- Frontiers in Sociology
- Media Governance and the Public Sphere
- Research Topics

Social Media and Political Participation: Unpacking the Role of Social Media in Contemporary Politics
Total Downloads
Total Views and Downloads
About this Research Topic
The rapid evolution of social media has transformed the landscape of contemporary politics and civil engagement. Social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, WhatsApp, and WeChat, in addition to less censored platforms such as Redditt and Telegram, among others, have emerged as ...
Keywords : social media, politics, political participation, Twitter, communication
Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Topic Editors
Topic coordinators, recent articles, submission deadlines.
| Manuscript | |
| Manuscript Extension |
Participating Journals
Manuscripts can be submitted to this Research Topic via the following journals:
total views
- Demographics
No records found
total views article views downloads topic views
Top countries
Top referring sites, about frontiers research topics.
With their unique mixes of varied contributions from Original Research to Review Articles, Research Topics unify the most influential researchers, the latest key findings and historical advances in a hot research area! Find out more on how to host your own Frontiers Research Topic or contribute to one as an author.
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
How does social media use influence political participation and civic engagement? A meta-analysis
2015 paper in Information, Communication & Society reviewing existing research on how social media use influences measures such as voting, protesting and civic engagement.
Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by John Wihbey, The Journalist's Resource October 18, 2015
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/politics-and-government/social-media-influence-politics-participation-engagement-meta-analysis/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
Academic research has consistently found that people who consume more news media have a greater probability of being civically and politically engaged across a variety of measures. In an era when the public’s time and attention is increasingly directed toward platforms such as Facebook and Twitter, scholars are seeking to evaluate the still-emerging relationship between social media use and public engagement. The Obama presidential campaigns in 2008 and 2012 and the Arab Spring in 2011 catalyzed interest in networked digital connectivity and political action, but the data remain far from conclusive.
The largest and perhaps best-known inquiry into this issue so far is a 2012 study published in the journal Nature , “A 61-Million-Person Experiment in Social Influence and Political Mobilization,” which suggested that messages on users’ Facebook feeds could significantly influence voting patterns. The study data — analyzed in collaboration with Facebook data scientists — suggested that certain messages promoted by friends “increased turnout directly by about 60,000 voters and indirectly through social contagion by another 280,000 voters, for a total of 340,000 additional votes.” Close friends with real-world ties were found to be much more influential than casual online acquaintances. (Following the study, concerns were raised about the potential manipulation of users and “digital gerrymandering.” )
There are now thousands of studies on the effects of social networking sites (SNS) on offline behavior, but isolating common themes is not easy. Researchers often use unique datasets, ask different questions and measure a range of outcomes. However, a 2015 metastudy in the journal Information, Communication & Society , “Social Media Use and Participation: A Meta-analysis of Current Research,” analyzes 36 studies on the relationship between SNS use and everything from civic engagement broadly speaking to tangible actions such as voting and protesting. Some focus on youth populations, others on SNS use in countries outside the United States. Within these 36 studies, there were 170 separate “coefficients” — different factors potentially correlated with SNS use. The author, Shelley Boulianne of Grant MacEwan University (Canada), notes that the studies are all based on self-reported surveys, with the number of respondents ranging from 250 to more than 1,500. Twenty studies were conducted between 2008 and 2011, while eight were from 2012-2013.
The study’s key findings include:
- Among all of the factors examined, 82% showed a positive relationship between SNS use and some form of civic or political engagement or participation. Still, only half of the relationships found were statistically significant. The strongest effects could be seen in studies that randomly sampled youth populations.
- The correlation between social-media use and election-campaign participation “seems weak based on the set of studies analyzed,” while the relationship with civic engagement is generally stronger.
- Further, “Measuring participation as protest activities is more likely to produce a positive effect, but the coefficients are not more likely to be statistically significant compared to other measures of participation.” Also, within the area of protest activities, many different kinds of activities — marches, demonstrations, petitions and boycotts — are combined in research, making conclusions less valid. When studies do isolate and separate out these activities, these studies generally show that “social media plays a positive role in citizens’ participation.”
- Overall, the data cast doubt on whether SNS use “causes” strong effects and is truly “transformative.” Because few studies employ an experimental design, where researchers could compare a treatment group with a control group, it is difficult to claim causality.
“Popular discourse has focused on the use of social media by the Obama campaigns,” Boulianne concludes. “While these campaigns may have revolutionized aspects of election campaigning online, such as gathering donations, the metadata provide little evidence that the social media aspects of the campaigns were successful in changing people’s levels of participation. In other words, the greater use of social media did not affect people’s likelihood of voting or participating in the campaign.”
It is worth noting that many studies in this area take social media use as the starting point or “independent variable,” and therefore cannot rule out that some “deeper” cause — political interest, for example — is the reason people might engage in SNS use in the first place. Further, some researchers see SNS use as a form of participation and engagement in and of itself, helping to shape public narratives and understanding of public affairs.
Related research: Journalist’s Resource has been curating a wide variety of studies in this field. See research reviews on: Effects of the Internet on politics ; global protest and social media ; digital activism and organizing ; and the Internet and the Arab Spring . For cutting-edge insights on how online organizing and mobilization is evolving, see the 2015 study “Populism and Downing Street E-petitions: Connective Action, Hybridity, and the Changing Nature of Organizing,” published in Political Communication .
Keywords: social media, Facebook, Twitter
About The Author
John Wihbey
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- The Political Environment on Social Media
- 3. Social media and political engagement
Table of Contents
- 1. Political content on social media
- 2. The tone of social media discussions around politics
- Acknowledgments
- Methodology
For those who are heavily interested in politics, social media offers an especially compelling environment for engaging with news, information and discussion about political issues. But although social media can help facilitate connections to the causes people care about, it can also expose these same users to negative or aggressive speech and require them to more attentively curate their social feeds.
This chapter of the report examines the experiences and attitudes of highly politically engaged social media users. For the purposes of this report, highly engaged Americans are defined as those who are registered to vote; who say that they always or almost always vote in elections; and who have volunteered or contributed money to political parties, campaigns or groups in the past year. 3
Social media users with high levels of political engagement take an active approach to curating the content they consume and the users they are connected to

Compared to those with lower levels of political engagement, highly-engaged social media users take a fairly active role when it comes to entering into political discussions or otherwise engaging with political content. Roughly one-in-five (19%) of these highly engaged social media users “often” comment, post or discuss political or government issues with others on social media, triple the share among social media users who are less politically engaged (6%).
These highly engaged users also take a more active role when it comes to curating their online political networks. For instance, they are more likely to follow political candidates or figures: 53% do so, compared with 21% of users with low levels of political engagement. And when one of their friends posts political content they disagree with, some 30% of highly engaged social media users say they typically respond with a comment or post of their own. That is more than double the share of less-engaged social media users who typically respond in this way (13%). In addition, 42% of these politically active users have changed their settings to see fewer posts from someone they follow because of politics (30% of less-engaged users have done so), and 34% have blocked or unfriended someone as a result of politics (compared with 26% of less-engaged users). However, the root causes that each group give for doing so are largely the same: by a substantial margin, both groups say that the top reason they take these steps is because someone posted political content that they found offensive.
Highly engaged social media users see greater levels of negativity in the tone of social media discussions – but also express greater optimism about the ability of social media to facilitate political action

When asked about the political interactions they see on social media, many politically engaged users are dismayed at the negativity and tone of political discourse. For instance, a slight majority of these users (53%) agree that the statement “people say things when discussing politics on social media that they would never say in person” describes social media very well; 38% of less-engaged users feel equally strongly.
These highly engaged social media users are also more likely to feel that the discussions they see on social media pertaining to politics are less enjoyable in a variety of ways than the political discussions they see occurring elsewhere. This is especially notable in the context of political correctness: Fully 57% of highly engaged social media users feel that social media conversations are less politically correct than those they see elsewhere: Just 39% of less-engaged users feel the same way. And a substantial majority of highly engaged users see social media as angrier, less civil and less respectful than other venues for discussing politics.
Yet even as they express heightened concern at the tone and tenor of social media conversations, highly politically engaged users also express greater appreciation for the ability of social media to foster inclusivity and to connect people to causes that are important to them. Nearly one-third of highly engaged social media users (31%) feel that social media bring new voices into the political discussion “very well” (vs. 20% of less engaged users). Similarly, 30% of highly engaged users say social media help people get involved with issues that matter to them “very well,” compared with 21% of less-engaged users. And these politically engaged users are around twice as likely as less-engaged users to say that they ultimately like seeing lots of political content on social media (35% do so, compared with 18% of less-engaged users).
- In total, 11% of all U.S. adults meet this definition of “highly engaged” politically. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
Most Popular
Report materials.
- American Trends Panel Wave 19
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- Campus News
- Campus Events
- Devotionals and Forums
- Readers’ Forum
- Education Week
- Breaking News
- Police Beat
- Video of the Day
- Current Issue
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- The Daily Universe Magazine, December 2022
- The Daily Universe, November 2022
- The Daily Universe Magazine, October 2022
- The Daily Universe Magazine, September 2022 (Black 14)
- The Daily Universe Magazine, March 2022
- The Daily Universe Magazine, February 2022
- The Daily Universe Magazine, January 2022
- December 2021
- The Daily Universe Magazine, November 2021
- The Daily Universe, October 2021
- The Daily Universe Magazine, September 2021
- Pathway to Education: Breaking Ground in Ghana
- Hope for Lahaina: Witnesses of the Maui Wildfires
- Auschwitz-Birkenau Memorial
- Remembering Rumbula: Preserving the memory of the WWII massacre in Riga
- The Black 14: Healing Hearts and Feeding Souls
- Camino de Santiago
- A Poor Wayfaring Man
- Palmyra: 200 years after Moroni’s visits
- The Next Normal
- Called to Serve In A Pandemic
- The World Meets Our Campus
- Defining Moments of BYU Sports
- If Any of You Lack Wisdom

