

EdD vs. PhD in Education: What’s the Difference?

Industry Advice Education
If you’re interested in pursuing a doctoral degree in education, one of the first questions you’ll face is: Should I apply for a Doctor of Education (EdD) or a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Education?
The decision between these two culminating degrees can be career-defining as each serves a very different purpose despite being equivalent in level. In order to ensure you choose the path that best aligns with your future goals and career path, it’s important to take the time to first understand the differences in program curriculum and future career opportunities that relate to each degree.
Read on to learn about the defining qualities and key differences of an EdD and a PhD in Education to determine which program is the right fit for you.
EdD vs. PhD in Education
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a professional degree designed for practitioners pursuing educational leadership roles. A PhD in education , on the other hand, is designed to prepare graduates for research and teaching roles.
“With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based on a theory or hypothesis,” Joseph McNabb , a professor of practice in Northeastern’s Graduate School of Education , explains. “Conversely, an EdD student starts with a problem of practice and [works to learn] the skills it will take to resolve that complex problem of practice.”

What is an EdD Degree?
An EdD, or Doctor of Education , is a professional doctorate best suited for experienced educators and mid- to senior-level working professionals who want to lead and implement change within their organization.
EdD candidates work in a broad range of fields ranging from K-12 and higher education to nonprofits, government, healthcare, and the military. What each share is a desire to transform their everyday environment and apply the lessons learned through their doctorate to a complex, critical issue facing their workplace.
The EdD is practice-based. Students in an EdD program don’t want to just research their area of interest, but leverage that research in ways that could positively influence their community or organization’s decision-making process.
Learn More: 5 Tips for Choosing Your EdD Concentration
Those who pursue an EdD focus on qualitative, exploratory research. Students collect data and conduct individual interviews, observations, or focus groups to construct hypotheses and develop strategies that can help solve or clarify a specific problem of practice, such as how to support student veterans transitioning to civilian life or how to foster more female leaders in higher education—two dissertation topics recently explored through Northeastern’s EdD program .
Download Our Free Guide to Earning Your EdD
Learn how an EdD can give you the skills to enact organizational change in any industry.
DOWNLOAD NOW
What Can You Do with an EdD Degree?
While an EdD can be applied to a variety of industries and career options—such as K-12, higher education, the nonprofit sector, or civic service—there are several job titles you’ll likely come across within your cohort of classmates. They include:
- Postsecondary Education Administrators: Postsecondary education administrators work in colleges or universities, and typically oversee faculty research, academics, admissions, or student affairs. Some job titles that fall under this category include president, vice president, provost, and dean. The average annual salary for a postsecondary education administrator rings in at $99,940 .
- Elementary and Secondary School Education Administrators: Superintendents, who are the top executives of a school district, fall under this category. They manage academic programs, spending, and the staffing of all educational facilities within their district, and typically earn an average of $106,850 per year .
- Top Executives : In education, a top executive could be a “chief learning officer” or “chief academic officer”—senior-level professionals who drive and develop strategies that help their organization meet critical business goals. Top executives make an average of approximately $100,090 per year .
- Instructional Coordinators : Instructional coordinators create and manage school curricula and other educational materials. They help teachers implement effective classroom learning strategies and measure the effectiveness of what’s being taught and how. The average annual salary for instructional coordinators is roughly $66,490 .

These are just a few of the many career opportunities available to EdD graduates.
Learn More: Top Careers with a Doctorate in Education
What is a PhD in Education?
A PhD in Education is a terminal degree best suited for individuals who want to pursue a career in academia or research at the university level.
Students in PhD or doctoral programs take a more theoretical, study-based approach to learning. In most cases, their goal is to master a specific subject or add their unique findings to a body of existing literature. PhD candidates conduct original research in the hopes of driving change in their field or inspiring others to make change based on their work.
A PhD is the degree most popular amongst those who aspire to become a professor or obtain a tenure position. Through these programs, students tend to focus on getting published in well-respected journals, presenting at national conferences, and learning how to teach future educators.
What Can You Do with a PhD in Education?
While some of the above roles can also be earned through a PhD program, the most common job titles for PhD-holders include:
- Postsecondary Teachers: Postsecondary teachers instruct students at a college or university. When they’re not in the classroom, they’re often focused on conducting research, attending conferences, and publishing scholarly papers and books. Postsecondary teachers earn an average $80,840 per year .
- Academic Researcher : Researchers often have the opportunity to create their own centers or institutes, hire staff to help carry out their work, and secure funding for that work. Salaries often vary by subject area, but a general academic researcher typically earns an average $83,971 per year .
EdD or PhD: Which is Better For You?
Once you’ve explored the differences between an EdD and PhD in Education, the most relevant question to consider will be: What’s the next step I want to take in my career, and which degree can help me achieve my professional goals? The answer to this question will determine which degree program you ultimately pursue.
Earning your doctorate can pay off no matter which path you choose. Professionals with a doctoral degree earn an average $98,000 a year —nearly $20,000 more a year than master’s degree holders. Similarly, doctoral degree holders see an unemployment rate of only one percent compared to the national unemployment rate of two percent.
Regardless of which degree you ultimately pursue, there is enormous potential for you to advance your career in the field of education. Evaluating your needs and values will help you understand whether an EdD or PhD in Education is best suited to your personal and professional goals.

This article was originally published in July 2017. It has since been updated for accuracy and relevance.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About scott w. o'connor, related articles.

What is Learning Analytics & How Can it Be Used?

Reasons To Enroll in a Doctor of Education Program

Why I Chose to Pursue Learning Analytics
Did you know.
The median annual salary for professional degree holders is $97,000. (BLS, 2020)
Doctor of Education
The degree that connects advanced research to real-world problem solving.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

5 Homeland Security Careers for the Future

The Top 3 Job Requirements For a Homeland Security Career

What Are Security Studies?

Should I Go To Grad School: 4 Questions to Consider
What’s the Difference Between a PhD and EdD in Education?

What Is an Ed.D. Degree?
What is a ph.d. in education, ed.d. vs ph.d. in education: key differences.
- Ed.D. vs Ph.D. in Education: Which is Right for You?
An Ed.D. degree is a doctoral degree in education focused on educational leadership. The abbreviation stands for Educationis Doctor, and the degree indicates that the person holding it has advanced leadership knowledge in teaching, administration, and education research. According to the Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate, the Ed.D. “prepares educators for the application of appropriate and specific practices, the generation of new knowledge, and for the stewardship of the profession.” (Source: https://www.cpedinitiative.org/page/framework)
Ed.D. degrees emphasize transformational leadership skills—that is, leadership that can change systems to better serve students and their communities, rather than leadership that merely manages efforts within the existing system. In the modern educational environment, where educators seek to provide an excellent education to students from an ever more diverse range of background and abilities, transformational leadership is in demand.
By completing an Ed.D. program, experienced educators can develop executive-level leadership skills, advanced education policy knowledge, pedagogical skills, and research capabilities to innovatively solve problems for the schools and students they serve.
Who Is a Good Fit for an Ed.D. Degree?
Ed.D. degrees are aimed at current education professionals working directly in their organizations outside of academia. These professionals may include:
- Pre-K-12 teachers, counselors, curriculum advisors, and other classroom personnel
- School principals and other administrators
- School district officials
- Administrators within government education departments
- College administrators
- Mid-career executives in educational consultancies or private businesses such as textbook publishers
Essentially, Ed.D. programs are ideal for experienced education professionals who hold a master’s degree and who do not want to work mostly within academic education research. While Ed.D. programs can also teach advanced classroom teaching skills, the primary role of an Ed.D. degree vs. a Ph.D. is to empower the professionals who are shaping and leading today’s schools and colleges.
Ed.D. Career Options
Ed.D. career options will vary depending on your previous work experience and your master’s degree field of study. However, the degree is designed to equip you for senior leadership roles.
- School District Administrator or Superintendent - An Ed.D. degree can equip you to lead in public school districts, either as an upper-level administrator or as the superintendent (in some larger cities known as the Chief Executive Officer). According to Payscale.com, the average salary for a school superintendent in the U.S. is currently $117,216. *Source
- Academic Dean - Usually found in colleges and universities but sometimes also in larger private K-12 schools, deans oversee a specific academic department or area of operations (e.g. student affairs). They manage instructors, analyze student performance data, help set curriculum plans, etc. According to Payscale.com, the average salary for an academic dean is $90,236. *Source
- Provost - A provost or vice president is a senior academic administrator who acts as deputy to a college president. Provosts are primarily responsible for directing the academic programs at a college or university and have authority over deans. Payscale.com currently estimates the average annual salary for provosts at $147,730. *Source
- College President - Earning your Ed.D. could prepare you to become the CEO or president of a college or university, ultimately responsible for setting the academic and social direction of your school, as well as ensuring it has the budgetary resources to change and expand with the times. Pay for college presidents can vary widely depending on the size and type of their institution, but in 2016, the median take-home pay for public university presidents was $431,000. *Source
- Company Executive - The skills you learn in an Ed.D. program can also apply to careers in private industry, particularly companies within the education sector such as textbook publishers or educational technology companies. However, the Ed.D. can also equip you to lead training efforts within large corporations unrelated to education. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, median pay for top executives in 2017 was $104,700 per year. * Source
Benefits of an Ed.D. Program
What are the benefits of an Ed.D. program? Aside from expanded pay potential and the opportunity for more responsibility, there are several.
- Advanced research with practical outcomes: In an Ed.D. program, you’ll be required to conduct research into an educational problem, and thanks to the program’s more practical focus, you can dive deep into an area which is of pressing concern to you at your current place of work.
- Raise your relevance: Earning your doctorate in education can help you stay up to date on policy, technology, and pedagogical ideas that are changing the field.
- Fill in skill and knowledge gaps: Most educators spend their time focused on one aspect of teaching or leadership. By completing your Ed.D., you can round out your knowledge and expertise with advanced course content in teaching methods, building community relationships, education law, etc.
- Time to completion: In general, an Ed.D. degree requires 60 credits of work beyond the master’s degree and a dissertation or capstone project. They usually take less time to complete than a Ph.D.—in some cases, depending on the program, as few as three years.
- Study while continuing to work: Because the Ed.D. is aimed more at administrators and practitioners, institutions often structure the program to accommodate working schedules, meaning you can “earn while you learn”.
A Ph.D. in Education is a research-intensive academic degree focused on producing leaders who can nurture new educators, either within college classrooms or as leaders within educational institutions. Ph.D. programs in education emphasize the production of scholarship-- the research and analysis which describes for practitioners and policy makers what works in education, what doesn’t work, and why that is.
Typically, Ph.D. in Education degrees aim to produce researchers who can also teach at the university level, ensuring that new teachers get off to a strong start in their careers and that mid-career teachers gain the advanced skills they need to serve students even more effectively, whether as master teachers, administrators, or school counselors. Education Ph.D. graduates may also serve as administrators, whether at the K-12 level, in higher education, or in government departments and private companies which serve education.
Who Is a Good Fit for a Ph.D. in Education?
While current teachers and administrators can make a good fit for Ph.D. in education programs, they should already have a demonstrated focus on research in their careers before applying. Other potential good fits for education Ph.D.s are academics from other fields who are interested in investigating specific problems within the field of education.
These may include:
- Sociologists
- Counselors or people with psychology degrees
- Child social workers
Ph.D. in Education Career Options
There is some overlap between the careers you can pursue with an Ed.D. and the careers you can pursue with a Ph.D. in Education. Your ability to pursue administrative roles will vary depending on your previous experience managing others within an education setting. Other roles may include:
- College Professor – Ph.D. graduates in education can often obtain work teaching in education programs at colleges and universities. They may work with new undergraduates, experienced teachers, administrators, or public policy students. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median 2017 salary for postsecondary teachers of all types was $76,000. *Source
- Sociologist – As a graduate of a Ph.D. in Education program, you could work in sociological research related to education, conducting surveys, analyzing data, and working to identify the impact of educational policies on schools and students. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that the median salary for sociologists in 2017 was $79,650. *Source
- Training and Development Manager – Private companies need skilled educational professionals who can help them develop effective training programs for employees and executives. As a training and development manager, you can put the knowledge gained in your education Ph.D. program to work researching and designing corporate training plans. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that training and development managers earned a median salary of $108,250 in 2017. *Source
- Public Policy Director – With your Ph.D. in Education, you may also qualify to lead policy creation and advocacy efforts within non-profit organizations or government departments. You would apply your research and analysis skills to this role, along with managerial skills as you direct the work of junior policy analysts and researchers. Payscale.com reports that the average annual salary for this role is $76,486. *Source
Benefits of a Ph.D. in Education Program
With its emphasis on research and teaching, the Ph.D. in Education demands full-time commitment, can take longer to complete than an Ed.D. and can be difficult to complete while continuing to work. However, it has its own benefits for those who truly want to follow a scholarly career path.
- More common degree: There are more Ph.D. programs in education available than there are Ed.D. programs. This means you will have more options when it comes to finding a college that suits you. It also means you will have more options in terms of choosing a specialization program.
- Funding is more available: Many colleges and universities provide funding for Ph.D. students to pay their tuition and some living costs while they study. In exchange, Ph.D. students assist their supervisors in research, perform graduate assistant teaching duties, and represent the university at conferences and other professional events. These are all excellent activities for building a resume in academia—and you could get paid to do them.
- Learn widely applicable research skills: The research methodologies you learn in a Ph.D. program go beyond those taught in an Ed.D. program and can apply to many career paths after graduation. This is especially true if you work with research involving large data sets and analysis software. Many companies are looking for data analysts, no matter what field of study their degree was in. *Source
The two doctoral degrees in education overlap in many ways, but also feature key differences in terms of their intended student prospects, aims, goals, and formats.
Career Path Direction
When it comes to deciding on a Ph.D. vs. Ed.D., consider where you’ve come from and where you want to go. If you are an established classroom teacher or administrator and want advanced skills to continue solving complex problems as a leader in that area, choose an Ed.D. If you have a more academic background and want to investigate major issues around education through research or want to contribute to the profession by training new teachers in colleges, choose the Ph.D.
Skill Set Emphasis
Related to the differing career path goals of a Ph.D. vs. Ed.D., the skills emphasized in each degree do vary. Ed.D. students will focus primarily on hands-on, transformational leadership skills within education settings at any level. Ph.D. students will cover many courses in research methodologies, spend more time producing a dissertation and other scholarly publications, and focus on teaching and mentoring college students.
Research Goals
Both Ed.D. and Ph.D. programs teach advanced research skills, including statistics, data analysis, and qualitative and quantitative methodologies such as surveys and other investigation tools. However, the research aims in each degree differ.
Ed.D. programs teach research skills to help students employ those processes to solve very specific problems through the application of evidence to practical solutions.
Ph.D. programs teach more open-ended academic inquiry skills, designed to contribute to the wider body of scholarship which informs education practice and policy.
Program Format and Completion Length
The final difference between Ed.D. programs vs. Ph.D. programs is the way the formats are commonly structured by colleges and universities. Because of its more practical, hands-on focus, the Ed.D. is usually a credit-based program that can be delivered via online study as well as on-campus study (or with some combination of the two). In addition, Ed.D. programs are often designed to accommodate working education professionals, whether they are teachers, curriculum designers, or administrators.
Finally, Ed.D. degree programs are typically shorter than other doctoral degrees in education, with programs lasting anywhere from two to four years in length. Ph.D. in Education programs are more likely to be full-time residential programs which require students to leave full-time jobs to pursue. While some Ph.D. programs focused on educational leadership may be structured for people who need to keep working, they are less common in other specialization areas. Ph.D. degrees are also competency-based, meaning whether you earn the degree or not depends on the defense of your dissertation. Because of this requirement, they are more likely to take in the region of 5-7 years to finish.
Ed.D. vs Ph.D. in Education: Which Is Right for You?
In summary, the chief difference between an Ed.D. and a Ph.D. is about the long-term career goals of the student. Which one is right for you will depend on where you’ve come from in your career to this point and where you want to go. Dedicated to solving problems in education through hands-on, transformational leadership? An Ed.D. program is likely to be the best bet for you. Passionate about scholarly research and policy development within academic settings? You may be ideal for a Ph.D. program. We hope this guide has helped you understand the differences between an Ed.D. in Education Leadership and a Ph.D. program in education with more clarity. Good luck with your career in education, no matter which degree you choose!
Get Started on Your Ed.D. Journey with GMercyU
Ready to help transform schools, colleges, and universities through advanced leadership? Contact Gwynedd Mercy University at 844-707-9064 to learn more about our Accelerated Online Ed.D. in Executive Educational Leadership today!
- Request Info Request Info
- Call (844-707-9064) Call
- Email ([email protected]) Email
By using this website, you consent to the use of cookies.
See our Privacy Policy for more details.

EdD vs PhD: Which Education Degree Should You Get?
Teachers that are looking to use their leadership skills to create change in policy, curriculum, and research can use a doctorate degree to get roles in research, postsecondary schools, and K-12 education. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), postsecondary education jobs are projected to grow 12% between 2020-2030.
However, teachers wanting to earn a high-level degree must choose between a doctor of education (EdD) or a doctor of philosophy in education (PhD) degree. While both are excellent options, the two degrees lead to very different coursework, requirements, and career outcomes.
What Are EdD and PhD In Education Degrees For?
A doctorate degree in education gives people a variety of career paths. The different programs can lead to private and public sector jobs including:
- Administrator
- Superintendent
- Policy maker
- Postsecondary teacher
- College president
- Education director
The EdD and PhD are both terminal degrees that make teachers and educators experts in their fields. A good job outlook and growth projections make a doctorate degree worth the time and money.
Picking Between an EdD or PhD In Education Program
The curriculum and job prospects of an EdD and PhD program are different. You should consider your interests and career goals when deciding which type of degree to obtain.
- A PhD program is rooted in research and theory and students learn to interpret research.
- And EdD program is rooted in leadership and application and students are taught how to apply the research to a real-world setting.
The EdD degree is available to professionals who already hold a master’s degree and want to advance their career and receive a boost in income.
The EdD program prepares students to apply research to real-world settings and to find work in educational leadership. This degree rewards students with the skill set and ability to create change in their professional environment by:
- Develop the tools to become a better administrator
- Résumé credibility and expanded career search
- Learn the latest technology in instructional design
- Qualify for senior educational leadership positions
The overall goal of getting an EdD degree is to become a good leader and transfer knowledge to an education environment to create positive change.
Coursework includes a focus on professional leadership, solutions, and solving problems in practice.
Teachers and administrators are best suited for an EdD. Many programs are geared towards the working professional and are offered online or in a hybrid model.
Those who complete an EdD degree often choose to work in a K-12 setting or in college administration.
On average, an EdD degree takes three years to complete including a dissertation. This timeframe can be dependent on:
- Previous education
- Online vs. in-person programs
- Part-time vs. full-time study
Since obtaining an EdD degree is both time-consuming and a financial commitment, finding a program that meets a person’s career goals, work-life balance, and interests is critical.
EdD Career Outcomes And Salaries
Careers in education are growing and the job outlook for this profession is positive. Someone with an EdD degree can expect an increase in income and responsibility.
A few examples of careers available to people with an EdD degree are highlighted below.
- Median Salary: $80,560
- Career Outlook: +912% (2020-2030)
Postsecondary teachers instruct students beyond high school. They are typically referred to as faculty or professors and may write books, conduct research, and publish papers.
- Median Salary: $97,500
- Career Outlook: +8% (2020-2030)
A postsecondary education administrator works in the college setting usually in student services, student affairs, admission, registrar’s office, or oversees faculty, research, and academics.
- Median Salary: $107,680
Top executives are usually in charge of the organization’s big picture. They create strategies and policies to meet goals.
- Median Salary: $98,490
School principals oversee all aspects of the school setting including managing staff, curriculum, and the health and safety of the students.
A PhD in education prepares people to critically analyze and interpret research.
Those that hold a PhD become experts in a given field of education such as teaching practices, inequity in education, and how learning environments shape student outcomes.
Coursework includes a focus on education, quantitative and qualitative research, and a close collaboration with faculty.
A PhD dissertation focuses on creating new research in a particular field whereas a dissertation in an EdD program focuses on solving a particular problem found in a school setting.
People who have a passion for new research and advanced theory along with the desire to become an expert in a particular education field are best suited for a PhD in education.
Career options for those that hold a PhD in education include:
- University professor
- Research scholar
- Policy researcher
PhD of education students will enjoy using their skill set to shape new research and create best practices that will affect teaching and learning for years to come.
On average, a PhD in education degree takes 4-6 years to complete including an original research dissertation.
Unlike the EdD degree, the PhD program is a full-time commitment and not well suited for the working professional. Not many schools offer an online PhD in Education program.
Program timeline may be dependent on:
- Student funding
- Dissertation complexity
Since obtaining a PhD degree is both time-consuming and a financial commitment, finding a program that meets a person’s career goals, work-life balance, and interests is critical.
PhD In Education Career Outcomes And Salaries
As with EdD careers, careers for PhD graduates are projected to see significant job growth. Someone with a PhD degree can expect an increase in income and responsibility.
While EdD professionals seek to obtain roles as superintendents, deans, principals, and other education administrative positions, PhD professionals seek roles as professors, scholars, and researchers.
- Career Outlook: +12% (2020-2030)
Postsecondary professors instruct students beyond high school. They may also be referred to as faculty. Professors often write books, conduct research, and publish papers.
Postsecondary education administrators who hold a PhD may oversee faculty research, or work in student affairs, attendance, and academics.
- Median Salary: $59,870
- Career Outlook: +4% (2020-2030)
Survey researchers conduct qualitative research and analyze the data for trends that can influence education policy and help shape education decisions and plans.
Doctor Of Education (EdD) vs Educational Specialist (EdS)
Another option for career advancement in education is the educational specialist (EdS). An EdS is a postgraduate degree for those that already have a master’s degree, but don’t want to pursue a doctorate. This program is designed for the working professional who wants to add to their skill set but in half the time it takes to complete an EdD program.
The EdS is a graduate certificate that does not require a dissertation or capstone project to complete and is geared towards those that work in the K-12 setting. However, this option is not designed for people who want to work in higher education or organizational leadership.
What To Look For In Educational Doctoral Degree Programs
When comparing different EdD and PhD programs, you should also consider factors outside of career outcomes such as online flexibility and accreditation.
Online vs. On-Campus Learning
While most PhD programs are full-time and conducted in person, online EdD programs are becoming more abundant, and many schools offer the option to complete the degree on a part-time or full-time basis to accommodate busy schedules and the working professional. The biggest benefits of online learning include:
- Flexibility and self-paced learning
- Better time management
- Improved virtual and communication and collaboration
- Faster graduation times
- Ability to work from anywhere
Accreditation
Accreditation is critical for any educational institute. It certifies that the school and its curriculum meet the appropriate standards and qualifications outlined by the U.S. Department of Education and/or the Council for Higher Education accreditation.
Choosing a school that is accredited is extremely important and it gives degrees credibility and validity and will be valued by employers.
Many programs and departments within a school may have a separate accreditation called programmatic accreditation. This accreditation elevates the credibility of the program and shows that the department has designed a program that meets a standard of excellence.
Programmatic accreditation also ensures that students will receive the appropriate training and knowledge to be successful in their given fields.
Applying To Education Doctoral Programs
Admissions requirements for education doctoral programs depend on the type of school, degree, and program modality desired. A master’s degree, letters of recommendation, GRE score, work experience, and prior grades are a few examples of typical education doctoral application requirements.
Admission Requirements For EdD and PhD Programs
Admission requirements for an EdD program typically include:
- A minimum grade point average of 3.0 in the last 60 units of upper-division courses taken
- Passing GRE score
- Three academic or professional letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
- Essay on an assigned topic
- Master’s or specialist degree in education
- Three years practical experience
- Currently employed as a full-time educator
- Application fee
Admission requirements for a PhD program typically include:
- Statement of purpose
- Three letters of recommendation
- College and university transcripts
EdD vs PhD in Education FAQ
- One degree is not considered “better” than the other. Both the PhD and EdD pathways end in a terminal doctorate degree and both programs are designed for different career goals and interests.
- An EdD is a terminal doctorate degree that is designed for the working educational professional (teacher or administrator) who wants to advance their career and apply research in a real-life setting.
- An EdD program is typically three years in length, while a PhD program typically takes four to six years to complete.
- The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that doctoral degrees in education are a growing profession that offers both rewarding and healthy salaries for those who pursue them.
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/postsecondary-teachers.htm
- https://rossier.usc.edu/phd-vs-edd-in-education-nine-expert-tips-to-help-you-choose-with-infographic/
- https://www.franklin.edu/blog/is-a-doctorate-in-education-worth-it
- https://www.eddprograms.org/resources/is-an-edd-worth-it/
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/postsecondary-education-administrators.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/top-executives.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/elementary-middle-and-high-school-principals.htm
- https://www.waldenu.edu/programs/education/resource/how-to-tell-if-i-want-an-edd-or-a-phd-in-education
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/survey-researchers.htm
- https://www.onlineeddprograms.com/faqs/edd-vs-eds-degree
- https://education.ufl.edu/curriculum-teaching/edd/admissions-requirements/
- https://ed.stanford.edu/admissions/application-reqs/phd
EdD vs. PhD in Education: Why Choose an EdD?

