- Harmful Effects Of Junk Food Essay

Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay
500+ words essay on harmful effects of junk food.
The word ‘junk’ refers to fast food, which is easy to make and contains a low nutritional value. There are various types of junk food that are available in restaurants, such as cold drinks, pizza, burgers, sandwiches etc. Nowadays, fast-food restaurants and their chains are increasing because people around the world like to eat junk food. Junk food has become more popular because of its great taste, better shelf life and easy transportation. Junk food advertisement also plays a great role in making them popular, but these junk foods create a lot of health problems. So, with the help of this Junk Food Essay, we will make students aware of the harmful effects of junk food. Also, this Junk Food Essay will help you know how we can avoid these junk foods and follow a healthier diet regimen. Students can also get the list of CBSE Essay topics to practise essays on different topics.
Why Do People Prefer Junk Food?
Food is a basic need for human beings which provides energy to our body and protects us from diseases. Today, it’s common to have junk food in our diet. Junk foods are immensely popular among the younger generation. Junk meals contain a lot of fat and sugars, oils, salt, and excessive calories and have low nutritional value and quality. Many people like junk food as it has a delicious flavour. Junk food has unique tastes as it lets in a solid bunch of spices that make it tasty. Children like junk food the most and want to have them for breakfast and as snacks in the evening. Whether it’s any occasion, party or celebration, people prefer to eat junk food. We all must have seen that different varieties of fast food items are served during weddings or birthday parties.
Our life is becoming busy day by day, so we are going for easily made food like fast food and junk food. The junk food is smooth and fast to prepare. People can cook them instantly and consume them quickly. For example, making Maggi noodles does not take much time as compared to parathas. Also, it has become a fashion to eat junk food while watching a favourite show, match or movie on the television. Junk food can be easily transported. Now with shipping and delivery online, delivery of junk food is just a click away. The meal reaches the doorstep within 20 to 30 minutes.
Harmful Effects of Junk Food on Health
Junk food has high cholesterol and poor concentration. They are less nutritious and provide us with less energy. By eating junk food, fat accumulates in the body, and we become lazy. It gives rise to various health problems like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, blood pressure, etc. Mental disorders, loss of balance and lack of concentration can also occur due to excessive eating of junk food. Consumption of junk in early childhood can result in behaviour-associated problems like hyperactivity, aggressiveness, etc. Dental cavities can also be formed due to the excess consumption of junk food.
Ways to Avoid Junk Food
Eliminating the temptation for junk food and developing an awareness of fitness can help in avoiding junk food. We should not let our children get habituated to junk food. We must stop them from eating outside and make them eat home-cooked food. Keeping good food nearby and having meals right on time may help in this direction. The habit of eating junk food can be avoided by strong willpower and awareness of the side effects associated with them. People must be educated about the harmful effects of junk food on health. This will surely help in avoiding junk food and developing healthy eating habits.
Students must have found the Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay useful for practising essay writing skills. They can get the study material and latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay
What are the impacts of junk food.
In the long run, junk food can cause stomach and colon upset, constipation, diarrhoea, skin rashes and infections.
Can junk food be addictive?
Yes, continuous consumption of junk food can lead to addiction in children and also adults. Certain additives in junk food can make us crave repetitive consumption of the same.
How to control the urge to have junk food?
Choose and select natural, home-cooked food which tastes similar to junk food.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Junk Food — Harmful Effects of Junk Food for Health and Well-being
Harmful Effects of Junk Food for Health and Well-being
- Categories: Fast Food Junk Food
About this sample

Words: 609 |
Published: Sep 5, 2023
Words: 609 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
1. adverse effects on physical health, 2. impact on mental well-being, 3. long-term implications for quality of life, 4. impact on environmental sustainability, conclusion: making healthier choices.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health
+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 836 words
2 pages / 1019 words
2 pages / 702 words
4 pages / 3148 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Junk Food
Cornelsen, L., Green, R., Dangour, A., & Smith, R. (2014). Why fat taxes won't make us thin. Journal of public health, 37(1), 18-23.Doshi, V. (2016, July 20).Tax on Junk food in Kerala leaves Indians with a bitter taste. The [...]
World Health Organization. (2018). Obesity and Overweight. Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/society/2012/may/16/fat-tax-unhealthy-food-effect
Government of Canada. (2006). The Health Risks of Obesity. Health Canada.Government of Canada. (2018). Obesity in Canada: A Whole-of-Society Approach for a Healthier Canada. Public Health Agency of Canada.Government of Canada. [...]
When it comes to the topic of junk food, there is a lot of debate and controversy. Some people argue that junk food should be avoided at all costs, while others believe that it is fine to indulge in moderation. In this [...]
I have chosen unhealthy diet as the lifestyle behavior that affects my health directly. An unhealthy diet is defined as the consumption of “high levels of high-energy foods, such as processed foods that are high in fats and [...]
Unhealthy eating is one of the most important health risk factors that can cause a range of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes and other conditions linked to obesity. Unhealthy eating can add [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay: 200, 250 and 300 Words

- Updated on
- October 9, 2024

Harmful effects of junk food essay: Junk food refers to highly processed and refined foods. It is considered less healthful than other options and causes us more harm. Junk food causes a variety of health problems in children and adults, including obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and even cancer. This type of meal contains harmful ingredients that quickly satisfy hunger but have serious effects. In this blog, we will discuss the harmful effects of junk food essay. It is a great tool to help young children realise the harmful effects of junk food.
Keep reading for 200, 250, and 300 words samples on the harmful effects of junk food essay. You can use these samples to score well in your English exam.
Table of Contents
- 1 Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 200 Words
- 2 Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 250 Words
- 3 Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 300 Words
- 4 FAQs
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 200 Words
Junk food contains excessive levels of sugar, salt, bad fats and artificial additives. These types of foods have grown popular in modern diets. Even though it is tempting due to its taste, junk food has many negative effects on your health.
Consuming junk foods contributes significantly to obesity. Excess calories from sugar, salt, and fat, when mixed with other factors, can cause weight gain. It also raises the risk of obesity-related issues like diabetes, heart disease and hypertension. Junk food has also been linked to poor digestion, which can cause constipation and bloating. Junk food also lacks dietary fibres which can affect the nutritional value of the food and can lead to regular health issues.
Moreover, the high sodium level of junk food raises blood pressure, while trans fats can lead to bad cholesterol, clog arteries, and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Regular junk food consumption is also harmful to mental health since it causes mood swings, anxiety, and even depression.
In simple words, while junk food may appear convenient, regular consumption can lead to long-term health problems. As a result, it is important to eat healthy, nutritional food and control the consumption of junk food.
Also Read: Essay on Junk Food: Samples in 150, 250 Words
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 250 Words
Junk food contains excessive levels of sugar, salt, bad fats, and artificial additives. It has become an increasingly popular food of modern diets due to its convenience and taste. However, regular consumption might have a significant negative impact on one’s health.
Consuming junk food contributes greatly to obesity. Junk food is high in calories but low in nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and fibre. A high intake of refined sugar and salt, along with unhealthy fats, causes weight gain and increases the risk of obesity-related problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease and hypertension. Excess sugar raises insulin levels, which can lead to diabetes.
Junk food not only causes weight gain, but it also has a harmful impact on heart health. Many junk foods contain trans and saturated fats, which can raise bad cholesterol while lowering good cholesterol. This imbalance can lead to clogged arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues . Junk food’s high salt content can raise blood pressure.
Junk food also has a negative impact on mental health , which increases the frequency of mood disorders such as anxiety and depression. Foods high in sugar may reduce nutrients and affect brain function and emotional stability. Furthermore, junk food can affect digestion, resulting in constipation, bloating and other gastrointestinal problems.
In conclusion, while junk food offers short-term pleasure, its long-term consequences are severe. That is why, it is important to moderate the intake of junk food and prioritize a balanced diet, that is rich in nutrients.
Also Read: Essay on Food for School Students: 100, 200, 300 Words
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 300 Words
Junk food, which contains excessive amounts of sugar, salt, harmful fats, and artificial additives, has become a popular food in many diets due to its flavour and cost. However, regular consumption of junk food can be hazardous to both physical and mental health.
