5G use cases: 31 examples that showcase what 5G is capable of
5G use cases are increasing in number, and in this post we take a look at the most innovative projects around the world today.

5G use cases tend to rely on the increased speed and consistency of 5G, as well as the latency reductions it offers, and they promise to disrupt both traditional and digital sectors. And there are a plethora of opportunities for 5G technology over the coming months, years and decades.
5G use cases will pave the way for automated vehicles, smart cities, automated factories, and a new wave of business communications. According to the results of a study by Accenture, 79% of businesses worldwide believe that 5G will have a significant impact on their organisation. And 57% of those believe that it will be revolutionary.

5G use cases across sectors
According to small business portal Bytestart , 5G will allow communication between a million devices per square kilometre (compared with 100,000 for 4G). The enabling of these IoT sensors, combined with speed and low latency, will lead to many benefits across a range of business and prosumer activities.
IoT connectivity will lead to fully integrated smart cities, which will be essential as urban populations grow. The United Nations (UN) predicts that 68 percent of the world’s population will be living in urban areas by 2050, which will place increasing pressure on our cities, such as pollution, crime, overcrowding, congestion, and social disorder.
There are already some amazing 5G use cases out there. That's what this feature is all about - the ways in which 5G is already being used across the globe. Because 5G networks are still being rolled out, many of these use cases are actually in the test or proof-of-concept phase, using prototype networks, devices or other technology. But the idea of gathering them here is to show the huge future potential of 5G technology .
1. Smart cities
Network operators are already looking to showcase what can be achieved with 5G technology , and one such 5G use case is the Alba Iulia Smart City , which has been developed in conjunction with Orange, and has seen congestion monitoring, parking sensors, and smart waste management introduced in the Romanian city.
Smart factories will also be enabled by 5G, including more robots in production lines, and drones in last mile delivery. It will also enable car to car communication around hazards and incidents, as well as fully automated cars.
SIGN UP FOR E-MAIL NEWSLETTERS
Get up to speed with 5G, and discover the latest deals, news, and insight!
2. Autonomous vehicles

The CTO of Waymo , which started life as the Google Self-Driving Car Project in 2009, believes that 5G is a crucial “enabler”, when it comes to developing the company’s autonomous car fleets.
“I think it’ll help in terms of communication [and with] latency and bandwidth,” explains Dmitri Dolgov, Waymo’s CTO. “Our cars still have to rely on onboard computation for anything that is safety-critical, but 5G will be an accelerator.”

O2 has also now announced a project to trial driverless cars in London using its 5G network. The UK's second-biggest phone network has partnered with the Smart Mobility Living Lab - a research organisation comprised of experts from the Transport Research Laboratory (TRL), DG Cities, Cisco, and Loughborough University - to develop what it claims to be the ‘most advanced driverless testbed in the world’.
The organisation is based in Greenwich as well as the Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park. The aim is to develop a road management system with the focus on a 10 percent reduction in the time that motorists spend in traffic. Other figures include a positive benefit to the economy of £880m a year from improved productivity as well as the reduction of CO2 emissions by 370,000 metric tonnes a year.
At the Consumer Electronics Show in January 2020, Samsung and BMW showcased the companies' efforts in connected cars, revealing the 5G TCU (Telematics Control Unit). The TCU will be included in the BMW iNext, coming in 2021. The iNext will include technology from Samsung subsidiary Harman. The companies are talking up the benefits of the technology as not only enabling greater levels of autonomy but also detailed and specific information such as whether there's something in your blind spot.
Elsewhere, Huawei, in partnership with Thailand National Broadcasting and Telecommunication Communication (NBTC) and Siriraj Hospital, has launched a new project to use 5G-powered self-driving vehicles to deliver medical supplies.
According to data from the UK’s Office for National Statistics, jobs such as bus drivers and hospital porters are particularly at risk from catching Covid-19 whilst at work, with both jobs in the top 20% when it comes to exposure. And this scheme enables the transportation of goods around the Siriraj Hospital campus in Thailand, where workers face a similar risk to those in the UK. In the initial stage of the project, driverless vehicles will be used to transport and distribute medicines, which will be delivered via a contactless system, which will help reduce workload and infection risk among frontline workers.
3. Improved viewing experience at sporting events

Connectivity is increasingly important at sporting events with, as an example, the average Bundesliga match attracting 43,000 spectators, who consume an average of 500GB – a figure which has risen by 50 percent over the past 12 months,.
Because of this, some sporting organisations fear that spectators will stay at home if they can't stay connected. However, existing mobile and Wi-Fi networks lack the capacity for such densely-populated environments, which is why venues and operators are so excited about 5G. Research from Amdocs and Ovum suggests 91 percent of the world’s leading mobile operators plan to hold trials of 5G sporting experiences at stadiums, with the likes of Verizon announcing the 5G availability at selected NFL stadiums.
This will not only increase fan satisfaction, but also enable new experiences. The German FA plans to let fans view data insights in real time – such as how fast a player is sprinting – using Augmented Reality.
4. Better crowd management at sporting venues

Verizon and Cisco are partnering to deliver a number of new capabilities to stadiums, such as the ability to use analytics to estimate waiting times at gates, restrooms and concession stands. Supporters will also have the ability to access digital signage, and via a mobile app they will also get tailored updates, information on crowd density, and tips on the best ways to avoid crowds and maintain social distancing.
To deliver these new 5G capabilities, venues in Cisco’s Sports and Entertainment portfolio will be able to access Verizon 5G Ultra Wideband with mobile edge computing (MEC) capabilities. Cisco innovations, which will be able to tap into Verizon’s MEC include Cisco DNA Spaces for secure location analytics; Cisco switching and data center technology; connected venue analytics; and more.
5. Sports broadcasting

Sports broadcasting is arguably the most developed use case for 5G to date, with ready-made innovations driving efficiencies and unlocking a raft of creativity options. 5G-enabled cameras eliminate the need to use cables, making it easier to cover sports that take place over a wide area. Fox Sports has trialled 5G at golf’s US Open (with Intel, AT&T, and Ericsson) allowing its team to cover more of the course, while 5G was used to capture some events at the 2018 Winter Olympics. In the UK, BT Sport is able to join football fans in the pub before the game, travel on the team bus, capture the game, and do post-match interviews using the same camera.
Meanwhile, 5G-enabled remote production enables video feeds to be sent back to a central hub, rather than an outside broadcast truck. This massively reduces costs and allows production teams to work across multiple events in a single day. Already, the likes of Verizon and Sony have joined forces to demonstrate how 5G can enhance live sports broadcasts.
6. 5G drones