EdD or PhD? This is one of the first decisions aspiring education leaders face when exploring options for advanced degrees. The need for leaders in the field has never been greater. Integrating new educational methods and technology, addressing diversity and other social issues, and managing growing requirements for remote learning—these are just a few of the issues currently challenging educators. Taking a step toward earning an EdD or a PhD requires that prospective students first explore the differences between them to determine which track best serves their interests and aspirations.
Both degrees prepare graduates for rewarding careers and leadership roles in the education field , but they vary significantly in terms of study focus and typical career paths. Future education leaders wondering why to get an EdD or a PhD should understand the differences between the two degrees before they choose to pursue one.
What Is a Doctor of Education (EdD) Degree?
An EdD is an advanced degree in the education field that prepares graduates to succeed in leadership roles in higher education. EdD curricula incorporate heavy coursework in education policy, research methods, current social and political issues impacting students and teachers, developing teams and procedures, collaborating with internal and external partners, and managing and planning budgets.
EdD programs provide a solid foundation in modern education system operations, as well as extensive tools to create strategies and implement solutions to help schools and educational organizations succeed. Someone who has an EdD can teach or serve as an educator, but the degree program is more focused on helping graduates become leaders of educational organizations.
What Is a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Degree?
A PhD is an advanced degree that individuals and professionals can typically earn after attaining a master’s degree. A PhD can be attained in several academic subjects, including education, and often prepares students for careers in more research-oriented positions, as well as university and college instructor roles. The curriculum for a PhD in education can vary by school, but it often includes coursework in educational research and evaluation, teaching methods, and a larger dissertation on topics or subjects in the education field.
Job Outlook
In broad terms, EdD programs help graduates gain a deep understanding of education as a field and profession, developing leadership expertise for various educational settings. The PhD track is more research oriented, helping graduates prepare for both the classroom and research aspects of teaching at a postsecondary institution. A closer look at career paths, salary projections, and growth outlooks can help differentiate the programs further.
EdD vs. PhD: Common Career Paths
When considering why to get an EdD or a PhD, it’s important to look at what happens after graduation. EdD and PhD programs’ different areas of focus mean each program best prepares graduates for different career options. The most common path for PhD recipients is to go right back into postsecondary education, with the hope of becoming tenured professors at a college or university. Gaining an EdD opens a variety of doors in the education sector.
Professional Options with an EdD
EdD graduates will have some research background, for example, in examining the implementation of a new curriculum and student response. EdD graduates also benefit from classes focused on leadership and strategic planning, which provide a more business-oriented viewpoint of education and illustrate how policies can impact education at all levels.
Educators who earn an EdD can choose to pursue any of a variety of paths throughout education. Most commonly, they go into elementary, secondary, or postsecondary administration, serving in such roles as college dean or school district superintendent. EdD graduates from a school such as American University can also become college professors or run education-based nonprofit organizations.
Professional Options with a PhD
PhD programs place greater emphasis on research, and graduates commonly work in academia or pursue academic research. Experts in their specific area of focus, they may choose to continue their research with students or other professors.
A person who holds a PhD in education can serve as a professor at a university, a consultant, or a researcher in a government education agency or organization, as well as in a larger leadership role in school or university administration.
EdD vs. PhD: Salary Comparison
Many education leadership roles can be filled by professionals who have earned either an EdD or a PhD, so their respective earning potential is difficult to define precisely. Salaries largely depend upon experience and geographic location. Salary ranges for postsecondary educators, for example, vary widely depending on whether an educator is working at the associate or assistant level or has attained a full professorship.
According to Payscale, the median annual salary for professionals with a PhD in education is approximately $80,000. Payscale notes that assistant professors of postsecondary/higher education have a median annual salary of roughly $69,000.
Doctoral degree holders who attain advanced roles in academia earn higher salaries: Deans with the degree have a median salary of around $93,000 annually, according to Payscale.
The median annual salary for EdD degree holders is around $80,000 in June 2022, according to Payscale. Salaries for EdD professionals can vary significantly by role. For example, Payscale reports the median annual salary of associate professors working in postsecondary/higher education is around $71,000, while EdD professionals serving in an executive director role have a median salary of around $104,000 per year.
Growth Outlook for EdD vs. PhD
The bright career outlook for degree holders is another reason to get an EdD or PhD. Advanced leadership roles for education professionals generally have a positive growth outlook. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the number of jobs for postsecondary teachers will grow by 12 percent between 2020 and 2030, which is much faster than the average 8 percent growth the BLS projects for all professions. The BLS estimates that over the same period, postsecondary education administrator positions will grow by 8 percent, which is on par with the national job growth average projected by the BLS.
Differences Between EdD and PhD
EdDs and PhDs are valuable to professionals seeking to become leaders in education. Both require significant commitments—a doctoral-level degree can take three years or more to complete. While there’s overlap between the coursework and career options for EdD and PhD programs, a review of the differences can help determine a good fit for prospective students.
The curricula for the degrees themselves prepare students for different career paths after they graduate. There are generally more options and specialties for PhD programs than there are for EdD programs. An EdD primarily prepares graduates to become leaders and strategists in the education field—for example, as superintendents, deans, provosts, and school district officials—while a PhD is more tailored to preparing graduates for instructional and research roles in education and higher education, for example, as professors and researchers.
This doesn’t mean that an EdD degree holder can’t serve as a professor or an instructor in a university environment or that a PhD in education degree holder can’t succeed as a superintendent or a dean. EdD programs just focus on the larger scope and strategy of an educational organization or institution, while PhD programs are more tightly focused on academic research.
EdD candidates learn about different educational and leadership styles and how education fits into the larger world. They explore policy at the local, state, national, and international levels. Ultimately they discover how to spearhead change throughout the educational system. EdD graduates can learn how to make strategic partnerships and forge meaningful relationships in the professional world.
PhD students focus much more on research methods and data collection. They typically explore a more narrowly focused dissertation than that of EdD students. PhD students often choose their specific area of research and then spend much of their time collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data so that they can draw informed conclusions. While EdD work looks at systemic progress and trends, PhD work typically examines education theory and methods, with the end goal of having them applied directly in the classroom.
Ultimately both degrees are associated with professionals who’ve earned leadership roles in education, and both degrees enable degree holders to make a positive impact on students’ lives and on educational communities.
Why Get an EdD?
One of the main reasons to get an EdD is that it can prepare graduates to take on leadership roles in different aspects of education. These are more commonly operational roles in academia, such as a higher education administrator. However, an EdD education can also lead to roles in a classroom setting, such as a professor.
The process of earning an EdD degree helps individuals gain expertise in concepts such as leadership, academic policy, and resource management. While these skills are often useful in administration, policy development and implication, and leadership contexts, an EdD can also give degree holders the foundational knowledge to conduct academic research.
Choosing an EdD Program
No two EdD programs are alike. Exploring their differences can help prospective students determine the program that’s the right fit for them. EdD programs may offer varying specializations, for example, education policy and leadership or school administration. Programs can also differ in delivery options, such as online versus in-person coursework.
Benefits of an Online EdD
Individuals who opt to pursue their EdD through an online program can benefit in several ways. A significant advantage is the flexibility of an online program, as its structure makes it possible for students to build their studies and coursework around their existing schedule.
Another benefit of an online EdD program is that students who are concurrently working full-time can immediately apply what they’ve learned to their job. Additionally, the flexibility of an online program fosters discipline, such as good time management, which is essential for professional success.
Become an Education Leader
As society continues to evolve, effective leadership will be needed to guide educational institutions toward a brighter future. Earning an EdD can prepare an individual to guide others confidently as an academic leader, either in the classroom or in an administrative role. Being fully able to lead this charge can make earning an EdD an immensely satisfying achievement.
American University’s online EdD in Education Policy and Leadership program offers students a flexible option to participate in an innovative EdD program from one of the nation’s leading universities. Because the program is online, professionals have the ability to pursue their educational leadership goals and connect with established thought leaders and decision makers, all while still being able to balance their other responsibilities.
Explore American University’s innovative program to learn more about how the EdD in Education Policy and Leadership program can help educators advance in their field and change lives.
5 Effective Principal Leadership Styles
Path to Becoming a School District Administrator
The Role of Educational Leadership in Forming a School and Community Partnership
Indeed, “FAQ: How Much Can You Earn With a Doctorate in Education?”
Indeed, “FAQ: Should I Get a Doctorate in Education? (Plus Career Options)”
Payscale, Doctor of Education (EdD) Degree
Payscale, Doctorate (PhD), Education Degree
United States Bureau of Labor Statistics, Postsecondary Education Administrators
United States Bureau of Labor Statistics, Postsecondary Teachers
Request Information

University Administration
- Careers @ USA
- For Current Students
- Request Information
- Master of Occupational Therapy (MOT)
- Doctor of Occupational Therapy (OTD)
- Post-Professional Doctor of Occupational Therapy (PPOTD)
- Master of Health Administration (MHA)
- Doctor of Education (EdD)
- Graduate Certificates
- Clinical Orthopedic Residency (OCS)
- Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Fellowship (OMPT)
- Continuing Professional Education (CPE)
- Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT)
- Non-Degree Physical Therapy Online Courses
- Master of Science in Speech-Language Pathology (MS-SLP)
- Post-Graduate Nursing Certificates
- Master of Science in Nursing (MSN)
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP)
- Browse All Degree-Programs
- Admissions & Aid Home
- Scholarships & Grants
- How to Apply
- Cost of Attendance
- Financial Aid
- Application Deadlines
- Academic Calendar
- Financial Aid FAQ
- Admissions FAQs
- Catalog/Handbook
- Our History
- Accreditation
- B Corp Certified
- Student Achievement Data
- Institutional Learning Outcomes (ILOs)
- Diversity & Inclusion
- San Marcos, California
- St. Augustine, Florida
- Miami, Florida
- Austin, Texas
- Dallas, Texas
- Our Faculty
- Board of Directors

Education EdD
| 27 July 2023
PhD vs. EdD in Education: How Do I Choose?

Aspiring educators can pursue an advanced degree if they want a more prominent teaching position. If you’re interested in a high-level career in education, you have two doctoral degree options: a Doctor of Education (EdD)or a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD).
In this guide, we highlight key differences in curricula, prerequisite requirements, application processes and typical career paths that graduates pursue. Keep reading to determine whether a PhD vs. EdD is a better choice for you.
PhD vs. EdD
| Career plan | Research and education | Leadership and administration |
| Average education length | 4–7 years | 3–5 years |
| Average program cost (tuition over 4 years) | $96,800 | $98,850 |
| Dissertation? | Yes | Most times |
| Possible concentrations | ADS Educational Technology Higher Education Counselor Education Special Education Teaching and Learning Curriculum and Instruction | Healthcare Special Education Curriculum and Instruction Instructional Design Reading and Literacy Adult Education Organizational Leadership Athletic Training Specialization Executive Leadership Specialization Nurse Educator Specialization Teaching and Learning Specialization |
While both degrees are at the doctoral level, the focus of each is unique. The main difference between a PhD and EdD is that a PhD is designed for graduates who are seeking careers in education or research-based roles , while an EdD is designed for candidates who want to pursue leadership positions with a real-world focus 1 .
For example, an EdD career path would be more aligned with becoming a university dean or director of research, while those pursuing a PhD would likely choose a career as a college professor or research scholar 2 .
The average program lengths also differ. The average time to complete a PhD in education is 4–7 years, whereas an EdD can take 3–5 years to complete. However, the number of years it will take for you to complete either program will depend on if you’re pursuing full-time or part-time schooling.
Below we’ll review each type of degree in depth, including their education requirements, career options, program costs and job outlook.
What Is a PhD in Education?
A PhD in Education is a Doctor of Philosophy degree designed for candidates pursuing a career in research and academia. Most PhD graduates work in a university as a professor, researcher or both. The PhD curriculum is typically more theory-based compared to an EdD degree 2 .
PhD candidates aim to become thought leaders in the field of education—conducting and publishing research on advanced theoretical topics within their specialization, as well as passing on their knowledge to the next generation of students. PhD graduates put an emphasis on research and devote their career to advancing the body of knowledge available within their field.
Education Requirements
Earning a PhD in Education is a time-intensive process, but it’s also the highest academic degree within the field. On average, it takes 4–7 years to complete a PhD 3 .
To obtain a PhD, candidates must hold at least a bachelor’s degree and complete the GRE or an equivalent entrance exam. Depending on the field of study, candidates will then complete either a master’s degree or proceed directly to PhD coursework. During the program, candidates will write a dissertation and defend it before receiving their PhD.
What Can I Do With a PhD?

Most PhD coursework is theoretical, and the degree is a popular choice for those who aspire to become tenured at a university. The most common career options for PhD candidates include:
- Professor: A professor, or postsecondary teacher, instructs college- or university-level students on advanced topics. In addition to teaching, many professors conduct research and publish papers on new topics within their field. Professors earned a median salary of $79,640 per year in 2021 4 .
- Senior School Administrator: PhD graduates may work at secondary schools in senior administrative roles such as a superintendent. Garnering an average salary of $106,690 in 2022, a role as a secondary school administrator is a popular choice for PhD graduates with a background in working with younger students 5 .
- Chief Learning Officer: PhD graduates who prefer to work in a corporate environment rather than at a university may pursue a career path as a Chief Learning Officer (CLO). Job responsibilities for CLOs include retaining top talent, implementing training and mentorship programs and improving the internal talent available within the company. As of 2021, the median annual salary for a top-level executive was $98,980 per year 6 .
- Medical Science Liaison (MSL): Another option for PhD graduates who want to work outside of academia is a career as a Medical Science Liaison (MSL), whose job responsibilities include building professional relationships with industry leaders in research-related areas. One of the key advantages of becoming an MSL is that it provides more freedom to learn, teach and travel than traditional PhD careers. In 2023, the average salary for an MSL is $147,283 7 .*
Job Outlook
PhD candidates typically pursue careers in academia, focusing on education or performing research in their field of study. For postsecondary educators and researchers, the projected job growth is 12% between 2021 and 2031 4 . This is due to the expected rise in enrollment at postsecondary institutions such as colleges and universities.
What Is an EdD?
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a practice-based professional degree that focuses on research applications and leadership roles. The first EdD degree was granted by Harvard University in 1921. The EdD degree was created to develop seasoned educators to serve as faculty at the university level. EdD candidates are solution-focused, aiming to identify and strategize ways to improve real-world problems 8 .
Along with core coursework, many EdD programs offer opportunities to specialize in areas such as healthcare education, teaching and learning and executive leadership. While specializations are optional when earning an EdD, they allow you to gain deeper knowledge and expertise in areas aligned with specific career goals.
To apply for an EdD program, candidates must hold a master’s degree and meet other requirements specific to each program applied to. Once the candidate is accepted into a program, earning an EdD typically requires 3–5 years of study.
EdD programs often attract students who are simultaneously working professionally in the field. For example, the Doctor of Education program at the University of St. Augustine for Health Sciences (USAHS) has a flexible online curriculum, allowing students to continue working while completing their degree at a pace that fits their lifestyle.
The EdD program culminates in a dissertation (or dissertation in practice) that allows EdD candidates to tackle real-world problems or contribute original research in their field of study.
What Can I Do With an EdD?

An EdD is a valuable degree in any number of fields, such as higher education, healthcare, government and nonprofit organizations. Some common EdD career paths include:
- Healthcare Educator: Some EdD programs focus on pedagogical strategies within specialized areas of expertise. For example, USAHS’ EdD program trains educators within the health sciences field. Graduates train the next generation of healthcare practitioners in nursing, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech-language pathology, athletic training and other areas, or they may teach and serve as mentors in healthcare administration. Teaching settings include universities, nursing schools, healthcare organizations and more. In 2021, the median pay for a health education specialist was $48,860 9 .
- Provost: A provost is typically a senior-level administrator at a college or university who functions as the school’s chief academic officer. Provosts help develop institutional goals and strategies, determine fund allocation, and assist with the school’s daily operations. In 2021, the median pay for a postsecondary education administrator, such as a provost, was $96,910 per year 10 .
- Dean: A dean is an upper-level university administrator who oversees several related departments or an entire college within the university. Deans may also work in operations-related positions, including dean of student affairs or dean of admissions. The median pay for postsecondary education administrators (including deans) in 2021 was $96,910 per year 10 .
- Top-Level Executive: An EdD degree can prepare candidates for executive roles such as a CLO or Chief Academic Officer (CAO) within an educational institution or a business with an educational component. In these positions, an executive can create strategies to solve business problems and help their organization develop and meet goals for business development. As of 2021, the median pay for a top-level executive was $98,980 per year 6 .
- Curriculum Designer: Curriculum designers develop educational programs and instructional materials—in print or online—for schools, organizations and companies. They can also help teachers and trainers implement the curriculum and evaluate learning outcomes. The median pay in 2021 for curriculum designers was $63,740 11 .
An EdD is a degree for experienced educators who want to further their knowledge to improve the education system in its entirety. Although most EdD graduates hold jobs in the education sector , other opportunities include leadership roles in business, government and nonprofit organizations 12 .
Postsecondary education administrators have a projected growth of 7% from 2021 to 2031, which is as fast as the national average for all occupations 10 .
PhD vs. EdD: 5 Factors To Consider

Here are some important factors to consider when determining whether an EdD or a PhD is right for you.
1. Career Goals
First, think about your career goals. If you’re interested in educating future students and publishing theory-based research, you might consider pursuing a PhD in Education. If you are more interested in applying research to real-world foundational and institutional issues, an EdD may be a better choice.
2. Day-to-Day Work
Consider what your day-to-day work would consist of as a graduate of each degree program. With a PhD, you would likely teach classes and work with graduate students to perform research. An EdD degree may lead to a career more focused on creating educational policy and developing leadership in educational institutions.
3. Types of Coursework
Completing a degree at the doctoral level is rigorous regardless of whether you choose an EdD or PhD. In PhD programs, coursework typically centers on conducting qualitative and quantitative research culminating in a dissertation. By contrast, EdD coursework focuses on leadership and education, treating research as a component rather than the main focus of the degree.
4. Online Programs
If you’re already working as an educator or aren’t able to commute, online programs give you the flexibility to complete an EdD or PhD at home and at your own pace.
Programs such as USAHS’ Doctor of Education are delivered almost completely online, with optional on-campus immersions where you can engage in discussions, presentations and Q&A sessions face-to-face with professors, guest speakers and fellow students.
5. Specialization Options
If you want to specialize within your degree, do some research to determine which EdD or PhD programs have options to concentrate on the area you’re interested in. While concentrations differ at each university, EdD and PhD programs have certain staples. PhD concentrations include areas such as educational psychology and special education, while popular EdD concentrations include educational leadership and teaching.
Both an EdD and PhD in Education offer excellent career options. Regardless of the decision you make, it’s essential to choose the career path that is right for you and best aligns with your career goals.
Take the Next Step With Your Education
Interested in pursuing higher education in health sciences? USAHS offers an EdD degree that allows you to specialize in healthcare education, like Nurse Educator, Teaching and Learning, Athletic Training and Executive Leadership. It’s an online program that also offers optional immersions.
Contact an enrollment advisor when you’re ready to apply to a one-of-a-kind program.
The University of St. Augustine for Health Sciences (USAHS) offers an online EdD program designed for working clinicians and healthcare educators, with optional on-campus immersions. Specializations include Nurse Educator, Athletic Training, Teaching and Learning, and Executive Leadership. Complete coursework when and where you want and earn your advanced degree while keeping your work and life in balance.
*The information provided on this website is based on self-reported data and is intended for general informational purposes only. PayScale is a limited data source that relies on voluntary submissions from individuals and employers.
Please be aware that the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the data may vary due to its voluntary nature and limited scope. While efforts are made to maintain the data’s accuracy, we cannot guarantee its absolute correctness or currency.
- University of The People, “What Is An Ed.D. And Why Is It Important For Your Future?,” University of The People , last modified July 2022, https://www.uopeople.edu/blog/what-is-doctor-of-education/
- School of Education Online Programs, “EdD vs. PhD in Education: Why Choose an EdD?,” SOEOnline , last modified October 2022, https://soeonline.american.edu/blog/edd-vs-phd/
- Coursera, “How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?,” Coursera , last modified June 2023, https://www.coursera.org/articles/how-long-does-it-take-to-get-a-phd
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Postsecondary Teachers,” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , last modified October 2022, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/postsecondary-teachers.htm
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “May 2022 Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics,” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , last modified Modified April 2023, https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes_nat.htm#00-0000
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Top Executives,” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , last modified September 2022, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/top-executives.htm
- Payscale, “Average Medical Science Liason Salary,” PayScale, last modified 2023, https://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Medical_Science_Liaison/Salary
- Harvard Graduate School of Education, “Doctor of Education Leadership,” Harvard Graduate School of Education , https://www.gse.harvard.edu/degrees/edld
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Health Education Specialists and Community Health Workers,” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , last modified October 2022, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/community-and-social-service/health-educators.htm
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Postsecondary Education Administrators,” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , last modified October 2022, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/postsecondary-education-administrators.htm
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Instructional Coordinators,” U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , last modified October 2022, https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/instructional-coordinators.htm
- Graduate Programs Staff, “8 Careers You Can Pursue with a Doctorate in Education,” Northeastern University Graduate Programs , last modified September 2019, https://graduate.northeastern.edu/resources/careers-with-doctorate-in-education/
ARE YOU INSPIRED?
There could be an article about you here one day. Take charge of your own life-story!
Take charge of your own life-story
More Education EdD Articles

How To Study Effectively? 10 Best Study Techniques | USAHS

Tuition Reduction Available for Select Programs When You Start Next Spring

Determining the Cost of Your Advanced Education
Upcoming education edd events.

Flex Doctor of Physical Therapy (Flex DPT) - Academic Webinar - June 12 @ 4:00 pm PDT
Fellowship & Residency Programs Webinar - June 12 @ 5:30 pm PDT

Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) - Academic Webinar - June 13 @ 4:00 pm PDT

Ed.D. vs. Ph.D.: What’s the Difference?
Reviewed by Jon Konen, District Superintendent
In essence, the primary difference between a Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) and a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) is that an Ed.D. focuses on practical skills, while a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) focuses on theory and research.
Those pursuing an Ed.D. typically want to work in education leadership roles, so they perform hands-on work while pursuing their degrees. Ph.D. candidates usually hope to work in educational research and high-level education, so they perform a lot of literature reviews and other types of academic study. However, both involve practical and theory-based work.
Do you want to earn a doctorate in education but can’t decide which type of program to choose? Then, look no further for the answers to your questions.
Here, we’ll discuss the difference between an Ed.D. and Ph.D., including the careers they’re both geared toward, what their respective course schedules look like, how long they take to get, and more.
What Is an Ed.D.?

If you are working towards your Ed.D., your curriculum will likely be geared towards solving on-the-ground problems in the educational system.
Projects for Ed.D. programs often include participating in workshops and research in the community, up to implementing a program in a classroom and reporting the findings. Specific coursework is determined by the area you specialize in. For instance, if you’re focusing on creating best practices for special education, you’ll likely spend time working in various special education rooms.
What Can I Do With an Ed.D.?
Those with Ed.D. degrees often seek positions in administration or community or district-wide leadership, seeking to improve schools and other educational resources in their communities.
If you choose to pursue the Ed.D. route, you may also choose to specialize in different leadership tracks such as:
- Educational Technology : Instructional technologists help create programs for classrooms, teach district leaders and educators how to best implement digital resources, and more.
- Education Policy : Education policy jobs involve helping officials to create policies that further and benefit education at the local through national levels.
- School or District Leadership : Principals and superintendents aren’t generally required to have doctorates, but the degrees can make them stand out among the crowd.
Salaries and Job Growth for Common Ed.D. Careers
There are many possible careers with Doctor of Education degrees, but salaries for the most common include:
- Educational Technologists: Average base salary of $64,125 per year ; growth unavailable
- Education Policymakers: Median salary of $125,350 per year (inclusive of all political scientists); 9% growth 2020-2030
- School or District Leaders: Median salary of $98,490 per year (inclusive of all administrative positions); 3% to 4% growth 2019-2029
What is a Ph.D. in Education?
A Ph.D. in education focuses on conducting research that enhances the profession and educational system. Most people with this doctorate spend some time working as a professor or postsecondary administrator.
Ph.D. in education programs generally require courses in research, independent study, and best practices, culminating in a dissertation.
That said, teaching-related internships and research are often needed.
What Can I Do With a Ph.D. in Education?
With a Ph.D. in education, you will usually seek employment as a college professor or educational researcher. This means you should want to teach and conduct research at the collegiate level. While some people can ultimately focus their efforts on research, being asked to teach is common.
While both Ed.D. and Ph.D. programs allow many of the same specialties, some more common with Ph.D. programs are:
- Adult Education : Adult education can mean college professors in the traditional sense or working with nontraditional learners on earning their GEDs.
- School Psychology: This program may be offered through a college’s education department or psychology department. It allows you to provide in-depth psychological services to students and families.
- Specific Subjects: You can focus on an academic subject you like most, such as math , language arts , history , special education, or even art and physical education , allowing you to create best practices for teachers, teach college students in the subject, research the psychology behind best practices, and work as a K-12 classroom teacher or teacher leader.
Salaries and Job Growth for Common Ph.D. in Education Careers
No matter the specialty, many Ph.D. holders work in college classrooms and administration. The salaries and job growth estimates for those areas are:
- Postsecondary Teachers: Median salary of $80,560 per year ; 12% growth between 2020 and 2030
- Postsecondary Education Administrators: Median salary of $97,500 per year ; 8% growth 2020-2030
Similarities Between Ed.D. and Ph.D. Degrees
Both a Ph.D. in education and an Ed.D. are intended to extend a teacher’s knowledge and ability in education. Each requires research in your intended field and the defense of a dissertation, capstone project, or other comprehensive final exploration of a topic.
You can refer to yourself as “doctor” whether you have a Ph.D. or Ed.D. However, you should be aware of the context in which you’re using it since almost everyone associates the term with medical doctors. In your classroom? Go ahead! In a place where it could be confusing? Consider leaving your title at home.
While common career paths were named under both the Ed.D. and Ph.D. sections above, you aren’t barred from entering those careers with the other doctorate. While it’s more common, for instance, for someone with an Ed.D. to work hands-on in the schools, someone with a Ph.D. can definitely do that too.
Some doctoral programs allow you to pick an area to specialize in, while others only enroll students for specific types of specialties. It’s rare for a student not to specialize—to work as a doctor in education, you need to have a particular area you’re passionate enough about to want to focus your studies on it.
Common specialization tracks for both degree types can include:
- Adult Education
- Curriculum, Instruction, and Learning
- Early Childhood Education (ECE)
- Special Education (SPED)
- Teacher Leadership
While you can have other degrees in all those specializations, doctoral degrees allow you to make bigger picture decisions.
For instance, someone with a master’s in ECE may serve as a consultant or manager of an ECE center, while someone with a doctorate is more likely to work at the policy level to ensure a community’s early childhood education goals are met. (If you want to teach ECE and not work in those levels, consider an associate or bachelor’s degree in the field, as those are typically all you need.)
Is Getting a Doctoral Degree in Education Worth It?
Getting a Ph.D. in education or an Ed.D. is worthwhile for some people and not for others. Here are some pros and cons to consider when deciding to pursue a doctoral degree in education:
Doctoral Degrees in Education: Pros
- Prestige: Getting a doctorate impresses many people.
- Additional Career Opportunities: Some careers that education-focused doctors can have are open to those with master’s degrees, but many (such as professors at major universities) often require doctorates.
- Research: Doctoral candidates and doctors in education often have more resources for researching their chosen field.
Doctoral Degrees in Education: Cons
- Potentially Harder to Get Some Jobs: If you want to work as a teacher in a K-12 school, you’ll likely be at the high end of the pay scale. If you decide to switch to a new school or district, you could find it hard to gain employment since you’re more expensive to hire.
- According to the National Center for Education Statistics , the most recent data on the cost of a graduate education at a public university shows the average to be $11,926 per year.
- At a private university, you’re looking at an average of $25,442 per year.
- You May Not Need One: Before committing the time and money to a doctoral degree in education, be sure you need one. In some cases, the costs outweigh the benefits.
Ed.D. vs. Ph.D.: Which is Right for Me?
Both doctoral degrees in education can lead to professional advancement. The two primary factors to consider are how much time you have to spend in school and what your careers goals are:
- Time in School: You should generally expect your D. in education to take between four and six years, depending on a few factors that will play out after you get started. An Ed.D. usually takes approximately three years.
- Career Goals: An Ed.D. involves more of a practical application of what you’re learning. You learn by doing and should want a career where you’re actively involved in education. Meanwhile, a D. in educationinvolves more theoretical and research-based work. You should favor jobs in research and development but also be comfortable teaching in a postsecondary environment.
Your Path to a Doctorate in Education
If you’re beginning to explore careers in education , you may have made it to this page as part of figuring out the path to your ideal career in the field. Remember: No matter what, you need a minimum of a bachelor’s degree to pursue a doctorate in education. Depending on the requirements of the programs that might be offered at your school of choice, you may also need a master’s degree .
However, if you’re getting ready to enter a specific job that requires a doctorate, it’s time to explore doctoral programs in your state or online.
Whether you choose an Ed.D., Ph.D., or choose to remain at the bachelor’s or master’s degree levels, a career in education—even one that seems a bit outside the box —means you’re likely to change lives. We at EducationDegree are here to help with our wealth of articles and other resources to set you up for success.
(Salary data reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in May 2020 for teachers and administrators . Figures represent national data, not school-specific information. Conditions in your area may vary. Information accessed October 2021.)
PhD vs. Ed.D. - What’s the Difference?