One of the most immediate consequences of eating junk food is weight gain. Junk food is high in calories but low in nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fibre. Excessive consumption of such meals increases body fat levels, leading to obesity. Obesity can lead to a variety of major health problems, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease and certain types of cancer. Junk food’s high sugar content can boost insulin levels, leading to diabetes, while unhealthy fats can raise bad cholesterol, blocking arteries and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Apart from physical health risks, it can also have an impact on an individual’s mental health. Research has revealed that eating highly processed foods increases the risk of mood disorders like anxiety and sadness. A lack of nutrients in foods that support brain function might cause emotional instability and cognitive decline. Furthermore, regular consumption of sugary foods generates blood sugar spikes and crashes, which can have a negative effect on mood and energy levels, resulting in irritability, fatigue, and even cravings for junk food.
Junk food also harms digestive health and can cause constipation, bloating and irritable bowel syndrome. Preservatives contained in junk food may upset gut bacteria, which can negatively impact the overall gut health.
In short, the convenience of junk food cannot outweigh its serious health implications. Regular consumption of such food can lead to obesity, chronic diseases, mental health issues, and digestive problems. It is important to restrict the consumption of junk food and prioritise a diet rich in whole, nutritious foods in order to preserve your overall well-being and health.
Related Posts on Essay
Junk food is often high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, which pose serious risks to health. One of the negative impacts of consuming junk food is weight gain. This weight gain can lead to obesity, which raises the risk of serious problems like type 2 diabetes, heart disease and high blood pressure. Junk food has low nutritional content, such as vitamins and fibre, making it harmful to one’s overall health. In addition to physical health, it has a negative impact on mental health too. This can result in mental disorders such as anxiety and depression, fatigue, irritability, and craving for more junk food. It can also affect digestion, which results in constipation and bloating. In short, while junk food can seem tempting its harmful impacts on physical and mental health are severe.
Research has revealed that eating highly processed foods increases the risk of mood disorders like anxiety and sadness. A lack of nutrients in foods that support brain function might cause emotional instability and cognitive decline.
The convenience of junk food cannot outweigh its serious health implications. Regular consumption of such food can lead to obesity, chronic diseases, mental health issues, and digestive problems. It is important to restrict the consumption of junk food and prioritise a diet rich in whole, nutritious foods in order to preserve your overall well-being and health.
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Bhumika Sharma
A writer with a fresh perspective on thoughts, I have an year of experience in writing the blogs on various topics. Here, you will find my blogs for the students and education purpose.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?


Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Frontiers for Young Minds
- Download PDF
The Impacts of Junk Food on Health
Energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods, otherwise known as junk foods, have never been more accessible and available. Young people are bombarded with unhealthy junk-food choices daily, and this can lead to life-long dietary habits that are difficult to undo. In this article, we explore the scientific evidence behind both the short-term and long-term impacts of junk food consumption on our health.
Introduction
The world is currently facing an obesity epidemic, which puts people at risk for chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Junk food can contribute to obesity and yet it is becoming a part of our everyday lives because of our fast-paced lifestyles. Life can be jam-packed when you are juggling school, sport, and hanging with friends and family! Junk food companies make food convenient, tasty, and affordable, so it has largely replaced preparing and eating healthy homemade meals. Junk foods include foods like burgers, fried chicken, and pizza from fast-food restaurants, as well as packaged foods like chips, biscuits, and ice-cream, sugar-sweetened beverages like soda, fatty meats like bacon, sugary cereals, and frozen ready meals like lasagne. These are typically highly processed foods , meaning several steps were involved in making the food, with a focus on making them tasty and thus easy to overeat. Unfortunately, junk foods provide lots of calories and energy, but little of the vital nutrients our bodies need to grow and be healthy, like proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Australian teenagers aged 14–18 years get more than 40% of their daily energy from these types of foods, which is concerning [ 1 ]. Junk foods are also known as discretionary foods , which means they are “not needed to meet nutrient requirements and do not belong to the five food groups” [ 2 ]. According to the dietary guidelines of Australian and many other countries, these five food groups are grains and cereals, vegetables and legumes, fruits, dairy and dairy alternatives, and meat and meat alternatives.
Young people are often the targets of sneaky advertising tactics by junk food companies, which show our heroes and icons promoting junk foods. In Australia, cricket, one of our favorite sports, is sponsored by a big fast-food brand. Elite athletes like cricket players are not fuelling their bodies with fried chicken, burgers, and fries! A study showed that adolescents aged 12–17 years view over 14.4 million food advertisements in a single year on popular websites, with cakes, cookies, and ice cream being the most frequently advertised products [ 3 ]. Another study examining YouTube videos popular amongst children reported that 38% of all ads involved a food or beverage and 56% of those food ads were for junk foods [ 4 ].
What Happens to Our Bodies Shortly After We Eat Junk Foods?
Food is made up of three major nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. There are also vitamins and minerals in food that support good health, growth, and development. Getting the proper nutrition is very important during our teenage years. However, when we eat junk foods, we are consuming high amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which are quickly absorbed by the body.
Let us take the example of eating a hamburger. A burger typically contains carbohydrates from the bun, proteins and fats from the beef patty, and fats from the cheese and sauce. On average, a burger from a fast-food chain contains 36–40% of your daily energy needs and this does not account for any chips or drinks consumed with it ( Figure 1 ). This is a large amount of food for the body to digest—not good if you are about to hit the cricket pitch!
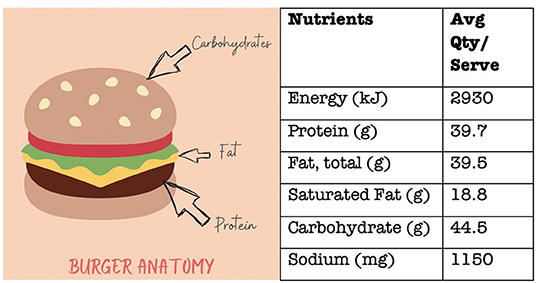
- Figure 1 - The nutritional composition of a popular burger from a famous fast-food restaurant, detailing the average quantity per serving and per 100 g.
- The carbohydrates of a burger are mainly from the bun, while the protein comes from the beef patty. Large amounts of fat come from the cheese and sauce. Based on the Australian dietary guidelines, just one burger can be 36% of the recommended daily energy intake for teenage boys aged 12–15 years and 40% of the recommendations for teenage girls 12–15 years.
A few hours to a few days after eating rich, heavy foods such as a burger, unpleasant symptoms like tiredness, poor sleep, and even hunger can result ( Figure 2 ). Rather than providing an energy boost, junk foods can lead to a lack of energy. For a short time, sugar (a type of carbohydrate) makes people feel energized, happy, and upbeat as it is used by the body for energy. However, refined sugar , which is the type of sugar commonly found in junk foods, leads to a quick drop in blood sugar levels because it is digested quickly by the body. This can lead tiredness and cravings [ 5 ].
- Figure 2 - The short- and long-term impacts of junk food consumption.
- In the short-term, junk foods can make you feel tired, bloated, and unable to concentrate. Long-term, junk foods can lead to tooth decay and poor bowel habits. Junk foods can also lead to obesity and associated diseases such as heart disease. When junk foods are regularly consumed over long periods of time, the damages and complications to health are increasingly costly.
Fiber is a good carbohydrate commonly found in vegetables, fruits, barley, legumes, nuts, and seeds—foods from the five food groups. Fiber not only keeps the digestive system healthy, but also slows the stomach’s emptying process, keeping us feeling full for longer. Junk foods tend to lack fiber, so when we eat them, we notice decreasing energy and increasing hunger sooner.
Foods such as walnuts, berries, tuna, and green veggies can boost concentration levels. This is particularly important for young minds who are doing lots of schoolwork. These foods are what most elite athletes are eating! On the other hand, eating junk foods can lead to poor concentration. Eating junk foods can lead to swelling in the part of the brain that has a major role in memory. A study performed in humans showed that eating an unhealthy breakfast high in fat and sugar for 4 days in a row caused disruptions to the learning and memory parts of the brain [ 6 ].
Long-Term Impacts of Junk Foods
If we eat mostly junk foods over many weeks, months, or years, there can be several long-term impacts on health ( Figure 2 ). For example, high saturated fat intake is strongly linked with high levels of bad cholesterol in the blood, which can be a sign of heart disease. Respected research studies found that young people who eat only small amounts of saturated fat have lower total cholesterol levels [ 7 ].
Frequent consumption of junk foods can also increase the risk of diseases such as hypertension and stroke. Hypertension is also known as high blood pressure and a stroke is damage to the brain from reduced blood supply, which prevents the brain from receiving the oxygen and nutrients it needs to survive. Hypertension and stroke can occur because of the high amounts of cholesterol and salt in junk foods.
