisis, this often is taken as a sign of educational breakdown; education, and educators, become scapegoats.
It is not surprising that such an important social domain has attracted the attention of philosophers for thousands of years, especially as there are complex issues aplenty that have great philosophical interest. Even a cursory reading of these opening paragraphs reveals that they touch on, in nascent form, some but by no means all of the issues that have spawned vigorous debate down the ages; restated more explicitly in terms familiar to philosophers of education, the issues the discussion above flitted over were: education as transmission of knowledge versus education as the fostering of inquiry and reasoning skills that are conducive to the development of autonomy (which, roughly, is the tension between education as conservative and education as progressive, and also is closely related to differing views about human “perfectibility”—issues that historically have been raised in the debate over the aims of education); the question of what this knowledge, and what these skills, ought to be—part of the domain of philosophy of the curriculum; the questions of how learning is possible, and what is it to have learned something—two sets of issues that relate to the question of the capacities and potentialities that are present at birth, and also to the process (and stages) of human development and to what degree this process is flexible and hence can be influenced or manipulated; the tension between liberal education and vocational education, and the overlapping issue of which should be given priority—education for personal development or education for citizenship (and the issue of whether or not this is a false dichotomy); the differences (if any) between education and enculturation; the distinction between educating versus teaching versus training versus indoctrination; the relation between education and maintenance of the class structure of society, and the issue of whether different classes or cultural groups can—justly—be given educational programs that differ in content or in aims; the issue of whether the rights of children, parents, and socio-cultural or ethnic groups, conflict—and if they do, the question of whose rights should be dominant; the question as to whether or not all children have a right to state-provided education, and if so, should this education respect the beliefs and customs of all groups and how on earth would this be accomplished; and a set of complex issues about the relation between education and social reform, centering upon whether education is essentially conservative, or whether it can be an (or, the ) agent of social change.
It is impressive that most of the philosophically-interesting issues touched upon above, plus additional ones not alluded to here, were addressed in one of the early masterpieces of the Western intellectual tradition—Plato's Republic . A.N. Whitehead somewhere remarked that the history of Western philosophy is nothing but a series of footnotes to Plato, and if the Meno and the Laws are added to the Republic , the same is true of the history of educational thought and of philosophy of education in particular. At various points throughout this essay the discussion shall return to Plato, and at the end there shall be a brief discussion of the two other great figures in the field—Rousseau and Dewey. But the account of the field needs to start with some features of it that are apt to cause puzzlement, or that make describing its topography difficult. These include, but are not limited to, the interactions between philosophy of education and its parent discipline.
1.1 The open nature of philosophy and philosophy of education
1.2 the different bodies of work traditionally included in the field, 1.3 paradigm wars the diversity of, and clashes between, philosophical approaches, 2.1 the early work: c.d. hardie, 2.2 the dominant years: language, and clarification of key concepts, 2.3 countervailing forces, 2.4 a new guise contemporary social, political and moral philosophy, 3.1 philosophical disputes concerning empirical education research, 3.2 the content of the curriculum, and the aims and functions of schooling, 3.3 rousseau, dewey, and the progressive movement, 4. concluding remarks, bibliography, other internet resources, related entries, 1. problems in delineating the field.
There is a large—and ever expanding—number of works designed to give guidance to the novice setting out to explore the domain of philosophy of education; most if not all of the academic publishing houses have at least one representative of this genre on their list, and the titles are mostly variants of the following archetypes: The History and Philosophy of Education , The Philosophical Foundations of Education , Philosophers on Education , Three Thousand Years of Educational Wisdom , A Guide to the Philosophy of Education , and Readings in Philosophy of Education . The overall picture that emerges from even a sampling of this collective is not pretty; the field lacks intellectual cohesion, and (from the perspective taken in this essay) there is a widespread problem concerning the rigor of the work and the depth of scholarship—although undoubtedly there are islands, but not continents, of competent philosophical discussion of difficult and socially-important issues of the kind listed earlier. On the positive side—the obverse of the lack of cohesion—there is, in the field as a whole, a degree of adventurousness in the form of openness to ideas and radical approaches, a trait that is sometimes lacking in other academic fields. This is not to claim, of course, that taken individually philosophers of education are more open-minded than their philosophical cousins!
Part of the explanation for this diffuse state-of-affairs is that, quite reasonably, most philosophers of education have the goal (reinforced by their institutional affiliation with Schools of Education and their involvement in the initial training of teachers) of contributing not to philosophy but to educational policy and practice. This shapes not only their selection of topics, but also the manner in which the discussion is pursued; and this orientation also explains why philosophers of education—to a far greater degree, it is to be suspected, than their “pure” cousins—publish not in philosophy journals but in a wide range of professionally-oriented journals (such as Educational Researcher , Harvard Educational Review , Teachers College Record , Cambridge Journal of Education, Journal of Curriculum Studies , and the like). Some individuals work directly on issues of classroom practice, others identify as much with fields such as educational policy analysis, curriculum theory, teacher education, or some particular subject-matter domain such as math or science education, as they do with philosophy of education. It is still fashionable in some quarters to decry having one's intellectual agenda shaped so strongly as this by concerns emanating from a field of practice; but as Stokes (1997) has made clear, many of the great, theoretically-fruitful research programs in natural science had their beginnings in such practical concerns—as Pasteur's grounbreaking work illustrates. It is dangerous to take the theory versus practice dichotomy too seriously.
However, there is another consequence of this institutional housing of the vast majority of philosphers of education that is worth noting—one that is not found in a comparable way in philosophers of science, for example, who almost always are located in departments of philosophy—namely, that experience as a teacher, or in some other education-related role, is a qualification to become a philosopher of education that in many cases is valued at least as much as depth of philosophical training. (The issue is not that educational experience is irrelevant—clearly it can be highly pertinent—but it is that in the tradeoff with philosophical training, philosophy often loses.) But there are still other factors at work that contribute to the field's diffuseness, that all relate in some way to the nature of the discipline of philosophy itself.
In describing the field of philosophy, and in particular the sub-field that has come to be identified as philosophy of education, one quickly runs into a difficulty not found to anything like the same degree in other disciplines. For example, although there are some internal differences in opinion, nevertheless there seems to be quite a high degree of consensus within the domain of quantum physics about which researchers are competent members of the field and which ones are not, and what work is a strong contribution (or potential contribution). The very nature of philosophy, on the other hand, is “essentially contested”; what counts as a sound philosophical work within one school of thought, or socio-cultural or academic setting, may not be so-regarded (and may even be the focus of derision) in a different one. Coupled with this is the fact that the borders of the field are not policed, so that the philosophically-untrained can cross into it freely—indeed, over the past century or more a great many individuals from across the spectrum of real and pseudo disciplines have for whatever reason exercised their right to self-identify as members of this broad and loosely defined category of “philosophers” (as a few minutes spent browsing in the relevant section of a bookstore will verify).
In essence, then, there are two senses of the term “philosopher” and its cognates: a loose but common sense in which any individual who cogitates in any manner about such issues as the meaning of life, the nature of social justice, the essence of sportsmanship, the aims of education, the foundations of the school curriculum, or relationship with the Divine, is thereby a philosopher; and there is a more technical sense referring to those who have been formally trained or have acquired competence in one or more areas such as epistemology, metaphysics, moral philosophy, logic, philosophy of science, and the like. If this bifurcation presents a problem for adequately delineating the field of philosophy, the difficulties grow tenfold or more with respect to philosophy of education.
This essay offers a description and assessment of the field as seen by a scholar rooted firmly in the formal branch of “philosophy of education”, and moreover this branch as it has developed in the English-speaking world (some of which, of course, has been inspired by Continental philosophy); but first it is necessary to say a little more about the difficulties that confront the individual who sets out, without presuppositions, to understand the topography of “philosophy of education”.
It will not take long for a person who consults several of the introductory texts alluded to earlier to encounter a number of different bodies of work (loosely bounded to be sure) that have by one source or another been regarded as part of the domain of philosophy of education; the inclusion of some of these as part of the field is largely responsible for the diffuse topography described earlier. What follows is an informal and incomplete accounting.
First, there are works of advocacy produced by those non-technical, self-identified “philosophers” described above, who often have an axe to grind; they may wish to destroy (or to save) common schooling, support or attack some innovation or reform, shore-up or destroy the capitalist mode of production, see their own religion (or none at all) gain a foothold in the public schools, strengthen the place of “the basics” in the school curriculum, and so forth. While these topics certainly can be, and have been, discussed with due care, often they have been pursued in loose but impressive language where exhortation substitutes for argumentation—and hence sometimes they are mistaken for works of philosophy of education! In the following discussion this genre shall be passed over in silence.
Second, there is a corpus of work somewhat resembling the first, but where the arguments are tighter, and where the authors usually are individuals of some distinction whose insights are thought-provoking—possibly because they have a degree of familiarity with some branch of educational activity, having been teachers (or former teachers), school principals, religious leaders, politicians, journalists, and the like. While these works frequently touch on philosophical issues, they are not pursued to any philosophical depth and can hardly be considered as contributions to the scholarship of the discipline. However, some works in this genre are among the classics of “educational thought”—a more felicitous label than “philosophy of education”; cases in point would be the essays, pamphlets and letters of Thomas Arnold (headmaster of Rugby school), John Wesley (the founder of Methodism), J.H. (Cardinal) Newman, T.H. Huxley, and the writings on progressive schooling by A.S. Neill (of Summerhill school). Some textbooks even include extracts from the writings or recorded sayings of such figures as Thomas Jefferson, Ben Franklin, and Jesus of Nazareth (for the latter three, in works spanning more than half a century, see Ulich, 1950, and Murphy, 2006). Books and extracts in this genre—which elsewhere I have called “cultured reflection on education”—are often used in teacher-training courses that march under the banner of “educational foundations”, “introduction to educational thought”, or “introduction to philosophy of education”.
Third, there are a number of educational theorists and researchers, whose field of activity is not philosophy but—for example—might be human development or learning theory, who in their technical work and sometimes in their non-technical books and reflective essays explicitly raise philosophical issues or adopt philosophical modes of argumentation—and do so in ways worthy of careful study. If philosophy (including philosophy of education) is defined so as to include analysis and reflection at an abstract or “meta-level”, which undoubtedly is a domain where many philosophers labor, then these individuals should have a place in the annals of philosophy or philosophy of education; but too often, although not always, accounts of the field ignore them. Their work might be subjected to scrutiny for being educationally important, but their conceptual or philosophical contributions are rarely focused upon. (Philosophers of the physical and biological sciences are far less prone to make this mistake about the meta-level work of reflective scientists in these domains.)
The educational theorists and researchers I have in mind as exemplars here are the behaviorist psychologist B.F. Skinner (who among other things wrote about the fate of the notions of human freedom and dignity in the light of the development of a “science of behavior”, and who developed a model of human action and also of learning that eschewed the influence of mental entities such as motives, interests, and ideas and placed the emphasis instead upon “schedules of reinforcement”); the foundational figure in modern developmental psychology with its near-fixation on stage theories, Jean Piaget (who developed in an abstract and detailed manner a “genetic epistemology” that was related to his developmental research); and the social psychologist Lev Vygotsky (who argued that the development of the human youngster was indelibly shaped by social forces, so much so that approaches which focused on the lone individual and that were biologically-oriented—he had Piaget in mind here—were quite inadequate).
Fourth, and in contrast to the group above, there is a type of work that is traditionally but undeservedly given a prominent place in the annals of philosophy of education, and which thereby generates a great deal of confusion and misunderstanding about the field. These are the books and reflective essays on educational topics that were written by mainstream philosophers, a number of whom are counted among the greatest in the history of the discipline. The catch is this: Even great philosophers do not always write philosophy! The reflections being referred-to contain little if any philosophical argumentation, and usually they were not intended to be contributions to the literature on any of the great philosophical questions. Rather, they expressed the author's views (or even prejudices) on educational rather than philosophical problems, and sometimes—as in the case of Bertrand Russell's rollicking pieces defending progressive educational practices—they explicitly were “potboilers” written to make money. (In Russell's case the royalties were used to support a progressive school he was running with his current wife.) Locke, Kant, and Hegel also are among those who produced work of this genre.
John Locke is an interesting case in point. He had been requested by a cousin and her husband—possibly in part because of his medical training—to give advice on the upbringing of their son and heir; the youngster seems to have troubled his parents, most likely because he had learning difficulties. Locke, then in exile in Europe, wrote the parents a series of letters in which alongside sensible advice about such matters as the priorities in the education of a landed gentleman, and about making learning fun for the boy, there were a few strange items such as the advice that the boy should wear leaky shoes in winter so that he would be toughened-up! The letters eventually were printed in book form under the title Some Thoughts Concerning Education (1693), and seem to have had enormous influence down the ages upon educational practice; after two centuries the book had run through some 35 English editions and well over thirty foreign editions, and it is still in print and is frequently excerpted in books of readings in philosophy of education. In stark contrast, several of Locke's major philosophical writings—the Essay Concerning Human Understanding , and the Letter on Toleration —have been overlooked by most educational theorists over the centuries, even though they have enormous relevance for educational philosophy, theory, policy, and practice. It is especially noteworthy that the former of these books was the foundation for an approach to psychology—associationism—that thrived during the nineteenth century. In addition it stimulated interest in the processes of child development and human learning; Locke's model of the way in which the “blank tablet” of the human mind became “furnished” with simple ideas that were eventually combined or abstracted in various ways to form complex ideas, suggested to some that it might be fruitful to study this process in the course of development of a young child (Cleverley and Phillips, 1986).
Fifth, and finally, there is a large body of work that clearly falls within the more technically-defined domain of philosophy of education. Three historical giants of the field are Plato, Rousseau, and Dewey, and there are a dozen or more who would be in competition for inclusion along with them; the short-list of leading authors from the second-half of the 20 th century would include Richard Peters, Paul Hirst, and Israel Scheffler, with many jostling for the next places—but the choices become cloudy as we approach the present-day, for schisms between philosophical schools have to be negotiated.
It is important to note, too, that there is a sub-category within this domain of literature that is made-up of work by philosophers who are not primarily identified as philosophers of education, and who might or might not have had much to say directly about education, but whose philosophical work has been drawn upon by others and applied very fruitfully to educational issues. (A volume edited by Amelie Rorty contains essays on the education-related thought, or relevance, of many historically-important philosophers; significantly the essays are almost entirely written by philosophers rather than by members of the philosophy of education community. This is both their strength and weakness. See Rorty, 1998.)
The discussion will turn briefly to the difficulty in picturing the topography of the field that is presented by the influence of these philosophers.