Updated on March 29, 2023
A Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) or Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Education each shapes the educational world in different ways. These degrees can chart different career paths in academia, the private sector and civil service.
A Doctor of Education and a PhD in Education each offers students ample opportunities for leadership, learning and research. However, each comes with distinctions and unique advantages.
Both a PhD and Ed.D. are terminal degrees that can help you affect the future of education , but understanding the differences and similarities can help you make the right educational investment.
PhD vs. Ed.D. : What Are They?
The main difference between an Ed.D. vs. a PhD is the end focus of the graduate’s career. An Ed.D. has a practical emphasis that may go outside of academia. A PhD in education is the more scholarly concentration of the two, more often than not culminating in research-based studies.
A PhD in Education
A PhD usually pursues a teaching career in academia and does first-hand research to help inform best practices. This allows candidates a primary exploration of their field.
A PhD is likely to take on the role of an academic in higher education. PhD candidates are likely to publish original research in academic journals and present research papers at conferences.
A Doctor of Education
A Doctor of Education degree tends to be more focused on the practical application of education within an organization. An Ed.D. is the more hands-on degree of the two, with more direct leadership opportunities. While many Doctor of Education graduates teach, conduct research and take on administrative roles in higher education, this degree may also culminate in non-academic settings, such as the private sector.
For those pursuing a career in education, government, the nonprofit sector or business, an Ed.D. degree may be ideal. Instead of fielding new research, an Ed.D. applies existing knowledge to solve problems within an organization. This enables them to exercise leadership and make data-informed decisions based on concepts like social assessments and organizational theory.
PhD vs. Ed.D .: How Are They Similar?
Both an Ed.D. and a PhD can open doors to career advancement. This brings the potential for promotion and greater compensation in comparison to that of a bachelor’s or master’s degree. In fact, employers and students are demanding advanced degrees more than ever.
An Ed.D. and a PhD in Education have key aspects in common. Each degree develops leadership within a candidate and equips them to understand both research and statistics.
- Both degrees are terminal (as high as a student can go in that academic path).
- Both focus on ways to enhance professional knowledge in different environments.
- Both benefit the candidate, making them more marketable and affording greater compensation.
- Both provide great benefits to the graduate’s employer.
- Both enable candidates to pursue careers in administration and supervision, training and development and curriculum and instruction in addition to teaching.
Marketability and Popularity
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, 24.1 million people in the United States have a master’s degree as their highest degree. The number of people with doctoral degrees is 4.7 million . These numbers total 14.4% of the U.S. population.
Total post-graduate degree enrollment increased by 10% between fall 2009 and fall 2020 — the most recent data due to the pandemic. By 2030, the total number of students enrolled in post-graduate programs is expected to increase to 3.3 million students, 6% higher than 2020 figures.
What’s more, according to a 2022 survey conducted by Public Agenda, 86% of Americans feel that earning a college education can help individuals further their careers.
Ed.D vs. PhD : How Are They Different?
Both a Doctor of Education and a PhD in Education are rigorous and authoritative degrees that focus on professional knowledge, innovation and problem-solving. Both advanced degrees are in the same field. But when you’re ready to advance your career, understanding the differences and similarities between these options is key.
Ideal Candidates
While an Ed.D. and a PhD are similar in some ways, each degree has a slightly different ideal candidate.
The Ideal Ed.D. Candidate
A person best suited to an Ed.D. degree is searching for a more concrete, real-world approach to education. An Ed.D. candidate will often already be working in education or a related field full time and want to pursue their Ed.D. degree to enhance their leadership skills and professional knowledge.
They may work for an educational institution or perhaps in a university setting. Other roles may include the nonprofit sector or a business focused on professional development or training, a government agency or even civil service.
An Ed.D. degree may be more suited to students who want:
- To effect transformation within an organization , the private sector or government
- To apply or add to existing scholarly studies to effect change
- To have an existing job they would like to keep while pursuing an advanced degree
- To implement established best practices in the real world
The Ideal PhD Candidate
A PhD candidate is traditionally focused on conducting research that drives changes. They may not necessarily be interested in implementing change but in conducting leading-edge research. Their work can influence education and public policy.
PhD students need to master their subject area and extend scholarly knowledge on that subject. This might focus on policy in education, leadership in education, child cognitive development, literacy or the sociology of education.
A PhD in Education may make sense for students who want to:
- Delve deeply into a research subject
- Inform best practices that others implement
- Devote their career to higher education
- Publish their findings in scholarly journals
While neither an Ed.D. or a PhD in education is better than the other, each degree offers unique benefits based on your career goals and other factors.
Benefits of Pursuing a Doctor of Education Degree
An Ed.D. candidate can enjoy:
- Implementing best practices in education and evaluating measurable change within an organization
- Going beyond academia into the private sector , non-profit organizations, school districts or government to lead and transform environments
- Remaining competitive in the dynamic field of education
- Maintaining a strong influence on educational practices within their work sphere
- Shaping not only educational research but educational process and policy
Benefits of Pursuing a PhD in Education
A PhD candidate can enjoy:
- Performing exploration and research into what intrigues them about their field
- Knowing that their research has the potential to shape best practices in their field
- Remaining competitive in their chosen field
The coursework for a PhD vs Ed.D. degree varies between two and six years of study and between 60 and 90 credit hours.
Typical Coursework for a Doctor of Education
- Requires two years of study
- Is primarily conducted within a classroom (face to face or virtual)
- Works heavily with applying theory to real-life situations while evaluating solutions from different and innovative perspectives
- May require a thesis but not writing and defending a dissertation
- Requires around 60 hours of coursework
- Focuses on the practical application of innovative solutions to improve the workplace
Typical Coursework for a PhD in Education
- Requires four to six years of study
- Works heavily with data, encompassing the scientific method, statistics and research
- Encompasses writing and defending a dissertation
- Requires around 90 hours of coursework
- Focuses on research more than practice
Jobs and Salaries
While some commonalities in career trajectory exist, these degrees see many graduates landing in different careers. The salary depends on the career path a graduate chooses, and there may also be additional influencing factors, such as years of experience and job location.
Typical Doctor of Education Salary
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports on the 2021 salary statistics for educational leadership positions that Ed.D. graduates can pursue:
- Education administrators, postsecondary: $111,260
- Education administrators, kindergarten through secondary: $102,650
- Clinical, counseling and school psychologists: $99,640
- Social and community service managers: $76,790
Typical PhD in Education Salary
PhD graduates tend to remain in research and higher education. The salary site Payscale reports that graduates with a PhD in Education made a median annual salary of approximately $89,000 as of March 2023.
Your Next Step Toward an Advanced Degree in Education
Deciding whether an Ed.D., PhD or another advanced degree is right for you depends on your career goals.
Marymount University’s Online Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) program can be instrumental in helping you achieve those goals. The fully online program is designed to allow you to cultivate knowledge and skills at your own pace, with a curriculum rooted in social justice, ethics and equity. Find out how Marymount can prepare you for a career with true impact.
Recommended Readings
- 4 Innovations in Higher Education Being Driven by Educational Leaders
- Is an EdD Worth It?
- 9 Educational Leadership Career Paths Explored
Requirements Not Met
To proceed with either the BSN to MSN FNP or the BSN to DNP FNP or the BSN to DNP PMHNP or the MSN PMHNP, you are required to have a bachelor’s degree and hold your RN license.
To proceed with either the PMC-FNP or the PMC-DNP or the PMC-PMHNP, you are required to have a master's degree and hold your RN license.
To proceed with the ABSN, you are required to have a bachelor's degree.
If you don’t meet these requirements but would still like further information, please contact us .
To proceed with the EdD in Educational Leadership and Organizational Leadership degree, you are required to have a master’s degree.
If you don’t meet this requirement but would still like further information, please contact us .
To proceed with the Doctor of Business Administration - Business Intelligence degree, you are required to have a master’s degree.
X Close Box
© 2024 Marymount University • All Rights Reserved • Privacy Policy • California Privacy Notice
- Schedule an Appointment
- Request Info

EdD vs. PhD in Education: What’s the Difference?
By Scott W. O’Connor
If you’re interested in pursuing a doctoral degree in education, one of the first questions you’ll face is: Should I apply for a Doctor of Education (EdD) or a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Education?

The decision between these two culminating degrees can be career-defining as each serves a very different purpose despite being equivalent in level. In order to ensure you choose the path that best aligns with your future career goals, it’s important to take the time to first understand the differences in program curriculum and future career opportunities that relate to each degree.
Read on to learn about the defining qualities of an EdD and a PhD in Education, and determine which program is the right fit for you.
EdD vs. PhD in Education
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a professional degree designed for practitioners pursuing educational leadership roles. A PhD in education , on the other hand, is designed to prepare graduates for research and teaching roles.
“With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based on a theory or hypothesis,” Joseph McNabb , a professor of practice in Northeastern’s Graduate School of Education , explains. “Conversely, an EdD student starts with a problem of practice and [works to learn] the skills it will take to resolve that complex problem of practice.”

What is an EdD Degree?
An EdD, or Doctor of Education , is a professional doctorate best suited for experienced educators and mid- to senior-level working professionals who want to lead and implement change within their organization.
EdD candidates work in a broad range of fields ranging from K-12 and higher education to nonprofits, government, healthcare, and the military. What each share is a desire to transform their everyday environment and apply the lessons learned through their doctorate to a complex, critical issue facing their workplace.
The EdD is practice-based. Students in an EdD program don’t want to just research their area of interest, but leverage that research in ways that could positively influence their community or organization’s decision-making process.
Learn More: 5 Tips for Choosing Your EdD Concentration
Those who pursue an EdD focus on qualitative, exploratory research. Students collect data and conduct individual interviews, observations, or focus groups to construct hypotheses and develop strategies that can help solve or clarify a specific problem of practice, such as how to support student veterans transitioning to civilian life or how to foster more female leaders in higher education—two dissertation topics recently explored through Northeastern’s EdD program .
What Can You Do with an EdD Degree?
While an EdD can be applied to a variety of industries—such as K-12, higher education, the nonprofit sector, or civic service—there are several job titles you’ll likely come across within your cohort of classmates. They include:
- Postsecondary Education Administrators: Postsecondary education administrators work in colleges or universities, and typically oversee faculty research, academics, admissions, or student affairs. Some job titles that fall under this category include president, vice president, provost, and dean. The average annual salary for a postsecondary education administrator rings in at $94,340 .
- Elementary and Secondary School Education Administrators: Superintendents, who are the top executives of a school district, fall under this category. They manage academic programs, spending, and the staffing of all educational facilities within their district, and typically earn an average of $98,880 per year .
- Top Executives : In education, a top executive could be a “chief learning officer” or “chief academic officer”—senior-level professionals who drive and develop strategies that help their organization meet critical business goals. Top executives make an average of approximately $104,980 per year .
- Instructional Coordinators : Instructional coordinators create and manage school curricula and other educational materials. They help teachers implement effective classroom learning strategies and measure the effectiveness of what’s being taught and how. The average annual salary for instructional coordinators is roughly $64,450 .
These are just a few of the many career opportunities available to EdD graduates.
Learn More: Top Careers with a Doctorate in Education
What is a PhD in Education?
A PhD in Education is a terminal degree best suited for individuals who want to pursue a career in academia or research at the university level.
Students in a PhD program take a more theoretical, study-based approach to learning. In most cases, their goal is to master a specific subject or add their unique findings to a body of existing literature. PhD candidates conduct original research in the hopes of driving change in their field or inspiring others to make change based off their work.
A PhD is the degree most popular amongst those who aspire to become a professor or obtain a tenure position. Through these programs, students tend to focus on getting published in well-respected journals, presenting at national conferences, and learning how to teach future educators.
What Can You Do with a PhD in Education?
While some of the above roles can also be earned through a PhD program, the most common job titles for PhD-holders include:
- Postsecondary Teachers: Postsecondary teachers instruct students at a college or university. When they’re not in the classroom, they’re often focused on conducting research, attending conferences, and publishing scholarly papers and books. Postsecondary teachers earn an average $78,470 per year .
- Academic Researcher : Researchers often have the opportunity to create their own centers or institutes, hire staff to help carry out their work, and secure funding for that work. Salaries often vary by subject area, but a general academic researcher typically earns an average $76,273 per year .
Taking the Next Step
Once you’ve explored the differences between an EdD and PhD in Education, the most relevant question to consider will be: What’s the next step I want to take in my career, and which degree can help me achieve my professional goals? The answer to this question will determine which degree you ultimately pursue.
Earning your doctorate can pay off no matter which path you choose. Professionals with a doctoral degree earn an average $3.65 million over their lifetime—nearly one million dollars more than master’s degree holders. Similarly, doctoral degree holders see an unemployment rate of only 1.5 percent compared to the national unemployment rate of 3.6 percent.
Regardless of which degree you ultimately pursue, there is enormous potential for you to advance your career in the field of education. Evaluating your needs and values will help you understand whether an EdD or PhD in Education is best suited to your personal and professional goals.
About Scott W. O’Connor
Scott W. O’Connor is a writer and SEO specialist for Northeastern University. He has been writing for both print and online publications for over 10 years and specializes in the higher education sector.
“With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based on a theory or hypothesis. Conversely, an EdD student starts with a problem of practice and [works to learn] the skills it will take to resolve that complex problem of practice.” Joseph McNabb Professor of practice in Northeastern’s Graduate School of Education
We use cookies to improve your experience on our sites. By continuing to use our sites, you agree to our Privacy Statement .
- Online Degrees
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Transferring Credit
- The Franklin Experience
Request Information
We're sorry.
There was an unexpected error with the form (your web browser was unable to retrieve some required data from our servers). This kind of error may occur if you have temporarily lost your internet connection. If you're able to verify that your internet connection is stable and the error persists, the Franklin University Help Desk is available to assist you at [email protected] , 614.947.6682 (local), or 1.866.435.7006 (toll free).
Just a moment while we process your submission.
Popular Posts

Ed.D. vs. Ph.D.: What’s The Difference?
Doctoral degrees are the pinnacle of achievement in higher education. They’re also particularly valuable if you want to become a leader in the education field. Whether you aspire to teach college, head a K-12 school system or become an organizational leader, you may be at a crossroads between choosing a Doctor of Education (Ed.D). or a Ph.D. in Education.
You’re probably wondering what the practical difference is between the Ed.D. and the Ph.D., as well as the career paths each prepares you for. We’re here to help answer those questions and more as we dive into the specifics of the Ed.D. vs. a Ph.D.
Ed.D.: The Professional Degree in Education
A Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) is a professional degree designed for practitioners who want to pursue roles as education or mission-driven leaders.
The Ed.D. degree originates over 100 years ago at Harvard University. Since its inception it has evolved into a multifaceted and nuanced program offered in varying forms at universities across the world. As this degree has grown, it is especially prevalent in online education.
According to labor market analytics firm EMSI, Ed.D. degrees earned through online programs grew 238% from 2012 to 2020.
As the popularity of the Ed.D. grows and its availability increases, many students are weighing the pros and cons of getting their Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. We’ve put together three lists to help you decipher the advantages, career paths and top considerations for potential Ed.D. students.
Top 3 Ed.D. Advantages
Leadership training. Ed.D. programs offer leadership and management training that is pivotal in creating thriving organizations and satisfied employees across industries.
Real-world application. Ed.D. degrees are focused on preparing professionals to solve real-world problems in education and other mission-driven organizations.
Flexible career options. An Ed.D. provides flexible career options, both in the field of education or as a leader in a mission-driven organization.
5 Popular Ed.D Career Paths
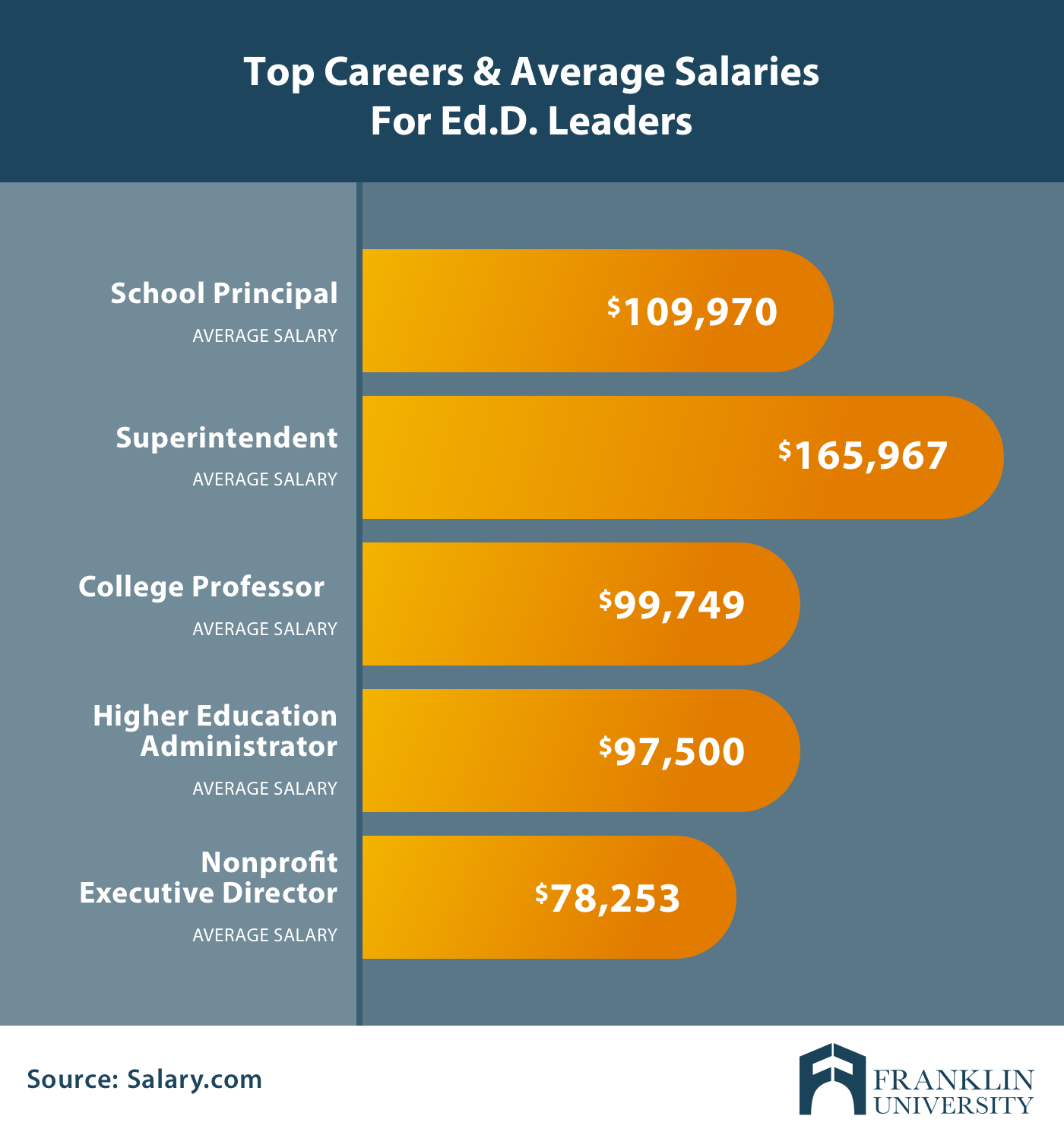
- School Principal: Principals act as the leader of K-12 schools, managing teachers and staff to set school goals and ensure students are meeting learning objectives. If you currently work in K-12 education, getting your Ed.D. is a great way to advance your career and increase your earning potential, as principals earn a median salary of $109,970.
- Superintendent: Superintendents are responsible for all school programs within their district. They work with school boards to create and carry out policies that will improve students’ learning outcomes. An Ed.D. degree is an ideal fit for this high-earning career, as superintendents can earn a median salary of $165,967 per year.
- College Professor: If you want to teach education full time at the college level, you will most likely need a doctoral degree. Professionals with Ed.D. degrees, especially those with industry experience, are a great fit for professional education programs at universities. College professors in the field of education earn an average base salary of $99,749.
- Higher Education Administrator: Administrators in higher education can work in a variety of departments and specialities. These professionals often oversee faculty, staff, curriculum, budgets and facilities within their department or college. Higher education administrators earn a median pay of $97,500 per year with projected job growth of 4% by 2029.
- Nonprofit Executive Director: These professionals develop goals, strategies and operational plans for nonprofit organizations. An Ed.D. with a focus in organizational leadership can prepare you for these roles that involve donor education, motivation and people management. Executive directors earn a median salary of $78,253 , with the top 10% earning over $114,053.
3 Big Considerations for Prospective Ed.D. Students
No universal standard across programs. Ed.D. curriculum is not standardized, meaning each Ed.D. program may be different in its focus. It’s important to thoroughly research each Ed.D. program to ensure the curriculum aligns with your goals.
Not ideal for academia. An Ed.D. degree may not be the right fit if you want to pursue a career in academia with a heavy research focus. Most tier one research universities seek out candidates with Ph.D. degrees who want to conduct and publish research on the university’s behalf.
J ust as rigorous as Ph.D. programs. Ed.D. programs are not easier than Ph.D. programs. If you’re considering an Ed.D. because you see it as a less intensive option than a Ph.D., that is a misconception. Be prepared for a rigorous academic program no matter which degree path you choose.
Earning a doctorate is challenging and rewarding, but do you know what to really expect? Download this free guide for tips and insights to help you prepare for success.
Ph.d.: the academic & research degree in education.
A Ph.D. in Education is a terminal degree that’s best suited for individuals who want a career in academia or research at the university level. Students in a Ph.D. program take a more theoretical approach to learning, which involves publishing original research to contribute to the field of education. A Ph.D. trains you to interpret existing knowledge, identify areas for exploration, and use critical analysis to move the discipline forward.
Let’s look at the advantages, career paths and considerations for pursuing a Ph.D. in Education so you can compare this degree option to the Ed.D. degree.
Top 3 Ph.D. Advantages
Stand out for academia and research positions. Gaining subject mastery and finely honed research skills can help you stand out for jobs at top tier research universities, research institutions or government agencies.
Advance education theory. Advance theory on a topic you’re passionate about while gaining professional credibility in that specialty. This may include advancing theory in areas such as cognitive learning theory, behaviorism learning theory, or connectivism learning theory, among others.
Contribute to research. Collaborate directly with faculty and researchers to contribute original research in the field. This could include addressing issues such as the gender gap in STEM programs, mandating school standards, or standardized testing as an indicator of future success.
5 Popular Ph.D. Career Paths
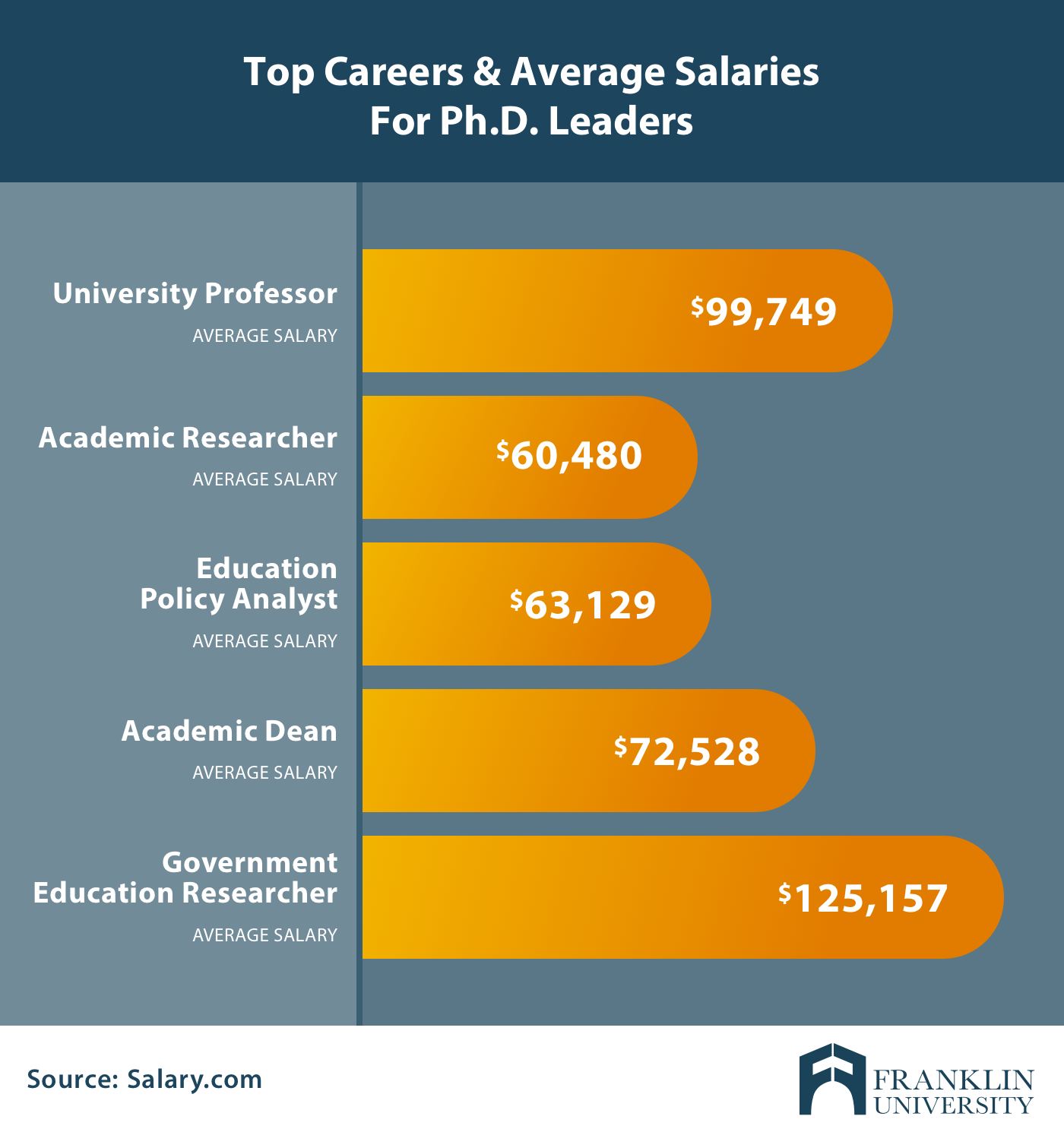
- University Professor: A Ph.D. degree will help you compete for jobs at universities of all sizes. If you want to participate in research while also teaching, a Ph.D. is a great fit. College professors in the field of education earn an average base salary of $99,749.
- Academic Researcher: Getting your Ph.D. in education can also qualify you to work solely as a researcher in a university setting. Many educational researchers use their subject matter expertise to design and test academic programs that assist schools and universities with curriculum and measuring student progress. An academic researcher can expect to make an average $60,480 per year , while some make as much as $144,500.
- Education Policy Analyst: These professionals have a desire to shape the future of education by identifying and researching educational challenges and proposing data-backed policy solutions. The average salary for an education policy analyst is $63,129.
- Academic Dean: Academic deans are the head of their respective academic unit within a university. A Ph.D. in Education can prepare you to lead the education department and shape the curriculum and student experience. The median salary for an academic dean is $72,528.
- Government Education Researcher: A Ph.D. in Education can qualify you to work with various government agencies, from local to federal, to conduct research that helps improve education quality. The average education researcher at the federal level can expect to earn $125,157.
3 Big Considerations for Prospective Ph.D. Students
Less flexible scheduling. Ph.D. programs may not accommodate part-time study and may require in-residence study and research. While some online programs are available, if you’re looking to compete for top jobs at research universities, a full-time Ph.D. program is likely your best option.
Longer duration to complete. Ph.D.s in Education usually require 90 credit hours to complete, compared to approximately 60 credit hours for an Ed.D. This means your degree will take longer to earn and will likely cost more than an Ed.D.
Less competitive wages. Ph.D. degrees most often lead to careers in academia, which often pay less than the variety of public, private and nonprofit sector jobs you can pursue with an Ed.D.
Making The Right Degree Choice For Your Career Goals
Choosing the right doctoral degree is key to your success as a future educator or organizational leader. If you want to pursue a degree that is ideal for working professionals while learning to apply research to real-world problems, an Ed.D. can take your career to the next level.
Franklin University offers an online Ed.D. program that can be completed in as few as 3 years. The no-fear dissertation process helps you define your dissertation topic and integrate it into your coursework, so you can finish faster. Franklin also offers three different focus areas in Organizational Leadership, PK-12 Leadership and Higher Education Leadership, so you can specialize in the career path you're most passionate about.
Learn more about Franklin’s Ed.D. program and how it can help you advance your career.