Furthermore, junk foods can trigger the “happy hormone,” dopamine , to be released in the brain, making us feel good when we eat these foods. This can lead us to wanting more junk food to get that same happy feeling again [ 8 ]. Other long-term effects of eating too much junk food include tooth decay and constipation. Soft drinks, for instance, can cause tooth decay due to high amounts of sugar and acid that can wear down the protective tooth enamel. Junk foods are typically low in fiber too, which has negative consequences for gut health in the long term. Fiber forms the bulk of our poop and without it, it can be hard to poop!
Tips for Being Healthy
One way to figure out whether a food is a junk food is to think about how processed it is. When we think of foods in their whole and original forms, like a fresh tomato, a grain of rice, or milk squeezed from a cow, we can then start to imagine how many steps are involved to transform that whole food into something that is ready-to-eat, tasty, convenient, and has a long shelf life.
For teenagers 13–14 years old, the recommended daily energy intake is 8,200–9,900 kJ/day or 1,960 kcal-2,370 kcal/day for boys and 7,400–8,200 kJ/day or 1,770–1,960 kcal for girls, according to the Australian dietary guidelines. Of course, the more physically active you are, the higher your energy needs. Remember that junk foods are okay to eat occasionally, but they should not make up more than 10% of your daily energy intake. In a day, this may be a simple treat such as a small muffin or a few squares of chocolate. On a weekly basis, this might mean no more than two fast-food meals per week. The remaining 90% of food eaten should be from the five food groups.
In conclusion, we know that junk foods are tasty, affordable, and convenient. This makes it hard to limit the amount of junk food we eat. However, if junk foods become a staple of our diets, there can be negative impacts on our health. We should aim for high-fiber foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits; meals that have moderate amounts of sugar and salt; and calcium-rich and iron-rich foods. Healthy foods help to build strong bodies and brains. Limiting junk food intake can happen on an individual level, based on our food choices, or through government policies and health-promotion strategies. We need governments to stop junk food companies from advertising to young people, and we need their help to replace junk food restaurants with more healthy options. Researchers can focus on education and health promotion around healthy food options and can work with young people to develop solutions. If we all work together, we can help young people across the world to make food choices that will improve their short and long-term health.
Obesity : ↑ A disorder where too much body fat increases the risk of health problems.
Processed Food : ↑ A raw agricultural food that has undergone processes to be washed, ground, cleaned and/or cooked further.
Discretionary Food : ↑ Foods and drinks not necessary to provide the nutrients the body needs but that may add variety to a person’s diet (according to the Australian dietary guidelines).
Refined Sugar : ↑ Sugar that has been processed from raw sources such as sugar cane, sugar beets or corn.
Saturated Fat : ↑ A type of fat commonly eaten from animal sources such as beef, chicken and pork, which typically promotes the production of “bad” cholesterol in the body.
Dopamine : ↑ A hormone that is released when the brain is expecting a reward and is associated with activities that generate pleasure, such as eating or shopping.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
[1] ↑ Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2013. 4324.0.55.002 - Microdata: Australian Health Survey: Nutrition and Physical Activity, 2011-12 . Australian Bureau of Statistics. Available online at: http://bit.ly/2jkRRZO (accessed December 13, 2019).
[2] ↑ National Health and Medical Research Council. 2013. Australian Dietary Guidelines Summary . Canberra, ACT: National Health and Medical Research Council.
[3] ↑ Potvin Kent, M., and Pauzé, E. 2018. The frequency and healthfulness of food and beverages advertised on adolescents’ preferred web sites in Canada. J. Adolesc. Health. 63:102–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.01.007
[4] ↑ Tan, L., Ng, S. H., Omar, A., and Karupaiah, T. 2018. What’s on YouTube? A case study on food and beverage advertising in videos targeted at children on social media. Child Obes. 14:280–90. doi: 10.1089/chi.2018.0037
[5] ↑ Gómez-Pinilla, F. 2008. Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 568–78. doi: 10.1038/nrn2421
[6] ↑ Attuquayefio, T., Stevenson, R. J., Oaten, M. J., and Francis, H. M. 2017. A four-day western-style dietary intervention causes reductions in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory and interoceptive sensitivity. PLoS ONE . 12:e0172645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172645
[7] ↑ Te Morenga, L., and Montez, J. 2017. Health effects of saturated and trans-fatty acid intake in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 12:e0186672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186672
[8] ↑ Reichelt, A. C. 2016. Adolescent maturational transitions in the prefrontal cortex and dopamine signaling as a risk factor for the development of obesity and high fat/high sugar diet induced cognitive deficits. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00189
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay

Essay on Harmful Effects of Junk Food
Junk food is easily accessible, convenient and affordable to everyone. These properties of junk foods entice many people around the world to consume them in excess. Junk food may be defined as nutrient-poor food items which are usually high in fat, sugar or salt. They lack essential elements like proteins, fibers, vitamins or minerals (Buzby et al., 2013). The excessive consumption of junk foods is associated with a wide range of health problems like obesity, diabetes, heart diseases and cancer.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that overweight and obesity are now epidemics in both developed and developing countries. They have further warned that the epidemic is spreading to the young generation at an alarming rate (WHO, 2012). According to a report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one-third of U.S. children and adolescents are obese or overweight (Ogden et al., 2014). The main reason for this is the excessive consumption of junk foods.
Junk food items are generally high in calories which lead to weight gain. Obesity is a serious health problem that increases the risk of many chronic diseases like heart disease, stroke, cancer and diabetes. A study published in the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA) showed that obese people are at increased risk for heart attacks, strokes and death from any cause (Flegal et al., 2013). Another study published in the journal The Lancet revealed that obese people are at risk of developing 13 different types of cancer (Flegal et al., 2013).
The high amount of sugar present in junk foods is also a major cause of concern. Excessive consumption of sugar can lead to obesity, diabetes and heart diseases. A study published in the journal Diabetes Care showed that people who consume excessive amounts of sugar are at risk of developing diabetes (Yoon et al., 2014). Another study published in the journal Circulation revealed that people who consume sugary drinks are at risk of heart diseases (Hu et al., 2012).
Junk foods are also high in saturated and trans fats. Saturated fats increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases like heart attacks and strokes (Smith et al., 2006). Trans fats can also increase the risk of coronary heart disease (Mozaffarian et al., 2006). Junk food items made from hydrogenated oils contain dangerous trans fats.
Long and Short Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in English
Short harmful effects of junk food essay.
In this short essay on the harmful effects of junk food, a brief account of the impact of junk food on our health and how important it is to avoid junk food are discussed.
We are all aware that the way we treat our bodies reflects the state of our mind and lifestyle that we are all leading. The food we consume directly affects our state of mind, and so when we eat healthy and nutritious food, we are happier, content and positive in life. Even though we know that we do not take care of our bodies and eat junk food that harms our bodies. Sadly, nowadays, kids want everything to be served quickly, and fast food serves this purpose rightly.
The production of junk and fast food is at an all-time high. The supply is more because of the increasing demand. It has a negligible amount of nutrients and nutritional value. It is oily, greasy, full of fats and sugars. The high levels of calories have resulted in an increase in obesity and high blood pressure. It has also worsened the digestive system and appetite. When this is combined with the comfy and lethargic lifestyle in today's times, it also results in inadequate growth and development of children. And from a very young age, they are more susceptible to mental health diseases like depression. The effects of such consumption are only negative when the world is trying to normalize conversations about such problems; we should also be doing our bit in taking care of our health and life.
Long Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay
In this long 600+ words harmful effects of junk food essay, the effects of junk food on body and life are discussed in detail.
It is very vital to take care of one's body because our body is our vehicle, the most important tool that helps us get through life and perform our daily activities. When we treat our body right, it reciprocates the same zeal and willpower required for us.
The first important way to treat our body right is via exercise or working out in any form, be it through yoga, pilates, functional training, or weight training. All of this will help keep us fit. Even with working out daily, we will not get our desired results of fitness if we do not eat well. A proper diet is the most important catalyst to lead a healthy life.
A proper diet includes a good amount of balance between calories, fats, proteins, fibers, and nutrition-rich food. We can find all these nutritional values in foods like green leafy vegetables, fruits, and rice for carbohydrates. It is good for the body and the mind.
Junk foods include fast foods like french fries, fried foods like churros, pastries, pizzas, cookies, candies, burgers, and chips. All of this has a very high sodium content, cheese, sugar, and oils that have no nutritional value. It is not a good source of nutrition, nor is it helping our body in any way.