As sketched earlier, the domain of education is vast, the issues it raises are almost overwhelmingly numerous and are of great complexity, and the social significance of the field is second to none. These features make the phenomena and problems of education of great interest to a wide range of socially-concerned intellectuals, who bring with them their own favored conceptual frameworks—concepts, theories and ideologies, methods of analysis and argumentation, metaphysical and other assumptions, criteria for selecting evidence that has relevance for the problems that they consider central, and the like. No wonder educational discourse has occasionally been likened to Babel, for the differences in backgrounds and assumptions means that there is much mutual incomprehension. In the midst of the melee sit the philosophers of education.
It is no surprise, then, to find that the significant intellectual and social trends of the past few centuries, together with the significant developments in philosophy, all have had an impact on the content and methods of argument in philosophy of education—Marxism, psycho-analysis, existentialism, phenomenology, positivism, post-modernism, pragmatism, neo-liberalism, the several waves of feminism, analytic philosophy in both its ordinary language and more formal guises, are merely the tip of the iceberg. It is revealing to note some of the names that were heavily-cited in a pair of recent authoritative handbooks in the field (according to the indices of the two volumes, and in alphabetical order): Adorno, Aristotle, Derrida, Descartes, Dewey, Habermas, Hegel, Horkheimer, Kant, Locke, Lyotard, Marx, Mill, Nietzsche, Plato, Rawls, Richard Rorty, Rousseau, and Wittgenstein (Curren 2003; Blake, Smeyers, Smith, and Standish 2003). Although this list conveys something of the diversity of the field, it fails to do it complete justice, for the influence of feminist philosophers is not adequately represented.
No one individual can have mastered work done by such a range of figures, representing as they do a number of quite different frameworks or approaches; and relatedly no one person stands as emblematic of the entire field of philosophy of education, and no one type of philosophical writing serves as the norm, either. At professional meetings, peace often reigns because the adherents of the different schools go their separate ways; but occasionally there are (intellectually) violent clashes, rivaling the tumult that greeted Derrida's nomination for an honorary degree at Cambridge in 1992. It is sobering to reflect that only a few decades have passed since practitioners of analytic philosophy of education had to meet in individual hotel rooms, late at night, at annual meetings of the Philosophy of Education Society in the USA, because phenomenologists and others barred their access to the conference programs; their path to liberation was marked by discord until, eventually, the compromise of “live and let live” was worked out (Kaminsky, 1996). Of course, the situation has hardly been better in the home discipline; an essay in Time magazine in 1966 on the state of the discipline of philosophy reported that adherents of the major philosophical schools “don't even understand one another”, and added that as a result “philosophy today is bitterly segregated. Most of the major philosophy departments and scholarly journals are the exclusive property of one sect or another” ( Time , reprinted in Lucas, 1969, 32). Traditionally there has been a time-lag for developments in philosophy to migrate over into philosophy of education, but in this respect at least the two fields have been on a par.
Inevitably, however, traces of discord remain, and some groups still feel disenfranchised, but they are not quite the same groups as a few decades ago—for new intellectual paradigms have come into existence, and their adherents are struggling to have their voices heard; and clearly it is the case that—reflecting the situation in 1966—many analytically-trained philosophers of education find postmodern writings incomprehensible while scholars in the latter tradition are frequently dismissive if not contemptuous of work done by the former group. In effect, then, the passage of time has made the field more—and not less—diffuse. All this is evident in a volume published in 1995 in which the editor attempted to break-down borders by initiating dialogue between scholars with different approaches to philosophy of education; her introductory remarks are revealing:
Philosophers of education reflecting on the parameters of our field are faced not only with such perplexing and disruptive questions as: What counts as Philosophy of Education and why?; but also Who counts as a philosopher of education and why?; and What need is there for Philosophy of Education in a postmodern context? Embedded in these queries we find no less provocative ones: What knowledge, if any, can or should be privileged and why?; and Who is in a position to privilege particular discursive practices over others and why? Although such questions are disruptive, they offer the opportunity to take a fresh look at the nature and purposes of our work and, as we do, to expand the number and kinds of voices participating in the conversation. (Kohli, 1995, xiv).
There is an inward-looking tone to the questions posed here: Philosophy of education should focus upon itself, upon its own contents, methods, and practitioners. And of course there is nothing new about this; for one thing, almost forty years ago a collection of readings—with several score of entries—was published under the title What is Philosophy of Education? (Lucas, 1969). It is worth noting, too, that the same attitude is not unknown in philosophy; Simmel is reputed to have said a century or so ago that philosophy is its own first problem.
Having described the general topography of the field of philosophy of education, the focus can change to pockets of activity where from the perspective of this author interesting philosophical work is being, or has been, done—and sometimes this work has been influential in the worlds of educational policy or practice. It is appropriate to start with a discussion of the rise and partial decline—but lasting influence of—analytic philosophy of education This approach (often called “APE” by both admirers and detractors) dominated the field in the English-speaking world for several decades after the second world war, and its eventual fate throws light on the current intellectual climate.
2. Analytic philosophy of education, and its influence
Conceptual analysis, careful assessment of arguments, the rooting out of ambiguity, the drawing of clarifying distinctions—which make up part at least of the philosophical analysis package—have been respected activities within philosophy from the dawn of the field. But traditionally they stood alongside other philosophical activities; in the Republic , for example, Plato was sometimes analytic, at other times normative, and on occasion speculative/metaphysical. No doubt it somewhat over-simplifies the complex path of intellectual history to suggest that what happened in the twentieth century—early on, in the home discipline itself, and with a lag of a decade or more in philosophy of education—is that philosophical analysis came to be viewed by some scholars as being the major philosophical activity (or set of activities), or even as being the only viable or reputable activity (for metaphysics was judged to be literally vacuous, and normative philosophy was viewed as being unable to provide compelling warrants for whatever moral and ethical positions were being advocated).
So, although analytic elements in philosophy of education can be located throughout intellectual history back to the ancient world, the pioneering work in the modern period entirely in an analytic mode was the short monograph by C.D. Hardie, Truth and Fallacy in Educational Theory (1941; reissued in 1962). In his Introduction, Hardie (who had studied with C.D. Broad and I.A. Richards) made it clear that he was putting all his eggs into the ordinary-language-analysis basket:
The Cambridge analytical school, led by Moore, Broad and Wittgenstein, has attempted so to analyse propositions that it will always be apparent whether the disagreement between philosophers is one concerning matters of fact, or is one concerning the use of words, or is, as is frequently the case, a purely emotive one. It is time, I think, that a similar attitude became common in the field of educational theory. (Hardie, 1962, xix)
The first object of his analytic scrutiny in the book was the view that “a child should be educated according to Nature”; he teased apart and critiqued various things that writers through the ages could possibly have meant by this, and very little remained standing by the end of the chapter. Then some basic ideas of Herbart and Dewey were subjected to similar treatment. Hardie's hard-nosed approach can be illustrated by the following: One thing that educationists mean by “education according to Nature” (later he turns to other things they might mean) is that “the teacher should thus act like a gardener” who fosters natural growth of his plants and avoids doing anything “unnatural”(Hardie, 1962, 3). He continues:
The crucial question for such a view of education is how far does this analogy hold? There is no doubt that there is some analogy between the laws governing the physical development of the child and the laws governing the development of a plant, and hence there is some justification for the view if applied to physical education. But the educationists who hold this view are not generally very much concerned with physical education, and the view is certainly false if applied to mental education. For some of the laws that govern the mental changes which take place in a child are the laws of learning …. [which] have no analogy at all with the laws which govern the interaction between a seed and its environment. (Hardie, 1962, 4)
About a decade after the end of the Second World War the floodgates opened and a stream of work in the analytic mode appeared; the following is merely a sample. D.J. O'Connor published An Introduction to Philosophy of Education (1957) in which, among other things, he argued that the word “theory” as it is used in educational contexts is merely a courtesy title, for educational theories are nothing like what bear this title in the natural sciences; Israel Scheffler, who became the paramount philosopher of education in North America, produced a number of important works including The Language of Education (1960), that contained clarifying and influential analyses of definitions (he distinguished reportive, stipulative, and programmatic types) and the logic of slogans (often these are literally meaningless, and should be seen as truncated arguments); Smith and Ennis edited the volume Language and Concepts in Education (1961); and R.D. Archambault edited Philosophical Analysis and Education (1965), consisting of essays by a number of British writers who were becoming prominent—most notably R.S. Peters (whose status in Britain paralleled that of Scheffler in the USA), Paul Hirst, and John Wilson. Topics covered in the Archambault volume were typical of those that became the “bread and butter” of analytic philosophy of education throughout the English-speaking world—education as a process of initiation, liberal education, the nature of knowledge, types of teaching, and instruction versus indoctrination.
Among the most influential products of APE was the analysis developed by Hirst and Peters (1970), and Peters (1973), of the concept of education itself. Using as a touchstone “normal English usage”, it was concluded that a person who has been educated (rather than instructed or indoctrinated) has been (i) changed for the better; (ii) this change has involved the acquisition of knowledge and intellectual skills, and the development of understanding; and (iii) the person has come to care for, or be committed to, the domains of knowledge and skill into which he or she has been initiated. The method used by Hirst and Peters comes across clearly in their handling of the analogy with the concept of “reform”, one they sometimes drew upon for expository purposes. A criminal who has been reformed has changed for the better, and has developed a commitment to the new mode of life (if one or other of these conditions does not hold, a speaker of standard English would not say the criminal has been reformed). Clearly the analogy with reform breaks down with respect to the knowledge and understanding conditions. Elsewhere Peters developed the fruitful notion of “education as initiation”.
The concept of indoctrination was also of great interest to analytic philosophers of education, for—it was argued—getting clear about precisely what constitutes indoctrination also would serve to clarify the border that demarcates it from acceptable educational processes. Unfortunately, ordinary language analysis did not lead to unanimity of opinion about where this border was located, and rival analyses of the concept were put forward (Snook, 1972). Thus, whether or not an instructional episode was a case of indoctrination was determined by: the content that had been taught; or by the intention of the instructor; or by the methods of instruction that had been used; or by the outcomes of the instruction; or, of course, by some combination of these. Adherents of the different analyses used the same general type of argument to make their case, namely, appeal to normal and aberrant usage. Two examples will be sufficient to make the point: (i) The first criterion mentioned above—the nature of the content being imparted—was supported by an argument that ran roughly as follows: “If some students have learned, as factual, some material that is patently incorrect (like ‘The capital city of Canada is Washington D.C.’), then they must have been indoctrinated. This conclusion is reinforced by the consideration that we would never say students must have been indoctrinated if they believe an item that is correct!” However, both portions of this argument have been challenged. (ii) The method criterion—how the knowledge was imparted to the students—usually was supported by an argument that, while different, clearly paralleled the previous one in its logic. It ran roughly like this: “We never would say that students had been indoctrinated by their teacher if he or she had fostered open inquiry and discussion, encouraged exploration in the library and on the net, allowed students to work in collaborative groups, and so on. However, if the teacher did not allow independent inquiry, quashed classroom questions, suppressed dissenting opinions, relied heavily on rewards and punishments, used repetition and fostered rote memorization, and so on, then it is likely we would say the students were being indoctrinated”. (The deeper issue in this second example is that the first method of teaching allows room for the operation of the learners' rationality, while the second method does not. Siegel, 1988, stresses this in his discussion of indoctrination.)
After a period of dominance, for a number of important reasons the influence of APE went into decline. First, there were growing criticisms that the work of analytic philosophers of education had become focused upon minutiae and in the main was bereft of practical import; I can offer as illustration a presidential address at a US Philosophy of Education Society annual meeting that was an hour-long discourse on the various meanings of the expression “I have a toothache”. (It is worth noting that the 1966 article in Time , cited earlier, had put forward the same criticism of mainstream philosophy.) Second, in the early 1970's radical students in Britain accused the brand of linguistic analysis practiced by R.S. Peters of conservatism, and of tacitly giving support to “traditional values”—they raised the issue of whose English usage was being analyzed?
Third, criticisms of language analysis in mainstream philosophy had been mounting for some time, and finally after a lag of many years were reaching the attention of philosophers of education. There even had been a surprising degree of interest in this arcane topic on the part of the general reading public in the UK as early as 1959, when Gilbert Ryle, editor of the journal Mind , refused to commission a review of Ernest Gellner's Words and Things (1959)—a detailed and quite acerbic critique of Wittgenstein's philosophy and its espousal of ordinary language analysis. (Ryle argued that Gellner's book was too insulting, a view that drew Bertrand Russell into the fray on Gellner's side—in the daily press, no less; Russell produced examples of insulting remarks drawn from the work of great philosophers of the past. See Mehta, 1963)
Richard Peters had been given warning that all was not well with APE at a conference in Canada in 1966; after delivering a paper on “The aims of education: A conceptual inquiry” that was based on ordinary language analysis, a philosopher in the audience (William Dray) asked Peters “ whose concepts do we analyze?” Dray went on to suggest that different people, and different groups within society, have different concepts of education. Five years before the radical students raised the same issue, Dray pointed to the possibility that what Peters had presented under the guise of a “logical analysis” was nothing but the favored usage of a certain class of persons—a class that Peters happened to identify with. (See Peters, 1973, where to the editor's credit the interaction with Dray is reprinted.)
Fourth, during the decade of the seventies when these various critiques of analytic philosophy were in the process of eroding its luster, a spate of translations from the Continent stimulated some philosophers of education in Britain and North America to set out in new directions, and to adopt a new style of writing and argumentation. Key works by Gadamer, Foucault, and Derrida appeared in English, and these were followed in 1984 by Lyotard's foundational work on The Postmodern Condition . The classic works of Heidegger and Husserl also found new admirers; and feminist philosophers of education were finding their voices—Maxine Greene published a number of pieces in the 1970s; the influential book by Nel Noddings, Caring: A Feminine Approach to Ethics and Moral Education , appeared the same year as the work by Lyotard, followed a year later by Jane Roland Martin's Reclaiming a Conversation . APE was no longer the center of interest.