Related Articles

Franklin University 201 S Grant Ave. Columbus , OH 43215
Local: (614) 797-4700 Toll Free: (877) 341-6300 [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Franklin University
Ph.D. vs. Ed.D.
By DeWitt Scott
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.
DeWitt Scott received his doctorate in Educational Leadership from Chicago State University. You can follow him on Twitter at @dscotthighered .
In today’s higher education climate, students who wish to pursue doctoral degrees have a plethora of options. Colleges and universities across the country have expanded their graduate offerings. The Ph.D. (Doctor of Philosophy) degree is now accompanied by the Psy.D. (Doctor of Psychology), DBA (Doctor of Business Administration), and Ed.D. (Doctor of Education) degrees. With so many options, prospective students often find themselves weighing opportunity costs of enrolling in certain programs, leading to questions, and sometimes debates, about which degree option is best for a particular student and his/her career path.
In no other discipline is this subject more frequently broached than in education. With both the Ph.D. and Ed.D. degrees available, education students have two legitimate options for obtaining a terminal degree. Dismissing the notion many “real scholars” hold about education not being a true, rigorous discipline like those in the humanities or natural sciences, I will use this space to give a comparison of the Ph.D. in education and Ed.D. degrees.
Strengths of a Ph.D. in Education
1. Research Intensive. Both the Ph.D. and Ed.D. require rigorous research and scholarship production, but the Ph.D. tends to have a greater focus on these areas. Students pursuing a Ph.D. in education typically are being trained to become scholars who spend much of their careers raising questions on best practices and outcomes for teaching and learning in K-12 and higher education settings. Ph.D. recipients often develop theories through research that can be tested and utilized in the classroom or on campus.
2. More Common for a Faculty Career. Although there are a number of Ed.D. recipients who become professors right out of graduate school, this tends to be a more common career path for Ph.D. recipients. Ph.D. programs specialize in producing scholars who tend to pursue careers cultivating other scholars. These programs train their graduates to focus predominantly on publishing in top-tier journals, presenting papers at national conferences, and obtaining tenure at all costs. Ph.D. programs in education normally breed future education professors.
3. More Program Options. There are far more Ph.D. programs in education than Ed.D. programs. Students desiring a Ph.D. in an education field (higher education, curriculum and instruction, educational policy, etc.) will have an easier time finding a degree program than those seeking strictly an Ed.D. More options means more opportunities in terms of institution, geographic location, quality faculty, etc.
4. Funding. This is a major strength. Ph.D. programs tend to—not always—fully fund students’ tuition while providing a stipend and living quarters. It is rare to find an Ed.D. program that will provide full funding. The major advantage here is that fully funded Ph.D. students can focus full-time on coursework and research. Ph.D. students have time to teach undergraduate courses, travel to conferences, and serve as teaching assistants , all valuable experiences for developing a resume to become a professor.
Strengths of an Ed.D.
1. Administration Focus. Most Ed.D. programs—not all—focus specifically on preparing students to assume formal administrative leadership positions in educational institutions, school districts, nonprofit organizations, government agencies, and the private sector. It is an applied, professional degree that aims to teach students how to solve problems and challenges that education administrators face on a daily basis. The average Ed.D. student usually does not have aspirations to be an academic .
2. Practical Over Philosophical. Related to the last point, pondering abstract concepts is not the primary focus of Ed.D. studies. While critically examining theoretical constructs is useful, Ed.D. students are seeking solutions that are directly applicable at this moment to managing large, complex organizations. Coursework and research is practitioner-based, and professors typically have spent time in the field doing what they are teaching rather than entering the academy directly from graduate school.
3. Able to Hold Full-Time Jobs. Because most Ed.D. programs are not fully funded, students tend to hold outside full-time jobs to support themselves and their families. While it might not seem that paying tuition is an asset, Ed.D. students who work do not have to endure the financially-strapped, poverty-stricken life most graduate students experience. Many Ed.D. students are K-12 principals, assistant principals, assistant superintendents, or college deans, assistant deans, and other administrators. These positions usually pay quite well and allow students to continue to support themselves while budgeting in the cost of their tuition to their life expenses.
4. Classmates as Professionals. Since most Ed.D. students tend to be working professionals, it can be normal to have a class or cohort of students who all hold significant administrative or professional positions. This gives students an opportunity to learn from each other about what works in the field. It also helps students build relationships and networks with people who may already be major players in their disciplines. I personally have seen classmates in an Ed.D. program hire each other for significant, high-paying positions based on connections made in class.
It is important to note that I am not saying one particular degree is better than the other. The one that is “better” is the one that fits your professional and personal needs and interests. I am hoping this explanation brings some clarity to the nature of the Ed.D. and how it differs from a Ph.D. in education. If you plan on pursuing a doctorate in education, think deeply about where you want to go in your career. Your long-term career goals will help you make the right decision.
What advice do you have for those seeking doctorates in education? In what ways do you believe the Ph.D. and Ed.D. overlap?
[Photo by Google Images user Pixbay used under a Creative Commons license]

A 3-Step Process for Gaining a Tenure-Track Job
Susanna Semerdzhyan, a first-generation college graduate, shares strategies that helped her overcome the obstacles.
Share This Article
More from gradhacker.

5 Productivity Practices That Helped Me Finish My Dissertation

Summer Planning Strategies

Holding Pattern
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Create Free Account

- July 28, 2022
- Academic Advice
EdD vs PhD in Education: What are the Differences?
UOTP Marketing

After a Master’s of Science in Education , getting a doctorate in education is the right step towards advancing your knowledge on the subject matter and implementing your ideas and projects in the community. You can take two different paths: an EdD (Doctorate of Education) and a Ph.D. (Doctorate of Philosophy in Education).
Both come with benefits that can suit different people, and this article will tell you all there is to know about the key differences between EdD vs PhD, what career paths you can take, and which doctorate is better for you.
What is an EdD Degree?

An EdD degree is an applied doctorate in education that best suits educators who want to pursue leadership roles in colleges or schools and implement government policies. By the end of their studies, the graduates can develop new projects and apply them to the community.
Career options with an EdD in Education
An EdD is handy in advancing your skills in training teachers, pushing for innovative policies, and researching specific fields. With the program’s flexibility for working hours, EdD helps students build their careers during their studies. Some of these career options include:
Elementary School Administrator
Elementary School Administrators are in charge of staffing and overseeing the management of elementary schools. Additionally, they develop academic programs and monitor teachers ‘and students’ progress.
Coordinators
Coordinators manage the curricula at elementary, secondary schools, and colleges. Moreover, coordinators help apply effective teaching strategies and increase the effectiveness of programs.
Director of Assessment
Directors of Assessment develop and lead assessment programs to aid the university’s strategic initiatives. Moreover, they oversee each stage of assessment programs and help with institutional decision-making.
How long does it take to get an EdD?
An EdD takes about three years to complete. Still, it can take up to four or five years, depending on your circumstances, such as occupation and family obligations, not sticking to plans, not receiving enough supervision, or other academic delays.
At the University of the Potomac, an EdD takes three years to complete for most students. Generally, the coursework takes about two years, whereas researching and writing the dissertation is done in the third year.
EdD salaries and job outlook
Getting an EdD opens doors for many job opportunities with a promising job outlook. For example, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) sees a job outlook of 8% for Principals in this decade, with annual pay of $98,420.
Other career choices in education with above-average salaries include Education Coordinators ( $46,986 ) and Directors of Assessment ( $66,927 ).
What is a PhD Degree?

A PhD in Education is a theoretical research-based doctorate in the education field. This doctorate is best suited for people who strive for an academic career as a professor or a researcher. As a PhD student, you will be encouraged to observe and research new solutions for old problems.
Career options with a PhD in Education
PhDs in Education offer many job opportunities in academia, though university professors and education administrators are the most common. Other career choices include:
Policy Makers
Policy makers can help secure funding and support in poorer school areas, raise teaching standards, reduce class overcrowding, and work with local school boards on how students can be educated best.
Academic Researchers
Academic researchers are responsible for publishing papers about problems and solutions in education. Additionally, they may supervise Master’s and PhD students during their academic projects.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
Educational Consultants
Educational consultants advise students, parents, schools, colleges, and universities on different educational matters such as college admissions, finding effective learning strategies, administering exams, training teachers, etc.
How long does it take to get a PhD?
A PhD in education takes about six to ten years . It all depends on the subject matter and the circumstances surrounding the student, which can be mental burnout, inconclusive results, weak mentorship, and family and work obligations.
PhD salaries and job outlook
Same as EdD careers , careers focused on academia for PhDs also have a great outlook in this decade. The BLS reports an 8% increase in the Postsecondary Education Administrators job outlook, with an annual salary of $96,910. Another promising-looking career for PhD graduates is the Postsecondary Teachers career, with a yearly salary of $79,640 and a job outlook of 12%.
EdD vs PhD in Education: What Are The Differences?
The two doctorates are equal in academic value and rigor; however, the main difference between an EdD and a PhD is the approach to the practicality of the acquired skills. On one hand, an EdD is more project-based and is of applied nature. On the other hand, a PhD is more research-based and theoretical in nature.
Regarding careers, EdD post-graduates are more focused on education leadership positions. Meanwhile, PhD career choices lean towards teaching and research roles. Moreover, an EdD career offers collaboration opportunities with people in the same field of study and builds networks that help implement policies and projects. PhDs, on the other hand, provide opportunities for individual research.
EdD vs PhD: Which is Better for You?

Either an EdD or a PhD in Education are great ways to advance in the educational field; however, you must consider all factors before choosing. If you want to have a closer role in the community or become an applied educational researcher, an EdD is perfect for you. On the other hand, if you want to become an educational theorist and have an academic research role, a PhD might be the right degree for you.
Even though both are equal in standing, the better doctorate is the doctorate closer to your path.
While it’s easy to put EdD vs PhD in Education and measure their worth, we have to consider the effort and time spent on each path and how much our educational system benefits from each person that chooses one or the other. EdDs and PhDs have a lot of benefits for the students pursuing them. They offer opportunities to advance in your field of study and help your community with more effective teaching.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

What Can You Do With a Hospitality Management Degree? Best Hospitality Careers

What Can You Do with an International Studies Degree [2024]

9 Benefits of Learning a Second Language

Associate’s vs. Bachelor’s: Which One To Choose?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information
- Search All Scholarships
- Exclusive Scholarships
- Easy Scholarships to Apply For
- No Essay Scholarships
- Scholarships for HS Juniors
- Scholarships for HS Seniors
- Scholarships for College Students
- Scholarships for Grad Students
- Scholarships for Women
- Scholarships for Black Students
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- College Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Scholarship Winners
- Scholarship Providers
Student-centric advice and objective recommendations
Higher education has never been more confusing or expensive. Our goal is to help you navigate the very big decisions related to higher ed with objective information and expert advice. Each piece of content on the site is original, based on extensive research, and reviewed by multiple editors, including a subject matter expert. This ensures that all of our content is up-to-date, useful, accurate, and thorough.
Our reviews and recommendations are based on extensive research, testing, and feedback. We may receive commission from links on our website, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. It’s accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted. You can find a complete list of our partners here .
EdD vs. the PhD in Education: Everything You Need to Know

Cece Gilmore is a Content Writer at Scholarships360. Cece earned her undergraduate degree in Journalism and Mass Communications from Arizona State University. While at ASU, she was the education editor as well as a published staff reporter at Downtown Devil. Cece was also the co-host of her own radio show on Blaze Radio ASU.
Learn about our editorial policies

Cari Schultz is an Educational Review Board Advisor at Scholarships360, where she reviews content featured on the site. For over 20 years, Cari has worked in college admissions (Baldwin Wallace University, The Ohio State University, University of Kentucky) and as a college counselor (Columbus School for Girls).

Maria Geiger is Director of Content at Scholarships360. She is a former online educational technology instructor and adjunct writing instructor. In addition to education reform, Maria’s interests include viewpoint diversity, blended/flipped learning, digital communication, and integrating media/web tools into the curriculum to better facilitate student engagement. Maria earned both a B.A. and an M.A. in English Literature from Monmouth University, an M. Ed. in Education from Monmouth University, and a Virtual Online Teaching Certificate (VOLT) from the University of Pennsylvania.

Are you passionate about being a part of the future of education? Well, in the world of education, two prestigious degrees stand out: the EdD and PhD in Education. Learn more about the EdD and PhD in Education degrees and the difference between the two below!
A Doctor of Education degree, known as an EdD, is a doctoral degree that is focused on professional practice in the field of education. An EdD is designed for students pursuing leadership roles in administration and policy within the education field. This degree emphasizes the practical application of knowledge in educational settings.
An EdD is designed to prepare individuals for leadership roles such as:
- School administration
- Educational policy development
- Curriculum design
- Instructional leadership
Also see: Top education scholarships
PhD in education
A PhD, or a “Doctor of Philosophy” in Education, is a doctoral degree that focuses on advanced research in the field of education. It is the highest academic degree that an individual can earn within the field of education.
A PhD in Education is ideal for students who want to conduct research. With a PhD in Education, a student will become an expert on a particular topic or range of topics within the field of education. Their focused research puts them in the position to make sound decisions on how practitioners should approach or implement education.
A PhD in education is designed to prepare individuals for leadership roles such as:
- Researchers
- Policymakers
- Administrators
- Consultants in educational institutions
Read more: Top fully funded PhD programs
EdD vs PhD chart
| Length of program | Typically 3-5 years | Typically 4-7 years |
| Focus areas | Prepare leaders in education with a focus on leadership, administration and policy | Research and scholarship in education with a docs on a wide range of educational topics |
| Research emphasis | Applied research, practical applications | Original research, theoretical contributions |
| Industries | Many industries | Mainly academia |
| Potential careers | Leadership, administration, policy | Professor, researcher, policy analyst, consultant |
Pros and cons of earning an EdD
| Less time than a PhD | Not as widely recognized as a PhD |
| Average cost for an EdD degree is less | May be less challenging than a PhD |
| Focuses on practical application | Less research-focused than a PhD |
| Offers flexibility in terms of coursework | May not offer as much job security |
Pros and cons of earning a PhD in Education
| More widely recognized | Takes longer to complete than an EdD |
| Offers opportunities for clinical experience | Can be more expensive |
| Focuses on research | Time commitment can be demanding |
| Can be tailored to your specific goals and interests | Not ideal for those interested in educational administration |
Tips for choosing between EdD and PhD in education
Time commitment.
EdD and PhD in Education programs are significant investments in time. Therefore, it is important to understand the amount of time each degree requires to determine which is better suited for your career goals. An EdD program will take around 3 to 5 years to complete, while a PhD in Education will typically require around 4 to 7 years to complete.
Career goals
There are many different careers you can choose from with EdD and PhD degrees. However, the careers that are available with each degree differ slightly. EdD programs prepare students for administration roles within education. PhD in Education programs make students desirable candidates for a range of research-oriented positions. Therefore, it’s important to review what career options there are so you can choose the best course of action for your goals.
Careers with an EdD in Education
- Superintendent
- University president
- Development manager
- Curriculum development
Careers with a PhD in Education
- University professor
- Research scholar
- Education director
- Policy researcher
EdD and PhD programs both typically require a dissertation. However, the EdD program may allow you to complete a dissertation based on a real-world application while a PhD dissertation may be more theoretical. In addition, EdD coursework will typically be more application based while PhD coursework is more research oriented.
Review the course description for any degree programs you are interested in order to become familiar with the topics you will study in your respective program.
Online availability
It’s no surprise that online schools provide a more flexible schedule for students. Therefore, if online school is something you desire, you are more likely to find online opportunities for an EdD program rather than a PhD program.
Read more: Top scholarships for online students
To help you choose between an EdD and a PhD in Education, it may be helpful to picture your daily life and routines in each of these programs. An EdD program focuses on the application of research, which means most of your time will be spent using your knowledge to solve challenges in the education field. In contrast, a PhD program is more research-heavy meaning that a majority of your time will be spent researching methodologies in education.
Taking the next step
Now that you have a better understanding of what an EdD is, what a PhD in education is, and what the difference between them is, you are probably wondering what now? Regardless of which degree you want to pursue, earning your doctorate can pay off no matter what.
Therefore, truly evaluate your current situation, career goals, and time commitment to determine if the EdD or PhD path is the right one for you. Ultimately, it is your decision, and you should choose the option that most aligns with your personal goals.
Now that you have picked which direction you want to go in, research universities and colleges that offer your desired degree program! Be sure to research their values and coursework to ensure it is a good fit for you. Don’t forget, Scholarships360 is here for you to help you find the right scholarships to help you fund your graduate education !
Start your scholarship search
- Vetted scholarships custom-matched to your profile
- Access exclusive scholarships only available to Scholarships360 members
Frequently asked questions about EdD vs PhD degrees
Are there any online edd programs, which degree is better for students aspiring to become educational administrators, how long does it take to complete an edd degree compared to a phd in education, are there any prerequisites that differ between the two programs, scholarships360 recommended.

10 Tips for Successful College Applications

Coalition vs. Common App: What is the difference?

College Application Deadlines 2023-2024: What You Need to Know
Trending now.

How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale

PSAT to SAT Score Conversion: Predict Your Score

What Are Public Ivy League Schools?
3 reasons to join scholarships360.
- Automatic entry to our $10,000 No-Essay Scholarship
- Personalized matching to thousands of vetted scholarships
- Quick apply for scholarships exclusive to our platform
By the way...Scholarships360 is 100% free!

- Online ABSN
- Online MSN-FNP
- Online MSN-AGACNP
- Online MSN-PMHNP
- Online FNP Post-Master's Certificate
- Online AGACNP Post-Master's Certificate
- Online PMHNP Post-Master's Certificate
- Online MSN Dual Track
- Online MSN in Nursing Leadership
- Online Ed.D. in Higher Education
- Online Ed.D. in K-12 Leadership
- Online Ed.D. in Health Care Education
- Online Ed.D. in Organizational Leadership
- Career Resources
- Why Rockhurst University Online?
- Message from the President
- Student Testimonials
- Student Services and Support
- Faculty Profiles
- State Authorization
- Placement Services
- Refer a Friend
Ed.D. vs. Ph.D.: What’s the Difference?

Professionals in fields like higher education and healthcare who want to continue to grow in their careers often consider further education. However, for the aspiring leader or educator who already holds a master’s degree, the question to consider is: what is the difference between an Ed.D. and Ph.D.?
While these degree programs have some overlap, they are distinct in their coursework and intended outcomes. Understanding these differences can help professionals choose the right program for them and ensure that their degree choice aligns with their professional goals. For example, a Ph.D. is research-intensive, while an Ed.D. is practitioner-based. The differences don’t stop there — the number of credit hours, program length, and goal of student projects vary between the Ph.D. and Ed.D. as well.
Consider the similarities and differences between the Ph.D. and Ed.D. to discover the best program for your professional path.
What is a Ph.D.?
A Ph.D., which is short for Doctor of Philosophy, is an academic degree that is heavily focused on research, data, and theory. A Ph.D. is the most advanced degree an individual can earn in a given area of study or professional field, also known as a terminal degree.
Typically, a Ph.D. program prepares students for faculty and/or researcher roles. While some graduates work as practitioners, most Ph.D.-holders tend to choose occupations in areas like academia or theoretical development.
Ph.D. programs usually feature around 90 credit hours and tend to take five or more years to complete.
What is an Ed.D.?
Short for Doctor of Education, an Ed.D. is a practitioner-focused doctorate that is specifically designed for professionals aspiring to education leadership roles in various fields. Like the Ph.D., the Ed.D. is considered a terminal degree in the field of education.
A primary difference between the Ph.D. and Ed.D. is that the Ph.D. focuses only on research while the Ed.D. emphasizes the practical application of research. Additionally, the Ph.D. tends to prepare graduates for roles in academia, while the Ed.D. has greater cross-industry potential. For example, an Ed.D. graduate may become a scholar or faculty member, but, depending on their experience and interests, they may also pursue an industry-specific role like Nurse Educator or Chief Learning Officer.
Students can typically complete their Ed.D. program in 2–3 years. The degree plan tends to comprise around 60 credit hours.
What are the benefits of earning a Ph.D.?
For professionals who are interested in an academic career path, the Ph.D. offers several benefits. Many fields of study require that professors or researchers hold a Ph.D. in the given subject. A terminal degree is almost always required for tenure-track professor positions at most universities, and in many fields, that terminal degree is a Ph.D.
Ph.D.-holders are also seen as credible experts in their areas of research. As a result, they may be called upon to contribute further to their field by researching, writing, writing and speaking.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , individuals who earn a Ph.D. also have low unemployment rates and relatively high earnings. In 2021, for example, doctoral-degree holders earned a median weekly rate of $1909 and a 1.5 percent unemployment rate. In contrast, master’s degree holders earned a median weekly rate of $1574 and faced an unemployment rate of 2.6 percent.
What are the benefits of earning an Ed.D.?
The Ed.D. is an ideal degree choice for the professional who wants to become a leader and educator in their industry field. Rather than focusing primarily on theoretical research, the Ed.D. prepares practitioners to apply research, data, and insights in the workplace.
Through coursework in educational leadership, managerial communications, and organizational behavior, Ed.D. students become equipped for the highest levels of leadership in various organizations.
Since the BLS does not distinguish between the Ph.D. and Ed.D., instead measuring the salary and unemployment standards among all doctoral degree holders, the median weekly wage of $1,909 and an unemployment rate of 1.5 percent apply here as well.
Learn more about RUO's Online Ed.D Programs
What can I do with a Ph.D.?
Individuals who earn a Ph.D. often decide to pursue career paths in academia, such as a faculty position at a college or university. Often called professors or faculty members, postsecondary teachers teach courses beyond the high school level. Often, they are also responsible for conducting ongoing research, publishing scholarly articles and books, and serving as an expert in their area of study.
As employees of a college or university, postsecondary teachers often perform job duties such as:
- Developing syllabi and course outlines
- Planning lessons, projects, quizzes, and tests
- Advising students
- Collaborating with colleagues on curriculum
Postsecondary teachers earn an average salary of $79,640 per year. Their job outlook rate is faster than average, with 12% growth expected between 2020–2030.
In addition to postsecondary teaching roles, Ph.D.-holders may also pursue opportunities as postdoctoral, academic, or professional researchers.
What can I do with an Ed.D.?
An important difference between the Ph.D. and Ed.D. is the range of practitioner-based roles available to professionals who earn an Ed.D.. Since the Ed.D. focuses on applying research and theory directly to the workplace, there are many leadership positions available to Ed.D. graduates who are already practiced in putting their knowledge to work in real-world ways.
Like Ph.D. graduates, Ed.D.-holding professionals may also become postsecondary teachers. Oftentimes, Ed.D. graduates who become faculty do so in highly practical fields like education or healthcare. They use their Ed.D. and industry knowledge to prepare the next generation of professionals in their field with both theory and practical application that directly applies to their careers.
Ed.D. graduates may also pursue industry-specific roles, each of which has specific duties, salaries, and job outlooks. A few examples include:
- Chief Learning Officer: Responsible for employee learning and development, the Chief Learning Officer develops strategies and programs that further educate and enrich a company’s employees in alignment with organizational goals and desired outcomes. The median annual wage for top executives was $98,720 in May 2021, and the projected job growth between 2020–2030 is 8 percent.
- Postsecondary Education Administrator: Working in roles like dean, provost, and registrar, postsecondary education administrators manage and direct various departments and colleges within higher education institutions. Their 2021 median pay was $96,910, and their projected job growth between 2020 and 2030 is as fast as average at 8 percent.
- Superintendent: As the highest-ranking official, a superintendent can be thought of as the chief executive officer in a school district. They oversee all academic and administrative endeavors of the elementary and secondary schools in their district. The median annual salary for Education Administrators, Kindergarten through Secondary was $98,420 in May 2021. Top executives project job growth rate between 2020 and 2030 is 8 percent.
How can I get a Ph.D.?
Individuals who are interested in a Ph.D. program first need to obtain the relevant bachelor’s or master’s degrees that are required in order to apply. Once enrolled, a Ph.D. program will require the completion of both coursework and a dissertation. While many Ph.D. programs take place in person, there are online Ph.D. programs available as well.
How can I get a Doctorate of Education?
At Rockhurst University, professionals can earn their Ed.D. degree fully online in just two years. Applicants can enroll with a master’s degree or 33 graduate credits. Upon acceptance, students will take courses and complete a doctoral capstone project that aligns with their area of concentration: Higher Education , K–12 Leadership , or Health Care Education .
Cohort-based classes support student success and facilitate positive connections between faculty and students. Recognizing that Ed.D. students are working professionals, the program is flexible, accessible, and has no travel requirement. One virtual residency and a doctoral capstone project ensure that each student is empowered to tailor their academic experience to their workplace goals and objectives.
Recent capstone projects from the program highlight the thoughtful, practical approach that characterizes the degree:
- Deferred action for childhood arrival (DACA) students in higher education (Laura Cordoba Dominquez, 2022): This research examines the experiences of DACA students in higher education. The researcher analyzes the challenges of DACA students, how they overcome these challenges, and what higher education institutions can do to help DACA students to be successful in U.S. colleges.
- Differences in the achievement of learning outcomes among various modalities at the U.S. Army (Ashley Richter, 2022): This research examines the differences in student learning outcomes amongst students who attended the US Army’s Command and General Staff College’s Staff Officers’ Course via varying modalities (including face-to-face, virtual synchronous, asynchronous, and computer-based instruction), explored possible reasons for these differences, and solutions to create equitable outcomes for all CGSOC students.
- What are the impacts of international service trips on the cultural competency and clinical skills of Doctor of Physical Therapy students? (Chris Johnson, 2022): This research evaluates the impact of international service-learning trips on the cultural competency and clinical skills of physical therapy students. The results of this study will provide insights for developing international service-learning projects in higher education.
As a Catholic, Jesuit, liberal arts university, Rockhurst University emphasizes comprehensive and supportive education that prepares students to engage the world as compassionate, thoughtful leaders. Learn more about Rockhurst’s online Ed.D. in Education and Leadership program.
About Rockhurst University's Online Programs
In the heart of Kansas City since 1910, Rockhurst University is dedicated to learning, leadership and service in the Jesuit tradition, and today is the #1 Regional University in Kansas City (2021 U.S. News and World Report).
Rockhurst University’s online programs are delivered by the highly reputable Saint Luke’s ™ College of Nursing and Health Sciences and the School of Education. As an educational leader serving exceptional students in the field of health care and education, we are committed to preparing the workforce of tomorrow with our unique programs designed to prepare graduates to meet the needs of diverse populations and work in various organizations.
To learn more about our highly competitive online programs, please visit onlinedegrees.rockhurst.edu , or read more here:
- Online/Hybrid ABSN
- MSN and FNP Post-Master's
- MSN and AGACNP Post-Master's
- MSN and PMHNP Post-Master's
- MSN in Nursing Leadership
- Ed.D. in Education & Leadership
Thank You For Your Interest
Unfortunately, your location is currently ineligible for our program but we’d like to help you continue your search. Visit OnlineABSNPrograms.com and enter your ZIP code to find a CCNE-accredited program near you.
Challenge Yourself | Inspire Others | Impact Our World
Requirements not met.
To proceed with either the BSN to MSN FNP or the BSN to DNP FNP, you are required to have a bachelor’s degree and hold your RN license.
If you don’t meet these requirements but would still like further information, please contact us .
To proceed with the EdD in Educational Leadership and Organizational Leadership, you are required to have a master’s degree.
If you don’t meet this requirement but would still like further information, please contact us .
X Close Box
- Ask an Advisor
- Request Info
© Rockhurst University Online • All Rights Reserved • Privacy Policy • California Privacy Notice