Verizon wants to be the first telco to use 5G to enable a million connected flights of 5G drones to take place. That's some ambition, but the idea has some backing since Verizon bought Skyward in 2016 - an organisation specializing in drone operations for businesses and enterprises.
Skyward provides drone operators with detailed mapping while operating industrial drones plus there are also tools for overseeing multiple drones in action and, basically, work out what needs to go where.
Verizon's plan is to enable as many drones as possible to be connected and to transmit video footage in real-time but also to relay back other intelligence such as levels of stock in a warehouse situation
“We've already started testing connected drones on 5G on the Verizon Network,” said Mariah Scott, president of Skyward . “We knew early on that connectivity would be critical for drones. And now 5G Ultra Wideband will usher in a new era in aviation, where we connect and integrate drones into the national airspace.”
Elsewhere, Irish startup Manna has partnered with Cubic Telecom to fly delivery 5G-connected delivery drones in Ireland and England by the end of 2020. It is currently testing the tech at a base in Pontypool, Wales.
The intention is for the drones to charge $1 per delivery. Each drone will have three batteries on board, meaning that they can make five deliveries per hour. Even so, that doesn't seem that profitable to us, but Manna believes that by keeping the drones flying as much as possible it can make it work.
7. Immersive entertainment

Verizon showcased its 5G tech in real-time rendering of effects from Star Wars: The Rise of Skywalker. The network partnered with Walt Disney Studios’ StudioLAB for a demo at the premiere afterparty in in Hollywood where guests were able to interact with Sith troopers in real-time.
Two actors played the troopers working in a remote location 15 miles away. Those who took part in the demo could approach a screen and interact with the two Sith troopers. The troopers were able to react in real-time.
“Both the StudioLAB and Verizon believe 5G will fundamentally change everything about how entertainment media is created, distributed and consumed,” said Nicki Palmer, chief product development officer at Verizon.
“The speed and low latency of 5G can unlock incredible creative capabilities,” added Ben Havey at Disney Studios StudioLAB. “We want to give storytellers early access to this new technology so they can continue to bring unparalleled experiences to audiences around the world.”
In November EE streamed a 360-degree augmented reality (AR) Bastille concert from Birmingham New Street station to Edinburgh and Liverpool.
As well as being covered by various media outlets, the stunt wasn't just for fun - the event will be featured in a new EE brand campaign by Saatchi & Saatchi
Members of the public in Edinburgh and Liverpool could watch the gig on devices provided by EE reps including the Samsung Galaxy Fold 5G and some AR glasses. Of course, AR visuals surrounded the band which could be seen on the glasses.
EE has used other music stars to promote 5G - it held a gig with Stormzy on the River Thames to promote the launch of its 5G network. The network also sponsors the Glastonbury Festival each year.
8. Overground trains

Virgin Trains has been testing out 5G-powered Wi-Fi on its trains. The company believes it is the first railway company to trial the new tech. The trial happened on services between London Euston and Birmingham New Street, and between London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly.
However, Virgin Trains hasn't yet said if and when it plans to offer 5G-powered Wi-Fi on board its trains.
The Vodafone 5G network was used to provide the 5G service - the red network has installed 5G in key transport locations including Birmingham New Street station.
Virgin says the speeds seen were up to ten times faster than current on-board Wi-Fi.
9. Going underground

Whilst companies such as Virgin Trains are looking to get 5G into the UK's biggest stations, a private and public sector consortium, led by Cisco, has gone underground to test 5G use cases on the Glasgow Subway.
5G RailNext has announced a pioneering new project to explore new 5G use cases for underground commuters, by setting up a unique private 5G network to connect passengers travelling by train on Scotland’s historic Glasgow Subway.
5G RailNext is a private and public sector consortium led by Cisco, and it includes companies and organisations across the technology, marketing and transport sectors, including the University of Strathclyde, Ampletime, Sublime, Strathclyde Partnership for Transport, and Glasgow City Council. And as part of the UK Government's £200 million 5G Testbeds & Trials Programme, it aims to maximise the opportunities around 5G applications and services.
10. Manufacturing

With 5G networks using URLLC (Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications) latency can theoretically reduce that to a single millisecond, essentially rendering the issue of latency meaningless. The advantages to manufacturers are many; think high-precision assembly lines where all machines and robots are perfectly in sync in real-time, the mass-adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), and even humans controlling machines via touch. However, the first generation of 5G networks tend to offer around 10ms latency, so, for now, latency is still an issue. Expect second-gen 5G networks to be mostly about reducing latency.
5G in a manufacturing context is not about making use of publicly available 5G connections as used by consumers. No, 5G for industry is about constructing custom-made, private 5G networks that essentially bring alive the idea of an Intelligent or ‘smart’ factory. Also known as Industry 4.0, this is about abandoning the old ways to embrace connected systems to encourage more streamlined automation in a closed environment. With the Internet of Things (IoT) in full deployment and connected sensors on every machine, the aim is to predict problems, see problems emerge in real-time, and reduce production downtime. The secret sauce will be AI-capable analytics software to crunch real-time data on every machine and piece of equipment.
11. Smart factories
In the US, mobile network Verizon has partnered with specialist glass maker Corning to investigate how 5G can improve the factory environment.
The maker of Corning Gorilla Glass (used on vast numbers of smartphones) are looking at how 5G can improve control across a factory environment on a large scale by tracking supplies across the whole complex, autonomous vehicles - so they can be called in from other parts of the facility - as well as moving product around.
"As artificial intelligence starts using this data and improving our process, making our processes more efficient, that's when we're going to start seeing the value," says Claudio Mazzalli, Corning's vice president of technology.
Could it actually save Corning money? "We are not speculating right now, but I can tell you that this question is a very important question for us. We don't want to start just adding devices everywhere if we don't see the value."
12. Connected cows and calving

Traditional industries such as agriculture will use 5G sensors to collate real-time information about fertilisation, livestock, and moisture needs, helping to conserve energy. And we are already seeing the emergence of smart farms, with services such as the MooCall calving sensor and app now being powered by 5G. MooCall is a sensor that attaches to the tail of cows, and then alerts farmers when a cow is about to give birth (cows move their tails more just before and during labour).
“With the growing prevalence of IoT and 5G, we expect to see increasing innovation in the agricultural sector,” says Anne Sheehan, Director, Vodafone Business. “By using digital tools, farmers can gain better control over processes such as raising livestock and growing crops, improving overall productivity, efficiency and financial performance … technologies such as IoT and 5G must be viewed as a priority for the farming sector.”
13. Healthcare

The health industry will offer remote diagnosis and operations, as well as e-health and responsive wearables, and AI assistants might help people with disabilities. Companies such as the interactive physiotherapy specialist Immersive Rehab are already looking at how 5G can improve their offering, and 5G is being used in various trials such as the Liverpool 5G Testbed .
5G has even made its way into the operating theatre, when Telefónica, with the help of a hospital in Malaga, already presented the first assistance system for surgery that runs entirely on 5G technology . The howcase took place at the IV Advanced Digestive Endoscopy Conference, where Telefónica broadcast medical training sessions live, and in 4K quality. It achieved this with “almost no latency,” according to Telefónica .
Elsewhere, O2 has developed a deal with Samsung and the NHS to test out “smart ambulances” equipped with 5G technology . O2 will test the technology on six ambulances which will allow for new services such as real-time video technology and high-quality scanners (read the full story here ).
14. Construction

