Online Master's in Education


Contact Information
Connect with program staff.
If you have program-specific questions, please contact OEL Associate Director Nicole Barone .
Additional Information
- Download the Master's Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
Today’s education landscape needs leaders like you — dynamic educators and innovators committed to making sustainable and scalable change for all students by building on your professional experience in PreK–12 classrooms and districts; on college and university campuses; or in philanthropies, nonprofits, policy organizations, and ed-tech initiatives.
That’s why the Harvard Graduate School of Education launched an online Master's in Education Leadership, a two-year, part-time Ed.M. program with Higher Education and PreK-12 pathways specifically designed for working education professionals who bring at least seven years of relevant or transferrable work experience. The program will strengthen the invaluable skills you’ve already developed and give you the tools to propel yourself to new leadership opportunities and to even greater impact.
“Skilled leadership is essential to creating opportunity and overcoming the longstanding inequities that create barriers to success. At HGSE, we are committed to helping you meet today’s complex challenges by becoming the type of leader education needs.” Bridget Long Dean and Saris Professor of Education and Economics Harvard Graduate School of Education
A New Option for Experienced Educators
The online Master's in Education Leadership from HGSE consists of a diverse cohort of professionals like you — leaders who are advancing in their careers, and who bring important perspectives grounded in real-world challenges. Our program is conducted almost exclusively online — except for one short on-campus experience, where you'll meet your cohort in person and build community prior to the start of the first fall semester.
The program offers a distinctive Harvard experience — including deep engagement and interaction with Harvard faculty and talented peers, as well as a lifelong professional network — within an intentionally designed curriculum and robust opportunities for mentorship and coaching. The program is career-embedded — so you can immediately apply what you are learning, in real time, to the work you are doing on the ground.
Two Pathways: Higher Education and PreK–12
In the online Master’s in Education Leadership, you will choose between two Professional Pathways — Higher Education or PreK–12 — that align with the area of practice or the student community in which your work will make an impact. Students interested in advancing into senior leadership roles in colleges and universities, or in organizations that impact higher education, should study in the Higher Education Pathway . Students who want to do change-making work within the education ecosystem on behalf of students from early childhood to secondary education levels should select the PreK–12 Pathway .
Our prescribed curriculum is intentionally designed to meet your professional needs. It is anchored in both foundational knowledge and core competencies in education leadership related to the U.S. education system. You will also complete pathway-specific courses to advance your leadership in higher education or preK–12 education, as well as the Foundations courses. You will also have the opportunity to select courses from a small subset of electives. A minimum of 42 credits are required to graduate with an Ed.M. degree from HGSE.
The main elements of the curriculum are:
Foundations Courses
Throughout the two-year program, you will participate in Foundations courses in four areas: How People Learn, Leading Change, Evidence, and Equity and Opportunity. Through the Foundations, you’ll build core skills central to the profession of education.
- The online Ed.M. program commences with How People Learn, which runs online June–July and requires a time commitment of 12–15 hours per week.
- Additional Foundations learning goals and experiences tied to Leading Change and Equity and Opportunity will be incorporated into other required courses during your two-year program.
Professional Pathways
All students will choose between the Higher Education and PreK–12 Pathways. Throughout the program, you will take both cross-pathway courses and pathway-specific courses. Cross-pathway courses will allow you to develop leadership skills that are important across sectors, as well as have discussions about how higher education and preK–12 can work more effectively together. Cross-pathway courses include:
- Real Talk: The Art and Practice of Communications
- Strategic Finance for Nonprofit Leaders
Pathway-specific courses are directed to the knowledge and skills important for leadership in the Pathway professional setting.
Elective Coursework
Students will have the opportunity to choose from a curated list of electives during the optional January terms, and during the fall and spring of their second year. Sample elective courses:
- Law and Higher Education
- Leading a School through Challenge and Crisis
- Race, Equity, and Leadership
- Teaching Exceptional Learners in Inclusive Classrooms
- Why Can’t Higher Education Change?
- Writing Workshop
Note: Though some courses may include comparative and international examples, applicants should expect a focus on leadership within U.S. domestic educational institutions and systems.
Leadership Core Competencies
To help you manage, lead, and implement change in complex organizations, our curriculum explores the core leadership competencies that you'll need to elevate your skills, knowledge, and expertise, wherever you are in your career. Throughout your coursework, you will strengthen your ability to:
- Lead change and think strategically
- Foster productive organizational conditions
- Navigate politics and practice political inclusion
- Communicate effectively
- Cultivate self-development and team professional development skills
Higher Education Pathway
All students will choose between the Higher Education and PreK–12 Pathways. The Higher Education Pathway prepares you to be a dynamic leader in a diverse range of postsecondary education contexts. It is designed to increase your knowledge of the practices, policies, processes, challenges, and opportunities in American postsecondary education. You will enhance your repertoire of strategies and management skills for tackling critical issues and introducing change — while preparing you to advance in your current career or move into other important leadership roles in higher education.
Sample courses for the Higher Education Pathway:
- Creating the Future of American Postsecondary Education
- Higher Education Leadership & Governance
- Student Affairs in Higher Education: Theory-Driven Practices to Help Students Thrive
You will also have the opportunity to engage with accomplished leaders through HGSE’s unique President-in-Residence program.
Students interested in the Higher Education Pathway currently hold administrative and mid-level leadership roles:
- Colleges and universities, including in academic affairs, student affairs, admissions and enrollment management, advancement, and institutional research
- Nonprofit education organizations
- State and federal government agencies
- Policy organizations focused on higher education
PreK–12 Pathway
All students will choose between the Higher Education and PreK–12 Pathways. The PreK–12 Pathway equips you to advance your leadership across the preK–12 landscape, including in such positions as teacher leader, principal, afterschool director, education agency representative, education nonprofit/philanthropic leader, or education entrepreneur.
Sample courses for the PreK–12 Pathway:
- Strategic Leadership in the PreK–12 Ecosystem
- Creating Conditions for Effective School, Family, and Community Partnerships
- Leading Learning
Students interested in the PreK-12 Pathway currently hold administrative and mid-level leadership roles in:
- PreK–12 schools, including as principals, assistant principals, and department heads
- Nonprofit education organizations (I.e., foundations, advocacy organizations, technical assistant organizations).
- Policy organizations focused on preK–12 education
Projected Time Commitment
Courses combine synchronous meetings and asynchronous work and assignments. Live or synchronous aspects of required courses will occur on weekdays (Monday–Friday) between 6 and 9 p.m. ET . Some elective courses, outside the required curriculum, may be offered at alternative times. On average, this degree requires 12 to 18 hours of work per week, though the weekly commitment will vary by term, courses taken, and students' own work styles. Students can expect to spend approximately five to seven hours per week in synchronous online class sessions with faculty members and classmates. The remaining hours will be spent working independently on asynchronous class preparation, in self-scheduled small-group work with other students or working on assignments.
Weekly Time Estimate
To complete the online Ed.M. in Education Leadership, students must complete 42 total credit hours of coursework over the two-year program. While the weekly time commitment varies, the graphic below provides a snapshot of the estimated weekly time commitment students may experience during the fall and spring semesters, when they will typically take 8 credits, the equivalent of two courses .
Synchronous
Includes live, scheduled sessions with faculty members and other students.
Asynchronous
Self-paced activities, discussion posts, and other course-related work.
Assignments
Readings, projects, papers, research, etc.
Total Estimated Weekly Hours
Hours reflect estimates and vary by term, course, and student work style.
Occurs between Monday-Friday, according to a specific schedule.
Asynchronous work and assignments will have clear deadlines or milestones, but students can set their own schedules to complete this work. Note that there may be days or weeks during the semester that are busier than average, requiring more than the estimated time shown.
Program Faculty
The faculty co-chair for the Higher Education Pathway is Francesca Purcell . The faculty co-chair for the PreK–12 Pathway is Irvin Scott .
Faculty Co-Chairs

Francesca Purcell
Francesca Purcell is a specialist in higher education policy and practice, with expertise on topics including college completion, student transfer, and developmental education.