Virtual Tour
Experience University of Idaho with a virtual tour. Explore now
- Discover a Career
- Find a Major
- Experience U of I Life
More Resources
- Admitted Students
- International Students
Take Action
- Find Financial Aid
- View Deadlines
- Find Your Rep

Helping to ensure U of I is a safe and engaging place for students to learn and be successful. Read about Title IX.
Get Involved
- Clubs & Volunteer Opportunities
- Recreation and Wellbeing
- Student Government
- Student Sustainability Cooperative
- Academic Assistance
- Safety & Security
- Career Services
- Health & Wellness Services
- Register for Classes
- Dates & Deadlines
- Financial Aid
- Sustainable Solutions
- U of I Library

- Upcoming Events
Review the events calendar.
Stay Connected
- Vandal Family Newsletter
- Here We Have Idaho Magazine
- Living on Campus
- Campus Safety
- About Moscow

The largest Vandal Family reunion of the year. Check dates.
Benefits and Services
- Vandal Voyagers Program
- Vandal License Plate
- Submit Class Notes
- Make a Gift
- View Events
- Alumni Chapters
- University Magazine
- Alumni Newsletter

U of I's web-based retention and advising tool provides an efficient way to guide and support students on their road to graduation. Login to VandalStar.
Common Tools
- Administrative Procedures Manual (APM)
- Class Schedule
- OIT Tech Support
- Academic Dates & Deadlines
- U of I Retirees Association
- Faculty Senate
- Staff Council
College of Education, Health and Human Sciences
Physical Address: 921 Campus Drive Moscow ID, 83844
General Contact: Phone: 208-885-6772 Email: [email protected]
Student Services: Phone: 208-885-6610
Fax: 208-885-1071
Mailing Address: University of Idaho Boise Center 322 E. Front Street Boise, ID 83702
Phone: 208-334-2999
Fax: 208-364-4035
Email: [email protected]
Web: Boise Center
Coeur d'Alene
Mailing Address: University of Idaho CDA Center 1031 N. Academic Way, Suite 242 Coeur d'Alene, ID 83814
Phone: 208-292-2519
Fax: 208-667-5275
Email: [email protected]
Web: CDA Center
Doctoral Degree Overview
The University of Idaho College of Education, Health and Human Sciences offers three doctoral degree programs. Students who are pursuing a doctoral degree in education have various areas of specialization to choose from.
Doctor of Education (Ed.D.)
The Doctor of Education prepares students as professional leaders, educators and practitioner-scholars who actualize the knowledge base in their respective field. Students will:
Create and model ethical evidence-based best practices
Lead organizational change
Establish a caring and collaborative learning community
Support the principles of teaching and learning practices
Utilize the principles of effective leadership
Develop proficiency utilizing and applying technologies
Evaluate the individual, organizational, and societal contexts of learning
Design research that addresses professional policy issues
Integrate ethical sensitivity toward diversity and social justice in research, teaching and learning
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
The Doctor of Philosophy prepares students as researchers, faculty and/or discipline-based scholars who contribute to the knowledge base of their respective fields. Students will:
Engage in ethical, empirical, theoretical, and/or conceptual inquiry
Develop an active research agenda
Engage in grant-writing, proposal and manuscript preparation and presentations
Develop understanding of pedagogies and content
Contribute to professional organizations, societies and/or academies
Engage in appropriate outreach/service
Doctor of Athletic Training (D.A.T.)
The Doctor of Athletic Training provides advanced knowledge in the field and improves professional clinical skills as a practicing certified athletic trainer. Students will:
Understand the history and wider context (including barriers and future potential) of athletic training
Become well-versed in manual therapy paradigms
Utilize state-of-the-art rehabilitation strategies to improve clinical outcomes
Integrate evidence-based practice and practice-based evidence into their clinical practice
Study manual therapy approaches and outcomes in multi-site research
Learn to treat patients from a holistic integrative approach
Participate in meaningful clinical research
Develop meaningful strategies and skills to help prepare the future generations of athletic trainers to effectively treat patients
The Doctoral Handbook will guide students through the steps necessary to be considered for admission to the doctoral program in the College of Education, Health and Human Sciences (EHHS) and College of Graduate Studies. For more information about our programs, contact us by email at [email protected] or call 208-885-6772.
For additional information
- View our Education doctoral pages
- View our Athletic Training doctoral pages
Questions on our Graduate Programs?
» Visit our Graduate Program FAQ page
Admission Details
Ed.D. or Ph.D.
- Next available: Fall 2025
- Application Deadline: Dec. 1
- Summer only
- Next available: Summer 2024
- Application Deadline: April 15
- Doctoral Handbook pdf
- EHHS Doctoral Core Course Rotation xlsx
- Doctoral Dissertation Proposal Approval pdf
EdDPrograms.org
Ed.D. Programs in Counseling and Psychology
Ed.D. programs in Counseling and Educational Psychology are open to K-20 administrators & educators, school psychologists, licensed counselors, and all kinds of research-focused education professionals. Explore our listings to find the ideal doctorate in your area of expertise. Learn more about accreditation standards and licensure issues. And use our guide to explore useful subspecialties, online Ed.D. programs, and career info!
What are Ed.D Programs in Educational Psychology and Counseling?
Ed.D. programs in Educational Psychology, Counseling, Counselor Education, and related fields are doctoral-level degrees that explore the intersection of psychology & education. These types of doctorates are geared toward working professionals who already hold a master’s degree or Ed.S. and have prior experience in their field.
- Educational Psychology: Doctoral students may seek to deepen their knowledge of cognitive, social, and emotional processes in order to improve how children and adults learn.
- School Psychology: Doctoral students may wish to explore new breakthroughs in the K-12 field.
- Counseling: Doctoral students may want to build on their existing counseling experience to improve current practices & influence the next generation of counselors.
As the title suggests, Ed.D. programs are always administered by a School or College of Education.
Types of Educational Psychology and Counseling Ed.D. Programs
Ed.d. in educational psychology & related fields.
Ed.D. programs in Education Psychology are often aimed at mid- to senior-level professionals who are currently involved in K-20 education or similar fields.
- Some Colleges of Education choose to offer Educational Psychology as a concentration within an Ed.D. in Educational Leadership (e.g. USC Rossier), Curriculum & Instruction (e.g. La Sierra University), or Learning & Teaching (e.g. Hofstra University).
- The Chicago School of Psychology even has an entire doctorate devoted to the intersection of Educational Psychology & Technology .
- However, there are alternatives. Aspen University uses its doctorate to focus on the broader topic of Organizational Psychology .
Ed.D. in School Psychology
It’s important to note that Ed.D. programs in School Psychology are specifically targeted at current or aspiring school psychologists. To that end, some education doctorates in school psychology will help prepare you for state certification or endorsements.
Ed.D. in Counseling & Related Fields
Ed.D programs with “Counseling” in the title are usually tailored toward those with experience—or a significant interest—in counseling, counseling education, or counseling leadership. Ed.D. programs in Counseling come in all kinds of professional flavors, including dedicated programs in Counselor Education & Supervision.
- You’ll find doctorates in education that focus on marriage, family & pastoral care counseling (e.g. Liberty University), counseling & rural education (e.g. UWA), and mental health counseling (e.g. UR).
- Universities may also offer counseling as a concentration within a major such as School Improvement (e.g. UWG) or Educational Leadership (e.g. UHCL).
Licensure & Accreditation for Ed.D. Programs in Educational Psychology or Counseling
Program accreditation.
All programs in our listings hold regional accreditation. In addition, there are two specialist organizations that accredit or approve Ed.D. programs in psychology & counseling:
- National Association of School Psychologists (NASP) : The NASP grants approval to School Psychology programs as part of the CAEP educator preparation provider accreditation process. Approval can be given at the Specialist Level (SL) or Doctoral Level (DL). View a list of NASP-Approved Programs in School Psychology .
- Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP) : The CACREP accredits doctoral level programs in counseling education. View a list of CACREP-Accredited Ph.D. & Ed.D. Programs in Counselor Education & Supervision .
You’ll notice that the majority of Ed.D. programs in our listings do not currently hold NASP or CACREP approval/accreditation. So it can be difficult to assess the relative necessity of accreditation at the Ed.D. level.
- If you intend to work in a position that requires licensure, and NASP or CACREP accreditation is required under your state’s licensure requirements, it stands to reason that accreditation is vital.
- If you’re already licensed—or don’t need licensure for the work you intend to do—it becomes less important.
Note: The American Psychological Association (APA) does not accredit Ed.D. programs in Counseling or Educational Psychology. It’s only concerned with accrediting Ph.D. or Psy.D. programs. If you’re interested in those options, check the APA-Accredited Program List .

National Certification & State Licensure
Ed.D. programs in Educational Psychology do not lead to state licensure as a K-12 administrator (e.g. Superintendent, Principal, etc.). Colleges of Education will expect you to have your licensure sorted before you apply.
- If you need this kind of license, choose your home state in our Menu Bar.
- Each State page contains a section devoted to state-approved Ed.D. programs for administrative licensure.
Check the Admissions section. Although some schools will expect you to hold a Professional Educator License as a School Psychologist before you apply for an Ed.D. (e.g. Loyola University Chicago ), there are doctoral programs that can help with credentials. For example:
- La Sierra University offers Ed.D. in School Psychology electives that lead to state licensure through the California Commission on Teacher Credentialing (CTC) and national certification through the Behavioral Analyst Certification Board (BACB).
- And even Loyola prepares Ed.D. graduates for a Director of Special Education endorsement or LPC/LCPC certification.
Check the Admissions section. A number of universities will expect Ed.D. in Counseling applicants to be licensed or license-eligible in counseling or a related field. However, there are exceptions. For example:
- UR’s Ed.D in Mental Health Counseling & Supervision CA5 prepares graduates for NYS Certification in Mental Health Counseling licensure.
Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. in Counseling or Educational Psychology
Anyone interested in counseling, learning development, or educational psychology has a choice between the Ph.D. and the Ed.D. Both are research-focused doctorates that include high-level coursework in theory & practice and large-scale projects (e.g. dissertation). Here’s what makes them different:
- Ed.D. Programs : Ed.D. programs deal with applied research & real-world applications—students are expected to tackle complex problems of practice during their course of their studies. That makes Ed.D. programs in Educational Psychology popular among K-20 professionals and folks in educational leadership roles. In a similar manner, graduates of Ed.D. programs in Counseling or Counselor Education often end up pursuing hands-on leadership opportunities, especially in areas that intersect with professional training or education.
- Ph.D. Programs: Ph.D. programs in Educational Psychology, School Psychology, or Counseling will focus heavily on original research—Ph.D. students are expected to make unique advances in their field. If you’re thinking of applying for academic positions in universities & higher education settings, or research positions in government agencies & educational organizations, the Ph.D. is probably going to be your best bet. For certain jobs, you may also prefer to have an APA-accredited doctorate on your résumé (e.g. counseling work that involves clinical research).
As always, we recommend you talk to recent Ed.D. and Ph.D. alumni before you make your decision. Job requirements often change and expectations shift within fields. If you do commit to a Ph.D., be aware that it will usually take longer than an Ed.D. and may require full-time study. You can learn more about your options in our Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. explainer .
Note: If you are interested in becoming a licensed clinical psychologist, you need to be looking at APA-accredited Ph.D. or Psy.D. programs in Clinical Psychology . Ed.D. programs do not deal with this subject.
Earning an Ed.D. in Counseling or Educational Psychology
Counseling & educational psychology prerequisites.
Ed.D. candidates are expected to have a master’s degree. A relevant Ed.S. will usually grant you advanced placement.
- Ed.D. in Educational Psychology & Related Fields: Schools will often ask for a master’s degree in education, psychology, or a closely related field. School Psychology applicants who haven’t graduated from an NASP-approved Specialist Level program may have to demonstrate that they have similar foundational coursework to students who did.
- Ed.D. in Counseling & Related Fields: Schools will often ask for a master’s degree in counseling or counseling-related field (e.g. psychology, counseling psychology, clinical social work, mental health counseling, community counseling, marriage and family therapy, school psychology, school counseling, or school social work). In some cases, the university will ask that your master’s degree be CACREP-accredited or have equivalent standards.
Some programs may also require a minimum GPA (e.g. 3.0), GRE scores, an admissions essay, letters of recommendation, a résumé, and/or work experience (e.g. 2-3 years). A few programs, such as Loyola University Chicago’s Ed.D. in School Psychology , specifically require that applicants be licensed in their field. Counseling programs may specify that you be licensed or license-eligible.
Counseling & Educational Psychology Coursework
- Ed.D. in Educational Psychology & Related Fields: The curriculum typically blends elements from an educational leadership program with relevant psychology coursework (e.g. Beliefs About Knowledge and Learning, Human Lifespan Development, Group Dynamics, Theories & Practice in Educational Psychology, etc.). As you might expect, doctorates in School Psychology will contain advanced coursework in School Psychological Services and Counseling.
- Ed.D. in Counseling & Related Fields: Coursework is often a mix of psychology subjects (e.g. Advanced Human Growth and Development, Social Bases of Behavior, Culture & Race, etc.), advanced counseling credits (e.g. Effective Interventions, Clinical Mental Health, Counselor Supervision, etc.), and clinical work/practicums. Ed.D. programs in Counseling and Supervision may also include leadership courses (e.g. Ethical Leadership, Advanced Appraisals, etc.).
Ed.D. programs in these fields tend to be practical, not academic. Sure, there are core courses in areas such as quantitative & qualitative research and research design, but the focus is usually vocational. Universities want to help you apply your coursework to your current situation.
Counseling & Educational Psychology Internship and Practicums
- Ed.D. in Educational Psychology & Related Fields: Unless you’ve chosen a concentration or electives that deal with hands-on work (e.g. counseling), Ed.D. programs in Educational Psychology may not include practicums. Having said that, you may still be expected to gather data and implement projects in your workplace. The one major exception to the rule is Ed.D. programs in School Psychology—these almost always have “on-the-ground” components such as internships & field practice.
- Ed.D. in Counseling & Related Fields: Because of the clinical nature of the field, Ed.D. programs in Counseling contain internships, practicums, or fieldwork requirements. For example, TSU’s Ed.D. in Counseling includes a 600-hour counseling internship in an appropriate clinical setting. Boston University’s Ed.D. in Counseling Psychology has a clinical core of 20-22 credits that includes 2-semester practicums and a separate internship.
Counseling & Educational Psychology Dissertation
All Ed.D. programs—regardless of the subject—are going to contain a research-based dissertation, Dissertation in Practice (DiP), or capstone project. For example, students in LaSierra University’s Ed.D. in Educational Psychology submit a portfolio based on fieldwork in lieu of a traditional dissertation. We explore the differences between these options in our guide to No Dissertation Ed.D. Programs .
Online Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Counseling Programs
Are ed.d. programs in educational psychology and counseling offered online.
Yes. You’ll see an “Offered Online” marker under all relevant programs in our listings . Some of them are in traditional subjects, like USC’s Online Ed.D. in Educational Leadership – Educational Psychology . Some are highly unusual, like the Chicago School of Professional Psychology’s Online Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Technology and its focus on cognitive science and human-computer interaction.
Are Online Ed.D. Programs CACREP- or NASP-Accredited?
- CACREP: We didn’t find any online counseling programs in our listings that were CACREP-accredited, but it’s always good to double-check! View a complete list of CACREP-Accredited Ph.D. & Ed.D. Programs in Counselor Education & Supervision .
- NASP: There are NASP-approved Ed.D. programs in our listings (e.g. Loyola University Chicago), but none of them are available online at the present time. View a complete list of NASP-Approved Doctoral Programs in School Psychology .
Note: It is worth reiterating that no Ed.D. programs in Educational Psychology or Counseling (online or otherwise) hold APA accreditation. The APA only accredits psychology & counseling doctorates that use the Psy.D. or Ph.D. designation.
Do Online Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Counseling Programs Contain Residency Requirements?
Yes. To date, every Online Ed.D. program in Educational Psychology or Counseling in our listings requires some visits to campus. But that doesn’t mean the residencies are always lengthy. For example:
- Students in the Chicago School of Professional Psychology’s Online Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Technology spend a grand total of 7 days on campus over the course of two 3-4 day residencies. The first residency covers a wide variety of relevant cutting-edge issues in a mini-seminar format; the second consists of a comprehensive exam.
- USC’s Online Ed.D. in Educational Leadership – Educational Psychology contains an initial on-campus immersion/orientation experience on the USC University Park Campus.
Educational Psychology and Counseling Careers
Ed.d. in educational psychology and counseling jobs.
Graduates of an Ed.D in Educational Psychology might pursue job titles such as:
- University Faculty in Education
- K-20 Administrator (e.g. Principal, Dean, etc.)
- Curriculum & Instruction Specialist
- Educational Technology Specialist
- School District Administrator
- Professional Development Provider
- Education Analyst in State and National-Level Agencies
- Education Consultant
- Research Associate in Education
Graduates of an Ed.D. in School Psychology qualify for jobs such as:
- School Psychologist
- School Counselor
- Educational Psychologist
Graduates of an Ed.D. in Counseling or Counselor Education with appropriate licensure qualifications seek positions such as:
- University Faculty in Counseling
- Clinical Services Director
- Approved Counselor Supervisor
- Administrator in Counseling Practice
- Mental Health Administrator
- Research Associate in Counseling-Related Fields (e.g. Public Health)
- Addiction Counselor
- Clinical Mental Health Counselor
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) ranks Psychologists and School and Career Counselors among the fastest-growing occupations in the country, with 14% and 13% growth projected, respectively, over the 2016-2026 period. But for licensed counselors who choose to work in private practice, these numbers are dwarfed by the anticipated 23% growth over the 2016-2026 period in the category of Substance Abuse, Behavioral Disorder, and Mental Health Counselors .
Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Counseling Salaries
Your salary bump with an Ed.D. will depend on your job title, location, and your employer’s policy on educational qualifications. You can get a broad sense of the territory by examining the BLS’s Occupational Employment Statistics. The Bureau provides median annual wage data & state wage maps for a number of relevant jobs, including:
- Clinical, Counseling, and School Psychologists
- Kindergarten through Secondary Education Administrators
- Postsecondary Education Teachers
- Postsecondary Education Administrators
In addition, salary sites like Glassdoor, Indeed, and Payscale will help you get a gauge on salary numbers for specific roles.
Is an Ed.D. in Educational Psychology or Counseling Worth It?
- If you wish to bring psychology to bear on administrative, curriculum-related, or technology-related roles in education—yes.
- If you’re already a licensed psychologist or counselor, and wish to expand your career horizons—yes.
- If you intend to become a licensed counselor (e.g. Clinical Mental Health Counselor), and the Ed.D. program satisfies licensure requirements in your state—yes.
If you’re interested in working as a school psychologist or counselor in a school setting, bear in mind that you must meet the specific licensure requirements of your state. The National Association of School Psychologists (NASP) and the American Counseling Association (ACA) have prepared useful reports addressing licensure requirements in each state.
Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Counseling Resources
- APA Division 15 : Although the APA does not accredit Ed.D. programs, the Educational Psychology division of the American Psychological Association is the gold standard for academic research and networking.
- American Counseling Association (ACA) : The ACA offers membership benefits, career development, continuing education, a magazine, a journal, conferences, public policy advocacy, and other related benefits for people who practice counseling as a profession in every U.S. context, including educational institutions.
- American School Counselor Association (ASCA) : The leading professional organization for U.S.-based school counselors, the ASCA promotes public policy initiatives, helps school counselors network and further develop their knowledge base, and publishes a magazine and volumes summarizing the latest research in the field.
- International Journal of Educational Psychology (IJEP) : IJEP covers educational psychology from an international and interdisciplinary point of view. It’s a peer-reviewed open-access journal, with articles available online and at no cost.
- National Association of School Psychologists (NASP) : In addition to approving and accrediting School Psychology programs, the NASP offers member benefits, a podcast, a speaker’s bureau, and other features useful to those working in the industry.
School Listings
26 Schools Found
The University of Alabama
Department of Educational Studies in Psychology, Research Methodology, and Counseling
Tuscaloosa, Alabama
PhD in Educational Psychology
- Curriculum Info
- How To Apply
University of West Alabama
College of Education
Livingston, Alabama
Online Ed.D in Rural Education - Counseling
Offered Online
La Sierra University
Department of Curriculum and Instruction
Riverside, California
Doctor of Education in Curriculum and Instruction - Educational Psychology
Doctor of education in educational psychology, doctor of education in educational psychology - mental health, doctor of education in school psychology, doctor of education in school psychology - bcba, university of southern california.
Rossier School of Education
Los Angeles, California
Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership - Educational Psychology
University of the pacific.
Benerd School of Education
Stockton, California
EdD in Education - Counseling Psychology
Edd in educational and school psychology - educational psychology, aspen university.
School of Education
Denver, Colorado
Online Doctor of Education in Leadership and Learning - Organizational Psychology
University of central florida.
Orlando, Florida
EdD in Curriculum and Instruction - Educational Psychology
University of west georgia.
Carrollton, Georgia
Online Doctor of Education in Professional Counseling and Supervision
Online doctor of education in professional counseling and supervision - accelerate, online doctor of education in school improvement - school counseling, boise state university.
Boise, Idaho
Online EdD in Curriculum and Instruction - Counselor Education and Supervision
University of idaho.
College of Education, Health, and Human Sciences
Moscow, Idaho
Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership - Leadership and Counseling
Online edd in educational leadership - leadership and counseling, governors state university.
University Park, Illinois
Doctor of Education in Counselor Education and Supervision
Loyola university chicago.
Chicago, Illinois
EdD in School Psychology - Data-Based Decision-Making
Edd in school psychology - mental health, the chicago school of professional psychology.
Department of Educational Psychology and Technology
Online Ed.D. in Educational Psychology and Technology - Higher Education Learning and Technology
Online ed.d. in educational psychology and technology - instructional design, online ed.d. in educational psychology and technology - k-12 education learning and technology, wichita state university.
Counseling, Educational Leadership, Educational and School Psychology Department
Wichita, Kansas
EdD in Educational Leadership - Educational Psychology track
Massachusetts, boston university.
Boston, Massachusetts
MSW/EdD Dual Degree Program
Minnesota state university-mankato.
Mankato, Minnesota
The University of Montana
Department of Counselor Education
Missoula, Montana
EdD in Counselor Education and Supervision
Hofstra university.
Hempstead, New York
Doctor of Education in Learning and Teaching - Human Development and Educational Psychology
University of rochester.
Rochester, New York
Doctor of Education in Counseling
Doctor of education in mental health counseling and supervision, houston baptist university.
College of Education and Behavioral Sciences
Houston, Texas
Doctor of Education in Executive Leadership in Mental Health and Human Services
Texas southern university.
Department of Counseling
University of Houston-Clear Lake
Department of Educational Leadership and Policy Analysis
EdD in Educational Leadership - Counseling
Liberty university.
School of Behavioral Sciences
Lynchburg, Virginia
Online Doctor of Education in Community Care and Counseling - Marriage and Family Counseling
Online doctor of education in community care and counseling - pastoral care & counseling, regent university.
Virginia Beach, Virginia
Online Doctor of Education in Educational Psychology
Seattle pacific university.
Seattle, Washington
EdD - School Counseling
Viterbo university.
College of Business, Leadership, and Ethics
La Crosse, Wisconsin
Ed.D. in Counselor Education and Supervision
- What is a PhD?
Written by Mark Bennett
A PhD is a doctoral research degree and the highest level of academic qualification you can achieve. The degree normally takes between three and four years of full-time work towards a thesis offering an original contribution to your subject.
This page explains what a PhD is, what it involves and what you need to know if you’re considering applying for a PhD research project , or enrolling on a doctoral programme .
The meaning of a PhD
The PhD can take on something of a mythic status. Are they only for geniuses? Do you have to discover something incredible? Does the qualification make you an academic? And are higher research degrees just for people who want to be academics?
Even the full title, ‘Doctor of Philosophy’, has a somewhat mysterious ring to it. Do you become a doctor? Yes, but not that kind of doctor. Do you have to study Philosophy? No (not unless you want to) .
So, before going any further, let's explain what the term 'PhD' actually means and what defines a doctorate.
What does PhD stand for?
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term ‘philosophy’ does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to ‘lover of wisdom’.
What is a doctorate?
A doctorate is any qualification that awards a doctoral degree. In order to qualify for one you need to produce advanced work that makes a significant new contribution to knowledge in your field. Doing so earns you the title 'Doctor' – hence the name.
So, is a PhD different to a doctorate? No. A PhD is a type of doctorate .
The PhD is the most common type of doctorate and is awarded in almost all subjects at universities around the world. Other doctorates tend to be more specialised or for more practical and professional projects.
Essentially, all PhDs are doctorates, but not all doctorates are PhDs.
Do you need a Masters to get a PhD?
Not necessarily. It's common for students in Arts and the Humanities to complete an MA (Master of Arts) before starting a PhD in order to acquire research experience and techniques. Students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) don't always need an MS/MSc (Master of Science) to do a PhD as you'll gain training in lab techniques and other skills during your undergraduate degree.
Whether a Masters is a requirement for a PhD also varies by country. Australian PhDs may require a Masters as the equivalent of their own 'honours year' (where students work on research). US PhD programmes often include a Masters.
We have a whole guide dedicated to helping you decide whether a PhD without a Masters is the right route for you.
The origin of the PhD
Despite its name, the PhD isn't actually an Ancient Greek degree. Instead it's a much more recent development. The PhD as we know it was developed in nineteenth-century Germany, alongside the modern research university.
Higher education had traditionally focussed on mastery of an existing body of scholarship and the highest academic rank available was, appropriately enough, a Masters degree.
As the focus shifted more onto the production of new knowledge and ideas, the PhD degree was brought in to recognise those who demonstrated the necessary skills and expertise.
The PhD process – what's required to get a PhD?
The typical length of a PhD is three to four years full-time, or five to six years part-time.
Unlike most Masters courses (or all undergraduate programmes), a PhD is a pure research degree. But that doesn’t mean you’ll just spend years locked away in a library or laboratory. In fact, the modern PhD is a diverse and varied qualification with many different components.
Whereas the second or third year of a taught degree look quite a lot like the first (with more modules and coursework at a higher level) a PhD moves through a series of stages.
A typical PhD normally involves:
- Carrying out a literature review (a survey of current scholarship in your field).
- Conducting original research and collecting your results .
- Producing a thesis that presents your conclusions.
- Writing up your thesis and submitting it as a dissertation .
- Defending your thesis in an oral viva voce exam.
These stages vary a little between subjects and universities, but they tend to fall into the same sequence over the three years of a typical full-time PhD.
The first year of a PhD
The beginning of a PhD is all about finding your feet as a researcher and getting a solid grounding in the current scholarship that relates to your topic.
You’ll have initial meetings with your supervisor and discuss a plan of action based on your research proposal.
The first step in this will almost certainly be carrying out your literature review . With the guidance of your supervisor you’ll begin surveying and evaluating existing scholarship. This will help situate your research and ensure your work is original.
Your literature review will provide a logical jumping off point for the beginning of your own research and the gathering of results . This could involve designing and implementing experiments, or getting stuck into a pile of primary sources.
The year may end with an MPhil upgrade . This occurs when PhD students are initially registered for an MPhil degree and then ‘upgraded’ to PhD candidates upon making sufficient progress. You’ll submit material from your literature review, or a draft of your research findings and discuss these with members of your department in an upgrade exam . All being well, you’ll then continue with your research as a PhD student.
PhDs in other countries
The information on the page is based on the UK. Most countries follow a similar format, but there are some differences. In the USA , for example, PhD students complete reading assignments and examinations before beginning their research. You can find out more in our guides to PhD study around the world .
The second year of a PhD
Your second year will probably be when you do most of your core research. The process for this will vary depending on your field, but your main focus will be on gathering results from experiments, archival research, surveys or other means.
As your research develops, so will the thesis (or argument) you base upon it. You may even begin writing up chapters or other pieces that will eventually form part of your dissertation .
You’ll still be having regular meetings with your supervisor. They’ll check your progress, provide feedback on your ideas and probably read any drafts your produce.
The second year is also an important stage for your development as a scholar. You’ll be well versed in current research and have begun to collect some important data or develop insights of your own. But you won’t yet be faced with the demanding and time-intensive task of finalising your dissertation.
So, this part of your PhD is a perfect time to think about presenting your work at academic conferences , gaining teaching experience or perhaps even selecting some material for publication in an academic journal. You can read more about these kinds of activities below.
The third year of a PhD
The third year of a PhD is sometimes referred to as the writing up phase.
Traditionally, this is the final part of your doctorate, during which your main task will be pulling together your results and honing your thesis into a dissertation .
In reality, it’s not always as simple as that.
It’s not uncommon for final year PhD students to still be fine-tuning experiments, collecting results or chasing up a few extra sources. This is particularly likely if you spend part of your second year focussing on professional development.
In fact, some students actually take all or part of a fourth year to finalise their dissertation. Whether you are able to do this will depend on the terms of your enrolment – and perhaps your PhD funding .
Eventually though, you are going to be faced with writing up your thesis and submitting your dissertation.
Your supervisor will be very involved in this process. They’ll read through your final draft and let you know when they think your PhD is ready for submission.
All that’s left then is your final viva voce oral exam. This is a formal discussion and defence of your thesis involving at least one internal and external examiner. It’s normally the only assessment procedure for a PhD. Once you’ve passed, you’ve done it!
Looking for more information about the stages of a PhD?
How do you go about completing a literature review? What's it like to do PhD research? And what actually happens at an MPhil upgrade? You can find out more in our detailed guide to the PhD journey .
Doing a PhD – what's it actually like?
You can think of the ‘stages’ outlined above as the basic ‘roadmap’ for a PhD, but the actual ‘journey’ you’ll take as a research student involves a lot of other sights, a few optional destinations and at least one very important fellow passenger.
Carrying out research
Unsurprisingly, you’ll spend most of your time as a PhD researcher… researching your PhD. But this can involve a surprisingly wide range of activities.
The classic image of a student working away in the lab, or sitting with a pile of books in the library is true some of the time – particularly when you’re monitoring experiments or conducting your literature review.
Your PhD can take you much further afield though. You may find yourself visiting archives or facilities to examine their data or look at rare source materials. You could even have the opportunity to spend an extended period ‘in residence’ at a research centre or other institution beyond your university.
Research is also far from being a solitary activity. You’ll have regular discussions with your supervisor (see below) but you may also work with other students from time to time.
This is particularly likely if you’re part of a larger laboratory or workshop group studying the same broad area. But it’s also common to collaborate with students whose projects are more individual. You might work on shorter projects of joint interest, or be part of teams organising events and presentations.
Many universities also run regular internal presentation and discussion groups – a perfect way to get to know other PhD students in your department and offer feedback on each other’s work in progress.
Working with your supervisor
All PhD projects are completed with the guidance of at least one academic supervisor . They will be your main point of contact and support throughout the PhD.
Your supervisor will be an expert in your general area of research, but they won’t have researched on your exact topic before (if they had, your project wouldn’t be original enough for a PhD).
As such, it’s better to think of your supervisor as a mentor, rather than a teacher.
As a PhD student you’re now an independent and original scholar, pushing the boundaries of your field beyond what is currently known (and taught) about it. You’re doing all of this for the first time, of course. But your supervisor isn’t.
They’ll know what’s involved in managing an advanced research project over three years (or more). They’ll know how best to succeed, but they’ll also know what can go wrong and how to spot the warning signs before it does.
Perhaps most importantly, they’ll be someone with the time and expertise to listen to your ideas and help provide feedback and encouragement as you develop your thesis.
Exact supervision arrangements vary between universities and between projects:
- In Science and Technology projects it’s common for a supervisor to be the lead investigator on a wider research project, with responsibility for a laboratory or workshop that includes several PhD students and other researchers.
- In Arts and Humanities subjects, a supervisor’s research is more separate from their students’. They may supervise more than one PhD at a time, but each project is essentially separate.
It’s also becoming increasingly common for PhD students to have two (or more) supervisors. The first is usually responsible for guiding your academic research whilst the second is more concerned with the administration of your PhD – ensuring you complete any necessary training and stay on track with your project’s timetable.
However you’re supervised, you’ll have regular meetings to discuss work and check your progress. Your supervisor will also provide feedback on work during your PhD and will play an important role as you near completion: reading your final dissertation draft, helping you select an external examiner and (hopefully) taking you out for a celebratory drink afterwards!
Professional development, networking and communication
Traditionally, the PhD has been viewed as a training process, preparing students for careers in academic research.
As such, it often includes opportunities to pick up additional skills and experiences that are an important part of a scholarly CV. Academics don’t just do research after all. They also teach students, administrate departments – and supervise PhDs.
The modern PhD is also viewed as a more flexible qualification. Not all doctoral graduates end up working in higher education. Many follow alternative careers that are either related to their subject of specialism or draw upon the advanced research skills their PhD has developed.
PhD programmes have begun to reflect this. Many now emphasise transferrable skills or include specific training units designed to help students communicate and apply their research beyond the university.
What all of this means is that very few PhD experiences are just about researching and writing up a thesis.
The likelihood is that you’ll also do some (or all) of the following during your PhD:
The work is usually paid and is increasingly accompanied by formal training and evaluation.
Conference presentation
As a PhD student you’ll be at the cutting edge of your field, doing original research and producing new results. This means that your work will be interest to other scholars and that your results could be worth presenting at academic conferences .
Doing this is very worthwhile, whatever your career plans. You’ll develop transferrable skills in public speaking and presenting, gain feedback on your results and begin to be recognised as an expert in your area.
Conferences are also great places to network with other students and academics.
Publication
As well as presenting your research, you may also have the opportunity to publish work in academic journals, books, or other media. This can be a challenging process.
Your work will be judged according to the same high standards as any other scholar’s and will normally go through extensive peer review processes. But it’s also highly rewarding. Seeing your work ‘in print’ is an incredible validation of your PhD research and a definite boost to your academic CV.
Public engagement and communication
Academic work may be associated with the myth of the ‘ivory tower’ – an insular community of experts focussing on obscure topics of little interest outside the university. But this is far from the case. More and more emphasis is being placed on the ‘impact’ of research and its wider benefits to the public – with funding decisions being made accordingly.
Thankfully, there are plenty of opportunities to try your hand at public engagement as a PhD student. Universities are often involved in local events and initiatives to communicate the benefits of their research, ranging from workshops in local schools to public lectures and presentations.
Some PhD programmes include structured training in order to help students with activities such as the above. Your supervisor may also be able to help by identifying suitable conferences and public engagement opportunities, or by involving you in appropriate university events and public engagement initiatives.
These experiences will be an important part of your development as a researchers - and will enhance the value of your PhD regardless of your career plans.
What is a PhD for – and who should study one?
So, you know what a PhD actually is, what’s involved in completing one and what you might get up to whilst you do. That just leaves one final question: should you do a PhD?
Unfortunately, it’s not a question we can answer for you.
A PhD is difficult and uniquely challenging. It requires at least three years of hard work and dedication after you’ve already completed an undergraduate degree (and probably a Masters degree too).
You’ll need to support yourself during those years and, whilst you will be building up an impressive set of skills, you won’t be directly progressing in a career.
But a PhD is also immensely rewarding. It’s your chance to make a genuine contribution to the sum of human knowledge and produce work that other researchers can (and will) build on in future. However obscure your topic feels, there’s really no such thing as a useless PhD.
A PhD is also something to be incredibly proud of. A proportionately tiny number of people go on to do academic work at this level. Whatever you end up doing after your doctorate you’ll have an impressive qualification – and a title to match. What’s more, non-academic careers and professions are increasingly recognising the unique skills and experience a PhD brings.
Other PhDs - do degree titles matter?
The PhD is the oldest and most common form of higher research degree, but a few alternatives are available. Some, such as the DPhil are essentially identical to a PhD. Others, such as the Professional Doctorate or DBA are slightly different. You can find out more in our guide to types of PhD .
Is a PhD for me?
There’s more advice on the value of a PhD – and good reasons for studying one – elsewhere in this section. But the following are some quick tips if you’re just beginning to consider a PhD.
Speak to your lecturers / tutors
The best people to ask about PhD study are people who’ve earned one. Ask staff at your current or previous university about their experience of doctoral research – what they enjoyed, what they didn’t and what their tips might be.
If you’re considering a PhD for an academic career, ask about that too. Are job prospects good in your field? And what’s it really like to work at a university?
Speak to current PhD students
Want to know what it’s like studying a PhD right now? Or what it’s like doing research at a particular university? Ask someone who knows.
Current PhD students were just like you a year or two ago and most will be happy to answer questions.
If you can’t get in touch with any students ‘face to face’, pop over to the Postgraduate Forum – you’ll find plenty of students there who are happy to chat about postgraduate research.
Take a look at advertised projects and programmes
This may seem like a strange suggestion. After all, you’re only going to study one PhD, so what’s the point of reading about lots of others?
Well, looking at the details of different PhD projects is a great way to get a general sense of what PhD research is like. You’ll see what different PhDs tend to have in common and what kinds of unique opportunity might be available to you.
And, with thousands of PhDs in our database , you’re already in a great place to start.
Read our other advice articles
Finally, you can also check out some of the other advice on the FindAPhD website. We’ve looked at some good (and bad) reasons for studying a PhD as well as the value of a doctorate to different career paths.
More generally, you can read our in-depth look at a typical PhD journey , or find out more about specific aspects of doctoral study such as working with a supervisor or writing your dissertation .
We add new articles all the time – the best way to stay up to date is by signing up for our free PhD opportunity newsletter .
Ready to find your PhD?
Head on over to our PhD search listings to learn what opportunities are on offer within your discipline.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