By the 1980s, the rather simple if not simplistic ordinary language analysis practiced in philosophy of education, was reeling under the attack from the combination of forces sketched above, but the analytic spirit lived on in the form of rigorous work done in other specialist areas of philosophy—work that trickled out and took philosophy of education in rich new directions. Technically-oriented epistemology, philosophy of science, and even metaphysics, flourished; as did the interrelated fields of social, political and moral philosophy. John Rawls published A Theory of Justice in 1971; a decade later MacIntyre's After Virtue appeared; and in another decade or so there was a flood of work on individualism, communitarianism, democratic citizenship, inclusion, exclusion, rights of children versus rights of parents, rights of groups (such as the Amish) versus rights of the larger polity. From the early 1990s philosophers of education have contributed significantly to the debates on these and related topics—indeed, this corpus of work illustrates that good philosophy of education flows seamlessly into work being done in mainstream areas of philosophy. Illustrative examples are Creating Citizens: Political Education and Liberal Democracy , Callan (1997); The Demands of Liberal Education , Levinson (1999); Social Justice and School Choice , Brighouse (2000); and Bridging Liberalism and Multiculturalism in American Education , Reich (2002). These works stand shoulder-to-shoulder with semi-classics on the same range of topics by Gutmann, Kymlicka, Macedo, and others. An excerpt from the book by Callan nicely illustrates that the analytic spirit lives on in this body of work; the broader topic being pursued is the status of the aims of education in a pluralistic society where there can be deep fundamental disagreements:
… the distinction must be underlined between the ends that properly inform political education and the extent to which we should tolerate deviations from those ends in a world where reasonable and unreasonable pluralism are entangled and the moral costs of coercion against the unreasonable variety are often prohibitive. Our theoretical as well as our commonsense discourse do not always respect the distinction…. If some of the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church conflict with our best theory of the ends of civic education, it does not follow that we have any reason to revise our theory; but neither does it mean we have any reason to impose these ends on Catholic schools and the families that they serve. (Callan, 1997, 44)
Callan and White (2003) have given an analysis of why the topics described above have become such a focus of attention. “What has been happening in philosophy of education in recent years”, they argue, mirrors “a wider self-examination in liberal societies themselves”. World events, from the fall of communism to the spread of ethnic conflicts “have all heightened consciousness of the contingency of liberal politics”. A body of work in philosophy, from the early Rawls on, has systematically examined (and critiqued) the foundations of liberalism, and philosophy of education has been drawn into the debates. Callan and White mention communitarianism as offering perhaps “the most influential challenge” to liberalism, and they write:
The debate between liberals and communitarians is far more than a theoretical diversion for philosophers and political scientists. At stake are rival understandings of what makes human lives and the societies in which they unfold both good and just, and derivatively, competing conceptions of the education needed for individual and social betterment. (Callan and White, 2003, 95-96)
It should be appended here that it is not only “external” world events that have stimulated this body of work; events internal to a number of democratic societies also have been significant. To cite one example that is prominent in the literature in North America at least, the US Supreme Court issued a ruling ( Wisconsin v. Yoder ) in which members of the Amish sect were allowed to withdraw their children from public schools before they had reached the age of sixteen—for, it had been argued, any deeper education would endanger the existence of the group and its culture. In assessing this decision—as of course philosophers have frequently done (see, for example, Kymlicka, 1995)—a balance has to be achieved between (i) the interest of civic society in having an informed, well-educated, participatory citizenry; (ii) the interest of the Amish as a group in preserving their own culture; and (iii) the interests of the Amish children, who have a right to develop into autonomous individuals who can make reflective decisions for themselves about the nature of the life they wish to lead. These are issues that fall squarely in the domain covered by the works mentioned above.
So much work is being produced on the complex and interrelated issues just outlined, that in a different context it seemed fair for me to remark (descriptively, and not judgmentally) that a veritable cottage industry had sprung up in post-Rawlsian philosophy of education. There are, of course, other areas of activity, where interesting contributions are being made, and the discusion will next turn to a sampling of these.
3. Other areas of contemporary activity
As was stressed at the outset, and illustrated with a cursory listing of examples, the field of education is huge and contains within it a virtually inexhaustible number of issues that are of philosophical interest. To attempt comprehensive coverage of how philosophers of education have been working within this thicket would be a quixotic task for a large single volume, and is out of the question for a solitary encyclopedia entry. Nevertheless, a valiant attempt to give an overview was made in the recent A Companion to the Philosophy of Education (Curren, 2003), which contained more than six-hundred pages divided into fourty-five chapters each of which surveyed a subfield of work. The following random selection of chapter topics gives a sense of the enormous scope of the field: Sex education, special education, science education, aesthetic education, theories of teaching and learning, religious education, knowledge and truth in learning, cultivating reason, the measurement of learning, multicultural education, education and the politics of identity, education and standards of living, motivation and classroom management, feminism, critical theory, postmodernism, romanticism, purposes of universities in a fluid age, affirmative action in higher education, and professional education.
There is no non-arbitrary way to select a small number of topics for further discussion, nor can the topics that are chosen be pursued in great depth. The choice of those below has been made with an eye to filling out—and deepening—the topographical account of the field that was presented in the preceding sections. The discussion will open with a topic that was not included in the Companion , despite it being one that is of great concern across the academic educational community, and despite it being one where adherents of some of the rival schools of philosophy (and philosophy of education) have had lively exchanges.
The educational research enterprise has been criticized for a century or more by politicians, policymakers, administrators, curriculum developers, teachers, philosophers of education, and by researchers themselves—but the criticisms have been contradictory. Charges of being “too ivory tower and theory-oriented” are found alongside “too focused on practice and too atheoretical”; but particularly since publication of the book by Stokes mentioned earlier, and also in light of the views of John Dewey and William James that the function of theory is to guide intelligent practice and problem-solving, it is becoming more fashionable to hold that the “theory v. practice” dichotomy is a false one.
A similar trend can be discerned with respect to the long warfare between two rival groups of research methods—on one hand quantitative/statistical approaches to research, and on the other hand the qualitative/ethnographic family. (The choice of labels here is its not entirely risk-free, for they have been contested; furthermore the first approach is quite often associated with “experimental” studies, and the latter with “case studies”, but this is an over-simplification.) For several decades these two rival methodological camps were treated by researchers and a few philosophers of education as being rival paradigms (Kuhn's ideas, albeit in a very loose form, have been influential in the field of educational research), and the dispute between them was commonly referred-to as “the paradigm wars”. In essence the issue at stake was epistemolgical: members of the quantitative/experimental camp believed that only their methods could lead to well-warranted knowledge claims, especially about the causal factors at play in educational phenomena, and on the whole they regarded qualitative methods as lacking in rigor; on the other hand the adherents of qualitative/ethnographic approaches held that the other camp was too “positivistic” and was operating with an inadequate view of causation in human affairs—one that ignored the role of motives and reasons, possession of relevant background knowledge, awareness of cultural norms, and the like. Few if any commentators in the “paradigm wars” suggested that there was anything prohibiting the use of both approaches in the one research program—provided that if both were used, they only were used sequentially or in parallel, for they were underwritten by different epistemologies and hence could not be blended together. But recently the trend has been towards rapprochement, towards the view that the two methodological families are, in fact, compatible and are not at all like paradigms in the Kuhnian sense(s) of the term; the melding of the two approaches is often called “mixed methods research”, and it is growing in popularity. (For more detailed discussion of these “wars” see Howe, 2003, and Phillips, 2008.)
The most lively contemporary debates about education research, however, were set in motion around the turn of the millenium when the US Federal Government moved in the direction of funding only rigorously scientific educational research—the kind that could establish causal factors which could then guide the development of practically effective policies. (It was held that such a causal knowledge base was available for medical decisionmaking.) The definition of “rigorously scientific”, however, was decided by politicans and not by the research community, and it was given in terms of the use of a specific research method—the net effect being that the only research projects to receive Federal funding were those that carried out randomized controlled experiments or field trials (RFTs). It has beome common over the last decade to refer to the RFT as the “gold standard” methodology.
The National Research Council (NRC)—an arm of the U.S. National Academies of Science—issued a report, influenced by postpostivistic philosophy of science (NRC, 2002), that argued this criterion was far too narrow. Numerous essays have appeared subsequently that point out how the “gold standard” account of scientific rigor distorts the history of science, how the complex nature of the relation between evidence and policy-making has been distorted and made to appear overly simple (for instance the role of value-judgments in linking empirical findings to policy directives is often overlooked), and qualitative researchers have insisted upon the scientific nature of their work.
Nevertheless, and possibly because it tried to be balanced and supported the use of RFTs in some research contexts, the NRC report has been the subject of symposia in four journals, where it has been supported by a few and attacked from a variety of philosophical fronts: Its authors were positivists, they erroneously believed that educational inquiry could be value-neutral and that it could ignore the ways in which exercise of power constrains the research process, they misunderstood the nature of educational phenomena, they were guilty of advocating “your father's paradigm”(clearly this was not intended as a compliment). One critic with postmodernist leanings asserted that educational research should move “toward a Nietzschean sort of ‘unnatural science’ that leads to greater health by fostering ways of knowing that escape normativity”—a suggestion that evokes the reaction discussed in Section 1.3 above, namely, one of incomprehension on the part of most researchers and those philosophers of education who work within a different tradition where a “way of knowing”, in order to be a “way”, must inevitably be normative.
The final complexity in the debates over the nature of educational research is that there are some respected members of the philosophy of education community who claim, along with Carr, that “the forms of human association characteristic of educational engagement are not really apt for scientific or empirical study at all” (Carr, 2003, 54-5). His reasoning is that educational processes cannot be studied empirically because they are processes of “normative initiation”—a position that as it stands begs the question by not making clear why such processes cannot be studied empirically.
The issue of what should be taught to students at all levels of education—the issue of curriculum content—obviously is a fundamental one, and it is an extraordinarily difficult one with which to grapple. In tackling it, care needs to be taken to distinguish between education and schooling—for although education can occur in schools, so can mis-education (as Dewey pointed out), and many other things can take place there that are educationally orthogonal (such as the provision of free or subsidized lunches, or the development of social networks); and it also must be recognized that education can occur in the home, in libraries and museums, in churches and clubs, in solitary interaction with the public media, and the like.
In developing a curriculum (whether in a specific subject area, or more broadly as the whole range of offerings in an educational institution or in a system), a number of difficult decisions need to be made. Issues such as the proper ordering or sequencing of topics in the chosen subject, the time to be allocated to each topic, the lab work or excursions or projects that are appropriate for particular topics, can all be regarded as technical issues best resolved either by educationists who have a depth of experience with the target age group or by experts in the psychology of learning and the like. But there are deeper issues, ones concerning the validity of the justifications that have been given for including particular subjects or topics in the offerings of formal educational institutions. (Why is evolution included, or excluded, as a topic within the standard high school subject Biology? Why is Driver Education part of the high school curriculum, and methods of birth control usually not—even though sex has an impact on the life of teenagers that at least is comparable to the impact of car-driving? Is the justification that is given for teaching Economics in some schools coherent and convincing? Does the justification for not including the Holocaust or the phenomenon of wartime atrocities in the curriculum in some countries stand up to critical scrutiny?)
The different justifications for particular items of curriculum content that have been put forward by philosophers and others since Plato's brilliant pioneering efforts all draw upon, explicitly or implicitly, the positions that the respective theorists hold about at least three sets of issues. First, what are the aims and/or functions of education (aims and functions are not necessarily the same), or alternatively, what constitutes the good life and human flourishing. These two formulations are related, for presumably our educational institutions should aim to equip individuals to pursue this good life. Thus, for example, if our view of human flourishing includes the capacity to act rationally and/or autonomously, then the case can be made that educational institutions—and their curricula—should aim to prepare, or help to prepare, autonomous individuals. How this is to be done, of course, is not immediately obvious, and much philosophical ink has been spilled on the matter. One influential line of argument was developed by Paul Hirst, who argued that knowledge is essential for developing a conception of the good life, and then for pursuing it; and because logical analysis shows—he argued—that there are seven basic forms of knowledge, the case can be made that the function of the curriculum is to introduce students to each of these forms. Luckily for Hirst, the typical British high school day was made up of seven instructional periods. (Hirst, 1965; for a critique see Phillips, 1987, ch.11.)
Second, is it justifiable to treat the curriculum of an educational institution as vehicle for furthering the socio-political interests and goals of a ruler or ruling class; and relatedly, is it justifiable to design the curriculum so that it serves as a medium of control or of social engineering? In the closing decades of the twentieth century there were numerous discussions of curriculum theory, particularly from Marxist and postmodern perspectives, that offered the sobering analysis that in many educational systems, including those in Western democracies, the curriculum did indeed reflect, and serve, the interests of the ruling class. Michael Apple is typical:
… the knowledge that now gets into schools is already a choice from a much larger universe of possible social knowledge and principles. It is a form of cultural capital that comes from somewhere, that often reflects the perspectives and beliefs of powerful segments of our social collectivity. In its very production and dissemination as a public and economic commodity—as books, films, materials, and so forth—it is repeatedly filtered through ideological and economic commitments. Social and economic values, hence, are already embedded in the design of the institutions we work in, in the ‘formal corpus of school knowledge’ we preserve in our curricula….(Apple, 1990, 8-9)
Third, should educational programs at the elementary and secondary levels be made up of a number of disparate offerings, so that individuals with different interests and abilities and affinities for learning can pursue curricula that are suitable? Or should every student pursue the same curriculum as far as each is able—a curriculum, it should be noted, that in past cases nearly always was based on the needs or interests of those students who were academically inclined or were destined for elite social roles. Mortimer Adler and others in the late twentieth century (who arguably were following Plato's lead in the Republic ), sometimes used the aphorism “the best education for the best is the best education for all”.
The thinking here can be explicated in terms of the analogy of an out-of-control virulent disease, for which there is only one type of medicine available; taking a large dose of this medicine is extremely beneficial, and the hope is that taking only a little—while less effective—is better than taking none at all! Medically, this probably is dubious, while the educational version—forcing students to work, until they exit the system, on topics that do not interest them and for which they have no facility or motivation—has even less merit. (For a critique of Adler and his Paideia Proposal , see Noddings, 2007.) It is interesting to compare the modern “one curriculum track for all” position with Plato's system outlined in the Republic , according to which all students—and importantly this included girls—set out on the same course of study. Over time, as they moved up the educational ladder it would become obvious that some had reached the limit imposed upon them by nature, and they would be directed off into appropriate social roles in which they would find fulfillment, for their abilities would match the demands of these roles. Those who continued on with their education would eventually be able to contemplate the metaphysical realm of the “forms”, thanks to their advanced training in mathematics and philosophy. Having seen the form of the Good, they would be eligible after a period of practical experience to become members of the ruling class of Guardians.
Plato's educational scheme was guided, presumably, by the understanding he thought he had achieved of the transcendental realm of fixed “forms”. John Dewey, ever a strong critic of positions that were not naturalistic, or that incorporated a priori premises, commented as follows:
Plato's starting point is that the organization of society depends ultimately upon knowledge of the end of existence. If we do not know its end, we shall be at the mercy of accident and caprice…. And only those who have rightly trained minds will be able to recognize the end, and ordering principle of things. (Dewey, 1916, 102-3)
Furthermore, as Dewey again put it, Plato “had no perception of the uniqueness of individuals…. they fall by nature into classes”, which masks the “infinite diversity of active tendencies” which individuals harbor (104). In addition, Plato tended to talk of learning using the passive language of seeing, which has shaped our discourse down to the present (witness “Now I see it!” when a difficult point has become clear).