Irvin Leon Scott
A former teacher, principal, assistant superintendent, chief academic officer, and foundation leader, Irvin Scott's focus is on education leadership and faith-based education.
James P. Honan

Karen L. Mapp

Timothy Patrick McCarthy

Mary Grassa O'Neill

Alexis Redding

On-Campus Experience
Prior to kicking off your first fall semester, you will participate in the On-Campus Institute, an immersive experience on the HGSE campus in Cambridge. This will provide the opportunity to not only form deep relationships with your cohort, but also learn together with the faculty and advisers with whom you will spend two years. The immersive residential experience is a core component to the two-year degree program that is required of all students in the program.
Over several days in late July and/or early August, you and your fellow peers will discuss your professional experiences and examine some of the persistent challenges in your organizations. You will immerse yourself in rich exercises and community building, set expectations of what it means to be in a rigorous HGSE degree program, and set intentions for yourself, your cohort, and your course of study.
Career Pathways
The Master's in Education Leadership Program prepares you to advance to a senior leadership role in a variety of career pathways, including:
- Academic affairs
- Admissions and financial aid
- Development
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Institutional research
- Student affairs
PreK-12 Pathway
- Education entrepreneur
- Executive director for an education nonprofit
- Principal* or head of school
- Program officer for a foundation
- School department head
- School designer and developer
- School district or network leader
- Teacher leader
Overall Program
- Education nonprofit CEO/COO
- Educational advocate and organizer
- Entrepreneur
*Note: This program is not able to provide principal certification at this time.
Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Online Master's in Education experience and the impact its community is making on the field:

The Impact We Hope to Have
Kamal James and Inella Ray will be honored with the Intellectual Contribution Award for the Online Master's in Education Program

Same Questions, One Year Apart
Online Master’s in Education students reflect on their first year in the program
Find the Best Online Master's in Education Programs
Some school districts require their teachers to earn an education master's degree within five years of entering the profession. Completing an education degree online can lead to career growth for current and future educators.
Best Online Education Programs
U.S. News evaluated several factors to rank the best online education degree programs, including faculty credentials, graduation rates and reputation.
Clemson, SC
Gainesville, FL
Charlottesville, VA

Online Education Program Specialty Rankings
Explore the best online education master’s programs offering the specialties below and get a feel for the curriculum and topics each area covers.
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Educational Administration
- Instructional Media
- Special Education
Online Education Program Concentration Rankings
See how online education master’s programs rank in concentrations offered, and discover more about where each focus area can take your career.
- Educational Administration and Supervision
- Educational Assessment, Evaluation, and Research
- Educational/Instructional Media Design
- Educational Psychology
- Education, General
- International and Comparative Education
- Bilingual, Multilingual and Multicultural Education
- Social and Philosophical Foundations of Education
- Special Education and Teaching
- Student Counseling and Personnel Services
- Teacher Education and Professional Development, Specific Levels and Methods
- Teacher Education and Professional Development, Specific Subject Areas
- Teaching Assistants/Aides
- Teaching English or French as a Second or Foreign Language
Online Graduate Education Degree Overviews
The degree types below can help you tailor your online education degree. Learn how an online early childhood education master's degree is different from an online education specialist degree, for example, to discover which is right for you.
- Adult Education
- Child Development
- Curriculum and Instruction (doctorate)
- Doctor of Education
- Early Childhood Education
- Education Administration
- Education Administration (doctorate)
- Education Leadership and Administration
- Education Specialist
- Educational Leadership (Doctorate)
- Educational Technology (Doctorate)
- Elementary Education
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Higher Education (doctorate)
- Higher Education Administration
- Instructional Technology
- Master of Arts in Teaching
- Master of Education
- Math Education
- Online Doctorate in Educational Psychology
- Online Teaching
- Reading and Literacy
- School Counseling
- Science Education
- Secondary Education
- Social Studies Education
- Special Education (doctorate)
Online Undergraduate Education Degree Overviews
Explore more in depth what it takes to earn an online education degree using the following guides.
- Early Childhood Education (Associate)
- Education (Associate)
- English Language Learning
FAQs about Online Education Master’s Programs
Online education degrees are respected when earned from an accredited program with a good reputation. Institutions must be accredited by an organization that has been recognized by either the U.S. Department of Education or the nonprofit Council for Higher Education Accreditation. Many institutions award the same graduate education degrees to students enrolled in online and on-campus programs. However, some schools do have different in-person and online degree offerings, so students should check that the specialization they’re interested in is offered online.
Employers want to know that you earned your online education degree from an accredited program and that you’re certified to teach in the state in which the job is located. If you enroll in a graduate program that offers state certification as part of the degree requirements, where you obtain your education master’s degree matters. In any case, hiring managers may be more interested in why you earned your degree and how it fits with your career goals than whether you earned it online or in person.
Enrolling in an online graduate education program is not an inherently easier option than enrolling in a traditional in-person program. Any format of an accredited graduate-level education program is rigorous. While the flexibility of online school helps students who are balancing work and family stay on track, many online programs have the same study materials and time commitments as on-campus programs.
Not everyone who enters an online education master’s program will attain a degree, either. According to U.S. News survey data, 73% of online master's in education students who entered in the 2018-2019 academic year graduated by June 2022. Online courses may require students to have more self-discipline to complete assignments. And some online programs still require in-person activities, like student teaching, for credit.
The time and effort to attain your education master’s degree may be worth it to earn a higher salary. Prospective students should weigh the cost of graduate student loans against the likely long-term payoff from a graduate degree. Opportunities for advancement in leadership positions are more likely for those who earn an education master’s degree than for those who have a bachelor’s degree alone. Education professionals with master’s degrees can become school principals or administrators, roles that earn a higher salary than most teaching positions. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , the median annual salary for elementary, middle and high school principals was $98,420 in 2021. High school teachers , who need at least a bachelor’s degree, earned a median salary of $61,820 in 2021.
A graduate education degree helps you advance your career to administrative and leadership roles and keeps you competitive for new opportunities. You can use your degree in settings including pre-K-12 schools, colleges and universities, nonprofits, government agencies, and policy organizations.
In addition to being prepared for higher paying principal positions, graduates of education-related master’s degrees can become postsecondary education administrators – a job which can take many forms, from helping students sign up for classes to coordinating the activities of a college while serving as dean. According to the BLS, these positions earned a median salary of $96,910 in 2021. In addition, training and development managers , who identify the training needs of an organization and create or select course content for training programs, earned a median salary of $120,130 in 2021. Some higher education institutions hire postsecondary teachers who have a master’s degree, while others require teachers to have earned a doctorate as well. In 2021, postsecondary teachers earned a median salary of $79,640.
- Alumni & Giving
- Faculty/Staff Directory

The Graduate School of Education and Human Development
- Accreditation
- Faculty & Staff Directory
Counseling & Human Development
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Educational Leadership
- Human and Organizational Learning
- Special Education and Disability Studies
- Individualized Master's Program
- PhD in Education
- Online Programs
- Prospective Students
Request Info
- How to Apply
- International Applicants
- Funding Your Education
- Admissions Events
Visit Campus
- Admitted Students
- Career Services
- Student FAQs
- Dates & Deadlines
- New Student Orientation
- New Student Guide
- Research Lab
- UNESCO Chair & Fellowship
- Futrell Scholars
- EdFix Podcast
- Feuer Consideration
- Refer a Student
- Fellowship and Summer Institute on Antisemitism & Jewish Inclusion in Educational Settings

ELEVATE YOUR
In Education, Leadership, Counseling & Policy
Discover GSEHD

See what makes GW and our grad programs in education and human development the best fit for you.
Learn more about our programs, schedule a campus tour, or register for an upcoming info session.
Connect with Admissions
Apply Today

Ready to take the next step in your career? Submit your application today. There’s no application fee!
Submit Application

It’s a saying engrained at the George Washington University . It means always striving to do your best, helping others, and aiming to change the world. At the Graduate School of Education and Human Development (GSEHD) , we’re focused on building scholar-practitioners who aim to connect practice with action. We’re here to elevate and amplify your voice, while giving you the tools to elevate and amplify others.
At GSEHD, you’ll find yourself amongst a diverse community of students who are committed to changing the lives of others through education, leadership, counseling, and policy. Our community of dedicated, lifelong learners define who we are today and what the nation and world can become.