The construction industry has always looked at new technologies as a way to improve safety and working practices, and 5G is no different.
KT and Hyundai Engineering & Construction have announced that they will work together to build 5G networks at construction sites, with a aim to develop construction and automation technology.Using 5G infrastructure, we could see autonomous construction robots, and 5G will also be used to improve other technologies with better productivity and monitoring at construction sites.
KT will help Hyundai to build these 5G networks at its construction sites. The trials of the 5G solutions will commence later this year. If the trial all goes to plan, then the two companies aim to apply their technologies to many more construction sites next year.
KT has said that its 5G technologies will provide "ultra-fast data transmission speeds and ultra-low latency with top notch security". And the companies have both said that the development of autonomous robots will give Hyundai the opportunity to carry out work on sites with limited to no human access (read the full story here ).
15. Energy preservation

There are many interesting user case studies, but the increased use of 5G connected drones or autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) for service or production delivery is one with some very interesting permutations. One of these might help with disaster relief situations via the sharing of real time data. They could help with search and rescue missions and deliver medical help, according to OnQ a blog from US telecom operator Qualcomm. And 5G drones can also be used as small cells to prevent gaps in 5G coverage.
Another interesting end result of 5G is the huge potential for energy savings. Including all the currently unconnected, energy consuming devices via 5G IoT connections into the grid will allow for better management of energy.
Where there are outages, 5G and smart grid technology can help with early diagnosis, speeding up repairs and reducing down time. Smart lighting will see street lights dimmed when no one is present, again saving power.
In fact, a recent McKinsey report, Future proofing infrastructure in a fast changing world, argued that cities deploying a range of smart solutions could cut greenhouse gas emissions by 10–15 percent.
16. IP broadcasting

The broadcasting industry is currently looking at whether 5G technology can deliver both linear, and nonlinear broadcasts, whilst supporting them with enhanced media services (EMS), which are a combination of both. (‘Linear media’ refers to conventional TV or radio channels where programmes such as news, sport, entertainment and documentaries are scheduled by a service provider to be viewed at the time of transmission; whereas ‘nonlinear media’ is a type of media content that is offered on-demand at the request of the user.)
In 2019, a consortium of European broadcasting companies – led by virtualized media production company, Nevion – received a grant of €2 million from the European Union to create a remote production studio, powered by 5G technology. The project, known as VIRTUOSA , was selected from a list of 225 applications, and it has announced that it has taken its first technical step, opening an IP-based production studio, at Nevion’s Service Operations Center (SOC) in Gdansk, Poland.
This initial phase involves setting up an IP-based studio, built on industry standards (SMPTE ST 2110 and NMOS) and integrating equipment from multiple vendors, including: video cameras, a vision mixer, and a server from Sony; a multiviewer from TAG Video Systems; an audio mixer from Stagetec; a media analyzer from Telestream; IP switches from Mellanox; a PTP-compliant time and frequency synchronization from Meinberg; software-defined media nodes from Nevion; and all of it managed by an orchestration and SDN control system from Nevion.
17. 5G-powered studio lighting

Telia, together with the government-owned subscription station TV2 Denmark, and leading lighting company BB&S, has developed a partnership to showcase 5G-connected lamps, which can be used in TV and film production, and could one day transform the broadcasting industry.
Telia is a Swedish multinational telecommunications company, and mobile network provider, which operates in Sweden, Finland, Norway, Denmark, Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia. And as a ‘Tier 1 network’ operator, it is particularly focussed on 5G, and its ability to deliver new services.
And Telia has worked closely with TV2 and BB&S to test how 5G networking could be employed to improve lightning set-up and cost efficiency in broadcasting.
Since it was founded in 1999, BB&S Lighting has worked with numerous broadcasting clients around the world, and on movie projects such as Star Wars - The last Jedi, Interstellar, Alien: Covenant, Pirates of Caribbean, and Independence Day 2.
These set-ups can consist of 100s of lamps, every one of which needs to be connected with a power and a control cable. But using 5G, lights can be managed remotely, in real-time, providing huge efficiency and cost benefits.
18. Oil and gas
Centrica Storage and Vodafone have entered a partnership that will build the “gas plant of the future” at their Easington site, providing a 5G-ready mobile private network (MPN) for the facility, which will be the first of its kind in the UK’s oil and gas sector.
The new 5G infrastructure will enable Centrica Storage to automate, monitor, and centralize much of its critical maintenance and engineering operations. Real-time data will enable Centrica Storage to monitor its facility, streamline operational resources, and reduce costs. And the 5G network will even improve safety, enabling engineers to use virtual reality headsets to undertake training and critical maintenance tasks.
The 5G mobile private network will be built by Vodafone using Ericsson equipment, and will enable a number of industrial 5G use cases, such as connecting workers to digital data and applications across the entire site, increasing productivity whilst reducing cost, and all in a much safer environment.
19. Communication

Although the first wave of video calls over 5G will be on phones (which is why most 5G phones have better front cameras), in the long term expect full HD, 4K and even 8K video streams to be exchanged between 5G-enabled augmented reality (AR) devices and virtual reality (VR) headsets. With 5G’s ability to stream high capacity data packets in real-time, video-calling applications are about to get super-charged and go 360°.

And once video calling over 5G has improved, expect another giant leap to be made with the advent of live 3D holographic phone calls. Last year UK network operator Vodafone conducted the UK’s first live holographic call using 5G technology, with England and Manchester City Women’s footballer Steph Houghton using 5G tech to make a holographic call from Manchester. She appeared as a live 3D hologram on stage in front of an audience at Vodafone’s UK HQ in Newbury. European network operator Cosmote in Greece has also used the same tech to ‘holoport’ musicians in different physical locations on to a virtual stage where they played a piece of music together. 3D holographic calls require about four times as much data as a streamed 4K video – itself pretty data-intensive – though 5G’s low latency is just as important. In the long term the tech has potential applications for medical imaging, video conferencing and gaming.
20. Quality control

Logistics company Ice Mobility is testing on Verizon’s on-site 5G Edge platform, integrated with Microsoft Azure.
“When I heard that [Verizon] were partnering with Microsoft, it kind of sealed the deal for me,” said Mike Mohr, CEO of Ice Mobility. “We have always been a Microsoft house for everything we do in our business, and so it became a natural selection at that point.
Ice Mobility is using 5G and MEC to help with computer vision assisted product packing. By gathering data on product packing errors, in what is essentially real-time, the company has the potential to improve on-site quality assurance and save 15% to 30% in processing time.
“The goal is to make sure that the customers have the right product on their shelves when they need to sell it, and one of the ways we've always achieved this by making sure we double check every single shipment so that it has the right product in the box,” said Mohr.
“We're improving our quality control process through computer vision. We were able to do this by installing a high definition camera above every one of our pick lines. These cameras are powered by the 5G network, matching the data for a particular order to what the high definition camera is looking at inside the box. This validates that it's the right materials, and flags it up if it's not. The mech is that it literally knows the entire journey of the box.”
21. Empowering the high street

