- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center

Customer Satisfaction Research: What it is + How to do it?

Customer satisfaction research is essential for businesses looking to build long-term customer relationships. It provides organizations with essential insights into their customers’ thinking and tastes.
Customers who are satisfied with the quality of service are more likely to become loyal customers. In this blog, we will explore customer satisfaction research and how to do it for customer-centric success.
What is customer satisfaction research?
Customer satisfaction research is a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data that allows companies to measure the satisfaction level of customers when purchasing a product or service from their brand.
This research is useful to identify satisfied customers who are loyal defenders of your brand and who are dissatisfied to follow up on their demands.
There are many reasons to measure customer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction research offers great insights, so your team can focus on meeting customer expectations or flagging potential issues that may affect your business growth.
Importance of conducting a satisfaction study
Customer satisfaction research allows business managers and owners to discover that keeping current customers costs less than getting new ones.
One way to collect information about customer satisfaction is by conducting online surveys, which will help you make the necessary changes to improve your business and maintain customer loyalty.
Responding to customer complaints and concerns don’t always mean knowing their needs. Satisfaction surveys allow companies to understand what is working, what needs to be improved, and why.
To provide better customer service, it’s important to understand how they feel and allow them to explain why they feel that way. Only then can you adapt your services and offer an experience that makes you stand out from the competition.
Companies carry out satisfaction studies for different objectives. Among the most important uses of this mechanism are:
- Know what are the areas that need to be improved in the business.
- Know the opinion of customers about your brand.
- Find out what the true needs of customers are.
- Create better customer retention strategies.
- Know if the market strategies that are carried out are working.
- Meet customer expectations.
How to carry out customer satisfaction research?
Customer satisfaction research takes several steps to get a thorough and accurate insight into your customer experiences and perspectives. Here’s a step-by-step method you can follow for carrying out customer satisfaction research:
Step 1: Define Research Objectives
Defining precise and well-structured research objectives is an essential first step in every customer satisfaction research project. These objectives will guide you through the whole research process and ensure that the research remains focused, relevant, and connected with your business goals.
To define research objectives, follow the steps outlined below:
- Identify the Objectives: Start by identifying the overall objectives of your customer satisfaction research.
- Break Down Objectives: Divide the purpose into specific objectives. Each objective should be specific and address a different component of customer satisfaction.
- SMART Criteria: Make sure your objectives are SMART—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Prioritize: If you have several objectives, prioritize them according to relevance and potential impact.
Step 2: Select Research Methodology
Selecting an appropriate research technique is a vital decision that will define your overall research process. Your approach will influence the type of data you gather, the level of insights you get, and the general validity of your findings. Here are some examples of research methodology.
- Surveys: Surveys are a popular and versatile method for collecting data on customer satisfaction. You can gather qualitative and quantitative data through structured questions.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is the most straightforward of the customer satisfaction survey methodologies. Surveys are well-suited for measuring customer satisfaction scores, Net Promoter Scores (NPS), and other quantitative metrics.
- Interviews: Interviews will enable you to have in-depth interactions with customers. You can get valuable qualitative insights into customer experiences through phone interviews or in-person chats.
- Focus Groups: In a focus group, a small group of customers shares their experiences, ideas, and impressions in a guided session. This strategy encourages group interactions by allowing participants to respond to each other’s comments.
- Observations: Observational research refers to directly monitoring customers as they interact with your products or services. This strategy will provide you insights into user behavior and reactions in real time.
Step 3: Develop Customer Satisfaction Surveys
Developing well-crafted customer satisfaction surveys is an important stage in customer satisfaction research. It serves as the primary tool for gathering customer data and insights.
A well-crafted customer satisfaction survey will ensure that you get relevant and meaningful data. It will also motivate you to make improvements and increase customer satisfaction. You can develop a robust customer satisfaction survey by following the steps below:
- Define Research Objectives: Before developing survey questions, ensure you understand the research objectives. Determine which aspects of customer satisfaction you want to measure and what insights you want to get.
- Choose Question Types: Remember the research objectives when creating customer satisfaction survey questions. Select appropriate question types that align with your research objectives. It will help you to capture different dimensions of customer satisfaction. To quantify responses, include closed-ended questions with Likert scales, multiple-choice options, and ranking scales. Include open-ended questions. It will encourage your customers to provide thorough comments and insights.
- Order and Flow: Organize the survey questions logically, begin with general questions, and then proceed to more specialized and complicated topics. Keep a balance between qualitative and quantitative questions.
- Avoid Leading Questions: Leading questions will unintentionally influence your respondents and compromise the accuracy of their responses. So, avoid including leading questions and design questions that are neutral and unbiased.
- Incorporate Demographic Questions: Demographic questions (e.g., age, gender, location) will help you to segment responses and analyze satisfaction across different customer segments. So include it.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: Make sure your survey is mobile-friendly and displays properly on different screen sizes.
Step 4: Sampling Strategy
Sampling ensures that the findings are representative of your whole customer base. It will enable you to make correct decisions and judgments. A well-planned sampling method will help you reduce biases and increase your findings’ generalization.
Depending on your research objectives and available resources, you can use a variety of sampling methods . Here are a few common approaches:
- Simple Random Sampling : It ensures that every person in the population has an equal chance of being chosen.
- Stratified Random Sampling : This sampling method divides your population into subgroups based on specified criteria.
- Convenience Sampling : This method selects participants who are easily accessible, such as customers who frequently visit your physical store or online store.
Step 5: Data Collection and Analysis
In this step, you will collect data from your target audience, arrange and evaluate the data systematically, and generate useful insights to make informed decisions.
Use statistical tools to analyze trends, correlations, and distributions for quantitative data. Calculate measures such as averages, percentages, and standard deviations. You can visually represent the findings using graphs, charts, and tables.
Use qualitative analysis tools for qualitative data. Content analysis, thematic analysis, and sentiment analysis are all common methodologies you can use. These strategies will help you identify repeating themes, attitudes, and patterns in open-ended responses.
Step 6: Implement Changes
The implementation phase of customer satisfaction research is where insights and recommendations are implemented. Here, you will turn data-driven findings into real improvements that directly influence the customer experience.
Create a detailed implementation plan for each identified improvement. Implementing changes based on research findings involves careful planning, cooperation, and a dedication to providing greater customer value.
Define specific tasks, time frames, responsible parties, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of each effort. Prioritize the actionable recommendations that are most likely to improve customer satisfaction and retention significantly.
Step 7: Communication and Regular Feedback Loop
Transparency is essential for maintaining trust and credibility with your customers. Share the research’s findings and the responses that were made. Let your customers know that their opinions are taken seriously and have resulted in concrete improvements.
Customer satisfaction will remain a dynamic and changing emphasis of your business strategy if you establish a continual feedback loop. Here are some tips for creating and keeping a consistent feedback loop:
- Scheduled Surveys: Conduct customer satisfaction surveys quarterly, semi-annually, or yearly.
- Incorporate Feedback Mechanisms: Integrate feedback mechanisms into various touchpoints, such as post-purchase follow-up emails, customer service interactions, or feedback forms on your website.
- Feedback Analysis: Analyze the customer feedback you received from each cycle in detail. Identify recurring themes, popular trends, and problem areas.
- Action Planning: Create action plans for additional improvements based on the newly acquired insight.
- Implementation: Implement the suggested modification and changes in every relevant part of your business.
Advantages of carrying out a satisfaction study
Carrying out a satisfaction study has great benefits for your organization:
- Obtain valuable information from customers
Doing customer satisfaction research allows you to obtain information about your customers, determine how happy they are with your company, and correct what is wrong.
- Establish priorities
The satisfaction study results allow you to discover which areas of your business need more attention, such as customer service, the sales closing process, etc.
- Customer retention
If your customers are satisfied with your products, it is possible that they will stay in your business. Maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction is extremely important to the overall success of your organization.
- Maintain your reputation
A satisfaction study allows you to interact with consumers and show them that you care about their needs and opinions. In particular, they offer to improve the customer experience if you make the changes.
- Maintain customer loyalty
If you want to maintain customer loyalty, a satisfaction survey will give you the opportunity to listen to their feedback and improve your brand.
- Get new customers
People feel more confident buying from transparent companies, so post the feedback you get from current customers to show that you allow any kind of feedback and value it.
- An advantage over the competition
There is a lot of competition in the market today, so any advantage you may have needs to be made known. Show current and potential customers the areas in which you excel.
Conducting customer satisfaction research with QuestionPro
One of the best ways to find out the opinion of customers and their needs is through online surveys, which allow you to collect information and perform data analysis to make better business decisions.
With QuestionPro, you can find out how satisfied your customers are by asking a Net Promoter Score question, which will let you know if consumers are promoters or detractors of your brand.
Other types of questions that will help you gather information for your study are:
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Closed questions
- Open text questions
- Order and Ranking Questions
You can track customer satisfaction and measure how happy your existing customers are with your business, brand, and customer initiatives by using QuestionPro’s customer satisfaction survey templates and survey questions. These customer satisfaction survey examples help ensure a higher survey completion and response rate for your market research.
Find out what customers think! Carry out customer satisfaction research and collect the necessary information to improve the consumer experience. Contact us and learn how to measure customer satisfaction using QuestionPro.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 10 Knowledge Management Tools to Enhance Knowledge Flow
Jul 10, 2024

CX Shenanigans: Booth Duty and Beyond — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jul 9, 2024
Negative Correlation: Definition, Examples + How to Find It?

Customer Marketing: The Best Kept Secret of Big Brands
Jul 8, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Top Marketing Research Articles Related to Customer Satisfaction Studies
Learn all about customer satisfaction studies. Quirks.com is the largest source of marketing research information.
Search Results
More Filters
Loading filters...
Article The Q Report: Researchers hope AI will boost listening-tool effectiveness Marlen Ramirez | July 1, 2024
Article Quick Take: Just measuring customer satisfaction isn’t enough Doug Berdie | July 1, 2024
Article 10 steps to enhance your customer experience strategy Mehul Nagrani | June 11, 2024
Article Strategies and tips to improve B2B customer retention Sara Melefsky | May 22, 2024
Article The challenges and benefits of AI-powered customer service Angel Vossough | May 15, 2024
Sponsored Article Want to Know What Your Customers Really Think? Simplify Your Satisfaction Survey! Rick Kieser | May 14, 2024
Article Trade Talk: Area man recounts CX nightmare Joseph Rydholm | January 1, 2024
Article How an aging population affects grocery retailers and CPG companies Katarina Weil | January 10, 2024
Article Voice of the customer: Five tips for an effective VOC program Marlen Ramirez | December 19, 2023
Article Utilizing user personas to improve customer experience Charles Adom | December 11, 2023
Sponsored Article KitchenAid Reveals “End-To-End” Global Consumer Journey Kelly Vrachimis | November 27, 2023
Article Unhappy customers are more costly in a tight economy, but data analytics can help Miika Mäkitalo | September 18, 2023
Article Transforming the customer service landscape: Marketing research and conversational AI Polat Goktas , Taskin Dirsehan | September 18, 2023
Article Use neuroscience to fine-tune your customer expectations strategy Terry Grapentine | September 1, 2023
Article How generative AI is transforming open-end analysis Rick Kieser | September 1, 2023
Measuring Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 03 December 2019
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Sebastian Hohenberg 4 &
- Wayne Taylor 5
1526 Accesses
2 Citations
Measuring customer satisfaction and customer loyalty represents a key challenge for firms. In response, researchers and practitioners have developed a plethora of options on how to assess these phenomena. However, existing measurement approaches differ substantially with regard to their complexity, sophistication, and information quality. Furthermore, guidance is scarce on how firms can leverage and combine these approaches to implement a state-of-the-art satisfaction and loyalty measurement system. This chapter attempts to address this vacancy. The authors first define and conceptualize customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. Next, the authors provide an overview of the different operationalization and measurement approaches that companies face when designing a customer satisfaction and loyalty measurement system. The authors also discuss some of the common modeling challenges associated with measuring loyalty, namely, dealing with self-selection bias. Finally, the authors project what the future holds in this area.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Measurement: A Two-Sided Approach

Customer Loyalty: An Empirical Investigation of Operationalized Measures of Loyalty
Ahn, H., & Powell, J. L. (1993). Semiparametric estimation of censored selection models with a nonparametric selection mechanism. Journal of Econometrics, 58 (l–2), 3–29.
Article Google Scholar
Aksoy, L. (2013). How do you measure what you can’t define? The current state of loyalty measurement and management. Journal of Service Management, 24 (4), 356–381.
Anderson, E. W. (1996). Customer satisfaction and price tolerance. Marketing Letters, 7 (3), 265–274.
Anderson. (2010). Meng marketing trends report 2010.
Google Scholar
Anderson, E. W., & Mittal, V. (2000). Strengthening the satisfaction-profit chain. Journal of Service Research, 3 (2), 107–120.
Anderson, E. W., Fornell, C., & Lehmann, D. R. (1994). Customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability: Findings from Sweden. Journal of Marketing, 58 (3), 53–66.
Anderson, E. W., Fornell, C., & Mazvancheryl, S. K. (2004). Customer satisfaction and shareholder value. Journal of Marketing, 68 (4), 172–185.
Ascarza, E. (2018). Retention futility: Targeting high-risk customers might be ineffective. Journal of Marketing Research, 55 (l), 80–98.
Ascarza, E., Fader, P. S., & Hardie, B. G. (2017). Marketing models for the customer-centric firm. In Handbook of marketing decision models (pp. 297–329). New York: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Athey, S. (2018). The impact of machine learning on economics. In The economics of artificial intelligence: An agenda . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Brakus, J. J., Schmitt, B. H., & Zarantonello, L. (2009). Brand experience: what is it? How is it measured? Does it affect loyalty?. Journal of Marketing, 73(3), 52–68.
Bain andCompany (2013). Management Tools & Trends 2013. http://www.bain.de/Images/BAIN_BRIEF_Management_Tools_%26_Trends_2013.pdf . Accessed 25 July 2016.
Bearden, W. O., & Teel, J. E. (1983). Selected determinants of consumer satisfaction and complaint reports. Journal of Marketing Research, 20 (l), 21–28.
Bergkvist, L., & Rossiter, J. R. (2007). The predictive validity of multiple-item versus single-item measures of the same constructs. Journal of Marketing Research, 44 (2), 175–184.
Bijmolt, T. H., Dorotic, M., Verhoef, P. C., et al. (2011). Loyalty programs: Generalizations on their adoption, effectiveness and design. Foundations and Trends® in Marketing, 5 (4), 197–258.
Blattberg, R., Kim, B., & Neslin, S. (2008). Database Marketing: Analyzing and Managing Customers . New York: Springer.
Book Google Scholar
Bolton, R. N. (1998). A dynamic model of the duration of the customer’s relationship with a continuous service provider: The role of satisfaction. Marketing Science, 17 (l), 45–65.
Boshoff, C. (1997). An experimental study of service recovery options. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 8 (2), 110–130.
Brandt, D. R., & Reffett, K. L. (1989). Focusing on customer problems to improve service quality. Journal of Services Marketing, 3 (4), 5–14.
Breugelmans, E., Bijmolt, T. H., Zhang, J., Basso, L. J., Dorotic, M., Kopalle, R., Minnema, A., Mijnlieff, W. J., & Wünderlich, N. V. (2015). Advancing research on loyalty programs: A future research agenda. Marketing Letters, 26 (2), 127–139.
Brooke. (2016). Rewards, returns, and ringside seats. Marketing News, 50 (6), 28–35.
Bruhn, M. (2003). Relationship marketing: Management of customer relationships . Harlow: Pearson Education.
Bruhn, M. (2016). Kundenorientierung: Bausteine fuer ein exzellentes Customer Relationship Management (CRM) (Vol. 50950). München: CHE Beck.
Cannon, J. P., & Perreault, W. D., Jr. (1999). Buyer-seller relationships in business markets. Journal of Marketing Research, 36 (4), 439–460.
Certo, S. T., Busenbark, J. R., Woo, H.-s., & Semadeni, M. (2016). Sample selection bias and heckman models in strategic management research. Strategic Management Journal, 37 (13), 2639–2657.
Chandrashekaran, M., Rotte, K., Tax, S. S., & Grewal, R. (2007). Satisfaction strength and customer loyalty. Journal of Marketing Research, 44 (1), 153–163.
