Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Top 10 Ph.D. Interview Presentation Templates With Samples and Examples
Mayuri Gangwal
Do you know that only 56 % of students complete their Ph.D.? Factors such as students' age, department, and lack of a good mentor sometimes contribute to the non-completion rate. Indeed, the journey to earning a doctoral degree is challenging. It involves years of research and extensive writing. However, most students find a lack of focus and motivation to be the primary reason for their failure.
If you prepare for the PhD interview, PhD presentation slides can benefit you in several ways. For instance, templates save considerable time and effort and allow to focus on content delivery. Furthermore, for amateurs creating presentations, templates help them to organize content effectively.
At the same time, candidates often face several challenges regarding content creation and delivery. Templates can help streamline the process, but being aware of potential pitfalls is essential. Here are some common challenges associated with using presentation templates for PhD interviews:
In a recent survey, 6 out of 10 students feel nervous and anxious before the final presentation. It is because they find it challenging to communicate the importance of their research effectively. Crafting visually appealing slides can be tricky, especially for those without a design background. Did you find this relatable? Yes, our PhD interview templates can be a valuable solution for you.
They serve as valuable tools for creating well-structured presentations and assist students in delivering a solid defense for their Doctoral theses. Let's dive in and learn more about these templates and see how they can be valuable resources in your academic journey.
Template 1: Thesis Research Paper Proposal Template
This template can elevate your academic presentations to the next level. It is tailored specially for scholars, researchers, and students. It helps them embark on the rigorous journey of thesis proposal development and ensures that their research proposals are remembered. This template's uniqueness is its visually appealing designs. It integrates text, graphs, and tables and provides a solid structure to your presentation. Whether it's for your academic review or seminars, this template empowers you with confidence and clarity.

Download this template and make your proposal more impactful.
Template 2: Research Proposal Steps Template
Use this template to streamline your research proposal creation process. It is a comprehensive resource covering every crucial aspect of a research proposal. You can use this template to craft an engaging cover letter for your proposal. Thus, this template ensures that your proposal is compelling and professionally presented. Additionally, this template simplifies the process of conveying complex research plans. This template is structured to guide you through the essential steps of the research proposal. It will help you present your research coherently and persuasively. Download now!

Download this template today and embark on a seamless journey of crafting your thesis proposal.
Template 3: Research Proposal for Thesis Template
This template can help you effectively present your thesis proposal. It also ensures that you get sponsors for your project by providing a professional look at your proposal. So, this template is a must for someone presenting their hypothesis, as it provides a solid foundation for the presentation. The template encompasses a variety of crucial elements, from the thesis statement to the project stages.

Download and leverage this template today to focus on critical market components.
Template 4: Abstract for Thesis Research Proposal Template
This PPT Set helps streamline the complex process of crafting compelling research proposals by providing a structured and intuitive design. The template is divided into two parts. The first consists of six sections briefly describing the thesis. The second part includes a summary and description of the content. Thus, it empowers users to articulate their research objectives and methodologies precisely so that their proposal not only meets but also exceeds expectations.

Download this template today and elevate your academic work to new heights.
Template 5: Research Method Overview Template
This template is designed for ambitious scholars to help them dive into the essence of academic precision. This template helps researchers by providing them with a robust and logical roadmap for their research. This not only increases their efficiency but also helps them select the best research method. This template provides a clear picture of the target audience and how to conduct the study. Thus, this template acts as a catalyst for boosting the proposal's effectiveness. Want to transform your proposal into a compelling narrative that commands attention and respect?

Download this template today.
Template 6: Method of Data Collection for Thesis Research Paper Proposal
It is the best template for someone looking to elevate their data collection methods. This template provides a clear and professional way to collect data for academic brilliance. It provides a structured framework to articulate the rationale behind the chosen manner. Thus, it is a template and a strategic tool for showcasing your research and methodology. It ensures that your proposal stands out to provide a deep understanding of your work. Additionally, this template helps you communicate complex methodologies in an accessible manner and develop a deeper connection with your audience.

Download this template today and transform your thesis proposal into a masterpiece.
Template 7: Work Plan with Timetable Template
It is a versatile template that is designed to help professionals across industries. It helps them organize and present their project plans clearly and precisely. The template is divided into three sub-templates to simplify the entire planning phase. The first template includes various activities associated with a specific completion month. It helps you stay organized by outlining different tasks and actions. The second template delves deeper into project activities by outlining a detailed weekly work plan. This way, it provides better visibility and time management. Additionally, it helps you allocate your resources efficiently and prioritize activities. The third and the last templates provide different stages with their names and timeframes, adding to the level of detail and enhancing the proposed research's feasibility.
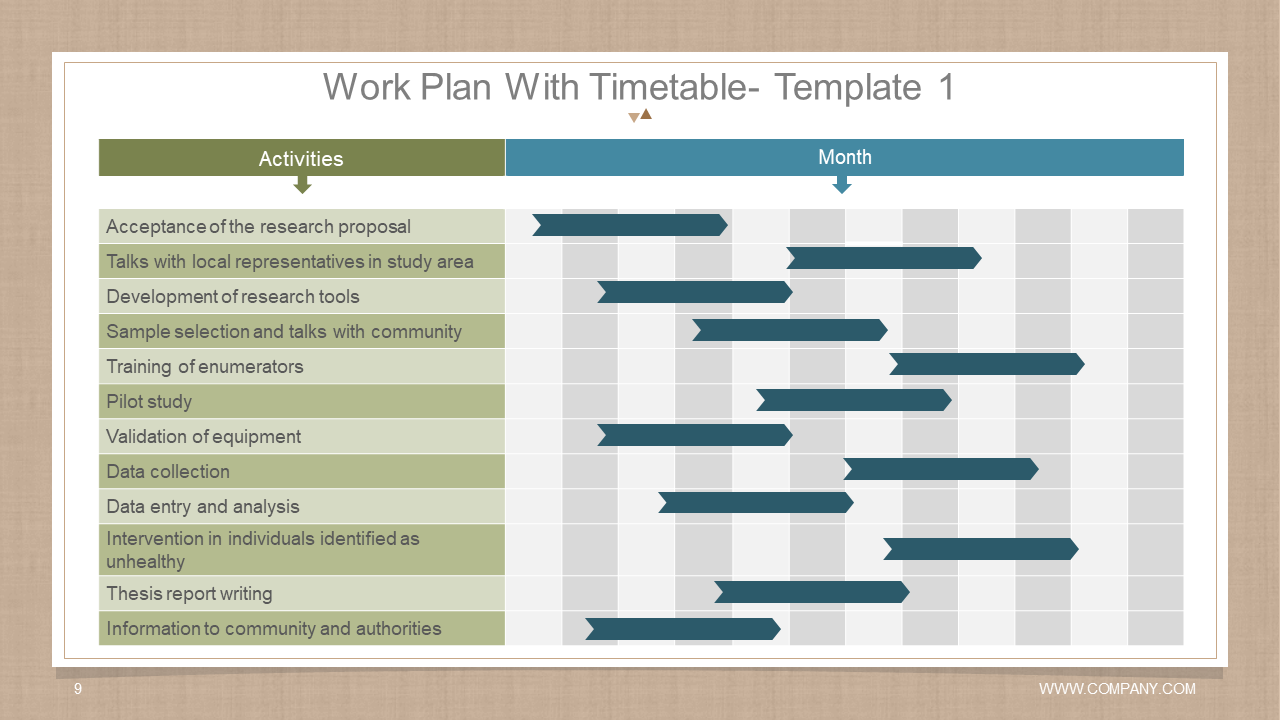
Download this template today to take the first step toward achieving project excellence.
Template 8: Implication of Research Template
This professional template helps you unlock the full potential of your research findings. It is a cornerstone for scholars and professionals eager to convey the significance of their research. The template is Structured as a four-stage process to help students present their research implications. The template's design not only presents data in a captive and visually appealing manner. But it also narrates the story behind your findings and their relevance in real-world applications. Further, this template gives the researcher the chance to explore a variety of angles and helps them consider different aspects of the issue, making research more comprehensive. It further makes research more versatile and applicable to various contexts, which makes it relevant to a broader audience.
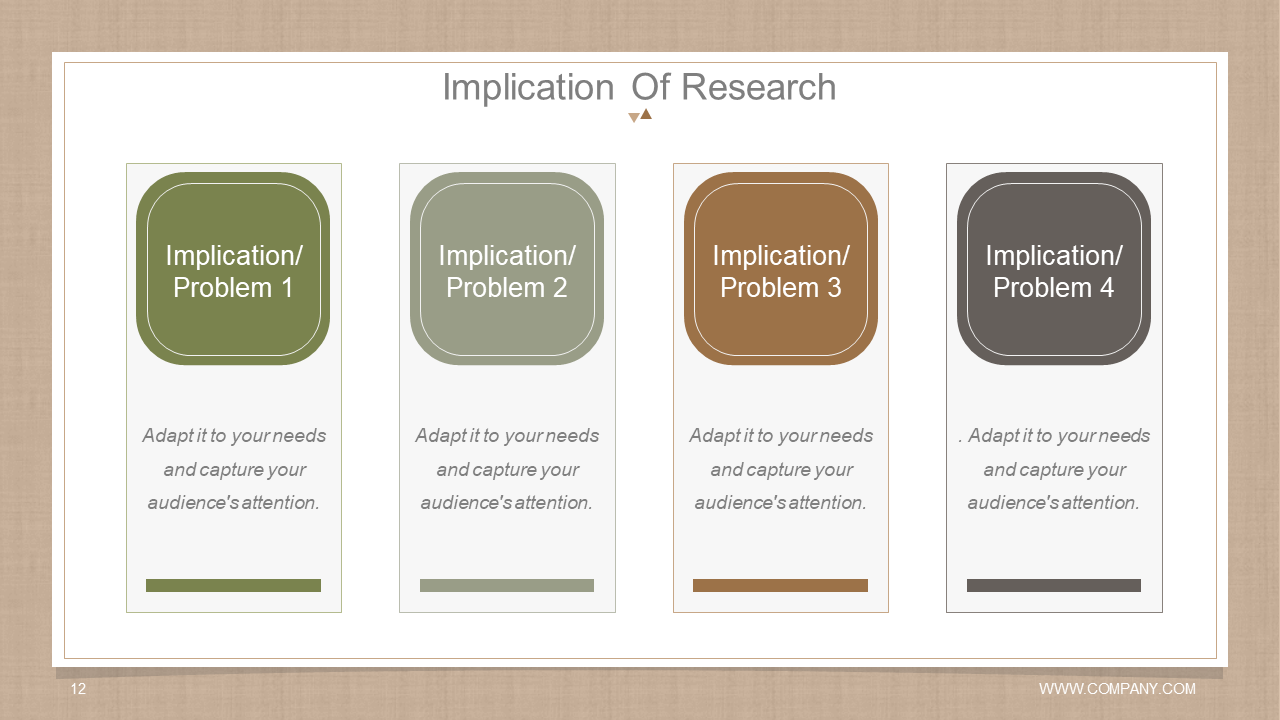
Download this template today and bridge the gap between academic research and applications.
Template 9: Aims and Objective of Research Proposal for Thesis Template (Slide 5)
This template is the blueprint for academic success. It is designed to elevate your doctoral thesis proposal. It helps you create a concise and compelling presentation outlining your research objectives. On one side, it highlights the study's objectives, while on the other, it highlights the expected outcome. This way, it ensures that your academic goals are understood easily because lack of clarity may confuse the audience. So, this template sets the stage by explaining what the study aims to achieve.

Download this template today to embark on a journey of research excellence.
Template 10: Dissertation Methodology Template
This comprehensive template can assist students through the complexities of the research approach. It can be their ultimate guide in structuring and presenting their methodology. This template subdivides the entire process into four distinguished subheadings to streamline the process. The first subheading outlines the resources that can be instrumental in research. The second subheading highlights the diversity of the research inputs and helps categorize and organize the gathered data. The following subheading details the analytical techniques for validating your findings. The last, but not least, subheadings discuss the various collection methods and illustrate the strategic approach for gathering comprehensive data.

