

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
Thesis and Dissertation Appendicies – What to Include
- By DiscoverPhDs
- August 12, 2020

An appendix is a section at the end of a dissertation that contains supplementary information. An appendix may contain figures, tables, raw data, and other additional information that supports the arguments of your dissertation but do not belong in the main body.
It can be either a long appendix or split into several smaller appendices. Each appendix should have its own title and identification letters, and the numbering for any tables or figures in them should be reset at the beginning of each new appendix.
Purpose of an Appendix
When writing the main body of your dissertation, it is important to keep it short and concise in order to convey your arguments effectively.
Given the amount of research you would have done, you will probably have a lot of additional information that you would like to share with your audience.
This is where appendices come in. Any information that doesn’t support your main arguments or isn’t directly relevant to the topic of your dissertation should be placed in an appendix.
This will help you organise your paper, as only information that adds weight to your arguments will be included; it will also help improve your flow by minimising unnecessary interruptions.
Note, however, that your main body must be detailed enough that it can be understood without your appendices. If a reader has to flip between pages to make sense of what they are reading, they are unlikely to understand it.
For this reason, appendices should only be used for supporting background material and not for any content that doesn’t fit into your word count, such as the second half of your literature review .
What to Include in a Dissertation Appendix
A dissertation appendix can be used for the following supplementary information:
Research Results
There are various ways in which research results can be presented, such as in tables or diagrams.
Although all of your results will be useful to some extent, you won’t be able to include them all in the main body of your dissertation. Consequently, only those that are crucial to answering your research question should be included.
Your other less significant findings should be placed in your appendix, including raw data, proof of control measures, and other supplemental material.
Details of Questionnaires and Interviews
You can choose to include the details of any surveys and interviews you have conducted. This can include:
- An interview transcript,
- A copy of any survey questions,
- Questionnaire results.
Although the results of your surveys, questionnaires or interviews should be presented and discussed in your main text, it is useful to include their full form in the appendix of a dissertation to give credibility to your study.
Tables, Figures and Illustrations
If your dissertation contains a large number of tables, figures and illustrative material, it may be helpful to insert the less important ones in your appendix. For example, if you have four related datasets, you could present all the data and trend lines (made identifiable by different colours) on a single chart with a further breakdown for each dataset in your appendix.
Letters and Correspondence
If you have letters or correspondence, either between yourself and other researchers or places where you sought permission to reuse copyrighted material, they should be included here. This will help ensure that your dissertation doesn’t become suspected of plagiarism.
List of Abbreviations
Most researchers will provide a list of abbreviations at the beginning of their dissertation, but if not, it would be wise to add them as an appendix.
This is because not all of your readers will have the same background as you and therefore may have difficulty understanding the abbreviations and technical terms you use.
Note: Some researchers refer to this as a ‘glossary’, especially if it is provided as an appendix section. For all intended purposes, this is the same as a list of abbreviations.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How to Format a Dissertation Appendix
In regards to format, you can include one lengthy appendix or structure it into several smaller appendices.
Although the choice is yours, it is usually better to opt for several different appendices as it allows you to organise your supplementary information into different categories based on what they are.
The following guidelines should be observed when preparing your dissertation appendices section:
- Each appendix should start on a new page and be given a unique title and identifying letter, such as “Appendix A – Raw Data”. This allows you to more easily refer to appendix headings in the text of your main body should you need to.
- Each appendix should have its own page numbering system, comprising the appendix identification letter and the corresponding page number. The appendix identification letter should be reset for each appendix, but the page number should remain continuous. For example, if ‘Appendix A’ has three pages and ‘Appendix B’ two pages, the page numbers should be A-1, A-2, A-3, B-4, B-5.
- The numbering of tables and figures should be reset at the beginning of each new appendix. For example, if ‘Appendix A’ contains two tables and ‘Appendix B’ one table, the table number within Appendix B should be ‘Table 1’ and not ‘Table 3’.
- If you have multiple appendices instead of a single longer one, insert a ‘List of Appendices’ in the same way as your contents page.
- Use the same formatting (font size, font type, spacing, margins, etc.) as the rest of your report.
Example of Appendices
Below is an example of what a thesis or dissertation appendix could look like.
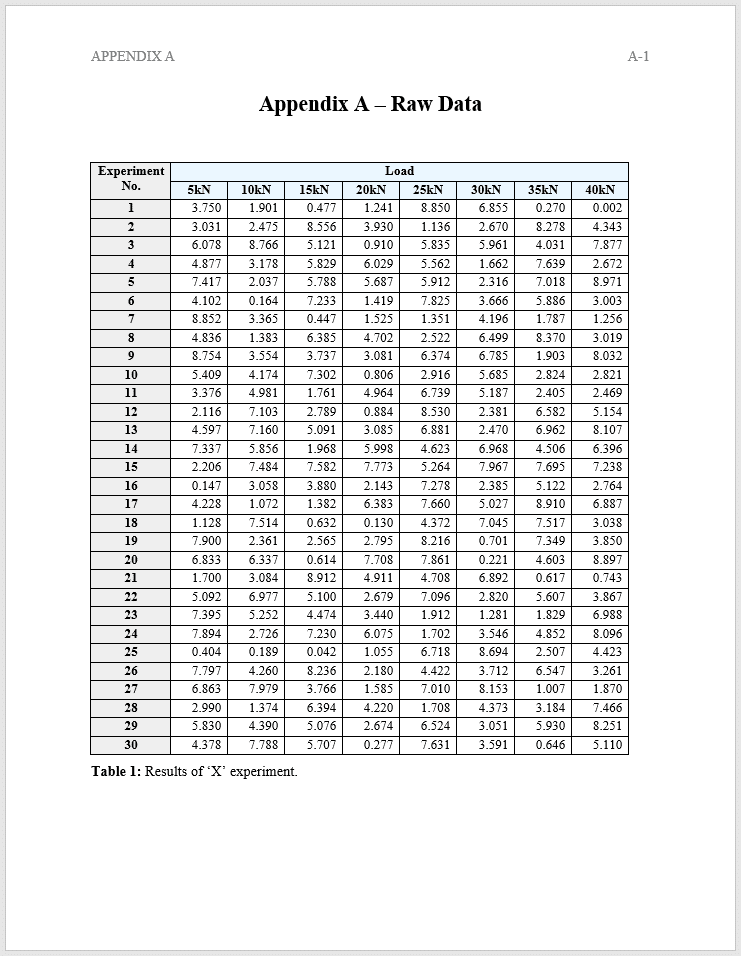
Referring to an Appendix In-Text
You must refer to each appendix in the main body of your dissertation at least once to justify its inclusion; otherwise, the question arises as to whether they are really needed.
You can refer to an appendix in one of three ways:
1. Refer to a specific figure or table within a sentence, for example: “As shown in Table 2 of Appendix A, there is little correlation between X and Y”.
2. Refer to a specific figure or table in parentheses, for example: “The results (refer to Table 2 of Appendix A) show that there is little correlation between X and Y”.
3. Refer to an entire appendix, for example: “The output data can be found in Appendix A”.
Appendices vs Appendixes
Both terms are correct, so it is up to you which one you prefer. However, it is worth noting that ‘appendices’ are used more frequently in the science and research community, so we recommend using the former in academic writing if you have no preferences.
Where Does an Appendix Go?
For a dissertation, your appendices should be inserted after your reference list.
Some people like to put their appendices in a standalone document to separate it from the rest of their report, but we only recommend this at the request of your dissertation supervisor, as this isn’t common practice.
Note : Your university may have its own requirements or formatting suggestions for writing your dissertation or thesis appendix. As such, make sure you check with your supervisor or department before you work on your appendices. This will especially be the case for any students working on a thesis.

Being a new graduate teaching assistant can be a scary but rewarding undertaking – our 7 tips will help make your teaching journey as smooth as possible.

Learn about defining your workspace, having a list of daily tasks and using technology to stay connected, all whilst working from home as a research student.

Reference management software solutions offer a powerful way for you to track and manage your academic references. Read our blog post to learn more about what they are and how to use them.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

The title page of your dissertation or thesis conveys all the essential details about your project. This guide helps you format it in the correct way.
Thinking about applying to a PhD? Then don’t miss out on these 4 tips on how to best prepare your application.

Dr Roberts gained her PhD from Duke University in 2014 in the field of biomedical engineering. She now runs her own business named Personal Finance for PhDs.

Julia’s in her final year of her PhD at University College London. Her research is helping to better understand how Alzheimer’s disease arises, which could lead to new successful therapeutics.
Join Thousands of Students
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
Published on 15 August 2022 by Kirsten Dingemanse and Tegan George. Revised on 25 October 2022.
An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper , dissertation , or thesis without making your final product too long.
Appendices help you provide more background information and nuance about your topic without disrupting your text with too many tables and figures or other distracting elements.
We’ve prepared some examples and templates for you, for inclusions such as research protocols, survey questions, and interview transcripts. All are worthy additions to an appendix. You can download these in the format of your choice below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What is an appendix in a research paper, what to include in an appendix, how to format an appendix, how to refer to an appendix, where to put your appendices, other components to consider, appendix checklist.
In the main body of your research paper, it’s important to provide clear and concise information that supports your argument and conclusions . However, after doing all that research, you’ll often find that you have a lot of other interesting information that you want to share with your reader.
While including it all in the body would make your paper too long and unwieldy, this is exactly what an appendix is for.
As a rule of thumb, any detailed information that is not immediately needed to make your point can go in an appendix. This helps to keep your main text focused but still allows you to include the information you want to include somewhere in your paper.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
An appendix can be used for different types of information, such as:
- Supplementary results : Research findings are often presented in different ways, but they don’t all need to go in your paper. The results most relevant to your research question should always appear in the main text, while less significant results (such as detailed descriptions of your sample or supplemental analyses that do not help answer your main question), can be put in an appendix.
- Statistical analyses : If you conducted statistical tests using software like Stata or R, you may also want to include the outputs of your analysis in an appendix.
- Further information on surveys or interviews : Written materials or transcripts related to things such as surveys and interviews can also be placed in an appendix.
You can opt to have one long appendix, but separating components (like interview transcripts, supplementary results, or surveys) into different appendices makes the information simpler to navigate.
Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Always start each appendix on a new page.
- Assign it both a number (or letter) and a clear title, such as ‘Appendix A. Interview transcripts’. This makes it easier for your reader to find the appendix, as well as for you to refer back to it in your main text.
- Number and title the individual elements within each appendix (e.g., ‘Transcripts’) to make it clear what you are referring to. Restart the numbering in each appendix at 1.
It is important that you refer to each of your appendices at least once in the main body of your paper. This can be done by mentioning the appendix and its number or letter, either in parentheses or within the main part of a sentence. It is also possible to refer to a particular component of an appendix.
Appendix B presents the correspondence exchanged with the fitness boutique. Example 2. Referring to an appendix component These results (see Appendix 2, Table 1) show that …
It is common to capitalise ‘Appendix’ when referring to a specific appendix, but it is not mandatory. The key is just to make sure that you are consistent throughout your entire paper, similarly to consistency in capitalising headings and titles in academic writing.
However, note that lowercase should always be used if you are referring to appendices in general. For instance, ‘The appendices to this paper include additional information about both the survey and the interviews.’
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The simplest option is to add your appendices after the main body of your text, after you finish citing your sources in the citation style of your choice . If this is what you choose to do, simply continue with the next page number. Another option is to put the appendices in a separate document that is delivered with your dissertation.
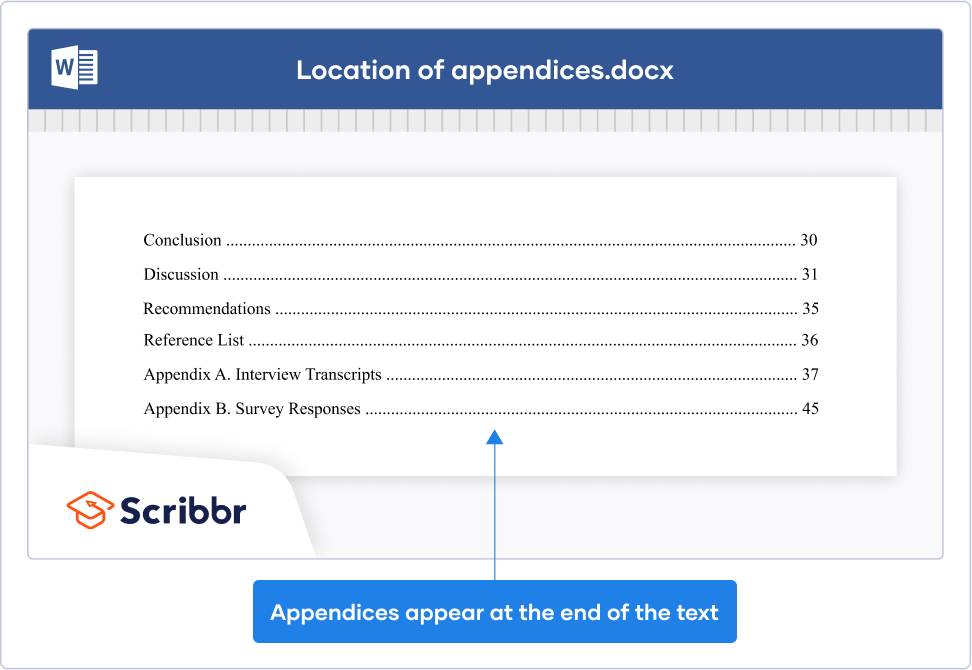
Remember that any appendices should be listed in your paper’s table of contents .
There are a few other supplementary components related to appendices that you may want to consider. These include:
- List of abbreviations : If you use a lot of abbreviations or field-specific symbols in your dissertation, it can be helpful to create a list of abbreviations .
- Glossary : If you utilise many specialised or technical terms, it can also be helpful to create a glossary .
- Tables, figures and other graphics : You may find you have too many tables, figures, and other graphics (such as charts and illustrations) to include in the main body of your dissertation. If this is the case, consider adding a figure and table list .
Checklist: Appendix
All appendices contain information that is relevant, but not essential, to the main text.
Each appendix starts on a new page.
I have given each appendix a number and clear title.
I have assigned any specific sub-components (e.g., tables and figures) their own numbers and titles.
My appendices are easy to follow and clearly formatted.
I have referred to each appendix at least once in the main text.
Your appendices look great! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Dingemanse, K. & George, T. (2022, October 25). Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 10 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/appendix/
Is this article helpful?
Kirsten Dingemanse
Other students also liked, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, dissertation title page, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- How to create an APA Style appendix
How to Create an APA Style Appendix | Format & Examples
Published on October 16, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 9, 2022.
An appendix is a section at the end of an academic text where you include extra information that doesn’t fit into the main text. The plural of appendix is “appendices.”
In an APA Style paper, appendices are placed at the very end, after the reference list .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Do i need an appendix, appendix format example, organizing and labeling your appendices, frequently asked questions.
You don’t always need to include any appendices. An appendix should present information that supplements the reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to the argument of your paper . Essential information is included in the main text.
For example, you might include some of the following in an appendix:
- Full transcripts of interviews you conducted (which you can quote from in the main text)
- Documents used in your research, such as questionnaires , instructions, tests, or scales
- Detailed statistical data (often presented in tables or figures )
- Detailed descriptions of equipment used
You should refer to each appendix at least once in the main text. If you don’t refer to any information from an appendix, it should not be included.
When you discuss information that can be found in an appendix, state this the first time you refer to it:
Note that, if you refer to the same interviews again, it’s not necessary to mention the appendix each time.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