Verizon has partnered with TechUnited:NJ – an organization set up to help empower entrepreneurs and innovators in the New Jersey area – to create the “5G Impact Challenge”, which aims to provide a number of small businesses with new ways to use 5G technology, from solving operational pain points to improving the shopping experience for customers.
"In times like these, the world leans on technology to help us stay connected,” said TJ Fox, president of business markets at Verizon. “This is especially true for our local communities and retail shops, which is why Verizon has joined in this effort to show small businesses how 5G connectivity can open the door to new and immersive solutions as a way to interact with customers."
TechUnited worked with Verizon to select five small businesses within Verizon’s 5G Ultra Wideband mobility service footprint.
“Without the help of technology, we wouldn’t still be in business today,” said Dominic Yun, owner of SOHO Flower & Garden. “Prior to COVID, we had a website but didn’t do online sales. Thankfully, we were able to quickly shift to online orders which helped us stay afloat."
The companies selected for the “5G Impact Challenge” received Inseego MiFi M2100 5G hotspots and Samsung Galaxy S10 5G phones , as well as access to Verizon’s suite of small business services.
One of the most innovative 5G use cases in the scheme involved giving visitors to SOHO Flower & Garden the opportunity to view flowers in an augmented reality environment, so they could see how they were going to look before deciding to purchase them.
22. 5G use cases in port authorities

In 2020, Zeebrugge, one of the world’s busiest ports, with 45.8 million tons of goods annually transshipped through its docks, announced the completion of the first phase of a 5G-ready, industrial-grade private wireless network for the port.
By implementing the Nokia Digital Automation Cloud platform Zeebrugge hopes to streamline the logistical challenge of moving and tracking almost one million tons of goods each week. And the new platform will provide private wireless connectivity to more than 100 endpoints across the entire port operations.
The network is now being used for connectivity with tugboats, air pollution detectors, security cameras and quay sensors. And this partnership will enable Zeebrugge to deliver a range of new and enhanced 5G use cases to improve the port’s operational performance, and also showcase Zeebrugge as a leader in port transformation and digitalization.

And in January 2021, Terminal 5 of the Port of Seattle joined Zeebrugge in utilizing Nokia's DAC platform, working with Tideworks Technology, a provider of terminal operating technology for maritime facilities, to deploy Nokia Digital Automation Cloud (DAC) at Terminal 5, which is part of the Northwest Seaport Alliance, one of the largest container gateways in North America.
The LTE/5G private wireless network will be used to augment Wi-Fi, for enhanced redundancy and availability, and will support cable-free port and terminal operations using overlapping LTE Bands (B53 and B48). And it will be a valuable addition to Nokia’s growing list of industrial 5G use cases.
The introduction of an industrial-grade LTE/5G private wireless network will, the companies say, deliver major increases in efficiency, worker safety and terminal handling performance by “reducing the complexity of port flow”.
“These use cases illustrate the benefits of private wireless in a port or intermodal terminal operation,” said Matt Young, vice president of US Enterprise Sales, Nokia Cloud and Networking Services.
The new network will deliver connectivity indoors, and out across Terminal 5 operations, cranes, trucks and lifts, with Nokia DAC also being incorporated into ruggedized tablets and smartphones for comms and inventory applications.
23. Improving education facilities with 5G

Nova Southeastern University is a private Hispanic-serving multi-campus research university, with around 20,000 students, and its main campus in Fort Lauderdale-Davie, Florida, which has partnered with Mobilitie to deliver 5G to its students.
“We’re thrilled to provide our students, faculty and staff with an ultra-fast, state-of-the-art wireless network across our Davie campus,” said Tom West, Chief Information Officer of NSU.
This partnership with Mobilitie, the largest privately-held wireless infrastructure firm in the US, will enable the deployment of a cutting-edge 5G network across the Davie, Florida campus of Nova Southeastern University.
The 5G network will cover the 314-acre campus, including offices, classrooms, the library, residence halls, computer labs and athletic facilities, providing 5G access to students and faculty.
24. Transforming tourist attractions

Azoomee/Da Vinci , a media company focussing on children’s entertainment, has released a new Augmented Reality (AR) experience, which enables young visitors to Vienna’s Rathaus building to experience digitally enhanced environments as they move through the building.
"Azoomee’s work in this space has been especially noted for the way it combines new technology with the city’s heritage." City of Vienna spokesperson.
“We’ve been very impressed with the quality of contributions to Vienna’s challenge to find new 5G use cases, but Azoomee’s work in this space has been especially noted for the way it combines new technology with the city’s heritage,” said Dipl.-Vw. Klemens Himpele, chief information officer (CIO) der Stadt Wien. “The way its AR app transforms the Rathaus into a digital environment that combines both fun and learning for children is the perfect example of what we hope to achieve with 5G. We are excited by the possibilities that this AR experience could be adapted to other locations both in Vienna and beyond.”
The Azoomee/Da Vinci AR app enables kids to see historical figures jumping on trampolines, playing football, and performing skateboard tricks, whilst also transforming the landscape, even placing some rooms underwater, with sub-aquatic creatures swimming around features and furniture.
25. 5G-powered service bots

At the 2021t Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Shanghai, OrionStar, a company specialising in robotics tech, launched three service robots that include Qualcomm technology, enabling 5G connectivity and enhanced AI processing capabilities.
Powered by AI tech, OrionStar’s 5G Robotic Coffee Master served up beverages to attendees visiting Qualcomm Technologies’ booth at MWC Shanghai 2021. And based on the Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 5G Modem-RF System, this 5G bot can make 1,000 cups of coffee every day.
Elsewhere, the OrionStar Restaurant Service Robot roamed the convention floor, delivering beverages to guests. Whilst the 5G HomeBot was on display at the ‘5G mmWave’ booth, where it used Qualcomm’s Robotics Platform to answer questions from guests, conduct live Q&As, and provide personalized tours.
26. 5G IoT via nanosatellite

Open Cosmos , a UK company that specializes in satellite-based technology, has launched two commercial nanosatellites, one of which is a 5G IoT satellite for telecom operator Sateliot – the first of its kind to provide continuous IoT connectivity, merging satellite and terrestrial networks under the 5G protocol.
Both nanosatellites were created entirely at the Open Cosmos HQ in Harwell, known as the heart of the UK’s space industry, with the company having dedicated £4 million in R&D to the project, courtesy of funding from the UK Space Agency and European Space Agency.