Download this template to set a solid foundation for your dissertation.
Conclusion
A student takes 4 to 7 years to complete his Ph.D., requiring strategic planning, dedication, and dedication. Additionally, writing and publishing journals is not a cakewalk. It needs exceptional scholars' writing skills along with critical thinking. Our thesis-dissertation templates can open doors to various opportunities and establish you as a credible and competent researcher.
Additionally, our thesis timeline templates help you streamline your project planning. It also bridges the gap between academic reading and research with real-world applications.
Download these templates today and pave the way for a successful and impactful career.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Must-Have Software Migration Plan Templates with Examples and Samples

Top 10 Hedge Fund Pitch Deck Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

--> Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

--> Sales funnel results presentation layouts
--> 3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

--> Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Future plan powerpoint template slide

--> Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

--> Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

--> Agenda powerpoint slide show

--> Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

--> Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

--> Meet our team representing in circular format


PhD Dissertation Defense Slides Design: Start
- Tips for designing the slides
- Presentation checklist
- Example slides
- Additional Resources
Purpose of the Guide
This guide was created to help ph.d. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. the guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from ph.d. graduates. the tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can be used in designing other types of presentations such as conference talks, qualification and proposal exams, and technical seminars., the tips and examples are used to help students to design effective presentation. the technical contents in all examples are subject to copyright, please do not replicate. , if you need help in designing your presentation, please contact julie chen ([email protected]) for individual consultation. .
- Example Slides Repository
- Defense slides examples Link to examples dissertation defense slides.
Useful Links
- CIT Thesis and dissertation standards
- Dissertations and Theses @ Carnegie Mellon This link opens in a new window Covers 1920-present. Full text of some dissertations may be available 1997-present. Citations and abstracts of dissertations and theses CMU graduate students have published through UMI Dissertation Publishing. In addition to citations and abstracts, the service provides free access to 24 page previews and the full text in PDF format, when available. In most cases, this will be works published in 1997 forward.
- Communicate your research data Data visualization is very important in communicating your data effectively. Check out these do's and don'ts for designing figures.
Power Point Template and other Resources
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 1
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 2
Source: CEE Department Resources https://www.cmu.edu/cee/resources/index.html
- CMU Powerpoint Slide Template
Source: CMU Marketing and Communications
https://www.cmu.edu/marcom/brand-standards/downloads/index.html
- Use of CMU logos, marks, and Unitmarks
Email me for questions and schedule an appointment

Top 7 tips for your defense presentation
1. show why your study is important, remember, your audience is your committee members, researchers in other fields, and even the general public. you want to convince all of them why you deserve a ph.d. degree. you need to talk about why your study is important to the world. in the engineering field, you also need to talk about how your study is useful. try to discuss why current practice is problematic or not good enough, what needs to be solved, and what the potential benefits will be. , see how dr. posen and dr. malings explained the importance of their studies..
- Carl Malings Defense Slides with Notes
- I. Daniel Posen Defense Slides with Notes
2. Emphasize YOUR contribution
Having a ph.d. means that you have made some novel contributions to the grand field. this is about you and your research. you need to keep emphasizing your contributions throughout your presentation. after talking about what needs to be solved, try to focus on emphasizing the novelty of your work. what problems can be solved using your research outcomes what breakthroughs have you made to the field why are your methods and outcomes outstanding you need to incorporate answers to these questions in your presentation. , be clear what your contributions are in the introduction section; separate what was done by others and what was done by you. , 3. connect your projects into a whole piece of work, you might have been doing multiple projects that are not strongly connected. to figure out how to connect them into a whole piece, use visualizations such as flow charts to convince your audience. the two slides below are two examples. in the first slide, which was presented in the introduction section, the presenter used a flow diagram to show the connection between the three projects. in the second slide, the presenter used key figures and a unique color for each project to show the connection..

- Xiaoju Chen Defense Slides with Notes
4. Tell a good story
The committee members do not necessarily have the same background knowledge as you. plus, there could be researchers from other fields and even the general public in the room. you want to make sure all of your audience can understand as much as possible. focus on the big picture rather than technical details; make sure you use simple language to explain your methods and results. your committee has read your dissertation before your defense, but others have not. , dr. cook and dr. velibeyoglu did a good job explaining their research to everyone. the introduction sessions in their presentations are well designed for this purpose. .
- Laren M. Cook Defense Slides with Notes
- Irem Velibeyoglu Defense with Notes
5. Transition, transition, transition
Use transition slides to connect projects , it's a long presentation with different research projects. you want to use some sort of transition to remind your audience what you have been talking about and what is next. you may use a slide that is designed for this purpose throughout your presentation. , below are two examples. these slides were presented after the introduction section. the presenters used the same slides and highlighted the items for project one to indicate that they were moving on to the first project. throughout the presentation, they used these slides and highlighted different sections to indicate how these projects fit into the whole dissertation. .

You can also use some other indications on your slides, but remember not to make your slides too busy. Below are two examples. In the first example, the presenter used chapter numbers to indicate what he was talking about. In the second example, the presenter used a progress bar with keywords for each chapter as the indicator.

Use transition sentences to connect slides
Remember transition sentences are also important; use them to summarize what you have said and tell your audience what they will expect next. if you keep forgetting the transition sentence, write a note on your presentation. you can either write down a full sentence of what you want to say or some keywords., 6. be brief, put details in backup slides , you won't have time to explain all of the details. if your defense presentation is scheduled for 45 minutes, you can only spend around 10 minutes for each project - that's shorter than a normal research conference presentation focus on the big picture and leave details behind. you can put the details in your backup slides, so you might find them useful when your committee (and other members of the audience) ask questions regarding these details., 7. show your presentation to your advisor and colleagues, make sure to ask your advisor(s) for their comments. they might have a different view on what should be emphasized and what should be elaborated. , you also want to practice at least once in front of your colleagues. they can be your lab mates, people who work in your research group, and/or your friends. they do not have to be experts in your field. ask them to give you some feedback - their comments can be extremely helpful to improve your presentation. , below are some other tips and resources to design your defense presentation. .
- Tips for designing your defense presentation
How important is your presentation, and cookies?

- Next: Tips for designing the slides >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 11:18 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/c.php?g=883178

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
Wharton Stories
How to prepare a strong phd application.
Doctoral candidates and departmental coordinators at the Wharton School outline a few tips to help you navigate the PhD application process.
It’s no secret the application process can be intimidating. Where do you start? What exactly are schools looking for on your application? What materials do you need to submit? Doctoral candidates and departmental coordinators at the Wharton School have outlined a few tips to help you navigate the process.
Don’t Delay the Process
A successful PhD applicant starts thinking about their application months or even years before the deadlines. For Alejandro Lopez Lira , a third year student in Finance, the application process began a year before he actually submitted the paperwork. He said, “I spoke to my advisors way before, like one year before, about my letters of recommendation, where to apply, everything involved in the process.”
Each program has different requirements, which can make for a tedious process. Karren Knowlton , a third year in Management, said, “I took a little while to draft a personal statement. I had my mom, who teaches creative writing, and a few other people that I trust just read over it. Then you have to tweak it for different schools because they want slightly different things.”
Taking time to prepare your application is critical. Starting the process sooner rather than later gives you several advantages:
- It allows your letter of recommendation writers enough time in advance to thoughtfully prepare a letter that speaks to who you are as a PhD candidate.
- It gives you more time to review your materials, fix any errors, and proofread, proofread, proofread.
- Finally, it means a lot less stress when the deadline starts rapidly approaching. By planning ahead, you’ll have a much smoother process applying.
Get Letters of Recommendation
Prof. Matthew Bidwell , who previously served as the doctoral coordinator for the Management program , said a common mistake he sees are letters of recommendations from employers. Although he said it is impressive to see work experience, having an employer write a letter is not the best choice.
“We don’t pay very much attention to those because rightly or wrongly, we worry that they’re not looking for the kinds of things that we’re looking for,” he said. “If you have one, it’s not a disaster, but when you see people with two or three — most of their recommendations coming from their work — that kind of heightens our concern. You’re committing to a fairly specialized career, do you really know what that career entails?”
Instead, he suggests getting to know an academic who will be able to write a recommendation attesting to your ability to manage doctoral-level research and work.
Include Research/Work Experience in Your Field
Each program has a unique set of criteria to evaluate applicants, but several doctoral coordinators agree that some research and work experience in your field of interest will strengthen your application overall.
Prof. Fernando Ferreira , doctoral coordinator for the Business Economics and Public Policy and Real Estate programs, thinks work experience can be useful in demonstrating an applicant’s abilities. He said, “Any work experience after undergraduate school is important. If that experience is more related to research it’s even better, but work experience in general is always good.”
Prof. Guy David , doctoral coordinator for the Health Care Management & Economics program , thinks that work experience benefits applicants in terms of giving them a broader view of business. “Work experience creates retrospection about how the world works, how organizations make decisions, and how people function in various situations,” he said.
However, he warns that spending too much time away from an academic setting can have its drawbacks too. “It may lead people to start their PhD later when they are not in the habit of immersing themselves in rigorous studies and have a shorter horizons to develop a name for themselves,” he said.
Although having both research and work experience can strengthen your application, you will not be denied entry because you are lacking either.
Prof. Bidwell said, “I think research experience does give us some confidence that people have some idea about what it is that we do. In terms of work experience, I think we don’t have a strong view. We quite like work experience, but we also take people straight out of undergrad.”
Prepare for the Standardized Tests
Most PhD programs require students to take the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE). Having high test scores is a key part of an application as it tests skills learned over the course of many years in school. Quantitative skills are especially important when applying to doctoral programs in business areas. Much like any other standardized test, the GRE requires preparation.
Karren, who took the GRE twice to ensure her scores were high enough, offered advice to those who may be struggling. “I would absolutely recommend practicing the writing beforehand. Look up examples and have your outline structured,” she said. “So much of it is just getting the right structure and how you formulate your arguments so knowing what they’re looking for is key.”
Test prep can be time-consuming, but like anything else, practice makes perfect. There are multiple text books and online sites to help you prepare for the exam. Karren aimed to improve her math scores the second time she took the GRE and recommended this site to help strengthen math skills.
Taking advantage of resources to help you study can limit the number of times you need to take the GRE while ensuring you score high enough to remain in the applicant pool.
Watch a Webinar with Former Wharton Vice Dean Catherine Schrand
Posted: August 4, 2017
- Admissions and Applying
- Advancement and Transition
Doctoral Programs
Start your doctoral journey.
Whether you’re just starting your research on PhD programs or you’re ready to apply, we’ll walk you through the steps to take to become a successful PhD candidate.
Deciding to get a PhD
You might be surprised to find out what you can do with a PhD in business.
Is an Academic Career for You ? What Makes a Successful PhD Student
Preparing for the Doctoral Path
The skills, relationships, and knowledge you need to prepare yourself for a career in academics.
How the PhD Program Works How to Become a Successful PhD Applicant
Choosing the right program
What’s the difference between PhD programs? Find out how to choose one that fits your goals.
What to Consider When Choosing a Doctoral Program What Differentiates R1 Universities?
Starting an application
Tips for a successful application process.
Application Requirements Preparing Your PhD Application
Related Content

How to Build a Strong Brand Through Design

How This Penn Alum Founded a Startup Pioneering Innovation in Brain Research

How Wharton’s EMBA Program Helped this Alum Transition from Software Entrepreneur to Chief Strategy Officer

Kiersa Sanders: Beating the Odds and Finding Community

PhD Candidate Matthew Caulfield Became an Election Technology Expert — As an Undergrad

Student Combines Real Estate, Military, and Business Experiences in African Venture

Does It Pay to Have a Monarchy? The Answer Might Surprise You

Making a Career Transition, From Seoul to Philly

8 Resources This Seattle-Based Accountant Leveraged to Land a Promotion

How to Create the Infrastructure to Accommodate a Rapidly Changing Growth Enterprise

MBA Student on Exploring Career Switches Through Exposure in the Core

An EMBA Student Shares Her Strategic Study Plan for the Executive Assessment

The Role of the CFO Explained

Why This PhD Student Says Wharton Makes It Easy to Be Successful

What to Know About the Moelis Advance Access Program Before You Apply
- The PhD Interview – What to Expect and How to Prepare
Written by Mark Bennett
Most PhD applications include an interview of some sort. This allows your university (and perhaps even your prospective supervisor) to discuss the PhD with you in more detail.
They’ll ask questions about your background, goals and project. You may also be required to give a presentation.
On this page you can find out what happens at an interview, including advice on how to prepare for a PhD interview.
You can also read our separate guide for a detailed overview of PhD interview questions (and answers!).
Create a my FindAPhD account
Set-up an account to make your search easier. You can save programmes, send enquiries to institutions, view upcoming events, and see the latest news and updates, all in one place.
What happens at a PhD interview?
The format for a PhD interview can vary, depending on your subject area and the circumstances of your application.
You might be in front of a recruitment panel. Or you might just meet your supervisor in the campus coffee shop and chat about your research interests.
This makes it quite difficult to describe a ‘standard PhD interview’.
There’s a bit of a difference between going over the finer points of your MSc thesis before a panel and discussing your favourite historians in a canteen.
But two things unite both formats. Each hinges on a discussion of your academic interests, achievements and goals. And that discussion is important, however it takes place.
Even the most ‘informal’ interview aims to establish this.
Depending on the format for your PhD interview it could involve:
- A formal question and answer session in front of a postgraduate recruitment panel.
- A presentation , based on your research proposal or area of expertise.
- A one-to-one discussion with your prospective supervisor.
- An informal lunch with your prospective supervisor, other members of your interview panel and / or current PhD students.
- Various ‘orientation’ activities . These might include visits to research spaces and opportunities to chat with staff and students.
PhD interview presentation
Depending on the format of your interview, you may be asked to prepare a presentation on the advertised PhD project or your research proposal.
When you’re invited to an interview, your prospective department will let you know what their expectations are for the presentation. They’ll usually specify:
- How long the presentation should be – usually this won’t be any more than 15 minutes
- What they want your presentation to cover – for example, your academic background, your research methods, the ‘impact’ of your research
- How the presentation should be delivered – this will usually be PowerPoint but you might need to provide supplementary materials for your audience or deliver the presentation remotely over a video call
You’ll normally be speaking before a small committee of staff members, who will ask you questions about your research after the presentation.
PhD interview length
As you can imagine, the length of a PhD interview varies according to its format.
Some interviews involve several components activities, over an entire day. You could greet your panel in the morning, have lunch, visit your department and then sit down for a formal interview.
Or you might just meet your supervisor for coffee and discuss your ideas with them for an hour or so.
You can read more about what to expect in different circumstances and subject areas below.
Interviews for advertised PhD positions
Most PhDs in Science , Medicine and Engineering are specific pre-designed projects , with pre-defined aims and objectives.
They normally take place in a group that’s pursuing broader research objectives, to which your PhD will make a small (but important) contribution.
Such projects may have funding secured in advance (as part of the budget for their laboratory or workshop). Or they may have funding available in principle, confirmed if the project meets certain conditions. (These could include attracting a suitable PhD student!).
Interview goals
An interview for one of these projects needs to ensure that the applicant can complete a specific project. And that they deserve the funding available for it.
Imagine a PhD that involves analysing a specific kind of protein folding. Just being a talented life scientist may not be enough to complete this project. You’d also need to have some knowledge of the proteins in question, as well as the kinds of equipment and techniques required to analyse them.
Or, what about a digital humanities project involving the latent semantic indexing of a periodicals database? A general Masters in literature may not be enough here. You’ll also need to be able to use this kind of database. (And ideally know what latent semantic indexing is).
This isn’t to say that you have to be an expert in your research topic before you begin it. That would defeat the function of the PhD as an academic training exercise.
But you will need to be the kind of student who can develop the necessary skills and expertise in the time available. Your interview is when the university will do its best to make sure of this.

