

Phrasal Verbs
What are phrasal verbs.
Table of Contents
Easy Examples of Phrasal Verbs
Real-life examples of phrasal verbs, transitive and intransitive phrasal verbs, separable and inseparable phrasal verbs, particle or a preposition, why phrasal verbs are important.

- to break in
- to catch up
- to break down
- to cut back
- to put up with
- to go out with
- to check up on
- to cut down on
- Damn your principles! Stick to your party. (Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli)
- When people find out you're an actress, they Google you. (Actress Laverne Cox)
- Meditation helps me to calm down . (Singer Lady Gaga)
- Do I exaggerate? Boy, do I, and I'd do it more if I could get away with it. (Comedian David Sedaris)
- Fill in the form as quickly as possible.
- Did you go over those reports last night?
- I will look into it immediately.
- I felt compelled to hand the purse in .
- If you're unhappy, please stand up .
- The lorry is starting to drop back .
- The tree could fall down .
- Do not give in .
- She will show up soon.
- She will show up the opposition.
- I will make you up to look like a princess.
- She talked her father into letting her attend the party.
- She looks up to her sister .
- You must stick to the plan at all costs.
- He looked my address up on the National Voter Register.
- He looked up my address on the National Voter Register.
- She takes after her mother.
- Please think it over .
- I can stand in for you next week.
(Reason to Avoid 1) Phrasal verbs sound informal.
- We will congregate in the foyer. (preferable in a formal email)
- We've put the meeting off until Tuesday. (okay, if a little informal)
- The meeting is postponed until Tuesday. (preferable in a formal email)
(Reason to Avoid 2) Some phrasal verbs eat up your word count unnecessarily.
- I cannot face up to this problem. (okay)
- I cannot face this problem. (better, more succinct)
- Try this new garlic dip out . (okay)
- Try this new garlic dip. (better, more succinct)
- She will not stand for shoddy work. (okay)
- She will not stand shoddy work. (better, more succinct)
- Even I don't wake up looking like Cindy Crawford. (Model Cindy Crawford)
(Reason to Avoid 3) A phrasal verb often puts a preposition at the end of your sentence.
- It is a situation I will not put up with . (okay)
- It is a situation I will not tolerate. (safer and more succinct)
- Can you sort it out ? (okay)
- Can you resolve it? (safer and more succinct)
(Reason to Embrace 1) A phrasal verb might better fit your image.
- We would not expect you to tolerate a second-rate service. (corporate)
- Don't put up with bad service. (engaging)
(Reason to Embrace 2) Phrasal verbs are easily understood.
- The framework is required to concatenate the disparate elements.
- The framework is required to join up each element.
- Phrasal verbs sound natural, and they're easily understood. However, they can sound too informal for business or academic writing. Strike the balance you need.
- Sometimes, the preposition that accompanies the main verb in a phrasal verb is unnecessary. If it doesn't add anything, delete it.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips
Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips
Published on April 23, 2015 by Shane Bryson . Revised on November 7, 2022.
A phrasal verb combines two or more words to describe a specific action. Phrasal verbs can be difficult to get right, as their meaning usually has nothing to do with the definitions of the component words.
This means that phrasal verbs must be treated as distinct pieces of vocabulary. You have to learn them as a single unit of meaning, just like you would learn any single word.
Phrasal verbs are very common in everyday speech, but in academic writing, it’s best to replace them with one-word alternatives where possible.
47 phrasal verbs and one-word alternatives
Table of contents
What is a phrasal verb, when to use phrasal verbs, separating phrasal verbs.
A verb (e.g., “It goes ”) becomes a phrasal verb with the addition of one preposition (e.g., “The light goes out ”) or more (e.g., “She goes out with him”). Each additional preposition completely changes the meaning of the verb.
It is very important to remember that a phrasal verb should be considered one unit of meaning, just like a distinct verb. In the above examples, the phrasal verb “goes out” is as different from the verb “goes” as the verb “goes” is different from the verb “stays.”
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Although the best choice is usually to avoid phrasal verbs, they are so common that finding adequate replacements every time will be difficult. Change them when you can, and when you “run out” of ideas for rephrasing, “cheer up,” “believe in” yourself, and “write down” your phrasal verbs conscientiously.
Phrasal verbs do have their uses, after all. For example, they convey a casual tone, and while this is not usually desirable in academic writing , the best academic writers can vary their tone at will.
Accordingly, you should think of phrasal verbs as a stylistic option, even though you will often be best advised to eliminate them rather than add them.
Some phrasal verbs can be separated by intervening words, while others have to stay together in the sentence. There is no rule to tell whether a phrasal verb can be separated, so you have to learn by memory and practice—one good reason to avoid them when you can.
One helpful pointer, though, is that phrasal verbs that can be separated must be separated when their object is a pronoun (e.g., it , her , them).
Example: Separable
- Call the meeting off .
- Call off the meeting.
Note that if a phrasal verb is separable, it must be separated when its object is a pronoun (e.g., it , her , them).
- Call it off .
- Call off it.
Example: Inseparable
- The message didn’t come across well.
- The message didn’t come well across .
Example: Must be separated
Some phrasal verbs always have to be separated, but this is comparatively rare.
- Oscar will take Sven up on the offer.
- Oscar will take up Sven on the offer.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Bryson, S. (2022, November 07). Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved July 17, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/phrasal-verbs/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
List of 47 phrasal verbs and their one-word substitutions, subject-verb agreement | examples, rules & use, verb tenses in academic writing | rules, differences & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Phrasal Verbs – List, Uses & Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
You guessed it; as the name suggests, a phrasal verb is a type of verb that comes in phrases. Learning these different phrasal verbs improved my vocabulary and communication so I’m putting everything I know into this handy guide for you.
You’ll learn more about phrasal verbs and their different types as I explain. I also provided an extensive list of phrasal verbs with their definitions and sample sentences.
What are Phrasal Verbs?

Phrasal verbs in English are groups of words or multi-word verbs that show action. This verb usually includes a normal verb and an adverb or preposition.
Keep in mind the meaning of a phrasal verb is usually unrelated to the definition of the main verb. For example:
- We passed out two hours after the social event.
The phrasal verb in this sentence is passed out, which means become unconscious, sleep, or blackout. But the base verb, pass, takes on a different meaning. This single-word verb means to move or cause to move in a specified direction.
Here’s another example.
- The team members come up with the best project ideas at night.
The phrasal verb above is come up, meaning present itself. It’s different from the base verb, come, which means arrive .
English phrasal verbs can be confusing because their definitions are not explicit or painless to speculate. It takes memorization to understand the meaning of every phrasal verb.
Whether it’s a regular or irregular verb, remember that phrasal verbs act like normal verbs in sentences. They can express action while showing time. That means you can also conjugate them into every type of verb form and any verb tenses.
What are the Four Types of Phrasal Verbs?
Understanding phrasal verbs will help you master their placement and functions in sentences. Here are the four categories to remember.
Transitive Phrasal Verbs
A transitive phrasal verb acts like normal transitive verbs. A transitive verb always includes a direct object. For example:
- I will go over the phone book to look for his telephone number.
- We will get through this difficult time.
The phrasal verb in the first statement has a different meaning from the original verb, go . The phrase go over means to examine or look at something carefully. Its direct object is phone book because it is the receiver of the action.
In the second sentence, the phrasal verb is get through, meaning overcome. The receiver of the action is difficult time.
Here’s a list of transitive phrasal verbs you can use.
- Bring back.
- Pass around.
- Switch off.
Intransitive Phrasal Verbs
This is a verb that doesn’t include a direct object. I remember that a direct object is a noun or pronoun that accepts the action. Take a look at the sentences containing intransitive phrasal verbs below.
- We need to catch up without mobile phones and other distractions.
- Please step aside for the cyclists.
In the first sentence, the verb catch up stands on its own without a direct object. The same is true with the second sentence. Step aside stands on its own without a noun or pronoun receiving the action.
Here are more examples of intransitive phrasal verbs.
- Came about.
- Come through
- Stand by. Turn in.
Separable Phrasal Verbs
Separable phrasal verbs are transitive verbs where we can put the direct object between the words. For example, instead of saying, “pick up you,” we say, “ pick you up.” Below are more sentence examples.
- Please don’t let me down.
- Marvin is planning to take Lily out on a date.
You can even put long groups of words or a noun phrase between separable phrasal verbs. For example:
- I know you would never let Hazel, Jason, and the rest of the organization down.
Remember that some separable phrasal verbs can still be placed together in a sentence. The sentences below are both correct.
- I will pick up the package today.
- I will pick the package up today.
It’s also important that not all transitive phrasal verbs can be separated. For example:
- Incorrect: Let’s go these pages over.
Correct: Let’s go over these pages.
There’s a special rule for pronouns regarding separable verbs. If the direct object is a pronoun, position it in the middle of a phrasal verb. For example:
- Incorrect: The men will pick up it later.
Correct: The men will pick it up later.
Here are some examples of separable phrasal verbs.
- Bring about.
- Bring over.
- Quiet down.
Inseparable Phrasal Verbs
An inseparable phrasal verb is a phrasal verb that you should not split up. These phrasal verbs are always beside each other, whether there’s a direct object or not. Below is an example of an inseparable phrasal verb with a direct object.
- Incorrect: The mother wants to stick her principles to.
Correct: The mother wants to stick to her principles.
Here’s another example of an inseparable phrasal verb without a direct object. In other words, it’s also an intransitive phrasal verb.
- The orphan carried on with his life.
Some of the most common non-separable phrasal verbs in the English language are:
- Back out of.
- Come along with.
- Check up on.
- Disagree with.
- Drop in at/on.
- Drop out of.
- Fall back on.
- Fall out with.
- Get away with.
- Look after.
- Put up with.
- Run away with.
Rules for Using Phrasal Verbs
We have specific rules when using phrasal verbs. I laid them all out here for you to study.
Phrasal Verbs Have Different Definitions from the Main Verb
Combining a normal verb with a preposition or adverb gives it a different meaning from the original action verb. The sentences below will prove it.
- Justine came down with a cold and fever after playing in the rain for hours.
- I only came here to see the headmaster.
In the first sentence, the phrasal verb came down with is in its past form, meaning became sick. But in the second example, the verb came means arrived.
Below are more examples.
- Julia promised not to back down from the fight. ( Back down means to withdraw, while back means to give support).
- Let’s get away for the weekend. ( Get away means to escape, while get means to receive).
- You keep on messaging me. ( Keep on means continue doing, while keep means have or retain possession of).
Phrasal Verbs Can Be Verbals
Since phrasal verbs are no different from ordinary verbs, they can also function as other parts of speech, such as a noun , adverb, or adjective. These are called verbals.
One type of verbal is a gerund, a verb in its present participle form acting as a noun. Here’s an example of the phrasal verb get over acting as a gerund.
- Getting over that incident was a traumatizing experience.
Another type of verbal is the infinitive. Here, the word to plus the base form of the verb act as a noun, adjective, or adverb in the sentence. For example:
- To get over a long-term ex-partner is challenging. ( To get over as a noun)
- But I don’t want to get over him yet. ( To get over as an adverb)
Phrasal verbs can also be participles. Participles are verb forms used as adjectives or parts of specific tenses. Below are examples of the present and past participle forms of get over in sentences.
- Jamie is still getting over her breakup. (present participle used in the present progressive tense)
- Having gotten over the accident, Jamie is now ready to walk on her feet again. (past participle is used in the present perfect tense)
Conjugating Phrasal Verbs
As the main verb of the entire sentence, we conjugate a phrasal verb by only changing the action verb. Then, you should leave the other words, such as the preposition or adverb.
For example, the present progressive form of look forward is is/are/am looking forward. The word forward remains the same.
- I’m looking forward to the charity event in three days time.
Here’s another set of sentence examples. The phrasal verb used is get up, where get is an irregular verb. That means it doesn’t follow the typical conjugation pattern for its simple past and past participle forms.
- Simple present tense: She gets u p at 12 noon each day.
Simple past tense: She got up at 12 noon yesterday.
Simple future tense: She will get up at 12 noon tomorrow.
All Intransitive Phrasal Verbs are Inseparable
You already know that all separable phrasal verbs are transitive. However, not all transitive phrasal verbs are separable. However, all intransitive phrasal verbs are inseparable because they do not have a direct object. For example:
- My mother wakes up the earliest in our family.
- The competitive student wants to get ahead of everyone academically.
- The elderly couple keeps on coming back to their first home every summer.
All Three-Word Phrasal Verbs are Inseparable
Some phrasal verbs actually have more than one particle after the main verb. All these three-word phrasal verbs are inseparable. That means a direct object cannot come between them. Check out the sentences below.
- The finance department has to come up with a better plan for the 2023 budget.
- Teachers must be role models because the children look up to them.
- The stepmother and biological mother get along with each other.
All Three-Word Phrasal Verbs are Transitive
Three-word phrasal verbs end with prepositions, so there’s likely an object that will follow them. Some examples include come up with (something), look forward to (something), look up to (someone), and put up with (something.) Consider these sentences.
- Did you come up with this plan by yourself?
- I get along with him sometimes.
- I can’t put up with your poor manners anymore. You need to change it.
What is the Formula for Phrasal Verbs?

There are three possible formulas for producing phrasal verbs.
Verb + Adverb
The most basic structure of a phrasal verb is the main verb followed by an adverb. These can either be transitive or intransitive. Some examples include put off, turn down, and set off.
- I suggest you don’t put it off until tomorrow.
- I turned down his offer because he wouldn’t compromise.
- We should set off at 3 PM to miss the rush hour traffic.
In these sentences, off and down are adverbs instead of prepositions. That’s because the proceeding words are not objects of the prepositions.
Verb + Preposition
This type of phrasal verb is also known as a prepositional verb. Note that every preposition should have an object. For example:
- I believe in the theory of evolution.
In this sentence, believe in is the phrasal verb. The prepositional phrase is in the theory of evolution.
Other examples of prepositional verbs are look after and talk about. Here are some sentence examples.
- Please look after my daughter while I’m away.
- We talked about sociolinguistics, politics, and different economic systems the whole day.
This phrasal verb structure is inseparable. That means the direct object should not be between the verb and the preposition. For instance, it’s incorrect to say, “Please look my daughter after while I’m away.”
Verb + Adverb + Preposition
The last type of phrasal verb is composed of the main verb, an adverb, and a preposition. They are also known as phrasal-prepositional verbs or three-word phrasal verbs. Some examples include get on with, get out of, and run out of.
I made up some examples so you know how to use phrasal verbs in a sentence.
- He hasn’t gotten on with Maya since kindergarten.
- The agent wants to get out of working the night shift.
- We ran out of milk today.
What are the 20 Most Used Phrasal Verbs?
Check out this list of the most common phrasal verbs examples.
- Figure out.
- Throw away.
- Turn on/off.
- Turn up/down.
What are the Most Used Three-Word- Phrasal Verbs?
The most common three-word phrasal verbs are:
- Come up with.
- Get along with.
- Get around to.
- Look forward to
- Look up to.
- Look down on.
- Keep up with
- Make up for.
What are the Phrasal Verbs I Can Use in a Phone Conversation?
Now that you know the grammatical rules for phrasal verbs, here are some examples you can use in phone conversations.
- Get through.
- Put through.
- Get back to someone.
Are Idioms Phrasal Verbs?
One of the most common questions about phrasal verbs is whether they are considered idioms or not. Phrasal verbs have more than one word that results in a different meaning.
Therefore, the final compound verb can be idiomatic. That’s because its definition cannot be derived from the different parts’ dictionary meanings.
Extensive Phrasal Verbs List
| Phrasal Verb | Definition | Example |
| Abide by | To obey a law, rule, or decision | You must abide by the rules and regulations of the company if you don’t want to be fired. |
| Advise against | To suggest not to do one thing | I strongly advise against texting when your emotions are all over the place. |
| Agree with | Have similar opinions | I agreed with the lawyer when he mentioned the importance of swallowing one’s righteous indignation. |
| Allow for | To consider | The event organizers are allowing for additional fees and schedule interruptions. |
| Apply for | To request something formal, such as a loan, job, or permit | I want to apply for a scholarship this coming school year. |
| Back down | Concede, accept defeat | I will not back down on your threats. |
| Black out | Lose consciousness | Sheila blacked out after the night out. |
| To get angry, to be popular online | Your tweet isn’t going to blow up if you have a private account. | |
| Calm down | To relax after an anxious, irritated, or energetic state. | Drinking tea instead of coffee might help you calm down. |
| Check out | Verify an object or thing, Flirtatiously look at a person | Several girls will check you out if you wear those sweatpants. |
| Clean up | Be successful in sports, business, or any endeavor | The basketball team cleaned up during the finals. |
| Deal with | Take care of a situation, manage a problem | Dealing with a kid’s tantrums can be stressful. |
| Dive into | Occupy oneself with something | Let’s dive into the Twilight Saga tonight. |
| Ease off | Become less severe, slow down | My skin irritation eases off after summertime. |
| Fall through | To not happen, fail | My plan to start a business and pursue law fell through. |
| Figure out | Discover, find the answer, understand | Three years later, I’m still figuring out why my laptop broke. |
| Get ahead | Progress | The company wants to get ahead in terms of branding and online presence. |
| Get at | Imply | I do not understand what you’re getting at. |
| Give in | To cease opposition | This country will never give in to despotic laws. |
| Hang up | End a conversation on the cell phone or telephone | Don’t hang up. We’ll talk about a lot of things |
| Hurry up | To be quick | Hurry up because I don’t want to be late for class. |
| Join in | participate | All the students should join in the online discussion. |
| Keep up with | Stay at an equal level as someone | I can’t keep up with the latest news about him. |
| Let down | disappoint | No matter the mistakes you commit, you will never let me down. |
| Let go of | Release or free | Don’t let go of your belongings every time you’re in public. |
| Look down on | To consider inferior | It’s rude to look down on people in the service industry. |
| Make fun of | Make jokes about | Do not make fun of someone else’s insecurities. |
| Make up | invent | Stop making up excuses for not working out. |
| Nod off | Fall asleep | Jackie nodded off on the couch. |
| Own up | Confess something | Own up to your mistakes. |
| Pass away | To die | I heard that my favorite professor passed away in his sleep last week. |
| Pick up | Collect somebody | Jeff will pick me up at 8 PM tomorrow. |
| Point out | To direct attention to something | What are you trying to point out? I’ve already understood your message. |
| Rely on | Depend on | We don’t have to rely on them anymore. |
| Run out of | To have no more of something | We are running out of rice and potatoes. |
| Show off | To want to be admired, to brag | The valedictorian rightfully showed off her medals and certificates. |
| Stand up | Rise | My parents taught me to stand up when greeting a visitor. |
| Take care of | To look after | Please take care of my computer. |
| Turn down | Say no or reject | I turned down Mr. Rooney’s offer last year because I found a better opportunity in Miami. |
| Top off | Fill something to the top, to finish something | He topped off my beverage. |
| Use up | Finish a product | I used up all the shampoo and conditioner. Let’s go grocery shopping. |
| Watch out | Be careful | Watch out for any falling debris. |
| Wear out | To be unusable, be exhausted | I’ve been worn out after hours of running and lifting barbells. |
| Work out | To perform physical exercise | Is jogging considered working out? |
| Wipe off | clean | Please wipe off all surfaces in your room, including your bedside table and desk. |
Practice Using Phrasal Verbs
I hope this help! Just remember that phrasal verbs are groups of words that act as a single verb. They are composed of a standard verb and a preposition or adverb. Learning the different phrasal verbs and their definitions will help you expand your vocabulary. Do you have other suggestions for phrasal verbs not mentioned in my guide?
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of phrasal verb in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- The phrasal verb ' heal up' is intransitive .
- Some phrasal verbs consist of three words, such as ' look up to'.
- bare infinitive
- non-progressive
- passivization
- present participle
- subjunctive
- the active voice
- the future perfect
- the past continuous
- the past tense
phrasal verb | American Dictionary
Examples of phrasal verb, translations of phrasal verb.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
the moon when it is shaped like a crescent, or a time when it is shaped like this