It only satisfies our taste buds because all junk foods taste good. But we must realize, in order to satisfy the cravings of our tongue, we are ruining our body and depriving it of a healthy lifestyle. This short-term fulfillment of mere cravings can have long-term impacts on our health, with life-threatening diseases that will leave a lasting negative impact on our bodies. It results in the following:-
On the Brain and Mental Health - the sodium content in junk food leads to headaches which will help lose focus and motivation even for mundane tasks. The risk of depression and other mental illnesses increases with the increased consumption of processed foods.
On the Respiratory System - due to heavy and oily foods the children are consuming these days and leading a lazy lifestyle, they are at high risks of shortness of breath, and according to the studies it is also found that such children also suffer from asthma even to their adult and old age.
On the Cardiovascular System - Cholesterol consumption blocks the blood flow to and from the heart because of the deposition of fats and leads to blood pressure-related issues. There is also the risk of premature heart diseases like heart failure, arrhythmia, etc. A weak heart results in many other bodily diseases due to improper and inadequate supply of blood to others.
On the Digestive Tract - When such processed food is consumed, it is very difficult to digest because our bodies are not designed to do so. When digestion is slowed, the metabolism also becomes slower, and it results in weight gain and obesity. Other such problems are food poisoning, acid reflux, constipation, and indigestion, and in severe cases may also lead to kidney failure.
On the Skin - Processed food contains very high levels of sugar, eventually leading to obesity. In such conditions, the blood sugar level also sees a spike, and this causes the outbreak of acne in the skin and face.
Curbing the intake of Junk food: - It is important to have healthy food due to the aforementioned reasons but surely one is attracted to junk food regardless. In such a case, we must reduce the intake of junk and processed foods and have it less often rather than making it a habit. Incorporating healthy food will allow you to have an active lifestyle and lead a fulfilling life. It will keep the heart in check, and energy levels will always soar high, which is the optimal way of living.
Being aware of your own health and knowing the possibilities of the very harmful effects junk foods have on our body can be very helpful. This awareness will help one make healthier choices. A proper workout is incomplete without a balanced diet, so it is important to cater to the body's needs without indulging in your cravings and taste requirements. Long-term effects last a lifetime and rob you of your childhood and youth, so starting a healthier diet for a better lifestyle is never too late.
FAQs on Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay
1. What are the health effects of junk food?
Junk foods are also very much high in saturated and trans fats. Saturated fats increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases like heart attacks and strokes (Smith et al., 2006). Trans fats can also increase the risk of coronary heart disease (Mozaffarian et al., 2006). Junk food items made from hydrogenated oils contain dangerous trans fats. Junk and processed foods have a high sodium content, cheese, sugar, and oils that have no nutritional value. They only satisfy our taste buds because all junk foods taste good. But we must consider that in order to satisfy the cravings of our tongue, we are ruining our body and shearing it off a healthy lifestyle. This short-term fulfillment of mere cravings can have long-term impacts on our health, with life-threatening diseases that will leave a lasting negative impact on our bodies.
On Brain and Mental Health - The sodium content in junk food leads to headaches which will help lose focus and motivation even for mundane tasks which are very dangerous. The risk of depression and other mental illnesses increases with the increased consumption of processed foods.
On the Respiratory System - Due to heavy and oily foods the children are consuming these days and leading a lazy lifestyle, they are at high risks of the absence of breath, and according to the studies it is also found that such children also suffer from asthma even to their adult and old age.
On the Cardiovascular System - Cholesterol consumption interrupts the blood flow to and from the heart because of the deposition of fats and leads to blood pressure-related issues. There is also the risk of early heart diseases like heart failure, arrhythmia, etc. A weak heart results in many other bodily diseases due to improper and Insufficient supply of blood to others.
2. What are the foods that can be classified as junk food?
Any food that is manufactured with the addition of artificial colors, flavors, sweeteners or preservatives qualifies to be junk food. The foods that are high in calories but offer no nutritional value like soda, candy bars, chips, and other fried snacks fall under this category. These foods are usually easy and cheap to find. It's best to avoid these foods as much as possible. These foods are very harmful and have the potential to cause great damage to our body and possibly increase the risk of some life-threatening diseases.
3. What exactly causes obesity?
There are some pathophysiological causes for obesity, namely, genetic disorders such as Prader-Willi syndrome and leptin receptor mutations, developmental causes like brain tumors or injury, some autoimmune conditions like Cushing's syndrome, and medications like antipsychotics and steroids. However, the majority of obese people have no identifiable cause for their weight gain. Many experts believe that excessive consumption of junk food is a major contributing factor to obesity. When people eat foods that are high in calories but offer no nutritional value, their bodies don't get the nutrients they need. Over time, this can lead to weight gain.
4. What are the long term effects of junk food?
Some experts say that since junk food is readily available, it becomes easy to eat more than one should usually be allowed to consume. Eating junk food can lead to obesity and other health conditions like glucose intolerance, type 2 diabetes, hypertension etc. A study found that children who consumed fast foods three times a week were more likely to develop asthma. Junk food can also lead to tooth decay and other oral health problems. Long term effects of junk food are obesity, weight gain, heart diseases, diabetes etc.
5. How can we prevent our children from eating junk food?
It is important for parents to set a good example for their children and teach them about the importance of healthy eating. Parents can try to make healthy meals at home that their children will enjoy, and they can also pack healthy snacks for their children to take to school or on trips. It is important to be aware of the foods that are being sold at schools and in other places where children might be tempted to eat unhealthy foods. Parents can also talk to their children about the dangers of eating junk food and make sure they understand the benefits of eating whole foods.
6. What are the Junk Foods to Avoid at any Cost?
Any junk food that has high levels of damaging chemicals and sugars to add taste and flavour to the food must be kept at bay at any cost. And such junk foods and processed food often have harmful preservatives that will cause many diseases. Such foods can be pizzas, burgers, chips, cakes, cookies, cookies, fried and grilled food is extremely oily with unuseful fats. Broiled food must be avoided. Drinks containing high amounts of sugar are also unhealthy and harmful.
7. Is any Junk Food Healthy?
Chips are considered to be a portion of junk food but now there are many vegan chips available that can be extremely healthy and will aid in fulfilling your cravings and not harm your body and lifestyle. A few of those are Kale chips, sweet potato chips, and spinach chips. They are healthy with no trans-fat or saturated fats. And these are easily available now. All these can be an alternative to potato chips.

An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
The Hidden Dangers of Fast and Processed Food *
Joel fuhrman , md.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Joel Fuhrman, MD, Nutritional Research Foundation, 4 Walter E. Foran Boulevard, Flemington, NJ 08822; e-mail: [email protected]
Condensed and adapted from Fast Food Genocide (HarperCollins 2017) for a lecture given at the ACLM annual conference Tuscan, Arizona, October 2017.
Collection date 2018 Sep-Oct.
The fundamental concern as we look to reform health in America is the known reality that most chronic diseases that afflict Americans are predominantly lifestyle induced; and the belief is that the vast majority of heart attacks and strokes could be prevented if people were willing to adopt healthy lifestyle behaviors. In addition, healthy lifestyles would impact a significant number of cancers which are also believed to be related to lifestyle exposures, especially to obesity, cigarettes, and other toxins.
Over the past 50 years, the health of Americans has gotten worse, and now 71% of Americans are overweight or obese—not 66%, which was reported 5 years ago. 1 That means a staggering 100 million people in America are obese. Today, eating processed foods and fast foods may kill more people prematurely than cigarette smoking. 2
Authorities determined the 71% figure by classifying people with a body mass index (BMI) over 25 kg/m 2 as overweight or obese. Yet in long-lived societies such as in the “Blue Zones” (Ikaria, Greece; Sardinia, Italy; Okinawa, Japan; the Nicoya Peninsula of Costa Rica; and Loma, Linda California) and wherever we find groups of centenarians, we observe a healthy BMI below 23 kg/m 2 , not 25 kg/m 2 . If we use above 23 kg/m 2 as the demarcation for overweight or obesity, then we find that 88% of Americans are overweight. And out of the approximately 10% that are of normal weight, the majority of those so-called “normal weight individuals” are either cigarette smokers, or suffer from alcoholism, drug addiction or dependency, autoimmune disease, occult cancers, inflammatory disorders, autoimmune conditions, digestive disorders, irritable bowel syndrome, and other illnesses that lower their body weight. Therefore, perhaps that only about 5% of the American population is at a normal weight as a result of eating healthy and living a healthy life. A recent study documented that only 2.7% of Americans adopt a relatively healthy lifestyle by combining exercise with healthy eating. 3 The Standard American Diet (SAD) is clearly not a healthy diet.