Churchill, G. A., Jr., & Surprenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Research, 19 (4), 491–504.
Davis, D. F., Golicic, S. L., & Boerstler, C. N. (2011). Benefits and challenges of conducting multiple methods research in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 39 (3), 467–479.
DeWulf, K., Odekerken-Schrôder, G., & Iacobucci, D. (2001). Investments in consumer relationships: A cross-country and cross-industry exploration. Journal of Marketing, 65 (4), 33–50.
Diamantopoulos, A. (2011). Incorporating formative measures into covariance-based structural equation models. MIS Quarterly, 35 , 335–358.
Dreze, X., & Nunes, J. C. (2008). Feeling superior: The impact of loyalty program structure on consumers’ perceptions of status. Journal of Consumer Research, 35 (6), 890–905.
Ernst & Young (2011), The digitisation of everything: How organizations must adapt to changing consumer behaviour, available at: http://www.ey.com/Publication/vwLUAssets/The_digitisation_of_everything_-_How_organisations_must_adapt_to_changing_consumer_behaviour/$FILE/EY_Digitisation_of_everything.pdf , retrieved on 2016-07-25.
Ellickson, P. B., & Misra, S. (2012). Enriching interactions: Incorporating outcome data into static discrete games. Quantitative Marketing and Economics, 10 (1), 1–26.
Fornell, C., Johnson, M. D., Anderson, E. W., Cha, J., & Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American customer satisfaction index: Nature, purpose, and findings. Journal of Marketing, 60 (4), 7–18.
Fuerst, A. (2012). Verfahren zur Messung der Kundenzufriedenheit im Ueberblick. Kundenzufriedenheit: Konzepte–Methoden–Erfahrungen, 8 , 123–154.
Gremler, D. D. (2004). The critical incident technique in service research. Journal of Service Research, 7 (l), 65–89.
Griffin, A., Gleason, G., Preiss, R., & Shevenaugh, D. (1995). Best practice for customer satisfaction in manufacturing firms. MIT Sloan Management Review, 36 (2), 87.
Grigoroudis, E., & Siskos, Y. (2009). Customer satisfaction evaluation: Methods for measuring and implementing service quality (Vol. 139). Springer Science & Business Media.
Gupta, S., & Zeithaml, V. (2006). Customer metrics and their impact on financial performance. Marketing Science, 25 (6), 718–739.
Gustafsson, A., & Johnson, M. D. (2004). Determining attribute importance in a service satisfaction model. Journal of Service Research, 7 (2), 124–141.
Halstead, D. (1999). The use of comparison standards in customer satisfaction research and management: A review and proposed typology. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 7 (3), 13–26.
Hartmann, W., & Viard, B. (2008). Do frequency reward programs create switching costs? A dynamic structural analysis of demand in a reward program. Quantitative Marketing and Economics, 6 (2), 109–137.
Hauser, J. R., Urban, G. L., Liberali, G., & Braun, M. (2009). Website morphing. Marketing Science, 28 (2), 202–223.
Hayes, B. E. (2008). Measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty: Survey design, use, and statistical analysis methods . ASQ Quality Press.
Heckman, J. J. (1979). Sample selection bias as a specification error. Econometrica, 47 (1), 153–161.
Homburg, C., & Fuerst, A. (2005). How organizational complaint handling drives customer loyalty: An analysis of the mechanistic and the organic approach. Journal of Marketing, 69 (3), 95–114.
Homburg, C., Fürst, A. (2010). Überblick über die Messung von Kundenzufriedenheit und Kundenbindung. In Bruhn, M. and Homburg, C. (Eds.): Handbuch Kundenbindungsmanagement (pp. 599–634). Wiesbaden: Gabler.
Homburg, C. and Klarmann, M. (2012). Die indirekte Wichtigkeitsbestimmung im Rahmen von Kundenzufriedenheitsuntersuchungen: Probleme und Loesungsansaetze. Homburg, C. (Eds.): Handbuch Kundenzufriedenheit: Konzepte - Methoden - Erfahrungen. Wiesbaden: Gabler.
Homburg, C., & Stock, R. M. (2004). The link between salespeoples job satisfaction and customer satisfaction in a business-to-business context: A dyadic analysis. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 32 (2), 144.
Homburg, C., Koschate, N., & Hoyer, W. D. (2005). Do satisfied customers really pay more? A study of the relationship between customer satisfaction and willingness to pay. Journal of Marketing, 69 (2), 84–96.
Homburg, C., Koschate, N., & Hoyer, W. D. (2006). The role of cognition and affect in the formation of customer satisfaction: A dynamic perspective. Journal of Marketing, 70 (3), 21–31.
Homburg, C., Mueller, M., & Klarmann, M. (2011). When should the customer really be king? On the optimum level of salesperson customer orientation in sales encounters. Journal of Marketing, 75 (2), 55–74.
Homburg, C., Ehm, L., & Artz, M. (2015). Measuring and managing consumer sentiment in an online community environment. Journal of Marketing Research, 52 (5), 629–641.
Howard, J. A. & Sheth, J. N. (1969). The Theory of Buyer Behavior. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Hunt, H. K. (1977). Conceptualization and measurement of consumer satisfaction and dissatisfaction (pp. 77–103). Cambridge, MA: Marketing Science Institute.
Jarvis, C. B., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, P. M. (2003). A critical review of construct indicators and measurement model misspecification in marketing and consumer research. Journal of Consumer Research, 30 (2), 199–218.
Keiningham, T. L., Cooil, B., Andreassen, T. W., & Aksoy, L. (2007). A longitudinal examination of net promoter and firm revenue growth. Journal of Marketing, 71 (3), 39–51.
Klarmann, M. (2008). Methodische Problemfelder der Erfolgsfaktorenforschung: Bestandsaufnahme und Empirische Analysen. Ph.D. thesis.
Kozinets, R. V., De Valck, K., Wojnicki, A. C., & Wilner, S. J. (2010). Networked narratives: Understanding word-of-mouth marketing in online communities. Journal of Marketing, 74 (2), 71–89.
Kumar, V., & Reinartz, W. (2012). Customer relationship management: Concept, strategy, and tools . Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Kumar, V., & Shah, D. (2004). Building and sustaining profitable customer loyalty for the 21st century. Journal of Retailing, 80 (4), 317–329.
Kumar, V., Dalla Pozza, I., & Ganesh, J. (2013). Revisiting the satisfaction–loyalty relationship: Empirical generalizations and directions for future research. Journal of Retailing, 89 (3), 246–262.
Larivière, B., Keiningham, T. L., Aksoy, L., Yalgin, A., Morgeson, F. V., III, & Mithas, S. (2016). Modeling heterogeneity in the satisfaction, loyalty intention, and shareholder value linkage: A cross-industry analysis at the customer and firm levels. Journal of Marketing Research, 53 (1), 91–109.
Liu, J., & Toubia, O. (2018). A semantic approach for estimating consumer content preferences from online search queries. Marketing Science, 37 (6), 930–952.
Liu, Y., & Yang, R. (2009). Competing loyalty programs: Impact of market saturation, market share, and category expandability. Journal of Marketing, 73 (1), 93–108.
Luo, X., & Homburg, C. (2007). Neglected outcomes of customer satisfaction. Journal of Marketing, 71 (2), 133–149.
Ma, L., Sun, B., & Kekre, S. (2015). The squeaky wheel gets the grease - an empirical analysis of customer voice and firm intervention on twitter. Marketing Science, 34 (5), 627–645.
McAlexander, J. H., Schouten, J. W., & Koenig, H. F. (2002). Building brand community. Journal of Marketing, 66 (l), 38–54.
McAlexander, J. H., Kim, S. K., & Roberts, S. D. (2003). Loyalty: The influences of satisfaction and brand community integration. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 11 (4), 1–11.
McCall, M., & Voorhees, C. (2010). The drivers of loyalty program success: An organizing framework and research agenda. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 51 (l), 35–52.
McCollough, M. A., Berry, L. L., & Yadav, M. S. (2000). An empirical investigation of customer satisfaction after service failure and recovery. Journal of Service Research, 3 (2), 121–137.
McNeal, J. U. (1969). Consumer satisfaction-measure of marketing effectiveness. MSU Business Topics-Michigan State University, 17 (3), 31–35.
Mellens, M., Dekimpe, M., & Steenkamp, J. (1996). A review of brand-loyalty measures in marketing. Tijdschrift voor economic en management, 4 , 507–533.
Morgan, N. A., & Rego, L. L. (2006). The value of different customer satisfaction and loyalty metrics in predicting business performance. Marketing Science, 25 (5), 426–439.
Morgan, N. A., Anderson, E. W., & Mittal, V. (2005). Understanding firms customer satisfaction information usage. Journal of Marketing, 69 (3), 131–151.
Morgeson, F. V., Mithas, S., Keiningham, T. L., & Aksoy, L. (2011). An investigation of the cross-national determinants of customer satisfaction. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 39 (2), 198–215.
Oliver, R. L. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. Journal of Marketing Research, 17 (4), 460–469.
Oliver, R. L. (1981). Measurement and evaluation of satisfaction processes in retail settings. Journal of Retailing, 57 , 25.
Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of Marketing, 63 (4_suppl 1), 33–44.
Palmatier, R. W., Dant, R. P., Grewal, D., & Evans, K. R. (2006). Factors influencing the effectiveness of relationship marketing: A meta-analysis. Journal of Marketing, 70 (4), 136–153.
Peters, L. D., Pressey, A. D., & Greenberg, P. (2010). The impact of CRM 2.0 on customer insight. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 25 , 410.
Peterson, R. A., & Wilson, W. R. (1992). Measuring customer satisfaction: Fact and artifact. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 20 (1), 61.
Reeves, M., & Deimler, M. (2011). Adaptability: The new competitive advantage. Harvard Business Review, 89 (4), 134–141.
Reichheld, F. F. (1996). Learning from customer defections. Harvard Business Review, 74 , 56–69.
Reichheld, F. F. (2003). The one number you need to grow. Harvard Business Review, 81 (12), 46–55.
Richins, M. L. (1983). Negative word-of-mouth by dissatisfied consumers: A pilot study. Journal of Marketing, 47 (l), 68–78.
Roehm, M., Pullins, E., & Jr, H. R. (2002). Designing loyalty-building programs for packaged goods brands. Journal of Marketing Research, 39 (2), 202–213.
Rust, R. T., & Zahorik, A. J. (1993). Customer satisfaction, customer retention, and market share. Journal of Retailing, 69 (2), 193–215.
Sarstedt, M., Mooi, E., (2019). A Concise Guide to Market Research: The Process, Data, and Methods Using IBM SPSS Statistics (3rd edition). Springer
Schwartz, E. M., Bradlow, E. T., & Fader, R. S. (2017). Customer acquisition via display advertising using multi-armed bandit experiments. Marketing Science, 36 (4), 500–522.
Shankar, V., Smith, A. K., & Rangaswamy, A. (2003). Customer satisfaction and loyalty in online and offline environments. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 20 (2), 153–175.
Sheppard, B. H., Hartwick, J., & Warshaw, P. R. (1988). The theory of reasoned action: A meta-analysis of past research with recommendations for modifications and future research. Journal of Consumer Research, 15 (3), 325–343.
Sheth, J. N. (1970). Measurement of multidimensional brand loyalty of a consumer. Journal of Marketing Research, 7 (3), 348–354.
Shugan, S. (2005). Brand loyalty programs: Are they shams? Marketing Science, 24 (2), 185–193.
Singh, J., & Pandya, S. (1991). Exploring the effects of consumers’ dissatisfaction level on complaint behaviours. European Journal of Marketing, 25 (9), 7–21.
Smith, A. K., & Bolton, R. N. (1998). An experimental investigation of customer reactions to service failure and recovery encounters: Paradox or peril? Journal of Service Research, 1 (1), 65–81.
Szymanski, D. M., & Henard, D. H. (2001). Customer satisfaction: A meta-analysis of the empirical evidence. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 29 (l), 16–35.
Umashankar, N., Bhagwat, Y., & Kumar, V. (2017). Do loyal customers really pay more for services? Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (6), 807–826.
Van Doorn, J., & Verhoef, P. C. (2008). Critical incidents and the impact of satisfaction on customer share. Journal of Marketing, 72 (4), 123–142.
Verhoef, P. (2003). Understanding the effect of customer relationship management efforts on customer retention and customer share development. Journal of Marketing, 67 (4), 30–45.
Watson, G. F., Beck, J. T., Henderson, C. M., & Palmatier, R. W. (2015). Building, measuring, and profiting from customer loyalty. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43 (6), 790–825.
Weinberg, B. D., Milne, G. R., Andonova, Y. G., & Hajjat, F. M. (2015). Internet of things: Convenience vs. privacy and secrecy. Business Horizons, 58 (6), 615–624.
Wieseke, J., Alavi, S., & Habel, J. (2014). Willing to pay more, eager to pay less: The role of customer loyalty in price negotiations. Journal of Marketing, 78 (6), 17–37.
Woodruff, R. B., Cadotte, E. R., & Jenkins, R. L. (1983). Modeling consumer satisfaction processes using experience-based norms. Journal of Marketing Research, 20 (3), 296–304.
Zairi, M. (2000). Managing customer satisfaction: A best practice perspective. The TQM Magazine, 12 (6), 389–394.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
McCombs School of Business, The University of Texas, Austin, TX, USA
Sebastian Hohenberg
Cox School of Business, Southern Methodist University, Dallas, TX, USA
Wayne Taylor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sebastian Hohenberg .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Universität Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany
Christian Homburg
Inst. Informations Systems and Marketing Marketing & Sales Research Group, Karlsruher Institut für Technologie, Karlsruhe, Germany
Martin Klarmann
LS für ABWL und Marketing I, Universität Mannheim, Mannheim, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
Arnd Vomberg
Section Editor information
University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Hohenberg, S., Taylor, W. (2020). Measuring Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty. In: Homburg, C., Klarmann, M., Vomberg, A. (eds) Handbook of Market Research. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05542-8_30-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05542-8_30-1
Received : 17 September 2019
Accepted : 17 September 2019
Published : 03 December 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-05542-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-05542-8
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Business and Management Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 15 September 2016
An empirical research on customer satisfaction study: a consideration of different levels of performance
- Yu-Cheng Lee 1 ,
- Yu-Che Wang 2 ,
- Shu-Chiung Lu 3 , 4 ,
- Yi-Fang Hsieh 6 ,
- Chih-Hung Chien 3 , 5 ,
- Sang-Bing Tsai 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 &
- Weiwei Dong 13
SpringerPlus volume 5 , Article number: 1577 ( 2016 ) Cite this article
23k Accesses
32 Citations
Metrics details
Customer satisfaction is the key factor for successful and depends highly on the behaviors of frontline service providers. Customers should be managed as assets, and that customers vary in their needs, preferences, and buying behavior. This study applied the Taiwan Customer Satisfaction Index model to a tourism factory to analyze customer satisfaction and loyalty. We surveyed 242 customers served by one tourism factory organizations in Taiwan. A partial least squares was performed to analyze and test the theoretical model. The results show that perceived quality had the greatest influence on the customer satisfaction for satisfied and dissatisfied customers. In addition, in terms of customer loyalty, the customer satisfaction is more important than image for satisfied and dissatisfied customers. The contribution of this paper is to propose two satisfaction levels of CSI models for analyzing customer satisfaction and loyalty, thereby helping tourism factory managers improve customer satisfaction effectively. Compared with traditional techniques, we believe that our method is more appropriate for making decisions about allocating resources and for assisting managers in establishing appropriate priorities in customer satisfaction management.
Traditional manufacturing factories converted for tourism purposes, have become a popular leisure industry in Taiwan. The tourism factories has experienced significant growth in recent years, and more and more tourism factories emphasized service quality improvement, and customized service that contributes to a tourism factory’s image and competitiveness in Taiwan (Wu and Zheng 2014 ). Therefore, tourism factories has become of greater economic importance in Taiwan. By becoming a tourism factory, companies can establish a connection between consumers and the brand, generate additional income from entrance tickets and on-site sales, and eventually add value to service innovations (Tsai et al. 2012 ). Because of these incentives, the Taiwanese tourism factory industry has become highly competitive. Customer satisfaction is seen as very important in this case.