The appendix label appears at the top of the page, bold and centered. On the next line, include a descriptive title, also bold and centered.
The text is presented in general APA format : left-aligned, double-spaced, and with page numbers in the top right corner. Start a new page for each new appendix.
The example image below shows how to format an APA Style appendix.
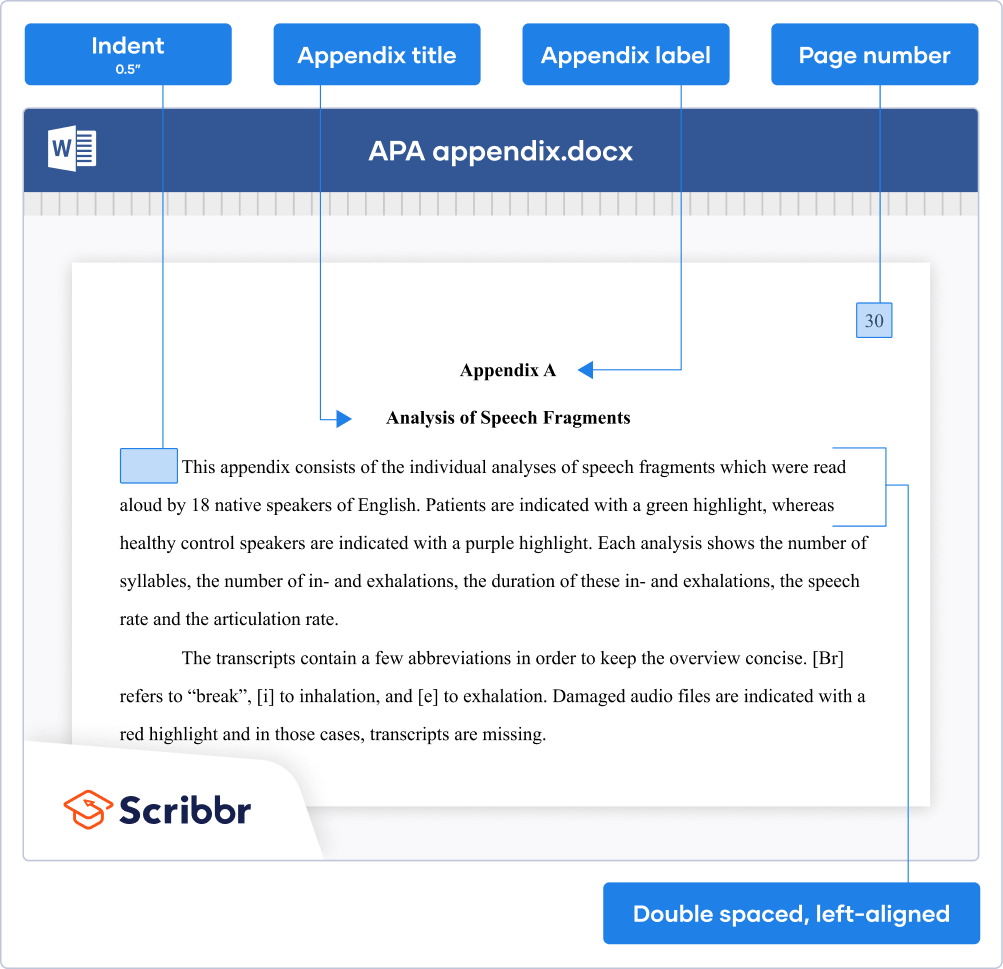
If you include just one appendix, it is simply called “Appendix” and referred to as such in-text:
When more than one appendix is included, they are labeled “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on.
Present and label your appendices in the order they are referred to in the main text.
Labeling tables and figures in appendices
An appendix may include (or consist entirely of) tables and/or figures . Present these according to the same formatting rules as in the main text.
Tables and figures included in appendices are labeled differently, however. Use the appendix’s letter in addition to a number. Tables and figures are still numbered separately and according to the order they’re referred to in the appendix.
For example, in Appendix A, your tables are Table A1, Table A2, etc; your figures are Figure A1, Figure A2, etc.
The numbering restarts with each appendix: For example, the first table in Appendix B is Table B1; the first figure in Appendix C is Figure C1; and so on. If you only have one appendix, use A1, A2, etc.
If you want to refer specifically to a table or figure from an appendix in the main text, use the table or figure’s label (e.g. “see Table A3”).
If an appendix consists entirely of a single table or figure, simply use the appendix label to refer to the table or figure. For example, if Appendix C is just a table, refer to the table as “Appendix C,” and don’t add an additional label or title for the table itself.
An appendix contains information that supplements the reader’s understanding of your research but is not essential to it. For example:
- Interview transcripts
- Questionnaires
- Detailed descriptions of equipment
Something is only worth including as an appendix if you refer to information from it at some point in the text (e.g. quoting from an interview transcript). If you don’t, it should probably be removed.
Appendices in an APA Style paper appear right at the end, after the reference list and after your tables and figures if you’ve also included these at the end.
When you include more than one appendix in an APA Style paper , they should be labeled “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on.
When you only include a single appendix, it is simply called “Appendix” and referred to as such in the main text.
Yes, if relevant you can and should include APA in-text citations in your appendices . Use author-date citations as you do in the main text.
Any sources cited in your appendices should appear in your reference list . Do not create a separate reference list for your appendices.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, August 09). How to Create an APA Style Appendix | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/appendices/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, creating an apa style table of contents, how to format tables and figures in apa style, apa format for academic papers and essays, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
The Graduate College at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Appendix(es) (optional).
Refer to either the Sample (Straight Numbering) or Sample (Decimal Numbering) pages as you read through this section. Note: For the Appendices, you should use the same numbering style you chose for the Main Text.
The appendix is a section that is placed at the end of the thesis and may contain material such as tables, figures, maps, photographs, raw data, computer programs, musical examples, interview questions, sample questionnaires, CDs, and many other types of material.
- An appendix is considered a chapter equivalent and the appendix title should be formatted like a chapter title.
- Multiple appendices should be numbered A, B, C, and so on. Each appendix should be treated as a separate chapter equivalent and will therefore start on a new page.
- Page numbers used in the appendix must continue from the main text.
- As a best practice, include your IRB approval letter (if applicable) in an appendix.
- Do not include a curriculum vitae or author's biography in your thesis; the Graduate College no longer accepts these sections.
As part of the thesis, any appendix materials must be reviewed and approved by the director of research and committee.
The thesis or dissertation itself should be understandable without the supplemental appendix materials.
As part of the ETD submission, students may upload supplemental electronic files as part of their thesis or dissertation. These files are considered appendix items, and an appendix page must be included as part of the thesis and should be numbered accordingly. This page should include an appendix title, such as “Appendix A: Interview Transcriptions,” and a brief description of the material along with the name of the file in which the material is contained.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
Appendices within Manuscript
Appendices may be included as part of the manuscript. These typically appear after the Bibliography or References section.
- List the Appendices in the Table of Contents
- Do not restart page numbering for your Appendices. For example, if the last page of your Bibliography is 195, your first Appendix page number should be 196.
Appendices as Supplemental Files
Electronic or audiovisual data may be included as Supplemental Files in an ETD submission. Your committee should agree that the information contained in the supplemental files is of such a character that a medium other than text is necessary.
When uploading your manuscript to ProQuest, there is a place to upload Supplemental Files separate from the main PDF upload (see screen capture below).

- << Previous: Figures and Illustrations
- Next: IV. Using Previously Published Material >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 9:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- « Thesis & Dissertation Resources
- The Graduate School Home
- Introduction
- Copyright Page
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, Preface (optional)
- Table of Contents
- List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
- List of Abbreviations
- List of Symbols
Non-Traditional Formats
Font type and size, spacing and indentation, tables, figures, and illustrations, formatting previously published work.
- Internet Distribution
- Open Access
- Registering Copyright
- Using Copyrighted Materials
- Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Submission Steps
- Submission Checklist
- Sample Pages

II. Formatting Guidelines
All copies of a thesis or dissertation must have the following uniform margins throughout the entire document:
- Left: 1″ (or 1 1/4" to ensure sufficient room for binding the work if desired)
- Right: 1″
- Bottom: 1″ (with allowances for page numbers; see section on Pagination )
- Top: 1″
Exceptions : The first page of each chapter (including the introduction, if any) begins 2″ from the top of the page. Also, the headings on the title page, abstract, first page of the dedication/ acknowledgements/preface (if any), and first page of the table of contents begin 2″ from the top of the page.
Non-traditional theses or dissertations such as whole works comprised of digital, artistic, video, or performance materials (i.e., no written text, chapters, or articles) are acceptable if approved by your committee and graduate program. A PDF document with a title page, copyright page, and abstract at minimum are required to be submitted along with any relevant supplemental files.
Fonts must be 10, 11, or 12 points in size. Superscripts and subscripts (e.g., formulas, or footnote or endnote numbers) should be no more than 2 points smaller than the font size used for the body of the text.
Space and indent your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- The text must appear in a single column on each page and be double-spaced throughout the document. Do not arrange chapter text in multiple columns.
- New paragraphs must be indicated by a consistent tab indentation throughout the entire document.
- The document text must be left-justified, not centered or right-justified.
- For blocked quotations, indent the entire text of the quotation consistently from the left margin.
- Ensure headings are not left hanging alone on the bottom of a prior page. The text following should be moved up or the heading should be moved down. This is something to check near the end of formatting, as other adjustments to text and spacing may change where headings appear on the page.
Exceptions : Blocked quotations, notes, captions, legends, and long headings must be single-spaced throughout the document and double-spaced between items.
Paginate your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:
- Use lower case Roman numerals (ii, iii, iv, etc.) on all pages preceding the first page of chapter one. The title page counts as page i, but the number does not appear. Therefore, the first page showing a number will be the copyright page with ii at the bottom.
- Arabic numerals (beginning with 1, 2, 3, 4, etc.) start at chapter one or the introduction, if applicable. Arabic numbers must be included on all pages of the text, illustrations, notes, and any other materials that follow. Thus, the first page of chapter one will show an Arabic numeral 1, and numbering of all subsequent pages will follow in order.
- Do not use page numbers accompanied by letters, hyphens, periods, or parentheses (e.g., 1., 1-2, -1-, (1), or 1a).
- Center all page numbers at the bottom of the page, 1/2″ from the bottom edge.
- Pages must not contain running headers or footers, aside from page numbers.
- If your document contains landscape pages (pages in which the top of the page is the long side of a sheet of paper), make sure that your page numbers still appear in the same position and direction as they do on pages with standard portrait orientation for consistency. This likely means the page number will be centered on the short side of the paper and the number will be sideways relative to the landscape page text. See these additional instructions for assistance with pagination on landscape pages in Microsoft Word .

Format footnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- Footnotes must be placed at the bottom of the page separated from the text by a solid line one to two inches long.
- Begin at the left page margin, directly below the solid line.
- Single-space footnotes that are more than one line long.
- Include one double-spaced line between each note.
- Most software packages automatically space footnotes at the bottom of the page depending on their length. It is acceptable if the note breaks within a sentence and carries the remainder into the footnote area of the next page. Do not indicate the continuation of a footnote.
- Number all footnotes with Arabic numerals. You may number notes consecutively within each chapter starting over with number 1 for the first note in each chapter, or you may number notes consecutively throughout the entire document.
- Footnote numbers must precede the note and be placed slightly above the line (superscripted). Leave no space between the number and the note.
- While footnotes should be located at the bottom of the page, do not place footnotes in a running page footer, as they must remain within the page margins.
Endnotes are an acceptable alternative to footnotes. Format endnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- Always begin endnotes on a separate page either immediately following the end of each chapter, or at the end of your entire document. If you place all endnotes at the end of the entire document, they must appear after the appendices and before the references.
- Include the heading “ENDNOTES” in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the first page of your endnotes section(s).
- Single-space endnotes that are more than one line long.
- Number all endnotes with Arabic numerals. You may number notes consecutively within each chapter starting over with number 1 for the first note in each chapter, or you may number notes consecutively throughout the entire document.
- Endnote numbers must precede the note and be placed slightly above the line (superscripted). Leave no space between the number and the note.
Tables, figures, and illustrations vary widely by discipline. Therefore, formatting of these components is largely at the discretion of the author.
For example, headings and captions may appear above or below each of these components.
These components may each be placed within the main text of the document or grouped together in a separate section.
Space permitting, headings and captions for the associated table, figure, or illustration must be on the same page.
The use of color is permitted as long as it is consistently applied as part of the finished component (e.g., a color-coded pie chart) and not extraneous or unprofessional (e.g., highlighting intended solely to draw a reader's attention to a key phrase). The use of color should be reserved primarily for tables, figures, illustrations, and active website or document links throughout your thesis or dissertation.
The format you choose for these components must be consistent throughout the thesis or dissertation.
Ensure each component complies with margin and pagination requirements.
Refer to the List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations section for additional information.
If your thesis or dissertation has appendices, they must be prepared following these guidelines:

- Appendices must appear at the end of the document (before references) and not the chapter to which they pertain.
- When there is more than one appendix, assign each appendix a number or a letter heading (e.g., “APPENDIX 1” or “APPENDIX A”) and a descriptive title. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., 1, 2 or A, B), or you may assign a two-part Arabic numeral with the first number designating the chapter in which it appears, separated by a period, followed by a second number or letter to indicate its consecutive placement (e.g., “APPENDIX 3.2” is the second appendix referred to in Chapter Three).
- Include the chosen headings in all capital letters, and center them 1″ below the top of the page.
- All appendix headings and titles must be included in the table of contents.
- Page numbering must continue throughout your appendix or appendices. Ensure each appendix complies with margin and pagination requirements.
You are required to list all the references you consulted. For specific details on formatting your references, consult and follow a style manual or professional journal that is used for formatting publications and citations in your discipline.