Interview format
An interview for a funded PhD project will be a formal process. The main component will be a question and answer session in front of a designated postgraduate recruitment panel.
This panel will usually involve three or more people. They could include:
- Your project supervisor (or supervisors). They will assess your academic and personal suitability for the role.
- A member of the university or department’s postgraduate admissions staff . They will normally chair the panel and ensure the interview is properly conducted. This person could also represent any structured PhD programme your project might form part of.
- The lead investigator for your prospective research group. This is the academic with overall responsibility for the research your PhD will be part of. Normally they will be your supervisor, but this may not be the case for larger laboratories or departments. If so, they might attend your interview.
- A funding representative . If an external body funds your PhD they may have a presence at your interview. This won’t normally be the case for Research Council studentships (which are managed by universities) but it could occur for other organisations.
The bulk of your interview will involve the panel asking you questions and listening to your answers. These will focus on your academic background, research interests and goals. You may also be invited to expand upon parts of your PhD application.
Some interviews may ask you to give a more specific presentation as well as answering questions. This won’t normally be long or complicated. You may be asked to talk through your research proposal in more detail, or provide a summary of a previous research project (such as a Masters dissertation).
Once your panel has finished asking its questions, you will be invited to ask questions of your own . This is an opportunity to show your enthusiasm for the subject whilst also finding out more about it.
Interviews for self-proposed PhD projects
In some subjects, such as the Arts, Humanities and some Social Sciences, pre-defined (and pre-funded) PhD projects are less common.
This isn’t always the case, of course. Arts and Humanities research can involve huge ongoing projects, focussing on the collaborative analysis of vast archives. Many branches of the Social Sciences also undertake long-term data gathering and analysis.
Yet, the majority of PhDs in these areas tend to be original projects, proposed by the student seeking to undertake them.
If this is the case for your project, you will normally apply to a university’s PhD programme , rather than a specific PhD ‘position’.
If accepted, you will have the freedom to do your own independent research. But you’ll benefit from the resources, training and support available within your programme.
Because these projects and their funding aren’t pre-defined, their interviews can be more flexible.
It won’t be necessary to confirm that you have the specific skills needed for a specific project. Or that you are the student most deserving of a designated studentship.
But this doesn’t mean that the interview for a self-proposed PhD is easier than one for an advertised position. If anything, greater scrutiny may be paid to your project proposal and to your suitability for independent research.
The university itself hasn’t identified this research topic. It needs to ensure that the project is viable, that you understand what’s involved in completing it and that you care enough about it to do so.
Interviews for self-proposed PhD projects may be more informal, but this isn’t always the case.
You could still find yourself discussing your application in front of a panel. If so your experience will be like to that outlined for advertised projects, above.
Or, you may simply be invited to chat with your prospective supervisor. This could take place in their office or in an informal setting on campus.
Don’t underestimate the importance of such a meeting. A relaxed interview can seem less serious. Yet the discussion it enables will still play a crucial role in assessing your potential for PhD study.
Your supervisor may not need to assess your suitability for a specific project, but they still need to be sure that you have the knowledge and skills to carry out research in their field.
Equally, there may not be funding available, but your prospective supervisor is still considering investing three years (or more) of their time and effort guiding your project and assisting your development.
Whether you chat with a supervisor or sit before a panel, you can expect to spend some time discussing your research proposal . This may involve formal questions and answers, or it might simply involve ‘talking through’ what you’ve written. Make sure you’re familiar with the contents of that proposal – and ready to expand upon any areas where more detail might be requested.
Other questions may focus on your previous work, on your career goals and your reasons for undertaking a PhD.
Informal interviews are unlikely to include a presentation . However, you may still be invited to talk freely about your academic interests or offer an overview of previous research work.
If there is an opportunity to allocate funding to your project (through a Research Council studentship, or similar) this may be discussed at your interview. In most cases funding is merit-based, so make sure you are prepared to talk up the specific value of your project.
Research proposals
Our guide to writing a research proposal has more detail on how you can make a success of this important part of a PhD application.
Preparing for a PhD interview
Whatever form your PhD interview takes, you should prepare for it carefully. Even a more informal discussion will touch on aspects of your previous work and explore your current research proposal.
Reviewing these materials in advance will allow you to discuss them with confidence.
The following are some good tips on how to prepare for a PhD interview:
- Review your research proposal – If you submitted a research proposal as part of your PhD application, make sure you re-familiarise yourself with it. It’s highly likely that you’ll be invited to discuss this document at your interview. Be prepared to talk in more detail about your plans and ideas. You should also be able to back up any claims you have made.
- Re-read previous academic work – There’s a good chance your interview will touch on your Bachelors and / or Masters experience. If you are applying for a specified project, this allows the panel to check the relevance of your previous studies. If you are proposing your own project a discussion of your academic background can help reveal the development of your interests and your enthusiasm for the PhD. You won’t be ‘examined’ on any of this prior work, but it can be helpful to refresh yourself.
- Read some of your supervisors’ current research – Whatever form your PhD will take, it makes sense to be familiar with what your supervisor is currently working on. This will show that you take the prospect of working with them seriously. Needless to say, it also proves that you understand the nature of the work they do! If you don’t know who your supervisor will be, take a look at some of the research currently being done within your prospective laboratory or department.
- Look at other current research in your field – By the same token, it makes sense to have some idea of the current state of academic scholarship in your area. Remember: a PhD needs to be an original piece of research. Make sure you know what’s going to be unique and original about yours. This step is especially important if you’ve taken a break from academia and aren’t up to date on current work in your area.
- Check the details of your project or programme – This may seem obvious, but it can be easy to overlook. If you’re applying for an advertised position, make sure you know it inside out. Know what its objectives are. Know who else (other than your supervisor) is involved in the research. Know about any external funders. The same applies to the PhD programme that will ‘host’ a self-proposed PhD. Find out what other research is currently being carried out there. Look up past and present students. Check what training and development is available.
- Practice any presentation material – If you’ve been asked to prepare a presentation for your PhD interview, make sure you practice it. This is particularly helpful if you aren’t familiar with public speaking. The interview panel will be supportive and encouraging, but you want to look as confident and capable as possible.
What to wear
Regardless of your interview format, you should pay some attention to your appearance.
Academic workplaces are fairly relaxed on a day-to-day basis, but your PhD interview isn’t too dissimilar from a job application. Show that you’re serious about the opportunity and dress accordingly.
A chat in your supervisor’s office can probably be treated more casually than a formal panel interview, but there’s no harm in erring on the safe side.
What to bring
You won’t necessarily need to bring anything specific to a PhD interview, unless you’ve been asked to.
You may wish to bring copies of previous academic work. It may be appropriate to mark-up key passages for reference during the interview. Or you could simply have the material available to re-read whilst you wait.
If you submitted a research proposal, you should have a copy handy. Your interviewer/s will probably refer to it.
You’ll also need to bring any presentation materials you’ve been asked to prepare. Make sure you have these in a suitable format. The last thing you need at a PhD interview is malfunctioning presentation software.
Finally, a pen and paper won’t go amiss (handy if you want to make notes as a question is asked).
Getting the most out of your PhD interview
This may seem like a slightly odd topic. Sure there’s only one thing you want to get out of a PhD interview: a place on a PhD?
Well, yes and no.
You’ll want to make sure you come across as well as possible during your interview and give a fair impression of your academic potential. Hopefully the advice on this page will help with that.
But the PhD interview isn’t just an opportunity for your university to learn about you. It’s also a unique chance for you to learn about your university.
After all, you’re considering committing a significant amount of time and energy to a PhD with them. And this may be one of the few occasions when you visit the campus and meet staff and students before actually starting your project.
With that in mind, here are a few ways to take advantage of the opportunities a PhD interview offers:
- Visit your prospective laboratory or department – You’re going to be spending a lot of time in your university’s academic workspaces, using its facilities. Take the opportunity to look at these whilst you’re on campus. You may find that a brief tour is part of your interview format. If it isn’t, ask if you can have a quick look around – if nothing else, this demonstrates your interest.
- Chat to current PhD students – If you do visit your prospective department, take the opportunity to speak to any current PhD students you meet. They’ll be happy to answer questions about what it’s actually like to study at this university (or with this supervisor…).
- Explore the campus – This may seem a little trivial, but arriving early and having the time to explore your university can be a nice way to relax before your interview. It could also give you something to chat about later.
- Ask good questions – Whatever format your interview takes, you’ll have a chance to ask questions as well as answer them. This is important, because it allows you to show your motivation and engagement with the project or programme. But it’s also a way for you to find out useful things about the university, your supervisor and expectations of you as a student. Make sure you know the right questions to ask .
Still searching for a PhD?
Head over to our PhD course search to find the latest opportunities .
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

Are you preparing for a PhD interview? Learn some of the do's and don'ts from our expert who has been through the process to help you ace yours.

Holly is officially coming to the end of her first year of PhD study. She talks to some other students to compare experiences and lessons learnt along the way.

Our guest blogger, Holly sat down with an expert on Imposter Syndrome to find out what it really is and how to tackle it.

A PhD is a great way to help you make a difference. We spoke to Josephine Agyeman-Duah about her PhD journey to improve outcomes for babies born preterm.

PhD Hard-talk is an online community for postgraduates and researchers to share their work and advice. We sat down to chat with the project founder, Noma Mguni to learn what PhD Hard-talk can do for you.

After winning our PhD Supervisor of the Year Award, we caught up with Clive Palmer to see how he got to where he is now and what life is like as a supervisor.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

education technology
253 templates
19 templates

88 templates

meet the teacher
30 templates

14 templates

welcome back to school
112 templates
PhD Dissertation
It seems that you like this template, phd dissertation presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
In order to achieve the highest academic degree there is, you need the best presentation for your dissertation. Years of hard work will pay off with this free template by Slidesgo, which can help you focus on your message without having to worry about the visual design.
The color palette is neutral, as it plays with gray, conveying maturity. You’ll find several inspiring pictures with a grayish blue filter, and these come with a nice variety of topics that reinforce the human side of things. Use our slides to place quotes, tables, timelines and graphs to properly display references, data, schedule and statistics. You’ll find it very easy to distribute your text within the composition, and the typography focuses on seriousness and stability. Everyone will soon address you as Doctor!
Features of this template
- A professional presentation template with a minimalist look and inspiring pictures
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 16 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics and maps
- Includes 1000+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online
Introduce yourself in a PhD interview (4 simple steps + examples)

The opening of an application interview for a PhD position usually starts with short introductions of everyone participating in the conversation. Many applicants wonder how to best introduce themselves in a PhD interview. Four simple steps (including examples) help you to develop a powerful self-introduction .
Introductions in a PhD interview
On the other hand, you may feel much more vulnerable during an interview than when sending a carefully crafted application letter.
A self-introduction summarises who you are and why you want the PhD position. A powerful self-introduction can set the tone for the whole interview.
If you are unprepared, there is a risk of going in all directions when it is your turn to introduce yourself. It may throw you off and make you extra nervous for the remainder of the interview.
What to do in a PhD interview introduction
What not to do in a phd interview introduction.
Several things are best to be avoided when you introduce yourself in a PhD interview:
Step 1: State your full name
| .” |
Step 2: Give a brief overview of your educational (and professional) background
Therefore, it is useful to provide a brief summary of your educational background. Those who have work experience also benefit from including it.
Step 3: Explain why you are interested in the PhD position
Step 4: thank everyone for the opportunity to be interviewed.
The final step is to thank everyone for the opportunity to be interviewed. Be gracious and polite, and express your enthusiasm for the interview. This will create a comfortable atmosphere in which questions can be freely asked and answered.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, 10 key skills of successful master's students, clever strategies to keep up with the latest academic research, related articles, 10 things to do when you feel like your dissertation is killing you, 13 awesome academic phrases to write your methodology (+ real examples), creating awesome gantt charts for your phd timeline, energy management in academia.