In contrast, for Dewey each individual was an organism situated in a biological and social environment in which problems were constantly emerging, forcing the individual to reflect and act, and learn. Dewey, following William James, held that knowledge arises from reflection upon our actions; and the worth of a putative item of knowledge is directly correlated with the problem-solving success of the actions performed under its guidance. Thus Dewey, sharply disagreeing with Plato, regarded knowing as an active rather than a passive affair—a strong theme in his writings is his opposition to what is sometimes called “the spectator theory of knowledge”. All this is made clear enough in a passage containing only a thinly-veiled allusion to Plato's famous analogy of the prisoners in the cave whose eyes are turned to the light by education:
In schools, those under instruction are too customarily looked upon as acquiring knowledge as theoretical spectators, minds which appropriate knowledge by direct energy of intellect. The very word pupil has almost come to mean one who is engaged not in having fruitful experiences but in absorbing knowledge directly. Something which is called mind or consciousness is severed from the physical organs of activity. (164)
This passage also illuminates a passage that many have found puzzling: “philosophy is the theory of education” (387). For in the sentences above it is easy to see the tight link between Dewey's epistemology and his views on education—his anti-spectator epistemology morphs directly into advocacy for anti-spectator learning by students in school—students learn by being active inquirers. Over the past few decades this view of learning has inspired a major tradition of research by educational psychologists, and related theory-development (the “situated cognition” framework); and these bodies of work have in turn led to innovative efforts in curriculum development. (For a discussion of these, see Phillips, 2003.)
The final important difference with Plato is that, for Dewey, each student is an individual who blazes his or her unique trail of growth; the teacher has the task of guiding and facilitating this growth, without imposing a fixed end upon the process. Dewey sometimes uses the term “curriculum” to mean “the funded wisdom of the human race”, the point being that over the course of human history an enormous stock of knowledge and skills has accumulated and the teacher has the task of helping the student to make contact with this repertoire—but helping by facilitating rather than by imposing. (All this, of course, has been the subject of intense discussion among philosophers of education: Does growth imply a direction? Is growth always good—can't a plant end up misshapen, and can't a child develop to become bad? Is Dewey some type of perfectionist? Is his philosophy too vague to offer worthwhile educational guidance? Isn't it possible for a “Deweyan” student to end up without enough relevant knowledge and skills to be able to make a living in the modern world?)
Dewey's work was of central importance for the American progressive education movement in its formative years, although there was a fair degree of misunderstanding of his ideas as progressives interpreted his often extremely dense prose to be saying what they personally happened to believe. Nevertheless, Dewey became the “poster child” or the “house philosopher” of progressive education, and if he didn't make it onto many actual posters he certainly made it onto a postage stamp.
His popularity, however, sharply declined after the Soviets launched Sputnik, for Dewey and progressive education were blamed for the USA losing the race into space (illustrating the point about scapegoating made at the start of this essay). But he did not remain in disgrace for long; and for some time has been the focus of renewed interest—although it is still noticeable that commentators interpret Dewey to be holding views that mirror their own positions or interests. And interestingly, there now is slightly more interest in Dewey on the part of philosophers of education in the UK than there was in earlier years, and there is growing interest by philosophers from the Continent (see, for example, Biesta and Burbules, 2003).
To be a poster child for progressivism, however, is not to be the parent. Rather than to Dewey, that honor must go to Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and to his educational novel written in soaring prose, Emile (1762). Starting with the premise that “God makes all things good; man meddles with them and they become evil” (Rousseau, 1955, 5), Rousseau held that contemporary man has been misshapen by his education; the “crushing force” of social conventions has stifled the “Nature within him”. The remedy adopted in the novel is for the young Emile to be taken to his family estate in the country where, away from the corrupting influence of society, and under the watchful eye of his tutor, “everything should … be brought into harmony with these natural tendencies”. (This idea of education according to nature, it will be recalled, was the object of Hardie's analytic attention almost two centuries later.)
Out in the countryside, rather than having a set curriculum that he is forced to follow, Emile learns when some natural stimulus or innate interest motivates him—and under these conditions learning comes easily. He is allowed to suffer the natural consequences of his actions (if he breaks a window, he gets cold; if he takes the gardener's property, the gardener will no longer do him favors), and experiences such as these lead to the development of his moral system. Although Rousseau never intended these educational details to be taken literally as a blueprint (he saw himself as developing and illustrating the basic principles), over the ages there have been attempts to implement them, one being the famous British “free school”, A.S. Neill's Summerhill. (It is worth noting that Neill claimed not to have read Rousseau; but he was working in a milieu in which Rousseau's ideas were well-known—intellectual influence can follow a less than direct path.) Furthermore, over the ages these principles also have proven to be fertile soil for philosophers of education to till.
Even more fertile ground for comment, in recent years, has been Rousseau's proposal for the education of girls, developed in a section of the novel (Book V) that bears the name of the young woman who is destined to be Emile's soul-mate, Sophy. The puzzle has been why Rousseau—who had been so far-sighted in his discussion of Emile's education—was so hide-bound if not retrograde in his thinking about her education. One short quotation is sufficient to illustrate the problem: “If woman is made to please and to be in subjection to man, she ought to make herself pleasing in his eyes and not provoke him …her strength is in her charms” (324).
The educational principles developed by Rousseau and Dewey, and numerous educational theorists and philosophers in the interregnum, are alive and well in the twenty-first century. Of particular contemporary interest is the evolution that has occurred of the progressive idea that each student is an active learner who is pursuing his or her own individual educational path. By incorporating elements of the classical empiricist epistemology of John Locke, this progressive principle has become transformed into the extremely popular position known as constructivism, according to which each student in a classroom constructs his or her own individual body of understandings even when all in the group are given what appears to be the same stimulus or educational experience. (A consequence of this is that a classroom of thirty students will have thirty individually-constructed, and possibly different, bodies of “knowledge”, in addition to that of the teacher!) There is also a solipsistic element here, for constructivists also believe that none of us—teachers included—can directly access the bodies of understandings of anyone else; each of us is imprisoned in a world of our own making. It is an understatement to say that this poses great difficulties for the teacher. The education journals of the past two decades contain many thousands of references to discussions of this position, which elsewhere I claimed has become a type of educational “secular religion”; for reasons that are hard to discern it is particularly influential in mathematics and science education. (For a discussion of the underlying philosophical ideas in constructivism, and for an account of some of its varieties, see the essays in Phillips, ed., 2000.)
As stressed earlier, it is impossible to do justice the whole field of philosophy of education in a single encyclopedia entry. Different countries around the world—France, Germany, the Netherlands, Japan, to mention only a few—have their own intellectual traditions, and their own ways of institutionalizing philosophy of education into the academic universe, and no discussion of any of this appears in the present essay. But even in the Anglo-American world, there is such a diversity of approaches to the discipline that any author attempting to produce a synoptic account will quickly run into the borders of his or her areas of competence. Clearly this has happened in the present case.
Fortunately, in the last twenty years or so resources have become available that significantly alleviate these problems. There has been a flood of encyclopedia entries, commenting on the field as a whole or on many specific topics not well-covered in the present essay (see, as a sample, Burbules, 1994; Chambliss, 1996; Phillips, 1985; Siegel, 2007; Smeyers, 1994); two large volumes—a “Guide” (Blake, Smeyers, Smith and Standish, 2003) and a “Companion” (Curren, 2003)—have been produced by Blackwell in their well-known philosophy series; and the same publisher recently released an anthology, with 60 papers considered to be important in the field, and which also are representative of the range of work that is being done (Curren, 2007). Several encyclopedias of philosophy of education have been published or are in the works (for example, Chambliss, 1996; Siegel, 2008); there is a dictionary of key concepts in the field (Winch and Gingell, 1999), and a good textbook or two (see Noddings, 2007); in addition there are numerous volumes both of reprinted selections and of specially commissioned essays on specific topics, some of which were given short shrift in the present work (for another sampling see A. Rorty, 1998; Smeyers and Marshall, 1995; Stone, 1994); and several international journals appear to be flourishing— Educational Philosophy and Theory , Educational Theory , Journal of Philosophy of Education , Studies in Philosophy and Education , Theory and Research in Education . Thus there is enough material available to keep the interested reader busy, and to provide alternative assessments to the ones presented in this present essay.
- Apple, M., 1990, Ideology and Curriculum , New York: Routledge, 2 nd . Editon.
- Archambault, R., (ed.), 1965, Philosophical Analysis and Education , London: Routledge.
- Biesta, G., and Burbules, N., 2003, Pragmatism and Educational Research , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Blake, N., Smeyers, P., Smith, R., and Standish, P., (eds.), 2003, The Blackwell Guide to the Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Brighouse, H., 2000, Social Justice and School Choice , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Burbules, N., 1994, “Marxism and Educational Thought”, in The International Encyclopedia of Education , (Volume 6), T. Husen and N. Postlethwaite (eds.), Oxford: Pergamon, 2 nd . Edition, pp. 3617-22.
- Callan, E., 1997, Creating Citizens: Political Education and Liberal Democracy , Oxford: Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- Callan, E., and White, J., 2003, “Liberalism and Communitarianism”, in The Blackwell Guide to the Philosophy of Education , N. Blake, P. Smeyers, R. Smith and P. Standish (eds.), Oxford: Blackwell, pp.95-109.
- Carr, D., 2003, Making Sense of Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy and Theory of Education and Teaching , London: RoutledgeFalmer.
- Chambliss, J., 1996, “History of Philosophy of Education”, in Philosophy of Education: An Encyclopedia , J. Chambliss (ed.), New York: Garland, pp.461-72.
- Cleverley, J., and Phillips, D.C., 1986, Visions of Childhood , New York: Teachers College Press.
- Curren, R., (ed.), 2003, A Companion to the Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Curren, R., (ed.), 2007, Philosophy of Education: An Anthology , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Dewey, J., 1916, Democracy and Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Education , New York: Macmillan.
- Gellner, E., 1959, Words and Things , London: Gollancz.
- Hardie, C., 1962, Truth and Fallacy in Educational Theory , New York: Teachers College Bureau of Publications.
- Hirst, P., 1965, “Liberal Education and the Nature of Knowledge”, in Philosophical Analysis and Education , R. Archambault, (ed.), London: Routledge, pp. 113-138.
- Hirst, P., and Peters, R., 1970, The Logic of Education , London: Routledge.
- Howe, K., 2003, Closing Methodological Divides: Toward Democratic Educational Research . Dordrecht: Kluwer.
- Kaminsky, J., 1996, “Philosophy of Education: Professional Organizations In”, in Philosophy of Education: An Encyclopedia , J. Chambliss, (ed.), New York: Garland, pp. 475-79.
- Kohli, W., (ed.), 1995, Critical Conversations in Philosophy of Education , New York: Routledge.
- Kymlicka, W., 1995, Multicultural Citizenship , Oxford: Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- Levinson, M., 1999, The Demands of Liberal Education , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Lucas, C., (ed.), 1969, What is Philosophy of Education? London: Macmillan.
- Martin, J., 1985, Reclaiming a Conversation , New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press.
- Mehta, V., 1963, Fly and the Fly-Bottle : London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
- Murphy, M., (ed.), 2006, The History and Philosophy of Education: Voices of Educational Pioneers , New Jersey: Pearson.
- Noddings, N., 1984, Caring: A Feminine Approach to Ethics and Moral Education , Berkeley: University of California Press.
- –––, 2007, Philosophy of Education , Boulder, CO: Westview, 2 nd . Edition.
- National Research Council (NRC), 2002, Scientific Research in Education , Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
- O'Connor, D., 1957, An Introduction to Philosophy of Education , London: Routledge.
- Peters, R., (ed.), 1973, The Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Phillips, D.C., 1985, “Philosophy of Education”, in International Encyclopedia of Education, T. Husen and N. Postletwaite, (eds.), pp.3859-3877.
- –––, 1987, Philosophy, Science, and Social Inquiry , Oxford: Pergamon.
- –––, (ed.), 2000, Constructivism in Education: Opinions and Second Opinions on Controversial Issues , (Series: 99 th . Yearbook of the National Society for the Study of Education), Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- –––, 2003, “Theories of Teaching and Learning”, in A Companion to the Philosophy of Education , R. Curren, (ed.), Oxford: Blackwell, pp. 232-245.
- –––, 2008, “Empirical Educational Research: Charting Philosophical Disagreements in an Undisciplined Field”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Education , H. Siegel (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, in press.
- Reich, R., 2002, Bridging Liberalism and Multiculturalism in American Education , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Rorty, A., (ed.), 1998, Philosophers on Education: New Historical Perspectives , New York: Routledge.
- Rousseau, J-J., 1955, Emile , B. Foxley, (tr.), London: Dent/Everyman.
- Scheffler, I., 1960, The Language of Education , Illinois: Thomas.
- Siegel, H., 1988, Educating Reason: rationality, Critical Thinking, and Education , New York: Routledge.
- –––, 2007, “Philosophy of Education”, in Britannica Online Encyclopedia , [ Available online ].
- –––, (ed.), 2008, The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Oxford University Press, in press.
- Smeyers, P., 1994, “Philosophy of Education: Western European Perspectives”, in The International Encyclopedia of Education , (Volume 8), T. Husen and N. Postlethwaite, (eds.), Oxford: Pergamon, 2 nd . Edition, pp. 4456-61.
- Smeyers, P., and Marshall, J., (eds.), 1995, Philosophy and Education: Accepting Wittgenstein's Challenge , Dordrecht: Kluwer.
- Smith, B., and Ennis, R., (eds.), 1961, Language and Concepts in Education , Chicago: Rand McNally.
- Snook, I., 1972, Indoctrination and Education , London: Routledge.
- Stokes, D., 1997, Pasteur's Quadrant: Basic Science and Technological Innovation , Washington, DC: Brookings.
- Stone, L., (ed.), 1994, The Education Feminism Reader , New York: Routledge.
- Ulich, R., 1954, Three Thousand Years of Educational Wisdom , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, Revised Ed.
- Winch, C., and Gingell, J., 1999, Key Concepts in the Philosophy of Education , London: Routledge.
- PES (Philosophy of Education Society, North America)
- PESA (Philosophy of Education Society of Australasia)
- PESGB (Philosophy of Education Society of Great Britain)
- INPE (International Network of Philosophers of Education)
- UNESCO/International Bureau of Education: Thinkers on Education
autonomy: personal | -->Dewey, John --> | feminist (interventions): ethics | feminist (interventions): liberal feminism | feminist (interventions): political philosophy | -->feminist (topics): perspectives on autonomy --> | feminist (topics): perspectives on disability | Foucault, Michel | Gadamer, Hans-Georg | liberalism | Locke, John | -->Lyotard, Jean François --> | -->ordinary language --> | Plato | postmodernism | Rawls, John | rights: of children | -->Rousseau, Jean Jacques -->
Analytic Philosophy of Education and the Concept of Liberal Education
Cite this chapter.