Your reference pages must be prepared following these guidelines:
- If you place references after each chapter, the references for the last chapter must be placed immediately following the chapter and before the appendices.
- If you place all references at the end of the thesis or dissertation, they must appear after the appendices as the final component in the document.
- Select an appropriate heading for this section based on the style manual you are using (e.g., “REFERENCES”, “BIBLIOGRAPHY”, or “WORKS CITED”).
- Include the chosen heading in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the page.
- References must be single-spaced within each entry.
- Include one double-spaced line between each reference.
- Page numbering must continue throughout your references section. Ensure references comply with margin and pagination requirements.
In some cases, students gain approval from their academic program to include in their thesis or dissertation previously published (or submitted, in press, or under review) journal articles or similar materials that they have authored. For more information about including previously published works in your thesis or dissertation, see the section on Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials and the section on Copyrighting.
If your academic program has approved inclusion of such materials, please note that these materials must match the formatting guidelines set forth in this Guide regardless of how the material was formatted for publication.
Some specific formatting guidelines to consider include:

- Fonts, margins, chapter headings, citations, and references must all match the formatting and placement used within the rest of the thesis or dissertation.
- If appropriate, published articles can be included as separate individual chapters within the thesis or dissertation.
- A separate abstract to each chapter should not be included.
- The citation for previously published work must be included as the first footnote (or endnote) on the first page of the chapter.
- Do not include typesetting notations often used when submitting manuscripts to a publisher (i.e., insert table x here).
- The date on the title page should be the year in which your committee approves the thesis or dissertation, regardless of the date of completion or publication of individual chapters.
- If you would like to include additional details about the previously published work, this information can be included in the preface for the thesis or dissertation.
Previous: Order and Components
Next: Distribution

Graduate College Formatting Guide
- Page Numbers (Microsoft Word)
- Page Numbers (Google Docs)
- Page Breaks and Section Breaks
- Headings, Subheadings, and Table of Contents (Microsoft Word)
- Headings, Subheadings, and Table of Contents (Google Docs)
- Inserting Tables and Figures
- Comments and Track Changes
- References, Bibliography, Works Cited
- Landscape Pages & Special Materials
Using Appendices
Some theses/dissertations need space for extra materials relevant to the work but not appropriate in the main body of text, such as IRB approvals. For these, appendices are useful.* Appendices should go after your references/works cited list, should be formatted as Heading 1, and as such should appear in your Table of Contents. Any Tables or Figures that appear in an appendix should also appear in its respective list. Finally, when referring to an appendix within the body of the work, please refer to them as "Appendix A," "Appendix B," etc.
*Note: the following example screenshots will have the "Show/hide formatting marks" option toggled on. To see how to enable/disable this feature, see Landscape Pages & Special Materials.
To add an appendix, first create a new page after your references list (to do so, see Page Breaks and Section Breaks). Type Appendix A at the top and set it to Heading 1.

Most students prefer to title their appendices, though this step is optional.

You can repeat this process as many times as necessary to include all of your extra materials.
Updating the Table of Contents for Appendices
If you've already inserted a Table of Contents in your document, appendices won't appear immediately in this table once they're added. To show your changes, right click anywhere inside of your Table of Contents and click Update Field

You might receive a pop-up asking if you want to update the entire table or just the page numbers. Select Update entire table.

Any added appendices should now appear in your Table of Contents.

- << Previous: References, Bibliography, Works Cited
- Next: Landscape Pages & Special Materials >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 2:45 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uni.edu/grad-college-format
Graduate School
- Make a Gift
Organizing and Formatting Your Thesis and Dissertation

Learn about overall organization of your thesis or dissertation. Then, find details for formatting your preliminaries, text, and supplementaries.
Overall Organization
A typical thesis consists of three main parts – preliminaries, text, and supplementaries. Each part is to be organized as explained below and in the order indicated below:
1. Preliminaries:
- Title page (required)
- Copyright page (required)
- Abstract (required) only one abstract allowed
- Acknowledgments (optional) located in the Preliminary Section only
- Preface (optional)
- Autobiography (optional)
- Dedication (optional)
- Table of Contents (required)
- List of Tables (optional)
- List of Figures (optional)
- List of Plates (optional)
- List of Symbols (optional)
- List of Keywords (optional)
- Other Preliminaries (optional) such as Definition of Terms
3. Supplementaries:
- References or bibliography (optional)
- Appendices (optional)
- Glossary (optional)
- List of Abbreviations (optional)

Preliminaries
These are the general requirements for all preliminary pages.
- Preliminary pages are numbered with lower case Roman numerals.
- Page numbers are ½” from the bottom of the page and centered.
- The copyright page is included in the manuscript immediately after the title page and is not assigned a page number nor counted.
- The abstract page is numbered with the Roman numeral “ii”.
- The remaining preliminary pages are arranged as listed under “Organizing and Formatting the Thesis/Dissertation” and numbered consecutively.
- Headings for all preliminary pages must be centered in all capital letters 1” from the top of the page.
- Do not bold the headings of the preliminary pages.

A sample Thesis title page pdf is available here , and a sample of a Dissertation title page pdf is available here.
Refer to the sample page as you read through the format requirements for the title page.
- Do not use bold.
- Center all text except the advisor and committee information.
The heading “ Thesis ” or “ Dissertation ” is in all capital letters, centered one inch from the top of the page.
- Your title must be in all capital letters, double spaced and centered.
- Your title on the title page must match the title on your GS30 – Thesis/Dissertation Submission Form
Submitted by block
Divide this section exactly as shown on the sample page. One blank line must separate each line of text.
- Submitted by
- School of Advanced Materials Discovery
- School of Biomedical Engineering
- Graduate Degree Program in Cell and Molecular Biology
- Graduate Degree Program in Ecology
If your department name begins with “School of”, list as:
- School of Education
- School of Music, Theatre and Dance
- School of Social Work
If you have questions about the correct name of your department or degree, consult your department. Areas of Study or specializations within a program are not listed on the Title Page.
Degree and Graduating Term block
- In partial fulfillment of the requirements
- For the Degree of
- Colorado State University
- Fort Collins, Colorado (do not abbreviate Colorado)
Committee block
- Master’s students will use the heading Master’s Committee:
- Doctoral students will use the heading Doctoral Committee:
- The Master’s Committee and Doctoral Committee headings begin at the left margin.
- One blank line separates the committee heading and the advisor section.
- One blank line separates the advisor and committee section.
- Advisor and committee member names are indented approximately half an inch from the left margin.
- Titles before or after the names of your advisor and your members are not permitted (Examples – Dr., Professor, Ph.D.).
Copyright Page
- A sample copyright page pdf is available here.
- A copyright page is required.
- A copyright page is included in the manuscript immediately after the title page.
- This page is not assigned a number nor counted.
- Center text vertically and horizontally.
- A sample abstract page pdf is available here – refer to the sample page as you read through the format requirements for the abstract.
- Only one abstract is permitted.
- The heading “ Abstract ” is in all capital letters, centered one inch from the top of the page.
- Three blank lines (single-spaced) must be between the “ Abstract ” heading and your title.
- Your title must be in all capital letters and centered.
- The title must match the title on your Title Page and the GS30 – Thesis/Dissertation Submission Form
- Three blank lines (single-spaced) must be between the title and your text.
- The text of your abstract must be double-spaced.
- The first page of the abstract is numbered with a small Roman numeral ii.
Table of Contents
- A sample Table of Contents page pdf is available.
- The heading “ Table of Contents ” is in all capital letters centered one inch from the top of the page.
- Three blank lines (single-spaced) follow the heading.
- List all parts of the document (except the title page) and the page numbers on which each part begins.
- The titles of all parts are worded exactly as they appear in the document.
- Titles and headings and the page numbers on which they begin are separated by a row of dot leaders.
- Major headings are aligned flush with the left margin.
- Page numbers are aligned flush with the right margin.
The text of a thesis features an introduction and several chapters, sections and subsections. Text may also include parenthetical references, footnotes, or references to the bibliography or endnotes.
Any references to journal publications, authors, contributions, etc. on your chapter pages or major heading pages should be listed as a footnote .

- The entire document is 8.5” x 11” (letter) size.
- Pages may be in landscape position for figures and tables that do not fit in “portrait” position.
- Choose one type style (font) and font size and use it throughout the text of your thesis. Examples: Times New Roman and Arial.
- Font sizes should be between 10 point and 12 point.
- Font color must be black.
- Hyperlinked text must be in blue. If you hyperlink more than one line of text, such as the entire table of contents, leave the text black.
- Margins are one inch on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right).
- Always continue the text to the bottom margin except at the end of a chapter.

- Please see preliminary page requirements .
- Body and references are numbered with Arabic numerals beginning with the first page of text (numbered 1).
- Page numbers must be centered ½” from the bottom of the page.
Major Headings
- A sample page pdf for major headings and subheadings is available here.
- Use consistent style for major headings.
- Three blank lines (single-spaced) need to be between the major heading and your text.
- Each chapter is started on a new page.
- The References or Bibliography heading is a major heading and the formatting needs to match chapter headings.
Subheadings
- A sample page pdf for major headings and subheadings is available here .
- Style for subheadings is optional but the style should be consistent throughout.
- Subheadings within a chapter (or section) do not begin on a new page unless the preceding page is filled. Continue the text to the bottom of the page unless at the end of a chapter.
- Subheadings at the bottom of a page require two lines of text following the heading and at least two lines of text on the next page.
Running Head
Do not insert a running head.
When dividing paragraphs, at least two lines of text should appear at the bottom of the page and at least two lines of text on the next page.
Hyphenation
The last word on a page may not be divided. No more than three lines in succession may end with hyphens. Divide words as indicated in a standard dictionary.
- The text of the thesis is double-spaced.
- Bibliography or list of reference entries and data within large tables may be single-spaced. Footnotes should be single spaced.
- Footnotes and bibliography or list of reference entries are separated by double-spacing.
- Quoted material of more than three lines is indented and single-spaced. Quoted material that is three lines or fewer may be single-spaced for emphasis.
Poems should be double-spaced with triple-spacing between stanzas. Stanzas may be centered if lines are short.
- Consult a style manual approved by your department for samples of footnotes.
- Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout the entire thesis.
- Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which the reference is made.
- Footnotes are single-spaced.
- Consult a style manual approved by your department for samples of endnotes.
- Endnotes are numbered consecutively throughout the entire thesis.
- Endnotes may be placed at the end of each chapter or following the last page of text.
- The form for an endnote is the same as a footnote. Type the heading “endnote”.
Tables and Figures
- Tables and figures should follow immediately after first mentioned in the text or on the next page.
- If they are placed on the next page, continue the text to the bottom of the preceding page.
- Do not wrap text around tables or figures. Text can go above and/or below.
- If more clarity is provided by placing tables and figures at the end of chapters or at the end of the text, this format is also acceptable.
- Tables and Figures are placed before references.
- Any diagram, drawing, graph, chart, map, photograph, or other type of illustration is presented in the thesis as a figure.
- All tables and figures must conform to margin requirements.
- Images can be resized to fit within margins
- Table captions go above tables.
- Figure captions go below figures.
- Captions must be single spaced.
Landscape Tables and Figures
- Large tables or figures can be placed on the page landscape or broadside orientation.
- Landscape tables and figures should face the right margin (unbound side).
- The top margin must be the same as on a regular page.
- Page numbers for landscape or broadside tables or figures are placed on the 11” side.
Supplementaries
These are the general requirements for all supplementary pages.
- Supplementary pages are arranged as listed under “Organizing and Formatting the Thesis/Dissertation” and numbered consecutively.
- Headings for all supplementary pages are major headings and the formatting style needs to match chapter headings.

References or Bibliography
- The References or Bibliography heading is always a major heading and the formatting style needs to match chapter headings.
- References or Bibliography are ordered after each chapter, or at the end of the text.
- References or Bibliography must start on a new page from the chapter text.
- References are aligned flush with the left margin.
- The style for references should follow the format appropriate for the field of study.
- The style used must be consistent throughout the thesis.
- Appendices are optional and used for supplementary material.
- The Appendices heading is a major heading and the formatting style needs to match chapter headings.
- As an option the appendix may be introduced with a cover page bearing only the title centered vertically and horizontally on the page. The content of the appendix then begins on the second page with the standard one inch top margin.
- Quality and format should be consistent with requirements for other parts of the thesis including margins.
- Page numbers used in the appendix must continue from the main text.
A Foreign Language Thesis
Occasionally, theses are written in languages other than English. In such cases, an English translation of the title and abstract must be included in the document.
- Submit one title page in the non-English language (no page number printed).
- Submit one title page in English (no page number printed).
- Submit one abstract in the non-English language (page number is ii).
- Submit one abstract in English (page number is numbered consecutively from previous page – example: if the last page of the abstract in the foreign language is page ii the first page of the abstract in English is numbered page iii).
Multipart Thesis
In some departments, a student may do research on two or more generally related areas which would be difficult to combine into a single well-organized thesis. The solution is the multi-part thesis.
- Each part is considered a separate unit, with its own chapters, bibliography or list of references, and appendix (optional); or it may have a combined bibliography or list of references and appendix.
- A single abstract is required.
- The pages of a multi-part thesis are numbered consecutively throughout the entire thesis, not through each part (therefore, the first page of Part II is not page 1).
- The chapter numbering begins with Chapter 1 for each part, or the chapters may be numbered consecutively.
- Pagination is consecutive throughout all parts, including numbered separation sheets between parts.
- Each part may be preceded by a separation sheet listing the appropriate number and title.