In for a penny, in for a pound: Idioms in The Thursday Murder Club

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Translations
- All translations
To add phrasal verb to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add phrasal verb to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

What are Phrasal Verbs?
A phrasal verb is a phrase or expression that consists of a verb plus another word or two, like this:
[verb + adverb] e.g: look up
[verb + preposition] e.g: look after
[verb + adverb + preposition] e.g: look forward to
The whole phrase acts as a verb, and has a different meaning to the original verb. For example, look up , look after and look forward to do NOT mean the same as look .
Because we cannot always work out the meaning of a phrasal verb from its individual words, phrasal verbs are usually "idiomatic". They are very common in spoken English, and less common in formal written English.
Some phrasal verbs can be split by their object. They are said to be "separable" because the object can go between the verb and the rest of the phrase. For example, in the following sentences the phrasal verb "turn on" is separable, so the object ("the radio") can go after the phrasal verb OR in the middle of the phrasal verb:
- Mary turned on the radio.
- Mary turned the radio on .
Here are some more example sentences with phrasal verbs:
- They had to put off their wedding for a year.
- What time do you get up in the morning?
- I was disappointed that they turned my invitation down .
- Who is looking after your dog while you're away?
- She didn't get on with her boss so she was glad when he left.
- Luckily, we didn't run out of petrol and we got home okay.
See a list of phrasal verbs
Study the grammar of phrasal verbs
Order "1000 Phrasal Verbs in Context" ebook
What Are Phrasal Verbs In English And How Are They Used?

Table of Contents
Introduction, what are phrasal verbs, form of phrasal verbs.
| Verb | One Particle |
|---|---|
| get | up |
| go | through |
| write | down |
| take | after |
| Verb | Particle #1 | Particle #2 |
|---|---|---|
| look | forward | to |
| put | up | with |
| sit | in | for |
| run | out | of |
Exploring Meaning Shifts Through Particle Changes
| Verb & Meaning | Verb + Particle (Phrasal Verb) | Different Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| – “Take or go with (someone or something) to a place.” | Bring up | To mention or introduce a topic into conversation. |
| – “Put, lay, or stand (something) in a specified place or position.” | Set up | To establish or arrange something. |
| – “To grasp or obtain” | Take off | To remove or lift off, especially in aviation. |
| “to rotate or change direction” | Turn on | To activate or switch on a device. |
| – “To transfer or offer” | Give up | To surrender, quit, or stop trying. |
| – “To direct one’s gaze toward someone or something” | look for | To search or seek |
Literal or Idiomatic?
Phrasal verb meanings can be either literal or idiomatic. While some phrasal verbs maintain a straightforward, tangible interpretation rooted in their constituent words, others transcend their literal origins to convey idiomatic nuances.
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Run out | To physically exit a location | Literal: “I ran out of the room.” |
| To deplete or exhaust the supply of something | Idiomatic: “I ran out of milk.” | |
| Put in | To place something inside | Literal: “I put my keys in my bag.” |
| To invest time or effort in something | Idiomatic: “I put in a lot of time into the project.” | |
| Take out | To remove or extract something from a location | Literal: “I took out my wallet from my bag.” |
| To eliminate or withdraw someone or something | Idiomatic: “They want to take out the sniper.” | |
| Look out | To direct one’s gaze outward or be watchful | Literal: “She looked out of the window.” |
| To be cautious or be aware of something | Idiomatic: “The police have warned storekeepers to look out for forged bills.” |
Types of Phrasal Verbs
Transitive and intransitive phrasal verbs, separable or inseparable phrasal verbs, separable phrasal verbs:.
| Separable Phrasal Verb | Non-Separable Example | Separable Example |
|---|---|---|
| Turn on | “She the lights before entering the room.” | “She the lights before entering the room.” |
| Take off | “The plane smoothly, heading for its destination.” | “The plane the passengers smoothly.” |
| Put off | “Let’s the meeting until next week.” | “Let’s the meeting until next week.” |
| Pick up | “I need to groceries on my way home.” | “I need to the groceries on my way home.” |
| Bring up | “During the discussion, she an important point.” | “During the discussion, she an important point .” |
| Set up | “They a new system to improve efficiency.” | “They a new system to improve efficiency.” |
| Give back | “Don’t forget to the book you borrowed.” | “Don’t forget to the book you borrowed.” |
| Turn off | “He the television before leaving the room.” | “He the television before leaving the room.” |
| Look up | “I often unfamiliar words in the dictionary.” | “I often unfamiliar words in the dictionary.” |
| Break up | “They decided to after years of dating.” | “They decided to the relationship after years of dating.” |
Inseparable Phrasal Verbs:
| Inseparable Phrasal Verb | Example |
|---|---|
| Look after | “She always her younger brother.” |
| Stand by | “I will you during difficult times.” |
| Carry on with | “After the interruption, the speaker decided to the presentation.” |
| Come across | “During my trip, I an old bookstore.” |
| Get in | “She the car and drove to work.” |
| Get over | “It takes time to a loss.” |
| Do without | “We’ll have to milk as there isn’t any left.” |
| Put up with | “I can’t his rude behavior any longer.” |
| Run out of | “We ran out of milk, so I need to buy some more.” |
| Look forward to | “I always look forward to the weekend.” |
| Take care of | “She takes care of her plants with great dedication.” |
Frequently Used Phrasal Verbs
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Look after | To take care of or be responsible for someone. |
| Set up | To establish or arrange something. |
| Bring up | To mention or introduce a topic into conversation. |
| Turn down | To reject or decline an offer or invitation. |
| Run into | To unexpectedly encounter or meet someone. |
| Put off | To postpone or delay an event or task. |
| Come across | To find or discover unexpectedly. |
| Bring about | To cause or make something happen. |
| Take off | To remove or lift off, especially in aviation. |
| Look forward to | To anticipate or be excited about a future event. |
| Give up | To quit or stop trying. |
| Get along with | To have a good relationship with someone. |
| Take care of | To attend to or manage a situation or person. |
| Go on | To continue or proceed. |
| Bring in | To introduce or involve someone or something. |
| Put up with | To tolerate or endure. |
| Bring down | To reduce or lower. |
| Show up | To appear or arrive. |
| Hold on | To wait or pause. |
| Break up | To end a relationship. |
| Look up | To search for information. |
| Figure out | To understand or solve a problem. |
| Bring out | To reveal or produce. |
| Check out | To examine or investigate. |
| Take on | To accept or undertake a task or responsibility. |
| Put out | To extinguish a fire or release a product. |
| Bring down | To cause a downfall or reduce. |
| Take over | To assume control or responsibility. |
| Look into | To investigate or examine closely. |
| Pick up | To lift or collect; to learn or acquire. |
Phrasal Verbs: Understanding and Using Them Correctly
Phrasal verbs are a crucial part of the English language, especially in informal contexts. They are made up of a verb and one or two particles that can change the meaning of the verb. For example, “pick up” means to grab or lift, which is very different from the meanings of “pick” and “up” alone.
In this article, we will explore phrasal verbs in-depth, providing definitions, examples, and tips for using them correctly. We will also discuss the differences between separable and inseparable phrasal verbs, and how to identify them. By the end of this article, readers should have a solid understanding of phrasal verbs and feel confident in using them in their daily conversations and writing.