Numerous empirical studies have indicated that service quality and customer satisfaction lead to the profitability of a firm (Anderson et al. 1994 ; Eklof et al. 1999 ; Ittner and Larcker 1996 ; Fornell 1992 ; Anderson and Sullivan 1993 ; Zeithaml 2000 ). Anderson and Sullivan ( 1993 ) stated that a firm’s future profitability depends on satisfying current customers. Anderson et al. ( 1994 ) found a significant relationship between customer satisfaction and return on assets. High quality leads to high levels of customer retention, increase loyalty, and positive word of mouth, which in turn are strongly related to profitability (Reichheld and Sasser 1990 ). In a tourism factory setting, customer satisfaction is the key factor for successful and depends highly on the behaviors of frontline service providers. Kutner and Cripps ( 1997 ) indicated that customers should be managed as assets, and that customers vary in their needs, preferences, buying behavior, and price sensitivity. A tourism factory remains competitive by increasing its service quality relative to that of competitors. Delivering superior customer value and satisfaction is crucial to firm competitiveness (Kotler and Armstrong 1997 ; Weitz and Jap 1995 ; Deng et al. 2013 ). It is crucial to know what customers value most and helps firms allocating resource utilization for continuously improvement based on their needs and wants. The findings of Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI) studies can serve as predictors of a company’s profitability and market value (Anderson et al. 1994 ; Eklof et al. 1999 ; Chiu et al. 2011 ). Such findings provide useful information regarding customer behavior based on a uniform method of customer satisfaction, and offer a unique opportunity to test hypotheses (Anderson et al. 1997 ).
The basic structure of the CSI model has been developed over a number of years and is based on well-established theories and approaches to consumer behavior, customer satisfaction, and product and service quality in the fields of brands, trade, industry, and business (Fornell 1992 ; Fornell et al. 1996 ). In addition, the CSI model leads to superior reliability and validity for interpreting repurchase behavior according to customer satisfaction changes (Fornell 1992 ). These CSIs are fundamentally similar in measurement model (i.e. causal model), they have some obvious distinctions in model’s structure and variable’s selection. Take full advantages of other nations’ experiences can establish the Taiwan CSI Model which is suited for Taiwan’s characters. Thus, the ACSI and ECSI have been used as a foundation for developing the Taiwan Customer Satisfaction Index (TCSI). The TCSI was developed by Chung Hua University and the Chinese Society for Quality in Taiwan. The TCSI provides Taiwan with a fair and objective index for producing vital information that can help the country, industries, and companies improve competitiveness. Every aspect of the TCSI that influences overall customer satisfaction can be measured through surveys, and every construct has a cause–effect relationship with the other five constructs (Fig. 1 ). The relationships among the different aspects of the TCSI are different from those of the ACSI, but are the same as those of the ECSI (Lee et al. 2005 , 2006 ).
The Taiwan Customer Satisfaction Index model
The traditional CSI model for measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty is restricted and does not consider the performance of firms. Moreover, as theoretical and empirical research has shown, the relationship between attribute-level performance and overall satisfaction is asymmetric. If the asymmetries are not considered, the impact of the different attributes on overall satisfaction is not correctly evaluated (Anderson and Mittal 2000 ; Matzler and Sauerwein 2002 ; Mittal et al. 1998 ; Matzler et al. 2003 , 2004 ). Few studies have investigated CSI models that contain different levels of performance (satisfaction), especially in relation to satisfaction levels of a tourism factory. To evaluate overall satisfaction accurately, the impact of the different levels of performance should be considered (Matzler et al. 2004 ). The purpose of this study is to apply the TCSI model that contains different levels of performance to improve and ensure the understanding of firm operational efficiency by managers in the tourism factory. A partial least squares (PLS) was performed to test the theoretical model due to having been successfully applied to customer satisfaction analysis. The PLS is well suited for predictive applications (Barclay et al. 1995 ) and using path coefficients that regard the reasons for customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction and providing latent variable scores that could be used to report customer satisfaction scores. Our findings provide support for the application of TCSI model to derive tourist satisfaction information.
Literature review
National customer satisfaction index (csi).
The CSI model includes a structural equation with estimated parameters of hidden categories and category relationships. The CSI can clearly define the relationships between different categories and provide predictions. The basic CSI model is a structural equation model with latent variables which are calculated as weighted averages of their measurement variables, and the PLS estimation method calculates the weights and provide maximum predictive power of the ultimate dependent variable (Kristensen et al. 2001 ). Many scholars have identified the characteristics of the CSI (Karatepe et al. 2005 ; Malhotra et al. 1994 ).
Although the core of the models are in most respects standard, they have some obvious distinctions in model’s structure and variable’s selection so that their results cannot be compared with each other and some variations between the SCSB (Swedish), the ACSI (American), the ECSI (European), the NCSB (Norwegian) and other indices. For example, the image factor is not employed in the ACSI model (Johnson et al. 2001 ); the NCSB eliminated customer expectation and replaced with corporate image; the ECSI model does not include the customer complaint as a consequence of satisfaction. Many scholars have identified the characteristics of the CSI (Karatepe et al. 2005 ; Malhotra et al. 1994 ). The ECSI model distinguishes service quality from product quality (Kristensen et al. 2001 ) and the NCSB model applies SERVQUAL instrument to evaluate service quality (Johnson et al. 2001 ). A quality measure of a single customer satisfaction index is typically developed according to a certain type of culture or the culture of a certain country. When developing a system for measuring or evaluating a certain country or district’s customer satisfaction level, a specialized customer satisfaction index should be developed.
As such, the ACSI and ECSI were used as a foundation to develop the TCSI. The TCSI was developed by Chung Hua University and the Chinese Society for Quality. Every aspect of the TCSI that influences overall customer satisfaction can be measured through surveys, and every construct has a cause–effect relationship with the other five constructs. The TCSI assumes that currently: (1) Taiwan corporations have ability of dealing with customer complaints; customer complaints have already changed from a factor that influences customer satisfaction results to a factor that affects quality perception; (2) The expectations, satisfaction and loyalty of customers are affected by the image of the corporation. The concept that customer complaints are not calculated into the TCSI model is that they were removed based on the ECSI model (Lee et al. 2005 , 2006 , 2014a , b ; Guo and Tsai 2015 ; Tsai et al. 2015a , b ; 2016a ).
TCSI model and service quality
Service quality is frequently used by both researchers and practitioners to evaluate customer satisfaction. It is generally accepted that customer satisfaction depends on the quality of the product or service offered (Anderson and Sullivan 1993 ). Numerous researchers have emphasized the importance of service quality perceptions and their relationship with customer satisfaction by applying the NCSI model (e.g., Ryzin et al. 2004 ; Hsu 2008 ; Yazdanpanah et al. 2013 ; Chiu et al. 2011 ; Temizer and Turkyilmaz 2012 ; Mutua et al. 2012 ; Dutta and Singh 2014 ). Ryzin et al. ( 2004 ) applied the ACSI to U.S. local government services and indicated that the perceived quality of public schools, police, road conditions, and subway service were the most salient drivers of satisfaction, but that the significance of each service varied among income, race, and geography. Hsu ( 2008 ) proposed an index for online customer satisfaction based on the ACSI and found that e-service quality was more determinative than other factors (e.g., trust and perceived value) for customer satisfaction. To deliver superior service quality, an online business must first understand how customers perceive and evaluate its service quality. This study developed a basic model for using the TCSI to analyze Taiwan’s tourism factory services. The theoretical model comprised 14 observation variables and the following six constructs: image, customer expectations, perceived quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction, and loyalty.
Research methods
The measurement scale items for this study were primarily designed using the questionnaire from the TCSI model. In designing the questionnaire, a 10-point Likert scale (with anchors ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree) was used to reduce the statistical problem of extreme skewness (Fornell et al. 1996 ; Qu et al. 2015 ; Tsai 2016 ; Tsai et al. 2016b ; Zhou et al. 2016 ). A total of 14 items, organized into six constructs, were included in the questionnaire. The primary questionnaire was pretested on 30 customers who had visited a tourism factory. Because the TCSI model is preliminary research in the tourism factory, this study convened a focus group to decide final attributes of model. The focus group was composed of one manager of tourism factory, one professor in Hospitality Management, and two customers with experience of tourism factory.
We used the TCSI model (Fig. 1 ) to structure our research. From this structure and the basic theories of the ACSI and ECSI, we established the following hypotheses:
Image has a strong influence on tourist expectations.
Image has a strong influence on tourist satisfaction.
Image has a strong influence on tourist loyalty.
Tourist expectations have a strong influence on perceived quality.
Tourist expectations have a strong influence on perceived values.
Tourist expectations have a strong influence on tourist satisfaction.
Perceived quality has a strong influence on perceived value.
Perceived quality has a strong influence on tourist satisfaction.
Perceived value has a strong influence on tourist satisfaction.
Customer satisfaction has a strong influence on tourist loyalty.
The content of our surveys were separated into two parts; customer satisfaction and personal information. The definitions and processing of above categories are listed below:
Part 1 of the survey assessed customer satisfaction by measuring customer levels of tourism factory image, expectations, quality perceptions, value perceptions, satisfaction, and loyalty toward their experience, and used these constructs to indirectly survey the customer’s overall evaluation of the services provided by the tourism factory.
Part 2 of the survey collected personal information: gender, age, family situation, education, income, profession, and residence.
The six constructs are defined as follows:
Image reflects the levels of overall impression of the tourism factory as measured by two items: (1) word-of-mouth reputation, (2) responsibility toward concerned parties that the tourist had toward the tourism factory before traveling.
Customer expectations refer to the levels of overall expectations as measured by two items: (1) expectations regarding the service of employees, (2) expectations regarding reliability that the tourist had before the experience at the tourism factory.
Perceived quality was measured using three survey measures: (1) the overall evaluation, (2) perceptions of reliability, (3) perceptions of customization that the tourist had after the experience at the tourism factory.
Perceived value was measured using two items: (1) the cost in terms of money and time (2) a comparison with other tourism factories.
Customer satisfaction represents the levels of overall satisfaction was captured by two items: (1) meeting of expectations, (2) closeness to the ideal tourism factory.
Loyalty was measured using three survey measures: (1) the probabilities of visiting the tourism factory again (2) attending another activity held by the tourism factory, (3) recommending the tourism factory to others.
Data collection and analysis
The survey sites selected for this study was the parking lots of one food tourism factory in Taipei, Taiwan. A domestic group package and individual tourists were a major source of respondents who were willing to participate in the survey and completed the questionnaires themselves based on their perceptions of their factory tour experience. Four research assistants were trained to conduct the survey regarding to questionnaire distribution and sampling.
To minimize prospective biases of visiting patterns, the survey was conducted at different times of day and days of week—Tuesday, Thursday, Saturday for the first week; Monday, Wednesday, Friday and Sunday for the next week. The afternoon time period was used first then the morning time period in the following weeks. The data were collected over 1 month period.
Of 300 tourists invited to complete the questionnaire, 242 effective responses were obtained (usable response rate of 80.6 %). The sample of tourists contained more females (55.7 %) than males (44.35 %). More than half of the respondents had a college degree or higher, 28 % were students, and 36.8 % had an annual household income of US $10,000–$20,000. The majority of the respondents (63.7 %) were aged 20–40 years.
Comparison of the TCSI models for satisfied and dissatisfied customers
Researchers have claimed that satisfaction levels differ according to gender, age, socioeconomic status, and residence (Bryant and Cha 1996 ). Moreover, the needs, preferences, buying behavior, and price sensitivity of customers vary (Kutner and Cripps 1997 ). Previous studies have demonstrated that it is crucial to measure the relative impact of each attribute for high and low performance (satisfaction) (Matzler et al. 2003 , 2004 ). To determine the reasons for differences, a satisfaction scale was used to group the sample into satisfied (8–10) and dissatisfied (1–7) customers.
The research model was tested using SmartPLS 3.0 software, which is suited for highly complex predictive models (Wold 1985 ; Barclay et al. 1995 ). In particular, it has been successfully applied to customer satisfaction analysis. The PLS method is a useful tool for obtaining indicator weights and predicting latent variables and includes estimating path coefficients and R 2 values. The path coefficients indicate the strengths of the relationships between the dependent and independent variables, and the R 2 values represent the amount of variance explained by the independent variables. Using Smart PLS, we determined the path coefficients. Figures 2 and 3 show ten path estimates corresponding to the ten research hypothesis of TCSI model for satisfied and dissatisfied customers. Every path coefficient was obtained by bootstrapping the computation of R 2 and performing a t test for each hypothesis. Fornell et al. ( 1996 ) demonstrated that the ability to explain the influential latent variables in a model is an indicator of model performance, in particular the customer satisfaction and customer loyalty variables. From the results shown, the R 2 values for the customer satisfaction were 0.53 vs. 0.50, respectively; and the R 2 value for customer loyalty were 0.64 vs. 0.60, respectively. Thus, the TCSI model explained 53 vs. 50 % of the variance in customer satisfaction; 64 vs. 60 % of that in customer loyalty as well.
Path estimate of the TCSI model for satisfied customers. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
Path estimate of the TCSI model for dissatisfied customers. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
According to the path coefficients shown in Figs. 2 and 3 , image positively affected customer expectations (β = 0.58 vs. 0.37), the customer satisfaction (β = 0.16 vs. 0.11), and customer loyalty (β = 0.47 vs. 0.16). Therefore, H1–H3 were accepted. Customer expectations were significantly related to perceived quality (β = 0.94 vs. 0.83). However, customer expectations were not significantly related to perceived value shown as dotted line (β = −0.01 vs. −0.20) or the customer satisfaction, shown as dotted line (β = −0.21 vs. −0.32). Thus, H4 was accepted but H5 and H6 were not accepted. Perceived value positively affected the customer satisfaction (β = 0.27 vs. 0.14), supporting H7. Accordingly, the analysis showed that each of the antecedent constructs had a reasonable power to explain the overall customer satisfaction. Furthermore, perceived quality positively affected the customer satisfaction (β = 0.70 vs. 0.62), as did perceived value (β = 0.83 vs. 0.74). These results confirm H8 and H9. The path coefficient between the customer satisfaction and customer loyalty was positive and significant (β = 0.63 vs. 0.53). This study tested the suitability of two TCSI models by analyzing the tourism factories in Taiwan. The results showed that the TCSI models were all close fit for this type of research. This study provides empirical evidence of the causal relationships among perceived quality, image, perceived value, perceived expectations, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty.
To observe the effects of antecedent constructs of perceived value (e.g., customer expectation and perceived quality), customer expectations were not significantly related to perceived value for either satisfied or dissatisfied customers. Furthermore, satisfied customers were affected more by perceived quality (β = 0.83 vs. 0.74), as shown in Table 1 . Regarding the effect of the antecedents of customer satisfaction (e.g., image, customer expectations, perceived value and perceived quality), the total effects of perceived quality on the customer satisfaction of satisfied and dissatisfied customers were 0.92 and 0.72. The total effects of image on the customer satisfaction of satisfied and dissatisfied customers were 0.45 and 0.19. Thus, the satisfaction level of satisfied customers was affected more by perceived quality. Consequently, regarding customer satisfaction, perceived quality is more important than image for satisfied and dissatisfied customers. Numerous researchers have emphasized the importance of service quality perceptions and their relationship with customer satisfaction by applying the CSI model (e.g., Ryzin et al. 2004 ; Hsu 2008 ; Yazdanpanah et al. 2013 ; Chiu et al. 2011 ; Temizer and Turkyilmaz 2012 ; Mutua et al. 2012 ; Dutta and Singh 2014 ). This is consistent with the results of previous research ( O’Loughlin and Coenders 2002 ; Yazdanpanah et al. 2013 ; Chiu et al. 2011 ; Chin and Liu 2015 ; Chin et al. 2016 ).
With respect to the effect of the antecedents of customer loyalty (e.g., image and customer satisfaction), the total effects of image on customer loyalty for satisfied and dissatisfied customers were 0.57 and 0.21. In other words, the customer loyalty of satisfied customers was affected more by customer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction was significantly related to the customer loyalty of both satisfied and dissatisfied customers, and satisfied customers were affected more by customer satisfaction ( β = 0.63 vs. 0.14). Consequently, regarding customer loyalty, customer satisfaction is more important than image for both satisfied and dissatisfied customers. Numerous studies have shown that customer satisfaction is a crucial factor for ensuring customer loyalty (Barsky 1992 ; Smith and Bolton 1998 ; Hallowell 1996 ; Grønholdt et al. 2000 ). This study empirically supports the notion that customer satisfaction is positively related to customer loyalty.