- Library Catalogue
Formatting your thesis: Appendices & supplemental material

On this page
Introduction, materials included in appendices, supplementary material or research data files, order of appendices, appendix headings, formatting help.
Appendices provide supplementary information to the main thesis and should always appear after the references/bibliography. If you are unsure about whether content should be included in the thesis or in an appendix, consult with your supervisor. The thesis and appendices must be uploaded in a single file.
For more information about appendices, please see the Thesis Template Instructions .
Note: Signatures, personal phone numbers, or personal email addresses (ones that contains part of a person’s name) must be redacted from your thesis. This means that the text is fully removed, and cannot be copied & pasted out of the document.
If including copyrighted materials as appendices, see Copyright at SFU .
Examples of material included in appendices are as follows--also refer to Formatting Help .
- interview questions
- participant letters / forms
- surveys / questionnaires (if not your own work, these require copyright permission)
- supplemental tables / figures / graphs / image
Supplementary material or research data files associated with your thesis can also be uploaded to your library submission record. We recommend publishing such files to Summit (the SFU Research Repository) as they will be available alongside your thesis. This is preferred to hosting such files externally or on personal cloud storage.
Temporary instructions : Contact [email protected] if you wish to upload such files with your thesis submission -- please do not upload them to the Thesis Registration System at this time. Data Services will require basic descriptive information for each of your files and will also help you organize your research data appropriately pending publication.
If you are including supplementary material or research data files in your submission, you must include an appendix within your thesis document which contains an overall description of the supplementary material or research data files, authorship credits, and file name(s). This assists in “linking” your thesis document to any additional files, as well as providing further information and context about the file(s). The maximum file size for each file is 2GB. If you have a larger file size, please contact [email protected] .
Appendix examples:
- video file example
- data file example
Note : if your Ethics approval requires that supplementary material or research data files be destroyed after a certain period, then such files cannot be published to Summit (the SFU Research Repository). Please contact [email protected] to identify other possible solutions in this case.
Accepted supplementary material or research data file types:
aac, cif, csv, docx, dta, epub, exe, gdb, geojson, gif, iso, jp2, jpg, jpeg, json, kml, kmz, las, mp3, mp4, mpv, odt, pdf, png, pptx, py, qgs, qgz, r, rar, rmd, rtf, shp, tex, tif, tiff, txt, wav, xlsx, zip
It is recommended to use the best file formats to allow for data files to be openly accessible for the long term, so that they remain usable through software upgrades and changes in the computing environment. See the Research Data Management (RDM) website for more information about the handling and organization of data during your research.
Appendices appear in the order in which they are introduced in the text.
You may include one appendix or a number of appendices.
If you have more than one appendix, you would letter each accordingly (i.e., Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.). Write your appendix headings in the same manner as your chapter headings.
- Transfer the text and re-format using the template styles as necessary, or
- Convert the documents into images and insert them into your document, one image per page.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Dissertation Advice: How to Use the Appendix

3-minute read
- 5th June 2017
Unlike the human appendix, the appendices at the end of your dissertation are very valuable… OK, we know that research has shown that the human appendix is useful. But we needed a snappy opening line and we’ll be damned if we let scientific evidence get in our way!
Anyway, our point is that you can often get extra marks on an academic paper by using the appendices effectively. In this blog post, we explain how.
What to Put in the Appendix
An appendix is where extra information goes. What you include, and how many appendices you need, will depend on what you’re writing about. Common examples include:
- Raw test data
- Technical figures, graphs and tables
- Maps, charts and illustrations
- Letters and emails
- Sample questionnaires and surveys
- Interview transcripts
These are all things you might want to reference in your main essay without including them in full. For example, even if you quote an interview in the results and discussion section of an essay, you would not usually include the full transcript. Instead, you would write:
Participant 4 claimed to experience ‘dizziness and nausea’ (see Appendix B).
This points the reader to the appendix if they want to see where the quote came from.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
How to Format Appendices
The correct way to format appendices will depend on your university, so make sure to check your style guide . But in general, the following rules should be followed:
- Place appendices at the end of your document after the reference list
- Divide appendices by topic (e.g. separate sections for test results, illustrations and transcripts)
- Start each appendix on a new page and label it with a letter or number, along with a title clarifying content (Appendix A: Instrument Diagrams, Appendix B: Test Results, etc.)
- List appendices in the table of contents at the beginning of your document
Doing these things will make it easier for your reader to find information in the appendices.
Appendices and the Word Count
Appendices are not usually included in the word count for your paper. This means you can cut non-essential information from the main chapters and add it to an appendix without worrying about exceeding the word limit.
But be warned! This is not an excuse to cut vital information from your work. You must included all important data in your main essay. If you put essential information in the appendices, it could count against you when your work is marked.
Some universities include appendices in the word count, though, so there are better ways to ensure that your work doesn’t end up too wordy!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Appendix – Components, Format & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

An appendix is an integral part of every dissertation paper, serving as supplementary material that enhances and supports the research study. However, only a few people understand what the section is, where it must be placed, and why it must be included in a dissertation . Therefore, while not typically central to the dissertation’s argument, the appendix adds valuable context and transparency to the academic work. This post will cover everything there is to know about a dissertation appendix, from its definition and purpose to the components and format.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Appendix – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation appendix
- 3 Purpose of a dissertation appendix
- 4 Dissertation appendix: Components
- 5 Dissertation appendix: Format
- 6 Referring to a dissertation appendix
- 7 Dissertation Appendix: Checklist
Dissertation Appendix – In a Nutshell
- An appendix is not part of the main body of the dissertation, but is still relevant to it.
- A dissertation appendix encapsulates all explanations that cannot be included in the main body of the dissertation.
- Appendices must be well-structured, and their components systemically organized to serve their purpose correctly.
Definition: Dissertation appendix
A dissertation appendix (plural –appendices) is an index at the end of a dissertation that provides additional information related to the dissertation paper. The section helps academic writers present background information related to the dissertation, but doesn’t directly answer the research question. These can include tables, illustrations and other graphics.
Purpose of a dissertation appendix
The primary purpose of a dissertation appendix is to help keep your dissertation paper organized and within the required word limit. It contains any additional information that isn’t directly relevant to the research topic.
Typically, texts that strengthen your arguments appear in your dissertation paper’s main body. However, there is additional information that isn’t directly beneficial to your research but might be helpful to your readers. That is where a dissertation appendix comes in.
Although they provide additional information, your audience should be able to understand the contents of your dissertation paper even without looking at the dissertation appendix. So, ensure you include all important texts in the main body.
Dissertation appendix: Components
A dissertation appendix can include different types of information, such as:

Research results can be presented in various ways, including tables and figures. However, not all of these findings need to appear in the main body of your dissertation. Only results that are essential in answering the research topic should be included in the paper. Additional results (less significant findings), such as raw data and supplemental analyses, should go into the dissertation appendix.
Further information
Besides supplementary results, additional information related to surveys and interviews can be included in a dissertation appendix. These can include types of interviews, interview transcripts, survey questions, and details of questionnaires. Although these details are not critical to answering your research question, including them in the dissertation appendix gives credibility to your research.

Copies of relevant forms
It is essential to include a list of abbreviations and acronyms and a glossary in the appendix if your dissertation paper contains many words that your audience might not recognize. This helps enhance readability and minimize confusion for readers. Your list of abbreviations and acronyms, and glossary should appear after the table of contents section.
Figures, tables, graphics
You can also include tables, figures, illustrations, and other graphics in the dissertation appendix if your research contains a lot of them. The appendix is the appropriate platform to include less important ones. Use tables and figures that support your research question but cannot be included in the main body.
Dissertation appendix: Format
There is no restriction to how you can format your dissertation appendix. You can opt to have one long appendix if you don’t feel the need to break it into smaller sections with different components. However, it might be a good idea to separate the components (such as interview transcripts and supplementary results) into various appendices to enhance readability.
If you choose to have multiple appendices in your dissertation, always start each appendix on a new page. Additionally, ensure you assign each page a number or letter. For instance, you can use ‘Appendix 2 – Interview Transcripts.’ Giving a unique identifier (number and title of each element) to each appendix makes it easier for the reader to navigate through the information and for you to refer to it in the main dissertation body.
When numbering tables and figures in multiple appendices, you should reset the numbering as you move to the next appendix (next page). For instance, if your ‘Appendix 1 –Raw Data’ has two tables and ‘Appendix 2 – Interview Transcripts’ has one table, the table in ‘Appendix 2’ should be ‘Table 1’ and not ‘Table 3’ .
Referring to a dissertation appendix
It is crucial to refer to each dissertation appendix at least once when crafting the dissertation’s main body. That helps justify the inclusion of appendices in your study.
There are two primary ways you can refer to a dissertation appendix in the main body:
- Refer to an entire appendix
“The interview transcripts can be found in Appendix 1 –Interview Transcripts”.
- Refer to an appendix component
There are two ways you can refer to an appendix component:
- Refer to specific figures or tables in brackets (parenthetical reference). For example, “The results (refer to Table 1 Appendix 3) indicate a slight decline in the number of new infections”.
- Include the reference in a sentence within the main body (descriptive reference). For example, “As shown in Table 1 of Appendix 3, there is a slight decline in the number of new infections” .
If your paper has one long dissertation appendix, it is good practice to refer to its components in uppercase, but it is not mandatory. However, it is important to maintain consistency throughout your entire paper, the same way you capitalize your headings and titles in academic work.
Although you are free to choose what case to use, you should always use lower-case when referring to appendices in general.
“The appendices at the end of this paper contain additional information about the area of research.”
Dissertation Appendix: Checklist
- Each dissertation appendix starts on a fresh page
- My appendices contain relevant information, but they are not essential in answering my research question
- I have referred to each of my appendices at least once in the main body
- The content of my appendices (tables and figures) are clearly labelled
- My appendices are easy to understand and refer to
What is a dissertation appendix?
A dissertation appendix is a section of your dissertation that you use to provide additional data related to your main study but is not essential to answering the primary research question.
What should I include in my appendix?
Your appendix should contain additional information relevant to the dissertation but not directly important to answering your main questions. These can include supplementary results, tables, interview questions and transcripts.
Do I need an appendix in my dissertation?
If you have a lot of additional information, it is important to have an appendix in your dissertation. Appendices help provide readers with details that support your research without breaking the flow of the main body.
Can my dissertation paper have multiple appendices?
Yes. Your dissertation paper can have more than one appendix. Ensure you properly label each appendix (Appendix A or Appendix 1) if your paper has multiple appendices.
Is it appendices or appendixes?
Appendices and appendixes are both correct plurals for the term appendix. However, many scholars prefer using ‘appendices’ over ‘appendixes.’
I am so so happy I found BachelorPrint!!! I was first working with Book1One,...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
- How it works

What is Appendix in the Dissertation?
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On June 13, 2023
“Appendix or appendices (plural) is/are used to provide additional data related to your dissertation research project.”
An appendix section in dissertation helps you to provide background data related to your topic; present tables, illustrations, and figures that are not directly relevant to your research questions in order to avoid disrupting the flow of the text; to make sure that your dissertation paper’s word count does not go beyond the limit. This article explains what is an appendix in the dissertation.
The Purpose of an Appendix
The main body of the dissertation paper generally contains text that adds weight to your arguments. However, some information that is not directly relevant to the topic of research but might be useful to your audience could be provided under the appendices section.
Any additional information that does not directly support your in-text arguments goes into appendices. This helps to keep your paper organised and within the word limit. It is important to make sure that your readers can understand the contents of your dissertation paper without having to look at the appendices. Any information that is important should be mentioned in the main body.
Items Included in Appendices in Dissertation
An appendix, which is also known as a postscript, includes the following:
Research findings can be presented in several ways. Findings including tables, illustrations and figures that are directly relevant to your research questions or research problem are included in the main body.
However, there are certain text, tables and figures —such as supplemental analyses—that really need to be shown and cannot be ignored, but (due to less significance) can’t be included in the main body as it can disturb the flow of the text.
Such tables and figures are then included in the appendix section. The appendix includes more of the illustrations and findings as a result of data analysis that doesn’t directly address the research question but are essential to be shown.
Also Read: How to Write Dissertation Acknowledgements
Surveys/Interviews
Appendices are helpful in mentioning extra information related to surveys , interviews or focus groups. You can clearly mention how respondents responded to underpin your findings.
Include Abbreviations Section
If you have utilised a lot of abbreviations or jargon, it might be difficult for lay-person to understand those terms. You can include the abbreviations section or a glossary section in the appendix, which are sometimes positioned at the start of the dissertation.

Tables, Figures and/or Graphs
Your dissertation may include a lot of tables, figures and/or graphs due to the nature of research . The appendix is the appropriate platform to include all this information, including illustrations.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue, then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Appendix Format
You can carry on with just one long appendix (if you don’t want to break it into different components and want it to be the only appendix in your dissertation).
On the other hand, you might want to have separate sections in appendices such as questionnaire responses, findings, key phrases and key terms; it would be easier to figure out the information provided in appendices.
If you decide to include multiple sections within your appendices, each appendix should start on a new page with a clearly assigned title and number, for instance, ‘Appendix 7. Survey questions’ . It allows for each section of the appendix to be clearly visible to the reader and researcher.
It is also recommended to mention the number and title against each element that is directly linked to the appendix so that the reader will be able to know what you are referring to in the main body.
While numbering tables and figures, make sure that you re-start the numbering for each appendix. This means that each table and figure in a new appendix would be titled Table 1 or Figure 1.
Referring to the Appendix in the Main Body of the Dissertation
It is recommended to indicate all appendices at least once in the main body of your dissertation. Make sure that you mention the appendix number (enclosed in brackets, called parenthetical reference ) or within text in the main body (called descriptive reference ) as highlights for the readers.
It is not mandatory to capitalise it as that typically depends on the researcher’s will. You can also refer to certain elements within the appendix (which can be a specific illustration or table).
Example #1. When you are referring to an entire appendix
The focus-group interview (see Appendix 1) shows that… Appendix 2 describes how we gathered data from the sample population….
Example #2. While you are referring to an appendix component
These findings (see Appendix 1, Table 2) show that… Table 2 in Appendix 1 describes the factors which result in the increase in sales.
It would be a good practice to mention Appendix in upper-case, especially when referring to a specific component. However, this is not compulsory and you can choose to use lower-case, i.e., ‘The appendices provided at the end of the documents contain relevant content about the questionnaire responses.’
Here are some more appendix examples for you .
Which is More Appropriate: Appendices or Appendixes?
Both of these words (spellings) are true in their sense and can be used, but appendices is more appropriate according to APA style. However, it is important to ensure consistency throughout the thesis document. Don’t use alternative words in different sections of the dissertation .
Where to Include Appendices?
The general idea in this regard is to include appendices after the main body, i.e., the reference section. If you opt for this option, you need to continue with the same page number format. You can also submit appendices as a separate document with your dissertation project.
You should write down appendices (including titles and page numbers) in the table of contents.
Even if you are still unsure about what an appendix in a dissertation is, our writers can help with this chapter of your paper. All you have to do is complete our online order form , select the dissertation part/chapter as the required service type, attach your dissertation draft, and let us know your deadline. We guarantee that the writer we will assign to your order will have the expertise and qualification to create the appendices to your exact requirements.
FAQs About Appendices in Dissertation
What should i not include in a dissertation appendix.
Don’t include any irrelevant and/or vague information. It will only distract your readers from understanding your study’s overall purpose, significance, etc.
What can I include in an appendix?
You can include in it things like figures and/tables that are too lengthy to be included within the dissertation ; maps, photographs, raw data like participant score lists, computer programs like SPSS, musical examples like audios etc., interview questions and/or sample questionnaires, etc.
Can I include web URLs in an appendix?
Not really, although you can include PDF documents or weblinks to such documents within your dissertation appendix.
You May Also Like
Not sure how to write the findings of a dissertation. Here are some comprehensive guidelines for you to learn to write a flawless findings chapter.
When writing your dissertation, an abstract serves as a deal maker or breaker. It can either motivate your readers to continue reading or discourage them.
Dissertation conclusion is perhaps the most underrated part of a dissertation or thesis paper. Learn how to write a dissertation conclusion.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Privacy Policy