How social media impacts political views
Leer en español: Cómo las redes sociales impactan las opiniones políticas

Social media platforms have recently facilitated the organization of protests around racism across the country and even prompted teenagers and K-Pop fans to register for a Trump rally in June with no intention of attending.
But social media use affects young users’ political views and involvement in other ways like exposing users to certain views or determining their understanding of current events.
Different viewpoints or echo chambers?
According to a report from the Pew Research Center , the majority of surveyed teens said they felt social media exposed them to people with different backgrounds and views and helped them show support for causes and issues important to them.
For BYU students, the results of the report mirror their thoughts on how social media platforms influence their political views.
In an informal Instagram poll on The Daily Universe’s account, 89% of the 273 respondents said they believe social media has affected their political views and involvement. When asked for specifics, the majority of commenters said social media has exposed them to different viewpoints and a few said social media can create echo chambers.
BYU student Abby Bjorkman said social media has helped her see views beyond her own community, which is predominantly white. “Especially with the Black Lives Matter movement, I have been able to educate myself on others’ experiences in America besides my own, which is the perspective of a white female.”
While Bjorkman acknowledged it can be easy to fall into an echo chamber and only see posts from those with similar views, she feels she has followed a wide enough variety of people to hear opposing opinions.
“Some users can feel extreme on both sides and can almost be intimidating, but it is up to the user to manipulate how much they want to see,” Bjorkman said.
BYU public relations professor Pamela Brubaker said social media users sometimes only interact with content that reflects their own views, which then leads to the apps suggesting other similar content.
“News and information are pushed to us based upon the content we engage with and the people we engage with online,” Brubaker said. “As a result, if your friends are more politically active on Facebook or Instagram, you are more likely to have higher levels of exposure to political content.”
Social media as a primary news source
Another recent Pew Research Center study shows that people who turn to social media to stay up to date about current events generally pay less attention to and are less knowledgeable about the news and politics. The study found that 48% of young adults age 18-29 fall into this category and primarily get their news from social media.
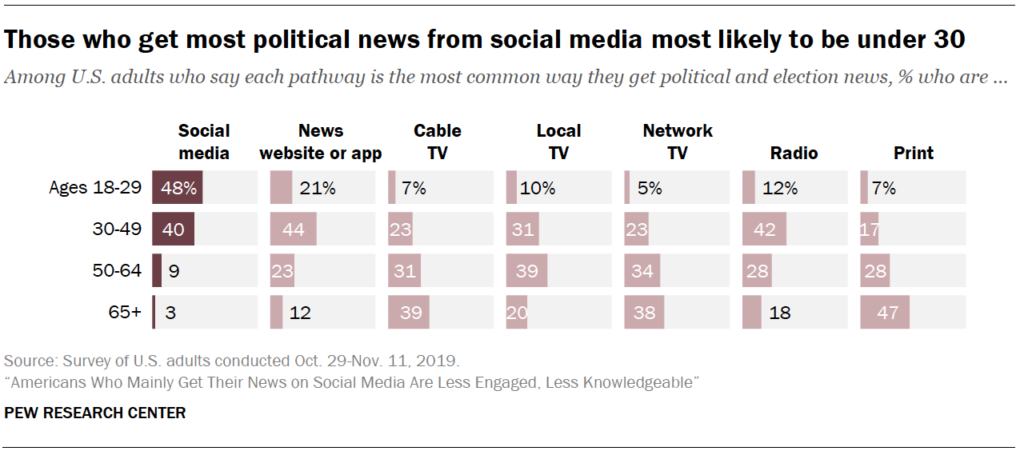
The study used data from five different surveys conducted from October 2019 to June 2020. During this time major news and political events like the impeachment and the outbreak of the coronavirus occurred. Researchers asked respondents questions to measure their understanding of these events.
The results show that 57% of people who rely on social media for news had low political knowledge and only 17% had high political knowledge. The only group with a larger percentage of low political knowledge was individuals who get their news from local TV stations.
According to the study, those who primarily get news from social media are “more likely than other Americans to have heard about a number of false or unproven claims.”
Brubaker said the increased reliance on social media could stimulate more political discussions both online and offline, but it also might limit the political views and information users are exposed to. “To stay politically informed, it’s important to expand our sources. We should rely on more than the news that’s pushed to us. We should also actively seek to be informed.”
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Byu big 12 media day recap, salt lake city plans to revitalize areas downtown, renovate delta center, multicultural students participate as soar counselors.
Detecting Political Polarization Using Social Media Data
- Conference paper
- First Online: 27 June 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- Erdogan Dogdu 6 ,
- Roya Choupani 6 &
- Selim Sürücü 7
Part of the book series: Communications in Computer and Information Science ((CCIS,volume 2113))
Included in the following conference series:
- Southwest Data Science Conference
20 Accesses
Political polarization is a world wide problem observed everywhere. It is on the increase due to increasing digital communication and use of social media. Election times are especially important, increasing political polarization tremendously, causing social and political problems in the society. In this study, we take the case of last Turkish local elections, which was highly contentious, leading to the renewal of elections in the most-populated major metropolitan city of Istanbul with a population of 15 million people. We used Twitter data to measure the political polarization, collected over 90 million tweets and retweets, introduced the inter retweet ratio metric to quantitatively measure the political polarization. Our results show that political polarization increases tremendously by double digit decreases in inter community interactions towards the election days, and comes back to normal after the elections are over.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2018/mar/17/facebook-cambridge-analytica-kogan-data-algorithm .
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2019_Turkish_local_elections .
https://developer.twitter.com/en/docs/twitter-api .
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Political_polarization .
https://spark.apache.org/ .
https://networkx.org/ .
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/python/ .
Adamic, L.A., Glance, N.: The political blogosphere and the 2004 U.S. election: divided they blog. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery, LinkKDD ’05, pp. 36–43. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2005). https://doi.org/10.1145/1134271.1134277
Barberá, P.: Social media, echo chambers, and political polarization. Social Media Democ. State Field Prospects Reform 34 (2020)
Google Scholar
Bedi, P., Sharma, C.: Community detection in social networks. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 6 (3), 115–135 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1178
Article Google Scholar
Blondel, V.D., Guillaume, J.L., Lambiotte, R., Lefebvre, E.: Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008 (10), P10008 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-5468/2008/10/p10008
Borge-Holthoefer, J., Magdy, W., Darwish, K., Weber, I.: Content and network dynamics behind Egyptian political polarization on twitter, CSCW 2015, pp. 700-711. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2675133.2675163
Chen, T., Singh, P., Bassler, K.E.: Network community detection using modularity density measures. J. Stat. Mech: Theory Exp. 2018 (5), 053406 (2018)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Conover, M., Ratkiewicz, J., Francisco, M., Gonçalves, B., Menczer, F., Flammini, A.: Political polarization on twitter. In: Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, vol. 5, pp. 89–96 (2011)
Darwish, K.: Quantifying polarization on twitter: the kavanaugh nomination (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2001.02125
Garimella, K., Weber, I.: A long-term analysis of polarization on twitter (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1703.02769
Girvan, M., Newman, M.E.J.: Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99 (12), 7821–7826 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.122653799
Golbeck, J.: Chapter 3 - network structure and measures. In: Golbeck, J. (ed.) Analyzing the Social Web, pp. 25–44. Morgan Kaufmann, Boston (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-405531-5.00003-1
Gui, X., Li, L., Cao, J., Li, L.: Dynamic communities in stock market. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014 , 723482 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/723482
Javed, M.A., Younis, M.S., Latif, S., Qadir, J., Baig, A.: Community detection in networks: a multidisciplinary review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 108 , 87–111 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.02.011
Lu, L., Zhang, M.: Edge Betweenness Centrality, pp. 647–648. Springer, New York (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9863-7_874
McDiarmid, C., Skerman, F.: Modularity of erdős-rényi random graphs. Rand. Struct. Algor. 57 (1), 211–243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/rsa.20910
Morales, A.J., Borondo, J., Losada, J.C., Benito, R.M.: Measuring political polarization: twitter shows the two sides of venezuela. Chaos Interdisc. J. Nonlinear Sci. 25 (3), 033114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4913758
Newman, M.: Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices. Phys. Rev. E, Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 74 , 036104 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.036104
Oyelade, J., Oladipupo, O., Obagbuwa, I.: Application of k means clustering algorithm for prediction of students academic performance. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 7 (2010). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1002.2425
Ozer, M., Kim, N., Davulcu, H.: Community detection in political twitter networks using nonnegative matrix factorization methods. In: 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), pp. 81–88 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ASONAM.2016.7752217
Raghavan, N., Albert, R., Kumara, S.: Near linear time algorithm to detect community structures in large-scale networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 76 , 036106 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.76.036106
Rashed, A., Kutlu, M., Darwish, K., Elsayed, T., Bayrak, C.: Embeddings-based clustering for target specific stances: the case of a polarized turkey (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2005.09649
Ríos, S.A., Videla-Cavieres, I.F.: Generating groups of products using graph mining techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 35 , 730–738 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2014.08.155
Schaeffer, S.E.: Graph clustering. Comput. Sci. Rev. 1 (1), 27–64 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2007.05.001
Shi, J., Malik, J.: Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22 (8), 888–905 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.868688
Traag, V.A., Waltman, L., van Eck, N.J.: From louvain to leiden: guaranteeing well-connected communities. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 5233 (2019)
Waller, I., Anderson, A.: Quantifying social organization and political polarization in online platforms. Nature 600 (7888), 264–268 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04167-x
Xing, Y., Meng, F., Zhou, Y., Zhu, M., Shi, M., Sun, G.: A node influence based label propagation algorithm for community detection in networks. Sci. World J. 2014 , 627581 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/627581
Yanrui, D., Zhen, Z., Wenchao, W., Yujie, C.: Identifying the communities in the metabolic network using ‘component’ definition and girvan-newman algorithm. In: 2015 14th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Applications for Business Engineering and Science (DCABES), pp. 42–45 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/DCABES.2015.18
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Computer Science, Angelo State University, San Angelo, TX, USA
Erdogan Dogdu & Roya Choupani
Department of Computer Engineering, Çankırı Karatekin University, Çankırı, Turkey
Selim Sürücü
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Erdogan Dogdu .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Baylor University, Waco, TX, USA
Belmont University, Nashville, TN, USA
Erich Baker
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Dogdu, E., Choupani, R., Sürücü, S. (2024). Detecting Political Polarization Using Social Media Data. In: Han, H., Baker, E. (eds) Next Generation Data Science. SDSC 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 2113. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61816-1_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61816-1_4
Published : 27 June 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-61815-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-61816-1
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Research Topics & Ideas: Politics
100+ Politics-Related Research Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project

Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation or thesis. If you’ve landed on this post, chances are you’re looking for a politics-related research topic , but aren’t sure where to start. Here, we’ll explore a variety of politically-related research ideas across a range of disciplines, including political theory and philosophy, comparative politics, international relations, public administration and policy.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas. This is the starting point, but to develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. Also, be sure to sign up for our free webinar that explores how to find a high-quality research topic from scratch.
Overview: Politics-Related Topics
- Political theory and philosophy
- Comparative politics
- International relations
- Public administration
- Public policy
- Examples of politics-related dissertations
Topics & Ideas: Political Theory
- An analysis of the impact of feminism on political theory and the concept of citizenship in Saudi Arabia in the context of Vision 2030
- A comparative study of the political philosophies of Marxism and liberalism and their influence on modern politics
- An examination of how the Covid-19 pandemic affected the relationship between individual freedom and collective responsibility in political philosophy
- A study of the impact of race and ethnicity on French political philosophy and the concept of justice
- An exploration of the role of religion in political theory and its impact on secular democracy in the Middle East
- A Review of Social contract theory, comparative analysis of the political philosophies of Hobbes, Locke, and Rousseau
- A study of the concept of the common good in political philosophy and its relevance to the ongoing refugee crisis in Europe
- An examination of the relationship between political power and the rule of law in developing African countries
- A study of the impact of postmodernism on political theory and the concept of truth, a case study of the US
- An exploration of the role of virtue in political philosophy and its impact on the assessment of moral character in political leaders

Topics & Ideas: Comparative Politics
- A comparative study of different models of federalism and their impact on democratic governance: A case Study of South American federalist states
- The impact of ethnic and religious diversity on political stability and democracy in developing countries, a review of literature from Africa
- An analysis of the role of civil society in promoting democratic change in autocratic regimes: A case study in Sweden
- A comparative examination of the impact of globalization on political institutions and processes in South America and Africa.
- A study of the factors that contribute to successful democratization in authoritarian regimes, a review of the role of Elite-driven democratization
- A comparison of the political and economic systems of China and India and their impact on social development
- The impact of corruption on political institutions and democracy in South East Asia, a critical review
- A comparative examination of the impact of majoritarian representation (winner-take-all) vs proportional representation on political representation and governance
- An exploration of Multi-party systems in democratic countries and their impact on minority representation and policy-making.
- A study of the factors that contribute to successful decentralization and regional autonomy, a case study of Spain

Topics & Ideas: International Relations
- A comparative analysis of the effectiveness of diplomacy and military force in resolving international conflicts in Central Africa.
- The impact of globalization on the sovereignty of nation-states and the changing nature of international politics, a review of the role of Multinational Corporations
- An examination of the role of international aid organizations in promoting peace, security, and development in the Middle East.
- A study of the impact of economic interdependence on the likelihood of conflict in international relations: A critical review of weaponized interdependence
- A comparative analysis of the foreign policies of the EU and the US and their impact on international stability in Africa
- An exploration of the relationship between international human rights and national sovereignty during the Covid 19 pandemic
- A study of the role of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO)s in international politics and their impact on state behaviour
- A comparative analysis of the effectiveness of international regimes in addressing global challenges such as climate change, arms control, and terrorism in Brazil
- An examination of the impact of the rise of BRICS on the international system and global governance
- A study of the role of ideology in shaping the foreign policies of states and the dynamics of international relations in the US

Tops & Ideas: Public Administration
- An analysis of the impact of digital technology on public administration and the delivery of public services in Estonia
- A review of models of public-private partnerships and their impact on the delivery of public services in Ghana
- An examination of the role of civil society organizations in monitoring and accountability of public administration in Papua New Guinea
- A study of the impact of environmentalism as a political ideology on public administration and policy implementation in Germany
- An exploration of the relationship between public administration and citizen engagement in the policy-making process, an exploration of gender identity concerns in schools
- A comparative analysis of the efficiency and effectiveness of public administration, decentralisation and pay and employment reform in developing countries
- A study of the role of collaborative leadership in public administration and its impact on organizational performance
- A systematic review of the challenges and opportunities related to diversity and inclusion in police services
- A study of the impact of corrupt public administration on economic development and regional growth in Eastern Europe
- An exploration of the relationship between public administration and civil rights and liberties, including issues related to privacy and surveillance, a case study in South Korea

Topics & Ideas: Public Policy
- An analysis of the impacts of public policy on income inequality and poverty reduction in South Sudan
- A comparative study of the effectiveness of legal and regulatory, economic and financial, and social and cultural instruments for addressing climate change in South Korea
- An examination of the role of interest groups in shaping public policy and the policy-making process regarding land-use claims
- A study of the impact of globalization on the development of public policies and programs for mitigating climate change in Singapore
- An exploration of the relationship between public policy and social justice in tertiary education in the UAE
- A comparative analysis of the impact of health policies for the management of diabetes on access to healthcare and health outcomes in developing countries
- Exploring the role of evidence-based policymaking in the design and implementation of public policies for the management of invasive invertebrates in Australia
- An examination of the challenges and opportunities of implementing educational dietary public policies in developing multicultural countries
- A study of the impact of public policies on urbanization and urban development in rural Indonesia
- An exploration of the role of media and public opinion in shaping public policy and the policy-making process in the transport industry of Malaysia
Examples: Politics Dissertations & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a politics-related research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various politics-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- We, the Righteous Few: Immoral Actions of Fellow Partisans are Judged as Less Possible (Varnam, 2020)
- Civilizing the State: Civil Society and the Politics of Primary Public Health Care Provision in Urban Brazil (Gibson, 2012)
- Political regimes and minority language policies: evidence from Taiwan and southeast Asia (Wu, 2021)
- The Feminist Third Wave: Social Reproduction, Feminism as Class Struggle, and Contemporary Women’s Movements (Angulo, 2019)
- The Politics of Immigration under Authoritarianism (Joo, 2019)
- The politics of digital platforms: Sour Dictionary, activist subjectivities, and contemporary cultures of resistance (Okten, 2019)
- Vote choice and support for diverse candidates on the Boston City Council At-Large (Dolcimascolo, 2022)
- The city agenda: local governance and national influence in the policy agenda, 1900-2020 (Shannon, 2022)
- Turf wars: who supported measures to criminalize homelessness in Austin, Texas? (Bompiedi, 2021)
- Do BITs Cause Opposition Between Investor Rights and Environmental Protection? (Xiong, 2022)
- Revealed corruption and electoral accountability in Brazil: How politicians anticipate voting behavior (Diaz, 2021)
- Intersectional Solidarity: The Political Consequences of a Consciousness of Race, Gender and Sexuality (Crowder, 2020)
- The Congressional Hispanic Caucus and the Coalitional Representation of Latinxs in the U.S. House of Representatives (Munoz, 2019)
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. In other words, to create a top-notch research topic, you must be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.
Get 1:1 Help
If you’re still feeling a bit unsure about how to find a research topic for your dissertation or research project, check out our Topic Kickstarter service below.
Interesting thesis.
I really appreciate your work which will greatly help me rethink on my topic
Please how can I get the full thesis?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
share this!
July 10, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
Unregulated online political ads pose a threat to democracy
by Steven Caplan, The Conversation