“These launches mark a major milestone for Open Cosmos, demonstrating the capacity of low-cost satellites to provide IoT connectivity to remote parts of the world and collect data,” said Rafel Jordá, founder and CEO of Open Cosmos. “With £300bn of wider UK GDP supported by satellite services, Open Cosmos is key to unlocking these services and making them more accessible for businesses and governments across the world."
27. 5G-in-a-box

5G isn't merely an iterative change in existing network technology; it's a step change of an update, which enables a plethora of new opportunities, especially for the industrial sector.
One challenge, though, is how you test whether 5G is the right technology for you, without a massive commercial investment?
Thankfully, Singte is one company addressing this problem, with the launch of GENIE, the world’s first portable 5G platform. This new 5G technology will allow enterprises to experience 5G’s capabilities and trial use cases at their own premises.
GENIE creates an independent 5G network at any location where it is deployed, without the need for prior installation of equipment or infrastructure. And it has been designed to be compact and transportable, coming in a suitcase-sized container, which consists of a 5G network control kit and a standing mount with 5G radio antenna.
28. 5G 'digital twin' technology

Digital twin technology, as it sounds, enables you to create a digital version of a physical object or environment, which can then be interacted with remotely. This could entail the virtual recreation of a work space, where people could train safely using VR equipment, or, as is the case at Hyperbat, one of the UK’s largest independent vehicle battery manufacturers, it can be used to create ‘digital twins’ of products, which can be manipulated and viewed using VR headsets.
The Coventry-based company has partnered with BT, Ericsson and NVIDIA, to enable remote teams to connect, collaborate, and interact using a virtual 3D engineering model. And this digital twin project will be a world-first, which will allow design and engineering teams to walk around, and interact with, a 3D life-size model in real time.
Hyperbat colleagues in different locations will be able to work with a 1:1 product scale hologram of the design in-situ on the factory floor, review designs in real time, and manage workflows much more effectively.
29. 5G in airports

China is currently pushing ahead of western countries with its 5G roll-out, and it has now announced the world's first wall-to-wall gigabit 5G available in an airport.
China Mobile Chengdu used Huawei's 5G distributed Massive MIMO solution to deliver 5G in the new Chengdu Tianfu International Airport. Huawei's field tests showed that the user-perceived rate across the check-in areas exceeded 1Gbps, with the single-user rate increasing by 26% on average over common 5G networks, up to a peak of 1.25Gbps.
With major airlines like Chengdu Tianfu International Airport launching 5G-based smart travel services, such as VIP recognition, luggage tracking, and AR map navigation, to improve travel experience, high 5G speed is essential. In using Huawei's digital indoor small cells combined with 5G distributed Massive MIMO software functions, Chengdu Tianfu International Airport certainly achieves this.
30. World’s first 5G substation

Constellation, a smart substation trial from UK Power Networks , will utilize Vodafone 5G connectivity to help make them more efficient, and enable the freeing up of capacity for clean energy, in a bid to help reach the UK’s target of net zero carbon emissions by 2050.
UK Power Networks is the UK’s biggest electricity distributor, delivering power to more than eight million homes and businesses across London, the South East, and the East of England. (Electricity network operators, unlike energy suppliers, who focus on selling electricity, take care of the maintenance and operation of power lines and substations.)
The Constellation project is a world-first in 5G use cases, and will connect parts of the UK’s electricity network with high-speed 5G connectivity, with computers being installed in electricity substations so they can communicate with each other in real-time to improve efficiency.
Initially the Constellation project team will select multiple testing locations across UK Power Networks areas in the south-east of England, and at the University of Strathclyde’s Power Networks Demonstration Centre. And the companies say that it could save 63,702 tonnes of CO2 by 2050, which is the equivalent of 38,607 return flights from London to New York.
31. Indoor farm monitoring

AeroFarms and Nokia Bell Labs have announced that they have formed a multi-year partnership to combine their expertise and expand their joint capabilities in cutting-edge networking, autonomous systems, and integrated machine vision and machine learning technologies to identify and track plant interactions at the most advanced levels.
Nokia Bell Labs, the industrial research arm of Nokia, will contribute its ground-breaking autonomous drone control and orchestration systems, private wireless 5G networks, robust image and sensor data pipelines, and innovative artificial intelligence (AI) enabled mobile sensor technologies. Meanwhile, AeroFarms, a Certified B Corporation and global leader in indoor vertical farming, will contribute its commercial growing expertise, comprehensive environmental controls, an agriculture-focused data platform, and machine vision core foundation. This combination of innovative technologies allows AeroFarms to reach the next level of imaging insights that further enhance its capabilities as an industry-leading operator of world-class, fully connected smart vertical farms that grow the highest quality plants all year round.

How should you get 5G ready?
Prosumers and business owners will need to swap their old phones for a 5G ready version. There are already several 5G smartphones on the market, and EE markets five of them (the Oppo Reno 5G, Samsung Galaxy S10 5G , LG V50 ThinQ 5G, the OnePlus 7 Pro 5G and Huawei Mate 20 X 5G ). You can also pre-order the Samsung Galaxy Note 10 Plus. Similarly, you will also need a 5G plan, either from one of the big telecoms operators, or an MVNO. We are likely to see more offerings from mobile operators as 5G develops.
- Discover the best 5G networks in the UK and US
- Get your hands on the hottest 5G phones
- Millimeter wave : the secret sauce behind 5G
- The complete guide to 5G security
- We reveal the latest 5G use cases
- Discover the truth behind 5G dangers
- 5G towers : everything you need to know
Nicola Brittain is a freelance journalist with expertise in technology, telecoms, media and finance. She worked as news and analysis editor at Computing Magazine, and more recently has freelanced for Diginomica, Investment Week and Portfolio Adviser. She is currently writing a novel.
- 2 Apple’s iPhone SE 3 5G phone tipped to convert a billion Android phone users
- 3 Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners to acquire 5G innovator Dense Air
- 4 2G and 3G to be phased out by 2033 increasing the capacity of the UK’s 5G coverage
- 5 Ericsson and Vodafone to launch new 5G lab in Spain

Move fast, think slow: How financial services can strike a balance with GenAI

Take on Tomorrow @ the World Economic Forum in Davos: Energy demand

Perspectives from the Global Entertainment & Media Outlook 2024–2028

Climate risk, resilience and adaptation

Business transformation

Sustainability assurance

The Leadership Agenda

Global Workforce Hopes and Fears Survey 2024

The s+b digital issue: The CEO’s sustainability checklist

The New Equation

PwC’s Global Annual Review

Committing to Net Zero

The Solvers Challenge
Loading Results
No Match Found
The Impact of 5G: Creating New Value across Industries and Society
21 January, 2020

Going beyond theory for the future of 5G
In collaboration with the World Economic Forum (WEF) we have published a new whitepaper, Creating New Value across Industries and Society, outlining the ways to realize the large estimated economic output potential of 5G by taking a bottom-up approach through a use-case-driven analysis. You can view the full paper here .
Rolling out 5G is critical because it will enable unprecedented levels of connectivity, upgrading 4G networks with five key functional drivers: superfast broadband, ultra-reliable low latency communication, massive machine-type communications, high reliability/availability and efficient energy usage. Together, these defining features will transform many sectors, such as manufacturing, transportation, public services and health.
The economic and social value of 5G networks
The analysis of 40 sample use cases in a wide range of key industries within this paper establishes linkages between commercial and societal impact of 5G, discussing how the functional drivers of 5G could enhance the output of these use cases as 5G networks evolve.
What is clearly apparent is that there is significant economic and social value to be gained from the widespread deployment of 5G networks. Technological applications, enabled by a set of key functional features, will both facilitate industrial advances—improving their bottom line—and enhance city and citizen experiences.
However, to accelerate the adoption of 5G, new collaboration models among stakeholders are needed, along with clear methodologies to estimate the social value creation, which will enhance the business case for 5G. This in turn will require the development of new business models, particularly within the Telecommunications industry, a topic we have covered in our whitepaper Making 5G Pay .
The 40 use cases outlined in this paper clearly demonstrate that 5G is here, now
However, the transition to 5G networks can only be achieved when all stakeholders—citizens, the private sector, regulators, national governments and cities—collaborate to effectively address these issues. The insights and recommendations in this white paper aim to pave the way towards accelerating a global, sustainable and inclusive transition to 5G networks, creating significant economic and social value.
You can view the full paper here The Impact of 5G: Creating New Value across Industries and Society
Related content
Making 5G pay
Telecoms are set to invest heavily in 5G. But to get a fair return, companies should explore new service offerings, use cases and business models.
The key functional drivers of 5G will unlock a broad range of opportunities, including the optimization of service delivery, decision-making, and end-user...
Technology, Media & Telecommunications (TMT)
Our industry professionals deliver consulting, tax and audit insights and advice to the world's leading TMT companies. Explore how PwC can create value for you.