The TCSI model has a predictive capability that can help tourism factory managers improve customer satisfaction based on different performance levels. Our model enables managers to determine the specific factors that significantly affect overall customer satisfaction and loyalty within a tourism factory. This study also helps managers to address different customer segments (e.g., satisfied vs. dissatisfied); because the purchase behaviors of customers differ, they must be treated differently. The contribution of this paper is to propose two satisfaction levels of CSI models for analyzing customer satisfaction and loyalty, thereby helping tourism factory managers improve customer satisfaction effectively.
Fornell et al. ( 1996 ) demonstrated that the ability to explain influential latent variables in a model, particularly customer satisfaction and customer loyalty variables, is an indicator of model performance. However, the results of this study indicate that customer expectations were not significantly related to perceived value for either satisfied or dissatisfied customers. Moreover, they were affected more by perceived quality of customer satisfaction. Numerous researchers have found that the construct of customer expectations used in the ACSI model does not significantly affect the level of customer satisfaction (Johnson et al. 1996 , 2001 ; Martensen et al. 2000 ; Anderson and Sullivan 1993 ).
Through the overall effects, this study derived several theoretical findings. First, the factors with the largest influence on customer satisfaction were perceived quality and perceived expectations, despite the results showing that customer expectations were not significantly related to perceived value or customer satisfaction. Hence, customer expectations indirectly affected customer satisfaction through perceived quality. Accordingly, perceived quality had the greatest influence on customer satisfaction. Likewise, our results also show that satisfied customers were affected more by perceived quality than dissatisfied customers. This study determined that perceived quality, whether directly or indirectly, positively influenced customer satisfaction. This result is consistent with those of Cronin and Taylor ( 1992 ), Cronin et al. ( 2000 ), Hsu ( 2008 ), Ladhari ( 2009 ), Terblanche and Boshoff ( 2010 ), Deng et al. ( 2013 ), and Yazdanpanah et al. ( 2013 ).
Second, the factors with the most influence on customer loyalty were image and customer satisfaction. The results of this study demonstrate that the customer loyalty of satisfied customers was affected more by customer satisfaction. Consequently, regarding customer loyalty, customer satisfaction is more important than image for satisfied customers. Lee ( 2015 ) found that higher overall satisfaction increased the possibility that visitors will recommend and reattend tourism factory activities. Moreover, numerous studies have shown that customer satisfaction is a crucial factor for ensuring customer loyalty (Barsky 1992 ; Smith and Bolton 1998 ; Hallowell 1996 ; Su 2004; Deng et al. 2013 ). In initial experiments on ECSI, corporate image was assumed to have direct influences on customer expectation, satisfaction, and loyalty. Subsequent experiments in Denmark proved that image affected only expectation and satisfaction and had no relationship with loyalty (Martensen et al. 2000 ). In early attempts to build the ECSI model, image was defined as a variable involving not only a company’s overall image but products or brand awareness; thus image is readily connected with customer expectation and perception. Therefore, this study contributes to relevant research by providing empirical support for the notion that customer satisfaction is positively related to customer loyalty.
In addition to theoretical implications, this study has several managerial implications. First, the TCSI model has a satisfactory predictive capability that can help tourism factory managers to examine customer satisfaction more closely and to understand explicit influences on customer satisfaction for different customer segments by assessing the accurate causal relationships involved. In contrast to general customer satisfaction surveys, the TCSI model cannot obtain information on post-purchase customer behavior to improve customer satisfaction and achieve competitive advantage.
Second, this study not only indicated that each of the antecedent constructs had reasonable power to explain customer satisfaction and loyalty but also showed that perceived quality exerts the largest influence on the customer satisfaction of Taiwan’s tourism factory industry. Therefore, continually, Taiwan’s tourism factories must endeavor to enhance their customer satisfaction, ideally by improving service quality. Managers of Taiwan’s tourism factories must ensure that service providers deliver consistently high service quality.
Third, this research determined that the factors having the most influence on customer loyalty were image and customer satisfaction. Therefore, managers of Taiwan’s tourism factories should allow customer expectations to be fulfilled through experiences, thereby raising their overall level of satisfaction. Regarding image, which refers to a brand name and its related associations, when tourists regard a tourism factory as having a positive image, they tend to perceive higher value of its products and services. This leads to a higher level of customer satisfaction and increased chances of customers’ reattending tourism factory activities.
Different performance levels exist in how tourists express their opinions about various aspects of service quality and satisfaction with tourism factories. Customer segments can have different preferences depending on their needs and purchase behavior. Our findings indicate that tourists belonging to different customer segments (e.g., satisfied vs. dissatisfied) expressed differences toward service quality and customer satisfaction. Thus, the management of Taiwan’s tourism factories must notice the needs of different market segments to meet their individual expectations. This study proposes two satisfaction levels of CSI models for analyzing customer satisfaction and loyalty, thereby helping tourism factory managers improve customer satisfaction effectively. Compared with traditional techniques, we believe that our method is more appropriate for making decisions about allocating resources and for assisting managers in establishing appropriate priorities in customer satisfaction management.
Limitations and suggestions for future research
This study has some limitations. First, the tourism factory surveyed in this study was a food tourism factory operating in Taipei, Taiwan, and the present findings cannot be generalized to the all tourism factory industries. Second, the sample size was quite small for tourists (N = 242). Future research should collect a greater number of samples and include a more diverse range of tourists. Third, this study was preliminary research on tourism factories, and domestic group package tourists were a major source of the respondents. Future studies should collect data from international tourists as well.
Anderson EW, Sullivan M (1993) The antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction for firms. Mark Sci 12:125–143
Article Google Scholar
Anderson EW, Mittal V (2000) Strengthening the satisfaction-profit chain. J Serv Res 3(2):107–120
Anderson EW, Fornell C, Lehmann DR (1994) Customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability: findings from Sweden. J Mark 58:53–66
Anderson EW, Fornell C, Rust RT (1997) Customer satisfaction, productivity, and profitability: differences between goods and services. Mark Sci 16(2):129–145
Barclay DW, Higgins C, Thompson R (1995) Interdepartmental conflict in organizational buying: the impact of the organizational context. J Mark Res 28:145–159
Barsky JD (1992) Customer satisfaction in the hotel industry: meaning and measurement. J Hosp Tour Res 16(1):51–73
Google Scholar
Bryant BE, Cha J (1996) Crossing the threshold. Mark Res 8(4):20
Chin T, Liu RH (2015) Understanding labor conflicts in Chinese manufacturing: A Yin-Yang harmony perspective. Int J Confl Manag 26(3):288–315
Chin T, Liu RH, Yang X (2016) Reverse internationalization in Chinese firms: A study of how global startup OEMs seek to compete domestically. Asia Pac Bus Rev 22(2):201–219. doi: 10.1080/13602381.2015.1055087
Chiu SI, Cheng CC, Yen TM, Hu HY (2011) Preliminary research on customer satisfaction models in Taiwan: a case study from the automobile industry. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):9780–9787
Cronin Jr JJ, Taylor SA (1992) Measuring service quality: a reexamination and extension. J Mark 56(3):55–68
Cronin JJ, Brady MK, Hult GTM (2000) Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments. J Retail 76(2):193–218
Deng WJ, Yeh ML, Sung ML (2013) A customer satisfaction index model for international tourist hotels: integrating consumption emotions into the American customer satisfaction index. Int J Hosp Manag 35:133–140
Dutta K, Singh S (2014). Deriving Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty from Organized Retailer’s Sales Promotion Activities in India. ISSN 2045-810X, 21
Eklof JA, Hackl P, Westlund A (1999) On measuring interactions between customer satisfaction and financial results. Total Qual Manag 10(4–5):514–522
Fornell C (1992) A national customer satisfaction barometer: the swedish experience. J Mark 56 (1):6
Fornell C, Johnson MD, Anderson EW, Cha J, Bryant BE (1996) The American customer satisfaction index: nature, purpose, and findings. J Mark 60:7–18
Grønholdt L, Martensen A, Kristensen K (2000) The relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty: cross-industry differences. Total Qual Manag 11(4–6):509–514
Guo JJ, Tsai SB (2015) Discussing and evaluating green supply chain suppliers: a case study of the printed circuit board industry in China. S Afr J Ind Eng 26(2):56–67
Hallowell R (1996) The relationships of customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and profitability: an empirical study. Int J Serv Ind Manag 7(4):27–42
Hsu SH (2008) Developing an index for online customer satisfaction: adaptation of American Customer Satisfaction Index. Expert Syst Appl 34(4):3033–3042
Ittner CD, Larcker DF (1996) Measuring the impact of quality initiatives on firm financial performance. Adv Manag Organ Qual 1(1):1–37
Johnson MD, Nader G, Fornell C (1996) Expectations, perceived performance, and customer satisfaction for a complex service: the case of bank loans. J Econ Psychol 17(2):163–182
Johnson MD et al (2001) The evolution and future of national customer satisfaction index models. J Econ Psychol 22(2):217–245
Karatepe OM, Yavas U, Babakus E (2005) Measuring service quality of banks: scales development and validation. J Retail Consum Serv 12(5):373–383
Kotler P, Armstrong G (1997) Marketing: an introduction. Prentice-Hall, New York
Kristensen K, Juhl HJ, Østergaard P (2001) Customer satisfaction: some results for European retailing. Total Qual Manag 12(7–8):890–897
Kutner S, Cripps J (1997) Managing the customer portfolio of healthcare enterprises. Healthc Forum J 40(5):52–54
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ladhari R (2009) Service quality, emotional satisfaction, and behavioural intentions. Manag Serv Qual Int J 19(3):308–331
Lee C-F (2015) Tourist satisfaction with factory tour experience. Int J Cult Tourism Hosp Res 9:3
Lee YC, He LY, Jiang JS, Lian QY (2005) Foundation of the Taiwan customer satisfaction index model. Qual Mag 41(12):52–56
Lee YC, He LY, Jiang JS, Lian QY (2006) The Taiwan customer satisfaction index model in related to sample decision. Qual Mag 42(4):74–77
CAS Google Scholar
Lee YC, Chen CY, Tsai SB, Wang CT (2014a) Discussing green environmental performance and competitive strategies. Pensee 76(7):190–198
Lee YC, Wu CH, Tsai SB (2014b) Grey system theory and fuzzy time series forecasting for the growth of green electronic materials. Int J Prod Res 299(8):1395–1406
Malhotra NK, Ulgado FM, Agarwal J, Baalbaki IB (1994) International service marketing: a comparative evaluation of the dimensions of service quality between developed and developing countries. Int Mark Rev 11(2):5–15
Martensen A, Gronholdt L, Kristensen K (2000) The drivers of customer satisfaction and loyalty: cross-industry findings from Denmark. Total Qual Manag 11(4–6):544–553
Matzler K, Sauerwein E (2002) The factor structure of customer satisfaction: an empirical test of the importance grid and the penalty-reward-contrast analysis. Int J Serv Ind Manag 13(4):314–332
Matzler K, Sauerwein E, Heischmidt K (2003) Importance-performance analysis revisited: the role of the factor structure of customer satisfaction. Serv Ind J 23(2):112–129
Matzler K, Bailom, F, Hinterhuber HH, Renzl B, Pichler J (2004) The asymmetric relationship between attribute-level performance and overall customer satisfaction: a reconsideration of the importance–performance analysis. Ind Mark Manag 33(4):271–277
Mittal V, Ross WT, Baldasare PM (1998) The asymmetric impact of negative and positive attribute-level performance on overall satisfaction and repurchase intentions. J Mark 62:33–47
Mutua J, Ngui D, Osiolo H, Aligula E, Gachanja J (2012) Consumers satisfaction in the energy sector in Kenya. Energy Policy 48:702–710
O’Loughlin C, Coenders G (2002) Application of the european customer satisfaction index to postal services. Structural equation models versus partial least squares, No. 4. Working Papers of the Department of Economics, University of Girona. Department of Economics, University of Girona
Qu Q, Chen KY, Wei YM et al (2015) Using hybrid model to evaluate performance of innovation and technology professionals in marine logistics industry mathematical problems in engineering. Article ID 361275. doi: 10.1155/2015/361275
Reichheld FF, Sasser WE (1990) Zero defections: quality comes to services. Harvard Bus Rev 68(5):105–111
Ryzin GG, Muzzio D, Immerwahr S, Gulick L, Martinez E (2004) Drivers and consequences of citizen satisfaction: an application of the American customer satisfaction index model to New York City. Public Adm Rev 64(3):331–341
Smith AK, Bolton RN (1998) An experimental investigation of customer reactions to service failure and recovery encounters paradox or peril? J Serv Research 1(1):65–81
Temizer L, Turkyilmaz A (2012) Implementation of student satisfaction index model in higher education institutions. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 46:3802–3806
Terblanche NS, Boshoff C (2010) Quality, value, satisfaction and loyalty amongst race groups: A study of customers in the South African fast food industry. S Afr J Bus Manag 41(1):1–9
Tsai SB (2016) Using grey models for forecasting China’s growth trends in renewable energy consumption. Clean Technol Environ Policy 18:563–571
Tsai CH, Peng YJ, Wu HH (2012, October). Evaluating service process satisfaction of a tourism factory—using Brands’ Health Museum as an example. In: 2012 6th international conference on new trends in information science and service science and data mining (ISSDM), pp 244–247
Tsai SB, Chien MF, Xue Y, Li L et al (2015a) Using the fuzzy DEMATEL to determine environmental performance: a case of printed circuit board industry in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0129153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129153
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Tsai SB, Saito R, Lin YC, Chen Q et al (2015b) Discussing measurement criteria and competitive strategies of green suppliers from a Green law Perspective. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 229(S1):135–145
Tsai SB, Huang CY, Wang CK, Chen Q et al (2016a) Using a mixed model to evaluate job satisfaction in high-tech industries. PLoS ONE 11(5):e0154071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154071
Tsai SB, Xue Y, Zhang J, Chen Q et al (2016b) Models for forecasting growth trends in renewable energy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.06.001
Weitz BA, Jap SD (1995) Relationship marketing and distribution channels. J Acad Mark Sci 23:305–320
Wold H (1985) Partial least squares. In: Kotz S, Johnson N (eds) Encyclopedia of statistical sciences. Wiley, New York, pp 581–591
Wu SI, Zheng YH (2014) The influence of tourism image and activities appeal on tourist loalty–a study of Tainan City in Taiwan. J Manag Strategy, 5(4):121
Yazdanpanah M, Zamani GH, Hochrainer-Stigler S, Monfared N, Yaghoubi J (2013) Measuring satisfaction of crop insurance a modified American customer satisfaction model approach applied to Iranian Farmers. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 5:19–27
Zeithaml VA (2000) Service quality, profitability, and the economic worth of customers: what we know and what we need to learn. J Acad Mark Sci 28(1):67–85
Zhou J, Wang Q, Tsai SB et al (2016) How to evaluate the job satisfaction of development personnel. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2519860
Download references

Authors’ contributions
Writing: S-CL; providing case and idea: Y-CL, Y-CW, Y-FH, C-HC; providing revised advice: S-BT, WD. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Department of Technology Management, Chung-Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan. This work was supported by University of Electronic Science Technology of China, Zhongshan Institute (414YKQ01 and 415YKQ08).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Technology Management, Chung-Hua University, Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan
Yu-Cheng Lee
Department of Business Administration, Chung-Hua University, Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan
Yu-Che Wang
PhD Program of Technology Management, Chung-Hua University, Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan
Shu-Chiung Lu & Chih-Hung Chien
Department of Food and Beverage Management, Lee-Ming Institute of Technology, New Taipei City, 243, Taiwan
Shu-Chiung Lu
Department of Business Administration, Lee-Ming Institute of Technology, New Taipei City, 243, Taiwan
Chih-Hung Chien
Department of Food and Beverage Management, Taipei College of Maritime Technology, New Taipei City, 251, Taiwan
Yi-Fang Hsieh
Zhongshan Institute, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Dongguan, 528402, Guangdong, China
Sang-Bing Tsai
School of Economics and Management, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai, 201306, China
Law School, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071, China
School of Business, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, 124221, China
College of Business Administration, Dongguan University of Technology, Dongguan, 523808, Guangdong, China
Department of Psychology, Universidad Santo Tomas de Oriente y Medio Día, Granada, Nicaragua
School of Economics and Management, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai, 201418, China
Weiwei Dong
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Sang-Bing Tsai or Weiwei Dong .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lee, YC., Wang, YC., Lu, SC. et al. An empirical research on customer satisfaction study: a consideration of different levels of performance. SpringerPlus 5 , 1577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3208-z
Download citation
Received : 25 April 2016
Accepted : 02 September 2016
Published : 15 September 2016
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3208-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Customer satisfaction
- Tourism factory industry
- Partial least squares
- Business management
- Service management
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Service quality and customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world: a study of saudi auto care industry.