I use the term “Fast Food Genocide” because most don’t understand the depth and breadth of the harm as a large segment of our society eats a diet worse than the dangerous SAD. Many people recognize that junk food, fast food, processed food, white flour, sugar, maple syrup, honey, agave nectar, and all the junk people are eating contribute to in obesity, diabetes, heart attacks, strokes, dementia and cancer, but many don’t realize the strong causative role an unhealthy diet may have in mental illness. Currently, 1 in 5 Americans suffers from a psychiatric disorder. And many people don’t realize the harm that processed foods have on Americans living in urban areas where they don’t have easy access to whole, fresh foods.
These unfortunate folks live in what we call “food deserts,” with reduced availability to fresh fruits and vegetables. Because of the limited access to supermarkets, they eat more unhealthy fast and processed foods and end up having 7 times the risk of early-life stroke (before age 45), putting people in nursing homes in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. 4 - 7
The vulnerable poor in these areas also have double the risk of heart attack, double the risk of diabetes, and 4 times the risk of renal failure 8 - 10 ; Unfortunately, the decrease in life span due to food inequality is shocking but rarely discussed. A substantial proportion of people in these urban environments are overweight, prediabetic, or fully diabetic. Researchers determined that compared with other areas in America with easy access to supermarket food, that the YPLL (Years of Potential Life Lost) for an overweight diabetic living in a zone classified as a food desert was a shocking 45 years! 11 , 12
A link may even exist between fast food, processed food, commercial baked goods, and sweets and destruction of brain cell and a lowering of intelligence. Candy and sweetened baked goods may even stimulate the brain in an addictive fashion, which can lead to more serious illnesses.
The nutritional fundamentals accepted by the World Health Organization and most nutritional authorities today include vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds, and fruit as healthy foods; and salt, saturated fat, and excess sugar as disease causing. Excessive amounts of animal products may lead to premature aging, increased risk of chronic disease and higher all-cause mortality. Multiple studies have been published on hundreds of thousands of people, followed for decades showing that the objective endpoint of death is increased with higher amounts of animal product consumption. 13 - 17 Furthermore, refined carbohydrates may not just lead to being overweight and diabetic but also contribute to dementia, mental illness, and cancer. 18 - 21 There is considerable evidence today that heart disease is not only promoted by saturated fat and increased animal products but also by refined carbohydrates, including white rice, white bread, sugar, honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar. 22 - 25
Research has shown that excess calories shorten lifespan, whereas moderate caloric restriction slows the aging process and protects the body and brain. Americans consume more calories than any other population; and they consume foods, many of which have minimal or no nutritional value (soda and alcohol as examples). So let’s consider the individual who is consuming 50 excess calories per day. What will be the short- and long-term result? Fifty excess calories per day, over and above your basic metabolic needs, over a 10-year period, adds about 50 pounds of extra body weight. The excess weight increases the risk of multiple chronic illnesses, cancers, and also takes many years of life away from the individual simply as a result of consuming only 50 calories a day too many.
Conversely, if an individual consumed 50 calories a day less that their metabolic requirements what would happen then? Would he or she become too thin, anorexic, and unhealthy? Would their bones fall apart? Obviously not! When you moderately caloric-restrict, even a small amount such as 50 to 100 calories a day, weight remains about the same, the person is slim, not too thin, and healthy. He or she will have a lower body fat percentage, and the skeletal mass, bones, and muscle mass are strong. In this scenario, the metabolic rate would slow down accordingly. The respiratory quotient, (the number of calories lost through respiration) would decrease, the body temperature would lower, and thyroid function would decrease slightly, all lowering the metabolic rate, which overall may result in a slowing of the aging process. The secret to a long life and freedom from chronic disease may be simply to moderately reduce calories in order to slow down our metabolic rate. The only behavior proven scientifically to dramatically increase life span in every species of animals, including primates, is to lower caloric intake while maintaining an environment of micronutrient adequacy, assuring that we have exposure to every micronutrient humans need. The American diet is also deficient in antioxidants and phytochemicals that are needed for normal immune function, for maximizing brain health, protecting against dementia, chronic illness, cancer, and premature aging.
A nutritarian diet is designed to establish excellent micronutrient intake without excess calories . A nutritarian diet is designed to help prolong human life span, decrease the risk of cancer, and keep the brain functioning well for many years. This principle is represented by the equation I use: H = N /C, which means your healthy life expectancy (H) is proportional to the micronutrient (N) per calorie intake (C) over your life span. This means that we are encouraged to seek out foods that are rich in nutrients. We should try to limit or exclude empty-calorie foods and drinks. We should also limit or avoid calorically dense foods, and not eat for recreation or when we are not hungry.
A nutritarian diet is rich in phytochemicals and antioxidants. It is a vegetable-based, utilizing a wide assortment of colorful vegetables, root vegetables, green vegetables, peas, beans, mushrooms, onions, nuts, seeds, and some intact whole grains. While the standard American diet and most traditional diets are grain-based and lack sufficient exposure to the broad spectrum of antioxidants and phytochemicals (with their anticancer effects), it is important to note that not all plant-based diets are equally cancer-protective. As an example, a rice-heavy, macrobiotic diet limits phytochemical diversity, and brown rice produced in this country is contaminated with arsenic, extensively documented by Consumer Reports and white rice is refined, high glycemic food, and therefore not a healthy starch.
In comparison, the SAD is almost the opposite of a nutritarian diet. Over 55% of the SAD’s calories are processed foods, and about 33% of calories come from animal products. If we are looking at the amount of fresh produce (fruits and vegetables) consumed in America, the food consumption data reports about 10%; but in actuality, it is less than 5%, because they include French fries and ketchup in the definition of “produce!” The point here is that processed foods such as bread, pasta, salad oil, mayonnaise, doughnuts, cookies, rice cakes, breakfast bars, chips, soda, candy, and popcorn do not contain a significant micronutrient benefit. A piece of chicken is like a bagel, because they are both rich sources of macronutrients (calories), but neither one contains the necessary amounts of micronutrients, especially the antioxidants and phytochemicals only found in plants.
The high glycemic white flour products with added sweetening agents, flood the bloodstream with glucose without fiber, nutrients, or phytochemicals; and these baked goods are also high in acrylamides and advanced glycation end-products, further increasing the glycoproteins in our tissues. The resulting spike in glucose leads to abnormally high amounts of insulin, which will also promote angiogenesis, which fuels the growth of fat cells, increases cellular replication and tumor growth. The liberal amount of animal protein (including chicken which many incorrectly believe is the more healthy meat) consumed by most Americans promotes excessive insulin-like growth factor–1 (IGF-1), making a synergistic “sandwich” of insulin and IGF-1, which may accelerate aging of the brain, interfere with cellular detoxification and repair, and promote cancer. 26 The SAD has created a nutritional disaster and a significant health crisis that will not be solved by governmental “health care reform.”
Now when we think about “fast food” we’re not just referring to the food in fast food restaurants. Fast foods include chips, soda, cookies, candy, breakfast cereals, bars, French fries, burgers, pizza, white flour baked goods, and all other high-calorie, low-nutrient foods that people often eat multiple times per day. These are processed foods and for many, are the primary source of calories. These fast foods have certain characteristics: They can be accessed easily and quickly; they don’t need to be prepared; they come out of a bag or box ready to go right into your mouth. You can eat them rapidly and they’re absorbed very quickly into the bloodstream. These fast foods typically contain multiple chemicals and synthetic ingredients. They are calorically dense, highly flavored, and nutritionally barren. Fast foods typically contain extra corn syrup, sugar, artificial sweeteners, salt, coloring agents, and other potentially disease promoting chemicals.
When calories flood the bloodstream rapidly they have dramatic biological effects. Let’s compare 200 calories of white bread to 200 calories of beans. The white bread would be metabolized into simple sugars (glucose) which enters the bloodstream in 5 to 10 minutes. This requires a rapid increase in insulin; and the rapid insulin response will remain for hours. On the other hand, the carbohydrates from beans will take much more time to be digested and, as a result these calories enter the bloodstream slowly. Essentially, the calories will trickle in over hours. When eating beans, a small amount of glucose enters the blood each minute and therefore you won’t need much of an insulin response to deal with this amount of sugar. As mentioned above, the buildup of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) accelerates aging and chronic disease. 27 , 28 When a diabetic suffers from kidney failure, blindness, or a leg amputation, a major causative factor is the buildup of AGEs in the tissues. Interestingly, these same glycated end-products and glycoproteins build up in the tissues of people who are not diabetic but who continually expose themselves to excess sugar and white flour products.