What Are Phrasal Verbs?
Phrasal verbs are a type of compound verb that consists of a verb and one or more particles. The particles can be prepositions or adverbs , or a combination of both. When combined with a verb, the meaning of the phrasal verb is often different from the meaning of the individual words.
Phrasal verbs are commonly used in spoken and informal English. They are also used in written English, particularly in novels and other creative writing. However, their use in academic writing is generally discouraged.
Phrasal verbs are an essential part of the English language. They are used to express a wide range of meanings, from simple actions to complex ideas. For example, the phrasal verb “take off” can mean to remove something, to leave a place quickly, or to become successful.
Phrasal verbs are often idiomatic, which means that their meaning cannot be easily predicted from the meaning of the individual words. For example, the phrasal verb “look up” can mean to search for information, but it can also mean to respect or admire someone.
Types of Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs are a combination of a verb and one or more particles, which can be prepositions or adverbs. They are commonly used in English and can be classified into different types based on their usage and structure. Here are the three main types of phrasal verbs:
Transitive Phrasal Verbs
Transitive phrasal verbs are those that require a direct object to complete their meaning. The direct object can come before or after the particle, depending on the context. For example, “pick up the phone” and “pick the phone up” mean the same thing. Here are some common transitive phrasal verbs:
- put up with
Intransitive Phrasal Verbs
Intransitive phrasal verbs do not require a direct object and can stand alone as a complete sentence. They are often used to describe a change in direction or movement. Here are some common intransitive phrasal verbs:
- come across
Separable and Inseparable Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs can also be classified based on whether they can be separated by other words or not. Separable phrasal verbs can be separated by an object or adverb, while inseparable phrasal verbs cannot be separated. Here are some examples of separable and inseparable phrasal verbs:
- Separable: “I will look the report over” or “I will look over the report.”
- Inseparable: “I will look into the matter.”
It’s important to note that the meaning of a phrasal verb can change depending on whether it is separable or inseparable.
List of Common Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs are an essential part of the English language, and they are commonly used in both spoken and written English. Here is a list of some of the most common phrasal verbs:
Phrasal Verbs with Get
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Get away | To escape or leave a place |
| Get along | To have a good relationship with someone |
| Get over | To recover from an illness or a difficult situation |
| Get up | To wake up and get out of bed |
| Get in | To enter a vehicle or a building |
| Get out | To leave a place |
| Get off | To leave a vehicle or a mode of transport |
| Get on | To board a vehicle or a mode of transport |
| Get by | To manage to survive or cope with a difficult situation |
| Get through | To complete a task or a difficult situation |
| Get ahead | To make progress in one’s career or life |
| Get down | To feel sad or depressed |
| Get together | To meet with friends or family |
| Get out of | To avoid doing something |
| Get back | To return to a place |
| Get around | To move from place to place |
| Get in touch | To contact someone |
| Get away with | To do something wrong without being punished |
| Get rid of | To dispose of something |
| Get on with | To continue doing something |
| Get the hang of | To understand how to do something |
| Get into | To become interested in something |
| Get off on | To enjoy something |
| Get lost | To go away or leave someone alone |
| Get a hold of | To obtain or acquire something |
Phrasal Verbs with Look
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Look after | To take care of someone or something |
| Look around | To explore or examine a place |
| Look away | To avert one’s gaze or attention |
| Look back | To remember or reflect on the past |
| Look down on | To have a negative attitude towards someone or something |
| Look for | To search for something |
| Look forward to | To anticipate or be excited about something in the future |
| Look into | To investigate or examine something |
| Look out | To be careful or watchful |
| Look over | To review or examine something |
| Look up | To search for information or a word in a dictionary |
| Look up to | To admire or respect someone |
| Look through | To browse or examine quickly |
| Look upon | To consider or regard something in a particular way |
| Look beyond | To consider something in a broader context |
| Look out for | To watch out for someone or something |
| Look to | To rely on or seek help from someone |
| Look in on | To visit someone briefly |
| Look for trouble | To intentionally seek out conflict or problems |
| Look sharp | To hurry or be quick |
| Look someone in the eye | To make direct eye contact with someone |
Phrasal Verbs with Take
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Take after | To resemble or have similar traits to a family member |
| Take apart | To disassemble or break something down into parts |
| Take away | To remove or subtract something |
| Take back | To retract or withdraw something that was said or done |
| Take down | To write or record information |
| Take in | To understand or comprehend something |
| Take off | To leave the ground (for a plane) or to remove clothing |
| Take on | To accept responsibility or a challenge |
| Take out | To remove something or to go on a date with someone |
| Take over | To assume control or responsibility |
| Take up | To begin a new activity or hobby |
| Take care of | To look after or attend to someone or something |
| Take advantage of | To use or exploit a situation for one’s benefit |
| Take a break | To rest or take a pause from an activity |
| Take a chance | To take a risk or gamble |
| Take a hike | To go away or leave |
| Take a look | To examine or inspect something |
| Take a stand | To make a firm decision or position on an issue |
| Take a step back | To pause and reassess a situation |
| Take a turn | To change direction or course |
| Take it easy | To relax or slow down |
| Take someone for granted | To not appreciate or value someone |
| Take the plunge | To take a big risk or make a major decision |
Phrasal Verbs with Put
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Put away | To tidy up or store something |
| Put down | To criticize or belittle someone |
| Put off | To postpone or delay something |
| Put on | To wear clothing or makeup |
| Put out | To extinguish a fire or to inconvenience someone |
| Put up | To accommodate or host someone |
| Put together | To assemble or create something |
| Put aside | To save or reserve something |
| Put forward | To propose or suggest something |
| Put in | To install or contribute something |
| Put through | To connect or transfer a phone call |
| Put up with | To tolerate or endure something |
| Put money on | To bet on something |
Phrasal Verbs with Up
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Add up | To make sense or be logical |
| Back up | To support or confirm something |
| Bring up | To raise or mention a topic |
| Cheer up | To make someone feel happier or more positive |
| Clean up | To tidy or clean a space |
| Dress up | To wear formal or fancy clothing |
| End up | To eventually reach or become something |
| Fix up | To repair or improve something |
| Give up | To quit or surrender |
| Grow up | To mature or become an adult |
| Hang up | To end a phone call or to hang clothing on a hook |
| Hold up | To delay or hinder something |
| Keep up | To maintain or continue something |
| Look up | To search for information or to improve |
| Make up | To reconcile or create something |
| Pick up | To lift or collect something |
| Put up | To accommodate or host someone |
| Show up | To arrive or appear |
| Speak up | To speak louder or more confidently |
| Stand up | To rise from a seated position or to defend oneself |
| Take up | To begin a new activity or hobby |
| Team up | To collaborate or work together |
| Turn up | To increase in volume or to appear unexpectedly |
| Wake up | To become alert or to awaken from sleep |
Phrasal Verbs with Break
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Break away | To escape or separate from a group |
| Break down | To stop functioning or to have an emotional collapse |
| Break in | To wear something in or to interrupt someone |
| Break into | To enter a building or a conversation |
| Break off | To end a relationship or a piece of something |
| Break out | To escape or to start suddenly |
| Break through | To make a breakthrough or to penetrate a barrier |
| Break up | To end a relationship or to disperse a group |
| Break the ice | To initiate conversation or to make a situation less tense |
| Break the news | To inform someone of something important or difficult |
| Break the rules | To violate or disobey established rules |
| Break the bank | To spend or lose a large amount of money |
| Break a habit | To stop doing something that has become routine |
| Break a leg | A superstitious phrase used to wish someone good luck |
| Break bread | To share a meal with someone |
| Break even | To have expenses equal to income |
| Break ground | To begin construction or to make progress |
| Break the cycle | To put an end to a negative pattern |
| Break the mold | To do something different or unconventional |
| Break the silence | To speak up or to end a period of silence |
| Break the news gently | To deliver bad news in a sensitive way |
| Break ranks | To deviate from a group or organization |
| Break free | To escape or to become independent |
| Break wind | To pass gas or to fart (informal) |
Phrasal Verbs with Turn
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Turn around | To reverse direction or to change one’s attitude |
| Turn away | To refuse or reject something or someone |
| Turn back | To return or to change one’s mind |
| Turn down | To refuse or reject an offer or request |
| Turn in | To submit or hand in something |
| Turn off | To switch off or to disgust someone |
| Turn on | To switch on or to excite someone |
| Turn out | To attend or to produce a result |
| Turn over | To flip or to transfer ownership |
| Turn to | To seek help or advice from someone |
| Turn up | To arrive or to increase in volume |
| Turn against | To become hostile or opposed to someone or something |
| Turn into | To transform or to change into something else |
| Turn over a new leaf | To start fresh or to change one’s behavior |
| Turn a blind eye | To ignore or overlook something |
| Turn the tables | To reverse a situation or outcome |
| Turn the corner | To make progress or to recover from a difficult situation |
| Turn the page | To move on from a past event or situation |
| Turn up the heat | To increase pressure or intensity |
| Turn heads | To attract attention or admiration |
| Turn a profit | To earn money or make a financial gain |
| Turn the other cheek | To forgive or tolerate an offense |
| Turn to stone | To become petrified with fear or shock |
Phrasal Verbs with Do
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Do away with | To get rid of or eliminate something |
| Do up | To fasten or to renovate something |
| Do without | To manage or survive without something |
| Do over | To redo or to repeat something |
| Do in | To exhaust or to kill someone |
| Do for | To ruin or to defeat someone |
| Do out of | To deprive someone of something |
| Do up in | To dress in fancy or formal clothing |
| Do the dishes | To wash the dishes |
| Do the laundry | To wash and dry clothing |
| Do time | To serve a prison sentence |
| Do a favor | To help someone out |
| Do a job on | To criticize or damage something |
| Do a number on | To deceive or manipulate someone |
| Do a double take | To take a second look or to be surprised |
| Do business | To conduct transactions or to work together |
| Do drugs | To use illegal drugs |
| Do harm | To cause harm or damage |
| Do justice | To treat fairly or to represent accurately |
| Do research | To investigate or study a topic |
| Do the trick | To solve a problem or satisfy a need |
| Do well | To perform successfully or to prosper |
| Do your best | To try your hardest |
| Do your homework | To prepare or research something thoroughly |
Phrasal Verbs with Make
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Make up | To invent or create something, to reconcile after a disagreement |
| Make out | To see or hear something with difficulty, to understand, to kiss passionately |
| Make up for | To compensate for something, to make amends |
| Make up one’s mind | To decide |
| Make for | To head towards a destination |
| Make off | To leave quickly or secretly |
| Make do | To manage with what one has |
| Make over | To renovate or transform something, to transfer ownership |
| Make out with | To engage in sexual activity with someone |
| Make a point | To emphasize or stress something |
| Make a difference | To have an impact or effect |
| Make a living | To earn money |
| Make a fool of | To embarrass or humiliate someone |
| Make a break for it | To try to escape |
| Make a mess | To create a disorderly or untidy state |
| Make a scene | To cause a public disturbance |
| Make good | To succeed or fulfill a promise |
| Make light of | To treat something as unimportant or insignificant |
| Make sense | To be logical or understandable |
| Make the most of | To take advantage of an opportunity |
| Make up to | To try to gain someone’s favor or affection |
| Make waves | To cause trouble or controversy |
| Make way for | To clear a path for someone or something |
These are just a few examples of the many phrasal verbs in the English language. Each phrasal verb consists of a verb and one or more particles that modify the meaning of the verb.
Using Phrasal Verbs in Context
When it comes to using phrasal verbs, context is key. As mentioned in the search results, phrasal verbs can have more than one meaning, and the meaning can change depending on the context. Here are a few tips on how to use phrasal verbs in context:
- Consider the situation: Think about the situation in which the phrasal verb is being used. Is it a formal or informal situation? Is it a conversation between friends or a business meeting? This can help you determine which phrasal verb to use and how to use it.
- Look at the surrounding words: Pay attention to the words that come before and after the phrasal verb. This can help you understand the meaning of the phrasal verb in that specific context.
- Use the correct particle: The particle in a phrasal verb can often change the meaning of the verb. Make sure to use the correct particle in the correct context. For example, “put up with” means to tolerate , while “put up” means to hang something on a wall.
- Practice: The best way to get better at using phrasal verbs in context is to practice. Read and listen to English in different contexts, and try to use phrasal verbs in your own conversations and writing.
Phrasal Verbs with Prepositions and Adverbs
Phrasal verbs are a common feature of the English language. They are formed by combining a verb with a preposition or adverb to create a new meaning. Prepositions are words like in, on, at, up, down, etc., while adverbs are words that describe verbs. When used in phrasal verbs, prepositions and adverbs can change the meaning of the verb completely.
Phrasal verbs with prepositions and adverbs are often used in everyday English. They can be separable or inseparable, depending on whether the object can be placed between the verb and the particle. Here are some examples:
- Separable phrasal verb: He turned off the lights. / He turned the lights off.
- Inseparable phrasal verb: She put on her coat. / She couldn’t put her coat on.
Prepositional verbs are another type of verb that includes a preposition and an object. Unlike phrasal verbs, the object always comes after the preposition. Here are some examples:
- Prepositional verb: She listened to the radio. / He looked at the picture.
It is important to note that prepositions and adverbs can have different meanings depending on the context in which they are used. For example, the preposition “up” can mean “to increase” in the sentence “The company’s profits are up,” but can mean “to complete” in the sentence “I need to finish up my work.”
Phrasal Verbs Exercises
Exercise 1 : Choose the correct phrasal verb to complete the sentence.
- I need to _________ up early tomorrow for my flight. a) wake b) wake off c) wake up
- Can you _________ the music? It’s too loud. a) turn on b) turn up c) turn off
- I’m going to _________ my old clothes to charity. a) give out b) give up c) give away
- She _________ her keys and couldn’t find them. a) lost out b) lost off c) lost
- He always _________ his work until the last minute. a) puts off b) puts up c) puts on
Answers: 1) c, 2) c, 3) c, 4) c, 5) a
Exercise 2 : Rewrite the sentences using the phrasal verbs in brackets.
- I’m going to stop smoking. (give up)
- She’s going to start a new job next week. (take on)
- Can you please explain the concept again? (go over)
- The teacher postponed the test until next week. (put off)
- We need to clean the kitchen before the guests arrive. (tidy up)
Answers: 1) I’m going to give up smoking. 2) She’s going to take on a new job next week. 3) Can you please go over the concept again? 4) The teacher put off the test until next week. 5) We need to tidy up the kitchen before the guests arrive.
FAQs on Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs can be tricky to understand, so here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify their meaning and usage.
What are phrasal verbs?
Phrasal verbs are combinations of a verb and one or more particles, such as prepositions or adverbs. Together, they create a new meaning that is different from the individual words used. For example, “take off” means to remove clothing or to leave quickly by airplane.
Are phrasal verbs only used in informal English?
No, phrasal verbs can be used in both formal and informal English. However, they are more common in spoken and informal English than in written and formal English.
How can I tell if a phrasal verb is separable or inseparable?
A separable phrasal verb can have the particle separated from the verb and placed in a different position in the sentence. For example, “I took off my shoes” and “I took my shoes off” are both correct. In contrast, an inseparable phrasal verb cannot be separated, such as “I’m looking forward to the party.”
Are there any rules for using phrasal verbs?
There are no strict rules for using phrasal verbs, but there are some general guidelines to follow. For example, it is important to use the correct particle to convey the intended meaning. Additionally, some phrasal verbs are more common in certain contexts or regions, so it can be helpful to study them in context.
How can I learn and practice phrasal verbs?
One way to learn phrasal verbs is to study them in context, such as in news articles or TV shows. Another way is to use flashcards or quizzes to practice identifying and using phrasal verbs. Additionally, it can be helpful to use phrasal verbs in your own writing and speaking to become more comfortable with them.
Related resources:
Related Posts:


- Grammar & vocab
Phrasal verbs
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
What is a phrasal verb?
A phrasal verb is a verb that is made up of a base verb and one or two particles, such as off , up , or on .
These particles change the meaning of the base verb in various ways. Phrasal verbs are an important part of the English language, and they are often used in everyday conversation and writing.
Common phrasal verbs
Some of the most common verbs used in phrasal verbs include get , take , put , make , and do .
The verb get can be combined with the particle off to form the phrasal verb get off , which means to depart or leave.
We can combine take with on to form the phrasal verb take on , which means to assume or undertake.
Put can be combined with the particle off to form the phrasal verb put off , meaning to postpone or delay.
Make can be combined with up to form the phrasal verb make up – to invent or fabricate.
Do can be combined with the particle over to form the phrasal verb do over , which means to redo or repeat.
Phrasal verbs can be a bit tricky to learn
Phrasal verbs are often quite difficult to learn (or remember) because their meanings are often not directly related to the meanings of the individual words that make them up. However, with practice and exposure, you can become more comfortable with using phrasal verbs in your own communication.
| Structure of phrasal verbs | |
| A phrasal verb can be made up of: | |
Examples of phrasal verbs
- Phrasal verbs with put put down, put in, put off . . .
- Phrasal verbs with come come across, come out with, come round . . .
- Exercises section: Phrasal verbs practice, upper-intermediate level
- Grammar section: Phrasal verbs vs. prepositional verbs: position of the object
- Vocabulary section: 10 important phrasal verbs for elementary learners
- Stuart’s article on phrasal verbs: Seven ways to make learning phrasal verbs easier
- Stuart’s article: 4 phrasal verbs with look
Related Posts
- Phrasal verbs vs. prepositional verbs: position of the object
- Transitive vs. intransitive phrasal verbs
- How to learn phrasal verbs more easily
- Four phrasal verbs with “look”
- Upper-intermediate vocabulary exercise (B2 level): phrasal verbs with ‘up’
- Using “it” with phrasal verbs
- Vocabulary: phrasal verbs with “come”
- Upper-intermediate vocabulary exercise (B2 level): phrasal verbs – clear up, come up with, drop off, let down, point out
- 10 important phrasal verbs for elementary learners
- Upper-intermediate vocabulary exercise (B2 level): phrasal verbs ex. 4
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips
Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips
Published on 20 October 2022 by Shane Bryson . Revised on 23 May 2023.
A phrasal verb combines two or more words to describe a specific action. Phrasal verbs can be difficult to get right, as their meaning usually has nothing to do with the definitions of the component words.
This means that phrasal verbs must be treated as distinct pieces of vocabulary. You have to learn them as a single unit of meaning, just like you would learn any single word.
Phrasal verbs are very common in everyday speech, but in academic writing, it’s best to replace them with one-word alternatives where possible.
47 phrasal verbs and one-word alternatives
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What is a phrasal verb, when to use phrasal verbs, separating phrasal verbs.
A verb (e.g., ‘It goes ‘) becomes a phrasal verb with the addition of one preposition (e.g., ‘The light goes out ‘) or more (e.g., ‘She goes out with him’). Each additional preposition completely changes the meaning of the verb.
It is very important to remember that a phrasal verb should be considered one unit of meaning, just like a distinct verb. In the above examples, the phrasal verb ‘goes out’ is as different from the verb ‘goes’ as the verb ‘goes’ is different from the verb ‘stays’.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Although the best choice is usually to avoid phrasal verbs, they are so common that finding adequate replacements every time will be difficult. Change them when you can, and when you ‘run out’ of ideas for rephrasing, ‘cheer up’, ‘believe in’ yourself, and ‘write down’ your phrasal verbs conscientiously.
Phrasal verbs do have their uses, after all. For example, they convey a casual tone, and while this is not usually desirable in academic writing , the best academic writers can vary their tone at will.
Accordingly, you should think of phrasal verbs as a stylistic option, even though you will often be best advised to eliminate them rather than add them.
Some phrasal verbs can be separated by intervening words, while others have to stay together in the sentence. There is no rule to tell whether a phrasal verb can be separated, so you have to learn by memory and practice – one good reason to avoid them when you can.
One helpful pointer, though, is that phrasal verbs that can be separated must be separated when their object is a pronoun (e.g., it , her , them).
Example: Separable
- Call the meeting off .
- Call off the meeting.
Note that if a phrasal verb is separable, it must be separated when its object is a pronoun (e.g., it , her , them).
- Call it off .
- Call off it.
Example: Inseparable
- The message didn’t come across well.
- The message didn’t come well across .
Example: Must be separated
Some phrasal verbs always have to be separated, but this is comparatively rare.
- Oscar will take Sven up on the offer.
- Oscar will take up Sven on the offer.
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Bryson, S. (2023, May 23). Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 17 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/verb/phrasal-verb/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
Verb tenses in academic writing | rules, differences & examples, subject-verb agreement | examples, rules & use.
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal Verbs - Meaning, Definition and Examples
Want to know how to speak English in a polished and sophisticated manner? Try using phrasal verbs in the place of normal verbs. As speakers of the English language , we use a lot of verbs and phrasal verbs in our everyday communication. Most of the time, we are not aware that we are making use of these verbs. This article on phrasal verbs will enlighten you with the meaning, definition and examples of phrasal verbs. Try out the practice questions as well to check your understanding of phrasal verbs and their usage.
Table of Contents
Definition of a phrasal verb, types of phrasal verbs, conjugating phrasal verbs, using the right word order, examples of phrasal verbs, check your understanding of phrasal verbs, frequently asked questions on phrasal verbs in english, what are phrasal verbs.
Phrasal verbs can be said to be formed by the combination of a verb and an adverb or a preposition . In some cases, it is a combination of all the three parts of speech – verb, adverb and preposition. Though each of these parts of speech have different functions, they play the role of the verb when they are put together. They can also act as a phrase and that is why these verbs are called phrasal verbs.
The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines a phrasal verb as “a verb combined with an adverb or a preposition, or sometimes both, to give a new meaning, for example, ‘go in for’, ‘win over’ and ‘see to’.” According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, a phrasal verb is defined as “a phrase (such as take off or look down on) that combines a verb with a preposition or adverb or both, and that functions as a verb whose meaning is different from the combined meanings of the individual words.” The Cambridge Dictionary defines a phrasal verb as “a phrase that consists of a verb with a preposition or adverb or both, the meaning of which is different from the meaning of its separate parts.”
Phrasal verbs can be divided into four main types or rather two main categories based on how they behave when used in sentences. They are:
Transitive Phrasal Verbs
Intransitive phrasal verbs, separable phrasal verbs, inseparable phrasal verbs.
Just like normal transitive verbs , a transitive phrasal verb can be identified by its demand for an object.
For example :
- It was not possible for Veena to do away with all of it as they brought back so many memories of the past.
- Can you fill in the required details so that we can move forward with the screening process.
Intransitive phrasal verbs behave exactly like intransitive verbs. They do not require an object to complete the sentence they are used in or make sense of the context.
For example:
- My car broke down all of a sudden while driving through the ghat section.
- It has been years since we met, we should definitely catch up.
Separable phrasal verbs include transitive phrasal verbs which have the characteristic property of separating the phrasal verb with the object in between. There is, however, a word order which should be taken into account when separating the phrasal verb.
- I am not the kind of person who holds all of this against you.
- Dhiraj is the one who is taking care of the applications for gold loan. Can you please hand it over to him?
Inseparable phrasal verbs, as the name suggests, cannot be separated from each other and have to be used together, no matter what.
- You will have to account for all the losses that have been incurred.
- Harish was asked to check out of the hotel before 9 p.m. on Tuesday.
How to Use Phrasal Verbs?
As fun and interesting as it is to use phrasal verbs, there are a few pointers you have to keep in mind when using them in your daily communication. Following a particular word order and conjugating it to represent the tense of the sentence are the two things you have to learn and put into practice.
As far as the conjugation part is concerned, all you have to remember is to employ the same rules of conjugation you would if the verb stands by itself. When the phrasal verb is used as a main verb , you have to conjugate the verb alone according to the respective tense and not change the preposition in the phrasal verb.
- Heera dropped out of school due to her illness. (Drop out)
- My friend, Sharon, had broken up with her boyfriend last month. (Break up)
- The security guard asked around the whole building to know whose car was parked right in front of the gate. (Ask around)
- I hung out with my friends after the wedding reception. (Hang out)
Note that, in the above sentences, the prepositions remain the same whereas the verbs ‘dropped’, ‘asked’ and ‘hung’ have been conjugated in the simple past form and the verb ‘broken’ has been conjugated in the past participle form. Keep in mind that irregular verbs take the same spellings as they do when used as normal verbs conjugated in the different forms.
Word order comes into the picture mainly when you are attempting to split up the phrasal verbs. Always bear in mind that intransitive phrasal verbs and inseparable phrasal verbs have to be used together. The verb and the participle /preposition should go next to each other.
With separable phrasal verbs, it is different. They are transitive and always have a direct object to complete them. You can separate the phrasal verb by putting the direct object in between the verb and the preposition.
- Kate let me down when she did not show up for my court hearing.
Some phrasal verbs will always require to be separated by the direct object in between.
- We are very glad that we have you around during this difficult time.
When noun phrases act as the object, it can also be placed in between the verb and the preposition.
- He was asked to leave all of it out for approval.
Phrasal verbs are most often a topic that confuses a lot of people, especially second language learners and new learners of the language. Since the multiple words used in a phrasal verb have different meanings and have a completely different meaning when used together, they end up being a slightly puzzling topic for some.
Phrasal verbs can be conjugated to suit the tense of the sentence and can be used like a normal verb. Here are a few examples of phrasal verbs. Identify how many of them you know and how often you use them in your regular communication.
Give up – combination of a verb (give) and a preposition (up)
Individually, the verb ‘give’ means to give something to someone and the preposition ‘up’ shows the position of some object. The magic happens or the confusion begins when both the verb and the preposition are used together. The phrasal ‘give up’ means to surrender or to stop making an effort in doing something.
Let us look at how the phrasal verb ‘give up’ can be conjugated to represent the different verb forms in English.
- Simple Past Form
The captain gave up at the last quarter.
- Infinitive Form
It was not easy for the coach to give up trying to encourage the team even in such a hopeless situation.
- Gerund Form
Giving up is not the solution to the problem, it is just the easiest choice.
- Past Participle Form
I have given up on them.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most appropriate phrasal verbs from the list of phrasal verbs given below. Conjugate them to suit the tense of the sentence.
(stand for, narrow down, hold on, run into, check out, go through, fall apart, pull off, fill in, hold against)
1. Make sure you _________ of the hotel at the right time, else they will charge you extra.
2. Levin was asked to _______ for Suresh.
3. ________ the whole itinerary before you make a decision.
4. Tom and Jerry ___________ after their last meeting.
5. Please _________ for a minute, I forgot to take my car keys.
6. It is not good to _______ such a silly issue _______ her for so many years.
7. Do you think Andreah would be able to _____ it _____ all by herself?
8. We have _____________ the possibilities of them finding us.
9. Do you know who we _______ on our way here?
10. Nelson Mandela ________ for the rights of his people.
Check your answers here.
1. Make sure you check out of the hotel at the right time, else they will charge you extra.
2. Levin was asked to fill in for Suresh.
3. Go through the whole itinerary before you make a decision.
4. Tom and Jerry fell apart after their last meeting.
5. Please hold on for a minute, I forgot to take my car keys.
6. It is not good to hold such a silly issue against her for so many years.
7. Do you think Andreah would be able to pull it off all by herself?
8. We have narrowed down the possibilities of them finding us.
9. Do you know who we ran into on our way here?
10. Nelson Mandela stood up for the rights of his people.
What are phrasal verbs?
Phrasal verbs can be said to be formed by the combination of a verb and an adverb or a preposition. In some cases, it is a combination of all the three parts of speech – verb, adverb and preposition. Though each of these parts of speech have different functions, they play the role of the verb when they are put together. They can also act as a phrase and that is why these verbs are called phrasal verbs.
What is the definition of a phrasal verb?
The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines a phrasal verb as “a verb combined with an adverb or a preposition, or sometimes both, to give a new meaning, for example, go in for’, ‘win over’ and ‘see to’.” According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, a phrasal verb is defined as “a phrase (such as take off or look down on) that combines a verb with a preposition or adverb or both, and that functions as a verb whose meaning is different from the combined meanings of the individual words.” The Cambridge Dictionary defines a phrasal verb as “a phrase that consists of a verb with a preposition or adverb or both, the meaning of which is different from the meaning of its separate parts.”