What happens during a typical PhD, and when? We've summarised the main milestones of a doctoral research journey.

The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to know about the PhD dissertation.

This page will give you an idea of what to expect from your routine as a PhD student, explaining how your daily life will look at you progress through a doctoral degree.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a PhD in the USA.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

Best Online Doctoral Programs for 2024 Top Consensus Ranked Schools for Online PhD Programs
Ready to start your journey.

Created on October 25, 2023 Updated: February 27, 2024

Online doctoral programs have gained popularity in recent years due to their flexibility, accessibility, and diverse offerings. These programs provide a convenient option for working professionals or individuals with other commitments, allowing them to pursue advanced degrees without the constraints of traditional on-campus attendance. The increasing acceptance of online education, advancements in technology, and the availability of virtual research opportunities contribute to the growing popularity of online doctoral programs. As universities expand their online offerings across various fields, more individuals are choosing these programs to advance their education and careers while balancing personal and professional responsibilities.
With more accredited online Ph.D. and other doctorate-level programs available than ever before, it’s important to be able to distinguish between the good, the bad, and the degree mills. That’s where the College Consensus rankings of the Best Online Doctoral Programs for 2024 can help. We’ve highlighted the most highly rated and positively reviewed online colleges and universities offering accredited online doctorates. These are the “best of the best” schools from around the country currently offering an online professional doctorate or online Ph.D. program in at least one subject. Many of the schools listed in our ranking offer several accredited online doctoral programs to choose from. If you’re interested in a master’s level program, see our rankings of the Best Online Grad Schools for Master’s Programs .
Methodology: Ranking the Best Online Doctoral Programs
College Consensus rankings are unique. We combine the results of the most respected college ranking systems with the averaged ratings of thousands of real student reviews from around the web to create a college meta-ranking unlike any other. This approach offers a comprehensive and holistic perspective missing from other college rankings. Visit our about page for information on which rankings and review sites are in this year’s consensus rankings.
The Best Online Doctoral Degree category is limited to schools offering at least one fully online program . Information about the number and types of online doctoral degree programs offered was taken directly from the school’s website.
- Washington Monthly
- Wall Street Journal
- Grad Reports
- U.S. News Reviews
Summary of Top 10 Best Accredited Online Doctoral Programs
| 1. | 4-year, Private not-for-profit | Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Commission on Colleges | 2 | 89.8 | |
| 2. | 4-year, Private not-for-profit | Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Commission on Colleges | 4 | 89.5 | |
| 3. | 4-year, Private not-for-profit | Middle States Commission on Higher Education | 2 | 89.1 | |
| 4. | 4-year, Public | Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Commission on Colleges | 9 | 87.7 | |
| 5. | 4-year, Private not-for-profit | WASC Senior College and University Commission | 6 | 86.8 | |
| 6. | 4-year, Public | Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Commission on Colleges | 3 | 85 | |
| 7. | 4-year, Public | Higher Learning Commission | 5 | 83.5 | |
| 8. | 4-year, Private not-for-profit | Middle States Commission on Higher Education | 2 | 83.5 | |
| 9. | 4-year, Public | Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Commission on Colleges | 1 | 83.2 | |
| 10. | 4-year, Public | Higher Learning Commission | 2 | 81.9 |
Recommended Online Doctoral Programs
Visit sites to learn more about enrollment, tuition, and aid
Duke University Durham, NC
Total online doctoral programs: 2
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Ministry, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Learn more: Duke Online Doctoral Programs
Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN
Total online doctoral programs: 4
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), Online Ph.D. in Nursing Science, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP), Online Doctor of Ministry
Learn more: Vanderbilt Online Learning
University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA
Notable programs: Online Doctorate in Clinical Social Work, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Learn more: UPenn Online Learning
University of Florida Gainesville, FL
Total online doctoral programs: 9
Notable programs: Online PhD in Classical Civilization, Online EdD in Educational Leadership, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP)
Learn more: UF Online Doctorate Degrees
University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA
Total online doctoral programs: 6
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership, Online Doctor of Regulatory Science (Pharmacy), Online Doctor of Physical Therapy, Online Doctor of Social Work
Learn more: USC Online Doctoral Programs
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Chapel Hill, NC
Total online doctoral programs: 3
Notable programs: Online Executive Doctoral Program in Health Leadership (DrPH), Online BSN to DNP in Health Leadership, Online MSN to DNP
Learn more: UNC Online
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Champaign, IL
Total online doctoral programs: 5
Notable programs: Online Doctorate in Global Studies in Education (Ed.D.), Online Doctorate in Human Resources Management, Online Doctorate in Learning Design & Leadership
Learn more: Illinois Online
Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Public Health (DrPH), Online Doctor of Eucation (Ed.D.)
Learn more: JHU Online
University of Virginia-Main Campus Charlottesville, VA
Total online doctoral programs: 1
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Education in Curriculum & Instruction (Ed.D.)
Learn more: Online Education @UVA
University of Wisconsin-Madison Madison, WI
Notable programs: Online DNP in Population Health Nursing, Online DNP in Systems Leadership & Innovation
Learn more: UW Professional Degrees & Certificates
Featured Schools
Explore our featured online programs to find the right match for you today.
Florida State University Tallahassee, FL
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP), Online PhD in Nursing Education, Online Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership & Policy (EdD)
Learn more: Distance @ FSU
Wake Forest University Winston-Salem, NC
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Nursing Practice, Online Doctor of Ministry
Learn more: WFU Office of Online Education
Texas A & M University-College Station College Station, TX
Total online doctoral programs: 7
Notable programs: Online PhD in Biomedical Sciences, Online Doctorate of Engineering, Online PhD in Plant Breeding
Learn more: Texas A&M Distance Education
Purdue University-Main Campus West Lafayette, IN
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Technology, Online PhD in Higher Education
Learn more: Purdue University Online Doctorate Degrees
North Carolina State University at Raleigh Raleigh, NC
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Design
Learn more: NC State Online Doctor of Design
New York University New York, NY
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Occupational Therapy for Practicing Therapists, Online EdD in Leadership & Innovation
Learn more: NYU Online & Hybrid Degrees
Indiana University-Bloomington Bloomington, IN
Total online doctoral programs: 12
Notable programs: Online PhD in Music Therapy, Online EdD in Art Education, Online PhD in Nursing Science
Learn more: IU Online Doctoral Degree Programs
George Washington University Washington, DC
Notable programs: Online PhD in Systems Engineering, Online Doctor of Public Health (DrPH), Online Doctor of Engineering in Artificial Intelligence & Maching Learning
Learn more: GWU Online Engineering Doctorates
Boston University Boston, MA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Ministry, Online Doctor of Music Education, Online Doctorate of Occupational Therapy
Learn more: BU Online Programs
Ohio State University-Main Campus Columbus, OH
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Nursing Practice, Online Doctor of Nursing Education
Learn more: Ohio State Online
University of Illinois Chicago Chicago, IL
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Public Health in Leadership
Learn more: UIC Online
Clemson University Clemson, SC
Total online doctoral programs: 8
Notable programs: Online PhD in Healthcare Genetics, Online PhD in Parks, Recreation, and Tourism Management, Online PhD in Special Education
Learn more: Clemson Online
University of San Diego San Diego, CA
Notable programs: Online PhD in Education for Social Justice
Learn more: USD Online PhD
University of Arizona Tucson, AZ
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Nursing Practice, Online Doctorate of Education in Educational Leadership, Online DNP in Nurse-Midwifery
Learn more: Arizona Online
University of South Florida Tampa, FL
Notable programs: Online Doctore of Business Administration, Online PhD in Career & Workforce Education, Online Doctor of Public Health (DrPH)
Learn more: USF Online Graduate Degrees
Towson University Towson, MD
Notable programs: Online PhD in Instructional Technology, Online PhD in Occupational Science, Online Occupational Therapy OTD
Learn more: Towson Online Programs
University of Central Florida Orlando, FL
Online doctoral programs: 5
Notable programs: Online Doctorate in Curriculum & Instruction, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice, Online PhD in Nursing
Learn more: UCF Online Doctorates
Messiah University Mechanicsburg, PA
Notable programs: Online DNP Family Nurse Practitioner, Online DNP Nursing Leadership
Learn more: Messiah graduate degrees
University of Missouri-Columbia Columbia, MO
Notable programs: Online PhD in Agricultural Studies, Online PhD in Architectural Studies, Online Occupational Therapy Doctorate
Learn more: Missouri Online
Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester, MA
Notable programs: Online PhD in Systems Engineering
Learn more: WPI Online Systems Engineering PhD
Butler University Indianapolis, IN
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD)
Learn more: Butler Doctor of Pharmacy Online
Tulane University of Louisiana New Orleans, LA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Social Work (DSW), Online Doctor of Public Health (DrPH)
Learn more: Tulane online graduate degrees
University of Pittsburgh-Pittsburgh Campus Pittsburgh, PA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Learn more: Pitt Online degree programs
American University Washington, DC
Notable programs: Online EdD in Education Policy & Leadership
Learn more: American University Online EdD
University at Buffalo Buffalo, NY
Notable programs: Online PhD in Informational Science, Online EdD in Learning & Teaching in Social Contexts, Online Doctorate in Educational Administration
Learn more: SUNY Online Programs
Fordham University Bronx, NY
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Ministry, Online EdD in Educational Leadership, Online PhD in Religion & Practice
Learn more: Fordham Online Learning Programs
Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Health Science, Online Doctor of Midwifery, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Learn more: Jefferson Online Programs
Pennsylvania State University-Main Campus University Park, PA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Education, Online Doctor of Engineering, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Learn more: Penn State World Campus doctoral programs
University of Oklahoma-Norman Campus Norman, OK
Notable programs: Online PhD in Nursing, Online Doctor of Education in Educational Administration
Learn more: OU Online Graduate Programs
The University of Tennessee-Knoxville Knoxville, TN
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Social Work, Online PhD in Industrial Engineering, Online PhD in Nursing
Learn more: Vols Online – doctoral degrees
California State University-Fresno Fresno, CA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership
Learn more: Fresno State Online EdD
Drexel University Philadelphia, PA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Couples & Family Therapy, Online Doctor of Health Science, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Learn more: Drexel accredited online doctorate programs
Loyola Marymount University Los Angeles, CA
Notable programs: Online EdD in Educational Leadership for Social Justice
Learn more: LMU Online EdD
Michigan Technological University Houghton, MI
Notable programs: Online PhD in Civil Engineering, Online PhD in Mechanical Engineering
Learn more: Michigan Tech Global Campus
Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, FL
Notable programs: Online PhD in Computer Science, Online PhD in Computer Engineering, Online PhD in Electrical Engineering
Learn more: FAU Online
Saint Louis University Saint Louis, MO
Notable programs: Online PhD in Aviation, Online Doctor of Nursing Practice, Online PhD in Nursing
Learn more: SLU online doctoral programs
SUNY at Albany Albany, NY
Notable programs: Online PhD in Curriculum & Instruction, Online PhD in Literacy
Learn more: Albany Online Graduate Programs
University of New Hampshire-Main Campus Durham, NH
Online doctoral programs: 1
Learn more: UNH Online
Duquesne University Pittsburgh, PA
Notable programs: Online Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD), Online Doctor of Nurse Anasthesia Practice (DNAP), Online PhD in Nursing Ethics
Learn more: Duquesne University Online
Sam Houston State University Huntsville, TX
Notable programs: Online EdD in Instructional Systems Design, Online EdD in Higher Education Leadership
Learn more: SHSU Online
Pros and Cons of Earning a Doctorate Online
Pros of online doctoral degrees:.
- Flexibility: One of the key advantages of pursuing a doctoral degree online is the flexibility it offers. Online programs allow students to manage their coursework around other commitments, making it more accessible for working professionals.
- Geographical Accessibility: Online programs eliminate geographical constraints, enabling students to enroll in prestigious universities without relocating. This accessibility expands the pool of potential programs and faculty members.
- Cost Savings: Online doctoral programs often reduce costs associated with commuting, housing, and campus fees. Additionally, students can continue working while pursuing their degree, potentially offsetting tuition expenses.
- Diverse Learning Environment: Online doctoral programs attract a diverse cohort of students from various backgrounds and locations. This diversity enriches discussions, bringing different perspectives to academic discourse.
- Technology Integration: Online programs leverage advanced technology, providing access to a variety of digital resources, virtual libraries, and collaborative platforms. This enhances the learning experience and allows students to engage with cutting-edge tools.
Cons of Online Doctoral Degrees:
- Limited Networking Opportunities: Online programs may offer fewer networking opportunities compared to traditional on-campus experiences. Building professional relationships and collaborations can be challenging in a virtual environment.
- Potential for Isolation: Doctoral studies can already be isolating, and online programs may exacerbate this by limiting face-to-face interactions with peers and faculty. The lack of a physical campus environment may lead to feelings of isolation.
- Varied Program Quality: The quality of online doctoral programs can vary. Prospective students must thoroughly research programs to ensure they meet academic standards and offer the necessary resources for research and dissertation work.
- Technical Challenges: Online learning relies heavily on technology, and technical issues such as poor internet connectivity or platform malfunctions can disrupt the learning experience. This may hinder participation in live discussions or access to materials.
- Perceived Credibility: While online education is becoming more widely accepted, some employers and academics may still harbor reservations about the credibility of online doctoral degrees. It’s crucial to choose a reputable institution to mitigate this concern.
Are Online PhD Programs Respected?
When professionals think of pursuing their doctorate degrees, what comes to their mind is “are online PhDs respected?”All online programs are respected as long as they are from institutions that are accredited by relevant bodies, and online degree programs are no exemption. Of course, not all online programs offering doctoral degrees are the same. Look for online doctoral degrees offered from reputable institutions. Ask yourself- are the online programs at this institution the same as the campus counterparts? Is the same faculty teaching within the online programs?
Most people who want to pursue a doctorate degree are busy professionals who are not able to accommodate a traditional course of study. Maybe they are a Nurse Practitioner and they would like to step up to a Doctor of Nursing Practice. Online doctoral degrees can help them achieve this. The best online PhD programs are offered in regionally accredited institutions. An independent body such as WSCUC reviews the degree programs offered in the institution and judges them on different factors before giving accreditation.
Accredited best online PhD programs are available in many U.S. universities, both public and private. Online PhDs are just as challenging as traditional PhDs. Students that choose to pursue a doctorate degree online are self-motivated and enjoy the freedom of choosing how long they want to take to finish their doctorate. This aspect of online education helps students prove to their employers or prospective employers that they are disciplined and self-driven. Actually, 79% of organizations see the value of online degrees and say that they had hired an applicant with an online degree in the last year according to research by Society for Human Resources Management.
The Most Popular Types of Doctoral Degrees
NCES data shows that healthcare (or health sciences) professionals earn nearly 44% of all doctoral degrees (desperate need for doctor of nursing practice). The second-highest rate of doctoral degrees is graduate programs in Law at just under 19%. Data from NCES also indicates that only about 5%-7% of professionals in the remaining disciplines of educational leadership, engineering, and biological sciences hold doctoral degrees. See below for descriptions of some of the most common doctoral degrees, including the Ed.D., Ph.D., and MD.
- Health professions and related (mostly nursing practice program) –44%
- Legal professions and studies — 19%
- Education (mostly higher education administration) — 7%
- Engineering and engineering technologies — 6%
- Biological and biomedical sciences — 4%
Source : NCES
You may not be able to get your MD 100% online, but you can get an online Doctor of Public Health or a Doctor of Nursing Practice. Online doctorates or an online PhD are available in many basic majors including:
- Engineering
- Health Sciences (Doctor of Nursing Practice)
- Computer Science
- Social Work
- Educational Leadership
Building on your experience as a working professional, and using cutting-edge technology, you can complete an online doctorate in a year or two in some cases, often without ever having to go to campus. Not from fly-by-night diploma mills, but from trusted institutions with vast reach and job market advantages.
Many online programs at the doctoral degree level are available for prospective students post a bachelor’s degree. A doctoral degree, and more specifically an online doctoral program can give prospective students the flexibility they need to advance in their career. Make sure the doctoral program you are looking at will achieve that goal!
| Doctor of Philosophy Ph.D. | $106,860 | Up to 8 Years |
| Psy.D. Psychology | $204,000 | 4-5 Years |
| Ph.D. Engineering | $43,200 | 5-7 Years |
| Ph.D. Law | $146,500 | 3-5 Years |
| Doctorate of Education Ed.D | $112,350 | 7-8 Years |
| Doctorate in Business Administration DBA | $140,400 | 3 Years** |
How Long Do Accredited Online PhD Programs Take?
Enrolling in a doctorate program after a bachelor’s degree is a big commitment and a huge step towards advancing one’s career and achieving excellence in any field. The length of time it takes to complete an online doctorate program depends on the type of program and how many credits it requires to complete. Most traditional PhD programs take between four to seven years but online students are allowed up to ten years to complete.
Online programs allow students to pursue their doctorate at their own pace. There are accelerated doctoral degree programs online that take as short as one year to complete. The length also depends on whether you have a master’s degree or you are pursuing a direct entry PhD. A master’s degree may allow online students to transfer some credits to their doctorate. On the other hand, direct entry programs may require students to take extra credits. The shortest doctoral degree programs online are found in public service, law, government, engineering, educational leadership, and arts programs.
The quickest PhD ever is a PhD in philosophy. As long as one already has some publications, one can become a doctor of philosophy in less than a year. One can also pursue 1-year Ph.D degree programs online in other fields of study as long as they are ready to spend enough time studying and researching.
Reasons to Get an Online Ph.D.
Whether you earn a Ph.D. or doctorate ultimately depends on your academic interests and how you want to shape your career or contribute to a body of knowledge.