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How to Make an Impressive Ph.D. Proposal Presentation to the University Panel

I’d like to share a personal story that highlights the challenges and valuable lessons I learned during my PhD proposal presentation to the university panel. It was a pivotal moment in my academic journey, one that taught me the importance of preparation, adaptability, and resilience.
Fresh off completing my Master of Technology (MTech), I made the ambitious decision to pursue a PhD. Eager to build upon the foundation laid by my previous project, I chose to continue exploring the problem statement that had captivated my interest.
Determined to leave no stone unturned, I meticulously prepared my presentation, meticulously crafting over 100 slides packed with intricate details. However, in my enthusiasm to cover every aspect of my research, I overlooked a crucial factor: time management.
As I stood before the panel, ready to deliver my meticulously prepared presentation, I quickly realized that I had underestimated the constraints of time. Within minutes, the panel members interrupted, kindly but firmly asking me to halt my presentation after only 10 minutes.
This unexpected setback left me feeling disheartened and flustered. I had assumed that the panel members were experts in my field, familiar with the intricacies of the technology I was discussing. However, I soon discovered that they represented a diverse range of backgrounds, including policymakers with limited technical knowledge.
Struggling to convey complex concepts in a language accessible to all, I found myself reverting to my mother tongue, further complicating the flow of my presentation. It became evident that I had failed to communicate my data collection strategies and methodology effectively, leaving panel members with unanswered questions.
Yet, despite these challenges, I was met with a surprising level of receptivity from the panel members. Rather than dismissing my shortcomings, they patiently listened to my presentation, offering constructive feedback and guidance along the way.
In particular, the policymakers played a pivotal role in helping me align my objectives with the needs of society, emphasizing the importance of making my research relevant and impactful. Their insights prompted me to reconsider my approach and develop a contingency plan, ensuring that I was prepared for any challenges that might arise during implementation.
Despite the setbacks, the panel members recognized my potential and allowed me to register for my PhD, offering me the opportunity to continue my academic journey. Their belief in my abilities served as a source of encouragement, motivating me to redouble my efforts and strive for excellence in my research endeavours.
In the end, while my PhD proposal presentation may not have gone as smoothly as I had hoped, it was a humbling and enlightening experience. It taught me the importance of humility, adaptability, and perseverance in the face of adversity.
Armed with the valuable feedback and guidance provided by the panel members, I emerged from the experience with a newfound sense of clarity and purpose. I am grateful for the lessons learned and the opportunity to grow as both a researcher and a person.
Introduction
- Format of Ph.D. Proposal Presentation
Points to Ponder During Ph.D. Proposal Presentation
Slide 1: title slide, slide 2: introduction, slide 3: literature review, slide 4: motivation and research problem, slide 5: research question and objectives, slide 6: study design and methods, slide 7: predicted outcomes, slide 8: resources, slide 9: societal impact, slide 10: gantt chart, slide 11: potential challenges, slide 12: conclusion, ph.d. proposal presentation ppt download, how to convert my ph.d. proposal presentation to a survey paper, as a new ph.d. student, how can i improve my presentation skills for a ph.d. proposal presentation.
- How should Ph.D. students overcome the fear and anxiety of giving a Ph.D. proposal presentation?
What are the most common reasons for rejecting a Ph.D. proposal?
- What kind of profile is required to get into top Ph.D. programs?
Is it very essential to have publications for getting accepted to the Ph.D. program?
As part of the Ph.D. selection process, all students are required to present their Ph.D. proposal for approval to the Ph.D. Scrutiny Committee at the University. The goal of the Ph.D. proposal presentation and approval process is to receive constructive feedback on the proposal and ensure that the Ph.D. proposal is feasible and appropriate for Ph.D. work. The panel also can look into the timeline of the proposed work to ensure its feasibility within the given time frame. Above all, it gives an opportunity to the research scholar to face the panel during the Ph.D. proposal presentation at the early stage of his research.
Please note, before making the presentation you need to submit the 10-12 page PhD proposal Report to the University and then make a presentation in front of the selection panel. The selection panel will go through both your report and presentation to make selection. If you are not familiar with writing PhD proposal report, please visit my blog post on “Writing PhD Proposal Report to the University” for a clear understanding of how to write the PhD proposal report in a a concise and professional manner.
Format of Ph.D. Proposal Presentation
The time duration of the presentation will be around 15-20 minutes. The presentation slides should be simple, well-structured, and effective.
The presentation slides should include the following:
- The Title of the work along with the candidate and supervisor details along with their affiliations.
- Introduction to the proposal
- A brief review of relevant literature
- Motivation for the work
- Statement of the research problem and goals
- Research question, objectives of the proposal
- Study design, methods for data collection, measures
- Predicted outcomes if everything goes according to plan
- Resources to complete the work
- Societal impact
- A timetable of activities ( Gantt Chart )
- Potential challenges
Maintaining the time limitation of the Ph.D. proposal presentation is crucial otherwise the panel members may stop the presentation after the time limit and the candidate may lose his chance to clearly explain the idea.
After the Ph.D. proposal presentation, the candidate has to face the panel for clearing their doubts regarding the proposal. For this session to run smoothly, prior to this presentation the candidate has to present his work to his guide and other fellow researchers of his choice several times to get acquainted with the concepts and queries.
During the discussion, the panel may ask the following questions to the candidate
- What is the (social, scientific) significance of the proposal?
- How will you approach your research question?
- Is your proposal novel? How is it related/compared to prior works?
- What difficulties do you expect to encounter during the implementation?
- What will be the impact of this proposal on research/society?
- Show the sample of data you are planning to collect.
- What research has already been done in the proposed area? What deficiencies or gaps need attention?
- In the proposed domain, can you list the other ongoing research works?
- Why do you think your research is reliable?
- Why do you think your research is valid?
- How do you validate your outcomes?
- In what way(s) does your research proposal contributes to knowledge?
- What research methodology do you use?
- Why did you use a particular research methodology?
- Can you bridge any gap in your work?
- What are the limitations of the proposal?
- Which programming language will you use to write your program? (for computer science students)
- What source of data will be employed for the research? whether you are data is benchmarked?
- Have you taken permission to use the data set you are planning to use in your research?
- What is the strongest point in your proposal?
- In what way your research is environment friendly?
- Suppose the proposed method does not work then what alternate solution you have planned for?
- Who are the experts you are in contact with in the domain you are working?
- What are the gaps you have identified in paper XYZ shown in your references?
- How is your method better than the method proposed in paper PQR?
During the Ph.D. proposal presentation, the following points should be given prime importance
- Use simple color combinations (contrasting colors) for your slides
- Make eye contact with your panel members
- Do not have any other personal material on the pen drive or External Hard Disk in which you carry your presentation
- Do not write an entire paragraph in slides.
- Add a story to your presentation . This story which you will discuss can be a problem you have seen in a specific domain where you are planning to work and explain how your research proposal may solve that problem.
- Do not start teaching the basic concepts. The panel members already know the basic concepts. Only concentrate on objectives and methodology.
- Start your presentation by disclosing a surprising /shocking fact, about the work you are considering. This will create interest in the panel members
- Highlight the papers presented/ workshops attended by you relating to your research.
- Acknowledge the domain experts with whom you are interacting to collect the data sets ( This will indirectly show the quality of the data sets you are planning to use ).
- Use pause in between your presentation. A pause is an effective way to grab attention.
- Offer alternative solutions/backup plans for your research work.
- Do not cross the time limit
- Have Backup slides
- If you do not know the answer to any of the questions say confidently that you have not come across that concept or you do not have a clear idea regarding the same. Do not bluff. This may leave a wrong impression on the panel.
Ph.D. Proposal Presentation Template
- Title of the work
- Candidate’s name and affiliation
- Supervisor’s name and affiliation
- Briefly introduce the topic
- Explain why the topic is important and relevant
- Provide a brief overview of what the presentation will cover
- Summarize the key findings of relevant literature
- Identify gaps and limitations in the existing research
- Explain how your work will contribute to filling these gaps
- Explain the motivation behind your work
- Clearly state the research problem you are addressing
- State your research question
- Clearly articulate your research objectives
- Explain your study design and why you chose it
- Describe your data collection methods and measures
- Present your predicted outcomes if everything goes according to plan
- Explain how these outcomes will contribute to the field
- Identify the resources you will need to complete your work
- Explain how you will obtain these resources
- Describe the potential societal impact of your work
- Explain how your work will benefit society
- Present a Gantt chart representing the timetable of the activities planned
- Explain how you will manage your time to complete your work on schedule
- Identify potential challenges you may encounter during your research
- Explain how you plan to address these challenges
- Summarize the key points of your presentation
- Conclude by emphasizing the significance of your work and its potential impact
Slide 13: Questions
- Encourage the audience to ask questions
- Thank the audience for their attention
Remember to keep your presentation simple, well-structured, and effective. Use clear and concise language, and make sure your presentation is visually engaging. Good luck with your PhD proposal presentation!
- Title of the work: “A Comparative Study of Deep Learning Techniques for Image Recognition in Medical Imaging”
- Candidate’s name and affiliation: Sarah Johnson, Department of Computer Science, University of ABC
- Supervisor’s name and affiliation: Dr. Robert Lee, Department of Computer Science, University of ABC
In this slide, you have to include the title of your work, your name and affiliation as the PhD candidate, and your supervisor’s name and affiliation. The title should be concise and descriptive, conveying the essence of your research.
- Briefly introduce the topic: Deep Learning Techniques for Image Recognition in Medical Imaging
- Explain why the topic is important and relevant: Accurate and efficient image recognition in medical imaging is crucial for diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of patient progress. However, the current state-of-the-art algorithms still have limitations in handling the complexities of medical images, such as noise, variation in size and shape, and variation in imaging protocols.
- Provide a brief overview of what the presentation will cover: In this presentation, I will introduce my proposed research on a comparative study of deep learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging. I will briefly cover the literature review, the research problem and goals, the study design, and the expected outcomes of the research.
In this slide, you have to provide an introduction to your research topic, explaining its importance and relevance in the field. The introduction should set the context for your research and explain why it matters.
- Summarize the key findings of relevant literature: Previous research has shown that deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), have achieved state-of-the-art results in various image recognition tasks, including medical image recognition. However, the performance of these techniques can be affected by factors such as the size and complexity of the dataset, the selection of hyperparameters, and the choice of architecture.
- Identify gaps and limitations in the existing research: While previous studies have compared the performance of different deep learning techniques for image recognition in general, there is a lack of research that compares and evaluates the performance of these techniques specifically in medical imaging. Additionally, there is a need for research that investigates the effectiveness of transfer learning, data augmentation, and other techniques for improving the performance of deep learning models in medical image recognition tasks.
- Explain how your work will contribute to filling these gaps: The proposed research aims to contribute to filling these gaps by conducting a comparative study of various deep learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging. The study will also investigate the effectiveness of transfer learning, data augmentation, and other techniques for improving the performance of these techniques in medical image recognition tasks. The results of this study will provide valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of different deep-learning techniques in medical imaging, and help inform the development of more accurate and efficient algorithms in the future.
In this slide, you have to summarize the key findings of relevant literature in your research area, identify gaps and limitations in the existing research, and explain how your work will contribute to filling these gaps.
| Slide 3: Literature Review |
|---|
| – Deep learning techniques (e.g. CNNs, RNNs) have achieved state-of-the-art results in various image recognition tasks, including medical image recognition. |
| – Performance can be affected by factors such as dataset size and complexity, hyperparameter selection, and architecture choice. |
| – Lack of research comparing and evaluating deep learning techniques specifically in medical imaging. |
| – Need for investigation of transfer learning, data augmentation, and other techniques for improving deep learning model performance in medical image recognition tasks. |
| – Conduct a comparative study of various deep learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging. |
| – Investigate the effectiveness of transfer learning, data augmentation, and other techniques for improving deep learning model performance in medical image recognition tasks. |
| – Provide valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of different deep learning techniques in medical imaging, and help inform the development of more accurate and efficient algorithms in the future. |
In this format, the information is organized into three sections: key findings, gaps and limitations, and contribution of proposed work. Each section is presented as a bullet point, with the main idea in bold, followed by a brief explanation. This format can be useful for presenting information in a clear and concise manner, while still providing enough detail to convey the main points.
| Slide 4: Motivation and Research Problem |
|---|
| – Medical image recognition is an important application with significant potential for improving patient outcomes. |
| – Deep learning techniques have shown promise in this area, but their effectiveness depends on various factors, and there is still room for improvement. |
| – A comprehensive study of deep learning techniques for medical image recognition could help identify the most effective approaches and guide future research. |
| – The goal of this research is to conduct a comparative study of deep learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging and investigate the effectiveness of transfer learning, data augmentation, and other techniques for improving model performance. |
| – Specifically, we aim to address the following research questions: |
| – What are the relative strengths and weaknesses of different deep-learning techniques for medical image recognition? |
| – How can transfer learning and data augmentation be used to improve model performance? |
| – What are the key factors affecting model performance, and how can they be optimized? |
In this format, the motivation and research problem are presented as two separate sections, with each section consisting of bullet points. The motivation section explains why the topic is important and why the proposed research is needed, while the research problem section clearly states the specific questions that the research will address. This format can help ensure that the motivation and research problem are clearly articulated and easy to understand.
| Slide 5: Research Question and Objectives |
|---|
| – What are the most effective deep-learning techniques for medical image recognition, and how can they be optimized for improved performance? |
| – To conduct a comparative study of deep learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and hybrid models. |
| – To investigate the effectiveness of transfer learning, data augmentation, and other techniques for improving model performance. |
| – To identify the key factors affecting model performance, including dataset size, complexity, and quality, and optimize these factors for improved accuracy and efficiency. |
| – To develop a comprehensive set of guidelines for using deep learning techniques in medical image recognition, based on the results of the study. |
In this format, the research question and research objectives are presented as two separate sections, with each section consisting of bullet points. The research question clearly states the specific problem that the research will address, while the research objectives explain the specific goals that the research aims to achieve in order to answer the research question. This format can help ensure that the research question and objectives are clearly articulated and easy to understand.
| Slide 6: Study Design and Methods |
|---|
| – Comparative study of deep learning techniques for medical image recognition. |
| – Experimental design with three groups: one using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), one using recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and one using hybrid models. |
| – Randomized assignment of datasets to groups to control for confounding factors. |
| – Datasets: Publicly available medical image datasets, including the MURA, ChestX-ray8, and DeepLesion datasets. |
| – Measures: Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and AUC for image recognition. |
| – Methods: Each group will train and test their models on the same datasets, with performance measures recorded for each model. |
In this format, the study design and data collection methods are presented as two separate sections, with each section consisting of bullet points. The study design section provides an overview of the design of the study, including the specific groups being compared and the methods used to control for confounding factors. The data collection methods section describes the datasets and measures being used, as well as the specific methods being employed to train and test the deep learning models. This format can help ensure that the study design and methods are clearly explained and easy to understand.
| Slide 7: Predicted Outcomes |
|---|
| – The CNN group is predicted to achieve the highest accuracy and AUC scores for medical image recognition. |
| – The hybrid model group is predicted to achieve high sensitivity and specificity scores, making it well-suited for certain medical applications. |
| – The RNN group is predicted to perform well on image sequences, such as those in medical videos or time-lapse images. |
| – This study will provide a comparative analysis of deep learning techniques for medical image recognition, helping to identify which techniques are most effective for different applications. |
| – The study will contribute to the development of improved medical image recognition models, which can have a significant impact on patient care and treatment outcomes. |
In this format, the predicted outcomes are presented as bullet points, along with an explanation of how they will contribute to the field. The predicted outcomes are based on the study design and methods described in previous slides and can help to demonstrate the potential impact of the proposed research.
| Slide 8: Resources |
|---|
| – Access to medical image databases with labeled images for model training and testing. |
| – Powerful computing resources, such as GPUs, for running deep learning algorithms. |
| – Software tools for image pre-processing, deep learning model training, and model evaluation. |
| – Technical support for troubleshooting and optimizing software and hardware issues. |
| – Medical image databases will be obtained through collaborations with healthcare institutions and research organizations. |
| – Computing resources will be obtained through the university’s high-performance computing center. |
| – Software tools will be obtained through open-source repositories and commercial licenses as needed. |
| – Technical support will be provided by the university’s IT department and by contacting software vendors and community forums as needed. |
This slide presents the resources needed to complete the work, along with an explanation of how these resources will be obtained. This can help to demonstrate that the necessary resources have been identified and that a plan is in place to obtain them.
| Slide 9: Societal Impact |
|---|
| – Improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical image analysis can lead to more accurate and timely diagnoses, which can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. |
| – Developing robust and interpretable deep learning models can help to build trust in these technologies and enable their widespread adoption in clinical practice. |
| – Generating new insights into brain tumor growth and progression can help to guide treatment decisions and lead to more personalized and effective therapies. |
| – By improving medical image analysis, our work can help to reduce the time and cost of diagnosis, increase the accuracy of treatment planning, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. |
| – By developing more interpretable and trustworthy deep learning models, our work can help to facilitate their integration into clinical practice and improve patient care. |
| – By providing new insights into brain tumor growth and progression, our work can help to guide the development of more targeted and effective treatments. |
This slide presents the potential societal impact of the work and how it will benefit society. This can help to demonstrate the broader implications and significance of the research.