Home » Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples
Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples
Table of Contents

Definition:
Appendices refer to supplementary materials or documents that are attached to the end of a Book, Report , Research Paper , Thesis or other written work. These materials can include charts, graphs, tables, images, or other data that support the main content of the work.
Types of Appendices
Types of appendices that can be used depending on the content and purpose of the document. These types of Appendices are as follows:
Statistical Appendices
Statistical appendices are used to present raw data or statistical analysis that is relevant to the main text but would be too bulky to include in the main body of the document. These appendices may include tables, graphs, charts, or other types of visual aids that help to illustrate the data.
Technical Appendices
Technical appendices are used to provide detailed technical information that is relevant to the main text but would be too complex or lengthy to include in the main body of the document. These appendices may include equations, formulas, diagrams, or other technical details that are important for understanding the subject matter.
Bibliographical Appendices
Bibliographical appendices are used to provide additional references or sources that are relevant to the main text but were not cited in the main body of the document. These appendices may include lists of books, articles, or other resources that the author consulted in the course of their research.
Historical Appendices
Historical appendices are used to provide background information or historical context that is relevant to the main text but would be too lengthy or distracting to include in the main body of the document. These appendices may include timelines, maps, biographical sketches, or other historical details that help to contextualize the subject matter.
Supplemental Appendices
Supplemental appendices are used to provide additional material that is relevant to the main text but does not fit into any of the other categories. These appendices may include interviews, surveys, case studies, or other types of supplemental material that help to further illustrate the subject matter.
Applications of Appendices
Some applications of appendices are:
- Providing detailed data and statistics: Appendices are often used to include detailed data and statistics that support the findings presented in the main body of the document. For example, in a research paper, an appendix might include raw data tables or graphs that were used to support the study’s conclusions.
- Including technical details: Appendices can be used to include technical details that may be of interest to a specialized audience. For example, in a technical report, an appendix might include detailed calculations or equations that were used to develop the report’s recommendations.
- Presenting supplementary information: Appendices can be used to present supplementary information that is related to the main content but doesn’t fit well within the main body of the document. For example, in a business proposal, an appendix might include a list of references or a glossary of terms.
- Providing supporting documentation: Appendices can be used to provide supporting documentation that is required by the document’s audience. For example, in a legal document, an appendix might include copies of contracts or agreements that were referenced in the main body of the document.
- Including multimedia materials : Appendices can be used to include multimedia materials that supplement the main content. For example, in a book, an appendix might include photographs, maps, or illustrations that help to clarify the text.
Importance of Appendices
Appendices are important components of research papers, reports, Thesis, and other academic papers. They are supplementary materials that provide additional information and data that support the main text. Here are some reasons why appendices are important:
- Additional Information : Appendices provide additional information that is too detailed or too lengthy to include in the main text. This information includes raw data, graphs, tables, and charts that support the research findings.
- Clarity and Conciseness : Appendices help to maintain the clarity and conciseness of the main text. By placing detailed information and data in appendices, writers can avoid cluttering the main text with lengthy descriptions and technical details.
- Transparency : Appendices increase the transparency of research by providing readers with access to the data and information used in the research process. This transparency increases the credibility of the research and allows readers to verify the findings.
- Accessibility : Appendices make it easier for readers to access the data and information that supports the research. This is particularly important in cases where readers want to replicate the research or use the data for their own research.
- Compliance : Appendices can be used to comply with specific requirements of the research project or institution. For example, some institutions may require researchers to include certain types of data or information in the appendices.
Appendices Structure
Here is an outline of a typical structure for an appendix:
I. Introduction
- A. Explanation of the purpose of the appendix
- B. Brief overview of the contents
II. Main Body
- A. Section headings or subheadings for different types of content
- B. Detailed descriptions, tables, charts, graphs, or images that support the main content
- C. Labels and captions for each item to help readers navigate and understand the content
III. Conclusion
- A. Summary of the key points covered in the appendix
- B. Suggestions for further reading or resources
IV. Appendices
- A. List of all the appendices included in the document
- B. Table of contents for the appendices
V. References
- A. List of all the sources cited in the appendix
- B. Proper citation format for each source
Example of Appendices
here’s an example of what appendices might look like for a survey:
Appendix A:
Survey Questionnaire
This section contains a copy of the survey questionnaire used for the study.
- What is your age?
- What is your gender?
- What is your highest level of education?
- How often do you use social media?
- Which social media platforms do you use most frequently?
- How much time do you typically spend on social media each day?
- Do you feel that social media has had a positive or negative impact on your life?
- Have you ever experienced cyberbullying or harassment on social media?
- Have you ever been influenced by social media to make a purchase or try a new product?
- In your opinion, what are the biggest advantages and disadvantages of social media?
Appendix B:
Participant Demographics
This section includes a table with demographic information about the survey participants, such as age, gender, and education level.
Age Gender Education Level
- 20 Female Bachelor’s Degree
- 32 Male Master’s Degree
- 45 Female High School Diploma
- 28 Non-binary Associate’s Degree
Appendix C:
Statistical Analysis
This section provides details about the statistical analysis performed on the survey data, including tables or graphs that illustrate the results of the analysis.
Table 1: Frequency of Social Media Platforms
Use Platform Frequency
- Facebook 35%
- Instagram 28%
- Twitter 15%
- Snapchat 12%
Figure 1: Impact of Social Media on Life Satisfaction
Appendix D:
Survey Results
This section presents the raw data collected from the survey, such as participant responses to each question.
Question 1: What is your age?
Question 2: What is your gender?
And so on for each question in the survey.
How to Write Appendices
Here are the steps to follow to write appendices:
- Determine what information to include: Before you start writing your appendices, decide what information you want to include. This may include tables, figures, graphs, charts, photographs, or other types of data that support the main content of your paper.
- Organize the material: Once you have decided what to include, organize the material in a logical manner that follows the sequence of the main content. Use clear headings and subheadings to make it easy for readers to navigate through the appendices.
- Label the appendices: Label each appendix with a capital letter (e.g., “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” etc.) and provide a brief descriptive title that summarizes the content.
- F ormat the appendices: Follow the same formatting style as the rest of your paper or report. Use the same font, margins, and spacing to maintain consistency.
- Provide detailed explanations: Make sure to provide detailed explanations of any data, charts, graphs, or other information included in the appendices so that readers can understand the significance of the material.
- Cross-reference the appendices: In the main text, cross-reference the appendices where appropriate by referring to the appendix letter and title (e.g., “see Appendix A for more information”).
- Review and revise: Review and revise the appendices just as you would any other part of your paper or report to ensure that the information is accurate, clear, and relevant.
When to Write Appendices
Appendices are typically included in a document when additional information needs to be provided that is not essential to the main text, but still useful for readers who want to delve deeper into a topic. Here are some common situations where you might want to include appendices:
- Supporting data: If you have a lot of data that you want to include in your document, but it would make the main text too lengthy or confusing, you can include it in an appendix. This is especially useful for academic papers or reports.
- Additional examples: I f you want to include additional examples or case studies to support your argument or research, but they are not essential to the main text, you can include them in an appendix.
- Technical details: I f your document contains technical information that may be difficult for some readers to understand, you can include detailed explanations or diagrams in an appendix.
- Background information : If you want to provide background information on a topic that is not directly related to the main text, but may be helpful for readers, you can include it in an appendix.
Purpose of Appendices
The purposes of appendices include:
- Providing additional details: Appendices can be used to provide additional information that is too detailed or bulky to include in the main body of the document. For example, technical specifications, data tables, or lengthy survey results.
- Supporting evidence: Appendices can be used to provide supporting evidence for the arguments or claims made in the main body of the document. This can include supplementary graphs, charts, or other visual aids that help to clarify or support the text.
- Including legal documents: Appendices can be used to include legal documents that are referred to in the main body of the document, such as contracts, leases, or patent applications.
- Providing additional context: Appendices can be used to provide additional context or background information that is relevant to the main body of the document. For example, historical or cultural information, or a glossary of technical terms.
- Facilitating replication: In research papers, appendices are used to provide detailed information about the research methodology, raw data, or analysis procedures to facilitate replication of the study.
Advantages of Appendices
Some Advantages of Appendices are as follows:
- Saving Space: Including lengthy or detailed information in the main text of a document can make it appear cluttered and overwhelming. By placing this information in an appendix, it can be included without taking up valuable space in the main text.
- Convenience: Appendices can be used to provide supplementary information that is not essential to the main argument or discussion but may be of interest to some readers. By including this information in an appendix, readers can choose to read it or skip it, depending on their needs and interests.
- Organization: Appendices can be used to organize and present complex information in a clear and logical manner. This can make it easier for readers to understand and follow the main argument or discussion of the document.
- Compliance : In some cases, appendices may be required to comply with specific document formatting or regulatory requirements. For example, research papers may require appendices to provide detailed information on research methodology, data analysis, or technical procedures.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

References in Research – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
The Appendix (How to Use One in an Essay)

2-minute read
- 30th March 2017
The appendices in an essay are not typically essential, but they can play an important supporting role. Not everyone knows how to use an appendix in academic writing , though, so we’ve prepared this handy guide.
What Is an Appendix?
An appendix (plural: appendices ) is a section at the end of a book or essay containing details that aren’t essential to your work, but which could provide useful context or background material.
In the main body of your essay, you should indicate when you’re referring to an appendix by citing it in parentheses. For example:
The interviews show that most people like ice cream (see Appendix C).
What Should Go in the Appendices?
Appendices can include many things depending on your topic. Common examples of information added to an appendix include:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
- Raw data from tests
- Technical figures, graphs or tables
- Maps, charts or images
- Letters or emails used in research
- Sample questionnaires or surveys
- Full interview transcripts
What these have in common is that you might need to refer to them in an essay without going into too much detail. For example, you might summarise the results of a test in the ‘Results’ section of a dissertation, then include the full data in appendices to ensure clarity.
How to Format Appendices
Exactly how to format appendices can vary between universities, so you should always check your style guide. Generally, though, appendices should:
- Appear at the end of your document, often after the reference list
- Be divided into sections depending on topic (e.g. separate sections for questionnaire results and interview transcripts)
- Have each appendix section start on a new page
- Be labelled with a letter or number, along with a title clarifying content (Appendix A: Instrument Diagrams, Appendix B: Test Results, etc.)
- Appear in the table of contents at the beginning of your document

Are Appendices Included in the Word Count?
Appendices are not usually included in the word count for an essay. Consequently, you can focus on key information in your work and place extra data in an appendix without worrying about the word count.
However, you should always check your style guide on this. And remember that if you rely on something in your main essay, it needs to be included there: you can’t just shuffle it into the appendices to reduce the word count !
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Appendix Dissertation: What to Write & How to Use
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
Appendix Dissertation: What to Write & How to Use