Career Advancement and Earnings Potential Considered terminal or professional degrees, PhDs, and professional doctorates will help advance your career and demonstrate your dedication and expertise in your chosen field. Whether your interests are in theory, research, creating (or contributing) to a knowledge base, or expanding your expertise in an applied profession, earning a Ph.D. and/or doctorate is the logical step.
Professional Expertise Among the top Ph.D. disciplines are science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Education, Law, and Business also rank highly in the most sought-after programs.
If you’re particularly passionate about a topic or field and want to do a deep dive into the subject and conduct research to enhance the field, earning an online Ph.D. or doctorate is the logical next step.
Networking Ph.D. programs will allow you to interact with other professionals with similar interests as yours. You’ll be able to share knowledge, and it will give you a base to explore research grants, other funding opportunities, and employment options.
Earnings In 2023 the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that people holding a Ph.D. degree experienced lower unemployment and significantly higher salaries than people who had less education. BLS cites those with doctoral or professional degrees can earn a median salary of $103,820.
ZipRecruiter, an online employment service, states the average hourly rate for a doctorate is around $68 an hour, although some are in the $191 range. Salaries and compensation will vary depending on location, skills, and years of experience but average $141,097.
Cost Although Ph.D.s can be costly, online programs can save you significant money by reducing travel expenses. Frequently, colleges and universities charge out-of-state students in-state tuition which will save you money.
Convenience The convenience of an online academic program can’t be overstated. Unless you’ve won the PowerBall, online programs save you time and money and allow you to continue to work to support yourself or a family.
Accredited online Ph.D.s and doctorates greatly expand your geographic reach, making it possible for you to enter a program in another state that best suits your objectives.
Coursework can frequently be presented over the Internet, allowing you to study at a time and place that works best for you. Access to online libraries saves time traveling to a university campus or public library.
Interactions with classmates, subject matter experts, and professors can be conducted using online video apps such as Zoom, Vimeo, or Google Meet. Depending on your program, you may be required to attend on-campus intensives, which are usually held over weekends or at designated times.
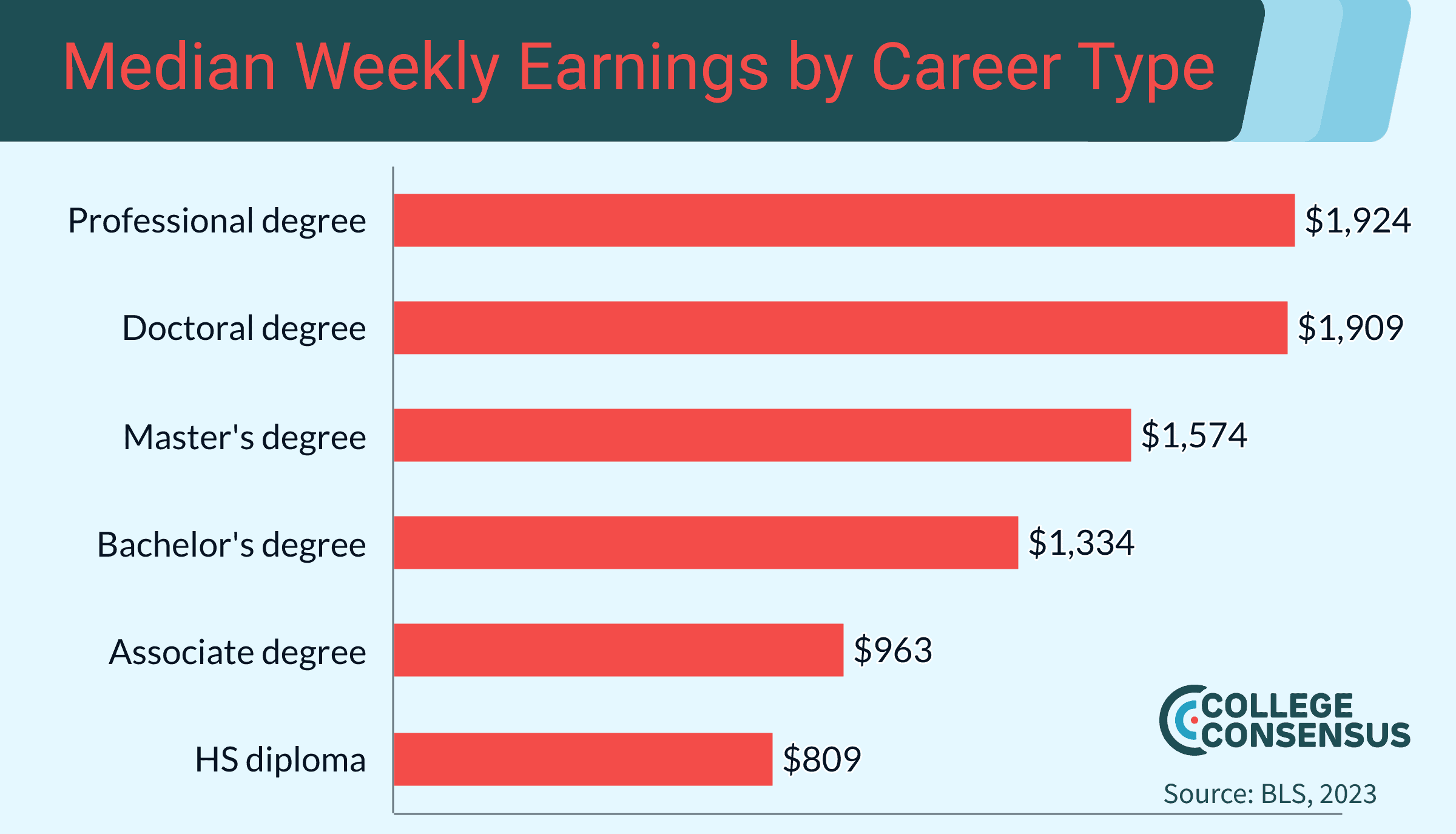
How Much Do Online PhD Programs Cost?
If your professional goal is to teach at the university level, snag a high-level executive position, or conduct ground-breaking research, a Ph.D. or doctorate is your foot in the door. Inevitably, the final decision to pursue a PhD or doctorate will probably boil down to if you can afford it. Advanced degrees aren’t necessarily cheap and may cause you to go into debt, but depending on the discipline, they can be affordable and worth the expense.
School Choice – Several factors, such as your school choice and field of study, can influence your costs for a Ph.D. Naturally, there are differences in tuition at a public college or university and private institutions. Prestige also plays a part. Ivy League schools may charge a premium for their doctorate programs.
Ph.D./Doctorates
Tuition costs for doctorates and Ph.D.s can vary, depending on the type of degree, program length, whether you’re working full-time or part-time on your degree and the school’s location per academic year.
The average length of a Ph.D. program is five to eight years, with an estimated of $106,860.
A doctorate from an eight-year public university program can range from $93,670 to $129,395.
Doctorate of Education Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. in Education – The differences between an Ed.D. and a Ph.D. can influence your cost due to the amount of time spent earning the degree. An Ed.D. may take 3-5 years, and a Ph.D. will take longer.
Doctorate of Psychology Psy.D. vs. Ph.D. – Again, like the doctorate in Education, there’s a difference in length of study, with the Psy.D. taking up to 4-5 years and the Ph.D. requiring 5-7 years.
Financial Assistance
Colleges and universities frequently fund Ph.D. and doctoral candidates. Funding may come in the form of waived tuition and fees as well as providing a stipend. While difficult for online Ph.D. programs, internships, assistantships, and fellowships may also be available.
If you’re working, your employer may be willing to provide some assistance, especially if the degree relates directly to your employment. For example, if you work in a healthcare setting and are pursuing a Doctor of Nursing Practice, it benefits your employer to support you in earning an advanced degree.
Federal student loans are also available for doctoral students, and you can borrow up to $20,500 each year in Direct Unsubsidized Loans. These loans are fixed and usually at a lower interest rate than commercial loans or credit cards. Repayment options are typically flexible. You’ll want to discuss your options with the Financial Aid Office.
Do I Have to Write a Dissertation for an Online PhD?
As much as getting a doctoral degree has many benefits, the work that goes into achieving it requires much dedication. There are many roadblocks on the road to achieving your PhD, including family responsibilities, work, time, and money. Many professionals looking to further their educations are always asking, “What is the easiest doctorate degree?” Well, there are no dissertation PhD programs. Accelerated PhD programs do not require a dissertation to graduate and take one year to complete. One-year doctorate programs are available in select universities across the country but are more intensive and require students to study full time. Some of the programs that do not require a dissertation include Doctor of Management (DM), Juris doctorates, law degree (JD), Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT), and Doctor of Education (EdD).
The most common doctorate degree online no dissertation is the Doctorate in Leadership . This is a doctorate that applies in many disciplines including Organizational Leadership, Leadership and Management, and Higher Education Leadership. A traditional doctoral program uses dissertations to assess the student’s knowledge in the field. Universities that offer accelerated doctoral degree programs understand that it is not the only way to assess the student’s knowledge in the field and they use other parameters such as doctoral capstone projects (along with online courses). Online students that already have published books and journals can also begin their degree without a dissertation.
Are There Any Online PhD Programs Without GRE or GMAT Requirements?
The online no GRE PhD programs are gaining popularity in many universities. These universities instead use the student’s professional experience, academic merits, and their motivation among other factors to admit them to their graduate programs. The GRE can be a big hurdle for online students who want to pursue their PhD programs but do not have the time and money to invest in studying for the standardized exams. There are a number of online degree PhD programs that do not require GRE online and others that the GRE can be waived under special circumstances.
Do I Need a Master’s Degree to Enroll in an Online Doctoral Degree Program?
There are a number of PhD programs without requiring a master’s degree in many universities in the U.S. Some accept students with undergraduate degrees into their degree programs and award them the master’s degree during the course after a certain amount of coursework has been completed. Others have specific stipulations for students applying for their doctoral programs without a master’s degree. For example, many universities will allow registered nurses to pursue their doctoral degrees if they pass an interview. There are universities that will confer a master’s degree once a student is admitted to the doctoral program. Universities offering PhD without a master’s admit exceptional students with outstanding grades and sometimes at least two years of professional experience.
Related Online Programs:
Best Online Graduate Schools
Best Online Colleges & Universities
Best Online Doctorate in History Programs

Most Affordable Online Doctorate in Education (EdD) Programs for 2024
Organizations require great leadership to reach their full potential and weather the worst storms. If you are looking to become a more effective and thoughtful manager or team leader, you may be considering a graduate degree program. For people who are further along in their careers and looking for a more flexible option, an online Ed.D. program in organizational leadership may be a good fit. But earning a doctorate degree requires a big investment of both time and money. So Fortune has ranked eight online Doctorate in Education (Ed.D.) programs by affordability. Tuition amounts were compiled using data provided by schools for our ranking of the best online Ed.D. programs in 2022. If schools did not provide the total tuition cost of the program, we multiplied the cost per credit amount by the minimum credit hours required to graduate. Cost per credit amounts were either provided by schools or taken from the program webpage. This ranking was last updated December 2022.
Online Ed.D. from Top-5-Ranked Peabody College

1. Trevecca Nazarene University
- ACCEPTANCE RATE
- CREDITS REQUIRED TO GRADUATE
- RETENTION RATE
2. Abilene Christian University

3. Spalding University

Hawai‘i Pacific University M.Ed. in Educational Leadership

4. Virginia Commonwealth University

5. University of Dayton

6. Drexel University

7. Baylor University

8. Vanderbilt University

Maryville University’s Doctor of Education | Online

2024-2025 Catalog
Doctoral degrees.
The University of Idaho awards the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in recognition of high achievement in scholarly and research activity. The degree of Doctor of Education is granted for high scholarly attainment and in recognition of the completion of academic preparation for professional practice. See the "Ph.D. and Ed.D. Procedures" tab for more details. The Doctor of Athletic Training is offered through the College of Education and the Department of Movement Sciences (see the "DAT Procedures" tab for more details).
The major professor and program offering a particular doctoral program indicate the general philosophy of the degree program, the objectives of courses and seminars, the research specialties available, and requirements unique to the department. Admission to the doctoral program is granted only to those who have a recognized potential for completing the degree.
Requirements for Doctoral Degrees
Credit requirements.
For the Ph.D. and Ed.D., a minimum of 78 credits beyond the bachelor's degree is required.; At least 52 credits must be at the 500 level or above and at least 33 of the 78 credits must be in courses other than 600 (Doctoral Research and Dissertation). A maximum of 45 research credits in 600 (Doctoral Research and Dissertation) including 6 credits of 599 (Non-thesis Research) or 500 (Master's Research and Thesis) may be in the 45 research credits used toward the degree. For the D.A.T., a minimum of 66 credits is required and follows a prescribed set of courses set by the program.
Courses numbered below 300 may not be used to fulfill the requirements for a doctoral degree; courses numbered 300-399 may be used only in supporting areas and are not to be used to make up deficiencies. Individual programs may require additional course work. Applicants having a doctoral degree may obtain a second doctoral degree subject to the approval of the Graduate Council. The Graduate Council will establish the requirements for the second degree.
Credit Limitations for Transfer, Correspondence Study, and Non-degree
For the Ph.D. and Ed.D. degrees, a student must complete at least 39 of the 78 required credits at the University of Idaho (U of I) while matriculated in the College of Graduate Studies. Credits can be transferred to U of I with the consent of the student's major professor, the committee (if required by the program), the program's administrator, and the dean of the College of Graduate Studies. Credits can be transferred only if the institution from which the credits are being transferred has a graduate program in the course's discipline. All credits used toward graduate degrees must be from regionally accredited American institutions or from non-US institutions recognized by the appropriate authorities in their respective countries. Transfer credits are subject to all other College of Graduate Studies rules and regulations. Correspondence study courses may be applied to the degree only with the prior written approval of the College of Graduate Studies. Courses used toward an undergraduate degree, professional development courses, and courses on a professional development transcript are not available to be used toward a doctoral degree.
Time Limits
Of the credits submitted to satisfy the requirements for a Ph.D. or Ed.D. degree, a maximum of 30 may be more than eight years old when the degree is conferred, provided the student's committee and program administrator determine that the student has kept current in the subjects concerned. Graduation must occur no later than five years after the date on which the candidate passed their preliminary or general examination. These time limitations can be extended only on recommendation of the committee and approval by the Graduate Council.
Awarding Doctoral Degrees to Members of the Faculty
Regulations are outlined in Section 4920 of the Faculty-Staff Handbook.
Particular Requirements for the Ed.D. Degree
A period of professional practice is required for the Doctor of Education degree; the period involved is determined by the student's supervisory committee. While the Ed.D. is a College of Education degree, you should consult with the departments in the College of Education to learn of specific emphasis requirements.
Procedures for Doctor of Philosophy and Doctor of Education Degrees
Appointment of major professor and committee.
Refer to " Appointment of Major Professor and Committee for All Degree Seeking Graduate Students " in the preceding General Graduate Regulations section. In addition, a doctoral supervisory committee consists of at least four people: the major professor as chair and at least one additional UI faculty member from the program, the balance of the committee may be made up of faculty members from a minor or supporting area, and faculty members from a discipline outside the major. If the committee has a co-chair, the minimum number of committee members is five.
Qualifying Examination
The qualifying examination is a program option and serves to assess the background of the student in both the major and supporting fields and to provide partially the basis for preparation of the student's study program. A particular program may or may not require a master's degree as a prerequisite for the qualifying evaluation. As soon as the program's qualifications are met, a supervisory committee is appointed.
Preparation of Study Plan
Refer to " Preparation and Submission of Study Plan " in the preceding General Graduate Regulations section.
Preliminary Examination for Ph.D. Degree
The preliminary examination should be scheduled only after the student has completed the majority of the courses on their study plan. The student is required to be registered during the semester the preliminary examination is taken. The student's committee certifies to the College of Graduate Studies the results of the preliminary examination and if passed, the student is advanced to candidacy. Graduation must occur no later than five years after the date on which the candidate passed their examination. If the preliminary examination is failed, it may be repeated only once; the repeat examination must be taken within a period of not less than three months or more than one year following the first attempt. If a student fails the preliminary examination a second time, or the program does not allow the student to repeat the examination after the first failure or the student does not retake the examination within one year, the student is automatically moved to unclassified enrollment status and is no longer in the degree program.
General Examination for Ed.D . Degree
When the student approaches the end of their course work, has completed the professional experience requirement, and has outlined the dissertation subject in detail, the supervisory committee approves the holding of the general examination. The student is required to be registered during the semester the general examination is taken. The examination is both written and oral and is intended to assess progress toward degree objectives. The student's committee certifies to the College of Graduate Studies the results of the general examination and if passed, the student is advanced to candidacy. Graduation must occur no later than five years after the date on which the candidate passed their examination. If the general examination is failed, it may be repeated only once; the repeat examination must be taken within a period of not less than three months or more than one year following the first attempt. If a student fails the general examination a second time, or the program does not allow the student to repeat the examination after the first failure or the student does not retake the examination within one year, the student is automatically moved to unclassified status and is no longer in the degree program.
See the General Graduate Regulations section regarding application for advanced degree, registration requirements, final defense and dissertation requirements.
Procedures for Doctor of Athletic Training
The culminating clinical project.
Students enrolled in the Doctor of Athletic Training (D.A.T.) will engage in research projects during the curricular phase of the program. These project(s) will lead to at least two publication ready manuscripts, and all students must meet professional authorship requirements (regardless of order). See the Department of Movement Sciences and Doctor of Athletic Training webpages for more information.
The Team (Committee)
All D.A.T. project team committees will have at least four committee members: two members of the athletic training faculty (all with graduate faculty status), the student's attending clinician (who is the student's on-site mentor during the student's residency), and an expert in the student's chosen area of clinical research. The athletic training faculty members will always chair the CCP, provide research guidance, and serve as the experts in the development of advanced practice in Athletic Training. A situation may arise in which one or both of the members of the committee that are outside of the AT program faculty may have a degree less than that of which the student is seeking; however, the intent of the third and fourth D.A.T. committee membership is to provide outside validation of the student's progress toward advanced practice and clinical utility of action research studies.
Culminating Clinical Project Hours
These dissertation hours may be used in instances when the CCP has not been successfully completed and the curricular phase of program has been completed.
Print Options
Send Page to Printer
Print this page.
Download Page (PDF)
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Psychology Degree Guide: Courses, Careers And Online Options