Wilson Chow
Global Technology, Media and Telecommunications (TMT) Industry Leader, PwC China

Hazem Galal
Partner, Global Cities and Local Government Leader, and Global Smart Mobility Co-Leader, PwC Middle East

© 2017 - 2024 PwC. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.
- Legal notices
- Cookie policy
- Legal disclaimer
- Terms and conditions
Development of the Digital Economy: A Case Study of 5G Technology
- Conference paper
- First Online: 22 April 2022
- Cite this conference paper

- Yuchan Wang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5050-1028 12 , 13
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Information Systems and Organisation ((LNISO,volume 54))
2080 Accesses
4 Citations
Digital technology is widely used in related industries of the national economy and has become a new driving force for economic development. This paper takes 5G as an example to discuss the integration development of the digital economy. As a new type of communication technology, 5G is playing an increasingly important role in modern society. At present, more and more industry fields have developed and used 5G technology. The competition of 5G is not only competition in the communications field but also competition between industries and economies, between countries and regions. It is also a good opportunity to open up various industries and enter the information revolution. The 5G technology will completely change the current operating mode of many industries and bring greater convenience to people. Compared with traditional communication technology, 5G technology has outstanding features in all aspects, such as new network architecture, flexible spectrum sharing technology, fast transmission speed, strong transmission stability, and short delay.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Introduction to 5G and Beyond