Gnatt chart representing the timetable of the activities planned
You have to create a Gantt chart to represent the activities that are planned for completing this research work within the given time frame. The time frame can change depending on the Univesity’s stipulated guidelines for full-time and part-time Ph.D. programs.
The chart is divided into five different stages, which are:
- Completion of the Course Work: You need to complete the coursework papers as per University Guidelines. This stage is expected to take 12 months.
- Literature review: In this stage, we will review and analyze the existing literature to identify gaps and limitations in the research. This stage is expected to take 06 months.
- Data collection: In this stage, we will collect the required data by conducting experiments and surveys. This stage is expected to take 06 months.
- Data analysis: In this stage, we will analyze the collected data to draw meaningful insights and conclusions. This stage is expected to take 3 months.
- Model development: In this stage, we will develop the proposed model and implement it. This stage is expected to take 12 months.
- Results and Analysis: In this stage, we will gather the results from various dimensions of the proposed model and analyze them. This stage is expected to take 03 months.
- Writing and submission: In this stage, we will write and submit the final research report and the thesis. This stage is expected to take 06 months.
You have to allocate appropriate time for each stage to complete the work on schedule. You have to keep track of the progress regularly and make necessary adjustments to the plan to ensure the timely completion of the research work.
In this section, you have to discuss some potential challenges which you may encounter during your research and how you plan to address them.
Potential Challenges:
- Access to data: Since we are planning to collect data from several sources, it may be challenging to obtain access to all the necessary data.
- Time constraints: We have a strict timeline to follow, and any delays could affect the overall success of the project.
- Technical difficulties: There is always a risk of encountering technical difficulties during data collection or analysis.
Addressing the Challenges:
- Data access: We will communicate with the relevant authorities and request access to the data needed for our research. We will also explore alternative sources of data if necessary.
- Time constraints: We will break down our research into smaller, more manageable tasks and allocate sufficient time for each. We will also build in extra time in case of unexpected delays.
- Technical difficulties: We will test our data collection and analysis tools thoroughly beforehand to minimize the risk of technical difficulties. We will also have contingency plans in place in case of any issues that may arise.
By identifying potential challenges and having a plan in place to address them, you can ensure that your research progresses smoothly and efficiently.
In conclusion, this presentation has outlined a research proposal for a comparative study of deep learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging. The key points covered in this presentation are:
- The importance of developing accurate and efficient image recognition techniques for medical imaging, which can assist in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions
- A review of the relevant literature in this field has identified the need for further research to compare the performance of different deep-learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging
- The research problem, objectives, and research question, aim to address this need by comparing the performance of different deep-learning techniques for image recognition in medical imaging
- The study design and methods, which will involve collecting and analyzing medical imaging data using various deep-learning techniques
- The predicted outcomes of the study, which could contribute to improving the accuracy and efficiency of image recognition in medical imaging
- The resources required to complete the study, including access to medical imaging data and computational resources
- The potential societal impact of the study, which could benefit patients and healthcare providers by improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical imaging
- The timetable of activities, which has been represented in a Gantt chart to ensure that the study is completed on schedule
- The potential challenges that may be encountered during the research, and the strategies that will be used to address these challenges.
Overall, this research proposal has the potential to contribute to the field of medical imaging by providing valuable insights into the performance of different deep-learning techniques for image recognition. By improving the accuracy and efficiency of image recognition in medical imaging, this research could ultimately benefit patients and healthcare providers.
Please enter your details to download the PPT of the PhD proposal presentation.
Here is an interesting thing. You may be wondering about the amount of effort you have put into preparing the Ph.D. proposal material and its further usage. Here is a quick tip. In fact, after finishing my Ph.D. proposal presentation my supervisor asked me to convert that material into a survey paper so that it can be showcased in the first Doctoral committee meeting to gain some brownie points from the members. I did the same and got lots of admiration from the committee members.
To convert your Ph.D. proposal material to a survey paper, you can start by using your existing literature review as the foundation. Expand your literature review to include a broader range of sources and provide a comprehensive overview of the research area. Use your research question and objectives to structure your paper and provide a detailed analysis of existing research, highlighting gaps and potential areas for future research.
Check out our blog posts listed below on how to write a survey paper and a structured literature review for more guidance on structuring and writing your paper.
How to write a better Survey Paper in 06 easy steps?
The Art of Conducting a Systematic Literature Review (SLR): Expert Advice for Researchers
Unlock Exclusive Access to the PhD Navigator Tool – for a Streamlined Research Experience for FREE!
Dear fellow researchers,
If you are a PhD research scholar or planning to pursue PhD, I understand the value of time in your PhD journey. That’s why I have organized my blog posts related to PhD meticulously, categorizing more than 100 articles into various stages of PhD (from planning of PhD to careers after PhD).
You can get this tool ABSOLUTELY FREE , by sending an email to [email protected] with the subject line “Subscribe: PhD Navigator Tool-1.0” By subscribing not only will you gain free access to this invaluable tool, but you’ll also receive regular updates on this tool and our blog’s latest insights, tips, and resources tailored for researchers.
Happy researching!
Best regards,
Dr Vijay Rajpurohit
A Ph.D. proposal presentation is a crucial step in obtaining approval for your research project. It requires careful planning, organization, and presentation skills to effectively communicate the significance, goals, and methods of your proposed research to the review committee.
By following the tips and guidelines discussed in this blog post, you can create an impressive and compelling presentation that showcases your expertise and potential to make a significant contribution to your field of study.
Remember to emphasize the importance and potential impact of your research, address potential challenges, and provide a clear timeline and plan for your project.
With a well-prepared presentation, you can increase your chances of obtaining approval for your Ph.D. proposal and embarking on a successful research journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
To get yourself accepted by the Ph.D. panel you need to do lots of research regarding the domain of interest in which you plan to pursue your Ph.D. Read the base paper thoroughly so that you will be clear regarding the basic implementation details. You need to do lots of rehearsals in front of your friends and family members, and in front of the mirror.
How should Ph.D. students overcome the fear and anxiety of giving a Ph.D. proposal presentation ?
By improving their domain knowledge; interacting with domain experts; listening to podcasts and youtube videos related to the concerned domain; and honing their communication skills, Ph.D. students can overcome fear and anxiety while giving the presentation.
The main reasons for rejecting the proposal are the limited literature survey; incomplete research gap analysis of the domain; non-coherent objectives; and the poor link between the aim and the objectives.
What kind of profile is required to get into top Ph.D. programs?
One or two good publications or conference presentations in the related domain of research will boost the chances of getting into top Ph.D. programs.
It is not essential to have publications for getting accepted to the Ph.D. programs. With thorough knowledge of the domain of research and clearly defined aims and objectives, one can impress the research panel to consider the applicant for the PhD admission.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- Student/Faculty Portal
- Learning Hub (Brightspace)
- Continuous Professional Development
- Admissions and Application Process
Prerequisites and Requirements
- Financial Support
- Curriculum Overview
- Initiative for Maximizing Student Development (IMSD)
- Career Development Internships
- Tracks Overview
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Biomedical Engineering and Physiology
- Clinical and Translational Science
- Molecular Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
- Neuroscience
- Regenerative Sciences
- Virology and Gene Therapy
- Find a Mentor
- Student Life Overview
- Student Organizations
- Graduate Student Workspaces
- Events and Programs
- Alumni Perspectives
Before applying to the Ph.D. Program at Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, review our full list of prerequisite information and complete admission requirements. The admissions committee reviews all completed applications through a holistic review process to select candidates for interviews.
Prerequisites
Candidates for the Ph.D. Program must meet the following eligibility requirements:
- Completion of a bachelor's degree, preferably in the biological or physical sciences, from an accredited institution.
- A minimum cumulative undergraduate GPA of 3.0 on a 4.0 scale.
- Degree conferral before the program begins (program begins in July).
Suggested undergraduate coursework:
- Applicants to our Ph.D. program are encouraged to have completed coursework with demonstrated proficiency (B average or above) in their math and science courses. Additionally, advanced courses in biology, chemistry, and physiology are encouraged.
- Applicants interested in applying to the Biomedical Engineering and Physiology Track are advised to take courses in quantitative science and engineering, such as signal processing, computer science, and instrumentation.
Holistic review
Our Ph.D. program prepares students to translate scientific discoveries into applications that improve patient care. This requires a wide range of skills, aptitudes, and characteristics. Along with the basic set of prerequisites, the track admissions committees take a holistic approach to admissions; meaning, they take into consideration the many factors that make up an applicant. These acceptance factors include:
- Academic performance
- Letters of recommendation
- Personal statement
- Research experience
Transfer student policy
The only pathway to matriculation at Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences is through application during the annual application window, September 1 - December 4.
The Ph.D. program does not accept transfer students; however, transfer credits for graduate courses taken at another institution may be considered if appointed to our Ph.D. program.
Application window
Apply between Sept. 1 and Dec. 4 for the following academic year.
To get in touch with the Ph.D. Program, fill out the form on the Contact Us page .

Create moving, zooming presentations that grab attention and keep it.

Appear right alongside your content while presenting to your audience.