Give some examples of phrasal verbs.
Here are some examples of phrasal verbs which you can use in your daily communication – stand up, go through, check in, fall apart, make up, stop over, put up with, do away with, hold up, get through, give in, etc.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
210+ Most Common English Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs are when we combine a verb with a preposition of another grammatical element, and end up with a completely new meaning.
They’re used constantly by native speakers in spoken and written English, which makes them important to know.
In this English phrasal verbs list, we’ll show you 210+ of the most common phrasal verbs , with audio and example sentences included.
Afterwards, you’ll find a complete lesson on what phrasal verbs are, how to form them and how to learn them effectively.
Before we jump into the list, here’s a quick video explanation:
The Most Common English Phrasal Verbs
Separable, transitive phrasal verbs, inseparable, transitive phrasal verbs, inseparable, intransitive phrasal verbs, more useful english phrasal verbs, what is a phrasal verb, types of phrasal verbs .
- Transitive
Intransitive
Inseparable, how to use phrasal verbs, conjugation, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
To start off, we’ll be going over the top English phrasal verbs that you’ll hear in everyday situations. You can get a taster with this video, which features 15 useful English phrasal verbs (plus example sentences):
Here’s a more detailed list of common English phrasal verbs, but right before the list, there’s two things you need to know about phrasal verbs in English:
- They can be separable or inseparable
- They can be transitive or intransitive (like all verbs in English)
I’ll go over these concepts more just after these handy lists!
- Thousands of learner friendly videos (especially beginners)
- Handpicked, organized, and annotated by FluentU's experts
- Integrated into courses for beginners

1. Pay back — To give someone back money that you owe
Thanks for getting me lunch when I forgot my wallet at home! I’ll pay you back tomorrow.
2. Give out (1) — To hand out or distribute something
He has a lot of contacts because he gives out his business card to everyone he meets.
3. Look up — To check the meaning of something
If you don’t know the meaning of a word, you should look it up in the dictionary.
- Interactive subtitles: click any word to see detailed examples and explanations
- Slow down or loop the tricky parts
- Show or hide subtitles
- Review words with our powerful learning engine
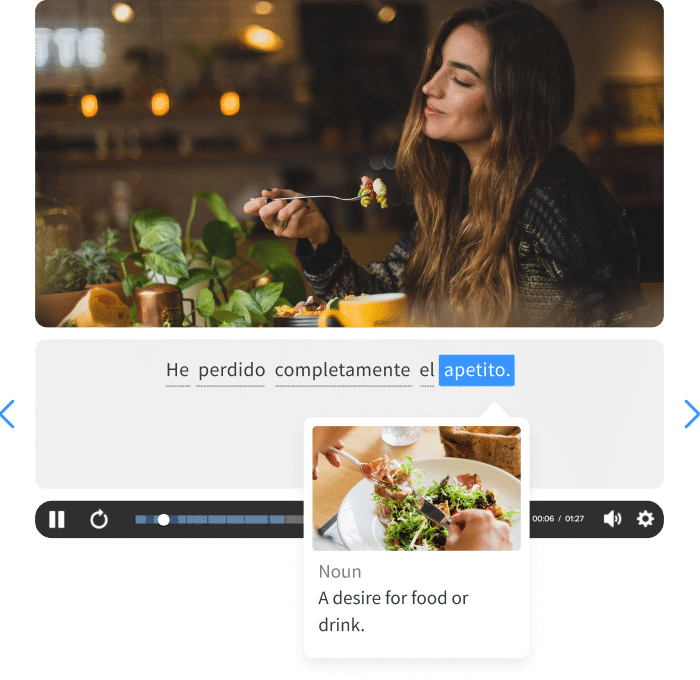
4. Give up — To stop trying, surrender
After two weeks of trying to build my own table, I gave up and just bought one.
5. Give away — To hand things out for free
When Linda’s cat had kittens, she gave them all away to good homes.
6. Hold back — To stop yourself from doing or saying something
Amy has a great voice, but whenever she’s singing in public, she feels shy and holds back .
7. Drop off — To take someone or something somewhere and leave them/it there
- Learn words in the context of sentences
- Swipe left or right to see more examples from other videos
- Go beyond just a superficial understanding

Can you drop me off at the grocery store on your way home?
8. Work (something) out — To come up with a solution or a compromise
Don’t worry, I’m sure we can work something out so that everyone is happy.
9. Drop in — To visit someone without making an appointment
Drop in to my office anytime.
10. Check out — To see or try something out to learn more about it
Check out my new car!
- FluentU builds you up, so you can build sentences on your own
- Start with multiple-choice questions and advance through sentence building to producing your own output
- Go from understanding to speaking in a natural progression.
11. Take out (1) — To remove something, like from a pocket or a bag
The children sat at their desks and took out their pens and paper.
12. Take out (2) — To take someone on a date
He took her out to the most expensive restaurant in the city.
13. Turn on / Turn off — To switch a machine or light on or off
Turn off the light, I’m trying to sleep!
- Images, examples, video examples, and tips
- Covering all the tricky edge cases, eg.: phrases, idioms, collocations, and separable verbs
- No reliance on volunteers or open source dictionaries
- 100,000+ hours spent by FluentU's team to create and maintain
14. Cheer on — To support someone through words of encouragement
Even though Samantha was in last place, her brother cheered her on through the entire race.
15. Fill in (for someone) — To do someone else’s job temporarily
Can you fill in for me while I’m on vacation?
16. Put out (1) — To extinguish a fire.
The firefighters managed to put out the fire before it spread to other houses.