Published: Jun 7, 2024, 4:43pm

Key Takeaways
- Psychology degrees offer students an array of valuable skills they can use to work as psychologists or in other related professions.
- Psychology degrees combine the quantitative rigors of the natural sciences with the qualitative analyses of the humanities and social sciences.
- Psychology students can specialize in subfields such as neuroscience, clinical psychology and behavior analysis.
Why do we feel, think, and act the way we do? Psychologists offer science-based insight into the enigmas that surround the human condition.
More than any other field, psychology can be viewed as the study of human behavior and what motivates us to live our lives the way we do. Psychology combines the empirical rigors of the hard sciences with the sociocultural qualitative analysis of the social sciences and humanities.
If you have ever made a “Freudian slip” while speaking, talked about someone doing something “unconsciously” or tried to interpret your dreams, you’ve been influenced by the vocabulary and theories of psychology.
Although the origins of psychology as a scientific field of study can be found in 19th-century Germany, philosophers and scientists have been hypothesizing for millennia about the way our behavior is engendered by the dynamic relationship that exists between our brains and our emotions. The formalization of such inquiries has led to an ever-growing field that now includes studying children, adults, animals and even machines.
Why You Can Trust Forbes Advisor Education
Forbes Advisor’s education editors are committed to producing unbiased rankings and informative articles covering online colleges, tech bootcamps and career paths. Our ranking methodologies use data from the National Center for Education Statistics , education providers, and reputable educational and professional organizations. An advisory board of educators and other subject matter experts reviews and verifies our content to bring you trustworthy, up-to-date information. Advertisers do not influence our rankings or editorial content.
- 6,290 accredited, nonprofit colleges and universities analyzed nationwide
- 52 reputable tech bootcamp providers evaluated for our rankings
- All content is fact-checked and updated on an annual basis
- Rankings undergo five rounds of fact-checking
- Only 7.12% of all colleges, universities and bootcamp providers we consider are awarded
What Is a Bachelor’s in Psychology?
A bachelor’s degree in psychology provides students with a holistic understanding and appreciation for the myriad ways in which psychology is used in the medical, therapeutic and professional worlds. Broadly defined as the science of human and animal behavior, psychology is currently being redefined by cutting-edge undergraduate programs to include the behavior of machines and artificial intelligence.
Psychology students are immersed in the theoretical and experiential foundations of psychological science by taking courses that focus on the behavioral, cognitive, developmental and social aspects of psychological studies. In other words, psychology aims to figure out why we feel, think and do the things we feel, think and do.
A bachelor’s degree in psychology is typically seen as the most effective gateway to earning the graduate degrees that allow you to become a psychiatrist or psychologist. However, because psychology majors are seen as individuals with multiple skill sets, more than 70% of recent graduates with a bachelor’s degree in psychology work outside of the field.
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), psychology degree holders work in areas as diverse as web development, architecture, journalism and education. After all, a psychology major’s keen insight into the human mind can prove beneficial to many businesses and organizations looking to build their customer and client base.
Degree Finder
Types of psychology degrees.
Below, explore the various types of degrees you can earn in psychology.
Associate of Arts (A.A.), Associate of Science (A.S.) or Associate of Applied Science (A.A.S.)
An associate degree in psychology usually takes two years to earn at a community college. Because job options in psychology are limited for those who only have an associate degree, most associate in psychology graduates use this degree as an affordable stepping stone to earning a bachelor’s degree.
An A.A. approaches psychology with a liberal arts focus. A.S. and A.A.S. programs in psychology are similar to A.A. programs, but with a more practice-focused approach.
Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) or Bachelor of Science (B.S.)
A B.A. in psychology usually requires a more well-rounded liberal arts education with a mix of courses in the humanities, the social sciences and general education. A B.A. is a good option for students who want to enter career fields where understanding human behavior is a strong asset. This degree usually takes four years to earn.
A B.S. in psychology usually requires more math and natural science courses that emphasize quantitative analysis. A B.S. is a good option for students who want to work in laboratories and do research that requires empirical methodologies. This degree usually takes four years to earn.
Typical courses for both the B.A. and B.S. tracks at most universities can include cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, statistics, psychopathology and mental health, social psychology and research methods.
Master of Science (M.S.) or Master of Arts (M.A.)
Typically lasting two to three years, the M.S. in psychology tends to take a practice-based approach to advanced education in psychology. Learners who plan to enter the workforce directly after earning their master’s might benefit from a Master of Science in psychology.
The psychology M.A., on the other hand, caters to students who plan to transfer into doctoral programs after completing their master’s. An M.A. in psychology delivers advanced education in the field through a liberal arts-focused lens.
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) or Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.)
A Ph.D. in psychology delivers research-based psychology education at the doctoral level. Students seeking careers in academia or research may benefit most from earning a Ph.D. in psychology. This degree typically takes four to seven years to complete, though completion times vary drastically depending on each student’s program, area of emphasis and enrollment status.
A Doctor of Psychology is another doctoral-level psychology degree, but it’s more practiced-focused than a Ph.D. in psychology. Students who want to practice clinical psychology may benefit most from earning a Psy.D. Though they often include practice requirements, Psy.D. programs often run shorter than Ph.D. programs, taking four to five years to complete.
Psychology Specializations
Aspiring psychology majors may consider the following specializations. This list represents only a few possible areas of emphasis for psychology students.
Counseling Psychology
Counseling psychology focuses on our everyday interactions with others and ourselves. A great specialization for students who want to be social workers and mental health counselors, a counseling psychology specialty combines theoretical approaches and research methods to provide students with the opportunity to conduct clinically relevant research.
Neuroscience
A neuroscience specialty, also known as a behavioral and cognitive neuroscience specialty, expands upon environmental life sciences to closely examine the entire nervous system with a focus on cognitive, behavioral and brain functions.
Behavior Analysis
Behavior analysts study how environmentally influenced behavior is established and how it can be modified. With a focus on creating practical solutions to various behavioral problems, these programs often help students become Board Certified Behavior Analysts®.
What Can You Do With a Psychology Degree?
We sourced salary data for this section from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in June 2024.
Psychologist
Median Annual Salary: $92,740 Minimum Required Education: Master’s degree in psychology or a related field Job Overview: Psychologists study and help modify how individuals, families and organizations interact with one another from cognitive, emotional and behavioral perspectives. Psychologists can work in clinical, educational and industrial-organizational settings to offer insight and support on individual or group levels.
Social Worker
Median Annual Salary: $58,380 Minimum Required Education: Bachelor’s degree, but usually a master’s degree in psychology or a related field Job Overview: Social workers provide individuals, groups and families with the support they need to navigate the problems they encounter in their everyday lives. This support can take the form of helping a family receive food stamps, getting a battered spouse into a domestic abuse shelter or providing a student who is suffering from depression with mental health counseling.
Substance Abuse, Behavioral Disorder or Mental Health Counselor
Median Annual Salary: $53,710 Minimum Required Education: Bachelor’s degree in psychology or a related field Job Overview: Substance abuse, behavioral disorder and mental health counselors provide education and training on how to prevent and treat problematic behaviors related to alcoholism, substance abuse and addiction. They also provide support to individuals who are dealing with depression and other mental health issues.
Human Resources Specialist
Median Annual Salary: $67,650 Minimum Required Education: Bachelor’s degree in human resources or a related field Job Overview: Human resources specialists help organizations manage employees from the recruitment and hiring phase to training and development and retention and retirement. Human resources specialists ensure that employers and employees are in compliance with labor laws and company policies and also help arbitrate and settle disputes and grievances.
Registered Nurse
Median Annual Salary: $86,070 Minimum Required Education: Associate in nursing , some employers may require a Bachelor of Science in Nursing Job Overview: Registered nurses provide critical care to patients in hospitals and other healthcare settings. Nurses also provide education and training on health issues to help prevent negative health outcomes in the community. Holders of a bachelor’s degree in psychology can either take an accelerated undergraduate nursing program or enroll in a master’s program that accepts the clinical hours of a psychology program, internship or job.
School and Career Counselor and Advisor
Median Annual Salary: $61,710 Minimum Required Education: Master’s in counseling psychology or a master’s in school counseling Job Overview: Working primarily in K-12 schools and colleges and universities, school and career counselors provide students with the academic and personal support they need to do well in their classes. School counselors can connect students with academic tutors and provide them with guidance on the courses they need to graduate.
Career counselors can help high school and college students who need to work outside of school balance their school and work schedules while maintaining an eye on long-term career goals. Counselors can also provide students with support when facing social or behavioral challenges.
Should You Earn a Degree in Psychology Online?
Degrees earned from online programs are just as reputable as degrees earned from in-person programs as long as they are from accredited universities and psychology departments. The most important factor in deciding on whether to earn your degree online is what type of learning format best suits your learning style and day-to-day scheduling needs.
You should also consider whether an online program offers networking, internship and group project opportunities that might only be available in in-person settings.
Featured Online Schools
Learn about start dates, transferring credits, availability of financial credit and much more by clicking 'Visit Site'
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Psychology Degrees
Are psychology degrees worth it.
Yes. You cannot become a licensed psychologist, a clinical social worker or a certified mental health therapist without a formal degree. While you may not need a bachelor’s degree in psychology to earn an advanced degree in psychology, it helps. At a minimum, though, you need a bachelor’s degree to pursue a graduate degree in psychology or a related field.
What degree is best for psychology?
The best degree depends on your career goals because psychology is such a broad field. While a bachelor’s degree in psychology will cover many areas, a bachelor’s degree in sociology or social work may be more suitable for laying the foundation for an advanced degree more closely aligned to your desired career.
However, if you want to be a licensed psychologist, a bachelor’s degree in psychology will prepare you for the coursework you will need to complete in graduate school.
Are psychology degrees difficult?
Psychology degrees are just as challenging to earn as other bachelor’s degrees that combine the social and natural sciences with the humanities. However, a psychology degree requires more math- and science-intensive courses than majors such as social work and sociology. Those who prefer qualitative analysis over quantitative analysis should reconsider majoring in psychology.
What grades do I need to study psychology?
Generally speaking, the higher your GPA, the stronger your chances are of being accepted into the university and program of your choice. Research the requirements of the programs in which you are interested. More competitive programs may require certain minimum grades in psychology, biology and mathematics classes.
- Best Online Master’s in Counseling
- Best Master's In ABA Online Degrees
- Best Online Master’s In Counseling Psychology
- Best Online Psychology Degrees
- Best Online Psychology Master’s Degrees
- Best Online Psy.D. Programs
- Best Online Counseling Degrees
- How To Become A Counseling Psychologist
- Careers In Psychology
- What Can You Do With An Associate Degree In Psychology?
- Earning An Online Bachelor’s Degree In Counseling
- CACREP Accreditation
- How Much Does A Psychologist Make?
- Psychology BA vs BS Degree
- Psychology Degrees, Specializations And Career Paths
- Psychotherapist Vs. Psychologist
- Psy.D. Vs. Ph.D.: Which Is The Right Fit For You?
- Sociology Vs. Psychology

Best Online Doctorates In Psychology Of 2024
Best Online Ph.D. In Organizational Psychology Programs Of 2024
Best Online Ph.D.s In Counseling Of 2024
How To Become A Psychiatrist: A Step-By-Step Guide
Best Online Associate Degrees In Psychology Of 2024

Best Online MFT Programs Of 2024
With more than two decades of experience in higher education, cultural criticism and politics, Horacio Sierra's writing and public speaking aims to demystify higher education and promote the democratic values of the arts and humanities.

- Helpful Resources
- Graduate Advisors & Plan Codes
- Graduate Student Employment
- Freqently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Graduation Information
- Diploma Orders
- Transcripts
- Arts and Letters
- Fowler College of Business
- Engineering
- Graduate Studies
- Health and Human Services
- SDSU Library
- Professional Studies and Fine Arts
- Weber Honors College
- SDSU Georgia
- SDSU Global Campus
- SDSU Imperial Valley
- SDSU Mission Valley
Current Students
Dr.ph and ed.d. dissertation publication steps.
First, please see the Doctoral Programs page for very important information.
- Dr.PH and Ed.D. students must publish their dissertation at SDSU.
- Publication deadlines are set by the College of Graduate Studies (CGS) in consultation with the Graduate Council and Montezuma Publishing. See below for deadlines.
- As of May 2020, all official SDSU communications must use official SDSU emails . The form requires being logged into your SDSU email account.
- Completed DrPH5 or EDD5
- Completed Dissertation Signature Page
- Certificate of Completion of the Survey of Earned Doctorates from sedsurvey.org
- Completed Dissertation
- Within five (5) business days of submitting the form, the doctoral program specialist < [email protected] > in the CGS will evaluate your academic record and submitted documents then will send the dissertation and associated documents to Montezuma Publishing (MP). An email will be sent to you, your doctoral program director, doctoral program coordinator, and MP informing everyone that your documents have been approved and moved forward.
- Respond promptly to MP’s requests for submission payment, any required revisions, and the final publication payment. MP will inform CGS once you have successfully published. Dissertation publication is a degree requirement and the dissertation is not “published” until final payment is made.
- If you have any questions please consult with your SDSU doctoral director .
Dr.PH and Ed.D. Dissertation Deadlines
Below are the Dr.PH and Ed.D. dissertation deadlines by academic year. Please consult with your committee chair and doctoral program director to ensure that you will meet your targeted deadlines.

Welcome to SDSU
- Tin tức & bài viết
- Văn phòng Find nearest IDP offices IDP Australia IDP Bahrain IDP Bangladesh IDP Cambodia IDP Canada IDP China IDP Egypt IDP Ghana IDP Hong Kong IDP India IDP Indonesia IDP Iran IDP Jordan IDP Kenya IDP Korea IDP Kuwait IDP Lebanon IDP Malaysia IDP Mauritius IDP Middle East IDP Nepal IDP New Zealand IDP Nigeria IDP Oman IDP Pakistan IDP Philippines IDP Saudi Arabia IDP Singapore IDP Sri Lanka IDP Taiwan IDP Thailand IDP Turkey IDP UAE IDP Global IDP Corporate
- Vietnamese Vietnamese English
- Các bước để du học
- Tại sao nên đi du học?
- Học ở đâu và học ngành gì?
- Làm thế nào để nộp hồ sơ?
- Sau khi nhận thư mời nhập học
- Chuẩn bị lên đường
- Sự kiện và hỗ trợ cho tân du học sinh khi đến nơi
- Du học Canada
- Du học Ireland
- Du học New Zealand
- Tìm khóa học
- Tư vấn khóa học
- Các khóa học có tính năng Fastlane
- Tìm kiếm học bổng
- Xếp hạng các trường Đại Học -THE
- Xếp hạng các trường Đại Học - CUG
- IELTS là gì?
- Đăng ký thi IELTS
- Lịch thi IELTS
- Lệ phí thi IELTS
- Thi thử IELTS
- Chương trình ưu đãi IELTS
- Tải các mẫu đơn IELTS
- Các câu hỏi thường gặp IELTS
- Dịch vụ sinh viên
- Chuyển tiền
- Bảo hiểm y tế dành cho du học sinh
- Dịch vụ ngân hàng dành cho du học sinh
- Mạng di động
- Dịch vụ giám hộ và phúc lợi xã hội
- Giới thiệu về IDP
- Lịch sử hình thành
- Tại sao chọn IDP
- Chính sách bảo mật
- Tìm kiếm văn phòng gần nhất
- Find nearest IDP offices
- IDP Australia
- IDP Bahrain
- IDP Bangladesh
- IDP Cambodia
- IDP Hong Kong
- IDP Indonesia
- IDP Lebanon
- IDP Malaysia
- IDP Mauritius
- IDP Middle East
- IDP New Zealand
- IDP Nigeria
- IDP Pakistan
- IDP Philippines
- IDP Saudi Arabia
- IDP Singapore
- IDP Sri Lanka
- IDP Thailand
- IDP Corporate
- Trình chuyển đổi ngôn ngữ
- English - US
From inspiring a global mindset to enhancing your career prospects, studying abroad opens doors for a world of opportunities.
Lost in a maze of choices and don't know where to begin? IDP helps you navigate study abroad options with ease.
Now that you’ve shortlisted your dream course and university, get a head start with our expert tools and support to fast-track your application process.
Got an offer from a university you applied to? Now, let's help you take the next steps towards making your study abroad dream a reality.
Ready to embark on your study abroad adventure? Let’s help set you up for the journey ahead.
Touch down in your new home and pave your own path to success. Learn how to make the most of your study abroad experience.

- IDP Education /
Education systems – PhD
Trên trang này, the traditional phd (pure research), the new route phd, part-time phd, professional doctorate in business administration, dba, professional doctorate in education, edd.
Chủ đề được đề cập
- 8 June 2024
A PhD is generally regarded as the highest degree that can be granted by institutions of higher education. Students are required to conduct original research and write a thesis, making a major contribution to their field of study, demonstrating that they possess the abilities expected of a PhD. The title used with this degree, duration of study and requirements for the doctorate vary by country. We provide PhD application services for the UK, USA, Australia, Ireland, Canada, and other countries. We have listed some common types of doctoral degrees below.
The traditional PhD, focused on research, is the most common but is also often seen as quite daunting as one needs to find a suitable supervisor to ensure that you can successfully complete the programme. To do this, you need to write a proposal which will include a literature review, hypothesis, methodology and indicate what original contribution you believe this research will make. The proposal is hugely important as it will demonstrate your understanding of the field and will show if you are sufficiently prepared to take on a PhD programme. The traditional PhD usually takes around 3 years to complete but can take longer depending on your field of study and difficulty of research.
The most difficult parts of applying for a PhD programme are writing a research proposal and finding a university and supervising professor that suit your area of research. But don’t worry, IDP’s advisors have decades of experience in assisting with PhD applications, we can guide you through the process!
Established in 2001, this type of programme was designed to cater for overseas students that have not been exposed to the same level of research as their UK counterparts. The new route programme (or integrated PhD) is completed over 4 years where students will have in-depth tuition on their subject and will also be taught a variety of research techniques.
In some instances, students are allowed to go to the UK for the 1st year of their PhD and are then allowed to return to their home country to collect data. This is often done at the discretion of the professor and is determined by the nature of the data that needs to be collected. Students will need to return to the UK to analyse the data and write up their thesis under the guidance of the professor.
This programme is designed for people that have a lot of experience in the field of business and management and helps them to develop practical skills and ideas that can be applied to management theory. The programme is academically demanding but differs from the traditional PhD in that it does not prepare candidates to become research active or to lecture in the field of management.
This works in a similar way to the DBA in that it allows experienced individuals to examine and research issues in the field of education and allows them to develop new practical skills.
Giải quyết mọi nhu cầu du học chỉ với một tài khoản
Bạn hãy tạo hồ sơ để khám phá nhiều tính năng tuyệt vời, bao gồm: gợi ý dành riêng cho bạn, xét duyệt hồ sơ nhanh chóng và nhiều hơn thế nữa!
Những bài viết liên quan

7 Unique courses to study in New Zealand
- December 20, 2024
- 10 min read

Understanding the CGPA Grading System
- October 29, 2024

- June 08, 2024

Read this before you use ChatGPT to write your university application cover letter
- May 28, 2024

7 Ways A Business Degree Can Be Your Global Ticket To A Successful Career

Never run out of topics again – stay connected with your loved ones while studying abroad

Pursuing a degree in political and social science abroad: what you must know

7 Reasons Why You Should Get A Postgraduate Degree In The UK
- May 27, 2024

Pursuing a degree in history abroad: what you must know

Masters in the UK
- May 25, 2024
Book an appointment
We'll call you back
Environmental Science and Engineering, PhD
Environmental Science and Engineering is an interdisciplinary program with the common goal of understanding, predicting, and responding to human-induced environmental change. You will learn that addressing environmental issues requires perspectives from a diverse set of scientific disciplines, including atmospheric physics and chemistry, oceanography, glaciology, hydrology, geophysics, ecology, and biogeochemistry.
Your research will be strongly interdisciplinary, with many connections to Earth and Planetary Sciences and other science and policy programs at Harvard. You will learn to think about environmental processes in an integrated fashion, preparing you to manage the environmental challenges we face.
Examples of projects current and past students have worked on include building bio-inspired robotics and developing personalized exosuits to assist in real-world walking.
APPLY NOW >
Environmental Science & Engineering Degree
Harvard School of Engineering offers a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D) degree in Engineering Sciences - Environmental Science & Engineering , conferred through the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (Harvard Griffin GSAS). Prospective students apply through the Harvard Griffin GSAS. In the online application, select “Engineering and Applied Sciences” as your program choice and select "PhD Engineering Sciences: Environmental Science and Engineering" in the area of study menu.
The Environmental Science & Engineering program does not offer an independent Masters Degree.
Environmental Science & Engineering PhD Career Paths
Graduates of the program have gone on to a range of careers in organizations like the World Bank, the Earth System Research Laboratory at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and Tesla. Others have positions in academia at Georgia Tech, Oregon State University, and University of Rochester. More generally, students with a PhD in Environmental Science and Engineering can go on to careers in academic research/teaching, consulting, law, energy, policy, government, or jobs in the private sector. Read more about some of the our Environmental Science and Engineering alumni .
Admissions & Academic Requirements
Please review the admissions requirements and other information before applying. Our website also provides admissions guidance , program-specific requirements , and a PhD program academic timeline .
Academic Background
Our graduate students come to Harvard with diverse undergraduate preparations. Some have studied environmental fields such as meteorology oceanography, atmospheric chemistry, or biogeochemistry. Many others have little prior training in environmental science, but enter with backgrounds in applied math, biology, chemistry, engineering or physics.
Standardized Tests
GRE General: Not Accepted
Environmental Science & Engineering Faculty & Research Areas
View a list of our Environmental Science & Engineering faculty and Environmental Science & Engineering affiliated research areas , Please review our faculty members’ research pages to learn about specific opportunities and how they match with your interests. Please note that faculty members listed as “Affiliates" or "Lecturers" cannot serve as the primary research advisor.
Environmental Science & Engineering Centers & Initiatives
View a list of the research centers & initiatives at SEAS and the Environmental Science & Engineering faculty engagement with these entities .
Graduate Student Clubs
Graduate student clubs and organizations bring students together to share topics of mutual interest. These clubs often serve as an important adjunct to course work by sponsoring social events and lectures. Graduate student clubs are supported by the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin School of Arts and Sciences. Explore the list of active clubs and organizations .
Funding and Scholarship
Learn more about financial support for PhD students.
- How to Apply
Learn more about how to apply or review frequently asked questions for prospective graduate students.
In Environmental Science & Engineering
- Undergraduate Engineering at Harvard
- Concentration Requirements
- How to Declare
- Who are my Advisors?
- Sophomore Forum
- ABET Information
- Senior Thesis
- Research for Course Credit (ES 91R)
- AB/SM Information
- Peer Concentration Advisors (PCA) Program
- Student Organizations
- PhD Timeline
- PhD Model Program (Course Guidelines)
- Qualifying Exam
- Committee Meetings
- Committee on Higher Degrees
- Guidelines for Advisor-Student Discussions
- Research Interest Comparison
- Collaborations
- Cross-Harvard Engagement
- Clubs & Organizations
- Centers & Initiatives
- Alumni Stories

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Ph.D. program, in contrast, emphasizes research over practice. These programs incorporate more theory, research, and policy-focused courses. Students might take classes in educational research, educational psychology, and learning theory. Focus: An Ed.D. focuses on education practice, while a Ph.D. focuses on research.
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a professional degree designed for practitioners pursuing educational leadership roles. A PhD in education, on the other hand, is designed to prepare graduates for research and teaching roles. "With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based ...
Finally, Ed.D. degree programs are typically shorter than other doctoral degrees in education, with programs lasting anywhere from two to four years in length. Ph.D. in Education programs are more likely to be full-time residential programs which require students to leave full-time jobs to pursue.
The EdD and PhD are both terminal degrees that make teachers and educators experts in their fields. A good job outlook and growth projections make a doctorate degree worth the time and money. Picking Between an EdD or PhD In Education Program. The curriculum and job prospects of an EdD and PhD program are different.
An EdD primarily prepares graduates to become leaders and strategists in the education field—for example, as superintendents, deans, provosts, and school district officials—while a PhD is more tailored to preparing graduates for instructional and research roles in education and higher education, for example, as professors and researchers.
For example, an EdD career path would be more aligned with becoming a university dean or director of research, while those pursuing a PhD would likely choose a career as a college professor or research scholar2. The average program lengths also differ. The average time to complete a PhD in education is 4-7 years, whereas an EdD can take 3-5 ...
Doctor of Education (EdD) vs. PhD in Education. Earning an advanced degree can be both a life achievement and an effective tool for career advancement. But even with closely related areas, like the EdD vs PhD in education, you can find more than a few significant differences.
Flexible Time-Frame: Doctor of Education programs tend to be much shorter than Ph.D. in Education programs. The quickest paths are 2-Year Ed.D. Programs, but even standard Ed.D. programs can be finished in 3 years. If you need extra time, many universities will allow you up to 7 years to complete your doctorate.
In essence, the primary difference between a Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) and a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) is that an Ed.D. focuses on practical skills, while a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) focuses on theory and research. Those pursuing an Ed.D. typically want to work in education leadership roles, so they perform hands-on work while pursuing ...
An Ed.D. and a PhD in Education have key aspects in common. Each degree develops leadership within a candidate and equips them to understand both research and statistics. Both degrees are terminal (as high as a student can go in that academic path). Both focus on ways to enhance professional knowledge in different environments.
An EdD, also known as a Doctor of Education, is a professional doctorate focused on the practice of education. Both on-campus and online EdD programs provide doctoral students with the tools and skills necessary to implement research-based practices in the classroom. EdD programs are primarily designed to take existing research and apply it to ...
A Doctor of Education (EdD) is a professional degree designed for practitioners pursuing educational leadership roles. A PhD in education, on the other hand, is designed to prepare graduates for research and teaching roles. "With a PhD, [students are] reviewing the research, seeing a gap in the literature, and generating new knowledge based ...
Longer duration to complete. Ph.D.s in Education usually require 90 credit hours to complete, compared to approximately 60 credit hours for an Ed.D. This means your degree will take longer to earn and will likely cost more than an Ed.D. Less competitive wages.
While there are many similarities between an EdD and a PhD, there are also some key differences. As the BLS points out for an EdD vs PhD, one of the main differences is that an EdD is geared more toward practical application or research, while a PhD is more focused on theoretical research. Another difference is that an EdD can typically be ...
3. More Program Options. There are far more Ph.D. programs in education than Ed.D. programs. Students desiring a Ph.D. in an education field (higher education, curriculum and instruction, educational policy, etc.) will have an easier time finding a degree program than those seeking strictly an Ed.D. More options means more opportunities in ...
EdD vs PhD in Education: What Are The Differences? The two doctorates are equal in academic value and rigor; however, the main difference between an EdD and a PhD is the approach to the practicality of the acquired skills. On one hand, an EdD is more project-based and is of applied nature. On the other hand, a PhD is more research-based and ...
EdD and PhD in Education programs are significant investments in time. Therefore, it is important to understand the amount of time each degree requires to determine which is better suited for your career goals. An EdD program will take around 3 to 5 years to complete, while a PhD in Education will typically require around 4 to 7 years to complete.
For example, a Ph.D. is research-intensive, while an Ed.D. is practitioner-based. The differences don't stop there — the number of credit hours, program length, and goal of student projects vary between the Ph.D. and Ed.D. as well. Consider the similarities and differences between the Ph.D. and Ed.D. to discover the best program for your ...
Ed.D. Ph.D. Lead positive change in local education. This program prepares education professionals for leadership positions in public or private education systems, including K-12 districts and community colleges. The degree is designed for experienced educators who want to perform and apply research to address practical problems relevant to ...
The University of Idaho College of Education, Health and Human Sciences offers three doctoral degree programs. Students who are pursuing a doctoral degree in education have various areas of specialization to choose from. Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Doctor of Athletic Training (D.A.T.)
Ed.D. programs in Educational Psychology, Counseling, Counselor Education, and related fields are doctoral-level degrees that explore the intersection of psychology & education. These types of doctorates are geared toward working professionals who already hold a master's degree or Ed.S. and have prior experience in their field.
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
Doctorate of Education Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. in Education - The differences between an Ed.D. and a Ph.D. can influence your cost due to the amount of time spent earning the degree. An Ed.D. may take 3-5 years, and a Ph.D. will take longer. Doctorate of Psychology Psy.D. vs. Ph.D.
1. Trevecca Nazarene University. Nashville, TN. Trevecca Nazarene University ranked No. 3 among Fortune's best online doctorate in education (Ed.D.) programs in 2022. The school doesn't ...
PhD & EdD Procedures. DAT Procedures. The University of Idaho awards the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in recognition of high achievement in scholarly and research activity. The degree of Doctor of Education is granted for high scholarly attainment and in recognition of the completion of academic preparation for professional practice.
Social Worker. Median Annual Salary: $58,380. Minimum Required Education: Bachelor's degree, but usually a master's degree in psychology or a related field. Job Overview: Social workers ...
Online Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) degrees are rising across the board. According to Fortune, the best online Ed.D. programs have seen a steady upward trend of enrollment and completion rates due to the promising value the degree holds in the field of education. Unlike a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) degree, an Ed.D. tells the world that you have obtained the necessary education to transform ...
Below are the Dr.PH and Ed.D. dissertation deadlines by academic year. Please consult with your committee chair and doctoral program director to ensure that you will meet your targeted deadlines. Welcome to SDSU. Apply Visit Get Info. youtube; facebook; instagram; tiktok; 619-594-5200 5500 Campanile Drive San Diego, CA 92182. Maps;
The traditional PhD (pure research) The traditional PhD, focused on research, is the most common but is also often seen as quite daunting as one needs to find a suitable supervisor to ensure that you can successfully complete the programme. To do this, you need to write a proposal which will include a literature review, hypothesis, methodology ...
Environmental Science and Engineering, PhD. Environmental Science and Engineering is an interdisciplinary program with the common goal of understanding, predicting, and responding to human-induced environmental change. You will learn that addressing environmental issues requires perspectives from a diverse set of scientific disciplines ...