- 1 College of Business Administration, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Khobar, Saudi Arabia
- 2 Department of Management Sciences, University of Baluchistan, Quetta, Pakistan
The aim of this research is to examine the impact of service quality on customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in auto care industry. The car care vendor in the study made effective use of social media to provide responsive updates to the customers in the post pandemic world; such use of social media provides bases for service quality and customer satisfaction. The study examined the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction using the SERVQUAL framework. According to the findings, empathy, reliability, assurance, responsiveness, and tangibles have a significant positive relationship with customer satisfaction. Our findings suggest that it is critical for workshops to recognize the service quality factors that contribute to customer satisfaction. Findings also suggest that empathy, assurance, reliability, responsiveness, and tangibles contribute to customer satisfaction. Auto repair industry must regularly provide personal attention, greet customers in a friendly manner, deliver cars after services, notify customers when additional repairs are required, and take the time to clarify problems to customers. Furthermore, workshops must screen and hire courteous staff who can clearly communicate the services required to customers both in-person and online and effectively communicate the risks associated with repairs. Service quality seems to be aided by prompt services.
Introduction
The previous studies on the effect of pandemic have focused on the behavior related to preventative measures to protect the health of the customers; however, less attention has been paid to the influence of pandemic on customer outcomes. To fill this gap, the SERVQUAL framework was employed to examine the changes in customers’ social media behaviors that have occurred since the pandemic was declared ( Mason et al., 2021 ). In the post pandemic world, the parameters for customer satisfaction have changed considerably ( Monmousseau et al., 2020 ; Srivastava and Kumar, 2021 ; Wu et al., 2021 ). Pandemic has made personal interaction more challenging ( Brown, 2020 ). To be less vulnerable to becoming severely ill with the virus, customers prefer touchless digital mediums of communications. For example, Mason et al. (2021) concluded that pandemic has altered customers’ needs, shopping and purchasing behaviors, and post purchase satisfaction levels. Keeping in view the public healthcare concerns, the governmental pandemic mitigation policies also promotes touchless mediums for shopping; therefore, the role of social media as a communication tool stands to increase at a time when social distancing is a common practice; social media provides avenues for buyers to interact with sellers without physical contact. Thus, the use of social media gains critical importance, especially after the pandemic ( Mason et al., 2021 ), and the businesses may find new opportunities to gain competitive advantage through their use of effective social media strategies.
The car care industry uses traditional means of customer communications. The company in this study made use of social media in improving their service quality through effective and safe communication with their customers. The use of social media to provide updates to customers played a significant role in improving service quality and satisfaction ( Ramanathan et al., 2017 ). The company in the study used Snapchat to provide updates on the work, thus minimizing the customers’ need to physically visit the car care facility. This use of social media gave a significant boost to the responsiveness aspect of the service quality.
Service quality and customer satisfaction are important aspects of business since a company’s growth is largely dependent on how well it maintains its customers through service and how well they keep their customers satisfied ( Edward and Sahadev, 2011 ). According to Chang et al. (2017) ; customer satisfaction is expected to result from good service efficiency, which will improve customer engagement and interrelationship. González et al. (2007) asserted that customer satisfaction is linked to high service quality, which makes businesses more competitive in the marketplace. This study uses the SERVQUAL framework to define service quality. This framework uses five dimensions to account for service quality, namely, tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Identifying issues in service and customer satisfaction can lead to high service quality. Furthermore, service quality can be characterized by analyzing the variations between planned and perceived service. Service quality and customer satisfaction have a positive relationship.
Recognizing and meeting customer expectations through high levels of service quality help distinguish the company’s services from those of its rivals ( Dominic et al., 2010 ). Social media plays a critical role in shaping these service quality-related variables. Specifically, in the context coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), where customers hesitated to visit auto workshops physically, the importance of online platforms such as auto workshops’ social media pages on Instagram and Facebook has increased, where customers try to get information and book appointment. For example, responsiveness is not only physical responsiveness but also digital means of communication. The car care company in this study uses social media as mode of communication with their customers due to physical interaction restriction caused by the pandemic.
Service quality becomes a critical element of success in car care industry because customer contact is one of the most important business processes ( Lambert, 2010 ). Saudi Arabia is one of the Middle East’s largest new vehicle sales and auto part markets. Saudi Arabia’s car repair industry has grown to be a significant market for automakers from all over the world. As a result, the aim of this research was to see how service quality affects customer satisfaction in the Saudi auto repair industry.
This aim of this research was to answer the following research questions:
(i) What is the contribution of individual dimensions of SERVQUAL on customer perceived service quality of car care industry in Saudi Arabia?
(ii) What is the impact of perceived service quality on customer satisfaction in car care industry in Saudi Arabia?
Literature Review
The concept of service has been defined since the 1980s by Churchill and Surprenant (1982) together with Asubonteng et al. (1996) , who popularized the customer satisfaction theory through measuring the firm’s actual service delivery in conformity with the expectations of customers, as defined by the attainment of perceived quality, and that is meeting the customers’ wants and needs beyond their aspirations. With this premise, Armstrong et al. (1997) later expanded the concept of service into the five dimensions of service quality that comprised tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy.
Extant literature on service delivery focuses on the traditional emphasis on the contact between the customer and service provider ( Mechinda and Patterson, 2011 ; Han et al., 2021 ). Doucet (2004) explained that the quality in these traditional settings depends on the design of the location and the behavior of the service provider. More recently, the proliferation of the internet has led to the emergence of the online service centers. In these cases, communication both in-person and online plays a critical role in the quality of service rendered. It follows that service quality in hybrid settings depends on quality of communications on social media as well as the behavioral interactions between the customer and the service provider ( Doucet, 2004 ; Palese and Usai, 2018 ). These factors require subjective assessments by the concerned parties, which means that different persons will have varied assessments of the quality of service received.
SERVQUAL Dimensions
Service quality has been described with the help of five quality dimensions, namely, tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Definitions relating to these variables have been modified by different authors. The relationship between various dimensions of service quality differs based on particular services.
The tangible aspects of a service have a significant influence on perception of service quality. These comprise the external aspects of a service that influence external customer satisfaction. The key aspects of tangibility include price, ranking relative to competitors, marketing communication and actualization, and word-of-mouth effects ( Ismagilova et al., 2019 ), which enhance the perception of service quality of customers ( Santos, 2002 ). These aspects extend beyond SERVQUAL’s definition of quality within the car care industry settings. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1a: Tangibles are positively related with perceived service quality.
Reliability
Reliability is attributed to accountability and quality. There are a bunch of precursors that likewise aid basic methodology for shaping clients’ perspectives toward administration quality and reliability in the car care industry in Saudi ( Korda and Snoj, 2010 ; Omar et al., 2015 ). A portion of these predecessors is identified with car repair benefits and includes the convenient accessibility of assets, specialist’s expertise level and productive issue determination, correspondence quality, client care quality, an exhibition of information, client esteem, proficiency of staff, representatives’ capacity to tune in to client inquiries and respond emphatically to their necessities and protests, security, workers’ dependability, more limited holding up time and quickness, actual prompts, cost of administration, accessibility of issue recuperation frameworks, responsibility, guarantees, for example, mistake-free administrations, generally association’s picture and workers’ politeness, and responsiveness. Despite the innovative changes happening in the car care industry and the instructive degree of car administrations suppliers in Saudi Arabia, car care suppliers in the territory are taught about the need to continually refresh their insight into the advancements in the area of vehicle workshops and the components of administration. Thus, we argued that reliability is important to enhance the perception of service quality of customers.
Hypotheses 1b: Reliability is positively linked with perceived service quality.
Responsiveness
Responsiveness refers to the institution’s ability to provide fast and good quality service in the period. It requires minimizing the waiting duration for all interactions between the customer and the service provider ( Nambisan et al., 2016 ). Nambisan et al. (2016) explained that responsiveness is crucial for enhancing the customers’ perception of service quality. Rather, the institution should provide a fast and professional response as to the failure and recommend alternative actions to address the customer’s needs ( Lee et al., 2000 ). In this light, Nambisan summarizes responsiveness to mean four key actions, i.e., giving individual attention to customers, providing prompt service, active willingness to help guests, and employee availability when required. These aspects help companies to enhance the customers’ perception of service quality. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1c: Responsiveness is positively linked with perceived service quality.
Assurance refers to the skills and competencies used in delivering services to the customers. Wu et al. (2015) explains that employee skills and competencies help to inspire trust and confidence in the customer, which in turn stirs feelings of safety and comfort in the process of service delivery. Customers are more likely to make return visits if they feel confident of the employees’ ability to discharge their tasks. Elmadağ et al. (2008) lists the factors that inspire empathy as competence, politeness, positive attitude, and effective communication as the most important factors in assuring customers. Besides, other factors include operational security of the premises as well as the proven quality of the service provided to the customers. Thus, the assurance has significant contribution in the perception of service quality.
Hypotheses 1d: Assurance is positively related with perceived service quality.
Empathy refers to the quality of individualized attention given to the customers. The service providers go an extra mile to make the customer feel special and valued during the interaction ( Bahadur et al., 2018 ). Murray et al. (2019) explains that empathy requires visualizing the needs of the customer by assuming their position. Murray et al. (2019) lists the qualities that foster empathy as including courtesy and friendliness of staff, understanding the specific needs of the client, giving the client special attention, and taking time to explain the practices and procedure to be undertaken in the service delivery process. Therefore, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypotheses 1e: Empathy is positively related with perceived service quality.
Perceived Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction refers to the level of fulfillment expressed by the customer after the service delivery process. This is a subjective assessment of the service based on the five dimensions of service quality. Customer satisfaction is important due to its direct impact on customer retention ( Hansemark and Albinsson, 2004 ; Cao et al., 2018 ; Zhou et al., 2019 ), level of spending ( Fornell et al., 2010 ), and long-term competitiveness of the organization ( Suchánek and Králová, 2019 ). Susskind et al. (2003) describes that service quality has a direct impact on customer satisfaction. For this reason, this research considers that five dimensions of service quality are the important antecedents of customer satisfaction.
Service quality refers to the ability of the service to address the needs of the customers ( Atef, 2011 ). Customers have their own perception of quality before interacting with the organization. The expectancy-confirmation paradigm holds that customers compare their perception with the actual experience to determine their level of satisfaction from the interaction ( Teas, 1993 ). These assessments are based on the five independent factors that influence quality. Consequently, this research considers service quality as an independent variable.
This study attempts to quantify perceived service quality though SERVQUAL dimensions. We proposed that customers place a high premium on service quality as a critical determinant of satisfaction. Moreover, it is argued that satisfaction prompts joy and reliability among customers in Saudi Arabia. These discoveries infer that the perception of service quality is significantly related to satisfaction, and quality insight can be applied across different cultures with negligible contrasts in the result. Car care industry in Saudi Arabia has grave quality problems. To rectify this situation, it is essential to apply quality systems as tools for development. The SERVQUAL is one of these system options. It is used to gauge the service quality using five dimensions that have been time-tested since 1982. Thus, the significance of SERVQUAL in car care industry in Saudi Arabia cannot be overemphasized. The study further suggests that the SERVRQUAL dimension increases the perceived service quality, which in turn increases customer satisfaction. Thus, we proposed the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: The perceived service quality of car care customers is positively linked with their satisfaction.
Methods and Procedures
In this study, we employed a cross-sectional research design. Using a paper-pencil survey, data were collected form auto care workshops situated in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. According to the study by Newsted et al. (1998) , the survey method is valuable for assessing opinions and trends by collecting quantitative data. We adapted survey instruments from previous studies. The final survey was presented to a focus group of two Ph.D. marketing scholars who specialized in survey design marketing research. The survey was modified keeping in view the recommendations suggested by focus group members. We contacted the customers who used social media to check the updates and book the appointment for their vehicle’s service and maintenance. We abstained 130 surveys, 13 of which were excluded due to missing information. Therefore, the final sample encompassed 117 (26 female and 91 male) participants across multiple age groups: 10 aged less than 25 years, 46 aged between 26 and 30 years, 28 aged between 31 and 35 years, 21 aged between 36 and 40 years, and 12 aged older than 40 years (for details, refer to Table 1 ). Similarly, the averaged participants were graduates with more than 3 years of auto care service experience.
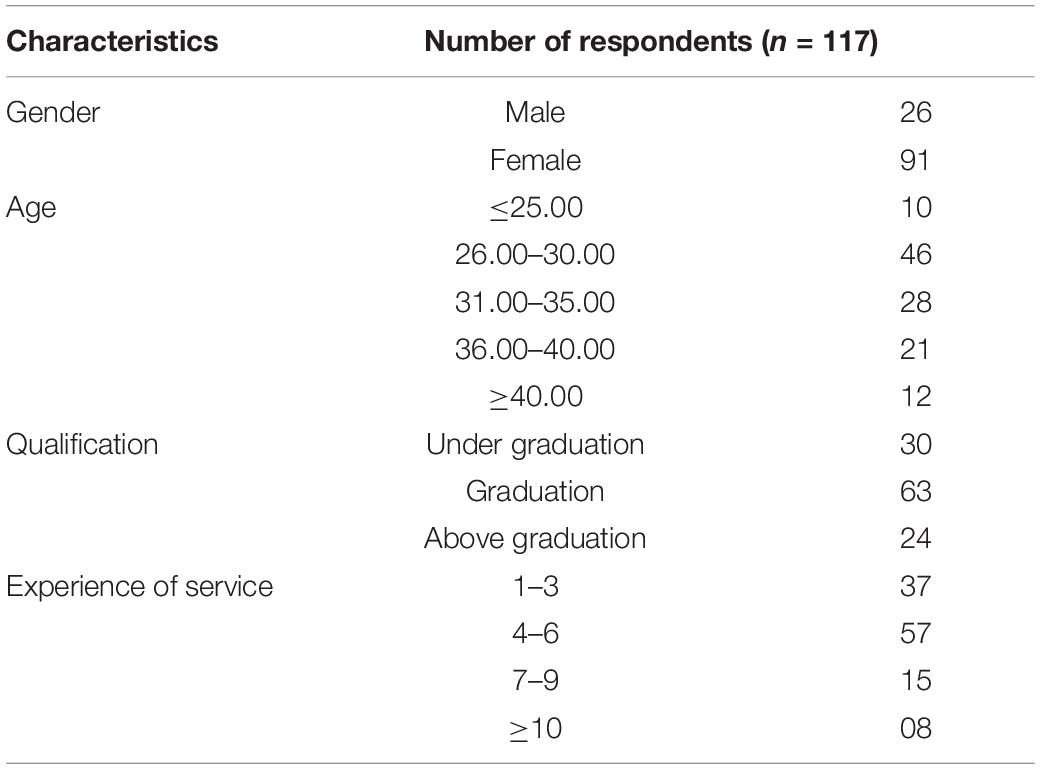
Table 1. Demographic information.
We measured service quality dimensions using 20 indicators. Customer satisfaction of the restaurant customers was assessed using 4-item scale (for detail, refer to Table 2 ). In this research, the 5-point Likert scale from 1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree was used.

Table 2. Constructs and items included in the questionnaire.
Control Variables
Following the previous research, customer’s gender and age were controlled to examine the influence of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction.
Data Analysis and Results
For data analysis and hypotheses testing, we employed the structural equation modeling (SEM) based on the partial least squares (PLS) in Smart-PLS. Smart-PLS 3 is a powerful tool, which is used for the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and SEM ( Nachtigall et al., 2003 ). Research suggests that CFA is the best approach to examine the reliability and validity of the constructs. We employed SEM for hypotheses testing because it is a multivariate data analysis technique, which is commonly used in the social sciences ( González et al., 2008 ).