Think back to the last time you scrolled through your social media feed and encountered a political ad that perfectly aligned with your views—or perhaps one that outraged you. Could you tell if it was from a legitimate campaign, a shadowy political action committee or even a foreign entity? Could you discern who paid for the ad? Chances are you couldn't.
While television and radio political ads have been subject to strict disclosure requirements for decades, their online counterparts exist in a regulatory vacuum. Social media giants like Facebook, X—formerly Twitter—and Instagram have become central battlegrounds for political campaigns . Yet they operate without the transparency mandated for traditional broadcast media. This allows advertisers to use sophisticated microtargeting to tailor messages to voters, often exploiting detailed personal data.
Welcome to the unregulated Wild West of online political advertising, where transparency is scarce and accountability is lacking. With the 2024 U.S. presidential election in full swing, this digital frontier poses an unprecedented threat to the integrity of American democracy.
The good old days
The McCain-Feingold Act became law over two decades ago. The law, officially known as the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 , was designed to curb the influence of money in politics and increase transparency in campaign financing. The landmark legislation, championed by Senators John McCain (R-Ariz.) and Russ Feingold (D-Wis.), includes the regulation of issue advocacy ads on television and radio.
The McCain-Feingold Act addressed the need for disclaimers and the "Stand by Your Ad" provision, which required candidates to personally endorse their messages in TV and radio ads. Such regulations have proved effective in maintaining a level of accountability and transparency in traditional media.
The media landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation since the bill's passage, however. As a communications scholar who studies online advertising , I see the lack of similar regulatory measures governing online political advertisements as a glaring absence. This vacuum leaves platforms responsible for providing transparency.
At the same time, Federal Election Commission rules governing disclosure on digital political ads remain murky at best . The lack of clarity makes tracking and analyzing digital political ads a daunting task for researchers, journalists and concerned citizens.
Ad transparency studies
A recent study conducted by open internet advocacy organization Mozilla and Finnish internet research firm Check First reveals significant deficiencies in the ad transparency tools provided by major tech platforms. Ad transparency tools are collections and analysis of ads that the social media companies make publicly available. Researchers, policymakers and advocacy groups use the tools to understand ads and their effects. The deficiencies raise concerns about the potential for manipulation and deception in the lead-up to the presidential election.
The study examined the ad transparency tools of 11 major tech platforms, including X, Apple's App Store, Google, Meta, TikTok and LinkedIn. The study found that these tools often provide incomplete data, have broken search functions and are difficult to use effectively. Among the tech giants the study evaluated, X emerged as the worst performer, with a dismal record of providing meaningful data for watchdogs and users alike.
Notably, the study focused on the efforts of these platforms to comply with the European Union's Digital Services Act , which mandates a certain level of ad transparency. The United States, however, has no comparable requirements, leaving voters vulnerable to potential manipulation and disinformation campaigns.
Recent academic research offers some insights into the potential effectiveness of political ad labeling. One study tested various transparency information disclosures based on enacted regulations, including the EU's Digital Services Act , and proposed regulations, including the U.S. Honest Ads Act .
The Digital Services Act is a broad set of regulations that requires online platforms to provide real-time information about which posts are ads and who produced and financed them. The U.S. bill aims to require platforms to maintain publicly accessible records of any political ads purchased by a person or group who spends more than $500 on ads in a calendar year. It also seeks to ensure that foreign entities are not purchasing political ads to influence U.S. elections.
The researchers found that transparency measures based on these regulations were most effective in increasing users' ability to recognize and understand persuasion attempts in advertising. However, the academic study also highlighted significant challenges in implementing ad labeling. Only 30% of participants remembered noticing the transparency information, underscoring the difficulty of making such measures effective in the fast-paced world of social media.
The importance of ad transparency was spotlighted by a recent report from AI Forensics, a European nonprofit that investigates influential and opaque algorithms. The report, titled " No Embargo in Sight: Meta Lets Pro-Russia Propaganda Ads Flood the EU ," revealed that a massive network of pro-Russian propaganda targeted voters in France and Germany. It reached 38 million user accounts in just six months. Meta failed to identify and label the vast majority of these ads as political in a timely manner, allowing the disinformation to spread rapidly.
Experts are increasingly concerned about the potential for similar disinformation campaigns to target American voters. With wars raging in multiple global hot spots and platforms like X and Facebook struggling to monitor and report on political ads effectively, the risks of electoral interference and voter manipulation are significant.
Despite the Honest Ads Act's high-profile bipartisan sponsors and the potential effectiveness suggested by academic research, most analysts predict that partisan gridlock and tech industry lobbying will keep the legislation from being passed before the November 2024 election. This lack of legislative action leaves the U.S. without robust ad transparency tools, making it difficult for the public to identify the sources behind political ads on digital platforms.
Advocates have called on tech platforms to prioritize the development of more robust and user-friendly ad transparency tools ahead of the election. They argue that without meaningful reforms, the integrity of the democratic process is at risk, leaving voters vulnerable to manipulation and deception .
Provided by The Conversation
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Researchers develop model to study heavy-quark recombination in quark-gluon plasma
29 minutes ago

A new species of extinct crocodile relative rewrites life on the Triassic coastline
11 hours ago

New method achieves tenfold increase in quantum coherence time via destructive interference of correlated noise

Mars likely had cold and icy past, new study finds
12 hours ago

Study: Nanoparticle vaccines enhance cross-protection against influenza viruses

New tools are needed to make water affordable, says study

Researchers demonstrate how to build 'time-traveling' quantum sensors

Lion with nine lives breaks record with longest swim in predator-infested waters
13 hours ago

New multimode coupler design advances scalable quantum computing

High-speed electron camera uncovers new 'light-twisting' behavior in ultrathin material
14 hours ago

Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better.
3 hours ago
Today's Fusion Music: T Square, Cassiopeia, Rei & Kanade Sato
6 hours ago
Japanese Translation Issues with Google Translate
Who is your favorite jazz musician and what is your favorite song.
21 hours ago
Biographies, history, personal accounts
Jul 8, 2024
Music to Lift Your Soul: 4 Genres & Honorable Mention
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories

How the Meta algorithm influences election advertising
Jun 26, 2024

Report builds framework for 'digital political ethics' in 2020
Jan 8, 2020

New, enhanced AdObservatory.org provides transparency and insights on digital political spending
Aug 5, 2022

EU probes Facebook, Instagram over election disinformation worries
Apr 30, 2024
Google tightens political ad rules ahead of Europe elections
Nov 22, 2018

US lawmakers move to regulate online political ads (Update)
Oct 19, 2017
Recommended for you
Motivated to disagree: What can be learned about rapid polarization from the Israeli judicial reform?
Jul 5, 2024

Lie-detection AI could provoke people into making careless accusations, researchers warn
Jun 27, 2024

Sharing false political information on social media may be associated with positive schizotypy, research suggests

Reframing voting as 'duty to others' could be key to increasing engagement, turnout
Jun 21, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
234 Social Media Research Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 2646 words
- Icon Clock 12 min read
Social media research encompasses a broad range of different topics that delve into the ever-evolving digital landscape. People investigate the impact of social platforms on society, exploring subjects, such as online identity formation, self-presentation, the psychology of virtual interactions, and others. Additionally, studies examine the influence of social media on politics, activism, and public opinion, uncovering patterns of information dissemination and polarization. Privacy concerns, cyberbullying, and online safety are also explored in-depth, seeking strategies to mitigate the associated risks. In this article, people can find many social media research topics, ideas, and examples.
Hot Social Media Research Topics
- Impacts of Social Media and Internet Algorithms on User Experience
- The Rise of TikTok: A Socio-Cultural Analysis
- Dealing With Cyberbullying: Strategies and Solutions
- Understanding the Phenomenon of Social Media ‘Cancel Culture’
- NFTs and Social Media: The Future of Digital Art?
- Ethical Concerns in the Era of Influencer Marketing
- Social Media’s Role in Accelerating E-Commerce Growth
- Impacts of Internet and Social Media on Journalism and News Reporting
- Understanding the Psychology of Viral Challenges on Social Platforms
- Cryptocurrency and Social Media: The Intersection
- Mitigating Misinformation and ‘Fake News’ on Social Media
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Social Media: A Game Changer?
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Political Campaigns
- Social Media’s Influence on Fashion and Beauty Trends
- Privacy, Safety, and Security Concerns in the Age of Social Networking
- Roles of Free Access and Social Media in Promoting Sustainable Practices
- Implications of Social Media Addiction on Mental Health
- Examining Social Media’s Role in Crisis Communication
- The Power of User-Generated Content in Branding
- Influence of Social Media on Food Culture and Dining Trends
Easy Social Media Research Topics
- Impacts of Online Videos and Social Media on Mental Health
- Influencer Marketing: Efficacy and Ethical Concerns
- Evolution of Privacy Policies Across Social Platforms
- Understanding Virality: What Makes Content Shareable?
- Cyberbullying: Prevalence and Prevention Strategies
- Social Media and Political Polarization: An In-Depth Study
- Role of Social Media in Modern Business Strategies
- Effect of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships
- Social Platforms as Tools for Social Change
- Navigating Online Hate Speech: A Legal Perspective
- Emerging Trends in Social Media Advertising
- Online Identity Construction and Self-Presentation
- The Psychology of Social Media Addiction
- Social Media’s Role in Crisis Management and Communication
- Sentiment Analysis in Social Media and Its Implications
- Social Media Algorithms: Bias and Implications
- The Phenomenon of Cancel Culture on Social Platforms
- Cybersecurity Threats in the Era of Social Media
- Analyzing Adverse Impacts of Social Media on Consumer Behavior