- Stefaan E. Cuypers 2
Part of the book series: Springer International Handbooks of Education ((SIHE))
5264 Accesses
1 Citations
In the second half of the twentieth century, two persons had an enormous impact on one branch of philosophy: that branch was the philosophy of education, and these persons were R.S. Peters and I. Scheffler, the founding fathers of the analytic approach in this philosophical subdiscipline. This chapter, first, introduces and contextualizes the analytic school of thought in the philosophy of education. Preliminary, the identity of analytic philosophy as such is outlined. The focus is primarily on showing how analytic philosophy of education is actually done, and not so much on enumerating theories or dropping names ([Curren R, Robertson E, Hager P, The analytical movement. In: Curren R (ed) A companion to the philosophy of education. Blackwell, Oxford, 2003] already gave an informative catalog). Next, as an example of the analytic approach, the chapter details conceptions of liberal education and delineates justifications of its value.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Analytical Philosophy of Education: A Critique from Marxist Lens

R.S. Peters

Introduction: Why Learn about Paradigms of Education?
Soames 2003 and 2006 .
Rorty 1967 .
See Scheffler 1954 , pp. 10–13 for a concise illustration of Russell’s logical analysis.
Coffman and Hedberg n.d .
Tomassi 1999 , chap. 1.
To clarify some terminology, a sentence (consisting of words) expresses a proposition (consisting of concepts). Loosely speaking, a proposition (concept) is a direct bearer of meaning, whereas a sentence (word) is an indirect bearer of meaning (via the meaning of the proposition (concept) it expresses). For my purposes, there is no need to distinguish between meaning as reference (extension) and meaning as sense (intension).
Earle 1992 , pp. 5–6.
Gettier 1963 .
Russell 1948 , pp. 170–71.
McGinn 2012 .
Margolis and Laurence 2014 .
Smith and Medin 1981 . For the empirical critique, see pp. 33–51.
Wittgenstein 1953 , part I, pp. 66–71.
For example, McGinn 2012 .
Williamson 2014 .
Rorty 1980 , Putnam 1981 , McDowell 1994 .
The ‘London Line’, a term coined to refer to Peters’ group and their work, includes P.H. Hirst, R. Dearden, R.K. Elliott, D. Cooper, and J. White. The second generation of analytic philosophers comprises, among others, D. Carr, T. McLaughlin, and J. Wilson in Great Britain and R. Barrow, H. Siegel, and E. Callan in North America.
Hardie 1942 and perhaps also O’Connor 1957 are important forerunners.
For instance, Scheffler 2000 . See also, Holma 2004 .
For the full story, see Cuypers and Martin 2013 . I draw upon material I wrote for this book in what follows.
The reaction of Peters’ ‘London Line’ to the 1967 Plowden report on Children and Their Primary School is a noteworthy example of the real-world impact of the analytic approach on British educational policy. See Peters 1969a .
Scheffler 1963 and Peters 1973 .
Scheffler 1964 and Peters 1969a .
Peters and Hirst 1970 , Winch and Gingell 1999 .
Peters 1967 and 1970 . See also, Carr 2003 and 2010 .
Ryle 1949 , pp. 131–135
Peters 1969b , pp. 34–35.
Evers ( 1993 ) criticizes the analytic method on the bases of the untenable analytic (or conceptual)/synthetic distinction (in the line of Quine) and the hopelessness of delivering necessary conditions for concept application (in the spirit of Wittgenstein). These bases are, however, controversial. See Russell 2008 for a defense of the distinction and McGinn 2012 for a defense of conceptual essentialism.
A good example of the contemporary methodological pluralism is Heyting, Lenzen, and White 2001 , a collection of essays on children’s rights.
Among others, Siegel 1988 and 1997 . The following argument is taken from Cuypers and Martin 2013 , p. 227.
Oakeshott 1989 .
For the detailed picture, see Cuypers and Martin 2013 , chap. 5. Below, I have drawn from this chapter.
By, for instance, Levinson 1999 .
Suissa 2006 .
Moreover, the dichotomy between ‘for its own sake’ and ‘for practical ends’ is inadequate because practical activities can also be pursued for their own sake on the one hand and theoretical activities can also be infected by purely instrumental, practical ends on the other.
See, for example, Hook et al. 1975 and Bailey 1984 for a detailed treatment of the justificatory issue(s).
For my purposes, there is no need to distinguish between the humanities in a narrow sense (only including literature and the fine arts, history, religion, and philosophy) and in a broad sense (also including the ‘human sciences’, i.e., the social sciences).
Small 2013 .
Cuypers ( forthcoming ) details this claim as follows. This article gives the full argumentation.
Bailey, C. (1984). Beyond the present and the particular: A theory of liberal education . London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Google Scholar
Carr, D. (2003). Philosophy and the meaning of ‘education’. Theory and Research in Education, 1 (2), 195–211.
Carr, D. (2010). Education, contestation and confusions of sense and concept. British Journal of Educational Studies, 58 (1), 89–104.
Article Google Scholar
Coffman, E. J. & Hedberg, T. (n.d.). Finding, clarifying, and evaluating arguments . Retrieved from http://web.utk.edu/~ecoffma1/FCEA.pdf
Curren, R., Robertson, E., & Hager, P. (2003). The analytical movement. In R. Curren (Ed.), A companion to the philosophy of education . Oxford: Blackwell.
Chapter Google Scholar
Cuypers, S. E. (forthcoming). The existential concern of the humanities. R.S. Peters’ justification of liberal education. Educational Philosophy and Theory
Cuypers, S. E., & Martin, C. (2013). R. S. Peters . London: Bloomsbury.
Earle, W. J. (1992). Introduction to philosophy . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Edel, A. (1972). Analytic philosophy of education. In P. H. Hirst & P. White (Eds.), Philosophy of Education. Major themes in the analytic tradition (pp. 39–60). London: Routledge, 1998.
Evers, C. W. (1993). Analytic and post-analytic philosophy of education: Methodological reflections. In P. H. Hirst & P. White (Eds.), Philosophy of Education. Major themes in the analytic tradition (pp. 120–132). London, Routledge, 1998.
Gettier, E. L. (1963). Is justified true belief knowledge? Analysis, 23 (6), 121–123.
Hardie, C. D. (1942). Truth and fallacy in educational theory . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Heyting, F., Lenzen, D., & White, J. (Eds.). (2001). Methods in philosophy of education . London: Routledge.
Hirst, P. H. (1965). Liberal education and the nature of knowledge. In P. H. Hirst (Ed.), Knowledge and the curriculum (pp. 30–53). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1974.
Holma, K. (2004). Plurealism and education: Israel Scheffler’s synthesis and its presumable educational implications. Educational Theory, 54 (4), 419–430.
Hook, S., Kurtz, P., & Todorovich, M. (Eds.). (1975). The philosophy of the curriculum: The need for general education . Buffalo: Prometheus Books.
Husserl, E. (1900/1901). Logical Investigations [ Logische Untersuchungen ], Volume 1 and 2 (Translated by J. N. Findlay, edited by D. Moran). London: Routledge, 2001.
Levinson, M. (1999). The demands of liberal education . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Margolis, E. & Laurence, S. (2014). Concepts. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy . Retrieved from http://plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2014/entries/concepts/
McDowell, J. (1994). Mind and world . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
McGinn, C. (2012). Truth by analysis: Games, names, and philosophy . New York: Oxford University Press.
Moore, G. E. (1903). The refutation of idealism. In G. E. Moore (Ed.), Philosophical studies (pp. 1–30). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1922.
Oakeshott, M. (1989). The voice of liberal learning . Indianapolis: Liberty Fund, 2001.
O’Connor, D. J. (1957). An introduction to the philosophy of education . London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Peters, R. S. (1966). Ethics and education . London: George Allen and Unwin Ltd.
Peters, R. S. (1967). What is an educational process? In R. S. Peters (Ed.), The concept of education (pp. 1–23). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1967.
Peters, R. S. (Ed.). (1969a). Perspectives on Plowden . London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Peters, R. S. (1969b). The meaning of quality in education. In R. S. Peters (Ed.), Education and the education of teachers (pp. 22–45). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1977.
Peters, R. S. (1970). Education and the educated man. In R. S. Peters (Ed.), Education and the education of Teachers (pp. 3–21). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1977.
Peters, R. S., & Hirst, P. H. (1970). The logic of education . London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Peters, R. S. (1973). Education as an academic discipline. In R. S. Peters (Ed.), Education and the education of Teachers (pp. 167–180). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1977.
Putnam, H. (1981). Reason, truth and history . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Rorty, R. M. (1980). Philosophy and the mirror of nature . Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
Rorty, R. M. (Ed.). (1967). The linguistic turn. Essays in philosophical method . Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Russell, B. (1948). Human knowledge: Its scope and limits . London: George Allen and Unwin Ltd..
Russell, G. (2008). Truth in virtue of meaning: A defence of the analytic/synthetic distinction . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ryle, G. (1949). The concept of mind . London: Routledge, 2009.
Scheffler, I. (1954). Toward an analytic philosophy of education. In I. Scheffler (Ed.), Reason and Teaching (pp. 9–17). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1974.
Scheffler, I. (1960). The language of education . Springfield: Charles C Thomas.
Scheffler, I. (1963). Is education a discipline? In I. Scheffler (Ed.), Reason and Teaching (pp. 45–57). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1974.
Scheffler, I. (1964). Concepts of education: Reflections on the current scene. In I. Scheffler (Ed.), Reason and Teaching (pp. 58–66). London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1974.
Scheffler, I. (2000). A Plea for Plurealism. Erkenntnis, 52 (2), 161–173.
Siegel, H. (1988). Educating reason. Rationality, critical thinking, and education . New York: Routledge.
Siegel, H. (1997). Rationality redeemed? Further dialogues on an educational ideal . New York: Routledge.
Small, H. (2013). The value of the humanities . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Smith, E. E., & Medin, D. L. (1981). Categories and concepts . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Soames, S. (2003). Philosophical analysis in the twentieth century, volume 1 and 2 . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Soames, S. (2006). Analysis, philosophical. In D. M. Borchert (Ed.), Encyclopedia of philosophy (Vol. 1, 2nd ed., pp. 144–157). Detroit: Thomson Gale.
Suissa, J. (2006). Anarchism and education: A philosophical perspective . London: Routledge.
Tomassi, P. (1999). Logic . London: Routledge.
Williamson, T. (2014). How did we get here from there? The transformation of analytic philosophy. Belgrade Philosophical Annual, 27 , 7–37.
Winch, C., & Gingell, J. (1999). Key concepts in the philosophy of education . London: Routledge.
Wittgenstein, L. (1953). Philosophical investigations . Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
KU Leuven—University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Stefaan E. Cuypers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefaan E. Cuypers .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Psychology and Educational Sciences, Ghent University and KU Leuven, Ghent, Belgium
Paul Smeyers
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cuypers, S.E. (2018). Analytic Philosophy of Education and the Concept of Liberal Education. In: Smeyers, P. (eds) International Handbook of Philosophy of Education. Springer International Handbooks of Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72761-5_48
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72761-5_48
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-72759-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-72761-5
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Global Education
By: Hannah Ritchie , Veronika Samborska , Natasha Ahuja , Esteban Ortiz-Ospina and Max Roser
A good education offers individuals the opportunity to lead richer, more interesting lives. At a societal level, it creates opportunities for humanity to solve its pressing problems.
The world has gone through a dramatic transition over the last few centuries, from one where very few had any basic education to one where most people do. This is not only reflected in the inputs to education – enrollment and attendance – but also in outcomes, where literacy rates have greatly improved.
Getting children into school is also not enough. What they learn matters. There are large differences in educational outcomes : in low-income countries, most children cannot read by the end of primary school. These inequalities in education exacerbate poverty and existing inequalities in global incomes .
On this page, you can find all of our writing and data on global education.
Key insights on Global Education
The world has made substantial progress in increasing basic levels of education.
Access to education is now seen as a fundamental right – in many cases, it’s the government’s duty to provide it.
But formal education is a very recent phenomenon. In the chart, we see the share of the adult population – those older than 15 – that has received some basic education and those who haven’t.
In the early 1800s, fewer than 1 in 5 adults had some basic education. Education was a luxury; in all places, it was only available to a small elite.
But you can see that this share has grown dramatically, such that this ratio is now reversed. Less than 1 in 5 adults has not received any formal education.
This is reflected in literacy data , too: 200 years ago, very few could read and write. Now most adults have basic literacy skills.
What you should know about this data
- Basic education is defined as receiving some kind of formal primary, secondary, or tertiary (post-secondary) education.
- This indicator does not tell us how long a person received formal education. They could have received a full program of schooling, or may only have been in attendance for a short period. To account for such differences, researchers measure the mean years of schooling or the expected years of schooling .
Despite being in school, many children learn very little
International statistics often focus on attendance as the marker of educational progress.
However, being in school does not guarantee that a child receives high-quality education. In fact, in many countries, the data shows that children learn very little.
Just half – 48% – of the world’s children can read with comprehension by the end of primary school. It’s based on data collected over a 9-year period, with 2016 as the average year of collection.
This is shown in the chart, where we plot averages across countries with different income levels. 1
The situation in low-income countries is incredibly worrying, with 90% of children unable to read by that age.
This can be improved – even among high-income countries. The best-performing countries have rates as low as 2%. That’s more than four times lower than the average across high-income countries.
Making sure that every child gets to go to school is essential. But the world also needs to focus on what children learn once they’re in the classroom.

Millions of children learn only very little. How can the world provide a better education to the next generation?
Research suggests that many children – especially in the world’s poorest countries – learn only very little in school. What can we do to improve this?
- This data does not capture total literacy over someone’s lifetime. Many children will learn to read eventually, even if they cannot read by the end of primary school. However, this means they are in a constant state of “catching up” and will leave formal education far behind where they could be.