17. Put out (2) — To irritate someone by asking them for a favor
I’d ask you to make me dinner but I don’t want to put you out .
18. Put on — To get your clothes or makeup on
Every morning she puts on her dress, lipstick, shoes and hat—in that order.
19. Take off (1) — To remove clothing
She was very happy when she finally got home and took off her shoes. They had been hurting her feet all day!
20. Fill out — To complete a form by providing required information
Please fill out the application form and submit it by Friday.
21. Cheer up — To show support to someone who seems sad or to try to make someone happier
Andrew was having a bad day, so his girlfriend cheered him up by taking him out for ice cream.
22. Cut off — To interrupt or stop something
His father is rich but he cut him off without any money of his own.
23. Cut (it) out — To stop it
Hey , cut it out ! I was watching that movie, so stop changing the channel!
24. Call off — To cancel something
We had to call off the picnic because of the rain.
25. Bring up — To mention something
Mark was sick and had to miss the party, so please don’t bring it up , I don’t want him to feel bad for missing it.
26. Bring on — To cause something to happen, usually something negative
His lung cancer was brought on by years of smoking.
27. Bring it on! — To accept a challenge with confidence
You want to have a race? Bring it on ! I can beat you!
28. Call on (1) — To visit someone
I’ll call on you this evening to see how you’re feeling.
29. Warm up to — To start liking someone or something more as you spend more time with them
The new puppy was scared of my husband when we first got him, but he warmed up to him pretty quickly.
30. Come across — To meet or find by chance
I was cleaning the attic and I came across my high school uniform. Can you believe it still fits?
31. Get back at — To get revenge on someone
Her ex-husband took her house so she got back at him by taking his dogs.
32. Go out with — To go on a date with someone
Sarah was so happy when Peter finally asked her to go out with him!
33. Log in — To sign in to your account on a website or computer
Don’t forget to log in to your account to learn English better and faster.
34. Pay for — To give someone money for a particular purpose
She used her credit card to pay for the hotel reservation.
35. Pay for — To suffer because of something you did.
He’ll pay for all the problems he caused me by being late today!
36. Fall for (someone) — To fall in love with someone
He fell for her the moment he saw her.
37. Cut in — To interrupt a conversation or activity
The teacher cut him in and asked him to explain the answer to the class.
38. Call on (2) — To use someone’s or something’s knowledge
I may need to call on the university’s excellent professors in order to answer your question.
39. Come up (with something) — To think of an idea
I came up with this idea for a TV show about a woman living with her best friend and daughter. I call it ‘Two and a Half Women.’
40. Drop out — To quit or stop participating in something
She was a straight-A student, but she dropped out of college to pursue her dream of becoming an artist.
41. Log out / Log off — To sign out of your account
You should always log out of your accounts when you use a public computer.
42. Look out — To watch out for something
Look out , there’s a baseball coming your way!
43. Come up (1) — To bring up a topic
I wanted to tell her that I got a new job but the chance never came up .
44. Come up (2) — When something happens unexpectedly
I was going to meet my friends for dinner, but something came up so I had to cancel.
45. Come in — To enter
‘ Come in , the door is open!’ said the grandmother to the wolf.
46. Come forward — To volunteer information about something, like a crime
The police are encouraging people to come forward with any information about the kidnapped girl.
47. Check in — To register at a hotel for a stay
We haven’t checked in at the hotel yet.
I was in the neighborhood, so I decided to drop in on my sister and see how she was doing.
48. End up — To eventually be in a particular place or situation
After driving around for hours, we finally ended up at the beach.
49. Fall apart — To stop working or break into pieces
The old chair fell apart when I sat on it.
50. Fall down — To collapse or fall to the ground
The little girl tripped and fell down the stairs.
51. Fall off — To decline in quality or quantity
Sales fell off during the holiday season.
52. Give out (2) — To break down or stop working
The city had to rebuild the bridge completely because it was about to give out and fall down.
53. Go ahead — To go in front of someone, or to give permission
You can go ahead and start the meeting without me.
54. Grow up — To tell someone to stop acting childish
Some people tell Steve he needs to grow up , but he loves acting like a child.
55. Grow apart — To get distant from someone, like a friend
When my friend moved to a different country, I tried to stay close with her, but we slowly grew apart .
56. Hang on — To keep something
When everyone else was getting fired, Paul managed to hang on to his job.
57. Hang out — To spend time with someone, casually
My friends and I used to hang out in the park after school.
58. Hang up — To end a phone call, especially if before the other person is ready
I was in the middle of a sentence, and he hung up on me! How rude.
59. Hold on (1) — To hold something tightly
You’d better hold on to your hat; it’s windy out there!
60. Hold on (2) — To ask someone to wait for a moment
Hold on , I’ll be right back.
61. Give in — To surrender, especially in a fight or argument
Ben’s mother gave in and let him stay out late with his friends.
62. Take off (2) — To leave for a journey
The plane will take off in a few minutes.
63. Turn around — To move so you’re facing the opposite direction
Sally was about to get on the plane, but she turned around when someone called her name.
64. Turn up — When something that was lost is found unexpectedly
Anything I lose usually turns up under the couch. It’s my cat’s favorite hiding place.
65. Work out — To exercise
I try to work out every morning, by repeatedly lifting a heavy donut to my mouth.
| Phrasal Verb | Meaning | Example | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| To perform a role or behavior | a scene from the play. | Separable, transitive | |
| To behave inappropriately or malfunction | and froze. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To request or invite someone to do something | help with this difficult task. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To support or assist someone or something | your claims with evidence? | Separable, transitive | |
| To reverse or move backward | the car so I can park? | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To be suited or suited for a particular role or occupation | a career in medicine. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To explode or burst into pieces | in the sky tonight. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To lose one's temper or become angry | at his colleague during the meeting. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To escape or separate from a group or organization | from their captors. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To enter a building or place forcibly or illegally | to the house. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To end a relationship or conversation abruptly | their engagement. | Separable, transitive | |
| To escape or start suddenly and violently | in the city center. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To overcome an obstacle or make a significant achievement | the language barrier. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To bring someone or something with you | your passport. | Separable, transitive | |
| To introduce or earn a certain amount of money | new customers with the marketing campaign. | Separable, transitive | |
| To dismiss or ignore someone or something casually | my suggestion and continued with his plan. | Separable, transitive | |
| To develop or expand on something already existing | the success of our previous project. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To require or demand something | immediate action. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To request someone's presence or services | to investigate the crime scene. | Separable, transitive | |
| To shout or say something loudly and clearly | the answer to the question. | Separable, transitive | |
| To make a telephone call | the restaurant and make a reservation. | Separable, transitive | |
| To become overly excited or emotional in a situation | and spent all her savings on the shopping spree. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To continue or proceed with an activity or action | with our plans despite the challenges. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To complete or perform a task or action | a thorough investigation. | Separable, transitive | |
| To understand or grasp something, usually quickly | to the new concept. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To mark or indicate that something has been completed or verified | the items on the list as we go. | Separable, transitive | |
| To review or examine something carefully | the document for any errors. | Separable, transitive | |
| To verify or investigate the condition or progress of something | your recovery. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To empty or remove the contents of something | the garage and get rid of old items. | Separable, transitive | |
| To tidy or make something clean and neat | the room before the guests arrive. | Separable, transitive | |
| To happen or occur | , but I'm glad it did. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To make progress or improve | ? | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To accompany or join someone | to the party with me? | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To return to a place or situation | and visit us next year. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To obtain or acquire something | some concert tickets for tonight. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To move from a higher to a lower position | the stairs. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To criticize or reprimand someone heavily | him for consistently being late to work. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To become ill with a particular illness or condition | the flu and had to stay home from work. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To offer oneself for a task, position, or help | and speak to the authorities. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To enter a place | . | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To succeed or be accomplished | really well. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To detach or be removed from something | . | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To encourage or urge someone | , you can do it! | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To be revealed or made public | after years of speculation. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To visit someone's place | to my house this weekend? | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To arise or occur | and I couldn't pass it up. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To produce or provide something, especially an idea or solution | a plan to solve this problem. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To rely on or trust someone or something | me for support. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To reduce the amount or quantity of something | caffeine. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To handle or manage a situation or problem | this issue immediately. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To eliminate or get rid of something | unnecessary paperwork. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To fasten or decorate something | her hair and put on a beautiful dress for the party. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To wear formal or fancy clothing for a special occasion | for the wedding. | Separable, transitive | |
| To consume all the food | his entire meal in just a few minutes. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To rely on something as a last resort or backup | my savings. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To collapse inward or form a line or formation | after years of neglect. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To have a disagreement or argument | over a trivial issue and stopped speaking to each other. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To unintentionally drop an object | of her pocket. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To fail to happen or be completed as planned | due to bad weather. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To understand or solve something | the solution to the puzzle. | Separable, transitive | |
| To discover or obtain information | what time the meeting starts. | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To have a harmonious relationship or rapport with someone | her coworkers very well. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To escape or go on a vacation | from the city and relax at the beach. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To manage or survive with the available resources or income | with their current budget. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To enter or arrive at a place | before the meeting starts. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To leave or disembark from a vehicle or transportation | the bus at the next stop. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To make progress or continue | with his work. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To have a good relationship or get along with someone | my coworkers. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To leave or to remove something | of this dangerous situation. | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To recover from an illness or emotional distress | the loss of her pet. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To finish or complete | today. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To emit or produce | a pleasant fragrance. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To leave or depart | and leave me alone? | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To return to a previous location or time | to visit our hometown every summer. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To pass or elapse | so quickly when you're having fun. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To continue or proceed | with your presentation. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To leave one's place of residence or to socialize for entertainment | for dinner tonight. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To experience or endure | a lot of difficulties to achieve her goals. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To match or be suitable for | my dress perfectly. | Separable, transitive | |
| To distribute or give | worksheets to the students. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To linger or wait around | in the park after school. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To spend time in a place without any specific purpose | the mall when we were teenagers. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To wait or remain on the line | while I transfer your call. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To retain or maintain something within a confined space or boundary | his emotions and rarely shows them. | Separable, Transitive | |
| To continue doing something | trying. | Separable, transitive | |
| To maintain the same pace or level as | the latest technological advancements. | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To demolish or destroy | the old building and construct a new one. | Separable, transitive | |
| To terminate someone's employment | several employees due to financial problems. | Separable, transitive | |
| To omit or exclude | an important detail in her report. | Separable, transitive | |
| To disappoint or fail someone | us when he didn't show up. | Separable, transitive | |
| To allow someone to enter | me the room; I forgot my key. | Separable, transitive | |
| To release or excuse from a punishment | him with a warning. | Separable, transitive | |
| To take care of or watch over | her younger siblings while their parents are away. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To view with contempt or consider inferior | people who don't have a college education. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To anticipate or be excited about | our vacation next month. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To investigate or examine | the matter and take appropriate action. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To watch or be vigilant for something or someone | any signs of danger. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To admire or respect someone | my older sister for her achievements. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To understand or see something unclear or distant | the words on the sign from here. | Separable, transitive | |
| To engage in passionate kissing | in the park. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To invent or create a story or excuse | a silly excuse for being late. | Separable, transitive | |
| To reconcile or restore a friendly relationship | and be friends again. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To confuse or mistake something or someone | our names. | Separable, transitive | |
| To die | last night. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To transmit or convey something | the message to the team. | Separable, transitive | |
| To faint or lose consciousness temporarily | during the presentation. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To miss or decline an opportunity | the chance to travel the world. | Separable, transitive | |
| To result in success or bring a positive outcome | when he won the competition. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To give someone the money owed, usually to settle a debt. | his debts and became debt-free. | Separable, transitive | |
| To choose or select something | a beautiful dress for the party. | Separable, transitive | |
| To collect or gather something or someone | some groceries on your way home? | Separable, transitive | |
| To indicate or draw attention to something or someone | the mistake in the report. | Separable, transitive | |
| To succeed in achieving something difficult or impressive | a flawless performance on stage. | Separable, transitive | |
| To propose or suggest something | a new idea for the project. | Separable, transitive | |
| To postpone or delay something | the meeting until next week. | Separable, transitive | |
| To tolerate or endure something | his constant complaining. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To assemble or display | their artwork for the gallery show. | Separable, transitive | |
| To escape or flee from a place or situation | from home. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To meet or encounter someone by chance | an old friend at the grocery store. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To leave quickly or suddenly | without saying goodbye. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To use up or exhaust the supply of something | milk, so I need to go to the store. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To start a journey or trip | early in the morning to avoid traffic. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To trigger or initiate something, such as a series of events | a heated debate among the panelists. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To establish or arrange something | a new business together. | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To calm down or become established in a stable life | in a small town. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To become accustomed or get comfortable in a new place | their new home. | Inseparable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To pay a debt or resolve financial matters | the bill before leaving the restaurant. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To display or demonstrate one's skills or possessions | his new car to everyone. | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To arrive or appear, especially unexpectedly or at a specified time | at the party wearing a stunning dress. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To close or stop the operation of a business or system | its manufacturing plant. | Separable, transitive / intransitive | |
| To dismiss or reject an idea, proposal, or argument | his suggestion. | Separable, transitive | |
| To take a seat or position oneself comfortably | and discuss the details of the project. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To be noticeably different or exceptional | among the other contestants. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To confront or resist someone or something | the bully. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To remain or stay in a place or situation | until I finish this task? | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To resemble or have similar traits as someone | her mother in terms of looks and personality. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To disassemble or dismantle something | the furniture before moving it. | Separable, transitive | |
| To retract or withdraw a statement or offer | what I said earlier. | Separable, transitive | |
| To return something to its original location or owner | this book to the library? | Separable, transitive | |
| To write or record something | the important points of the meeting. | Separable, transitive | |
| To understand or comprehend something | all the information at once. | Separable, transitive | |
| To undertake or accept a responsibility or challenge | the project despite the difficulties. | Separable, transitive | |
| To assume control or become dominant | the department next week. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To start or begin a hobby, activity, or occupation | playing the piano. | Separable, transitive | |
| To discuss or consider something with others | the details of the project. | Separable, transitive | |
| To consider or reflect on something | your proposal. | Separable, transitive | |
| To discard or get rid of something | the old magazines. | Separable, transitive | |
| To attempt to achieve or obtain something | a promotion at work. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To test or experiment with wearing something | the dress before buying it. | Separable, transitive | |
| To test or evaluate something | the new software. | Separable, transitive | |
| To reject or refuse an offer or request | the job offer because of the low salary. | Separable, transitive | |
| To deplete or exhaust the supply or quantity of something | all the printer ink. | Inseparable, transitive | |
| To stop sleeping and become conscious | early in the morning. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To leave or abandon a situation or relationship | from the argument. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To leave suddenly or in protest | during the boring performance. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To be cautious or vigilant | for the step, it's slippery. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To gradually fade or disappear | in a few hours. | Inseparable, intransitive | |
| To eliminate or reduce through physical activity or effort | the extra calories I consumed. | Separable, transitive | |
| To develop or generate a particular feeling or state | the courage to ask her out. | Separable, transitive | |
| To record or write something on paper | the important details. | Separable, transitive | |
| To consider something as a loss or failure | the damaged goods. | Separable, transitive | |
| To write a report, summary, or account of something | the meeting minutes. | Separable, transitive | |
| To fasten or close a zipper | her jacket before going outside. | Separable, transitive |
As you’ve probably figured out from the lists above, a phrasal verb is a phrase that’s made up of a verb and another word or two—usually a preposition but sometimes an adverb . The same verb can be used in several phrasal verbs, such as give in, give away and give up, but the meaning will be different.
There are also phrasal verbs that you’re more likely to say with friends ( hang out , cut it out ), while others are pretty common at work emails and meetings:
To understand phrasal verbs, it’s important to know what verbs , prepositions and adverbs are.
- A verb is an action word. It describes something happening (e.g. hearing, seeing ), a state of being (e.g. to live, to sleep ) or an action being done (e.g. to read, to sing ).
- A preposition describes the relationship between two words. For example, the bees are above the table or under the table, but not inside the table (hopefully). Prepositions mainly deal with location or direction (e.g. on, through, around) and time (e.g. “by” or “around” a certain time).
- An adverb is a word that describes a verb. For example, you can run quickly or slowly and arrive to class early or late .
You put these words together to form phrasal verbs.
It’s easier than you think. For example, you probably already know the phrase “come on”—that’s a phrasal verb!
The word “come,” on its own, means to move towards something. Together with the preposition “on,” though, the phrase “come on” becomes a phrase of encouragement.
If the idea of phrasal verbs still takes some getting used to, you can pick them up more naturally by watching English movies , TV clips or online videos and then trying to notice the phrasal verbs that come up. English shows make great material for this because they often use everyday language.
Sometimes it can be tricky to do on your own, though. As an English learning resource, FluentU makes this more approachable.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
Phrasal verbs are such an important part of English that you’ll hear them everywhere!
As mentioned above, phrasal verbs can be either transitive or intransitive and separable or inseparable.
Transitive
Transitive phrasal verbs have a direct object (a thing or person that’s being acted on).
For example, let’s take the phrasal verb “put on”:
She’ll put on some makeup before stepping on stage.
In this sentence, “some makeup” is the direct object. You can’t say “she’ll put on before stepping on stage” because with transitive verbs, there needs to be a direct object—what exactly is she putting on?
Here are some other transitive phrasal verbs:
We’re already indoors, take off your hat.
This is really tough, but the team’s confident that they can work out a solution.
I’m ready for this challenge, bring it on !
On the other hand, intransitive phrasal verbs don’t have a direct object. You can just use them in a sentence as is:
When I’ve had a really good nap, it’s hard to get up !
My friends want to hang out at this interesting café that just opened.
Separable phrasal verbs are phrasal verbs that can be split up, with a word or phrase in the middle:
Since you weren’t at the party yesterday, I’ll fill you in on the funny things that happened.
He had to take his jacket off because he was sweating.
One thing to remember is that separable phrasal verbs are always transitive—it’s the direct object that gets inserted into the middle of the phrase.
Usually, if the direct object is a noun, the word order is a bit more flexible. You can place it either inside the phrasal verb or simply add it afterwards:
I’m going to turn my phone off because there’s no signal here in the mountains.
I’m going to turn off my phone because there’s no signal here in the mountains.
There’s an exception to this, though. If the direct object is a pronoun (me, you, he, she, it, them), it would have to be inserted into the phrasal verb:
Correct: We brought a gift to cheer her up .
Incorrect: We brought a gift to cheer up her.
With inseparable phrasal verbs, you can’t break them up! If there’s a direct object, it has to come after the phrasal verb, even if it’s a pronoun:
Correct: Can you stay nearby so we can call on you if an emergency happens?
Incorrect: Can you stay nearby so we can call you on if an emergency happens?
Inseparable phrasal verbs can be either transitive or intransitive:
She came across her old school photos and felt surprised about how different she looked back then. (Transitive)
As a teenager, he was excited to grow up and live in his own apartment. (Intransitive)
The catch is that there’s no definite way to tell whether a phrasal verb is separable or inseparable, so if you encounter a new phrasal verb, you’ll have to observe how it’s used!
Phrasal verbs are used just like verbs—you can use them anywhere they make sense.
First, you have to remember if a phrasal verb is separable or inseparable.
Inseparable verbs need to have the verb and preposition said together, like in the phrase fall down.
For separable verbs, though, you can also separate the verb and the preposition by putting other words in between them—both ways are correct. For example:
T urn off the TV
Turn the TV off
The verb part of the phrase should be changed depending on the tense and subject of the sentence . For example, take out can transform like this:
He took out his water bottle from his bag. (Past tense)
She takes out the trash every Thursday. (Present tense)
They often take out their dog for a walk in the park. (Present tense)
I’ll take out the boxes from the storage room tomorrow. (Future tense)
Here’s another example (call off) :
They called off the meeting due to a scheduling conflict. (Past tense)
We’re calling off our plans to go hiking because it might rain. (Present continuous tense)
She will call off the event if not enough people RSVP. (Future tense)
How many of these English phrasal verbs did you already know? Phrasal verbs are everywhere! Don’t be afraid of how many there are—just start with a few at a time and soon you’ll be an expert.
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


100 Phrasal Verbs, Meanings and Example Sentences
100 phrasal verbs.
Phrasal verbs are an essential part of English grammar and are commonly used in daily conversations. They consist of a verb and a preposition or adverb, and their meanings can often be quite different from the individual words.
In this list, we have compiled 100 common phrasal verbs along with their meanings and example sentences to help you understand and use them correctly in your own writing and speaking.
- Ask out – to invite someone on a date Example: He finally asked her out to dinner.
- Back up – to support or defend someone or something Example: I will back you up on this decision.
- Break down – to stop working properly Example: My car broke down on the way to work.
- Bring up – to mention something in conversation Example: I don’t like to bring up politics at the dinner table.
- Call off – to cancel an event or meeting Example: They had to call off the meeting because of bad weather.
- Carry on – to continue doing something Example: He told her to carry on with her work.
- Catch up – to reach the same level as someone or something else Example: I need to catch up on my reading.
- Check in – to arrive and register at a hotel, airport or hospital Example: We need to check in at the hotel before we go sightseeing.
- Cheer up – to make someone feel better Example: I tried to cheer him up by telling him a joke.
- Clean up – to tidy and clean a place Example: We need to clean up the kitchen before guests arrive.
- Come across – to find or meet unexpectedly Example: I came across an old friend on my way to work.
- Come up with – to think of or suggest an idea or plan Example: We need to come up with a new marketing strategy.
- Count on – to rely on someone or something Example: I can always count on my best friend to help me.
- Cut off – to stop or interrupt someone or something Example: The teacher cut off the student in the middle of his sentence.
- Deal with – to handle or manage a problem or situation Example: I need to deal with this issue before it becomes worse.
- Do away with – to get rid of something Example: They decided to do away with the old furniture and buy new.
- Dress up – to wear formal clothes or make oneself look better Example: She likes to dress up for special occasions.
- Drop off – to take someone or something to a particular place Example: I need to drop off the package at the post office.
- End up – to finally reach or do something Example: They ended up staying home instead of going to the party.
- Fall apart – to break into pieces or fail completely Example: The old car finally fell apart after years of use.
- Fill in – to provide information that is missing or incomplete Example: I had to fill in the missing details on the form.
- Find out – to discover or learn something Example: I need to find out what time the movie starts.
- Get along – to have a good relationship with someone Example: I get along well with my colleagues.
- Get away – to escape or take a break from something Example: I need to get away from work for a few days.
- Get back – to return to a place or activity Example: He will get back to work on Monday.
- Get by – to manage to live or do something with limited resources Example: They were able to get by on very little money.
- Get off – to leave a vehicle or mode of transportation Example: We need to get off the train at the next stop.
- Get on – to board a vehicle or mode of transportation Example: We need to get on the bus before it leaves.
- Get out – to leave a place or situation Example: I need to get out of this meeting.
- Get over – to recover from an illness or emotional experience Example: It took him a long time to get over his breakup.
- Give up – to stop doing something or trying to achieve something Example: She decided to give up smoking.
- Go ahead – to proceed or continue with something Example: You can go ahead and start the presentation.
- Go out – to leave one’s home to go somewhere, usually for social reasons Example: We’re planning to go out for dinner tonight.
- Grow up – to become an adult or mature Example: He needs to grow up and start taking responsibility.
- Hand out – to distribute something to a group of people Example: She handed out the brochures at the conference.
- Hang up – to end a phone call Example: He hung up on me before I could finish speaking.
- Hold on – to wait or pause for a moment Example: Please hold on while I transfer your call.
- Keep up – to maintain a certain level or pace Example: It’s important to keep up with your studies.
- Knock out – to defeat or render unconscious Example: The boxer knocked out his opponent in the first round.
- Look after – to take care of someone or something Example: She looks after her younger siblings.
- Look up – to search for information in a reference source Example: I need to look up the meaning of that word.
- Make up – to invent or fabricate something, or to reconcile after an argument Example: He made up a story to explain his absence.
- Mess up – to make a mistake or create a mess Example: I accidentally messed up the report.
- Pass away – to die Example: Her grandfather passed away last week.
- Pay back – to return money that is owed Example: He promised to pay back the loan by next month.
- Pick up – to lift or collect something, or to improve or learn something quickly Example: She picked up the book from the table.
- Point out – to draw attention to something or someone Example: He pointed out the mistake in the report.
- Put off – to postpone or delay something Example: They decided to put off the meeting until next week.
- Put up with – to tolerate or endure something unpleasant Example: She can’t put up with the noise from the construction site anymore.
- Read out – to read aloud Example: She read out the names of the winners.
- Run into – to meet someone unexpectedly Example: I ran into an old friend at the mall.
- Set up – to arrange or establish something Example: They set up a meeting to discuss the new project.
- Show off – to display one’s abilities or possessions to impress others Example: He likes to show off his new car.
- Sort out – to resolve a problem or organize something Example: We need to sort out the issue with the supplier.
- Stand by – to support or be loyal to someone or something Example: I will stand by you no matter what.
- Stand out – to be noticeable or outstanding Example: Her bright red coat made her stand out in the crowd.
- Take off – to remove clothing, or to become popular or successful Example: She took off her shoes and sat down.
- Take on – to accept a challenge or responsibility Example: She decided to take on the new project.
- Take over – to gain control or authority over something Example: The new manager took over the department last month.
- Talk over – to discuss something in detail with someone Example: We need to talk over the plans for the weekend.
- Tear up – to rip into pieces Example: She tore up the letter in anger.
- Think over – to consider something carefully before making a decision Example: He needs to think over the job offer before accepting it.
- Throw away – to discard or dispose of something Example: She threw away the old magazines.
- Try on – to wear clothing to see if it fits or looks good Example: She tried on several dresses before finding the perfect one.
- Turn down – to refuse or reject something or someone Example: He turned down the job offer because of the low salary.
- Turn up – to arrive or appear unexpectedly Example: He turned up at the party uninvited.
- Use up – to exhaust or deplete a supply of something Example: We used up all the paper in the printer.
- Wait for – to remain in a place until someone or something arrives Example: I will wait for you at the entrance.
- Wake up – to stop sleeping and become alert or conscious Example: He wakes up early every morning.
- Warm up – to prepare the body for exercise or activity, or to become friendlier or more enthusiastic Example: She always warms up with stretching before running.
- Watch out – to be careful or cautious Example: Watch out for that slippery patch of ice.
- Wear out – to become worn or exhausted Example: His shoes were worn out from all the walking.
- Work out – to exercise or train, or to solve a problem Example: She likes to work out at the gym every day.
- Write down – to record something in writing Example: He wrote down the phone number on a piece of paper.
- Zip up – to close a zipper or fastener Example: She zipped up her jacket to keep warm.
- Act out – to express one’s emotions or feelings through behavior Example: The child was acting out because he was upset.
- Back up – to support or provide assistance, or to make a copy of data Example: She backed up her important files on an external hard drive.
- Blow up – to explode or increase suddenly, or to become angry Example: The balloon blew up when she tried to inflate it.
- Break down – to stop functioning, or to become emotional and start crying Example: The car broke down on the highway.
- Bring up – to raise or mention a topic, or to raise a child Example: She brought up the issue during the meeting.
- Brush up on – to review or improve one’s skills or knowledge of something Example: He needs to brush up on his French before his trip to Paris.
- Burn down – to completely destroy a building or structure by fire Example: The old warehouse burned down last night.
- Call off – to cancel or abandon something Example: They called off the wedding due to a family emergency.
- Carry on – to continue with an activity or task Example: She carried on with her work despite the distractions.
- Catch up – to reach the same level or pace as someone else, or to update oneself on news or events Example: She needs to catch up on the latest developments in the industry.
- Check in – to register one’s arrival at a hotel or airport Example: We need to check in at the hotel before 3 pm.
- Cheer up – to become happier or to make someone else happier Example: The sunny weather cheered her up.
- Clean up – to tidy or remove dirt or clutter from a place Example: They cleaned up the beach after the party.
- Come across – to encounter or discover something or someone unexpectedly Example: She came across an interesting article on the internet.
- Come back – to return to a place or activity Example: He will come back to work after his vacation.
- Count on – to rely or depend on someone or something Example: They know they can count on their parents for support.
- Cut off – to stop or interrupt something suddenly Example: The phone cut off in the middle of our conversation.
- Deal with – to handle or manage a situation or problem Example: We need to deal with the customer complaints as soon as possible.
- Die down – to become less intense or loud Example: The storm died down after a few hours.
- Do over – to repeat or redo something Example: She had to do the project over because of a mistake.
- Draw up – to prepare or create a plan or document Example: They drew up a proposal for the new project.
- Drop off – to fall asleep, or to leave someone or something at a specific location Example: She dropped off to sleep on the couch.
- Eat out – to dine at a restaurant instead of at home Example: They decided to eat out at their favorite restaurant.
- Figure out – to understand or solve a problem Example: He needs to figure out a way to fix the machine.
- Fill out – to complete a form or document with information Example: She filled out the application for the job.
Phrasal verbs can be challenging for non-native English speakers to master, but with practice and familiarity, they can become an essential part of your language skills. We hope this list of 100 phrasal verbs, meanings, and example sentences has been helpful in expanding your understanding and usage of these important language structures.
Download Word Coach Application
English word search game, related posts:.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download the Word coach App on your Android phone
Word Coach - IELTS and GRE Vocabulary Builder & word coach Quiz (10 Words a Day) application helps, you and your friends to improve English Vocabulary and help you become the smartest among your group.