Interesting Social Media Research Topics
- Evaluating the Effects of Social Media on Language and Communication
- Roles of Social Media in Fostering Political Engagement
- Misinformation and Propaganda Spread Through Social Platforms
- Analyzing the Shift From Traditional Media to Social Media
- Dark Patterns in Social Media: Hidden Manipulative Tactics
- Social Media and Digital Activism: Revolutionizing Advocacy
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Its Impact on Social Networking
- Exploring Cybersecurity Issues in Social Media Platforms
- Roles and Effects of Social Media and News in Mental Health Promotion
- Strategies for Effective Social Media Crisis Management
- The Power of Live Streaming for Brands and Influencers
- Using Social Media to Enhance Classroom Learning
- Analyzing the Influence of Memes on Internet Culture
- Impacts of Social Media Algorithms on User Behavior
- Assessing the Correlation Between Social Media and Loneliness
- Geotagging and Its Implications for Personal Privacy
- Social Media and E-commerce: A Cross-Industry Study
- The Ethics of Digital Advertising on Social Platforms
- Understanding the Psychology of Social Media Trolls
- The Cultural Shift Caused by Social Media Localization
Social Media Research Paper Topics for High School
- The Phenomenon of Cyberbullying: Prevention and Strategies
- How Does Social Media Influence Teen Body Image?
- Evaluating the Educational Potential of Social Media Platforms
- Impacts of Social Media on Adolescents’ Self-Esteem
- Roles of Free Connection and Social Media in Modern Political Activism
- Exploring the Concept of ‘Digital Citizenship’ Among Teenagers
- The Ethics of Social Media Privacy: User Rights and Responsibilities
- Social Media Addiction: Understanding Its Causes and Effects
- Influence of Social Media on Modern Communication Styles
- Analyzing Positive Roles of Social Media in Promoting Reading Culture
- Social Media and Mental Health: Correlation or Causation?
- The Role of Social Media in Global Environmental Awareness
- Examining Social Media’s Impact on Real-Life Social Skills
- Social Media Platforms: Tools for Personal Branding or Narcissism?
- Influence of Social Media Trends on Youth Fashion Choices
- Impacts of Social Media on Teenagers’ Sleep Patterns
- Online Safety: The Role of Parents and Schools in Social Media Usage
- How Does Social Media Influence Teenagers’ Views on Relationships?
- Social Media and Empathy: Does Online Interaction Decrease Compassion?
Social Media Research Paper Topics for College Students
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
- The Influence of Social Media on Voting Patterns Among Young Adults
- Social Media as a Valid Tool for Social Change: A Case Study Approach
- Unveiling the Psychology of Social Media Addiction
- Social Media’s Role in Modern Journalism: Opportunities and Challenges
- Privacy Implications of Data Collection on Social Media Platforms
- Cyberbullying in the Age of Social Media: Scope and Solutions
- The Ethical Aspects of Social Media Influencer Marketing
- Roles and Effects of Social Media in Crisis Communication and Management
- Social Media and Its Effects on Interpersonal Communication Skills
- Analyzing Social Media Strategies of Successful Businesses
- Impacts of Internet Use and Social Media on Mental Health Among College Students
- The Roles That Social Media Has in Modern Political Campaigns
- Understanding the Social Media Algorithm: Bias and Implications
- Social Media and Consumer Behavior: The Power of Influencer Marketing
- Fake News, Authors, and Disinformation Spread Through Social Media Platforms
- Exploring Direct Links Between Social Media Use and Academic Performance
- Social Media’s Role in Promoting Sustainable Lifestyle Choices
- Regulation of Hate Speech and Offensive Content on Social Media
- The Power and Peril of Virality in the Age of Social Media
Social Media Research Paper Topics for University
- The Effect That Social Media Has on Global Politics
- The Ethics of Data Mining in Social Media
- Roles of Social Media in Business Marketing Strategies
- Social Media, Internet Use, and Their Impacts on Mental Health: A Systematic Review
- Algorithmic Bias in Social Media Platforms: Causes and Consequences
- The Influence of Colors and Social Media on Consumer Behavior
- Exploring Possible Relationships Between Social Media Use and Academic Performance
- Privacy, Morality, and Security Concerns in the Age of Social Media
- Social Media as a Platform for Digital Activism
- Impacts of Social Media on Interpersonal Communication and Relationships
- Cyberbullying on Social Media: Scope, Impact, and Preventive Measures
- The Role of Social Media in Spreading Health-Related Misinformation
- Analyzing the Effect of Social Media on Journalism Practices
- Understanding the Influence of Social Media on Body Image Perceptions
- Social Media’s Role in Crisis Management: Case Studies
- The Power and Effectiveness of Influencer Marketing on Social Media
- Fake News and Disinformation in the Social Media Age
- Regulatory Approaches to Hate Speech on Social Media Platforms
- The Economic Implications of Social Media: From Startups to Giants
Social Media Research Paper Topics for Masters
- Advanced Algorithms and Their Role in Shaping Social Media Interactions
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Democratic Processes Globally
- The Intersection of Privacy, Data Mining, and Ethics in Social Media
- Quantitative Analysis of Social Media’s Impact on Consumer Buying Behavior
- Cybersecurity Threats in Social Media: Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
- Analyzing the Psychological Implications of Social Media Addiction
- Using Social Media Data to Predict Market Trends: An Econometric Approach
- Role of Social Media in Crisis Management: A Comparative Study
- The Sociolinguistic Impact of Social Media on Communication
- Machine Learning and AI in Social Media: An Examination of Emerging Trends
- Social Media as a Valid Tool for Public Health: Opportunities and Challenges
- Social Media’s Influence on Modern Journalism: A Critical Analysis
- Mapping Social Networks: A Graph Theory Approach
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Social Media Campaigns in Social Change Movements
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Corporate Reputation Management
- Data Privacy Laws and Social Media: A Comparative Study
- The Use of Small and Big Data Analytics in Social Media Marketing
- Social Media and Its Role in Strengthening Democracy: A Deep Dive
- The Impact of Social Media on Cultural Assimilation and Identity
- Ethics of Artificial Intelligence in Social Media Content Moderation
Social Media Research Paper Topics for Ph.D.
- Analyzing the Impact of Social Media Algorithms on User Behavior and Perceptions
- Deciphering the Influence of Social Media on Political Campaign Strategies
- Examining the Role of Social Media in Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives
- Social Media and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Studies
- Effects of Social Media and Internet Use on Consumer Buying Behavior: An Econometric Approach
- Social Media and Digital Diplomacy: A Critical Analysis
- Ethical Implications of Data Mining Techniques in Social Media Platforms
- Unpacking the Psychological Mechanisms of Social Media Addiction
- Role of Social Media in Contemporary Journalism: Opportunities and Challenges
- Social Media and Privacy: A Comparative Study of Data Protection Laws
- Machine Learning and AI in Social Media: Identifying Future Trends
- Social Media’s Possible Influence on People, Body Image, and Self-Esteem: A Meta-Analysis
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Crisis Management and Communication
- Impacts of Social Media on Different Language and Communication Styles
- Cybersecurity in Social Media: An Analysis of Current Threats and Mitigation Strategies
- Social Media as a Good Tool for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
- Effects of Social Media on Children and Their Parents: Social Skills and Interpersonal Relationships
- Roles of Social Media in Promoting Gender Equality and Women’s Rights
- Social Media and its Influence on Cultural Assimilation and Identity Formation
Social Media Research Topics for Argumentative Papers
- Impacts of Social Media on Social and Political Discourses: Enhancing or Hindering Democratic Engagement?
- Social Media and Mental Health: Exploring the Association Between Excessive Usage and Psychological Well-Being
- Fostering Online Activism and Social Movements: The Role of Social Media
- Balancing Personal Information Sharing and Data Protection: Social Media and Privacy
- Exploring the Effects of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
- Social Media and Political Polarization: Reinforcing Echo Chambers or Encouraging Diverse Perspectives?
- Youth Culture and Identity Formation: The Influence of Social Media
- Fake News and Misinformation: Combating Inaccurate Information in the Era of Social Media
- Social Media and Cyberbullying: Examining the Impact on Mental Health and Well-Being
- The Ethics of Social Media Research: Privacy, Informed Consent, and Ethical Considerations
- Relationships in the Digital Age: Exploring the Influence of Social Media Use
- The Influence of Internet, Technology, and Social Media on Consumer Behavior and Buying Decisions
- Analyzing the Role of Online Platforms in Elections: Social Media and Political Campaigns
- Social Media in Education: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Integration in the Classroom
- Impacts of Social Media and Interface on News Consumption and Journalism Practices
- Body Politics in the Digital Space: Examining Representations of Gender, Race, and Body Image on Social Media
- Addressing Ethical and Security Concerns in the Digital Age: Social Media and Cybersecurity
- Shaping Consumer Behavior and Brand Perception: The Role of Social Media Influencers
- Civic Engagement in the Digital Era: Assessing the Role of Social Media Platforms
- The Influence of Social Media Algorithms on Information Consumption and Personalization
Social Media Research Topics for Persuasive Papers
- The Power of Social Media in Driving Social and Political Change
- Promoting Digital Literacy: Empowering Users to Navigate the Complexities of Social Media
- Social Media as a Catalyst for Social Justice Movements: Amplifying Marginalized Voices
- Countering Fake News and Misinformation on Social Media: Strategies for Critical Thinking
- Harnessing the Influence of Social Media for Environmental Activism and Sustainability
- The Dark Side of Social Media: Addressing Online Harassment and Cyberbullying
- Influencer Marketing: Ethical Considerations and Consumer Protection in the Digital Age
- Leveraging Social Media for Public Health Campaigns: Increasing Awareness and Behavioral Change
- Social Media and Mental Health: Promoting Well-Being in a Hyperconnected World
- Navigating the Privacy Paradox: Balancing Convenience and Personal Data Protection on Social Media
- Roles of Social Media and Internet in Fostering Civic Engagement and Democratic Participation
- Promoting Positive Body Image on Social Media: Redefining Beauty Standards and Empowering Individuals
- Enhancing Online Safety: Developing Policies and Regulations for Social Media Platforms
- Social Media and the Spread of Disinformation: Combating the Infodemic
- Roles of Social Media and Technology in Building and Sustaining Relationships: Connecting in a Digital Era
- Influencer Culture and Materialism: Examining the Impact on Consumer Behavior
- Social Media and Education: Maximizing Learning Opportunities and Bridging the Digital Divide
- The Power of Viral Hashtags: Exploring Social Movements and Online Activism
- Social Media and Political Polarization: Bridging Divides and Encouraging Constructive Dialogue
Social Media Topics for Pros and Cons Research Papers
- Examining the Social Effects of Digital Connectivity: Pros and Cons of Using Social Media
- Balancing Privacy Concerns in the Digital Age: Evaluating the Cons and Risks of Social Media Use
- Information Sharing in the Digital Era: Uncovering the Advantages of Social Media Platforms
- Building Online Communities: Analyzing the Strengths and Weaknesses of Social Media Interaction
- Navigating Political Discourse in the Digital Age: The Disadvantages of Social Media Engagement
- Mental Health in the Digital Sphere: Understanding the Benefits and Drawbacks of Social Media
- Combating Cyberbullying: Addressing the Negative Side of Online Social Interactions
- Personal Branding in the Digital Landscape: Empowerment vs. Self-Objectification on Social Media
- Establishing Meaningful Connections: Exploring the Pros and Cons of Social Media Relationships
- Leveraging the Educational Potential of Digital Platforms: Examining the Benefits of Social Media in Learning
- Body Image and Self-Esteem in the Age of Social Media: Weighing the Positives and Negatives
- From Digital Activism to Political Change: Assessing the Opportunities and Limitations of Social Media
- Unraveling the Influence: Social Media and Consumer Behavior in the Digital Marketplace
- Misinformation in the Digital Landscape: The Pros and Cons of Social Media in the Spread of Disinformation
- Crisis Communication in the Digital Age: Navigating the Benefits and Challenges of Social Media
- Tackling Fake News: Navigating Misinformation in the Era of Social Media
- Maximizing Business Opportunities: Evaluating the Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media Marketing
- The Psychology of Social Media: Analyzing the Upsides and Downsides of Digital Engagement
- Exploring the Impact of Social Media on Socialization: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Implications
- Online Activism: The Power and Limitations of Social Media Movements
Social Media Topics for Cause and Effect Research Papers
- Enhancing Political Activism: Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media and Civic Engagement
- The Psychological Effects of Digital Connectivity: Investigating the Relationship Between Mental Health of People and Social Media Use
- Political Polarization in the Online Sphere: Understanding the Impact of Digital Networks
- Disrupted Sleep Patterns in the Digital Era: Exploring the Role of Online Platforms
- Digital Distractions and Academic Performance: Analyzing the Effects of Online Engagement
- Navigating Online Relationships: Understanding the Impacts of Digital Interactions
- The Digital Marketplace: Exploring Consumer Behavior in the Age of Online Platforms
- The Loneliness Epidemic: Investigating the Relationship Between Social Media Use and Social Isolation
- Redefining Political Participation: The Influence of Digital Networks on Democracy
- Unmasking Digital Identities: The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use
- News Consumption in the Digital Era: Exploring the Impacts of Online Platforms
- Cyberbullying in the Virtual World: Analyzing the Effects of Online Interactions
- The Digital Campaign Trail: Investigating the Influence of Online Platforms on Voter Behavior
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) in the Digital Age: Exploring the Psychological Consequences
- Body Dissatisfaction in the Digital Sphere: Understanding the Impacts of Online Presence
- Information Overload: Coping With the Digital Deluge in the Information Age
- Privacy Concerns in the Online Landscape: Analyzing the Implications of Digital Footprints
- Unveiling the Dark Side: Exploring the Relationship Between Online Activities and Substance Abuse
- Bridging the Political Divide: The Impact of Digital Networks on Sociopolitical Polarization
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