Next, it is important to understand that oils are also processed foods. When consumed, oil enters the bloodstream rapidly similar to high glycemic carbohydrates. Anything cooked in oil should be considered a fast food. Beans, nuts, and seeds are whole foods whose calories are absorbed gradually over hours. In contrast, the calories from oil are absorbed rapidly, and are largely empty calories (with insignificant micronutrients and no fiber)—a combination that leads to obesity, disease, and premature aging.
If I set up a buffet dinner and I asked all the guests to form 2 lines and then gave everyone on the right side a tablespoon of olive oil, and each of those on the left side an apple to consume while they were waiting in line, those who ate the 65-calorie apple will generally eat 65 less calories from the buffet. But those who had the 120-calorie tablespoon of oil will not usually consume 120 calories less. The oil contains neither fiber, nor micronutrients and contains nothing to decrease the appestat. A matter of fact, if you put oil on food, it may actually increase one’s appetite. Not only will these individuals not eat fewer calories—they will eat even more than the 120 calories from the oil. 29 When added or mixed into food, oil drives overeating behavior.
Nutrients and fiber are needed to control the appestat, so you consume a healthy amount of calories. My experience has demonstrated with thousands of patients, the more nutrient and fiber dense your diet becomes the lower your drive to overeat. 30 This is extremely important, because even a moderate amount of extra fat on the body induces more rapid aging and increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease and cancer. A mild degree of caloric restriction becomes comfortable and achievable when the diet is high in micronutrients and fiber. When you have enough micronutrients and fiber in your diet, you don’t feel driven to overeat. But when you don’t have enough micronutrients and fiber in your diet, you become a food-craving, overeating machine.
Even worse is what happens when you eat food fried in oil because fried food may create carcinogenic and mutagenic aldehydes. 31 Food that is fried such as in a fast food restaurant is usually cooked in oil that has been heated and used multiple times. One serving of French fries or fried chicken that is cooked in a fast food restaurant has 100 times the level of aldehydes designated as safe by the World Health Organization. Even the fumes are so toxic they increase the risk of cancer. People working in restaurants that fry the food, or those working in a movie theater making popcorn, have a heighted risk of lung and other cancers, even if they don’t eat any of the fried foods. 32
The explosion of fast food restaurants has significantly increased the intake of fried foods, and people are now eating 1000 times the amount of soybean oil compared with the early 1900s. 33 Humans never ate 400 calories of oil a day the way people do in America, especially in the Southern states—which are known for the highest stroke and heart attack rates in the world. 34 When you use nuts and seeds as your source of fat as opposed to oil, we see the opposite effect.
The Physician’s Health Study, the Nurses’ Health Study, Iowa Women’s Health Study, the Adventist Health Study—any study with large numbers of people followed for decades—demonstrates the relationship between nut and seed consumption and longer life span. We always have to give more credence to clinical research studies that involve large numbers of people followed over decades using objective endpoints such as mortality. When you do that, you find that people who consume nuts and seeds regularly have lower cancer rates, lower cardiovascular death rates, lower sudden cardiac death, less irregular heartbeats, and an increase in life span.
A 2015 meta-analysis that included over 44 000 deaths demonstrated an almost 40% decrease in cardiovascular mortality for people eating nuts and seeds regularly (one serving a day). The European PreviMed study, which randomized 7216 individuals to nuts or olive oil as part of a Mediterranean diet showed a 39% decrease in all-cause mortality in the nut eaters. 35
When we look at the health implications of animal protein we should compare this type of nutrition with plant-based proteins, especially when an individual has cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, or even cancer. When your protein comes from beans, nuts, seeds, and greens, the body more gradually assimilates a complete array of amino acids to make functional proteins and hormones, keeping IGF-1 production much lower. Adequate amounts of plant protein keep IGF-1 in that moderate range, between 100 and 175, which is where it should be. The average American’s IGF-1 level is around 225, which is a level which has been linked to cancer promotion. When we eat a variety of plants, we get a full balance of amino acids, which slowly enter the blood—and we also digest some of the bacteria in the digestive track and some of the cells that slough off of the villi endothelium, enabling the utilization of partially incomplete plant proteins, now made complete. Conversely, when you eat large portions of meat, eggs, or cheese, the amino acid mix enters the bloodstream faster and because it is already biologically complete, it stimulates excessive amounts of IGF-1, again increasing the risk of cancer. 36 - 43
The average American consumes 10 to 20 ounces a day of animal products, whereas the safe level of consumption is likely less than 10 ounces per week . My estimate of 10% of calories as an upper limit of safe consumption is for a person with favorable genetics and is still likely more animal products than ideal for the nonelderly adults. It may be the case that under 5% of calories from animal products would be more ideal for life span and for facilitating disease reversal. Of course, any diet designed to optimize health should include a broad array of colorful plants with phytochemicals and antioxidants, which have been shown to increase life span and prevent cancer.
The animal products served at fast food restaurants are making the health of the population much worse, creating dangerous carcinogens from the food being grilled, barbecued, and fried at high temperatures. The World Health Organization has classified processed meats (hot dogs, sausage, bacon, and lunch meats) a class 1 carcinogen. AGEs are also highest in barbecued and fried animal products which also contain cancer-causing chemicals such as heterocyclic amines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and lipid peroxidases, which are mutagenic.
There are 2 phases of the digestive cycle: the anabolic phase, when you are eating and digesting, and the catabolic phase, when digestion has ceased. When you are eating and digesting food, the body turns those calories into stored glycogen, increasing fat storage and the storage of waste. During this phase of the digestive cycle, growth hormones and fat storage hormones are activated.
When your body is finished digesting, you enter the catabolic phase, where the stored glycogen and fat are utilized for energy. This is the phase when your body can most effectively detoxify and enhance cellular repair. It is the time when the liver and kidneys work together to remove aldehydes, AGEs, and other toxic metabolites. Repair and healing is enhanced during the catabolic phase when you are not eating food.
Most Americans have made their bodies so toxic, that when they enter the catabolic phase of the digestive cycle, they feel uncomfortable. That means they feel fatigue, headache, stomach cramping or fluttering, anxiety, or other uncomfortable symptoms when they stop digesting food and the body starts to mobilize waste and repair the damage. They typically interpret these symptoms as hunger or low blood sugar, because they feel better if they eat again—even though there is no biological need for calories at this time; and so they just get fatter and sicker. Every addiction has a “high” during the caloric rush and a “low” during withdrawal and repair from the disease-causing diet and resultant metabolic wastes and toxins that accrue from it. The American diet results in withdrawal symptoms and discomfort which promotes overeating and too-frequent eating. The lower the quality of the food consumed, the more discomfort felt when not eating and digesting, which makes it very difficult to maintain a healthy body weight.
If you’re healthy and eating nutritious food, you feel nothing when you enter the catabolic phase, with no desire to eat again until glycogen stores are nearly exhausted. True hunger is a mild sensation felt in the throat and base of the neck. True hunger heightens taste sensitivity too, making eating more pleasurable. True hunger directs when you should eat and therefore it’s more difficult to become overweight if you pay attention to the signs your body sends to your brain. Being overweight requires eating outside of the demands of true hunger, either recreationally or because of withdrawal symptoms from improper eating, stimulating the overconsumption of calories.
Enhanced detoxification—reduction of metabolic waste, aldehydes, and AGEs—occurs most effectively in the catabolic phase. That means the longer you live in the catabolic phase of the digestive cycle, the longer you live. If you finish dinner earlier or have a lighter dinner, and you have a 13-hour window between the end of dinner and the start of breakfast, you are going to live longer. A recent study had women with breast cancer followed for 10 years and found that those who finished dinner earlier and had a 13-hour window before the start of breakfast had a 26% reduction in the risk of death or recurrence from breast cancer. 44 , 45 The increased nighttime window was also linked to improved glycemic control and a lower HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin). They had no better diet, no different number of calories, no better food; they just finished dinner earlier.
The goal for excellent health is to eat as infrequently as possible. Many people believe just the opposite and eat frequent small meals that increase endothelial dysfunction leading to an increased risk for arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. In addition, all the fad diets encourage people to make the wrong choices about what and when to eat. Many suggest the use of frequent high-protein meals so as not to feel the effects of normal detoxification. When the digestive track is continually busy, it results in accelerated aging.