Summary and Analysis of Typical Technologies in 5G
Towards the fulfillment of 5g network requirements: technologies and challenges.
Badic, B., Drewes, C., Karls, & Mueck, I. M. (2016). Rolling Out 5G: Use Cases, Applications, and Technology Solutions . Munich, Germany: Intel Deutschland GmbH.
Google Scholar
Chen, S. Z., Sun, S. H., & Wang, Y. M. (2015). A comprehensive survey of TDD-based mobile communication systems from TD-SCDMA 3G to TD-LTE(A) 4G and 5G directions. China Communications, 12 (05), 40–60. https://doi.org/10.1109/CC.2015.7084401
Article Google Scholar
Chen, X. H. (2020). 5G + Block-chain: Adding “fast + security” dual power to the digital economy. Journal of Tianjin Vocational College of Business, 02 , 3–16.
Dai, L. L., Wang, B. C., & Yuan, Y. F. (2015). Non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G: Solutions, challenges, opportunities, and future research trends. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53 (06), 74–81.
Dai, Z., Wang, X. Q., & Wang, W. (2020). Research on 5G edge computing business continuity technology for autonomous driving. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 32 (09), 808–815.
Ding, Z. G., Lei, X. F., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2017). A survey on non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G network. Research Challenges and Future Trends, 35 (02), 2181–2195. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2017.2725519
Dong, W., & Zhou, Y. (2020). Application of 5G communication technology in urban rail transit video monitoring system. Urban Rail Transit Research, 23 (05), 153–155.
Felita, C., & Suryanegara, M. (2013). 5G key technologies: Identifying innovation opportunity. In International Conference on QiR, Yogyakarta (pp. 235–238).
IEEE Spectrum. (2017). Everything You Need to Know About 5G . Retrieved November 8, 2021, from https://spectrum.ieee.org/everything-you-need-to-know-about-5g#toggle-gdpr
Jia, X. X. (2020). Application of 5G communication technology under the situation of Internet of Things. Digital World , 23–24.
Larsson, E. G., Edfors, O., & Tufvesson, F. (2014). Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52 (04), 186–195. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2014.6736761
Li, J. Q. (2020). The development and research of virtual reality technology and augmented reality technology in the field of construction machinery. China Market, 04 , 171–173.
Liu, X. C., & Dong, W. (2020). Talking about the application of 5G technology in the construction of smart cities. Computer Products and Circulation, 03 , 46–47.
Pan, B. L. (2019). New 5G network technology and core network architecture. Information and Computer (Theoretical Edition), 06 , 172–173.
Pradels, J. L. (1974). The Guide: An Information System (Ph.D. Thesis). University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign .
Ren, X. (2020). Research on the development of in-depth integration of contemporary 5G communication technology and artificial intelligence. Farm Staff, 08 , 131–136.
Schwab, K. (2016). The Fourth Industrial Revolution . World Economic Forum.
Sen, Z. G. (2020). Discussion on 5G ultra-dense networking key technologies and networking architecture. Telecom Engineering Technology and Standardization, 33 (02), 64–67.
Shi, W. (2020). 5G + Industrial Internet construction technology and economic model. Information and Communication Technology and Policy, 03 , 1–7.
Singh, R. K., Bisht, D., & Prasad, R. C. (2017). Development of 5G mobile network technology and its architecture. International Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering & Research (IJRTER), 03 (10), 195–201.
Wang, H. C., Xu, H., Cheng, Z. M., & Wang, K. (2015). Current research and development trend of 5G network technologies. Telecommunications Science, 31 (9), 149–155.
Wang, L., & Yang, F. M. (2020). Analysis of key technologies and practical applications based on 5G networks. Digital World, 05 , 30–32.
Yi, Z. L., Sun, Q., Wu, J., & Duan, R. (2020). Standards and application progress of artificial intelligence in 5G wireless networks. Information and Communication Technology and Policy, 03 , 23–30.
You, M. H., Yan, M. L., & He, M. Z. (2020). Analysis of green logistics capability expansion model driven by 5G application—taking Cainiao and Jingdong as examples. Business Economics Research, 02 , 103–106.
You, X. H. (2014). The 5G mobile communication: The development trends and its emerging key techniques. Science Sinica Information, 44 (5), 551–563.
Zhang, C. (2020). 5G in the application of environmental protection information. Computer Products and Circulation, 01 , 186–189.
Zheng, B. (2020). Application of information system in the prevention and treatment of new coronavirus. Computer System Application, 29 (01), 272–275.
Zheng, J. G. (2020). Application analysis of the internet of things based on 5G technology. Integrated Circuit Applications, 37 (04), 50–51.
Zheng, T. T., Yu, H., Song, X., Tan, L., & Yang, Z. (2020). The application prospect of 5G chain network in the digital economy. Wireless Internet Technology, 24 , 11–12.
Zhu, X. T. (2020). Research on 5G evolution technology of 3GPP R16. Electronic Technology Application, 46 (09), 1–7.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Economics, Southern Federal University, 88, M. Gorkogo St, Rostov-on-Don, 344002, Russian Federation
Yuchan Wang
Henan University of Economics and Law, Jinshui Road 180, Zhengzhou, 450046, Henan, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yuchan Wang .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Bristol Business School, University of the West of England, Bristol, UK
Vikas Kumar
State Key Laboratory of Precision Electronic Manufacturing Technology and Equipment, School of Mechanical Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
Department of Regional Industrial Policy and Economic Security, Institute of Economics, Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Ekaterinburg, Russia
Victoria Akberdina
Evgeny Kuzmin
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Wang, Y. (2022). Development of the Digital Economy: A Case Study of 5G Technology. In: Kumar, V., Leng, J., Akberdina, V., Kuzmin, E. (eds) Digital Transformation in Industry . Lecture Notes in Information Systems and Organisation, vol 54. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94617-3_16
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94617-3_16
Published : 22 April 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-94616-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-94617-3
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Newsletters
How to accelerate the world into the 5G era
The innovative yet consumer-centric groundwork enabling 5G smartphones to empower users en masse.
Provided by vivo
Demand for 5G smartphones is reaching an all-time high
In 2021, consumers and institutions alike are fast-tracking a digital revolution in an unprecedented era of social distancing and remote work—a trend that may continue long after the pandemic subsides.
The time is ripe for many commercialized products and services to ride the wave of unparalleled high-speed connectivity and minimal latency enabled by 5G. Yet, the technology at the forefront of them all is without a doubt the smartphone. By combining mobile telephone and computing functions within a singular multi-purpose device, smartphones have brought about a profound scale of mobility and accessibility with one-stop services that empower consumers across every aspect of their daily lives.
Some may look back fondly on the good old days of the mobile phone, when voice calls and text messaging were all we had access to, in the absence of addictive social media platforms and the seemingly endless barrage of notifications we receive nowadays. Nonetheless, the instantaneous connectivity of ever-improving mobile networks and increasingly diverse applications of smartphones will undeniably continue to bring value to users.
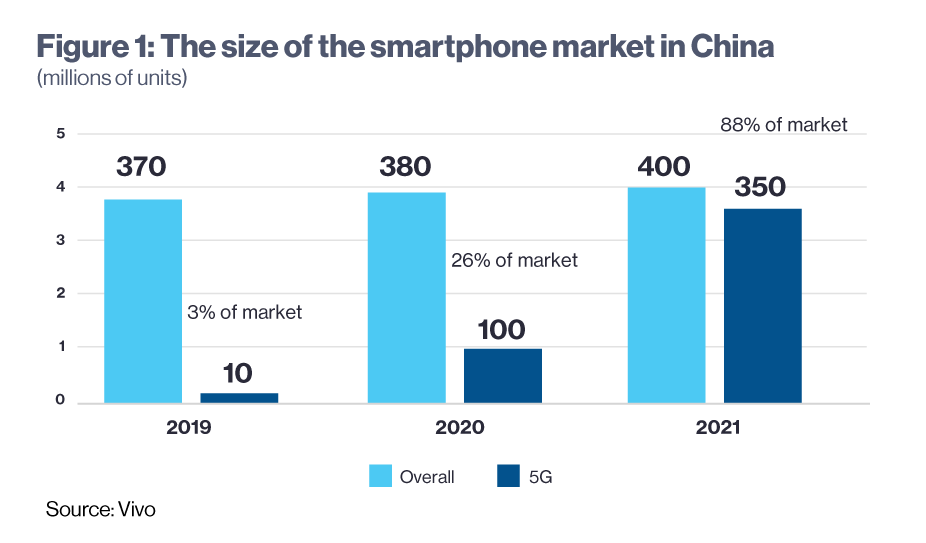
According to a forecast by vivo, one of the leading smartphone makers, demand for 5G devices is catching up to the entirety of the smartphone market as researchers recorded exponential growth between 2020 and 2021.
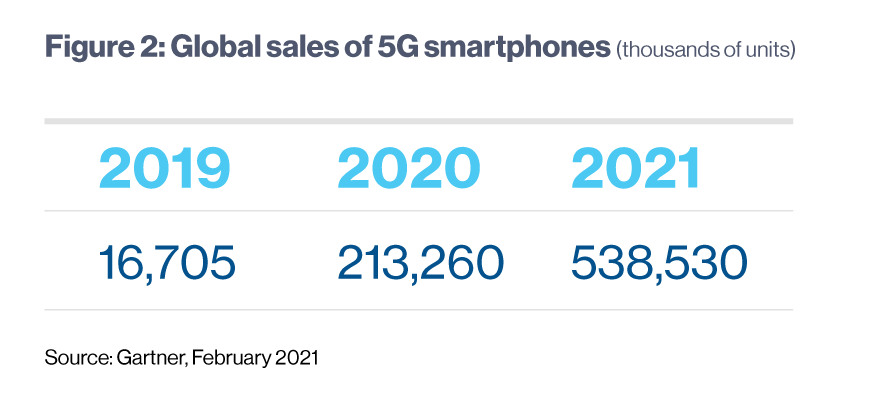
Another report, published by Gartner, showed that the worldwide demand for smartphones with 5G capabilities more than doubled this year. “In 2020, consumers reduced spending on smartphones, but the availability of new products will see users drive significant uptick in demand in 2021. Lower-end 5G smartphones, which are becoming more prevalent outside China, are poised to drive more momentum for 5G smartphones in 2021 across all regions,” said Anshul Gupta, senior research director at Gartner.
How did we get to where we are today, and how did smartphone brands take us here?
Defining the fifth generation
5G is the latest global wireless standard, otherwise known as the 5th generation of cellular mobile communication technology. Compared to 4G LTE technology, 5G increases flux density a hundredfold and connection density tenfold. This allows for a new kind of digital infrastructure that can connect virtually everything and everyone via peak data transmission speeds with minimal latency to provide a uniform experience to us all, culminating in higher efficiency and optimized performance to empower new user experiences.
Hundreds of thousands of industries are becoming integrated, owing to the reliable and streamlined network between machines, devices, and other digital objects. With many creative applications ranging from augmented reality/virtual reality experiences to vehicle-to-everything driverless cars and many more, 5G will provide humankind with the foundation to establish smart cities with comprehensive internet-of-things technologies that can efficiently restructure our lived environments and redefine our everyday lifestyles.