100+ Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Sentences

Explore 100+ Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Sentences through our comprehensive guide to phrasal verbs, providing detailed explanations and examples with sentences to help you understand and use them effectively. Whether you’re looking to improve your English vocabulary or seeking a refresher on Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples, this article is a valuable resource.
Definition of Phrasal verbs
Phrasal Verbs are the combinations of Verbs and adverbs or prepositions or both with completely new meanings and they consist of more than one word.
Most phrasal verbs consist of two words ; the first word is a simple monosyllabic Verb, and the second word is a particle i.e., a preposition or an adverb . For example,
- Put (simple monosyllabic Verb) + on (preposition) = Put on
It is nowadays called Phrasal because it represents the appearance of a two-word phrase rather than a single item . There are also some three-word phrasal verbs i.e.,
- to put up with ,
- to look down upon , and
- to leave up to .
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples
Phrasal Verbs are also called Group Verbs and Prepositional Verbs . We know that the word give means to contribute, supply, or transfer. If we add up after give ( i.e., Give up ), those two words express completely a new meaning and that is the wish to stop .
- Verb + Preposition / Adverb = A Phrase with completely one new meaning.
- Give + Up = Wish to stop
- Example: Here Give up is called Phrasal Verb.
If the object of a Transitive Phrasal Verb is a Noun , the particle ( preposition or adverb ) may be placed before or after the object; i.e.,
- He worked out the sum .
- He worked the same out.
If, however, the object of a Transitive Phrasal Verb is a Pronoun , the particle ( preposition or adverb ) must be placed after the pronoun . i.e.,
- He worked it out.
- (Not, he worked out it.)
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples Alphabetically
All the common and important Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples are arranged alphabetically in the following sentences. Expand your vocabulary and improve your English language skills with this comprehensive guide on Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples.
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples with Act
| We should not his opinion. | ||
| A solicitor his clients. | ||
| The medicine the heart. | ||
| He my suggestions. | ||
| He my expectation. |
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples with Bear
| He the first prize in school sports. | ||
| The king the enemy. | ||
| Shyamal the first prize in school sports. | ||
| These are issues that the welfare of society. | ||
| She did not your statement or she will me | ||
| The soldiers their courage against all odds. | ||
| You should a sick child. |
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples with Break
| The prisoner from captivity | ||
| His health has | ||
| Burglars the building last night. She tears when I told her the news. | ||
| The robbers the house in the dead of night. | ||
| He in the middle of the story. Anil her engagement with Sheila. | ||
| A devastating flood . Several prisoners from jail. | ||
| Lionel Messi the defense of his rival team. | ||
| The school at 4:30 PM. The sheep was into parts having been struck against the rock. | ||
| We should blind prejudices. | ||
| Why are you our conversation? |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Bring
| They their own ruin. | ||
| The price of essential commodities has been The subjects the tyrant. | ||
| Trees new tender leaves in spring./The news a cheer. | ||
| All these matters were in the meeting for discussion. | ||
| Idleness poverty.He has this disgrace to himself. The damp weather has his illness. | ||
| He will soon the new edition of his book.Adversity the good qualities of man. | ||
| Several girls painted in the heat but they were soon . | ||
| After the date of our parents the girl was by her aunt. | ||
| The king quickly the rebels. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Call
| I his house yesterday. | ||
| The occasion prompt action. | ||
| your speech an angry response from him. | ||
| He a doctor. The National Library has all overdue books. | ||
| The strike has been The journey has been due to some unavoidable circumstances. | ||
| I him yesterday. We him at his residence . | ||
| the fire brigade was by the authorities. | ||
| The old man could not past events. | ||
| I now the chief guest to address the meeting. I him to help me. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Carry
| He was by his passion. | ||
| India all the prices. | ||
| He the business in his father’s absence. | ||
| I shall what I have promised. | ||
| He the work successfully. His courage him difficulties. | ||
| The incident him to his childhood days. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Cast
| He has her family. | ||
| He has his old hat. | ||
| He was by his sans act. | ||
| He’s trying to his bad image. | ||
| I am for an opportunity to visit your village. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Come
| When did the accident ? | ||
| I my aunt in the street. | ||
| They us last night with a knife. | ||
| How did you this ring? | ||
| The roof of the house during the storm. Rain in torrents. | ||
| The boy the room. | ||
| He 1,000,000 rupees when his father died. | ||
| each speech for a great deal of criticism. | ||
| Vidyasagar a poor brahmin family. | ||
| The prize giving ceremony of our school yesterday. The experiment did not | ||
| The winter is . we will be late for the function. The project is nicely. | ||
| The truth ever When is your school magazine ? | ||
| He with a most extraordinary story. | ||
| He will never to our site.Why did Thomas to India? | ||
| When did the patient ? At last, he to our views. | ||
| His annual expenditures 10,000 rupees. | ||
| May the patient soon?A message had just here. | ||
| Your work has not the required standards. | ||
| I a dead horse. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Cry
| Don’t his achievements. | ||
| It’s no use the split milk. | ||
| There is no trader but his own goods. | ||
| They for help. | ||
| We said we should go but we had to at the last moment. | ||
| People are against dictatorship. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Cut
| You must your expenditure. Please the essay, it is much to lengthy. | ||
| Don’t your expenditure. She kept on our conversation. | ||
| He was in the prime of life. The baby is from its mother. | ||
| He is not an engineer. | ||
| The mother was terribly at the death of her own son. | ||
| They trimmed the plants the uneven branches. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Deal
| He rice. | ||
| the profits will be among the investors. | ||
| They try to politely the customers. He the difficult problem easily. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Do
| The death penalty has been in all civilised societies. We should this practice. The women tried to herself. | ||
| This desk he will do for a table. He is . | ||
| I am quite with the long journey. We are having the kitchen . | ||
| I cannot his insolence. | ||
| No minister can the service of a secretary. | ||
| He was so depressed that he felt like himself. He looked very . | ||
| He was by a gang of anti-socials. We are the drawing room. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Fall
| Our false friends when we fall into distress. Superstitions are here to from our society. | ||
| They are marriage finally | ||
| The enemy with the advance of our troops. | ||
| Finding no other means of livelihood, he up on begging. | ||
| France Germany in coal products and. | ||
| On his way to Kolkata, he his long lost father. The headmaster the decision of the committee. | ||
| The left tenant ordered the soldiers to . The roof of the building . | ||
| Don’t bad habits. | ||
| Attendance in classes has with the exams around the corner. False friends in adversity. | ||
| Miscreants or them. I have every time./The full cost of the program fell on or upon us. | ||
| Things as we had hoped She with me over a trifle. | ||
| The scheme for want of sufficient funds. | ||
| The hungry man meeting with great joy. | ||
| he was doing well on the exam until he fell down on the last essay question. | ||
| that case falls under the heading of errors of judgement. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Get
| The old woman is too weak to . The news of Mrs Indira Gandhi’s death fast. The news of the accident in different places. | ||
| How is your sister with her studies? | ||
| The fox could not the grapes. Truth is hard to . He failed to the witness. | ||
| The thief with my purse. The culprit can’t . | ||
| When did you last night? She has her last ring. | ||
| She cannot without him. | ||
| Did you his address?Let’s to our work. He from the tree. | ||
| The train five minutes early. | ||
| Don’t a moving train.Father me the school.Your son has bad habits.Me trouble or debt. | ||
| We the stadium after lunch.We were lucky to . | ||
| He will surely in life. | ||
| The boy is well with his studies. | ||
| The secret . When did the new book ? He got out of the room. | ||
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Give
| The minister the prizes at the sports meet. That remark his real feelings. Mr Roy has his whole property to his elder son. | ||
| The reveals to the government. Please your timecards. | ||
| You have not the books you borrowed from me. | ||
| The fire a dense smoke. | ||
| The blast furnace is a lot of heat. The wicked man that his wife had died of snake bite The minister he the handbills among the people. The fuel . She tried to with a song. | ||
| The fire a dense smoke. | ||
| The thief was to the police. Please this matter. You should not this matter. Before exams he to studies. | ||
| The boy has smoking.The Malaga himself to the police yesterday. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with ‘Go’
Phrasal verb – go.
| the Hawker is selling his articles. He his business at Daybreak. | ||
| the soldiers the enemy.everybody wealth. | ||
| These police will the public interest. | ||
| with your plan. | ||
| I shall with you as far as the charge. He with me on this point. | ||
| The man the policeman with a big knife. | ||
| he is the last man to upon his word. | ||
| a boy should what his parents say. Mr sane me without speaking a single word. | ||
| the price of rice has .he will in history as a despot. The sun has | ||
| The robbers the policeman. Mr sane a patriot in the country. | ||
| He will the exam this year. | ||
| I sell soon the matter. | ||
| the gun accidentally. Does your party all right? | ||
| I’m educated man wants to know what is in the world. with your work. | ||
| The lamp has . | ||
| Mr sane has to the Congress. The examiner the accounts. | ||
| this book 10 editions. I have the book. Mita great sufferings. | ||
| the price of fees is day by day. | ||
| I cannot you on this point. I shall you as far as the post of his. | ||
| the poor boy has often to food. | ||
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Hand
| This tradition has been to us from the past. | ||
| The minister has his resignation. | ||
| Samuel this magazine to me. | ||
| The teacher the books to the students. | ||
| The thief was to the police. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Hang
| Children always their mothers. | ||
| The Pak army how to | ||
| The unemployed young man in the office for a job. | ||
| Do not the open balcony.The meeting has been . | ||
| A notice was on the wall. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Hold
| Old years from saying unpleasant things. | ||
| You should your temper. | ||
| People revolt against the rulers who the people | ||
| Please for a minute. The rain for two hours. He tohis course of action through all opposition. | ||
| He a helping hand show me. The doctor a little hope of his recovery. | ||
| The match was on an hour. | ||
| We shoot our convictions. | ||
| The travellers where are bandits. | ||
| Many do not Co-education. | ||
| The matter is till the next meeting. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Keep
| You must your studies if you are serious. | ||
| He advised hits on to from bad company. | ||
| I sell nothing from you. | ||
| You must mark your anger. | ||
| bad habits. | ||
| I cannot him any longer. | ||
| Thousands of years ago man used to make a big fire to wild animals. | ||
| see talking. | ||
| Please your temper control. | ||
| of their quarrels. | ||
| One should always one’s promise. | ||
| skipper Virat Kohli always pressure on the England team. your courage in times of danger. | ||
| your son cannot the class. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Lay
| Father the offender with a big stick. | ||
| We should money for our old age. She led her to listen to me. We need to something for our bad days. | ||
| We should some money for a rainy day. | ||
| the rebels their arms. Our freedom fighters their lives to the cause of the country’s liberation. | ||
| Hoarders food for the future. | ||
| The factory had to many workers when it’s orders decreased. | ||
| The mother her hand her son’s head. Taxes were liquor. | ||
| He has all his money. | ||
| She is with typhoid. He has nothing for a rainy day. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Look
| I am still for a job. | ||
| Mother her children. | ||
| the moon. | ||
| Don’t the poor. | ||
| I am still a job. | ||
| We are his visit. | ||
| I shall next time. | ||
| I will soon the matter. | ||
| We the rare event of the full solar eclipse in 19 95. | ||
| The police were for the criminal. | ||
| A selfish man for nobody except himself. | ||
| They the application. | ||
| Please the letter. | ||
| You must your manners. We shall all you for help. | ||
| Please the word in the dictionary. The prices of necessaries are | ||
| They all look up to him as their leader. | ||
| I hard add my sister. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Make
| The cat the mouse. | ||
| He his father’s money. | ||
| The sheep the port. Early rising good health. Mr Roy the Andamans. | ||
| This chair is food. I can nothing what he says. | ||
| The thief with ornaments. | ||
| I could not anything what he said. He failed to his case. | ||
| He his property to the Trust. | ||
| We to come back. They have their quarrel. The government for the last. He the whole story. |
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples with Pass
| He last night. | ||
| One should not the faults of wants words. We his house every day. | ||
| He is a great scholar. | ||
| The prize giving ceremony of our school. yesterday. He tried to himself as a great scholar. | ||
| Mr Sen he her son’s faults. | ||
| He terrible sufferings in life. They endless hardships. |
Phrasal Verbs Meaning and Examples with Pull
| He me. | ||
| The old buildings was | ||
| The train on time. | ||
| Five men a robbery yesterday. | ||
| You will soon in our village. | ||
| The doctor says the patient will soon | ||
| He was by my father. |
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples with Put
| We all need to some amount of money for future use. | ||
| We all need to some amount of money for future use. | ||
| Ants food for the winter. | ||
| The king the rebellion by force of arms. the names of the successful candidates. | ||
| You must all your strength. Trees new leaves in spring. | ||
| He has a new theory. | ||
| He has a claim for compensation. | ||
| your shoes. She put on an air of innocence. | ||
| I my departure for a month. Getting back home we our clothes. You must your doubts in fear. | ||
| The fire should be properly | ||
| I at and in for the night. We a tent. KL Rahul a steep resistance against the Australian bowlers. A notice was | ||
| The measure was without opposition. | ||
| The committee his proposal vote. Don’t put me to Saint. She has been put to great difficulty. | ||
| None can such kind of behaviour. |
Phrasal Verbs with Run
| The policeman the thief. | ||
| The boy ran home and never returned. | ||
| The man ran a bag. | ||
| The tiger the deer. | ||
| The cyclist was by a minibus. The battery has | ||
| I will and see you this evening. | ||
| I an old friend of mine yesterday. He has debt | ||
| the man with my watch. | ||
| The stock of food | ||
| Don’t on your friends when they need you. | ||
| The old man was by a bus. He his notes before starting his lecture. | ||
| Bullets the body of the escaping terrorist. He has his fortune. | ||
| The book four hundred pages. |
Phrasal Verbs with See
| He promised to the matter. | ||
| I sell the matter. A great man the reality of things. | ||
| off | My parents were present at the airport to me . | |
| The headmaster himself the arrangement for the prize giving ceremony. |
Phrasal Verbs with Set
| The maid cleaning the room. | ||
| The court my claim | ||
| These seats are for ladies. | ||
| The old man a huge amount of money for the future. | ||
| The old man he’s bored and gently. The bass stopped to s an old man. The police the complaint. | ||
| In his speech he is religious views. | ||
| The rainy season in West Bengal about June. | ||
| He for Kolkata last night. | ||
| The dogs were the Jackal. | ||
| East out Jalpaiguri easily this morning. He his ideas clearly in this essay. He to collect all the wisdom of the world. | ||
| They were all hungry and at once eating. | ||
| He had a school. He had as a grocer. | ||
| The boy is being a doctor. The thieves him and beat him senseless. |
Phrasal Verb Meanings and Examples with Stand
| He the re- election of the president. | ||
| He always any agreements he makes. He will always me. | ||
| White purity. He total prohibits . | ||
| from their quarrel. | ||
| His work from that of others. | ||
| Let the matter until next meeting. | ||
| He always his promise. We should our principles. | ||
| He always the underdogs. |
Phrasal Verbs with Strike
| He is with paralysis. | ||
| The boy’s name was the school register. | ||
| the line. | ||
| I quickly an acquaintance with the new neighbour. |
Phrasal Verbs with Take
| He his father. | ||
| Many books were from the library. | ||
| I will not my words. | ||
| He the speech in shorthand. | ||
| I him a fool. | ||
| The foolish act is sure to his reputation as a sensible man. | ||
| He is the last man to be . I fail to the meaning of this passage. | ||
| The boy his shoes. The doctor his leg. Coronavirus has many lives in this year. When will the plane ? | ||
| He heavy responsibilities. | ||
| The dentist his teeth. | ||
| The new Prime Minister will the charge of the government . The government has the primary schools. | ||
| Recently he has been gambling. He has cultivation. | ||
| I sell the problem with the doctor. When did you your study of French? We shall the problem to solve it. |
Phrasal Verbs with Tell
| He us his hardships. | ||
| I cannot him his brother. | ||
| smoking started to or his health. | ||
| the teacher him for quarrelling with his classmate. |
Phrasal Verbs with Throw
| He is his money . | ||
| He and advantage. | ||
| Recently he has himself research work. | ||
| One must troublesome companions. | ||
| The bill was by the parliament. | ||
| When he became rich he all his old friends. | ||
| He his job. A country seldom a great political genius. |
Phrasal Verbs with Turn
| I shall never you. | ||
| We should not from the path of honesty. | ||
| he a beggar. | ||
| The headmaster did not our proposal. | ||
| The hermit the cat a dog. | ||
| Please the light. | ||
| Please the light or radio. The success of a picnic usually the weather. | ||
| Please the light. Our school has some first rate scholars. He to be a cheat. Dishonest students must be of the class. | ||
| He has his business to his successors. | ||
| The orphan has nobody to . | ||
| We cannot say what will next. He in time. |
Phrasal Verbs with Work
| He is Shakespeare’s sonnet. The sculptor making the statue. | ||
| He has been the evolution of the caste system. | ||
| He a few jokes the lecture. | ||
| New must take regular physical exercise to your excess weight. | ||
| The laborers the project. His speech ignorant villagers. | ||
| I will help you to the problem. He has a plan to save money. | ||
| He’s emotional speech the mob. |
Phrasal Verbs with Write
| I will him as a fool. | ||
| He an account of the sports meet. I will your debt. | ||
| Please a copy of the agreement. | ||
| I must my notes of the lecture. |
Related Posts:

- TheFreeDictionary
- Word / Article
- Starts with
- Free toolbar & extensions
- Word of the Day
- Free content
Phrasal Verbs
What is a phrasal verb, constructing phrasal verbs – particles vs. prepositions, particle phrasal verbs.
- “My table takes up too much room.” (The table occupies too much space.)
- “Please look over the proposal and let me know what you think.” (Please quickly examine the proposal.)
- “I can’t believe that you’re giving up !” (I’m surprised that you’re going to stop trying.)
- “There will always be setbacks that we have to allow for .” (We always have to consider and be ready for possible setbacks.)
- “We have to wait for the fire to die down before we can enter the building.” (We have to wait for the fire to become less intense.)
- “The plane took off an hour late.” (The plane rose into the air and began to fly later than scheduled.)
- “She is always making up excuses.” (She is always inventing excuses that are not true.)
- “When I am on the bus, I always give up my seat to the elderly.” (I vacate my seat and give it to an older passenger.)
Preposition phrasal verbs
- “He has been looking after his mother .” (He has been caring for his mother.)
- “I came across that old watch of mine when I was cleaning out the drawers.” (I found my old watch unexpectedly.)
- “Stop picking on your brother like that!” (Stop teasing or harassing your brother in that way.)
Particle-prepositional phrasal verbs
- “She comes across as a really confident person .” (She gives the impression of being confident by the way she acts.)
- “You’re going too fast, so I can’t keep up with you .”
- “I’ll make sure that she doesn’t get away with her plan .” (I’ll make sure she is caught and/or punished.)
- “A substitute teacher has been filling in for Mr. Davis all week.” (The substitute teacher is taking the place of Mr. Davis.)
- “I’ve been trying to cut back on junk food lately.” (I’m trying not to eat as much junk food as I had been before.)
Differentiating prepositional and particle verb phrases
Intransitive verbs.
- “Please don’t give up .”
- “I know you want me to lie, but I just wasn’t brought up that way.”
- “I hope that my idea came across well.”
Transitive verbs
- “Please look over the proposal and let me know what you think.”
- “Please look it over and let me know what you think.”
- “He has been looking after his mother .”
- “He has been looking after her .”
- “He has been looking her after .” (incorrect)
Transitive and intransitive phrasal verbs
- “I was a bit of a skinny kid, but I filled out nicely during high school.” ( Intransitive , meaning “to become larger or fuller in one’s figure.”)
- “Make sure that you fill out the form correctly.” ( Transitive , meaning “to complete (a document) by providing the required information.”)
- “The two friends made up after their bitter argument.” ( Intransitive , meaning “to reconcile or resolve a quarrel.”)
- “Please stop making up excuses .” ( Transitive , meaning “to fabricate or invent.”)
Prepositional verbs vs. phrasal verbs
- “Kelly asked for a raise.” (The literal meaning of to ask is to inquire . Kelly inquired about a raise, making it a prepositional verb.)
- “Kelly asked out Chad.” ( Ask out means to invite someone on a date , making it an idiomatic phrasal verb.)
- “They sailed through the waters with plenty of time to spare.”
- “They sailed through their exams with plenty of time to spare.”
Recognizing common phrasal verbs
1. Which of the following is not a component of a phrasal verb?
2. What is the primary difference between prepositional verbs and phrasal verbs?
3. What do prepositions do that particles cannot do in phrasal verbs?
4. Identify the phrasal verb in the following sentence. “It appears to me that you have thoroughly mucked up the case again.”
5. Which of the following can be separable in a sentence?
Chapter Sub-sections
- Common Phrasal Verbs
Conversations

- Facebook Share

Where people come to learn REAL English
42 Advanced Phrasal Verbs (That You Need to Know)
Phrasal verbs are very common in English conversation. Learning phrasal verbs is a great way to make your English sound more natural.
Some phrasal verbs are literal , which means the meaning is exactly what the words say . Some phrasal verbs are metaphorical , this means they have a completely different meaning than you would associate with the verb by itself .
| – | – |
| To go someplace and move around it to see what is there. | Be careful, something dangerous is coming. |
| .” | !” |
Another category of phrasal verbs is separable and inseparable . This simply means that some verbs can take a subject in between the verb and the particle and some cannot.
| separable – | inseparable – |
| To save something or keep it available to use | To be responsible for, or to take care of someone or something |
| money every month for when I retire.” | my kids while my wife and I are on vacation.” |
42 Advanced Phrasal Verbs
- Be up for Something – To want or be willing to do something.
- We’re going to go hiking this weekend, you can join us if you’re up for it .
- I’ll ask Kevin if he wants to come to the pub with us tonight but he had a long day, so I’m not sure he’ll be up for it .
- Be up to Something – To be doing something.
- Hey Jeff, what are you up to today?
*This can also mean to be doing something secretly.
- Todd has been sneaking around the office all morning, I think he’s up to something .
- Bounce back – To return to health or return to a good condition after an illness, injury, or difficulty.
- Lucas injured his shoulder in the rugby match last weekend but I’m sure he can bounce back in no time. He’s a tough guy.
*We can bounce back from something.
- Travel companies are starting to bounce back from the loss of business during the pandemic.
- Bounce s omething off someone – To share an idea or plans with someone so they can tell you what they think about it.
- I’ve been thinking about ways to increase company profits next year. I’d like to bounce some ideas off you if that’s okay. I would love to know what you think.
- Block off – to close a road or an opening by placing a barrier at one end or in front of it.
- The news just said that a water pipe burst downtown today. Emergency crews are trying to fix the damage and the police have blocked off Main Street. It must be a traffic nightmare.
*This is separable is a verb so we can put an object in between the verb and the preposition – block something off .
- The police have blocked Main Street off .
1) To become greater, stronger, or to increase in number.
- The movie had a nice steady build up until the big finale. It was fun.
2) Build somebody/something up – to give a very positive and enthusiastic description of somebody/something, often making them seem better than they really are.
- Really? I didn’t like the movie at all. It was built up to be the most exciting movie of the year but I was disappointed.
3) Build somebody/yourself up – To make somebody/yourself healthier or stronger.
- Did you see Anthony today? He has so much muscle! He really built himself up over the summer. She must have joined a gym.
- Bump into – To meet someone by chance.
- I bumped into Shannon this morning at the train station. She looked great, I think she lost weight.
- Call off – To cancel something.
- The boss called off the meeting today so we can all go home early. That’s great.
*This is separable phrasal verb so we can put an object in between the verb and the preposition – Call something off
- The boss called the 5:00 meeting off today.
- Catch up (with) – To reach somebody who is further ahead of you.
- You guys head to the restaurant now and I’ll catch up with you later. I’ve got a bit more work to do before I can leave.
*We can also catch someone up – Give someone information that was shared earlier that they didn’t receive.
- Smith was late today due to the heavy traffic on Main Street. Can you guys catch him up on this morning’s meeting?
- Clamp down on – To take strict action in order to prevent something, especially crime.
- The city has installed new traffic cameras to clamp down on people running red lights.
- Come across –
1)To be understood.
- After I did a practice presentation, I felt the message didn’t really come across in my speech. I need to rewrite it to make it clear.
2) To find or discover something by accident.
- I came across an old photo album in my grandmother’s attic. It was fun to see photos of my Dad when he was small.
- Come up with -To find or make an answer, an amount of money, etc.
- I need to come up with another $200 if I want to buy that new moped.
- If we work together I’m sure we can come up with a solution that works for everyone.
- Crack down on – To make more effort to prevent illegal activities and give stronger penalties to the people who do them.
- The police have set up a new task force to crack down on car theft in the city.
- Crank something out – To produce a lot of something quickly.
- The writer locked himself in a hotel room so he would have no distractions. His goal was to crank out 300 pages of his book over the weekend.
Do you want to learn even more phrasal verbs? You’ll find a list of common ones add my post here> Learn 50 Phrasal Verbs (List, Examples, Video, 42-page PDF)
- Crop up – To appear or happen unexpectedly.
- Who is Jonathan? I hear his name crop up in a lot of conversations around the office. Is he the new manager?
- Face up to – To accept or deal with something that is difficult.
- Rayleen had to face up to the fact that the relationship was over.
*The phrasal verb face up to is often paired with the fact .
- Fall out with – To end of friendly relationship with someone due to a disagreement or improper behavior.
- I fell out with Rory 6 months ago. We haven’t talked since.
*It’s common to use falling out as a noun phrase with the verb had .
- Rory and I had a falling out 6 months ago.
- Figure something out – 1) To think about somebody/something until you understand them/it.
- Sean is an odd guy, I could never figure him out .
- This is a small problem, I’m sure we can figure it out together.
2) To calculate an amount or the cost of something
- My wife wants to go to Hawaii, and I need to figure out how much it will cost.
- Freak out – To become or cause someone else to become very uncomfortable or excited.
- Try not to freak out but I might be able to sell my company 4 million dollars. Isn’t that amazing!
*This is separable is a verb so we can put an object in between the verb and the preposition – freak someone out
- My aunt has a creepy doll in her living room that looks like his eyes follow you wherever you go. That thing freaks me out every time I visit.
- Hash out – (informal, especially North American English) To discuss something carefully and completely in order to reach an agreement or decide something.
- The contract is almost ready, we just need to hash out some details, and then I can sign it.
- Iron out – To sort out any problems or difficulties.
- I like your business plan but before I invest any money we need to iron out a few details.
The phrasal verbs hash out and iron out are often used with the noun details .
- Jot down – To write something down quickly.
- I usually carry a small notepad with me so I can jot down any ideas that come to me.
- Lay off – (informal) 1. To stop pressuring or bothering someone.
- I think David is having a hard time at work, maybe we should lay off him for a while.
- (informal) To stop using something.
- Holy cow, I’ve gained 6 kg in 4 months. I need to lay off the fast food and start eating healthy.
- To stop employing somebody because there is not enough work for them to do.
- The company was losing money so they had to lay off 50 workers from their factory.
*This is separable is a verb so we can put an object in between the verb and the preposition – lay someone off
- The company will lay 50 workers off at the end of the summer.
- Look down on – If you look down on someone you think that you are better than them.
- I don’t like the way Melanie looks down on everyone. She thinks she’s so special but really she’s not.
- Look something over – To carefully look at something to check its condition and quality.
- My friend Martin is a licensed mechanic so I asked him to look the car over before I bought it.
- Mull something over – To carefully consider something.
- I understand your proposal, let me mull it over tonight and I’ll give you my answer tomorrow morning.
- Pass away – To die, this is used as a gentler way to talk about someone who is no longer with us.
- My high school Spanish teacher passed away last month, he was a great guy. Adios my friend, you will be missed.
- Plod along – To make very slow progress, especially with difficult or boring work.
- Filling out this paperwork is the most boring part of my job. I just have to plod along until it’s finished.
- Put up with – To tolerate something.
- Marcos is rude to all the girls in the office, they’re not going to put up with this any longer.
- Ramp up – To make something increase in amount.
- The whole team needs to ramp up our efforts to get this product launched on schedule.
- The factory has ramped up production to meet the surge in demand.
- Run something by – This phrasal verb’s meaning is similar to bounce off someone . You want to share a plan or an idea with another person to get their feedback.
- It’s a good idea, let’s run it by the manager to get his reaction. If he likes it, we can go ahead and start.
*We can also say run something past someone.
- Let me run this idea past Jonah first, he has experience in this area.
- See off – To take someone to the airport, bus/train station, etc. and say goodbye before they leave
- Tomorrow I’ll drive my son to the airport and see him off .
Visit my post > 74 Idioms and Phrasal Verbs with OFF (With Real Examples) and learn more ways to use OFF in conversation > https://worldenglishblog.com/idioms-and-phrasal-verbs-with-off/
- Sign up – to sign or add your name to a document, form, or contract that says you agree to do a job or to participate in something.
- Randall just walked into the Army recruiting office and signed up for five years. He has always wanted to be a soldier.
*We can also say sign on to do something.
- Randall signed on for five years.
Sign up for – To arrange to do a course of study by adding your name to the list of people doing it
- My local library offers free Japanese lessons for foreign people living in the area. I’m going to sign up for classes tomorrow.
If new circumstances or a new situation happens that we are not happy with, prepared for, or enjoying we often use the expression – I didn’t sign up for this .
- This is my third straight Saturday working overtime. At first, I was excited to work for this company but I didn’t sign up for all this overtime !
- Stem from – To be the result of something
- Bullying often stems from a difficult home life for the child. Unfortunately, it’s a cycle.
- Stick Up for – To support or defend yourself or someone else.
- I was big for my age in elementary school so I often stuck up for the smaller kids who were being bullied.
- Stock up on – To buy or prepare many things for later use.
- The weather says a big typhoon is coming in 2 days so we had better stock up on food and water now. It will be tough to go shopping when the storm hits.
- (To) muster up – The verb muster is often used with the prepositions up to mean to find as much support, courage, etc. as you can
- I mustered up the courage, walked to my boss’s office, and demanded a raise.
- Turn down – 1)To reject or refuse an offer, a proposal, etc. or the person who makes it
- I turned down the promotion because I didn’t want to move to the other side of the country.
2) Turn something down/Turn down something – To reduce the noise, heat, etc. produced by a piece of equipment by moving its controls
- Can you turn the TV down ? It’s too loud.
- I’m getting warm, does anyone mind if I turn down the heat?
*The opposite of Turn Down is Turn Up.
- I’m getting chilly, does anyone mind if I turn up the heat?
- Turn out – To be discovered to be; to prove to be
- I was worried about running a half marathon but it turned out to be easier than I thought.
- The antique watch that I bought at the market turned out to be very valuable.
- Weed out – To remove or get rid of people or things from a group because they are not wanted or are less good than the rest
- We look at the applications and weed out the candidates who are not suitable before we start the interviews.
*This is separable is a verb so we can put an object in between the verb and the preposition – weed something/someone out .
- Gangs and troublemakers had taken over the school. The new principal wanted to weed the bad students out so he could turn the school back into a place of learning.
- Weigh in – (informal) to join in a discussion, an argument, an activity, etc. by saying something important.
- It was a big decision so all the staff were asked to weigh in and share their opinions.
*The phrasal verb weigh in is sometimes followed by another preposition, on.
- Walter, you’ve been awfully quiet over there. Would you like to weigh in on the topic?
1) (informal) (of a person) to find yourself in a particular place or situation.
- When I was younger I never thought I would wind up working for my Dad’s company. My life is completely different than I imagined it, but I am happy.
2) wind up something/wind something up – To end something that has been happening, like a speech or a meeting.
- Okay everyone, let’s wind up this meeting and head home.
- Okay everyone, let’s wind this meeting up and head home.
3) wind up somebody/wind somebody up – (British English, informal) to deliberately say or do something to annoy somebody.
- Don’t listen to Alexander, he likes to wind up the staff on Monday mornings with his stupid comments. Just ignore him.
- He likes to wind the staff up on Monday mornings, just ignore him.
* DID YOU NOTICE? The title of this post is 42 Advanced Phrasal Verbs but the last verb on this list is numbered 43. There was an error when my word processing software numbered the Phrasal Verbs because I had to change the formatting. Some phrasal verbs have several meanings. This caused a problem in counting and somehow my list of Phrasal Verbs lost the number 19. Without number 19 on the list, the total is really 42! I left it in as a challenge to see who could find it.
Which Phrasal Verbs from this post were new for you? Which Phrasal Verbs have you already heard? Tell me in the comments .
- Learn 50 Phrasal Verbs (List, Examples, Video, 42-page PDF) May 13, 2024
- 42 Advanced Phrasal Verbs (That You Need to Know) February 16, 2024
- GET and TAKE Phrasal Verbs and Collocations (More than 50) November 26, 2022
- Phrasal Verbs With Stop (Compound Nouns and Adjectives too) September 30, 2022
- How to Learn Phrasal Verbs – Tips from an ESL Teacher (PDF) September 26, 2022
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Related Posts
Use these in and out phrasal verbs and improve your confidence, break in and break up (video + quiz) english phrasal verbs, master 6 phrasal verbs with cut (17 easy to understand examples).
Photo by Pavel Danilyuk on Pexels.com
How to use “Break down” 4 ways (Learn Phrasal Verbs)
Discover more from world english blog.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
phrasal verb
Definition of phrasal verb
Word history.
1925, in the meaning defined above
Articles Related to phrasal verb