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A dissertation appendix is an optional section that offers additional details. This can include survey results, raw data, statistics, calculations, photographs and other visual sources.
Appendix of a dissertation is one of the essential research components. It is an application that shows work you have conducted. Like other elements of scientific work, appendices should be drawn up accordingly. This article includes detailed information on how to do an appendicx for a dissertation.
What if you need someone more qualified to ' do my dissertation ?' Don't hesitate and check our solutions straight away!
What Is a Dissertation Appendix?
Appendix in dissertation is a section where non-standard format data is included. It is designed to improve quality of work, make it more evident and trustworthy. This section shows your readers the level of your competence and topic's depth. This part contains elements related to your research like tables, images, maps, documents, etc. Here should be any additional material which will not be added into general text. Just make sure you put data, which is not meant to be placed into the body of work. It includes vast material, for example, statistical data for calculation. Usually, the last pages are where you put this part of a dissertation. Appendixes' volume is not taken into account in total work size. If your research requires 70 pages, then your main text without attachments should be 70 pages. There are no volume requirements for the appendix itself. It can consist of 1 or 100 pages.
What Is the Purpose of Appendix in Dissertation?
Appendix in a dissertation includes all large materials that are not placed into worktext. This place is for informational or reference purposes only. Imagine there is disagreement about research conclusions. Then, detailed useful data from appendices will help you clarify the situation. For example, members of the defense commission had questions about certain conclusions. In turn, you can demonstrate application form and methodology for analyzing answers. It makes no sense to include these documents in work text due to their large volume. But this part is a super helpful place to prove the process's correctness.
Appendices or Appendixes
Wondering how to write correctly: appendices or appendixes ? You may think that both are correct. But which is more widespread? We'll explain it quickly! These are views of American English over past few decades: "Appendixes" was previously a completely incorrect plural form of "Appendix." This word was considered as a supplementary body part. Instead, the plural form was "Appendices." But it seems, many people made a mistake and preferred the wrong variant. So, with English being constantly evolving, it began to spread out quickly. This variant started to appear in academic and public materials. Both words are now considered correct according to modern dictionaries. "Appendixes" are becoming increasingly popular. We recommend you to look at other similar publications of your field. Check which word they are using.
What to Include in Dissertation Appendix?
Most often, your appendix for dissertation should include:
- Research Results Research results can be presented in tables and figures at the end or in the main text. So let's discover what information to submit in what form. Display main results that are relevant to your research question into the main text. Less significant results that do not help answer your main question can be placed in the appendix. This includes a detailed description of your sample or additional tests you have performed. For example, if you used software for statistics, including the results of your analysis.
- Questionnaires and Interviews In this section, you can add written materials relevant to survey and interview. Include these points in your dissertation so that readers can see what you have drawn your conclusions from. But they are usually not in the main body of text.
- Tables and Figures Any material that is less important to the main text can be included in the appendix. This includes tables, figures, and other graphic elements (such as charts and illustrations).
- Personal/Used Correspondence This should include correspondence between you and other researchers. Maybe you have applied for permission to reuse copyrighted material. This will help protect your dissertation from suspicion of plagiarism.
- Abbreviations It would be wise if you added a list of abbreviations to the appendix. Not all of your readers can understand the abbreviated technical terms you use. Note: Some researchers call this a "glossary."
Dissertation Appendix: Format
Now it's time to discuss how to do a dissertation appendix ! Here are some format and style rules you should keep in mind while writing your work:
- Heading "Appendix" should be centered on the first page of the section.
- Each reference should have its own number. It is located at the top of the page (for example, Appendix 1).
- Type and font size should be the same as in main work.
- Each attachment should be placed on a separate sheet even if it does not occupy the entire page.
- A "page break" should be inserted at the end of the page. So that materials do not move when a file is opened in another version of Microsoft Word.
At different universities, format requirements may differ. So we recommend you consult with your starting supervisor.
How to Refer to Appendix in Dissertation In-Text
Now let's discuss how to use an appendix in a dissertation in-text. All attachments should be arranged in the same order in which they are mentioned in text. In text, mark results with links. For example: "See Appendix №." We also recommend you make a list of attachments as you write your work. For example, you mentioned in a text a survey conducted. Immediately add a questionnaire and essential processing method in the appendix. When work is finished, you can easily collect all materials for application. Consider dissertation help services if you lack time to start the work.
Dissertation Appendix: Example
Here you can see some dissertation appendix samples. Don't hesitate and double-check this part. It is important for you to make your experience of writing a dissertation understandable for every reader.
Appendix in Dissertation: Bottom Line
Appendix of a dissertation is not less important than any other part of writing a thesis paper . This section consists of materials that do not fit into the main body. These can be images, tables, questionnaires, diagrams, calculations, drawings. It shows your severe approach and ability for working with information and increases the value of all work. Check our recommendations provided above if you wanna cope quickly with this section. We provided all the necessary background for you to succeed. Also, we recommended reading about how to write a dissertation abstract , dissertation acknowledgments , or dissertation proposals .
If difficulties arise, you can always turn to our writing services online for expert help. They will deliver your dissertation quickly and efficiently!

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

No notifications.
Dissertation Appendix Writing Guide
What is an appendix.
An appendix is a section of the paper that is included at the end of a report or a dissertation. If there is more than one item being included in this section, the section plural is appendices.
Items that would usually be included as an appendix are relevant to the context of the study but may not be useful to have in the main body of the work. Each appendix should discuss a separate topic and should be listed separately.
When listing an appendix, it is common practice to list is as Appendix A, Appendix B, Appendix C, etc. As each appendix will be evidence of a different topic or will be on a different topic, as with figures within the work, you will be required to title each individual appendix separately within the appendices section.
Make sure you refer to them in-text by the appropriate name. If you do not refer to your appendix in the main text, it does not need to be there!

Do I Need an Appendix?
Not every dissertation will require an appendix or appendices! It depends on the type of research you are doing, the subject you are studying and the requirements of your university.
What Is Included in an Appendix?
Some examples of appendix items could include interview transcripts, full data sets (i.e., numerical data), a full breakdown of a company’s background or financial information, full PESTLE analysis, search strategy tables or an example of a survey or questionnaire, amongst many others.
Any work in the appendix does not usually count towards the overall word count of a piece of work. However, this rule is not the same with all universities and you must ensure that you check with your own university about their rules and regulations on appendices.
Even in the appendix, you must remember to reference! Ensure you include these references in your bibliography too.
Checklist: Dissertation Appendices
- Have I presented my appendices clearly?
- Have I labelled the appendices in order of appearance in the main body?
- Have I made certain that my appendix is suitably relevant to the text to be included?
Congratulations!
Well done on completing this checklist! You're doing great.
We can help
If you require assistance to write the appendix section of your dissertation, you may want to consider our helpful service which is a great way to get a head start on your work.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Our dissertation writing guide chapters .
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Dissertation Topic
- Dissertation Title
- Dissertation Proposal
- Dissertation Abstract
- Dissertation Introduction
- Dissertation Background
- Literature Review
- Dissertation Methodology
- Dissertation Results Section
- Dissertation Discussion
- Dissertation Conclusion
Study Resources
Free resources to assist you with your university studies!
- Dissertation Examples
- Dissertation Proposal Examples
- Example Dissertation Titles
- Example Dissertation Topics
- Free Resources Index
Need more assistance? Check out our suite of services to assist you further.
- Samples of our Service
- Full Service Portfolio
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Marking Service
- Deutschland
- United Kingdom
- How to write a PhD Thesis
Select Page
Appendices, References, Acknowledgements and Other Final Things
Posted by Rene Tetzner | Oct 22, 2023 | PhD Success | 0 |
4.6 Appendices, References, Acknowledgements and Other Final Things
4.6.1 Appendices
As I mentioned in Sections 1.4.1 and 3.5.3, appendices are not required in a thesis, but they are often included. If you are considering appendices for your thesis, check your university or department guidelines or discuss the idea with your supervisor to be certain that they will be received positively. It is also a good idea to revisit at this point any length or word count requirements or limitations set for doctoral theses by your university or department, because if you have already reached the upper limit, including appendices may require cutting other material, and in such situations appendices should only be considered if they are absolutely necessary. However, appendices are often preferable to extensive or overly long footnotes or endnotes or too much supplementary information in the main text of a thesis, both of which can distract readers from your main argument. For this reason, an effective strategy may be to move such material from the main text or notes into an appendix, since this sort of revision will not significantly alter the overall length or word count of your thesis. If, on the other hand, your thesis is a little shy of the minimum length requirement, you may want to add an appendix or two for supplementary information that you originally cut out of the thesis, but that could usefully be included: this can help you increase the word count to meet requirements. Your decision regarding the inclusion of appendices may also be simplified by the following information and advice.
As a general rule, appendices present subsidiary or supplementary material that is directly related to the material in the thesis itself and potentially helpful to readers, but which might prove distracting or inappropriate or simply too long were it included in the main body of the thesis or in notes (long footnotes in particular can make the layout of pages unattractive and should be avoided). An appendix is also a good format for material that is mentioned or discussed in more than one chapter, part or section of a thesis, because it helps the author avoid repetition while rendering the information readily available to readers. Appendices can contain a wide variety of material, such as texts discussed in the thesis, translations, chronologies, genealogies, examples of principles and procedures, descriptions of complex pieces of equipment, survey questionnaires, participant responses, detailed demographics for a population or sample, lists (particularly long ones), tables and figures, explanations or elaborations of any aspect of a study and any other supplementary information relevant to a thesis.
This material should not be included in an appendix simply because it is interesting and you happen to have it, however; instead, appendices should be included ‘only if they help readers to understand, evaluate, or replicate the study or theoretical argument being made’ ( Publication Manual of the APA , 2010, p.40). An appendix ‘should not be a repository for odds and ends that the author could not work into the text’ ( Chicago Manual of Style , 2003, p.27). Ideally, each appendix should have a specific theme, focus or function and gather materials of a particular type or relating to a particular topic, and it should bear a main heading that describes its content (e.g., ‘Appendix: Questionnaire 3 in Spanish and English’). If more than one theme or topic requires this sort of treatment, additional appendices should be preferred to subdividing a single long appendix, although appendices can certainly make use of internal headings and subheadings if necessary (on headings, see Section 6.1).
It is also best if appendices, like tables and figures, are able to stand on their own, so all abbreviations, symbols and specialised or technical terminology should be briefly defined or explained within each appendix, enabling the reader to understand the material without recourse to definitions and explanations in the rest of the thesis. All information in appendices that overlaps material in the main body of a thesis should match that material precisely in both content and format. Appendices can be set in the font size used in the main body of a thesis or a slightly smaller font to save space and they normally appear in the final matter before the endnotes (if there are any) or before the reference list or bibliography, although in some cases the appendices will be the last items in a thesis, so do check guidelines to determine if a specific position is required. The first appendix in a thesis usually begins on a new page, and subsequent appendices sometimes do the same, though they can run on instead with a little extra spacing between the end of one appendix and the beginning of the next. If there is only one appendix in a thesis, it will not need to be identified by a particular number or letter, but if you intend to include two or more appendices, they will need to be labelled with uppercase letters or with Arabic or Roman numerals according to the order in which the appendices are mentioned in the main text of the thesis, which should match the order of their appearance in the final matter (‘Appendix A,’ ‘Appendix B,’ ‘Appendix C’ etc., or ‘Appendix 1,’ ‘Appendix 2,’ ‘Appendix 3’ etc.). Appendices should always be referred to by these labels when they are discussed in the thesis, and each appendix should be referred to at least briefly in the main text of the thesis.
If a single table or figure makes up the whole of an appendix, the appendix label and heading are sufficient for the table or figure as well, but if an appendix contains more than a single table or figure, each table and figure will need to be numbered (and given a heading or caption), and this numbering should be separate from the tables and figures associated with the chapters of the thesis. If there is only one appendix, a capital A (for ‘Appendix’) should be used before each table or figure number – ‘Table A.1’ and ‘Figure A.2’ – but if more than one appendix is included, the specific letter or number of the appendix should be used as well as the table or figure number: ‘Table C.3,’ ‘Figure B.2,’ ‘Table II.4’ and ‘Figure IV.2.’ Please note that if you have more than one appendix in your thesis and any of those appendices contain more than one table or figure, the appendices should be labelled with letters or Roman numerals; if such appendices use Arabic numerals, it will be difficult to distinguish between tables and figures in chapters and those in the appendices (e.g., ‘Table 3.3’ could be the third table in Chapter 3 or the third table in Appendix 3, whereas ‘Table C.3’ is clearly the third table in Appendix C). Tables and figures may be embedded in appendices that also include text or they may appear at the end of each appendix, but if the university or department guidelines you are following indicate that tables and figures in general should be placed at the end of the thesis, those associated with appendices may need to appear there as well. For further information on tables and figures, see Sections 1.3 and 4.4.1.
4.6.2 Other Final Things
If you have not yet added (or revised and expanded since your proposal) any footnotes or endnotes that you intend to use for supplementary information in the thesis, now is the time to add them (see Section 3.4 above). It can be helpful to construct (or review) the supplementary notes and any appendices you plan to include at the same time so that you can decide which format is most appropriate for different kinds of material. If any ancillary lists are required – a list of abbreviations, for instance, or lists of tables and figures – these should be added at this point as well, either in the preliminary or final matter depending on university or department guidelines and/or personal preferences (see Sections 1.1.7–1.1.9). A list of abbreviations is usually arranged alphabetically by the abbreviations (rather than the full versions) with a colon between each abbreviation and its definition (see also Section 6.3):
ANOVA: Analysis of variance
CI: Confidence interval
ES: Effect size
Lists of tables and figures (on which, see also Sections 1.1.8 and 1.1.9), on the other hand, are arranged numerically according to the table or figure numbers and usually include the page number each table or figure appears on:
Table 1: Items in Questionnaire 1 . . . . . . . . 67
Table 2: Items in Questionnaire 2 . . . . . . . . 71
Table 3: Items in Questionnaire 3 . . . . . . . . 74
Tables are usually listed separately from figures, and shortened forms of table headings and figure captions are often used in these lists, especially if the headings and captions are long (consisting of more than a single sentence, for instance), but the table and figure numbers must match exactly the labels that appear on the tables and figures themselves and the order in which the tables and figures appear in the thesis. When tables and figures are reproduced or adapted from other sources, acknowledgements of those sources are sometimes included in such lists. For general advice on constructing lists, see Section 5.5.2.
Acknowledgements of any assistance you received in writing the thesis and in some cases of any materials you used from previous publications should be added to the thesis as well (see Section 1.1.6). Acknowledgements generally appear in the front matter of a thesis, but they can instead be added to the final matter, so you will need to determine which location is most appropriate for your thesis. Credits and permissions (if necessary) for material such as images, tables and long quotations borrowed from sources sometimes appear along with the borrowed material itself instead of (or in addition to) appearing in the acknowledgements (see Section 4.4.1, for instance). Acknowledgements in theses tend to be rather informal and sometimes intensely personal when compared with the formal scholarly text used in the rest of a thesis. As a general rule, this is fine – you have, after all, had a great deal of help in achieving the monumental goal of writing your thesis and it is only natural to want to thank with enthusiasm those who assisted you. Do beware, however, of letting your prose style slip beneath the required standard.
The acknowledgements may not be part of the scholarship in your thesis, but they are there for all to read, and a thesis is a professional document, so it is wise to maintain a professional perspective. Try to avoid arbitrary shifts between the first-, second- and third-person voices (e.g., ‘I would like to thank my friend and colleague Vicky for reading each and every chapter with such painstaking care – I wouldn’t have survived this thesis without you!’) and informal usage (contractions, for instance, such as ‘wouldn’t’ in my example, the second part of which would be better as ‘– I would not have survived this thesis without her!’). Keep in mind as well that some supervisors and committee members will feel embarrassed and uncomfortable when reading overly effusive expressions of gratitude aimed at themselves – yes, they have been wonderful, but supervising your work is their job, after all – so maintaining the dignity and comfort of everyone involved, including yourself, while expressing sincere and even enthusiastic gratitude is the best approach. Focussing precisely on exactly what each individual has done that specifically assisted you in completing your thesis will help you keep your acknowledgements relevant and professional.
Any dedication you wish to include in the thesis should be added to the front matter at this point as well. More importantly, if you have not yet written your abstract and chosen your keywords, they will need to be tackled, and if you have already worked on these earlier, revising them right after you have finished drafting the entire thesis is a good strategy (see Sections 1.1.2, 1.1.3 and 4.2). Finally, you will need to add or complete all the necessary citations, quotations and references in your thesis and compile the list of references, list of works cited or bibliography that should appear at the end of the thesis (or expand the one you submitted with your proposal: see Sections 1.2.6, 1.4.3, 2.1.2 and 3.5.4). It is very late in the game indeed to be deciding upon referencing methods and styles at this point, but if that is not yet a settled matter, a consistent and effective system must be adopted and applied throughout the thesis before it is considered a complete draft, and it is always wise to check your references carefully to be sure you have met the requirements set by your university, department and thesis committee. In Chapter 7 below I discuss in detail the main methods and styles of in-text referencing as well as reference lists and bibliographies, so please refer to that chapter for specific advice on bringing your references into line with scholarly standards, especially if you do not have specific guidelines to follow. If you use direct quotations in your thesis, see also Chapter 8, where I outline the ways in which direct quotations should be presented and integrated in academic and scientific prose.
Finally, once you have the entire thesis drafted, your table of contents will need to be completed by adding page numbers for the parts, chapters and sections of the thesis (and perhaps removing the summaries you used for your thesis outline if you have not already done so: see Section 4.1), or updated and checked if you are making use of a tool such as Word’s automatic table of contents function (see Section 6.1.1 for advice on creating an active table of contents). Make sure that all page numbers in the table of contents accurately indicate the pages on which those parts, chapters and sections actually appear in the thesis, and check the table of contents carefully to ensure that all titles and headings that appear in it match the corresponding headings in the thesis exactly in terms of order, wording, numbering (if used), punctuation and usually capitalisation as well (see Section 6.1 for further information on headings). Even something as simple as line spacing is important in this final stage. Although you may have single spaced your writing while sharing it with your supervisor and the other members of your committee without earning any complaints, double spacing is usual in the main body or running text of a thesis and it also tends to make your work more legible and easier on the eyes of your readers than single spacing does. Many universities will require double spacing, so do check for that in the guidelines and perhaps pay your readers (who are also your examiners) the courtesy of using it even if it is not required.
Why PhD Success?
To Graduate Successfully
This article is part of a book called "PhD Success" which focuses on the writing process of a phd thesis, with its aim being to provide sound practices and principles for reporting and formatting in text the methods, results and discussion of even the most innovative and unique research in ways that are clear, correct, professional and persuasive.
The assumption of the book is that the doctoral candidate reading it is both eager to write and more than capable of doing so, but nonetheless requires information and guidance on exactly what he or she should be writing and how best to approach the task. The basic components of a doctoral thesis are outlined and described, as are the elements of complete and accurate scholarly references, and detailed descriptions of writing practices are clarified through the use of numerous examples.
The basic components of a doctoral thesis are outlined and described, as are the elements of complete and accurate scholarly references, and detailed descriptions of writing practices are clarified through the use of numerous examples. PhD Success provides guidance for students familiar with English and the procedures of English universities, but it also acknowledges that many theses in the English language are now written by candidates whose first language is not English, so it carefully explains the scholarly styles, conventions and standards expected of a successful doctoral thesis in the English language.
Individual chapters of this book address reflective and critical writing early in the thesis process; working successfully with thesis supervisors and benefiting from commentary and criticism; drafting and revising effective thesis chapters and developing an academic or scientific argument; writing and formatting a thesis in clear and correct scholarly English; citing, quoting and documenting sources thoroughly and accurately; and preparing for and excelling in thesis meetings and examinations.
Completing a doctoral thesis successfully requires long and penetrating thought, intellectual rigour and creativity, original research and sound methods (whether established or innovative), precision in recording detail and a wide-ranging thoroughness, as much perseverance and mental toughness as insight and brilliance, and, no matter how many helpful writing guides are consulted, a great deal of hard work over a significant period of time. Writing a thesis can be an enjoyable as well as a challenging experience, however, and even if it is not always so, the personal and professional rewards of achieving such an enormous goal are considerable, as all doctoral candidates no doubt realise, and will last a great deal longer than any problems that may be encountered during the process.
Interested in Proofreading your PhD Thesis? Get in Touch with us
If you are interested in proofreading your PhD thesis or dissertation, please explore our expert dissertation proofreading services.
PhD Dissertation Proofreading
Our PhD dissertation proofreaders specialise in improving grammar, sentence structure, citations, references, clarity, logical flow and readability.
Master’s Dissertation Proofreading
To avoid failure and its consequences, send your dissertation to our master’s dissertation proofreading service.
Dissertation Proofreading Services
Our dissertation proofreaders specialise in correcting and perfecting the language, editorial styles and references across all science fields.
Headquarters
Dissertation-Proofreading.com Allia Future Business Centre The Guildhall Market Square Cambridge CB2 3QJ United Kingdom
More Expert Proofreading Services
Journal editing.
Journal article editing services
PhD Thesis Editing
PhD thesis editing services
Manuscript Editing
Scientific editing, medical editing services, psychology proofreading, appendices, references, acknowledgements - how to write a phd thesis, about the author, rene tetzner.
Rene Tetzner's blog posts dedicated to academic writing. Although the focus is on How To Write a Doctoral Thesis, many other important aspects of research-based writing, editing and publishing are addressed in helpful detail.
Related Posts
Phd success – how to write a doctoral thesis.
October 1, 2023
Table of Contents – PhD Success
October 2, 2023
The Essential – Preliminary Matter
October 3, 2023
The Main Body of the Thesis
October 4, 2023
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Is it okay to include a very long appendix (for MS thesis)?
I am currently doing my MS thesis and I have to include an appendix to describe a mathematical subject. However, I added extra details in that appendix and it is now too long.
My Prof. suggests I better not include it "at all", or if necessary just make it shorter (though he admits that it is very well written and referenced).
Is it unusual to include a very long appendix in a thesis?
- My thesis is now 150 Pages; 20 pages are for that appendix.
- 1 This is probably not unusual, but extrapolating from my own behavior: the longer it is the less likely i read it (it is an appendix after all ..) – CrepusculeWithNellie Commented Mar 1, 2016 at 21:24
- 3 The only part of your situation that seems odd to me is an advisor recommending you remove 20 pages of well written math. That I cannot understand. – Cliff AB Commented Mar 1, 2016 at 23:49
- 1 Just wait 'til you see a literature paper that includes a transcription ;-) If the source text is long enough, the appendix can be several times longer than the thesis/dissertation itself. But the big question is how necessary is it for people in the field to understand your work. He might think it's not necessary. If you really think it important, argue for it to go in the body (and maybe he'll settle for an appendix). – user0721090601 Commented Mar 2, 2016 at 0:38
- 2 20 pages appendix on a 150 page thesis is not long at all. 150 page appendix on a 20 page thesis, now that would be long. That's the ratio I've seen for some scientific proposals, where the format of the core proposal is so rigid that essentially all scientific information is in the appendices. – gerrit Commented Mar 2, 2016 at 11:03
2 Answers 2
This does not sound unusual to me. Just ask yourself, is there a possibility that the reader would need this?
I have seen theses and dissertations with no appendices and some with over 50 pages of appendices. In my field, these are often filled with user study materials, source code, or raw data which can easily eat up many pages.
I don't see any harm done with being conservative and including everything. In this case, I have seen people list two versions of their thesis online, one with and one without the appendices.
- Agreed: 20 pages on a 150 page thesis is quite a reasonable size. – jakebeal Commented Mar 1, 2016 at 19:59
From my knowledge, it is unusual, but you are missing the most important question: is everything you put there absolutely needed for any other person to understand the value of your work?And does removing any part of it decrease the value of your thesis? Try to see your thesis as an impartial, but knowledgeable person. If you answer these two questions, you will know what do do!
Edit: The number of pages of your appendix compared to your thesis is not much important. But I would like to let you know that my MSc thesis has 200 pages of which 50-60 are from several appendix
I hope I have helped you! Thanks, KingBaboon
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged thesis masters ..
- Featured on Meta
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
Hot Network Questions
- Should I apologise to a professor after a gift authorship attempt, which they refused?
- Keyboard Ping Pong
- Go the Distance
- Using grout that had hardened in the bag
- Error concerning projectile motion in respected textbook?
- Car stalls when coming to a stop except when in neutral
- Upgrading SQL Server Express 2008 R2 that seems to be tied with SQL Server Standard
- Implementation of Euler-Maruyama numerical solver
- Book read in the 80/90s about an alien microbe taking over creatures
- To be considered airworthy, are commercial aircraft fuselages required to support some amount of external overpressure without buckling?
- A model suffering from omitted variable bias can be said to be unidentified?
- Is it an option for the ls utility specified in POSIX.1-2017?
- Where are quantised states in QFT?
- Accommodating whiteboard glare for low-vision student
- What do American people call the classes that students go to after school for SATs?
- Is it possible to go back to the U.S. after overstaying as a child?
- Mechanism behind a pink human skeleton
- Questions about writing a Linear Algebra textbook, with Earth Science applications
- Which Präposition should I use with Erwartungen?
- Pattern on a PCB
- How will a planet on asteroid belt see Jupiter?
- Simple probability question - seeming contradiction
- APFS vs HFS+ which is better for storage and music/videos creating/editing?
- How to control arrowhead size in chemfig?
Thesis/Dissertation Formatting
- You may or may not have appendices depending on your content.
- Always start an appendix on a new page. Use the page break function to insert a blank page; do not use the Enter key multiple times.
- Type Appendix A: Title of Appendix on the top line; your appendices will be labeled sequentially starting at A and continuing with B, C, etc. If you only have one appendix, still label it Appendix A. Be sure to label this title as a page title heading to format it properly; see Content/Chapters for more information about headings.
- Leave the next line blank.
- Start your appendix.