Common Method Bias
To ensure that common method bias (CMB) is not a serious concern for our results, we employed procedural and statistical and procedural remedies. During data collection, each survey in the research contained a covering letter explaining the purpose of the study and guaranteed the full anonymity of the participants. Moreover, it was mentioned in the cover letter that there was no right and wrong questions, and respondents’ answers would neither be related to their personalities nor disclosed to anyone. According to Podsakoff et al. (2003) , the confidentiality of the responses can assist to minimize the possibility of CMB. Furthermore, CMB was verified through the Harman’s single-factor test ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). All items in this research framework were categorized into six factors, among which the first factor explained 19.01% of the variance. Thus, our results showed that CMB was not an issue in our research. Moreover, using both tolerance value and the variance inflation factors (VIFs), we assessed the level of multicollinearity among the independent variables. Our results indicate that the tolerance values for all dimensions of service quality were above the recommended threshold point of 0.10 ( Cohen et al., 2003 ), and VIF scores were between 1.4 and 1.8, which suggested the absence of multicollinearity; thus, it is not a serious issue for this study.
Measurement Model
We performed CFA to analyze the reliability and validity of the constructs. The measurement model was assessed by examining the content, convergent, and discriminant validities. To assess the content validity, we reviewed the relevant literature and pilot test the survey. We used item loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability (CR), and the average variance extracted (AVE) ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981b ) to assess the convergent validity. The findings of CFA illustrate that all item loadings are greater than 0.70. The acceptable threshold levels for all values were met, as the value of Cronbach’s alpha and CR was greater than 0.70 for all constructs ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981b ), and the AVE for all variables was above 0.50 ( Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007 ; see Table 3 ). Thus, these findings show acceptable convergent validity.
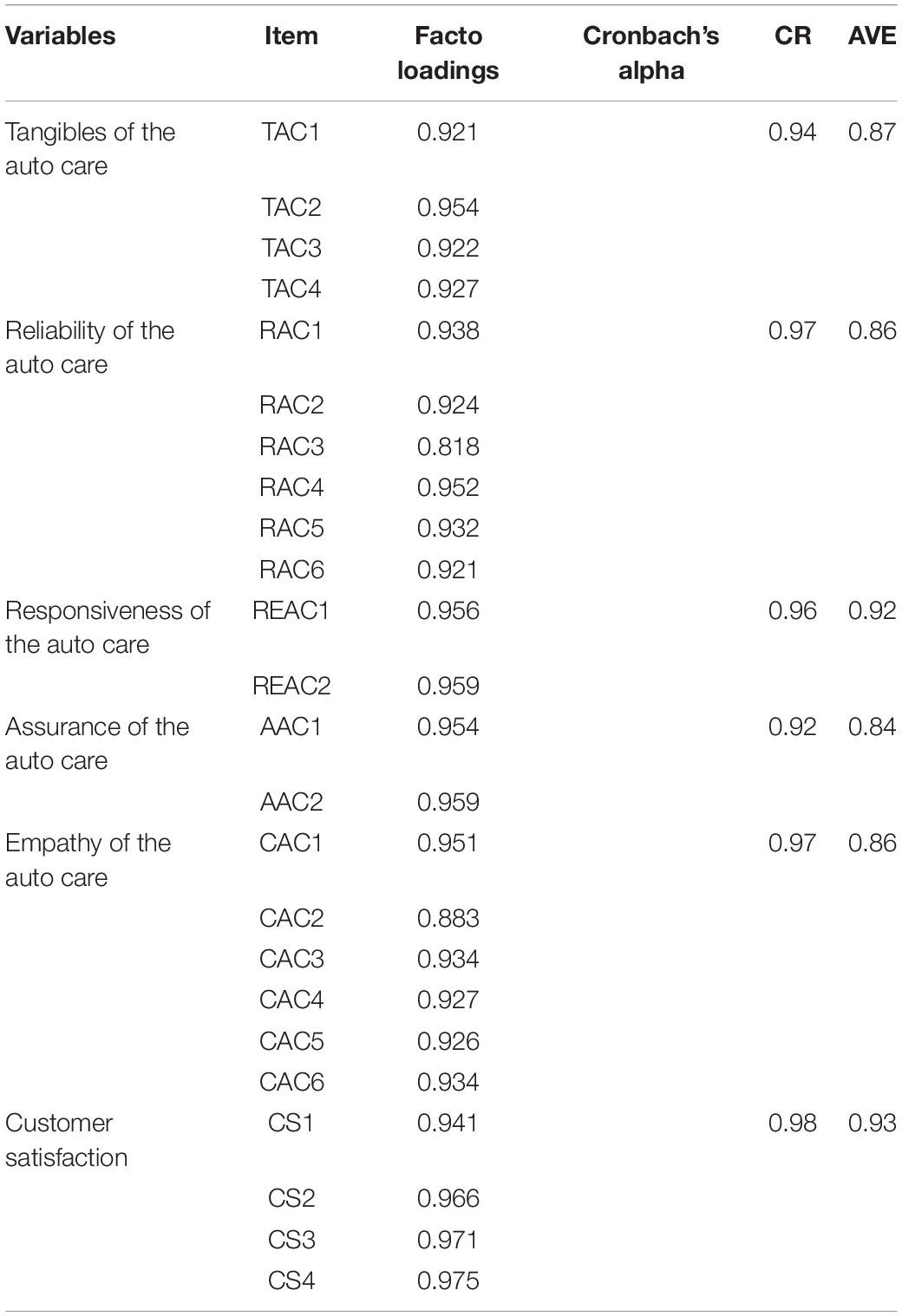
Table 3. Item loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability, and average variance extracted.
To analyze the discriminant validity, we evaluated the discriminant validity by matching the association between correlation among variables and the square root of the AVE of the variables ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981a ). The results demonstrate that the square roots of AVE are above the correlation among constructs, hence showing a satisfactory discriminant validity, therefore, indicating an acceptable discriminant validity. Moreover, descriptive statistics and correlations are provided in Table 4 .
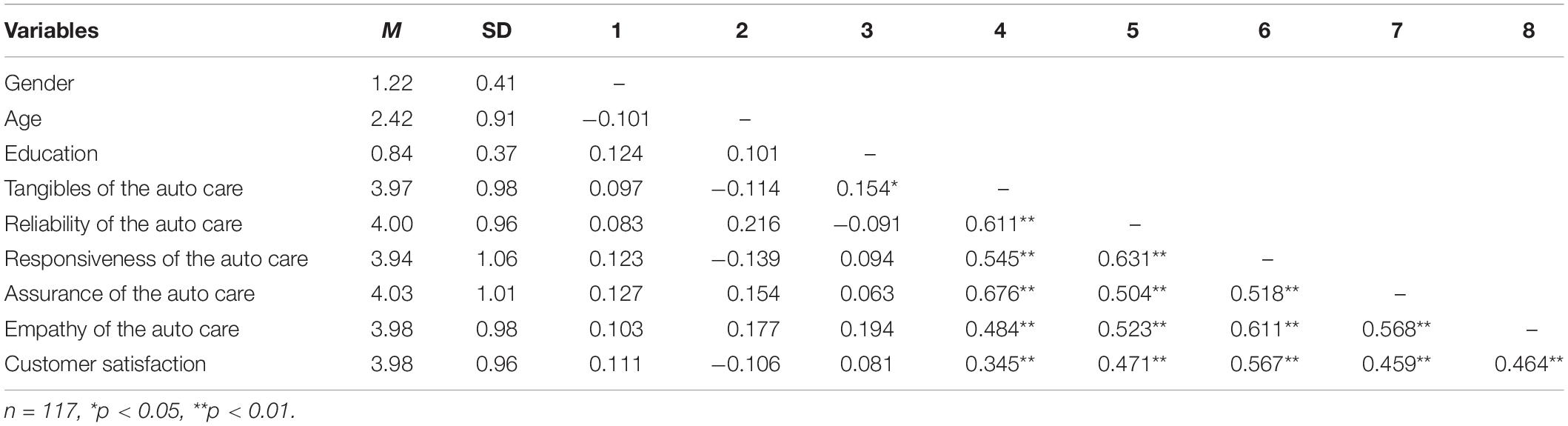
Table 4. Descriptive statistics and correlations.
Structural Model and Hypotheses Testing
After establishing the acceptable reliability and validity in the measurement model, we examined the relationship among variables and analyzed the hypotheses based on the examination of standardized paths. The path significance of proposed relations were calculated using the SEM through the bootstrap resampling technique ( Henseler et al., 2009 ), with 2,000 iterations of resampling. The proposed research framework contains five dimensions of service quality (i.e., tangibles of the auto care, reliability of the auto care, responsiveness of the auto care, assurance of the auto care, and empathy of the auto care) and customer satisfaction of auto care. The results show that five dimensions of service quality are significantly related to customer’s perception of service quality of auto care; thus, hypotheses 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, and 1e were supported. Figure 1 shows that the service quality of auto care is a significant determinant of customer satisfaction of auto care industry (β = 0.85, p < 0.001), supporting hypothesis 2. The result in Figure 1 also shows that 73.8% of the variation exists in customer satisfaction of auto care.
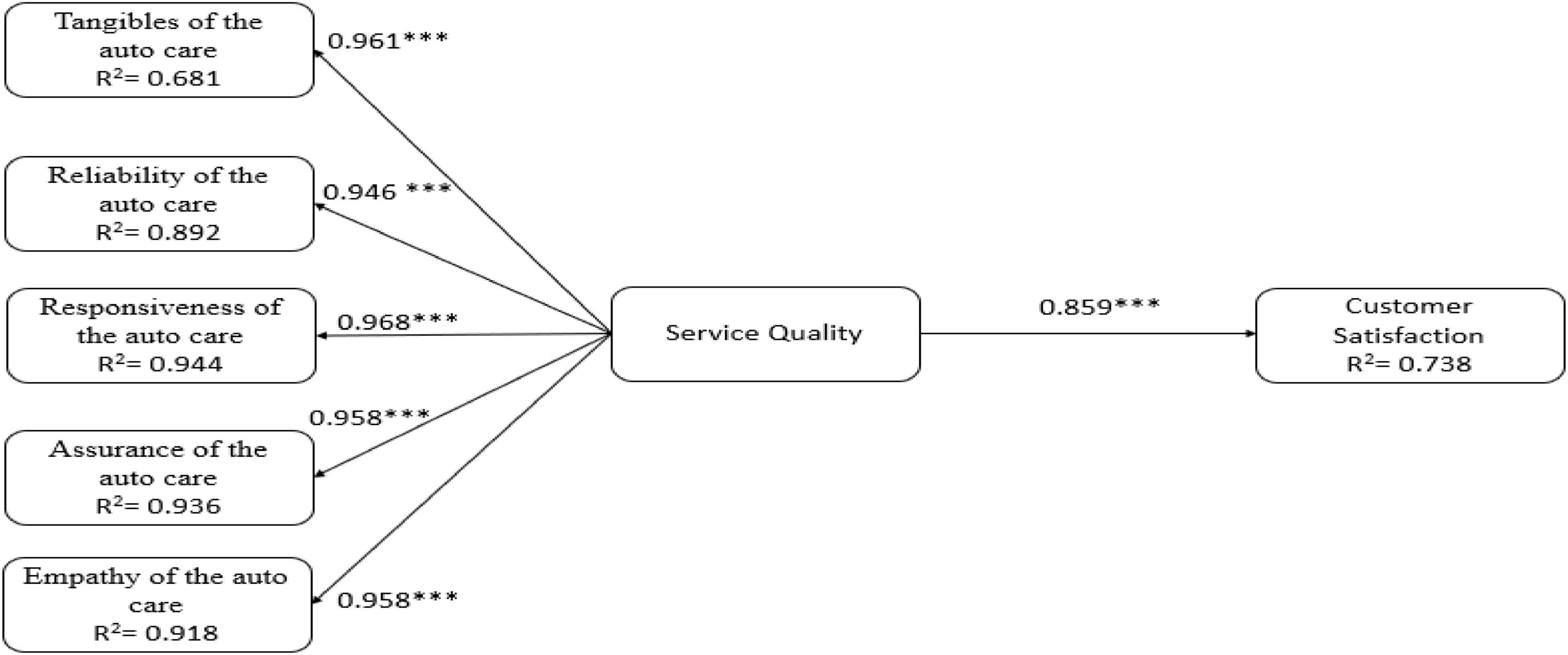
Figure 1. Results of the research model tests. *** p < 0.001.
The main purpose of this research was to assess the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in Saudi Arabia. This study was designed to examine how satisfaction of auto care customers is influenced by service quality, especially, when pandemic was declared, and due to health concerns, the customers were reluctant to visit workshops physically ( Mason et al., 2021 ). It appears that after the pandemic, customers were increasingly using online platforms for purchasing goods and services. This study reveals how customers of auto repair in Saudi perceive service quality and see how applicable SERVQUAL model across with five dimensions, including tangibles, responsiveness, reliability, assurance, and empathy measure service quality. The findings of this research show that five dimensions of SERVQUAL are positively related to the service quality perception of auto care customers in Saudi Arabia. Moreover, service quality perceptions are positively linked with customer satisfaction. These results indicate that auto care customers view service quality as an important antecedent of their satisfaction. The findings indicate that the customers perceive the service quality as a basic service expectation and will not bear the extra cost for this criterion. In this research, the positive connection between service quality and customer satisfaction is also consistent with previous studies (e.g., González et al., 2007 ; Gallarza-Granizo et al., 2020 ; Cai et al., 2021 ). Thus, service quality plays a key role in satisfying customers. These findings suggest that service organizations, like auto repair industry in Saudi Arabia could enhance satisfaction of their customers through improving service quality. Because of pandemic, people are reluctant to visit auto care workshops, and they try to book appointment through social media; so, by improving the quality of management of their social media pages, the workshops can provide accurate information for monitoring, maintaining, and improving service quality ( Sofyani et al., 2020 ). More specifically, social media, which allows individuals to interact remotely, appears to be gaining significant importance as a tool for identifying customers’ products and service needs. Increasingly, customers are also increasingly engaging with retailers through social media to search and shop for product and services options, evaluate the alternatives, and make purchases.
Furthermore, the research on the customer service quality can be held essential since it acts as a means for the promotion of the competitiveness of an organization. Precisely, the knowledge about the customers’ view concerning service quality can be used by organizations as a tool to improve their customer services. For example, knowledge of the required customer service would help in the facilitation of training programs oriented toward the enlightenment of the overall employees on the practices to improve and offer high-quality customer services. Besides, information concerning customer services would be essential in decision-making process concerning the marketing campaigns of the firm, hence generating competitive advantage of the organization in the marketplace. Findings show that customers demand more from auto repair, so the company must work hard to increase all service quality dimensions to improve customer satisfaction. Thus, organizations ought to venture in customer services initiatives to harness high-quality services.
Managerial Implications
The findings of this research indicate a strong association between SERVQUAL dimensions and perceived service quality. Perception of higher service quality leads to higher level of customer satisfaction among Saudi car care customers. In particular, the results indicate high scores for reliability, empathy, tangibles, and responsiveness. These are clear indications that the immense budgetary allocation has enabled these institutions to develop capacity. Nevertheless, the lack of a strong human resource base remains a key challenge in the car care industry. The effective use of social media plays a critical role in the responsiveness dimension of service quality. Companies need to develop their digital and social media marketing strategies in the post pandemic world to better satisfy their customers.
Saudi Arabia requires a large and well-trained human resource base. This requires intensive investment in training and development. Most of these workers have a limited contract, which reduced their focus on long-term dedication. Consequently, the government should provide longer-term contracts for workers in this critical sector. The contracts should include training on tailored courses to serve the identified needs in effective communication with the customers using digital media. We suggested that the auto car care workshops should provide training to their workers, particularly, on service technicians to enhance their skills that will help to deliver fast and reliable service to their auto customers.
Moreover, the auto car care workshops also provide customer care- or customer handling-related training especially for the service marketing personnel who handles customer directly for them to better understand the customer needs and expectations. This can be done at least once a year. This will help auto care workshops to improve their service quality.