Make stunning interactive charts, reports, maps, infographics, and more.
You're about to create your best presentation ever
Phd Interview Presentation Template

PhD Interview Presentation
Transcript: Interview for PhD position at University of Paris Academic Background Academic Background - High School Degree in Mathematics Chounen High School, 2016 - Bachelor Degree in Physics University of Djelfa, 2016-2019 - Master Degree in Astrophysics University of Constantine 1, 2019-2021 Courses Highlights M1 Courses First year of master degree Fundamental astronomy Astronomical data processing Interstellar medium computational physics general relativity Particle physics Courses Highlights M2 Courses Second year of master degree Standard model Astroparticle physics High-Energy Astrophysics Cosmic Rays Nuclear Astrophysics Vision Experience in data analysis Experience in correlation research Experience in scientific writing Experience in Python programming and Basic ML knowledge Why would I fit for this program Research Experience Research DRAFT Paper Algorithms Here are few algorithms used in my previous works correlation finder D'Agostni Fitting ML Algorithms Machine Learning Algorithms Support Vector Machines K-Nearest Neighbors Decision Trees Future Goals To do learn and develop machine learning algorithms for the search of neutrino-gamma correlations and analyze its data. Approach: - benefit from my previous experience -benefit from the AHE group -learn advanced machine/deep learning techniques THANK YOU

Transcript: Interview for PhD position at Utrecht University About Me! I am a Yemeni, lived 20 years in Malaysia. My interest has always revolved around giving back to either society and the planet. I am currently finialisng my Masters thesis at Radboud University, and also interning at a chemical manufaturing company. About Me Academic Background Bachelor’s degree in Banking and Finance, specialising in risk management and investment, - Asia Pacific University, 2014 - 2018 Pre-Masters in Environment and Society - Radboud University, 2021 - 2022 Master’s degree in Global Environment and Sustainability - Radboud University, 2022 - 2023 Academic Background Professional Background Professional Background Treasury Trainee; 2018 - 2019 skills: Financial Analysis and Risk management Sustainability Intern; 2020 - 2021 skills: Stakeholder Engagement and compliance Student Assitant (Quantitative methods); 2022 - 2023 skills: Literature Review, reporting and Data Analysis CSR & QHSE trainee; 2023 - 2023 skills: Communication and Collaboration, chemical and material science and solution based strategies Research Experience Research Bakgroynd Relevant research Research that are relevant Life cycle assessment on Radboud's greenhouse; 2022 - 2023 Operating bed covers and heat mattresses; 2022 - 2023 Master's Thesis; How are green and blue hydrogen are framed in European Media?; 2022 - 2023 Intenrship report: Map out waste streams and idetitfy opporunties of reuse and recycle; 2023- 2023 Master Thesis An indepth look into my master's thesis How has hydrogen technology been framed in European media between 2018 and 2023? What frames surrounding blue and green hydrogen technology emerged in European media? • Who are the key actors involved in shaping the narrative around blue and green hydrogen technology in media discourse, and how do they form coalitions? • How have broader societal and environmental concerns influence the framing of hydrogen technology, and what factors have contributed to its legitimacy? Why this topic? Motivations - Blue and green hydrogen as emerging technologies with potential to play a role in the transition to a low-carbon future. - Lack of research on how blue and green hydrogen are framed in the media. - Importance of raising public awareness of benefits and challenges of blue and green hydrogen. Theories Theories and Methodologies - Framing Theory by Gamson & Modigliani (1989) - Discourse Coalition by Hajer 2006 -->Technology legitmacy - Qualitative - Media Analysis + Two mode network - Atlas ti Methodologies Result My Candidancy Why I fit for this progam • Research background • Interdisciplinary skills • Methodological expertise • Passion for sustainability • Communication skills • Postdoctoral position • Energy sector • Knowledge exchange • Long term vision Future Goals My future goals

Transcript: Interview for PhD position at Maastricht University Academic Background - BS in Computer Engineering (IT branch) Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University, 2013-2017 - MS Degree in Computer Engineering Bilkent University, 2019-2022 Academic Background BS Courses Highlights Artificial Intelligence Decision Support and Expert Systems Database Systems Discrete Mathematics BS Courses MS Courses Highlights MS Courses Machine Learning Deep Learning Computer Vision Computational Geometry Parallel Computing Research Experience Research Applying Information Retrieval Paradigms in NL to SQL Translation Conditional text generation for query recommendation Explaining multi-class classification results TranSQLate MS Thesis improve the accuracy by 16.5% Learning with additional feratures Transformers DRAFT Paper Data Scientist 1001Epochs Work Experience Used LLMs to paraphrase Question-Answering model using Langchain Similarity search Vision Experience in data analysis Experience in correlation research Experience in scientific writing Experience in Python programming and Basic ML knowledge Why would I fit for this program Trustworthy Explainiability, Transparency, Traceability Trustworthy Conversational AI Scale Blending skills personality, knowledge, empathy Generation strategies beam search, next token sampling, and n-gram blocking Conversational AI Future Goals To do learn and develop machine learning algorithms for improving the quality of chatbots and Conversational AI Approach: - benefit from my previous experience -benefit from the great research envirnment at UM -learn advanced machine/deep learning techniques THANK YOU

PhD Interview Presentation Template
Transcript: Why I Have Applied for a PhD Program Project 2 Overview Diving into [Project Name], I delved into [brief description of the research questions]. The methods utilized, such as [mention specific methods], led to [highlight significant outcomes]. This project enhanced my expertise in [mention relevant skills or knowledge areas]. Mostafa Gharbawi Dissertation project: Synchronisation of Heterogeneous Oscillators in Power Networks Introduction: Unveiling My Academic Journey With a background in [mention field], I am deeply passionate about [add specific research interests]. Through my academic journey, I have honed my skills in [mention relevant skills] and aim to make impactful contributions to the field of [mention field]. A Stable Power Network: Aim: Online integration of renewables into the grid, Eliminating environmental impacts. Challenges: Operational and inertial dissimilarity, system instability, Asynchronisation and frequency disturbance, Uncertainty in availability of natural resources. Prepared for the Next Chapter Personal Background: Studied Engineering Mathematics, Skillful in data modeling, Worked on numerous group projects, Helped my employer to increase revenue, Highly receptive, enthusiastic, and discipline. Envisioned Power Network: Project 1 Overview Solutions: Conventional power network model, Kuramoto model. Results: Synchronisation and stability equivalence, Quantifying network connectivity, Synchronous parametric conditions. Future work: Feasible synchronisation conditions, Locally merging green generators. Involvement in Other Group Projects Automation of Manual Tasks Early Prediction of Sepsis Disease Objective: Service Quality, End-user experience. Tools: Challenges: Data pre-processing, Missing clinical records, Effective approach. Binary Probabilistic Classification: Maximum a Posteriori method, Naive Bayes Theorem. Outcome: Reduced completion time to 20%, Streamlined journal process, Improved invoicing quality. Why Am I the Ideal Candidate for This Project? My educational background, Possess genuine passion for this field, Result-driven and pragmatic in approach, Responsible for my own academic development, Believe in AI as a tool for the betterment of humanity. Assignment Using MAP: Skills Acquired: Data quality assurance, Coding reproducibility, Collaboration & improvement, Interpersonal & communication. Final Results: THANK YOU FOR LISTENING Improved input data Increased success rate from 45-60% Any questions? [email protected]

Transcript: Interview for PhD position at University of Antwerp Academic Background Academic Background High School Degree Exchange student in Canada for 6 months Master Degree in Physics Federal University of Pernambuco PhD in Physics Federal University of Penambuco Graduation in Physics Federal University of Pernambuco 2017-2019 2013 2020-2022 2022-2026 Courses Highlights Classical Electrodynamics Quantum Theory Statistical Mechanics Quantum Optics Master Courses Courses Highlights PhD Courses Advanced Classical Mechanics Computational Physics Magnetic Properties of Structures Advanced Classical Electrodynamics (ongoing) Teaching experience Experience teaching physics High School Teacher Colégio Fernando Ferrari High School Teacher Colégio Imaculado Coração de Maria Substitute Professor Federal University of Pernambuco Contract Professor Faculty of Igarassu 2021 2021 - 2023 2020 2023 High School Teacher National Commercial Apprenticeship Service - Senac 2023 Prizes Useful skills Checklist Experience using Latex for scientific writing Experience solving Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamic simulation Data analysis using OriginPro and Gnuplot Experience using OOMMF and Mumax3 for simulation of magnetic reversal and FMR Programming skills using Bash Script, C, Octave and Python Research Research Experience Algorithms Some previous algorithms Monte Carlo Molecular Dynamic Mumax3 + Bash Results a) b) c) d) Draft Paper Dipolar magnetic interactions in 3x3 arrays of rectangular Ni nanopillars Simulations of FMR for study the shape anisotropy in square hollow nanopillars Effects of the packing factor on magnetic anisotropy in a 3x3 array of square hollow Ni nanopillars Simulated FMR to study in plane magnetic anisotropy of 3x3 array constituted by square base nickel nanopillars Future Goals Learn Density Functional Theory 01 Using DFT to find magnetic parameters Calculations using VASP 02 Learn and use VASP in simulations Improve my scientific writing skills 03 04 Objectives Study and enhance my knowledge to publish more scientific papers Contribute with my expertise and proactivity Use my previous experiences to contribute to my fellow's work and keep a good labor environment Questions? ?

Transcript: PhD Interview Presentation Safety and Sustainability in Bio-based Composites' Structural Design Another point Remember to break up your words so your audience can follow. Academic Background Master's in Architecture, Building, and Planning (Eindhoven University of Technology) Specialization: Architectural Urban Design and Technology Thesis: Sustainable design of detached houses for extended Danish families Bachelor in Architecture (Sadjad University of Technology) Key Courses: Strength of Materials, Building Materials, Statics Willow Technologies, Ghana Source: Paul Yakubu. "Willow Technologies Transforms Agricultural By-Products Into Building Materials in Ghana" 28 Jul 2023. ArchDaily. Accessed 1 Jun 2024. <https://www.archdaily.com/1004645/willow-technologies-transforms-agricultural-by-products-into-building-materials-in-ghana> ISSN 0719-8884 Thank you for your time and consideration Skills and Competencies Technical Skills: Autodesk AutoCAD Autodesk Revit Rhinoceros 3D Adobe Creative Suite (InDesign, Illustrator, Photoshop) Python SQL SPSS Introduction Hasti Serajahmadi MSc in Architecture, Building, and Planning specializing in Architectural Urban Design and Technology BSc in Architecture Professional Experience Internship at UArchitects (May 2022 – Oct 2022) Collaborated on sustainable design projects and competitions such as MICROHOME Junior Architect/Assistant at Jam Silica Processing Company (Sept 2020 – Aug 2021)

PhD interview Presentation
Transcript: Input: Literature review Existing data sets Qualitative & quantitative data collected from case study regions Outputs: Create spatial framework Model various land use scenarios using framework at different spatio-temporal scales Present future scenarios in social ecological political contexts Glastir Woodland Creation Opportunities Phase 1 habitat map Project methodology Broadleaf woodland habitat network - Forest Research Various indexes: % cover, No. of patches, total edge, core area. Distribution of welsh woodland is spatially correlated rather than random and governed by topography, hydrology and land use (agriculture/plantation) Conifer plantations - highly correlated, broadleaf woodlands - less clustered Europe - percentage tree cover Ancient Woodland Inventory (2011) Northern forest Land cover thresholds (Forest Research) Peri-urban forest Afforestation - "50 million new trees" Urban/industrial and post-industrial landscape Shadows path of east-west M62 Biodiversity offsetting - masking woodland losses elsewhere? Only £5.7 million from Government from a projected total of £500 million Centre for Ecology and Hydrology - Land cover map 2015 Where can we see some of these drivers playing out in a UK context? Revive absent ecological processes Increase habitat connectivity. Core zones and buffer zones. Land already committed through NGO partners and public forest. Big change is bringing farmers onboard Precedents set by Pontbren project and MWT Pumlumon project (PES) Work on adapting commons concept Summit to Sea/O’r Mynydd i’r Môr Northern Forest Policy instruments Forest products markets Forest cultures Value of competing land uses Innovation - tech & skill Land abandonment Biodiversity - habitat protection Topography/Hydrology Thank you! Diolch yn fawr! Scale - at what spatio-temporal resolutions? Mapping between models and real world - applying landscape thresholds to random and actual landscapes. Modelling resilient, robust woodlands. "Crowded future landscapes" - competing land uses - woodland emergence within hostile matrix of intensive land use - disruption of open habitat networks. Interplay between spatial analysis and social research. Ethical dimension - respect for present landuse practice and social/cultural importance of this. Place spatial analysis within complex social ecological economic, politcal context. Before Adam Thorogood Summit to Sea Case studies 2016 Wales forest extent, loss & gain Land use change on a large scale involving multiple partners. Passive vs. Active afforestation National Forest Summit to Sea - terrestrial and marine, upland, agricultural Northern Forest - built environment, infrastruture, peri-urban National Forest - 28 years into project, peri-urban, afforestation Borders Forest Trust - Carrifran Wildwood, upland afforestation Knepp Castle - estate, ex-arable/dairy land, process-led wilding Trees for life - Scottish highlands, restore Caledonian forest Mersey Forest - community-led, partnership, peri-urban "Emerging spaces for native woodland growth in Britain's crowded future landscapes." Operationalising future planing PhD Interview presentation Adam Thorogood 10th Aug 2018 Useful Datasets What are the drivers and constraints for increase or decrease in forest cover? Trees for Life Slovenia forest extent, loss & gain Phase 1 habitat survey Ancient Woodland Inventory Glastir woodland creation opportunities Agricultural data sets - IBERS Sentinel 2 satellite data UK forest extent, loss & gain

Transcript: EDUCATION EXPERIENCE SKILLS RESEARCH PLAN [email protected] EXPERIENCE 2014-2020 2014-2020 Faculty Member | Instructor Islamic Azad University of Fariman 2016-2017 2016-2017 Islamic Azad University of Mashhad 2006-2014 2006-2014 Islamic Azad University of Bam EDUCATION Publications Ph.D. B.Sc. M.Sc. M.Sc. Bachelor's Degree Skilled gained: Master's Degree Skills gained: Thesis focus: Ph.D. Thesis: Thesis focus: Ph.D. Degree Publication Master's thesis: Master's Degree (Second M.S.) Course projects: Thesis focus: RESEARCH PLAN MANAGERIAL Language Skills Mother tongue (s) Other language (s) Language 1 Language 2 Language 1 Language 2 Language 3 Other Skills Name your Skills Skills description: Skills proficiency: Skill 1 Skill 2 Skill 3 TECHNICAL Name your Skills Skills description: Skills proficiency: Skill 1 Skill 2 Skill 3 COMPUTER Name your Skills Skills description: ARTISTIC RESEARCH PLAN MANAGERIAL Language Skills Mother tongue (s) Other language (s) Language 1 Language 2 Language 1 Language 2 Language 3 Other Skills Name your Skills Skills description: Skills proficiency: Skill 1 Skill 2 Skill 3 TECHNICAL Name your Skills Skills description: Skills proficiency: Skill 1 Skill 2 Skill 3 COMPUTER Name your Skills Skills description: ARTISTIC
Explore our templates for more presentation inspiration

Training - EDU
Description: A well-organized training presentation template is a critical tool for education professionals. From roadmaps to reviews, this training template will help you take your next EDU training presentation to the top of the class.