431 Music Essay Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 24 May 2023
- Icon Page 4272 words

Essay on My Escape From North Korea
- Icon Calendar 25 April 2023
- Icon Page 713 words
- Visual Story

- Entertainment
- Life & Style

To enjoy additional benefits
CONNECT WITH US

Political ads on social media rife with misinformation and scams, new research finds
A deep dive into political ads on facebook by researchers at syracuse university has revealed a sprawling web of advertisements that contain misleading information or scams.
Published - July 11, 2024 08:31 am IST - WASHINGTON
![Political advertisements on social media are one of the best ways for candidates to reach supporters and raise campaign cash [File] Political advertisements on social media are one of the best ways for candidates to reach supporters and raise campaign cash [File]](https://www.thehindu.com/theme/images/th-online/1x1_spacer.png)
Political advertisements on social media are one of the best ways for candidates to reach supporters and raise campaign cash [File] | Photo Credit: REUTERS
The online advertisement to Donald Trump supporters was clear enough: Click here, and receive a free Trump 2024 flag and a commemorative coin. All in exchange for taking a quick survey and providing a credit card number for the $5 shipping and handling.
“You’ll get two free gifts just by taking this quick poll in support of Trump,” says the ad's narrator.
The ad — which has appeared on Facebook, YouTube and other platforms — didn't mention the $80 charge that would later appear on credit card statements. Those that clicked were scammed.
Political advertisements on social media are one of the best ways for candidates to reach supporters and raise campaign cash. But as a new report from Syracuse University shows, weak regulations governing online ads and haphazard enforcement by tech companies also make ads a prime source for misleading information about elections — and a tantalizingly easy way for con artists to target victims.
(For top technology news of the day, subscribe to our tech newsletter Today’s Cache)
“There is very little regulation on the platforms," said Jennifer Stromer-Galley, the professor who led the research for the ElectionGraph Project at Syracuse University’s Institute for Democracy, Journalism & Citizenship. “It leaves the American public vulnerable to misinformation, disinformation and propaganda.”
Stromer's research examined more than 2,200 groups on Facebook or Instagram that ran ads between September and May mentioning one of the presidential candidates. Combined, the ads cost nearly $19 million and were seen more than 1 billion times.
Data connected to the ads (and made public by Meta, Facebook's owner) shows that both right- and left-leaning ads targeted older voters more than younger ones. Right-leaning ads were more likely to target men, progressive ads were more likely to target women.
Overall, conservative-leaning organisations bought more ads than progressive-leaning groups. Immigration was the top issue raised in right-leaning ads while the economy dominated progressive ads.
Many of the ads contained misleading information, or deepfake video and audio of celebrities supposedly crying during a speech by former First Lady Melania Trump. Stromer-Galley noted that falsehoods in ads about urban crime and immigration were especially common.
While most of the groups paying for the ads are legitimate, others seemed more interested in getting a user's personal financial data than boosting any particular candidate. Using a partnership with the data science firm Neo4j, Stromer-Galley found that some of the pages shared common creators, or ran virtually identical ads. When one page disappeared — perhaps removed by Facebook moderators — another would pop up quickly to take its place.
Many of the pages sold Trump-related merchandise such as flags, hats, banners and coins or advertised fictitious investment schemes. The true motive, apparently, was to get a user's credit card information.
The ads promising a free Trump flag were placed by a group called Liberty Defender Group. Emails sent to several addresses listed for the company were not returned, and a phone number for a company representative could not be found. One website associated with the group has moved on from politics, and is now selling devices that claim to improve home energy efficiency.
Meta removed most of the network's ads and pages earlier this year after researchers noticed their activity, but the ads are still visible on other platforms. The company says it prohibits scams or content that could interfere with the operation of an election and removes ads that violate the rules. In addition, the company urges its users not to click on suspicious links, or to hand over personal information to untrustworthy sources.
"Don’t answer messages asking for your password, social security number, or credit card information," the company said.
The Trump campaign, which has no known ties to the network, did not respond to a message seeking comment.
The researchers at Syracuse were only able to study ads on Meta platforms because other companies do not make such information public. As a result, Stromer-Galley said the public is in the dark about the true amount of misinformation and scams spreading on social media.
Related stories
Related topics.
technology (general) / internet / social networking / politics (general)
Top News Today
- Access 10 free stories every month
- Save stories to read later
- Access to comment on every story
- Sign-up/manage your newsletter subscriptions with a single click
- Get notified by email for early access to discounts & offers on our products
Terms & conditions | Institutional Subscriber
Comments have to be in English, and in full sentences. They cannot be abusive or personal. Please abide by our community guidelines for posting your comments.
We have migrated to a new commenting platform. If you are already a registered user of The Hindu and logged in, you may continue to engage with our articles. If you do not have an account please register and login to post comments. Users can access their older comments by logging into their accounts on Vuukle.
Media and Politics - Science topic

- asked a question related to Media and Politics
- Mar 31, 2012

- Nov 1, 2016
- 0 Recommendations

- Jul 4, 2016
- Jul 11, 2016
- 2 Recommendations

- Jul 2, 2016
- 4 Recommendations

- Feb 17, 2015

- May 6, 2016

- Mar 15, 2016

- Mar 16, 2016

- Nov 27, 2015
- Nov 30, 2015

- Dec 6, 2010

- Oct 13, 2015

- Mar 2, 2015

- Jul 3, 2015
- 7 Recommendations

- Mar 3, 2015

- 6 Recommendations

- Feb 7, 2015

- Feb 11, 2015
- Shared-Society 20 14.pdf 523.19 KB
- 16 Recommendations

- Jan 15, 2015

- Jan 16, 2015
- 12 Recommendations

- Sep 26, 2014

- Oct 22, 2014

- Feb 7, 2014

- Oct 7, 2014
- 8 Recommendations

- Jun 12, 2012

- Aug 7, 2013

- May 5, 2013
- May 24, 2013
- 5 Recommendations

- Mar 12, 2013

- Sep 21, 2012

- Feb 5, 2013

- Dec 7, 2010
- Nov 30, 2010
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Privacy Policy