What's the Past Tense of 'Creep'?
We don't want you to be creeped out, but...
Dictionary Entries Near phrasal verb
Cite this entry.
“Phrasal verb.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/phrasal%20verb. Accessed 17 Jul. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, flower etymologies for your spring garden, 12 star wars words, 'swash', 'praya', and 12 more beachy words, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, games & quizzes.

- General English Course
- IELTS Course
English phrasal verbs , English vocabulary
30+1 phrasal verbs for daily conversations + video.
What are the most common English phrasal verbs for daily conversations ? How and when should you use them? Stay with us in this lesson to get the answers to these questions!
First, let’s review what phrasal verbs are:
Phrasal verbs are like special pairs of words that work together to create a new meaning. They usually have two parts:
- A verb (an action word, like “run” or “look”).
- A little word called a particle (like “up,” “out,” or “in”).
When you put these two parts together, they often make a whole new meaning that’s different from the original verb. For example:
- “Give up” means to stop trying.
- “Look after” means to take care of someone.
The importance of using English phrasal verbs for daily conversations are as follows:
- Express More Ideas : Phrasal verbs let you say things in a more interesting way. Instead of just “stop,” you can say “give up,” which sounds more vivid.
- Understand Others : Many people use phrasal verbs in everyday conversations. If you know them, you’ll understand what people mean when they say things like “hang out” (spend time together) or “run into” (meet by chance).
- Sound Natural : Using phrasal verbs makes your speech sound more natural and fluent, like a native speaker. For example, “turn on” sounds more natural than “activate” when talking about a light or a TV.
- Be More Specific : Phrasal verbs can be more precise. “Turn off” specifically tells you to stop something from working, like a device, which is clearer than just saying “stop.
In this lesson, we are going to learn 21 phrasal verbs used in our daily conversations:
Bring sth up
Meaning : To start talking about something.
Example: He’s always bringing up the past.
Cheer on: Of phrasal verbs for daily conversations
Meaning : To encourage or support someone, usually with shouts.
Example: We arrived to cheer on the baseball team from our town in the championship game.

Meaning : To improve one’s mood, especially when someone is sad.
Example: Cheer up! Tomorrow’s another day!

Get across is also in the list of phrasal verbs for daily conversations that means:
Meaning : To manage to make someone understand or believe something.
Example: We tried to get our point across, but he just wouldn’t listen.
Meaning : To tell other people about something that you know, especially when it is a secret.
Example: If you know an important secret, you shouldn’t let on.
Jump in : Of phrasal verbs for daily conversations
Meaning : To interrupt when someone else is speaking.
Example: Why are you constantly jumping in my speech? Would you please let me finish my sentences?
Meaning : To interrupt a conversation or discussion or someone who is talking.
Example: He kept on butting in with silly comments.
Meaning : To meet someone you know when you have not planned to meet them.
Example: We bumped into Amy when we were downtown last week.

Read more: What are the traveling phrasal verbs in English?
Grapple with something
Meaning : To try to deal with or understand a difficult problem or subject.
Example: Today, many Americans are still grappling with poverty.

Pull sth off
Another item of the phrasal verbs for daily conversations is pulls sth of that means:
Meaning : To succeed in doing something difficult or unexpected.
Example: The company has pulled off one of the biggest financial problems of recent years.
Now let’s review these phrasal verbs in this conversation
Alex: Hey, Sam, have you heard about the new policy changes at work?
Sam: No, I haven’t. Can you bring it up during our meeting later? I’m curious.
Alex: Sure. Also, did you bump into Jerry this morning? He seemed upset.
Sam: Yeah! He’s grappling with some project issues, it seems.
Alex: That’s tough. We should cheer him on ; he might need some encouragement to get through this.
Sam: Good idea. Oh, and about the charity marathon, are you still planning to run?
Alex: Absolutely, I hope to pull it off ! I’ve been training every weekend.
Sam: I admire your dedication. Running isn’t really my thing.
Alex: Come on, it might cheer you up to participate. Plus, it’s for a good cause.
Sam: Maybe you’re right. I’ll think about it.
Meaning : To say something suddenly and without thinking, usually because you are excited or nervous.
Example: He blurted out everything out about our secret plan.
Meaning : To stop being available.
Example: Our main source of money has dried up and we will face a lot of problems.
Throw away: Of phrasal verbs for daily conversations
Meaning : To get rid of something that you no longer need.
Example: Let’s throw away all broken toys to clear a space for new ones.

Get (something) through (to someone)
Meaning : To succeed in making someone understand or believe something.
Example: We can’t get through to the manager just how serious the problem is!
Talk sth over (talk an issue/a plan over)
Meaning : To discuss a problem or situation with someone, often to find out their opinion or to get advice before making a decision.
Example: Employees had two weeks to talk the proposal over with their families before making a decision.
Talk someone around
Meaning : To persuade someone to agree or to be persuaded.
Example: He just kept talking around the subject and didn’t discuss the main issues.
Meaning : To continue or proceed.
Example: Sorry for the interruptions, please carry on with your story.
Meaning : If a business or a large piece of equipment stops operating.
Example: The manager has a plan to shut down four factories and cut 10,000 jobs.
Meaning : To support.
Example: Our plan is completely backed up by the manager.
Fall back on sth
Meaning : To use something to help when other things have failed.
Example: Jacob always has his professional experience to fall back on.
Give away: Of phrasal verbs for daily conversations
Meaning : To give something to someone for free.
Example: The company gave away a lot of coupons that could be used at any store.
Read more: What are the relationship phrasal verbs in English?
Let’s review the other mentioned phrasal verbs for daily conversations in this conversation:
Mia: I heard the café down the street is going to shut down . Have you heard about it?
Jake: Really? No, that’s news to me. It’s always dried up by the time I get there after work, but I didn’t think they’d close for good.
Mia: Yeah, it’s a shame. But on a brighter note, did you manage to get through to the customer service about the refund?
Jake: Oh, yes, finally. After several attempts, they understood the issue and processed it. By the way, have you seen the new fitness app? It’s backed up by some impressive research.
Mia: No, I haven’t. Sounds interesting . I need something new to fall back on now that my gym membership is ending.
Jake: I’ll send it across to you. It might give away some free subscription codes if you sign up now.
Mia: That would be great, thanks! Oh, and speaking of giving away , are you still giving away those old books?
Jake: Yes, I’m planning to. I thought it would be better than just throwing them away . Want to come over and see if there’s anything you’d like?
Mia: Absolutely, I might find a quick snack for my brain among those books. And, hey, we should talk over our plans for the hiking trip this weekend. I’m all for a slap-up meal afterwards.
Jake: Agreed, nothing like a good meal to cheer up after a day’s hike. Let’s plan it out.
Now let’s learn other useful phrasal verbs for speaking :
One of the common and useful phrasal verbs for speaking is “catch up” that means:
Meaning: To get up to date with someone or something.
When you’ve been away on vacation and you have a lot of emails waiting for you, you need to “catch up” on your emails.
Example: I need to catch up on my emails after being on vacation.
Turn down (Of useful phrasal verbs for speaking)
Meaning: To refuse or reject something.
If someone offers you a job but you don’t accept it because the salary isn’t enough, you “turn down” the job offer. You’re refusing or saying no to the job opportunity.
Example: She turned down the job offer because it didn’t pay enough.
Meaning: To unexpectedly encounter someone or something.
If you unexpectedly see an old friend while you’re shopping, you “run into” them. you didn’t plan to meet them.
Example: I ran into an old friend at the grocery store yesterday.
Come across
Another useful phrasal verbs for speaking is come across. This phrasal verb means:
Meaning: To find or meet by chance.
When you’re browsing the internet and you find an interesting article, you “come across” it. You look for something but find something else!
Example: I came across this interesting article while browsing the internet.
Bring up (Of useful phrasal verbs for speaking)
Meaning: To introduce a topic into conversation.
If there’s an important issue that needs to be discussed during a meeting, you should bring it up!
Example: I didn’t want to bring up the issue during the meeting.
Yesterday, I decided to catch up on my emails after being on vacation for a week. While going through my inbox, I ran into an old friend’s email, which I hadn’t seen in years. It was unexpected to come across his message among the others. Feeling nostalgic, I decided to bring up the idea of meeting for coffee!
Look forward to
This phrasal verb also in the list of useful phrasal verbs for speaking that means:
Meaning: To anticipate with pleasure.
When you’re excited about seeing someone again, like a friend you haven’t met in a long time, you “look forward to” meeting them. you feel happy about the upcoming event.
Example: I’m looking forward to seeing you again next week.
Meaning: To talk louder or express your opinion more clearly.
Imagine sitting in a noisy classroom, and your teacher is asking a question. You want to answer, but your voice is quiet. You need to “speak up” so everyone can hear you.
Example: Can you speak up? I can’t hear you very well.
Meaning: To postpone or delay something.
Picture having homework to do, but you want to play outside instead. You decide to play first and do your homework later. You “put off” doing your homework.
Example: They decided to put off their vacation until next year.
Meaning: To spend time relaxing or socializing with friends.
Think about spending time with your friends at the park. You laugh, play games, and have fun together. This is what it means to “hang out” with friends.
Example: Let’s hang out at the park this weekend.
Meaning: To experience or endure a difficult situation.
Imagine feeling sad because your favorite toy broke. You’re feeling upset, but you know you’ll feel better soon. You’re experiencing the emotions of being sad and then feeling better. This is what it means to “go through” a tough time.
Example: She’s going through a tough time right now.
I’m really looking forward to the weekend when I can hang out with my friends at the park. Last time, we had to put off our gathering due to bad weather and I didn’t say anything, but this time I’ll speak up !
Watch this video and review the last phrasal verbs mentioned in this article
Don’t forget to review all these phrasal verbs and use them in your daily conversations. If you want to learn more about phrasal verbs in English, we recommend that you take our online general English course . Level up your English and speak like a native!
related post

English phrasal verbs: Plans & Decisions + Video

The most common phrases about relationships+video

15 everyday idioms in English with example

How can we describe a movie in English? + video
85 Comments

English restaurant vocabulary with pictures + video

Idioms about money in English (Complete list)

Want alternatives in English: synonyms of want

Hotel vocabulary with pictures + Expressions & video
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

COMMENTS
A phrasal verb is a multi-word verb made up of a main verb and at least one preposition or a particle that changes the meaning of the verb from the original verb. 'To give up' and 'to run down' are examples of phrasal verbs. ... (parts of speech) hundreds more games and tests. read: parts-of-speech lists.
Phrasal verbs and multi-word verbs - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Phrasal Verbs | List, Definition, Examples & Tips. Published on April 23, 2015 by Shane Bryson. Revised on November 7, 2022. ... Phrasal verbs are very common in everyday speech, but in academic writing, it's best to replace them with one-word alternatives where possible. 47 phrasal verbs and one-word alternatives.
For example: We passed out two hours after the social event. The phrasal verb in this sentence is passed out, which means become unconscious, sleep, or blackout. But the base verb, pass, takes on a different meaning. This single-word verb means to move or cause to move in a specified direction. Here's another example.
PHRASAL VERB definition: 1. a phrase that consists of a verb with a preposition or adverb or both, the meaning of which is…. Learn more.
A phrasal verb is a verb like pick up, turn on or get on with. These verbs consists of a basic verb + another word or words. The two or three words that make up a phrasal verb form a short "phrase" - which is why we call them "phrasal verbs". But a phrasal verb is still a verb. Look is a verb.
A phrasal verb is a phrase or expression that consists of a verb plus another word or two, like this: [verb + adverb] e.g: look up. [verb + preposition] e.g: look after. [verb + adverb + preposition] e.g: look forward to. The whole phrase acts as a verb, and has a different meaning to the original verb. For example, look up, look after and look ...
Phrasal verbs that consist of more than one particle are inseparable. For instance, verbs like 'put up with,' 'come up with,' 'get rid of,' 'run out of,' and others, are always inseparable. Here's a table with 10 inseparable phrasal verbs and examples: "She always looks after her younger brother.".
Phrasal verbs are a type of compound verb that consists of a verb and one or more particles. The particles can be prepositions or adverbs, or a combination of both. When combined with a verb, the meaning of the phrasal verb is often different from the meaning of the individual words. Phrasal verbs are commonly used in spoken and informal English.
A phrasal verb is a verb that is made up of a base verb and one or two particles, such as off, up, or on. These particles change the meaning of the base verb in various ways. Phrasal verbs are an important part of the English language, and they are often used in everyday conversation and writing.
Phrasal verbs do have their uses, after all. For example, they convey a casual tone, and while this is not usually desirable in academic writing, the best academic writers can vary their tone at will. Accordingly, you should think of phrasal verbs as a stylistic option, even though you will often be best advised to eliminate them rather than ...
Phrasal Verbs: In this article, you will learn what is a phrasal verb, the definition of a phrasal verb and how it is used in sentences. Check out the list of phrasal verbs and try out the practice questions to find out how far you have understood. ... it is a combination of all the three parts of speech - verb, adverb and preposition. Though ...
210+ Most Common English Phrasal Verbs. Phrasal verbs are when we combine a verb with a preposition of another grammatical element, and end up with a completely new meaning.. They're used constantly by native speakers in spoken and written English, which makes them important to know.. In this English phrasal verbs list, we'll show you 210+ of the most common phrasal verbs, with audio and ...
Phrasal verbs can be challenging for non-native English speakers to master, but with practice and familiarity, they can become an essential part of your language skills. We hope this list of 100 phrasal verbs, meanings, and example sentences has been helpful in expanding your understanding and usage of these important language structures.
Phrasal Verbs are the combinations of Verbs and adverbs or prepositions or both with completely new meanings and they consist of more than one word. Most phrasal verbs consist of two words ; the first word is a simple monosyllabic Verb, and the second word is a particle i.e., a preposition or an adverb .
Phrasal verbs that can be divided by objects are commonly referred to as being separable; those that cannot be divided are known as being inseparable. "Please look overthe proposal and let me know what you think.". It might seem as though over does in fact introduce a prepositional phrase: over the proposal.
However, they are acceptable in informal writing and speech. Conclusion. Phrasal verbs can be challenging to understand and remember, but they are an essential part of the English language. ... By learning the 100 most common phrasal verbs list with meanings and examples, you can improve your communication skills and understanding of English ...
Phrasal verbs are very common in English conversation. Learning phrasal verbs is a great way to make your English sound more natural. Some phrasal verbs are literal, which means the meaning is exactly what the words say. Some phrasal verbs are metaphorical, this means they have a completely different meaning than you would associate with the verb by itself. literal - look aroundmetaphorical ...
phrasal verb: [noun] a phrase (such as take off or look down on) that combines a verb with a preposition or adverb or both and that functions as a verb whose meaning is different from the combined meanings of the individual words.
First, let's review what phrasal verbs are: Phrasal verbs are like special pairs of words that work together to create a new meaning. They usually have two parts: A verb (an action word, like "run" or "look"). A little word called a particle (like "up," "out," or "in"). When you put these two parts together, they often ...
Phrasal verbs are formed by the combination of two words, a verb and an adverb or a preposition, whose meaning is different from individual words. Check Phrasal verb definition, examples, types, list