Creativity-Paint
Description: For grant requests, funding pitches, program proposals, or any other kind of education or nonprofit presentation, this Prezi template is the way to generate interest and momentum. Like all Prezi education templates and Prezi nonprofit templates, it’s easily customizable.

Resume-Blue
Description: Rise way above the stacks and stacks of two-dimensional paper resumes on the hiring manager’s desk with a Prezi resume template. Simply personalize this Prezi presentation template to create your very own “Prezume” and impress them with your dynamism, originality, and cool.

Easy Book Presentation Template for Individual Design | Prezi
Description: When you need to clearly spell out your message, this creative Prezi template is the way to go. As with all Prezi education templates and Prezi nonprofit templates, this one is easy to customize to let you zoom in on your ideas or pull back to show the big picture.
Now you can make any subject more engaging and memorable
- The Science
- Conversational Presenting
- For Business
- For Education
- Testimonials
- Presentation Gallery
- Video Gallery
- Design Gallery
- Our Customers
- Company Information
- Prezi Support
- Prezi Classic Support
- Hire an Expert
- Data Visualization
- Infographics
June 30, 2024
June 28, 2024
May 31, 2024
- Latest posts
© 2024 Prezi Inc. Terms
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Preparing a very short presentation for a PhD interview [closed]
I have an interview for a PhD position for which I have to create a presentation. They say:
In this first stage interview you will be asked to give a four minute presentation on a project you have recently been involved and your suitability for this Ph.D. This will be followed by around 10-15 minutes of general questions from the panel.
My English is not very well and the interview is in English. Does anyone know how I should create a presentation? What topic I have to mention it?
What are their possible questions?
- presentation
- 2 What are possible questions - all are possible. Only the committee know what will they ask you . As per the 4-min presentation: the shortest I've given was a 6-7 mins one. I wrote down the whole text I intended to tell, and re-read it several times, also aloud, and said the presentation to a colleague. This was not learning it word-by-word by heart, but to have the exact plan of the presentation settle in my mind. – user68958 Commented May 30, 2019 at 12:53
- My recommendation for slides technology is LaTeX beamer . But that is just technology. The interview is to evaluate your oral communication skills (not mostly your English skills). Study existing slides of your field for preparing that – Basile Starynkevitch Commented May 30, 2019 at 12:56
- 1 A mistake (especially by beginners) is to have too much material for the time allotted. – GEdgar Commented May 30, 2019 at 13:13
- This is not answerable as a Stackexchange question, but I would add to what others have said - 4 minutes is a REALLY SHORT TIME , so you should be prepared for that, not include too much content, and have planned out exactly what you want to say (but not scripted, unless your level of English makes that unavoidable) – Flyto Commented May 30, 2019 at 17:45
3 Answers 3
It sound like you need to give an elevator pitch with slides. Short presentations are tough! You need to follow their instructions exactly and describe both a project and your fit to the program. You need to have this in mind: this is a sales pitch, so be short and to the point.
The objective is to sell yourself, so details on the project matter less than how you contributed in a way that’s relevant to the PhD program you’re applying to. So if your program is on graphic design focus on how your designs were used in the project, if it’s programming, focus on your code contribution etc.
In the part about you, try to show that you’ll be an amazing fit to the program: high-level plans, your agenda, your vision etc. you need to convince the committee that you’ll be a valuable asset to the program.
You must practice your talk several times till it’s perfect, and ask your friends to listen to it!
While conference talks are different, I highly recommend Simon Peyton Jones’ advice on how to give great talks, here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/give-great-research-talk/
The goal of this type of presentation is to allow your audience to see and hear your current level of communication skills along and your professional interests as they relate to research. The nature of PhD application packets is they are surprisingly large, yet surprisingly low on clear, reliable information content. This is a great opportunity to make up for that fundamental weakness in the system.
One big issue for the people interviewing you is that many people have a CV that probably looks a lot like yours in many ways. Lots of people mention they had some previous experience with a project of some kind, and it is completely unclear what their actual involvement was. So this is your chance to make it so they have a much clearer understanding of what your level of involvement and understanding of that project was.
Questions to Prepare For
There is no standard script, but you should prepare to answer questions like:
- What part of this project was the most challenging/hard/interesting?
- If you were going to do this project again, what would you do differently?
- Is this project the kind you would like to work on in the future?
- Do you have any experience with X? (you may have never heard of that before, ask if you don't know)
- Tell us more about your experience with X? (where X is generally pulled directly from your CV or personal statement - you should be prepared to talk in more detail about anything you put in your application materials)
- Why did you choose [some aspect of the project]? Ex: Why did you use multiple t-tests in the analysis (if you did stats)? Why did you make this as a web/phone application? Why did you choose to focus on revolutions in the 15th century? etc
- If you had your choice to work on any type of project in your first semester in the program here, what would you work on?
- Do you have any questions for us? (you don't have to have any)
They will not necessarily ask any/all of these questions - but I would expect you to be able to answer any of them on the spot reasonably well in such an interview.
General Short Presentation Outline
You can reorder things as you like, but in general I would expect for a short talk of only 4 minutes that you would cover:
- ~30 seconds: basic intro of yourself like name, university and major you are coming from, and where you work if you are not coming directly from college (and assuming it is relevant to research - no need to mention if you are working in a restaurant now, for example)
- ~30 seconds: background/motivation for the project you are talking about. Why was this project done, what reason would there be for anyone to care about it?
- ~1 minute: what you did on the project
- ~1 minute: what was the big takeaway, lesson learned, result, impact, whatever
- ~1 minute: how do you think this project (and or other projects you've done) prepare you for advanced studies? It should be clear how the skills and interests involved in this project directly relate to what you want to do during your graduate studies
The hardest part of short presentations is just how short they are. Generally I find I need to prepare double the material, or enough for about a 10 minute talk on my first personal practice attempt, to start with. Then I have to cut, cut, cut, and revise to get it down to 5 minutes, and that ends up being too much. You know it's too much when as you look at the time while you practice you feel you have to rush because you are running out of time. Don't rush - remove material.
I find it helpful to say the talk out loud quietly to myself, with a stopwatch running (clock app on your phone/computer works fine for this). This helps you practice what you want to say and how long it takes. The timing dictates you do not have time to get into very low levels of detail, because there is too much you would have to say - that's how these talks work, if they want details they will ask.
The project you pick should be as clearly related to your reasons for applying for a PhD and wanting to do research as possible. Applying for a Computer Science program to work in computer vision and then presenting a group project where you did a literature review for the historical legacy of Marxism in Eastern Europe would be...hard to pull off well.
Finally, do not worry about your English skills. Seriously. Focus on clarity of your communication, taking deep breaths to calm yourself before the interview helps most people, and try to speak in a steady and clear way. Many students are not especially confident English speakers, and in fact there are often professors at most Universities that aren't either. No one is tut-tutting your grammar or demanding you use exactly the right word for everything. Besides, your current level of skill is just your current level of skill - there really isn't any hiding it, so no sense in trying. Just try to be clear, speak in a measured and calm way, and this will help both you and your audience to get what they need from the presentation.
Oh, and one last thing, in case it may help - no one expects perfection here. Academics, as a group, give some of the worst presentations on the planet, even at very high levels of achievement and seniority. I have seen middle-school students give presentations that were more clear and pleasant than some of the talks given at the most prestigious conferences in the field by highly accomplished authors. This is not a TED talk, you are not interviewing to be an entertainer or orator. Focus on clarity and telling a story that shows you have applicable skills and reasonable, thought-out, applicable interests to the program you have applied to, and you will be fine. You will have to prepare and practice, but it should not be seen as a great obstacle - its just a chance to talk about one piece of your experience and your interests in a way that would be otherwise impossible to communicate in a typical 2 page application statement.
They told you what your ppt needs to be about:
Part 1. A project you were part of,
Part 2. Why you are a suitable candidate for the phd.
So a slide of intro, some slides of a project then some slides of motivation and close...
As for asking what are their possible questions - that has so many possibilities:
Questions about project ie points that were unclear,
Questions about you & motivation
Questions about your education so far
The list goes on.
- thank you how many slid do I need for four minutes? – hesam Commented May 30, 2019 at 5:23
- You need to decide - more than 4 but too many means they don’t have time to look at them. – Solar Mike Commented May 30, 2019 at 5:27
- More than four slides for a four minute talk is too much. A good rule of thumb is 1 to 2 minutes per slide. For a very short talk I would actually go towards the lower number: one title slide, one slide for the project and one slide about why you are an excellent candidate for a PhD position. And make sure that you actually give a talk and don't just read the slides to the audience. – user9482 Commented May 30, 2019 at 8:24
- @Roland there may be some images that warrant an extra slide for the project... And given the interview is next Monday, that means the OP does not have much time to craft the presentation and get some practice in... – Solar Mike Commented May 30, 2019 at 8:25
- 1 More than four slides as for this is not a talk. Focus of audience will be on candidate and his/her potential and motivation. No one expect a skilled presenter but rather an enthusiast though cool young persons. It then depends on the actual candidate. Asking in practice a former supervisor or teacher would be a good idea – Alchimista Commented May 30, 2019 at 10:56
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged presentation interview .
- Featured on Meta
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
Hot Network Questions
- Can someone explain the Trump immunity ruling?
- When did the four Gospels receive their printed titles?
- Boundary Conditions on the Inlet and Outlet in a Discontinuous Galerkin framework
- How much time do I need on my Passport expiry date to leave Australia for South Africa?
- How to maintain dependencies shared among microservices?
- Turning Misty step into a reaction to dodge spells/attacks
- Book in 90's (?) about rewriting your own genetic code
- Who originated the idea that the purpose of government is to protect its citizens?
- Why is a game's minor update on Steam (e.g., New World) ~15 GB to download?
- Phantom points in QGIS do not dissapear
- spath3 rotations shrink paths
- Do we know a lower bound or the exact number of 3-way races in France's 2nd round of elections in 2024?
- Why should I meet my advisor even if I have nothing to report?
- Staying in USA longer than 3 months
- Are there examples of triple entendres in English?
- Ideal diode in parallel with resistor and voltage source
- What does '\($*\)' mean in sed regular expression in a makefile?
- Does concentrating on a different spell end a concentration spell?
- Imagining Graham's number in your head collapses your head to a Black hole
- A chess engine in Java: generating white pawn moves - take II
- Powers of Gaussian primes are NOT collinear
- Why would a plane be allowed to fly to LAX but not Maui?
- Books using the axiomatic method
- Why didn't Jimmy Neutron realize immediately when he read the note on the refrigerator that the note is phony, as the note says "son or daughter..."?
- Career Advice
- Carpe Careers
How Your Ph.D. Prepares You to Be an Entrepreneur
You can deploy skills you develop as a grad student and postdoc in a variety of careers, including working for a start-up or founding your own, Chris Smith writes.
By Chris Smith
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