It goes without saying that 5G can facilitate limitless applications, on both industrial and consumer levels. For tech-savvy individuals accustomed to heavy device usage loads, 5G will be game-changing by elevating their collective digital devices into powerful, cloud-synced gateways capable of tapping into the most resource-intensive applications and data streams. Many industries are currently undergoing paradigm shifts as enterprises and countries race to propel society into the next phase of technological transformation.
Gearing up for the 5G race – a deep dive with vivo
The 5G technical standard was formed by a series of innovative R&D efforts led by companies such as vivo. The 5G products or services consumers are presented with today are actually a refined conglomeration of technologies formulated by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), a consortium of international telecom standards organizations that provide a stable platform for collaboration.
As the entire world becomes familiar with the limitless possibilities of contemporary mobile communications technology, consumers are looking to arm themselves with devices that contain cutting-edge capabilities in order to complement their connected and fast-paced daily lifestyles.
Corporations and governments are both racing to gear up in preparation for the new digital gold rush. Unbeknownst to many, battles are fought and alliances are formed every day as companies cannibalize each other in the race to hold the most patents for 5G technologies.
Vivo, one of the top players, has participated in the 3GPP 5G standard formulation for over five years. As one of many companies that set their sights on 5G technology, vivo established special 5G task forces back in December 2016 across Beijing and Shenzhen, China. One month later, vivo made its debut at the 2017 3GPP meeting. Since then, vivo has submitted over 5,000 5G proposals to the 3GPP, leading to 15 technical features and getting three technical projects approved. With more than 100 global standard experts staffed at its communication research institute, vivo now holds over 3,000 patents for 5G inventions.
User-oriented innovation
As a leading smartphone company with in-depth R&D capabilities, vivo is dedicated to accelerating the empowerment of consumers en masse in this new era by designing cutting-edge 5G smartphones that are available at every price point. Having amassed over 400 million users worldwide, vivo has a deep understanding of evolving consumer demands and strives to bridge users with the digital world by becoming one of the leading contributors to 5G technology in the industry.
“The main gateway for consumers to indulge in the new digital era must be the most accessible, portable, cost-effective, and readily available digital device of them all: the smartphone. A leader in both smartphone manufacturing and 5G connectivity, vivo has been designing a diverse lineup of products that are ready for the next generation of connectivity to bring joy to users worldwide at modest price points,” says Rakesh Tamrakar, 5G standards expert at vivo.
Tamrakar has 20 years of experience in the mobile communications industry. He is one of the lead delegates representing vivo in the 3GPP, holds numerous patents, and has chaired multiple 3GPP RAN1 sessions (which specify the physical layer of radio interfaces) that led to the successful standardization of MIMO, NR on unlicensed spectrum technologies. Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) is a key 5G technology that increases throughput and signal-to-noise ratio, while NR is a new radio interface and radio access technology for cellular networks. He has authored and contributed numerous technical papers on the subject of 3GPP RAN1 in 3G, 4G, and 5G standards.
“Brought to life by our strong R&D network across nine innovation centers and supported by research teams across the globe, vivo knows consumers best within the industry. We focus on innovations in hardware design and the software ecosystem to improve terminal performance and user experiences. Putting end users at the center of everything we do, vivo invests heavily into 5G connectivity to reach the stage of product realization and getting this technology into the hands of consumers,” he adds.
5G research, standardization, and industrialization by vivo
Vivo’s unique user-oriented innovation is the genesis behind its numerous patented contributions to 5G standards, many of which have been universally acclaimed at the 3GPP meeting and are currently already being adapted for everyday smartphone users.
One of vivo’s most notable contributions includes the standardization and performance enhancement of Rel-17 multi-SIM technology. Previously, an incoming voice call from one competing 5G SIM card would interrupt the data flow of the other, resulting in abysmal performance as one would cancel the other. Having discovered early on that consumers had a preference for 5G smartphones with dual-SIM card slots for greater flexibility in different usage scenarios, vivo researchers successfully sought to negate the clash, leading to the existence of multi-SIM 5G smartphones on the market today.
The initial implementation of 5G technology was initially found to be quite resource-draining compared to devices running on 4G. However, consumers had grown accustomed to the substantial usage time allowed by previous smartphones.
Always innovating with the user in mind, the Rel-16 terminal power-saving technology patented by vivo manages to simplify terminal actions. It lowers normal energy consumption by creating a new “dozing” state, allowing the device software to become inactive while the hardware becomes idle. 5G smartphones can now intelligently catch every chance to take a rest, thereby prolonging battery life.
Additionally, vivo underwent algorithm and system optimization to facilitate this technology, combined with 120-watt fast charging to ensure complete user satisfaction with their devices. Select vivo smartphones are housed with a superconducting carbon fiber liquid cooling system to prevent device overheating, which is especially prevalent during intensive multimedia entertainment or e-sports usage scenarios.
Another issue raised by 5G technology is the increasing number of antennas and components installed inside a smartphone. However, users are relentless in their pursuit for ultra-thin smartphones encased in sleek metallic exteriors. Never one to disappoint, vivo’s proprietary 3D stack design uniquely encases all of this industry-leading technology to allow new 5G smartphones to be even slimmer than its 4G predecessors.
6G visionary
As 5G commercial networks are gradually deployed around the world and progressively advanced devices increasingly permeate every aspect of our livelihoods, thought leaders of the mobile industry are already looking forward to its next generation: 6G.
Vivo is part of a select few that hold the extensive expertise and in-depth understanding of consumer needs in order to turn this vision into a reality. Along with leading companies, research groups, and academic institutions, this combined elite collective is expected to reach a consensus on the ideation and requirements for this future generation of connectivity. To kickstart this exciting new era, the vivo Communications Research Institute (VCRI) released two white papers in late 2020 that break down the facets of 6G technology. Providing a diverse set of hypothetical scenarios and case studies, vivo communication standard experts have analyzed how the sixth generation will embody much more than technological transformation as it merges our physical and digital worlds.
“Currently, mobile infrastructure is still relatively isolated from the physical world, existing solely as an auxiliary tool for consumer usage. An extreme degree of seamlessness will be required to dynamically connect our physical surrounding with the omnipresent digital systems. In 2030 and beyond, 6G standard technologies will begin to foster a ubiquitous, sophisticated, real-time, and fully integrated digital world. This new realm will revolutionize thousands of industries with an extraordinary variety of applications to result in an efficient, sustainable, and eco-friendly future world,” says Tamrakar.
6G communication systems will comprise many device terminals to realize the agile perception and accurate control between digital systems with our physical domain; this is comparable to the nerve endings that perceive essential information from every inch of the human body for our central nervous system to take responsive measures. As such, a large number of harmoniously connected and intelligent terminals in the form of smartphones or wearable devices will be fundamentally required in order for the entire IoE (internet-of-everything) system to be effective. To that end, vivo has launched a smartwatch, wireless earbuds, and Jovi AI assistant to introduce users to its own flourishing digital ecosystem.
Notwithstanding all of this exhaustive groundwork laid by technology companies, the 5G race and the 6G marathon are far from over. Nonetheless, affordable smartphones with innovative features will continue to act as the interface for everyday users to engage with the all-encompassing network infrastructure, to accelerate the impending intelligent transformation of society.
Keep Reading
Most popular.

The year is 2149 and …
Novelist Sean Michaels envisions what life will look like 125 years from now.
- Sean Michaels archive page

People are using Google study software to make AI podcasts—and they’re weird and amazing
NotebookLM is a surprise hit. Here are some of the ways people are using it.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page

AI and the future of sex
The rise of AI porn could change our expectations of relationships.
- Leo Herrera archive page

Beyond gene-edited babies: the possible paths for tinkering with human evolution
CRISPR will get easier and easier to administer. What does that mean for the future of our species?
- Antonio Regalado archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.

IMAGES
VIDEO