Processed and fast foods are also high in salt. The fast and processed food manufacturers don’t just put salt on the French fries and on the meat, they also put salt in the French fry batter and inside the chopped meat. They also include high fructose corn syrup in most foods. The added fat, sugar, and salt create a taste that makes people crave these foods, a sensation that many describe as an addiction. Both sugar and salt intake increase stroke risk, especially when consumed daily for years. Additionally, what is generally not appreciated is that the regular consumption of artificially sweetened soda creates more of a stroke risk. 46 High salt does not merely raise blood pressure; it also causes microvascular hemorrhaging, which damages the interior walls of the blood vessels in the brain and increases permeability and the propensity for hemorrhagic stroke. 47 , 48
Over the past 30 years, we’ve also seen an explosion of diabetes in Japan, Korea, and China, occurring at a lower body weight than we typically see in America, likely because the cumulative effects of eating more fast food, more oil and sugar, along with all of the white rice (a refined, high glycemic food), which they already had in their diet.
We know that people have the power to change when significant effort and attention is directed to the problems at hand. With good information, emotional support, increased food availability and food preparation instruction, we have found people enthused and willing to work together for change. They don’t have to be convinced of the tragic dangers of fast food; they see the obesity, diabetes, leg amputations, strokes, and blindness all around them. But if people don’t have good information, then they don’t have a choice. If they don’t have access to healthy, affordable food, and they don’t know how to make it taste good, then they are not given a chance to change.
The goal for physicians and other health care professionals is to work to transform America’s inner cities into zones of nutritional excellence. Our nation’s pride and heritage are based on the equal opportunity to achieve the American dream of prosperity and happiness. This critical information needs to be spread and put into action by community activists, teachers, educators, celebrities, health professionals, athletes, and politicians. The more people who know the critical importance of eating healthfully, and the more they take a stand, the greater the effect will be on transforming the health of all in America. By working together, we can save millions of lives.
Acknowledgments
This work was presented at Lifestyle Medicine 2017, October 22-25; Tucson, AZ.
Authors’ Note: The opinions presented in this article are those of the author and may not represent those of the Guest Editor, Editor, or the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval: Not applicable, because this article does not contain anystudies with human or animal subjects.
Informed Consent: Not applicable, because this article does not contain anystudies with human or animal subjects.
Trial Registration: Not applicable, because this article does not contain anyclinical trials.
- 1. National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United states, 2016: with chartbook on long-term trends in health. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus16.pdf#053 . Published May 2017. Accessed March 8, 2018. [ PubMed ]
- 2. Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, et al. ; US Burden of Disease Collaborators. The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013;310:591-608. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.13805. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Loprinzi PD, Branscum A, Hanks J, Smit E. Healthy lifestyle characteristics and their joint association with cardiovascular disease biomarkers in US adults. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:432-442. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Shikany JM, Safford MM, Newby PK, Durant RW, Brown TM, Judd SE. Southern dietary pattern is associated with hazard of acute coronary heart disease in the Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) Study. Circulation. 2015;132:804-814. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Chiuve SE, McCullough ML, Sacks FM, Rimm EB. Healthy lifestyle factors in the primary prevention of coronary heart disease among men: benefits among users and nonusers of lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications. Circulation. 2006;114:160-167. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Chomistek AK, Chiuve SE, Eliassen AH, Mukamal KJ, Willett WC, Rimm EB. Healthy lifestyle in the primordial prevention of cardiovascular disease among young women. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:43-51. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Howard G, Lackland DT, Kleindorfer DO, et al. Racial differences in the impact of elevated systolic blood pressure on stroke risk. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:46-51. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Fuchs FD. Why do black Americans have higher prevalence of hypertension? An enigma still unsolved. Hypertension. 2011;57:379-380. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Writing Group Members;Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38-e360. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. US Department Health and Human Services, Office of Minority Health. Diabetes and African Americans. http://minorityhealth.hhs.gov/omh/browse.aspx?lvl=4&lvlID=18 . Accessed March 8, 2018.
- 11. Gardner JW, Sanborn JS. Years of potential life lost (YPLL)—what does it measure? Epidemiology. 1990;1:322-329. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Mari Gallagher Research and Consulting Group. Examining the impact of food deserts on public health in CHICAGO—July 18, 2006. http://www.marigallagher.com/2006/07/18/examining-the-impact-of-food-deserts-on-public-health-in-chicago-july-18-2006/ . Accessed March 8, 2018.
- 13. Song M, Fung TT, Hu FB, et al. Association of animal and plant protein intake with all-cause and cause-specific mortality. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1453-1463. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.4182. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Fung TT, van Dam RM, Harkinson SE, Stampfer M, Willett WC, Hu FB. Low-carbohydrate diets and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: two cohort studies. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:289-298. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Lagiou RP, Sandin S, Lof M, Trichopoulos D, Adami HO, Weiderpass E. Low carbohydrate-high protein diet and incidence of cardiovascular disease in Swedish women: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2012;344:e4026. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 16. Levine ME, Suarez JA, Brandhorst S, et al. Low protein intake is associated with a major reduction in IGF-1, cancer, and overall mortality in the 65 and younger but not older population. Cell Metab. 2014;19:407-417. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. Wang X, Ouyang Y, Liu J, et al. Fruit and vegetable consumption and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ. 2014;349:g4490. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Sánchez-Villegas A, Toledo E, de Irala J, Ruiz-Canela M, Pla-Vidal J, Martínez-González MA. Fast-food and commercial baked goods consumption and the risk of depression. Public Health Nutr. 2011;15:424-432. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Gangwisch JE, Hale L, Garcia L, et al. High glycemic index diet as a risk factor for depression: analyses from the Women’s Health Initiative. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102:454-463. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.103846. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Kodi CT, Seaquist ER. Cognitive dysfunction and diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev. 2008;29:494-511. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 21. Sommerfield AJ, Deary IJ, Frier BM. Acute hyperglycemia alters mood state and impairs cognitive performance in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2335-2340. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 22. Halton TL, Willett WC, Liu S, et al. Low-carbohydrate-diet score and the risk of coronary heart disease in women. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1991-2002. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 23. Barclay AW, Petocz P, McMillan-Price J, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and chronic disease risk—a meta-analysis of observational studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:627-637. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 24. Mirrahimi A, de Souza RJ, Chiavaroli L, et al. Associations of glycemic index and load with coronary heart disease events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohorts. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012;1:e000752. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 25. Fan J, Song Y, Wang Y, Hui R, Zhang W. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and stroke mortality: a systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52182. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 26. Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D. The proliferating role of insulin and insulin-like growth factors in cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010;21:610-618. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 27. Uribarri J, Woodruff S, Goodman S, et al. Advanced glycation end products in foods and a practical guide to their reduction in the diet. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010;110:911-916.e12. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 28. Vitek MP, Bhattacharya K, Glendening JM, et al. Advanced glycation end products contribute to amyloidosis in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:4766-4770. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 29. The National Institute of Nutrition and Seafood Research (NIFES). Vegetable oils promote obesity. Excessive dietary omega-6 may increase our appetite and promote weight gain. http://sciencenordic.com/vegetable-oils-promote-obesity . Published June 2, 2012. Accessed March 8, 2018.