- Thesis/Dissertation Information
- Introduction & Help
- General Formatting
- Table of Contents
- Acknowledgments
- List of Tables
- List of Figures
- Content/Chapters
Experience Tech For Yourself
Visit us to see what sets us apart.
Quick Links
- Tech at a Glance
- Majors & Concentrations
- Colleges & Schools
- Student Life
- Research at Tech
- Tech Express
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Mission and Vision
- Facts about Tech
- University Rankings
- Accreditation & Memberships
- Maps & Directions
- Board of Trustees
- Office of the President
- Strategic Plan
- History of Tech
- Parents & Family
- International
- Military & Veteran Affairs
- Tuition & Fees
- Financial Aid
- Visit Campus
- Scholarships
- Dual Enrollment
- Request Information
- Office of the Provost
- Academic Calendar
- Undergraduate Catalog
- Graduate Catalog
- Volpe Library
- Student Success Centers
- Honors Program
- Study Abroad
- Living On Campus
- Health & Wellness
- Get Involved
- Student Organizations
- Safety & Security
- Services for Students
- Upcoming Events
- Diversity Resources
- Student Affairs
- Featured Researchers
- Research Centers
- ttusports.com
- Social Media
- Student Resources
- Faculty & Staff Resources
- Bookstore/Dining/Parking
- Pay Online - Eagle Pay
- IT Help Desk
- Strategic Planning
- Office of IARE
- Student Complaints
Find Info For
- Current Students
- Prospective Students
- Alumni and Friends
- Engage with Purdue
- Research and Innovation
Quick Links
- Departmental Format Advisors
- iThenticate Requests
- Copyright and Your Thesis
- Editing, Proofreading, and Translation Services
- Deposit Requirements
- Request a Consultation
- Deadlines
- Thesis & Dissertation Office
Thesis and Dissertation Policies and Practices
All thesis-option master’s students and doctoral students must follow the Thesis & Dissertation Policies that are outlined in the University Catalog – Policies and Procedures for Administering Graduate Student Programs .
Thesis Copyright Protection
Purdue University Policy I.A.1 , May 18, 2007, Intellectual Property , established that copyright ownership now resides with you, the author. The copyright symbol © is not required for works to be copyrighted. All candidates have the additional option of applying for registration of their copyright: This establishes a public record of theses/dissertations and confers additional legal rights, enabling individuals to file infringement suits and seek statutory damages as well as attorneys’ fees. Copyright registration can be filed here .
Specific questions regarding your rights and responsibilities under U.S. copyright law may be addressed to the Purdue University Copyright Office: 765.496.3864 or Stewart Center Room 246A.
Using Material Protected by Copyright
Purdue University promotes compliance with U.S. copyright law and understanding of the appropriate use of copyrighted works: Purdue University Policy I.A.3, January 1, 2015 Use of Copyrighted Materials for Educational and Research Purposes .
When quoting extensively from copyrighted material, the author must obtain written permission from the copyright holder. There is no precise relationship between the amount of text quoted and the requirement for written permission to use the material. The law governing copyright infringement is based on the fair use principle. Ordinarily, if you plan to quote more than 150 words of continuous text from copyrighted material, you should ask permission from the author. If the work you are quoting has significant commercial value, you should obtain permission to quote any complete or nearly complete text item or section. When your quotation of copyrighted material could have a negative impact on the existing commercial value of that material, obtain the copyright holder’s permission. Figures or other graphical material, including Web pages, should not be reprinted in your thesis without the author’s consent. Permission to use copyrighted material is usually granted on condition that acknowledgment is made. You will be responsible for any required payments.
You will be required to upload copyright permissions to HammerRR (Figshare) when depositing your thesis with the Purdue University Graduate School.
By depositing a thesis with the Purdue University Graduate School, you certify that all copyrighted material incorporated into the thesis complies with United States copyright law and that you have received written permission from the copyright owners for the use of their work, which is beyond the scope of the law. You also agree to indemnify and save harmless Purdue University from any and all claims that may be asserted or that may arise from any copyright violation.
Data subject to EAR, ITAR, DFARS Clause 252.204-7012, and other controlled data designators require increased security to establish compliancy with government regulations. Due to these increased security requirements an alternative method is required to be followed for controlled theses see Controlled Thesis Submission Process - Guidance Document - Controlled Thesis Submission Process.
Publication of the thesis or dissertation is a required part of the deposit process. The university currently uses HammerRR to publish the thesis after which, your thesis will become an Open Access document with no additional cost to you.
All theses submitted to HammerRR are considered the final copy and are required to undergo a format review. Candidates will upload their thesis to HammerRR and Graduate School administrators will review the thesis for any format errors. In the event format changes are required, the administration will provide you a list of necessary changes that you should make and re-submit to HammerRR as soon as possible. Format reviews will continue until your format is in an acceptable condition. You may schedule a Formatting Consultation before your Final Exam (Defense) to avoid an extensive format review during the deposit process.
To further promote and preserve the intellectual contributions of its degree recipients, Purdue is also partnering with ProQuest / Clarivate to disseminate its emerging scholarship through the ProQuest Dissertation & Theses Global and Web of Science databases, which reaches thousands of institutions and millions of researchers worldwide. ProQuest also partners with major search and discipline-specific indexes for additional amplification and provides all of these services free of charge. By distributing your work with ProQuest, you will increase its visibility and impact within the global research community. ProQuest recognizes the critical importance of embargos and will never publish a thesis until it has been released for dissemination by the university. You may withdraw your work from distribution at any time. You are eligible for a 10% royalty based upon sales and usage of the full text of the work. Please contact [email protected] with any questions and to set up your account to collect royalties.
Open Access Theses and Dissertations
Each student grants, without restriction, royalty free to Purdue University the nonexclusive right and license to reproduce, distribute, and display, in whole or in part, all theses and dissertations in any format now known or later developed for preservation and access in accordance with this agreement and will be made to the general public at no charge.
Benefits of an Open Access Thesis or Dissertation:
[1] Higher Citation Rates
The more users who can access a work, the more researchers that can cite that work.
[2] Better Global Visibility of Your Work
By making their work globally visible through open access, authors are allowing more scholars, more promising students and future scholars, less wealthy institutions, policy makers, news reporters, and the unexpected reader and citizen scholar to have access to their work who may not have otherwise had the ability or funds to access closed-access scholarship.
[3] Meeting the Land Grant Mission of the University
"Open access at Purdue can publicly showcase the scholarly output of the University and its community members, this provides greater visibility and traffic to your department, school, and ultimately the university. It can also show that scholars and researchers at Purdue think beyond their own disciplines by showcasing the interdisciplinary scholarship and research being created at Purdue. Finally, open access scholarship demonstrates accountability to the public that funds the university, while disseminating knowledge gained and created at Purdue; satisfying the public, land-grant mission of the university."
Students who wish to delay public release of their thesis must make the appropriate selection on the Electronic Thesis Acceptance Form (ETAF), provide the reasoning for the requested embargo, and make the same embargo selection in their HammerRR profile. The information that is provided to ETAF and HammerRR will be validated for consistency at the time of your thesis submission. If inconsistencies are present between the ETAF and HammerRR, the HammerRR profile will be updated by administrators to match what you have selected and what your committee chair has approved on the ETAF. Embargo periods are 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, or indefinite. During the embargo period, the deposited thesis abstract will be available for viewing; however, the main content will remain unpublished until the embargo period has expired. Students may embargo their thesis when applying for patents, have publications pending, or when proprietary rights are involved.
Confidentiality
Students who are applying for patents, are including sensitive ITAR/Export Controlled material, have a contract on file with Sponsored Program Services (SPS), or are including proprietary information may request confidentiality of their thesis. Confidentiality can be requested for one or two years and students who have contracts on file with SPS may request longer periods.
ADA Compliance and Accessible Documents
Before depositing your thesis with the Graduate School, the PDF copy of your thesis needs to be made accessible (the file will be accessible to screen readers and other assistive computer technologies) to the best of the author’s ability.
Word users: To check your thesis for accessibility it is recommended that you use Word 2013 or Word 2016 as these versions have a built-in accessibility checker. You can learn more about the accessibility checker from the Microsoft Accessibility Checker page. Once you convert your file to PDF, you should also verify that the accessible Word document has converted to an accessible PDF file.
LaTeX users: Authors using LaTeX should manually check the accessibility of their PDF document using Acrobat Pro.
Post-Facto Edits
The Graduate School expects candidates and departments to thoroughly review format and content of theses and dissertations prior to their electronic submission. The Graduate School does not generally permit post-facto revisions to ETDs once they have been accepted for deposit by the Thesis & Dissertation Office. Post acceptance changes are only permitted to correct significant textual, data, or mathematical errors affecting accuracy of content and which could be potentially embarrassing to Purdue University.
Exceptions to Graduate School policy will be considered on a case-by-case basis and may be requested by submitting a letter with justification for the exception to the Graduate School for consideration. Requests must be endorsed by the student’s major professor and the Head or Chair of the Graduate Program. The Graduate School may require additional approvals if the request may impact other offices within the University (see Section VII.I of the University Catalog).
A thesis authored at Purdue University should be structured and formatted using one of the below methods:
Traditional
A traditional thesis is a document that provides a complete and systematic account of your research. A typical traditional thesis suggests the following structure:
- Statement of Approval page
- Dedication (optional)
- Acknowledgments (optional)
- Table of Contents
- List of Tables
- List of Figures
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Conclusions and Recommendations
- Appendix (optional)
- Vita (optional)
- List of Publications (optional)
* Thesis structure may vary by department. Please consult your committee for specific departmental requirements.
Article-based
An article-based thesis is a collection of published (or will be published) research articles consisting of an introductory and concluding chapter. A typical article-based thesis suggests the following structure:
- Published Article #1
- Published Article #2
- Published Article #3
Theses authored using this structure will need to include acknowledgement of prior publication within the respective chapter. Although each journal may have specific statement requirements, the acknowledgment should be single spaced and appear 3 single spaces under the chapter title. Consult your publisher regarding required information that should appear in this acknowledgment.
Creative work
The Graduate School is prepared to accept theses in creative formats subject to departmental and committee approval. Students wishing to submit a creative work as their thesis requirement should consult with their committee chair and contact the Thesis & Dissertation Office with their proposal.
If the primary literature on a subject matter is in a language other than English and the thesis or dissertation addresses a community of scholars who publish in a language other than English, a student may elect to write the thesis in a language that all committee members speak and read and support its use in the thesis. In this case, the thesis should contain a title page and abstract page in English.
All West Lafayette , IUPUI , and Northwest candidates are required to submit the ETAF through their Plan of Study portal. This form should be submitted on the day of Defense or no later than the date of the Final Examination Deadline each semester.
Purdue Fort Wayne candidates are required to submit paper versions of Forms 9, 32, and 15 . Copies of these forms should be submitted to the Thesis & Dissertation Office prior to submitting the thesis to HammerRR.
Effective September 1, 2014, Purdue’s Graduate School requires that all theses and dissertations be reviewed using the iThenticate software and any issues identified by the software and any issues identified by the software addressed prior to the deposit of the final thesis or dissertation with the Graduate School. Satisfaction of this requirement will be certified by both committee chair and degree candidate on the ETAF. Click here for more information.
All master’s candidates are required to pay a Thesis Deposit Fee of $90 and Ph.D. candidates are required to pay a Thesis Deposit Fee of $125. The fees will be uploaded to a student’s myPurdue account within 5-10 business days after the HammerRR submission is approved.
West Lafayette, PFW, and PNW candidates will pay the fee through their local bursar’s office. IUPUI candidates will receive an e-bill following their successful thesis deposit.
Candidates are required to meet both departmental and Graduate School deadlines each term.
Thesis-option master’s and doctoral students are required to submit their thesis for a final format check to the Graduate School no later than the close of business (5:00pm ET) the day before the semester's designated deposit deadline date. Candidates who miss the semester's deposit deadline at 5:00, but still wish to graduate, must submit a request for a deposit extension (endorsed by committee chair and department head) to the Graduate School for full consideration. If approved, the student should expect to pay a Late Graduation Deadline Fee . Contact the Thesis & Dissertation Office for questions.
Ph.D. and master’s students are required to complete the Graduate School Exit Questionnaire (GSEQ). In addition to the GSEQ, Ph.D. candidates are required to complete the Survey of Earned Doctorates. These surveys will become available to complete during the semester the student registers as a candidate for graduation.
Communication
- OneCampus Portal
- Brightspace
- BoilerConnect
- Faculty and Staff
- Human Resources
- Colleges and Schools
- Find Workshops
- Funding Support
- Purdue Graduate Student Government
- Purdue Graduate Student Center
- Data Requests
- Staff Directory
- OGSPS Toolkit
- Catalogs, Manuals, Policies
- Report a Concern
- Publications
Ernest C. Young Hall, Room 170 | 155 S. Grant Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907-2114 | 765-494-2600
Contact OGSPS at [email protected] for accessibility issues with this page.
Empirical Thesis Structure JGU MIEPP Mainz