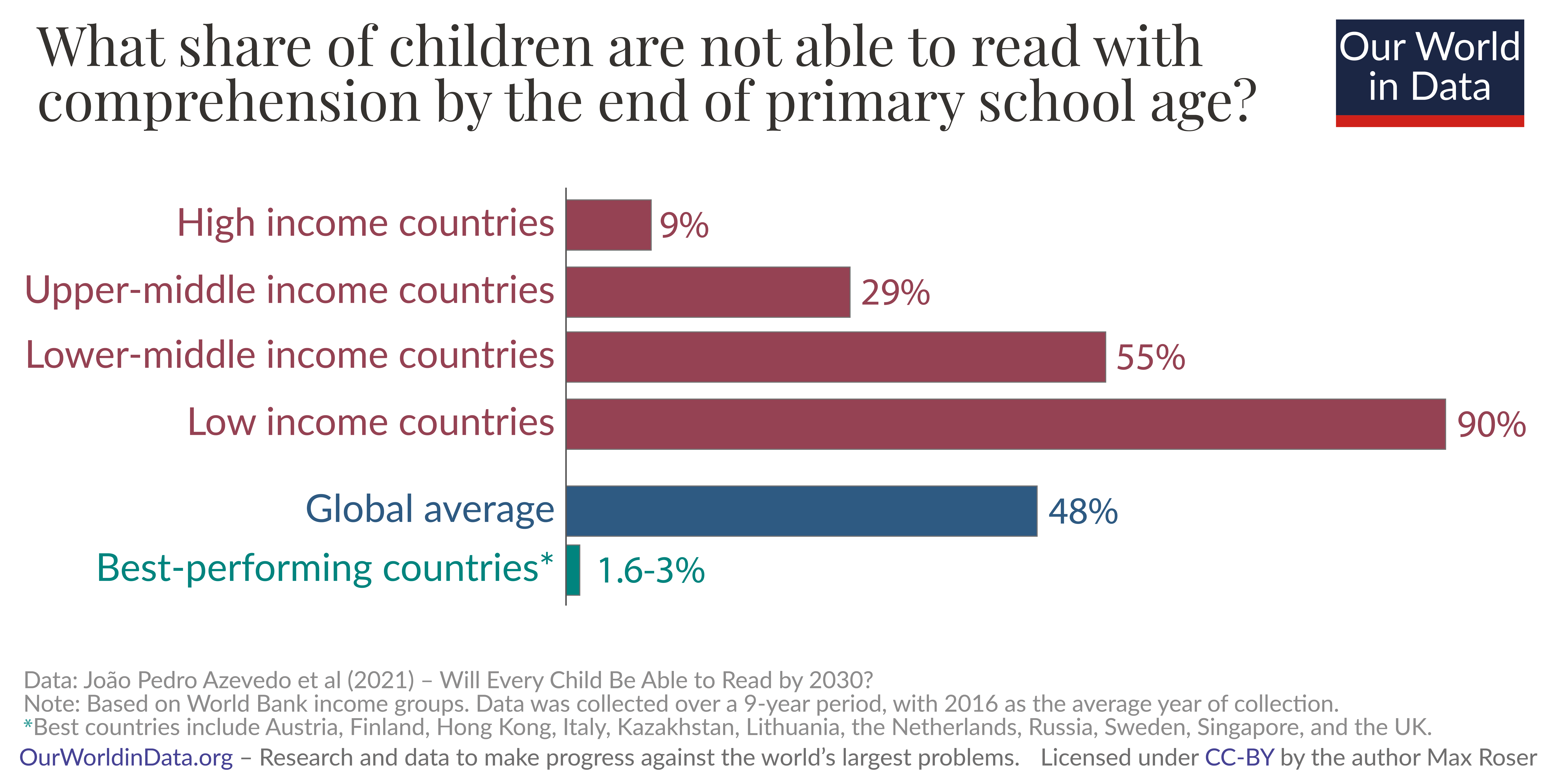
Children across the world receive very different amounts of quality learning
There are still significant inequalities in the amount of education children get across the world.
This can be measured as the total number of years that children spend in school. However, researchers can also adjust for the quality of education to estimate how many years of quality learning they receive. This is done using an indicator called “learning-adjusted years of schooling”.
On the map, you see vast differences across the world.
In many of the world’s poorest countries, children receive less than three years of learning-adjusted schooling. In most rich countries, this is more than 10 years.
Across most countries in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa – where the largest share of children live – the average years of quality schooling are less than 7.
- Learning-adjusted years of schooling merge the quantity and quality of education into one metric, accounting for the fact that similar durations of schooling can yield different learning outcomes.
- Learning-adjusted years is computed by adjusting the expected years of school based on the quality of learning, as measured by the harmonized test scores from various international student achievement testing programs. The adjustment involves multiplying the expected years of school by the ratio of the most recent harmonized test score to 625. Here, 625 signifies advanced attainment on the TIMSS (Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study) test, with 300 representing minimal attainment. These scores are measured in TIMSS-equivalent units.
Hundreds of millions of children worldwide do not go to school
While most children worldwide get the opportunity to go to school, hundreds of millions still don’t.
In the chart, we see the number of children who aren’t in school across primary and secondary education.
This number was around 244 million in 2023.
Many children who attend primary school drop out and do not attend secondary school. That means many more children or adolescents are missing from secondary school than primary education.

Access to basic education: almost 60 million children of primary school age are not in school
The world has made a lot of progress in recent generations, but millions of children are still not in school.
The gender gap in school attendance has closed across most of the world
Globally, until recently, boys were more likely to attend school than girls. The world has focused on closing this gap to ensure every child gets the opportunity to go to school.
Today, these gender gaps have largely disappeared. In the chart, we see the difference in the global enrollment rates for primary, secondary, and tertiary (post-secondary) education. The share of children who complete primary school is also shown.
We see these lines converging over time, and recently they met: rates between boys and girls are the same.
For tertiary education, young women are now more likely than young men to be enrolled.
While the differences are small globally, there are some countries where the differences are still large: girls in Afghanistan, for example, are much less likely to go to school than boys.

Research & Writing
Talent is everywhere, opportunity is not. We are all losing out because of this.
Access to basic education: almost 60 million children of primary school age are not in school, interactive charts on global education.
This data comes from a paper by João Pedro Azevedo et al.
João Pedro Azevedo, Diana Goldemberg, Silvia Montoya, Reema Nayar, Halsey Rogers, Jaime Saavedra, Brian William Stacy (2021) – “ Will Every Child Be Able to Read by 2030? Why Eliminating Learning Poverty Will Be Harder Than You Think, and What to Do About It .” World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 9588, March 2021.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
How much does the government spend on education? What percentage of people are college educated? How are kids doing in reading and math?
Table of Contents
What is the current state of education in the us.
How much does the US spend per student?
Public school spending per student
Average teacher salary.
How educated are Americans?
People with a bachelor's degree
Educational attainment by race and ethnicity.
How are kids doing in reading and math?
Proficiency in math and reading
What is the role of the government in education?
Spending on the education system
Agencies and elected officials.
The education system in America is made up of different public and private programs that cover preschool, all the way up to colleges and universities. These programs cater to many students in both urban and rural areas. Get data on how students are faring by grade and subject, college graduation rates, and what federal, state, and local governments spending per student. The information comes from various government agencies including the National Center for Education Statistics and Census Bureau.
During the 2019-2020 school year, there was $15,810 spent on K-12 public education for every student in the US.
Education spending per k-12 public school students has nearly doubled since the 1970s..
This estimate of spending on education is produced by the National Center for Education Statistics. Instruction accounts for most of the spending, though about a third includes support services including administration, maintenance, and transportation. Spending per student varies across states and school districts. During the 2019-2020 school year, New York spends the most per student ($29,597) and Idaho spends the least ($9,690).
During the 2021-2022 school year , the average public school teacher salary in the US was $66,397 .
Instruction is the largest category of public school spending, according to data from the National Center for Educational Statistics. Adjusting for inflation, average teacher pay is down since 2010.
In 2021 , 35% of people 25 and over had at least a bachelor’s degree.
Over the last decade women have become more educated than men..
Educational attainment is defined as the highest level of formal education a person has completed. The concept can be applied to a person, a demographic group, or a geographic area. Data on educational attainment is produced by the Census Bureau in multiple surveys, which may produce different data. Data from the American Community Survey is shown here to allow for geographic comparisons.
In 2021 , 61% of the Asian 25+ population had completed at least four years of college.
Educational attainment data from the Census Bureau's Current Population Survey allows for demographic comparisons across the US.
In 2022, proficiency in math for eighth graders was 26.5% .
Proficiency in reading in 8th grade was 30.8% ., based on a nationwide assessment, reading and math scores declined during the pandemic..
The National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) is the only nationally representative data that measures student achievement. NAEP is Congressionally mandated. Tests are given in a sample of schools based on student demographics in a given school district, state, or the US overall. Testing covers a variety of subjects, most frequently math, reading, science, and writing.
In fiscal year 2020, governments spent a combined total of $1.3 trillion on education.
That comes out to $4,010 per person..
USAFacts categorizes government budget data to allocate spending appropriately and to arrive at the estimate presented here. Most government spending on education occurs at the state and local levels rather than the federal.
Government revenue and expenditures are based on data from the Office of Management and Budget, the Census Bureau, and the Bureau of Economic Analysis. Each is published annually, although due to collection times, state and local government data are not as current as federal data. Thus, when combining federal, state, and local revenues and expenditures, the most recent year for a combined number may be delayed.
SIGN UP FOR THE NEWSLETTER
Keep up with the latest data and most popular content.

Four of the biggest problems facing education—and four trends that could make a difference
Eduardo velez bustillo, harry a. patrinos.

In 2022, we published, Lessons for the education sector from the COVID-19 pandemic , which was a follow up to, Four Education Trends that Countries Everywhere Should Know About , which summarized views of education experts around the world on how to handle the most pressing issues facing the education sector then. We focused on neuroscience, the role of the private sector, education technology, inequality, and pedagogy.
Unfortunately, we think the four biggest problems facing education today in developing countries are the same ones we have identified in the last decades .
1. The learning crisis was made worse by COVID-19 school closures
Low quality instruction is a major constraint and prior to COVID-19, the learning poverty rate in low- and middle-income countries was 57% (6 out of 10 children could not read and understand basic texts by age 10). More dramatic is the case of Sub-Saharan Africa with a rate even higher at 86%. Several analyses show that the impact of the pandemic on student learning was significant, leaving students in low- and middle-income countries way behind in mathematics, reading and other subjects. Some argue that learning poverty may be close to 70% after the pandemic , with a substantial long-term negative effect in future earnings. This generation could lose around $21 trillion in future salaries, with the vulnerable students affected the most.
2. Countries are not paying enough attention to early childhood care and education (ECCE)
At the pre-school level about two-thirds of countries do not have a proper legal framework to provide free and compulsory pre-primary education. According to UNESCO, only a minority of countries, mostly high-income, were making timely progress towards SDG4 benchmarks on early childhood indicators prior to the onset of COVID-19. And remember that ECCE is not only preparation for primary school. It can be the foundation for emotional wellbeing and learning throughout life; one of the best investments a country can make.
3. There is an inadequate supply of high-quality teachers
Low quality teaching is a huge problem and getting worse in many low- and middle-income countries. In Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, the percentage of trained teachers fell from 84% in 2000 to 69% in 2019 . In addition, in many countries teachers are formally trained and as such qualified, but do not have the minimum pedagogical training. Globally, teachers for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects are the biggest shortfalls.
4. Decision-makers are not implementing evidence-based or pro-equity policies that guarantee solid foundations
It is difficult to understand the continued focus on non-evidence-based policies when there is so much that we know now about what works. Two factors contribute to this problem. One is the short tenure that top officials have when leading education systems. Examples of countries where ministers last less than one year on average are plentiful. The second and more worrisome deals with the fact that there is little attention given to empirical evidence when designing education policies.
To help improve on these four fronts, we see four supporting trends:
1. Neuroscience should be integrated into education policies
Policies considering neuroscience can help ensure that students get proper attention early to support brain development in the first 2-3 years of life. It can also help ensure that children learn to read at the proper age so that they will be able to acquire foundational skills to learn during the primary education cycle and from there on. Inputs like micronutrients, early child stimulation for gross and fine motor skills, speech and language and playing with other children before the age of three are cost-effective ways to get proper development. Early grade reading, using the pedagogical suggestion by the Early Grade Reading Assessment model, has improved learning outcomes in many low- and middle-income countries. We now have the tools to incorporate these advances into the teaching and learning system with AI , ChatGPT , MOOCs and online tutoring.
2. Reversing learning losses at home and at school
There is a real need to address the remaining and lingering losses due to school closures because of COVID-19. Most students living in households with incomes under the poverty line in the developing world, roughly the bottom 80% in low-income countries and the bottom 50% in middle-income countries, do not have the minimum conditions to learn at home . These students do not have access to the internet, and, often, their parents or guardians do not have the necessary schooling level or the time to help them in their learning process. Connectivity for poor households is a priority. But learning continuity also requires the presence of an adult as a facilitator—a parent, guardian, instructor, or community worker assisting the student during the learning process while schools are closed or e-learning is used.
To recover from the negative impact of the pandemic, the school system will need to develop at the student level: (i) active and reflective learning; (ii) analytical and applied skills; (iii) strong self-esteem; (iv) attitudes supportive of cooperation and solidarity; and (v) a good knowledge of the curriculum areas. At the teacher (instructor, facilitator, parent) level, the system should aim to develop a new disposition toward the role of teacher as a guide and facilitator. And finally, the system also needs to increase parental involvement in the education of their children and be active part in the solution of the children’s problems. The Escuela Nueva Learning Circles or the Pratham Teaching at the Right Level (TaRL) are models that can be used.
3. Use of evidence to improve teaching and learning
We now know more about what works at scale to address the learning crisis. To help countries improve teaching and learning and make teaching an attractive profession, based on available empirical world-wide evidence , we need to improve its status, compensation policies and career progression structures; ensure pre-service education includes a strong practicum component so teachers are well equipped to transition and perform effectively in the classroom; and provide high-quality in-service professional development to ensure they keep teaching in an effective way. We also have the tools to address learning issues cost-effectively. The returns to schooling are high and increasing post-pandemic. But we also have the cost-benefit tools to make good decisions, and these suggest that structured pedagogy, teaching according to learning levels (with and without technology use) are proven effective and cost-effective .
4. The role of the private sector
When properly regulated the private sector can be an effective education provider, and it can help address the specific needs of countries. Most of the pedagogical models that have received international recognition come from the private sector. For example, the recipients of the Yidan Prize on education development are from the non-state sector experiences (Escuela Nueva, BRAC, edX, Pratham, CAMFED and New Education Initiative). In the context of the Artificial Intelligence movement, most of the tools that will revolutionize teaching and learning come from the private sector (i.e., big data, machine learning, electronic pedagogies like OER-Open Educational Resources, MOOCs, etc.). Around the world education technology start-ups are developing AI tools that may have a good potential to help improve quality of education .
After decades asking the same questions on how to improve the education systems of countries, we, finally, are finding answers that are very promising. Governments need to be aware of this fact.
To receive weekly articles, sign-up here
Get updates from Education for Global Development
Thank you for choosing to be part of the Education for Global Development community!
Your subscription is now active. The latest blog posts and blog-related announcements will be delivered directly to your email inbox. You may unsubscribe at any time.

Consultant, Education Sector, World Bank

Senior Adviser, Education
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
The Economics of Administration Action on Student Debt
Higher education financing allows many Americans from lower- and middle-income backgrounds to invest in education. However, over the past 30 years, college tuition prices have increased faster than median incomes, leaving many Americans with large amounts of student debt that they struggle or are unable to, pay off.
Recognizing the burden of this debt, the Biden-Harris Administration has pursued two key strategies for debt reduction and cancellation. The first, student debt relief (SDR), aims to address the ill effects of flaws in the student debt system for borrowers. The second, the SAVE plan, reforms the federal student loan system, improving student loan affordability for future students and providing current graduates with breathing room during the beginning of a new career.