Limitation and Future Research Direction
This research is not without limitations. First, the findings of this study are based on data collected from a single source and at a single point of time, which might be subjected to CMB ( Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). Future research can collect data from different points of time to validate the findings of this research. Second, this research was carried out with data obtained from Saudi auto car care customers; the findings of this research might be different because the research framework was retested in a different cultural context. Therefore, more research is needed to improve the understanding of the principles of service quality and customer satisfaction, as well as how they are evaluated, since these concepts are critical for service organizations’ sustainability and development. A greater sample size should be used in a similar study so that the findings could be applied to a larger population. Research on the effect of inadequate customer service on customer satisfaction, the impact of customer retention strategies on customer satisfaction levels, and the impact of regulatory policies on customer satisfaction is also recommended. Third, because most of the participants participated in this research are men, future studies should obtain data from female participants and provide more insights into the difference between male and female customers’ satisfaction levels. Moreover, due to limitation of time, the sample was collected from the eastern province. Consequently, further research should include a larger and more representative sample of the Saudi population. Because of the non-probability sampling approach used in this research, the results obtained cannot be generalized to a wide range of similar auto repair services situations, even though the methodology used in this study could be extended to these similar situations. Since the sample size considered is not that large, expectations could vary significantly. When compared with the significance of conducting this form of analysis, the limitations mentioned above are minor. Such research should be conducted on a regular basis to track service quality and customer satisfaction levels and, as a result, make appropriate changes to correct any vulnerability that may exist.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
SZ helped in designing the study. ZH helped in designing and writing the manuscript. MAA helped in data collection and analysis and writing the manuscript. SUR repositioned and fine-tuned the manuscript, wrote the introduction, and provided feedback on the manuscript.
This study was received funding from University Research Fund.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Armstrong, R. W., Mok, C., Go, F. M., and Chan, A. (1997). The importance of cross-cultural expectations in the measurement of service quality perceptions in the hotel industry. Int. J. Hospital. Manag. 16, 181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4319(97)00004-2
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Asubonteng, P., McCleary, K. J., and Swan, J. E. (1996). Servqual revisited: a critical review of service quality. J. Serv. Market. 10, 62–81. doi: 10.1108/08876049610148602
Atef, T. M. (2011). Assessing the ability of the Egyptian hospitality industry to serve special needs customers. Manag. Leisure 16, 231–242. doi: 10.1080/13606719.2011.583410
Bahadur, W., Aziz, S., and Zulfiqar, S. (2018). Effect of employee empathy on customer satisfaction and loyalty during employee–customer interactions: The mediating role of customer affective commitment and perceived service quality. Cog. Bus. Manag. 5:1491780. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2018.1491780
Brown, G. T. (2020). Schooling beyond COVID-19: an unevenly distributed future. Front. Edu. 8:82. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.00082
Cai, G., Hong, Y., Xu, L., Gao, W., Wang, K., and Chi, X. (2021). An evaluation of green ryokans through a tourism accommodation survey and customer-satisfaction-related CASBEE–IPA after COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 13:145. doi: 10.3390/su13010145
Cao, Y., Ajjan, H., and Hong, P. (2018). Post-purchase shipping and customer service experiences in online shopping and their impact on customer satisfaction: an empirical study with comparison. Asia Pacif. J. Market. Logist. 30:71. doi: 10.1108/APJML-04-2017-0071
Chang, M., Jang, H.-B., Li, Y.-M., and Kim, D. (2017). The relationship between the efficiency, service quality and customer satisfaction for state-owned commercial banks in China. Sustainability 9:2163. doi: 10.3390/su9122163
Churchill, G. A. Jr., and Surprenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. J. Mark. Res. 19, 491–504.
Google Scholar
Cohen, J., Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G. A., Leona, S., Patricia Cohen, S. G. W., et al. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Dominic, P., Goh, K. N., Wong, D., and Chen, Y. Y. (2010). The importance of service quality for competitive advantage–with special reference to industrial product. Int. J. Bus. Inform. Syst. 6, 378–397. doi: 10.1504/IJBIS.2010.035051
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Doucet, L. (2004). Service provider hostility and service quality. Acad. Manag. J. 47, 761–771. doi: 10.5465/20159617
Edward, M., and Sahadev, S. (2011). Role of switching costs in the service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction and customer retention linkage. Asia Pacif. J. Market. Logist. 23, 327–345. doi: 10.1108/13555851111143240
Elmadağ, A. B., Ellinger, A. E., and Franke, G. R. (2008). Antecedents and consequences of frontline service employee commitment to service quality. J. Market. Theory Pract. 16, 95–110. doi: 10.2753/MTP1069-6679160201
Fornell, C., Johnson, M. D., Anderson, E. W., Cha, J., and Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American customer satisfaction index: nature, purpose, and findings. J. Market. 60, 7–18. doi: 10.1177/002224299606000403
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981a). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 1987, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981b). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Market. Res. 1987, 382–388. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800313
Fornell, C., Rust, R. T., and Dekimpe, M. G. (2010). The effect of customer satisfaction on consumer spending growth. J. Market. Res. 47, 28–35. doi: 10.1509/jmkr.47.1.28
Gallarza-Granizo, M. G., Ruiz-Molina, M.-E., and Schlosser, C. (2020). Customer value in quick-service restaurants: a cross-cultural study. Int. J. Hospital. Manag. 85:102351. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.102351
González, J., De Boeck, P., and Tuerlinckx, F. (2008). A double-structure structural equation model for three-mode data. Psychol. Methods 13:337. doi: 10.1037/a0013269
González, M. E. A., Comesaña, L. R., and Brea, J. A. F. (2007). Assessing tourist behavioral intentions through perceived service quality and customer satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 60, 153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2006.10.014
Han, J., Zuo, Y., Law, R., Chen, S., and Zhang, M. (2021). Service Quality in Tourism Public Health: Trust, Satisfaction, and Loyalty. Front. Psychol. 12:279. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.731279
Hansemark, O. C., and Albinsson, M. (2004). Customer satisfaction and retention: the experiences of individual employees. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J . 14, 40–57. doi: 10.1108/09604520410513668
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing New challenges to international marketing. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 277–319. doi: 10.1108/S1474-7979(2009)0000020014
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E. L., Rana, N. P., and Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: A meta-analysis. Inform. Syst. Front. 2019, 1–24.
Korda, A. P., and Snoj, B. (2010). Development, validity and reliability of perceived service quality in retail banking and its relationship with perceived value and customer satisfaction. Manag. Glob. Trans. 8:187.
Lambert, D. M. (2010). Customer relationship management as a business process. J. Bus. Indus. Market. 25, 4–17. doi: 10.1108/08858621011009119
Lee, H., Lee, Y., and Yoo, D. (2000). The determinants of perceived service quality and its relationship with satisfaction. J. Serv. Market. 14, 217–231. doi: 10.1108/08876040010327220
Mason, A. N., Narcum, J., and Mason, K. (2021). Social media marketing gains importance after Covid-19. Cog. Bus. Manag. 8:797. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1870797
Mechinda, P., and Patterson, P. G. (2011). The impact of service climate and service provider personality on employees’ customer-oriented behavior in a high-contact setting. J. Serv. Market. 25, 101–113. doi: 10.1108/08876041111119822
Monmousseau, P., Marzuoli, A., Feron, E., and Delahaye, D. (2020). Impact of Covid-19 on passengers and airlines from passenger measurements: Managing customer satisfaction while putting the US Air Transportation System to sleep. Transp. Res. Interdiscipl. Persp. 7:179. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2020.100179
Murray, J., Elms, J., and Curran, M. (2019). Examining empathy and responsiveness in a high-service context. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2019:16. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-01-2019-0016
Nachtigall, C., Kroehne, U., Funke, F., and Steyer, R. (2003). Pros and cons of structural equation modeling. Methods Psychol. Res. Online 8, 1–22.
Nambisan, P., Gustafson, D. H., Hawkins, R., and Pingree, S. (2016). Social support and responsiveness in online patient communities: impact on service quality perceptions. Health Expect. 19, 87–97. doi: 10.1111/hex.12332
Newsted, P. R., Huff, S. L., and Munro, M. C. (1998). Survey instruments in information systems. Mis. Quart. 22:553. doi: 10.2307/249555
Omar, H. F. H., Saadan, K. B., and Seman, K. B. (2015). Determining the influence of the reliability of service quality on customer satisfaction: The case of Libyan E-commerce customers. Int. J. Learn. Dev. 5, 86–89. doi: 10.5296/ijld.v5i1.6649
Palese, B., and Usai, A. (2018). The relative importance of service quality dimensions in E-commerce experiences. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 40, 132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.02.001
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and rec-ommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., and Berry, L. (1988). SERVQUAL: a multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. J. Retail. 64, 12–40.
Ramanathan, U., Subramanian, N., and Parrott, G. (2017). Role of social media in retail network operations and marketing to enhance customer satisfaction. Int. J. Operat. Prod. Manag. 37:153. doi: 10.1108/IJOPM-03-2015-0153
Santos, J. (2002). From intangibility to tangibility on service quality perceptions: a comparison study between consumers and service providers in four service industries. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 12, 292–302. doi: 10.1108/09604520210442083
Srivastava, A., and Kumar, V. (2021). Hotel attributes and overall customer satisfaction: What did COVID-19 change? Tour. Manag. Persp. 40:100867. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100867
Sofyani, H., Riyadh, H. A., and Fahlevi, H. (2020). Improving service quality, accountability and transparency of local government: the intervening role of information technology governance. Cogent Bus. Manage. 7:1735690. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2020.1735690
Suchánek, P., and Králová, M. (2019). Customer satisfaction, loyalty, knowledge and competitiveness in the food industry. Eco. Res. Ekonomska istraživanja 32, 1237–1255. doi: 10.1080/1331677X.2019.1627893
Susskind, A. M., Kacmar, K. M., and Borchgrevink, C. P. (2003). Customer service providers’ attitudes relating to customer service and customer satisfaction in the customer-server exchange. J. Appl. Psychol. 88:179. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.1.179
Tabachnick, B., and Fidell, L. (2007). Multivariate analysis of variance and covariance. Multivar. Stat. 3, 402–407.
Teas, R. K. (1993). Consumer expectations and the measurement of perceived service quality. J. Prof. Serv. Market. 8, 33–54. doi: 10.1080/15332969.1993.9985048
Wu, G., Liang, L., and Gursoy, D. (2021). Effects of the new COVID-19 normal on customer satisfaction: can facemasks level off the playing field between average-looking and attractive-looking employees? Int. J. Hospit. Manag. 97:102996. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102996
Wu, Y.-C., Tsai, C.-S., Hsiung, H.-W., and Chen, K.-Y. (2015). Linkage between frontline employee service competence scale and customer perceptions of service quality. J. Serv. Market. 29, 224–234. doi: 10.1108/JSM-02-2014-0058
Zhou, R., Wang, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, L., and Guo, H. (2019). Measuring e-service quality and its importance to customer satisfaction and loyalty: an empirical study in a telecom setting. Elect. Comm. Res. 19, 477–499. doi: 10.1007/s10660-018-9301-3
Keywords : auto care, customer satisfaction, service quality, Saudi Arabia, pandemic (COVID-19)
Citation: Zygiaris S, Hameed Z, Ayidh Alsubaie M and Ur Rehman S (2022) Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in the Post Pandemic World: A Study of Saudi Auto Care Industry. Front. Psychol. 13:842141. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.842141
Received: 23 December 2021; Accepted: 07 February 2022; Published: 11 March 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Zygiaris, Hameed, Ayidh Alsubaie and Ur Rehman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zahid Hameed, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
100+ Customer Satisfaction Project Topics [Updated 2024]

In the dynamic landscape of business, one key factor stands out as a determinant of success – customer satisfaction. The concept is simple yet profound: a satisfied customer is a loyal customer. As organizations navigate the complexities of the modern market, understanding and optimizing customer satisfaction become paramount. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of customer satisfaction project topics, exploring their significance, selection criteria, and implementation strategies.
Understanding Customer Satisfaction
Table of Contents
Customer satisfaction is more than a fleeting emotion; it’s a multi-faceted concept encompassing a customer’s perception of a product or service. It involves the evaluation of various touch points throughout the customer journey, from initial contact to post-purchase interactions.
The impact of customer satisfaction on business success is profound, influencing customer loyalty, brand perception, and overall profitability.
Measuring customer satisfaction requires a nuanced approach. Key metrics, such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), serve as vital tools in gauging customer sentiment .
These metrics, when used effectively, provide actionable insights for businesses looking to enhance their customer experience.
| Unlock your path to academic success with our – expert guidance tailored to elevate your assignments and boost your grades, ensuring you stand out in your MBA journey! |
How to Choose the Right Customer Satisfaction Project Topic?
Choosing the right customer satisfaction project topic is crucial for the success of your research or initiative. Here are some steps to help you select a relevant and meaningful topic:
- Identify Your Objectives
- Clearly define the goals and objectives of your customer satisfaction project. What do you want to achieve? Understanding your objectives will guide you in choosing a relevant topic.
- Understand Your Audience
- Consider the audience for your project. Are you conducting research for a specific industry, company, or demographic? Tailor your topic to the interests and needs of your audience.
- Review Current Issues
- Stay informed about current trends and issues in customer satisfaction. Read industry reports, news articles, and academic papers to identify areas that need further exploration or improvement.
- Assess Organizational Needs
- If you are working on a project for a specific organization, consider their unique challenges and priorities. Discuss with key stakeholders to understand their concerns and identify areas where improvements in customer satisfaction are needed.
- Explore Emerging Technologies
- Investigate how emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, or data analytics, can be leveraged to enhance customer satisfaction. This can be a cutting-edge and relevant topic.
- Consider Industry Benchmarks
- Look at industry benchmarks and standards for customer satisfaction. Identify areas where performance is lagging and explore ways to address those gaps.
- Survey and Feedback Analysis
- If applicable, analyze existing customer surveys and feedback. Identify patterns or recurring issues that could be the focus of your project. This can help you address real concerns that customers are expressing.
- Review Academic Literature
- Look at academic literature related to customer satisfaction. Identify gaps in existing research that you can explore or areas where you can build upon existing knowledge.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders
- Collaborate with key stakeholders, including customer service teams, marketing, and product development. Their insights can help you identify areas that need improvement and guide your project topic selection.
- Feasibility and Resources
- Consider the feasibility of your project. Ensure that you have access to the necessary resources, data, and expertise to conduct thorough research on the chosen topic.
- Ethical Considerations
- Be mindful of ethical considerations, especially when dealing with customer data. Ensure that your project adheres to ethical standards and regulations.
- Innovation and Creativity
- Don’t be afraid to explore innovative and creative ideas. A unique approach to improving customer satisfaction can make your project stand out.
100+ Customer Satisfaction Project Topics
- The Impact of Online Customer Reviews on E-commerce Satisfaction.
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Customer Satisfaction.
- A Comparative Study of Customer Satisfaction in Retail vs. E-commerce.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Mobile App Usability.
- The Influence of Customer Service on Hotel Guest Satisfaction.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction in the Banking Sector.
- Evaluating the Impact of Loyalty Programs on Customer Satisfaction.
- Investigating the Relationship between Employee Satisfaction and Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Chatbots in Improving Customer Satisfaction.
- The Role of Packaging in Influencing Product Satisfaction.
- Examining the Impact of Personalization on E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Fast Food Industry.
- Assessing Customer Satisfaction in the Healthcare Sector.
- Exploring Customer Satisfaction in Subscription-based Services.
- The Impact of Website Design on E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction through Supply Chain Management.
- Investigating the Role of Trust in Online Customer Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Sustainable Business Practices.
- Analyzing the Influence of Brand Image on Customer Satisfaction.
- Customer Satisfaction in the Luxury Goods Market: A Case Study.
- Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in the Airline Industry.
- The Impact of Product Returns on E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- A Study on the Role of Community Engagement in Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Automotive Industry.
- The Influence of User Experience Design on Software Customer Satisfaction.
- Examining Customer Satisfaction in the Telecom Industry.
- The Impact of Pricing Strategies on Customer Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction in the Tourism and Hospitality Industry.
- A Comparative Analysis of Customer Satisfaction in B2B vs. B2C Markets.
- Investigating the Role of Customer Education in Improving Satisfaction.
- The Impact of Customer Feedback on Product Development and Satisfaction.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction through Omnichannel Retailing.