Explore Your Future at GSEHD
Experience life at GW! Schedule a tour, register for an info session, and connect with our Admissions team.

Ready to take your career to the next level?
Fall 2024 deadlines are quickly approaching. There's no application fee and the GRE isn't required for admission.
Apply to GSEHD Today

AI & Educational Leadership
As an educational administrator, learn how you can prepare to implement and guide policies around AI in the classroom.

Get the Inside Scoop
Join us in-person or online to learn more about financial aid, the admissions process, and more.
Register for an Open House or Virtual Info Session

EdFix: A Podcast About the Promise and Practice of Education
Join Dean Michael Feuer and top experts in the field as they take on some of education's most complex issues.
Listen to the latest episode, ChatGPT and Beyond: Teaching in the AI Era, featuring Dr. Ryan Watkins
Find the Program that Matches Your Career Goals

Address diverse and critical concerns within the field of counseling. Our programs prepare students to become practitioners in an expansive range of specialties, including school counseling, clinical mental health counseling, rehabilitation counseling, and career and workforce development.
Explore Programs >

Teacher Preparation & Curriculum Design
The curricular and pedagogical tools used in our nation’s schools are the foundation for educational and societal transformation. We offer the highest level of training for individuals preparing for a career in K-12 teaching, as well as for professionals aiming to become specialists in curriculum design.

Educational Leadership & Policy
Our programs in education policy, leadership, and administration equip alumni to solve problems, implement new policy, and drive change for good in ways that reform and transform communities worldwide. Students integrate theory with practice to become successful leaders in their fields.

Human and Organizational Leadership & Learning
Advance your leadership skills to effectively lead change and sustainably manage organizations of all types. Students work closely with faculty to learn theoretical applications, new research, and best practices in order to facilitate organizational growth.

Special Education & Disability Studies
Students in our special education programs are expertly trained to meet the diverse needs of youth with, or at-risk for, disabilities. Faculty offer mentorship to help students gain the knowledge and skills to make a lasting difference in schools and communities.

PhD in Education - Research Emphasis
Scholars make a direct impact on society and confront the most complex issues in the field of education, including evolving technology, leadership, policy, and more. Take a multi-disciplinary approach while honing your skills in a specific concentration.
Confront Complex Issues
Make an impact on society and drive progress. Our graduate programs foster exceptional leadership skills, empowering educators, administrators, counselors, researchers, and more to make a difference in their respective disciplines.
Turn Passion into Practice and Possibility
At GSEHD, we build and use rigorous methods to investigate important questions. Our faculty and students leverage their interests, knowledge, and analytical skills to improve education and advance social progress.

Better Lives for People with Disabilities
The Center for Rehabilitation Counseling Research and Education prepares professionals to work with people with disabilities to reach their employment goals and better integrate into society.

AI in Education
As AI tools like ChatGPT are changing daily aspects of our lives, Educational Technology Leadership faculty are leading the way in guiding educators on how to incorporate these tools into the classroom, as well as discussing hot topics such as ethics and potential implications.

Developing More Inclusive Organizations
The Humanistic Initiative , led by Dr. Shaista Khilji, fosters respect, dignity, compassion, and sustainability as the basis of leadership and organizations.
See How GSEHD is Making A Difference

Being a part of GSEHD has been one of the best decisions I have made. I now feel well prepared to serve the community while providing services to families and children in the DC area. Completing my education here has taught me to be independent, confident, and resilient. Thank you to GSEHD, my professors, peers, and family for your guidance and support!
Tatyana Suares (MA '20) Clinical Mental Health Counseling

GSEHD in the News
GSEHD Faculty and Students Published American Board of Vocational Experts Longitudinal Salary Survey
June 4, 2024
Alumna, Kathy Russell, Named 2024 Prince George's County Teacher of the Year
Alumnus, James D'Andrea, Named Principal of Andover High School
May 29, 2024
Upcoming Events
Request Information
Contact Admissions
Visit Campus
Student Resources

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
Education programmes, discover unicef's work worldwide..

← Back to Education
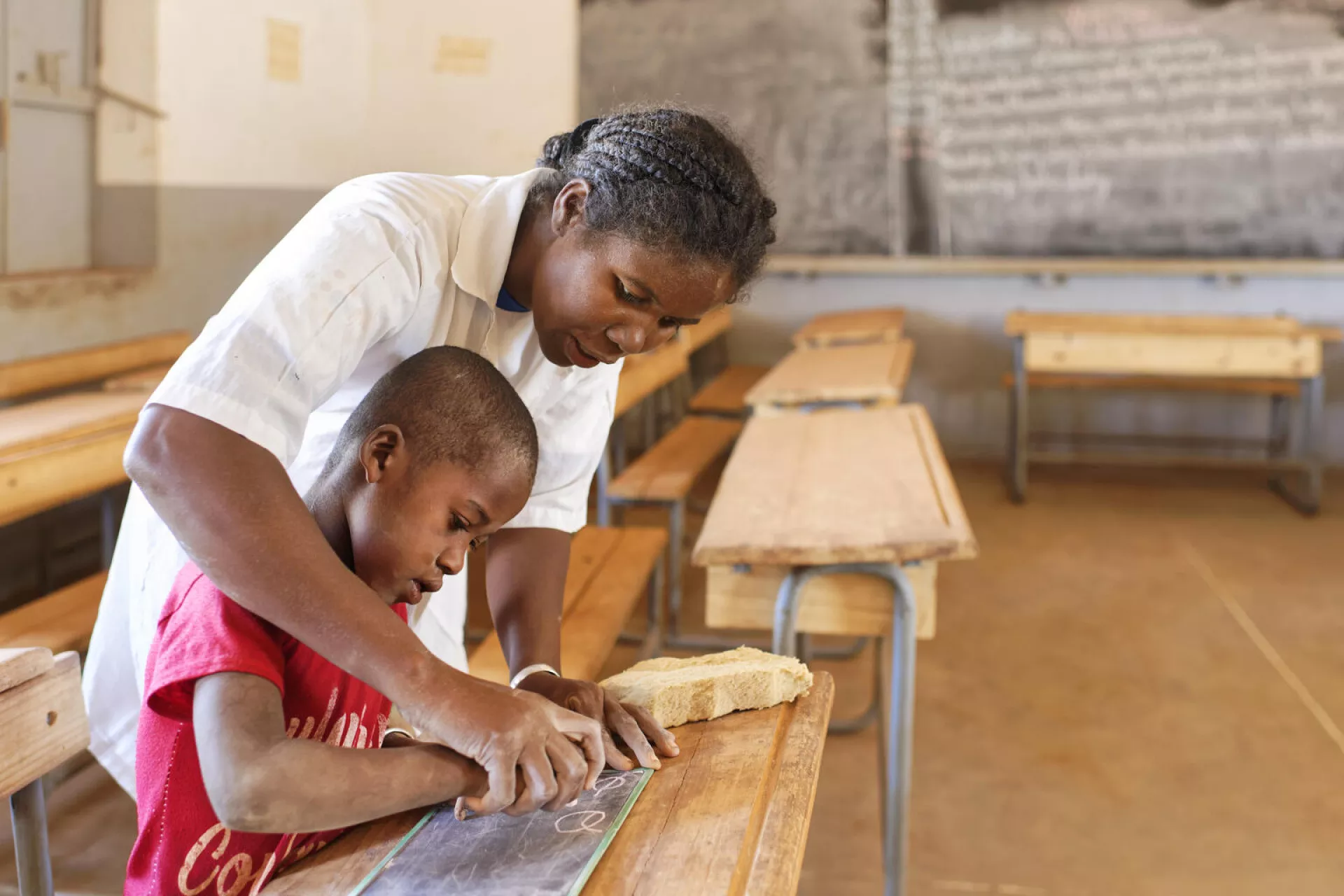
UNICEF works day in and day out, in some of the world’s toughest places, to protect children’s rights and safeguard their futures. On the ground in over 190 countries and territories, we reach more children and young people than any other international organization. Explore our education programmes, initiatives and partnerships.