Get in touch
Have you checked our knowledge base ?
Message sent! Our team will review it and reply by email.
Email:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader's understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper, dissertation, or thesis without making your final product too long.
Summary. An appendix is a section at the end of a dissertation that contains supplementary information. An appendix may contain figures, tables, raw data, and other additional information that supports the arguments of your dissertation but do not belong in the main body. It can be either a long appendix or split into several smaller appendices.
Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates. Published on 15 August 2022 by Kirsten Dingemanse and Tegan George. Revised on 25 October 2022. An appendix is a supplementary document that facilitates your reader's understanding of your research but is not essential to your core argument. Appendices are a useful tool for providing additional information or clarification in a research paper ...
Appendix format example. The appendix label appears at the top of the page, bold and centered. On the next line, include a descriptive title, also bold and centered. The text is presented in general APA format: left-aligned, double-spaced, and with page numbers in the top right corner. Start a new page for each new appendix.
If you only have one appendix in your thesis, adding that is pretty straightforward. It is mostly treated like another chapter, except "Chapter" is changed to "Appendix". When you have more than one appendix, it gets more complicated and you have to add a List of Appendices in the front matter part of the thesis. The video tutorial demonstrates ...
The appendix is a section that is placed at the end of the thesis and may contain material such as tables, figures, maps, photographs, raw data, computer programs, musical examples, interview questions, sample questionnaires, CDs, and many other types of material. An appendix is considered a chapter equivalent and the appendix title should be ...
For example, if the last page of your Bibliography is 195, your first Appendix page number should be 196. Appendices as Supplemental Files Electronic or audiovisual data may be included as Supplemental Files in an ETD submission.
If your thesis or dissertation has appendices, they must be prepared following these guidelines: ... When there is more than one appendix, assign each appendix a number or a letter heading (e.g., "APPENDIX 1" or "APPENDIX A") and a descriptive title. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., 1, 2 or A, B), or you ...
Appendices should go after your references/works cited list, should be formatted as Heading 1, and as such should appear in your Table of Contents. Any Tables or Figures that appear in an appendix should also appear in its respective list. Finally, when referring to an appendix within the body of the work, please refer to them as "Appendix A ...
As an option the appendix may be introduced with a cover page bearing only the title centered vertically and horizontally on the page. The content of the appendix then begins on the second page with the standard one inch top margin. Quality and format should be consistent with requirements for other parts of the thesis including margins.
Appendices provide supplementary information to the main thesis and should always appear after the references/bibliography. If you are unsure about whether content should be included in the thesis or in an appendix, consult with your supervisor. The thesis and appendices must be uploaded in a single file. For more information about appendices ...
Start each appendix on a new page and label it with a letter or number, along with a title clarifying content (Appendix A: Instrument Diagrams, Appendix B: Test Results, etc.) List appendices in the table of contents at the beginning of your document. Doing these things will make it easier for your reader to find information in the appendices.
An appendix is an integral part of every dissertation paper, serving as supplementary material that enhances and supports the research study. However, only a few people understand what the section is, where it must be placed, and why it must be included in a dissertation.Therefore, while not typically central to the dissertation's argument, the appendix adds valuable context and transparency ...
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On June 13, 2023. "Appendix or appendices (plural) is/are used to provide additional data related to your dissertation research project.". An appendix section in dissertation helps you to provide background data related to your topic; present tables, illustrations, and figures that ...
For example, in a book, an appendix might include photographs, maps, or illustrations that help to clarify the text. Importance of Appendices. Appendices are important components of research papers, reports, Thesis, and other academic papers. They are supplementary materials that provide additional information and data that support the main text.
An appendix (plural: appendices) is a section at the end of a book or essay containing details that aren't essential to your work, but which could provide useful context or background material. In the main body of your essay, you should indicate when you're referring to an appendix by citing it in parentheses.
Appendix in dissertation is a section where non-standard format data is included. It is designed to improve quality of work, make it more evident and trustworthy. This section shows your readers the level of your competence and topic's depth. This part contains elements related to your research like tables, images, maps, documents, etc.
Download: Dissertation/Thesis Template Download (choose by citation style): Formatting Checklist - Chicago Style or Formatting Checklist - APA Style Download the free Adobe Reader to complete the following template pages. Do not use browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, or any other PDF programs to fill out templates as they will be misaligned or missing customization components.
An appendix is a section of the paper that is included at the end of a report or a dissertation. If there is more than one item being included in this section, the section plural is appendices. Items that would usually be included as an appendix are relevant to the context of the study but may not be useful to have in the main body of the work.
For a PhD thesis (as indicated in the tags of your question), check your university's reference style guide. I suspect, however, that it doesn't go into that much detail. ... If appendix precedes references, just include citations in the regular reference list. If it follows, have a separate set of appendix-specific references. If it is ...
Finally, you will need to add or complete all the necessary citations, quotations and references in your thesis and compile the list of references, list of works cited or bibliography that should appear at the end of the thesis (or expand the one you submitted with your proposal: see Sections 1.2.6, 1.4.3, 2.1.2 and 3.5.4).
If you really think it important, argue for it to go in the body (and maybe he'll settle for an appendix). 20 pages appendix on a 150 page thesis is not long at all. 150 page appendix on a 20 page thesis, now that would be long. That's the ratio I've seen for some scientific proposals, where the format of the core proposal is so rigid that ...
Always start an appendix on a new page. Use the page break function to insert a blank page; do not use the Enter key multiple times. Type Appendix A: Title of Appendix on the top line; your appendices will be labeled sequentially starting at A and continuing with B, C, etc. If you only have one appendix, still label it Appendix A. Be sure to ...
Appendix (optional) References; Vita (optional) List of Publications (optional) * Thesis structure may vary by department. Please consult your committee for specific departmental requirements. Article-based. An article-based thesis is a collection of published (or will be published) research articles consisting of an introductory and concluding ...
A basic structure for an empirical thesis in the JGU Mainz. Specially usefull for MIEEP and QDEM students. An online LaTeX editor that's easy to use. ... % Set specific page number \setcounter{page}{8} % Example: start from Roman numeral VIII \centering \appendix \include{Appendix} % Declaration of Authorship \centering \include{Declaration ...
This study evaluated the intersectionality thesis, which suggests that the interaction of ethnicity, sex, and socioeconomic status significantly affects achievement in UK higher education. The study used a sample of 135,699 students from the Graduate Outcomes survey for the 2018/19 cohort, the last to leave higher education before the COVID-19 ...