- Analyzing the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Customer Satisfaction.
- Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in the Online Education Sector.
- The Influence of Word-of-Mouth on Customer Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction in the Gaming Industry.
- Examining the Role of Trust in Financial Services Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in Subscription-based Streaming Services.
- The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Customer Satisfaction.
- Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in the Real Estate Industry.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Grocery Retail Sector.
- The Influence of Packaging Design on Food Product Satisfaction.
- Analyzing the Impact of In-Store Technology on Retail Customer Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Personalized Marketing.
- Investigating the Role of Customer Empowerment in Satisfaction.
- The Impact of Environmental Sustainability on Hotel Guest Satisfaction.
- Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in the Fitness and Wellness Industry.
- Analyzing the Role of Emotional Intelligence in Customer Service Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Timely and Accurate Delivery.
- The Influence of Cross-Cultural Communication on International Customer Satisfaction.
- Assessing Customer Satisfaction in the Software as a Service (SaaS) Industry.
- The Impact of Virtual Assistants on Customer Satisfaction in Online Shopping.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Pharmaceutical Industry.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Electric Vehicle Market.
- Evaluating the Role of Virtual Reality in Enhancing Customer Satisfaction.
- The Influence of Social Responsibility in Corporate Customer Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through After-Sales Service.
- Investigating the Impact of Influencer Marketing on Brand and Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Renewable Energy Sector.
- The Role of Chat Support in E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction through Green Packaging Practices.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Digital Marketing Industry.
- The Impact of Cybersecurity Measures on E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- Evaluating the Role of Trust in Healthcare Provider Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Beauty and Cosmetics Industry.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Innovative Payment Solutions.
- The Influence of Augmented Reality in Retail Customer Satisfaction.
- Assessing Customer Satisfaction in the Ride-Sharing Industry.
- The Impact of Personal Data Protection on E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Pet Care Industry.
- Evaluating the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Hotel Guest Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Enhanced Customer Support.
- The Influence of Subscription Models on Media Streaming Customer Satisfaction.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Fitness App Industry.
- The Impact of In-App Purchases on Mobile Gaming Customer Satisfaction.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Luxury Travel and Hospitality Sector.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction through Smart Home Technology.
- Investigating the Role of Blockchain in E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- The Influence of Packaging Sustainability on Consumer Electronics Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Proactive Communication.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Electric Scooter Rental Industry.
- Analyzing the Impact of Omnichannel Customer Engagement on Retail Satisfaction.
- Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in the Agricultural Technology Sector.
- The Role of Predictive Analytics in Enhancing E-commerce Customer Satisfaction.
- The Influence of Virtual Events on Customer Satisfaction in the Event Industry.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction in the Fashion Retail Industry.
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in the Telemedicine and Virtual Health Industry.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction through Personalized Travel Experiences.
- The Impact of Data Privacy Measures on Customer Satisfaction in Financial Services.
- A Study on Customer Satisfaction in the Online Grocery Delivery Industry.
- The Influence of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Restaurant Customer Satisfaction.
- Evaluating the Role of Gamification in E-learning Customer Satisfaction.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction through Social Responsibility Initiatives.
- Analyzing the Impact of Subscription Models on Software Customer Satisfaction.
- The Role of Personalization in Enhancing Customer Satisfaction in the Fashion Industry.
- The Influence of Sustainable Packaging on Food Delivery Customer Satisfaction.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction in the Telecommunications Industry through Innovation.
- Analyzing the Impact of Voice Assistants on Smart Home Customer Satisfaction.
- Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in the Personal Finance App Industry.
- The Role of Data Security in Enhancing Cloud Computing Customer Satisfaction.
- Investigating the Influence of Employee Training and Development on Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in the Hospitality Industry.
Challenges and Solutions in Customer Satisfaction Projects
While customer satisfaction projects offer tremendous benefits, they are not without challenges. Common obstacles include misalignment with organizational goals, inadequate data quality, and resistance to change.
However, best practices, such as proactive communication, continuous monitoring, and a customer-centric culture, can overcome these hurdles.
Real-life examples of companies overcoming challenges provide valuable insights for project managers.
Future Trends in Customer Satisfaction Projects
As businesses evolve, so do customer expectations. Anticipated changes in customer preferences, emerging technologies, and the influence of sustainability on customer satisfaction are key considerations for future projects. Businesses that stay ahead of these trends can proactively adapt their strategies to meet evolving customer needs.
In the fast-paced world of business, customer satisfaction remains a cornerstone of success. By embarking on customer satisfaction projects, organizations can unlock new avenues for growth, loyalty, and brand advocacy.
This comprehensive guide has explored the various facets of customer satisfaction project topics, providing insights and strategies to empower businesses in their pursuit of customer-centric excellence.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Researching Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: How to Find out What People Really Think
Journal of Consumer Marketing
ISSN : 0736-3761
Article publication date: 1 April 2006
- Customer satisfaction
- Customer loyalty
- Market research methods
Goncalves, K.P. (2006), "Researching Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: How to Find out What People Really Think", Journal of Consumer Marketing , Vol. 23 No. 3, pp. 173-173. https://doi.org/10.1108/07363760610663349
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2006, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Paul Szwarc's Researching Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: How to Find out What People Really Think is a hybrid between the rigor and quantitative orientation of a textbook, and the “lightness” of a trade book. It is easy to read, well‐organized, easy to follow, and contains many helpful hints for practitioners new to commercial consumer research. The case studies throughout the book are likely to be especially interesting to new researchers. Senior researchers are not likely to find great value in this book.
Part I . Introduction and Theory (four chapters; 70 pages).
Part II . Getting Started (four chapters; 72 pages).
Part III . ‘Touching’ the Customer (one chapter; 20 pages).
Part IV . Outputs (two chapters; 45 pages).
Part V . What Lies Ahead? (one chapter; ten pages).
Part I provides useful background for anyone new to consumer satisfaction research. For example, Chapter 1 reminds readers that “customers” are really a wide array of stakeholders ranging from “external customers” to employees, stockholders, and prospective and lost customers. In chapter 2 the author reviews the important differences between strategic and operational research. He also takes the time to describe several well‐known customer service awards, as well as what some familiar terms mean (e.g. ISO 9002; Six Sigma).
“Instant feedback” must be the greatest concern of all moderators. Having just spent a couple of hours running a group, the moderator is asked to produce an instant summary of the “key findings” that emerged from the session. This does not allow any time for the moderator to reflect on all that has happened. Neither does it allow him or her to determine how different this group was from others her or she (or his/her colleagues) has conducted on the subject. Meanwhile, there is a risk that the client has drawn his or her own conclusions, and is keen to see if the moderator has similar “findings” (pp. 45‐6).
Chapter 4, on quantitative research, is where I had difficulty, because the author missed key points that may lead inexperienced researchers astray. For example, in the discussion of disadvantages of face‐to‐face interviewing, there is no mention of interviewer bias! Clearly, interviewer bias is a potential concern any time there is a live interviewer – telephone, in‐person, focus group moderation, etc. – so it should be included. In fact, bias is ignored or downplayed throughout the chapter, and experienced researchers know that bias can discredit any findings.
Aside from my disagreements with some of Chapter 4's content, it is easy to read, even for those who avoid the quantitative world of statistics, reliability levels, and sample size decisions. This alone, would make the chapter worth reading for new researchers, because it might help them overcome “numbers phobia”.
Part II addresses the research design process from when the research sponsor first develops its research objectives, until the formal research instrument is pre‐tested and ready for fieldwork. Chapters 5 and 6 provide both the “client” and “researcher” organizational perspectives – illuminating for those new to the field. These chapters also provide details such as who completes various tasks, how to handle budgets, and what to do when there are conflicts over methodology.
Chapter 7 moves on to sampling – who to reach, how to reach them, issues associated with certain types of samples, how many people to include, response rates, and other practical aspects of sampling that are hard to grasp until one has had to construct a sample. The author even includes a section on longitudinal research and how the samples, questionnaires, and research processes differ for one‐off projects versus those designed to be continuous or repeated at intervals.
Chapter 8 is a good overview of the questionnaire design process, from what to ask, to the role of order bias and how to handle sensitive questions. Szwarc's comments and advice are sound, and to a large degree, reflect what I have seen in my own practice. The sub‐headings he uses and some of the content are not exactly “purist” from an academic perspective, but they are very useful when designing commercial surveys.
What to do when you learn something confidential and time‐sensitive from a respondent, which should be shared with the client, but which is difficult (or impossible) to share given standard confidentiality rules.
Addressing misperceptions on the part of clients who have listened to or observed a small portion of the fieldwork, and then feel that anything which does not agree with their “knowledge” must be wrong.
Part IV (Chapters 10 and 11) are written in the same format as earlier sections but feel more like “checklists”, because they cover data cleaning, coding, entry, analysis and reporting. This is where many researchers seem to get lost, and these two chapters could easily be used to guide the data analysis and reporting process in an objective, logical fashion.
Part V, Chapter 12 shares the author's view of major global environmental shifts from demographics (the “aging” of the population in several countries) to technological change (internet, consumer electronics) to psychographics (consumer attitudes toward work, leisure and to the process of change itself). He also addresses how these shifts are affecting the market research process and industry. As he notes, everything is changing so rapidly, it is hard to keep up, and this chapter is a good example. No matter how recently the book was written, readers will find parts of this chapter sound dated – evidence that Szwarc is right!
Overall, this book is worthwhile for anyone new to market research. Junior staffers at research firms, as well as those who work for the companies that sponsor commercial research can benefit, and they may find that this becomes a reference work. It is easier to read than their marketing research textbook, and when in doubt about anything the author says, they can always refer to their textbook for a “purer”, more academic view of the world.
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Structure Customer Service Calls to Boost Satisfaction and Sales
- Jonah Berger,
- Grant Packard

Researchers found that service agents yield better results when they use warm language to start and end conversations, focusing on problem-solving in the middle.
We all know from our experience as customers that the things that salespeople say in a conversation affects our feelings and choices. A new study showed that the timing of language matters as well. By analyzing tens of thousands of moments or turns in service calls, researchers found that service agents get better customer satisfaction and purchase volume if they use warmer language at the start and finish of their interaction with a customer. Contrary to some common practices where a problem-solving mode is used right away, the results suggest that employees should use words that show competence only in the middle of a customer conversation.
Language plays a key role in almost every marketplace interaction. It’s how salespeople talk to prospects, leaders talk to teams, and customer service agents talk to customers. Recently, firms have been measuring and optimizing their language to manage the customer experience , automate service , and help make business decisions .
- Jonah Berger is a professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania and the author of Magic Words: What to Say to Get Your Way (Harper Business, 2023).
- Yang Li is an associate professor of marketing at the Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business in Beijing, China.
Grant Packard is an associate professor of marketing at the Schulich School of Business at York University in Toronto, Canada.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
New research on customer satisfaction from Harvard Business School faculty on issues such as the distinction between understanding and listening to customers, how to determine how much of a CEO's time should be spent interacting with customers, and how satisfied employees and customers can drive lifelong profit.
Furthermore, customer satisfaction is determined by the capability of the product or service to meet the concerned product performance (Lee et al., 2016), The primary objective of this paper ...
1. Introduction. Customer satisfaction, loyalty, product knowledge and competitive ability are variables which have been researched extensively across the globe. The relationships which tend to be researched the most are customer satisfaction and loyalty (e.g., Fornell, Johnson, Anderson, Cha, & Bryant, 1996; Türkyilmaz & Özkan, 2007 ).
These findings offer both theoretical contributions to the field of customer satisfaction research and practical implications for business strategies focused on customer engagement and loyalty ...
The authors synthesize research on the relationship of customer satisfaction with customer- and firm-level outcomes using a meta-analysis based on 535 correlations from 245 articles representing a combined sample size of 1,160,982. The results show a positive association of customer satisfaction with customer-level outcomes (retention, WOM, spending, and price) and firm-level outcomes (product ...
Step 1: Define Research Objectives. Defining precise and well-structured research objectives is an essential first step in every customer satisfaction research project. These objectives will guide you through the whole research process and ensure that the research remains focused, relevant, and connected with your business goals.
satisfaction, and loyalty. 1) integration of standardization and customization of. service offerings is essential to improve service quality; (2) standardization has a higher impact on service ...
ABSTRACT. Service quality and customer satisfac tion have been widely recognized as funda mental drivers in. the formation of pu rchase intentions. The concepts ar e important for companies to ...
This research aims to examine the trends in service quality and customer satisfaction research, identify the gaps, and propose future research agenda. The data for bibliometric analysis have been extracted from the Web of Science database. ... At the final stage, each article was reviewed with the title and abstracts to ensure data accuracy (X ...
Article Transforming the customer service landscape: Marketing research and conversational AI Polat Goktas , Taskin Dirsehan | September 18, 2023. Article Use neuroscience to fine-tune your customer expectations strategy Terry Grapentine | September 1, 2023. Article How generative AI is transforming open-end analysis Rick Kieser | September 1 ...
The existing state of customer experience research was assessed by reviewing 99 articles. Table 2 reveals that the customer experience has been studied in four categories; with most of the articles published in the context of experience with a brand (n = 35), followed by the context of experience with a product/service (n = 28), experience with a website or a specific medium (n = 19), and the ...
There is a desperate need for new research that will advance customer satisfaction (CS) and service quality (SO) methodologies in the hospitality industry. This comprehensive review of the theories and methodologies reported in CS and SQ studies cited in the hospitality literature provides suggestions for future CS and SQ research in the ...
Customer Satisfaction Research is defined as a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting feedback and data from customers to assess their level of satisfaction with a product, service, or overall experience provided by a company. This research aims to measure and understand customers' perceptions, expectations, and ...
The conceptualization of customer loyalty is more complicated. Although customer loyalty has been in the focus of marketing research and practice for a long time (Oliver 1999), there is no consensus among researchers on how to define customer loyalty (Aksoy 2013; Kumar and Reinartz 2012; McAlexander et al. 2003).Yet, most prior studies agree that customer loyalty is a complex, multidimensional ...
Customer satisfaction is the key factor for successful and depends highly on the behaviors of frontline service providers. Customers should be managed as assets, and that customers vary in their needs, preferences, and buying behavior. This study applied the Taiwan Customer Satisfaction Index model to a tourism factory to analyze customer satisfaction and loyalty. We surveyed 242 customers ...
1 College of Business Administration, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Khobar, Saudi Arabia; 2 Department of Management Sciences, University of Baluchistan, Quetta, Pakistan; The aim of this research is to examine the impact of service quality on customer satisfaction in the post pandemic world in auto care industry.
The impact of customer satisfaction on business success is profound, influencing customer loyalty, brand perception, and overall profitability. Measuring customer satisfaction requires a nuanced approach. Key metrics, such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), serve as vital tools in gauging customer sentiment .
Paul Szwarc's Researching Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: How to Find out What People Really Think is a hybrid between the rigor and quantitative orientation of a textbook, and the "lightness" of a trade book. It is easy to read, well‐organized, easy to follow, and contains many helpful hints for practitioners new to commercial consumer research.
The thesis research does not only discuss the concepts of customer satisfaction and loyalty, but also analyzes how customer satisfaction influences customer loyalty from the point of view of the research. As Hill et al. (2007, 7) also point out, "measuring customer satisfaction is to make decisions on how to improve it."
on customer satisfaction. The price of services in comparison to the quality of service has a positive impact on customer satisfaction. And the price of service directly influences service quality (Ismail, et al. 2006). Aga & Safakli (2007) suggest that empathy is significantly influential to customer satisfaction because it addresses the
Abstract. Customer satisfaction (CS) has attracted serious research attention in the recent past. This paper reviews the research on how to measure the level of CS, and classify research articles ...
2.2. Customer satisfaction Customer satisfaction emanates from the assessment of anticipated performance against the real perceived performance and the paid price (Abedi & Jahed, 2020). Customer satisfaction is a typical performance measure and is a result of the superiority of the customer experience and aspects
Customer satisfaction research is that area of marketing research, customer intelligence, and customer analytics which focuses on customers' perceptions with their shopping or purchase experience.. Companies are interested in understanding what their customers think about their shopping or purchase experience, because finding new customers is generally more costly and difficult than servicing ...
Researchers found that service agents yield better results when they use warm language to start and end conversations, focusing on problem-solving in the middle. We all know from our experience as ...