Inclusive education

Girls' education

Education in emergencies

Early childhood education

Primary education

Adolescent education and skills

Digital Education

Strengthening education systems and innovation
Global partnerships and initiatives, reimagine education.
In a world facing a learning crisis, digital learning should be an essential service. UNICEF aims to have every child and young person – some 3.5 billion by 2030 – connected to world-class digital solutions that offer personalized learning.

Learning Passport
A TIME Best Invention of 2021, the Learning Passport enables high-quality, flexible learning for children anywhere, to close the learning poverty gap.
Generation Unlimited
If the largest generation of young people in history is prepared for the transition to work, the potential for global progress is unlimited. We enable young people to become productive and engaged members of society.
The Giga Initiative was launched to connect every school to the internet and every young person to information, opportunity and choice.
Education Cannot Wait
Education Cannot Wait is the United Nations global fund for education in emergencies and protracted crises. We support and protect holistic learning outcomes so no one is left behind.
EdTech Hub is a global research partnership that empowers people by giving them the evidence they need to make decisions about technology in education.
Global Partnership for Education
GPE is the world’s only partnership and fund focused on providing quality education to children in lower-income countries.
Global Education Cluster
The Global Education Cluster works towards a predictable, equitable and well-coordinated response addressing education concerns of crisis-affected populations.
United Nations Girls' Education Initiative
Through evidence building, coordinated advocacy and collective action, the UNGEI partnership works to close the gender gap in education.
All in School
In collaboration with the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, this initiative provides governments with actionable data to identify barriers that lead to exclusion and develop policies and programmes that put more children on track to complete their education.

Children call for access to quality climate education
On Earth Day, UNICEF urges governments to empower every child with learning opportunities to be a champion for the planet

Teachers wanted
Empowering teachers at the forefront of the learning crisis

Climate action for a climate-smart world
UNICEF and partners are monitoring, innovating and collaborating to tackle the climate crisis

The inspiring journey of Steward Francis
How education transformed the life of a South Sudanese child refugee
Straight from the experts
Breaking news and analysis from UNICEF's Education team.

The Ph.D. in Education is an interdisciplinary doctoral program that combines advances in the social sciences, sciences, arts, and humanities with deep expertise in educational research, policy, and practice to train students for careers as academics, researchers, policymakers, and leaders who will improve educational outcomes in the United States and around the world. Ph.D. candidates will collaborate with faculty from across Harvard graduate and professional schools and conduct groundbreaking research — forging new fields of inquiry that will transform education practice and policy. Candidates for the Ph.D. in Education choose from among three concentrations: Culture, Institutions, and Society; Education Policy and Program Evaluation; or Human Development, Learning and Teaching.
All Ph.D.s are granted through the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences.
Could 3-year degree programs tackle concerns about college costs, return on investment?
With college costs rising and some students and families questioning the return on investment of a four-year degree, a few pioneering state universities are exploring programs that would grant certain bachelor’s degrees in three years.
The programs, which also are being tried at some private schools, would require 90 credits instead of the traditional 120 for a bachelor’s degree, and wouldn’t require summer classes or studying over breaks. In some cases, the degrees would be designed to fit industry needs.
Indiana recently enacted legislation calling for all state universities there to offer by 2025 at least one bachelor’s degree program that could be completed in three years, and to look into whether more could be implemented. The Utah System of Higher Education has tasked state universities with developing three-year programs under a new Bachelor of Applied Studies degree, which would still need approval by accreditation boards.
Graphics: How are college costs adding up these days and how much has tuition risen?
A dozen universities in 3-year pilot program
More than a dozen public and private universities are participating in a pilot collaboration called the College-in-3 Exchange, to begin considering how they could offer three-year programs. The public universities include the College of New Jersey, Portland State University, Southern Utah University, the Universities of Minnesota at Rochester and at Morris, the University of Wisconsin Oshkosh and Utah Tech University.
Proponents of the three-year degree programs say they save students money and set them on a faster track to their working life. But detractors, including some faculty, say they short-change students, particularly if they later change their minds on what career path they want to follow.
The Utah Board of Higher Education in March approved the new three-year degree category. Various areas of study would be tied to specific industry needs, with fewer electives required. These degrees are broader than two-year associate degrees but narrower than a full four-year bachelor’s.
“We told the institutions to start working on them now and developing the curriculum,” Geoff Landward, commissioner of the Utah System of Higher Education, said in an interview. “Also, we want them to find industry partners that would be willing to hire people with bachelor’s degrees of this type.”
He added: “We created a sandbox for our institutions to play in.”
Once created, individual programs would need both national accreditation and state Board of Higher Education approval.
Landward said he has taken note of criticism that the three-year programs might “cheapen” the bachelor’s degree by short-changing students who wouldn’t receive a broad college education. But he said students could save on tuition, get a head start in the workforce and meet the needs of industries that are looking for certain skilled workers to address shortages in the state.
That includes nursing, he said, where requiring a four-year degree means taking lots of electives that have nothing to do with the career.
Is college worth it?: The answer for half of Americans is striking.
Proponents say
Utah State University’s four-year nursing program , for example, suggests several electives along with the required anatomy, math and biology courses as prerequisites during freshman and sophomore years.
“We think if we are partnering with industry and they help us develop it, I don’t think it cheapens the degree,” Landward said. “I think it creates a very specific degree.”
Robert Zemsky, a University of Pennsylvania professor and founding director of the university’s Institute for Research on Higher Education, began proselytizing for the three-year college movement about a dozen years ago.
He said the idea has gotten traction recently because “we are wading in the deep waters of righteous anger” at colleges and universities because of the perception that four-year degrees are not worth their high costs.
A Pew Research Center survey released in May found only 1 in 4 American adults said it is extremely or very important to have a four-year college degree as a means to getting a good-paying job. Only 22% of the respondents said the cost is worth getting a four-year degree even if the student or their family has to take out loans.
Zemsky suggested a shorter time span also would lead to higher college completion rates. More than a third of students who began seeking a bachelor’s degree in fall 2014 at a four-year school failed to complete their education at the same institution in six years, according to the National Center for Education Statistics .
Zemsky said 27 colleges and universities have embarked on creating three-year pilot programs and predicted 100 would be doing so in another year.
Over the past 10 years, Zemsky said, schools have been ignoring the desires of students and instead creating their curricula around the preferences of faculty — which is where most of the opposition is coming from.
Last year, at a conference of the Association of Pennsylvania State College and University Faculties, a bargaining unit for professors, President Kenneth Mash said the overwhelming number of college faculty nationwide “have a visceral disdain for the idea.”
Opponents say college is more than for job prospects
In an interview with Stateline, he said three-year programs would hurt students, too, creating a “two-tiered” system under which wealthy students would get a full four-year education and lower-income students a cheapened three-year degree.
“If it’s not going to be a four-year degree, they should name it something that indicates it’s not a B.A.,” said Mash, who also is a political science professor at East Stroudsburg University. “We don’t know that employers will treat them the same.
“I’m on board, as most faculty are, with the notion that people want to increase their job opportunities. But that’s not all there is to a college degree,” he said. “Degrees prepare you to be a better citizen, a better parent and on and on.”
And he said a broad education is what makes it possible for students to change jobs and careers many times during their working lives. “It’s really that baking in liberal arts … that makes it possible for people to do different things in their lifetimes.”
Indiana’s new law
Indiana enacted a law in March that requires each public institution that offers bachelor’s degrees to review all the four-year degrees with an eye toward making some of them three years. And the law requires that by July 1, 2025, each state university offer at least one bachelor’s degree that can be completed in three years.
Indiana state Sen. Jean Leising, a Republican who sponsored the measure, pointed out that every extra year of college costs the students, their parents and the state.
But she noted that not all degrees lend themselves to compressed curricula. “If you’ve got a kid in pharmacy (studies), they are not going to be able to get through it in three years. Engineers aren’t going to be able to do it in three years. But some of the other kids will.”
Chris Lowery, Indiana’s commissioner for higher education, said the law will encourage schools to think about how to create 90-credit-hour bachelor’s degrees: “How feasible is this, would you still have the quality, would you still have the agency?”
Three-year degrees allow for choice, he added. His daughter, for example, had enough AP credits after high school to make a college degree feasible in three years, but opted to go to school for four because she wanted to have enough time to study so that she could get “straight As” as well as to have time for extracurricular activities.
“But for a lot of students, the finances are tighter,” he acknowledged.
Credentialing requirements
At both public and private universities, the new three-year degree programs that require fewer credits would need national accreditation.
The Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities, a regional credentialing agency, accredited several three-year bachelor’s degrees at two private schools, Brigham Young University-Idaho and Ensign College, last year. The degrees are in applied business management, family and human services, software development, applied health and professional studies.
Sonny Ramaswamy, the commission’s president, said in an interview that the three-year programs underwent two years of evaluation before being awarded accreditation.
He said the evaluation showed that competency in many professions could be attained in three years instead of four, and that graduate schools were willing to accept three-year bachelor’s as a credential for the pursuit of higher degrees. He noted that European college degrees often are completed in three years.
“We said, ‘We will approve you, but this is a pilot,’” Ramaswamy said. The schools will provide data to show their students have earned a good education, he added.
“My intuition is that it will head in the right direction,” he said. “The public is calling for innovation.”
Michael Poliakoff, president of the American Council of Trustees and Alumni, a nonprofit that says its mission is promoting academic freedom, excellence and accountability at colleges and universities, said “fluff” courses strengthen the case against a 120-credit hour bachelor’s degree.
“Let people get a good foundation with a strong general education core, strong skills and some electives,” Poliakoff said in an interview. “That’s what a responsible university should be doing.”
The council does an annual survey of higher education institutions and grades them A through F on what the group calls “core curricula” — the proportion of courses dedicated to mathematics, literature, composition, economics, laboratory science, American history and government, and foreign languages.
Poliakoff said the amount of debt students are accumulating over four years is “sinful” and unnecessary. Colleges and universities must meet the concerns of students and their families, he said.
“A 90-credit baccalaureate degree is a pretty good way to tighten up the bolts,” he said.
Elaine S. Povich covers education and consumer affairs for Stateline. Povich has reported for Newsday, the Chicago Tribune and United Press International. Stateline is part of States Newsroom , the nation’s largest state-focused nonprofit news organization.
- Share full article