Yutthana Gaetgeaw/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Innovation has become a hot topic in economic circles over the past few years. In March 2022, the United States’ National Science Foundation created its first new directorate in over 30 years : Technology, Innovation and Partnerships , or TIP. The passing of the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 helped fund the directorate, the mission of which is to “advance U.S. competitiveness and societal impact by nurturing partnerships that drive and accelerate diverse innovation ecosystems, technology translation and development, and workforce development.” The U.S. is investing heavily in research and innovation—which you can take advantage of as a Ph.D. researcher working in academia or beyond.
Graduate students and postdoctoral scholars already contribute much to research and innovation in the United States through their work on a variety of projects supported by the federal government and industry partners. But despite that fact, few consider a career focused on the leading edge of innovation: entrepreneurship.
Being willing to push the boundaries of human knowledge and forge new ideas into products is essential for entrepreneurs. And to secure backing, entrepreneurs must also work to articulate the value they and their products bring to individuals, organizations and the nation. Fortunately, plenty of resources are available to assist in those efforts, although many graduate students and postdocs may not be aware of them.
To encourage more technology commercialization and entrepreneurship, in the latter half of the 20th century the federal government established two funding programs for academics and others seeking to either move full-time to a start-up company or obtain funding to develop and commercialize new technologies. The Small Business Innovation Research program supports the growth of start-up companies, while the Small Business Technology Transfer program is aimed at technology commercialization.
Both the National Institutes of Health and NSF fund grants from both programs, and both offer a variety of other mechanisms to foster an innovation and entrepreneurial ecosystem in the United States. In addition, NIH provides numerous resources to educate people about entrepreneurship and special programs like the Small Business Transition Grant for New Entrepreneurs (see a webinar on the program here ), which helps researchers interested in transitioning to entrepreneurship via a mentor.
American universities also offer an increasing number of programs that either focus on training Ph.D.s for careers in the technology transfer space or assist them in learning how to commercialize technological and other innovations coming from their research work, as our Innovation Postdoctoral Fellowship here at Virginia Tech seeks to do. In addition, NSF’s Innovation Corps (I-Corps) provides a seven-week experiential training program that prepares scientists and engineers to extend their focus beyond the university laboratory and toward commercialization by engaging in customer discovery and other activities. Such programs can be a bridge between traditional academic research and exploring an entrepreneurial career or employment in the innovation and entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Many academics may mistakenly believe that entrepreneurial skills are only relevant if one is planning to run a start-up company. Yet most faculty members running research groups at large universities are effectively leading small businesses inside their institutions. They must articulate a value proposition to get hired and ultimately secure funding for their research. In addition, most faculty leaders or principal investigators are in charge of hiring those who work in their labs and must manage these individuals and their projects toward a larger, common goal. A faculty leader must create a vision for their group and think strategically about how the various projects align toward both short- and long-term goals. This is entrepreneurship in an academic research context.
And just as an entrepreneurial mindset is essential to a successful academic career, it is also extremely useful for any scholar looking to create their own company, independent of their institution.
Entrepreneurial Skills From Your Ph.D. or Postdoc
Ph.D. training offers graduate students and postdocs many experiences to help them navigate entrepreneurship and/or working in a start-up company, such as the following.
- Project planning and management. Completing a doctoral dissertation involves extensive project planning and management skills, from ideation to execution and dissemination. This directly translates to the ability to plan and manage large projects as an entrepreneur.
- Independent work. Ph.D. students, and especially postdocs, often work independently with minimal oversight, building the drive and accountability needed to accomplish tasks without rigid external deadlines—a crucial skill for entrepreneurs.
- Networking and collaboration. Entrepreneurs thrive on networking. Similarly, Ph.D. students and postdocs benefit from building strong connections—engaging with industry professionals, attending conferences and collaborating across disciplines to enhance their network. Such connections can lead to job opportunities, collaborations and funding.
Editors’ Picks
- DEI Ban Prompts Utah Colleges to Close Cultural Centers, Too
- The End of Chevron Deference
- U.S. Focused on Consumer Protection, Accountability in Rules Overhaul
- Thirst for knowledge. A core requirement for a Ph.D. is an insatiable desire to learn and expand one’s knowledge base. Entrepreneurs must constantly step out of their comfort zones and learn new skills, making this thirst for learning invaluable for Ph.D.s and postdocs looking to focus on entrepreneurship as a career.
- Research skills. Doctoral training equips individuals with the ability to seek out, evaluate and synthesize quality information from various sources—a vital skill when navigating the unfamiliar territories of entrepreneurship.
- Curiosity about the big questions. Starting a business requires asking and answering big questions about target audiences, value propositions and strategic direction. Ph.D.s are trained to take disparate information and craft cohesive narratives to address complex inquiries. Successful entrepreneurs do the same.
- Problem-solving. Overcoming research obstacles and failed experiments hones problem-solving abilities in Ph.D.s and postdocs. As entrepreneurs constantly face new challenges, this skill is indispensable for finding innovative solutions.
- Resilience and adaptability. Entrepreneurship involves risk-taking and overcoming failures. Ph.D. students and postdocs learn resilience by navigating setbacks. This adaptability prepares them for a dynamic marketplace for their products and ideas and the post-Ph.D. job market itself, where flexibility and the ability to pivot are critical.
In essence, the rigorous training and self-driven nature of doctoral programs and postdoc positions cultivate skills like project management, working both independently and collaboratively, learning agility, strategic thinking and problem-solving—all of which are invaluable assets for successful entrepreneurship. The key to honing these skills is taking increased agency in your projects so that you learn all aspects of the process of identifying a gap in knowledge or application, scoping out the current landscape of that area and working toward a solution. It is certainly not easy work, but it can help you in graduate school, postdoctoral training and beyond.
In sum, by embracing an entrepreneurial mindset in your job search, you identify opportunities in industry, start-ups, government or nonprofits or create your own position through entrepreneurship. And even if you don’t decide to go that direction, innovative thinking and treating one’s career development like a start-up can propel you to professional growth and success. The fact that cultivating the entrepreneurial skills I’ve described can also be significantly helpful for an academic researcher means leaning into them is a win-win for any graduate student or postdoc.
Chris Smith is the postdoctoral affairs program administrator at Virginia Tech. He serves on the National Postdoctoral Association’s Board of Directors and is a member of the Graduate Career Consortium—an organization providing an international voice for graduate-level career and professional development leaders.

Supporting Dissertation Writers Through the Silent Struggle
While we want Ph.D.
Share This Article
More from carpe careers.

STEM Trainees Must Master Writing Skills
Articulating discoveries, gaining funding and forging connections all require the ability to convey ideas, write Mabe

The Power of Confident and Impactful Communication
Scholars must convey complex concepts in ways that make an impression, write Diane A.

A Graduate Student’s Guide to Managing Change
Dinuka Gunaratne and Roshni Rao offer advice for handling all the new academic demands and social dynamics, so you ca
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
SEAS Sizzling This Summer with Research and Job-Readiness Programs for High School and College Students

July 1, 2024

Dr. Lara Thompson and participants in a summer biomedical engineering research program at UDC
The UDC School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) is serving up a slate of summer programs built to give students—from high school through college—impactful, job-ready training in STEM fields.
Among the professional growth opportunities is an eight-week biomedical engineering research program that focuses on aging-related issues, staffed by UDC faculty and graduate student mentors. The program is funded by a $1.9 million NIH National Institute on Aging grant and the National Science Foundation Alan T. Waterman Award , and serves Firebirds as well as students from universities outside the D.C. region.
“Our summer research experience program seeks to provide meaningful—and hopefully life-changing—exposure, professional training and research experiences for our student research scholars,” says Professor Lara Thompson, Ph.D., the principal investigator and UDC Biomedical Engineering Program’s founding director. In 2022, Thompson became the first principal investigator from an HBCU (Historically Black College or University) to win the Alan T. Waterman Award.
SEAS is also highly invested in outreach and engagement with prospective Firebirds. Multiple pre-college learning opportunities are on the SEAS summer menu, including the Johns Hopkins Engineering Innovation Program, Apple Swift Coding Camp at Anacostia High School, a UDC civil engineering program on the water-energy-food-climate nexus, and a calculus-ready summer bridge program. The highly competitive program is offering 30 recent high school graduates intensive training in algebra and precalculus to help prepare them for STEM programs in college. Led by UDC Mechanical Engineering Chair Kate Klein, Ph.D., and SEAS Student Engagement Director Ann Lankford, the program is funded by the Special Competitive Studies Project.
For Media Inquiries Rachel Perrone [email protected]
For General Requests [email protected] 202.274.5000

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This PPT Set helps streamline the complex process of crafting compelling research proposals by providing a structured and intuitive design. The template is divided into two parts. The first consists of six sections briefly describing the thesis. The second part includes a summary and description of the content.
For a mock interview with me, book here! https://www.fiverr.com/share/ebqE9gI show you my Oxford PhD interview presentation slides as an example of a researc...
Personal Presentation for PhD Admission. Oct 26, 2021 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 2 likes • 12,651 views. M. MD. Badiuzzaman Bodi. This is a personal presentation that can be used for PhD motivational interview or similar postgraduate admission. Also, can be modified for individual research projects or consultancy, or similar positions.
Slide 2 - Tell them why you want to do it (i.e. gap in knowledge you are addressing) Slide 3 - Tell them how qualified you are to complete it (i.e. your skills and experience) The contents and presentation skills go hand in hand, so prepare thoroughly. Unless you have a good reason, don't be too defensive of your approach.
3. I was selected for an interview for a PhD scholarship and asked to give a 10-minute presentation consisting of 10 slides including "summarising both your research experience and your research plan for the project". How should I set up the PPT? Is this way ok? How much detail should I go into when describing my thesis?
This template can be used by Ph.D. candidates from various fields who are preparing for their Ph.D. registration. Slide 1: Title Slide. Title of the work. Candidate's name and affiliation. Supervisor's name and affiliation. Slide 2: Introduction. Briefly introduce the topic. Explain why the topic is important and relevant.
The structure of a viva presentation plays a crucial role in bringing across the key messages of your PhD. Therefore, there are several factors to consider when developing a viva presentation structure: Available presentation time: Viva presentations usually last between 10 and 20 minutes, but every university has different regulations.
PhD Pre Application Presentation. Sep 7, 2019 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 2 likes • 4,051 views. AI-enhanced description. M. Michelle Chen. This document summarizes Michelle's background and proposed research for a PhD. Michelle has a computer science and software engineering background and experience developing games.
This Guide was created to help Ph.D. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. The Guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from Ph.D. graduates. The tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can ...
Simple, clean, and classic, these minimalist PhD dissertation slides are great as a Google Slides template, PowerPoint theme or Canva template. Keep the layout as it is or add, delete, and re-order slides. Choose your own color scheme and font combination. Upload images, photos, and illustrations. Easily add charts, graphs, and other figures.
Get prepared. The trick to giving a great presentation is to be prepared, know your stuff, and practice your talk until it feels completely natural to stand up in front of an audience. Perhaps your first presentation will be in an informal setting with other members of your lab during a weekly or monthly group meeting.
Prepare for the Standardized Tests. Most PhD programs require students to take the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE). Having high test scores is a key part of an application as it tests skills learned over the course of many years in school. Quantitative skills are especially important when applying to doctoral programs in business areas.
A member of the university or department's postgraduate admissions staff. They will normally chair the panel and ensure the interview is properly conducted. This person could also represent any structured PhD programme your project might form part of. The lead investigator for your prospective research group. This is the academic with overall ...
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. In order to achieve the highest academic degree there is, you need the best presentation for your dissertation. Years of hard work will pay off with this free template by Slidesgo, which can help you focus on your message without having to worry about the visual design.
I am soon attending a PhD Interview (Condensed matter Theory). The interview is divided in two steps: a first interview with a selection comitee, where I have to prepeare a presentation 6 minutes long, and a second, 1.30 hours long interview with possible PIs. The short (6' - 5 slides) presentation is supposed to deal with: Academic Background
What to do in a PhD interview introduction. What not to do in a PhD interview introduction. Step 1: State your full name. Example. Step 2: Give a brief overview of your educational (and professional) background. Example. Step 3: Explain why you are interested in the PhD position. Example.
The goal of the Ph.D. proposal presentation and approval process is to receive constructive feedback on the proposal and ensure that the Ph.D. proposal is feasible and appropriate for Ph.D. work. The panel also can look into the timeline of the proposed work to ensure its feasibility within the given time frame.
How to select a Research topic for PhD Interview?What should you have to mention in PPT necessarily?No. of Slides in a presentation of PhD Admission. Resear...
The admissions committee reviews all completed applications through a holistic review process to select candidates for interviews. Prerequisites. Candidates for the Ph.D. Program must meet the following eligibility requirements: Completion of a bachelor's degree, preferably in the biological or physical sciences, from an accredited institution.
PhD Interview Presentation. Transcript: Interview for PhD position at Utrecht University About Me! I am a Yemeni, lived 20 years in Malaysia. My interest has always revolved around giving back to either society and the planet. I am currently finialisng my Masters thesis at Radboud University, and also interning at a chemical manufaturing company.
PhD Admission PPT. WorldStar Consultants provides PhD admission services and guidance through the 12 levels of the PhD research process in India. They help with entrance exams, university admission, topic selection, guide appointment, synopsis preparation, coursework, publications, seminars, thesis preparation, and final defense.
The nature of PhD application packets is they are surprisingly large, yet surprisingly low on clear, reliable information content. This is a great opportunity to make up for that fundamental weakness in the system. ... They told you what your ppt needs to be about: Part 1. A project you were part of, Part 2. Why you are a suitable candidate for ...
You can deploy skills you develop as a grad student and postdoc in a variety of careers, including working for a start-up or founding your own, Chris Smith writes. Innovation has become a hot topic in economic circles over the past few years. In March 2022, the United States' National Science Foundation created its first new directorate in over 30 years: Technology, Innovation and ...
T. The document is an interview presentation by applicant Zhang XXXX from Jiujiang, China. It includes sections about the applicant's educational and professional background, works portfolio, and proposed research plan. The applicant studied art and design at Tongji University and Wuhan University of Technology, and currently teaches digital ...
The highly competitive program is offering 30 recent high school graduates intensive training in algebra and precalculus to help prepare them for STEM programs in college. Led by UDC Mechanical Engineering Chair Kate Klein, Ph.D., and SEAS Student Engagement Director Ann Lankford, the program is funded by the Special Competitive Studies Project.
2. About Us • We "WorldStar Consultants" is part of Group WorldStar World. • We have very active section of "PhD Admission" services. • Presently, we situated at: #193/4, Sector 24, ROHINI, New Delhi (INDIA) - 110085 • "Ph.D Course" have 12 levels to complete the PhD Research Degree. In coming slides, explain each level ...