This issue brief examines the factors that precipitated the current student debt landscape, and details how both SDR and SAVE will enhance the economic status of millions of Americans with student debt: enabling them to allocate more funds towards basic necessities, take career risks, start businesses, and purchase homes. This brief highlights credible research, underscoring how the Administration’s student debt relief could boost consumption in the short-term by billions of dollars and could have important impacts on borrower mental health, financial security, and outcomes such as homeownership and entrepreneurship. This brief also details how the SAVE plan makes repaying college costs more affordable for current borrowers and future generations. CEA simulations show that, under SAVE, an average borrower with a bachelor’s degree could save $20,000 in loan payments, while a borrower with an associate degree could see nearly 90 percent savings compared to the standard loan repayment plan. These changes enable more people to pursue education and contribute to the broader economy.
Why do borrowers need relief?
Over the last 20 years especially, the sticker price of college has risen significantly. Despite recent minor declines, sticker prices at public universities (which over 70% of undergraduate students in the United States attend) are 56% higher today than two decades ago. [1] While there are many reasons for this trend, the most rapid increases in tuition often occur during economic downturns as tuitions grow to fill the budgetary holes that are left when states cut their support to public colleges ( Webber, 2017 ; Deming and Walters 2018 ). This is especially problematic given many people choose to return to school during economic downturns ( Betts and MacFarland 1995 ; Hillman and Orians 2013 ). Unfortunately, contracting state appropriations have played a role in shifting the responsibility of financing away from public subsidies and toward students and families ( Turner and Barr, 2013 ; Bound et al., 2019 )–leading many students to take on more debt.
At the same time that college sticker prices have risen, the wage premium (the earnings difference between college goers and high school graduates) has not seen analogous growth. While obtaining a college degree remains a reliable entry point to the middle class, the relative earning gains for degree holders began to stagnate in the early 2000s after increasing for several decades. As shown in Figure 1b, since 2000, the wage premium for both bachelor’s degree holders and those with “some college” education (which includes anyone who enrolled in college but didn’t earn a BA) saw declines around the 2001-02 and 2008-10 recessions and a slow, inconsistent recovery thereafter. The decline is particularly notable for students who didn’t complete a four-year degree, a group that includes two-year college enrollees who have among the highest student loan default rates. [2]
Traditional economic theory tells us that individuals choose to invest in post-secondary education based on the expected costs and wage returns associated with the investment. But rapid and unforeseeable rises in prices and declines in college wage premia have contributed to decades of “unlucky” college-entry cohorts affected by a form of recessionary scarring . For example, a student who entered college in 2006 would have expected a sticker price of roughly $8,800 per year for a four-year college, but actually faced tuition of over $10,000 in their final year of college, a roughly 15% difference. This same student, upon graduation if they worked full time, would have earned about $3,500 less, on average, than what they would have expected upon entering. This example illustrates that many borrowers made sound borrowing decisions with available information, but as a result of these trends ended up with more debt than they could afford to pay off. [3] Consistent with this notion, the default rate for “unlucky” college entry cohorts of the 2000s is much higher than those of other cohorts, with undergraduate default rates doubling between 2000 and 2010: in 2017, 21 percent of undergraduate loan holders and 6 percent of graduate loan holders defaulted within 3 years ( CBO, 2020 ).
It is important to note that sticker prices for public institutions have declined 7 percent since 2021, the same period over which college wage premiums have been rising. Declining tuition, for the first time in decades, coincided with increased investment in higher education through pandemic-era legislation such as the American Rescue Plan, which allocated $40 billion in 2021 to support institutes of higher education and their students. Despite these improvements, as well as significant advances in the return on college investments over the last three years, many current borrowers still need some relief. The Administration has taken significant action to protect future cohorts from similar risks.
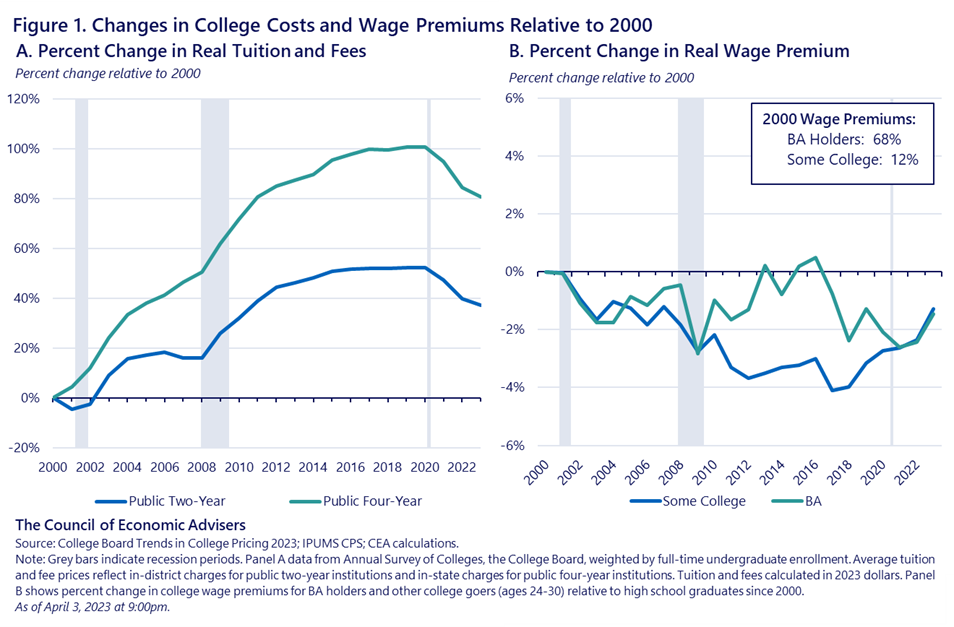
How the Administration is providing relief
Retrospective: Student Debt Relief Helps Existing Borrowers
In a commitment to help those who are overburdened with debt, the Administration has already approved Federal student debt cancellation for nearly 4 million Americans through various actions. Today , the Administration announced details of proposed rules that, if finalized as proposed, would provide relief to over 30 million borrowers when taken together with actions to date.
Importantly, much of this debt forgiveness comes from correcting program administration and improving regulations related to laws that were on the books before this Administration took office. This debt relief has affected borrowers from all walks of life, including nearly 900,000 Americans who have dedicated their lives to public service (such as teachers, social workers, nurses, firefighters, police officers, and others), borrowers who were misled and cheated by their institutions, and borrowers who are facing total or permanent disability, including many veterans. By relieving these borrowers of long-held, and in some cases very large burdens of debt, relief can have significant meaning and impact for borrowers, families, and their communities.
By reducing debtors’ liabilities, debt relief raises net worth (assets, including income less liabilities). Debt relief can also ease the financial burden of making payments—leading to greater disposable income for borrowers and their families, which enhances living standards and could positively influence decisions about employment, home buying, and mobility. While there are few direct estimates of the effect of debt cancelation in the literature, estimates based on the relationship between wealth and consumption suggest that this forgiveness could increase consumption by several billions of dollars each year in the next five to ten years.
Additionally, a recent study suggests that student debt cancellation can lead to increased earnings (due to greater geographic and career mobility), improved credit scores, and lower delinquency rates on other debts ( Di Maggio, Kalda, and Yao, 2019 ). This can facilitate access to capital for starting a business or buying a car or home. As home mortgages often require a certain debt-to-income ratio and depend heavily on credit scores, student debt cancellation could potentially increase home ownership. Indeed, based on the mechanical relationship between housing industry affordability standards and debt-to-income ratios, industry sources have suggested that those without student debt could afford to take out substantially larger mortgages ( Zillow, 2018 ). Other research also indicates a negative correlation between student loan debt and homeownership ( Mezza et al., 2020 ).

It is important to note that, while these pecuniary benefits are important, the benefits associated with debt relief are not merely financial. Experimental evidence has linked holding debt to heightened levels of stress and anxiety ( Drentea and Reynolds, 2012 ), worse self-reported physical health ( Sweet et al., 2013 ), and reduced cognitive capacity ( Robb et al., 2012 ; Ong et al., 2019 ). Studies also show that holding student debt can be a barrier to positive life cycle outcomes such as entrepreneurship ( Krishnan and Wang, 2019 ), and marriage ( Gicheva, 2016 ; Sieg and Wang, 2018 ). Student debt relief has the potential to improve these key outcomes for millions of borrowers.
Prospective: The SAVE Plan Helps Prevent Future Challenges
To address unaffordable education financing moving forward, the Administration has also introduced the Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) loan repayment program. The SAVE plan prospectively helps student borrowers by ensuring that once they graduate, they never have to pay more than they can afford towards their student loan debt. Importantly, the SAVE plan protects borrowers from being “unlucky” by ensuring that high tuition or low earnings do not result in loan payments that borrowers can’t afford. The CEA has detailed the real benefits of SAVE for borrowers in issue briefs and blogs , underscoring that SAVE is the most affordable student loan repayment program in U.S. history. By substantially reducing monthly payment amounts compared to previous income driven repayment (IDR) plans and reducing time to forgiveness to as little as 10 years for people who borrowed smaller amounts, the SAVE plan can mean tens of thousands of dollars in real savings for borrowers over the course of repayment.
Figure 2 gives the example of two representative borrowers. Take the first, a 4-year college graduate who has $31,000 in debt and earns about $40,500 per year. Under a standard repayment plan, this borrower would pay roughly $330 dollars each month for 10 years. Under SAVE, this borrower would pay about $50 per month for the first ten years, and on average about $130 per month for the next 10 years. Over a 20-year period, this borrower would make roughly $17,500 less in payments, not accounting for inflation over that period. This represents a 56 percent reduction in total payments compared to the standard repayment plan and includes considerable loan forgiveness. Similarly, the representative 2-year college graduate has $10,000 in debt and earns about $32,000 per year. Under a standard plan, this borrower would pay $110 dollars each month for 10 years. Under SAVE, this borrower would pay $0 per month for the first two years, and under $20 per month for the next eight years before their debt is forgiven at year 10. Overall, this borrower would be responsible for roughly $11,700 less in lifetime payments, not accounting for inflation. This borrower sees nearly 90 percent savings compared to the standard plan and receives considerable loan forgiveness.
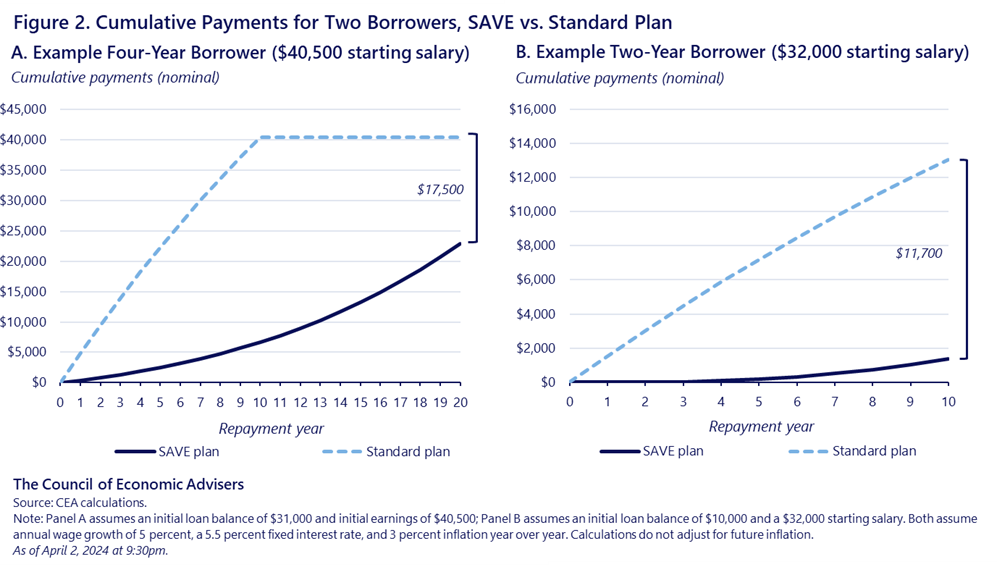
SAVE can also have benefits beyond the individual borrower. More money in borrowers’ pockets due to lower payment obligations under SAVE could boost consumption and give borrowers breathing room to make payments on other debt. This consumption effect is bolstered by a large literature documenting the benefits of easing liquidity constraints (see, for example, Aydin, 2022 ; Parker et al., 2022 ). Additionally, by shortening time to forgiveness for undergraduate borrowers, SAVE can lead to positive debt-relief outcomes (as discussed above) for many more borrowers.
Another key aspect of income-driven repayment plans like SAVE is that they protect borrowers from having to make large payments when incomes are low. Specifically, the required payments are not based on the initial loan balance, but on one’s income and household size so that those cohorts who need to borrow more to pay for college do not make larger payments unless they make more income. SAVE also protects more of a borrower’s income as discretionary and, when the full plan is implemented in Summer 2024, will limit monthly payments on undergraduate loans to 5 percent of discretionary income. In fact, for single borrowers who make less than $33,000 per year, the required monthly payments will be zero dollars. From a finance perspective, the SAVE plan provides a form of insurance against tuition spikes and economic downturns–taking some of the risk out of investing in one’s education while also bringing costs down.
A common concern, and one that could mute these benefits, is that increases in the generosity of education financing may encourage institutions to raise tuition and fees in response, a phenomenon commonly referred to as the Bennett Hypothesis (for an excellent overview of research, see Dynarski et al., 2022 ). Theoretically, in a market when sellers are maximizing profits, any policy that increases demand will also increase prices. However, this is less likely to impact the over 70% of U.S. undergraduates who attend public colleges, which are not profit-driven and often have statutorily set tuition. Consistent with this notion, the evidence in support of the Bennett Hypothesis primarily comes from for-profit colleges, which are highly reliant on students who receive federal financial aid ( Cellini and Goldin, 2014 ; Baird et al, 2022 ). [4] Importantly, although the for-profit sector enrolls some of the country’s most vulnerable students, enrollment in the sector in 2021 accounted for only 5 percent of total undergraduate enrollment, suggesting that aggregate tuition increases in response to changes in education financing may be modest. Furthermore, the Biden-Harris Administration has taken action to crack down on for-profit colleges that take advantage of, or mislead, their students. And, recent regulations, such as the Gainful Employment ( GE ) rule, add safeguards against unaffordable debt regardless of more generous education financing.
Although the SAVE plan stands to benefit borrowers of all backgrounds, the plan has important racial and socioeconomic equity implications because it is particularly beneficial for those borrowers with the lowest incomes. Centuries of inequities have led to Black, Hispanic, and Native households being more likely than their White peers to fall in the low end of the income distribution. This means that, mechanically, the SAVE plan’s benefits could accrue disproportionately to these groups. Indeed, using completion data from recent years, an Urban Institute analysis estimates that 59 percent of credentials earned by Black students and 53 percent of credentials earned by Hispanic students are likely to be eligible for some amount of loan forgiveness under SAVE, compared to 42 percent of credentials earned by White students ( Delisle and Cohn, 2023 ). Finally, the interest subsidy described in an August 2023 CEA blog , prevents ballooning balances when a borrower cannot cover their entire monthly interest payment, a phenomenon that has historically led to many borrowers in general, and Black borrowers in particular, to see loan balances that are higher than their original loan amount, even several years out from graduating with a bachelor’s degree ( NCES, 2023 ).