There’s a Program to Cancel Private Student Debt. Most Don’t Know About It.
A nonprofit group is publicizing the relief program that Navient, a large lender, created for students who attended for-profit schools that misled them.
Danielle Maynard took both federal and private loans to attend the New England Institute of Art. Credit... Simon Simard for The New York Times
Supported by

By Stacy Cowley
- May 30, 2024
More than a million borrowers who were defrauded by for-profit schools have had billions of dollars in federal student loans eliminated through a government aid program. But people with private loans have generally been excluded from any relief — until recently.
Navient, a large owner of private student loan debt, has created, but not publicized, a program that allows borrowers to apply to have their loans forgiven. Some who succeeded have jubilantly shared their stories in chat groups and other forums.
“I cried, a lot,” said Danielle Maynard, who recently received notice from Navient that nearly $40,000 in private loans she owed for her studies at the New England Institute of Art in Brookline, Mass., would be wiped out.
Navient, based in Wilmington, Del., has not publicized the discharge program that helped Ms. Maynard. Other borrowers have complained on social media about difficulties getting an application form. When asked about the program and the criticisms, a company spokesman said, “Borrowers may contact us at any time, and our advocates can assist.”
So a nonprofit group of lawyers has stepped in to ease the process: On Thursday, the Project on Predatory Student Lending , an advocacy group in Boston, published Navient’s application form and an instruction guide for borrowers with private loans who are seeking relief on the grounds that their school lied to them.
“We want to level the playing field and let people know, instead of having it be this closely held secret,” said Eileen Connor, the group’s director.
Senator Elizabeth Warren, Democrat of Massachusetts, and eight Senate colleagues sent Navient a letter last month with a lengthy list of questions about the program. Navient responded, but did not directly address many of the senators’ questions.
Navient’s new program — which it calls a “school misconduct discharge” — is something of a private parallel to a federal program known as “ borrower defense to repayment ,” which allows those who were seriously misled by their schools to have their federal student loans eliminated. Under President Biden, the Education Department revived the relief program and used it to cancel nearly $30 billion in debt owed by 1.6 million borrowers.
The Project on Student Predatory Lending backed a class-action lawsuit against the government that led to a 2022 settlement under which nearly 200,000 borrowers had their federal student debts eliminated. Ms. Maynard, who is 34, shed $38,000 in federal loans through that deal.
But she, like many borrowers, remained mired in private student loans. Ms. Maynard paid $700 a month to Navient for more than a decade for her private loans.

For nearly a decade, in the early 2000s, Navient — then known as Sallie Mae — struck deals with for-profit schools to issue private loans to their students. Lawsuits from state attorneys general later accused Navient of making those loans knowing that most would never be repaid . Many schools indemnified Navient for the private loans, agreeing to defray the company’s loss if the loans defaulted.
In 2022, Navient settled with 40 state attorneys general and canceled $1.7 billion in debt on those private loans — but only for borrowers who had already defaulted. Because those debts were unlikely to ever be repaid, the deal cost Navient only $50 million, the company said in regulatory filings. Borrowers who had kept paying their bills, like Ms. Maynard, remained stuck.
But a pressure campaign from lawmakers, federal regulators and lawyers representing borrowers prompted the company to create the “school misconduct discharge.”
Navient began sending a 12-page application form this year to some borrowers who complained about their private loans. The document lists dozens of types of impropriety by schools — such as inflating job placement rates and graduates’ earnings, or misrepresenting their educational programs — and asks borrowers to choose which apply to their experience. Applicants are required to submit documentation for their claims.
After Ms. Maynard’s federal loans were eliminated last year, she stopped making payments on her private loans and called Navient, seeking relief options.
A few months ago, Navient sent her its misconduct discharge form. Weeks later, she received the notice that her application had been approved.
The senators’ letter to Navient called its private loan discharge process “burdensome and confusing.” It also asserted a legal basis for borrowers’ claims that their loans should be canceled: the so-called holder-in-due-course rule, a 1975 regulation by the Federal Trade Commission that lets those who use certain types of loans contest the debt if the goods they bought were fraudulent.
The response that Navient sent the senators acknowledged the rule as a ground for claims. “We are committed to canceling all loans that meet the Holder Rule criteria,” Navient’s chief executive, David Yowan, wrote in the letter, which was reviewed by The New York Times.
The letter said Navient had discharged “some” loans for borrowers who raised claims under the rule, and had “recently introduced an enhanced process for borrowers to seek discharge,” which it described as “still in its early stages.”
Mr. Yowan told investors on a conference call in January that Navient had put $35 million in reserve for losses on school-misconduct claims. He cited “new regulatory expectations” as the reason. Navient has not disclosed how much of its $16.6 billion private student loan portfolio consists of loans that could be eligible for the debt cancellation program.
Senator Warren said in a written statement this week, “Navient has admitted responsibility for canceling their predatory loans but set up a process for cancellation that’s impossibly confusing for borrowers.”
Some trying to navigate the process have already failed.
Thomas Jean-Mastej had his federal loans for studies at American InterContinental University — a school cited by the Federal Trade Commission for deceptive recruiting tactics — canceled through the borrower defense program. In March, he filed a complaint with the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau about his private loans.
Navient responded by sending him the school misconduct discharge application form, which he submitted in mid-April. On May 10, he received a denial notice. It said Navient “carefully considers a variety of factors in determining whether a private loan should be discharged” but did not specify why his claim was rejected.
Mr. Jean-Mastej said he had hoped Navient “would have some compassion” — especially since he has, over the years, already repaid the company nearly $17,000 for a loan of just less than $7,000. He still owes almost $4,000.
Scores of others are in limbo, awaiting a response. Thomas Carter learned about Navient’s program on a Reddit forum . Following the steps recommended there, he filed a consumer bureau complaint, then received an application form from Navient. He sent it in three weeks ago.
“My thoughts were, like, why is this such a secret?” said Mr. Carter, who attended the Art Institute of York, in Pennsylvania. “You had to go through all these hoops to get the application.”
Stacy Cowley is a business reporter who writes about a broad array of topics related to consumer finance, including student debt, the banking industry and small business. More about Stacy Cowley
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
What Happened to Ad-Free TV?: Not long ago, streaming TV came with a promise: Sign up, and commercials will be a thing of the past. Here’s why ads are almost everywhere on streaming services now .
London Moves to Revive Its Reputation: As fears have grown that the city is losing its attractiveness for publicly traded businesses, Britain’s government is making changes to bring them back.
What Do Elite Students Want?: An increasing number of students desire “making a bag” (slang for a sack of money) as quickly as possible. Many of Harvard’s Generation Z say “sellout” is not an insult, appearing to be strikingly corporate-minded .
D.C.’s Empty Offices: Workers in Washington have returned to the office slowly , with a pervasive and pronounced effect on the local economy.
Trump’s Financial Future: Donald Trump has treated Trump Media, which runs his social network Truth Social, as a low-cost sideshow. Now a big portion of his wealth hinges on its success .
Advertisement