Home » 300+ Social Media Research Topics
300+ Social Media Research Topics

Social media has become an integral part of our lives, and it has transformed the way we communicate, share information, and interact with each other. As social media platforms continue to evolve and gain popularity, they have also become a rich source of data for researchers. Social media research is a rapidly growing field that encompasses a wide range of topics , from understanding the psychological and social effects of social media to analyzing patterns of user behavior and identifying trends in online conversations. In this era of data-driven decision-making, social media research is more important than ever, as it provides insights into how we use and are influenced by social media. In this post, we will explore some of the most fascinating and relevant social media research topics that are shaping our understanding of this powerful medium.
Social Media Research Topics
Social Media Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on mental health
- The role of social media in political polarization
- The impact of social media on relationships
- The use of social media by businesses for marketing
- The effects of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The influence of social media on consumer behavior
- The use of social media for education
- The effects of social media on language use and grammar
- The impact of social media on news consumption
- The role of social media in activism and social change
- The use of social media for job seeking and career development
- The effects of social media on sleep patterns
- The influence of social media on adolescent behavior
- The impact of social media on the spread of misinformation
- The use of social media for personal branding
- The effects of social media on political participation
- The influence of social media on fashion trends
- The impact of social media on sports fandom
- The use of social media for mental health support
- The effects of social media on creativity
- The role of social media in cultural exchange
- The impact of social media on language learning
- The use of social media for crisis communication
- The effects of social media on privacy and security
- The influence of social media on diet and exercise behavior
- The impact of social media on travel behavior
- The use of social media for citizen journalism
- The effects of social media on political accountability
- The role of social media in peer pressure
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships
- The use of social media for community building
- The effects of social media on gender identity
- The influence of social media on music consumption
- The impact of social media on academic performance
- The use of social media for social support
- The effects of social media on social skills
- The role of social media in disaster response
- The impact of social media on nostalgia and memory
- The use of social media for charity and philanthropy
- The effects of social media on political polarization in developing countries
- The influence of social media on literary consumption
- The impact of social media on family relationships
- The use of social media for citizen science
- The effects of social media on cultural identity
- The role of social media in promoting healthy behaviors
- The impact of social media on language diversity
- The use of social media for environmental activism
- The effects of social media on attention span
- The influence of social media on art consumption
- The impact of social media on cultural values and norms.
- The impact of social media on mental health
- The impact of social media on mental health.
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem.
- The use of social media for political activism and social justice movements.
- The role of social media in promoting cultural diversity and inclusivity.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships and dating.
- The use of social media for customer service and support.
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being among young adults.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and partisanship.
- The use of social media for health communication and behavior change.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards vaccination.
- The impact of social media on political participation and civic engagement.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and echo chambers.
- The use of social media for political campaigning and the manipulation of public opinion.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards vaccination and public health.
- The impact of social media on news consumption and trust in journalism.
- The use of social media for promoting sustainable fashion practices and ethical consumption.
- The role of social media in influencing beauty standards and body image.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and the role of social media influencers.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among healthcare professionals.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards gun violence and gun control policies.
- The impact of social media on social activism and advocacy.
- The use of social media for promoting cross-cultural communication and intercultural understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards climate change and environmental policies.
- The impact of social media on public health during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and access to financial services for low-income individuals.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards immigration policies and refugee crises.
- The impact of social media on political activism and social movements.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology education in developing countries.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards gender and sexual orientation.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior in the food and beverage industry.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among first responders.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards racial justice and police brutality.
- The impact of social media on privacy concerns and data security.
- The use of social media for promoting interfaith dialogue and religious tolerance.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards income inequality and economic justice.
- The impact of social media on the film and television industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among military personnel.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards privacy and data security.
- The impact of social media on the hospitality industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting intergenerational communication and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards animal welfare and animal rights.
- The impact of social media on the gaming industry and gamer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology skills among seniors.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards renewable energy and sustainability.
- The impact of social media on the advertising industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among children and adolescents.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards online privacy and security.
- The impact of social media on the beauty industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural preservation and heritage tourism.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards criminal justice reform.
- The impact of social media on the automotive industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among marginalized communities.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards sustainable development goals.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural communication in the workplace.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards mental health policies.
- The impact of social media on the travel industry and sustainable tourism practices.
- The use of social media for health information seeking and patient empowerment.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental activism and sustainable practices.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior and brand loyalty.
- The use of social media for promoting education and lifelong learning.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards mental health issues.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and fast fashion practices.
- The use of social media for promoting social entrepreneurship and social innovation.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun control.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of adolescents.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural exchange and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards climate change.
- The impact of social media on political advertising and campaign strategies.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy relationships and communication skills.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards police brutality and racial justice.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and personal finance management.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards LGBTQ+ rights.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and fan engagement.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among marginalized populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration and border policies.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of journalists.
- The use of social media for promoting community building and social cohesion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards healthcare policies.
- The impact of social media on the food industry and consumer behavior.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gender equality.
- The impact of social media on the sports industry and athlete-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting financial inclusion and access to banking services.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards animal welfare.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among college students.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards privacy and data security.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards income inequality and poverty.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology skills.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards renewable energy.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among elderly populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards online privacy and security.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards criminal justice reform.
- The impact of social media on online activism and social movements.
- The use of social media for business-to-business communication and networking.
- The role of social media in promoting civic education and engagement.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and sustainable fashion practices.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural diversity and inclusion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards police reform.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of frontline healthcare workers.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and investment education.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental sustainability and conservation.
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem among adolescent girls.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural dialogue and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration policies and refugees.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of healthcare professionals.
- The use of social media for promoting community resilience and disaster preparedness.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards the Black Lives Matter movement.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and artist-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy eating habits and nutrition education.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among college students.
- The impact of social media on the entertainment industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting workplace diversity and inclusion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards climate change policies.
- The impact of social media on the travel industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among military veterans.
- The role of social media in promoting intergenerational dialogue and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of educators.
- The use of social media for promoting animal welfare and advocacy.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards reproductive rights.
- The impact of social media on the sports industry and fan behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting financial inclusion and literacy among underprivileged populations.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among LGBTQ+ populations.
- The impact of social media on the food and beverage industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun ownership.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among caregivers.
- The role of social media in promoting sustainable tourism practices.
- The impact of social media on the gaming industry and gamer culture.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural heritage tourism and preservation.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards public transportation policies.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among homeless populations.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among immigrants and refugees.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and entrepreneurship among youth.
- The use of social media for political mobilization and participation in authoritarian regimes.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration policies.
- The impact of social media on the professional development of teachers and educators.
- The use of social media for emergency communication during public health crises.
- The role of social media in promoting LGBTQ+ rights and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on body positivity and self-acceptance among women.
- The use of social media for public diplomacy and international relations.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of marginalized communities.
- The use of social media for crisis management and disaster response in the corporate sector.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental activism and conservation.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of entrepreneurs.
- The use of social media for medical education and healthcare communication.
- The role of social media in promoting cultural exchange and understanding.
- The impact of social media on social capital and civic engagement among young adults.
- The use of social media for disaster preparedness and community resilience.
- The role of social media in promoting religious pluralism and tolerance.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- The use of social media for fundraising and philanthropy in the non-profit sector.
- The role of social media in promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the travel and tourism industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for customer engagement and brand loyalty in the retail sector.
- The impact of social media on the political attitudes and behaviors of young adults.
- The use of social media for promoting gender equality and women’s empowerment.
- The use of social media for promoting animal welfare and adoption.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among the elderly.
- The impact of social media on the art industry and artist-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy food choices and nutrition.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards income inequality.
- The use of social media for promoting political satire and humor.
- The role of social media in promoting disability rights and advocacy.
- The use of social media for promoting voter registration and participation.
- The role of social media in promoting entrepreneurship and small business development.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among incarcerated populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun violence prevention.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural heritage and preservation.
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being.
- The relationship between social media use and academic performance.
- The use of social media for emergency communication during natural disasters.
- The impact of social media on traditional news media and journalism.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and discourse.
- The use of social media for online learning and education.
- The impact of social media on the fashion and beauty industry.
- The use of social media for brand awareness and marketing.
- The impact of social media on privacy and security.
- The use of social media for job searching and recruitment.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and extremism.
- The use of social media for online harassment and cyberbullying.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental awareness and sustainability.
- The impact of social media on youth culture and identity formation.
- The use of social media for travel and tourism marketing.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior and decision-making.
- The role of social media in shaping beauty standards and body positivity.
- The use of social media for crisis communication and disaster response.
- The impact of social media on the music industry.
- The use of social media for fundraising and philanthropy.
- The role of social media in promoting healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- The impact of social media on sports fandom and fan behavior.
- The use of social media for political lobbying and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on the entertainment industry.
- The use of social media for healthcare communication and patient engagement.
- The role of social media in promoting gender equality and feminism.
- The impact of social media on the restaurant and food industry.
- The use of social media for volunteerism and community service.
- The role of social media in promoting religious tolerance and interfaith dialogue.
- The impact of social media on the art industry.
- The use of social media for political satire and humor.
- The role of social media in promoting disability awareness and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on the real estate industry.
- The use of social media for legal advocacy and justice reform.
- The role of social media in promoting intercultural communication and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the automotive industry.
- The use of social media for pet adoption and animal welfare advocacy.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and wellness for marginalized communities.
- The impact of social media on the retail industry.
- The use of social media for promoting civic engagement and voter participation.
- The impact of social media on the film and television industry.
- The use of social media for fashion and style inspiration.
- The role of social media in promoting activism for human rights and social issues.
- The effectiveness of social media for political campaigns.
- The role of social media in promoting fake news and misinformation.
- The impact of social media on self-esteem and body image.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships.
- The use of social media for online activism and social justice movements.
- The impact of social media on traditional news media.
- The impact of social media on interpersonal communication skills.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry.
- The use of social media for social support and mental health awareness.
- The use of social media for political lobbying and activism.
- The impact of social media on travel and tourism behavior.
- The use of social media for customer feedback and market research.
- The impact of social media on the restaurant industry.
- The role of social media in political activism
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication
- The relationship between social media use and body image concerns
- The impact of social media on self-esteem
- The role of social media in shaping cultural norms and values
- The use of social media by celebrities and its impact on their image
- The role of social media in building and maintaining personal relationships
- The use of social media for job searching and recruitment
- The impact of social media on children and adolescents
- The use of social media by political candidates during election campaigns
- The role of social media in education
- The impact of social media on political polarization
- The use of social media for news consumption
- The effect of social media on sleep habits
- The use of social media by non-profit organizations for fundraising
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion
- The influence of social media on language and communication patterns
- The use of social media in crisis communication and emergency management
- The role of social media in promoting environmental awareness
- The influence of social media on music preferences
- The impact of social media on body positivity movements
- The role of social media in shaping beauty standards
- The influence of social media on sports fandom
- The use of social media for health promotion and education
- The impact of social media on political participation
- The role of social media in shaping parenting practices
- The influence of social media on food preferences and eating habits
- The use of social media for peer support and mental health advocacy
- The role of social media in shaping religious beliefs and practices
- The influence of social media on humor and comedy
- The use of social media for online activism and social justice advocacy
- The impact of social media on public health awareness campaigns
- The role of social media in promoting cultural diversity and inclusion
- The influence of social media on travel behavior and decision-making
- The use of social media for international diplomacy and relations
- The impact of social media on job satisfaction and employee engagement
- The role of social media in shaping romantic preferences and dating behavior
- The influence of social media on language learning and language use
- The use of social media for political satire and humor
- The impact of social media on social capital and community building
- The role of social media in shaping gender identity and expression
- The influence of social media on fashion and beauty advertising.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Business Research Topics