Broader economic impacts
The benefits associated with SDR and SAVE for millions of Americans are considerable. In the short run, under both SDR and SAVE, those who receive relief may be able to spend more in their communities and contribute to their local economies. Summing the likely consumption effects of the Administration’s student debt relief and SAVE programs results in billions of dollars in additional consumption annually. Despite the modest effect on the macroeconomy as a whole (note that the U.S. economy is roughly $28 trillion with a population of roughly 320 million), these consumption effects represent incredibly meaningful impacts on individual borrowers’ financial security and the economic wellbeing of their communities.
SAVE, because it brings down the cost of taking out loans to go to college, has the potential to lead to longer-term economic growth if it leads to greater educational attainment. This increased attainment can occur both through improved retention and completion of post-secondary education, and also the movement of students into college who would not have otherwise enrolled. There is a long macroeconomics literature linking educational attainment in a nation to GDP growth (see, for example, Lucas, 1988 ; Hanushek and Woesmann, 2008 ). While identifying the causal effect of schooling on GDP is challenging, researchers, using a variety of approaches, find that a one-year increase in average education (for the entire working population) would increase the real GDP level by between 5 and 12 percent ( Barro and Lee, 2013 ; Soto, 2002 ) —a result that is in line with the micro-founded relationship between years of education and earnings ( Lovenheim and Smith, 2022 ).
To put this relationship in perspective and highlight the growth potential of increasing educational attainment, the CEA simulated the hypothetical effect on GDP of increasing the college-going rate by 1, 3, and 5 percentage points, respectively. This range represents the kinds of changes in college going that have been observed over several years: the college enrollment rate for 18- to 24-year-olds declined 4 percentage points between 2011 and 2021 after increasing by 6 percentage points between 2000 and 2011 ( NCES 2023 ). CEA simulations show that by 2055, a policy that increased the college going rate by 1, 3, and 5 percentage points could increase the level of GDP in 2055 (thirty years from now) by 0.2, 0.6, and 1 percent respectively. This represents hundreds of billions of dollars of additional economic activity in the long run.
While increased growth is an exciting possibility, it would only occur insofar as SAVE leads to increased educational attainment, which is uncertain. The academic literature has found that student loans can promote academic performance ( Barr, et. al. 2021 ), and increase educational attainment by increasing transfers from 2-year to 4-year colleges and increasing college completion among enrollees ( Marx and Turner, 2019 ). At the same time, increases in college-going due to SAVE are by no means guaranteed. While, historically, policies that reduce the cost of college through direct means—such as providing students with generous grant aid, or reducing tuition—have succeeded at raising college enrollment levels ( Dynarski, 2003 ; Turner, 2011 ), a pair of recent studies show that prospective students may only respond to cost changes when they are salient, i.e., they are framed and marketed in the right way ( Dynarski et al., 2021 ), and relatively certain ( Burland et al., 2022 ). However, evidence suggests that there is demand for plans like SAVE ( Balakrishnan et al., 2024 ), particularly as SAVE can provide sizable benefits to borrowers in terms of reducing their long-term debt burden and keep monthly payments low (dependent on a borrower’s income) after they finish school.
This highlights the importance of communicating the benefits of the SAVE program to prospective students who otherwise would not enroll in college due to cost concerns, including potential barriers to paying off student loans in the future. Doing so could lead to meaningful increases in college enrollment, and the resulting improvements in productive capacity could increase the size of the U.S. economy for years to come.
Concluding remarks
The Biden-Harris Administration has taken bold action to address a student debt problem that has been decades in the making. This student debt cancellation will provide well-deserved relief for borrowers who have paid their fair share, many of whom had the proverbial rug pulled out from under them with concurrent rapidly rising tuition and declining returns to a college degree. The relief has and will improve economic health and wellbeing of those who have devoted years of their life to public service, those who were defrauded or misled by their institutions, and those who have been doing all they can to make payments, but have still seen their loan balances grow. Looking to future generations, the Administration implemented the SAVE plan to protect borrowers against tuition spikes and poorer than expected labor market outcomes that often plague students graduating into a period of economic downturn ( Rothstein, 2021 ; Schwandt and von Wachter, 2023 ).
Both student debt relief and SAVE will enhance the economic status of millions of Americans with student debt: enable them to allocate more funds towards basic necessities, take career risks, start businesses, and purchase homes with the understanding that they will never have to pay more than they can afford towards their student loans. Moreover, the SAVE plan makes repayment more affordable for future generations, which helps borrowers manage monthly payments, but also enables more people from all walks of life to explore their full potential and pursue higher education, enhancing the potential of the U.S. workforce and the economy more broadly.
[1] In 2021, 51% of total undergraduates attended public 4-year universities and 21% attended public 2-years in 2021.
[2] The BA group excludes those with a graduate degree, or any education beyond a bachelor’s degree.
[3] Recent research shows that, despite a positive return on investment (ROI) for many, including the average student, the distribution of ROI has widened over the last several decades such that the likelihood of negative ROI is higher than it has historically been, particularly so for underrepresented minority students ( Webber 2022 ).
[4] There is also some evidence in support of the Bennett Hypothesis at the graduate level ( Black et al. 2023 ).
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
We couldn’t find any results matching your search.
Please try using other words for your search or explore other sections of the website for relevant information.
We’re sorry, we are currently experiencing some issues, please try again later.
Our team is working diligently to resolve the issue. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
News & Insights

SMCI Factor-Based Stock Analysis
October 23, 2024 — 08:06 am EDT
Written by John Reese for Validea ->
Below is Validea's guru fundamental report for SUPER MICRO COMPUTER INC ( SMCI ) . Of the 22 guru strategies we follow, SMCI rates highest using our Twin Momentum Investor model based on the published strategy of Dashan Huang . This momentum model looks for a combination of fundamental momentum and price momentum.
SUPER MICRO COMPUTER INC ( SMCI ) is a large-cap growth stock in the Computer Hardware industry. The rating using this strategy is 100% based on the firm’s underlying fundamentals and the stock’s valuation. A score of 80% or above typically indicates that the strategy has some interest in the stock and a score above 90% typically indicates strong interest.
The following table summarizes whether the stock meets each of this strategy's tests. Not all criteria in the below table receive equal weighting or are independent, but the table provides a brief overview of the strong and weak points of the security in the context of the strategy's criteria.
Detailed Analysis of SUPER MICRO COMPUTER INC
SMCI Guru Analysis
SMCI Fundamental Analysis
More Information on Dashan Huang
Dashan Huang Portfolio
About Dashan Huang : Dashan Huang is an Assistant Professor of Finance at the Lee Kong Chian School of Business at Singapore Management University. His paper "Twin Momentum" looked at combining traditional price momentum with improving fundamentals to generate market outperformance. In the paper, he identified seven fundamental variables (earnings, return on equity, return on assets, accrual operating profitability to equity, cash operating profitability to assets, gross profit to assets and net payout ratio) that he combined into a single fundamental momentum measure. He showed that stocks in the top 20% of the universe according to that measure outperformed the market going forward. When he combined that measure with price momentum, he was able to double its outperformance.
Additional Research Links
Top NASDAQ 100 Stocks
Top Technology Stocks
Top Large-Cap Growth Stocks
High Momentum Stocks
Top Chip Stocks
High Insider Ownership Stocks
About Validea : Validea is an investment research service that follows the published strategies of investment legends. Validea offers both stock analysis and model portfolios based on gurus who have outperformed the market over the long-term, including Warren Buffett, Benjamin Graham, Peter Lynch and Martin Zweig. For more information about Validea, click here
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.

Stocks mentioned
More related articles.
This data feed is not available at this time.
Sign up for the TradeTalks newsletter to receive your weekly dose of trading news, trends and education. Delivered Wednesdays.
To add symbols:
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to My Quotes by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
- Copy and paste multiple symbols separated by spaces.
These symbols will be available throughout the site during your session.
Your symbols have been updated
Edit watchlist.
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to Watchlist by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
Opt in to Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio is supported by our partner TipRanks. By connecting my portfolio to TipRanks Smart Portfolio I agree to their Terms of Use .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
O. Smith and R. H. Ennis edited the volume Language and Concepts in Education (1961); and R.D. Archambault edited Philosophical Analysis and Education (1965), consisting of essays by a number of prominent British writers, most notably R. S. Peters (whose status in Britain paralleled that of Scheffler in the United States), Paul Hirst, and John ...
The Functions of Education. Functional theory stresses the functions that education serves in fulfilling a society's various needs. Perhaps the most important function of education is socialization.If children need to learn the norms, values, and skills they need to function in society, then education is a primary vehicle for such learning.
This paper offers a critical examination of the nature of inequalities in relation to education and the pursuit of social justice. ... Marjoribanks K (1998) Family background, social and academic capital and adolescents' aspirations: A mediational analysis. Social Psychology of Education 2: 177-197. Crossref. Google Scholar. Marjoribanks K ...
This chapter gives an overall introduction to critical theories essential to education, as we lay out the histories, reasoning, needs, and overall structure of the Palgrave Handbook on Critical Theories of Education.We discuss the five groundings that are the conceptual and theoretical thematic constructions of the book as follows: praxis-oriented, fluidity, radical, utopic with countless ...
1. Problems in delineating the field. There is a large—and ever expanding—number of works designed to give guidance to the novice setting out to explore the domain of philosophy of education; most if not all of the academic publishing houses have at least one representative of this genre on their list, and the titles are mostly variants of the following archetypes: The History and ...
The limitations of Peters's analysis of the concept of education in his chapter on "Criteria of Education" are well known. In the chapter on "Education as Initiation," however, Peters offered a synthetic sketch of education that, Beckett argues, points us toward a more comprehensive definition of education, one which, he maintains, can ...
Philosophical analysis wants to be a toolbox philosophy for education and not a top-down philosophy applied to the domain of education. Footnote 21 So, the new, revolutionary approach identifies philosophy of education as an ahistorical, neutral, analytic method to handle (and hopefully resolve) concrete issues on the educational work floor.
What Is Sociology of Education? Theoretical Perspectives. CHAPTER 1. A . whole new perspective on schools and education lies in the study of sociology of education. How sociologists understand education can contribute to informed decision making and change in educational institutions. Sociologists of education focus on . interactions . between ...
Education production functions. Eric A. Hanushek, in The Economics of Education (Second Edition), 2020 Overview. Much of the analysis in the economics of education flows from a simple model of production. The common inputs are things like school resources, teacher quality, and family attributes; and the outcome is some measure of student achievement—frequently but not always student test scores.
Education, Economics of. E.A. Hanushek, in International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2001 The accumulated economic analysis of education suggests that current provision of schooling is very inefficient. Commonly purchased inputs to schools class size, teacher experience, and teacher education bear little systematic relationship to student outcomes, implying that ...
In addition to the analysis of Education for All, policy analysis should review several aspects that has affected the decision-making and implementation process of the educational sector. Quality education includes: learners, learning environments, content, process, and outcomes. EFA Global
Education is the transmission of knowledge, skills, and character traits and manifests in various forms. ... A meta-analysis by Engin Karadağ et al. concludes that, compared to other influences, factors related to the school and the teacher have the greatest impact on educational success.
It uses regular monitoring and evaluation to improve strategic plans: The strength of an education sector analysis, and of the resulting strategic plan, is highly dependent on the quality of the data used. Thus, one key element of strategic planning is improving the monitoring and evaluation system that collects fundamental educational data, as ...
An education sector analysis (ESA) is an in-depth, holistic diagnosis of an education system. It assists with understanding how an education system (and its subsectors) works, why it works that way, and how to improve it. An ESA provides the evidence base for decision-making and is the first step in preparing an education sector plan.
A good education offers individuals the opportunity to lead richer, more interesting lives. At a societal level, it creates opportunities for humanity to solve its pressing problems.. The world has gone through a dramatic transition over the last few centuries, from one where very few had any basic education to one where most people do.
To illustrate the importance of this sort of conceptual analysis in education, I track the educational impact of three concepts of knowledge: (1) the traditional philosophical concept of knowledge as justified, true belief; (2) Michael Young's concept of 'knowledge of the powerful'; and (3) Young's concept of 'powerful knowledge'. ...
Descriptive analysis in education: A guide for researchers. Whether the goal is to identify and describe trends and variation in populations, create new measures of key phenomena, or describe samples in studies aimed at identifying causal effects, description plays a critical role in the scientific process in general and education research in particular.
USAFacts categorizes government budget data to allocate spending appropriately and to arrive at the estimate presented here. Most government spending on education occurs at the state and local levels rather than the federal. Government revenue and expenditures are based on data from the Office of Management and Budget, the Census Bureau, and the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Biesta, G. (2011) Disciplines and theory in the academic study of education: a comparative analysis of the Anglo-American and continental construction of the field, Pedagogy Culture & Society, 19 (open in a new window) (2 (open in a new window)), 175-192. doi: 10.1080/14681366.2011.582255.
In 2022, we published, Lessons for the education sector from the COVID-19 pandemic, which was a follow up to, Four Education Trends that Countries Everywhere Should Know About, which summarized views of education experts around the world on how to handle the most pressing issues facing the education sector then.We focused on neuroscience, the role of the private sector, education technology ...
Why education level has become the best predictor for how someone will vote Analysis by Zachary B. Wolf, CNN 4 minute read Updated 4:14 PM EDT, Mon October 14, 2024 Link Copied! ...
Graduates with a special education master's with an ABA concentration can work in education, program management, speech pathology, social work, behavioral consulting and more. For example, in special education ABA is useful in helping students who face learning or behavior challenges such as autism or ADHD.
ensuring all students have access to higher education. With the 2024-25 FAFSA form, the U.S. Department of Education (Department) implemented two bipartisan pieces of legislation: the FAFSA Simplification Act and the Fostering Undergraduate Talent by Unlocking Resources for Education Act (FUTURE Act). Together, these laws make the most far ...
By: Luke Rhine, Deputy Assistant Secretary the Office of Career, Technical & Adult Education Dual enrollment works. The Biden-Harris Administration is deeply committed to the use and expansion of high-quality dual enrollment programs to improve student access to rigorous coursework and equitable postsecondary opportunities. Recently, the Department of Education hosted a webinar featuring a ...
In 2021, 51% of total undergraduates attended public 4-year universities and 21% attended public 2-years in 2021. The BA group excludes those with a graduate degree, or any education beyond a ...
Below is Validea's guru fundamental report for SUPER MICRO COMPUTER INC (SMCI). Of the 22 guru strategies we follow, SMCI rates highest using our Twin Momentum Investor model based on the ...