Exercise, Sport and Health Sciences: Community Health Education & Promotion
Building stronger communities through health advocacy.
Be actively involved in helping people develop healthy, active lifestyles in communities across the U.S. and abroad by pursuing a health sciences degree with an emphasis in community health education and promotion.
The CHEP program gives students hands-on teaching and community-engaged learning experiences and prepares you to address the complex health issues and disparities in any community through education, program planning, health communication, policy, advocacy and research.
Students study traditional health sciences classes with a focus on disease prevention, which gives you a competitive edge for graduate programs in public health, medicine, nursing, health administration and more.
This program could be a good fit if you:
- Want to promote active lifestyles and healthy communities.
- Seek to understand and address the root causes of poor health and health inequities.
- Like sharing health information and enjoy working with others.
- Plan to enter graduate school for a health-related profession.
- Enjoy challenges, systems thinking and biomedical sciences.
Career Outcomes
With this degree, you could become a/an:
- Health educator
- Health promotion specialist
- Public health specialist
- Prevention specialist
- Community health worker
- Health care coordinator
- Healthy schools coordinator
- Community health coordinator
- Public health physical activity specialist
- Maternal and child health specialist
- Worksite or corporate wellness specialist
- Health administrator
- Epidemiologist
- Other health professionals
Available Online and On-Campus
You may also be interested in:

Dance, B.S.
Prepare for a dance-related career with professional training in performance, choreography and teaching.

Elementary Education, B.S.Ed.
Gain the training and credentials to teach multiple subjects to students in grades K-8.
More degrees below. Enjoy!
Exercise, sport and health sciences: pre-physical therapy.
Blend classroom teaching, hands-on learning and service-learning projects in preparation for competitive graduate programs.
Secondary Education
Become prepared to teach a specific subject area to students in middle school or high school.
Elementary Education
Exercise, sport and health sciences: fitness, health and human performance.
Learn human anatomy and explore the effects of physical activity and inactivity on the body’s physiology, movement, performance and overall health.
Exercise, Sport and Health Sciences: Physical Education Teacher Certification
Learn how to improve fitness and health through games, sports and other physical activities in preparation for a career as a physical education teacher.
Recreation, Sport, and Tourism Management
Prepare to plan, organize and lead recreation programs for communities, tourism companies, youth groups, and other organizations.
Career & Technical Education: Business & Marketing
Prepare to teach business, marketing, and business technologies at the high-school or post-secondary level.
Career & Technical Education: Occupational Education
Learn to teach post-secondary students the defined skill sets they need for careers in professional-technical occupations.
Career & Technical Education
Learn to teach youth and adults the practical job skills they need to enter and succeed in today’s workforce.
Exercise, Sport and Health Sciences: Pre-athletic Training
Study human movement and exercise in preparation to engage in the two-year MSAT 3+2 program for athletic training.
Exercise, Sport, and Health Sciences
Learn the science and strategies to improve people’s quality of life through fitness and nutrition.
Career & Technical Education: Engineering & Technology
Prepare to teach engineering and technology subjects at a high school, community college, or in an industrial setting.
Doctor of Education Leadership

Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
America needs transformative leaders in preK–12 education whose passion for education quality and equity is matched by a knowledge of learning and development, the organizational management skills to translate visionary ideas into practical success, and a firm grasp of the role of context and politics in shaping leadership. Graduates of the three-year, multidisciplinary Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D.) Program at the Harvard Graduate School of Education will be prepared to become those leaders.
The Ed.L.D Program — taught by faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School — will train you for system-level leadership positions in school systems, state and federal departments of education, and national nonprofit organizations. Ed.L.D. is a full-time, three-year program built on a cohort learning model. Cohorts consist of up to 25 students from diverse professional backgrounds (including district/charter management leaders, nonprofit directors, principals, teachers, and policy researchers) who progress through the program together.
All Ed.L.D. students receive a full tuition funding package plus stipends, work opportunities, and a paid third-year residency at a partner organization.
The Ed.L.D. Program prepares graduates to do work for the public good in the American public education sector, whether that be at the system or state level. Specifically, the program is designed to accelerate the progress graduates make toward achieving meaningful impact in influential roles and/or crossing boundaries in the following spaces in the public education sector:
- PreK–12 district or CMO leadership roles : superintendent of schools, chief academic officer, and/or deputy superintendent
- Foundation/philanthropy roles: director, president and CEO, senior fellow
- Education nonprofit roles : president or executive director of backbone or collective impact organizations which support preK–12 schools. Ed.L.D. graduates will lead education nonprofits that explicitly focus on improving outcomes and opportunities for children, families, and communities.
- State or federal education leadership roles : commissioner or deputy commissioner roles. Could also include public education advocacy or education policy advisers to senior government officials.
- Social Entrepreneurship and Innovation roles: Founder, CEO, president
Curriculum Information
The Ed.L.D. curriculum is a balance of multidisciplinary coursework and practice-based learning. Core courses and electives are taught by recognized leaders from across Harvard’s graduate programs in fields like data-based education reform, organizational change and innovation, and effective leadership strategies for urban schools. You will develop and test your leadership skills through team projects and an immersive third-year residency.
All students in the cohort take the same classes in four foundational content areas: learning and teaching, leadership and organizational change, politics and policy, adult development, and leadership inside and out (including one-on-one executive coaching). Courses taken during the first-year focus on practice-based learning and serve as the framework of your first-year experience.
Sample HGSE Courses
- Leading Change
- How People Learn
- Ed.L.D. Proseminar
- Leadership, Entrepreneurship, and Learning
- Race, Equity, and Leadership
- Practicing Leadership Inside and Out
- Sector Change
- The Workplace Lab for System-Level Leaders
View all courses in the Academic Catalog.
Each cohort member works with program advisers to choose an individualized sequence of electives from any of the Harvard graduate schools. You will work closely with the program faculty and staff during your second year to determine the best match with a partner organization for your third-year residency. Matches are driven by mutual interest between the resident and the partner organization, and each student's career and learning goals and geographic preferences.
- Second Year Practicing Leadership Inside and Out
- Driving Change
- Education Sector Nonprofits
- Negotiation Workshop
- Coaching with Equity in Mind
- Ethnic Studies and Education
- Deeper Learning for All: Designing a 21st Century School System
- Institutional Change in School Organizations, Systems, and Sectors
You will take part in a 10-month paid residency at one of our partner organizations. There, you will work on a strategic project which synthesizes your experience and learning into a written Capstone project. You will stay connected to your Ed.L.D. cohort and HGSE through technology and by returning to Harvard periodically for intensive workshops.
Paid Residency
Our partner organizations include school systems and departments of education, as well as some of the nation's most influential and dynamic nonprofit, mission-based for-profit, and philanthropic organizations.
You will be intentionally pushed out of your comfort zones and asked to work systemically and make a significant contribution to the partner organization. In addition, the residency will provide you with the professional mentoring, practical experiences, and network of connections they need to position themselves as future leaders in the education sector.
Strategic Project
You will define (with supervisors from your partner organization) a strategic project on which to focus. You will have the opportunity to lead one or two major efforts on behalf of the organization, such as the creation or implementation of current initiatives. The project allows you to practice and improve leadership skills, add important value to the mission and strategy of the partner organization, work systemically, and hold high-level accountability.
During the residency period, you will produce a written Capstone. The Capstone is a descriptive, analytic, and reflective account of your third-year leadership contributions to a strategic project within an Ed.L.D. partner organization. It is a demonstration of your ability to engage others, develop strategy to successfully address and diagnose challenges, work toward a vision and goals, and learn from the results.
Sample Topics
- Accountability, Coherence, and Improvement: Leadership Reflection and Growth in the Los Angeles Unified School District
- Leadership Development for Entrepreneurial Education Leaders Working to Build Public & Private Sector Support
- Disrupting Teacher Preparation: Lessons in Collaboration and Innovation Across the Learning to Teach Community of Practice
- Pursuing Educational Equality for English Language Learners
Sample Summaries
- Breaking Down Silos in a School District: Findings from an Ed.L.D. Project in Montgomery County
- Expanding Students' Access to Meaningful STEM Learning Opportunities Through Strategic Community Partnerships
- Developing a New Teacher Leadership and Compensation System in Iowa: A Consensus-Based Process
- Finding Great Teachers for Blended-Learning Schools
GSE Theses and Dissertations from Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH)
Program Faculty
Ed.L.D. students learn with renowned faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, Harvard Business School, and Harvard Kennedy School. Faculty from the three schools share their individual expertise in the Ed.L.D. Program and work collaboratively to provide a challenging and coherent experience for students. Faculty who teach in the Ed.L.D. core curriculum and advise Ed.L.D. students include:
Faculty Director
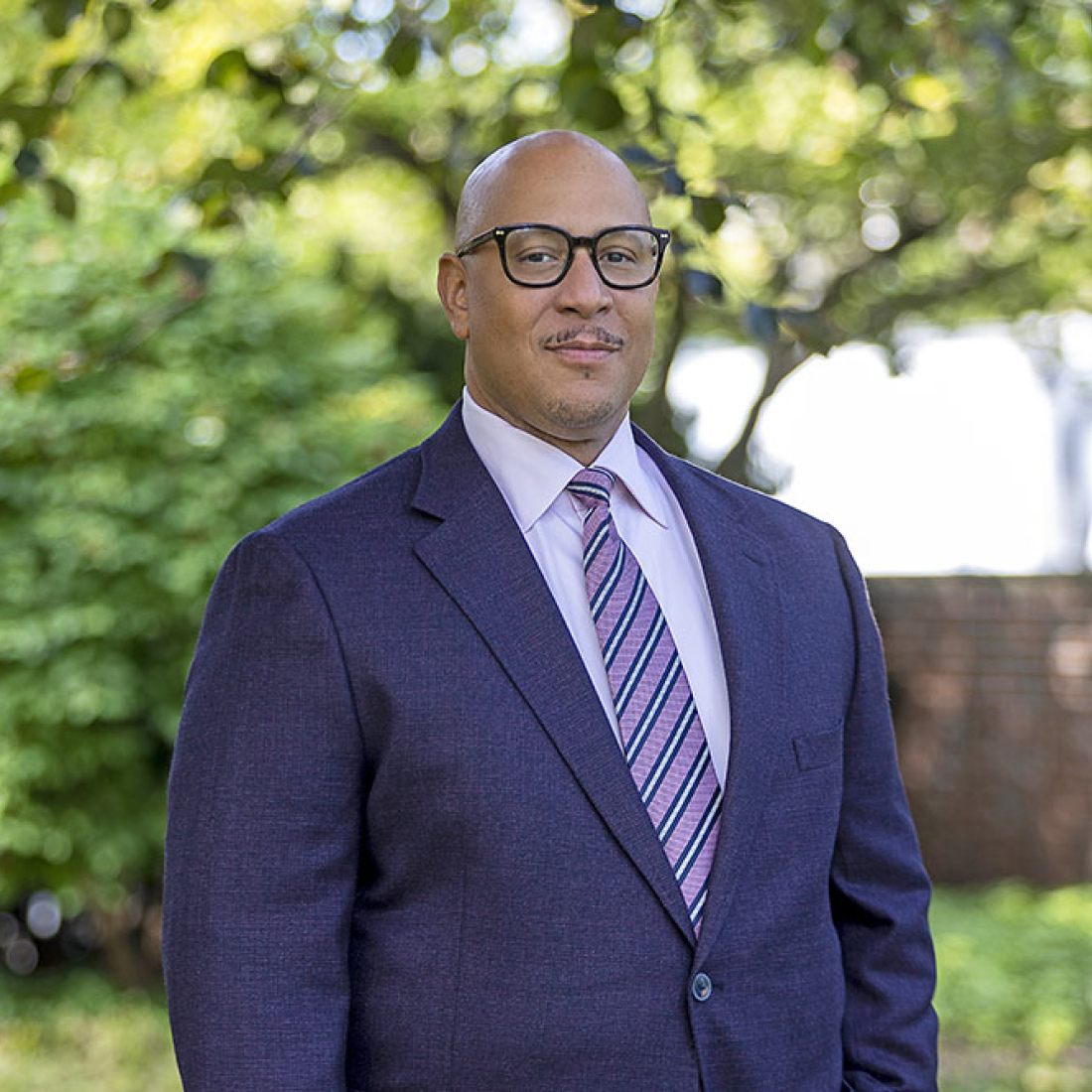

Frank D. Barnes
Frank Barnes is faculty director of the Doctor of Education Leadership Program. He has over 30 years experience as an educator, researcher, and organizer. As a chief accountability officer, he led turnaround efforts for large public school districts, including Boston Public Schools and Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools.
Kathryn Parker Boudett

Ebony N. Bridwell-Mitchell

Jennifer Perry Cheatham

Elizabeth City

Candice Crawford-Zakian

Marshall Ganz

Adria D. Goodson
Deborah helsing.

Monica C. Higgins

Deborah Jewell-Sherman

Lisa Laskow Lahey

Mary Grassa O'Neill

Irvin Leon Scott

Catherine Snow

Michael L. Tushman
Martin west.

Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Education Leadership experience and the impact its community is making on the field:
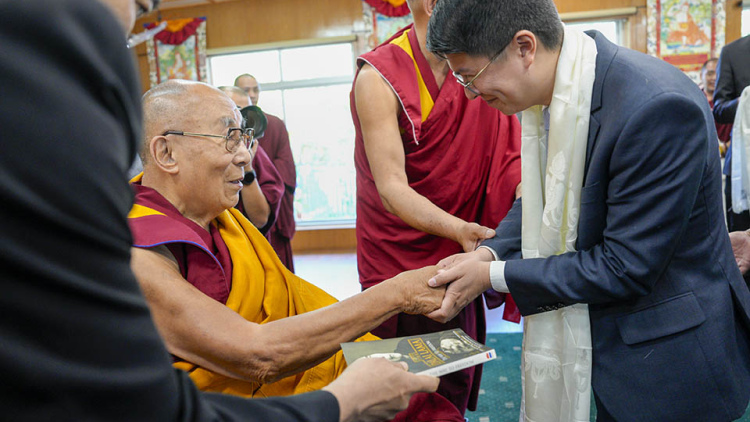

Do We Need Happiness Teachers?
After a trip to meet with the Dalai Lama, an Ed.L.D. student says we do

Combatting Chronic Absenteeism with Family Engagement
As post-COVID absenteeism rates continue unabated, a look at how strong family-school engagement can help
An official website of the United States government, Department of Justice.
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
OJJDP FY24 Title II Formula Grants Program
Download PDF, 310.21 KB
The OJJDP Title II Formula Grants Program supports state, Tribal, and local delinquency prevention, intervention, and juvenile justice system improvements. Funds are provided directly to states to assist them in planning, establishing, operating, coordinating, and evaluating projects directly or through grants and contracts with public and private agencies for the development and implementation of comprehensive juvenile justice plans based on the needs in their jurisdictions.
The Formula Grants Program is authorized under the Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (JJDP) Act of 1974, as amended, at 34 U.S.C. §§ 11131.
With this program, states can provide more effective education, training, research, prevention, diversion, treatment, and rehabilitation programs in the area of juvenile delinquency and programs to improve the juvenile justice system.
Eligibility
- State governments
FY 2024 Title II Formula Grant Resources
OJJDP FY 2024 Title II Formula Grants Program Solicitation Files On June 20, 2024, at 2 p.m. ET, OJJDP personnel will hold a webinar to provide a detailed overview of this solicitation and allow interested applicants to ask questions. Register to participate .
Supplemental Information
- OJJDP FY 2024 Title II Formula Grants Program Solicitation Files
- June 20, 2024 Solicitation Webinar
Similar Opportunities
- OJJDP FY24 Post-Secondary Education Opportunities for Child Protection Professionals
- OJJDP FY24 Supporting Effective Interventions for Youth With Problematic or Illegal Sexual Behavior Program
- OJJDP FY24 Juvenile Justice Evidence Translation Project

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Master's in Education (Ed.M.) prepares students with the skills needed to change the world through education. The online Master's in Education Leadership is a part-time, two-year Ed.M. program from the Harvard Graduate School of Education with Higher Education and PreK-12 pathways. The program is specifically designed for working ...
A New Option for Experienced Educators. The online Master's in Education Leadership from HGSE consists of a diverse cohort of professionals like you — leaders who are advancing in their careers, and who bring important perspectives grounded in real-world challenges. Our program is conducted almost exclusively online — except for one short ...
State for in-state tuition: Enrollment. 0 - 1,000+. School Type. For-Profit ( 1) Private ( 113) Public ( 200) Online Program Type. 100% Online ( 268) Fully integrated with on‑campus program ( 9 ...
U.S. News evaluated several factors to rank the best online education degree programs, including faculty credentials, graduation rates and reputation. See the methodology. #1. Clemson University ...
30-33 credits | $1,210 per credit. Tulane University's online master's in education program has four specialization options. Students design their curriculum around these specializations, including learning experience design and special education, to prepare them for their chosen career path. Visit Tulane's Programs.
Explore accredited online master's in education programs from top universities on edX.
Each state has its own specific requirements for obtaining a teaching license. Most states require prospective educators to possess a bachelor's degree in education or a related field, complete a teacher preparation program (usually offered through the college where you obtain your degree), participate in an internship or student teaching experience, and pass a standardized exam like the PRAXIS.
Special Education & Disability Studies. Students in our special education programs are expertly trained to meet the diverse needs of youth with, or at-risk for, disabilities. Faculty offer mentorship to help students gain the knowledge and skills to make a lasting difference in schools and communities. Explore Programs >
Discover thousands of offerings — from free courses to full degrees — delivered by world-class partners like Harvard, Google, Amazon and more.
UNICEF works day in and day out, in some of the world's toughest places, to protect children's rights and safeguard their futures. On the ground in over 190 countries and territories, we reach more children and young people than any other international organization. Explore our education programmes, initiatives and partnerships.
The mission of the Harvard Graduate School of Education is to prepare education leaders and innovators who will change the world by expanding opportunities and outcomes for learners everywhere. We're an institution committed to making the broadest impact possible, putting powerful ideas and evidence-based research into practice.
Movement Sciences. Promoting healthy active living through undergraduate, graduate and doctorate degrees. The College of Education, Health and Human Sciences is committed to innovation and research by providing undergraduate and graduate programs to meet the needs of aspiring students.
Guide to information on how to apply for an ED grant. Overview. ED offers three kinds of grants: Discretionary grants: awarded using a competitive process. Formula grants: uses formulas determined by Congress and has no application process. Student loans or grants: to help students attend college.
Value Knowledge, Educate. This program provides advanced professional foundational courses that emphasize teacher education. Students who have a bachelor's degree in the field they wish to teach may pursue this one-year program which will give them the teaching strategies and learning theories to facilitate student learning.
The Ph.D. in Education is an interdisciplinary doctoral program that combines advances in the social sciences, sciences, arts, and humanities with deep expertise in educational research, policy, and practice to train students for careers as academics, researchers, policymakers, and leaders who will improve educational outcomes in the United States and around the world.
WWAMI Medical Education Program. Train to serve others in the Pacific Northwest as a primary care doctor. Through a partnership between U of I, the University of Washington School of Medicine and the states of Washington, Wyoming, Alaska, Montana and Idaho, this cost-effective dual-enrollment program graduates medical professionals prepared to support their communities through quality health care.
The Parent-Directed Special Education Services (PDSES) program, previously, the Supplemental Special Education Services (SSES) program is a one-time $1,500 online grant for parents/guardians of eligible students served by special education and who are enrolled in a Texas public school. Parents/guardians of eligible students can use the online ...
The Utah System of Higher Education has tasked state universities with developing three-year programs under a new Bachelor of Applied Studies degree, which would still need approval by ...
For the third consecutive year, the ASPIRE529 program will again offer financial assistance to youth in or aging out of the foster care system seeking higher education according to State Treasurer Colleen Davis. "The high school graduation rate for youth in foster care in Delaware is just over 50 percent, with less than 5 percent of that same group graduating from a four-year college ...
Navient's new program — which it calls a "school misconduct discharge" — is something of a ... the Education Department revived the relief program and used it to cancel nearly $30 ...
The CHEP program gives students hands-on teaching and community-engaged learning experiences and prepares you to address the complex health issues and disparities in any community through education, program planning, health communication, policy, advocacy and research. Students study traditional health sciences classes with a focus on disease ...
Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides you with full access to the extraordinary resources of Harvard University and prepares you to assume meaningful roles as university faculty, researchers, senior-level education leaders, and policymakers.
The Experience Training, Education, and Coaching Advisor will collaborate closely with teammates and healthcare professionals to develop and implement interpersonal communication skills training. Virtual training and digital training development along with written conversational guides are primary roles of this position to assist leaders and ...
The Ed.L.D. curriculum is a balance of multidisciplinary coursework and practice-based learning. Core courses and electives are taught by recognized leaders from across Harvard's graduate programs in fields like data-based education reform, organizational change and innovation, and effective leadership strategies for urban schools.
The Formula Grants Program is authorized under the Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (JJDP) Act of 1974, as amended, at 34 U.S.C. §§ 11131. With this program, states can provide more effective education, training, research, prevention, diversion, treatment, and rehabilitation programs in the area of juvenile delinquency and programs ...