300+ Controversial Research Topics

500+ Educational Research Topics

500+ Music Research Topics

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Environmental Research Topics

COMMENTS
A majority of X users (59%) say keeping up with politics or political issues is a reason they use it, compared with 36% of TikTok users and even smaller shares of Facebook or Instagram users (26% each). There's a range of reasons people are drawn to social media platforms - even on X, where using it to keep up with politics is relatively ...
In a political environment defined by widespread polarization and partisan animosity, even simple conversations can go awry when the subject turns to politics.In their in-person interactions, Americans can (and often do) attempt to steer clear of those with whom they strongly disagree.. But online social media environments present new challenges.
Against this background, political communication scholars have explored two overarching research questions related to the normative role of social media in politics: first, whether social media increases democratic engagement, such as voting in elections or other forms of political participation (Boulianne, Citation 2020), and second, to what ...
The use of social media is becoming a feature of political and civic engagement for many Americans. Some 60% of American adults use either social networking sites like Facebook or Twitter and a new survey by the Pew Research Center's Internet & American Life Project finds that 66% of those social media users—or 39% of all American adults ...
Rising political polarization is, in part, attributed to the fragmentation of news media and the spread of misinformation on social media. Previous reviews have yet to assess the full breadth of research on media and polarization. We systematically examine 94 articles (121 studies) that assess the role of (social) media in shaping political ...
By examining previous research on social media's role in political campaigns within Sub-Saharan Africa, this study seeks to shed light on its potential to foster political participation, while also acknowledging the challenges that may constrain its efficacy within specific contexts (Chatora, 2012). Thus, this research aims to elucidate ...
Pew Research Center's research on the internet, social media and technology in the U.S. and around the world. Many of the topics explored in this report have been studied in depth in the U.S. by Pew Research Center's internet and technology team, which for more than two decades has conducted survey research on the social impact of digital technologies, such as internet and broadband ...
The rapid evolution of social media has transformed the landscape of contemporary politics and civil engagement. Social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, WhatsApp, and WeChat, in addition to less censored platforms such as Redditt and Telegram, among others, have emerged as powerful tools for political mobilization, civic engagement, and the dissemination of ...
The study's key findings include: Among all of the factors examined, 82% showed a positive relationship between SNS use and some form of civic or political engagement or participation. Still, only half of the relationships found were statistically significant. The strongest effects could be seen in studies that randomly sampled youth populations.
Meanwhile, 41% of users feel that social media discussions are less politically correct than other places where people discuss politics, but a majority feels that social media is either more politically correct (8%) or about the same as other venues (47%). Lastly, around one-third (34%) of users consider the political discussions they see on ...
9% of social media users say they often discuss, comment or post about politics or government on these platforms. Roughly one-third of social media users indicate they often (9%) or sometimes (23%) comment, discuss or post about government and politics on social media; meanwhile, nearly seven-in-ten indicate that they hardly ever (30%) or never ...
The study of social media use (SMU) and political participation (PP) has been rapidly expanding (Boulianne, 2015; Ekström et al., 2014).Findings suggest that the use of social media can promote various forms of political engagement (Boulianne, 2015; Dimitrova and Bystrom, 2013; Dimitrova et al., 2014; Halpern and Gibbs, 2013).Despite this large body of research, there is a lack of theorizing ...
This is especially notable in the context of political correctness: Fully 57% of highly engaged social media users feel that social media conversations are less politically correct than those they see elsewhere: Just 39% of less-engaged users feel the same way. And a substantial majority of highly engaged users see social media as angrier, less ...
The impact of social media in political campaigning around the world is undeniable. Latest statistics show that close to three fourth of U.S. adults use social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter, with social network use becoming almost ubiquitous among young adults, according to recent data from the Pew Research Center (2018).Globally, an estimated 2.62 billion people use social ...
Jun Liu is an Associate Professor at the Center for Tracking and Society at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark. His research spans political sociology, digital technologies, and comparative and computational social science. His latest work includes a monograph titled "Shifting Dynamics of Contention in the Digital Age," published by Oxford University Press.
Some have described journalists as political influencers when they post opinionated takes on political questions on social media (Peres-Neto, 2022; Schwemmer & Ziewiecki, 2018). ... The work presented here establishes a baseline in the domain of political influencer research. Future studies should focus on definitional work on influence and ...
Media is justified inasmuch as these have. democratized the process of news-making, and have made information more accessible. In this context, when we address the relation. between Social Media ...
First, prior research has found that using social media can help increase users' overall exposure to politics. As social media enable various kinds of information to be disseminated across a wide range of users, people are likely to stumble upon political information that is shared by their network of social contacts (Brundidge, 2010 ...
The research questions on the use of social media measured the frequencies of student's activities as follows: (a) receiving information related to politics, (b) sharing opinions relevant to current events, (c) following politicians, (d) posting experiences relating to politics, (e) re-sharing other people's comments, (f) arguing with other ...
In an informal Instagram poll on The Daily Universe's account, 89% of the 273 respondents said they believe social media has affected their political views and involvement. When asked for ...
tions. Based on the online survey results, majorit y of the people follow both politicians and politi cal candidates. Majority of youth. (67%) follow politics on various social media like face ...
Categorization of topic Figure 8 shows the four main topics that form the basis of the discussion of the theme of research on political communication in social media from Scopus-indexed articles ...
In recent years political polarization is also studied by data scientists due to the growing effect of internet and the digital platforms like social media. Now it is much more easier than ever to collect large volumes of big data from online social networks and study political polarization from multiple aspects and extract insights about the ...
Topics & Ideas: Political Theory. An analysis of the impact of feminism on political theory and the concept of citizenship in Saudi Arabia in the context of Vision 2030. A comparative study of the political philosophies of Marxism and liberalism and their influence on modern politics. An examination of how the Covid-19 pandemic affected the ...
Sharing false political information on social media may be associated with positive schizotypy, research suggests Jun 26, 2024 How the Meta algorithm influences election advertising
234 Social Media Research Topics & Ideas. Written by. Victor Hughes. 18 May 2024. 2646 words. 12 min read. Social media research encompasses a broad range of different topics that delve into the ever-evolving digital landscape. People investigate the impact of social platforms on society, exploring subjects, such as online identity formation ...
Political ads on social media rife with misinformation and scams, new research finds A deep dive into political ads on Facebook by researchers at Syracuse University has revealed a sprawling web ...
Relevant answer. Taimoor Ul Hassan. Jul 2, 2016. Answer. parties' messages, voter enrollment, mobilization of voters on voting day , party membership, political networking; but no significant ...
Social Media Research Topics are as follows: The effects of social media on mental health. The role of social media in political polarization. The impact of social media on relationships. The use of social media by businesses for marketing. The effects of social media on body image and self-esteem.
Project 2025 accuses social media networks—directly naming Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok—of jeopardizing young Americans' mental health and social ties by creating a form of addiction. "Federal policy cannot allow this to continue," it says.: 5-6 Immigration reforms