- 30. Fuhrman J, Sarter B, Glaser D, Acocella S. Changing perceptions of hunger on a high nutrient density diet. Nutr J. 2010;9:51. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 31. Zhang Q, Qin W, Lin D, Shen Q, Saleh AS. The changes in the volatile aldehydes formed during the deep-fat frying process. J Food Sci Technol. 2015;52:7683-7696. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 32. Lee T, Gary F. Cooking oil fumes and lung cancer: a review of the literature in the context of the US population. J Immigr Minor Health. 2013;15:646-652. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 33. Blasbalg TL, Hibbeln JR, Ramsden CE, Majchrzak SF, Rawlings RR. Changes in consumption of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the United States during the 20th century. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93:950-962. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 34. Howard G, Howard VJ, Katholi C, Oli MK, Huston S. Decline in US stroke mortality: an analysis of temporal patterns by sex, race, and geographic region. Stroke. 2001;32:2213-2220. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 35. Guasch-Ferré M, Bulló M, Martínez-González MÁ, et al. ; PREDIMED Study Group. Frequency of nut consumption and mortality risk in the PREVIMED nutrition intervention trial. BMC Med. 2013;11:164. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 36. Werner H, Bruchim I. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as an oncogene. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2009;115:58-71. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 37. Davies M, Gupta S, Goldspink G, Winslet M. The insulin-like growth factor system and colorectal cancer: clinical and experimental evidence. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006;21:201-208. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 38. Sandhu MS, Dunger DB, Giovannucci EL. Insulin, insulin-like growth factor–I (IGF-I), IGF binding proteins, their biologic interactions, and colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:972-980. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 39. Giovannucci E, Pollak MN, Platz EA, et al. A prospective study of plasma insulin-like growth factor–1 and binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal neoplasia in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000;9:345-349. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 40. Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, et al. Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:620-625. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 41. Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004;363:1346-1353. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 42. Shi R, Yu H, McLarty J, Glass J. IGF-I and breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2004;111:418-423. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 43. Rowlands MA, Gunnell D, Harris R, Vatten LJ, Holly JM, Martin RM. Circulating insulin-like growth factor peptides and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:2416-2429. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 44. Marinac CR, Natarajan L, Sears DD, et al. Prolonged nightly fasting and breast cancer risk: findings from NHANES (2009-2010). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2015;24:783-789. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 45. Marinac CR, Nelson SH, Breen CI, et al. Prolonged nightly fasting and breast cancer prognosis. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2:1049-1055. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 46. Pase MP, Himali JJ, Beiser AS, et al. Sugar- and artificially sweetened beverages and the risks of incident stroke and dementia: a prospective cohort study. Stroke. 2017;48:1139-1146. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 47. Ririje NMG, Engberink RHGO, Chahid Y, et al. Microvascular permeability after an acute and chronic salt load in healthy subjects: a randomized open-label crossover intervention study. Anesthesiology. 2018;128:352-360. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001989. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 48. Greaney JL, DuPont JJ, Lennon-Edwards SL, Sanders PW, Edwards DG, Farquhar WB. Dietary sodium loading impairs microvascular function independent of blood pressure in humans: role of oxidative stress. J Physiol. 2012;590:5519-5528. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (679.9 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

Essay on Junk Food
Students are often asked to write an essay on Junk Food in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Junk Food
The allure of junk food.
Junk food is popular for its taste, convenience, and affordability. It’s everywhere – in school cafeterias, at the cinema, and on our home tables.
The Downside of Junk Food
Despite its appeal, junk food can harm our health. It’s often high in sugars, fats, and salts, which can lead to obesity and heart diseases.
Healthy Alternatives
Instead of reaching for junk food, we should opt for healthier choices like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are not only tasty but also good for our health.
While junk food might be tempting, we must remember the importance of a balanced diet for our well-being.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Junk Food
- Paragraph on Junk Food
- Speech on Junk Food
250 Words Essay on Junk Food
Introduction.
Junk food, a term popularized in the latter half of the 20th century, refers to food that is high in calories but low in nutritional value. It is a pervasive element in modern societies, often associated with convenience, taste, and immediate gratification.
The appeal of junk food is multifaceted. It is typically easy to prepare, inexpensive, and designed to satisfy our innate preference for fat, sugar, and salt. Moreover, it’s often marketed with persuasive advertising strategies, making it an omnipresent temptation.
Nutritional Downfall
Despite its allure, junk food’s low nutritional value poses serious health risks. Its high sugar content can lead to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. High sodium levels can contribute to hypertension, and a dearth of essential nutrients can trigger a range of deficiencies.
Societal Impact
The ubiquity of junk food has significant societal implications. Its consumption is linked to a rise in chronic diseases, escalating healthcare costs, and decreased productivity. Moreover, it’s often more accessible in low-income communities, contributing to health disparities.
While junk food offers convenience and immediate satisfaction, its long-term effects on individual health and society are detrimental. It is crucial to promote healthier alternatives, regulate advertising, and improve nutritional education to mitigate these impacts. The challenge is not just a personal one, but a collective one that requires concerted effort and policy intervention.
500 Words Essay on Junk Food
Junk food, a term popularized in the latter half of the 20th century, refers to food items that are high in calories, sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, but lack essential nutrients. These foods, while alluring due to their taste and convenience, can have detrimental effects on health when consumed excessively.
Junk food’s popularity stems primarily from its convenience and addictive taste. Fast-paced modern lifestyles often leave little time for cooking or preparing nutritious meals. Junk food, easily accessible and ready-to-eat, fills this gap. Additionally, the high sugar, salt, and fat content in these foods stimulate the brain’s pleasure centers, creating a sense of satisfaction that encourages repeated consumption.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Despite their high calorie content, junk foods lack essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Regular consumption of such foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies. For instance, a diet rich in junk food but devoid of fruits and vegetables can result in Vitamin C and fiber deficiencies, leading to health issues like scurvy and constipation respectively.
Health Implications
Excessive intake of junk food can lead to various health problems. The high sugar content can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, while the high salt content can lead to hypertension. Furthermore, the unhealthy fats can lead to obesity and heart diseases. Research has also linked junk food consumption to mental health issues, including depression and anxiety.
The Role of Marketing
The marketing strategies employed by junk food companies play a significant role in promoting their products. These companies often target young audiences, using appealing packaging, catchy jingles, and celebrity endorsements. The influence of such marketing strategies can shape dietary habits from a young age, making it challenging to adopt healthier eating habits later in life.
Addressing the Issue
Addressing the junk food epidemic requires a multi-faceted approach. Education about the harmful effects of junk food and the benefits of a balanced diet is crucial. Schools and colleges should promote healthier food choices in their cafeterias. Governments can play a role by implementing policies such as taxing junk food, restricting their advertising, and mandating clear nutritional labeling. Individuals also have a responsibility to make conscious choices about their diet and lifestyle.
In conclusion, junk food, while convenient and tasty, poses significant health risks. It is essential to understand the allure of these foods, their nutritional deficiencies, and their health implications. Through education, policy changes, and personal responsibility, we can mitigate the impact of junk food on our health and society. The challenge lies not in completely eliminating junk food from our lives, but in striking a balance and making informed decisions about our dietary choices.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Julius Caesar
- Essay on John Proctor
- Essay on John Locke
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Harmful Effects of Junk Food. Junk Food is very harmful that is slowly eating away the health of the present generation. The term itself denotes how dangerous it is for our bodies. Most importantly, it tastes so good that people consume it on a daily basis. However, not much awareness is spread about the harmful effects of ...
By eating junk food, fat accumulates in the body, and we become lazy. It gives rise to various health problems like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, blood pressure, etc. Mental disorders, loss of balance and lack of concentration can also occur due to excessive eating of junk food. Consumption of junk in early childhood can result in behaviour ...
2. Impact on Mental Well-being. The effects of junk food extend beyond physical health to mental well-being. Research indicates a link between unhealthy diets and poor mental health outcomes such as depression, anxiety, and reduced cognitive function. Consumption of highly processed foods and sugary snacks can lead to rapid spikes and crashes ...
Harmful Effects of Junk Food Essay in 200 Words. Junk food contains excessive levels of sugar, salt, bad fats and artificial additives. These types of foods have grown popular in modern diets. Even though it is tempting due to its taste, junk food has many negative effects on your health. Consuming junk foods contributes significantly to obesity.
Junk food, a term popularly used to describe food with low nutritional value, is a staple in many people's diets. Despite its convenience and taste, it poses significant health risks. This essay aims to delve into the drawbacks of junk food consumption, with a focus on health, economic, and social implications.
Figure 2 - The short- and long-term impacts of junk food consumption. In the short-term, junk foods can make you feel tired, bloated, and unable to concentrate. Long-term, junk foods can lead to tooth decay and poor bowel habits. Junk foods can also lead to obesity and associated diseases such as heart disease.
A study found that children who consumed fast foods three times a week were more likely to develop asthma. Junk food can also lead to tooth decay and other oral health problems. Long term effects of junk food are obesity, weight gain, heart diseases, diabetes etc. 5.
Impact on Mental Health. The influence of junk food extends beyond physical health. Studies suggest a correlation between junk food consumption and mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. The high sugar content can cause fluctuations in mood and energy levels, while the lack of essential nutrients can impact brain function.
Over the past 50 years, the health of Americans has gotten worse, and now 71% of Americans are overweight or obese—not 66%, which was reported 5 years ago. 1 That means a staggering 100 million people in America are obese. Today, eating processed foods and fast foods may kill more people prematurely than cigarette smoking. 2.
500 Words Essay on Junk Food Introduction. Junk food, a term popularized in the latter half of the 20th century, refers to food items that are high in calories, sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, but lack essential nutrients. These foods, while alluring due to their taste and convenience, can have detrimental effects on health when consumed ...